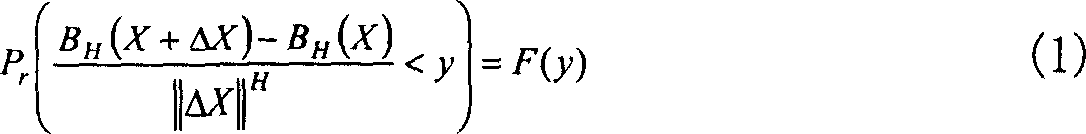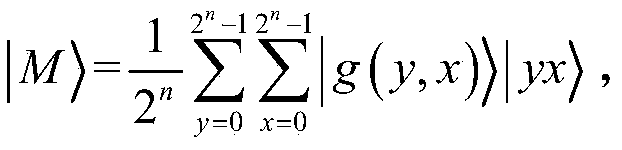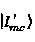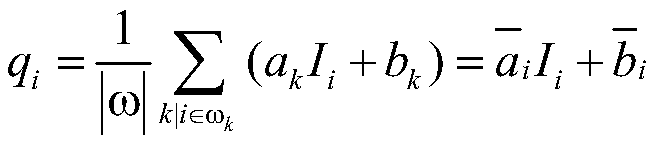Patents
Literature
109 results about "Quantum image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interactive virtual thematic environment
InactiveUS7373377B2Multiple digital computer combinationsImage data processing detailsTime informationInteractive software
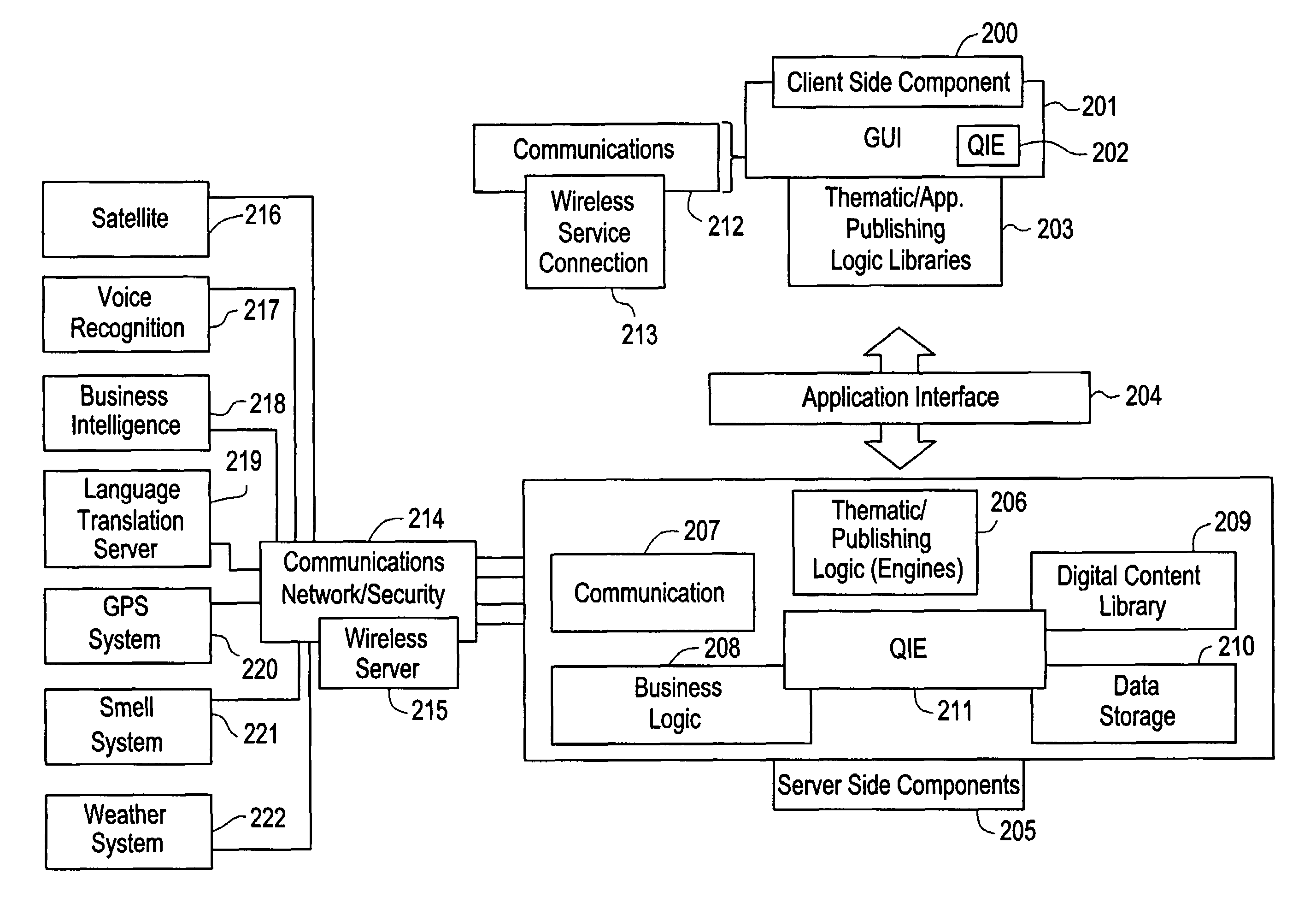
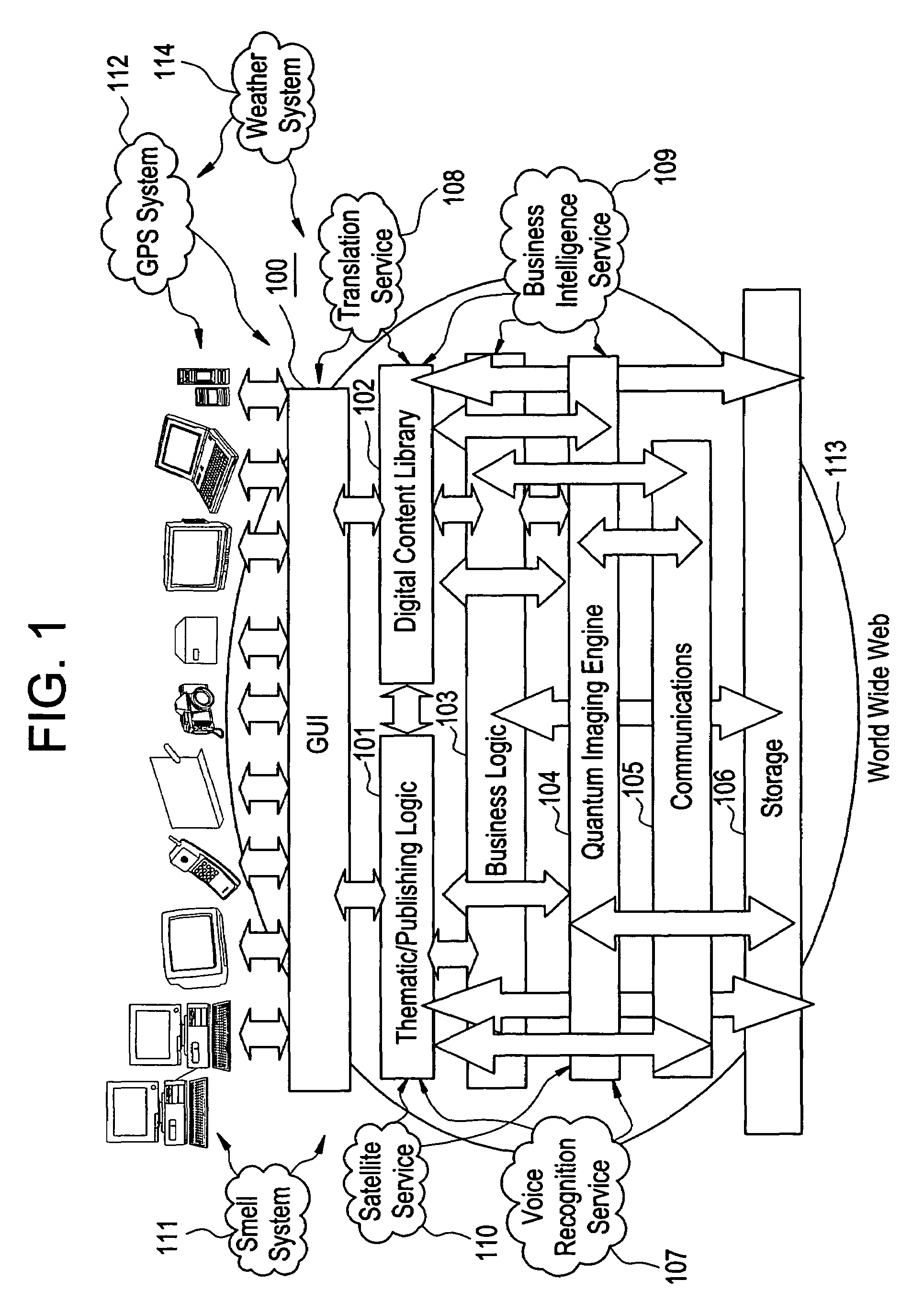
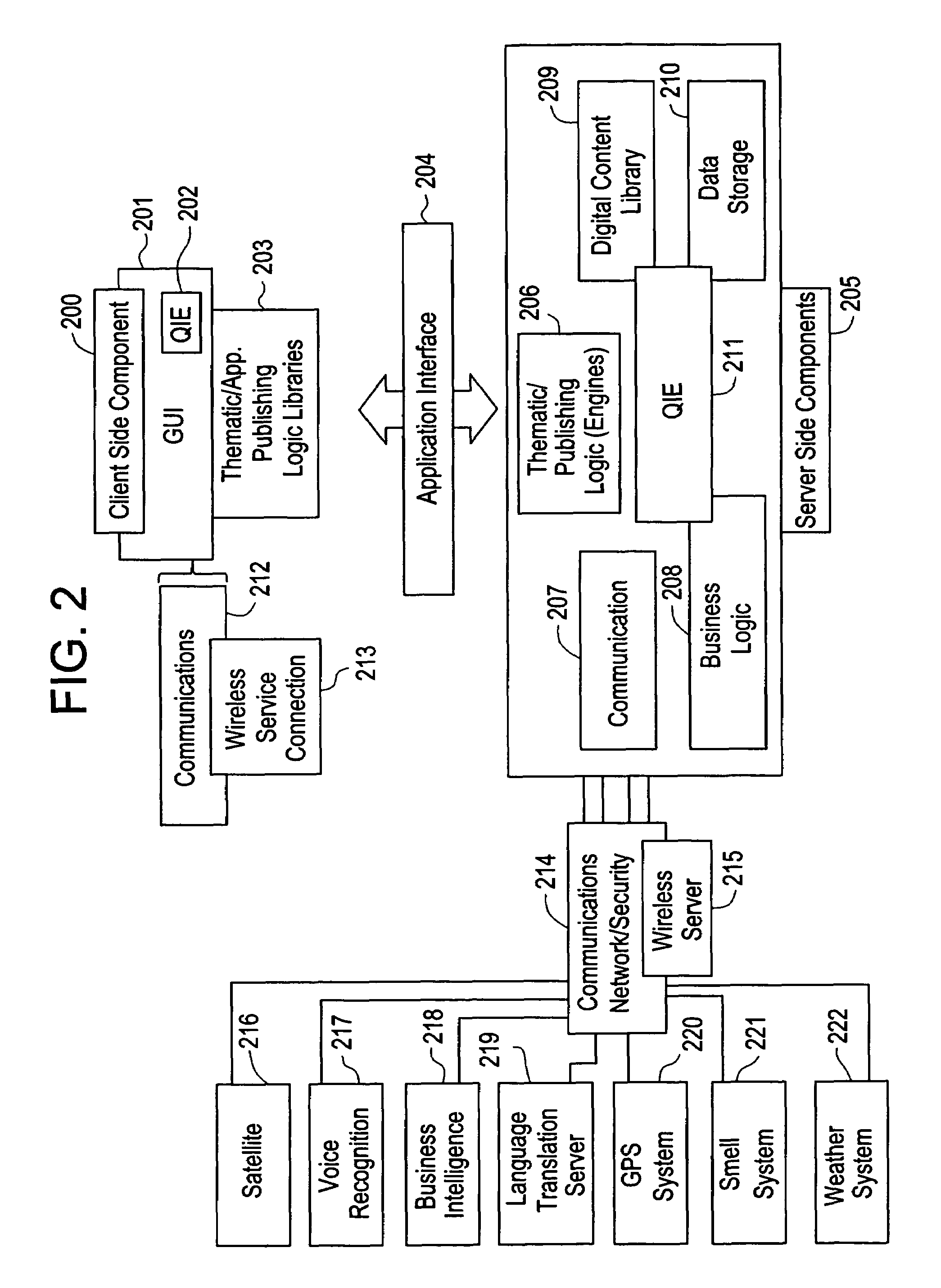
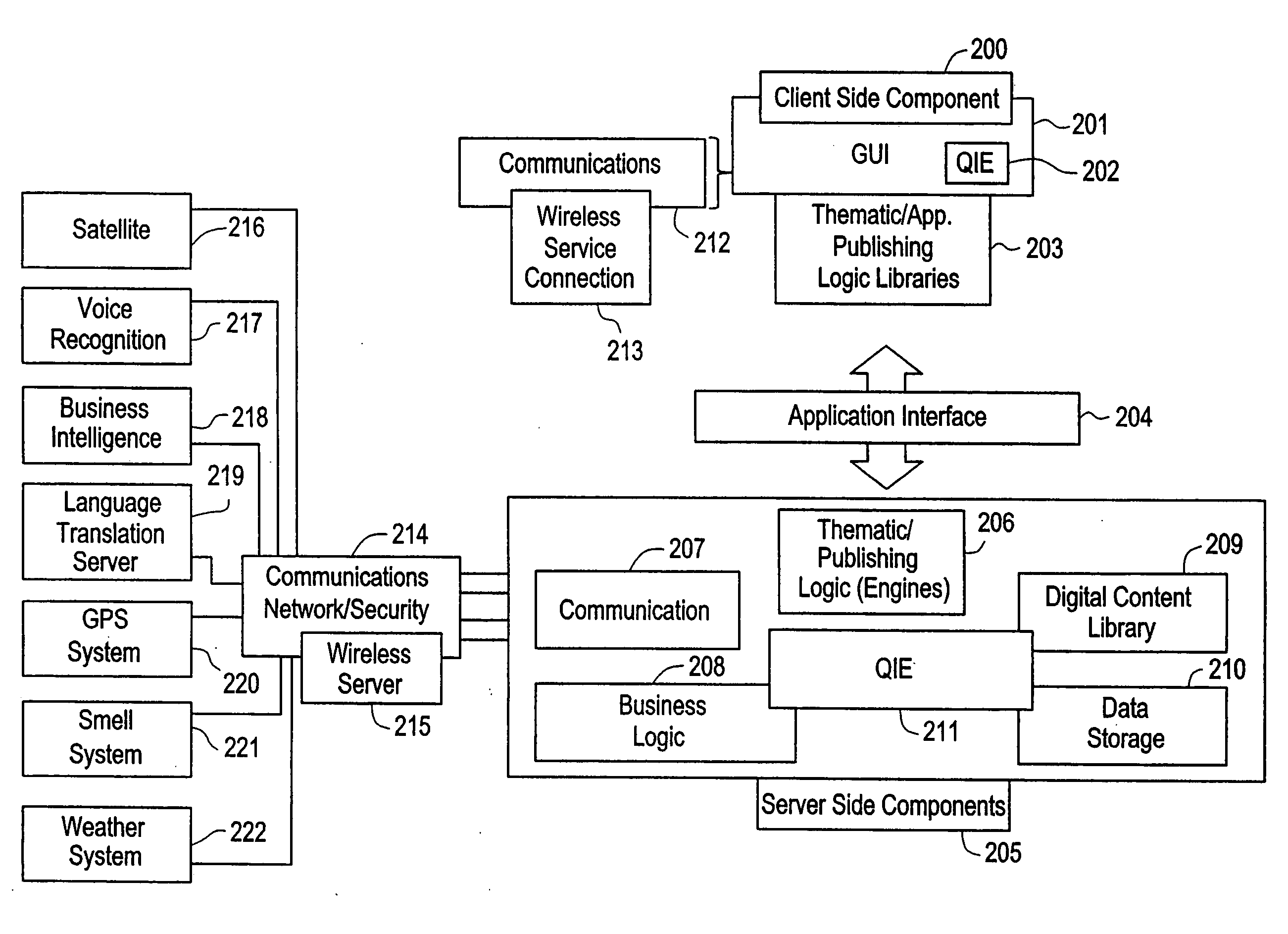
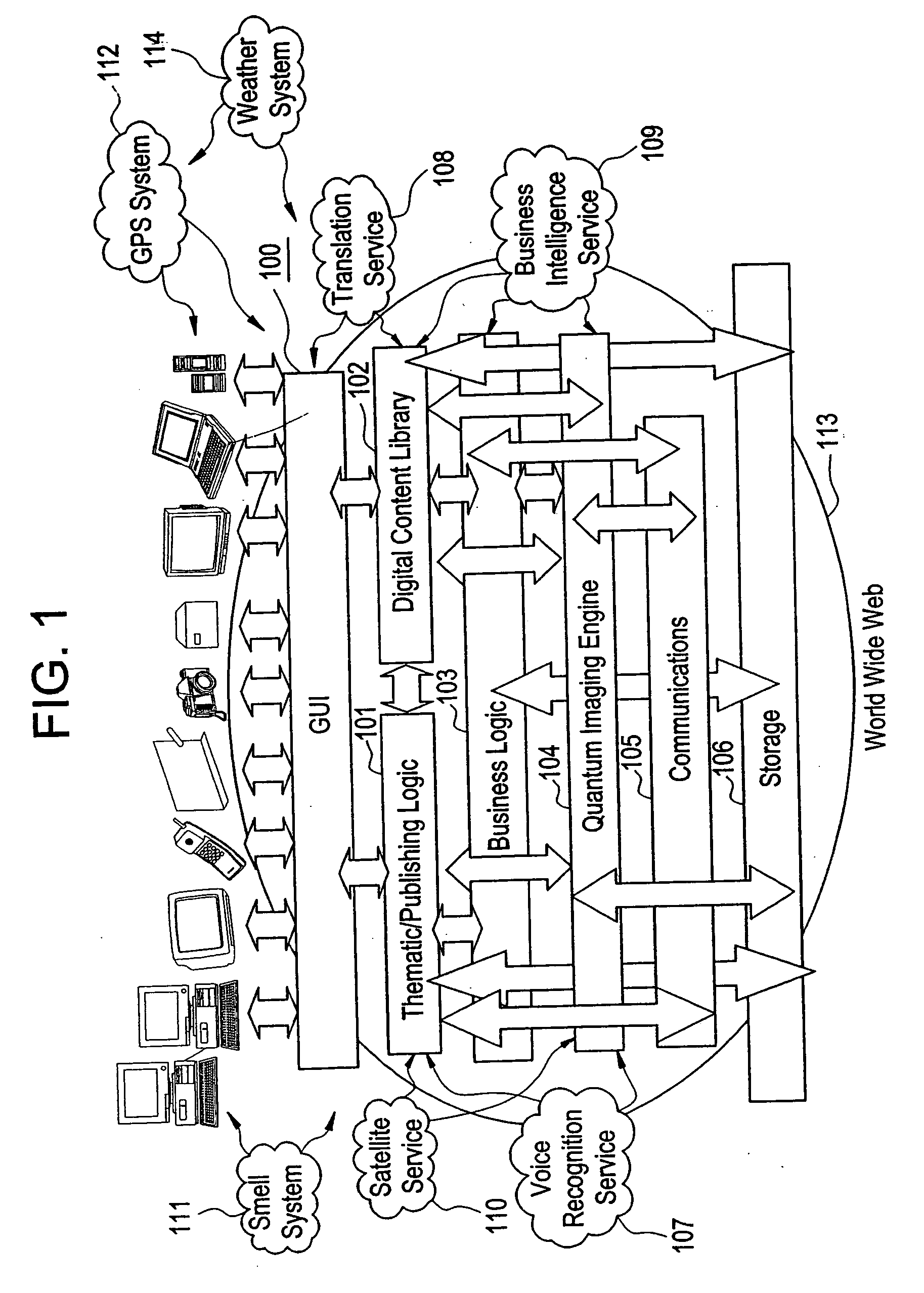
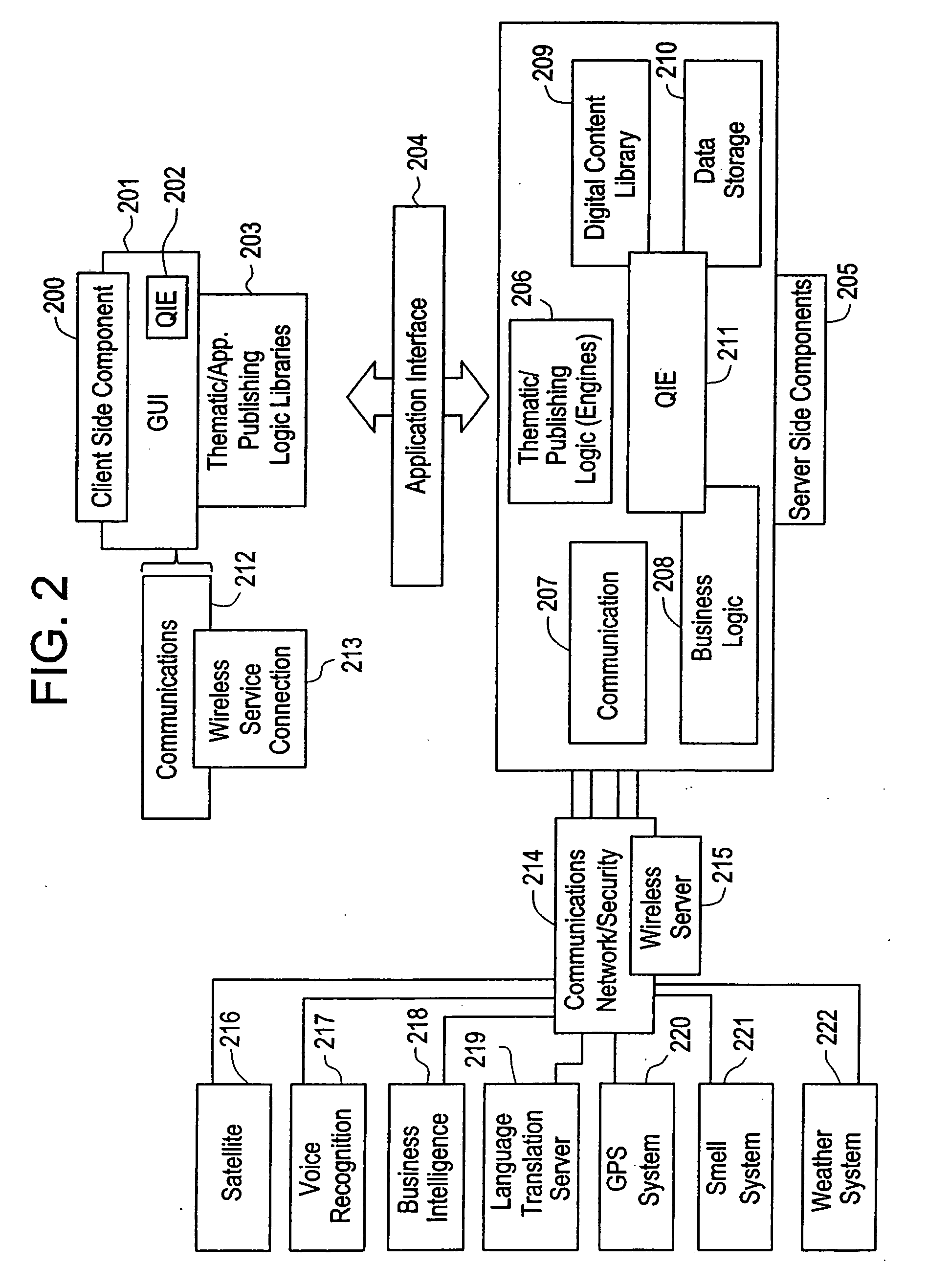
The present invention is directed to a method of integrating information, including real-time information, into a virtual thematic environment using a computer system, including accessing the stored information from a database or downloading the real-time information from a source external to the thematic environment; inserting the real-time information into the thematic environment; and displaying the information to a user within the thematic environment. In one embodiment, the computer system is connected to a holographic projection system such that the images from the thematic environment can be projected as holographic projections. The computer system includes an interactive software application platform having at least one thematic / publishing logic module which contains thematic environment rules; at least one digital content library module which provides content management on the thematic environment; and at least one quantum imaging environment (QIE) module which interprets content such that the content is manipulated and accessed by any device.
Owner:QUANTUM IMAGING LLC
Diamond components for quantum imaging, sensing and information processing devices
ActiveUS20160348277A1Reduce surface damageLong spin coherence timePolycrystalline material growthDiffusion/dopingInformation processingSurface roughness
A single crystal CVD diamond component comprising: a surface, wherein at least a portion of said surface is formed of as-grown growth face single crystal CVD diamond material which has not been polished or etched and which has a surface roughness Ra of no more than 100 nm; and a layer of NV− defects, said layer of NV− defects being disposed within 1 μm of the surface, said layer of NV− defects having a thickness of no more than 500 nm, and said layer of NV− defects having a concentration of NV− defects of at least 105 NV− / cm2.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX TECH LTD
Entangled quantum communications and quantum imaging
InactiveUS7536012B1Synchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesComputer hardwareSecure communication
An apparatus for generating a shared quantum key between a sender and a receiver comprises a sending apparatus which generates entangled photon pairs, and a receiving apparatus. A shared quantum key can be generated using temporal coincidences between photon detection events. For example, coincidences may be determined between sender and receiver photon detection events using detection data shared through a non-secure communications link between the sender and receiver. The quantum key can be used in encrypted communications. Similar apparatus and methods can be used for quantum imaging.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE THE
Interactive virtual thematic environment
The present invention is directed to a method of integrating information, including real-time information, into a virtual thematic environment using a computer system, including accessing the stored information from a database or downloading the real-time information from a source external to the thematic environment; inserting the real-time information into the thematic environment; and displaying the information to a user within the thematic environment. In one embodiment, the computer system is connected to a holographic projection system such that the images from the thematic environment can be projected as holographic projections. The computer system includes an interactive software application platform having at least one thematic / publishing logic module which contains thematic environment rules; at least one digital content library module which provides content management on the thematic environment; and at least one quantum imaging environment (QIE) module which interprets content such that the content is manipulated and accessed by any device.
Owner:QUANTUM IMAGING LLC
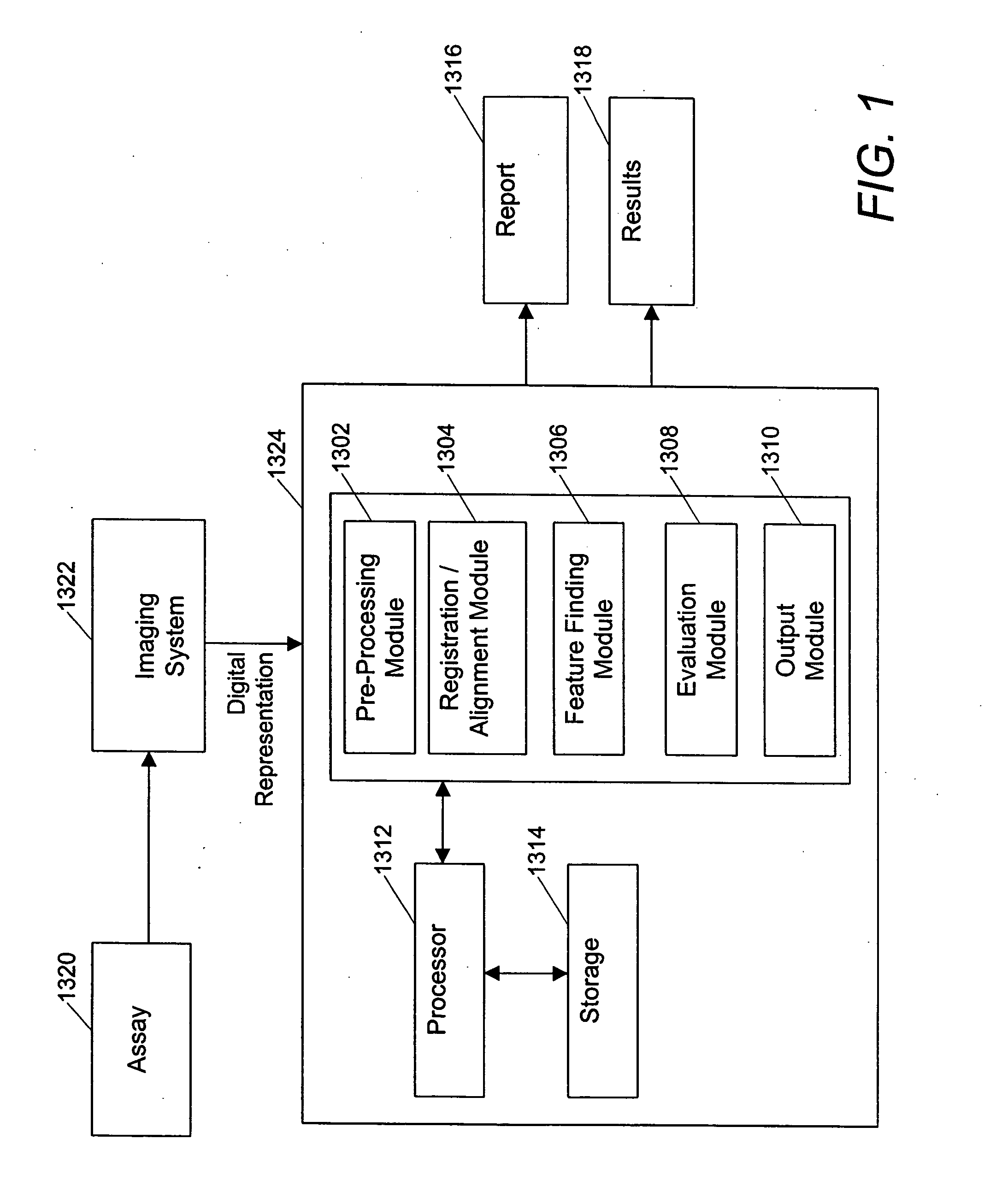
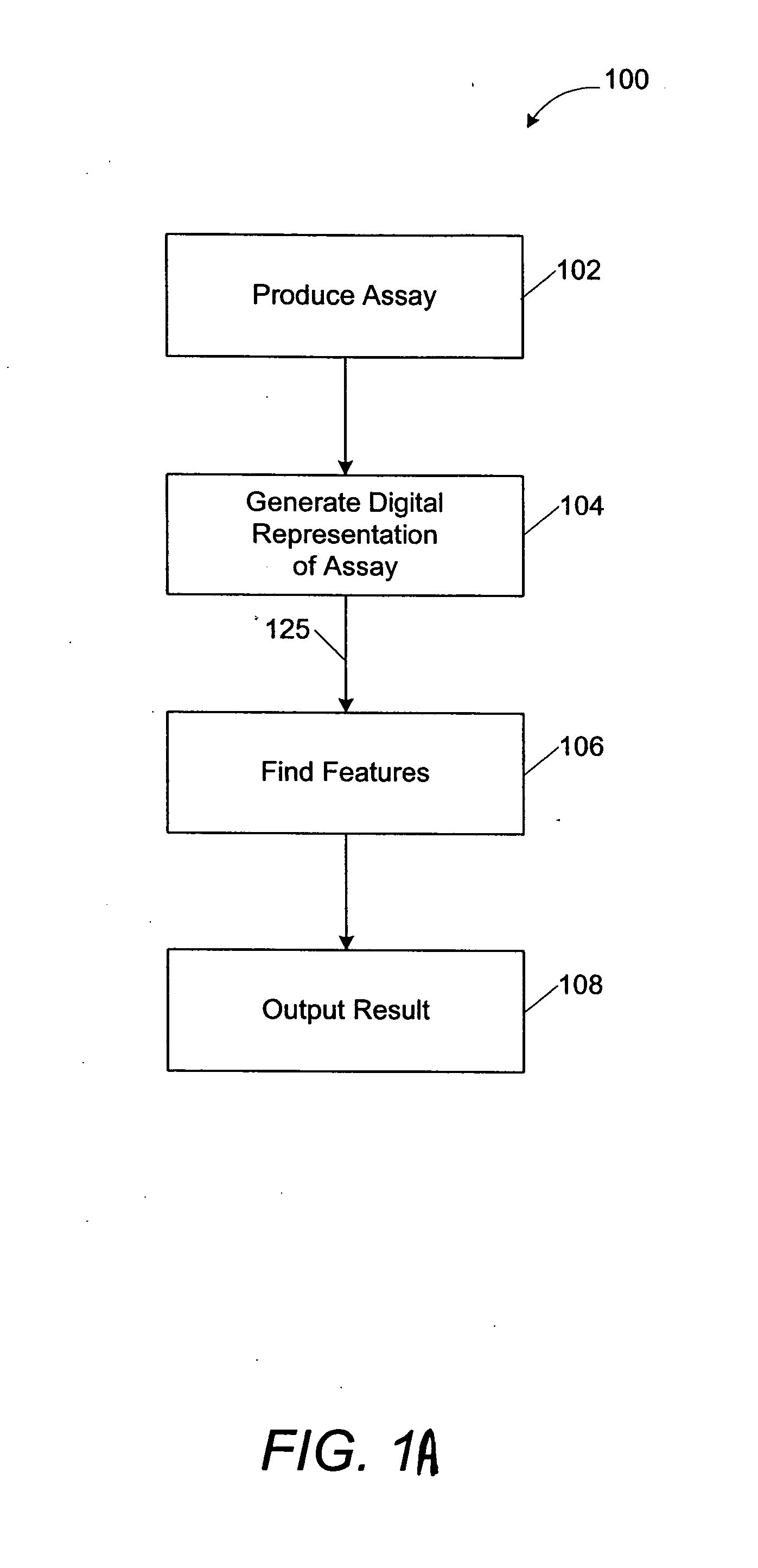
Spot finding algorithm using image recognition software
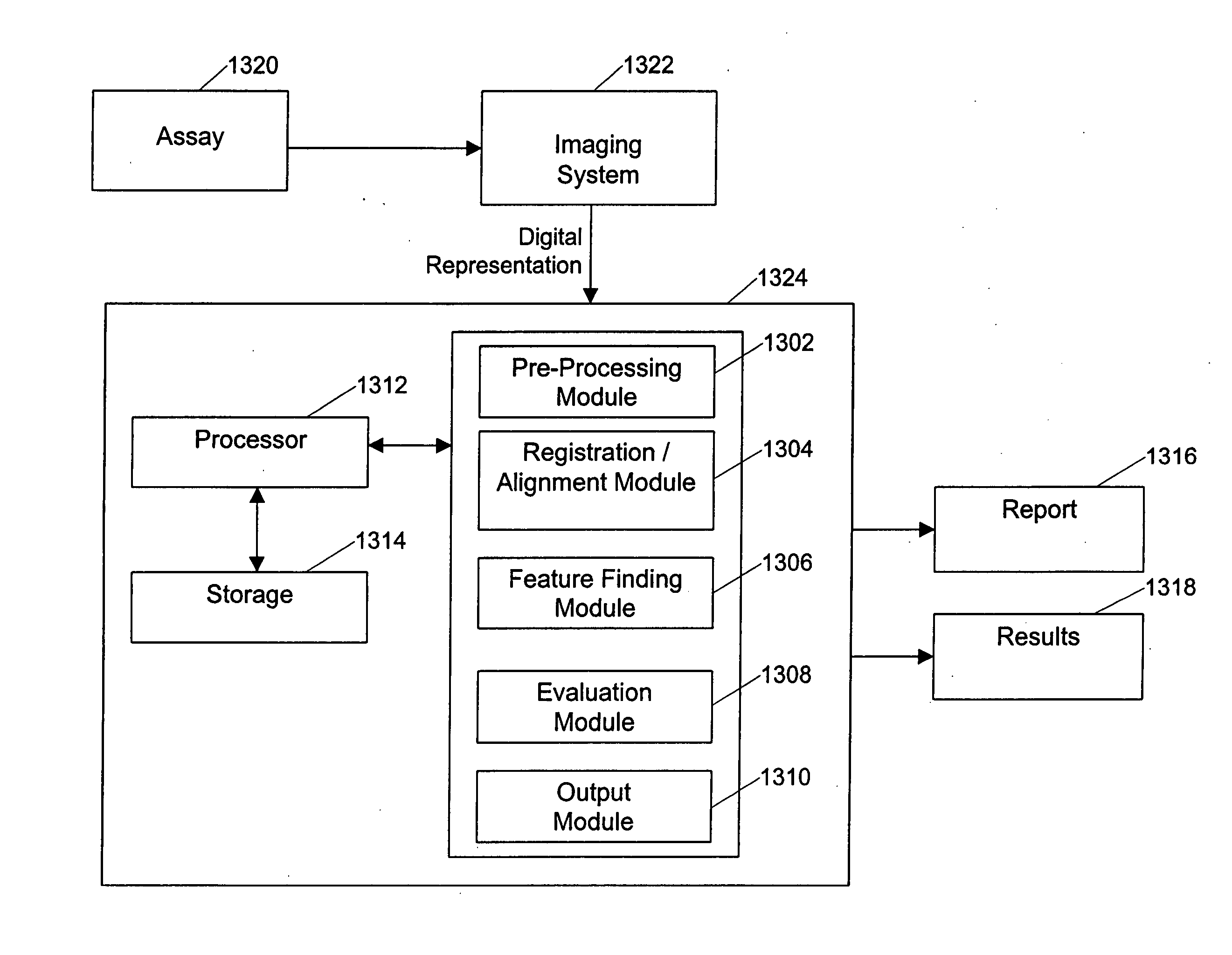
A plurality of samples are tested for their ability to enhance or inhibit a biological process in a multiplexed diffusive assay. The assay is imaged after the biological process has produced spots in a medium that indicate the tested enhancing or inhibiting ability of the samples. The image containing the resulting spots are evaluated to determine which samples caused the spots to form. The location of spots are identified by user selection or through a gradient triangulation technique that determines spot locations by analyzing the slope of pixel intensities in numerous subimages. The spots may also be analyzed by parametrically modeling the spots and comparing the spot characteristics in the image to a spot function, to determine the location of hit spots in the image. The hit spot locations, corresponding to the location of tested samples in the assay that enhanced or inhibited the biological process, are output to facilitate further analysis of the test samples.
Owner:DISCOVERY PARTNERS INT
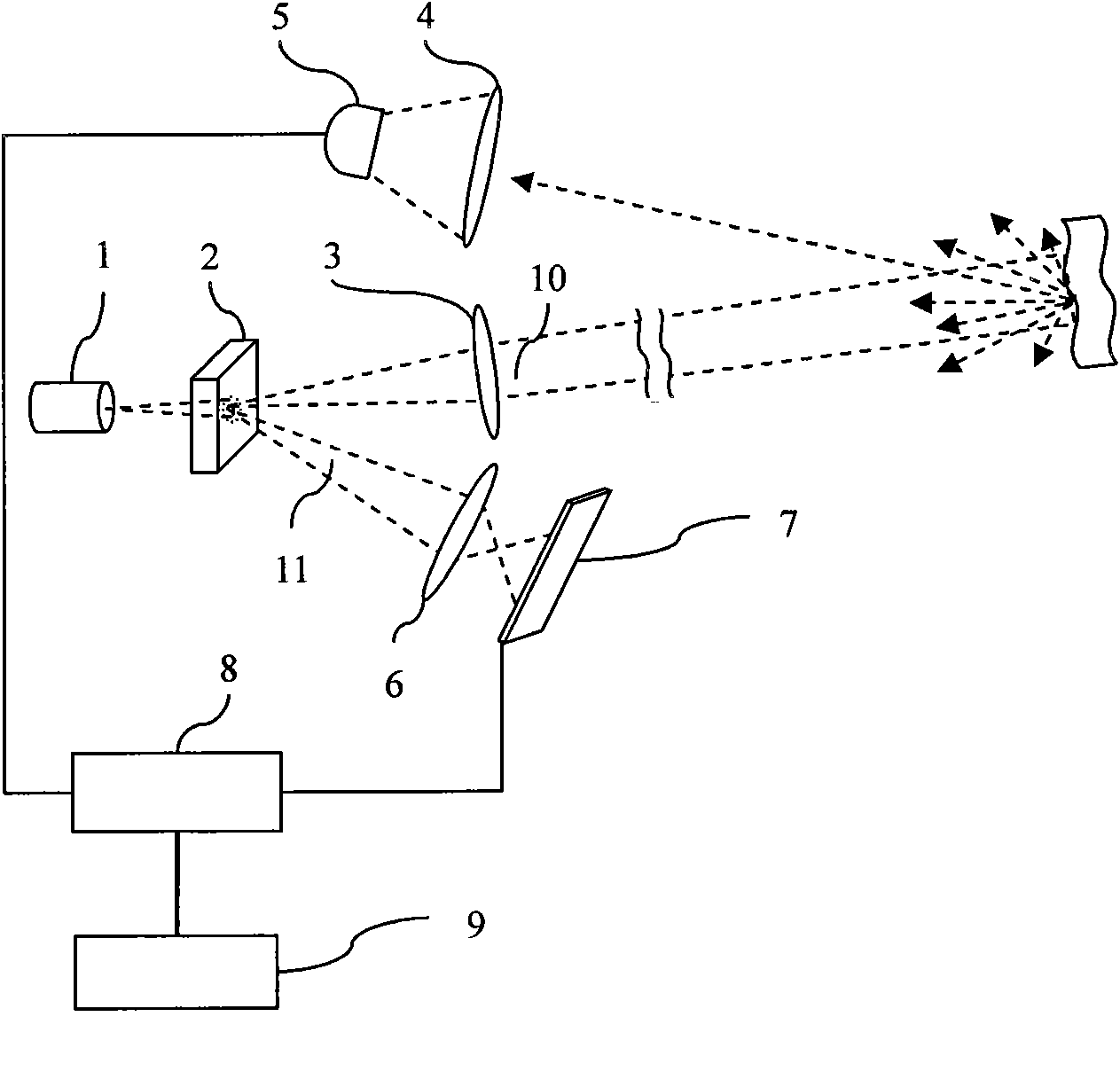
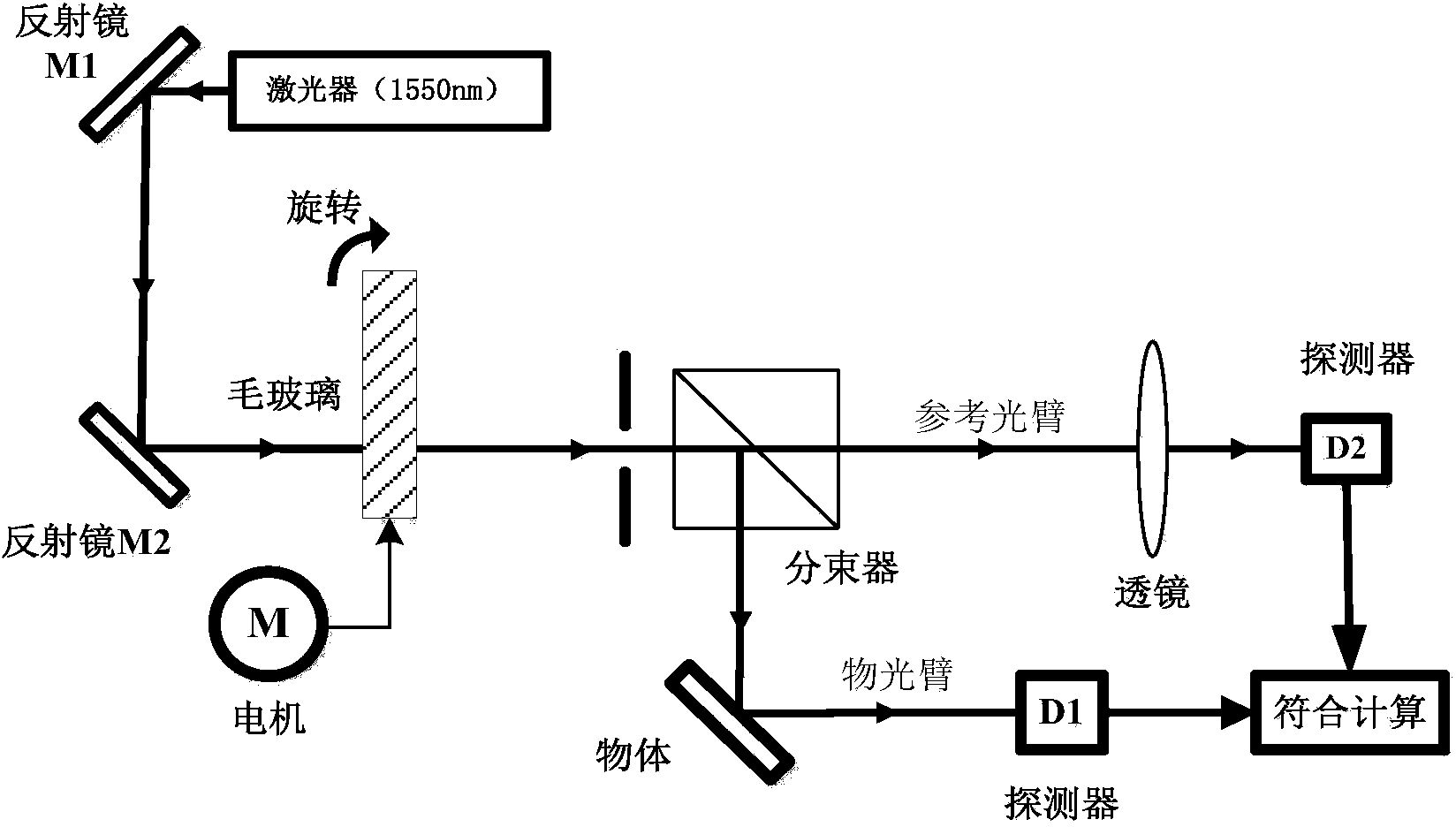
Laser radar based on highly-correlated quantum imaging principle
InactiveCN101846745AReduce lossRealize ultra-long-distance detectionElectromagnetic wave reradiationTime delaysDistance detection
The invention discloses laser radar based on a highly-correlated quantum imaging principle, which consists of a pulse laser, a parameter down-conversion non-linear device, a receiving lens, a photon detector, an imaging lens, an area-array detector, a time delay correlator and a signal processor. The pulse laser transmits laser pulse to generate two laser beams having different wavelengths and the highly correlation by parameter down-conversion non-linear device, one path of laser beam with long wavelength is irradiated on a measured object and is focused on a photon detector through a receiving lens to detector after being reflected, and a switch signal indicative of the detecting result of the photon is output; the other path of laser beam with short wavelength is irradiated to the area-array detector through an imaging lens to acquire a two-dimension photon image signal; and two paths of signals are correlated and integrated by the signal processor to acquire image and distance information of the measured object. The laser radar effectively solves the problem of transmission loss by using the laser with the long wavelength in an atmosphere window to realize the ultra-long distance detection and realize the super-resolution detection by using the highly-correction effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
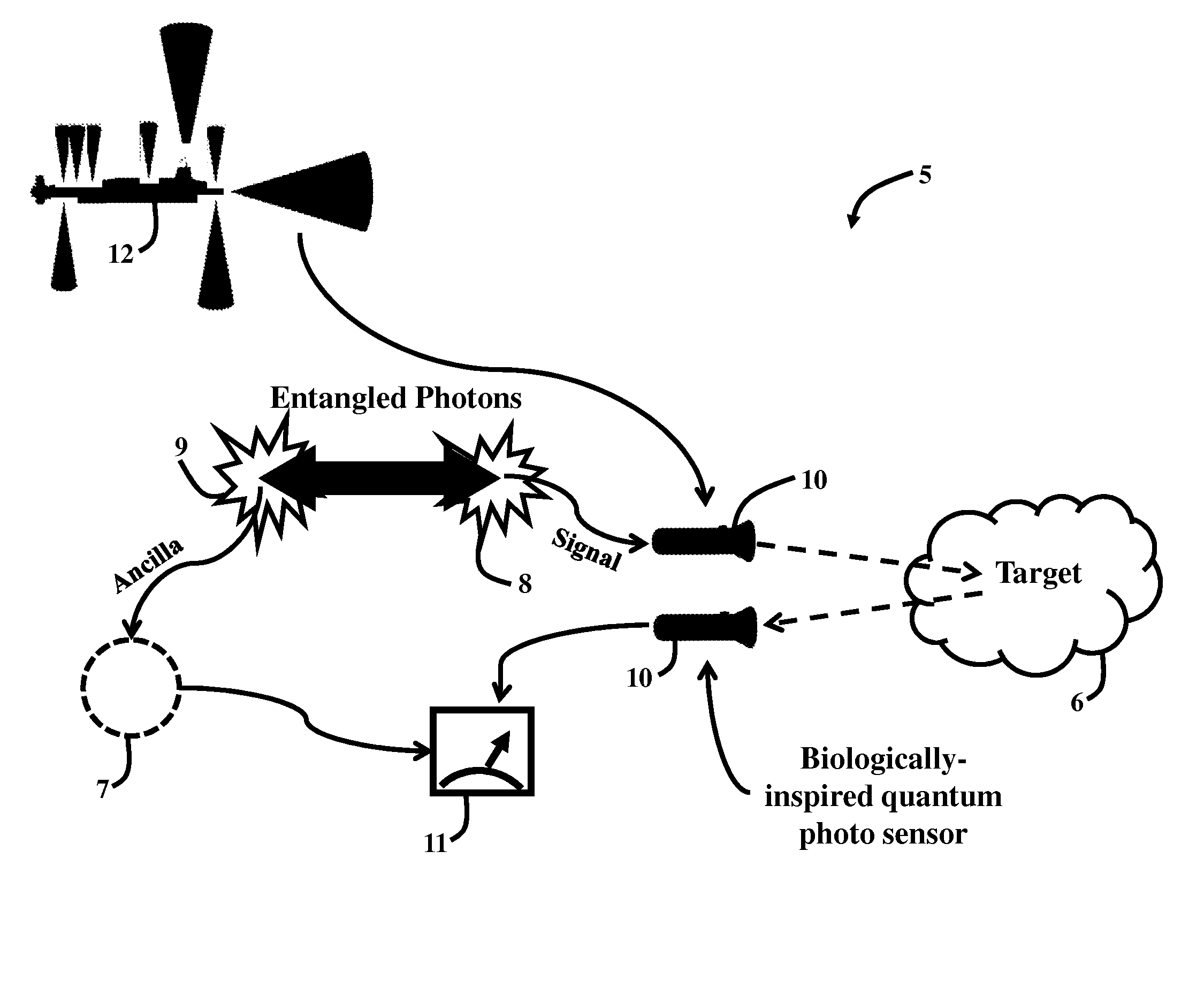
Quantum Imaging for Underwater Arctic Navigation
ActiveUS20160018525A1Optical rangefindersNavigational calculation instrumentsEnvironmental noisePhotonics
A quantum photonic imaging device used in an underwater vehicle for stealthy detection of underwater objects includes a photon generating module that generates an entangled pair of photons that includes a signal photon and an ancilla photon, wherein the ancilla photon is retained within the device; a transmitter that transmits the signal photon towards a region of space for detecting an underwater object; a receiver that detects an incoming photon to the device; and a correlation module that distinguishes the signal photon that is reflected back to the receiver due to a presence of the object from environmental noise photons, wherein the distinguishing includes determining an entanglement correlation of the detected photon with the ancilla photon, and wherein a presence of the entanglement correlation between the detected photon and the ancilla photon indicates that the detected photon is the signal photon reflected back from the object.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
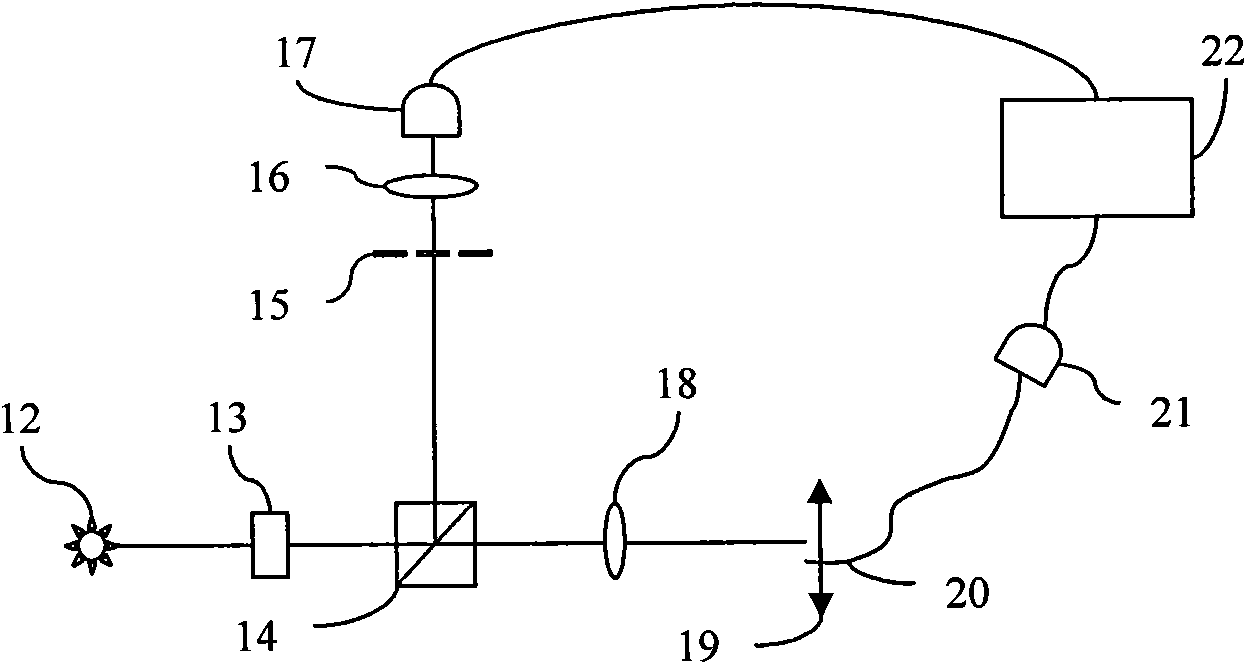
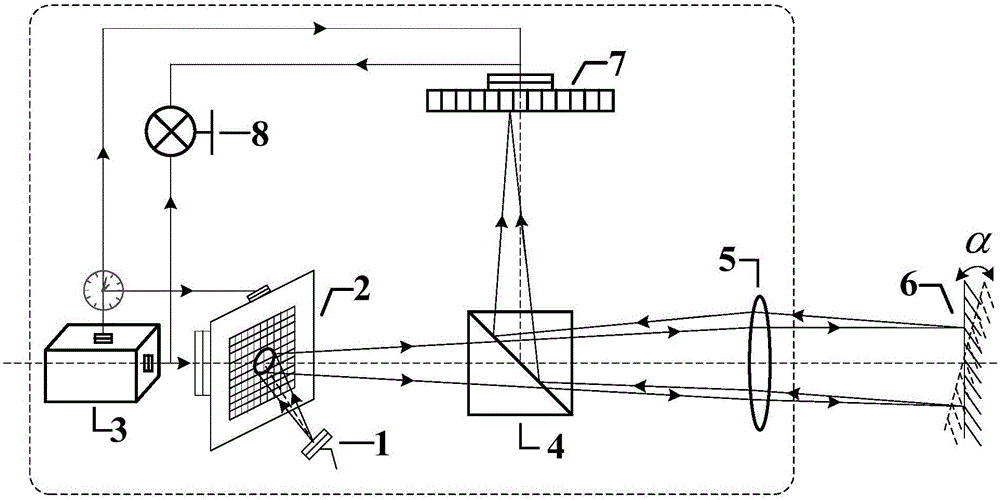
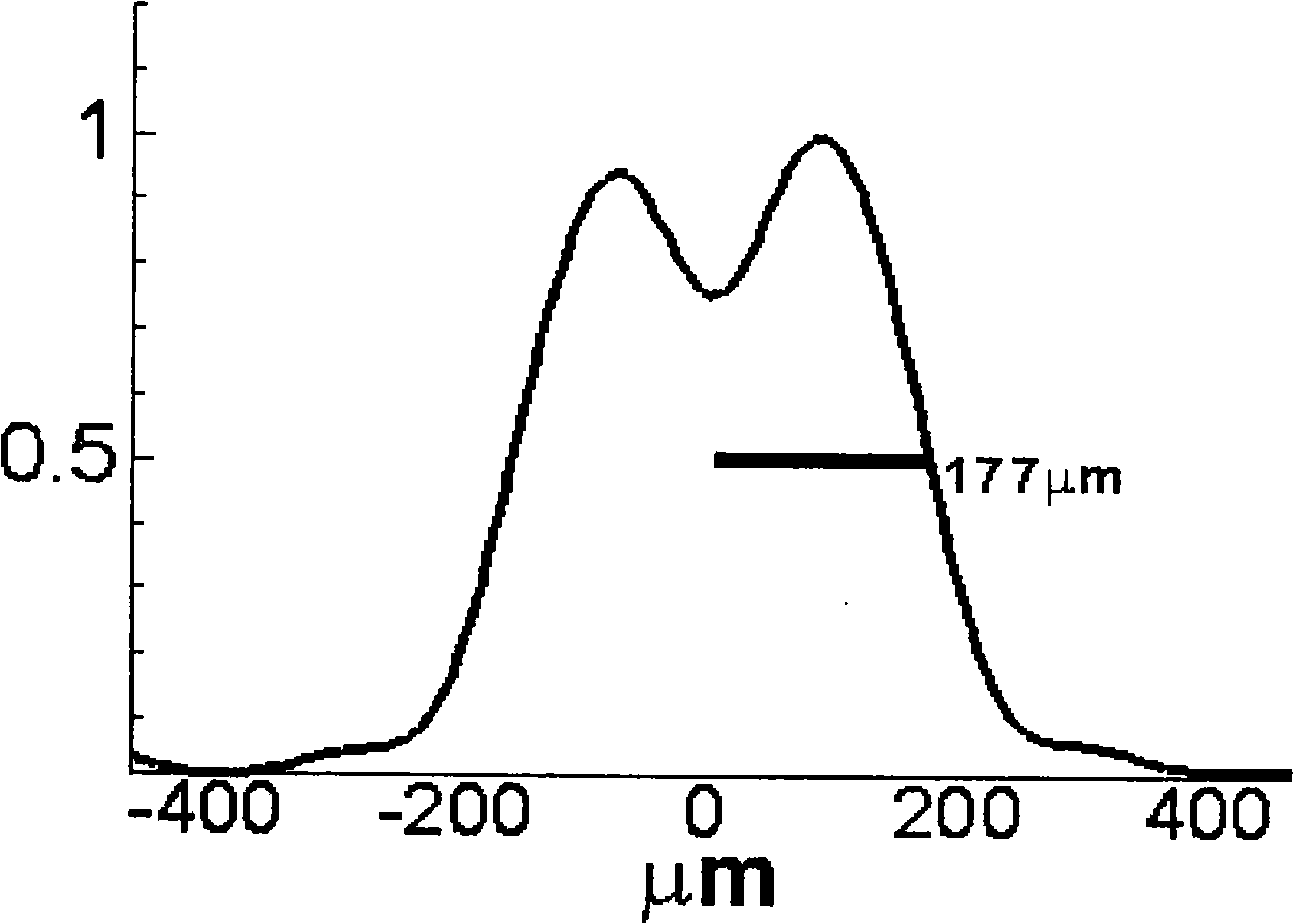
Calculated intensity correlated imaging autocollimator and measurement method
Disclosed are a calculated intensity correlated imaging autocollimator and a measurement method. The calculated intensity correlated imaging autocollimator comprises a light source, a digital micromirror device (DMD), a controller, a beam splitter, a lens, a device-under-test (DUT) reflective mirror, a CCD and an intensity correlated calculation module. A synchronous control module of the controller generates a synchronous clock signal which is applied to the DMD and the CCD. The intensity correlated calculation module records a light field modulation matrix generated by a light field modulation module and an echo signal received by the CCD simultaneously, and performs second-order intensity correlated calculation to indirectly calculate a tiny rotation angle of the DUT. The invention introduces a calculated correlated imaging method in quantum imaging technology to the design of the autocollimator, and can be used for effectively reducing the measurement errors caused by air turbulence and other factors and improving the sensitivity and stability of a system.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Quantum-imaging system and mode of operation and method of fabrication thereof
ActiveUS7781739B1Quality improvementIncrease catch rateElectric discharge tubesPhotometryOperation modeSpectrometer
A quantum-imaging system for detecting photons, including short-wavelength (<1 nm) photons, is provided. A quantum imaging system can include optical read-out and optical means, and can be configured to perform as both a photon counter and a photon spectrometer. A quantum-imaging system can function as a photon counter and be configured to measure photon beam fluences (e.g., in J / cm2) for both strong beams and weak beams, the latter ones, for example, in the intensity range of 1 pJ / cm2sec, or 0.1 μSv / h. The quantum-imaging system can also function as a photon spectrometer and can be configured to measure photon energies with high energy resolution such as, for example, 1% of photon energy.
Owner:MERCURY MISSION SYST LLC
Quantum image encryption method based on image association dissection
InactiveCN103778593AImplement encryptionImprove securityImage codingImage data processing detailsArray data structureBinary tree
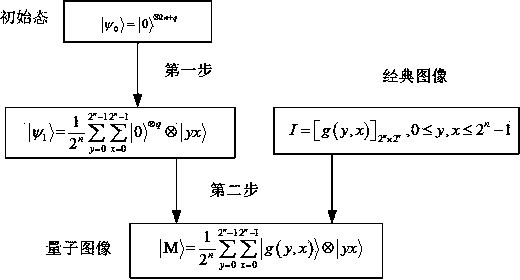
Disclosed is a quantum image encryption method based on image association dissection. A quantum-state superposition and measurement principle is used to establish correlation between image pixels. An image is dissected into superposition of a series of characteristic sub-images. Conversion operations are performed on the characteristic sub-images stored in a complete binary-tree digit group through use of a random phase door and a quantum rotating door and then a plurality of superpositions are performed on all the images through quantum-state superposition so as to obtain a cipher image. Schmidt orthogonal dissection is performed on the quantum random phase door, the quantum rotating door, a coefficient matrix and the cipher image so as to obtain a standard orthogonal ground state which is then used as a key. The quantum image encryption method based on the image association dissection has a larger key space so that strong attacks can be resisted and combination of a quantum-mechanical theory and an image encryption technology is realized. The method has classical information theory security and quantum information theory security so that quantum image encryption surpasses restriction of classical image encryption and compared with classical images, quantum images are higher in security.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
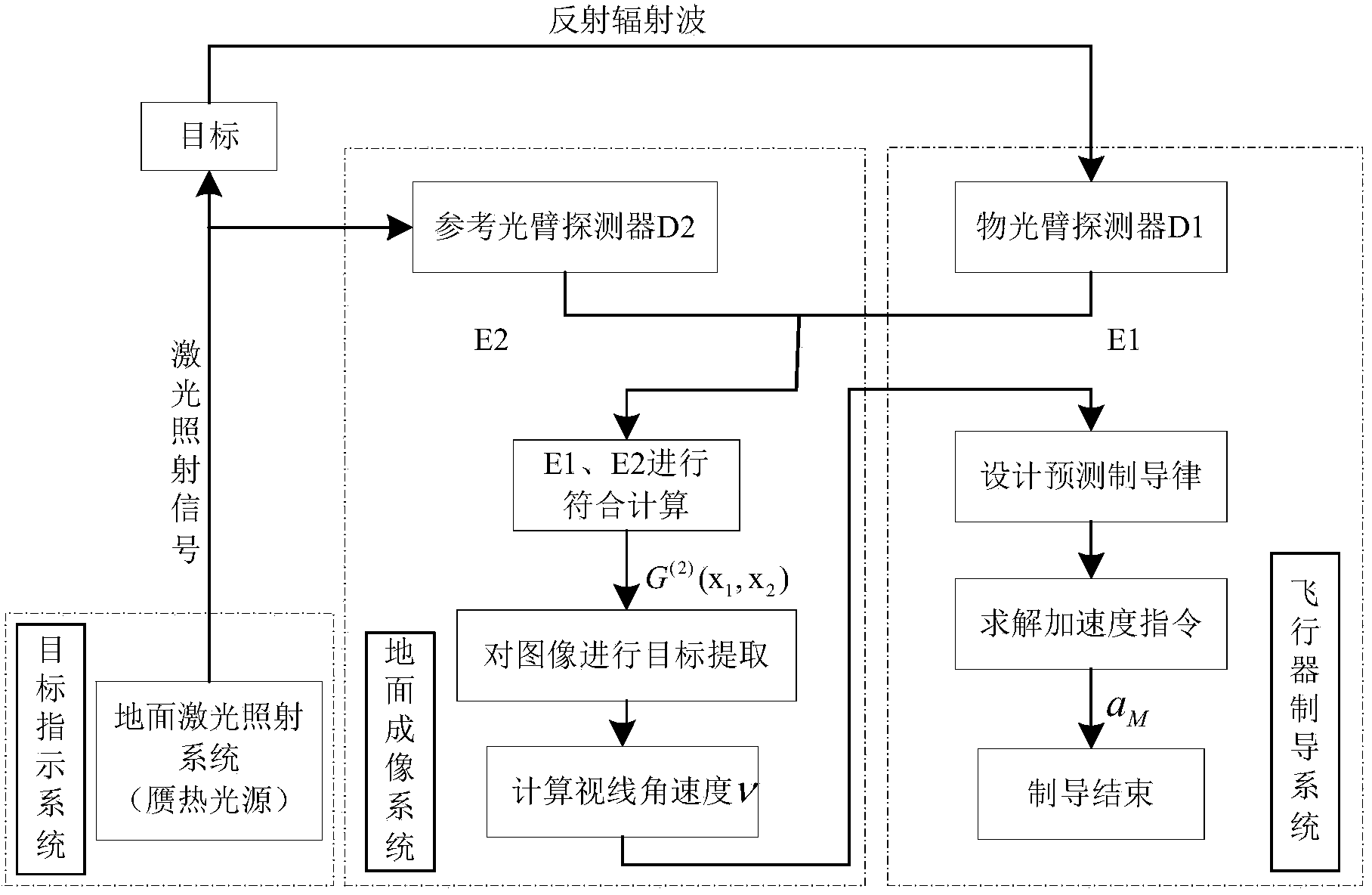
Aircraft forecast guidance scheme based on quantum imaging
ActiveCN104063623AImprove anti-interference abilityAdd dimensionTarget-seeking controlSpecial data processing applicationsFlight vehicleImage resolution
The invention relates to the field of the guidance technology based on optical imaging, in particular to an aircraft forecast guidance scheme based on quantum imaging. At preset, two main factors restricting guidance accuracy of an aircraft are that target detection resolution ratio is not high and affected by scattering particles easily, and imaging is difficult under extremely weak light; maneuvering targets cannot be tracked and guided quickly. According to the aircraft forecast guidance scheme based on quantum imaging, correlated imaging is performed by recording distribution strength of a radiation field and space fluctuation of a phase, and therefore, imaging resolution ratio is increased. However, the updating rate of measured data obtained from images is not high, so that a forecast guidance rule is adopted to overcome the shortcoming that guidance accuracy of the aircraft decreases due to low data updating rate of quantum imaging. By means of the aircraft forecast guidance scheme based on quantum imaging, quantum imaging can break up limitation of a diffraction limit, the resolution ratio can reach micron dimension, and guidance on the maneuvering targets can be improved by combining the forecast guidance rule. Therefore, the aircraft forecast guidance scheme based on quantum imaging is high in accuracy, strong in antijamming capability and suitable for guiding the aircraft to track the maneuvering targets.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Quantum imaging with undetected photons
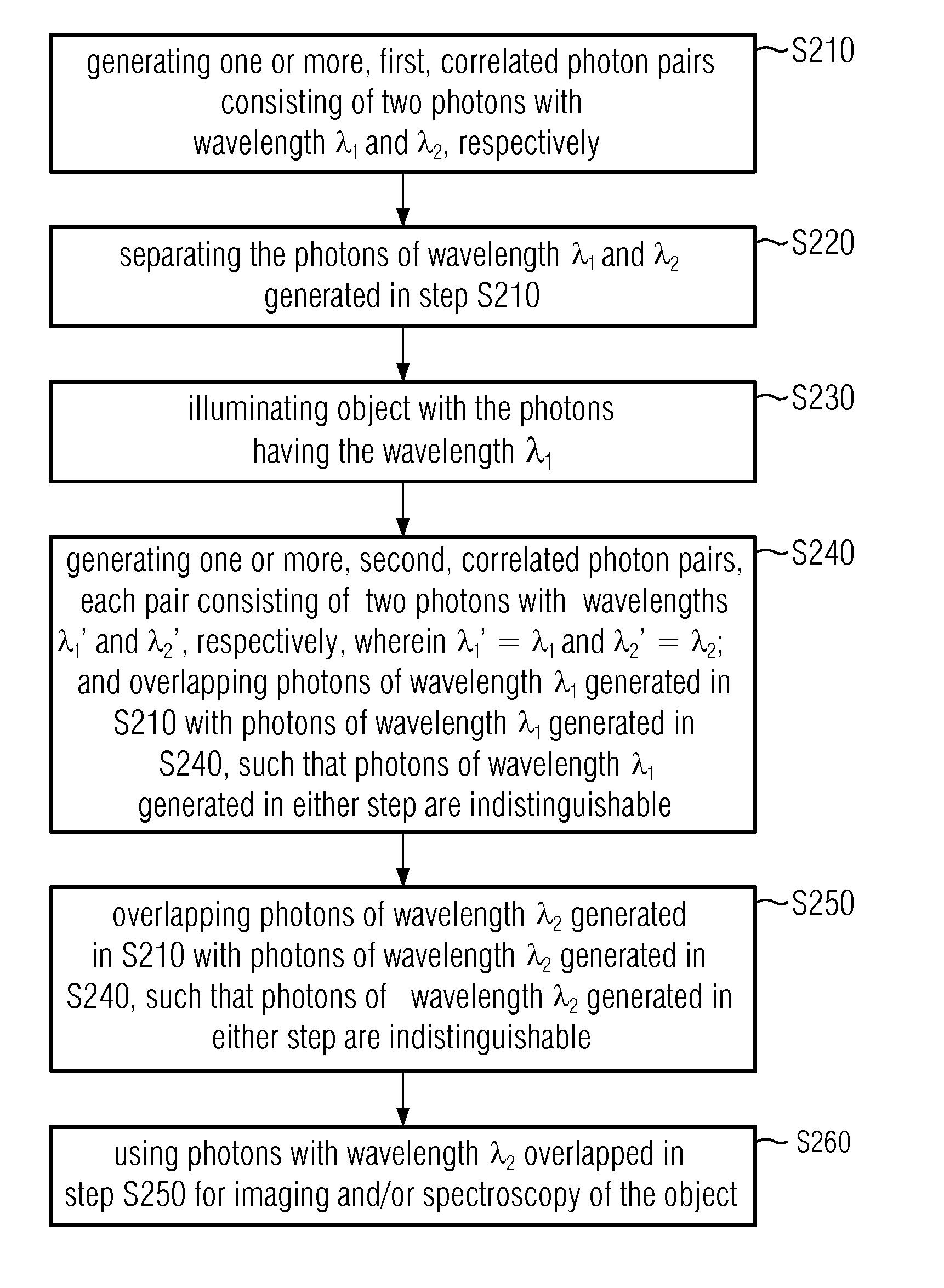
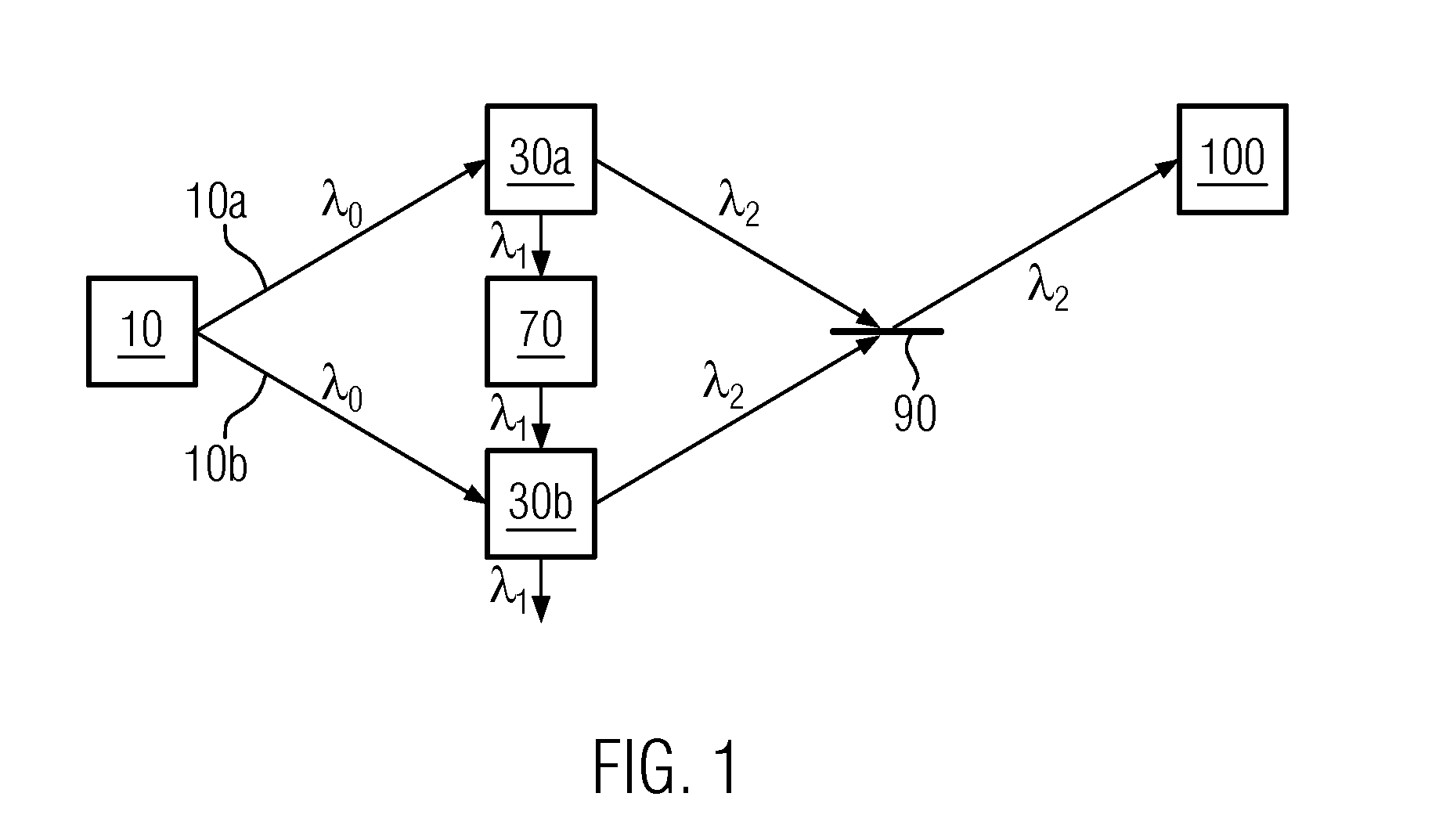
ActiveUS20150177128A1Simple methodRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectroscopyLength wave
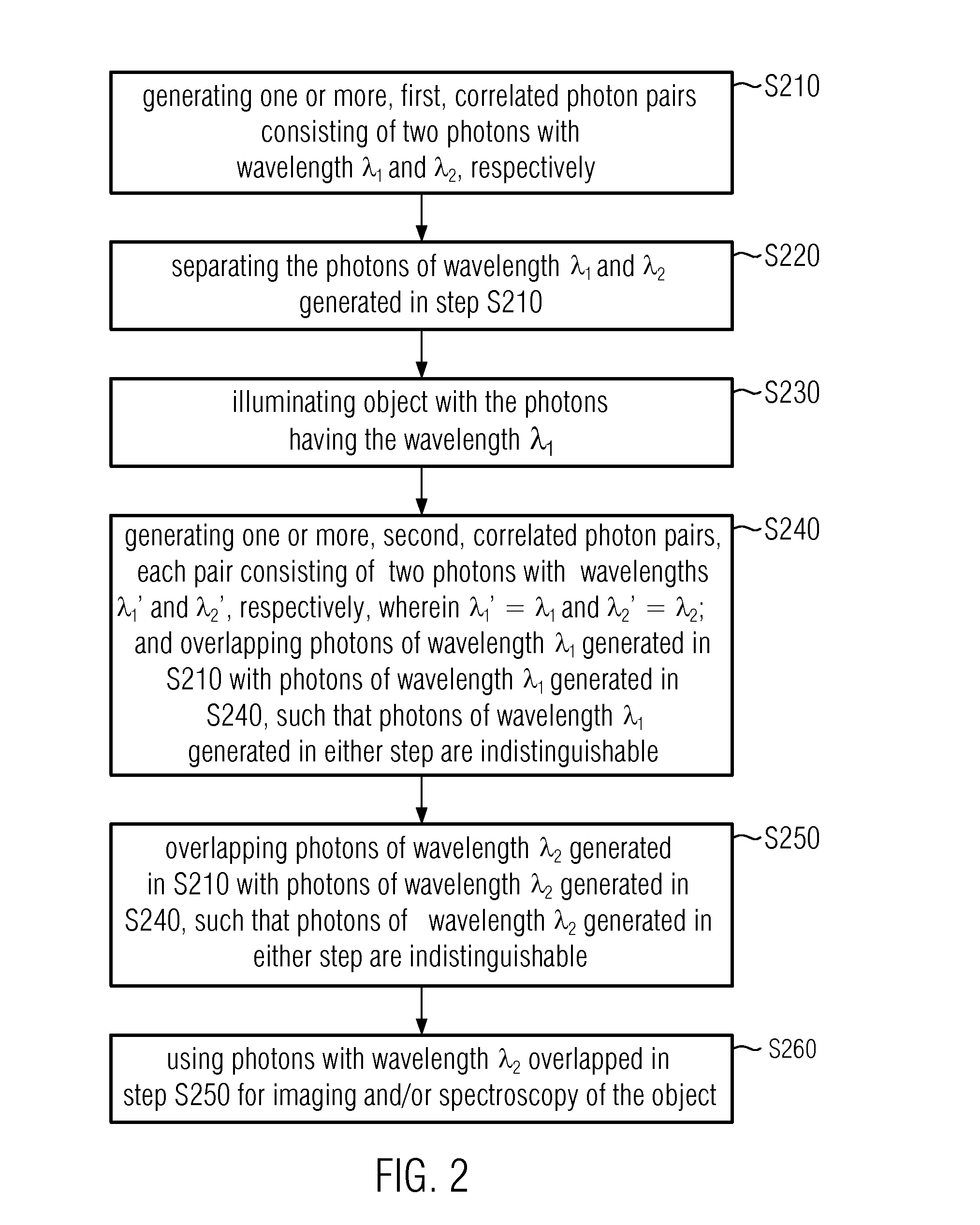
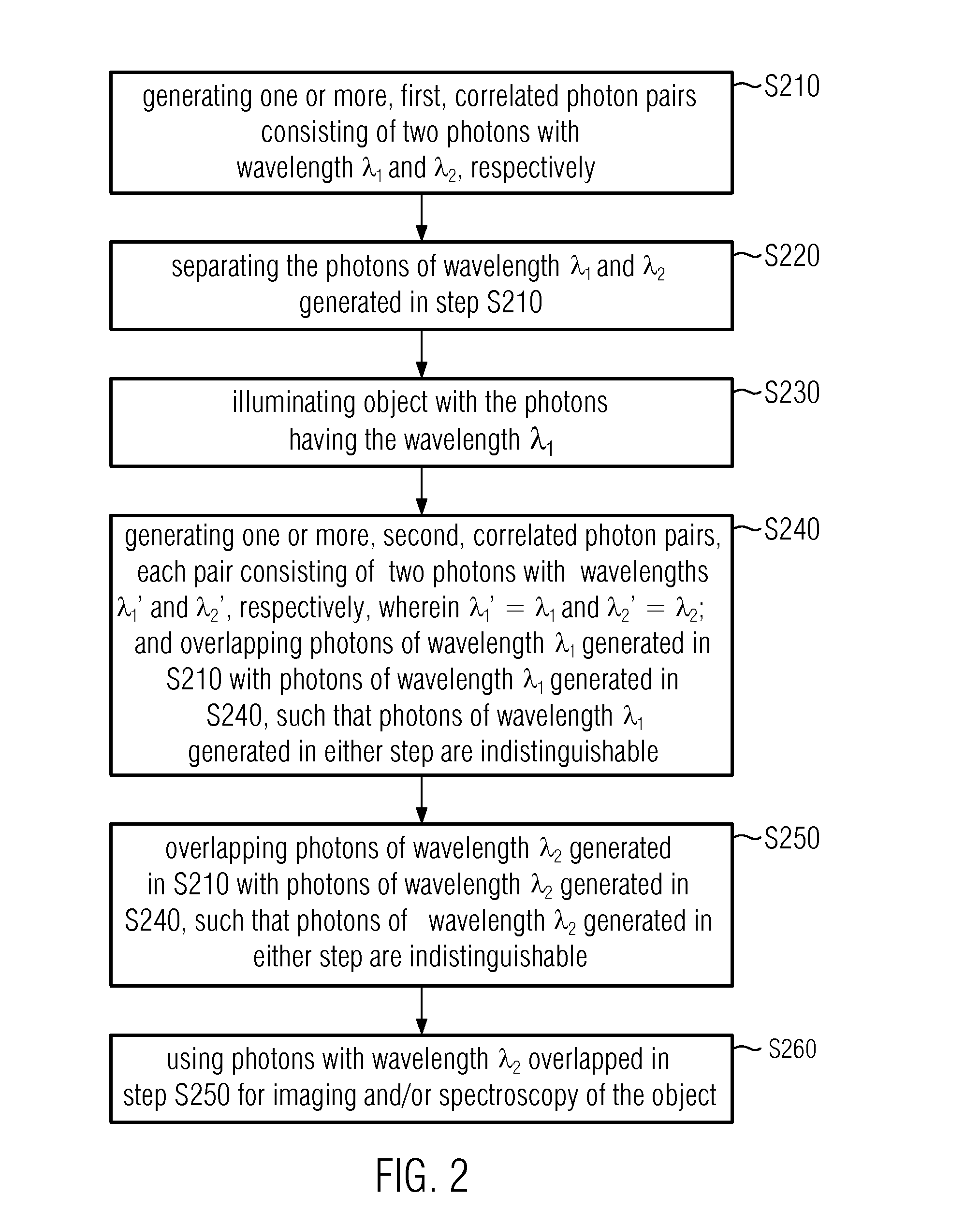
A method comprises: generating a first and a second correlated photon beam with wavelengths λ1 and λ2, respectively, wherein preferably λ1≠λ2; separating the first photon beam and the second photon beam; illuminating an object with the first photon beam; generating a third and a fourth correlated photon beam with wavelength λ1 and wavelength λ2, respectively; overlapping the first photon beam with the third photon beam such that photons of wavelength λ1 in either photon beam are indistinguishable; overlapping the second photon beam with the fourth photon beam such that photons of wavelength λ2 in either photon beam are indistinguishable; and using the overlapped photons of wavelength λ2 for imaging and / or spectroscopy of the object such that the photons that illuminate the object are not detected.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VIENNA +1
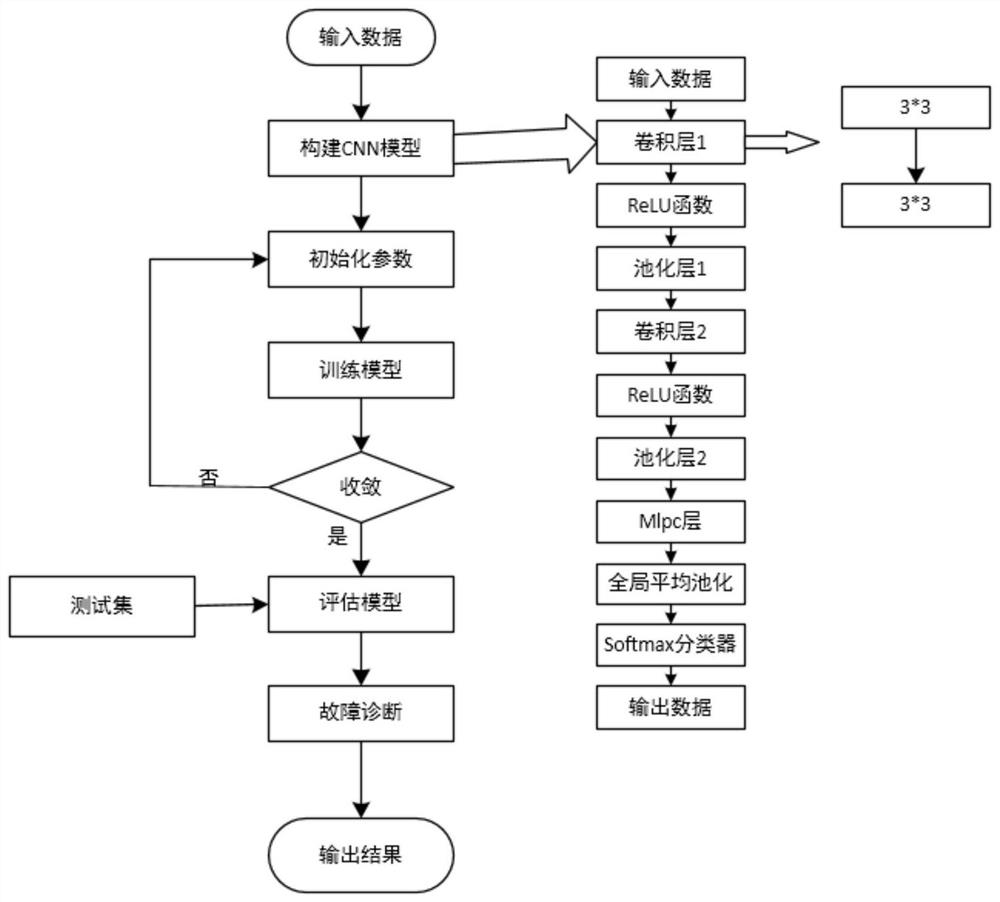
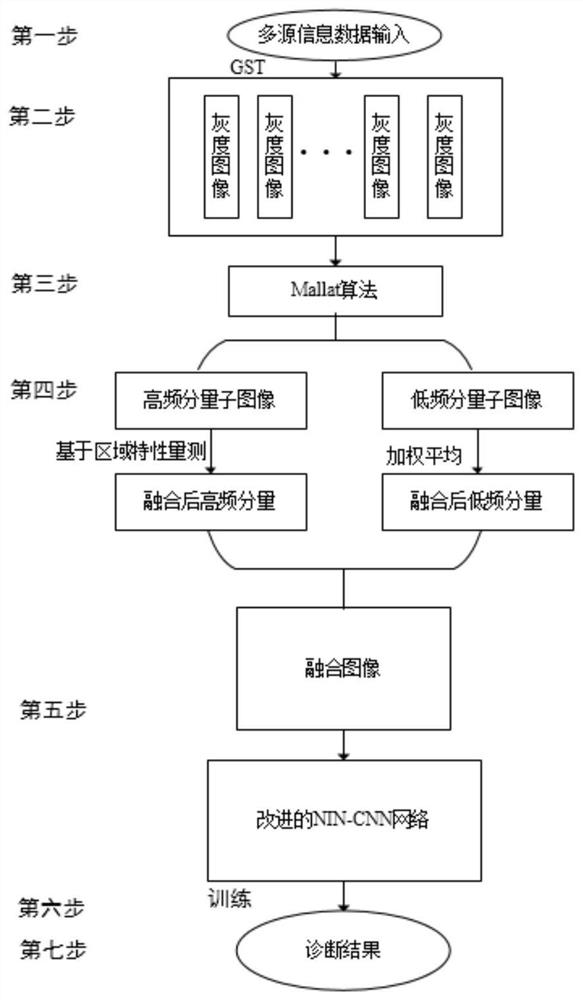
Power transformer winding fault diagnosis method based on GSMallat-NIN-CNN network
ActiveCN111751763AProblems with suppression strength varying with distanceImprove integrityImage enhancementImage analysisAlgorithmGray level
The invention discloses a power transformer winding fault diagnosis method based on a GSMallat-NIN-CNN network, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the measurement of a vibration condition of a transformer winding through a multi-channel sensor, and obtaining multi-source vibration data of a transformer; converting the multi-source vibration data obtained by measurement into grayscaleimages by using GST gray level transformation; decomposing each grayscale image into a high-frequency component sub-image and a low-frequency component sub-image layer by layer by adopting a Mallat algorithm, and performing image fusion on a high-frequency component sub-image and a low-frequency component sub-image; reconstructing the fused grayscale images, and encoding the vibration grayscale images according to the fault state of the transformer winding; establishing a transformer fault diagnosis model based on a GSMallat-NIN-CNN network; randomly initializing network parameters, dividinga training set and a test set, and training and optimizing the network through the training set; and storing the trained network, and testing the network through the test set. According to the method,t noise in a multi-source signal is effectively suppressed, the integrity of feature information is improved, the calculated amount is reduced, and the fault diagnosis accuracy is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
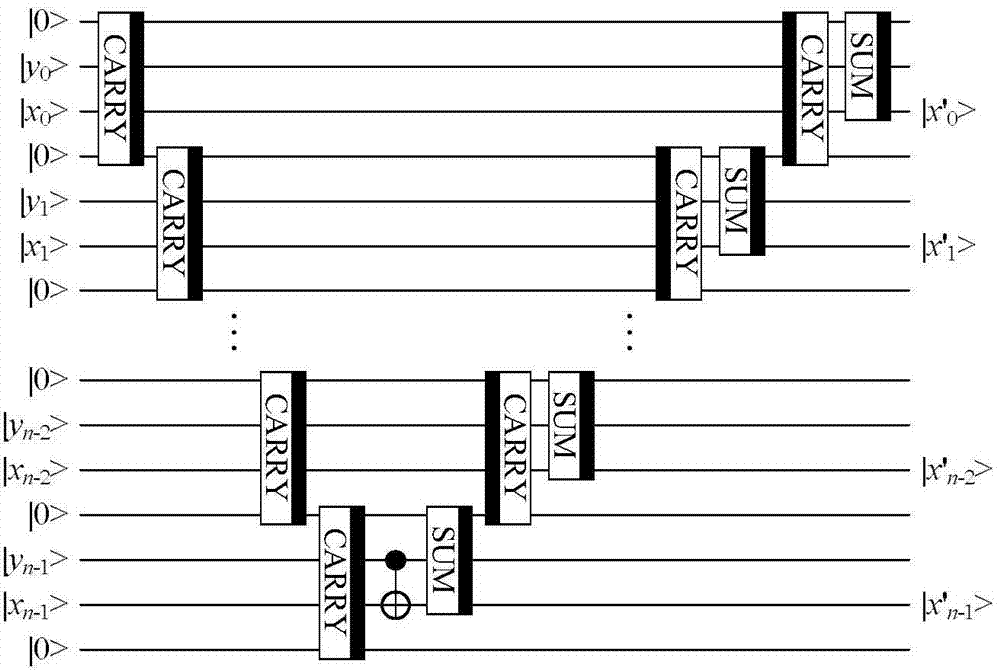
Quantum image matching method
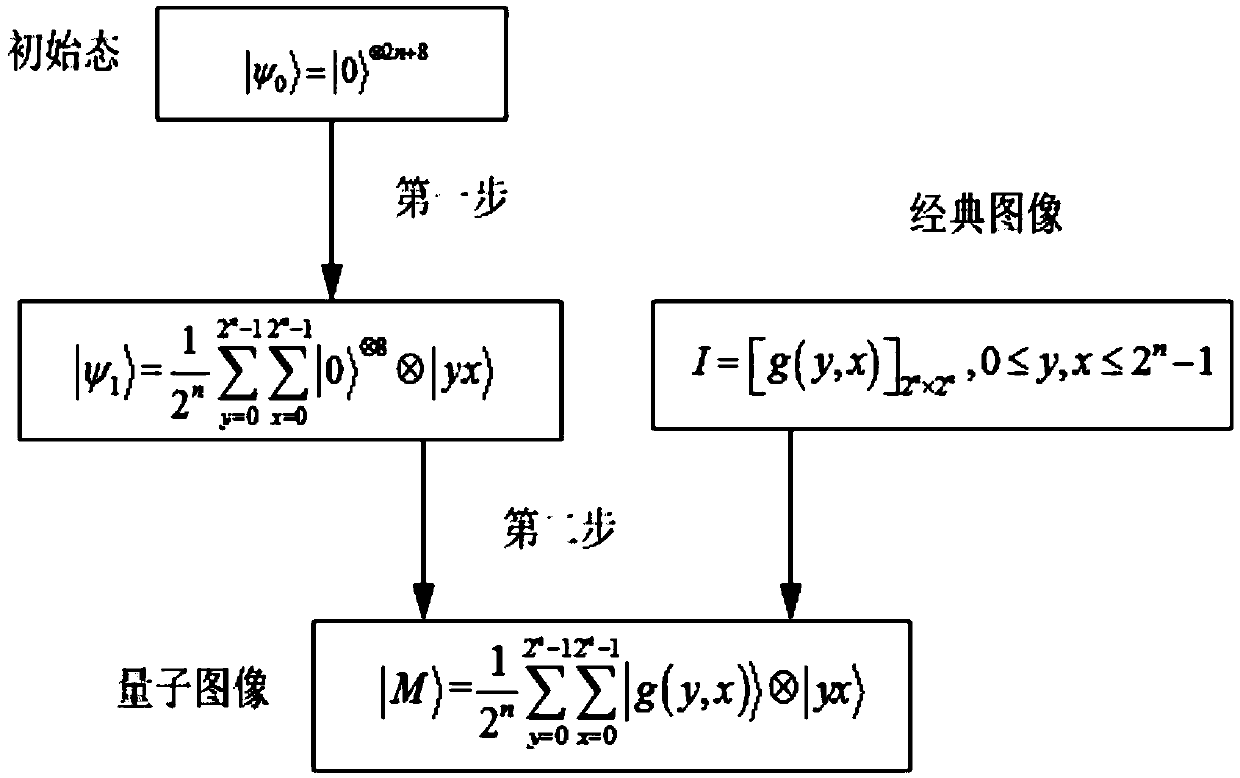
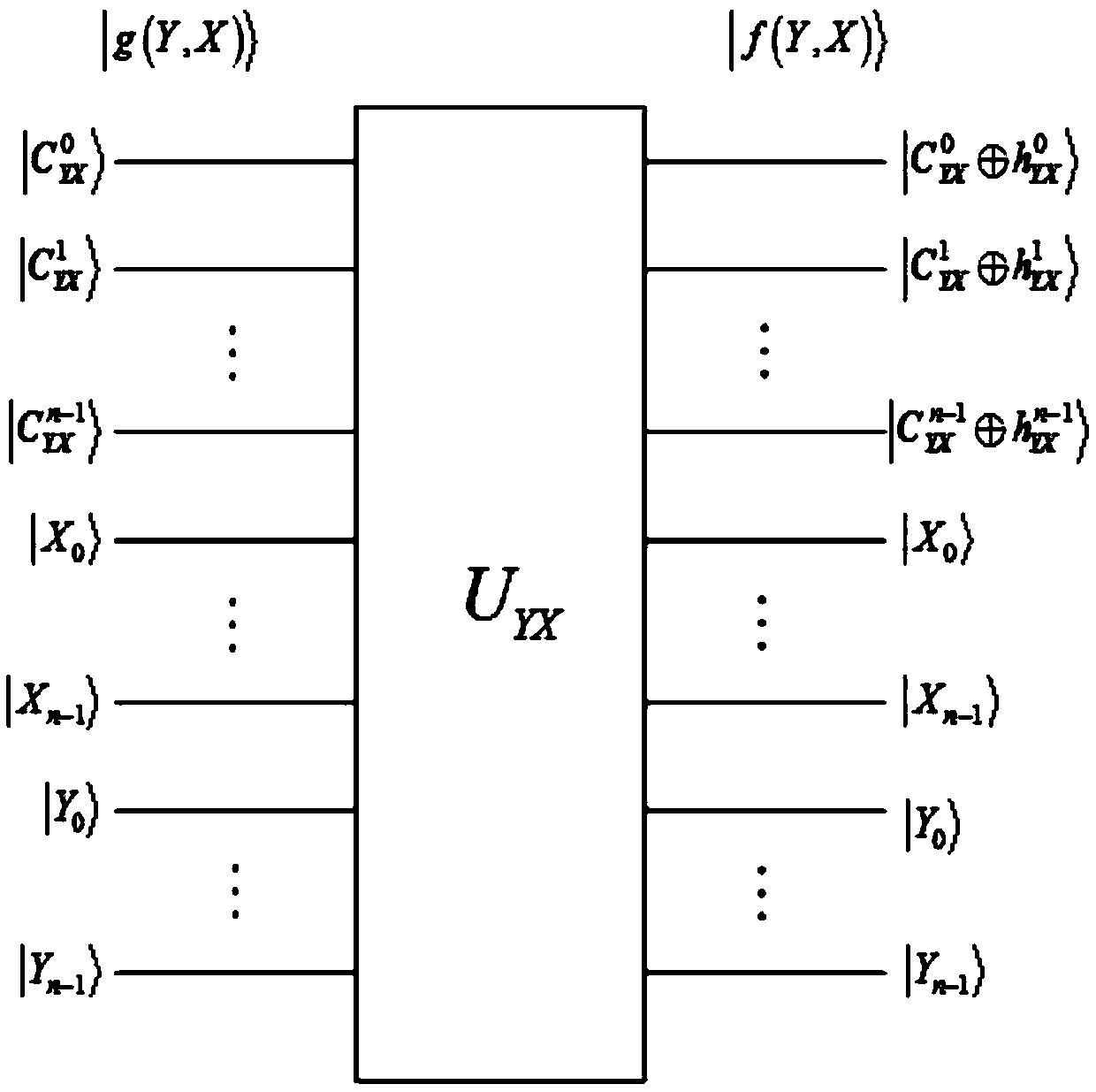
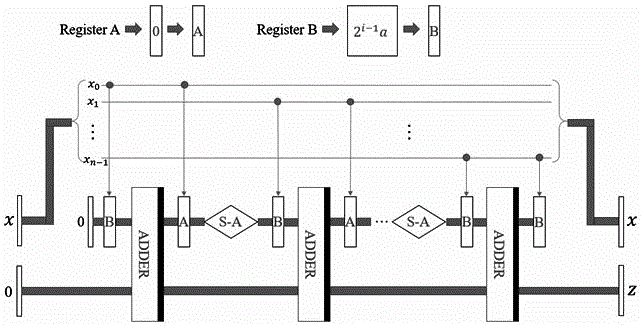
ActiveCN107204008AAchieve matchingFind the coordinates of the upper left corner exactlyImage analysisQuantum circuitImaging processing
The invention relates to a quantum image matching method. In combination with quantum calculation and classic computer image matching techniques, the method comprises steps as follows: S0, the size of a quantum reference image is set to be 2<n>*2<n>, and the size of a quantum template image is set to be 2<m>*2<m>; S1, the quantum reference image is prepared and stored in an NEQR manner, and an NEQR expression shown in the specification of the quantum reference image is obtained; S2, a quantum route U0 of the quantum reference image is designed, and the output state, shown in the specification, of the quantum reference image is obtained; S3, the quantum template image is prepared and stored in a classic image processing manner, a quantum route of the quantum template image is designed according to independent basic state expressions adopted for pixel point coordinates and corresponding pixel values, and the output state, shown in the specification, of the quantum template image is obtained; S4, quantum image matching is conducted according to the output state, shown in the specification, of the quantum reference image, the output state, shown in the specification, of the quantum template image as well as two added auxiliary quantum bits. Quantum image matching is realized by use of basic quantum bit gates and modular quantum routes, the matching efficiency is high, and the application range is wide.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Remote-sensing picture interpolation method based on small wave fractal
InactiveCN1892698AImprove spatial resolutionImprove application levelImage enhancementElectromagnetic wave reradiationSelf adaptiveWavelet transform
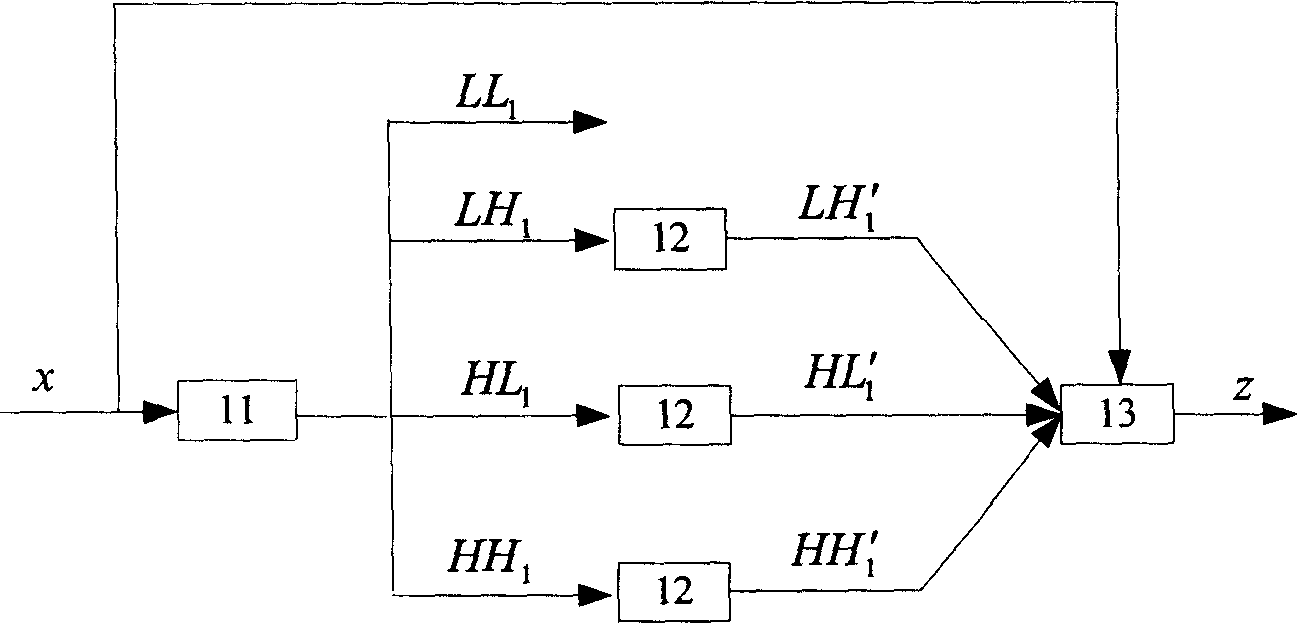
A wavelet fractal based on remotely sensed image interplation method adopts wavelet analysing and fractal technology adjoint to realize remotely sensed image interplation. It contains firstly making wavelet conversion to remotely sensed image to obtain remotely sensed image one low-frequency component and three high frequency component, dividing each high frequency component into mutually exclusive subimage block, utilizing image fractal character to calculate each subimage block fractal parameter and making self adaptive fractal interplation to every subimage block, then merging high frequency component subimage block and original image after fractal interplation, finally making inverse wavelet conversion to merged image to obtain high resolution remotely sensed image processed by wavelet fractal interplation.
Owner:GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI GSCAS
Strength relating quantum imaging microscope
InactiveCN101281292AIncrease the effective numerical apertureHigh-resolutionSurgeryMicroscopesBeam splitterData acquisition
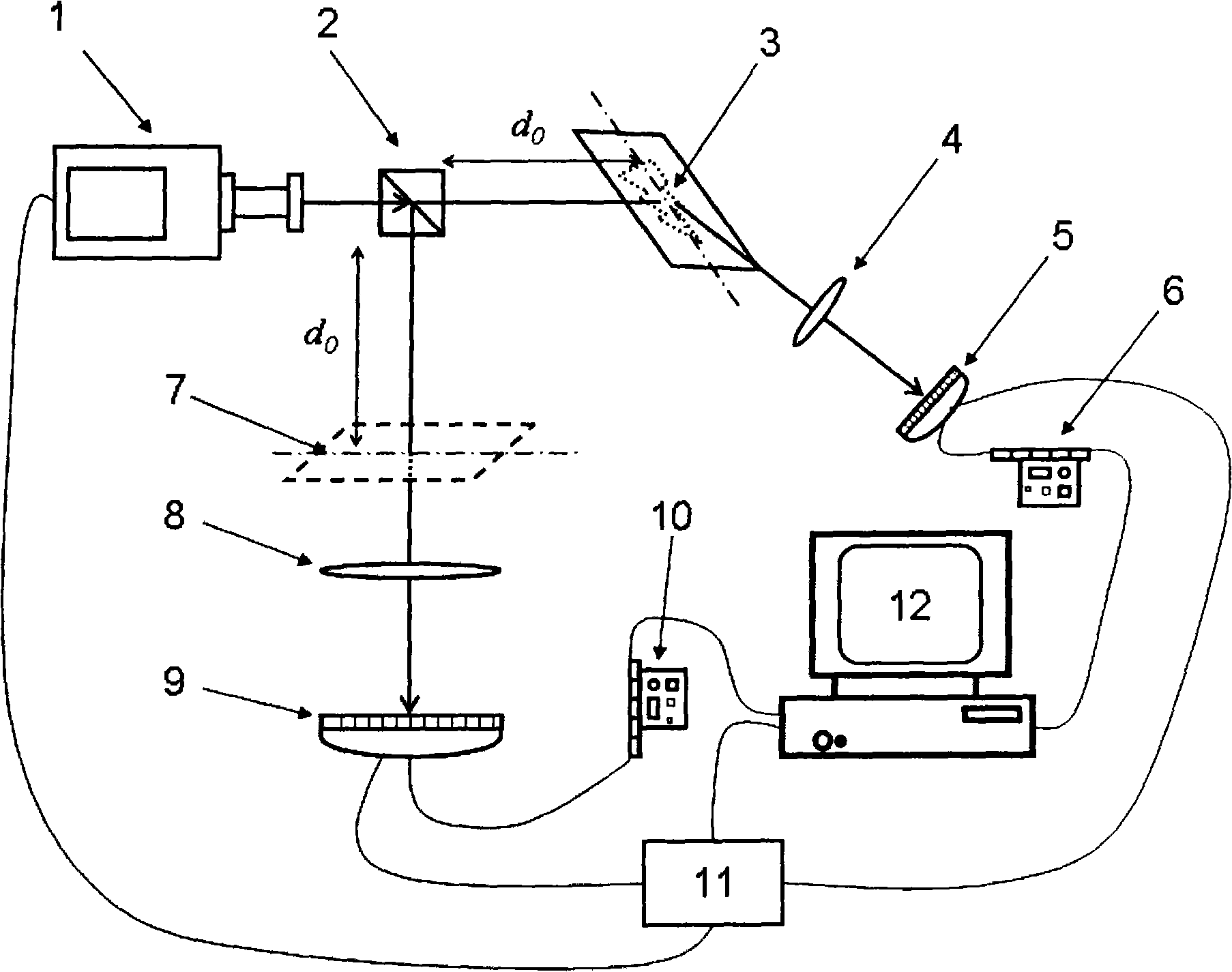
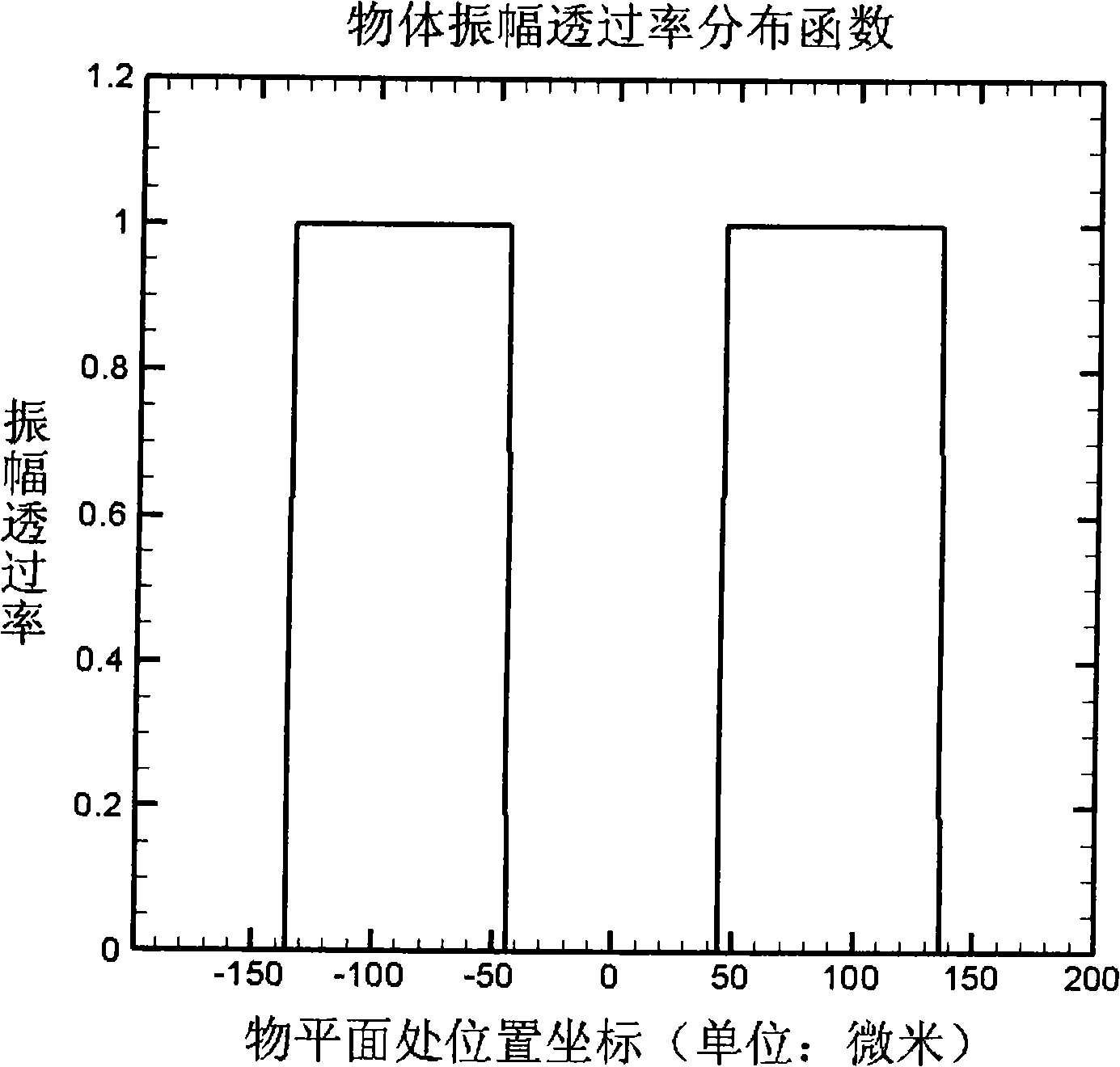
A strength related quantum imaging microscope is characterized by including a pulsed light source. The light beams generated by the pulse light source are divided into transmission light beams and reflectance light beams by a beam splitter; an object to be measured, an object arm imaging lens and an object arm detector are arranged in sequence at the transmission light beam direction to constitute an object arm, a virtual plane, a reference arm imaging lens and a reference arm detector are arranged in sequence at the reflection light beam direction to constitute a reference arm; the object arm detector and the reference arm detector are respectively connected to the computer through a first data acquisition card and a second data acquisition card, the computer is provided with a strength related arithmetic software, the computer is respectively connected to the pulse light source, the object arm detector and the reference arm detector through a synchronizing signal generator, and the reference arm imaging lens is provided with high numerical aperture. The invention can obtain a high resolutions image by increasing the numerical aperture of the reference arm imaging lens.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
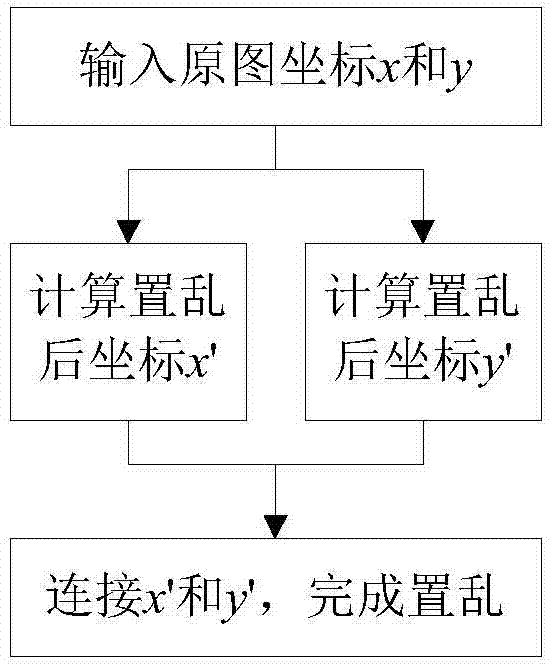
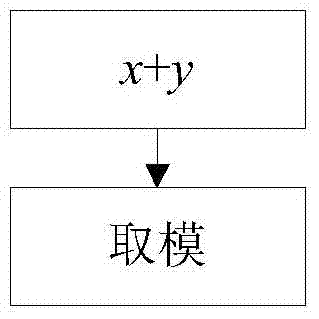
Method for achieving Arnold image scrambling effect on quantum computer
ActiveCN103886542AImplement Arnold scramblingGuaranteed to run directlyImage data processing detailsQuantum imageNetwork complexity
The invention relates to a method for achieving an Arnold image scrambling effect on a quantum computer. The method is characterized in that the Arnold image scrambling effect can be achieved on the quantum computer. The method includes the steps that an original quantum image is provided, Arnold scrambling conversion is carried out on an x-axis coordinate of the original image, and Arnold scrambling conversion is carried out on a y-axis coordinate of the original image; scrambling conversion carried out on the x-axis coordinate further includes the procedures of calculation of x+y and execution of a modular arithmetic on 2n; scrambling conversion carried out on the y-axis coordinate further includes the procedures of calculation of 2y, calculation of x+2y and execution of a modular arithmetic on 2n. The algorithm is provided in a quantum circuit form, and it is guaranteed that the algorithm can directly operate on the quantum computer; compared with an existing method for achieving the Arnold image scrambling effect on the quantum computer, a modular arithmetic operation can be achieved by ignorance of carry directly, and network complexity is greatly reduced.
Owner:上海华实投资有限公司
Compressed sensing imaging device and method based on entangled two-photon signal
ActiveCN108844464AReduce storagePromote recoveryImage enhancementUsing optical meansSpatial light modulatorImaging quality
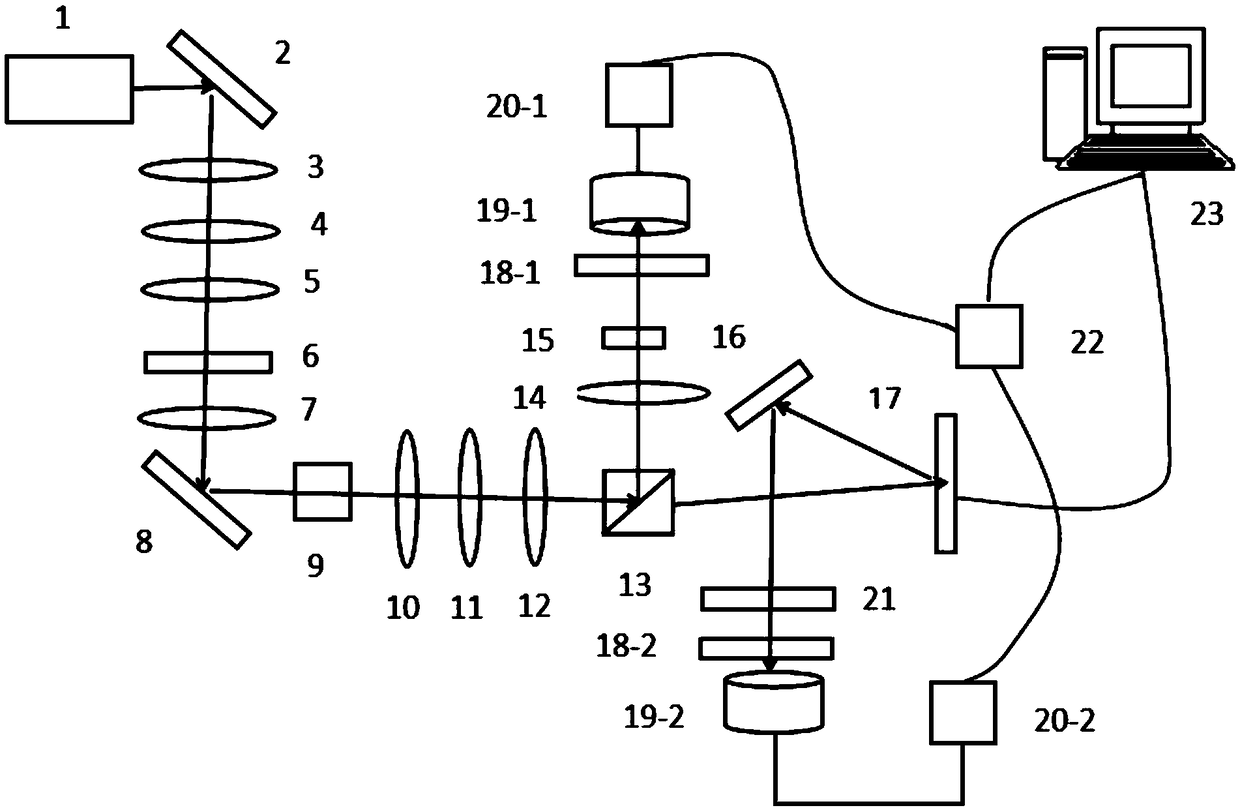
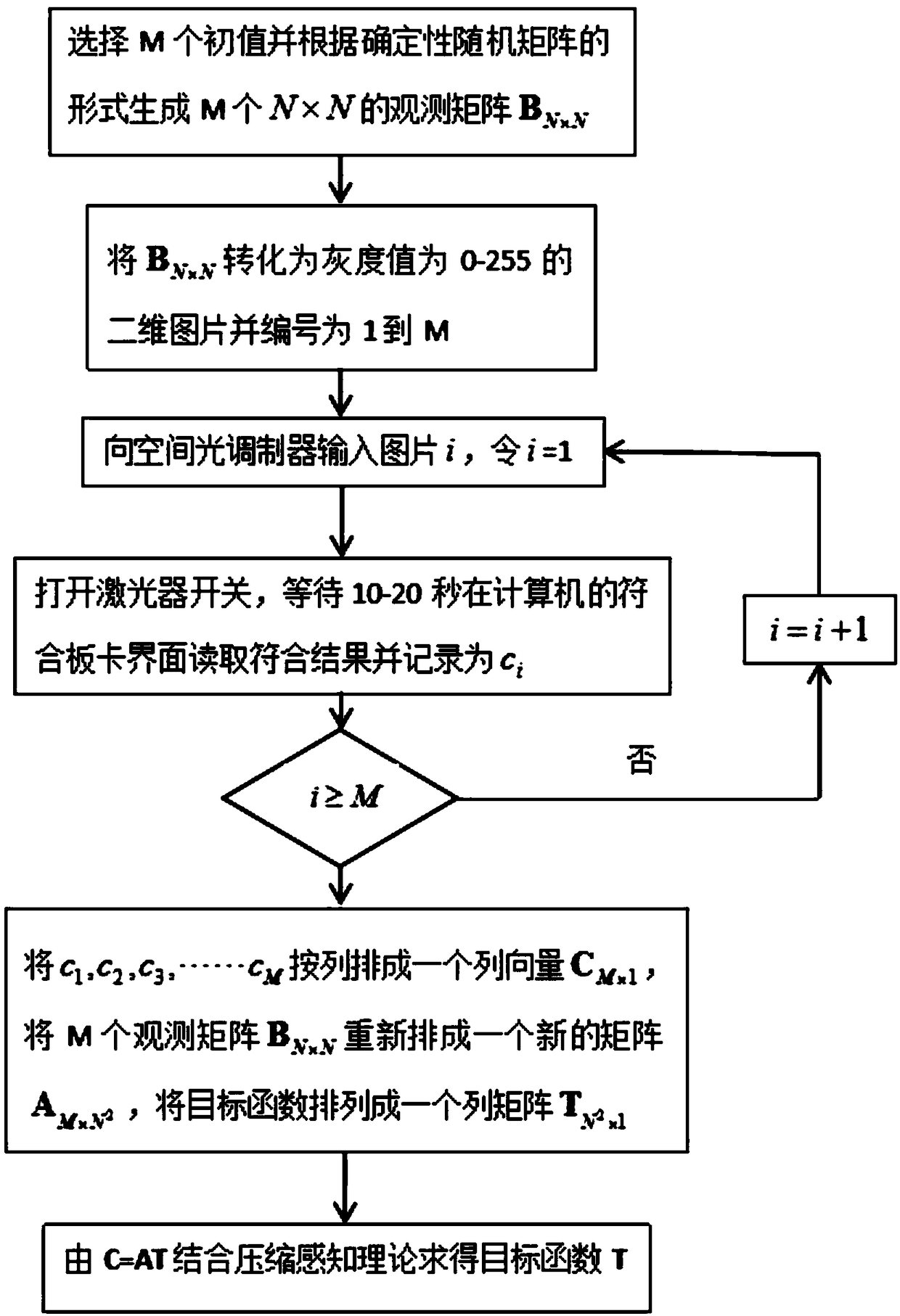
The invention discloses a compressed sensing imaging device and method based on an entangled two-photon signal, and solves the problem of not high imaging quality under the condition of low sampling number. According to the method, a deterministic determinacy random matrix is loaded in a spatial light modulator of an original quantum imaging device to complete imaging of a target object; and during preparation of entangled light, a telescoping system and a 0-degree incident heat mirror and a low-pass narrow-band filter which are placed along a laser transmission direction among the telescopingsystem are adopted to process laser. The imaging method includes producing a picture for being input to a spatial light modulator; inputting the picture to the spatial light modulator; preparing entangled light; obtaining a matched result value; loading a plurality of sets of modulated observation matrices and obtaining M matched results; constructing a quantum imaging mathematical model; and adopting a compressed sensing algorithm to solve a quantum imaging relational expression to restore an image of the target object. The entangled light prepared by the compressed sensing imaging device and method provided by the invention is high in purity and can well restore the image of the target object under the condition of a low sampling rate.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Hyperchaotic system based quantum image encryption method
ActiveCN105373739AImprove resistance to attackImprove securityChaos modelsDigital data protectionComputer hardwareQuantum
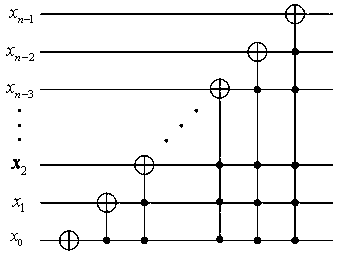
The invention discloses a hyperchaotic system based quantum image encryption method. The method comprises: finishing quantum image encryption by utilizing CNOT operation to realize XOR operation of a quantum image, namely, generating a hyperchaotic sequence by a Chen's hyperchaotic system, controlling unit transformation and NOT gate by a processed hyperchaotic sequence to construct CNOT transformation, and then, utilizing the CNOT operation to realize the XOR operation of the quantum image, thereby finishing the quantum image encryption. According to the method, the XOR operation of the quantum image is constructed for the first time and applied to the quantum image encryption, so that the attack resistance and security of an encryption algorithm can be enhanced; an initial condition of the Chen's hyperchaotic system serves as a secret key of the encryption algorithm, so that the effect of expanding secret key space is achieved; and the algorithm can resist strong attack, so that the secret key is easier to allocate, store and memorize.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
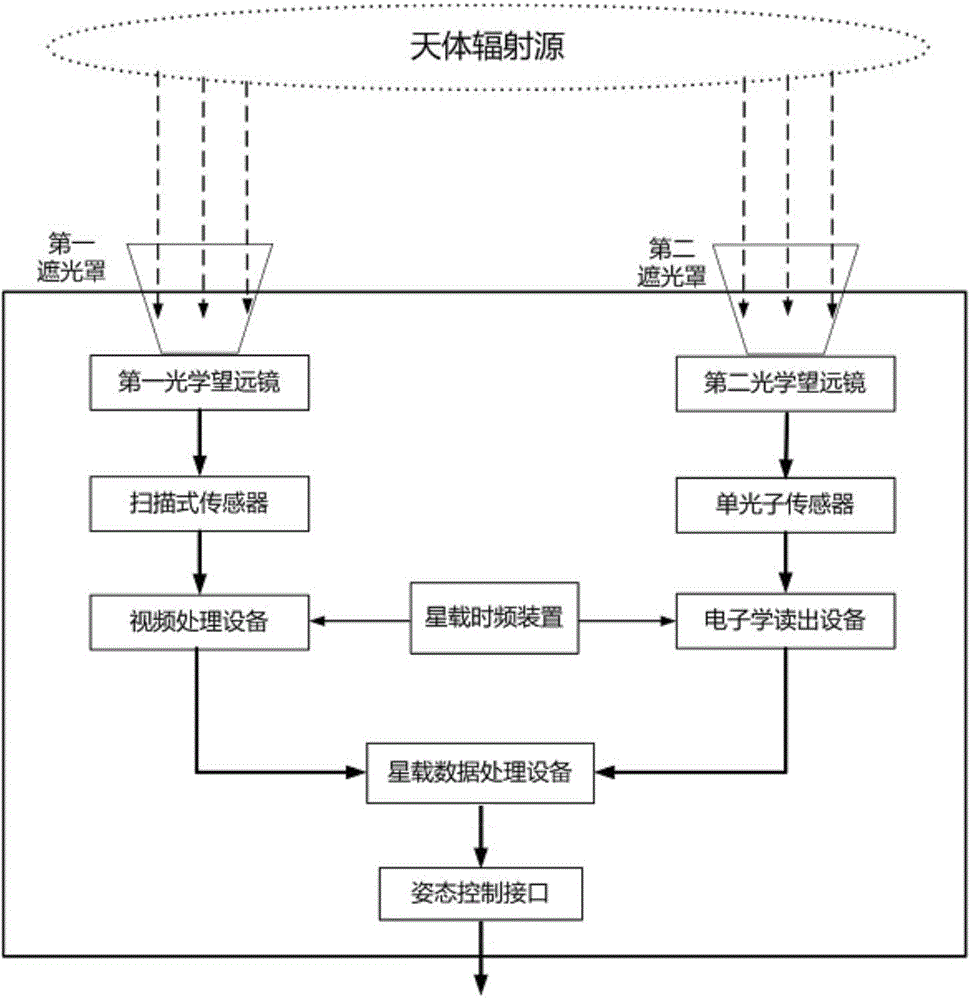
Intensity-correlation star sensor
ActiveCN104316046AEasy to implementHigh detection sensitivityNavigation by astronomical meansPhotonic sensorVIT signals
The invention provides an intensity-correlation star sensor which comprises a first lens hood, a second lens hood, a first optical telescope, a second optical telescope, a scanning type sensor, a single photon sensor, electronics read-out equipment, video processing equipment, a satellite-borne time-frequency device, satellite-borne data processing equipment and an interface. By using detection signals of two paths of optical detection systems, the obtained two paths of electric signals are subjected to time synchronization by using the satellite-borne time-frequency device, and are subjected to intensity-correlation signal processing in the satellite-borne data processing equipment. Therefore, on the basis of keeping an integral appearance shape of an optical system of an original star sensor unchangeable, an internal structure is locally regulated, and the engineering realization is easy. The starry sky is imaged by using an intensity-correlation method in a quantum imaging technology, and is searched by using the scanning type sensor; the single photon is used in the other path, relatively dark star bodies are relatively easily detected, and the detection sensitivity is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Quantum image shearing method based on NEQR expression
The invention relates to a quantum image shearing method based on an NEQR expression. The method is characterized in that an NEQR expression is used to compile a quantum image, the NEQR expression stores a gray value of a pixel through a basic state of a quantum sequence, therefore, image storage in a quantum system is realized through two tangled quantum sequences which express gray scale information and position information of a pixel, and a shearing operation of an NEQR quantum image can be divided into x axis shearing and y axis shearing; when the quantum image is shorn along an x axis, a translation amount of each row of pixels in the image along the x axis forms a positive correlation relationship with a y axis coordinate value of the row of pixels; and a quantum multiplier is used to calculate the translation amount of each row of the pixels in the quantum image during the shearing operation, and then, through a quantum interpolation operation, the translation amount is converted into an integer, and finally, a quantum adder is used to acquire position information of the quantum image after the shearing operation.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Design and implementation method of quantum image edge detection based on Sobel operator
The invention relates to a designing method for quantum image edge detection based on a Sobel operator, which establishes 9 quantum image sets by using a basic quantum logic gate, designs a quantum black box to calculate an image gradient value, classifies the gradient by a threshold operation, and finally obtains the edge of the quantum image. The complexity of the quantum circuit for the edge detection of the entire quantum image is at most, which the quantum image edge detection of the classic Sobel operator cannot achieve. The invention has great significance to the improvement and popularization of the application of the quantum computation theory.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Color quantum image encryption and decryption method based on multi-chaos and DNA operation
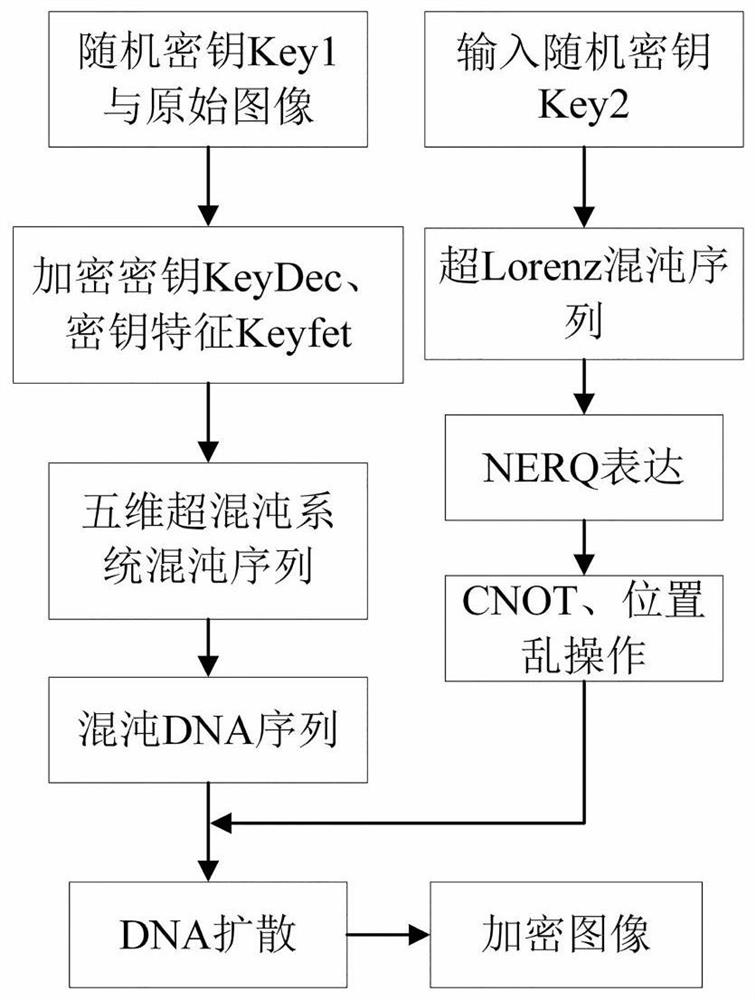
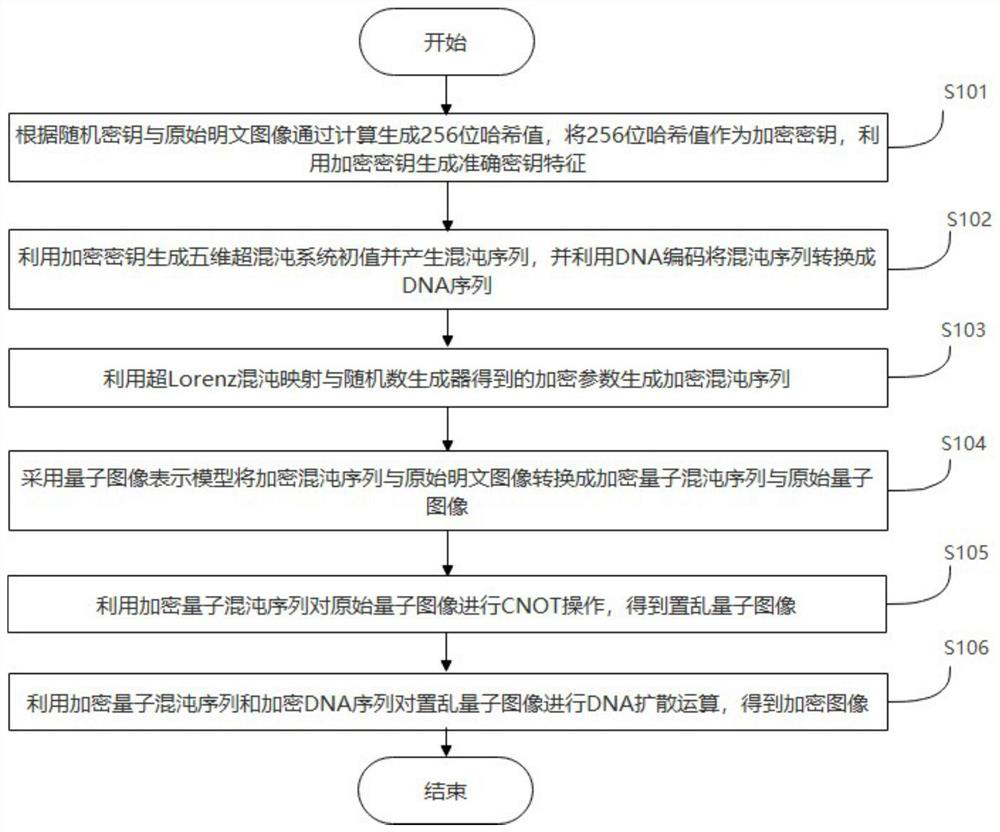
ActiveCN113297606AImprove securityAchieve scrambling effectImage enhancementImage codingTheoretical computer scienceChaotic systems
The invention provides a color quantum image encryption and decryption method based on multi-chaos and DNA operation, and the method comprises the steps: taking a hash value obtained by calculation of a random key and an original plaintext image as an encryption key, generating a five-dimensional hyper-chaos system initial value by the encryption key, generating a chaos sequence, and converting the chaos sequence into a DNA sequence by DNA coding; generating an encrypted chaotic sequence by the encryption parameters obtained by the super Lorenz chaotic mapping and the random number generator; converting the encrypted chaotic sequence and the original plaintext image into an encrypted quantum chaotic sequence and an original quantum image by adopting a quantum image representation model; performing CNOT operation on the original quantum image by using the encrypted quantum chaotic sequence to obtain a scrambled quantum image; and performing DNA diffusion on the scrambled quantum image by the encrypted quantum chaotic sequence and the encrypted DNA sequence to obtain an encrypted image. The encryption method disclosed by the invention is separated from the classic computer category, and the security of the encryption algorithm is improved.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
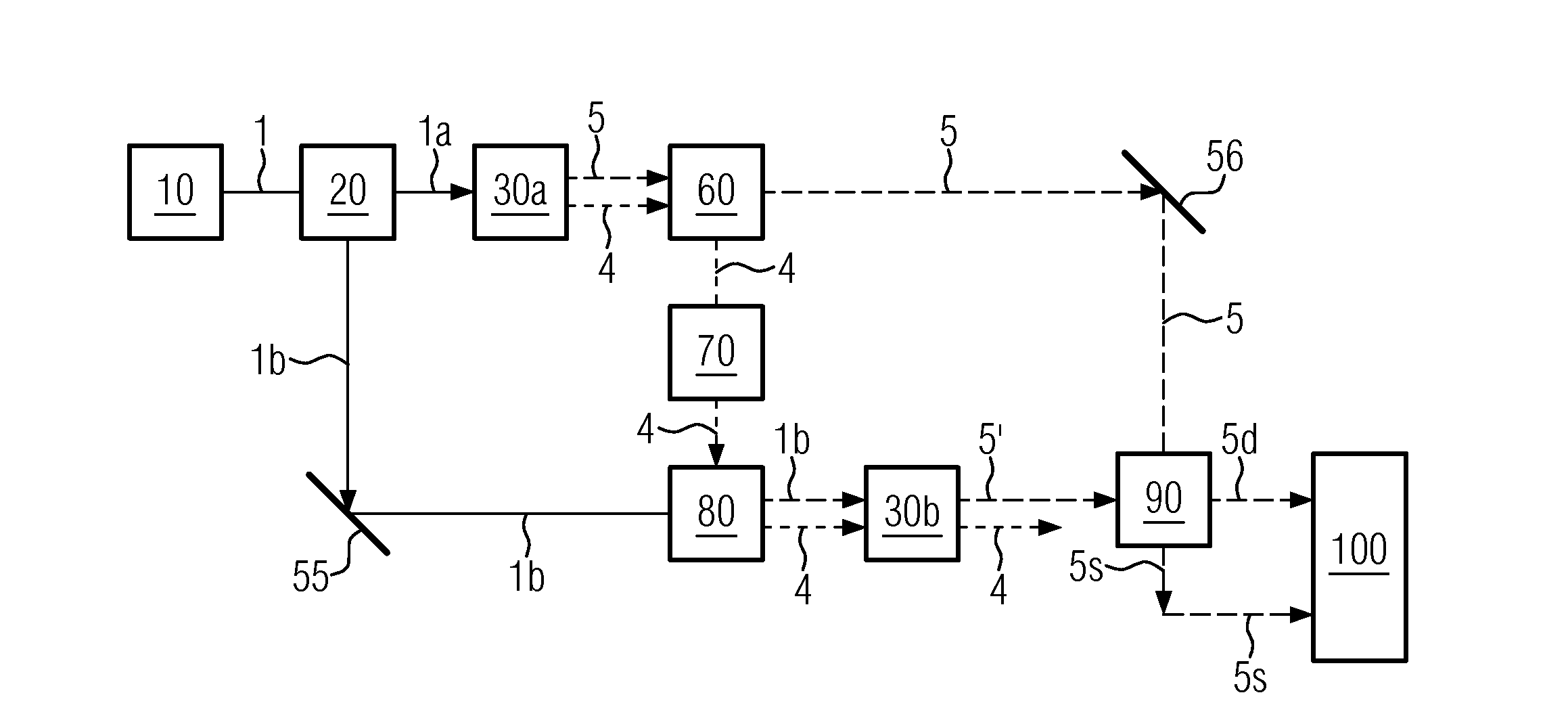
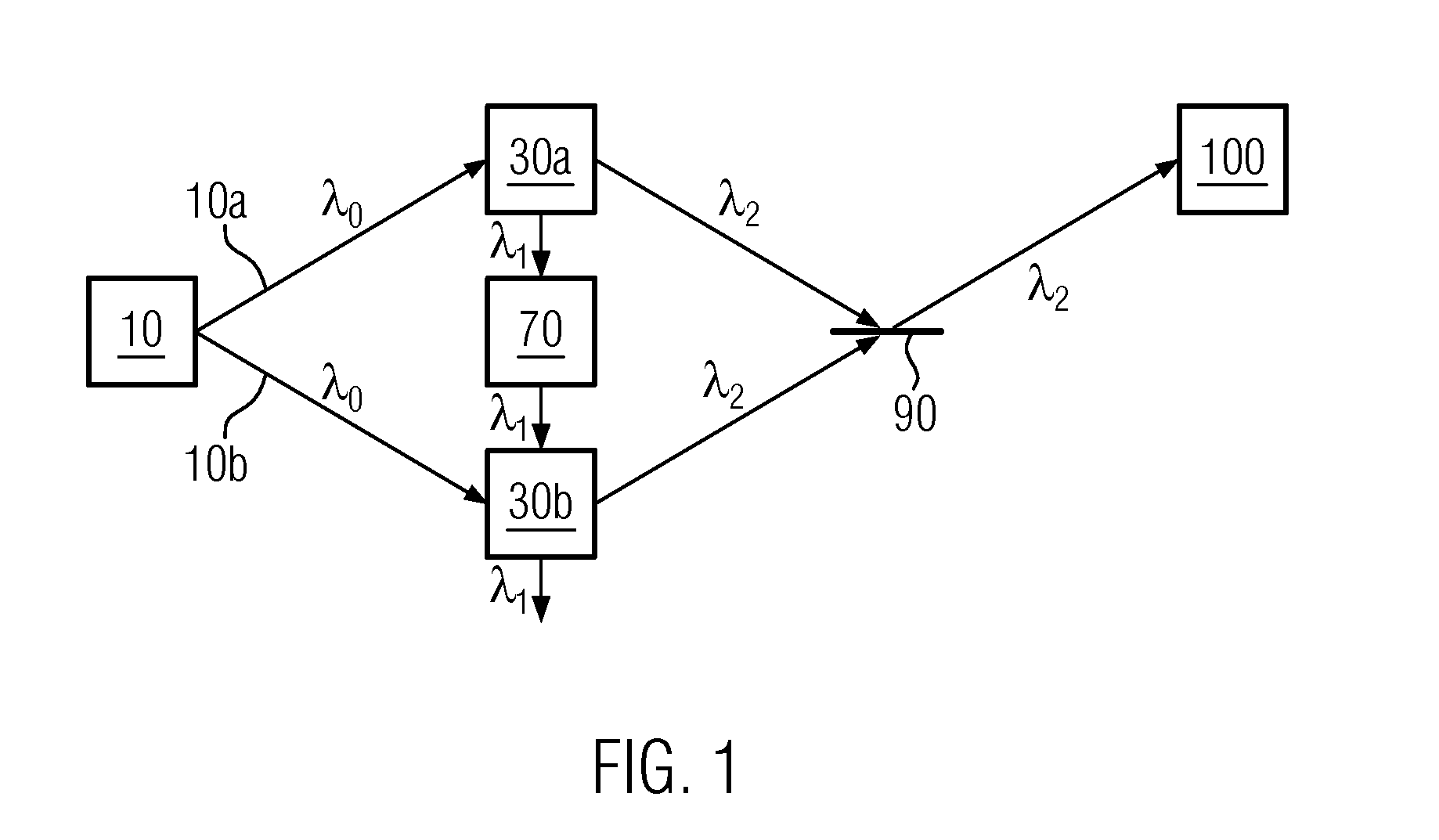
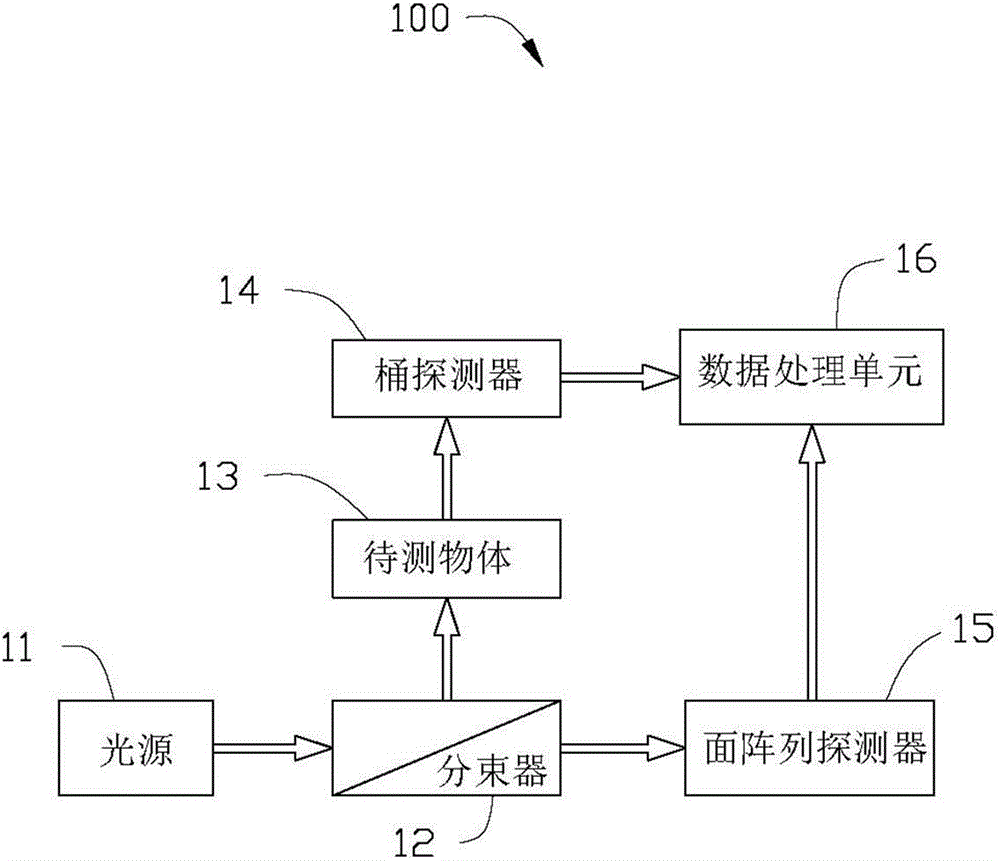
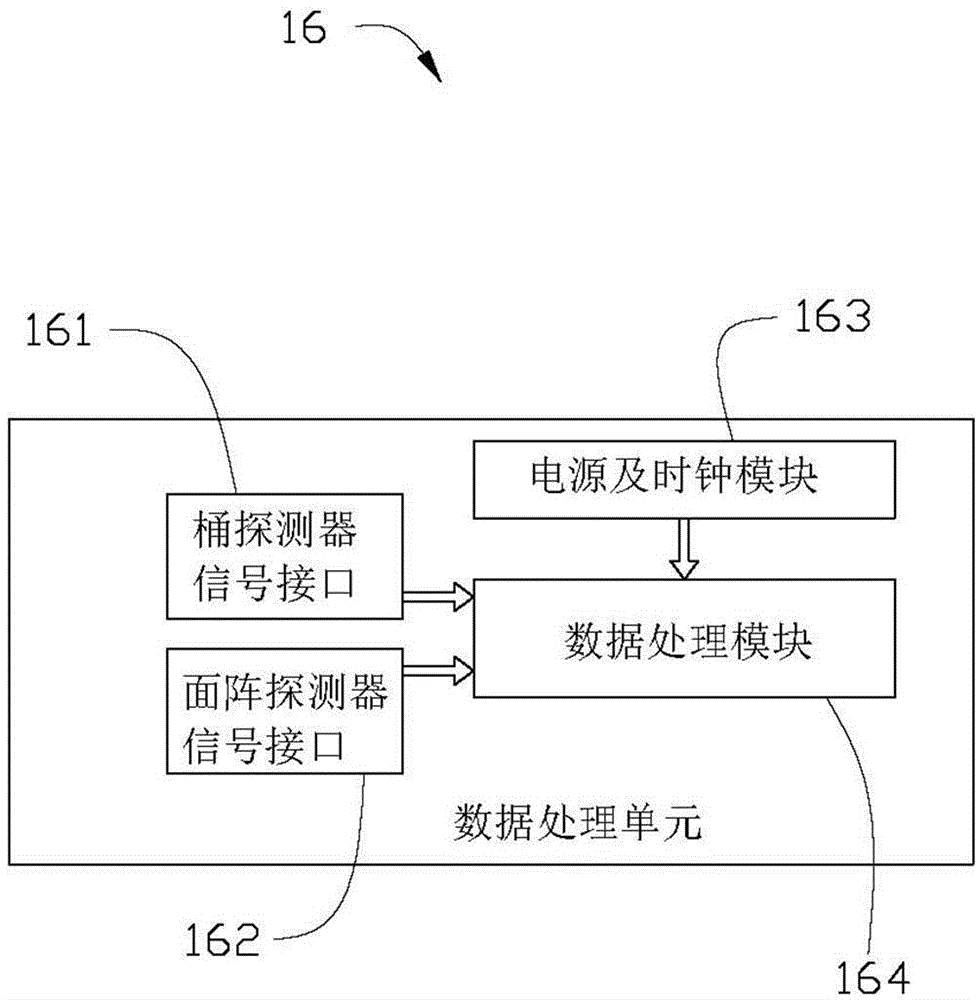
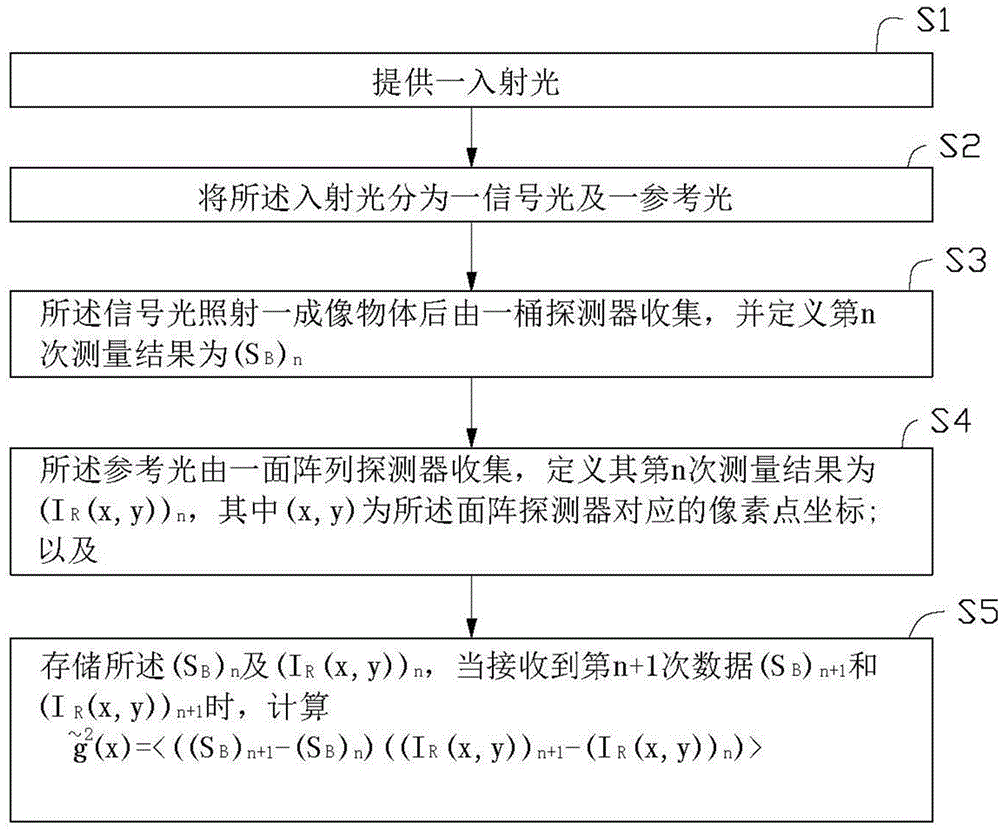
Quantum imaging method and quantum imaging system
The invention discloses a quantum imaging method and a quantum imaging system. The method comprises the following steps: S1) providing incident light; S2) splitting the incident light into signal light and reference light; S3) after the signal light irradiates an imaging object, collecting the light by a bucket detector and defining the nth measuring result as (SB)n; S4) collecting the reference light by a planar array detector, and defining the nth measuring result as (IR(x,y))n, wherein the (x,y) is pixel point coordinates corresponding to the planar array detector; and S5) storing the (SB)n and the (IR(x,y))n, and when receiving (n+1) data (SB)n+1 and the (IR(x,y))n+1, calculating g<~><2>(x)=<((SB)n+1- (SB)n)((IR(x,y))n+1-(IR(x,y))n)>.
Owner:北京坤煜量子科技有限责任公司
Quantum imaging with undetected photons
ActiveUS9557262B2Simple methodScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectroscopyLength wave
A method comprises: generating a first and a second correlated photon beam with wavelengths λ1 and λ2, respectively, wherein preferably λ1≠λ2; separating the first photon beam and the second photon beam; illuminating an object with the first photon beam; generating a third and a fourth correlated photon beam with wavelength λ1 and wavelength λ2, respectively; overlapping the first photon beam with the third photon beam such that photons of wavelength λ1 in either photon beam are indistinguishable; overlapping the second photon beam with the fourth photon beam such that photons of wavelength λ2 in either photon beam are indistinguishable; and using the overlapped photons of wavelength λ2 for imaging and / or spectroscopy of the object such that the photons that illuminate the object are not detected.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VIENNA +1
Quantum image encryption algorithm based on chaotic system and DNA dynamic coding
In order to guarantee the security of quantum information, the invention provides a quantum image encryption algorithm based on chaotic mapping and DNA coding in combination with a chaotic system anda DNA coding theory. According to the algorithm, first, quantum coding is performed on an image; second, a sequence generated in Logistic chaos is utilized to scramble the quantum image; third, Lorenzchaos is utilized to perform dynamic DNA coding and DNA additive operation to diffuse the quantum image; and finally the quantum image is measured to obtain a ciphertext image. Through combination ofthe parts, the quantum encryption algorithm is obtained, and through the algorithm, the quantum image can be encrypted by giving different chaotic initial values.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
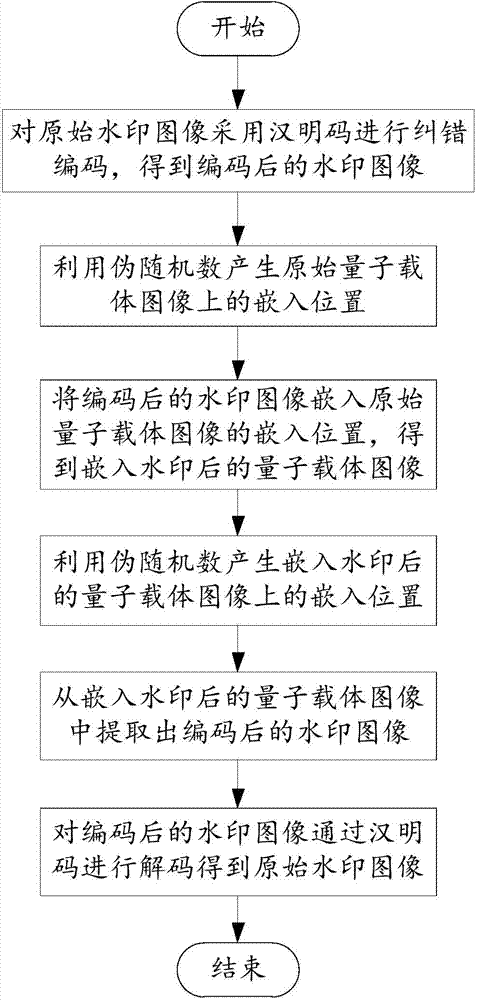
Hamming-code-based quantum image watermarking method
InactiveCN104715442AImprove integrityAchieve accuracyImage data processing detailsHamming codeComputer science
The invention provides a hamming-code-based quantum image watermarking method. The method comprises the following steps that the original watermark image is subjected to correcting coding through the hamming code; pseudo random numbers are utilized to generate a watermark embedding position on the original quantum carrier image; an auxiliary quantum bit sequence is additionally arranged to the original quantum carrier image during embedding of the watermark; the coded watermark image is decoded through the hamming code. With the adoption of the method, the completeness and accuracy of embedding and extracting of the watermark image can be achieved; the efficiency is high; the operation complexity is small; the robustness is high; the watermark can be embedded into part of the position of the quantum image; the original watermark image can be obtained without the original quantum carrier image; the method can be applied to encrypting of the gray image watermark and encrypting of the colored image watermark.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Single-photon polarization state quantum imaging system based on DMD micromirror array
InactiveCN110487427AIncrease chance of shootingLow priceInstrumentsStatistical analysisMicromirror array
The invention relates to a single-photon polarization state quantum imaging system based on a DMD micromirror array. The system comprises a laser transmitting device, a single-photon preparation system, a DMD control imaging device, and an EMCCD imaging receiving system; the laser transmitting device is a semiconductor laser and is used for emitting laser beams; the single-photon preparation system is used for converting the laser emitted by the laser transmitting device into single photon pulses in different polarization states; the MD control imaging device directly acts on the single photonpulses in different polarization states and reflects the single photon pulses to the EMCCD imaging receiving system; the EMCCD imaging receiving system images the single photons in different polarization states, performs statistical analysis on detected photon information, and also obtains an image measurement error rate and imaging reliability. The system is simple in structure, convenient to operate, accurate in measurement, high in feasibility and easy to apply.
Owner:QINGYUAN TIANZHIHENG SENSING TECH CO LTD
Encrypting method of multichannel quantum image
ActiveCN104217391AImprove securityImage data processing detailsComputational physicsComputer science
The invention relates to an encrypting method of a multichannel quantum image. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly giving three angle vectors, converting a quantum computer to a MCQI expression from an initial state through Hadamard door and controlled NOT gate transformation, transforming color information of the image by using a proposed color transform algorithm so as to acquire the encrypted image. Since the measurement on a quantum superposition state has collapsibility and a result is in existence with a certain probability, each measurement result and each performed color transform are updated, thereby greatly improving the safety performance of the image encryption.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
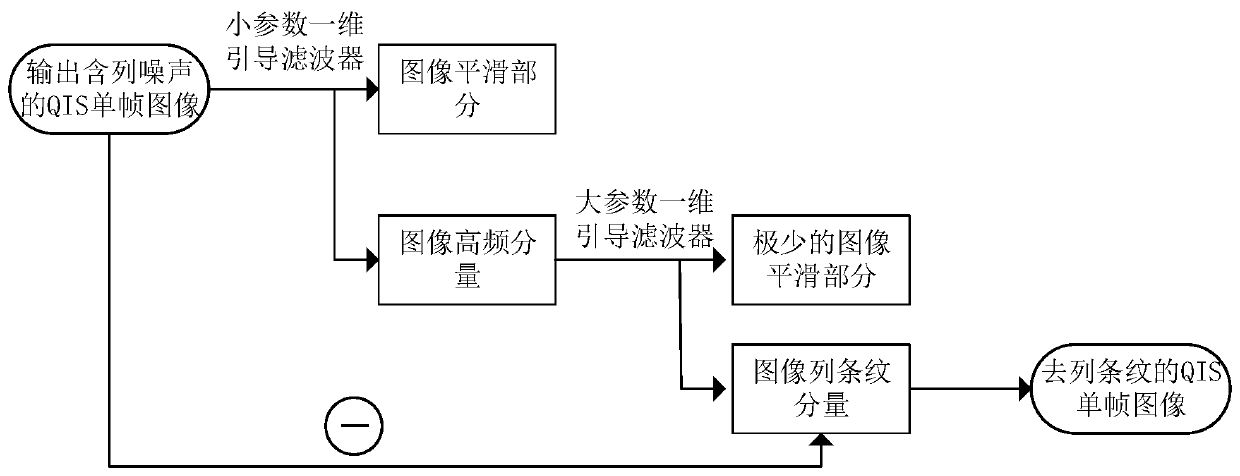
Column noise elimination method of a quantum image sensor based on a guide filter
The invention discloses a column noise elimination method of a quantum image sensor based on a guide filter. The method comprises the following steps: filtering a QIS single-frame image containing column noise by using a one-dimensional guide filter under a first set parameter, and separating a high-frequency component in the QIS single-frame image from an image smooth part to obtain a high-frequency component of the QIS single-frame image; Performing guided filtering on the high-frequency component by using the one-dimensional guided filter under a second set parameter, and separating columnnoise in the high-frequency component from a predetermined image smooth part to obtain a required noise component; And calculating a column mean value of the obtained noise components to obtain a column noise vector, and subtracting the column noise vector from the sensor output image to obtain a de-column noise image. The method has a good removal effect on the non-fixed column stripe noise of the QIS, and the algorithm is fast and effective.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com