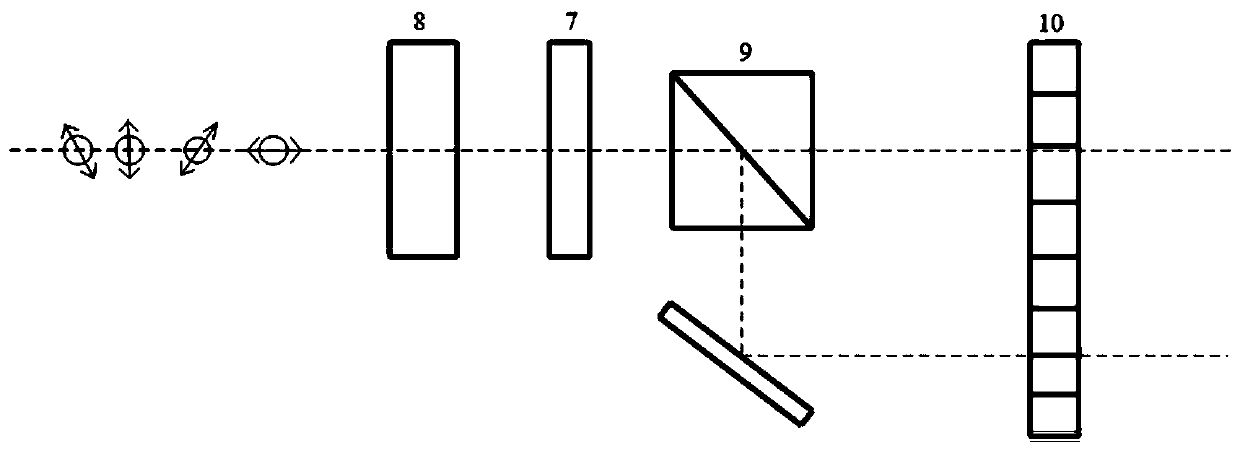
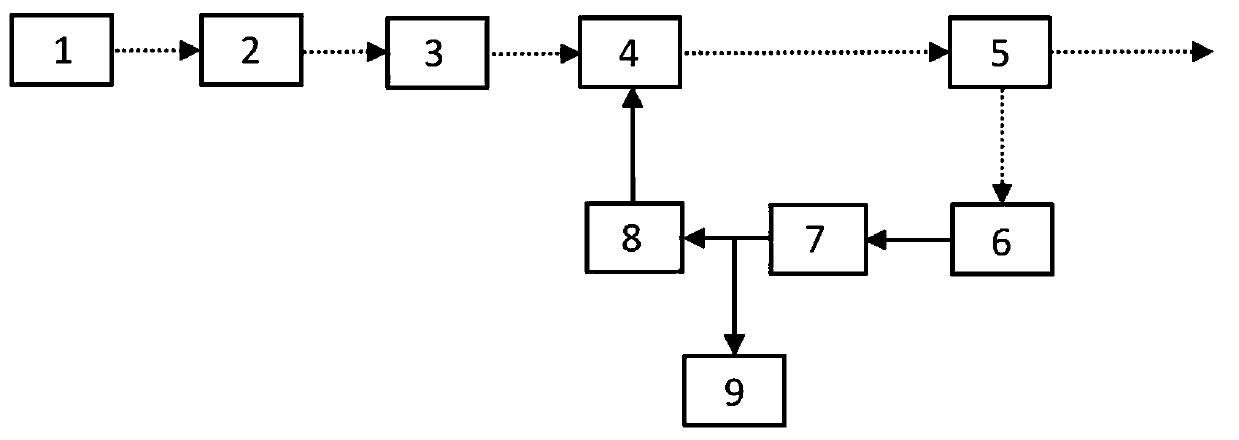
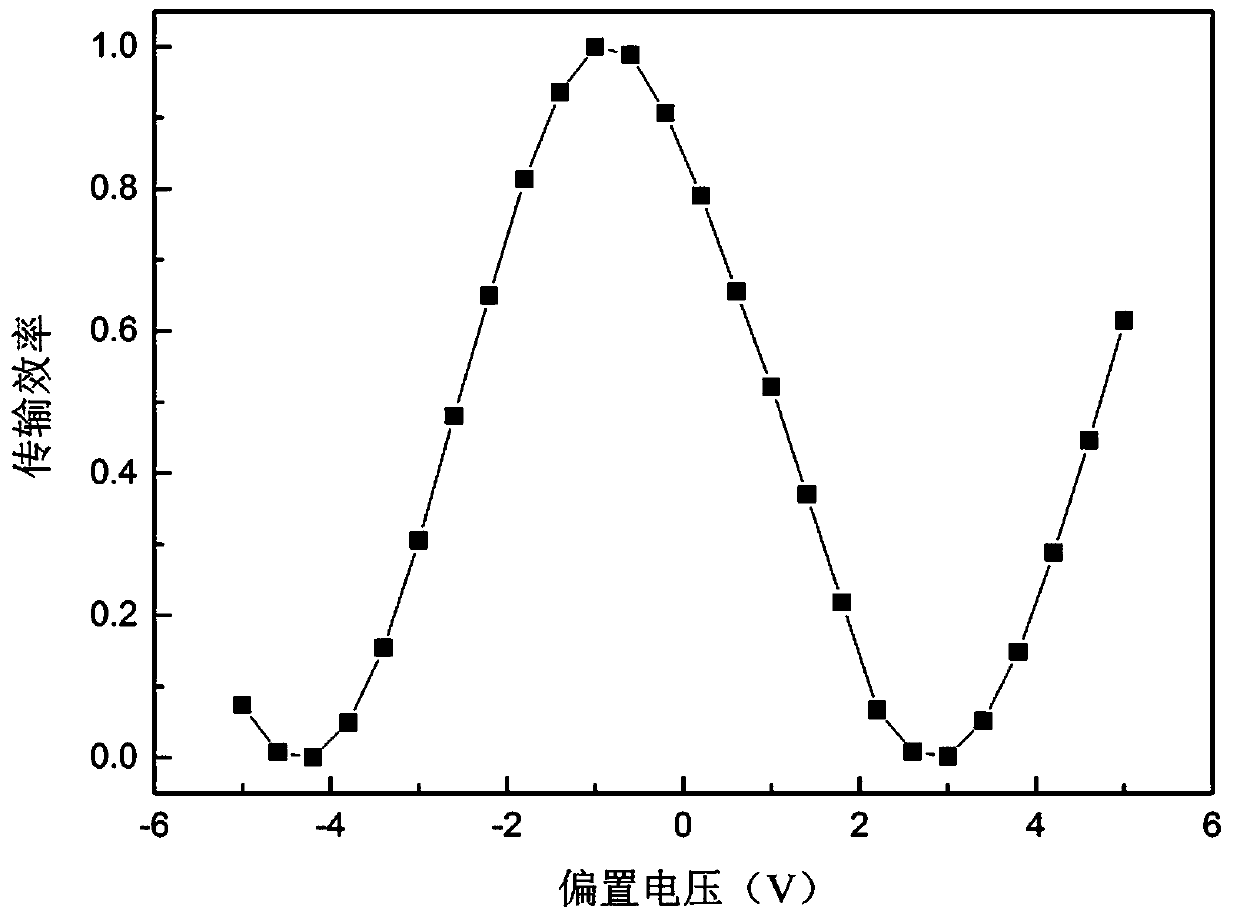
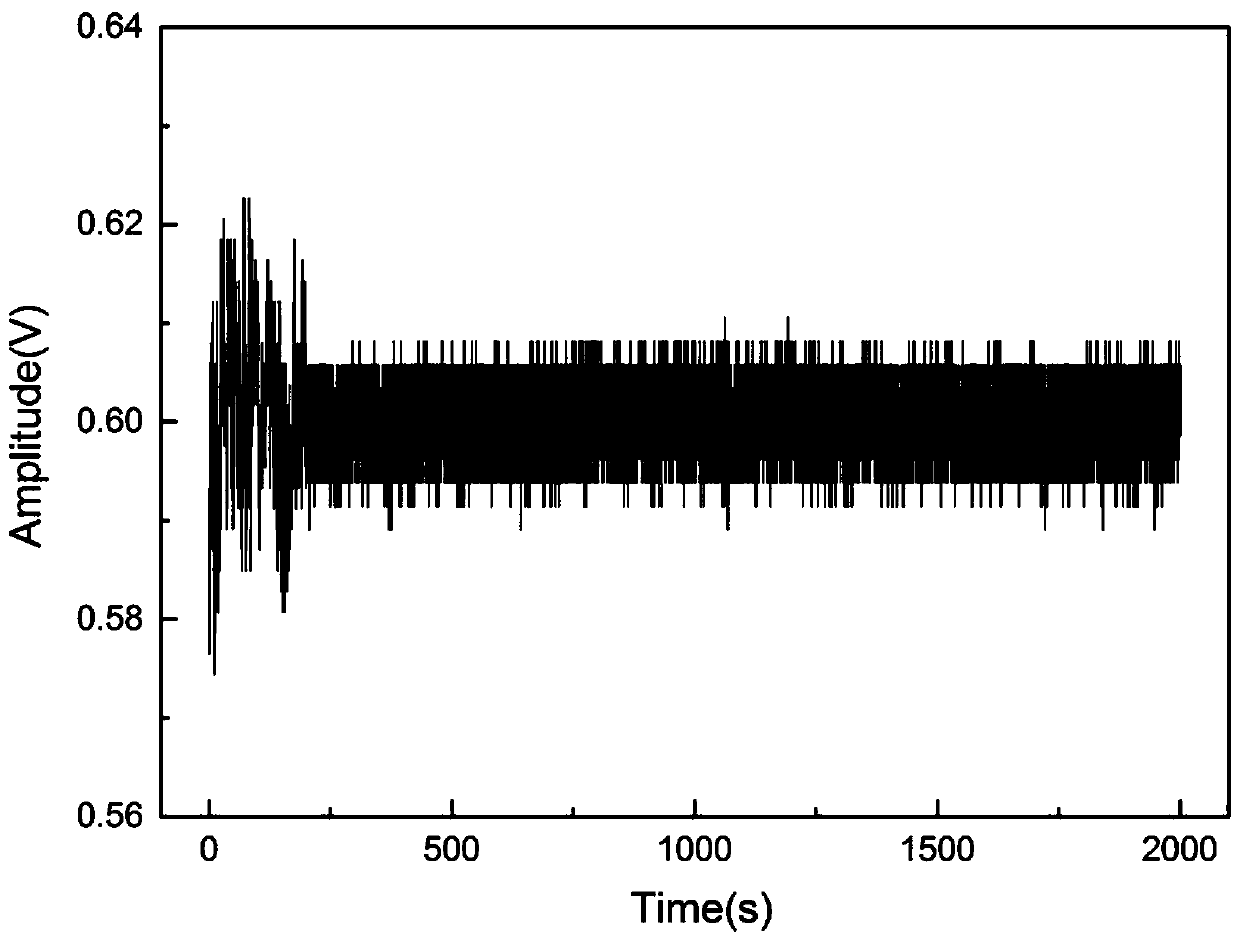
Patents
Literature
56 results about "Quantum imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Quantum imaging is a new sub-field of quantum optics that exploits quantum correlations such as quantum entanglement of the electromagnetic field in order to image objects with a resolution or other imaging criteria that is beyond what is possible in classical optics. Examples of quantum imaging are quantum ghost imaging, quantum lithography, and quantum sensing. Quantum imaging may someday be useful for storing patterns of data in quantum computers and transmitting large amounts of highly secure encrypted information. Quantum mechanics has shown that light has inherent “uncertainties” in its features, manifested as moment-to-moment fluctuations in its properties. Controlling these fluctuations—which represent a sort of “noise”—can improve detection of faint objects, produce better amplified images, and allow workers to more accurately position laser beams.
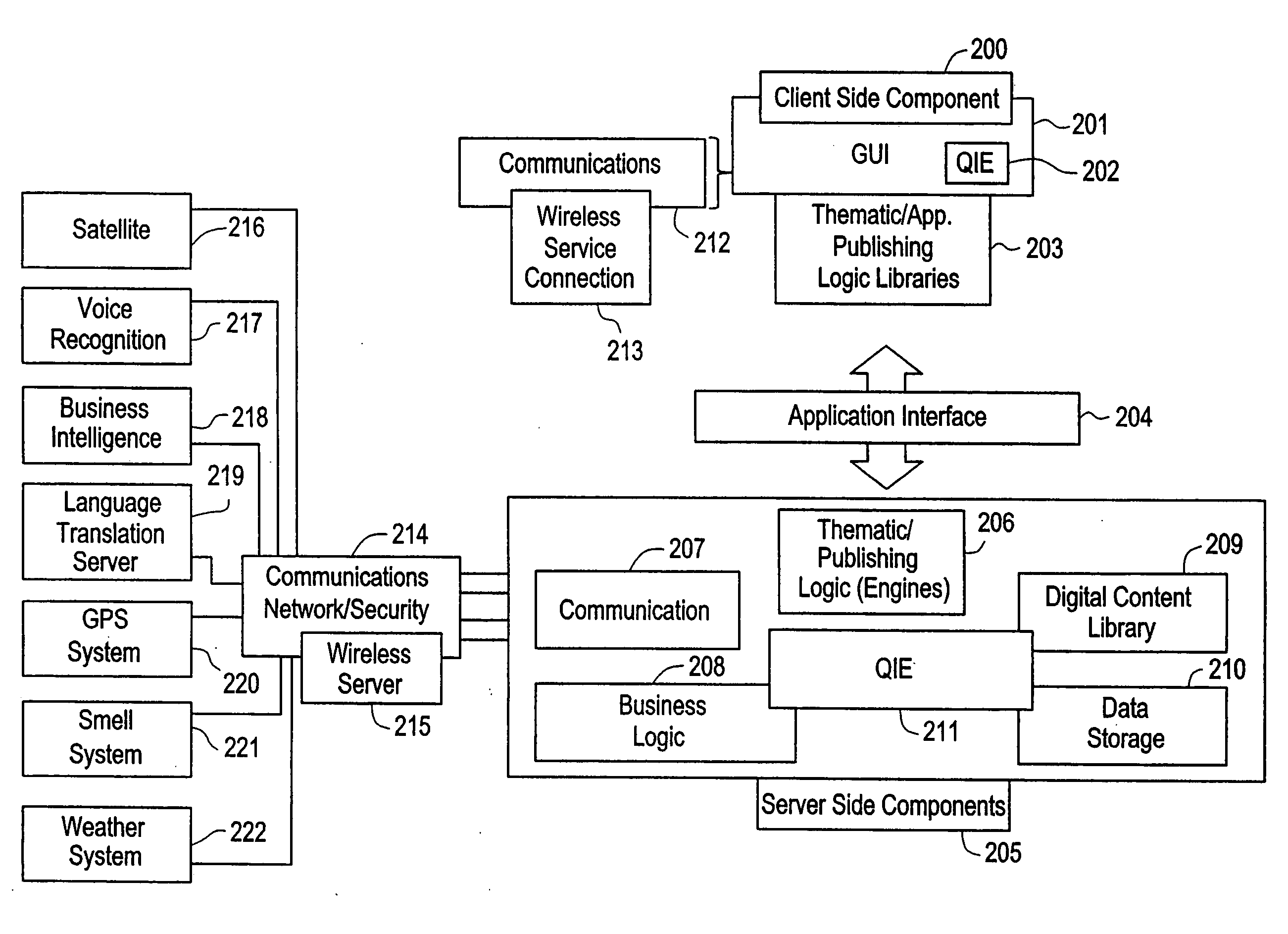
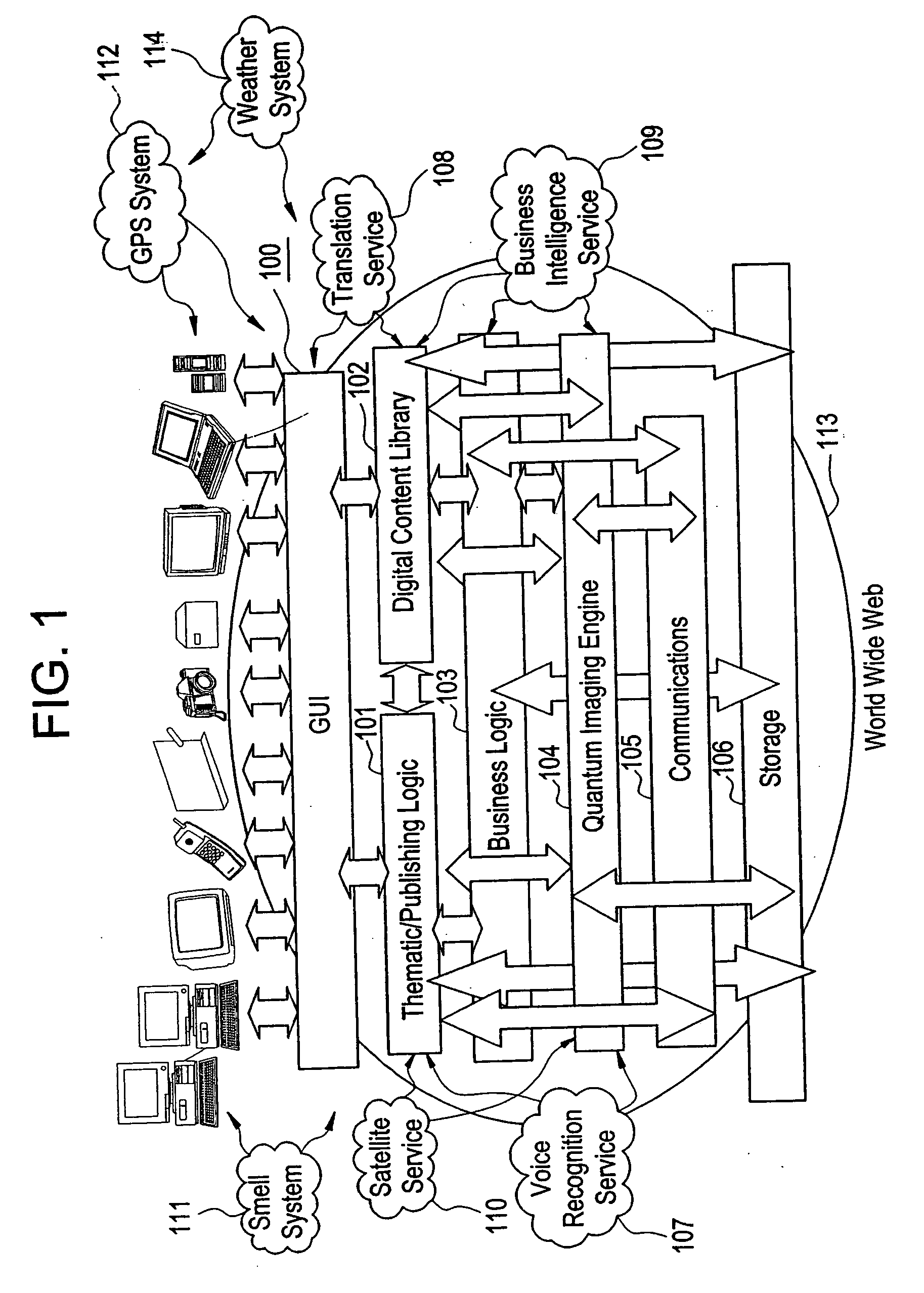
Interactive virtual thematic environment
InactiveUS7373377B2Multiple digital computer combinationsImage data processing detailsTime informationInteractive software
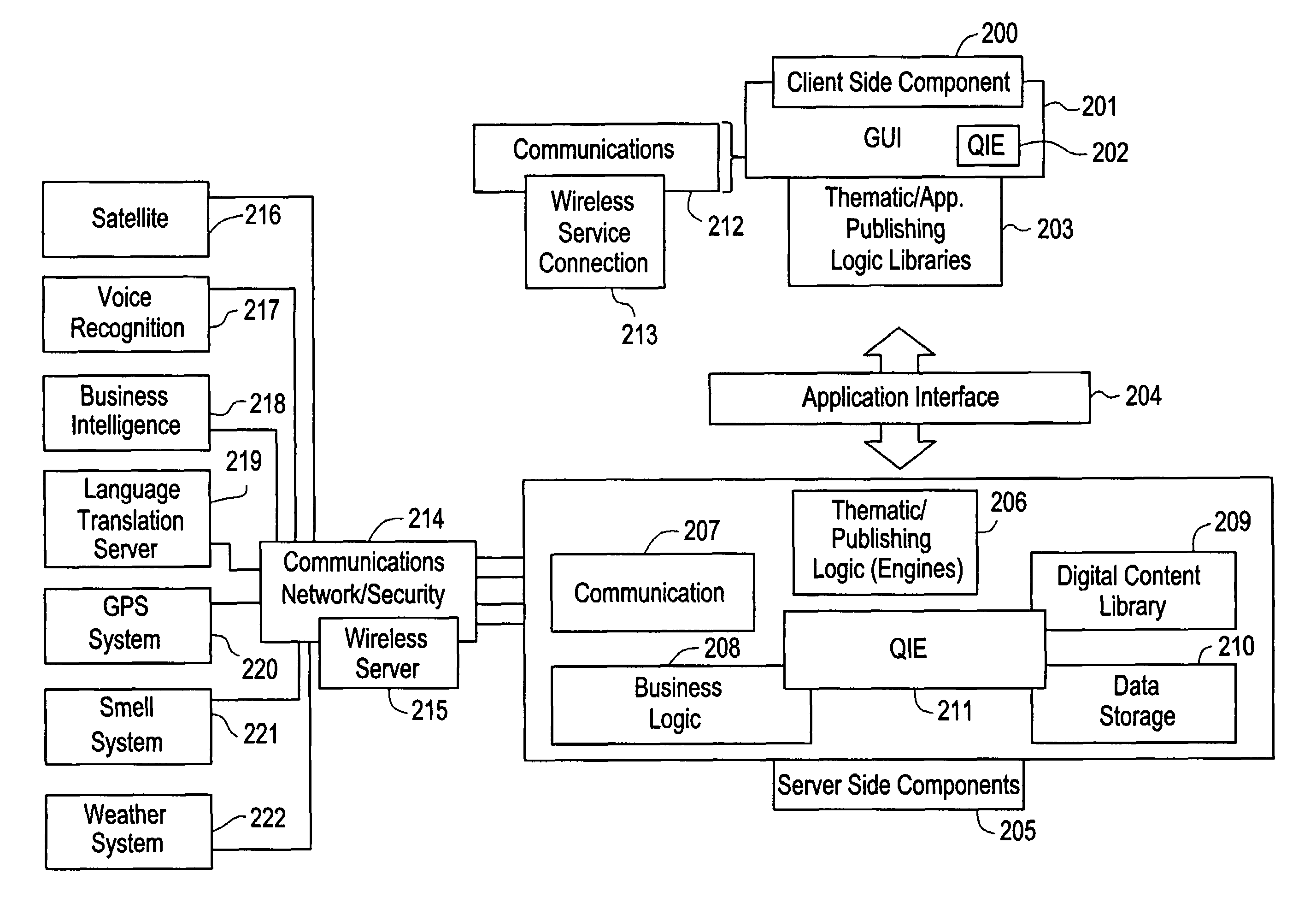
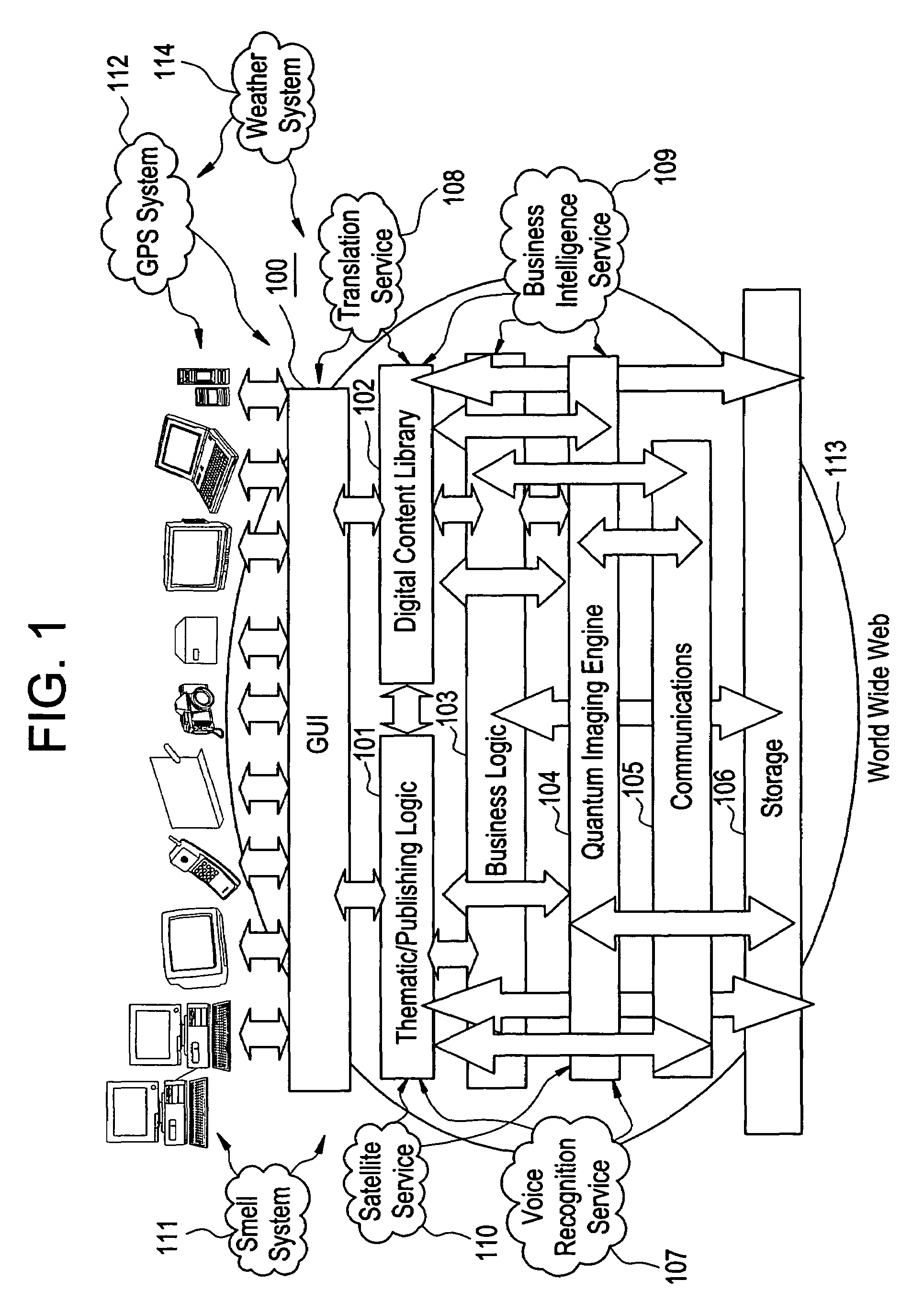
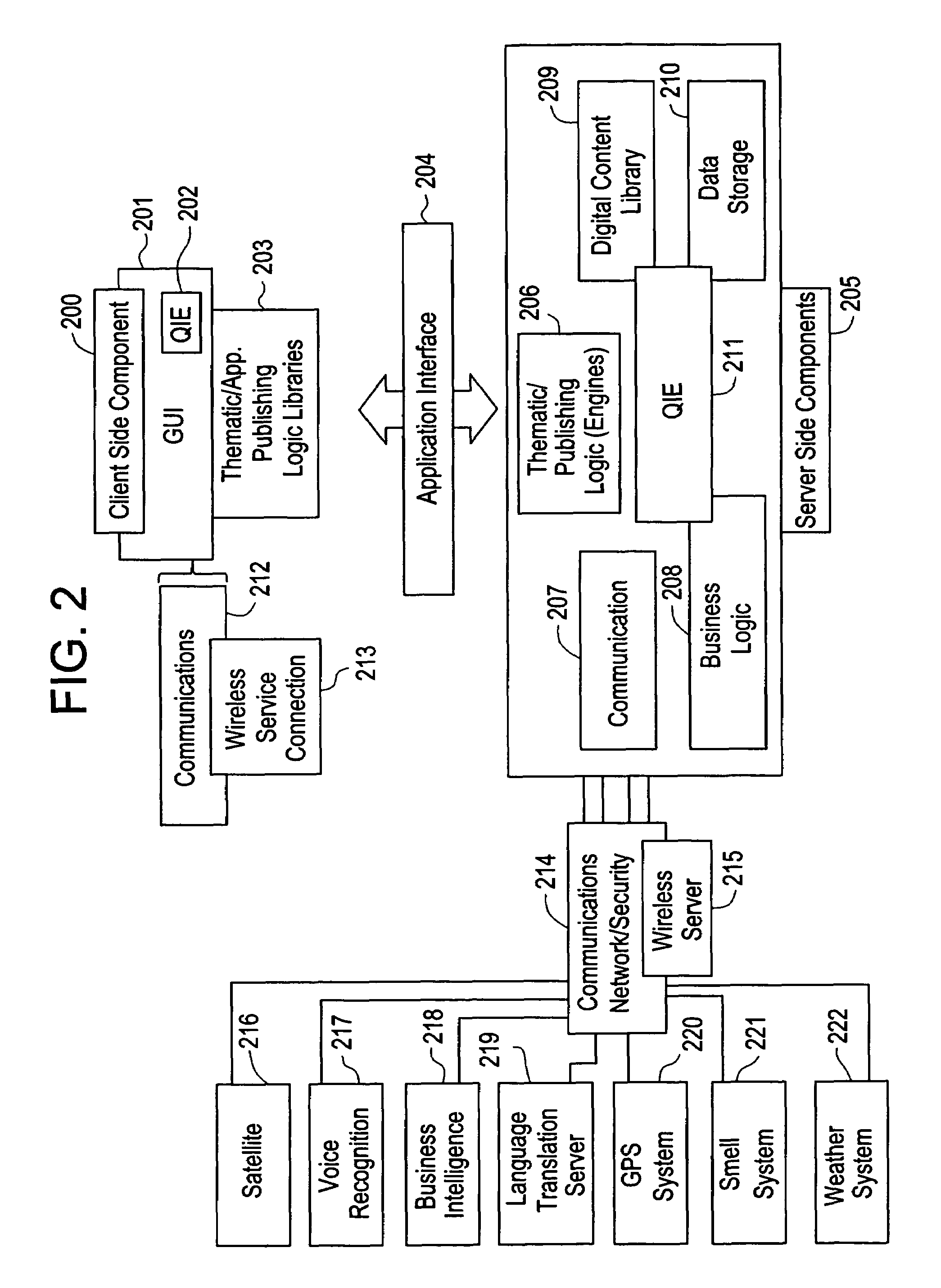
The present invention is directed to a method of integrating information, including real-time information, into a virtual thematic environment using a computer system, including accessing the stored information from a database or downloading the real-time information from a source external to the thematic environment; inserting the real-time information into the thematic environment; and displaying the information to a user within the thematic environment. In one embodiment, the computer system is connected to a holographic projection system such that the images from the thematic environment can be projected as holographic projections. The computer system includes an interactive software application platform having at least one thematic / publishing logic module which contains thematic environment rules; at least one digital content library module which provides content management on the thematic environment; and at least one quantum imaging environment (QIE) module which interprets content such that the content is manipulated and accessed by any device.
Owner:QUANTUM IMAGING LLC
Diamond components for quantum imaging, sensing and information processing devices
ActiveUS20160348277A1Reduce surface damageLong spin coherence timePolycrystalline material growthDiffusion/dopingInformation processingSurface roughness
A single crystal CVD diamond component comprising: a surface, wherein at least a portion of said surface is formed of as-grown growth face single crystal CVD diamond material which has not been polished or etched and which has a surface roughness Ra of no more than 100 nm; and a layer of NV− defects, said layer of NV− defects being disposed within 1 μm of the surface, said layer of NV− defects having a thickness of no more than 500 nm, and said layer of NV− defects having a concentration of NV− defects of at least 105 NV− / cm2.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX TECH LTD
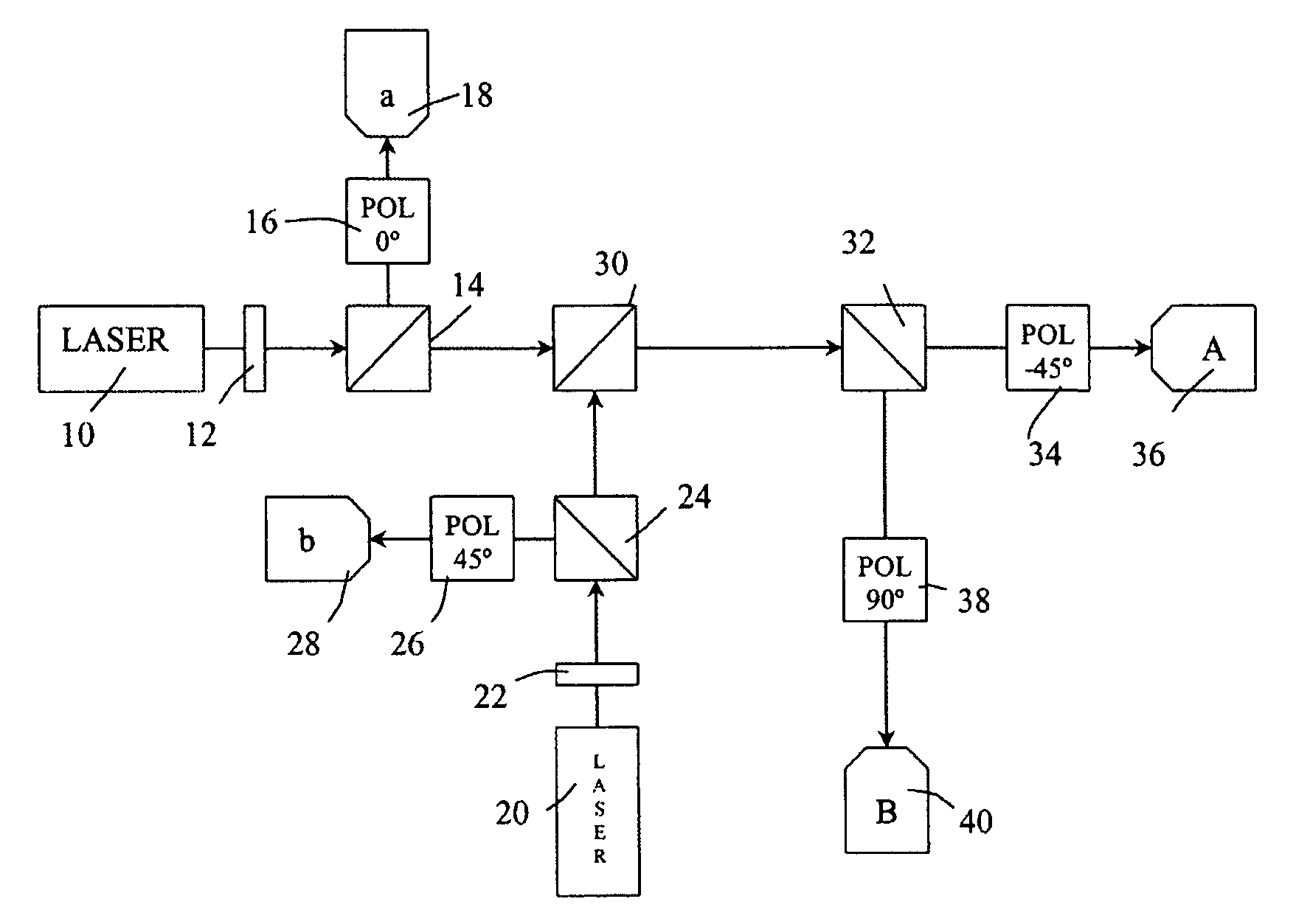
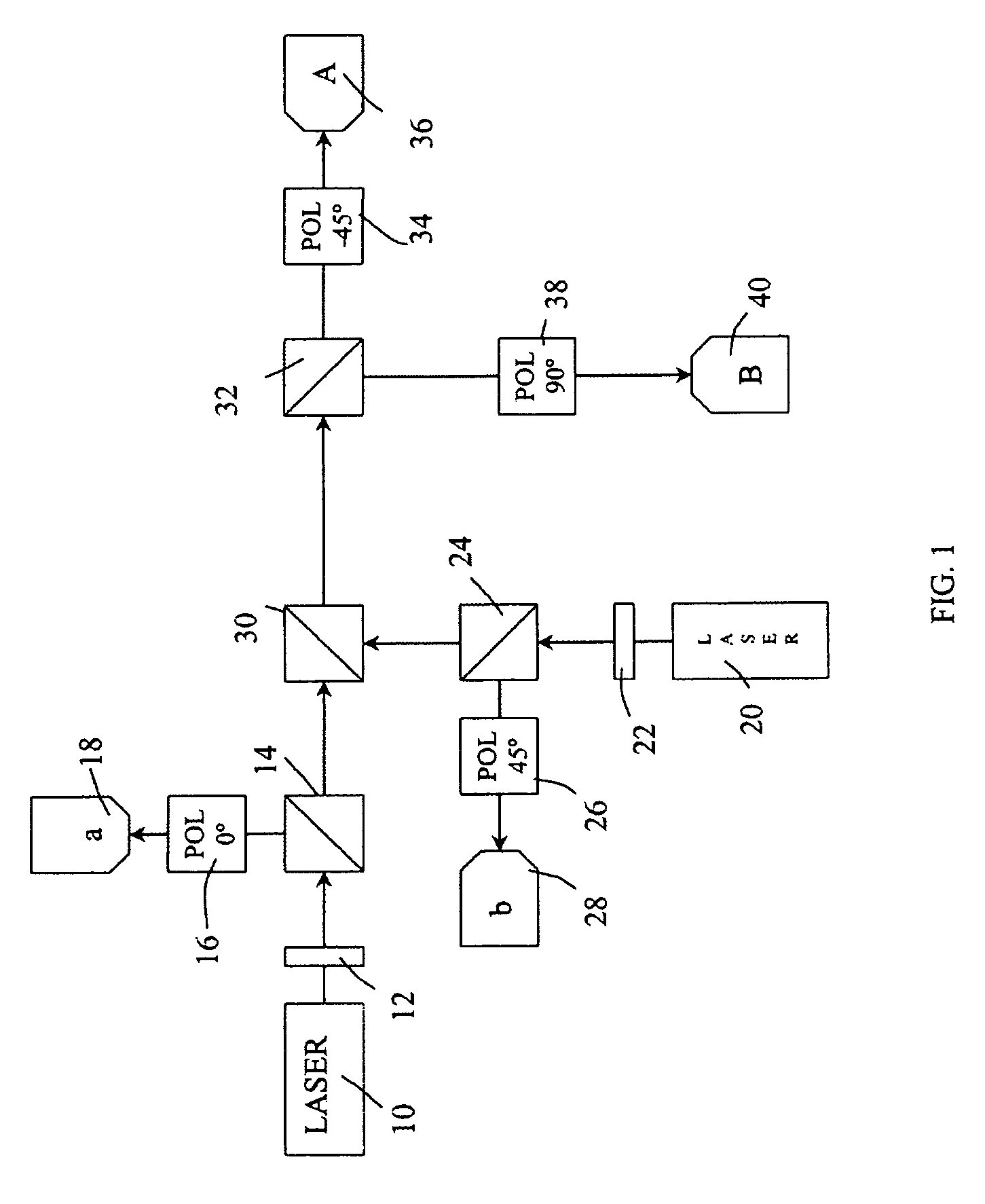
Entangled quantum communications and quantum imaging
InactiveUS7536012B1Synchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesComputer hardwareSecure communication
An apparatus for generating a shared quantum key between a sender and a receiver comprises a sending apparatus which generates entangled photon pairs, and a receiving apparatus. A shared quantum key can be generated using temporal coincidences between photon detection events. For example, coincidences may be determined between sender and receiver photon detection events using detection data shared through a non-secure communications link between the sender and receiver. The quantum key can be used in encrypted communications. Similar apparatus and methods can be used for quantum imaging.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE THE
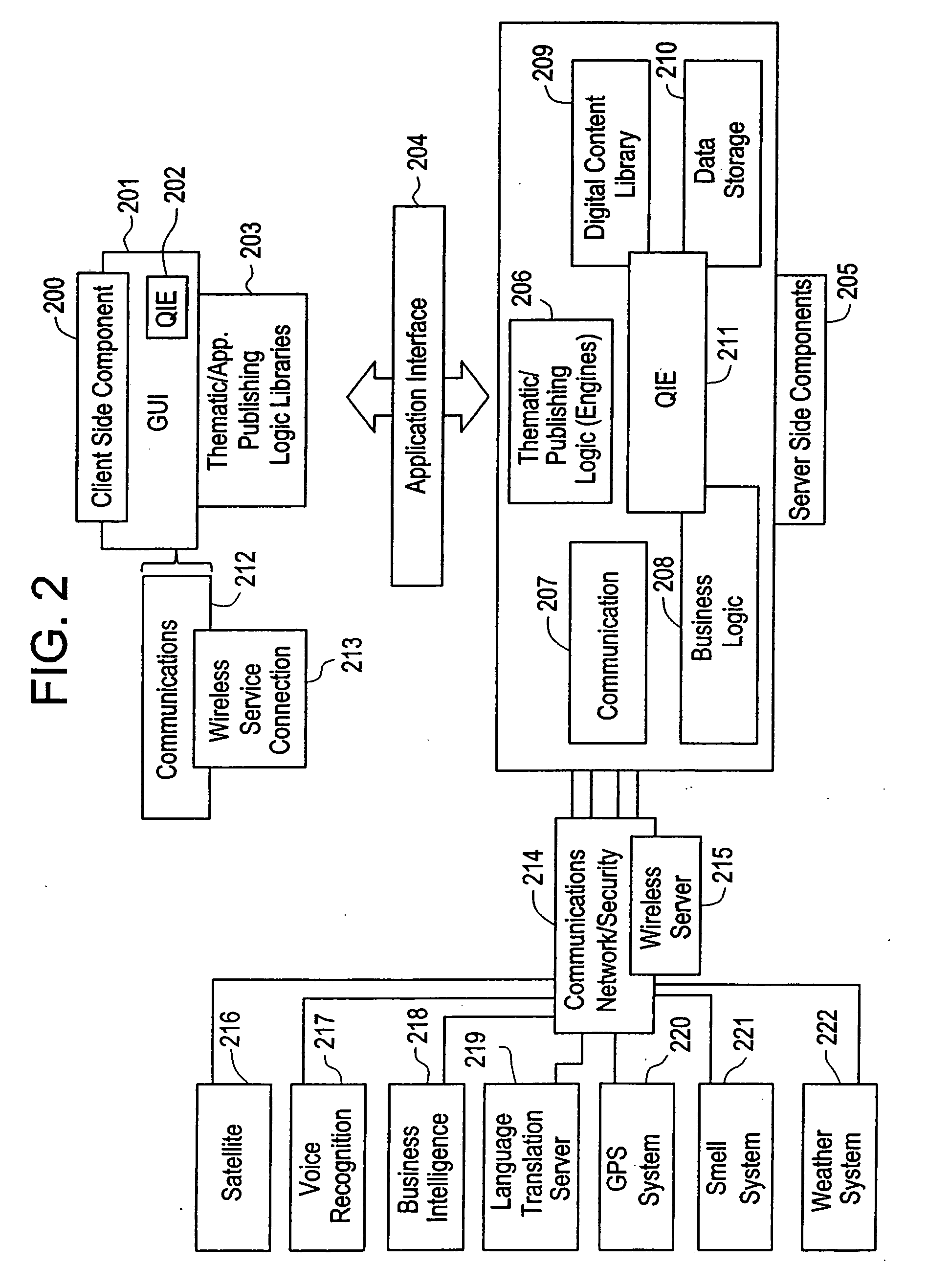
Interactive virtual thematic environment
The present invention is directed to a method of integrating information, including real-time information, into a virtual thematic environment using a computer system, including accessing the stored information from a database or downloading the real-time information from a source external to the thematic environment; inserting the real-time information into the thematic environment; and displaying the information to a user within the thematic environment. In one embodiment, the computer system is connected to a holographic projection system such that the images from the thematic environment can be projected as holographic projections. The computer system includes an interactive software application platform having at least one thematic / publishing logic module which contains thematic environment rules; at least one digital content library module which provides content management on the thematic environment; and at least one quantum imaging environment (QIE) module which interprets content such that the content is manipulated and accessed by any device.
Owner:QUANTUM IMAGING LLC
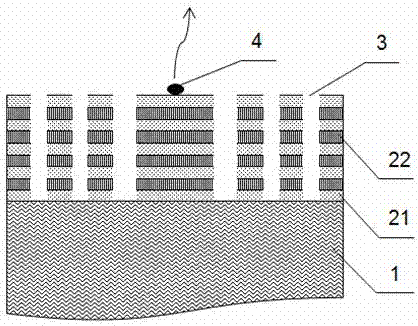
Hyperbolic metamaterial composite grating-enhanced high-frequency quantum-dot single photon source
ActiveCN107452844AIncrease spawn rateImprove production efficiencySemiconductor devicesGratingParticle physics
The invention discloses a hyperbolic metamaterial composite grating-enhanced high-frequency quantum-dot single photon source. The hyperbolic metamaterial composite grating-enhanced high-frequency quantum-dot single photon source comprises a substrate, a hyperbolic metamaterial and quantum dots, wherein a grating microstructure is arranged on a surface of the hyperbolic metamaterial or in the hyperbolic metamaterial, the hyperbolic metamaterial is of a one-dimensional periodic structure formed by alternatively arranging dielectric thin films and metal thin films or the dielectric thin films and metal-like thin films, and the quantum dots are arranged in the one-dimensional periodic structure or a near field of the hyperbolic metamaterial. Spontaneous radiation enhancement of wideband of the quantum dots is achieved by the hyperbolic metamaterial, the light emergent efficiency is improved by simultaneously combining directional coupling output characteristic of the grating, the photon generation ratio and the collection and utilization ratio of the quantum-dot single photon source are greatly improved, and the high-frequency, high-brightness and directional-emission quantum-dot single photon source of GHz or above can be achieved; and meanwhile, two excitation modes of optical pumping and electric pumping are compatible, and the quantum-dot single photon source is suitable for various wave bands to an infrared band from an ultraviolet band and can be widely applied to related fields of quantum information, quantum computation, quantum imaging, quantum authentication and quantum precision measurement.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS ENG CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
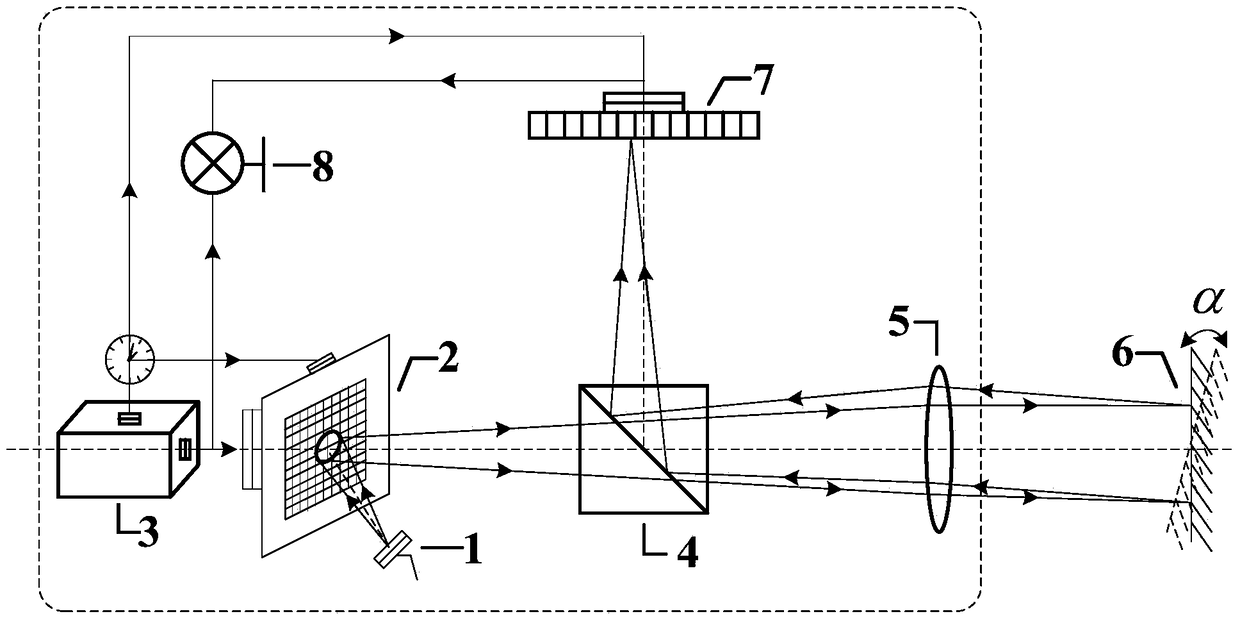
Laser radar based on highly-correlated quantum imaging principle
InactiveCN101846745AReduce lossRealize ultra-long-distance detectionElectromagnetic wave reradiationTime delaysDistance detection
The invention discloses laser radar based on a highly-correlated quantum imaging principle, which consists of a pulse laser, a parameter down-conversion non-linear device, a receiving lens, a photon detector, an imaging lens, an area-array detector, a time delay correlator and a signal processor. The pulse laser transmits laser pulse to generate two laser beams having different wavelengths and the highly correlation by parameter down-conversion non-linear device, one path of laser beam with long wavelength is irradiated on a measured object and is focused on a photon detector through a receiving lens to detector after being reflected, and a switch signal indicative of the detecting result of the photon is output; the other path of laser beam with short wavelength is irradiated to the area-array detector through an imaging lens to acquire a two-dimension photon image signal; and two paths of signals are correlated and integrated by the signal processor to acquire image and distance information of the measured object. The laser radar effectively solves the problem of transmission loss by using the laser with the long wavelength in an atmosphere window to realize the ultra-long distance detection and realize the super-resolution detection by using the highly-correction effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
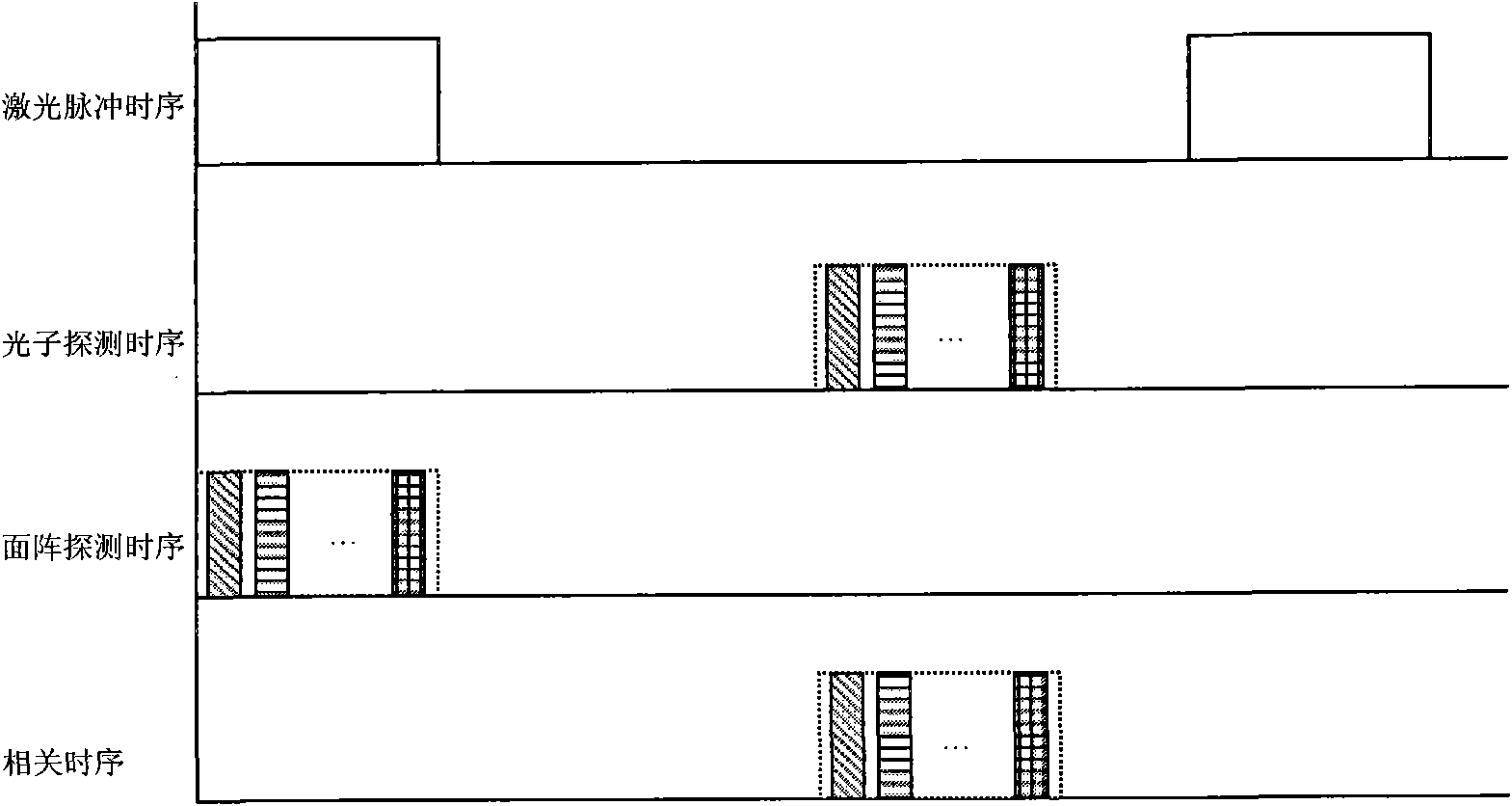
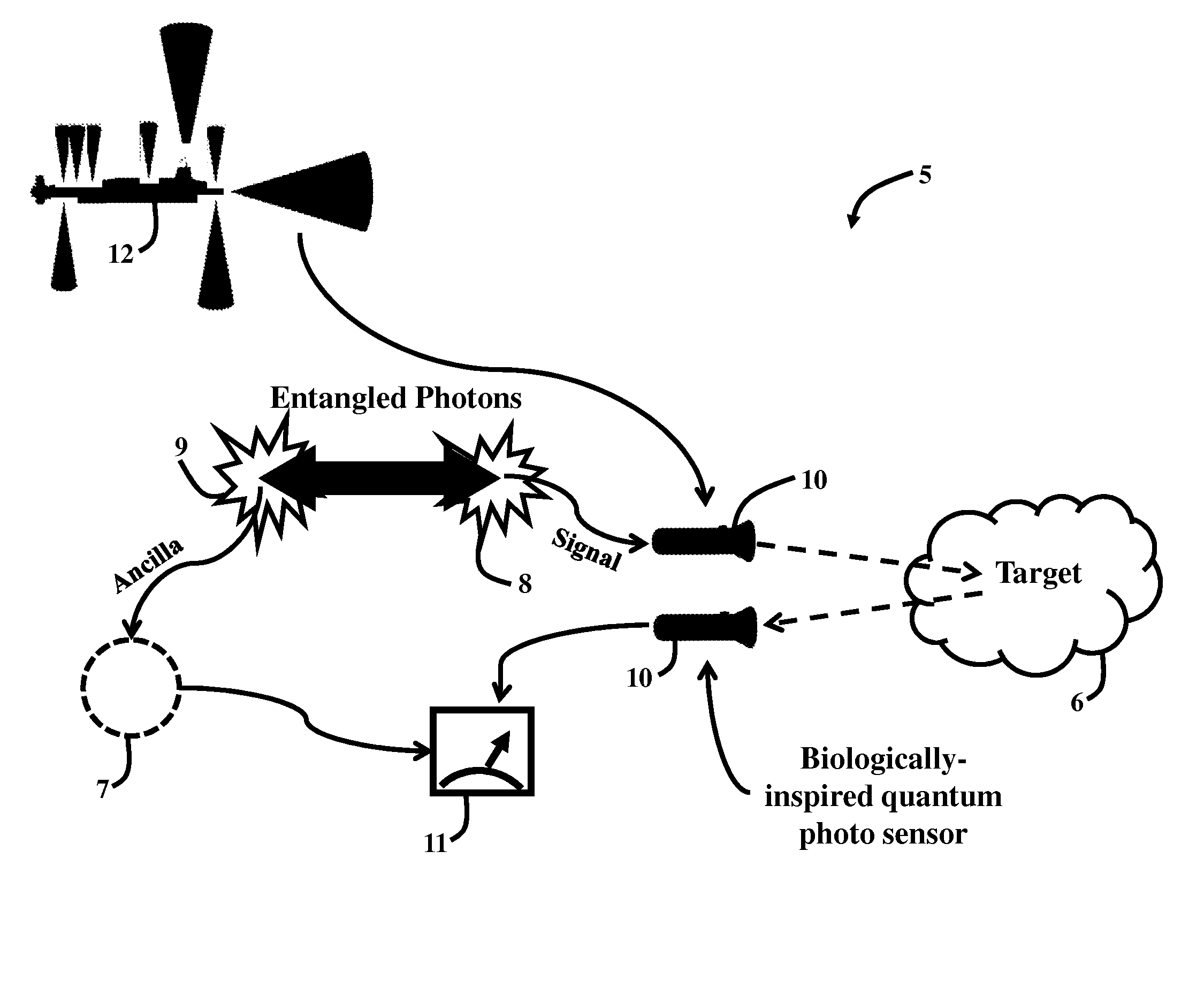
Quantum Imaging for Underwater Arctic Navigation
ActiveUS20160018525A1Optical rangefindersNavigational calculation instrumentsEnvironmental noisePhotonics
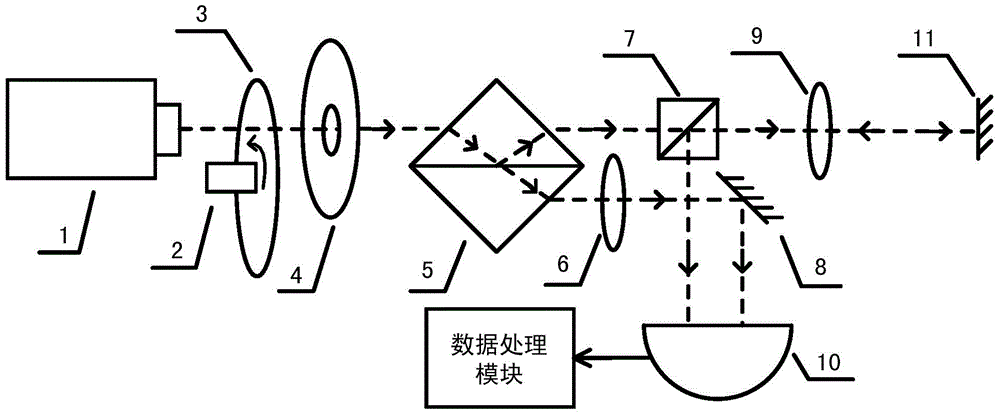
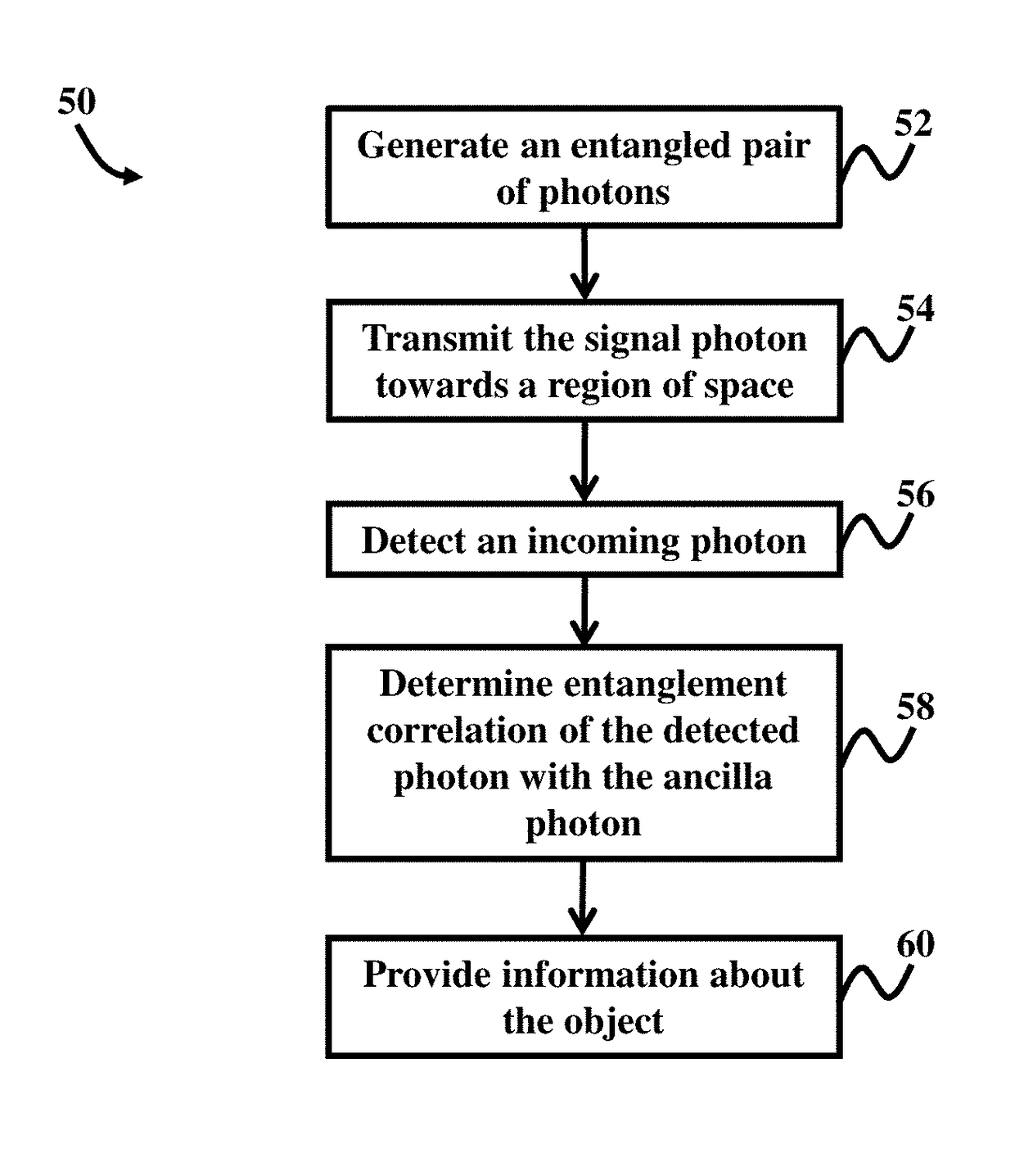
A quantum photonic imaging device used in an underwater vehicle for stealthy detection of underwater objects includes a photon generating module that generates an entangled pair of photons that includes a signal photon and an ancilla photon, wherein the ancilla photon is retained within the device; a transmitter that transmits the signal photon towards a region of space for detecting an underwater object; a receiver that detects an incoming photon to the device; and a correlation module that distinguishes the signal photon that is reflected back to the receiver due to a presence of the object from environmental noise photons, wherein the distinguishing includes determining an entanglement correlation of the detected photon with the ancilla photon, and wherein a presence of the entanglement correlation between the detected photon and the ancilla photon indicates that the detected photon is the signal photon reflected back from the object.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
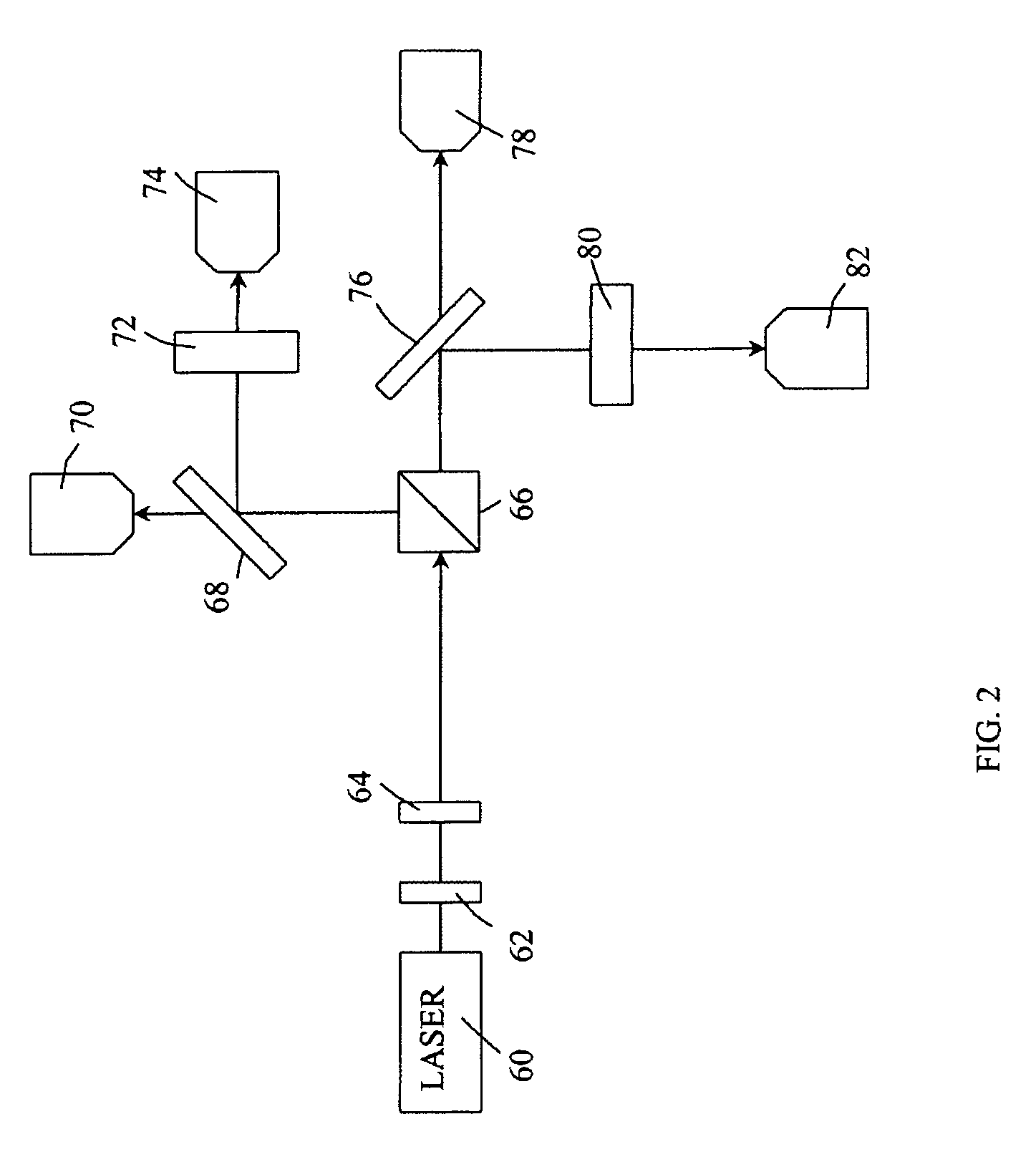
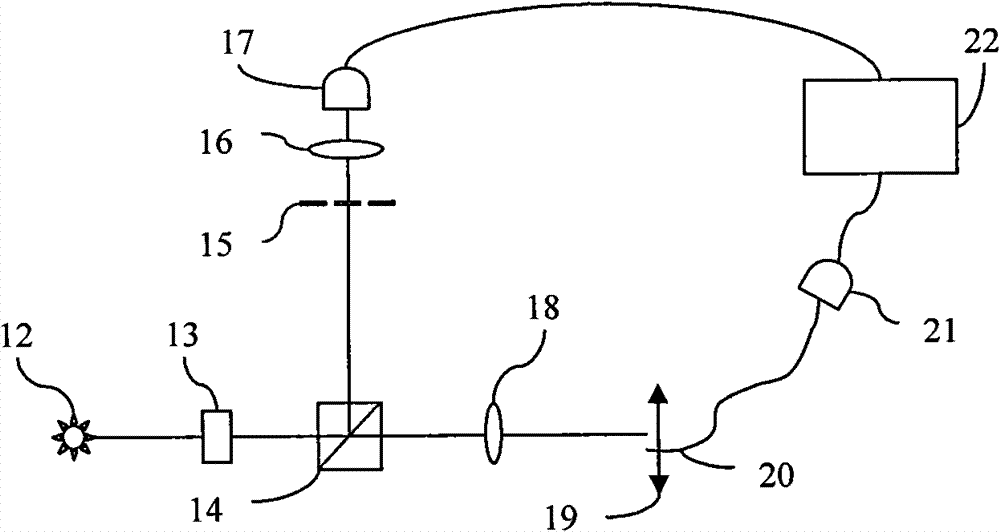
Calculated intensity correlated imaging autocollimator and measurement method
Disclosed are a calculated intensity correlated imaging autocollimator and a measurement method. The calculated intensity correlated imaging autocollimator comprises a light source, a digital micromirror device (DMD), a controller, a beam splitter, a lens, a device-under-test (DUT) reflective mirror, a CCD and an intensity correlated calculation module. A synchronous control module of the controller generates a synchronous clock signal which is applied to the DMD and the CCD. The intensity correlated calculation module records a light field modulation matrix generated by a light field modulation module and an echo signal received by the CCD simultaneously, and performs second-order intensity correlated calculation to indirectly calculate a tiny rotation angle of the DUT. The invention introduces a calculated correlated imaging method in quantum imaging technology to the design of the autocollimator, and can be used for effectively reducing the measurement errors caused by air turbulence and other factors and improving the sensitivity and stability of a system.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Quantum-imaging system and mode of operation and method of fabrication thereof
ActiveUS7781739B1Quality improvementIncrease catch rateElectric discharge tubesPhotometryOperation modeSpectrometer
A quantum-imaging system for detecting photons, including short-wavelength (<1 nm) photons, is provided. A quantum imaging system can include optical read-out and optical means, and can be configured to perform as both a photon counter and a photon spectrometer. A quantum-imaging system can function as a photon counter and be configured to measure photon beam fluences (e.g., in J / cm2) for both strong beams and weak beams, the latter ones, for example, in the intensity range of 1 pJ / cm2sec, or 0.1 μSv / h. The quantum-imaging system can also function as a photon spectrometer and can be configured to measure photon energies with high energy resolution such as, for example, 1% of photon energy.
Owner:MERCURY MISSION SYST LLC
Aircraft forecast guidance scheme based on quantum imaging
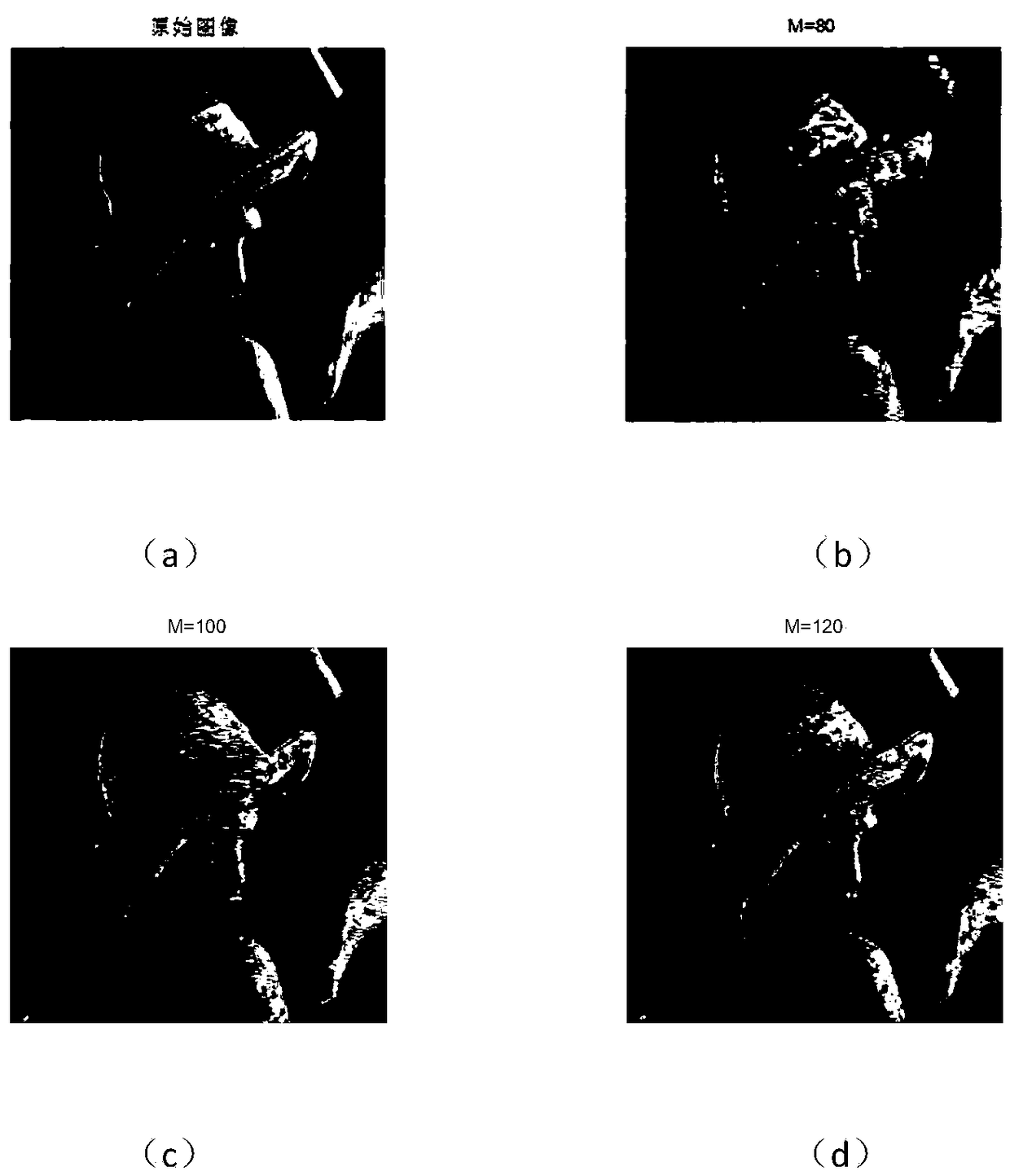
ActiveCN104063623AImprove anti-interference abilityAdd dimensionTarget-seeking controlSpecial data processing applicationsFlight vehicleImage resolution
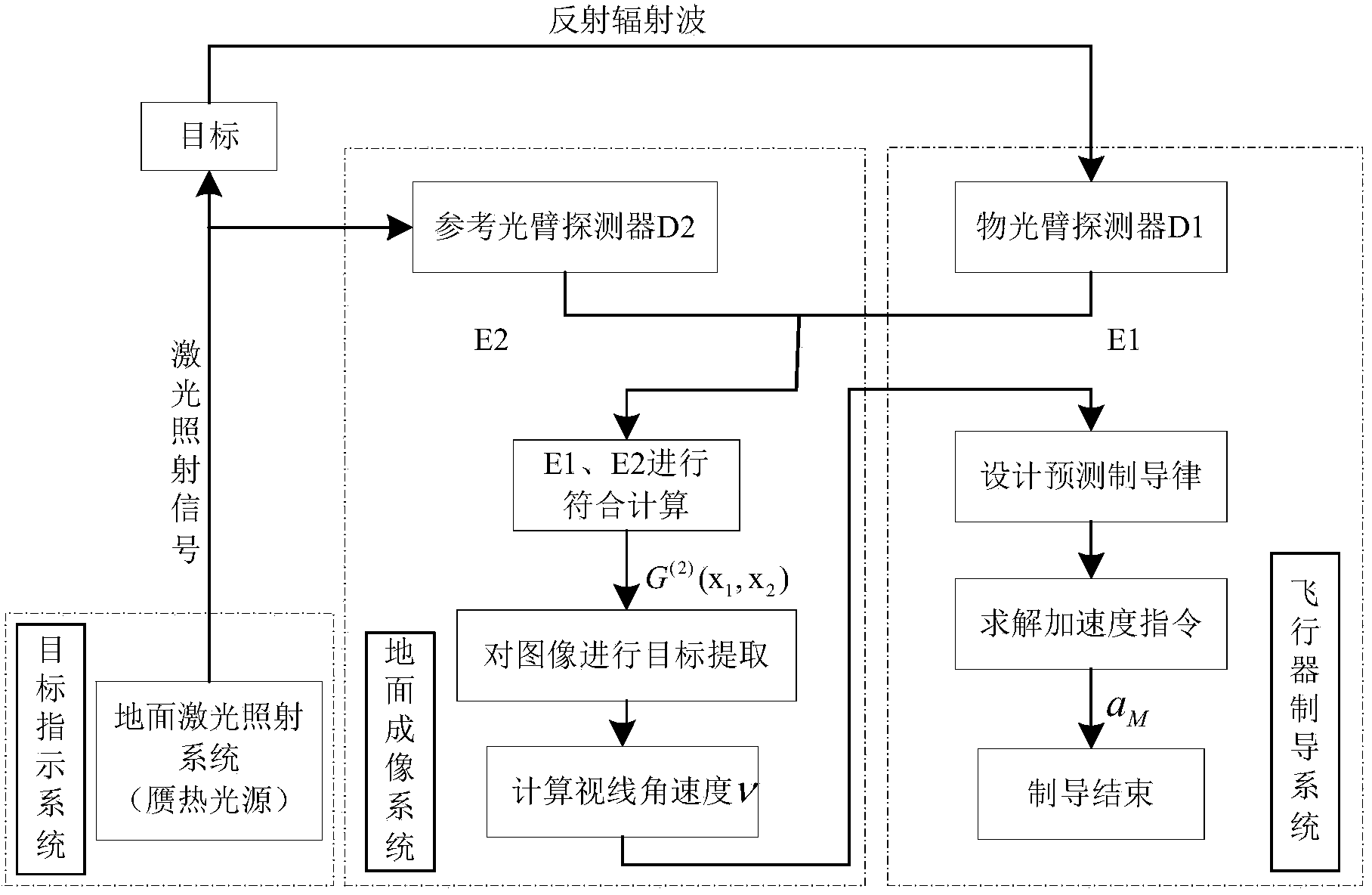
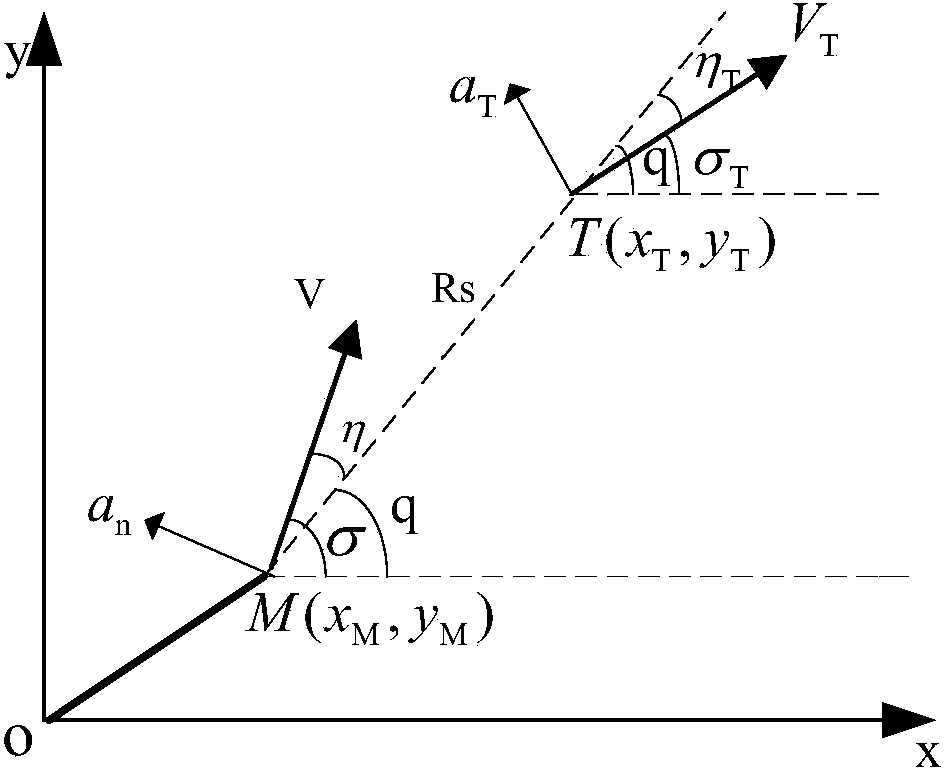
The invention relates to the field of the guidance technology based on optical imaging, in particular to an aircraft forecast guidance scheme based on quantum imaging. At preset, two main factors restricting guidance accuracy of an aircraft are that target detection resolution ratio is not high and affected by scattering particles easily, and imaging is difficult under extremely weak light; maneuvering targets cannot be tracked and guided quickly. According to the aircraft forecast guidance scheme based on quantum imaging, correlated imaging is performed by recording distribution strength of a radiation field and space fluctuation of a phase, and therefore, imaging resolution ratio is increased. However, the updating rate of measured data obtained from images is not high, so that a forecast guidance rule is adopted to overcome the shortcoming that guidance accuracy of the aircraft decreases due to low data updating rate of quantum imaging. By means of the aircraft forecast guidance scheme based on quantum imaging, quantum imaging can break up limitation of a diffraction limit, the resolution ratio can reach micron dimension, and guidance on the maneuvering targets can be improved by combining the forecast guidance rule. Therefore, the aircraft forecast guidance scheme based on quantum imaging is high in accuracy, strong in antijamming capability and suitable for guiding the aircraft to track the maneuvering targets.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Quantum imaging with undetected photons
ActiveUS20150177128A1Simple methodRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectroscopyLength wave
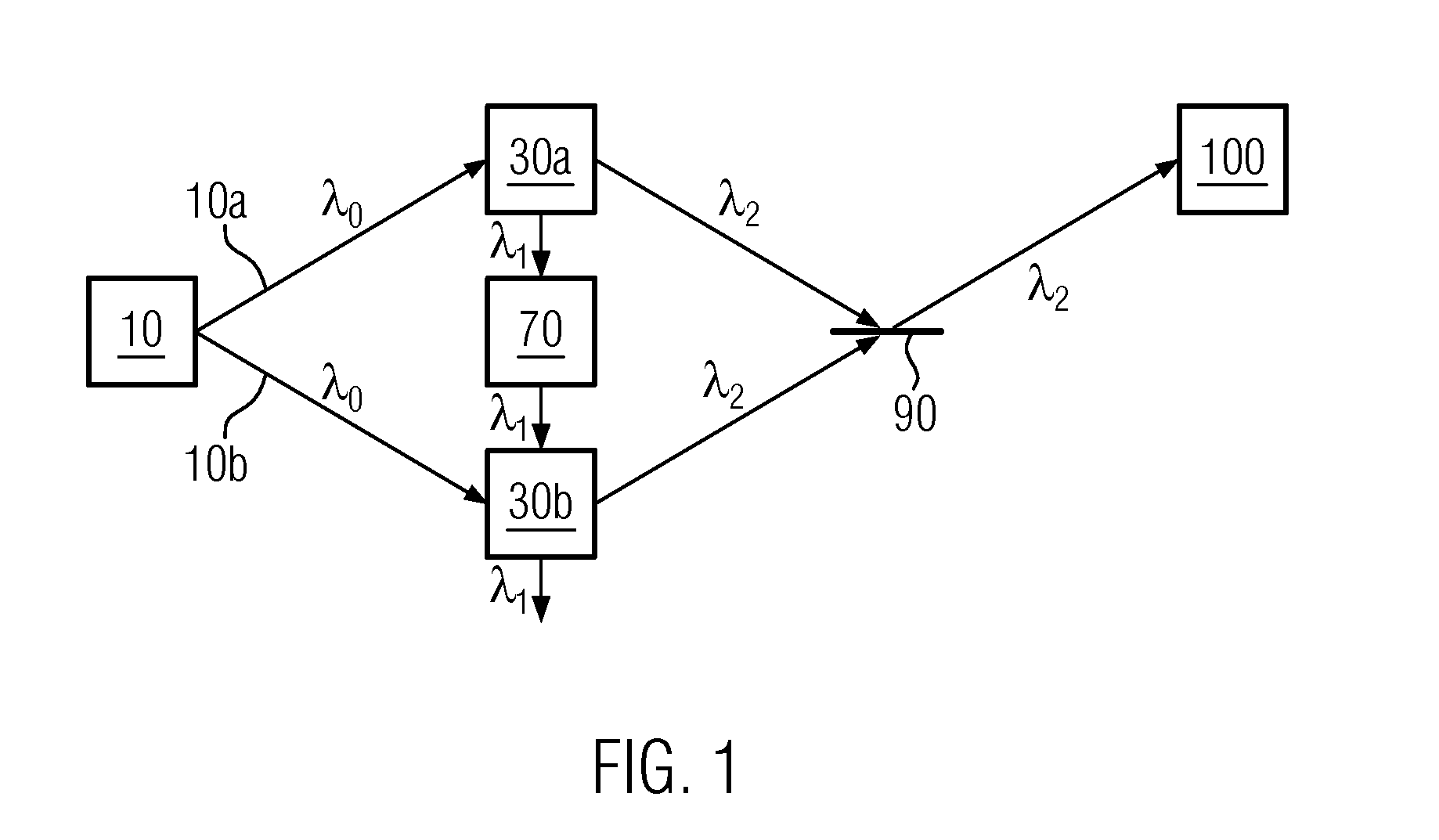
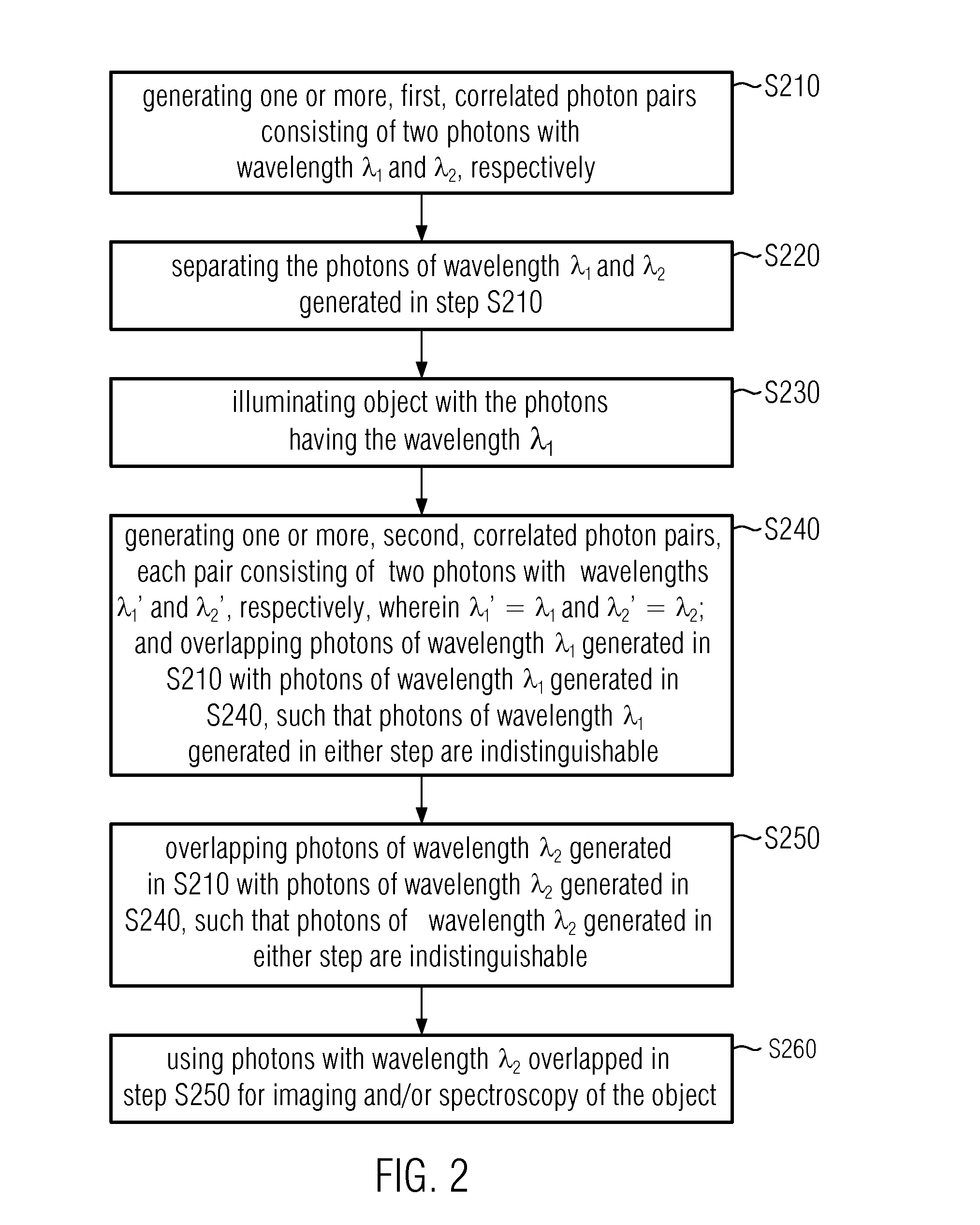
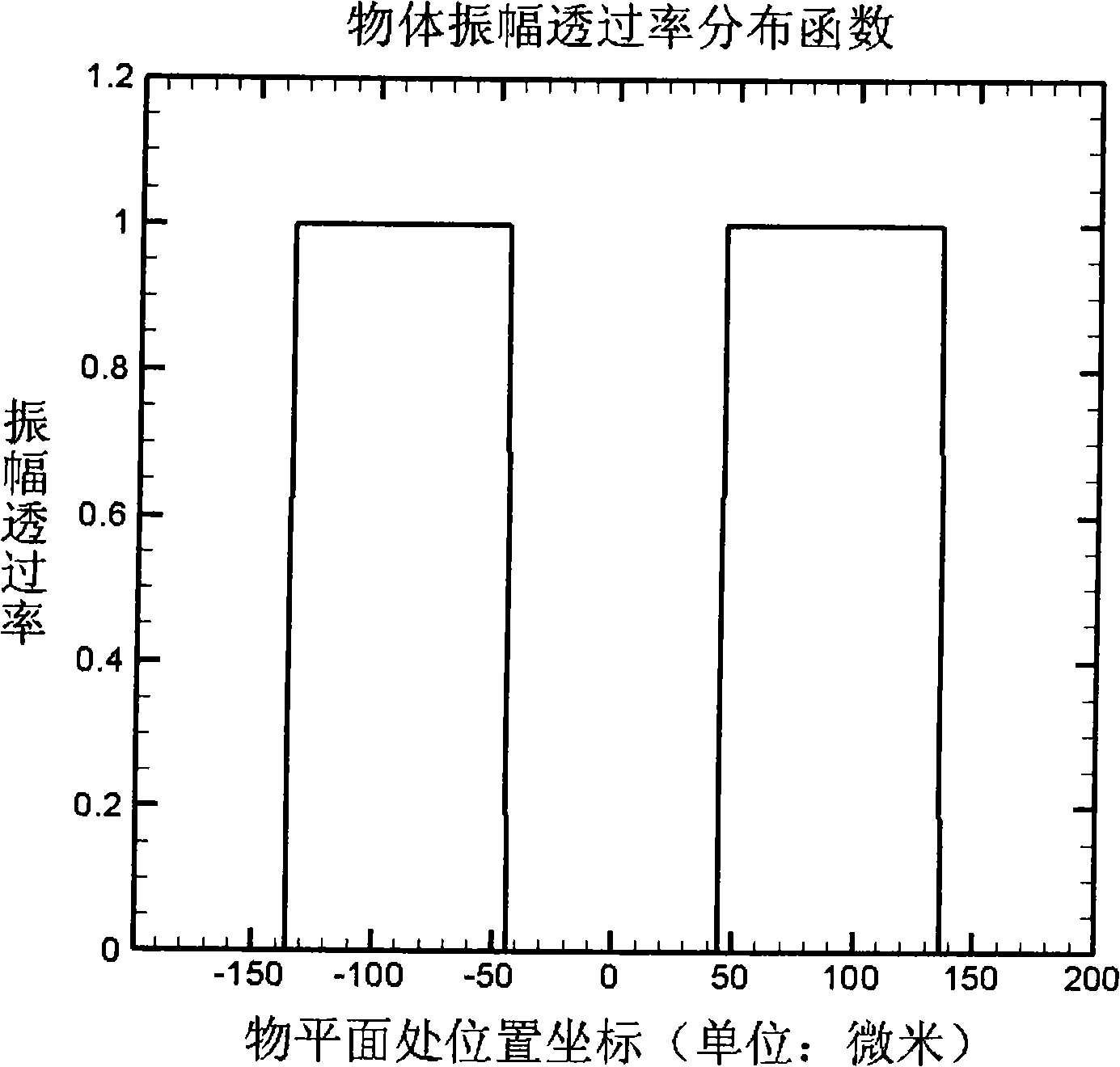
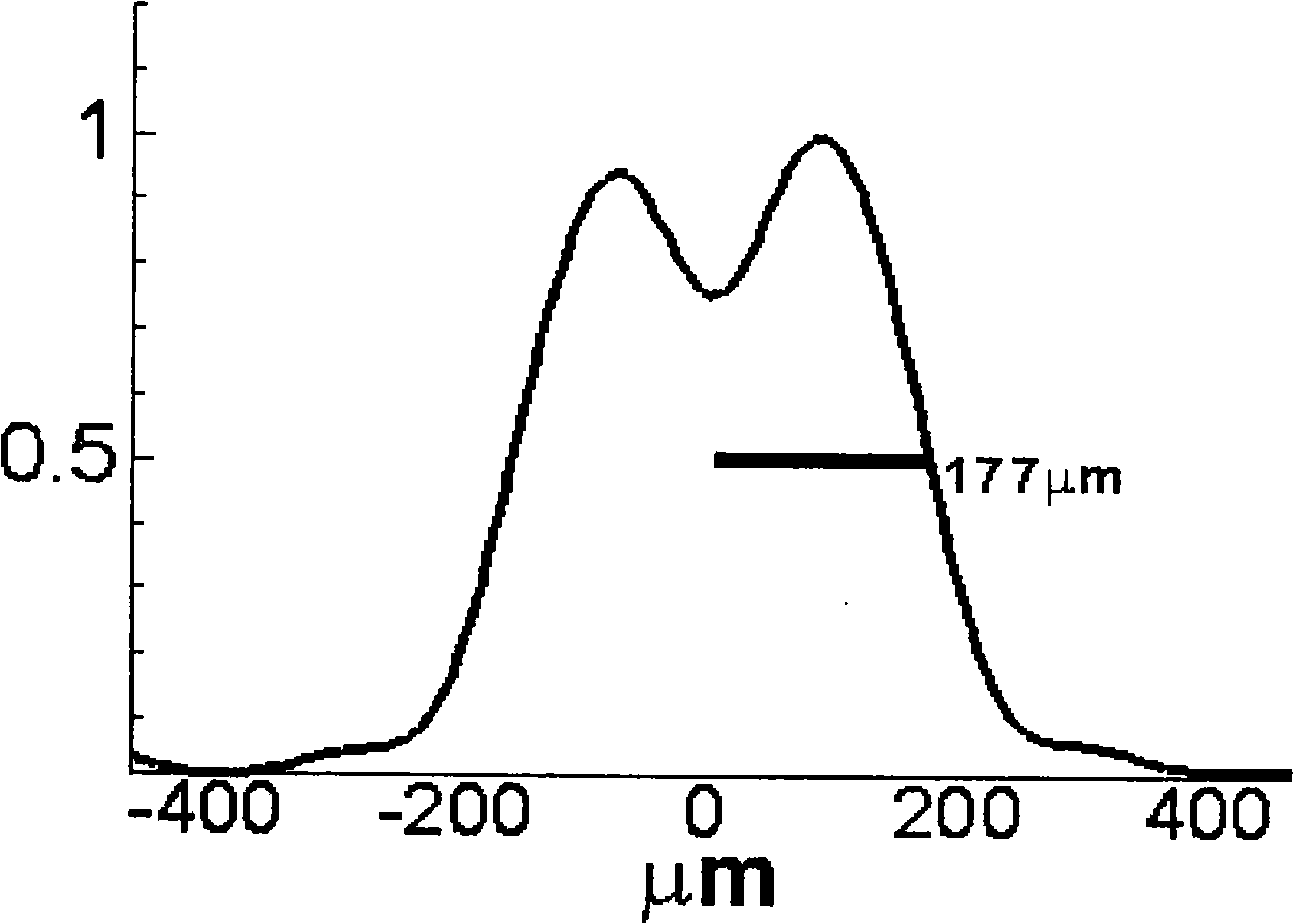
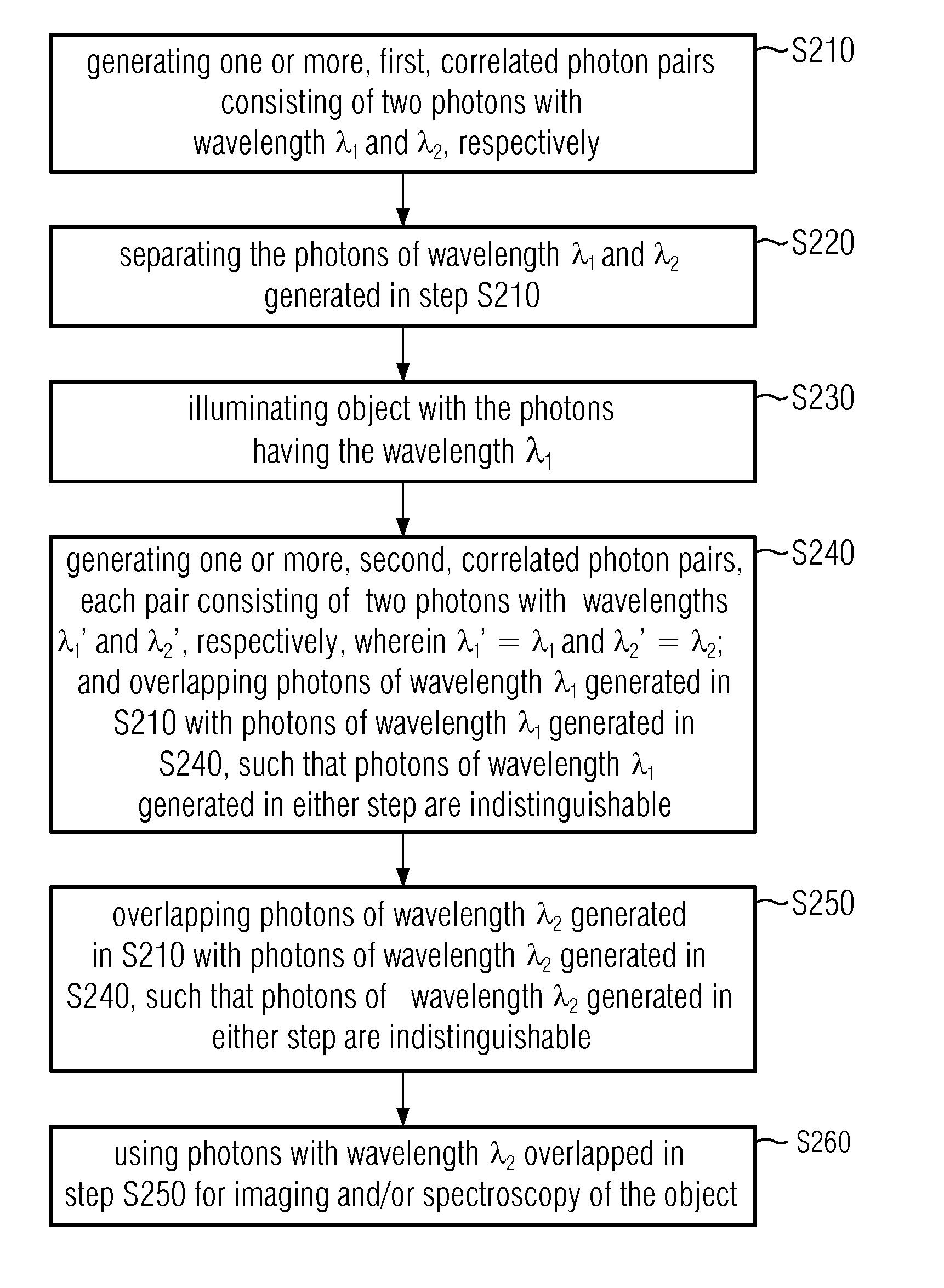
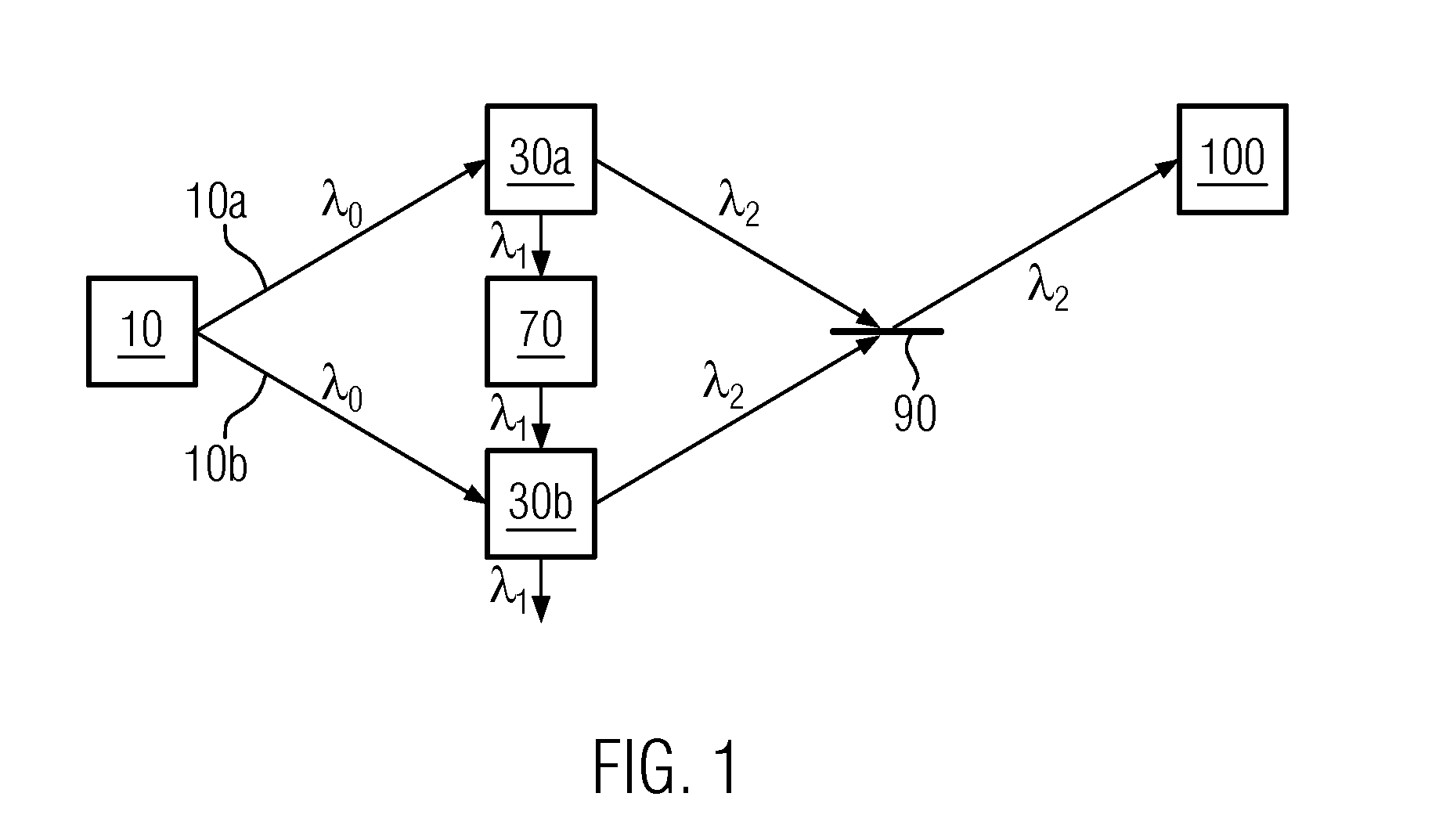
A method comprises: generating a first and a second correlated photon beam with wavelengths λ1 and λ2, respectively, wherein preferably λ1≠λ2; separating the first photon beam and the second photon beam; illuminating an object with the first photon beam; generating a third and a fourth correlated photon beam with wavelength λ1 and wavelength λ2, respectively; overlapping the first photon beam with the third photon beam such that photons of wavelength λ1 in either photon beam are indistinguishable; overlapping the second photon beam with the fourth photon beam such that photons of wavelength λ2 in either photon beam are indistinguishable; and using the overlapped photons of wavelength λ2 for imaging and / or spectroscopy of the object such that the photons that illuminate the object are not detected.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VIENNA +1
Single-pixel star sensor and target star sky detection method thereof
ActiveCN104567870AImproved low light detection capabilityHigh detection sensitivityNavigation by astronomical meansSpatial light modulatorPhoton detection
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Strength relating quantum imaging microscope
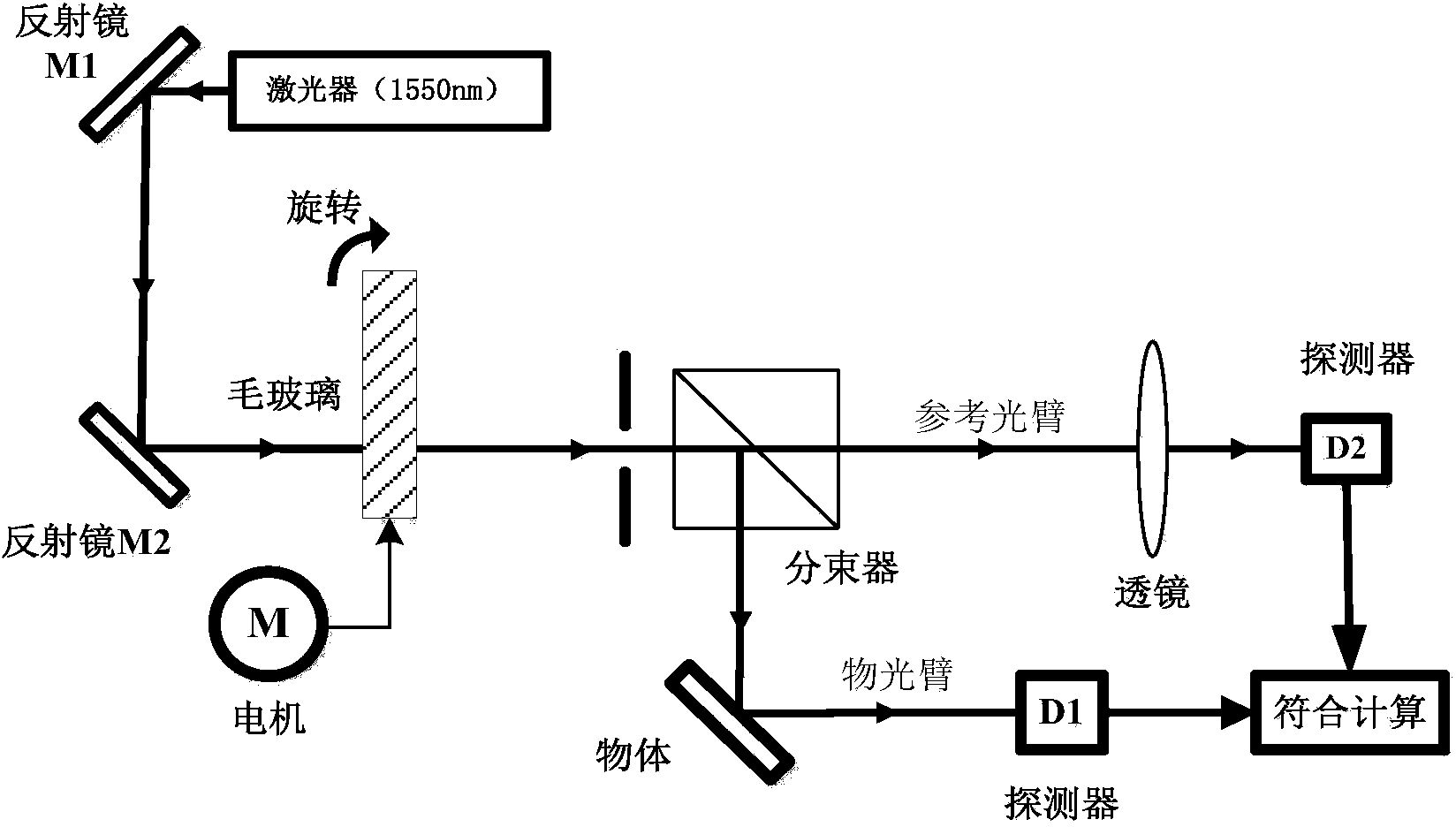
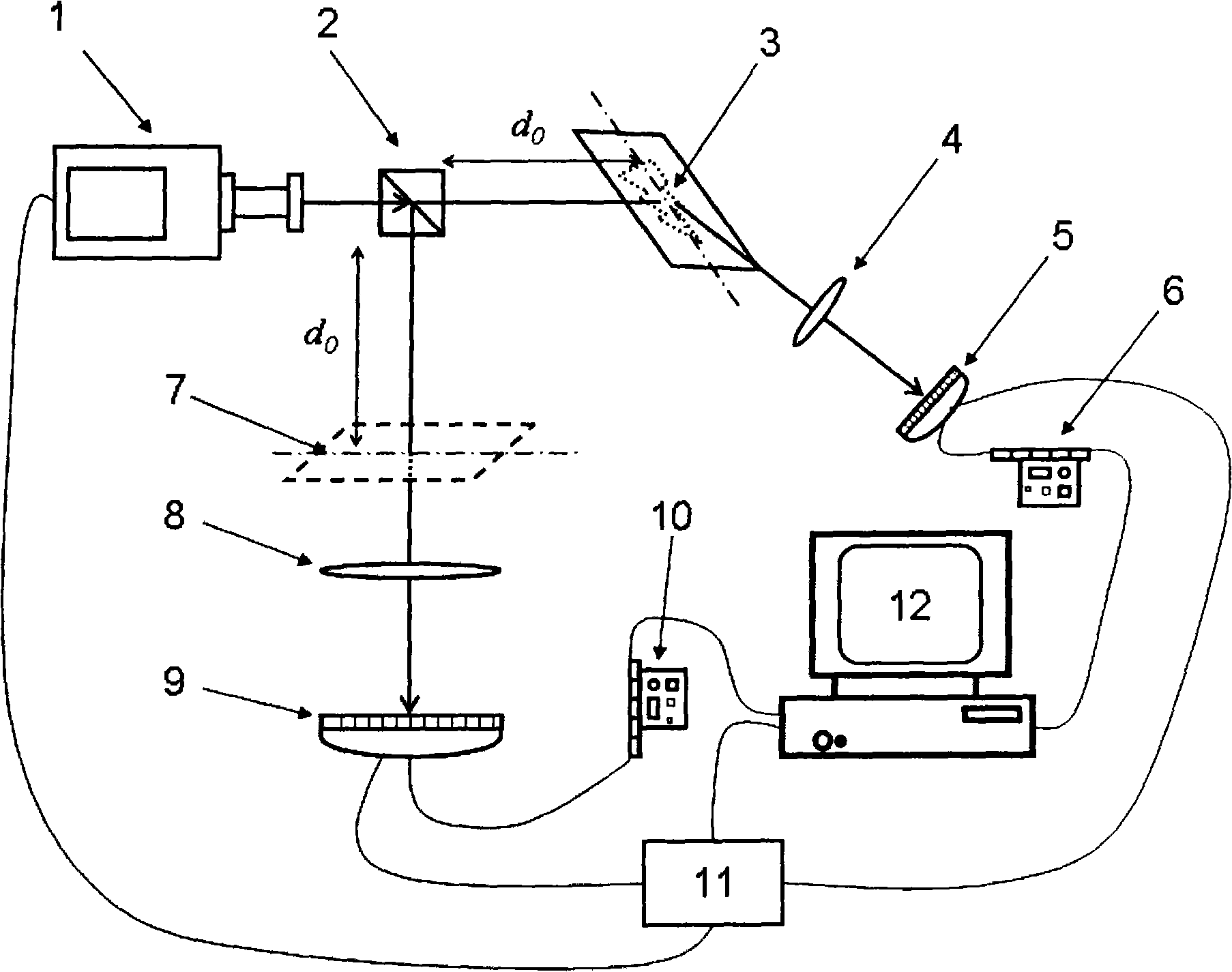
InactiveCN101281292AIncrease the effective numerical apertureHigh-resolutionSurgeryMicroscopesBeam splitterData acquisition
A strength related quantum imaging microscope is characterized by including a pulsed light source. The light beams generated by the pulse light source are divided into transmission light beams and reflectance light beams by a beam splitter; an object to be measured, an object arm imaging lens and an object arm detector are arranged in sequence at the transmission light beam direction to constitute an object arm, a virtual plane, a reference arm imaging lens and a reference arm detector are arranged in sequence at the reflection light beam direction to constitute a reference arm; the object arm detector and the reference arm detector are respectively connected to the computer through a first data acquisition card and a second data acquisition card, the computer is provided with a strength related arithmetic software, the computer is respectively connected to the pulse light source, the object arm detector and the reference arm detector through a synchronizing signal generator, and the reference arm imaging lens is provided with high numerical aperture. The invention can obtain a high resolutions image by increasing the numerical aperture of the reference arm imaging lens.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compressed sensing imaging device and method based on entangled two-photon signal
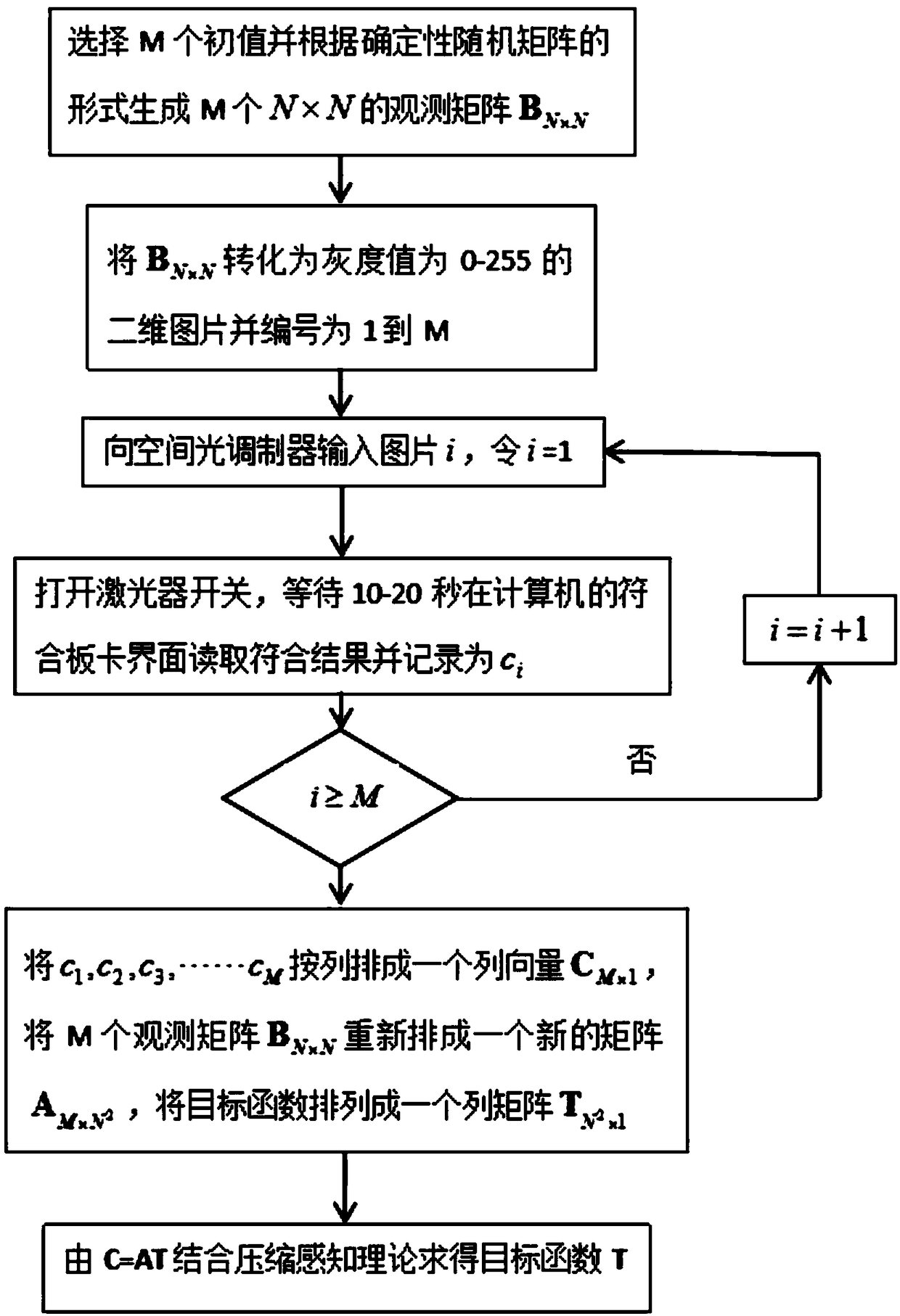
ActiveCN108844464AReduce storagePromote recoveryImage enhancementUsing optical meansSpatial light modulatorImaging quality
The invention discloses a compressed sensing imaging device and method based on an entangled two-photon signal, and solves the problem of not high imaging quality under the condition of low sampling number. According to the method, a deterministic determinacy random matrix is loaded in a spatial light modulator of an original quantum imaging device to complete imaging of a target object; and during preparation of entangled light, a telescoping system and a 0-degree incident heat mirror and a low-pass narrow-band filter which are placed along a laser transmission direction among the telescopingsystem are adopted to process laser. The imaging method includes producing a picture for being input to a spatial light modulator; inputting the picture to the spatial light modulator; preparing entangled light; obtaining a matched result value; loading a plurality of sets of modulated observation matrices and obtaining M matched results; constructing a quantum imaging mathematical model; and adopting a compressed sensing algorithm to solve a quantum imaging relational expression to restore an image of the target object. The entangled light prepared by the compressed sensing imaging device and method provided by the invention is high in purity and can well restore the image of the target object under the condition of a low sampling rate.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Intensity-correlation star sensor
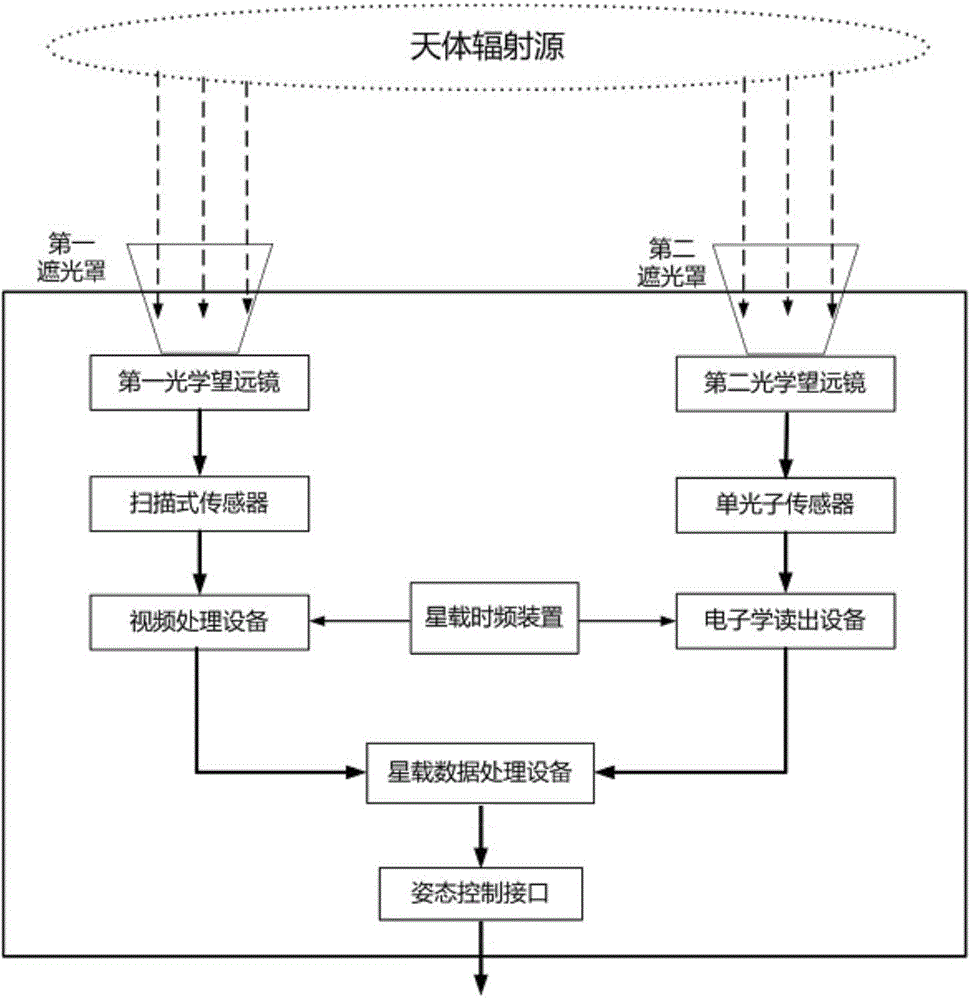
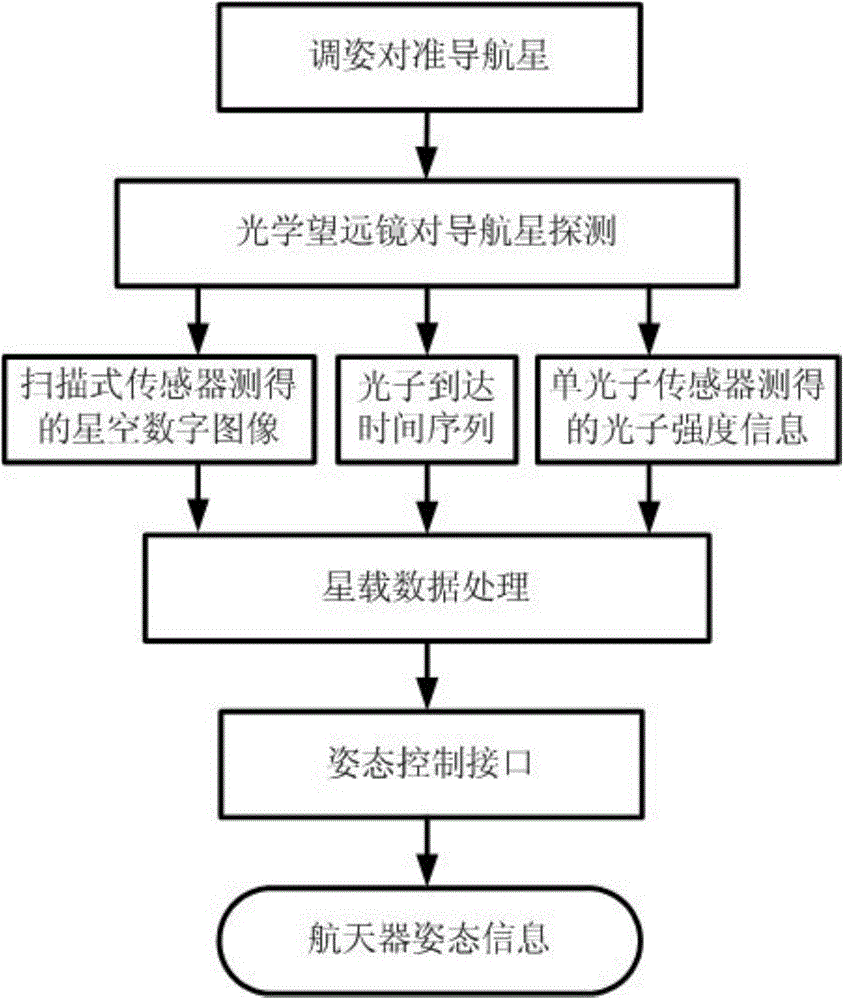
ActiveCN104316046AEasy to implementHigh detection sensitivityNavigation by astronomical meansPhotonic sensorVIT signals
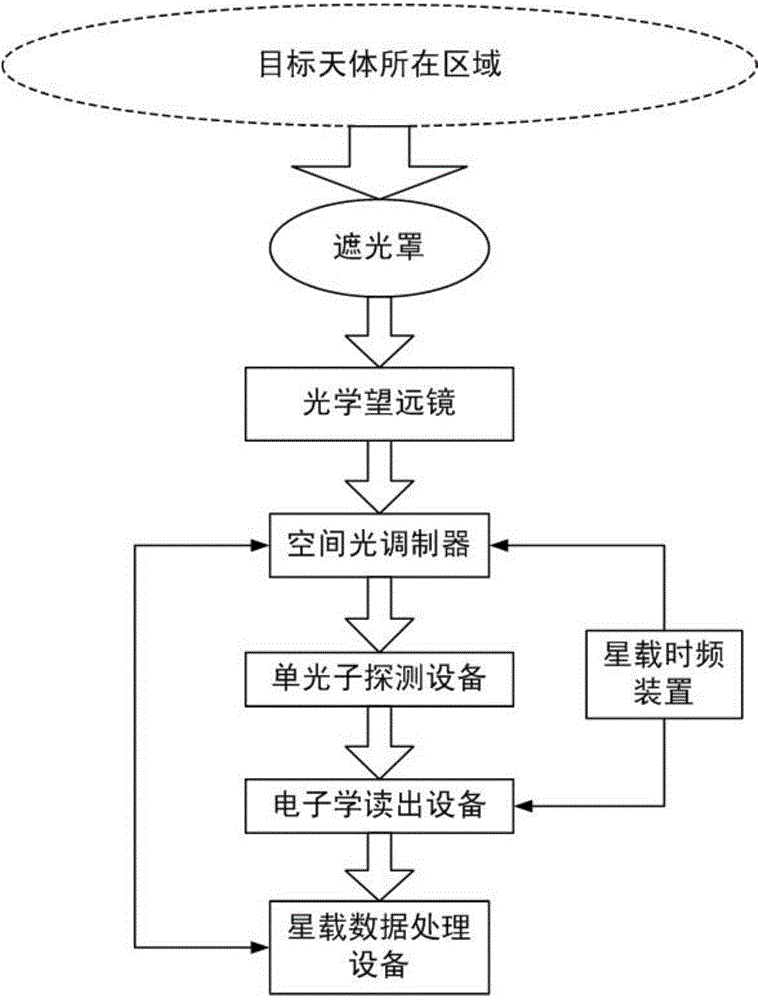
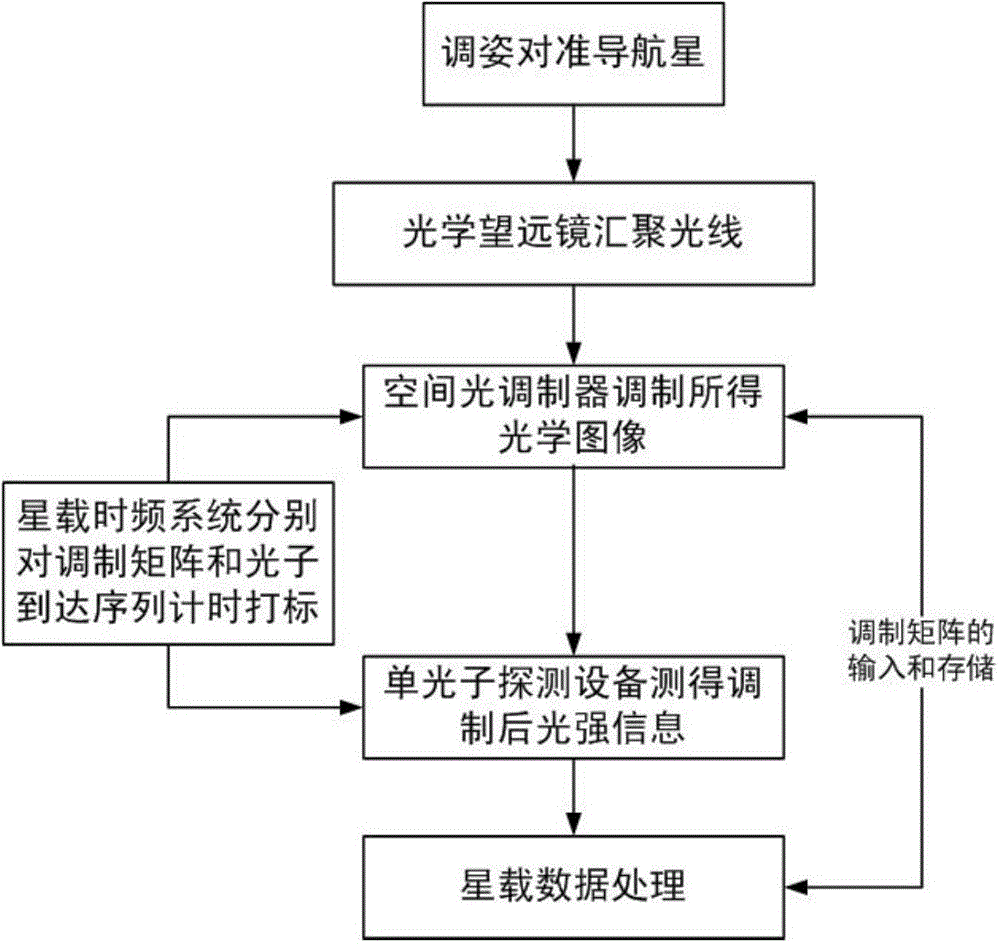
The invention provides an intensity-correlation star sensor which comprises a first lens hood, a second lens hood, a first optical telescope, a second optical telescope, a scanning type sensor, a single photon sensor, electronics read-out equipment, video processing equipment, a satellite-borne time-frequency device, satellite-borne data processing equipment and an interface. By using detection signals of two paths of optical detection systems, the obtained two paths of electric signals are subjected to time synchronization by using the satellite-borne time-frequency device, and are subjected to intensity-correlation signal processing in the satellite-borne data processing equipment. Therefore, on the basis of keeping an integral appearance shape of an optical system of an original star sensor unchangeable, an internal structure is locally regulated, and the engineering realization is easy. The starry sky is imaged by using an intensity-correlation method in a quantum imaging technology, and is searched by using the scanning type sensor; the single photon is used in the other path, relatively dark star bodies are relatively easily detected, and the detection sensitivity is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Steady quantum sparse imaging system and method
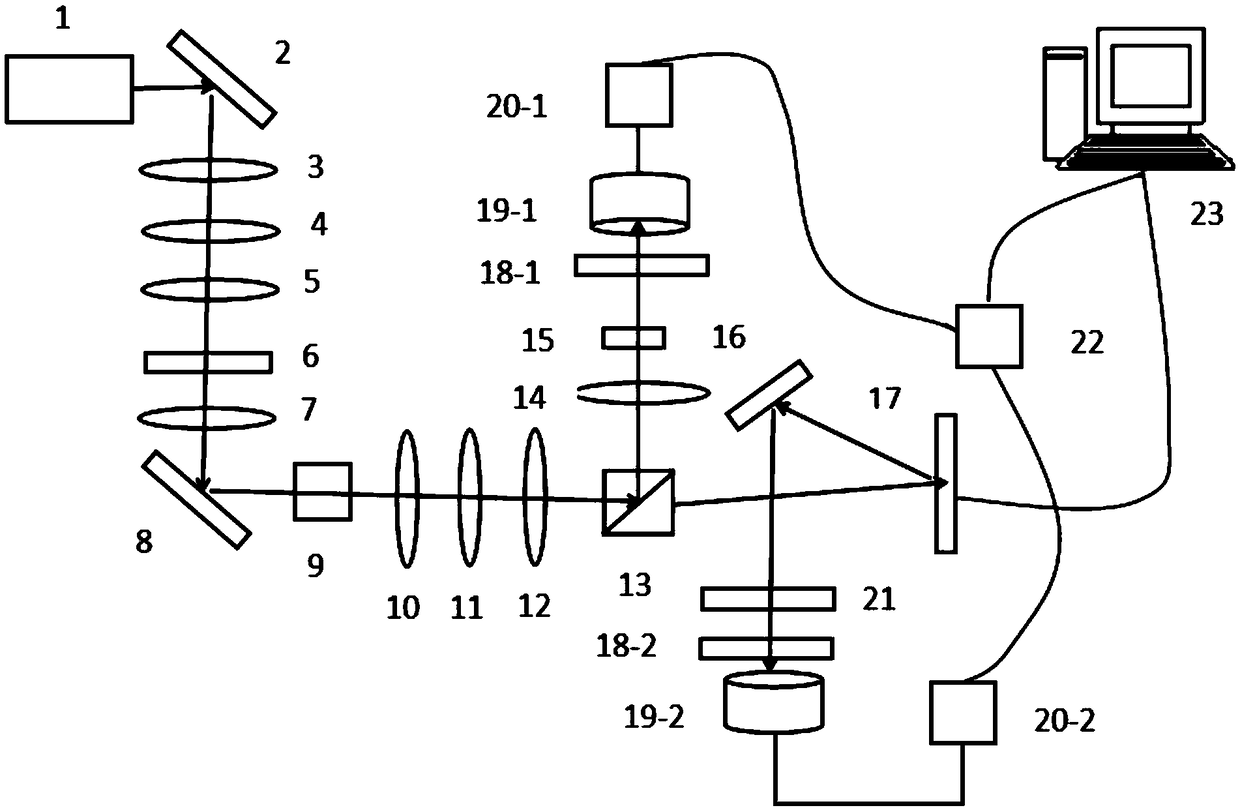
ActiveCN109115681AReduce mean square errorImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioColor/spectral properties measurementsBeam splitterTime correlation
The invention belongs to the technical field of quantum imaging, and discloses a steady quantum sparse imaging system and a method. The system comprises a laser, a half-wave plate, BBO (Barium Boron Oxide) crystal, a first focusing lens, a beam splitter, a second focusing lens, a spatial light modulator, a first single photon detector, a second single photon detector, a time correlation single photon counting card and a computer. Under the situation of interference and system errors, imaging robustness can be guaranteed.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
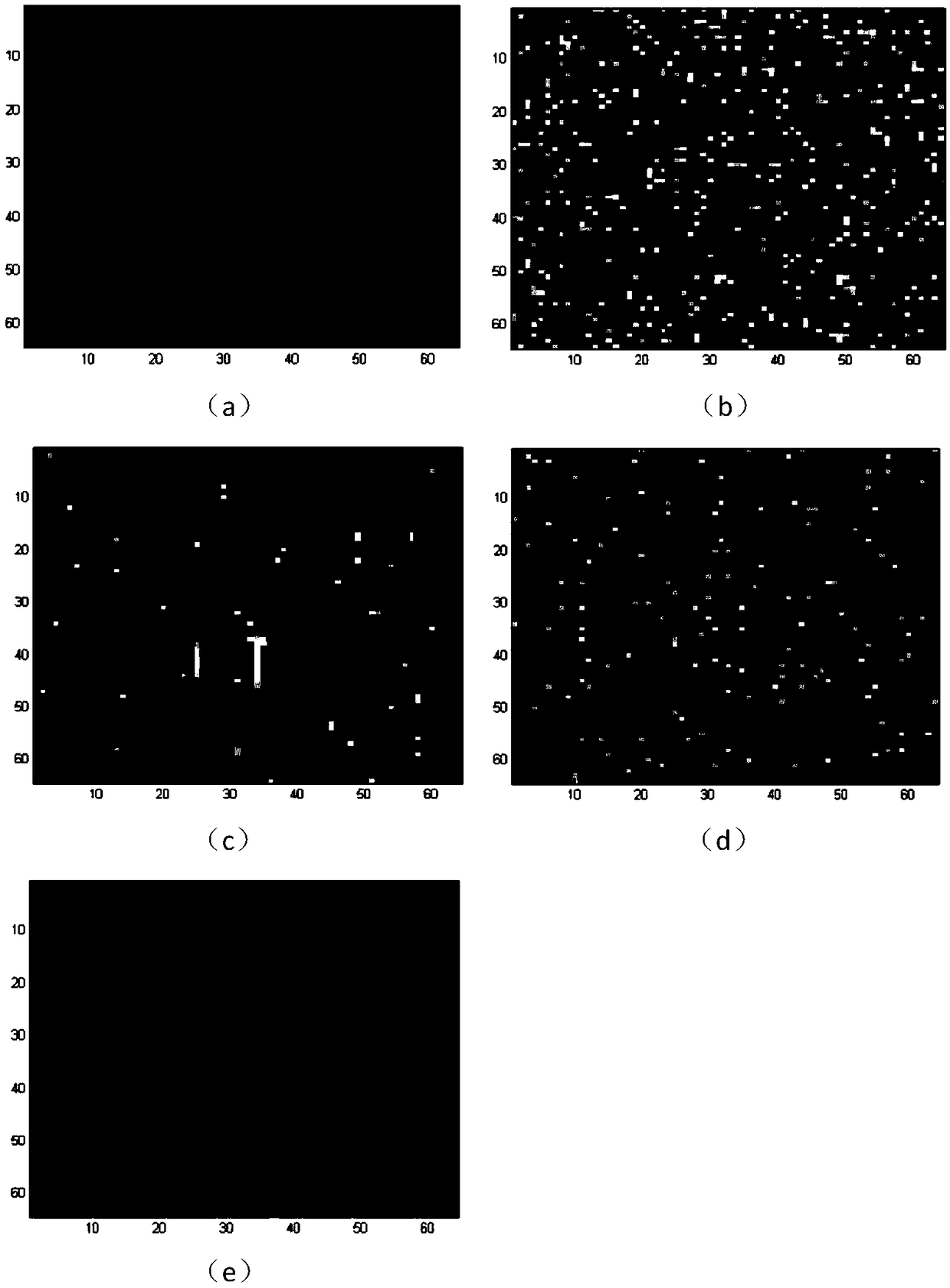
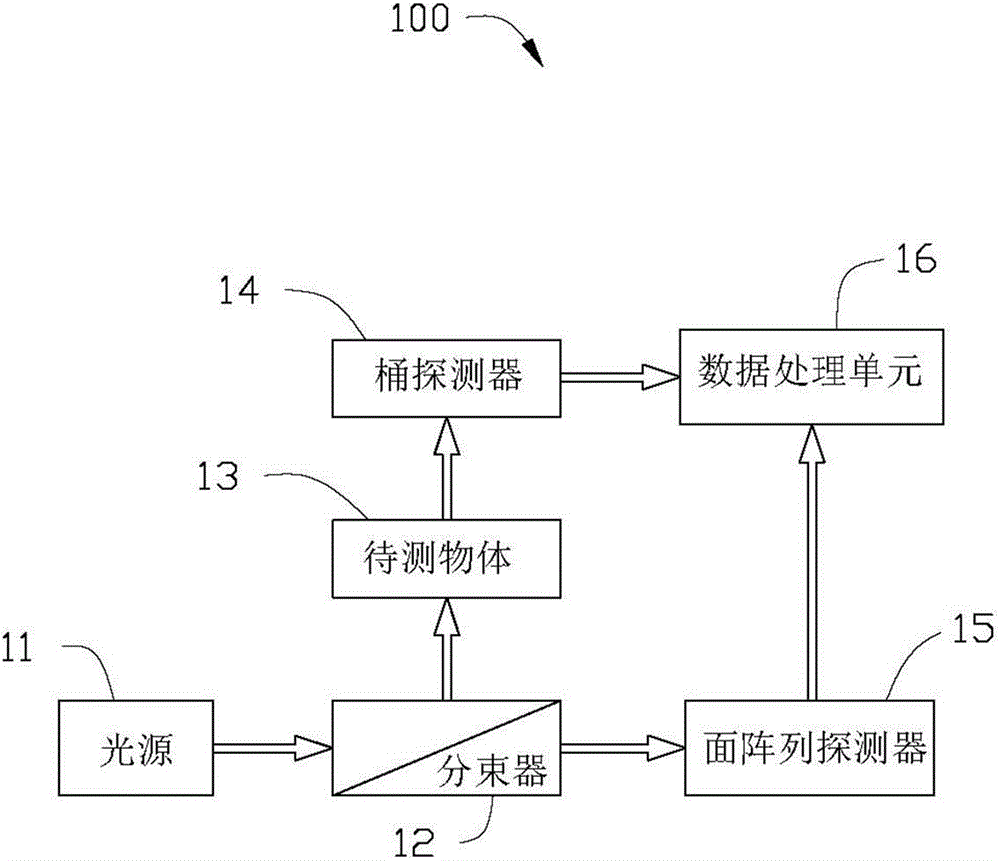
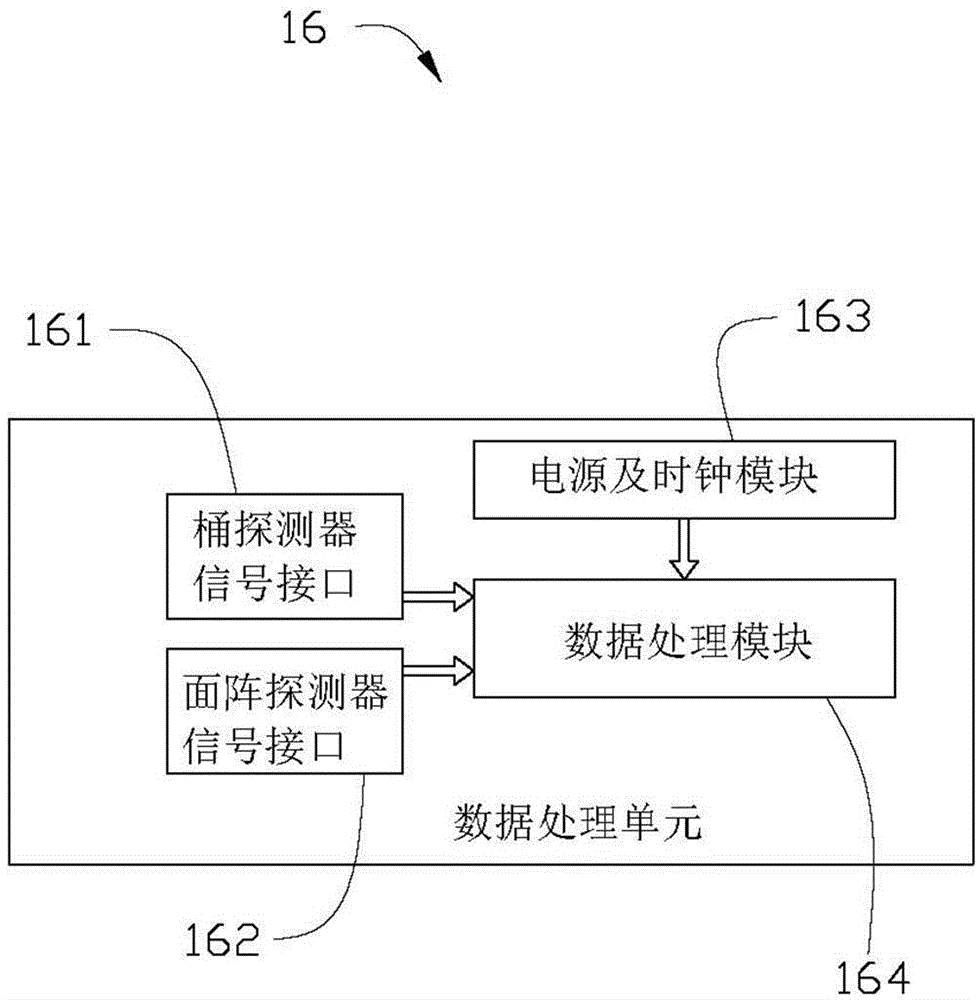
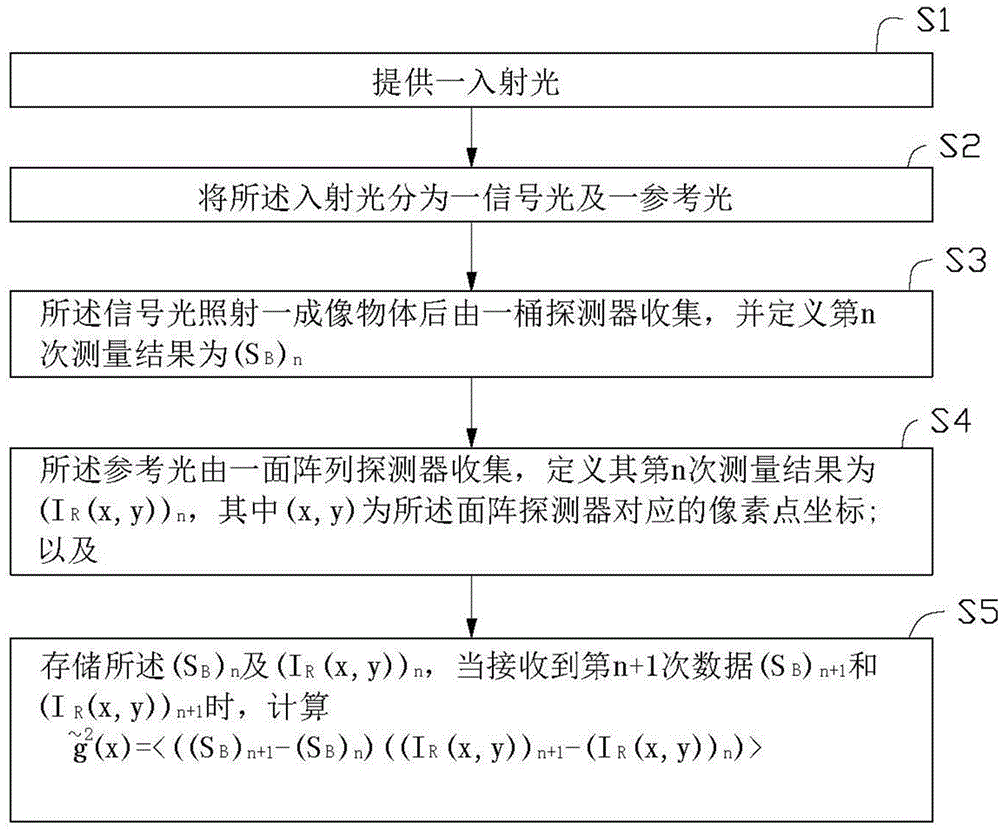
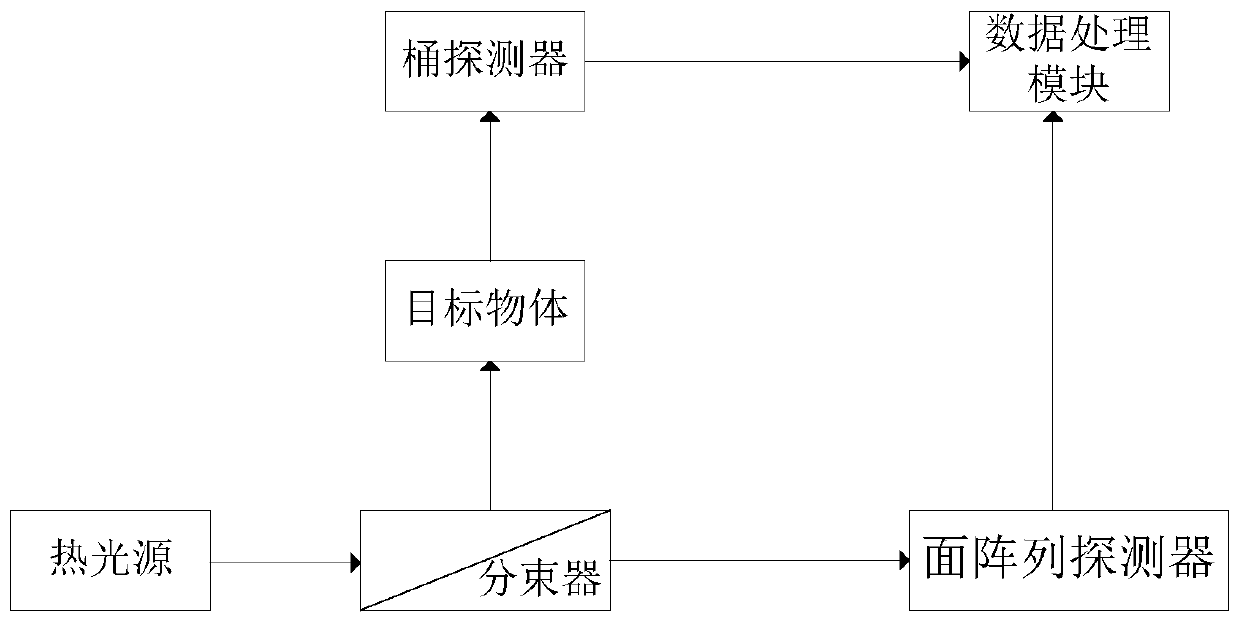
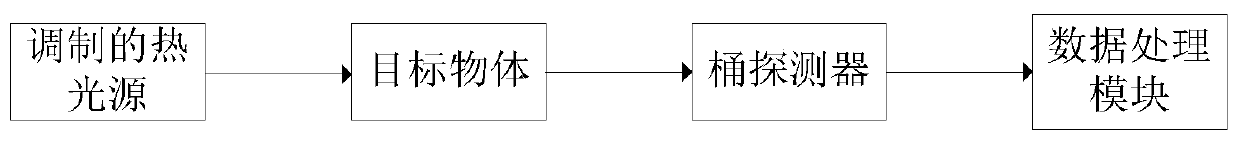
Quantum imaging method and quantum imaging system
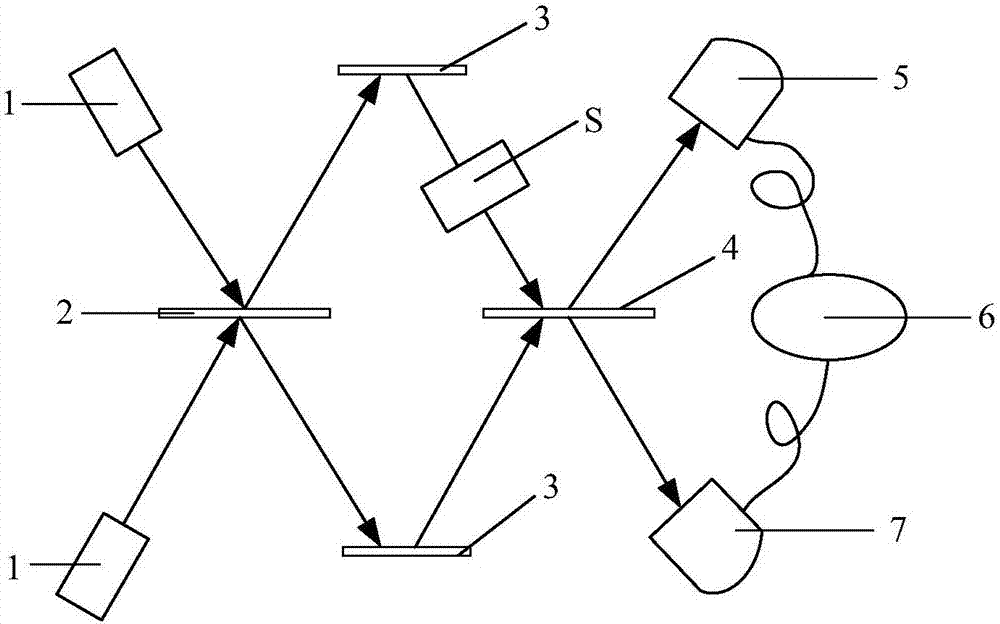
The invention discloses a quantum imaging method and a quantum imaging system. The method comprises the following steps: S1) providing incident light; S2) splitting the incident light into signal light and reference light; S3) after the signal light irradiates an imaging object, collecting the light by a bucket detector and defining the nth measuring result as (SB)n; S4) collecting the reference light by a planar array detector, and defining the nth measuring result as (IR(x,y))n, wherein the (x,y) is pixel point coordinates corresponding to the planar array detector; and S5) storing the (SB)n and the (IR(x,y))n, and when receiving (n+1) data (SB)n+1 and the (IR(x,y))n+1, calculating g<~><2>(x)=<((SB)n+1- (SB)n)((IR(x,y))n+1-(IR(x,y))n)>.
Owner:北京坤煜量子科技有限责任公司
Quantum imaging with undetected photons
ActiveUS9557262B2Simple methodScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectroscopyLength wave
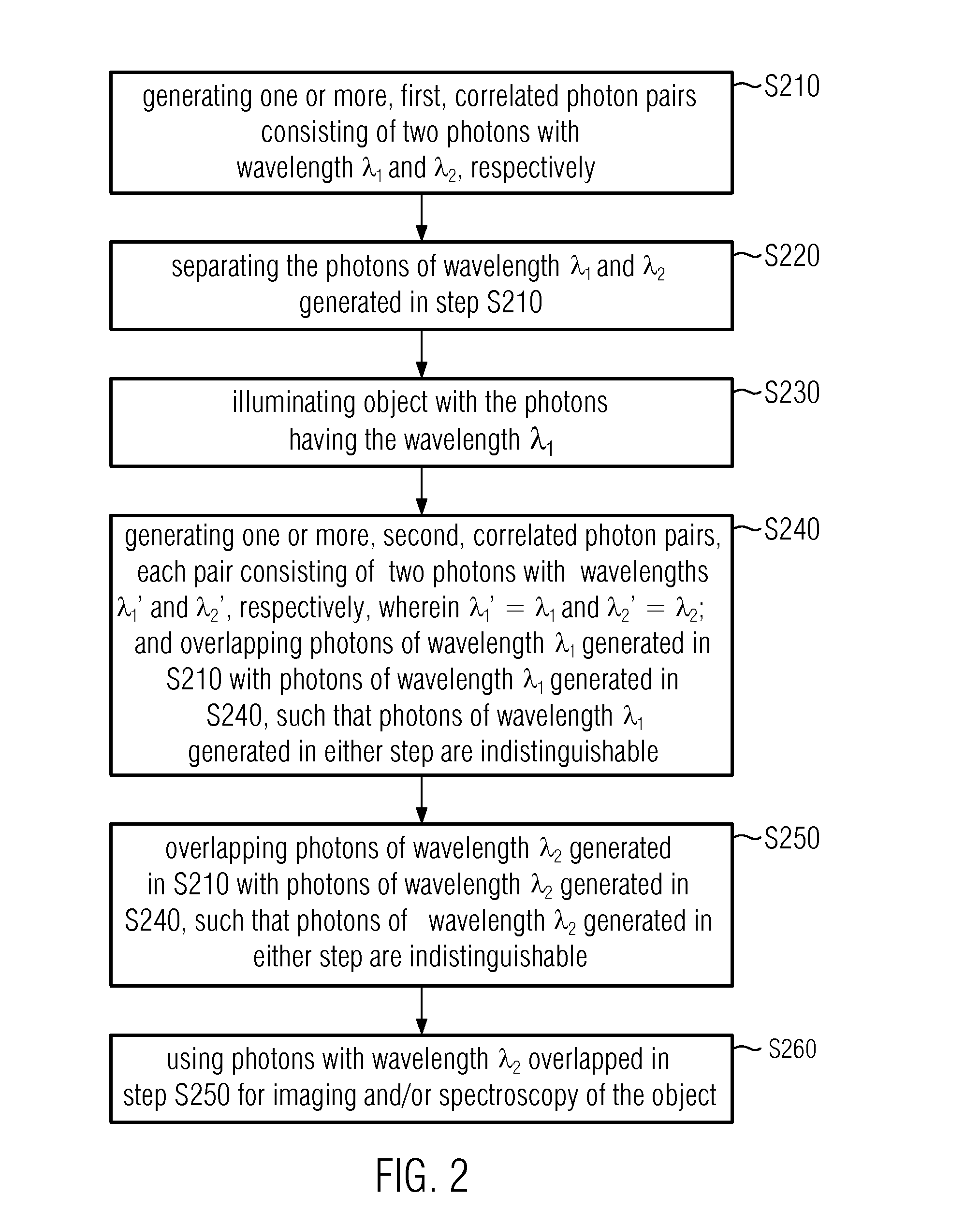
A method comprises: generating a first and a second correlated photon beam with wavelengths λ1 and λ2, respectively, wherein preferably λ1≠λ2; separating the first photon beam and the second photon beam; illuminating an object with the first photon beam; generating a third and a fourth correlated photon beam with wavelength λ1 and wavelength λ2, respectively; overlapping the first photon beam with the third photon beam such that photons of wavelength λ1 in either photon beam are indistinguishable; overlapping the second photon beam with the fourth photon beam such that photons of wavelength λ2 in either photon beam are indistinguishable; and using the overlapped photons of wavelength λ2 for imaging and / or spectroscopy of the object such that the photons that illuminate the object are not detected.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VIENNA +1
Imaging method of portable single-pixel camera implemented based on correlated imaging algorithm
ActiveCN109151191AImplement the imaging methodPicture reproducers using projection devicesTelephone set constructionsImaging algorithmComputer module
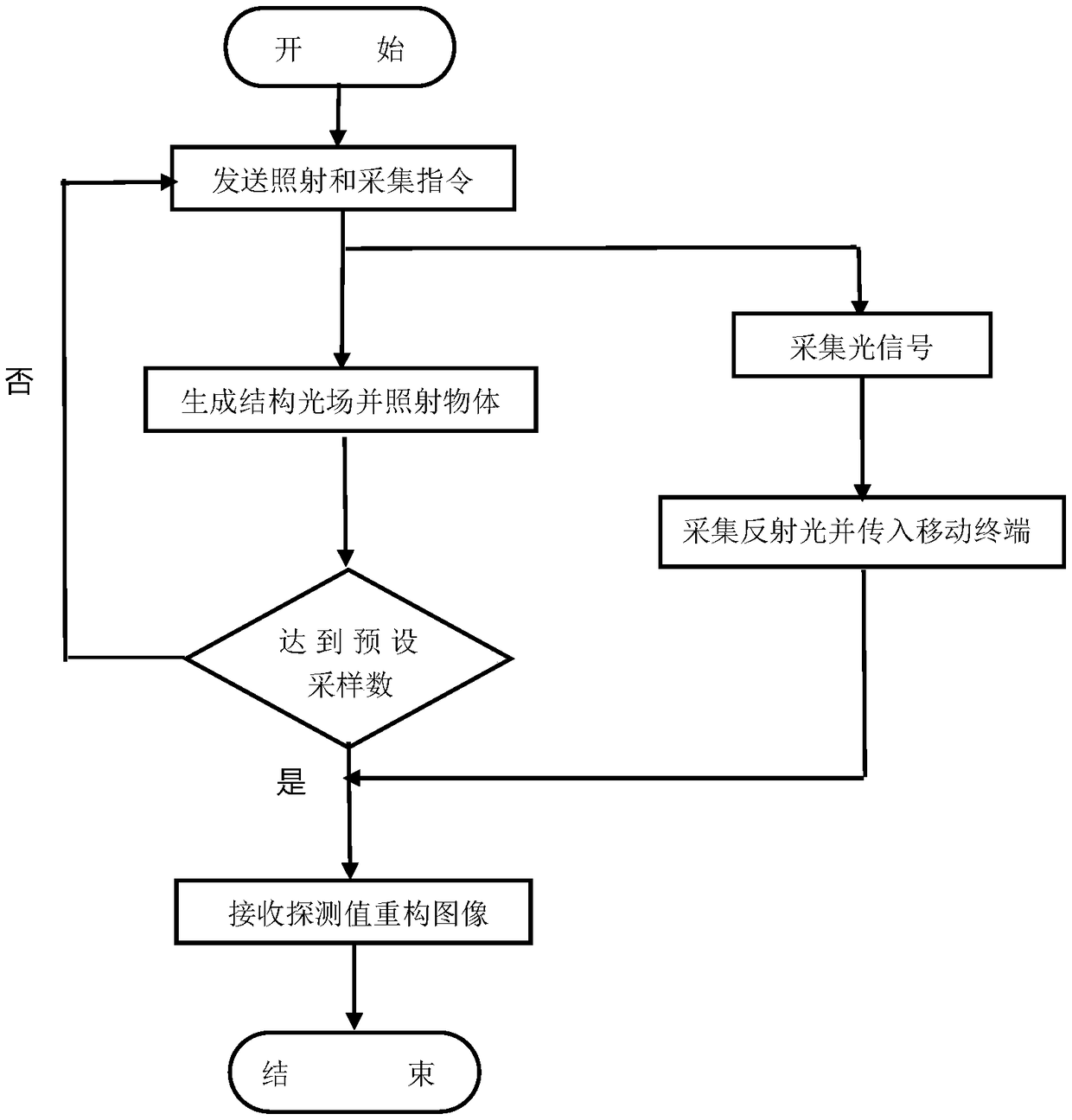
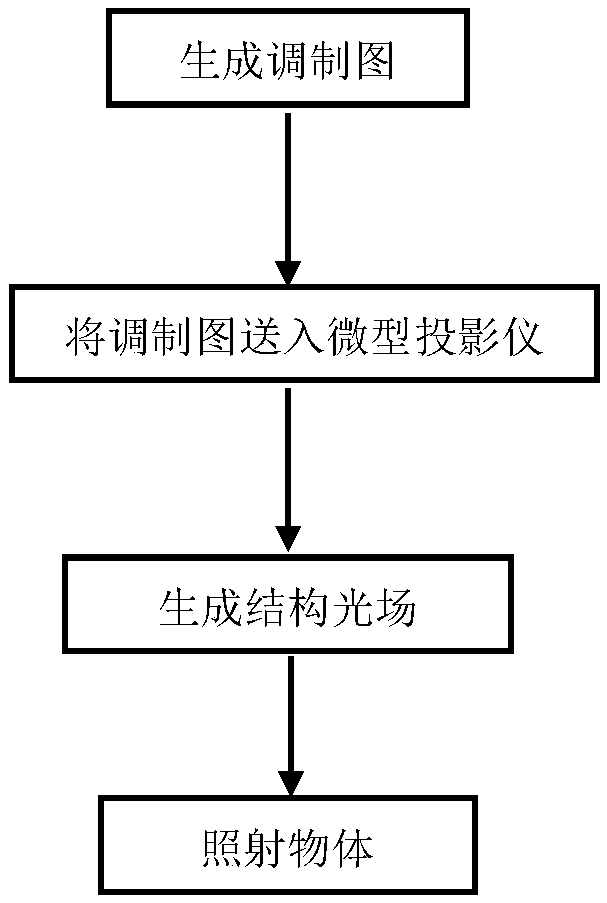
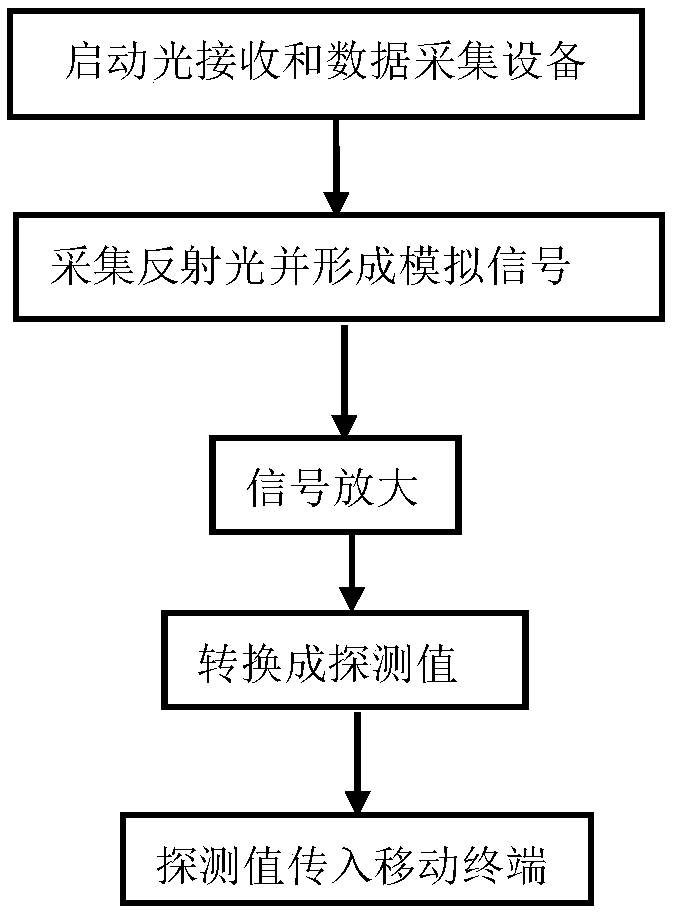
The invention discloses an imaging method of a portable single-pixel camera implemented based on a correlated imaging algorithm, and relates to the technical field of quantum imaging. The method comprises the following steps: enabling a single-pixel camera associated imaging APP application program to respond to an imaging request, generating a modulation map by using a modulation map generation function module, and transmitting the generated modulation map to a miniature projector for generating a structured light field; irradiating an object through the structured light field generated by the miniature projector; starting a light receiving and data collecting device to collect the reflected light of the object, performing the space-time integration of the reflected light field to form asingle point detection value, and transmitting the single point detection value to a mobile terminal; enabling the mobile terminal to receive the detection value and storing the detection value into an internal database; reconstructing an image of the object according to the pre-generated modulation map and the detection value. The method realizes the process of constructing a portable single-pixel camera using an existing miniature projector, the mobile terminal and the light receiving and data collecting device, and controlling the process of shooting and image reconstruction using the mobile terminal.
Owner:JILIN TEACHERS INST OF ENG & TECH
Single-photon polarization state quantum imaging system based on DMD micromirror array
InactiveCN110487427AIncrease chance of shootingLow priceInstrumentsStatistical analysisMicromirror array
The invention relates to a single-photon polarization state quantum imaging system based on a DMD micromirror array. The system comprises a laser transmitting device, a single-photon preparation system, a DMD control imaging device, and an EMCCD imaging receiving system; the laser transmitting device is a semiconductor laser and is used for emitting laser beams; the single-photon preparation system is used for converting the laser emitted by the laser transmitting device into single photon pulses in different polarization states; the MD control imaging device directly acts on the single photonpulses in different polarization states and reflects the single photon pulses to the EMCCD imaging receiving system; the EMCCD imaging receiving system images the single photons in different polarization states, performs statistical analysis on detected photon information, and also obtains an image measurement error rate and imaging reliability. The system is simple in structure, convenient to operate, accurate in measurement, high in feasibility and easy to apply.
Owner:QINGYUAN TIANZHIHENG SENSING TECH CO LTD
Device and method for locking single photon intensity in real time
PendingCN110146162ACompressive Strength FluctuationsEnables tunable outputPhotometry electrical circuitsNegative feedbackPhoton detection
The invention discloses a device and method for locking single photon intensity in real time. Through single photon detection, a discrete single photon signal is converted into a TTL pulse signal. A photon counter performs digital-to-analog conversion on the digital pulse signal to output an analog voltage signal of corresponding amplitude. An analog proportional integral derivative controller carries out negative feedback operation on the analog voltage signal and set reference voltage and outputs an error signal, and the error signal is loaded to the bias control port of an intensity modulator. The single photon intensity is locked to set intensity in real time by continuously adjusting the single photon intensity. According to the invention, the intensity fluctuation of a single photoncan be effectively compressed; the problems of unable single photon intensity locking and continuous tuning output are solved; and the device and method have the characteristics of simple structure, high practicability, high stability, tunable output and the like, and can be applied to the fields of quantum communication, sensing detection, quantum imaging and the like.
Owner:XINZHOU TEACHERS UNIV
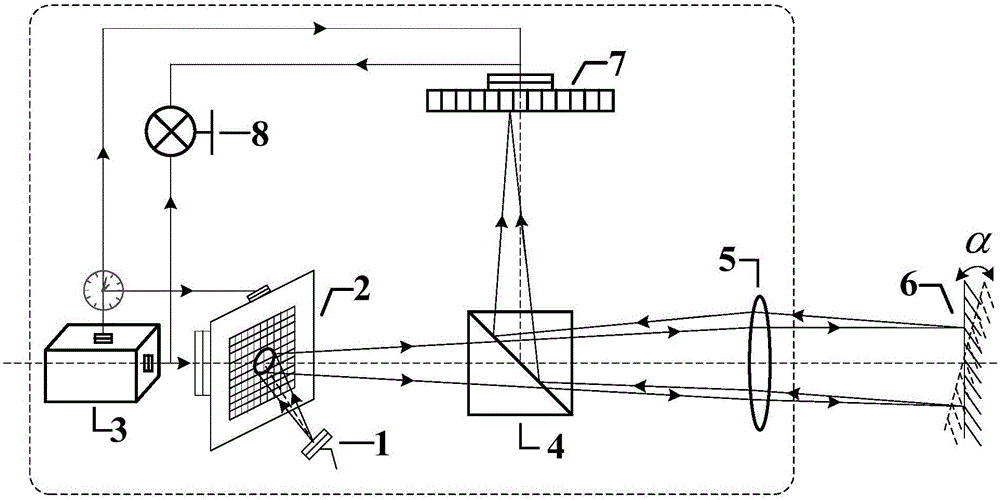
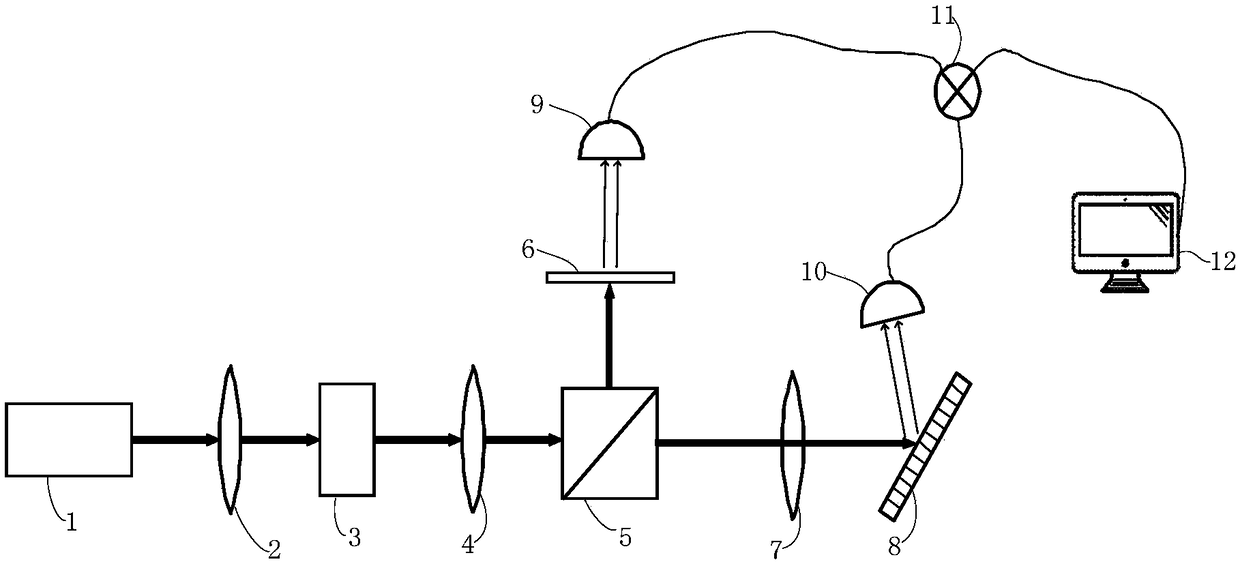
Intensity correlated autocollimator for single-CCD
ActiveCN105091797AEasy to implementHigh measurement accuracyUsing optical meansObservational errorImage signal
The invention discloses an intensity correlated autocollimator for a single-CCD, including an optical system and an image acquisition system and a data processing module, wherein the optical system is composed of a laser, ground glass, a motor, a reticle, a first spectroscope, a second spectroscope, a first lens and a second lens, and the image acquisition system includes an area array CCD. The area array CCD receives an image signal which is sent at the same time from the optical system through triggering of a synchronous signal sent from the image acquisition system. The two paths of images, after being acquired by the image acquisition system, are subject to intensity correlated calculation and signal processing in the data processing module, and finally a reading is displayed. According to the invention, a reference light path is added the optical system and the overall appearance of the traditional autocollimator are kept, and implementation in terms of engineering is easy. According to the invention, the intensity correlated method of quantum imaging technology is also introduced to the design of the autocollimator, which, can effectively increase the resolution and accuracy of measurement, can reduce errors of measurement caused by air disturbances, and the like, and can increase the sensitivity and stability of the autocollimator.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Quantum imaging for underwater arctic navigation
ActiveUS9798006B2Navigational calculation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingEnvironmental noisePhotonics
A quantum photonic imaging device used in an underwater vehicle for stealthy detection of underwater objects includes a photon generating module that generates an entangled pair of photons that includes a signal photon and an ancilla photon, wherein the ancilla photon is retained within the device; a transmitter that transmits the signal photon towards a region of space for detecting an underwater object; a receiver that detects an incoming photon to the device; and a correlation module that distinguishes the signal photon that is reflected back to the receiver due to a presence of the object from environmental noise photons, wherein the distinguishing includes determining an entanglement correlation of the detected photon with the ancilla photon, and wherein a presence of the entanglement correlation between the detected photon and the ancilla photon indicates that the detected photon is the signal photon reflected back from the object.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Solar-blind ultraviolet single-photon source and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107919604ALarge exciton binding energyLaunch applicableLaser active region structureFinal product manufactureSemiconductor materialsNanowire
The invention discloses a solar-blind ultraviolet single-photon source and a preparation method thereof. The solar-blind ultraviolet single-photon source includes a wide bandgap semiconductor p type layer, an i type intrinsic layer, a single quantum dot and a quantum dot embedded pin nanowire or a quantum dot embedded pin membrane composed of a n type layer. The width of a bandgap of a quantum dotin a pin structure is larger than 4.43 electron volts, the pin structure uses a semiconductor material of which the bandgap width is larger than the quantum dot, and thus a class quantum well structure is formed to enhance limitations on the single quantum dot. The solar-blind ultraviolet single-photon source is suitable for both excitation ways of optical pumping and electric pumping and can emit vertical to a substrate and can also emit parallel to the substrate, and hence the solar-blind ultraviolet single-photon source can be not only applied to a free space single-photon source but alsoapplied to an integrated single-photon source on a chip; the emission wavelength of the solar-blind ultraviolet single-photon source is in a solar-blind wave band smaller than 280 nm, and the wide bandgap quantum dot is suitable for room temperature single-photon emission even for high-temperature single-photon emission and can be broadly applied to the relevant fields of quantum information, quantum calculation, quantum imaging, quantum verification, near field secure communication and quantum precision measurement.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS ENG CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Quantum imaging method and quantum imaging system
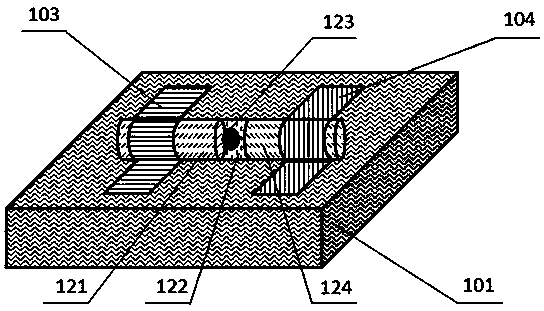
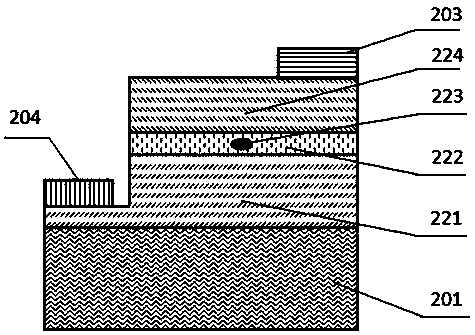
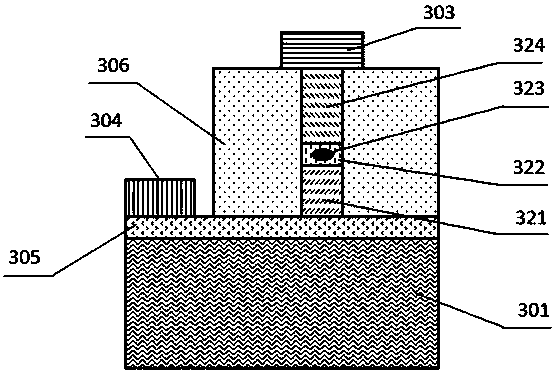
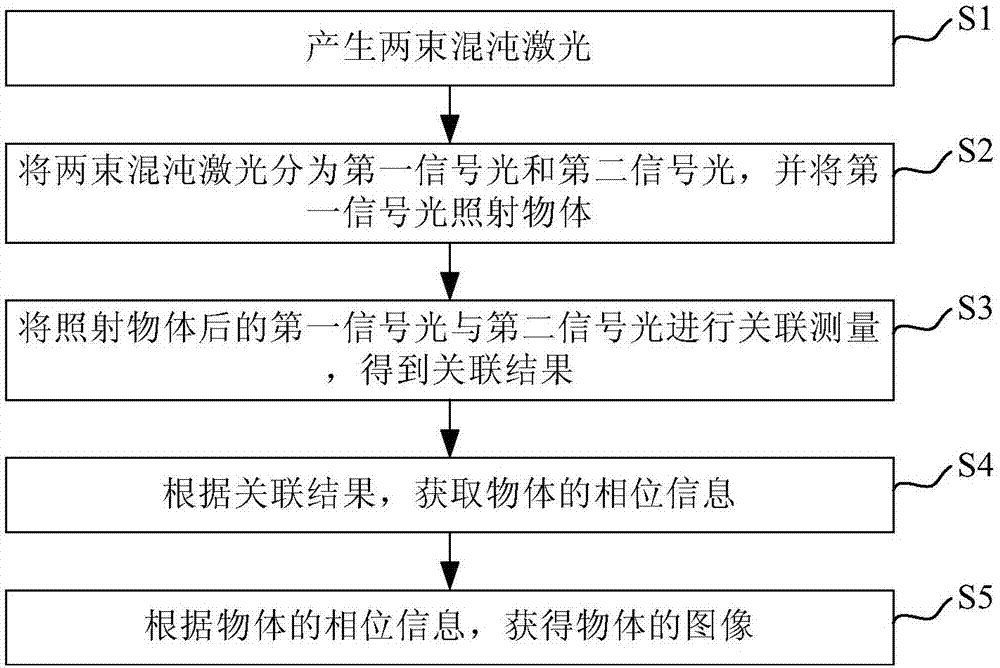
InactiveCN106932897AMuch phase informationImproving Quantum Imaging EffectsOptical elementsSignal lightQuantum
The invention provides a quantum imaging method and a quantum imaging system and belongs to the technical field of quantum imaging. The method and the system solve the problem that the existing quantum imaging method is poor in imaging effect in the prior art. The quantum imaging method comprises the following steps of generating two beams of chaotic lasers, dividing the two beams of chaotic lasers into a first signal light and a second signal light, illuminating an object by using the first signal light, correlating the first signal light with the second signal light after the object is illuminated by the first signal light so as to obtain a correlation result, obtaining the phase information of the object according to the correlation result, and obtaining the image of the object according to the phase information of the object.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
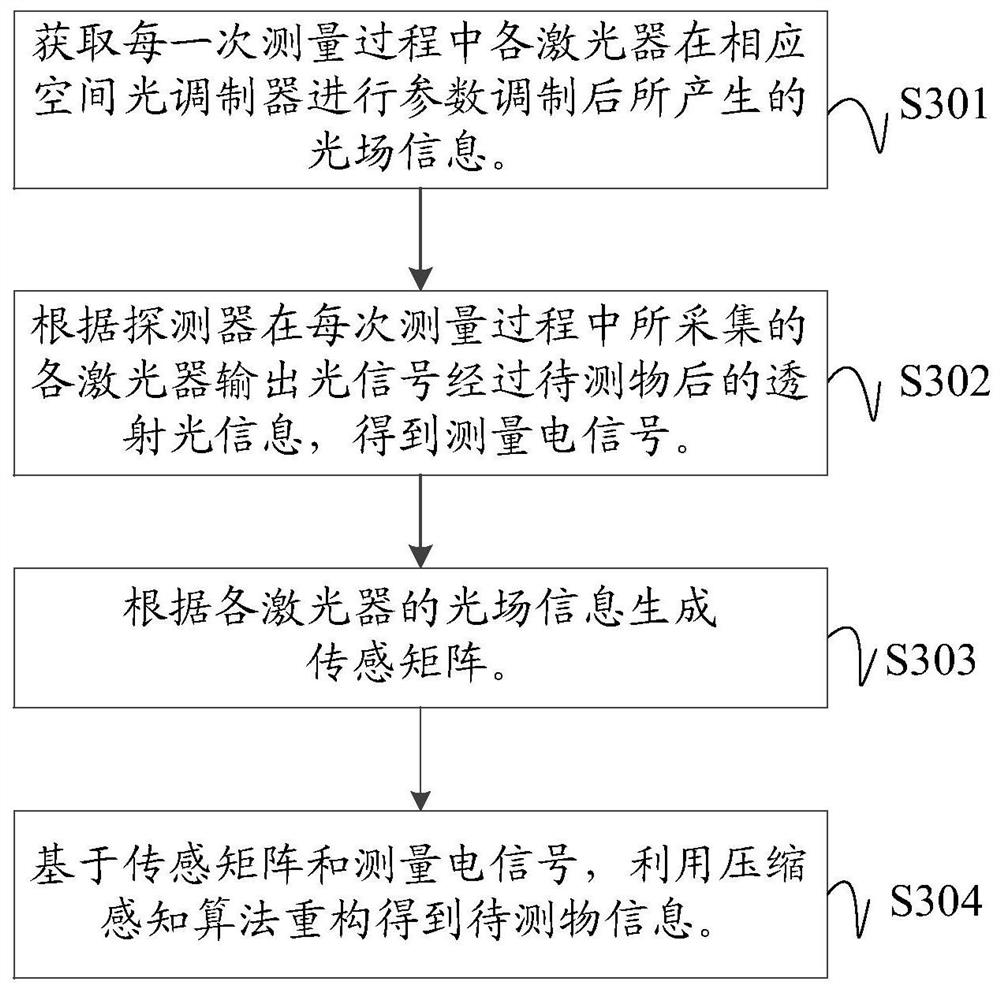
Distributed quantum imaging method, device and system and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN113066143AHigh-resolutionImprove efficiencyImage enhancement2D-image generationSpatial light modulatorImage resolution
The invention discloses a distributed quantum imaging method, device and system and a computer readable storage medium. The distributed quantum imaging system comprises a plurality of lasers placed at different spatial positions, a plurality of spatial light modulators, a detector and an imaging processor. Each laser uniquely corresponds to one spatial light modulator. Each spatial light modulator is used for modulating light field parameters generated by the corresponding laser in each measurement process and projecting modulated light signals to an object to be measured; the detector is used for collecting transmission light of light signals output by the lasers and passing through the to-be-measured object, converting the transmission light into corresponding measurement electric signals and sending the measurement electric signals to the imaging processor; and the imaging processor is used for obtaining information of the object to be measured by using a compressed sensing algorithm, a sensing matrix constructed based on light field information of multiple measurement processes and reconstruction of the measurement electric signals. The quantum imaging efficiency and the quantum imaging resolution can be effectively improved.
Owner:SHANDONG YINGXIN COMP TECH CO LTD
Quantum imaging method and quantum imaging system
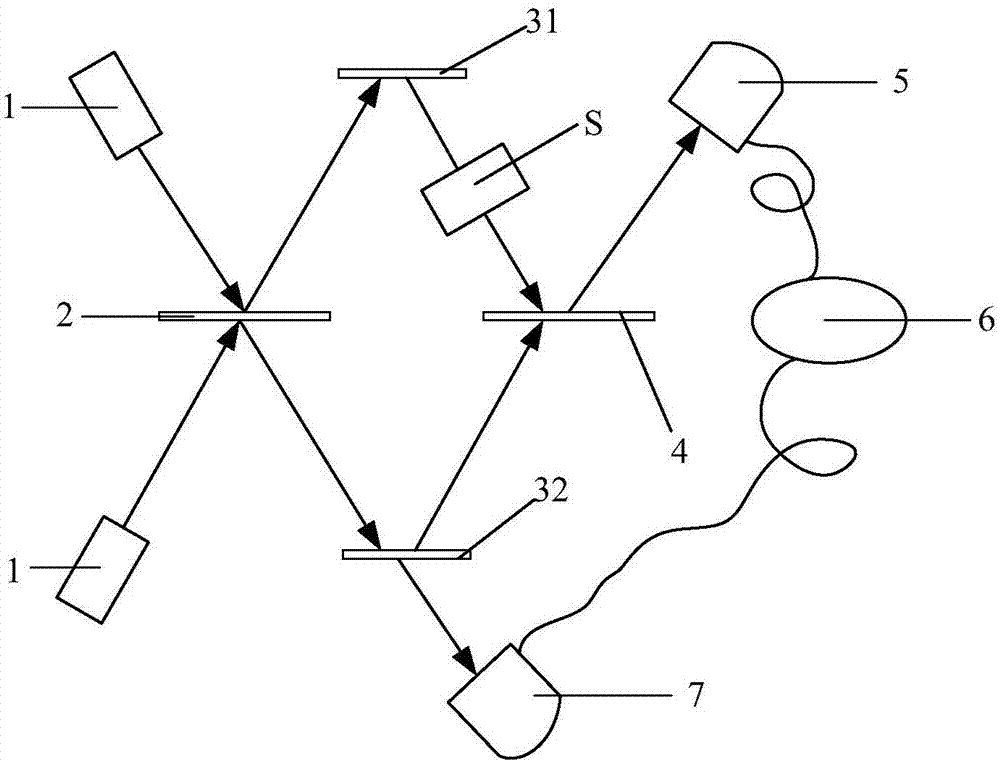
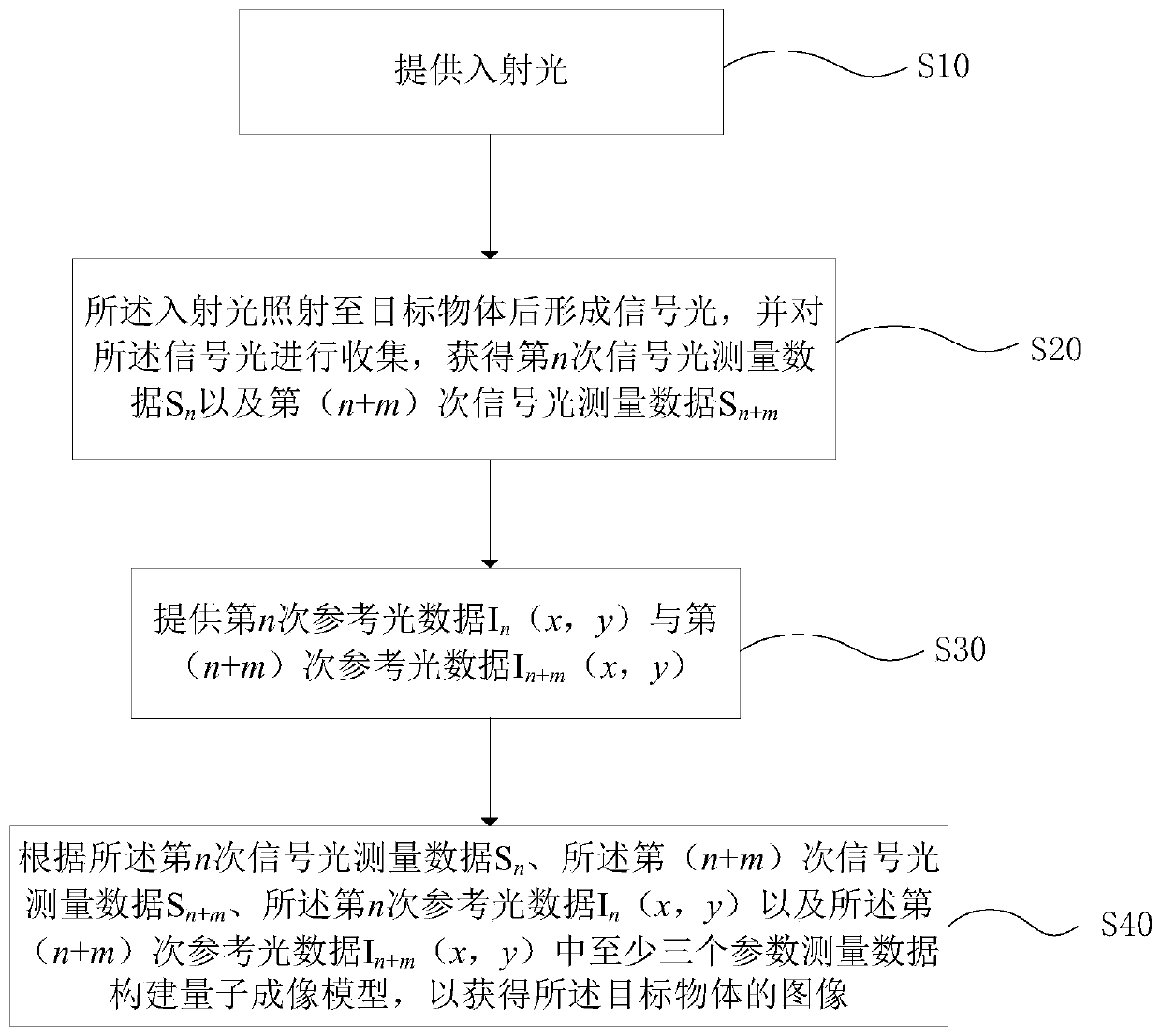
ActiveCN110568613AReduce the burden onDifficulty of SimplificationConverting sensor output opticallyOptical elementsMultiple frameHardware implementations
The invention provides a quantum imaging method and a quantum imaging system. According to the quantum imaging method, measurement data of at least any three parameters of Sn, Sn+m, In(x, y) and In+m(x, y) needs to be stored. Therefore, the amount of stored data is reduced in terms of overall implementation, and the burden of data storage is reduced. Meanwhile, computing resources involved in thequantum imaging method are correspondingly reduced, hardware implementation is simplified, and practical use of quantum imaging is facilitated. In the method, n and m in Sn, Sn+m, In(x, y) and In+m(x,y) are any positive integers. Data required for calculation through the quantum imaging method is not limited by adjacent frames, and imaging can be performed across multiple frames, so that quantumimaging is realized more flexibly. By means of the quantum imaging method, data processing is simplified, rapid and efficient imaging is achieved, the speed and efficiency of quantum imaging are improved, and therefore, online imaging can be achieved.
Owner:北京坤煜量子科技有限责任公司
Quantum imaging device and method of entangled photon pair time and position synchronization coincidence
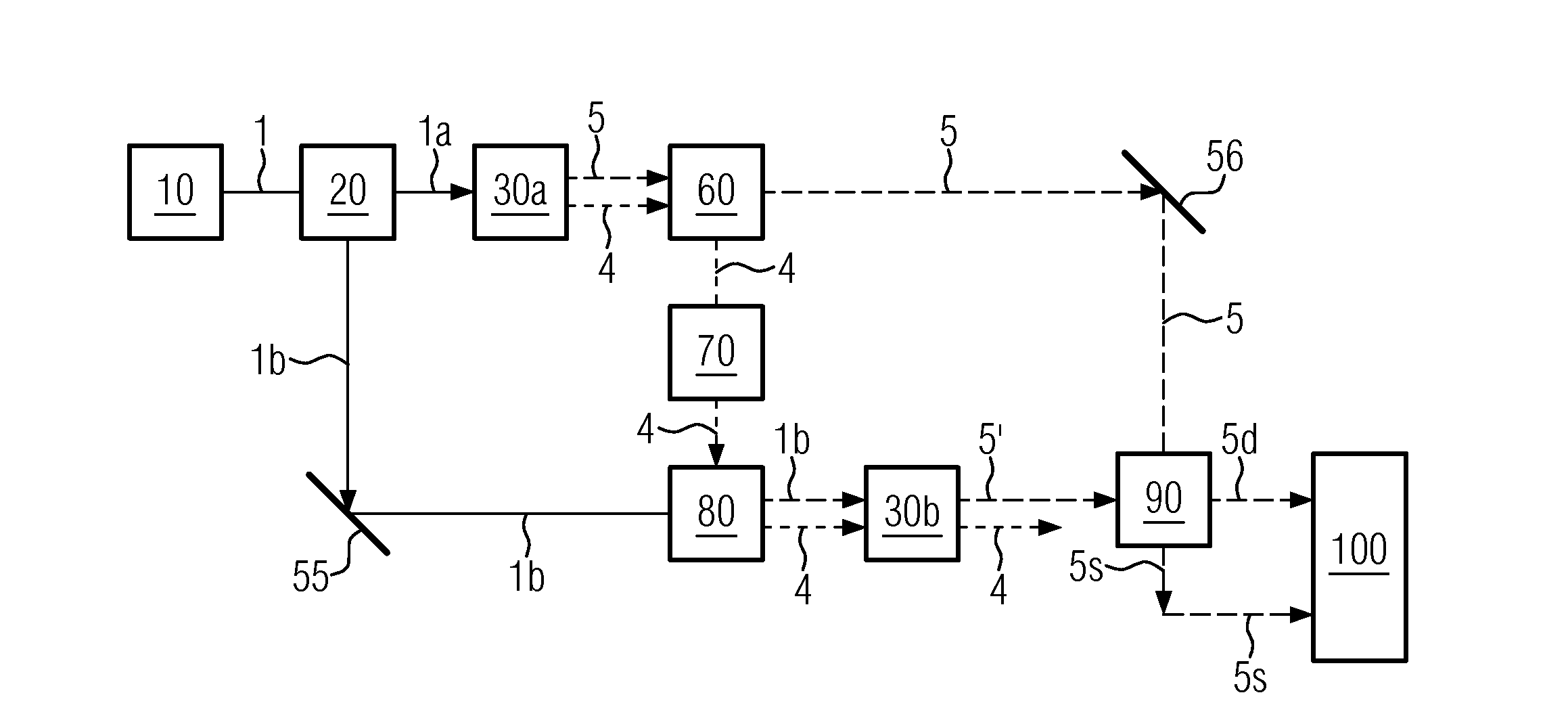
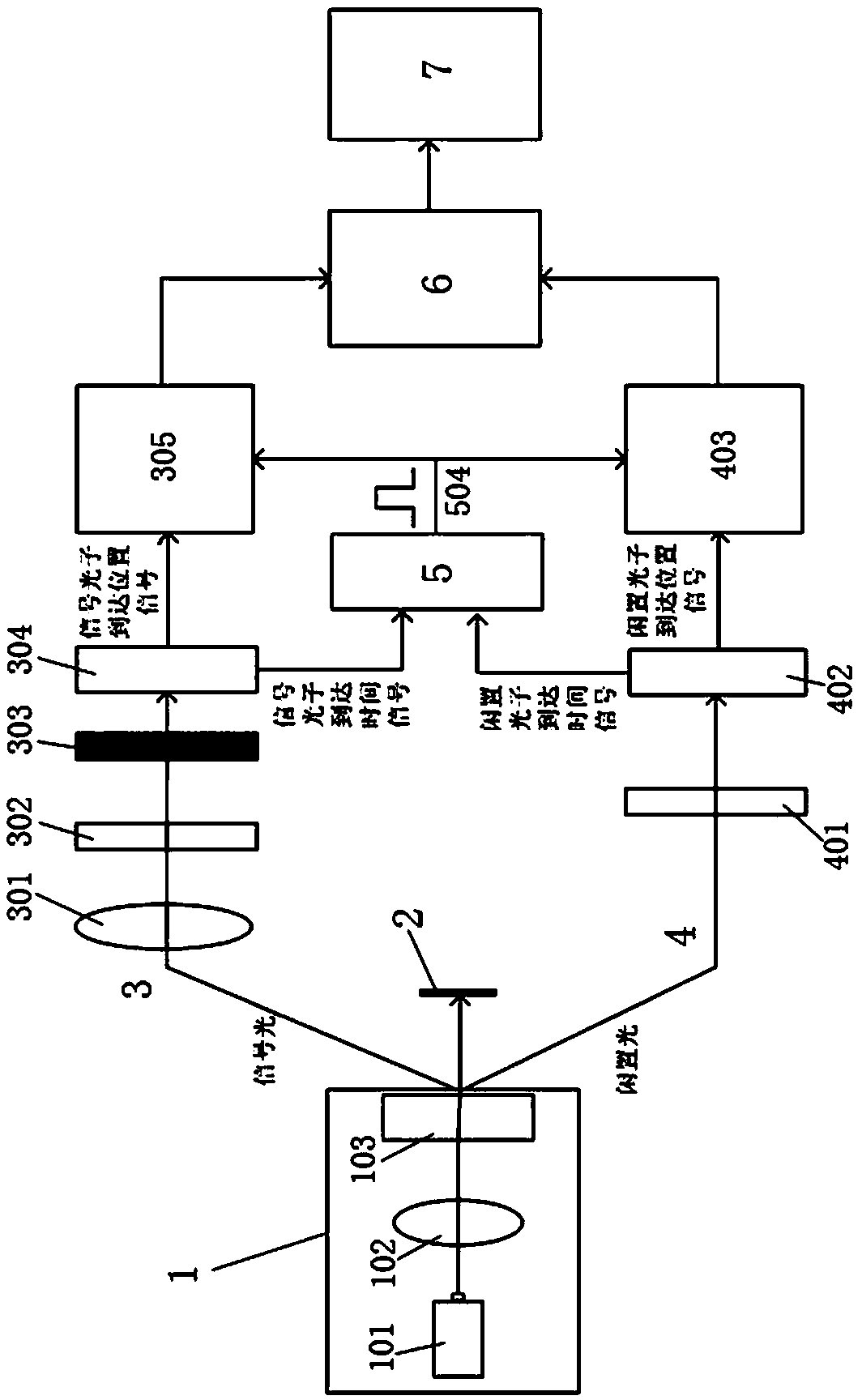
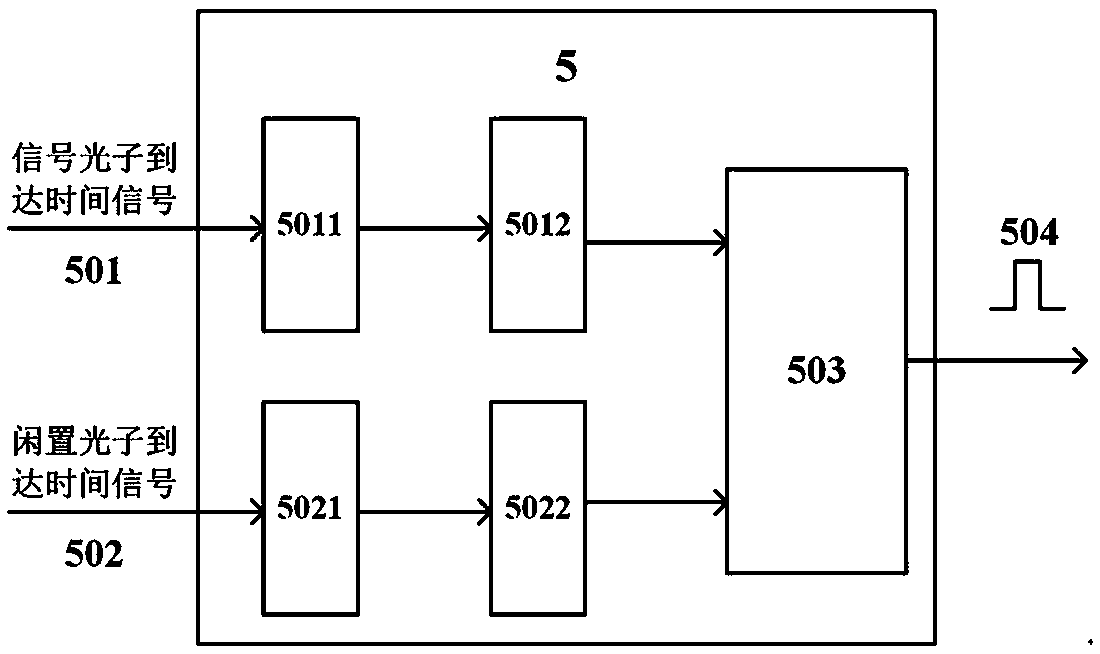
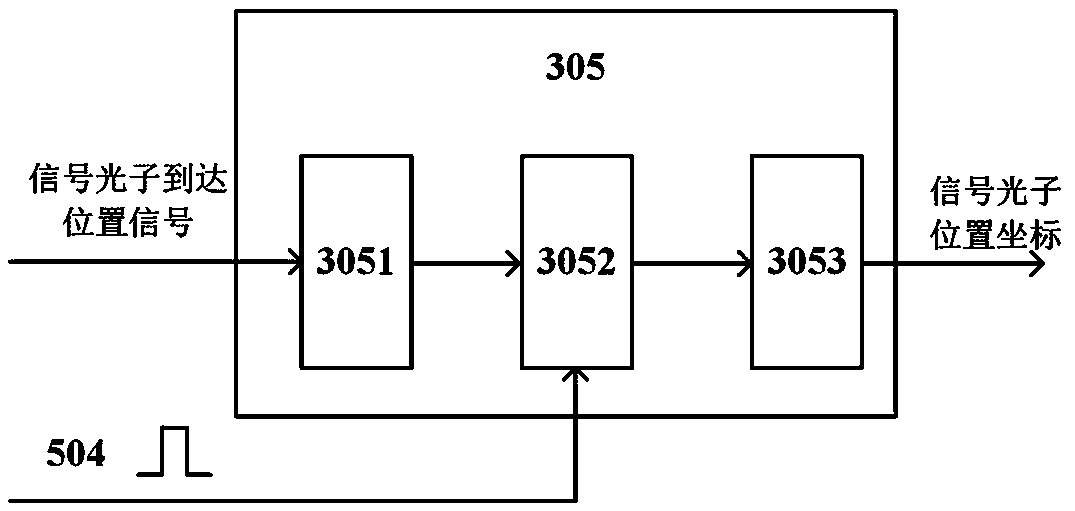
ActiveCN108469673AImprove collection efficiencyReduced imaging timeOptical elementsImaging lensQuantum
The invention relates to a quantum imaging device and method of entangled photon pair time and position synchronization coincidence. The device comprises an entangled source, a shading screen, a signal photon position measurement branch and an idle photon position measurement branch. The signal photon position measurement branch comprises an imaging lens, a first optical filter, a resolution plateand a first detector which are successively arranged. The first detector is connected to a signal photon position measurement module. The idle photon position measurement branch comprises a second optical filter and a second detector which are successively arranged. The second detector is connected to an idle photon position measurement module. The first detector and the second detector are connected to a time coincidence module. The signal photon position measurement module and the idle photon position measurement module are connected to the time coincidence module and a space coincidence module. The space coincidence module is connected to a photon counting image synthesis module. In the invention, photon collection efficiency is increased and imaging time is shortened.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Laser radar based on highly-correlated quantum imaging principle
InactiveCN101846745BReduce lossRealize ultra-long-distance detectionElectromagnetic wave reradiationTime delaysDistance detection
The invention discloses laser radar based on a highly-correlated quantum imaging principle, which consists of a pulse laser, a parameter down-conversion non-linear device, a receiving lens, a photon detector, an imaging lens, an area-array detector, a time delay correlator and a signal processor. The pulse laser transmits laser pulse to generate two laser beams having different wavelengths and the highly correlation by parameter down-conversion non-linear device, one path of laser beam with long wavelength is irradiated on a measured object and is focused on a photon detector through a receiving lens to detector after being reflected, and a switch signal indicative of the detecting result of the photon is output; the other path of laser beam with short wavelength is irradiated to the area-array detector through an imaging lens to acquire a two-dimension photon image signal; and two paths of signals are correlated and integrated by the signal processor to acquire image and distance information of the measured object. The laser radar effectively solves the problem of transmission loss by using the laser with the long wavelength in an atmosphere window to realize the ultra-long distance detection and realize the super-resolution detection by using the highly-correction effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A Computational Intensity Correlation Imaging Autocollimator and Measurement Method
A computational intensity correlation imaging autocollimator and measurement method, comprising: a light source, a digital micromirror array DMD, a controller, a beam splitter, a lens, a mirror of a test piece, a CCD and an intensity correlation calculation module; the synchronization of the controller The control module generates a synchronous clock signal to act on the digital micromirror array DMD and CCD. The intensity correlation calculation module simultaneously records the light field modulation matrix generated by the light field modulation module and the echo signal received by the CCD, and performs second-order intensity correlation calculation. The tiny rotation angle of the DUT is obtained through indirect calculation. The invention introduces the computational correlation imaging method in the quantum imaging technology into the design of the autocollimator, which can effectively reduce the measurement error caused by air disturbance and other factors, and improve the sensitivity and stability of the system.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com