Patents
Literature
604 results about "Zero voltage switching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Answer Wiki. Zero Voltage Switching means that the power to the load (heater or cooler or other device) is switched on or off only when the output voltage is zero volts. Zero Voltage Switching can extend the life of a controller and of the load being controlled.
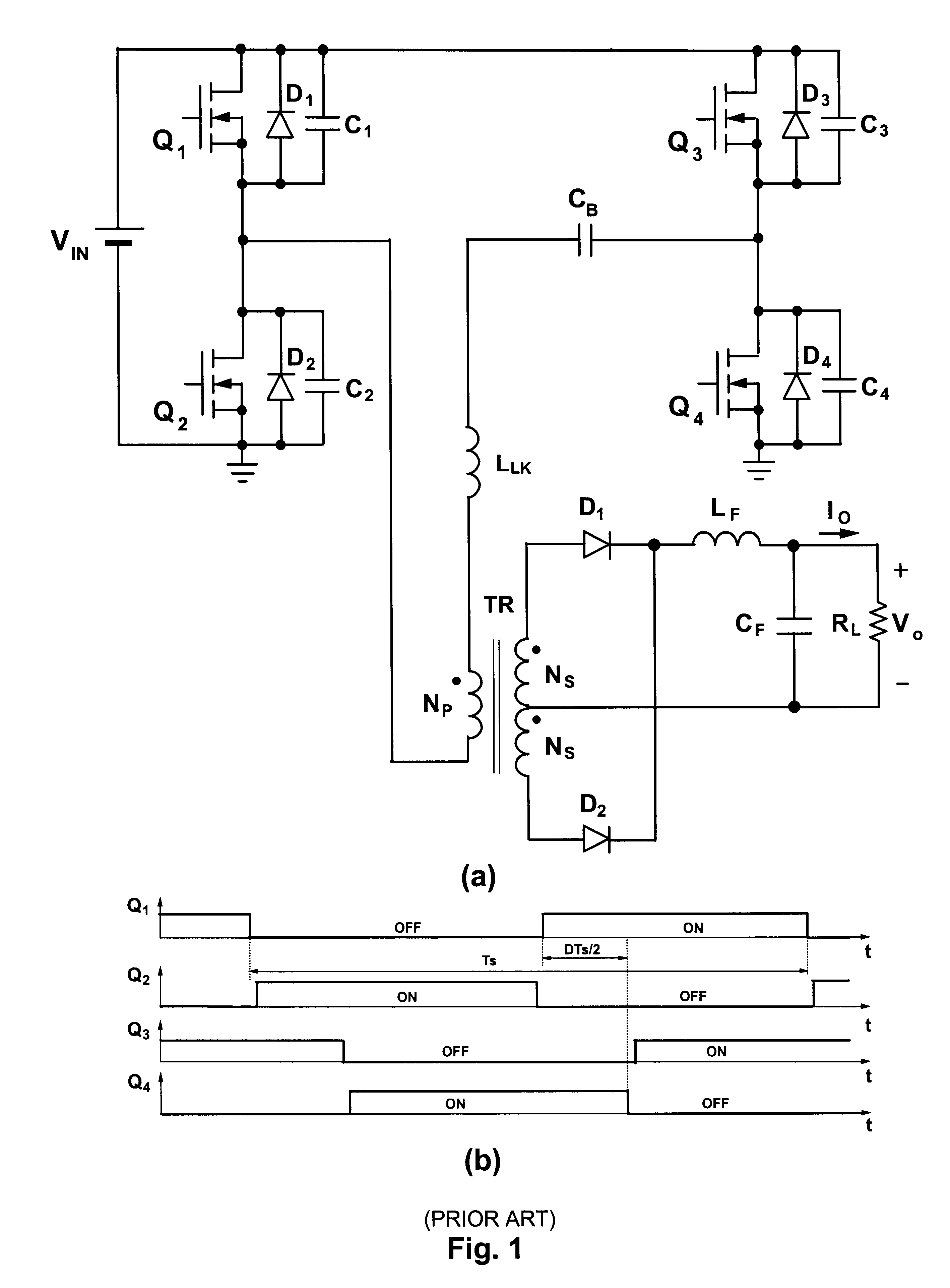
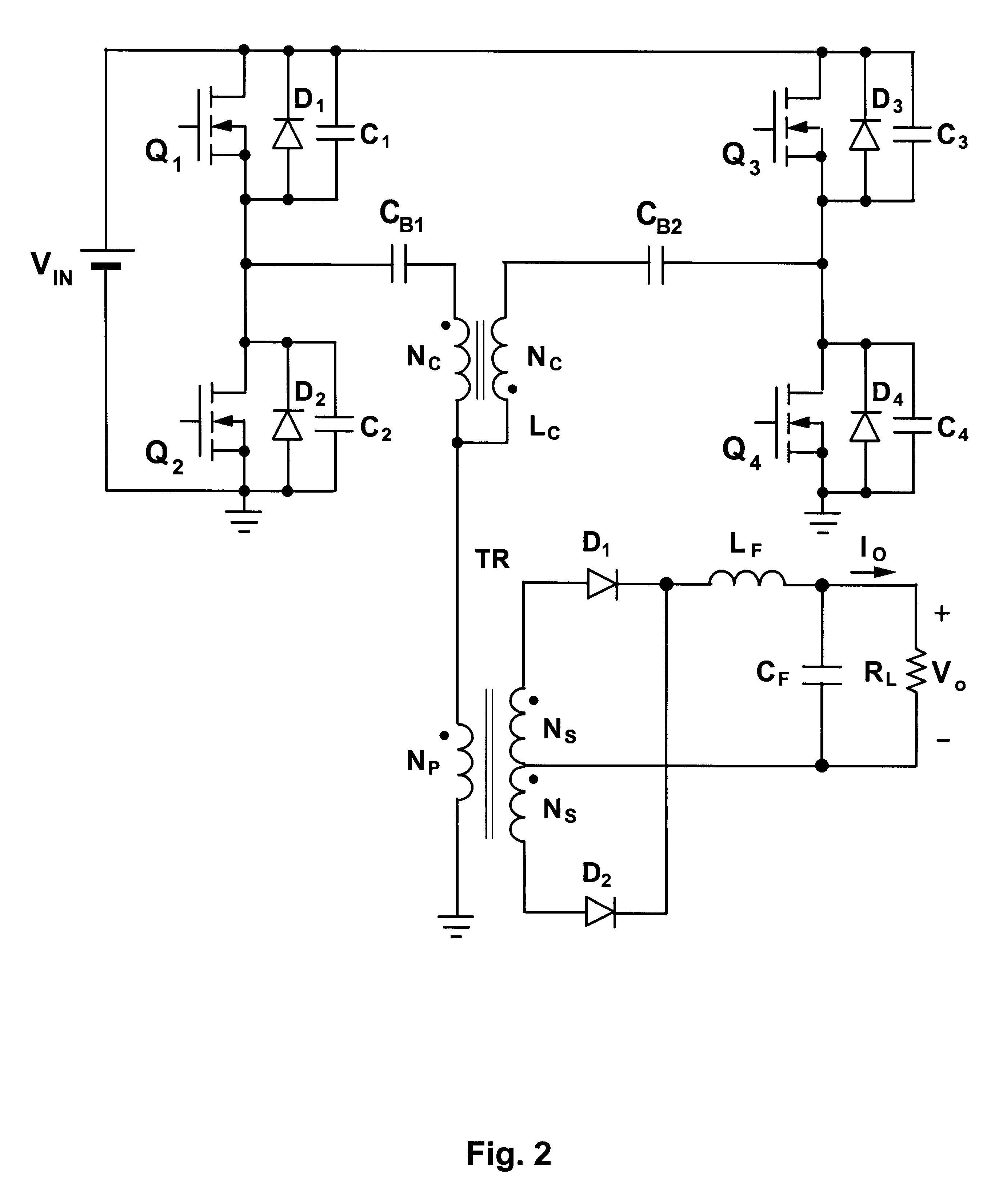
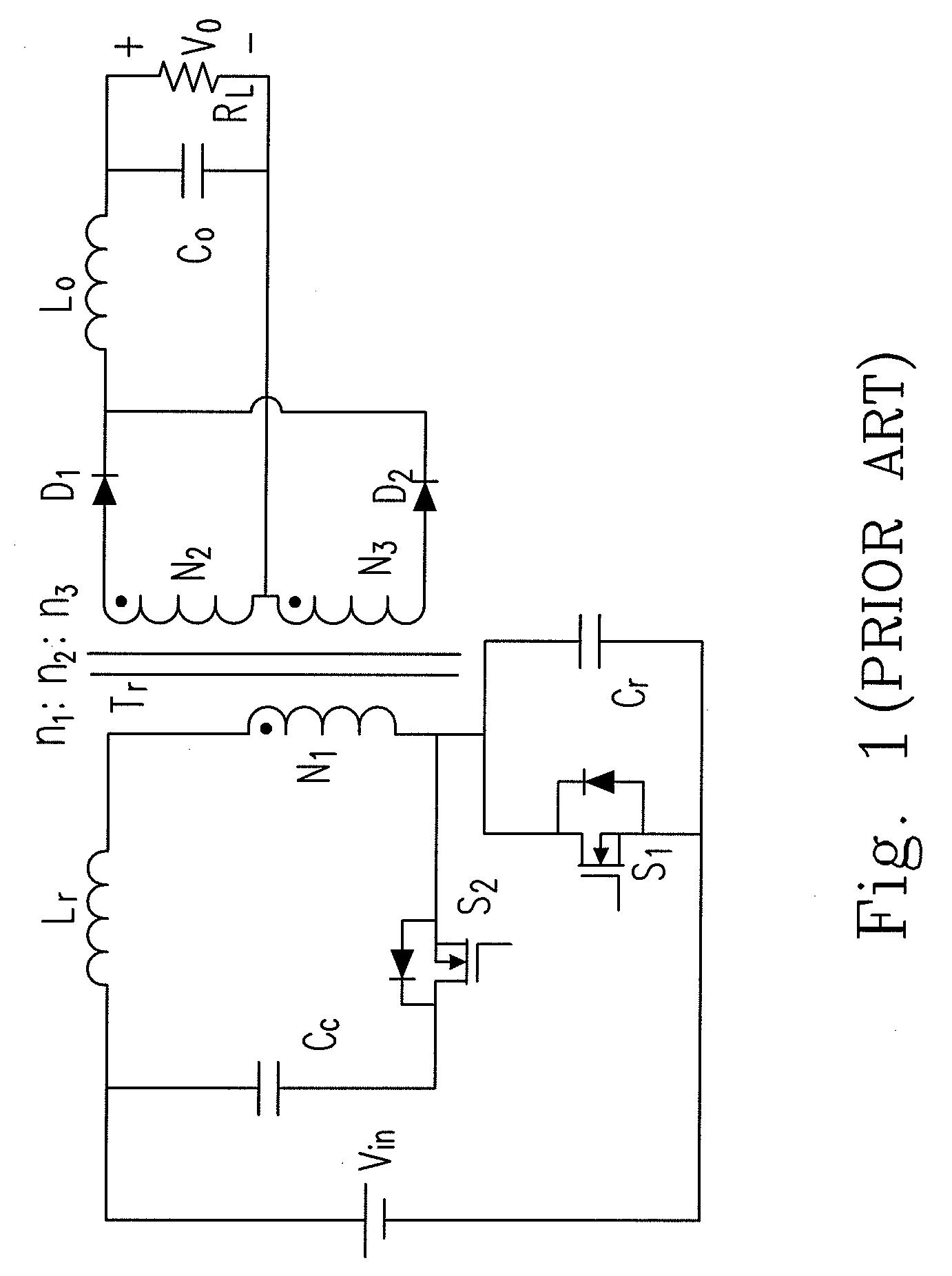
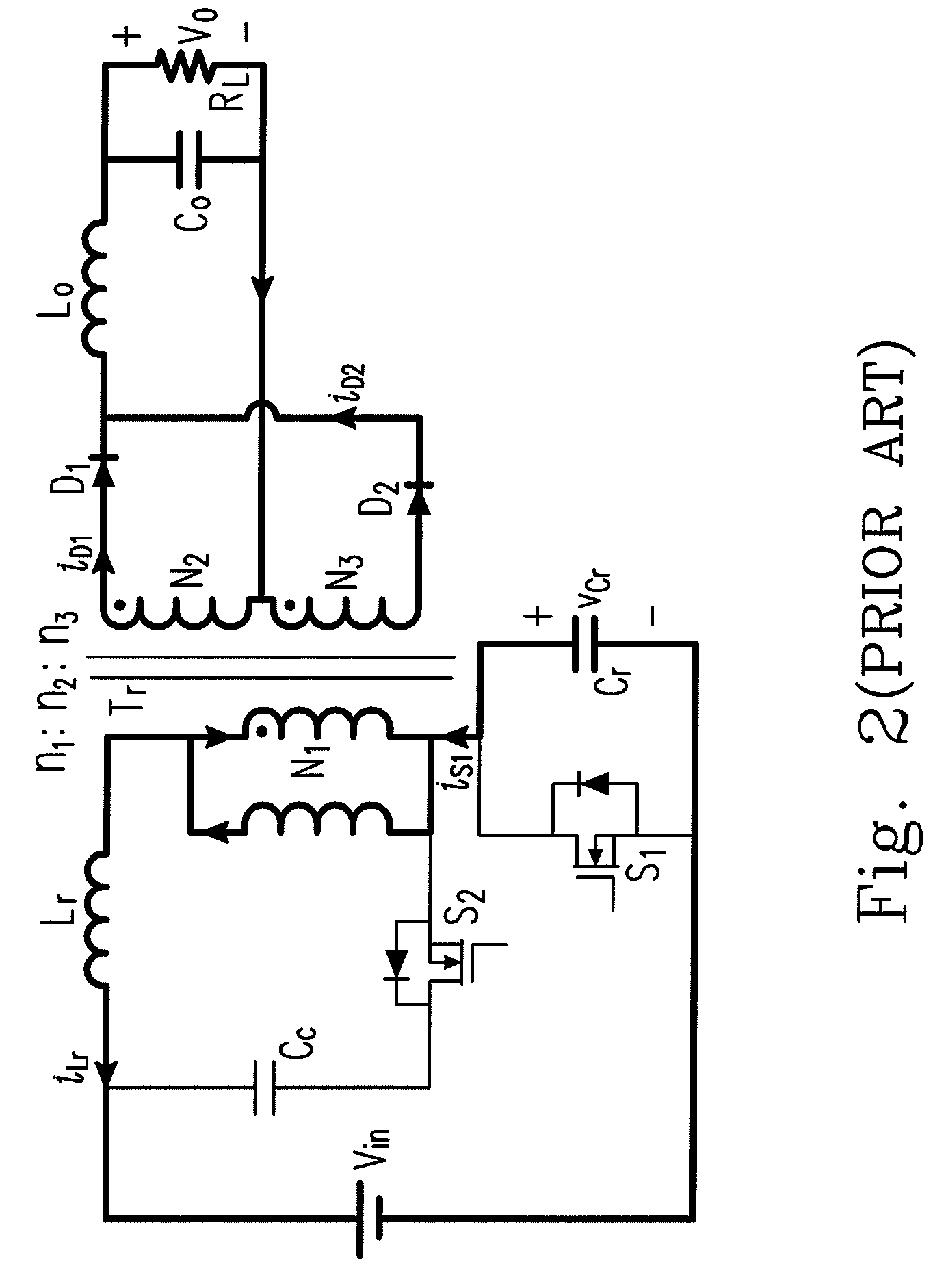
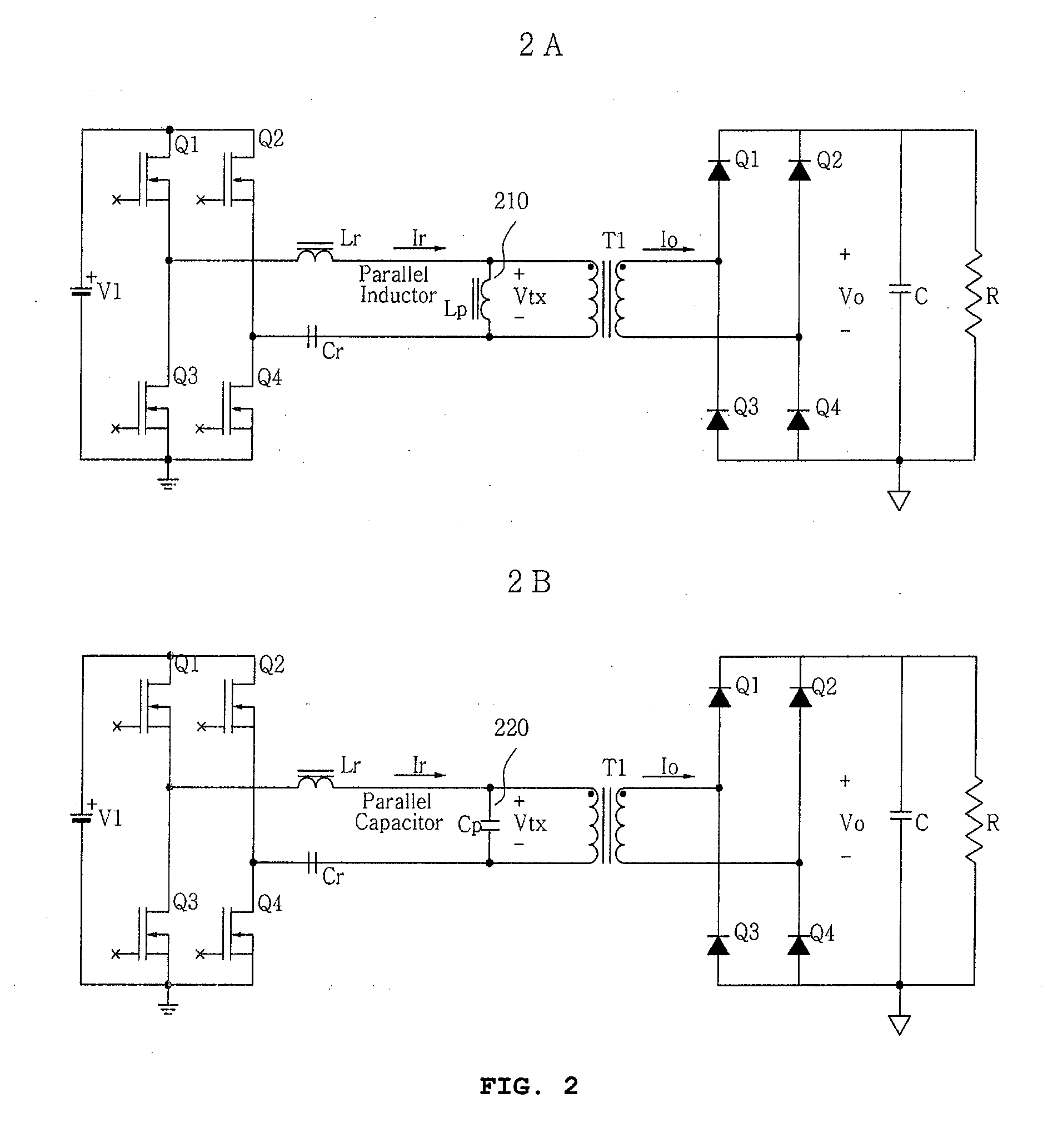
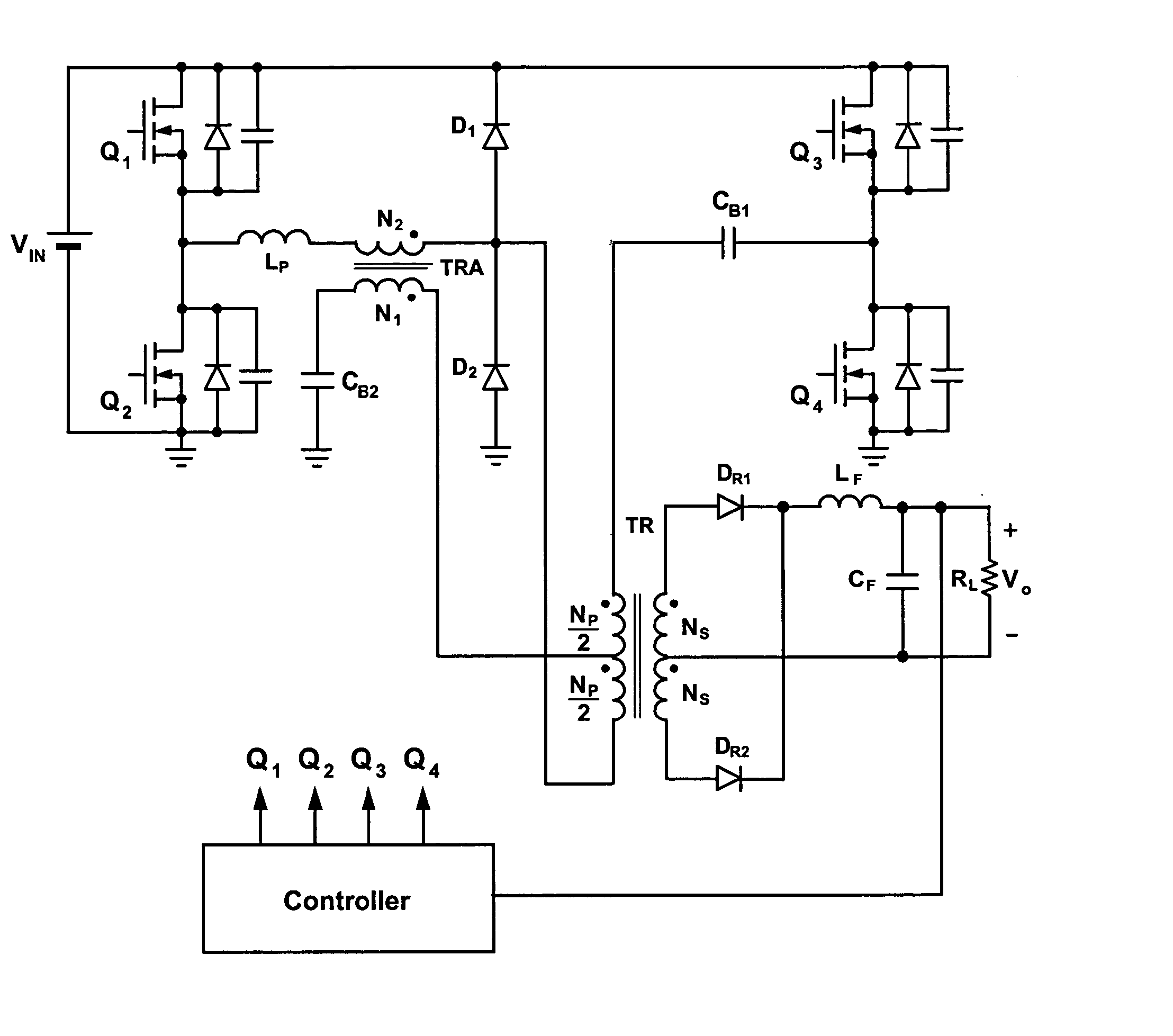
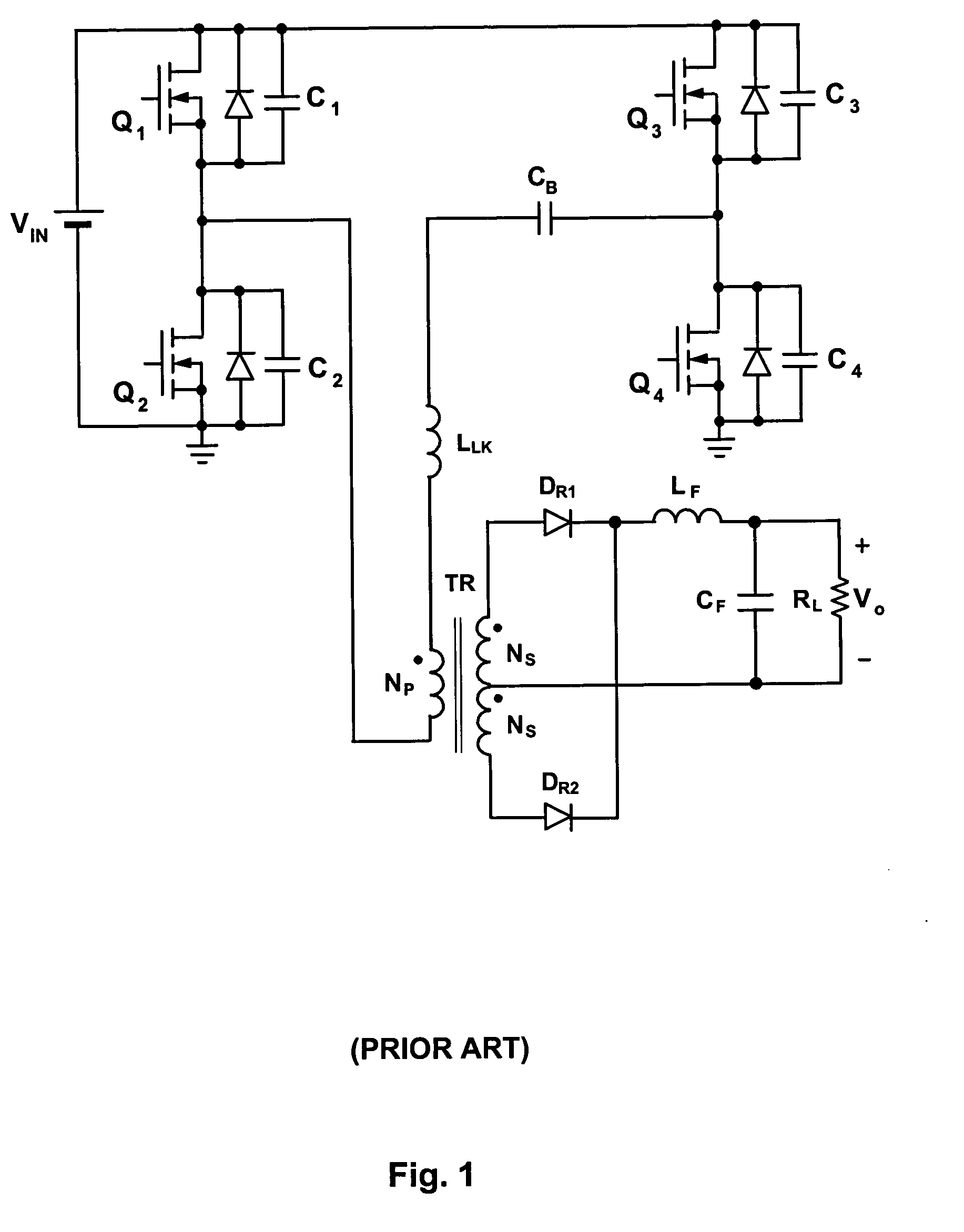
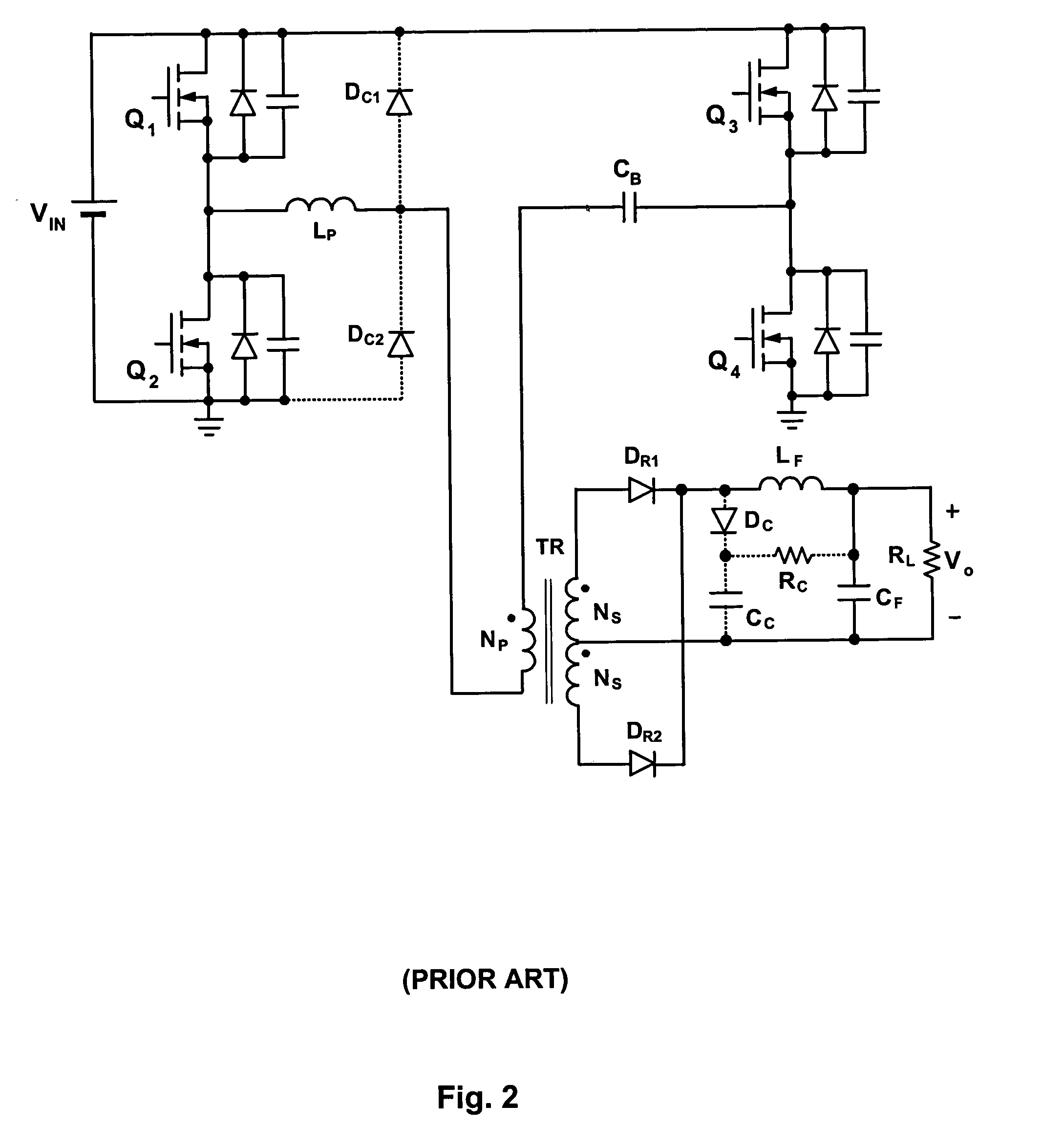
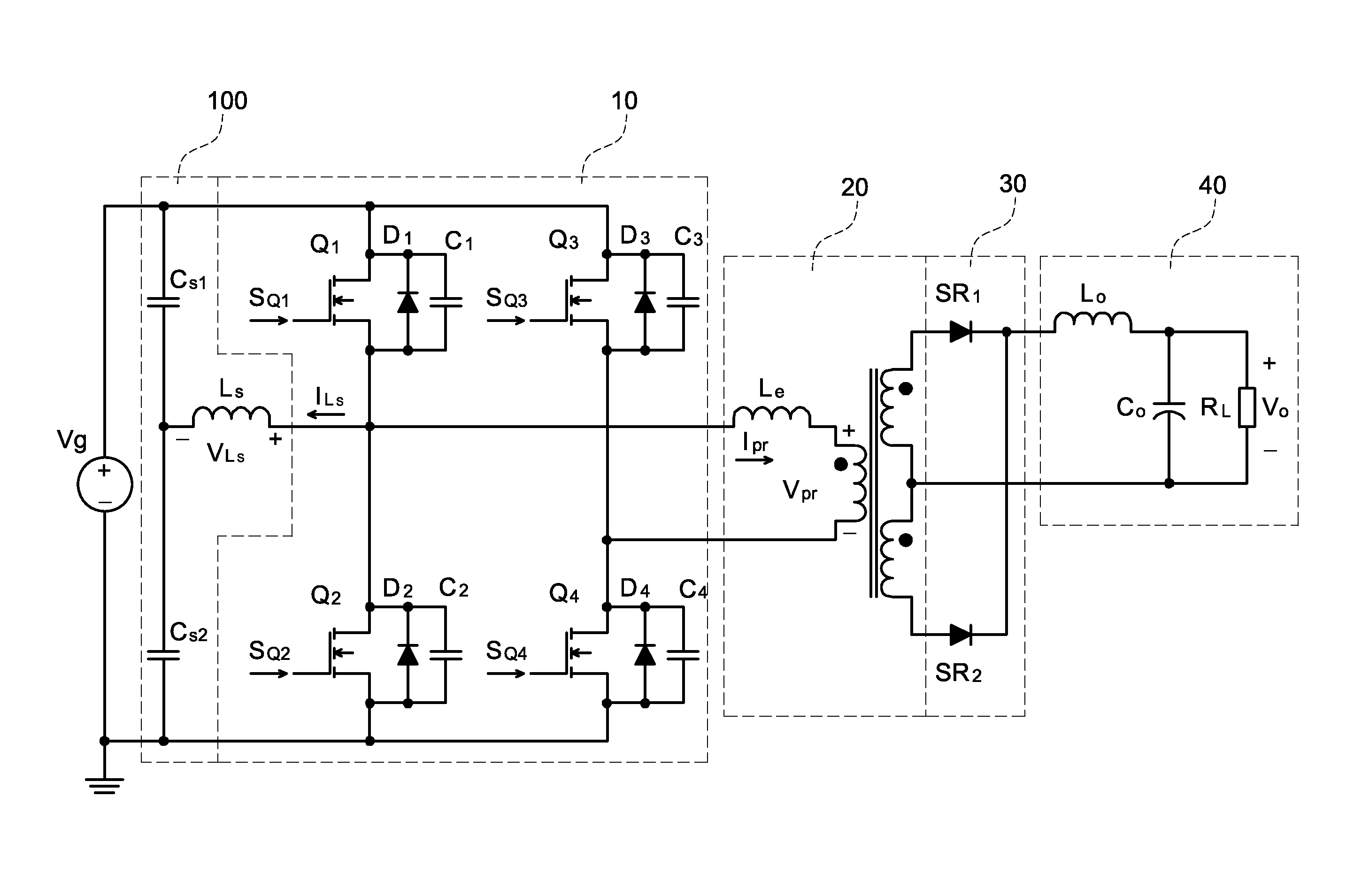
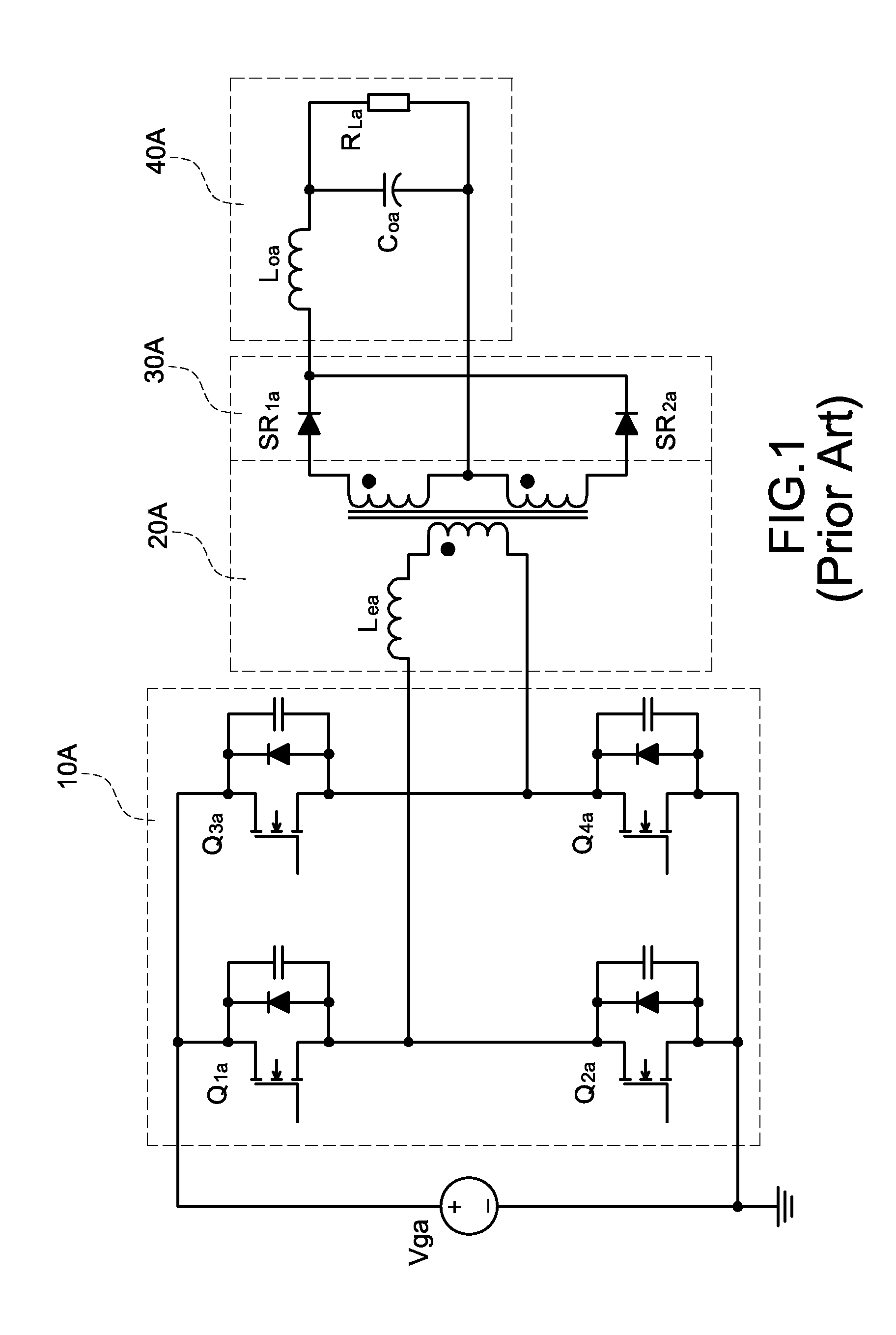
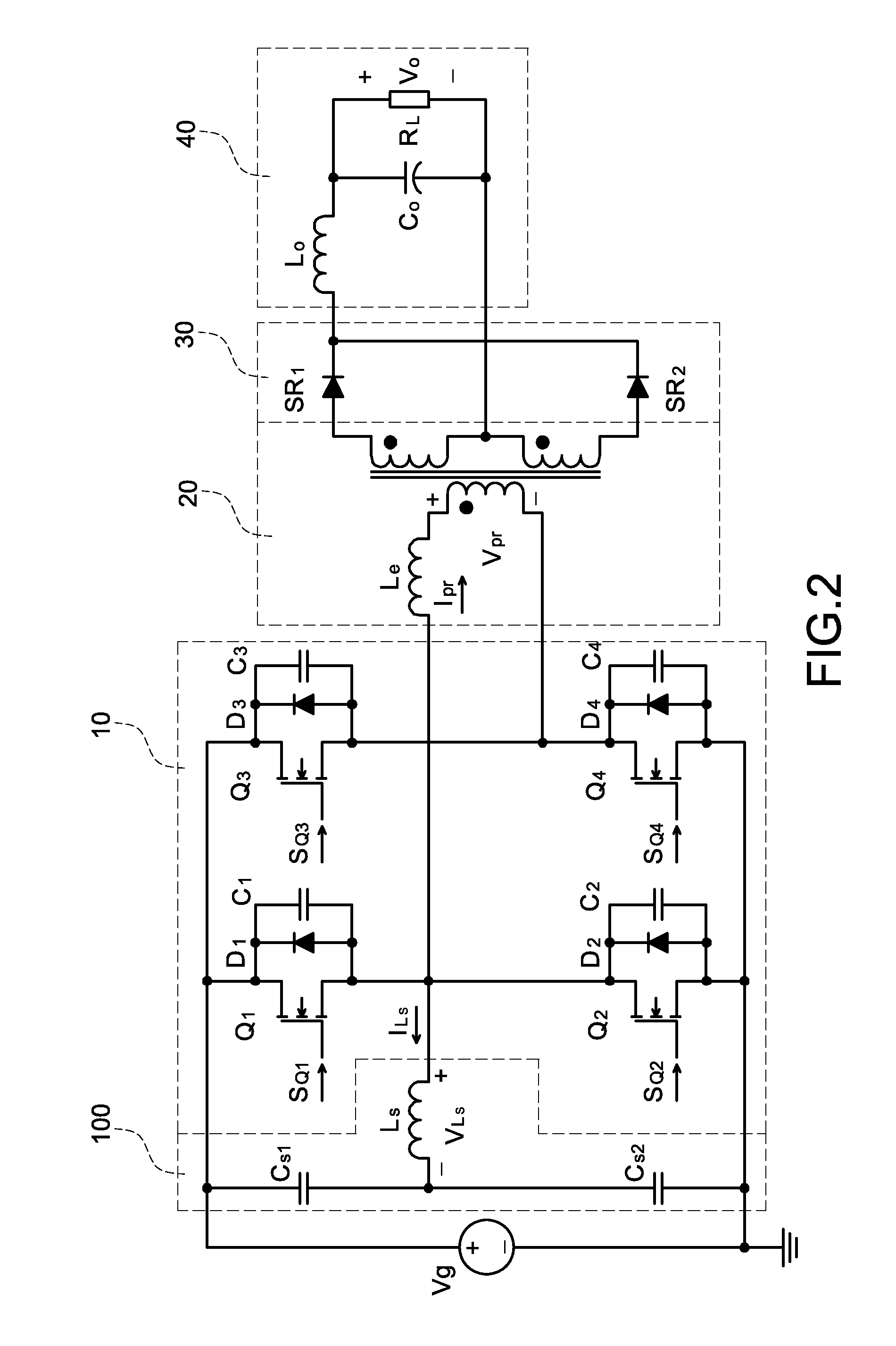
Zero Voltage Switching Half-Bridge Converters
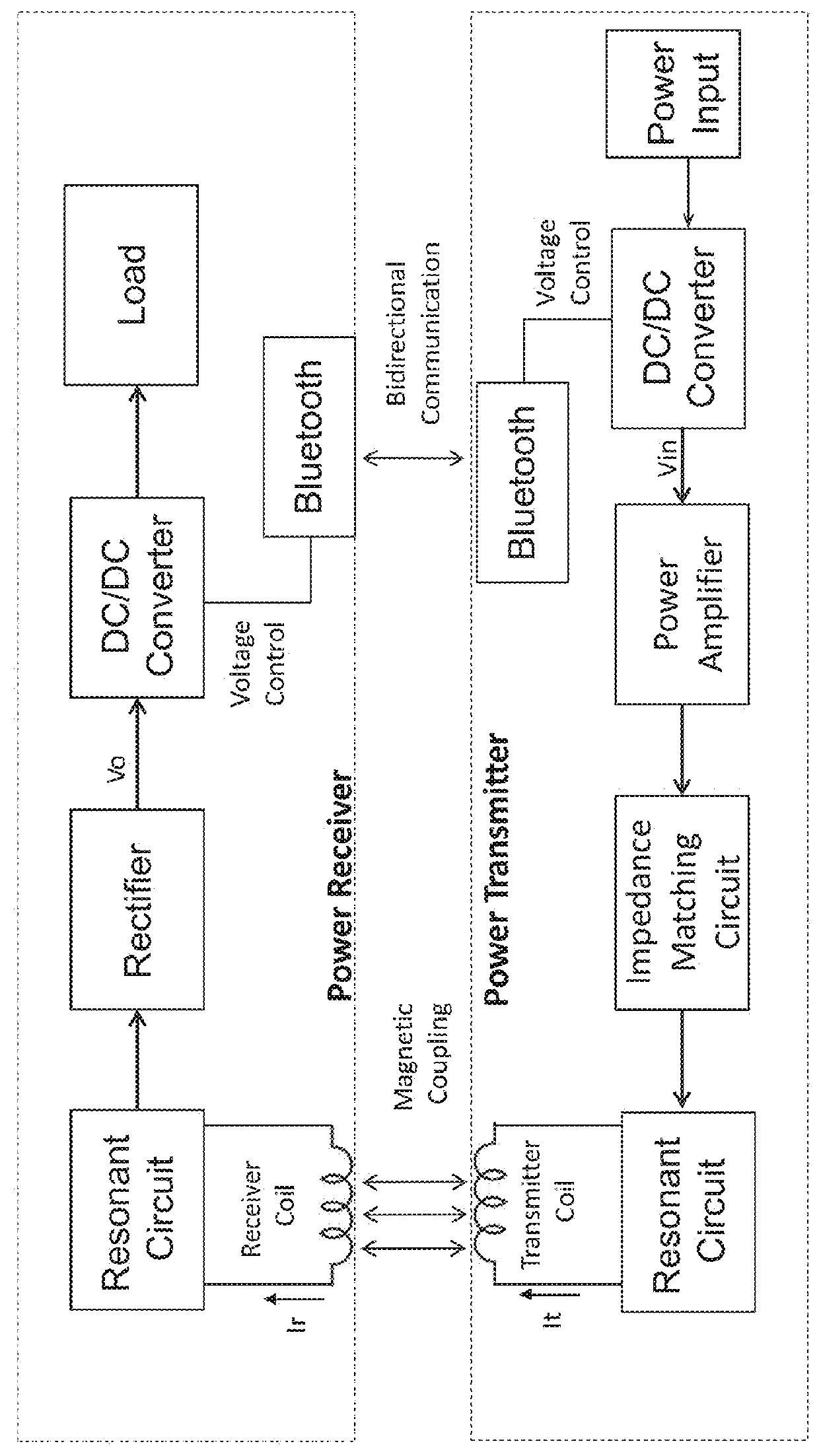
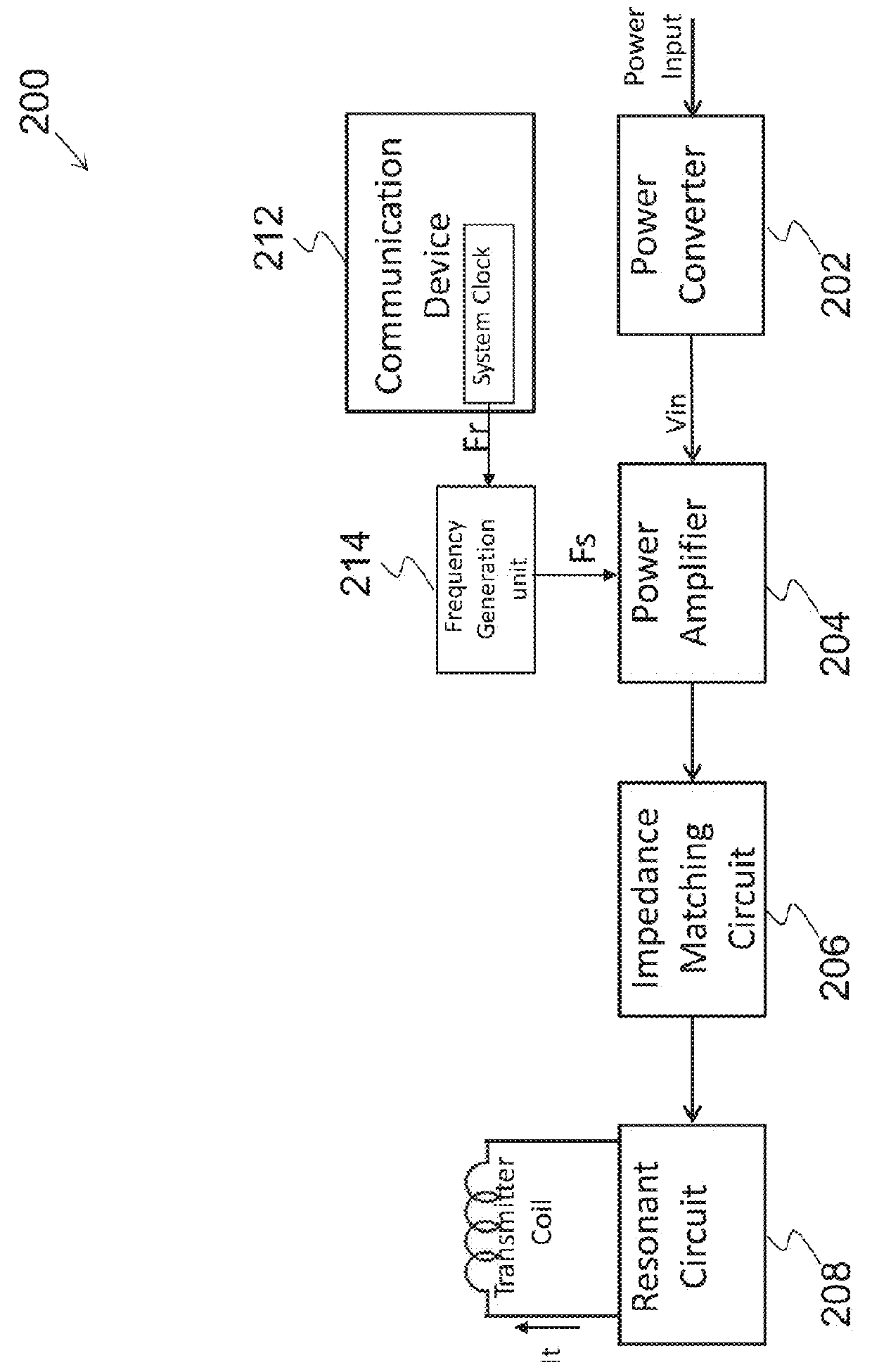
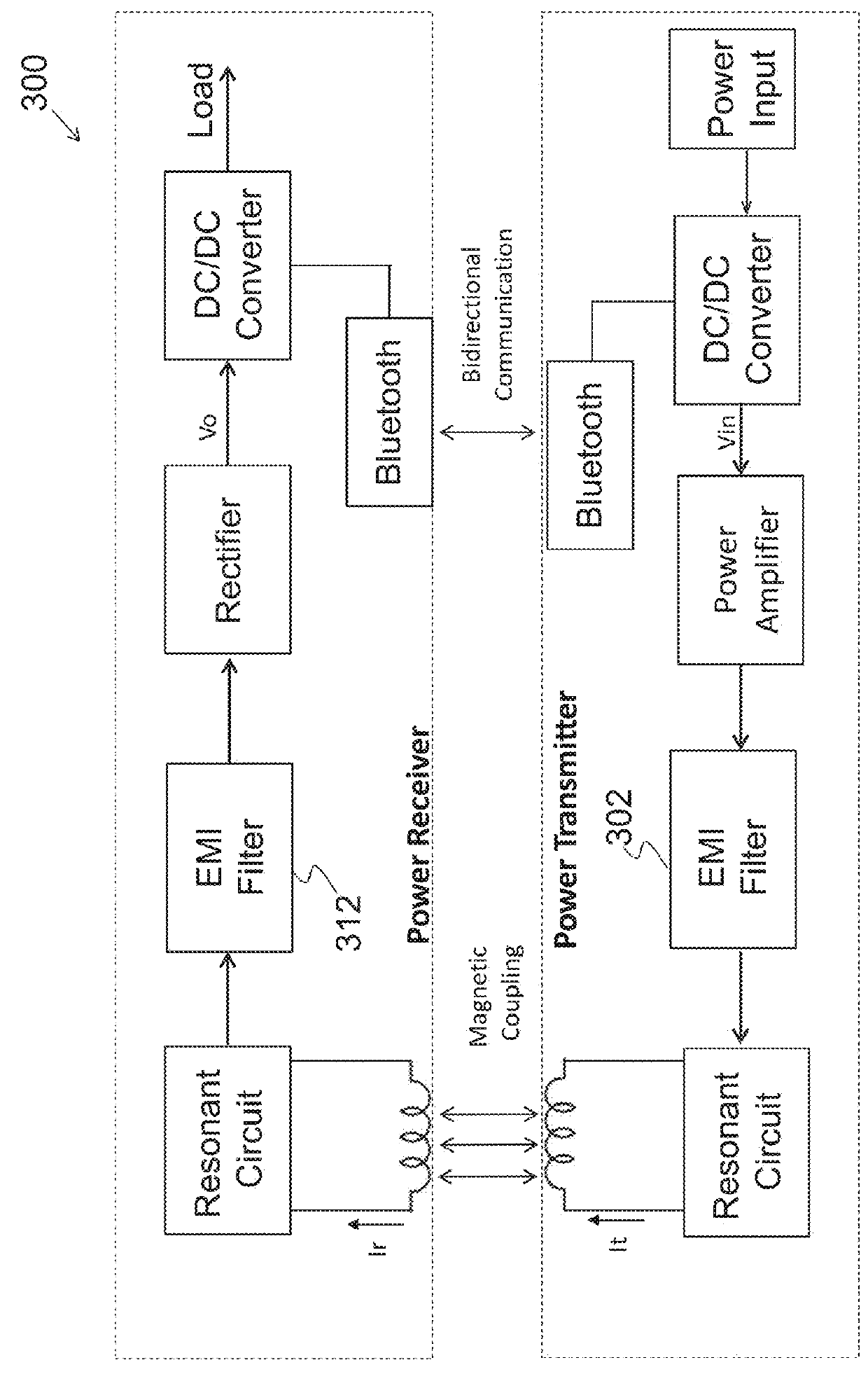
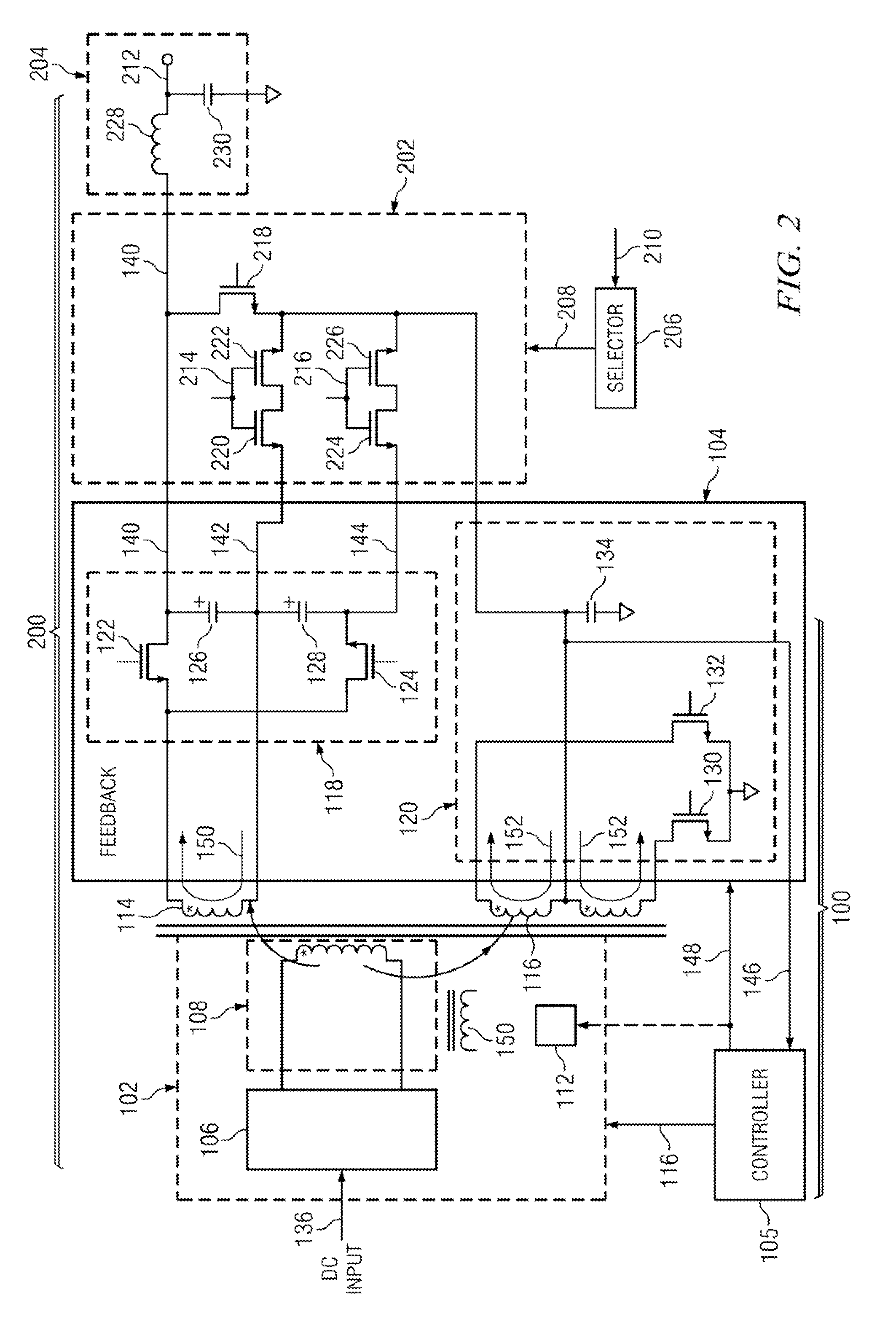
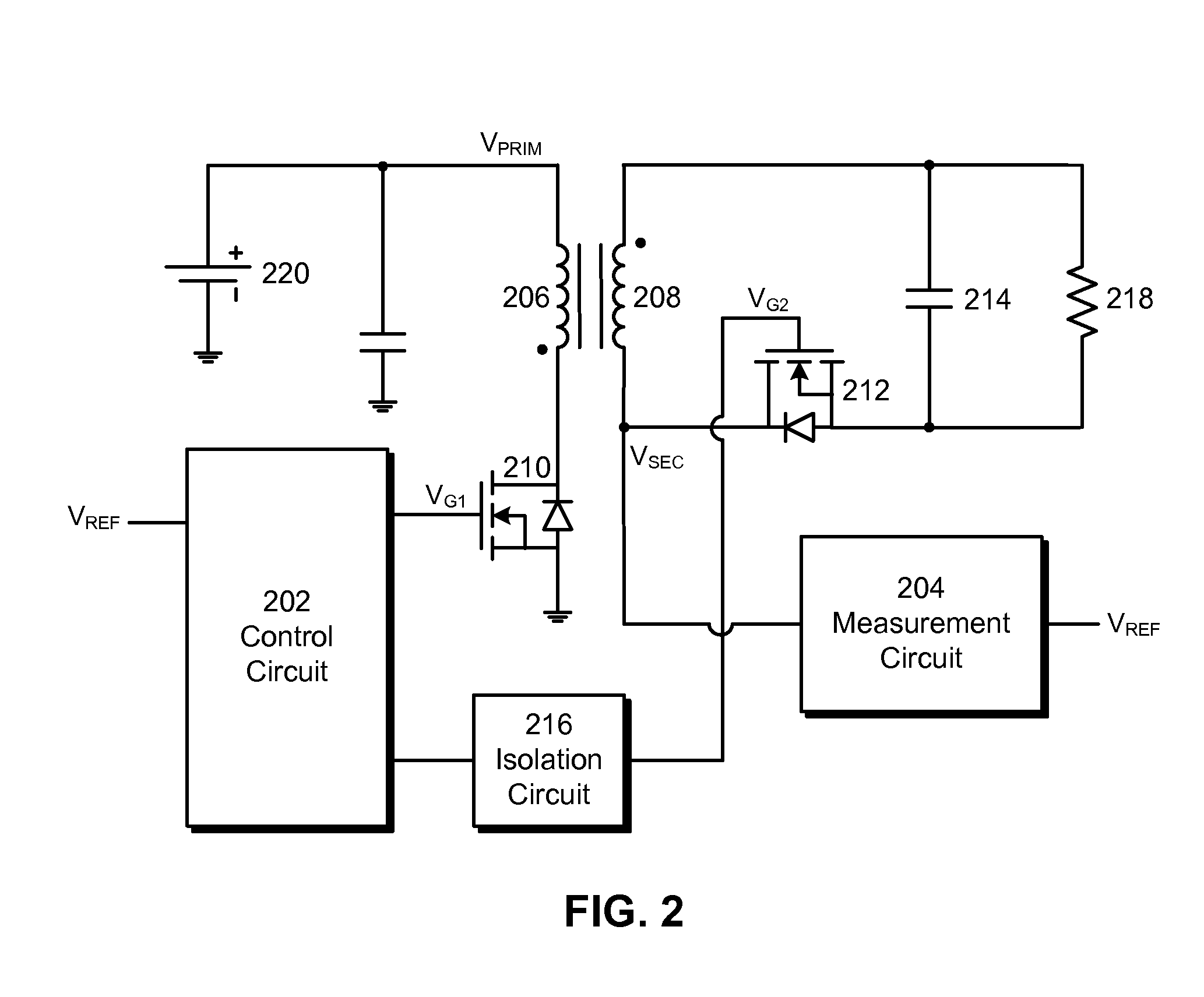
ActiveUS20160056640A1Improve efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemTransformerEngineering
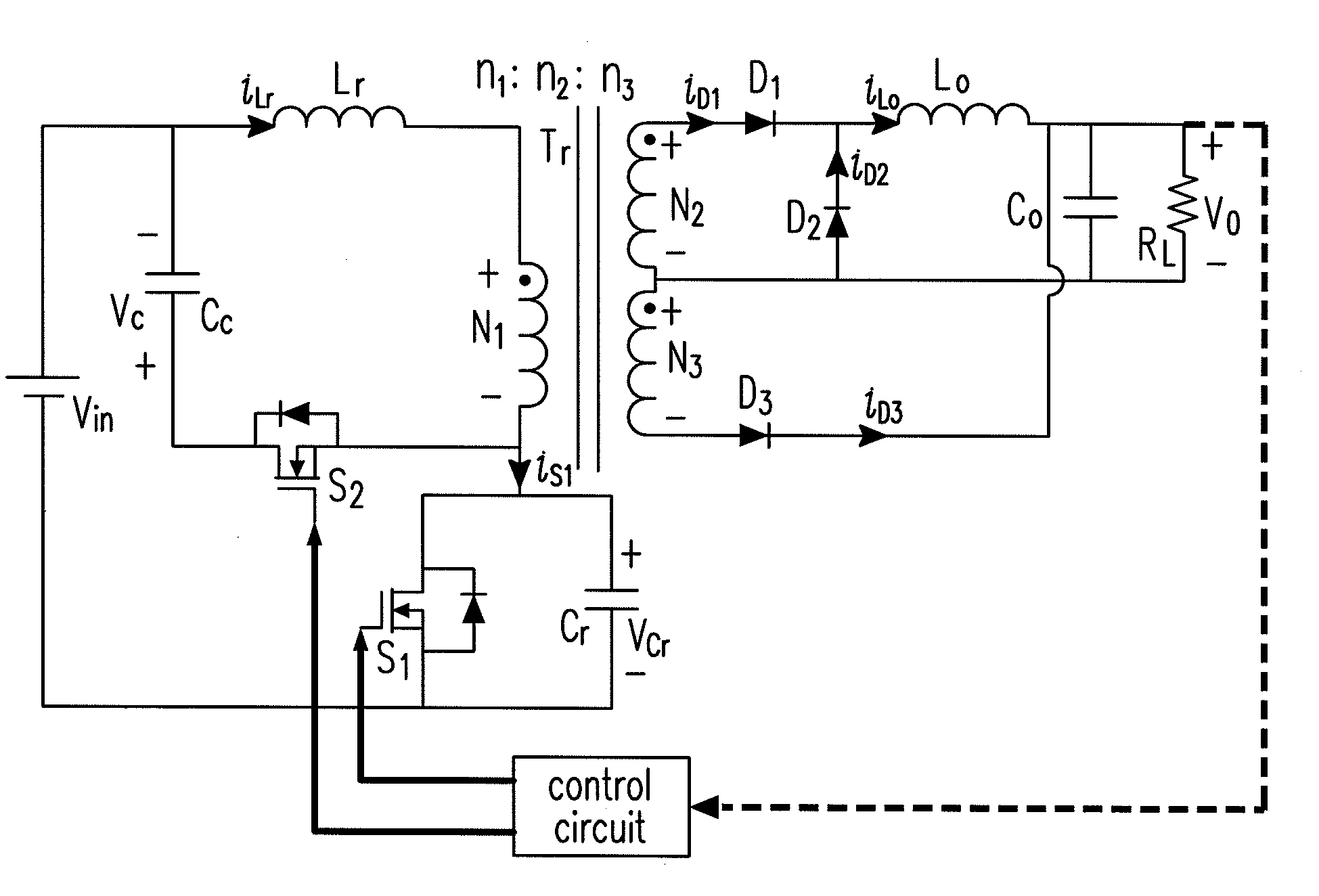
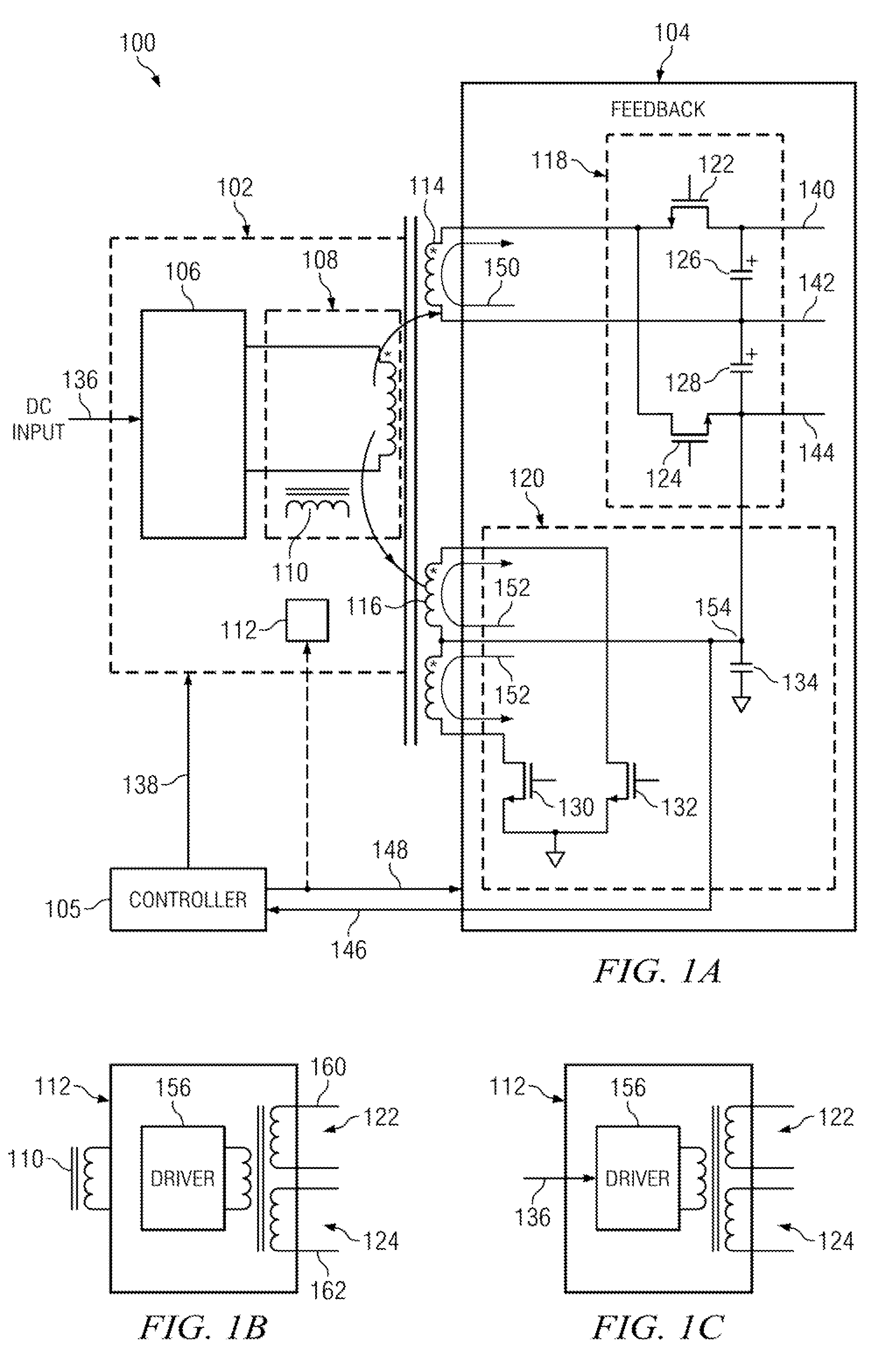
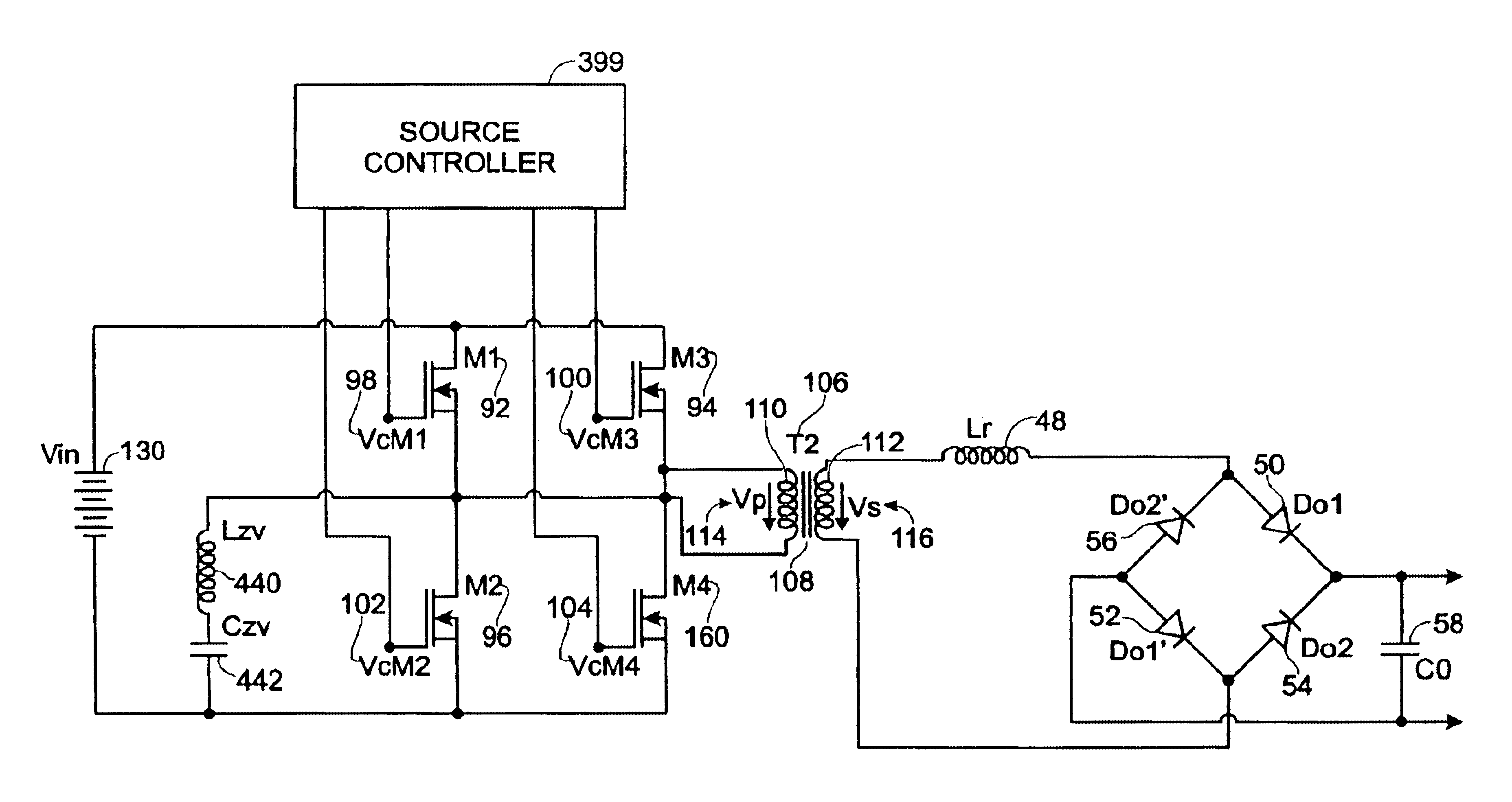
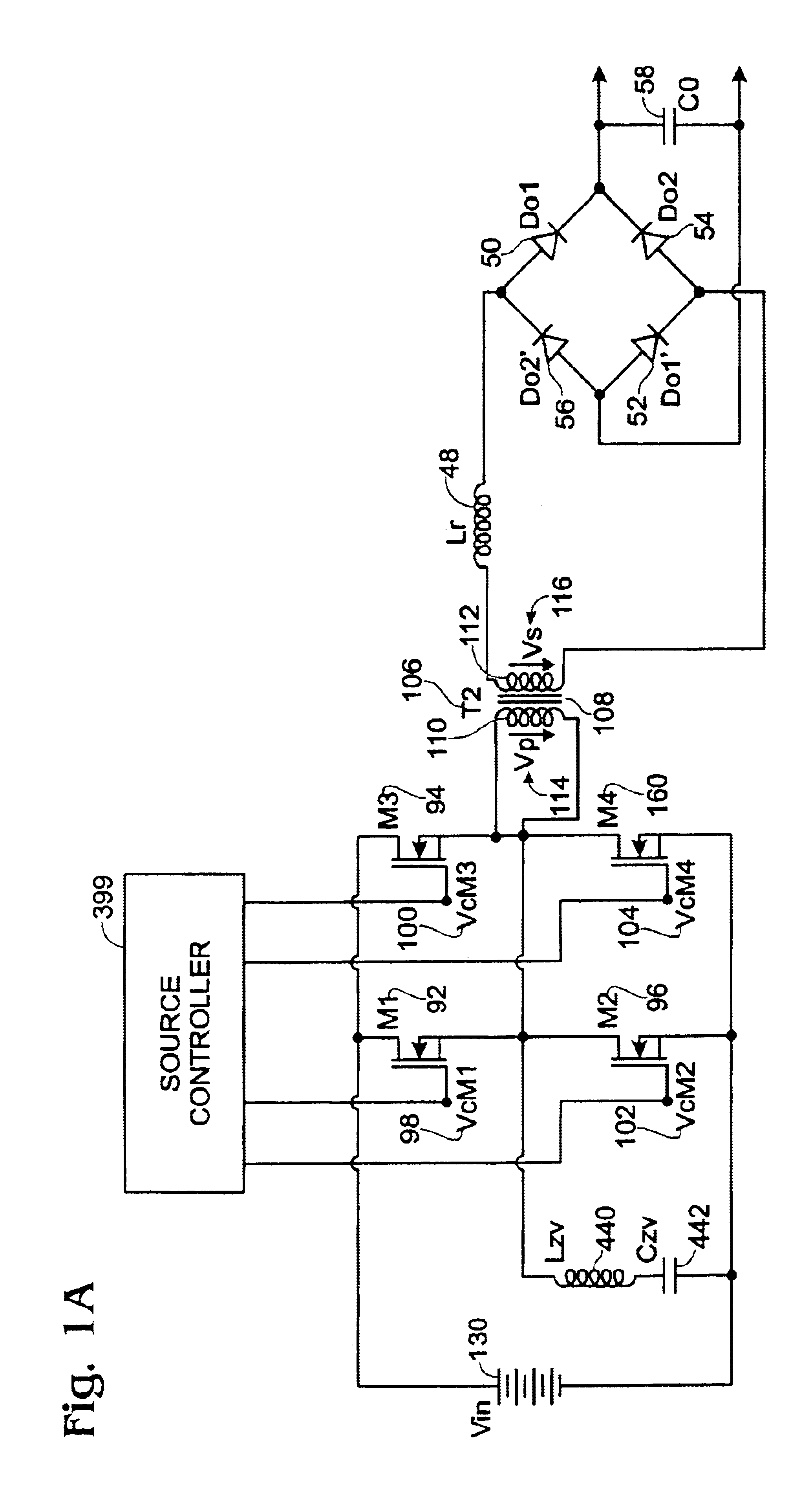
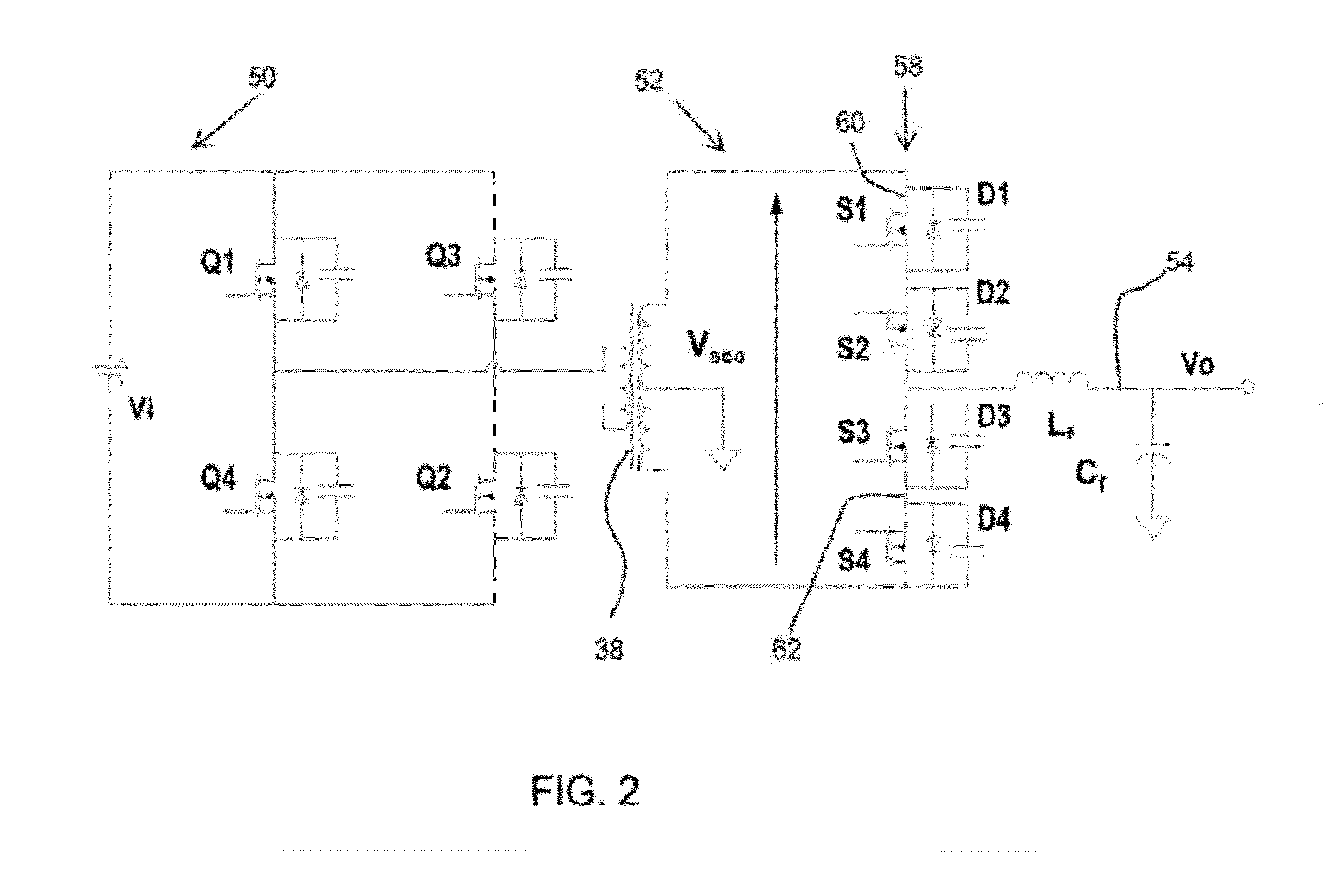
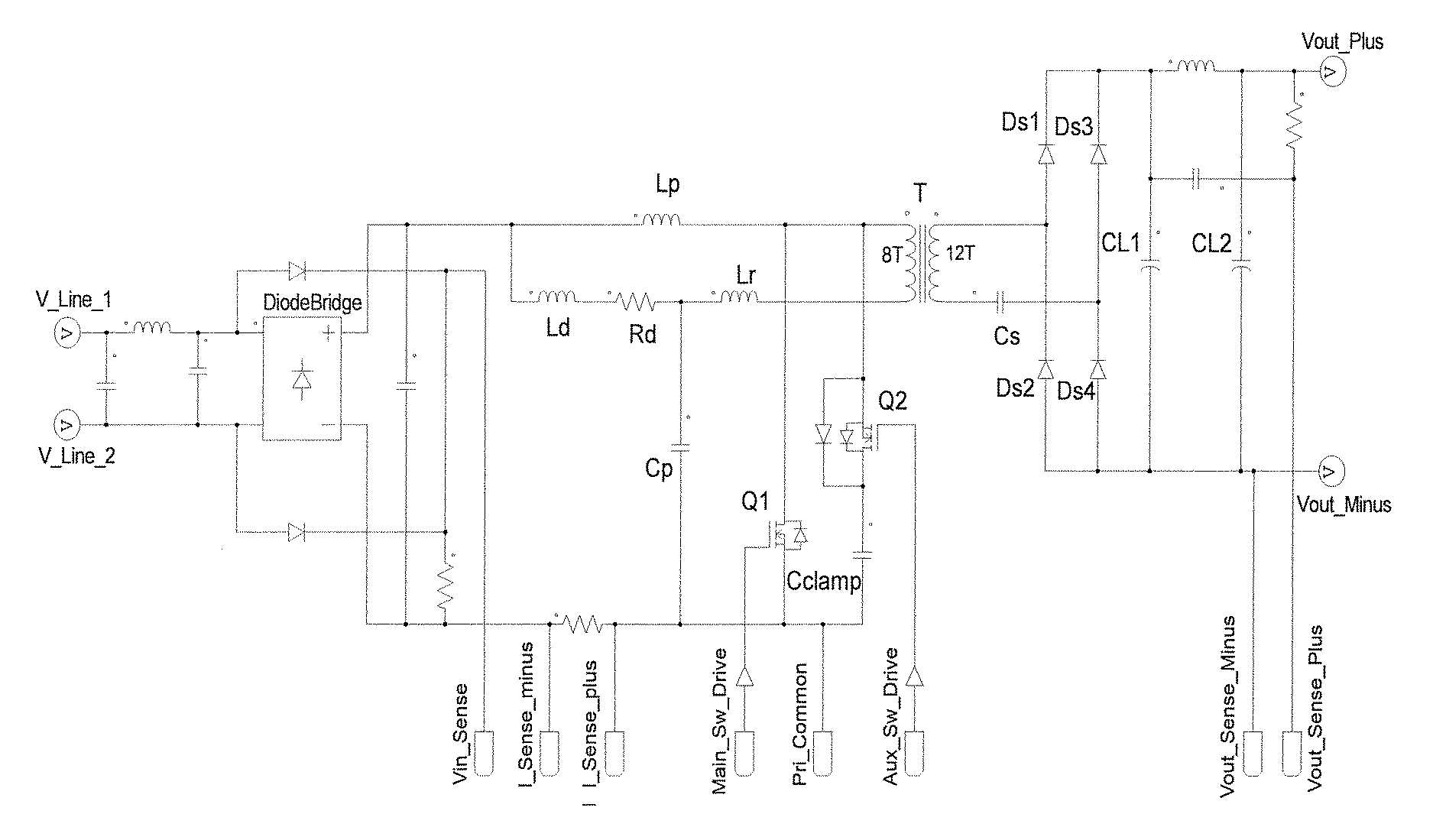
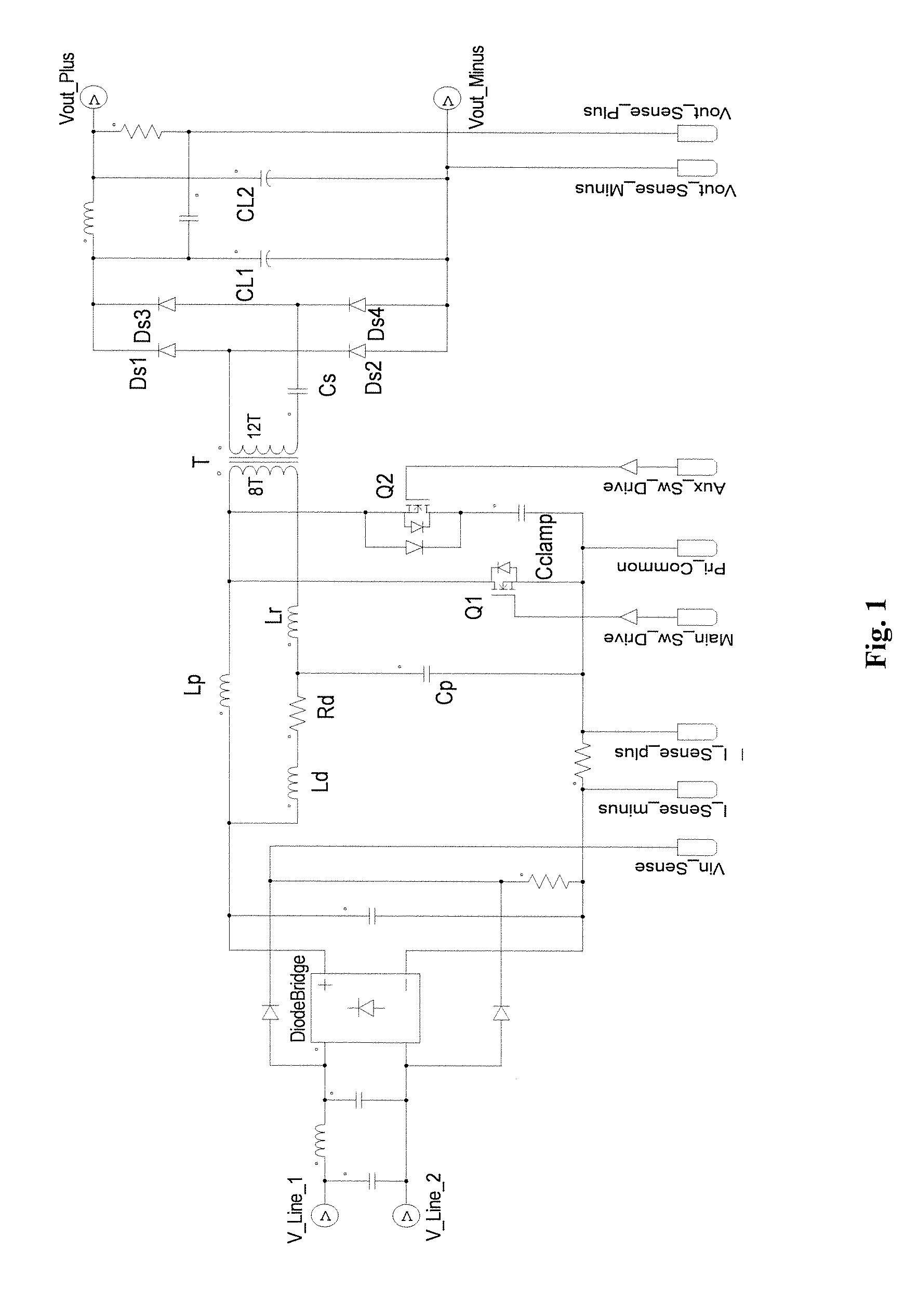
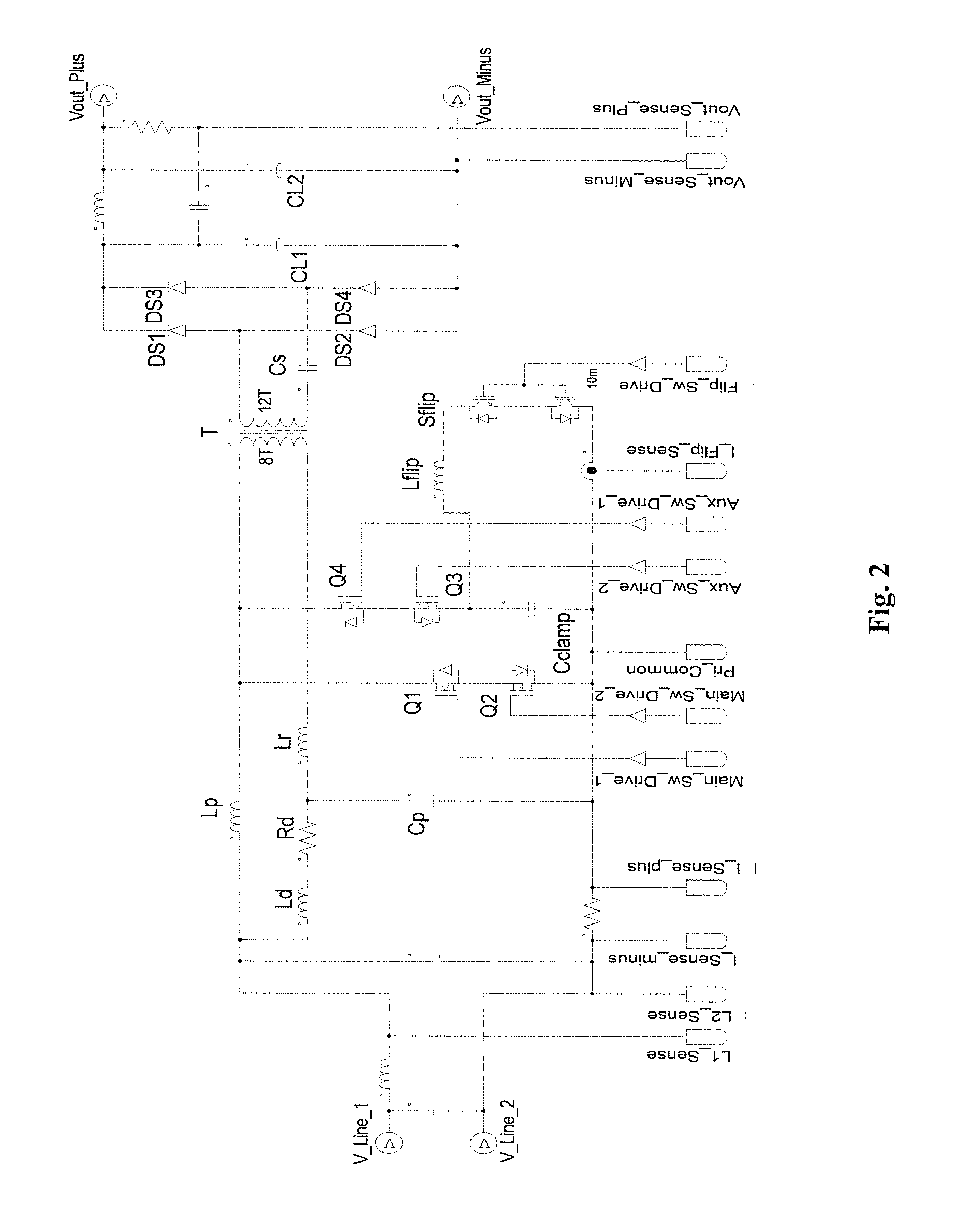
A power converter comprises a primary switch network coupled to a power source, wherein the primary switch network comprises a plurality of power switches, a controller configured to generate gate drive signals for the plurality of power switches, a secondary rectifier coupled to an output, a first transformer having a first winding coupled to the primary switch network, a second winding coupled to the secondary rectifier and a third winding coupled to the controller and a second transformer having a fourth winding coupled to the primary switch network, a fifth winding coupled to the secondary rectifier and a sixth winding coupled to the controller, wherein a voltage signal from the third winding and / or the sixth winding is processed to provide a feedback of a voltage at the output.
Owner:NUVOLTA TECH
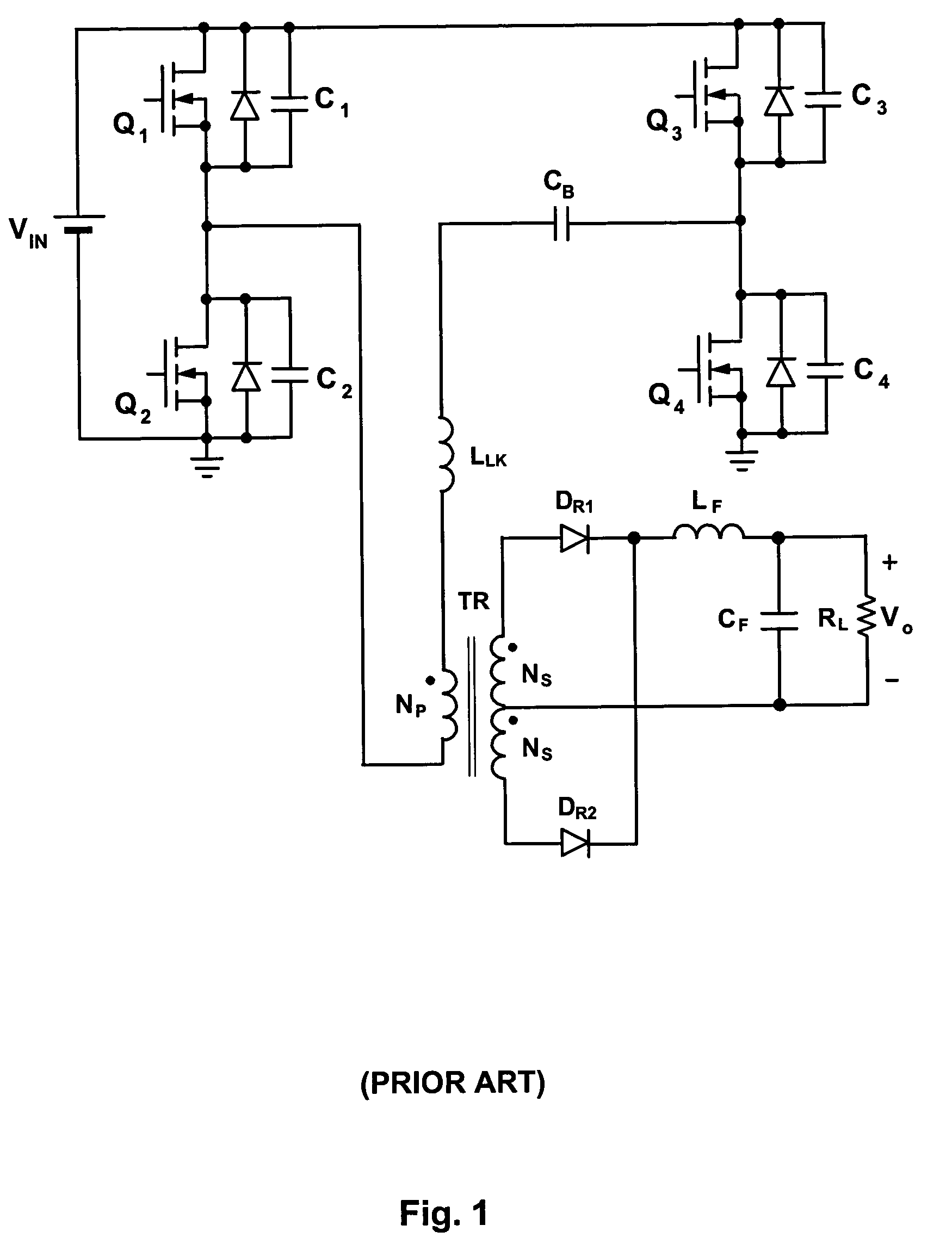
Soft-switched full-bridge converters
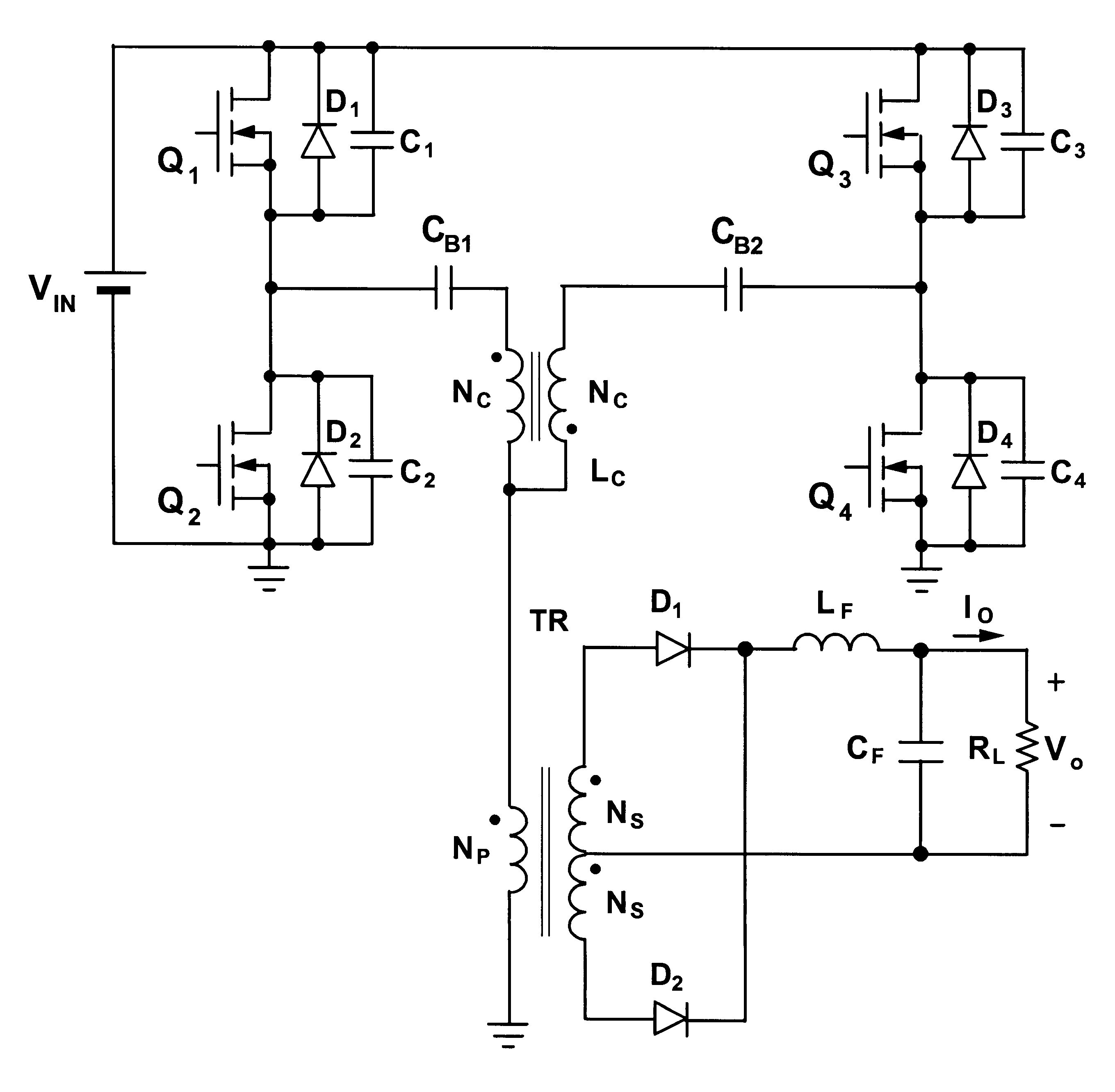
InactiveUS6356462B1Minimizes the duty-cycle lossImprove conversion efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionFull bridgeCirculating current
A family of soft-switched, full-bridge pulse-width-modulated (FB PWM) converters provides zero-voltage-switching (ZVS) conditions for the turn-on of the bridge switches over a wide range of input voltage and output load. The FB PWM converters of this family achieve ZVS with the minimum duty cycle loss and circulating current, which optimizes the conversion efficiency. The ZVS of the primary switches is achieved by employing two magnetic components whose volt-second products change in the opposite directions with a change in phase shift between the two bridge legs. One magnetic component always operates as a transformer, where the other magnetic component can either be a coupled inductor, or uncoupled (single-winding) inductor. The transformer is used to provide isolated output(s), whereas the inductor is used to store the energy for ZVS.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Control for an induction-based aerosol delivery device
An aerosol delivery device is provided that includes a substrate configured to carry an aerosol precursor composition, and includes an induction transmitter, induction receiver and control component. The induction transmitter is configured to generate an oscillating magnetic field. The induction receiver is positioned in proximity to the substrate, and configured to generate heat when exposed to the oscillating magnetic field and thereby vaporize components of the aerosol precursor composition. The control component is configured to direct current to the induction transmitter to drive the induction transmitter to generate the oscillating magnetic field, with the control component being configured to direct the current according to a zero voltage switching (ZVS) inverter topology.
Owner:RAI STRATEGIC HLDG INC
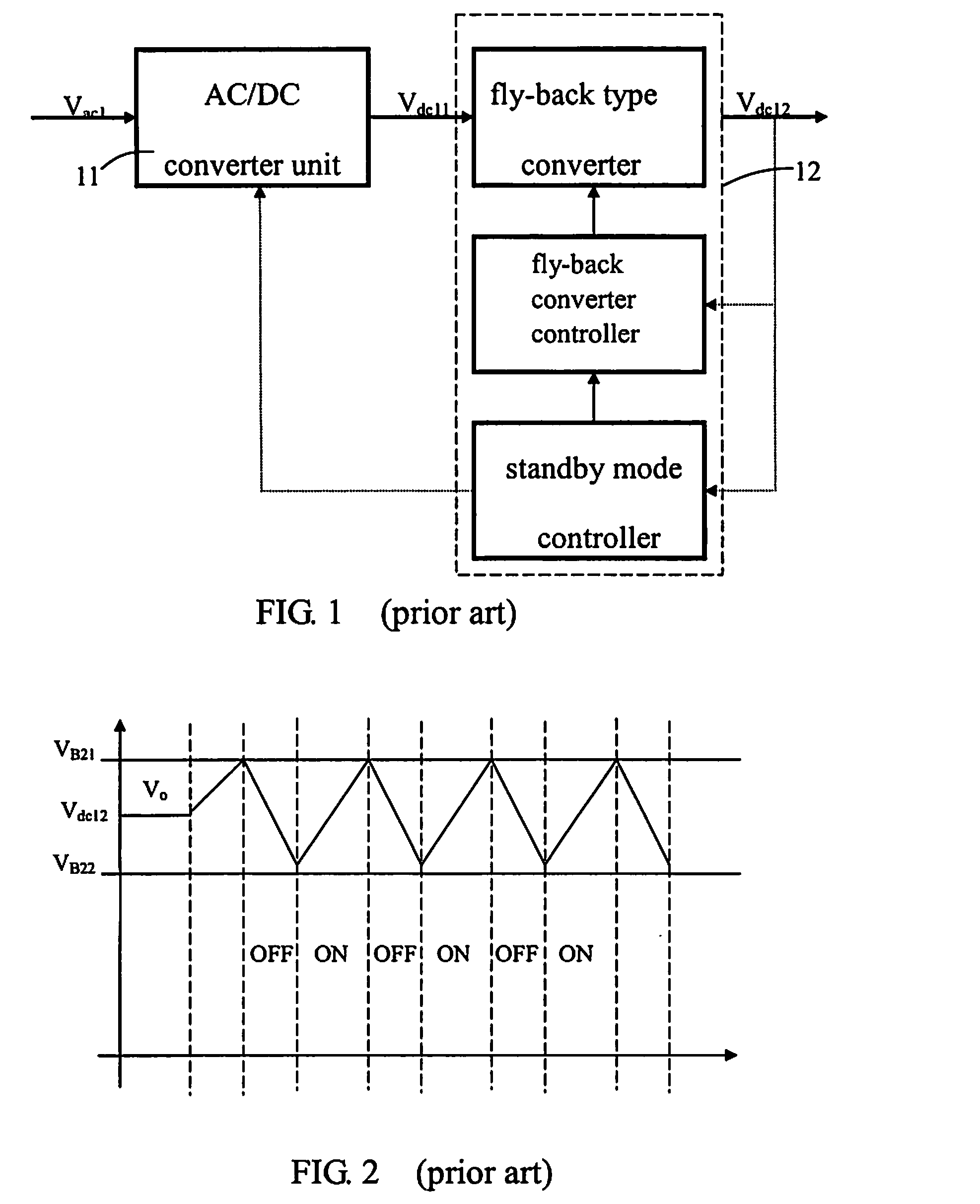
Forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit
ActiveUS20100067259A1Improve conversion efficiencyAdditional drawbackEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsHeavy loadCenter tap
The present invention discloses a forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit. The secondary side of the proposed converter is of center-tapped configuration to integrate a forward circuit and a flyback circuit. The flyback sub-circuit operating continuous conduction mode is employed to directly transfer the reset energy of the transformer to the output load. The forward sub-circuit operating discontinuous conduction mode can correspondingly adjust the duty ratio with the output load change. Under the heavy load condition, the mechanism of active-clamp flyback sub-circuit can provide sufficient resonant current to facilitate the parasitic capacitance of the switches to be discharged to zero. Under the light load condition, the time interval in which the resonant current turns from negative into positive is prolonged to ensure zero voltage switching function. Meanwhile, the flyback sub-circuit wherein the rectifier diode is reverse biased is inactive in order to further reduce the power losses.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
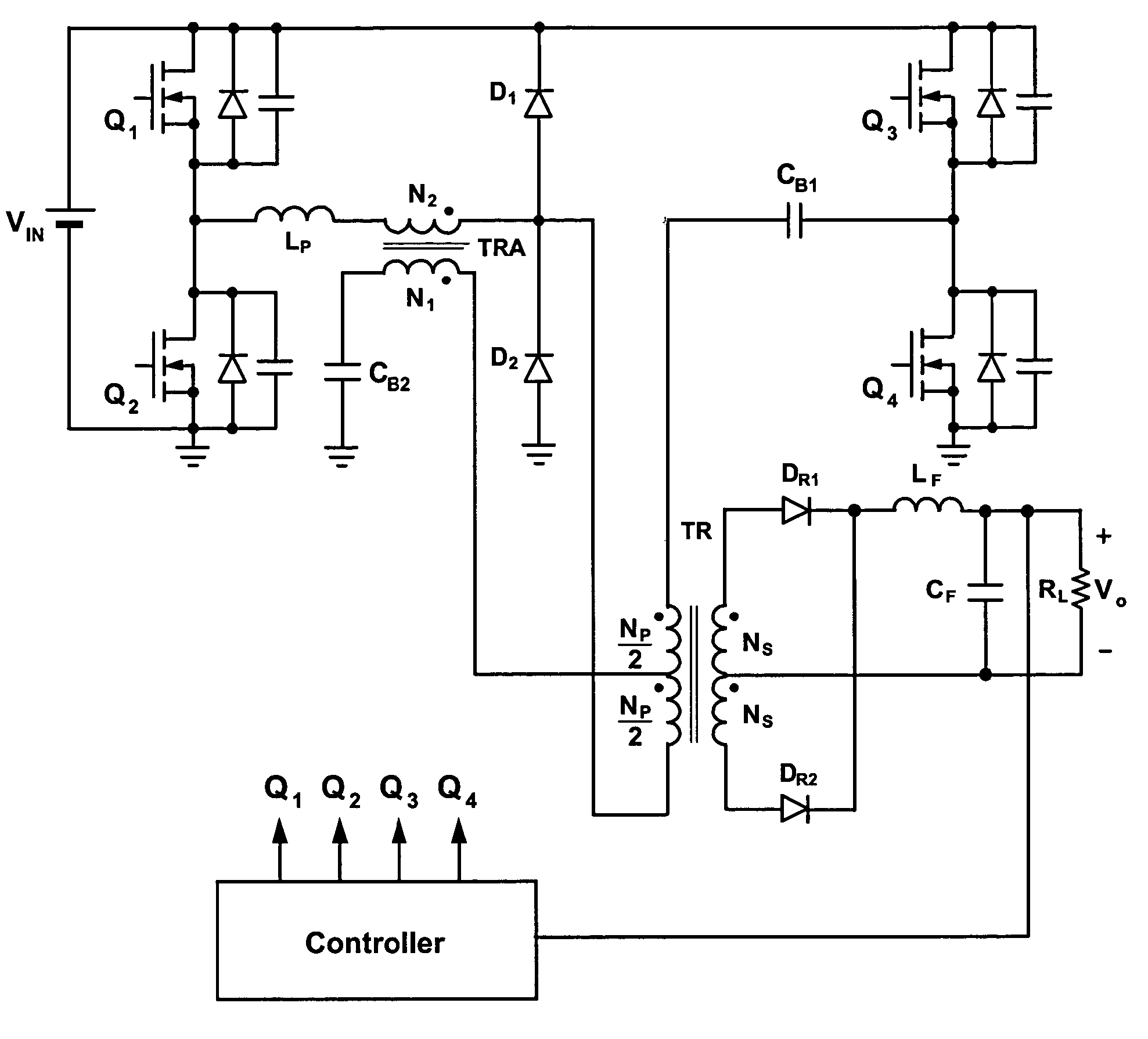
Phase-shifted dual-bridge DC/DC converter with wide-range ZVS and zero circulating current
ActiveUS20090196072A1Solve insufficient storage spaceMinimizes voltage ringingAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionFull wavePhase difference
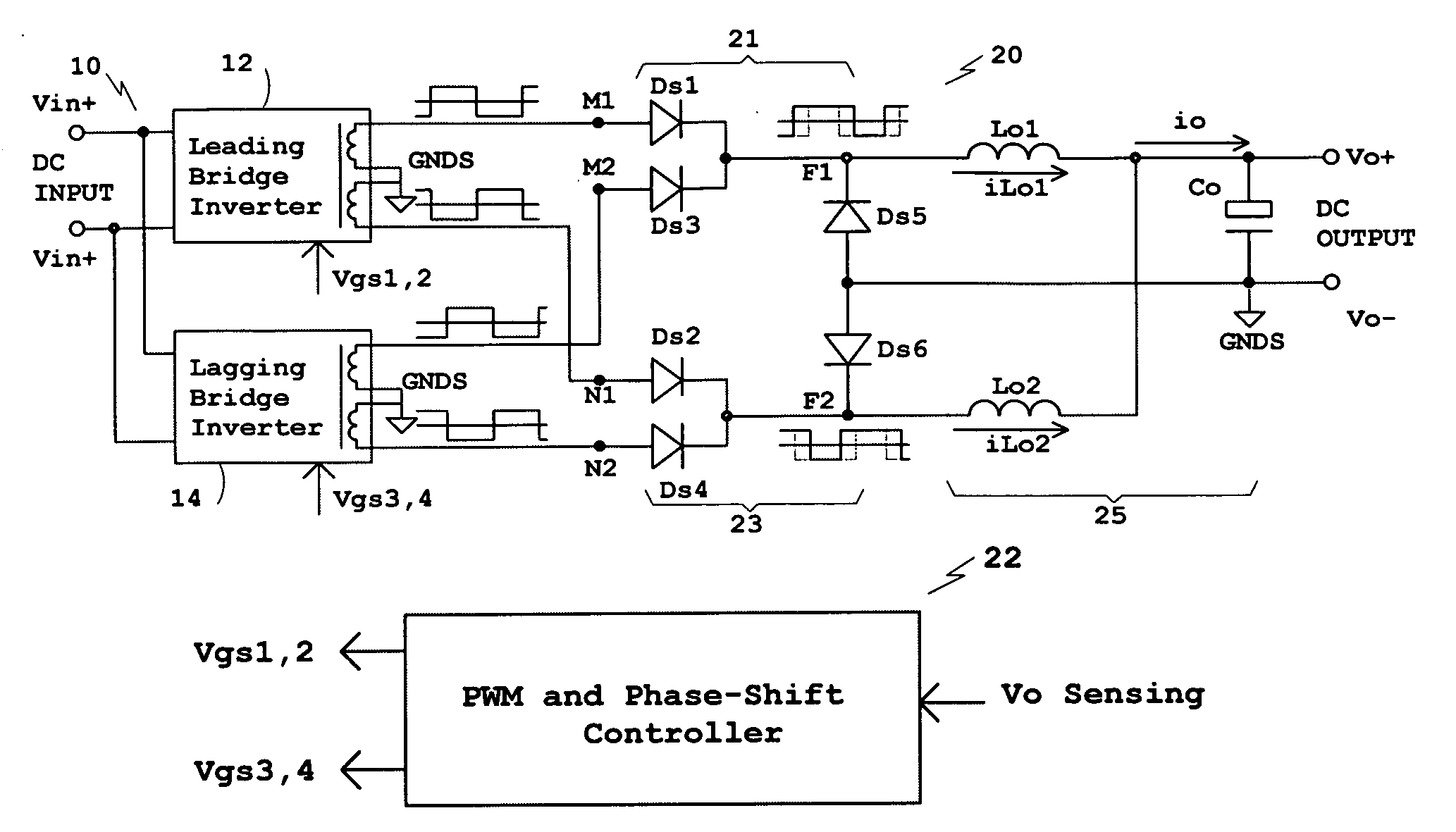
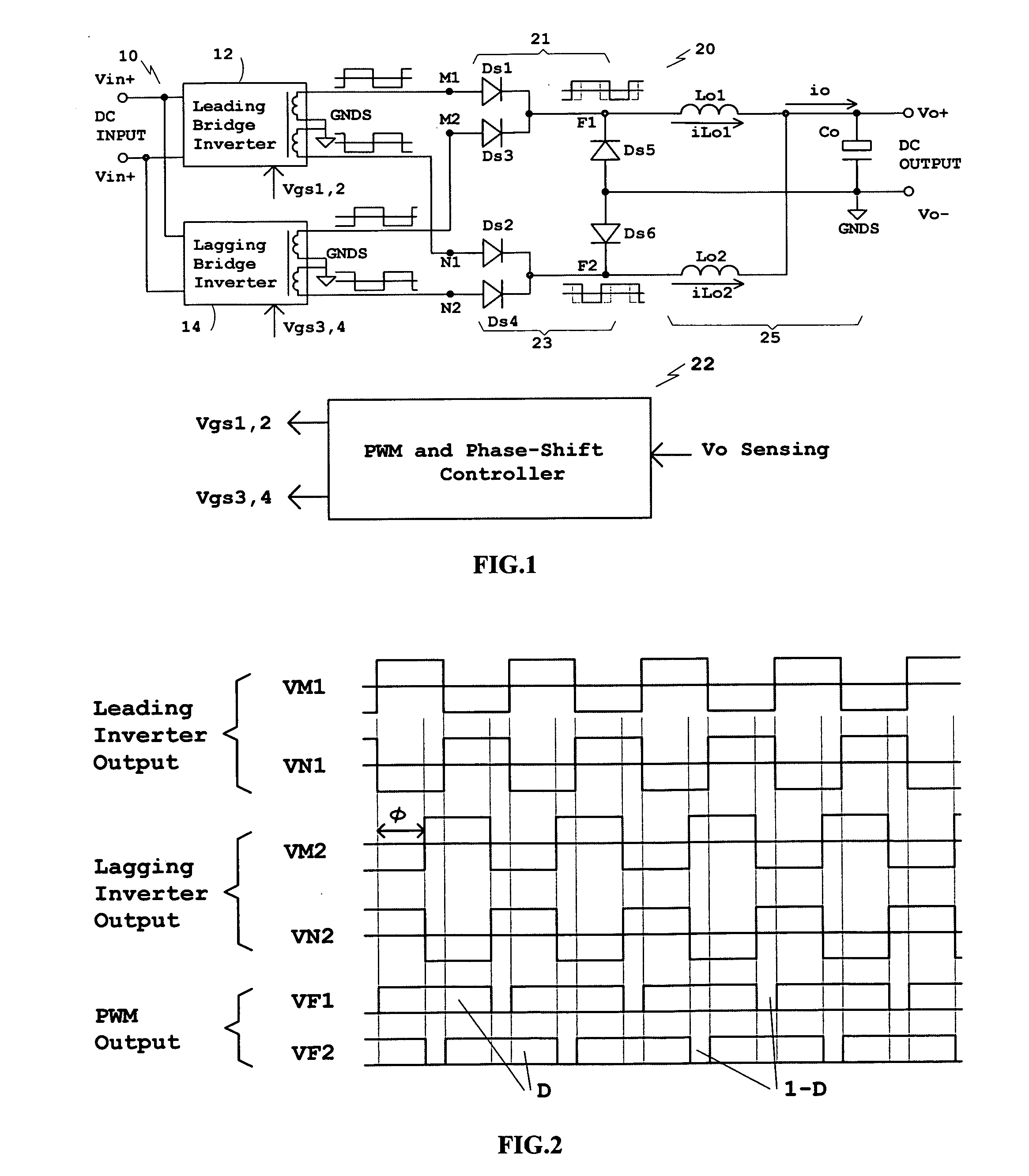
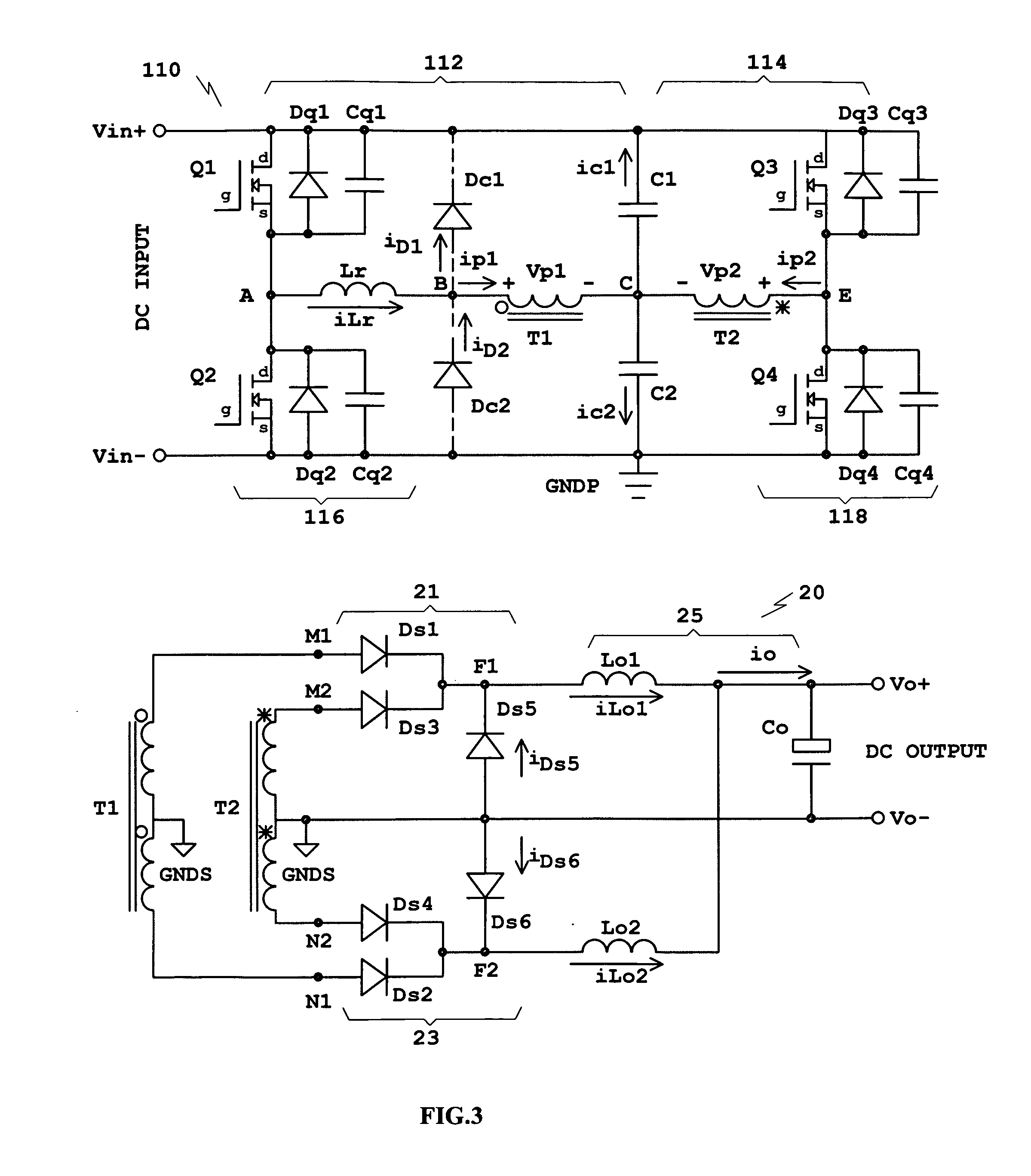
Disclosed is a family of new DC / DC converters and a new control method. The converter comprises two bridge inverters, two full-wave rectification circuits and a current-doubler filter. Each inverter is able to generate a symmetrical and isolated AC output voltage. Phase-shift control is employed to control the phase difference between the two bridge inverters. By shifting the phase, the converter changes the two inverters' output voltage overlapping area to regulate its output voltage. The bridge inverters always operate at 50% duty cycle, like an open loop Bus Converter, to achieve wide-range zero voltage switching and eliminate circulating current for normal operation. For low output voltage regulation and soft start, Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) control is used. The converters and the control method improve power conversion efficiency, maximize magnetic component utilization, reduce semiconductor stress and decrease EMI emission.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Zero voltage switching interleaved boost ac/dc converter
ActiveUS20130235631A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionPhase shiftedPower factor
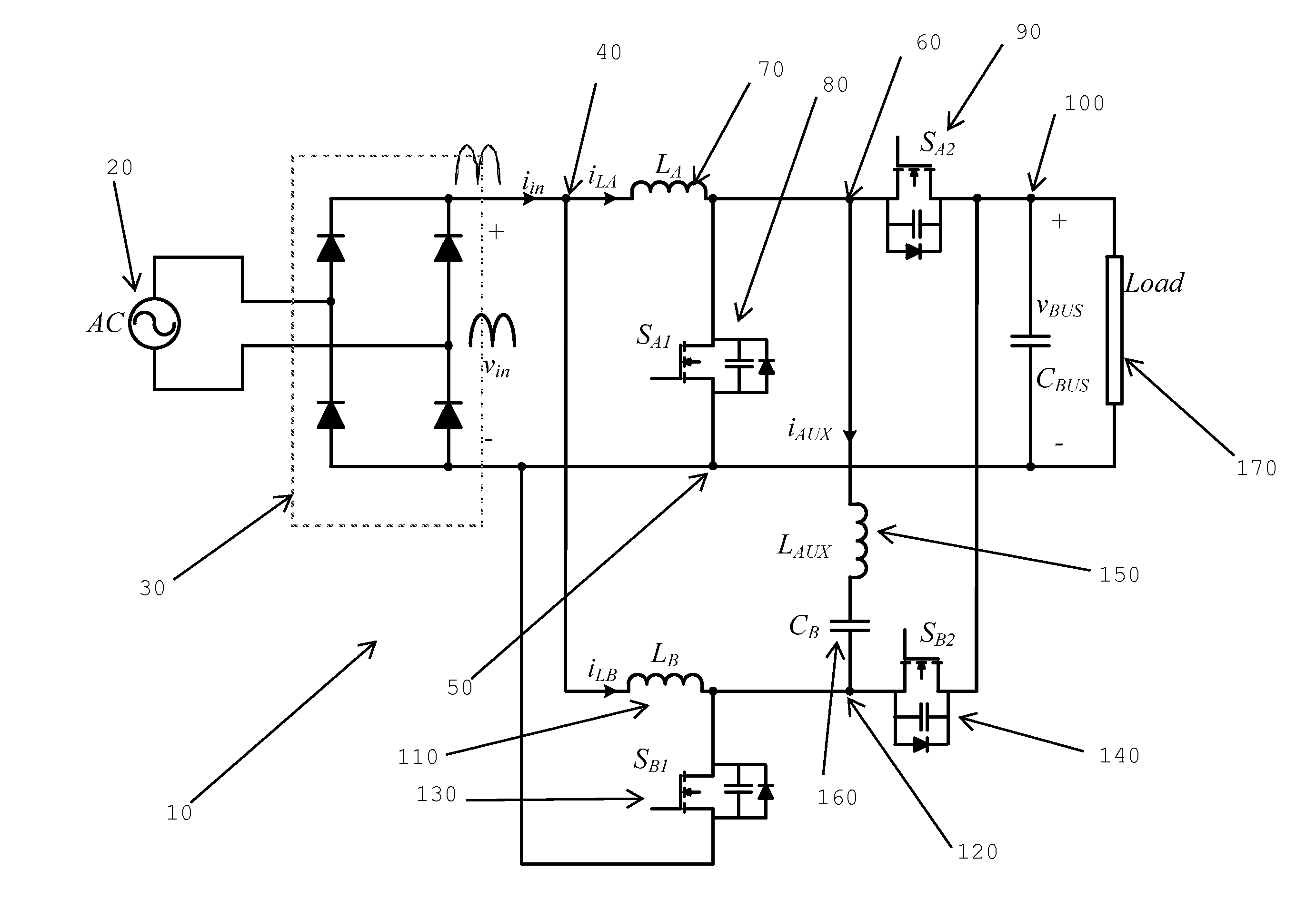
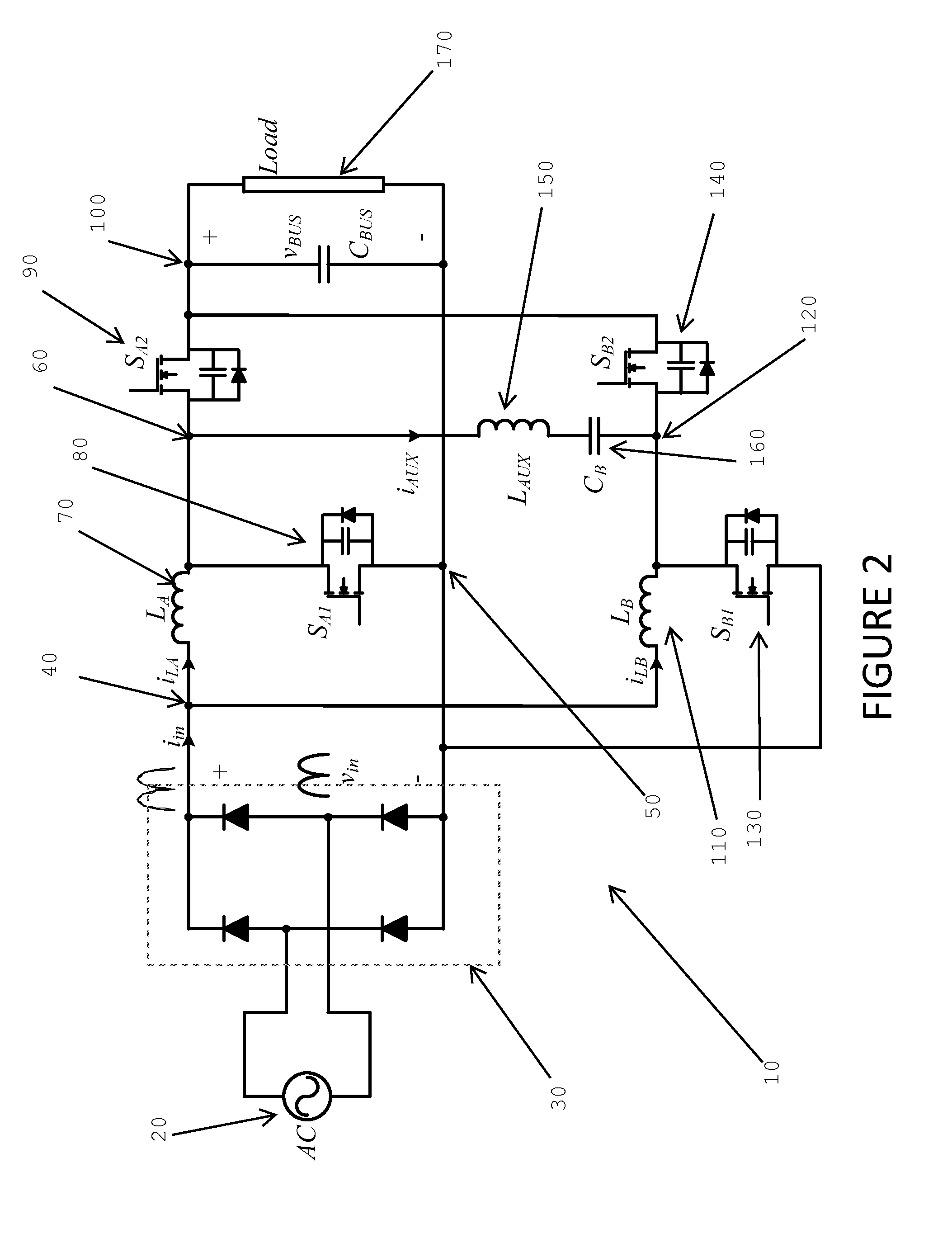
Circuits and methods relating to the provision of a reactive current to ensure zero voltage switching in a boost power factor correction converter. A simple passive circuit using a series connected inductor and capacitor are coupled between two phases of an interleaved boost PFC converter. The passive circuit takes advantage of the 180° phase-shift between the two phases to provide reactive current for zero voltage switching. A control system for adjusting and controlling the reactive current to ensure ZVS for different loads and line voltages is also provided.
Owner:SPARQ SYST INC
System and method for envelope tracking power supply
ActiveUS20130021827A1Reduce power lossImprove efficiencyHigh frequency amplifiersDc-dc conversionHigh bandwidthEngineering
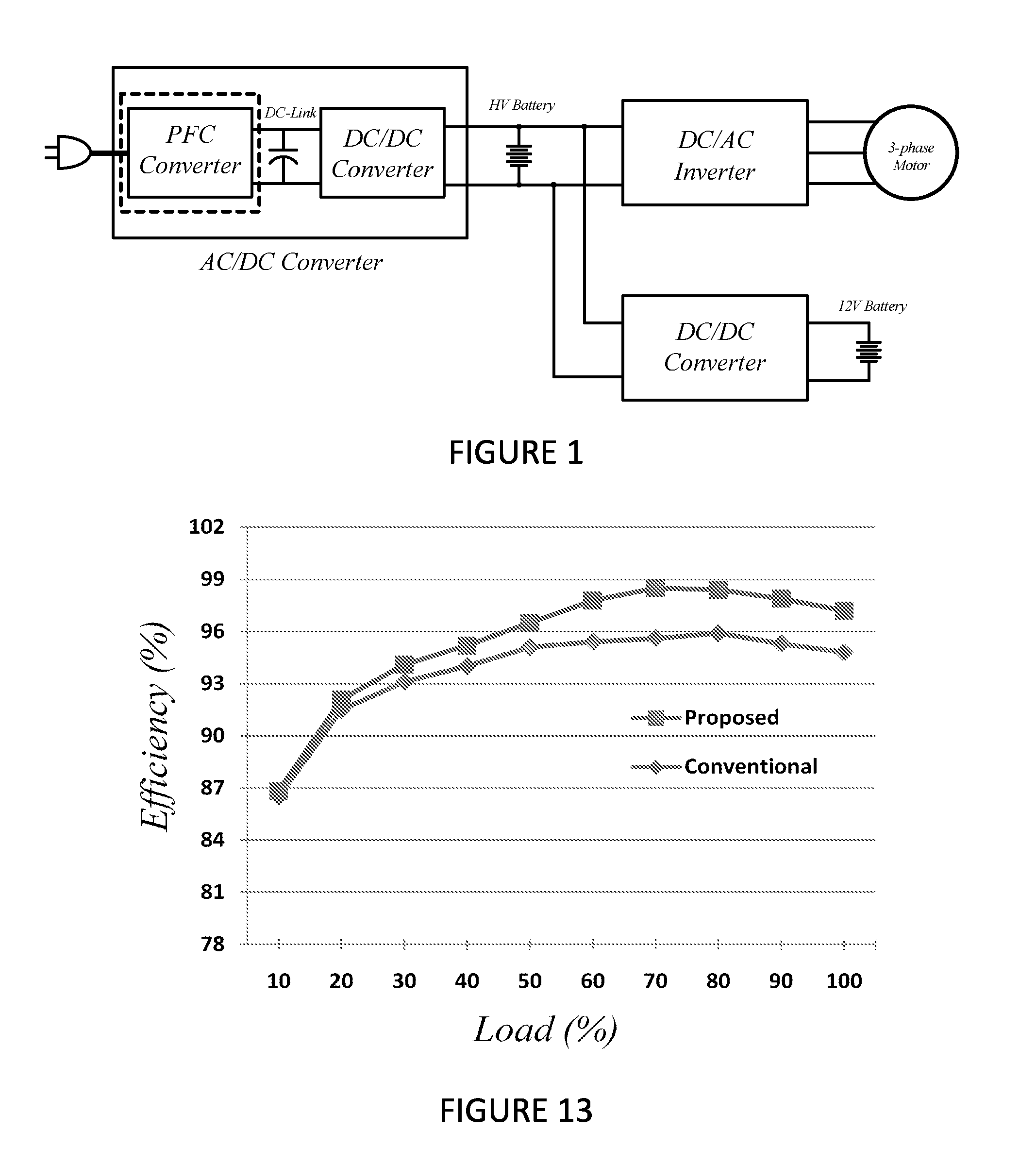
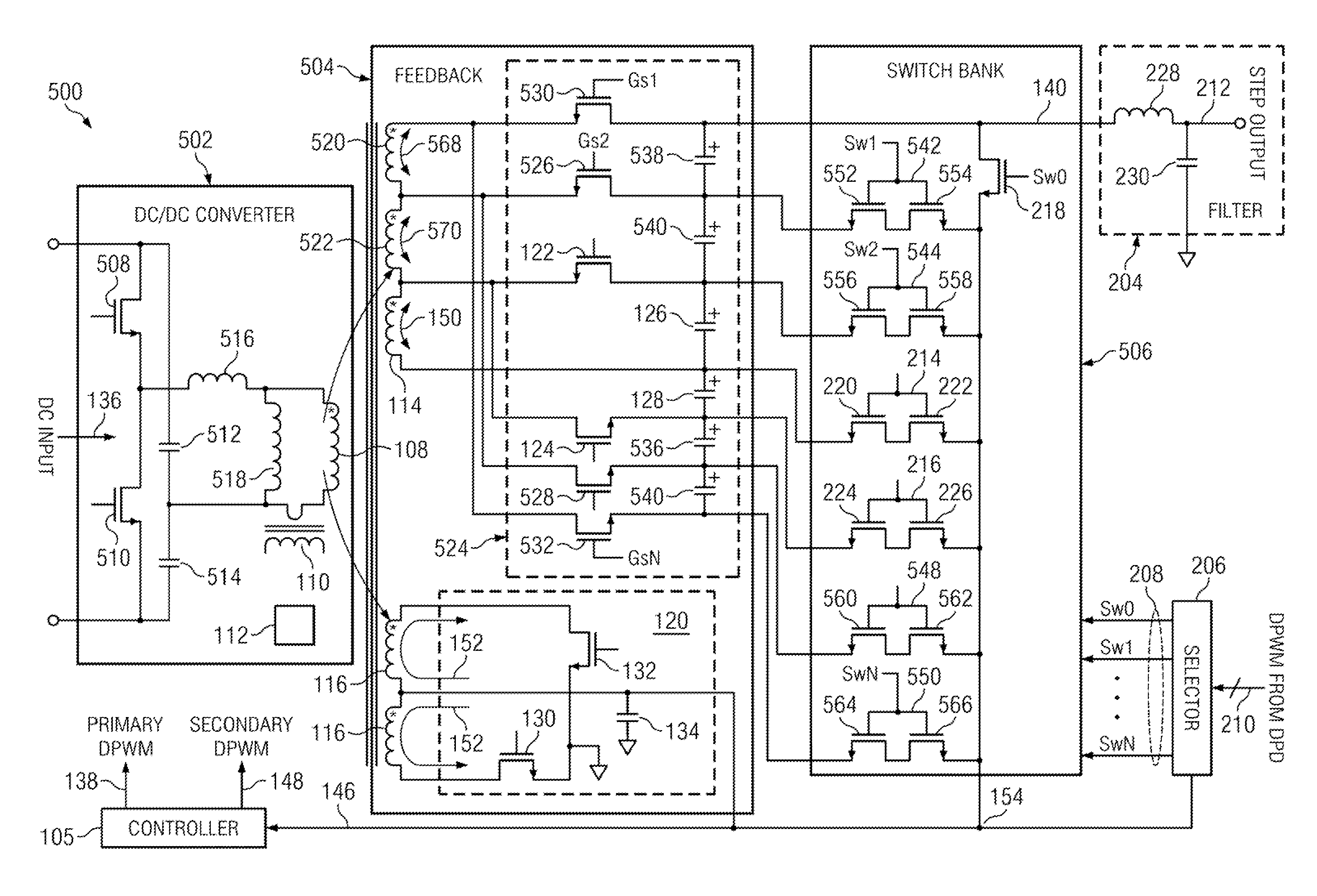
An envelope tracking power supply has a multiple-output DC / DC converter, a switch bank, an output voltage selector and an output filter. The DC / DC converter has an alternating current generating portion and a full rectifying portion. The alternating current generating portion, typically a LC circuit, can receive an input voltage and operate at zero voltage switching. The full rectifying portion includes at least one secondary winding and one voltage doubler output. Each voltage doubler has a first transistor, a second transistor, a first capacitor and a second capacitor. The transistors used as rectifier devices allow currents to flow bi-directionally and sink and source the currents from and to output capacitors to keep their voltage balance. Secondary windings and output capacitors are connected in series respectively. A switch bank selects a desired voltage from the series connected capacitors and connects it to the output filter. The switch bank receives an envelope tracking command from the voltage selector and provides a step voltage to the output. The output voltage is changed at switching speed to track a high bandwidth envelope signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Full bridge converter with ZVS via AC feedback
InactiveUS6992902B2Increase inductanceIncreases the amount of current deliveredConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionFull bridgeCirculating current
A soft-switched, full-bridge pulse-width-modulated converter and its variations provide zero-voltage-switching conditions for the turn-on of the bridge switches over a wide range of input voltage and output load. The FB PWM converters of this invention achieve ZVS with a substantially reduced duty cycle loss and circulating current. The ZVS of the primary switches is achieved by employing an auxiliary circuit having an inductor and transformer to store energy for ZVS turn-on of the bridge switches.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Three-Level Active Neutral Point Clamped Zero Voltage Switching Converter
ActiveUS20120218785A1Improve efficiencyHigh level conversionEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionThree levelSwitching cycle
A main circuit of a three-level active neutral point clamped voltage source converter having a pair of additional main switches provides two paths between an output node and a neutral point in which one of the paths involves only switches of an inner pair of switches that are operated at a high frequency. An auxiliary circuit operating at a high frequency for only a brief period during each high frequency switching cycle selects the path involving only the inner switches and provides operation with zero voltage switching and avoids reverse recovery of diodes connected antiparallel with the main and additional main switches. Accordingly, turn-on switching losses in the main switches is avoided and the voltage source converter can be operated at increased frequency to allow reduction in size of magnetic components and full potential power transfer to be achieved.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Power supply unit, hard disk drive and method of switching the power supply unit
InactiveUS20100232180A1Improve efficiencyBroadEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcCapacitanceHard disc drive
Zero volt switching during a light load is performed in such a manner that through an ON / OFF control of switches provided for a full bridge circuit and the synchronous rectifier switches in a rectifier and smoothing circuit, a resonant peak voltage necessary for the zero voltage switching determined by the output current flowing to output terminals, a resonant inductor and a resonant capacitor capacitance is ensured so that an energy accumulated in the rectifier and smoothing circuit is returned to the full bridge circuit so as to act as equivalent as when the output current is increased and to increase the current flowing through the full bridge circuit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Fully clamped coupled inductors in power conversion circuits
InactiveUS7606051B1Improve electromagnetic compatibilitySmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionActive clampLeakage inductance
The subject invention reveals improvement methods for circuits that use a coupled inductor wherein overshoot and ringing associated with leakage inductance of said coupled inductor is entirely eliminated by addition of non-dissipative active clamp networks that clamp each winding during each operating state of a power supply containing said coupled inductor. A further improvement applicable to zero voltage switching circuits that employ an inductor for driving a zero voltage turn on switching transition of a switch enables elimination of said inductor and preserves said zero voltage switching properties by adding leakage inductance to a coupled inductor without any adverse overshoot and ringing effects associated with said leakage inductance. The subject invention also reveals a coupled inductor with enhanced leakage inductance which can be used with said other improvements. Example circuits including zero voltage switching flyback and forward converters which require only one magnetic circuit element are revealed. Zero voltage switching tapped inductor buck and boost converters with a single magnetic circuit element are also revealed.
Owner:WITTENBREDER JR ERNEST HENRY
High efficiency coupled inductor soft switching power converters
InactiveUS6272023B1Reduce switching lossesLow component part countEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEngineeringVoltage source
The power converter of this invention accomplishes zero voltage switching at both turn on and turn off transitions of all primary switches. A pair of coupled inductors serve as both energy storage devices and isolation mechanisms. The placement of a small inductor in series with the coupled inductors enables the invariance of primary current direction throughout the switching transition which provides for zero voltage switching for all switches for all transitions. The power converter behaves as a pair of interleaved coupled inductor buck converters with oppositely directed magnetizing currents. During a first half cycle, while one inductor is coupled to the output, the other uncoupled inductor behaves as a current source, setting the primary winding currents for both inductors equal to the magnetizing current of the uncoupled inductor. The inductor which is coupled to the output appears as an output filter capacitor or voltage source to the uncoupled inductor during the first half cycle. During the alternate half cycle the roles of the two inductors are reversed.
Owner:TECHN WITTS
Hybrid switch for resonant power converters
ActiveUS20120057387A1Reduce conduction lossConstant voltage dropEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionResonant power convertersVoltage drop
A hybrid switch comprising two semiconductor switches connected in parallel but having different voltage drop characteristics as a function of current facilitates attainment of zero voltage switching and reduces conduction losses to complement reduction of switching losses achieved through zero voltage switching in power converters such as high-current inverters.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Switching-type power converter
An apparatus for increasing efficiency and reducing heat dissipation in power converters is disclosed. Zero-voltage-switching (ZVS) can reduce switching loss of power converters but it often results in a very complicated design and only works well under constant output current. In order to allow the ZVS to work over a wide loading range, the transformer secondary current is blocked when the primary starts to resonate. Hence, the resonant voltage waveform across the switch will not change even when the loading current is changing. Such a resonant voltage waveform is obtained with the aid of the transformer primary inductance and capacitor(s). Also provided is a novel driving circuit which controls the switching. Alternatives and variations of this apparatus can be made to satisfy different applications such as power conversion and power inversion. The subject power converter significantly lowers the heat loss and achieves higher efficiency for very wide loading ranges.
Owner:FUNG SZE WEI +1
Synchronous Rectifier Type Series Resonant Converter for Operating in Intermittence Mode
InactiveUS20080186742A1Reduce switching lossesMaximize conversion efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionLc resonant circuitResonance
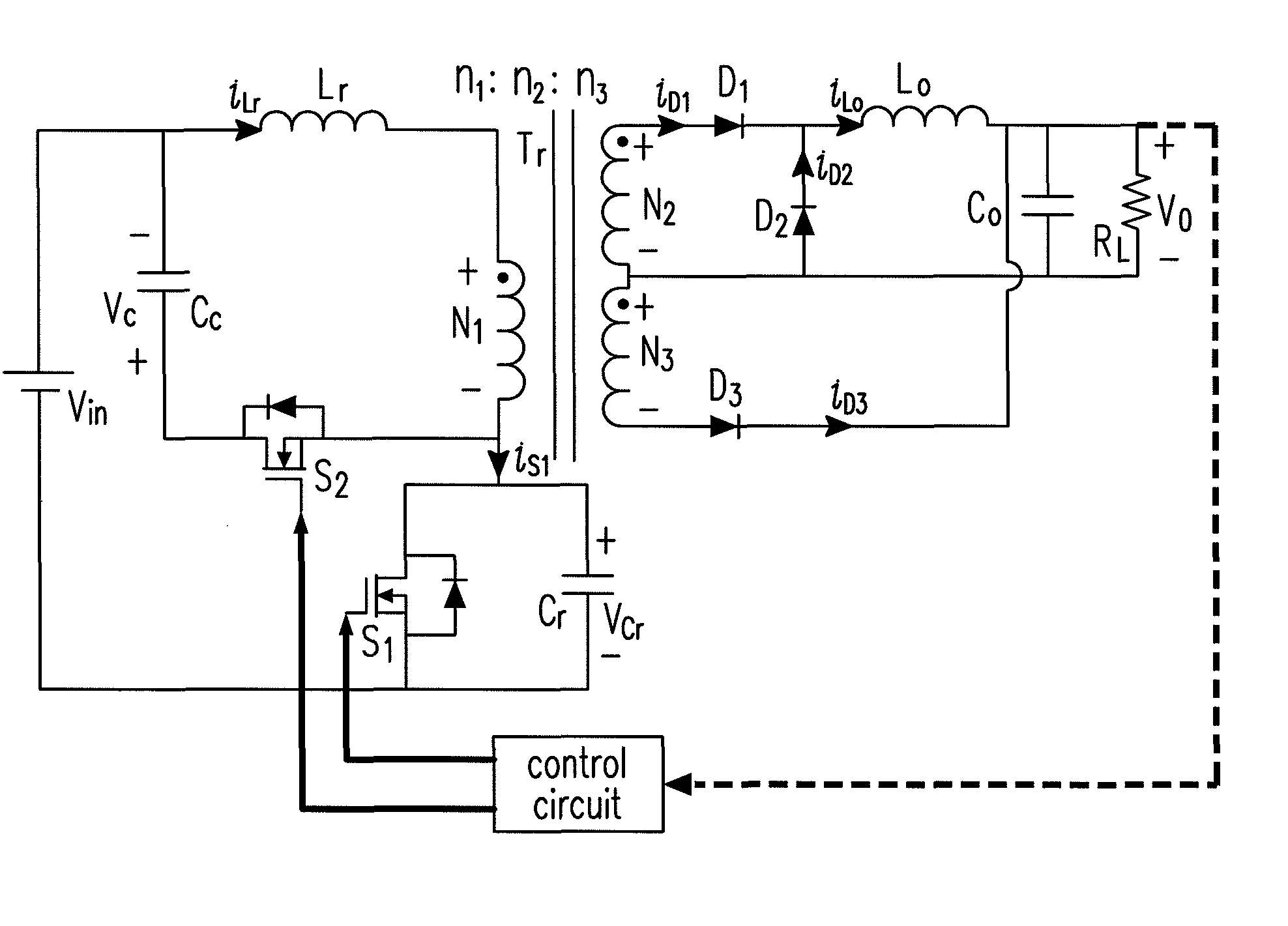
Disclosed is a synchronous rectifier type SRC for operating in an intermittence mode, which includes: an input power for supplying the input DC voltage; an input-side switching unit for switching four input-side switching devices to convert the input DC voltage to AC voltage, the input-side switching unit being connected to the input power, an LC resonance circuit for storing energy in a resonance inductor and a resonance capacitor by means of LC resonance, and outputting resonance voltage, the LC resonance circuit being connected to the input-side switching unit; a transformer with a primary winding and a secondary winding for converting the resonance voltage to voltage of a predetermined level according to a turn ratio to generate secondary voltage, and transferring the secondary voltage through the secondary winding, the primary winding being connected to the LC resonance circuit; an output-side switching unit for switching four output-side switching devices to convert the secondary voltage to the output DC voltage, the output-side switching unit being connected to the secondary winding of the transformer; and a gate driving circuit for detecting a polarity of secondary current flowing in the secondary winding, generating dead time, generating driving signals for driving the output-side switching device of the output-side switching unit according to the polarity, and then controlling turn-on or turn-off of the output-side switching devices, the gate driving circuit being connected to both the secondary winding of the transformer and the output-side switching unit. According to the synchronous rectifier type SRC, a no-load characteristic can be controlled with an easy scheme and a simple construction. In addition, a simple resistor is added, and thus dead time can be generated. Consequently, it is possible to simply reduce switching loss that may occur in zero voltage switching.
Owner:PS TECH CO LTD
Full bridge power converters with zero-voltage switching
InactiveUS20050041439A1Increase inductanceIncreases the amount of current deliveredConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionFull bridgeTransformer
A soft-switched, full-bridge pulse-width-modulated (FB PWM) converter and its variations provide zero-voltage-switching (ZVS) conditions for the turn-on of the bridge switches over a wide range of input voltage and output load. The FB PWM converters of this invention achieve ZVS with a substantially reduced duty cycle loss and circulating current, which optimizes the conversion efficiency. The ZVS of the primary switches is achieved by employing an auxiliary circuit comprising an inductor and transformer to store energy for ZVS turn-on of the bridge switches.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
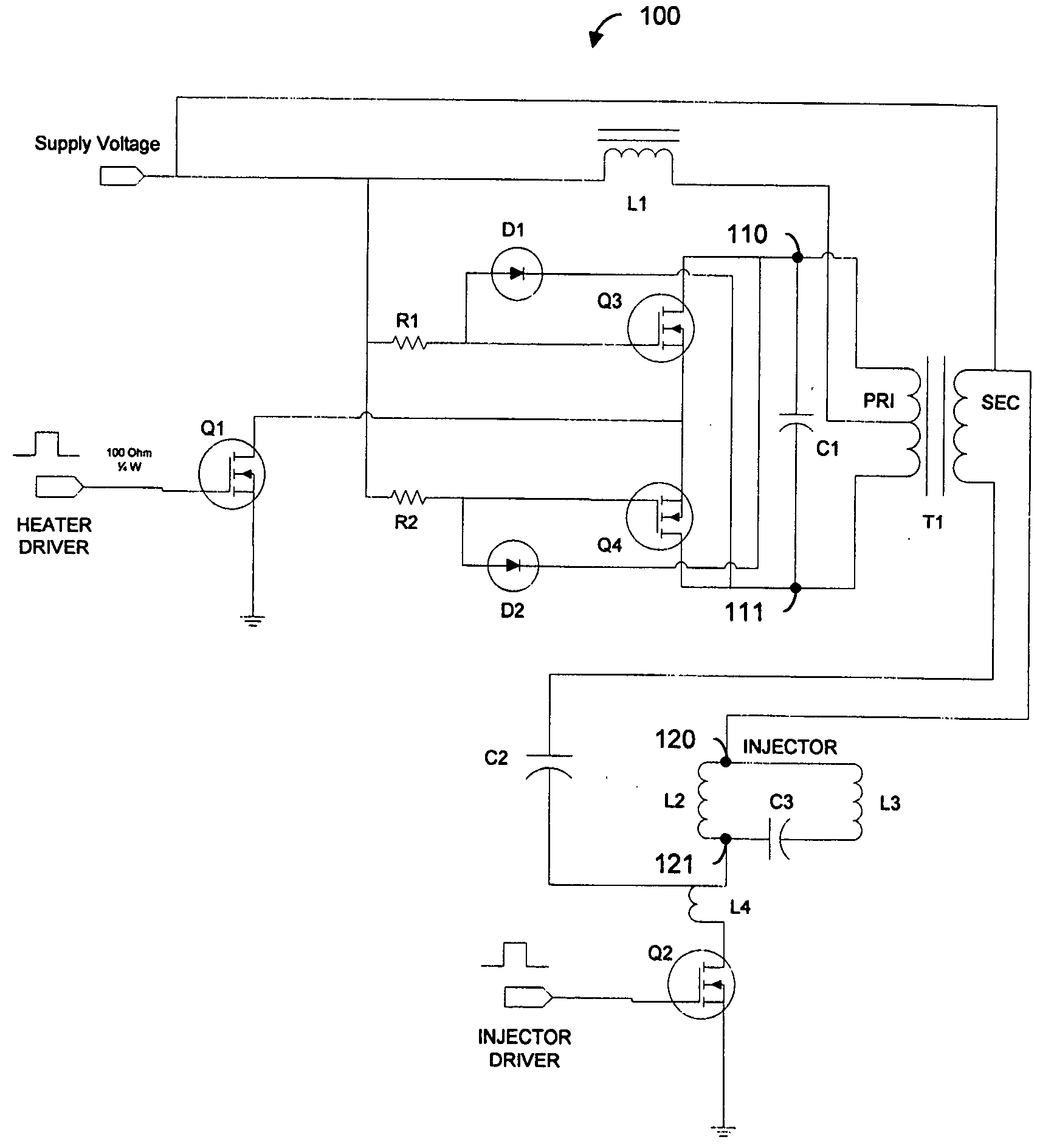
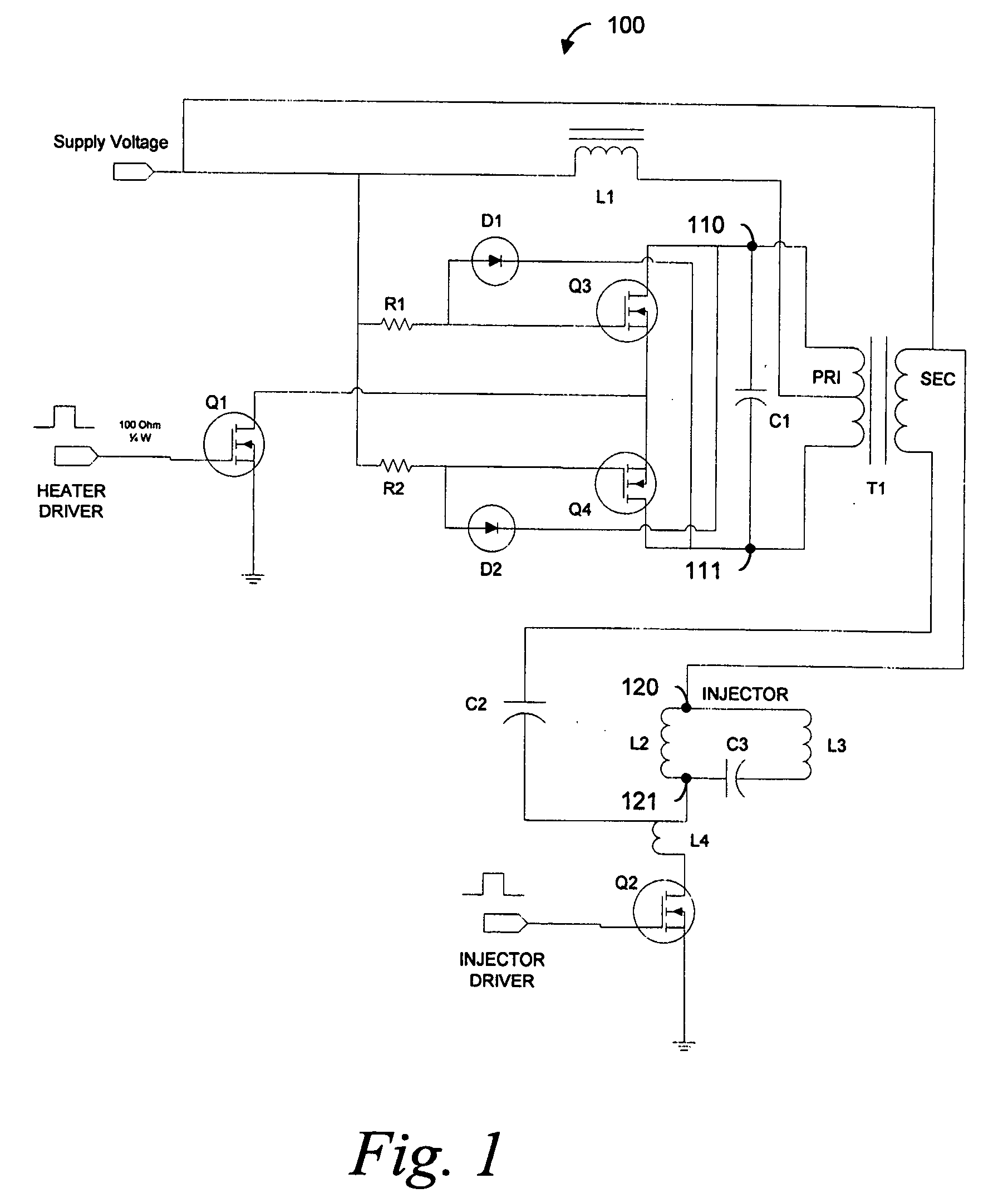
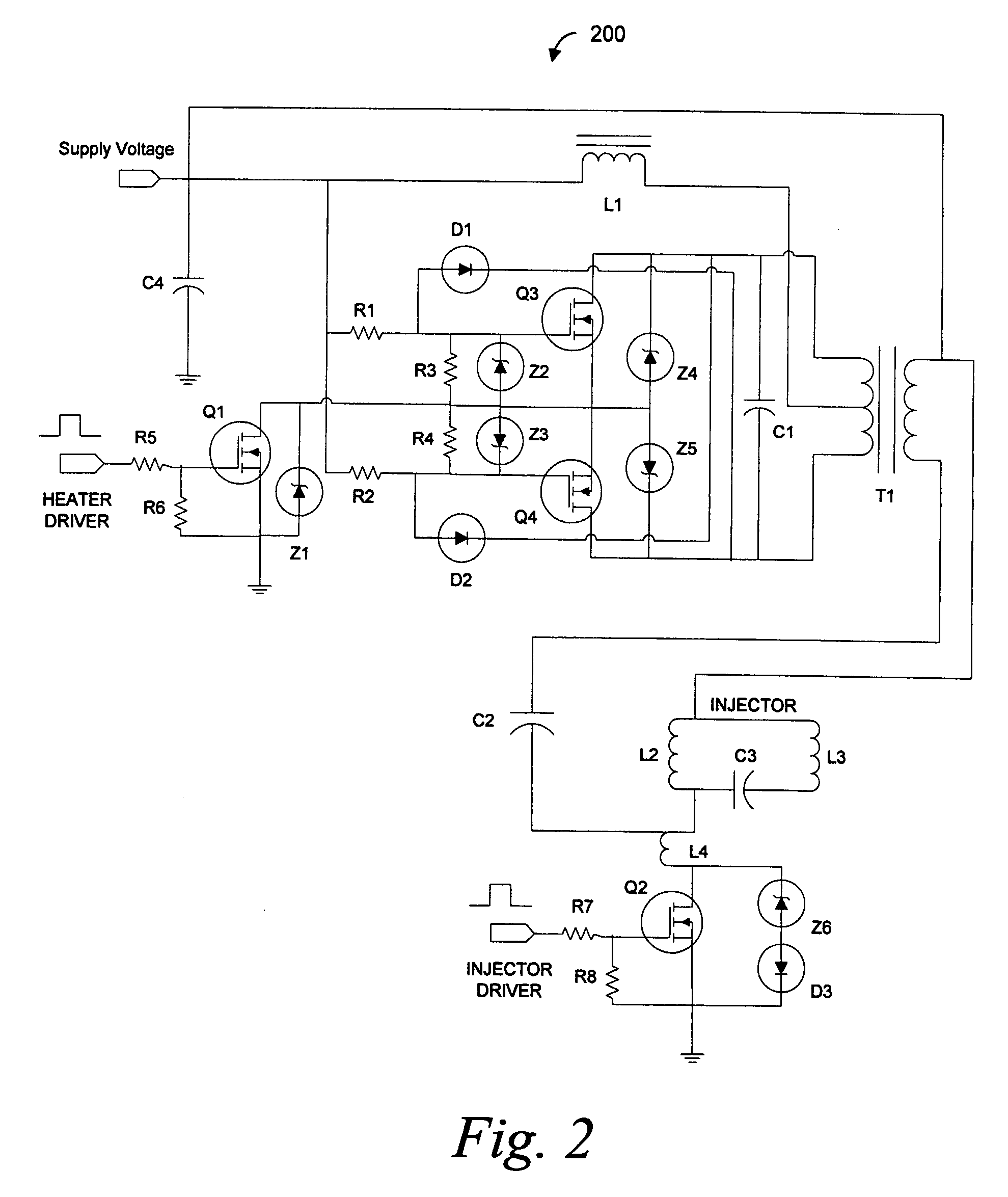
Constant current zero-voltage switching induction heater driver for variable spray injection
An electronic high frequency induction heater driver, for a variable spray fuel injection system, uses a zero-voltage switching oscillator that is impedance coupled to an imbedded multiple function signal separator and integrated with a conventionally implemented electronic fuel injector driver. The induction heater driver, upon receipt of a turn-on signal, multiplies a supply voltage through a self-oscillating series resonance, and couples the high frequency energy to a high pass filter such that the useful energy is utilized in an appropriate loss component so that fuel inside a fuel component is heated to a desired temperature.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
Soft transition converter
InactiveUS6862195B2Total current dropReduce reverse recovery lossEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSoft switchingFull bridge
The present invention is a circuit and method for reducing switching and reverse recovery losses in the output rectifiers while creating zero voltage switching conditions for the primary switchers. There are described two output configurations, one employing a soft commutation inductor element a bridge rectifier and a output filter capacitor, the second using a soft commutation inductor element a rectification-filtering bridge composed by two capacitors and two capacitors. Both secondary circuits can be driven by three primary circuits. A first circuit is a full bridge with phase shift control, and a second circuit is a half bridge topology with an additional bydirectional switch which achieves two goals, on to get soft switching commutation across all the primary switches, the second to create the right waveforms in the secondary suitable with the claims in this invention. The third topology is a phase shifted two transistors forward. The circuits claimed in this invention can provide soft commutation across the primary switching elements and secondary rectifier means, clamping the voltage across the rectifiers to the output voltage eliminating the need for snubbers circuits both in primary and the secondary section.
Owner:DELTA ENERGY SYST SWITZERLAND
Zero voltage switching in flyback converters with variable input voltages
ActiveUS20130148385A1Reduce power lossEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionBuck converterPeak value
The disclosed embodiments provide a system that operates a flyback converter. During operation, the system senses an input voltage for the flyback converter. Next, the system uses the input voltage to determine a negative peak current that enables zero voltage switching for a primary switch in the flyback converter. Finally, the system uses the negative peak current to perform the zero voltage switching for the primary switch based on the input voltage, wherein the negative peak current reduces a power loss of the flyback converter.
Owner:APPLE INC
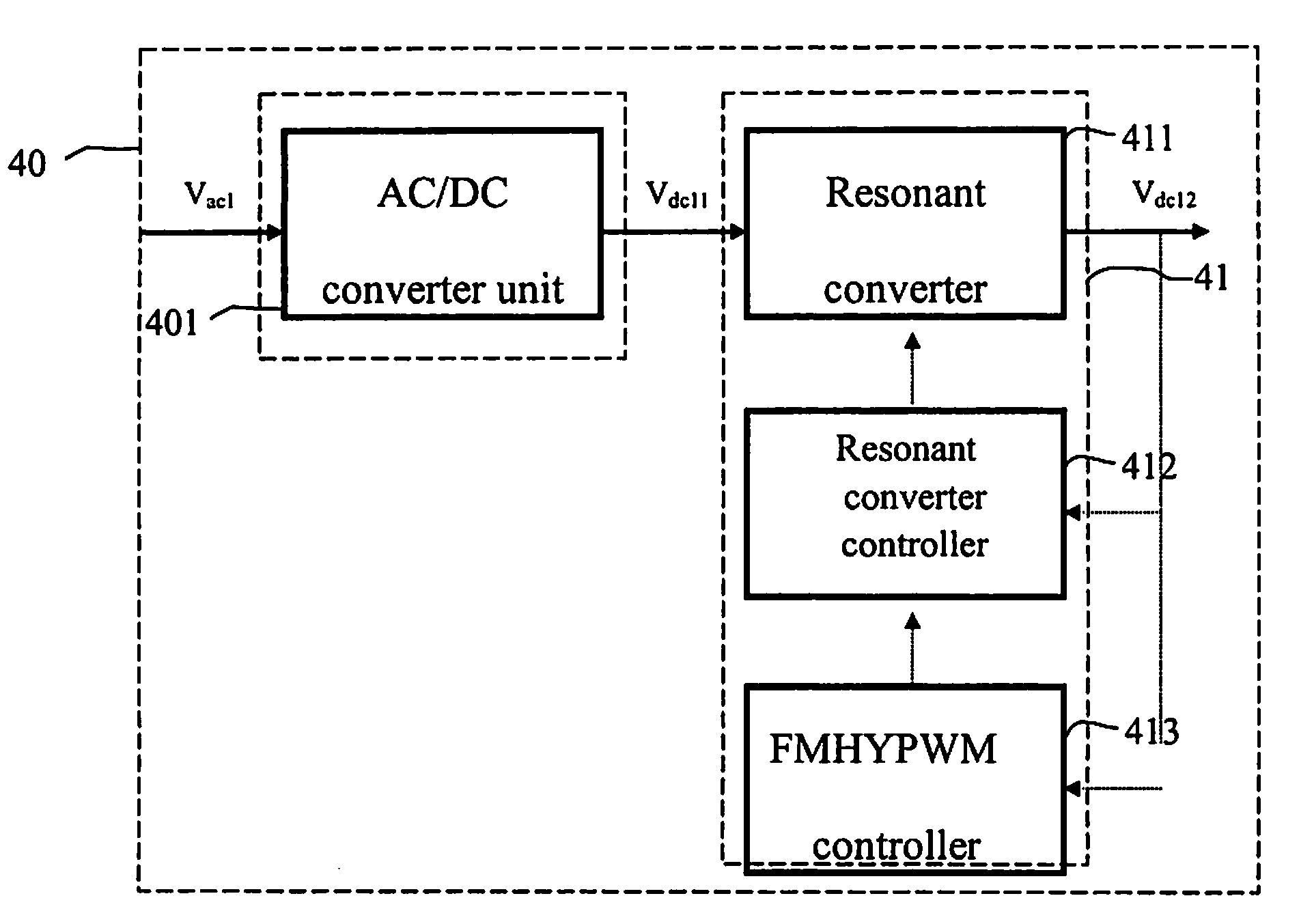
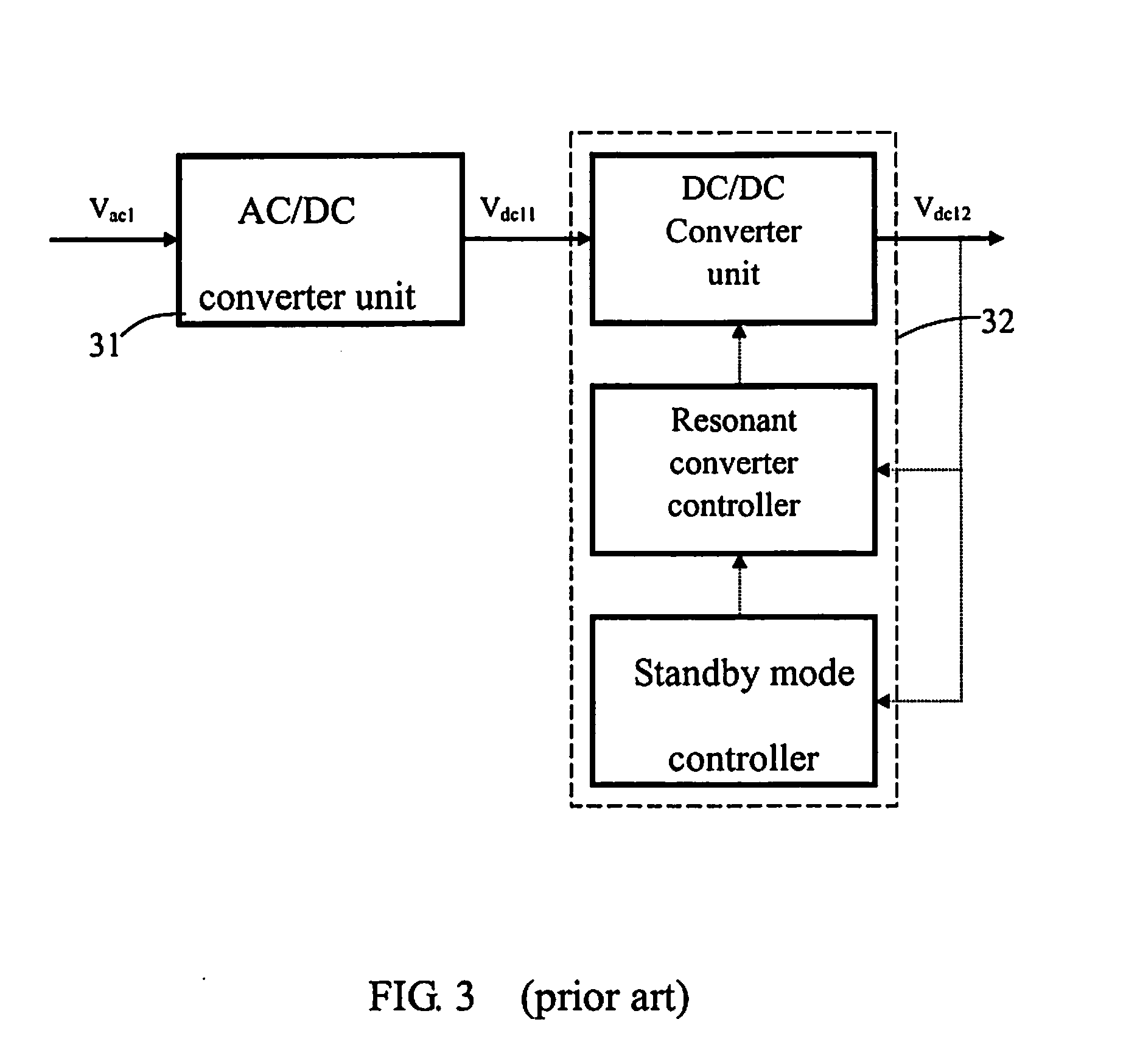
Control Method And Apparatus Of Resonant Type DC/DC Converter With Low Power Loss At Light Load And Standby
InactiveUS20090034298A1High converting effectReduce power consumptionEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionResonant converterSwitching frequency
The present invention discloses a control method and apparatus of resonant converter with low power loss at light load and standby. Based on the frequency response and loading condition of the resonant tank of a resonant converter, adjusts the switching frequency and the switching duty cycle to have a stable output voltage. Perform zero voltage switching and obtain higher converting efficiency by using the energy transfer in the resonant tank of the resonant type converter. Also have higher converting efficiency by combining with synchronize-rectify. Including: a resonant type converter, a controller of resonant type converter, and a regulated voltage mode (frequency modulation hybrid pulse width modulation, FMHYPWM) controller, and if the system specification require, a power factor correction or a double voltage rectifier circuit may be used in the advanced stage of the resonant type converter. The out put rectifier of the resonant type converter may be changed to a synchronized-rectifier.
Owner:CHAMPION MICROELECTRONICS
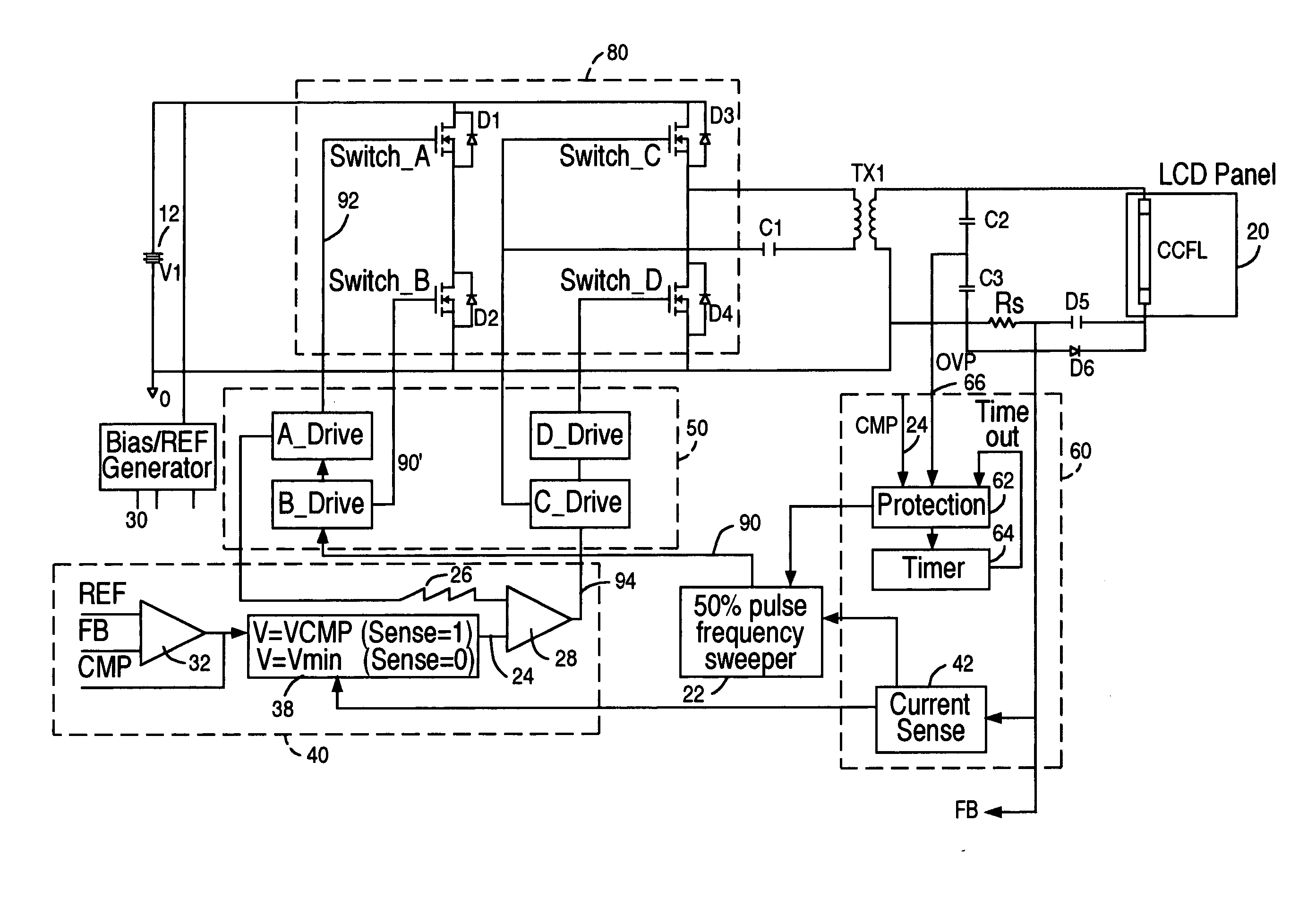
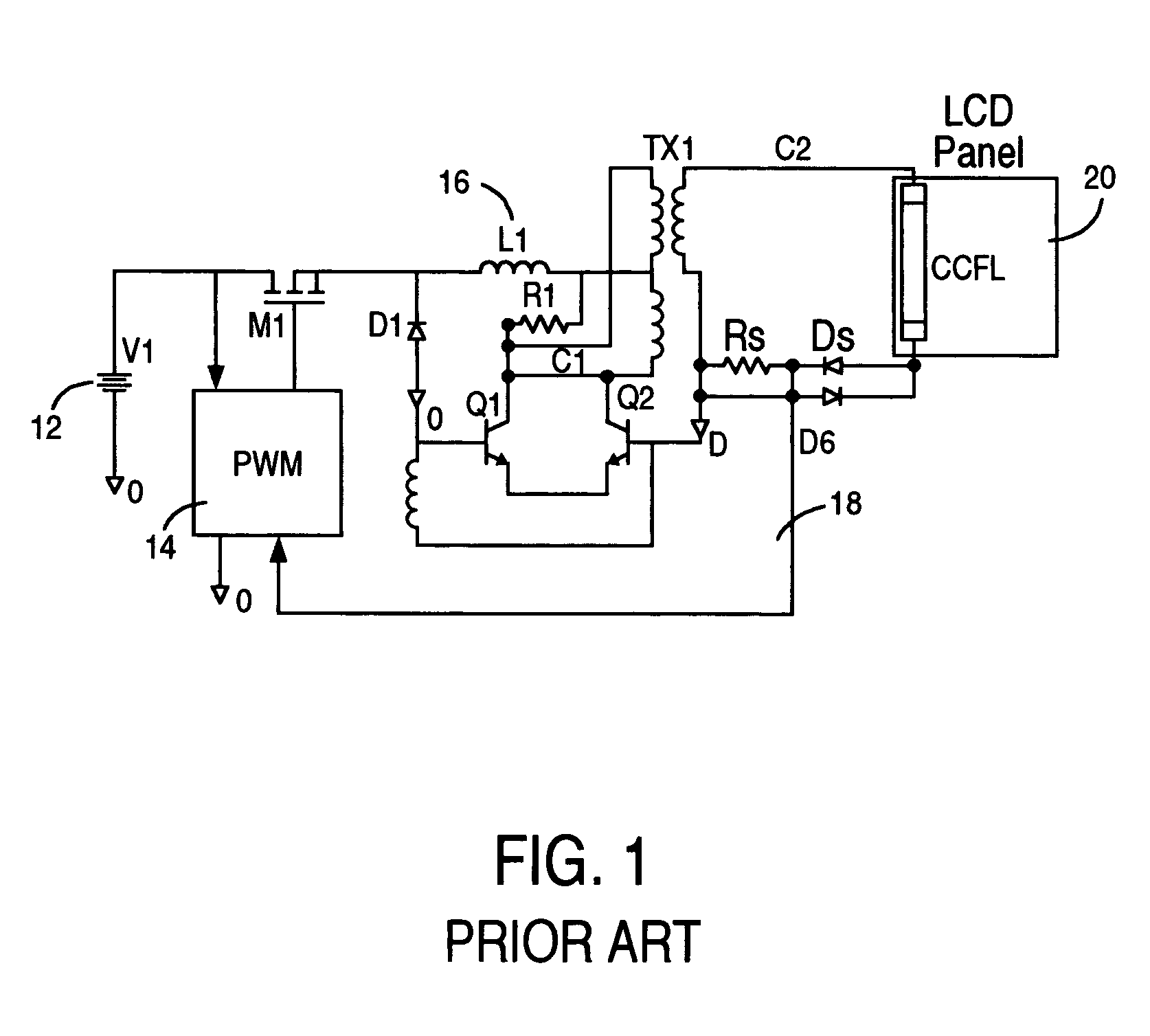
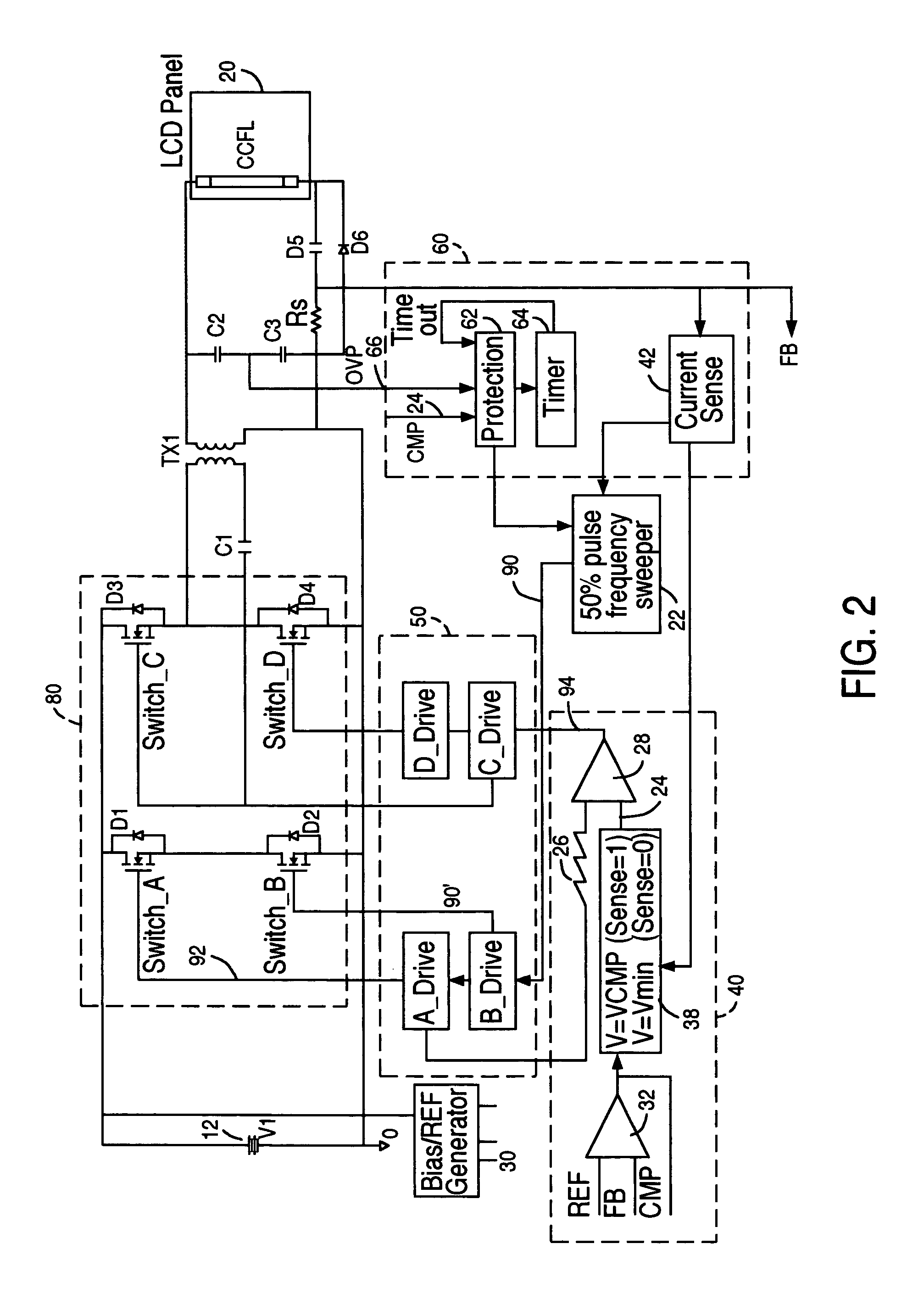
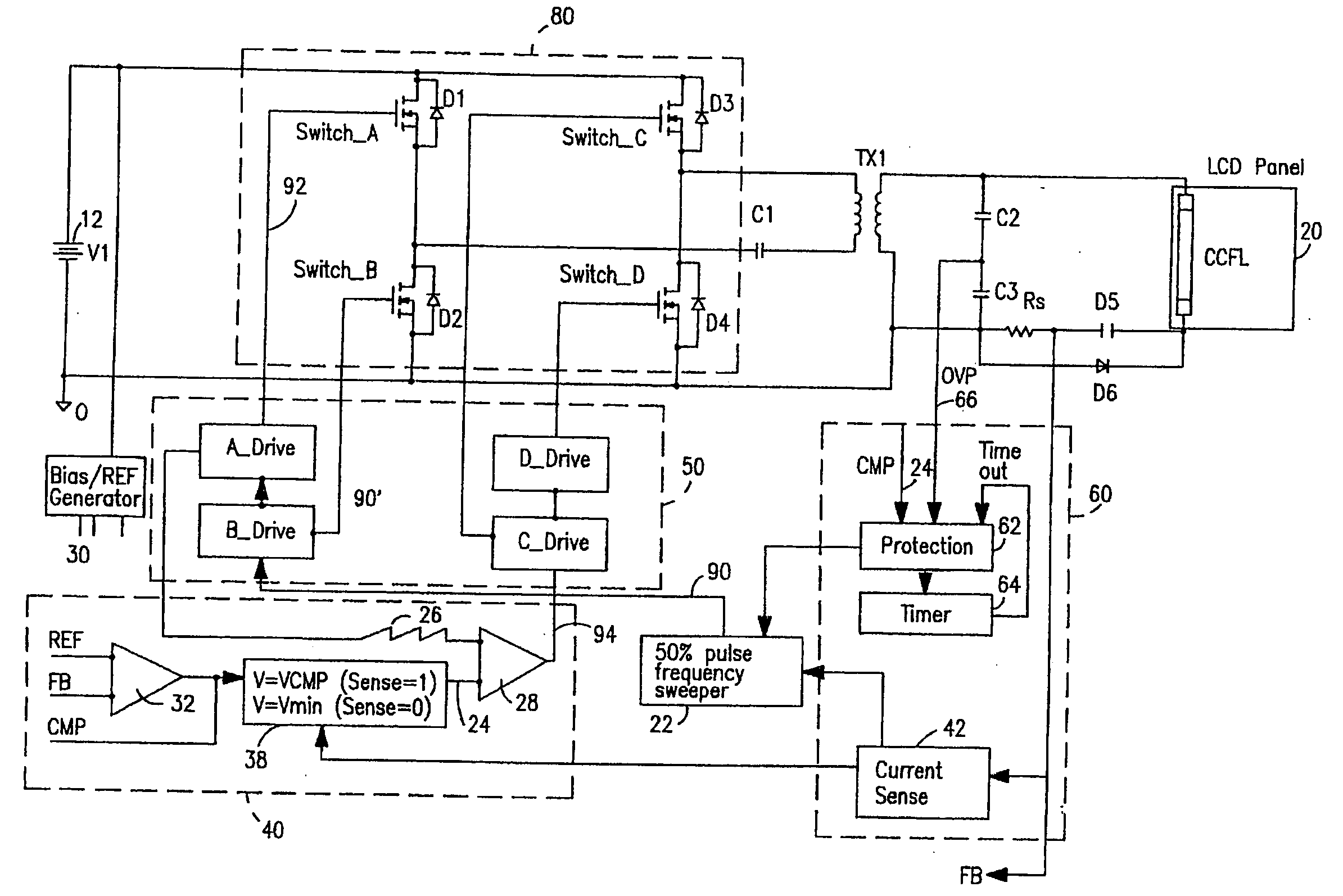
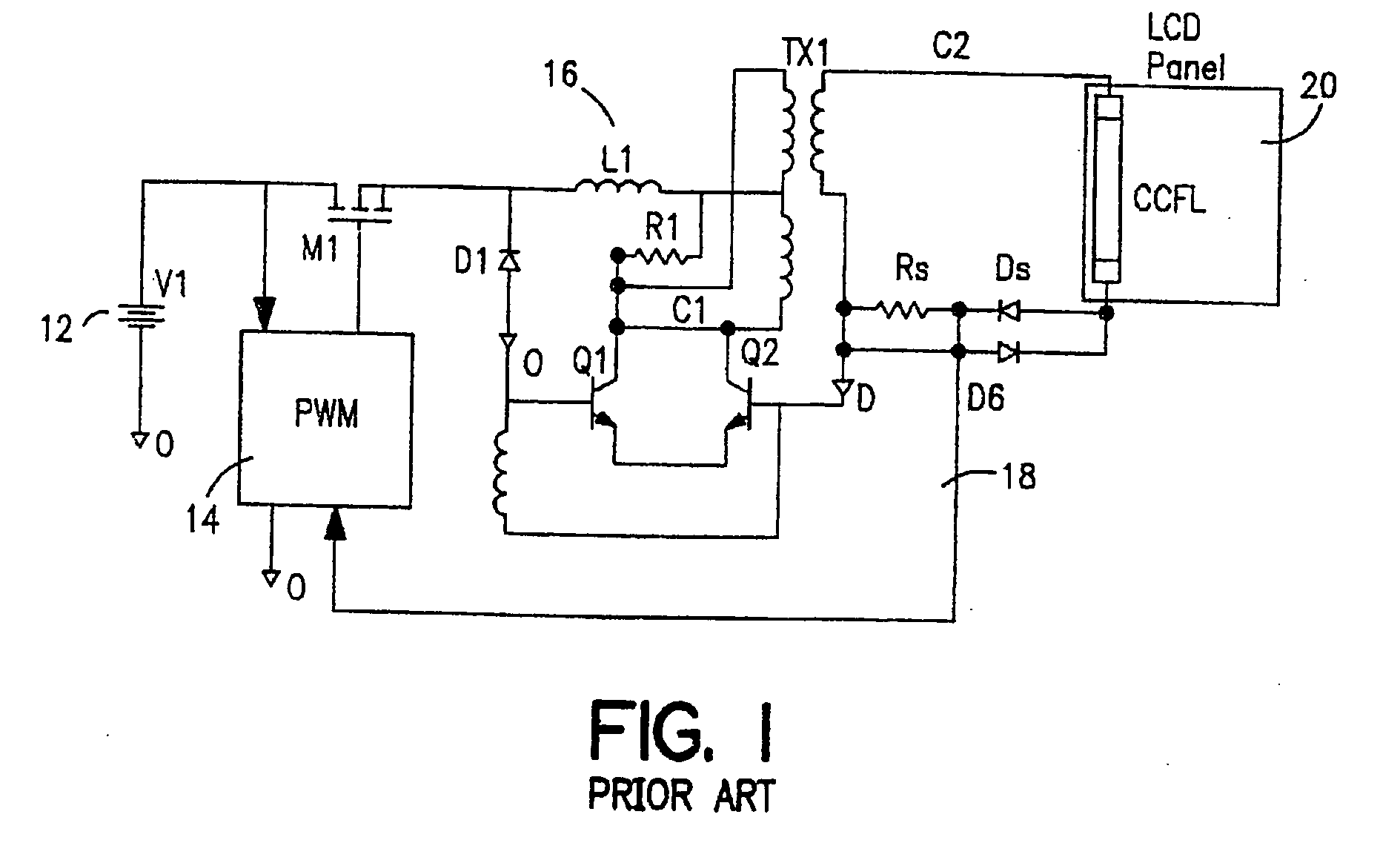
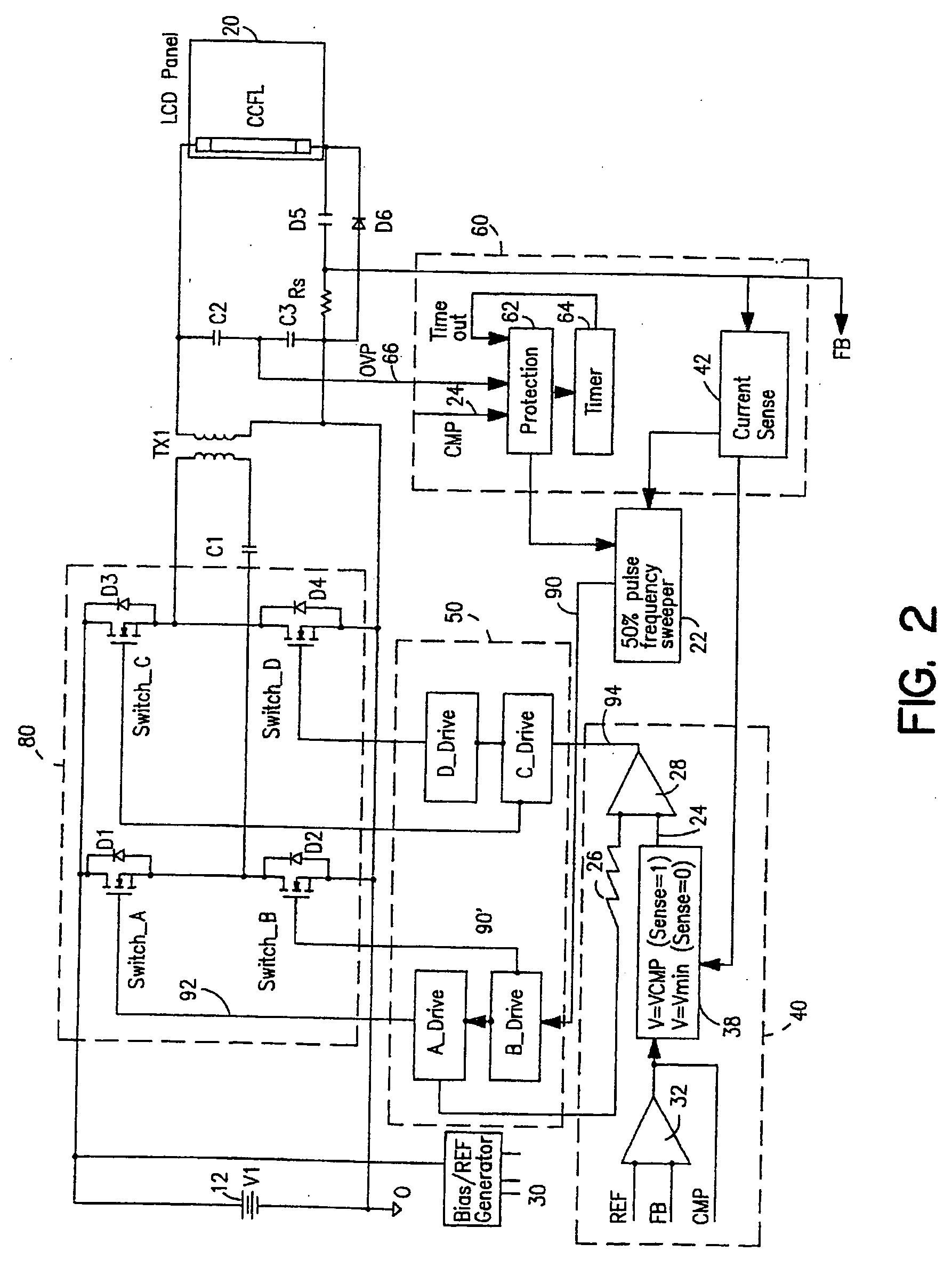
Liquid crystal display system with lamp feedback
InactiveUS7394209B2Reduce power supplyEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcLiquid-crystal displayParasitic capacitance
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
Methods and apparatus for a cascade converter using series resonant cells with zero voltage switching
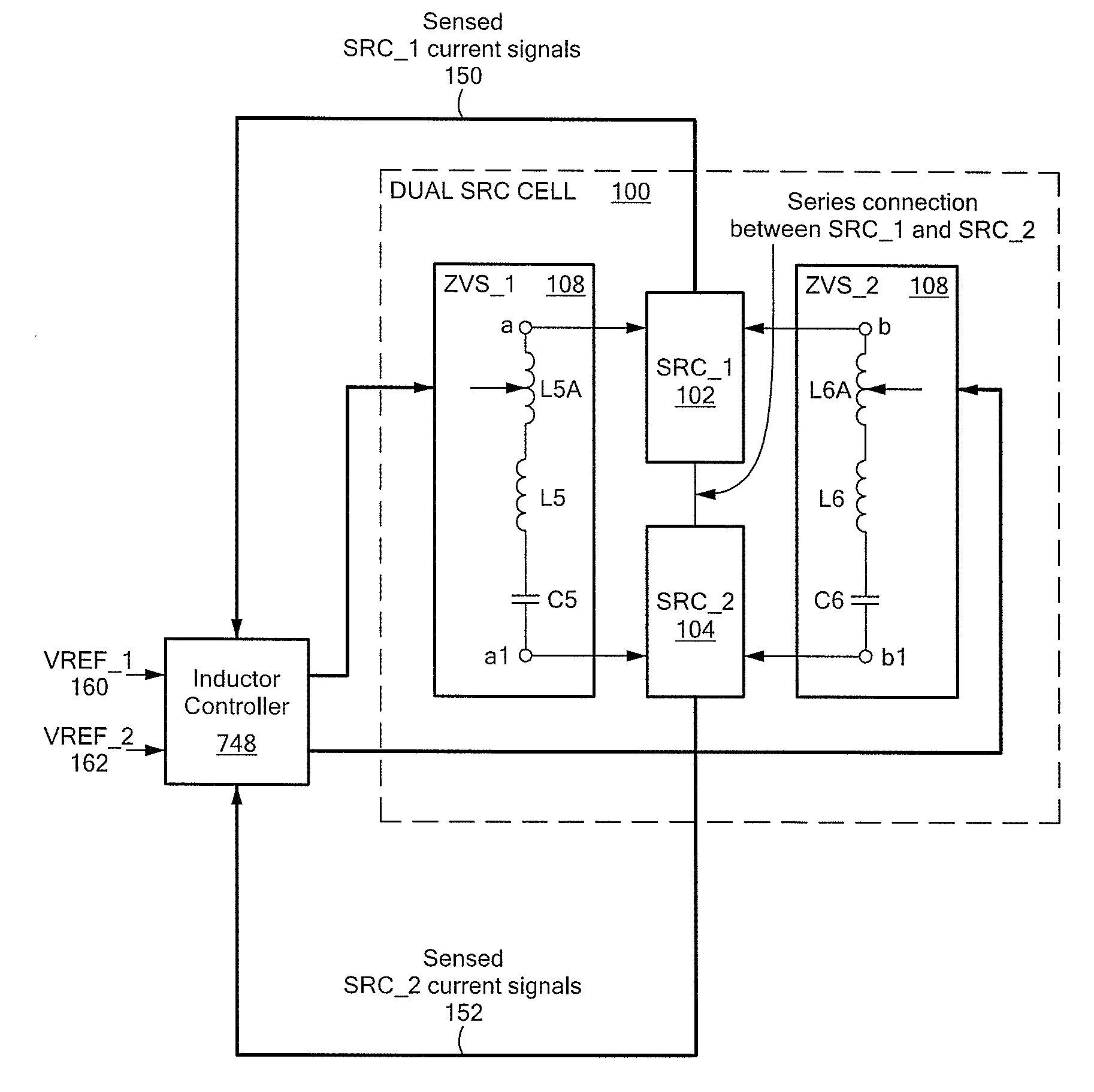
ActiveUS20090021966A1Efficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcCascade converterResonant converter
A method of providing power to a load is provided. A first series resonant converter is provided. A second SRC is operably coupled to the first SRC in a cascade connected arrangement. First and second zero voltage switching (ZVS)-assistance networks are operably coupled between the first SRC and the second SRC, such that the first and second ZVS-assistance networks are providing first and second ZVS-assistant currents flowing from each ZVS-assistance network to the cascade connected arrangement of SRCs. Power from a power source is received at the cascade connected arrangement of first and second SRCs, power from a power source. The cascade connected arrangement of first and second SRCs supplies an output voltage to the load in response to receiving power from the power source.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Zero-Voltage-Switching Scheme for High-Frequency Converter
ActiveUS20120063184A1Efficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcZero voltage switchingAC/AC converter
Method for operating an ac / ac converter circuit for a high-frequency-link converter. The ac / ac converter circuit converts an ac input voltage to an ac output voltage. When the ac input voltage is zero, each of a pair of switches for both first and second arms are caused to be on. Current flows through the first arm along a first direction and through the second arm along a second, opposite direction. Next, when the ac input voltage is zero, a selected switch in the second arm is caused to be turned off. The position of the switches can be maintained as the ac input voltage transitions to a dc level, reaches the dc level, approaches zero, and again reaches zero. When the ac input voltage again reaches zero, the selected switch for the second arm is caused to be turned on.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Switching power supply apparatus
InactiveUS20060187688A1Increase usageSmall sizeEmergency protective circuit arrangementsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsClamp capacitorSnubber capacitor
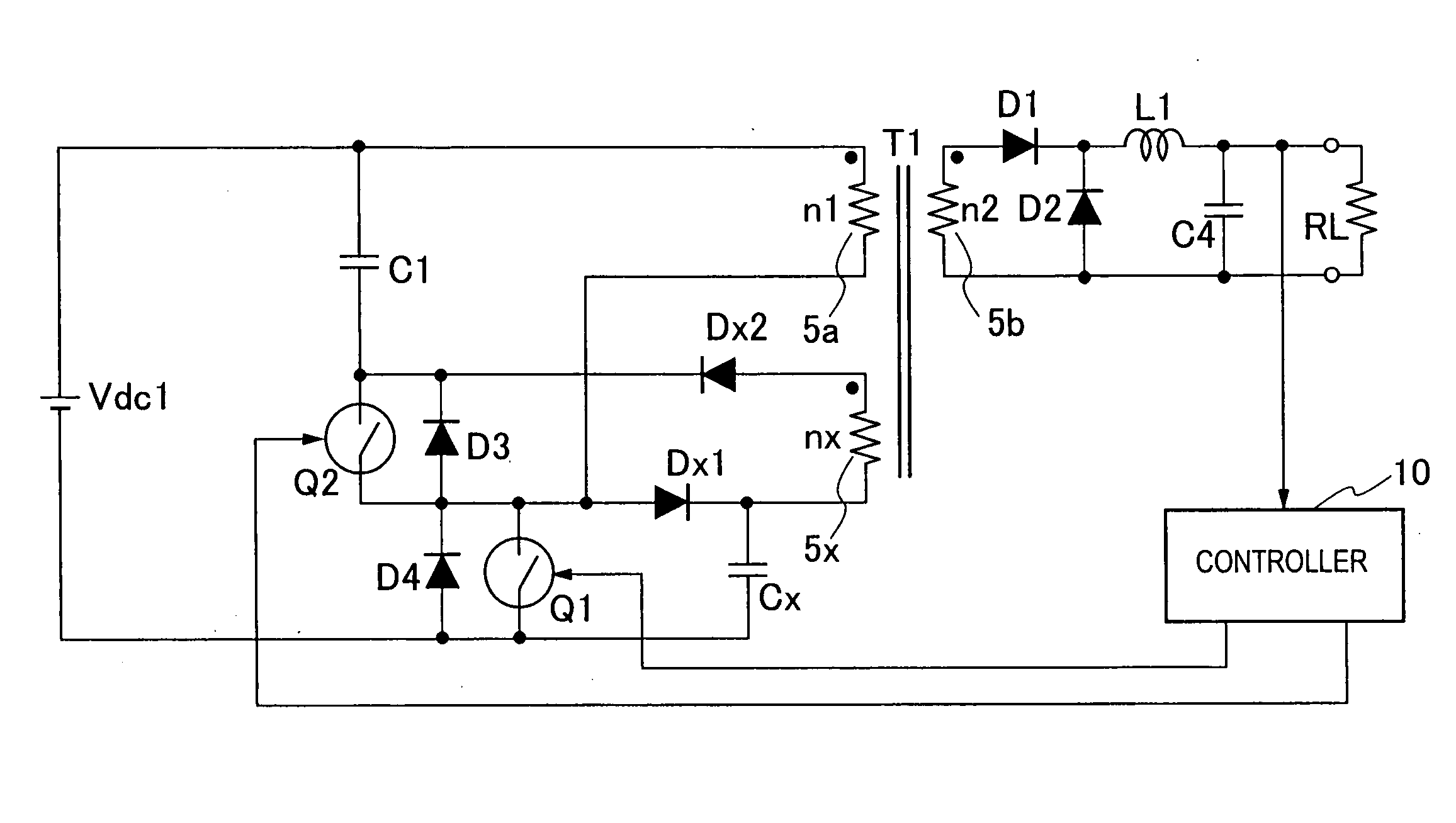
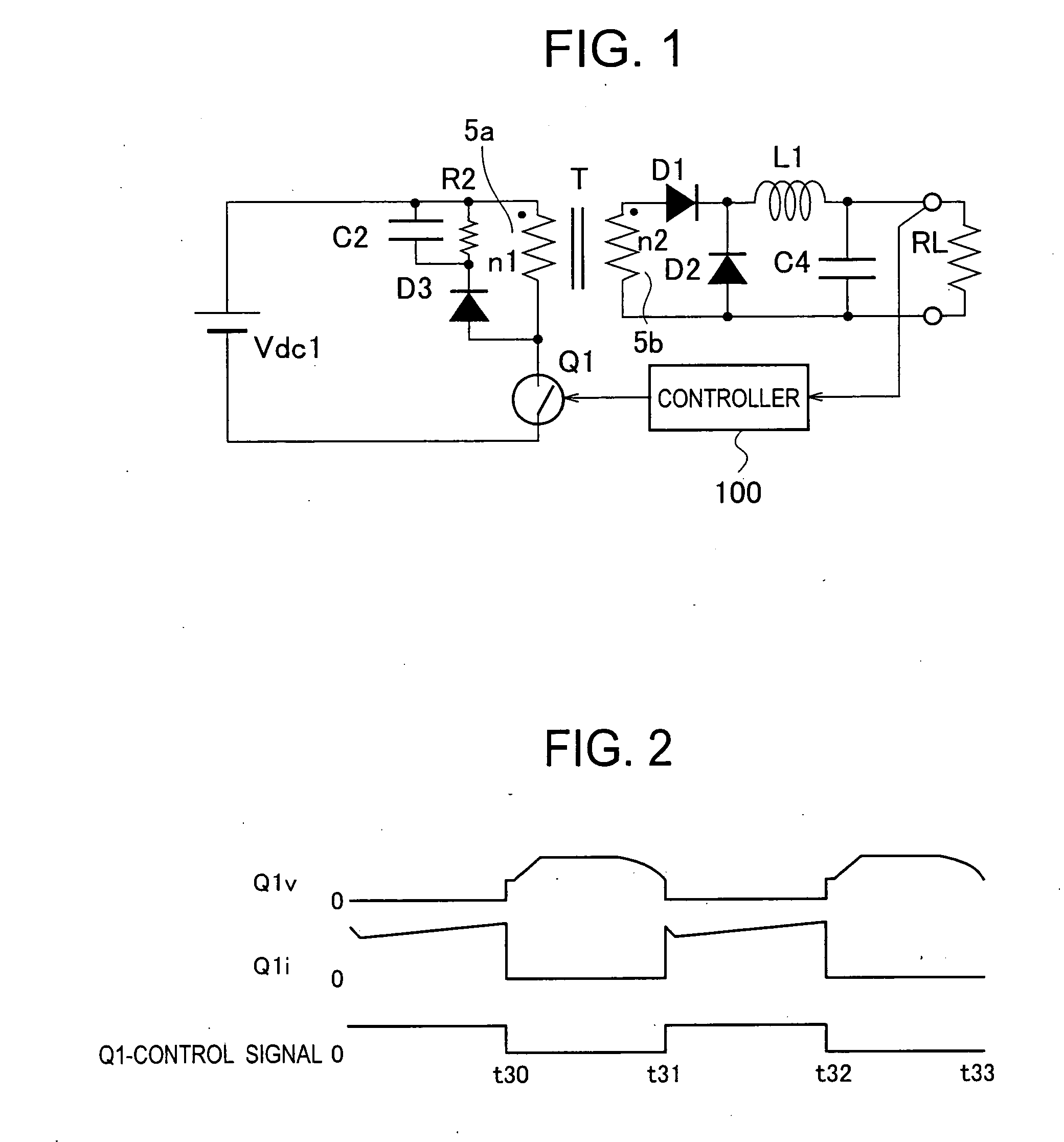
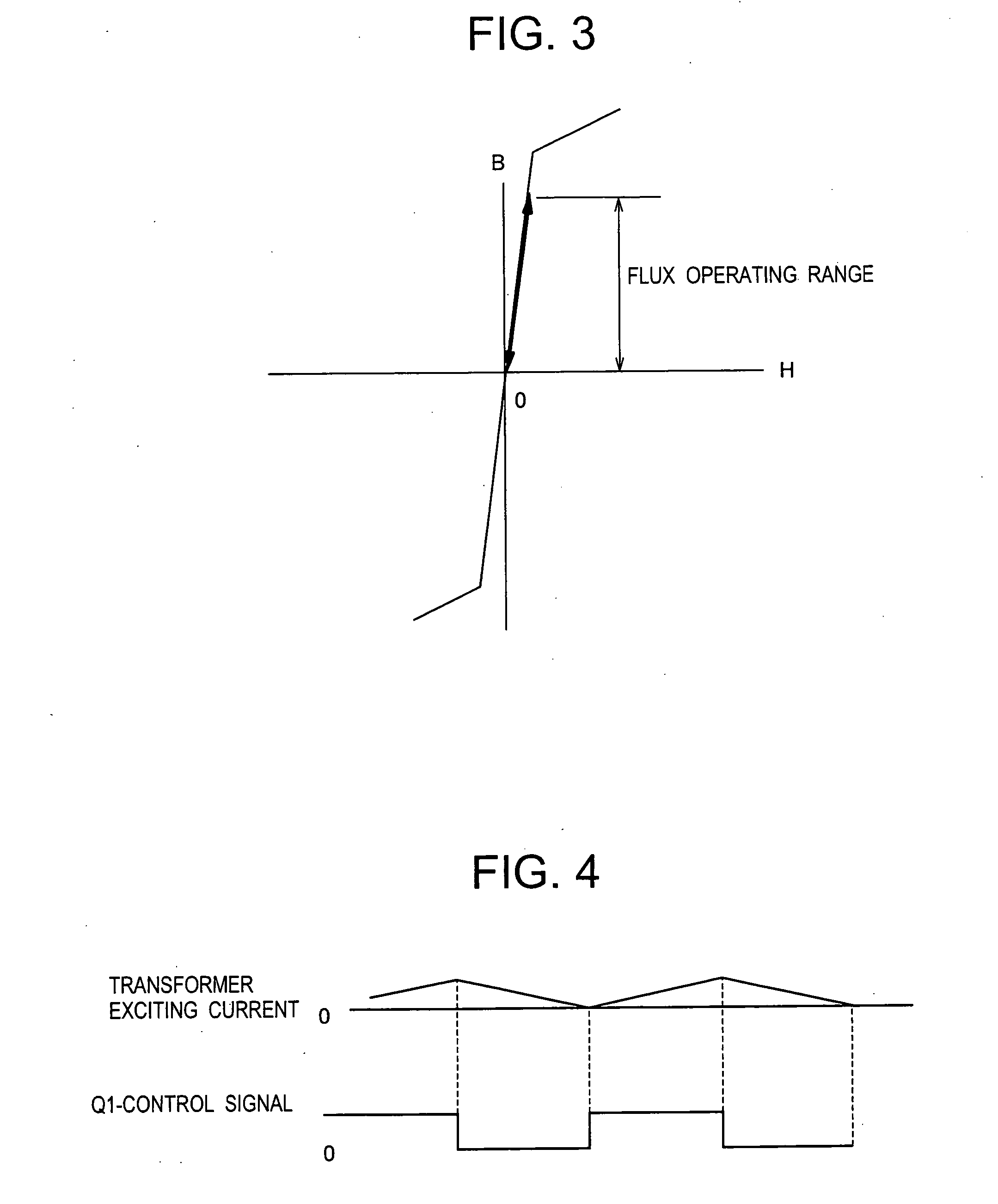
A switching power source apparatus can reduce the size of a transformer and realize the zero-voltage switching of a switch. The apparatus is compact, highly efficient, and low in noise. The apparatus has a series circuit connected to each end of a DC power source (Vdc1) and including a primary winding (5a) of a transformer (T) and a main switch (Q1), a rectifying-smoothing circuit to rectify and smooth a voltage that is outputted from a secondary winding (5b) when the main switch (Q1) is turned on, a series circuit connected to each end of the primary winding (5a) and including an auxiliary switch (Q2) and a clamp capacitor (C1), a series circuit connected to each end of the main switch (Q1) and including a diode (Dx1) and a snubber capacitor (Cx), a series circuit connected to a node between the diode (Dx1) and the snubber capacitor (Cx) and a node between the auxiliary switch (Q2) and the clamp capacitor (C1) and including an auxiliary winding (5x) and a diode (Dx2), and a control circuit (10) to alternately turn on / off the main switch (Q1) and auxiliary switch (Q2). When the main switch (Q1) is turned on, the snubber capacitor (Cx) is discharged through the auxiliary winding (5x) to the clamp capacitor (C1). When the main switch (Q1) is turned off, the snubber capacitor (Cx) is charged, to relax the inclination of a voltage increase of the main switch (Q1).
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
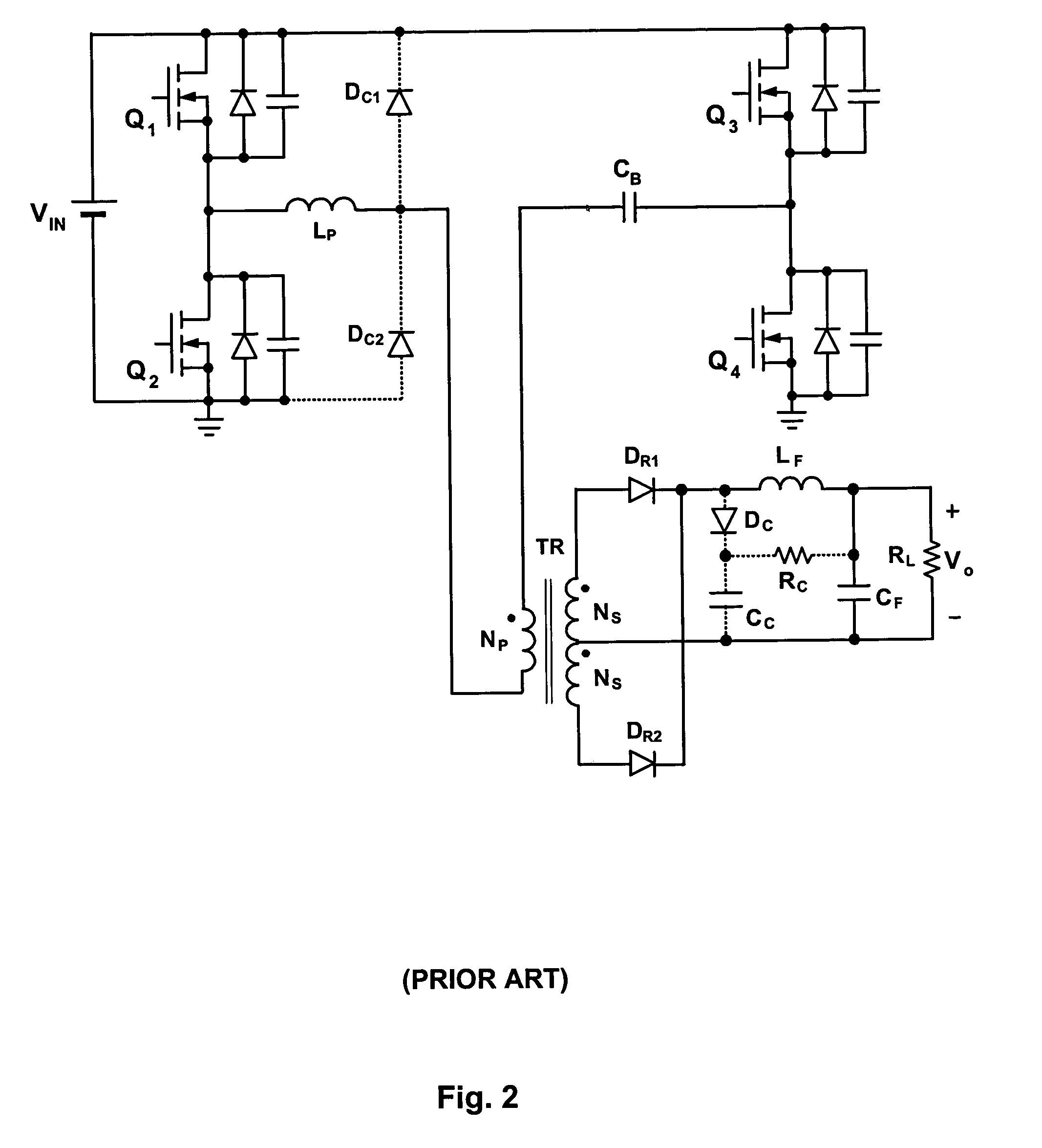
Single stage isolated ac/dc power factor corrected converter
ActiveUS20170025962A1Improve efficiencyReduce the burden onEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionClamp capacitorSingle stage
Two versions of an isolated single stage converter AC / DC Power Factor Corrected (PFC) converter topology have been invented. One is with a full bridge rectifier at its input and the other is a True Bridgeless version. The two versions of the topology feature new configurations and circuitry including a simplified damper circuit and a clamp capacitor flipping circuit and control methods that allow them to realize improved single stage isolated power factor converters which are suitable for high power operation, features Zero Voltage Switching to maximize conversion efficiency and to minimize Electro-Magnetic Interference generation, does not need an additional circuit to limit the inrush current, achieves reasonably low input current Total Harmonic Distortion (THD), and is easy to control. The second version provides a true bridgeless single stage isolated power factor converter with even higher efficiency and lower input current THD.
Owner:DAVIDSON CHRISTOPHER DONOVAN
Forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit
ActiveUS8009448B2Improve conversion efficiencyAdditional drawbackEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringHeavy load
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
High-efficiency adaptive DC/AC converter
InactiveUS20050030776A1Easy to operateImprove system reliabilityEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcParasitic capacitanceEngineering
A CCFL power converter circuit is provided using a high-efficiency zero-voltage-switching technique that eliminates switching losses associated with the power MOSFETs. An optimal sweeping-frequency technique is used in the CCFL ignition by accounting for the parasitic capacitance in the resonant tank circuit. Additionally, the circuit is self-learning and is adapted to determine the optimum operating frequency for the circuit with a given load. An over-voltage protection circuit can also be provided to ensure that the circuit components are protected in the case of open-lamp condition.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
Full-bridge phase-shift converter with auxiliary zero-voltage-switching circuit
InactiveUS20110273909A1Sufficient energyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationLeading edgePhase shifted
A full-bridge phase-shift converter with an auxiliary zero-voltage-switching circuit includes a full-bridge switching circuit, an isolated transformer, an auxiliary zero-voltage-switching (ZVS) circuit, a full-wave rectifying circuit, and a low-pass filtering circuit. The full-bridge phase-shift converter is used to send energy which is supplied from a DC input voltage to a load. Therefore, an auxiliary inductor of the auxiliary ZVS circuit is provided to reinforce sufficient inductive energy on a leading-edge leg, thus achieving normally zero-voltage-switching operations of the full-bridge phase-shift converter.
Owner:CHICONY POWER TECH CO LTD
Self-oscillation type resonant flyback converter utilizing charge stored effect of the P-N diode
InactiveUS6404654B1Increase powerEasy to switchEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsSelf-oscillationConductor Coil
A self-oscillation type resonant flyback converter includes a series combination of a primary winding and a switching transistor. A secondary winding is connected to a power diode and to an output capacitor. A feedback winding is connected to a delay driving circuit comprising a delay diode, a constant-current diode and a capacitor. The delay driving circuit is provided to delay a positive feedback signal from said feedback winding, so that when said power diode becomes non-conducting, said delay diode becomes in the reverse conduction state, starting a free resonance period that concludes when the said delay diode becomes non-conducting and the switching transistor is achieved at zero voltage switching.
Owner:INTEGRATED PROGRAMMABLE COMM
Zero-voltage-switching DC-DC converters with synchronous rectifiers
ActiveCN101047335AEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceDc dc converter
A DC-DC converter includes an inductor, a synchronous rectifier (SR) connected to the inductor, and an active switch connected to the inductor and the SR. An active resonant tank (ART) cell is connected to the SR or a transformer in parallel such that a resonant capacitor of the ART cell is charged through the active switch and discharged through the synchronous rectifier so that during a switch transition period energy is pumped out of the resonant capacitor by activating the ART cell to eliminate reverse recovery switching loss and achieve Zero Voltage Switching (ZVS).
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com