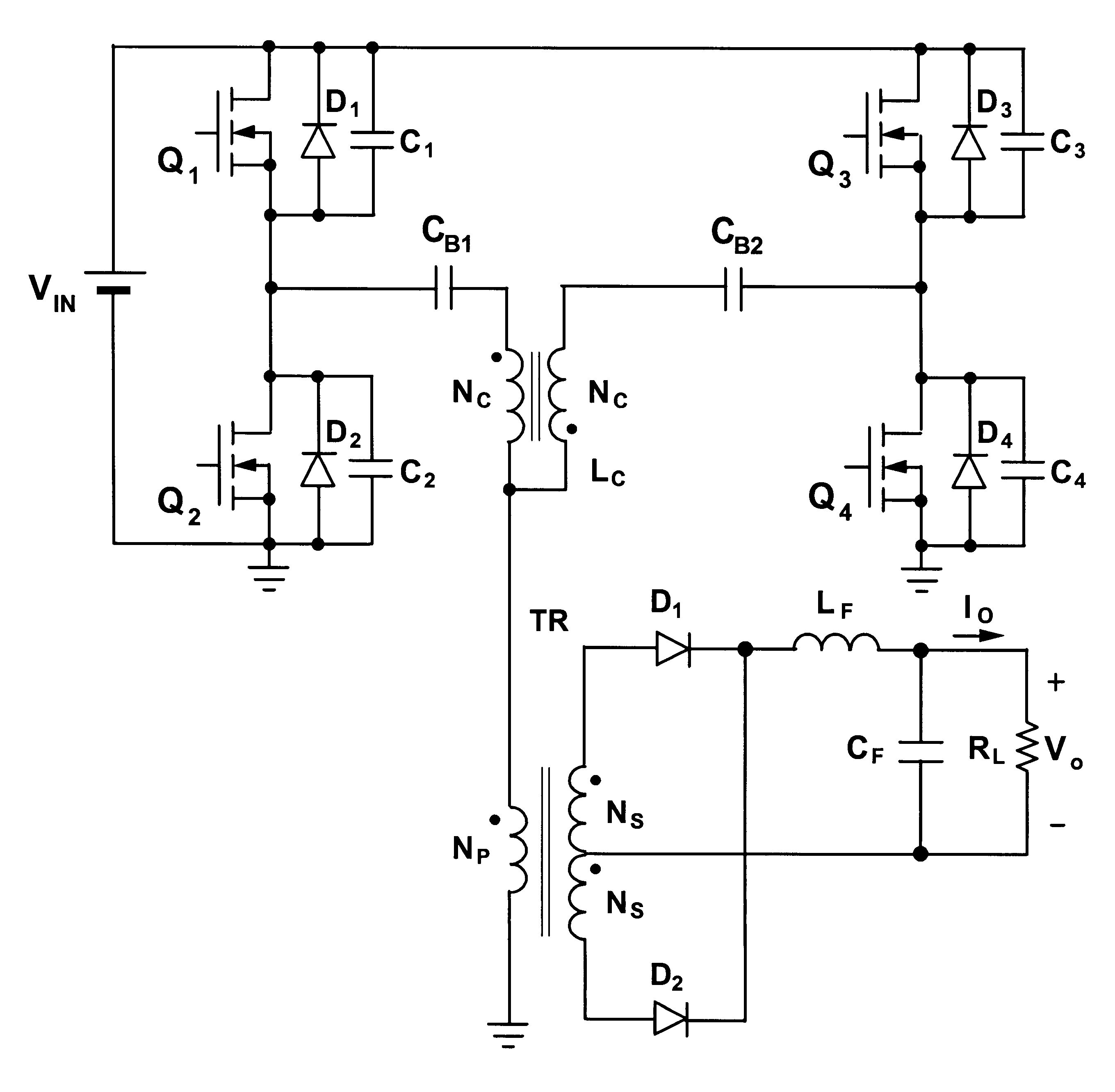
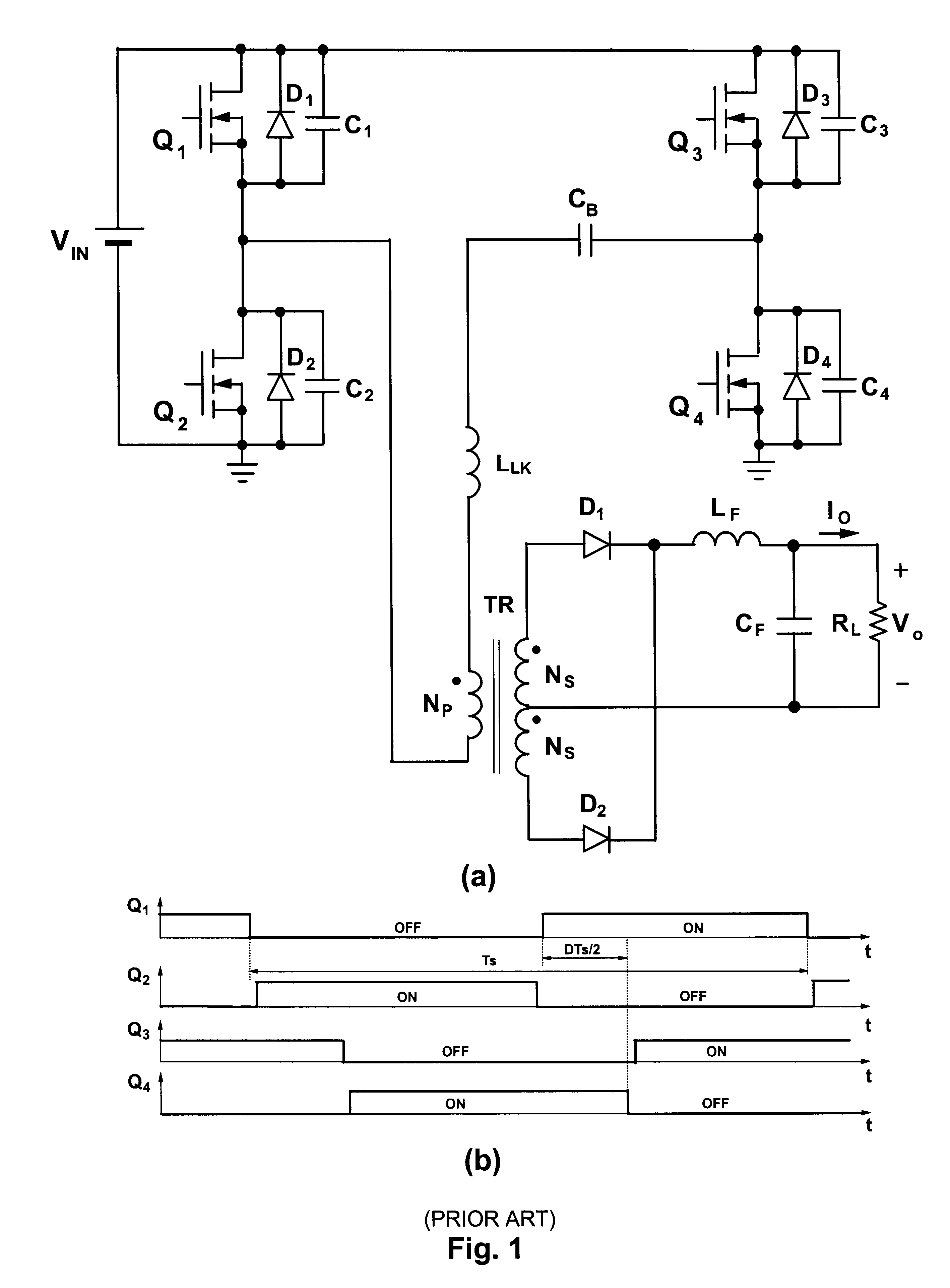
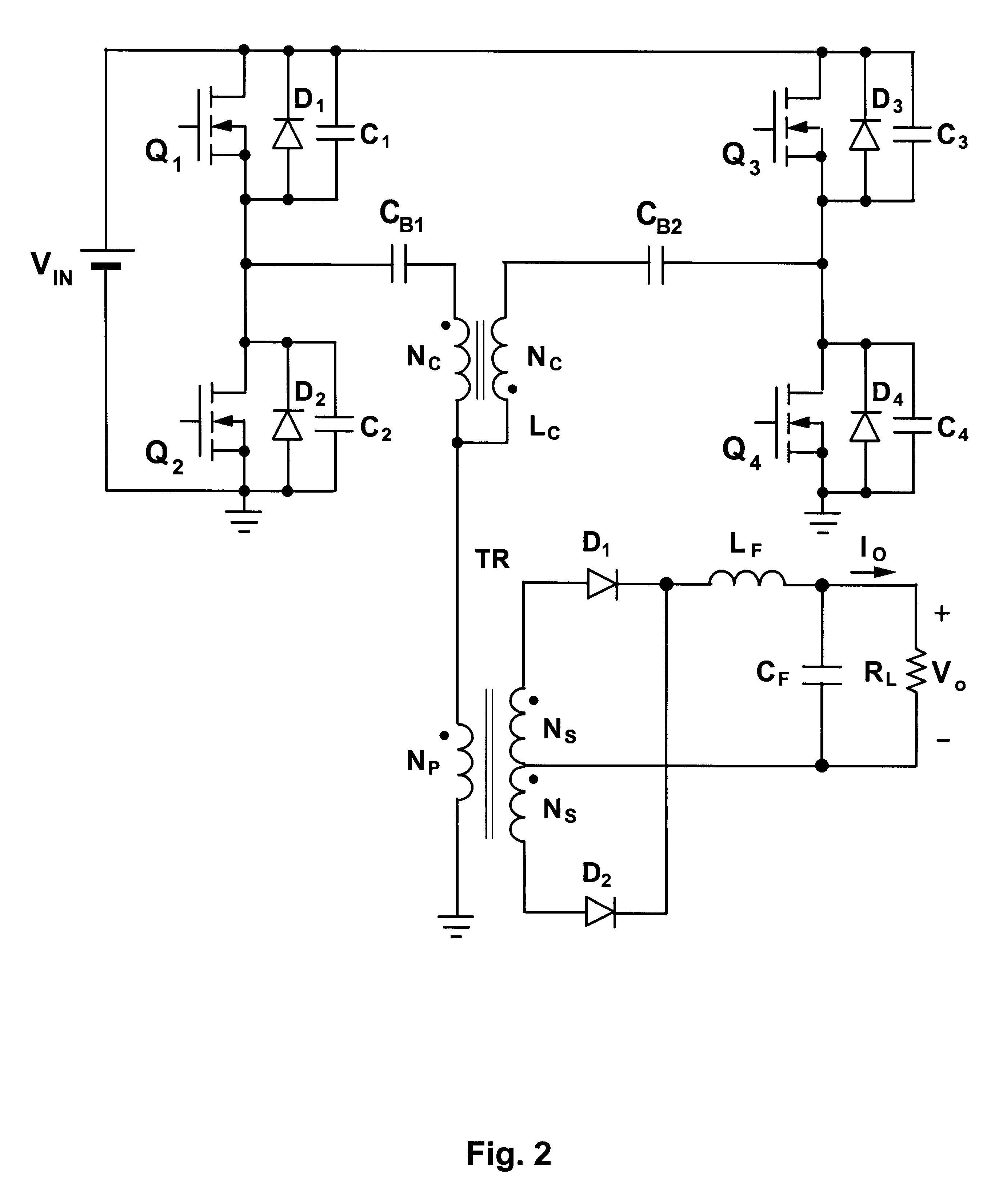
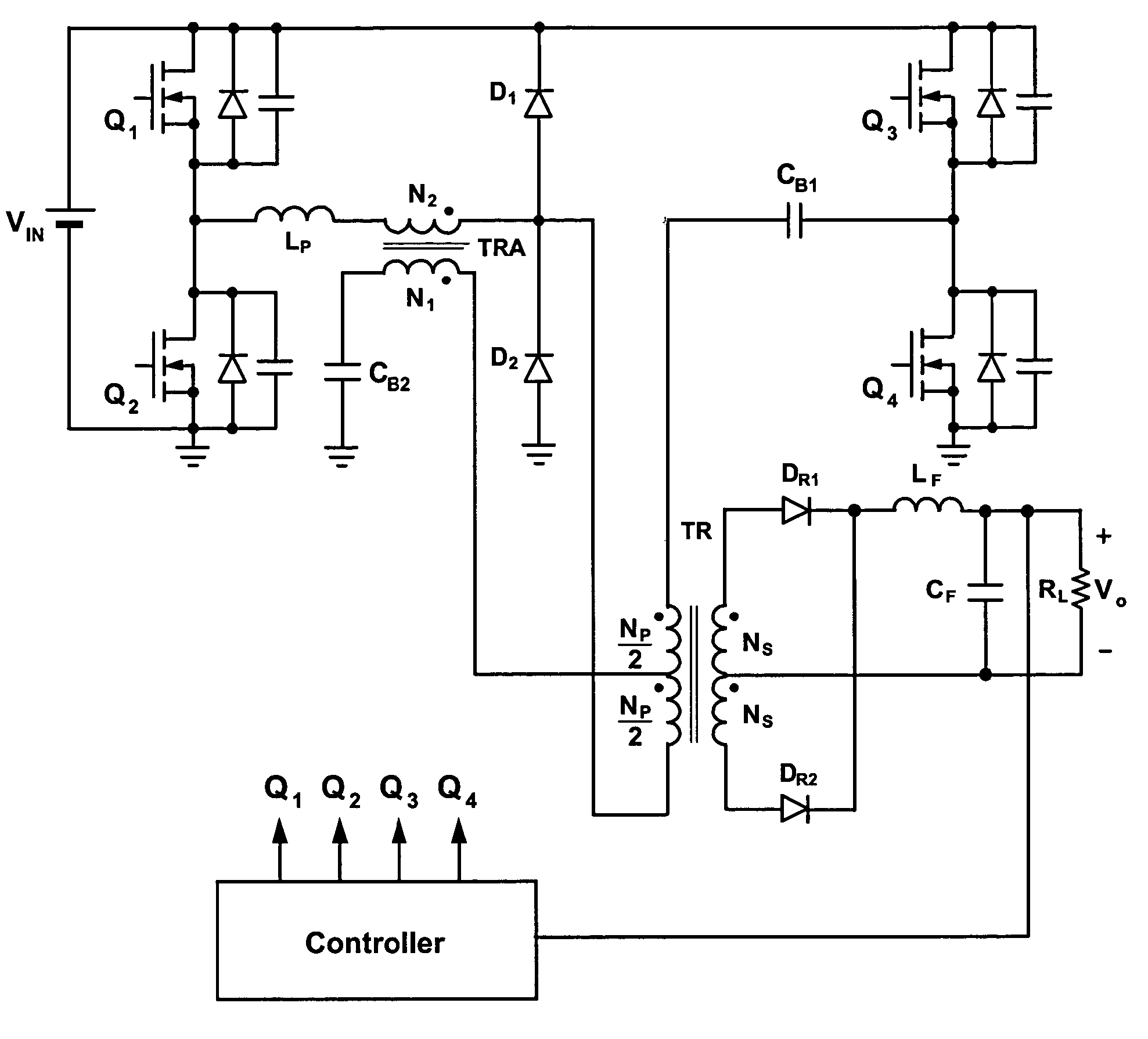
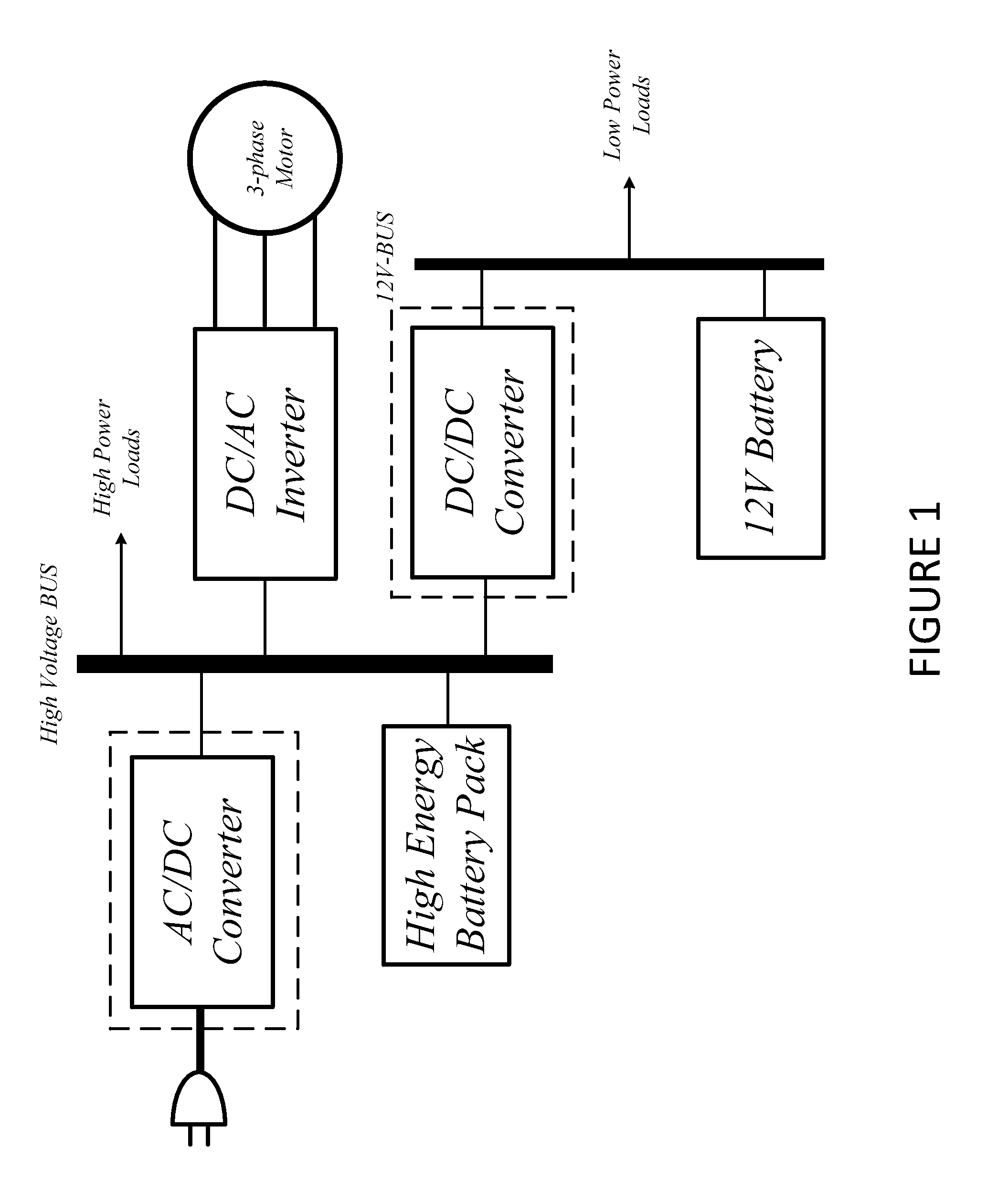
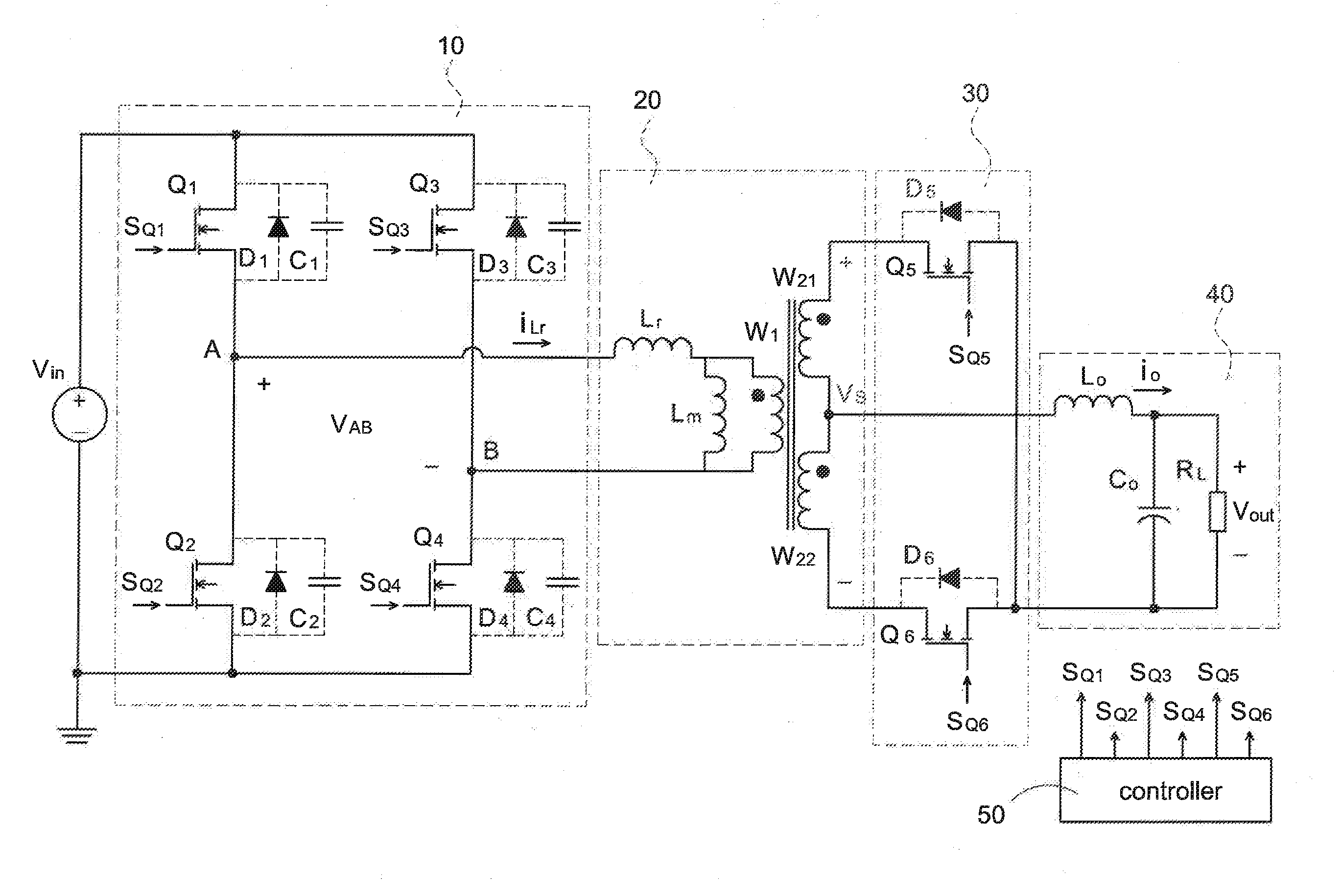
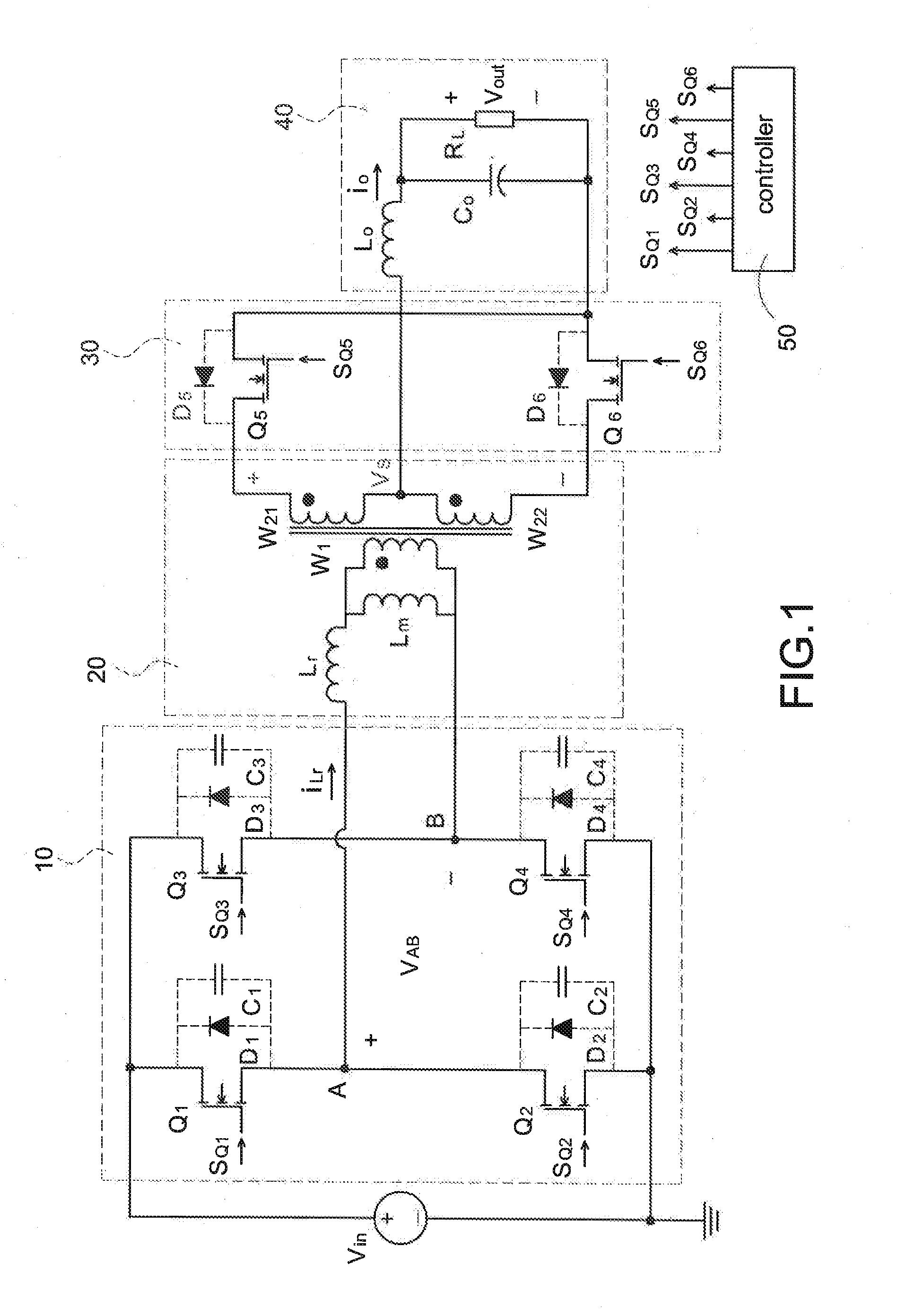
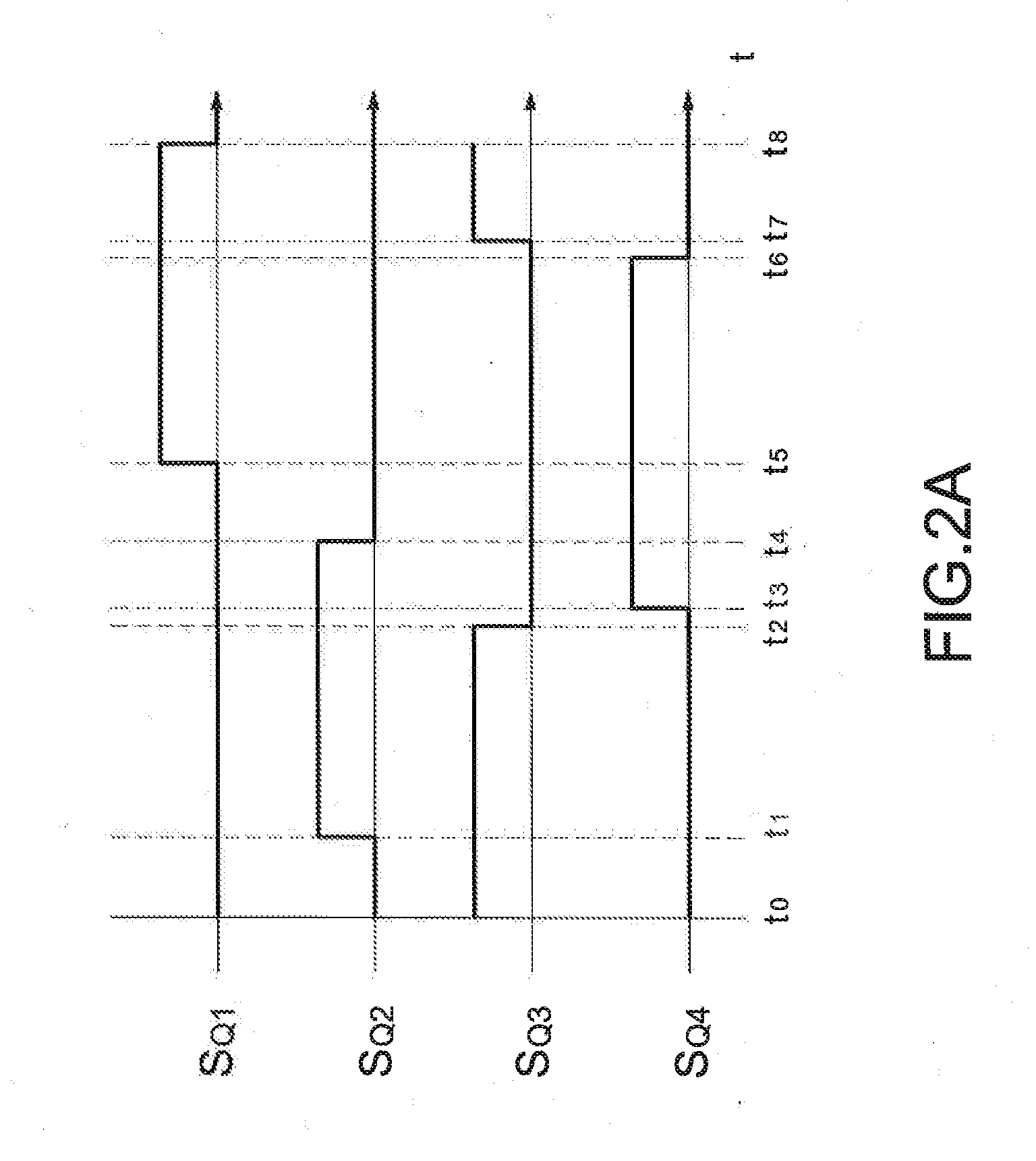
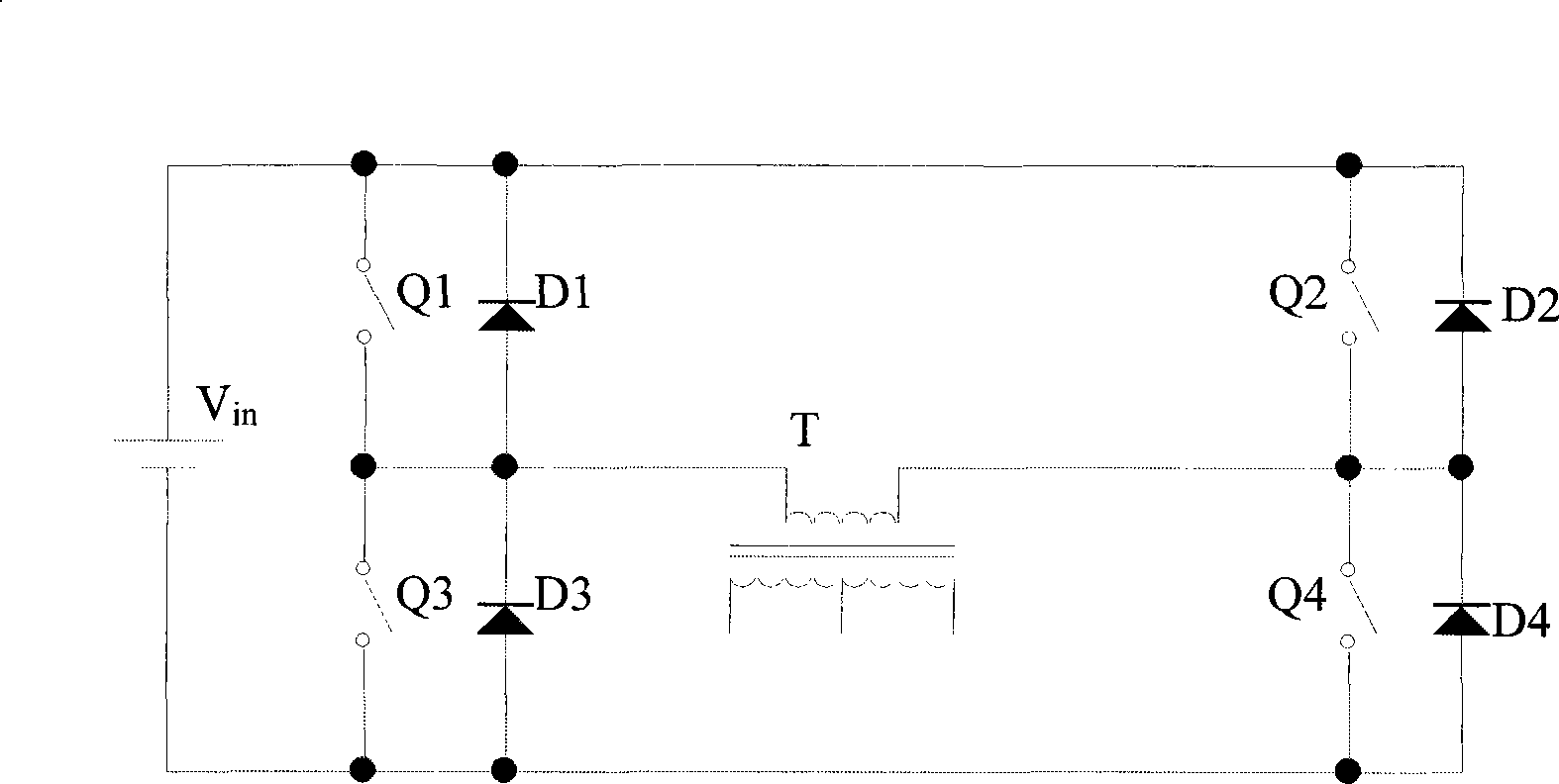
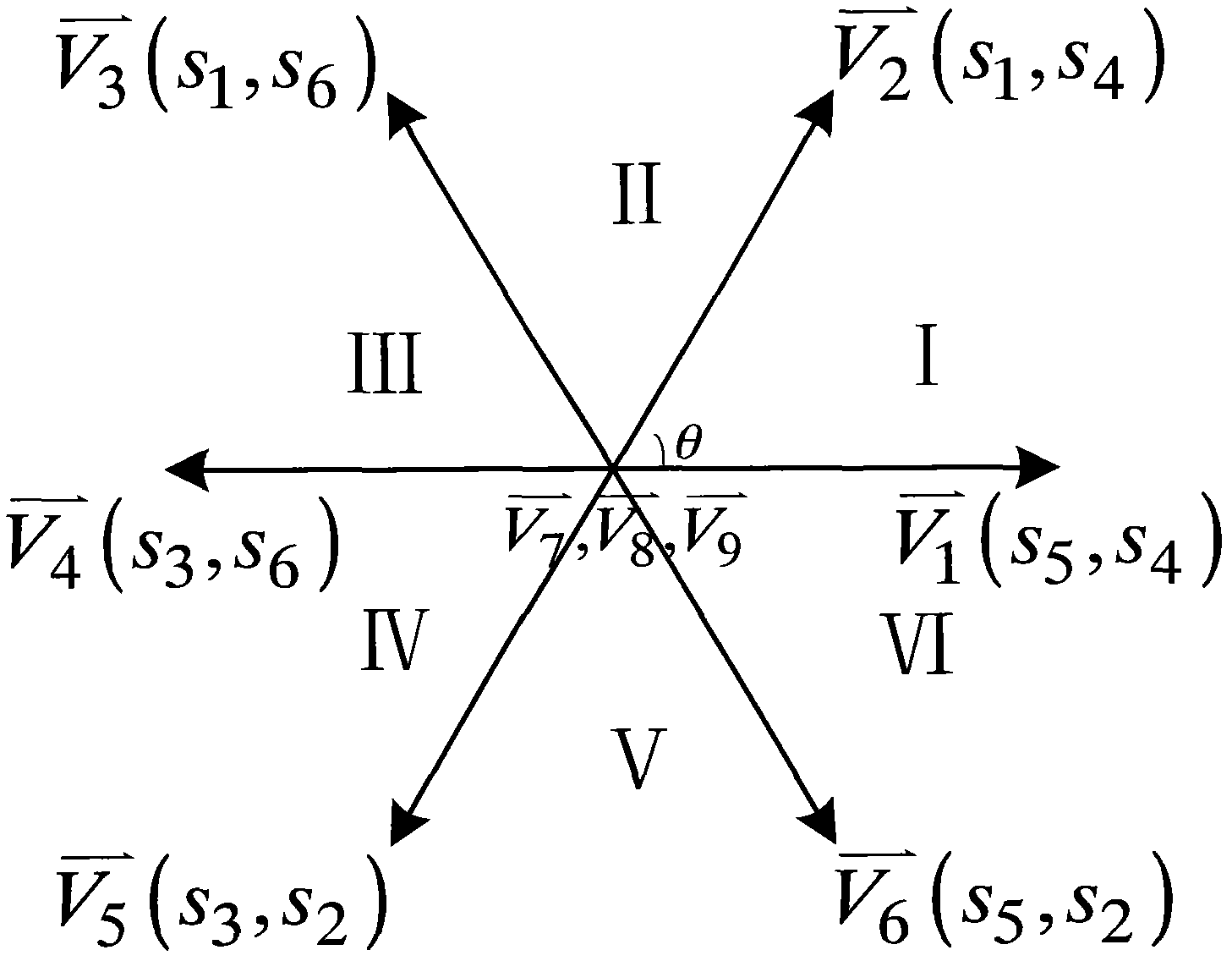Patents
Literature
355 results about "Full bridge converter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
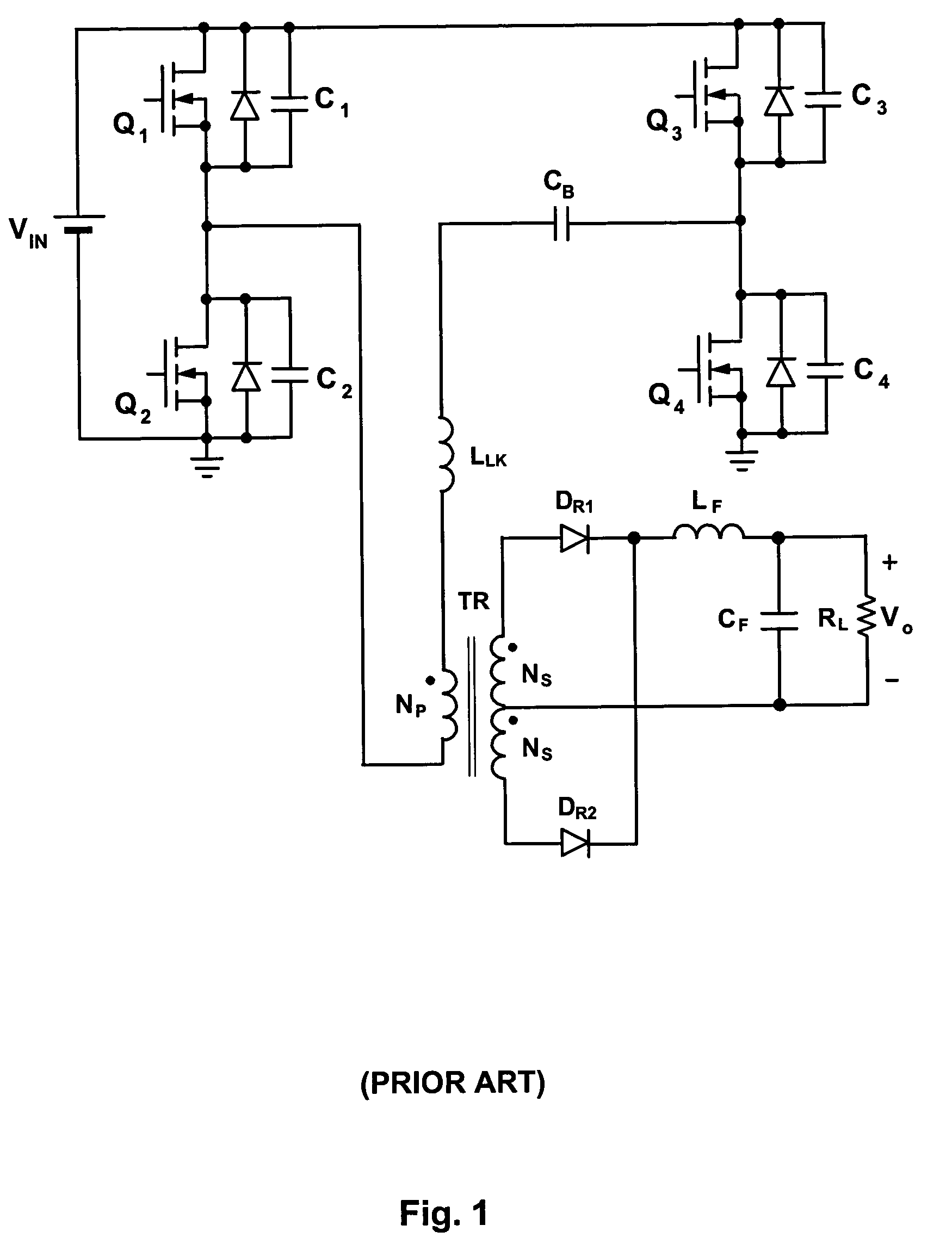
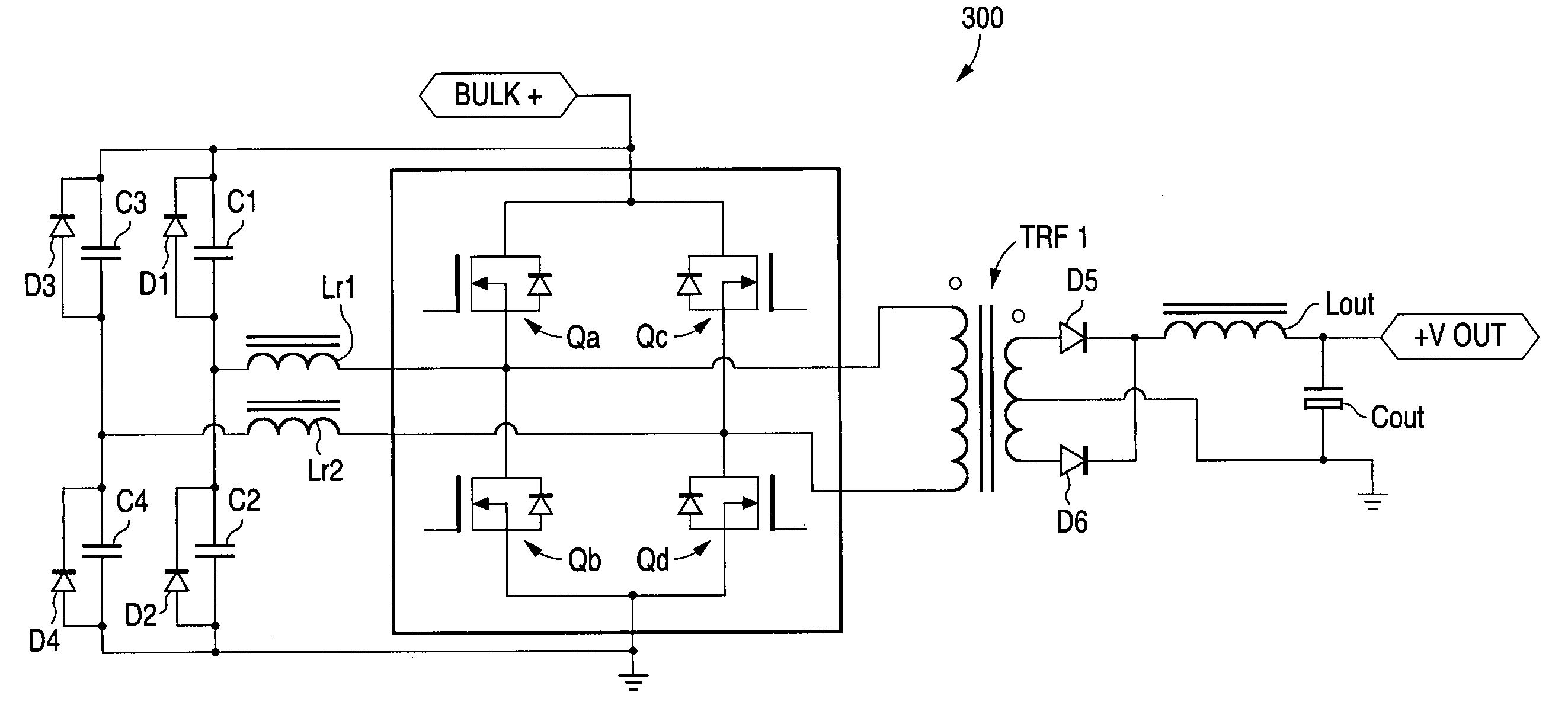
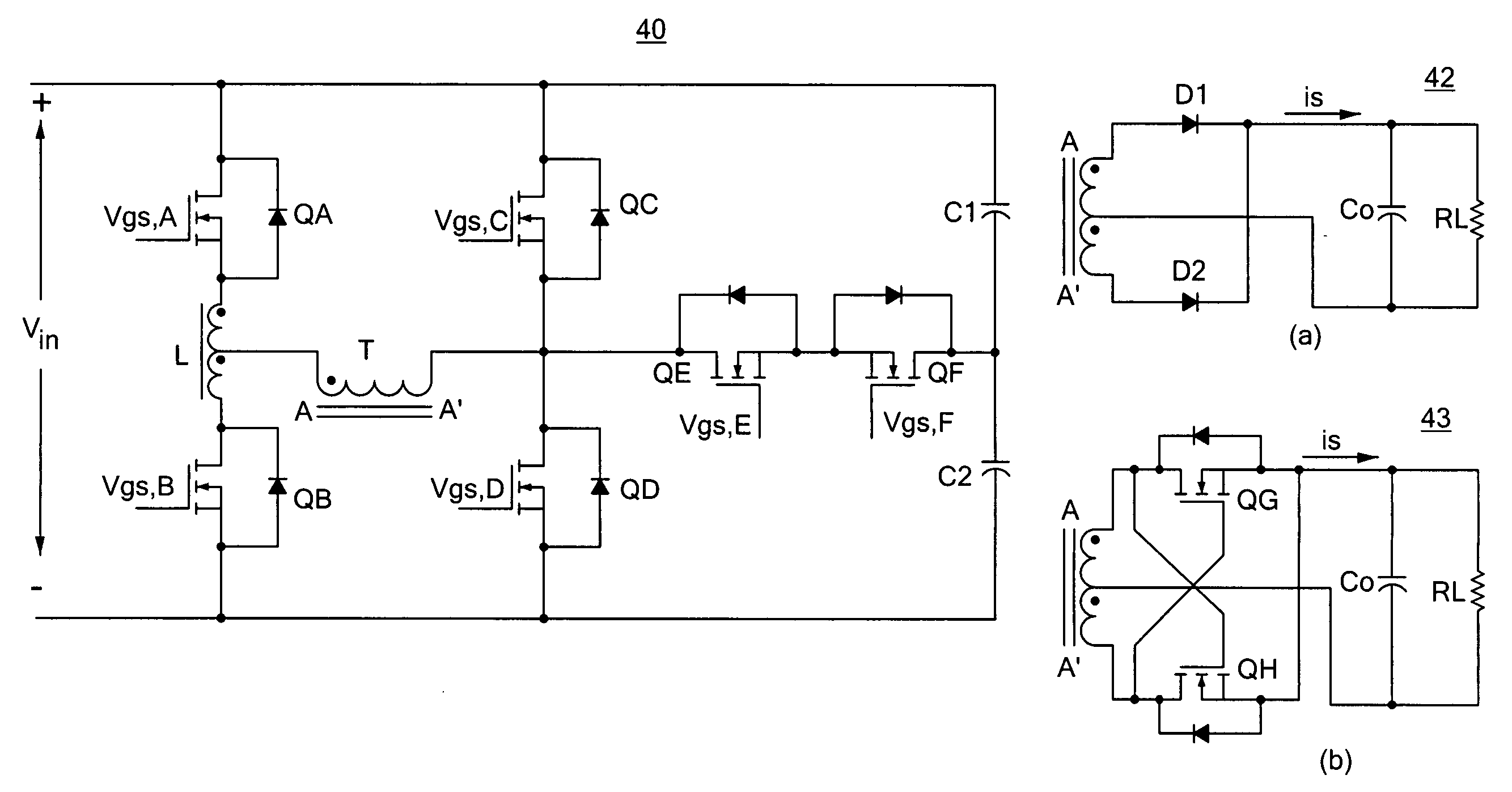
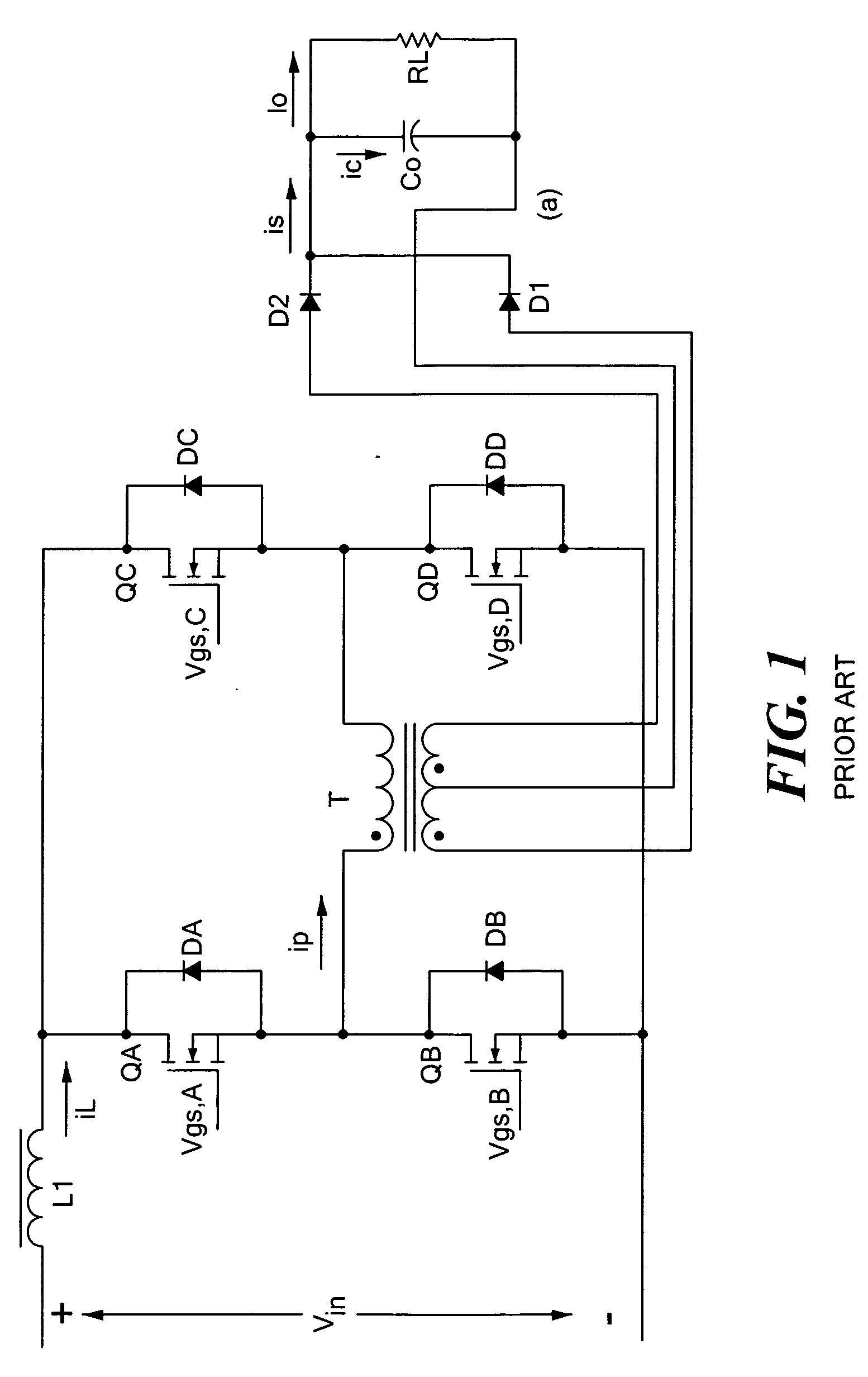
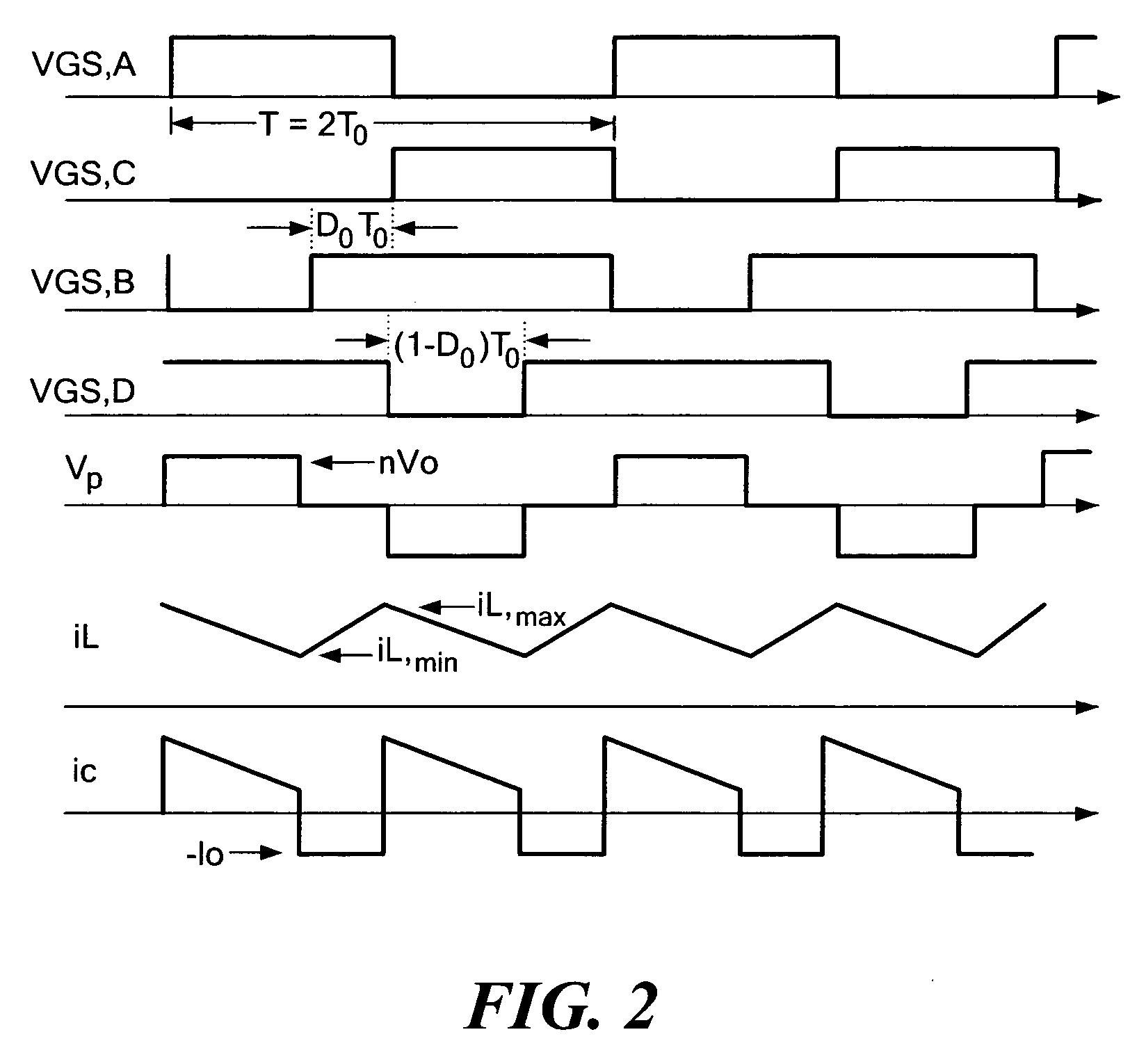
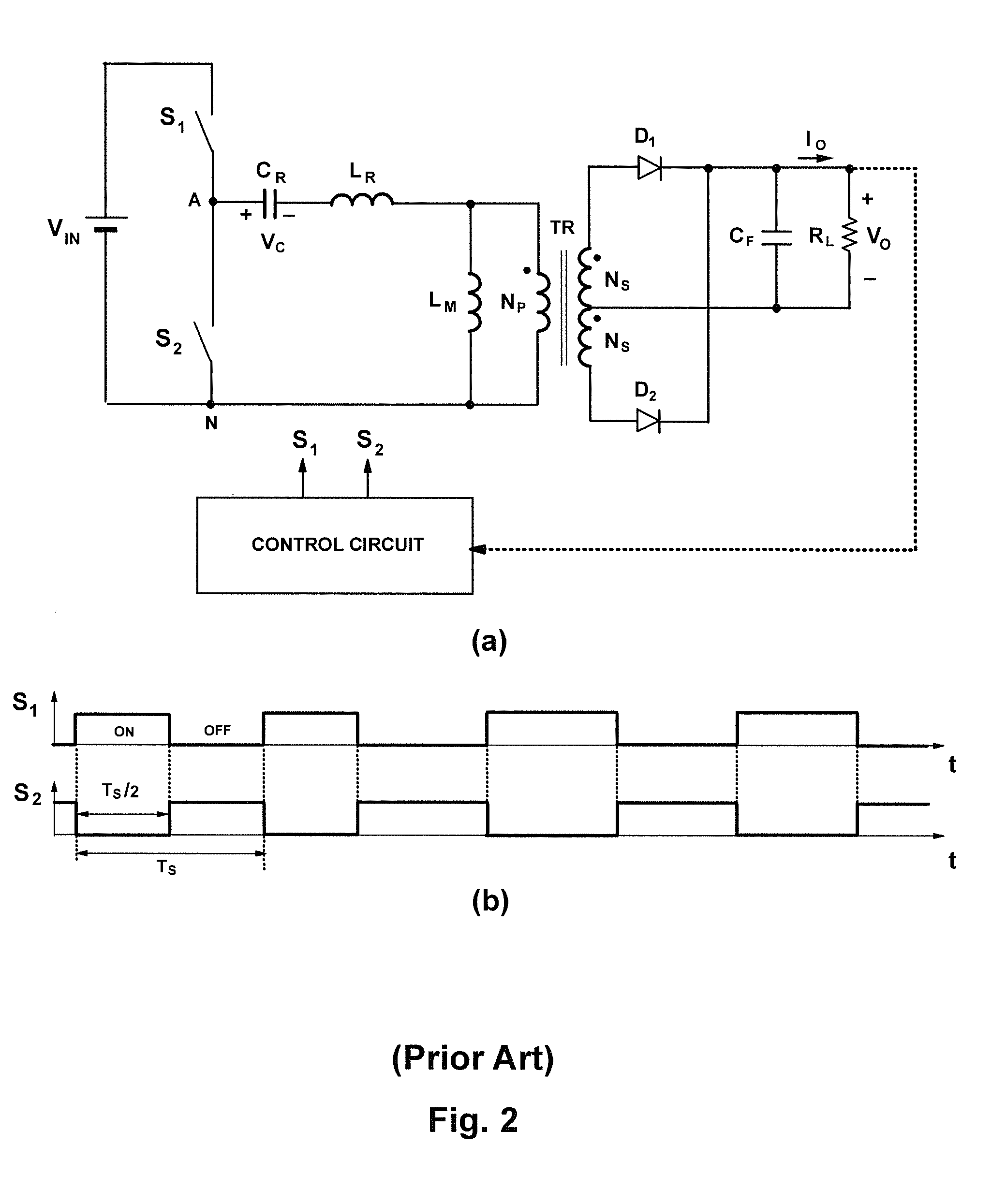
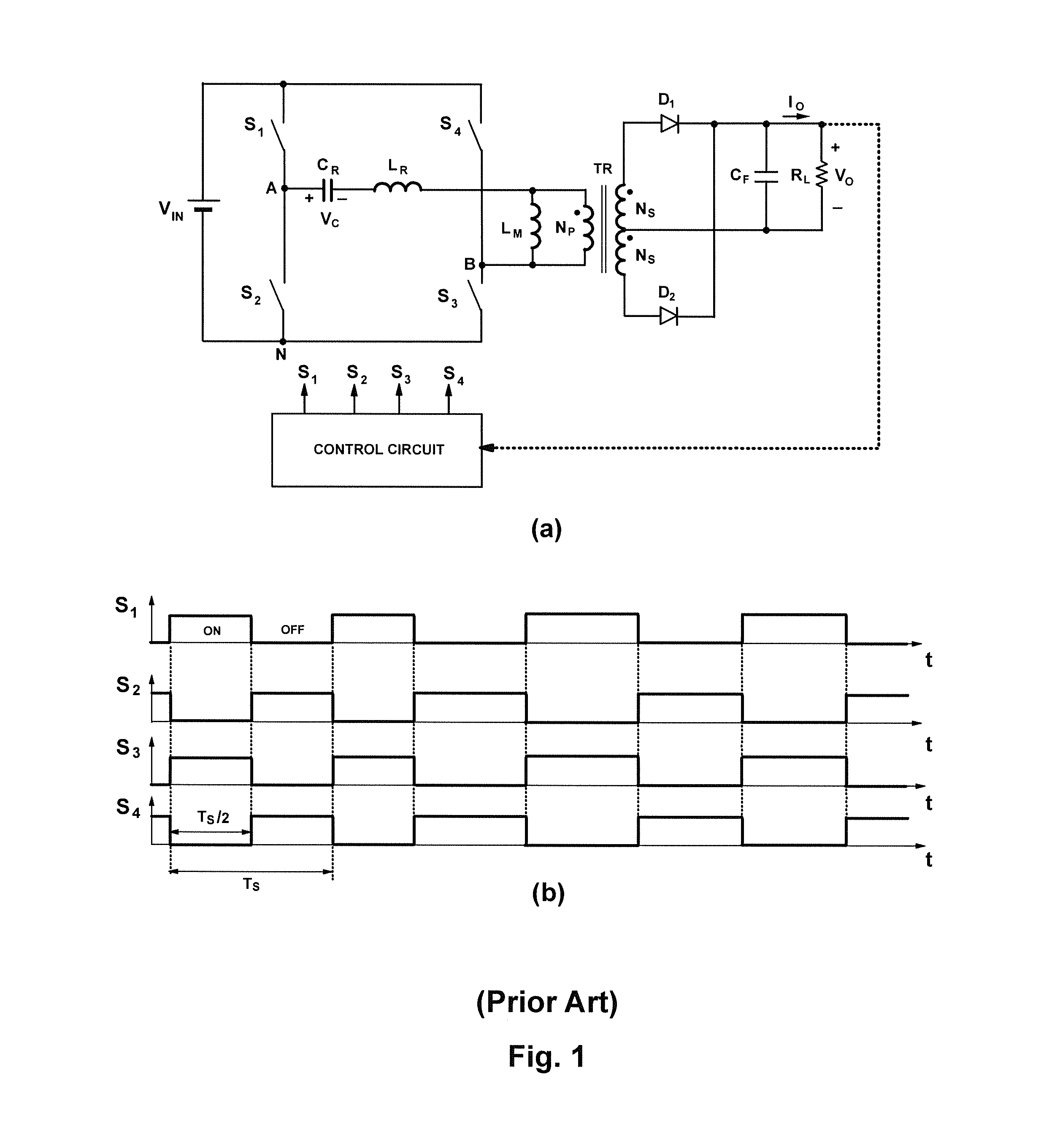
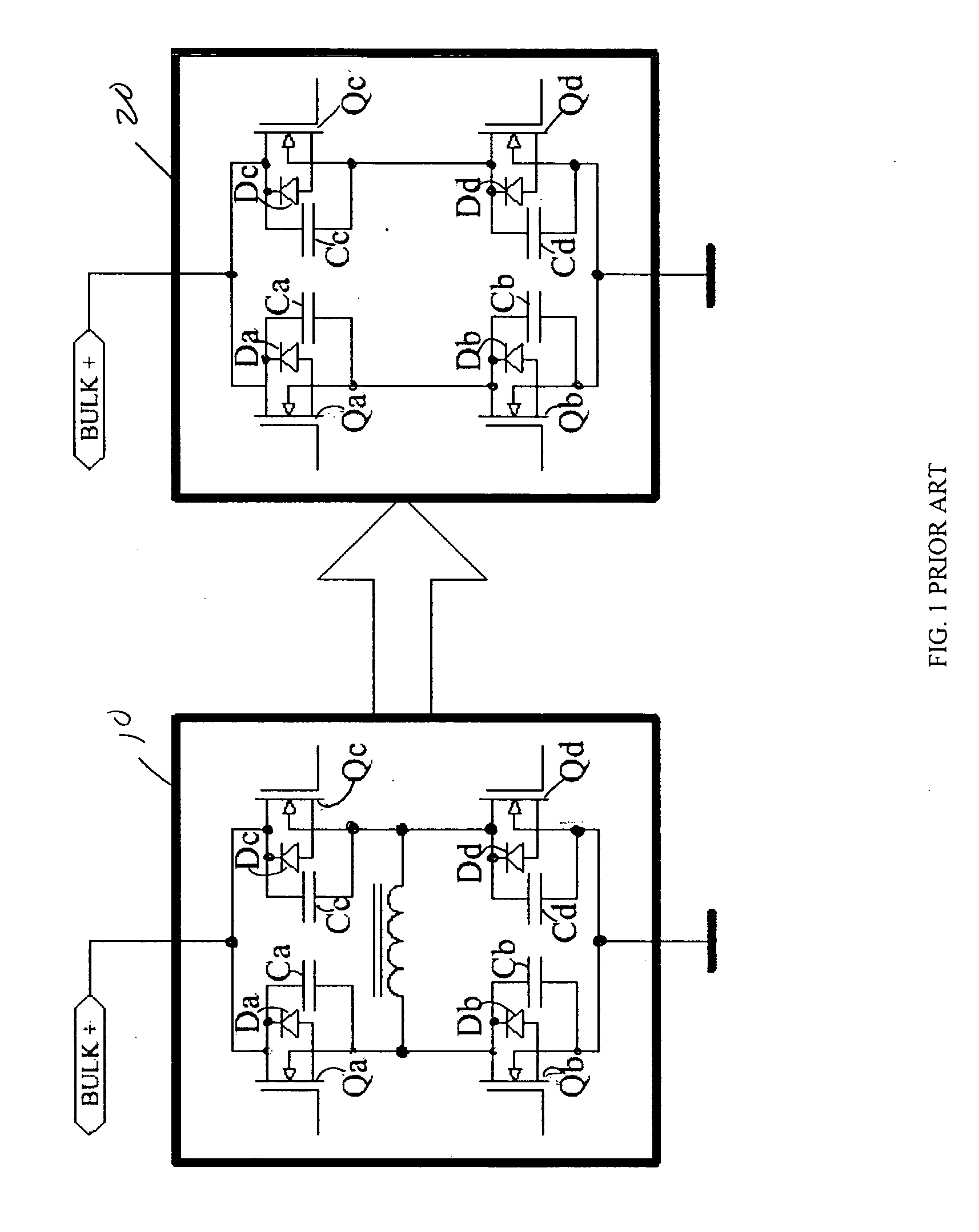
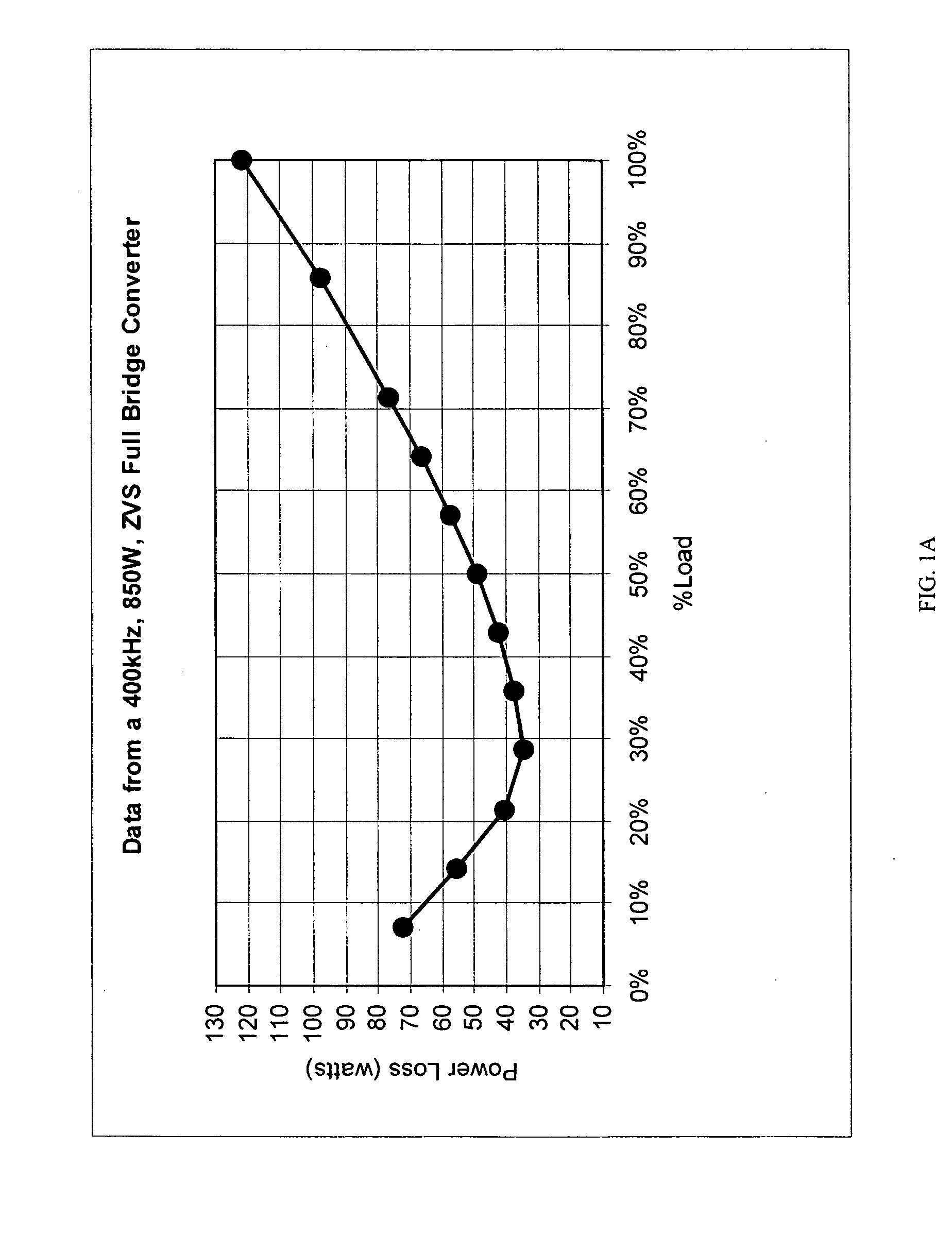
Soft-switched full-bridge converters
InactiveUS6356462B1Minimizes the duty-cycle lossImprove conversion efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionFull bridgeCirculating current
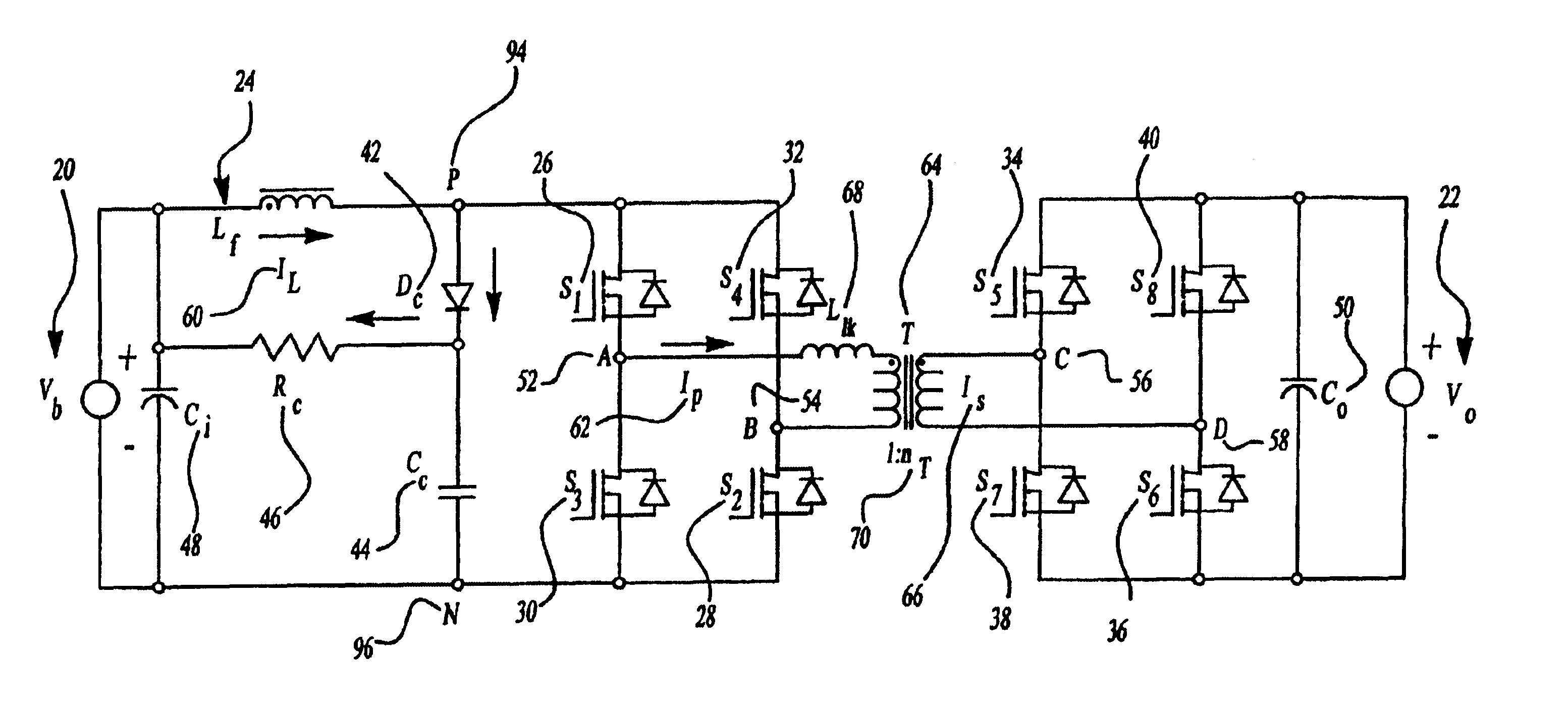
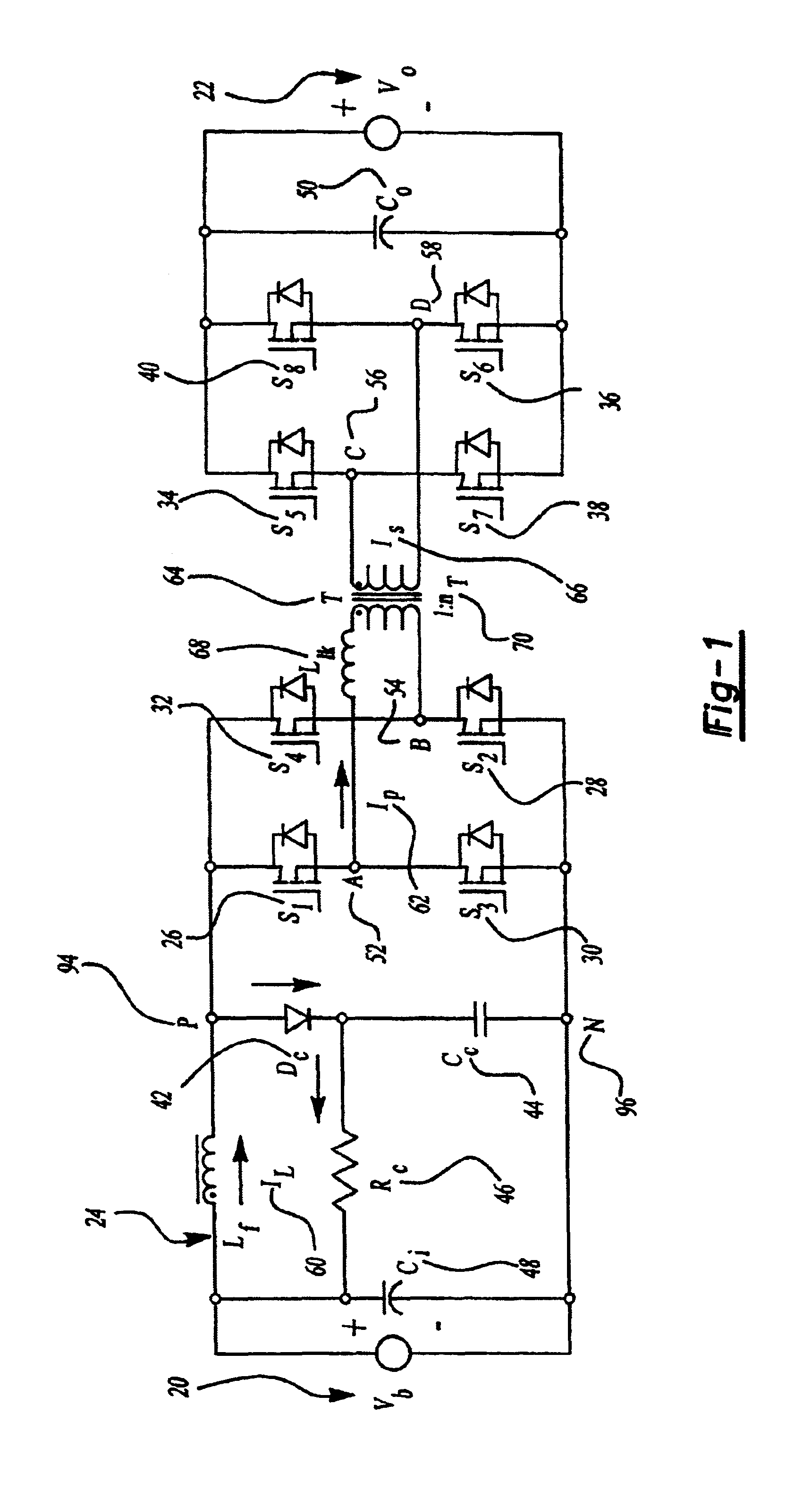
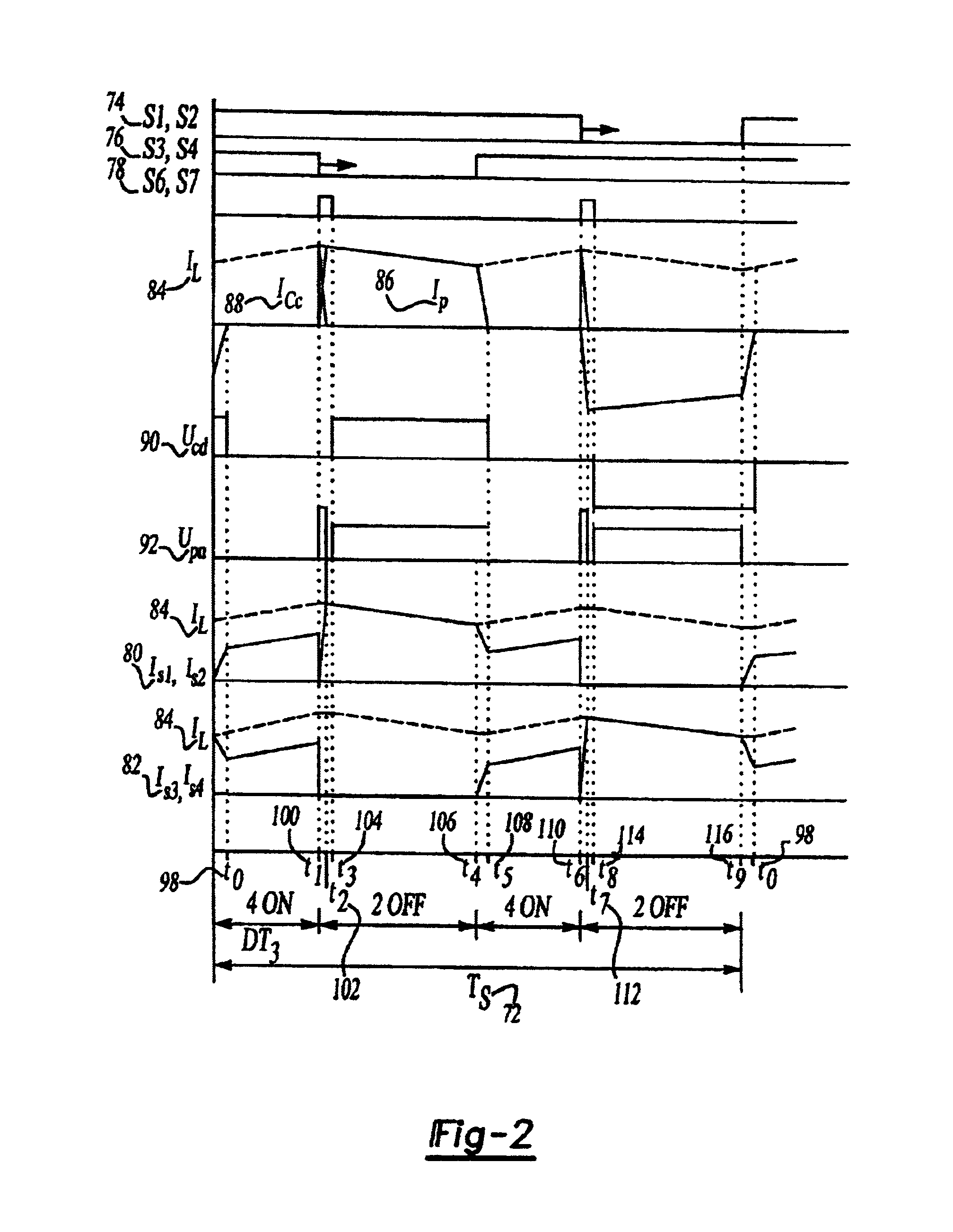
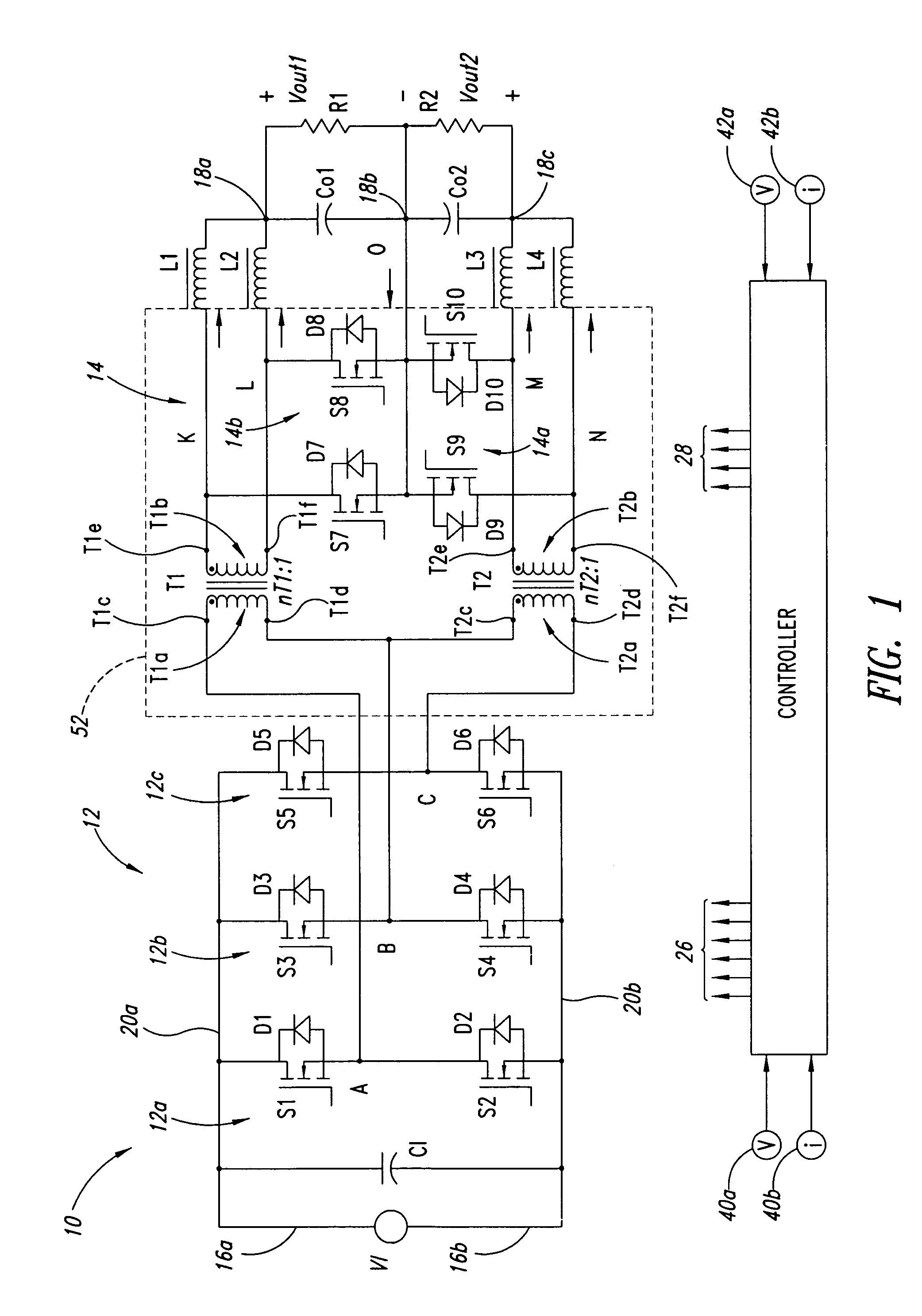
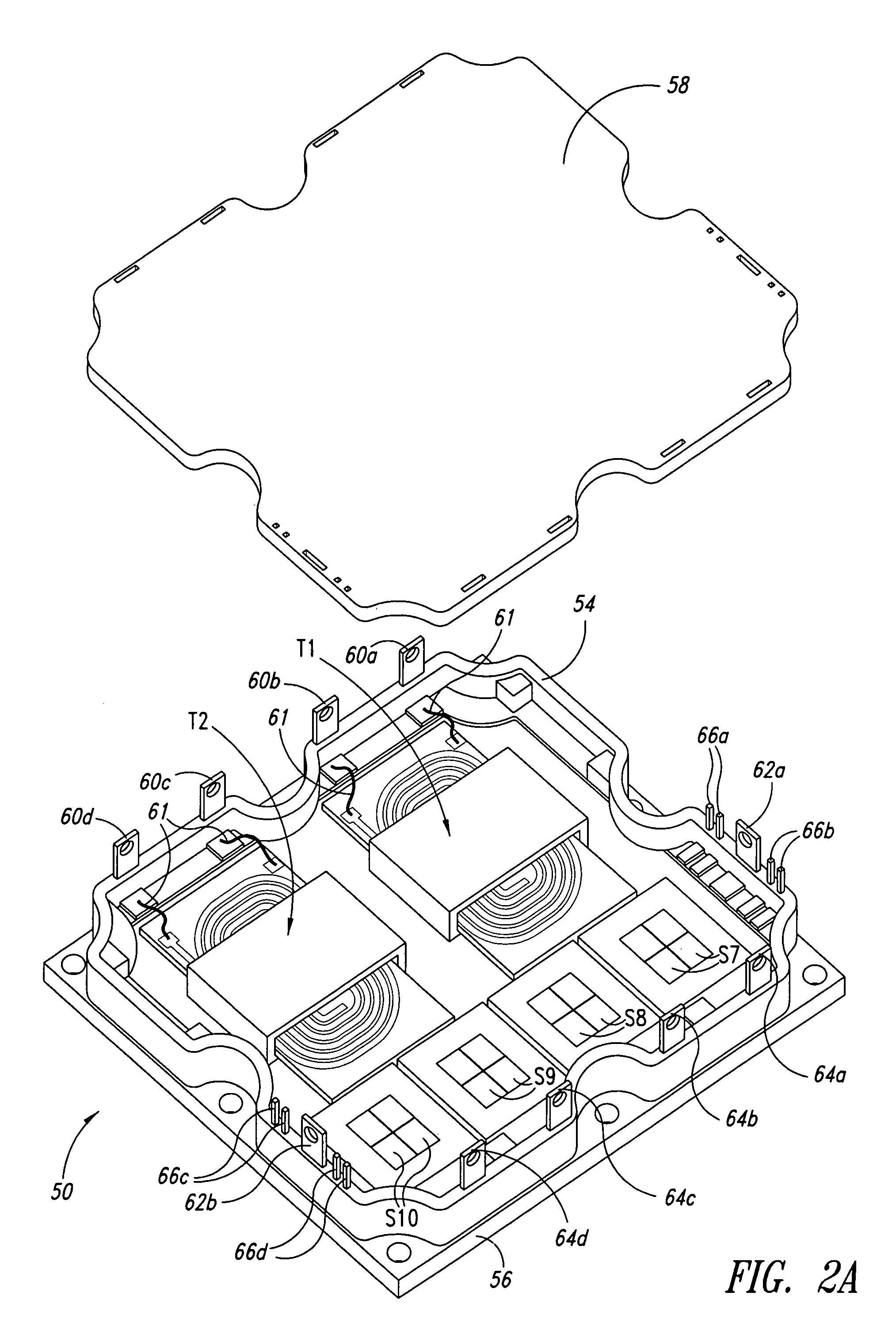
A family of soft-switched, full-bridge pulse-width-modulated (FB PWM) converters provides zero-voltage-switching (ZVS) conditions for the turn-on of the bridge switches over a wide range of input voltage and output load. The FB PWM converters of this family achieve ZVS with the minimum duty cycle loss and circulating current, which optimizes the conversion efficiency. The ZVS of the primary switches is achieved by employing two magnetic components whose volt-second products change in the opposite directions with a change in phase shift between the two bridge legs. One magnetic component always operates as a transformer, where the other magnetic component can either be a coupled inductor, or uncoupled (single-winding) inductor. The transformer is used to provide isolated output(s), whereas the inductor is used to store the energy for ZVS.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
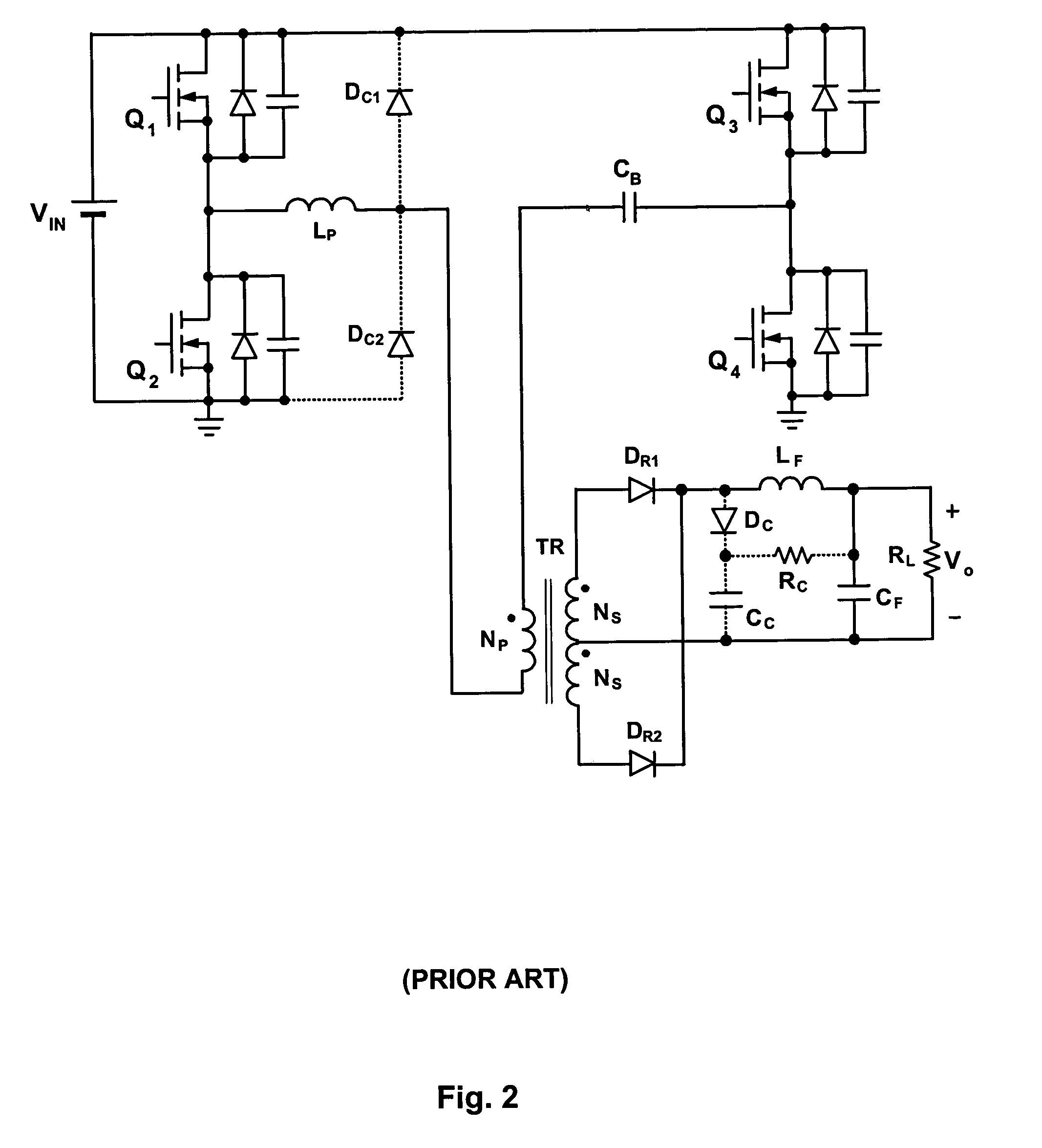
Full bridge converter with ZVS via AC feedback
InactiveUS6992902B2Increase inductanceIncreases the amount of current deliveredConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionFull bridgeCirculating current
A soft-switched, full-bridge pulse-width-modulated converter and its variations provide zero-voltage-switching conditions for the turn-on of the bridge switches over a wide range of input voltage and output load. The FB PWM converters of this invention achieve ZVS with a substantially reduced duty cycle loss and circulating current. The ZVS of the primary switches is achieved by employing an auxiliary circuit having an inductor and transformer to store energy for ZVS turn-on of the bridge switches.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
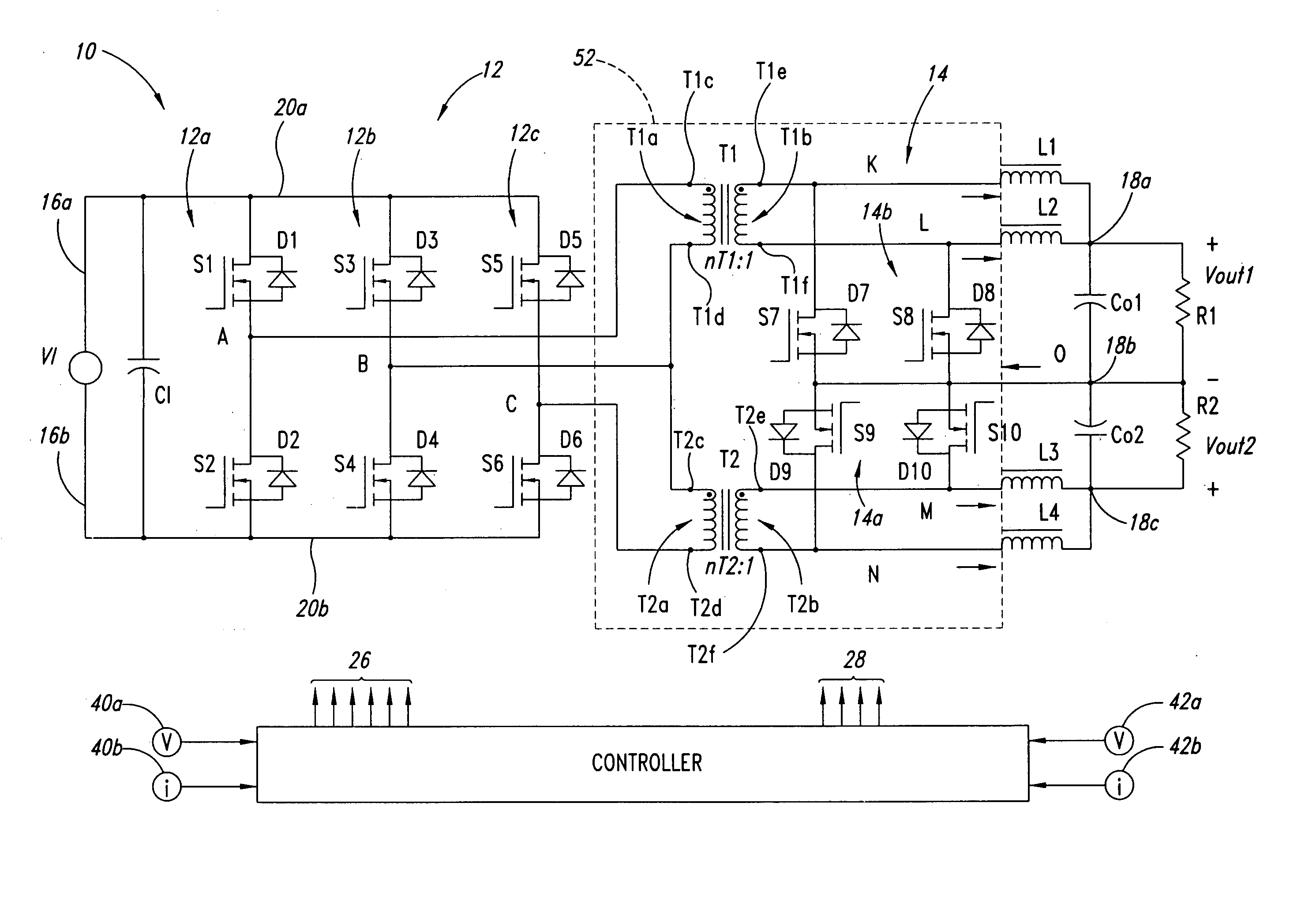
Interleaved power converter
ActiveUS20050270806A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsAc-dc conversionFull bridge converterDc converter
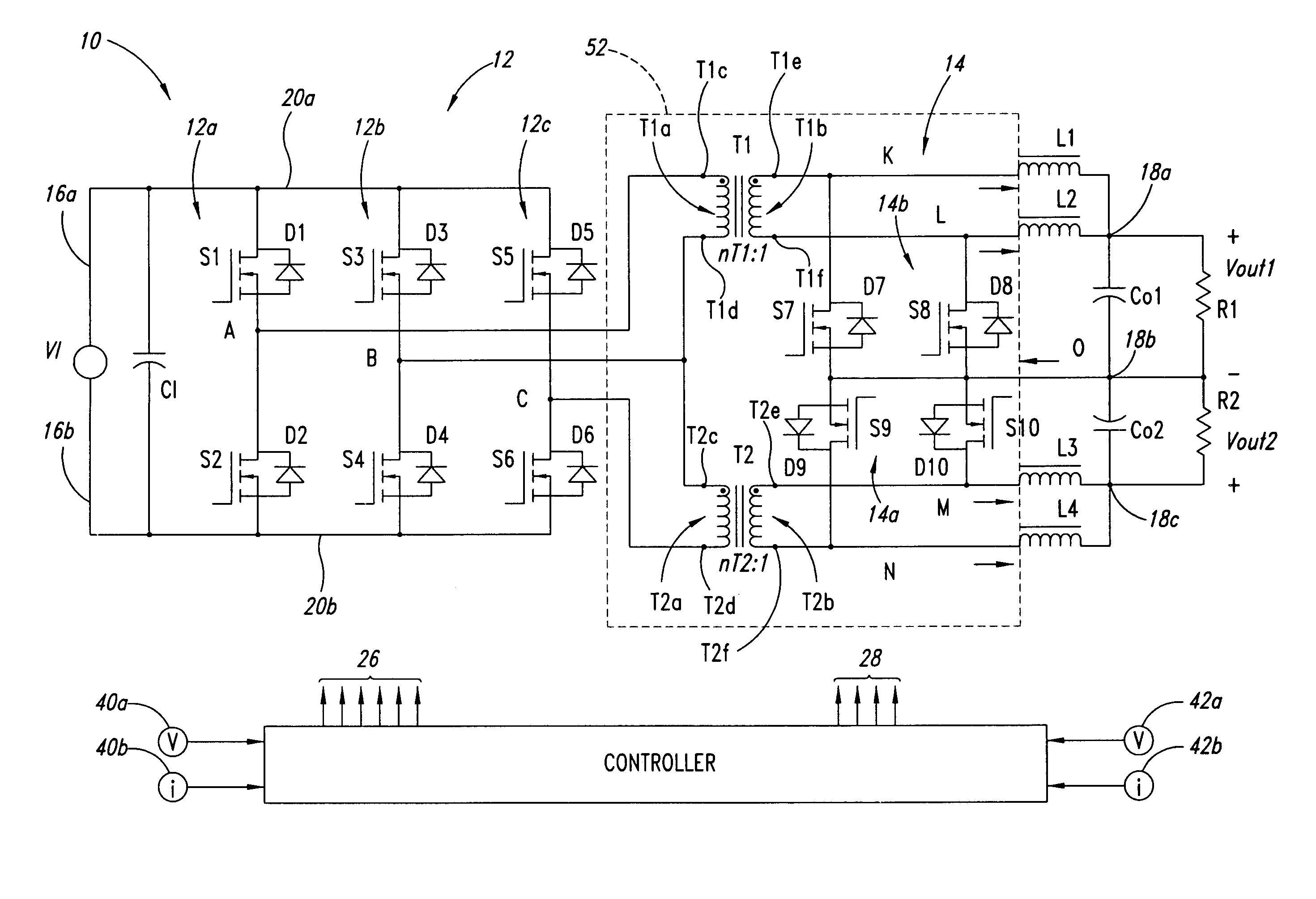
A power converter architecture interleaves full bridge converters to alleviate thermal management problems in high current applications, and may, for example, double the output power capability while reducing parts count and costs. For example, one phase of a three phase inverter is shared between two transformers, which provide power to a rectifier such as a current doubler rectifier to provide two full bridge DC / DC converters with three rather than four high voltage inverter legs.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
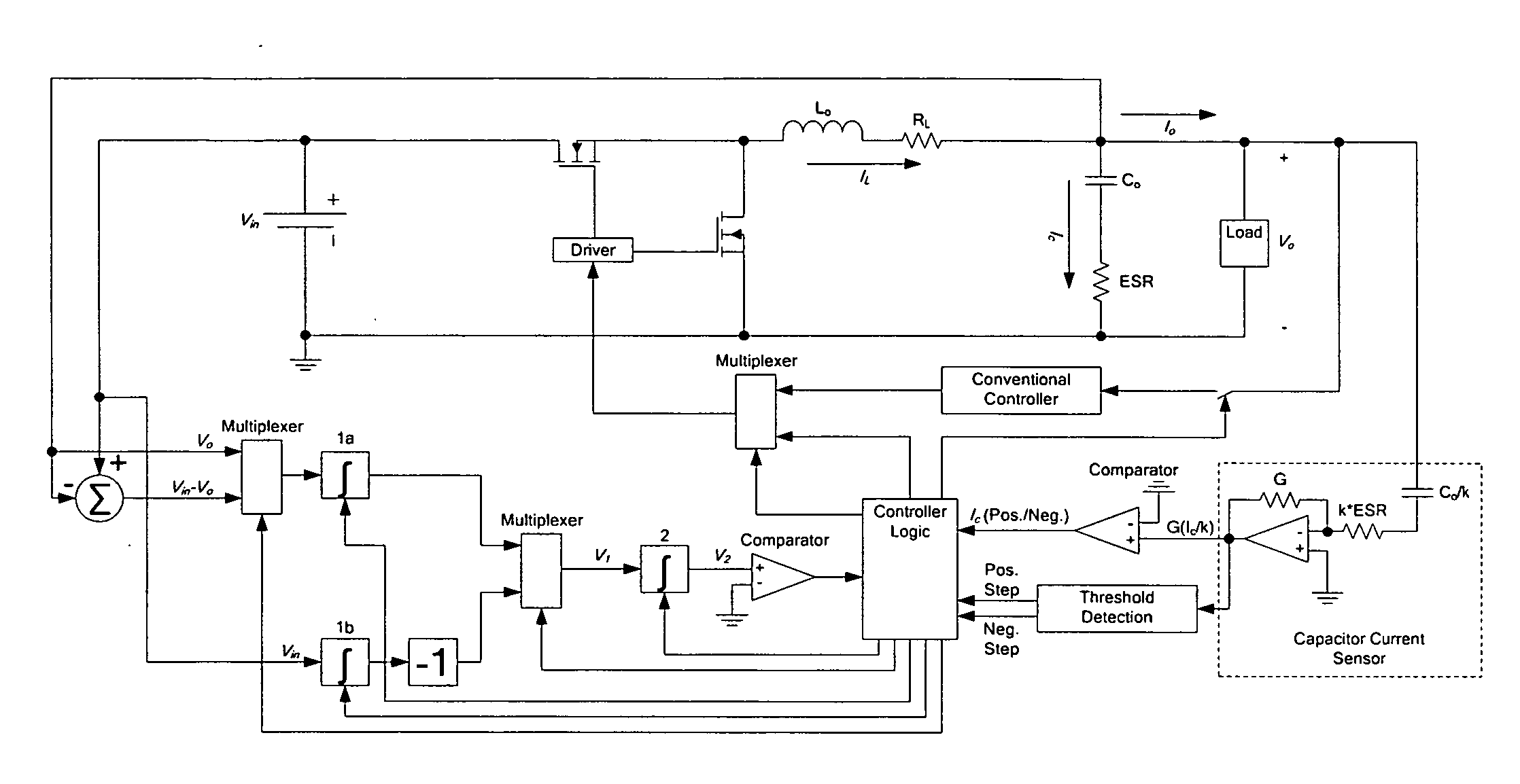
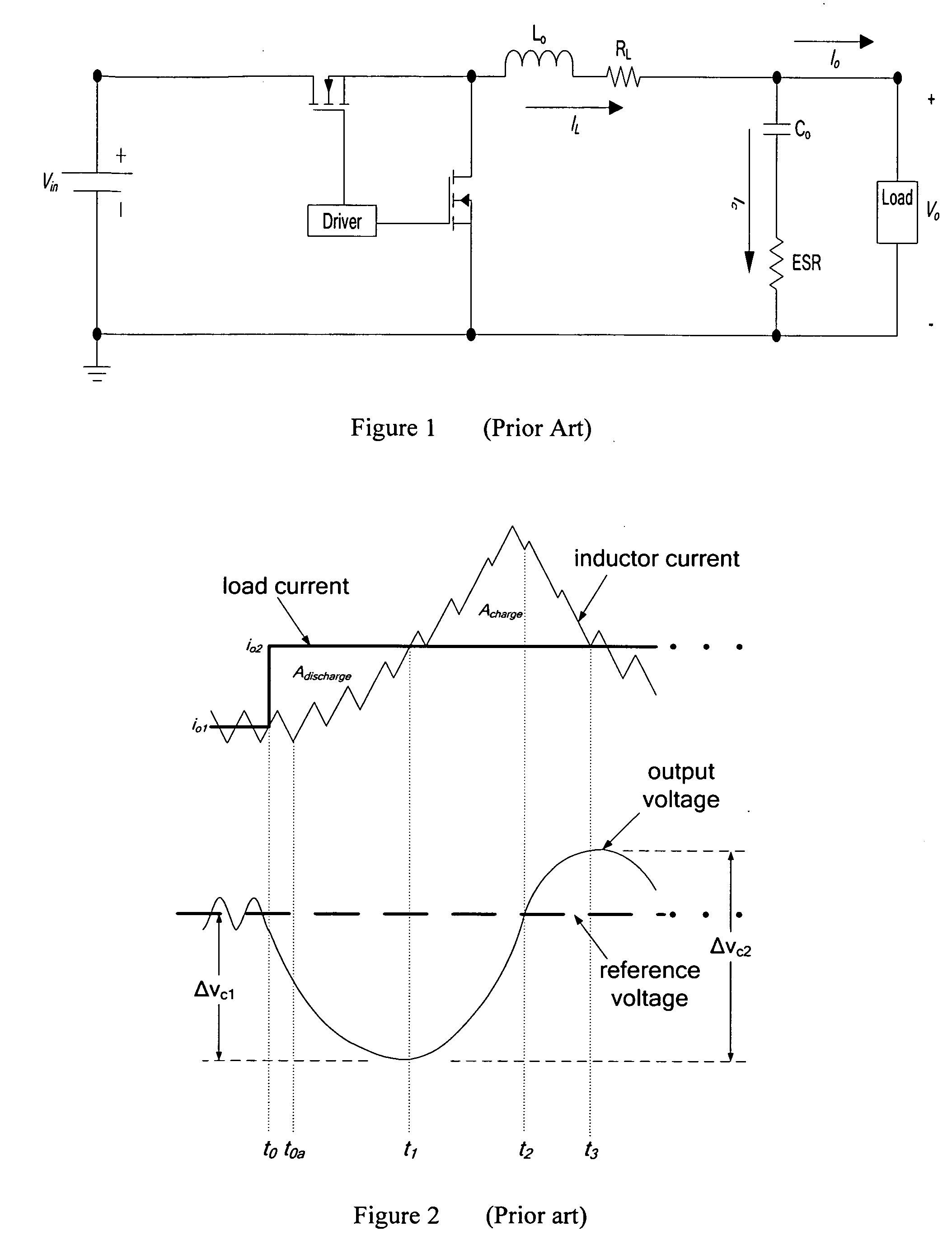
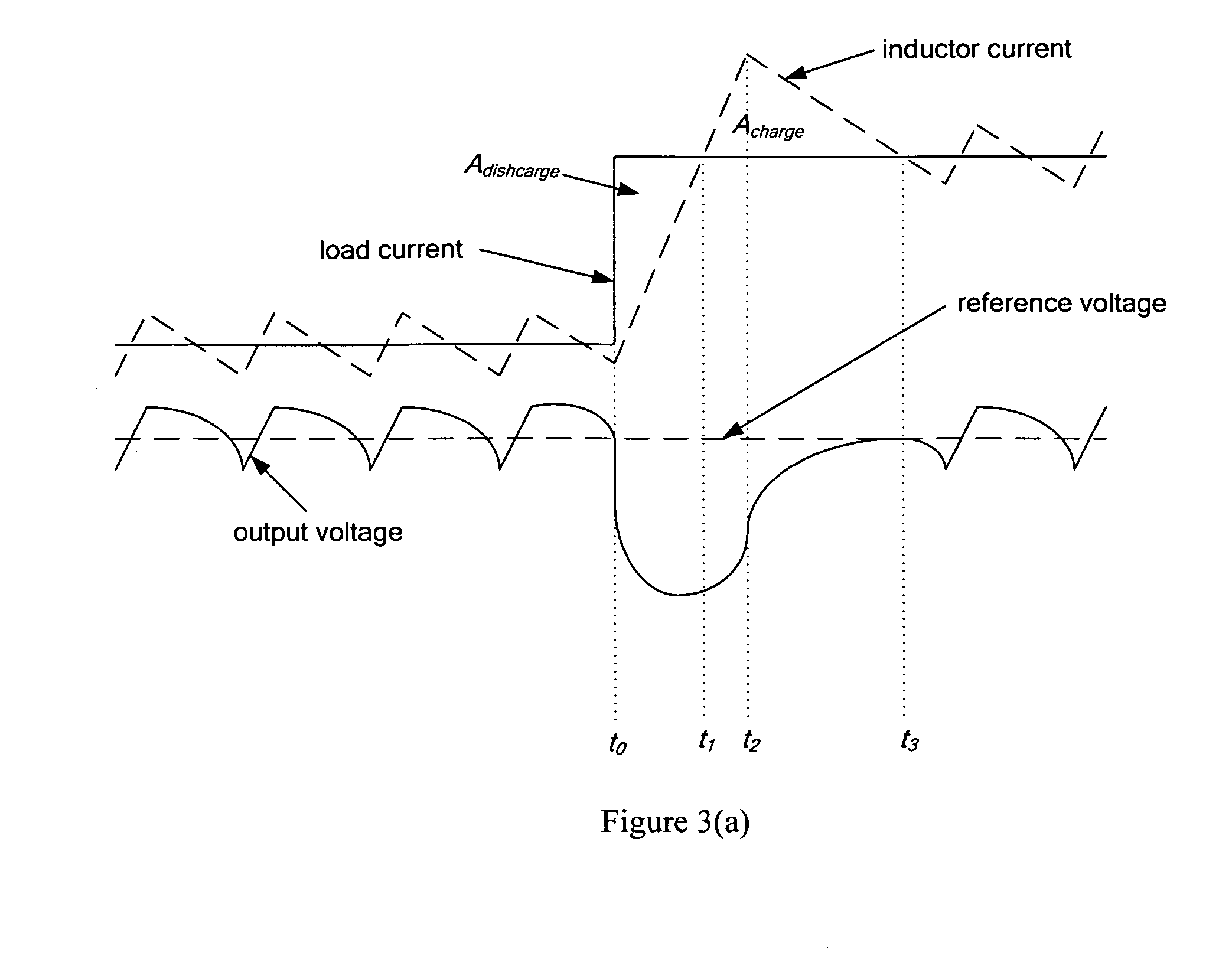
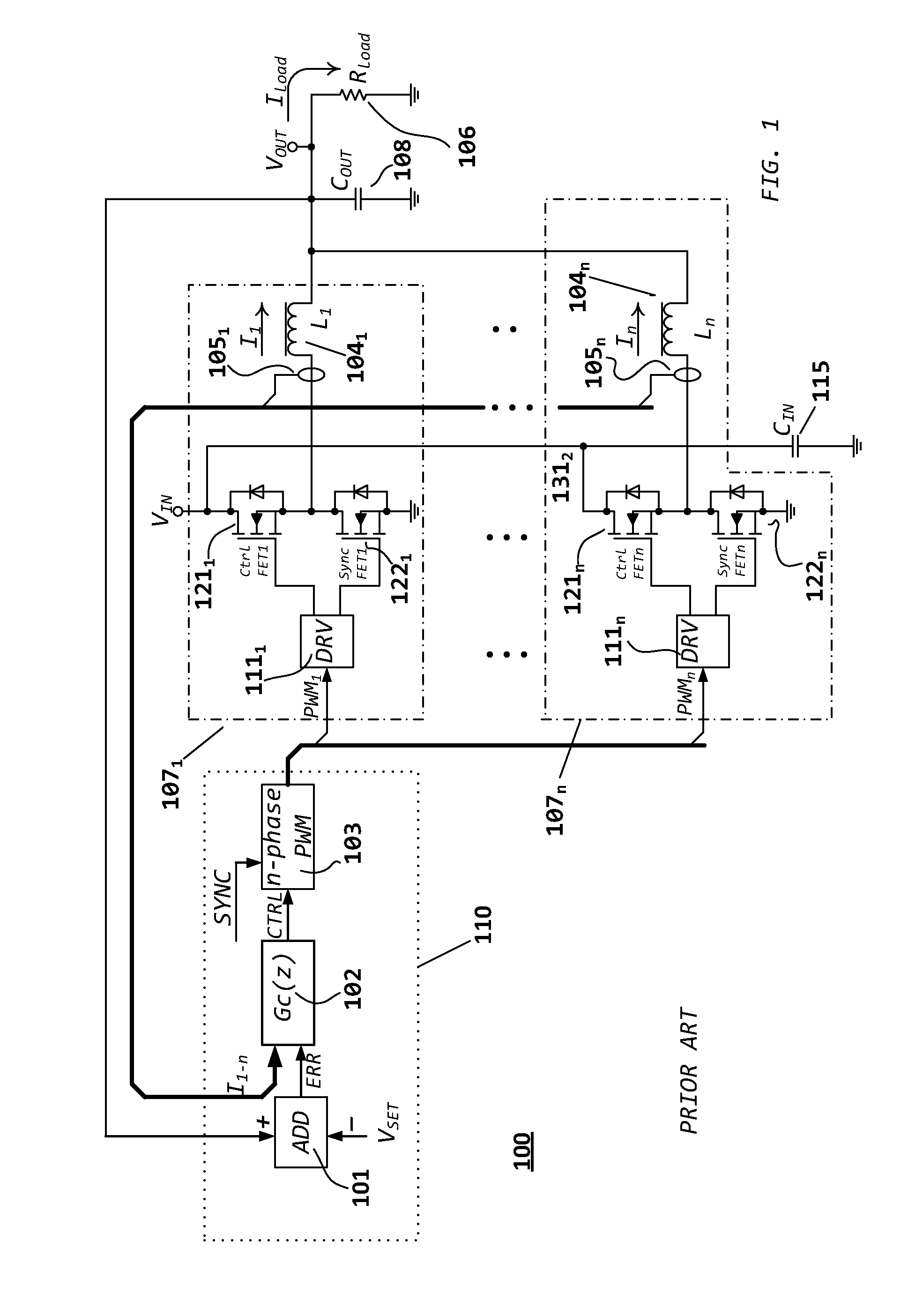
DC-DC converter with improved dynamic response
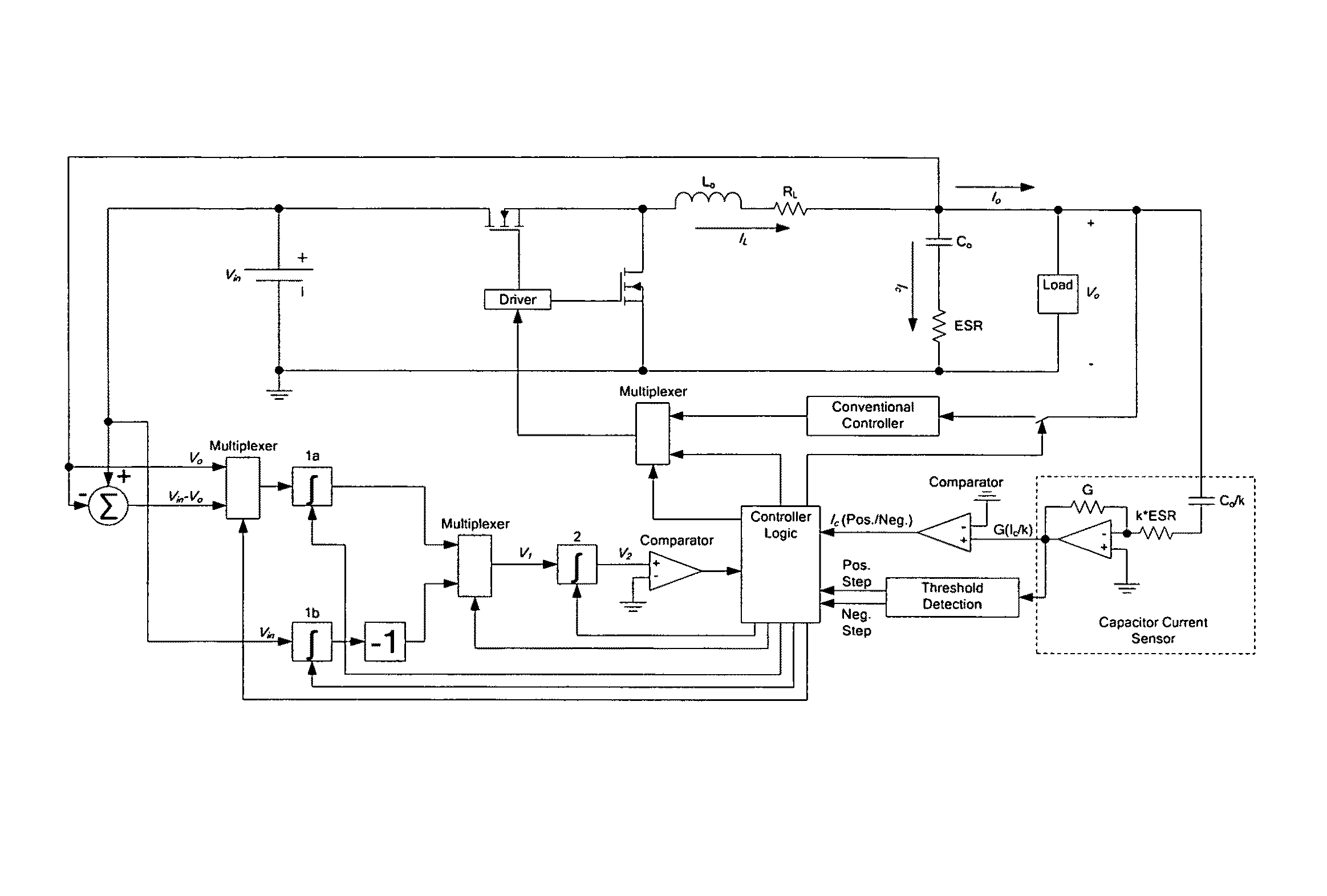
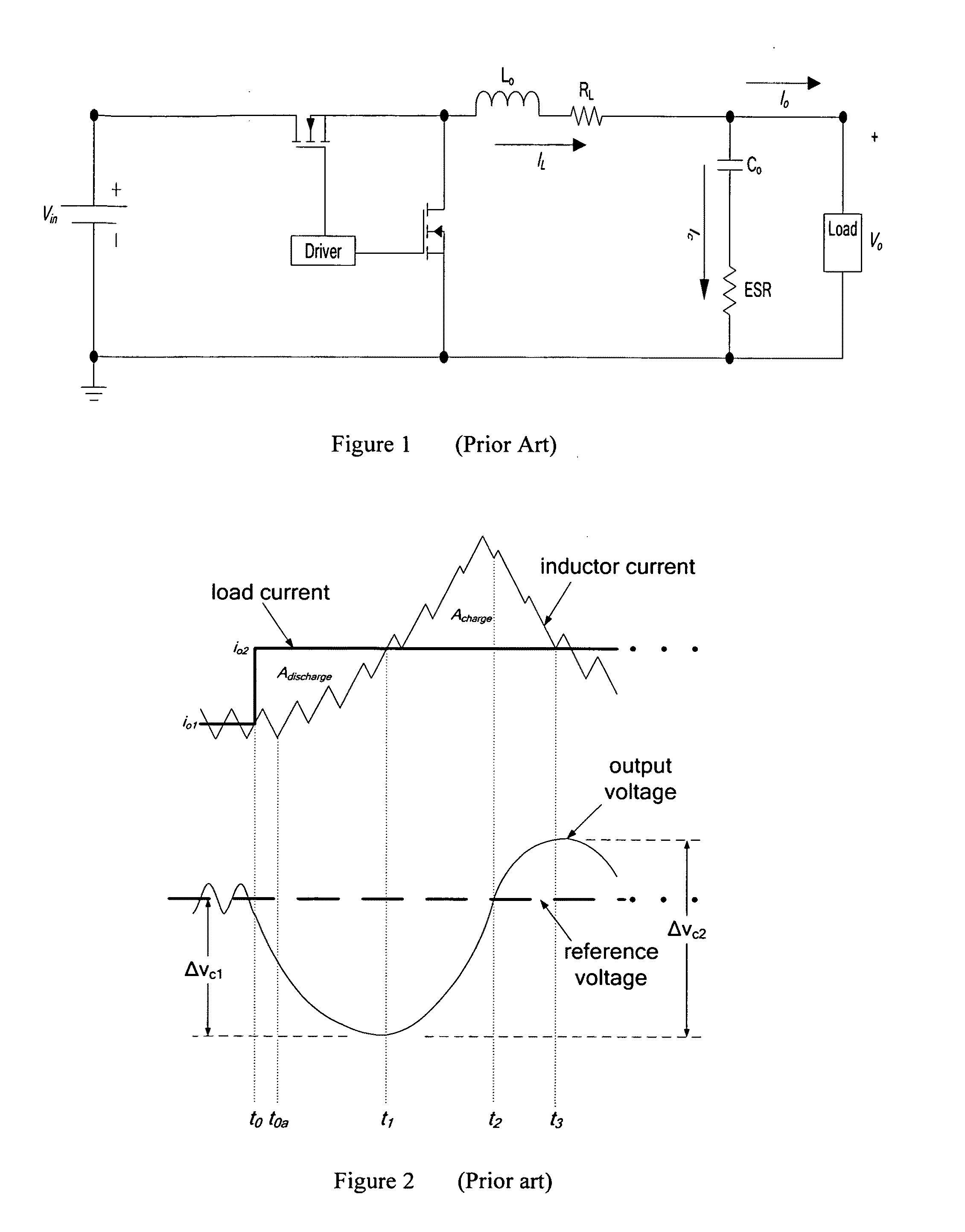
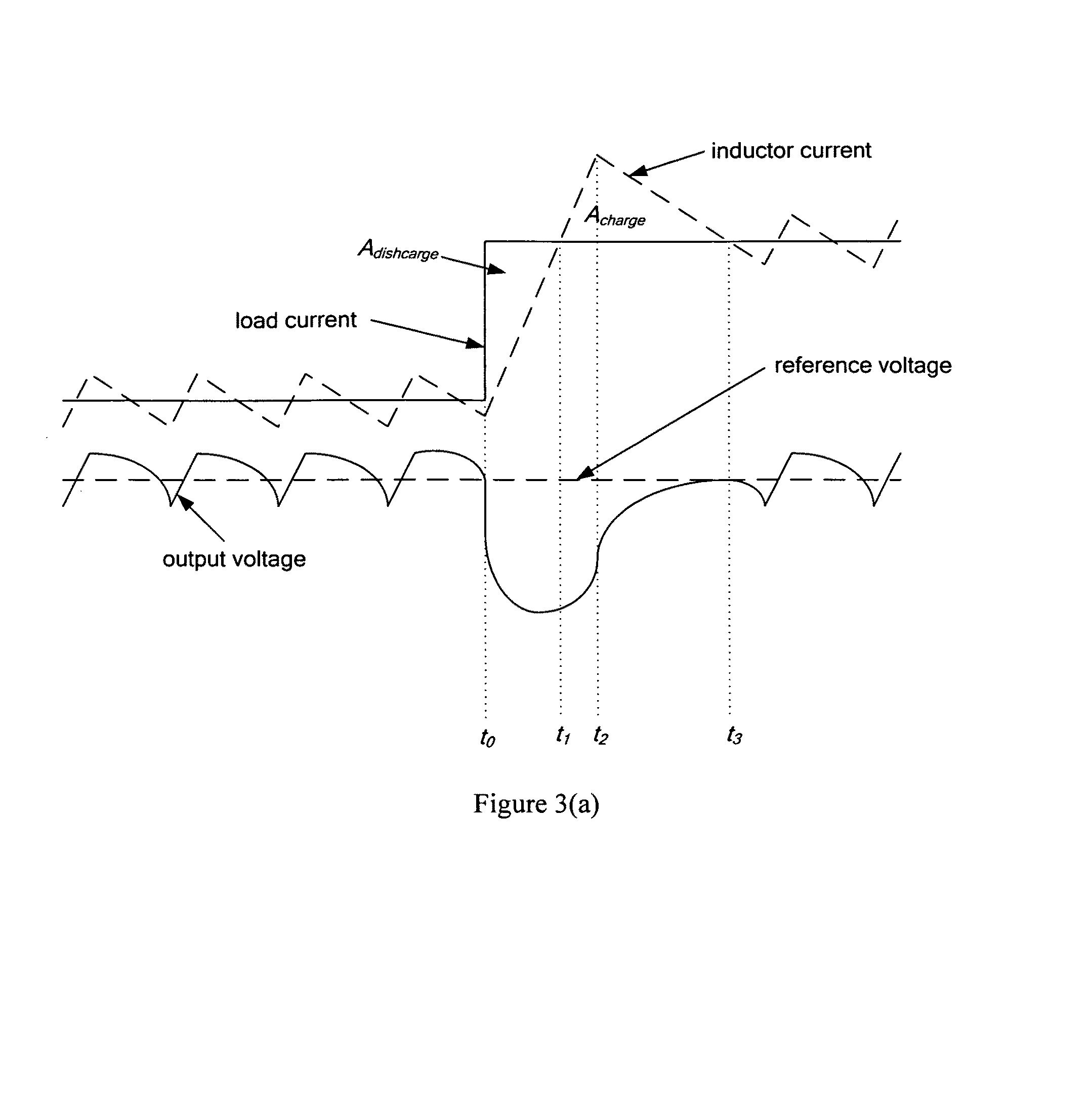
ActiveUS20080258701A1Improve dynamic performanceLow implementation costMultiple-port networksDc network circuit arrangementsFull bridgePush pull
The invention relates to a control method and a controller for a DC-DC converter, such as a synchronous Buck converter, which exploits the principle of capacitor charge balance to allow the converter to recover from a positive and / or negative load current step in the shortest achievable time, with the lowest possible voltage undershoot / overshoot. The control method may be implemented by either an analog or a digital circuit. The controller may be integrated with existing controller schemes (such as voltage-mode controllers) to provide superior dynamic performance during large-signal transient conditions while providing stable operation during steady state conditions. The invention also relates to a method and a modification of a DC-DC converter topology that comprises connecting a controlled current source between an input terminal and an output terminal of the DC-DC converter; detecting a load current step to a new load current; modifying a duty cycle of the DC-DC converter; and modifying current through a parallel output capacitor of the DC-DC converter by controlling current of the current source. The methods and circuits provided herein are applicable to Buck converters and Buck-derived converters such as forward, push-pull, half-bridge, and full-bridge converters.
Owner:GANPOWER SEMICON FOSHAN LTD
Accelerated commutation for passive clamp isolated boost converters
InactiveUS6876556B2Efficient and cost-effectiveImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsVoltage spikeBuck converter
An efficient and cost effective bidirectional DC / DC converter reduces switch voltage stress via accelerated commutation allowing use of a low-cost passive clamp circuit in boost mode. The converter includes a primary circuit, transformer and secondary circuit. The primary circuit takes the form of a “full bridge converter,” a “push-pull converter,” or an “L-type converter.”. The primary circuit may include a dissipator such as a snubber circuit or small buck converter. A secondary side of the transformer is momentarily shorted by the secondary circuit by, for example, turning on at least two switches in the secondary circuit simultaneously for a minimal calibratable period when a pair of primary circuit controllers turn off to protect the primary circuit switches from voltage spikes during switching conditions.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
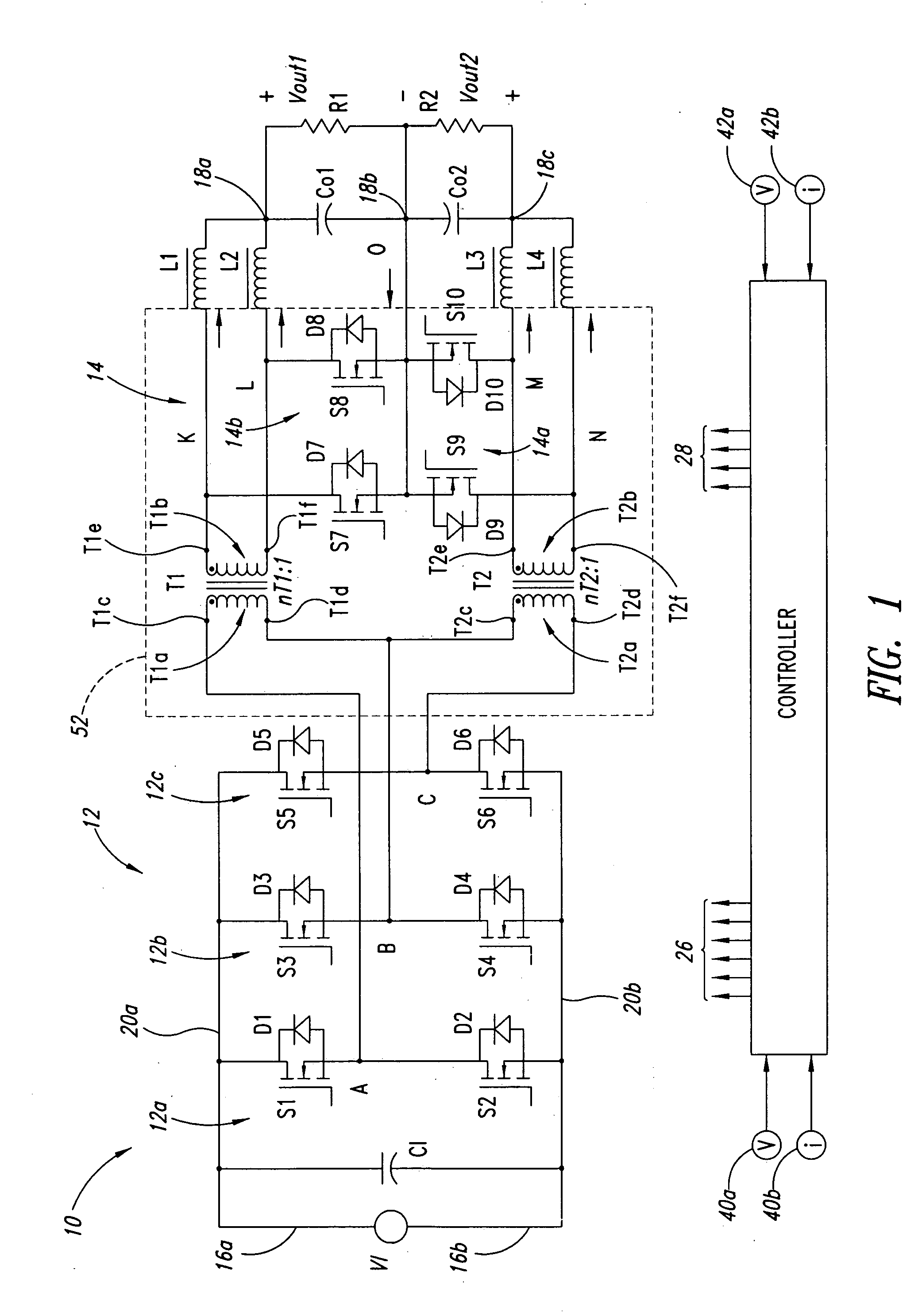
Interleaved power converter
ActiveUS7295448B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsAc-dc conversionPower capabilityFull bridge
A power converter architecture interleaves full bridge converters to alleviate thermal management problems in high current applications, and may, for example, double the output power capability while reducing parts count and costs. For example, one phase of a three phase inverter is shared between two transformers, which provide power to a rectifier such as a current doubler rectifier to provide two full bridge DC / DC converters with three rather than four high voltage inverter legs.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
Double salient-pole motor drive power tube fault diagnosis method
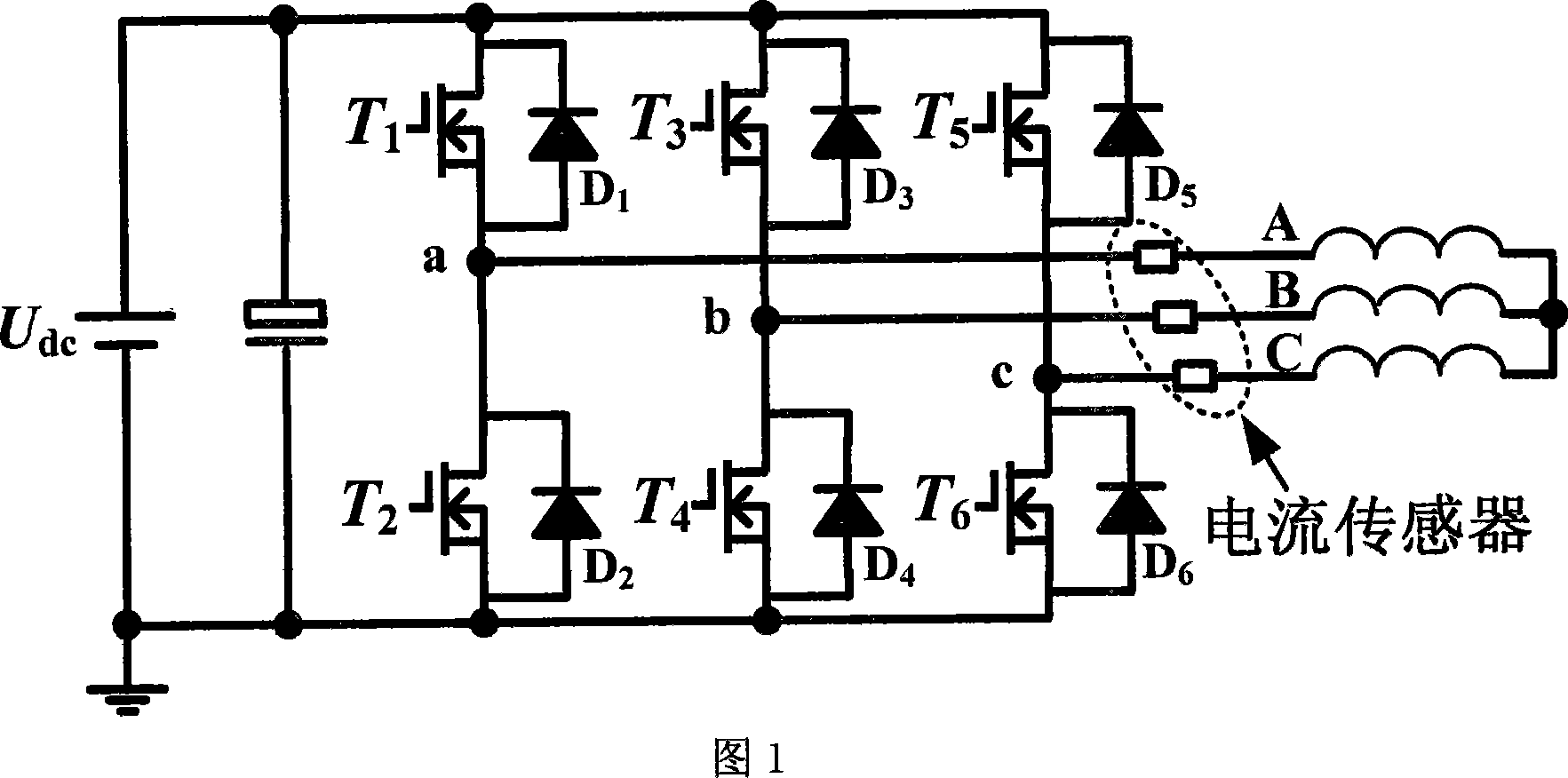
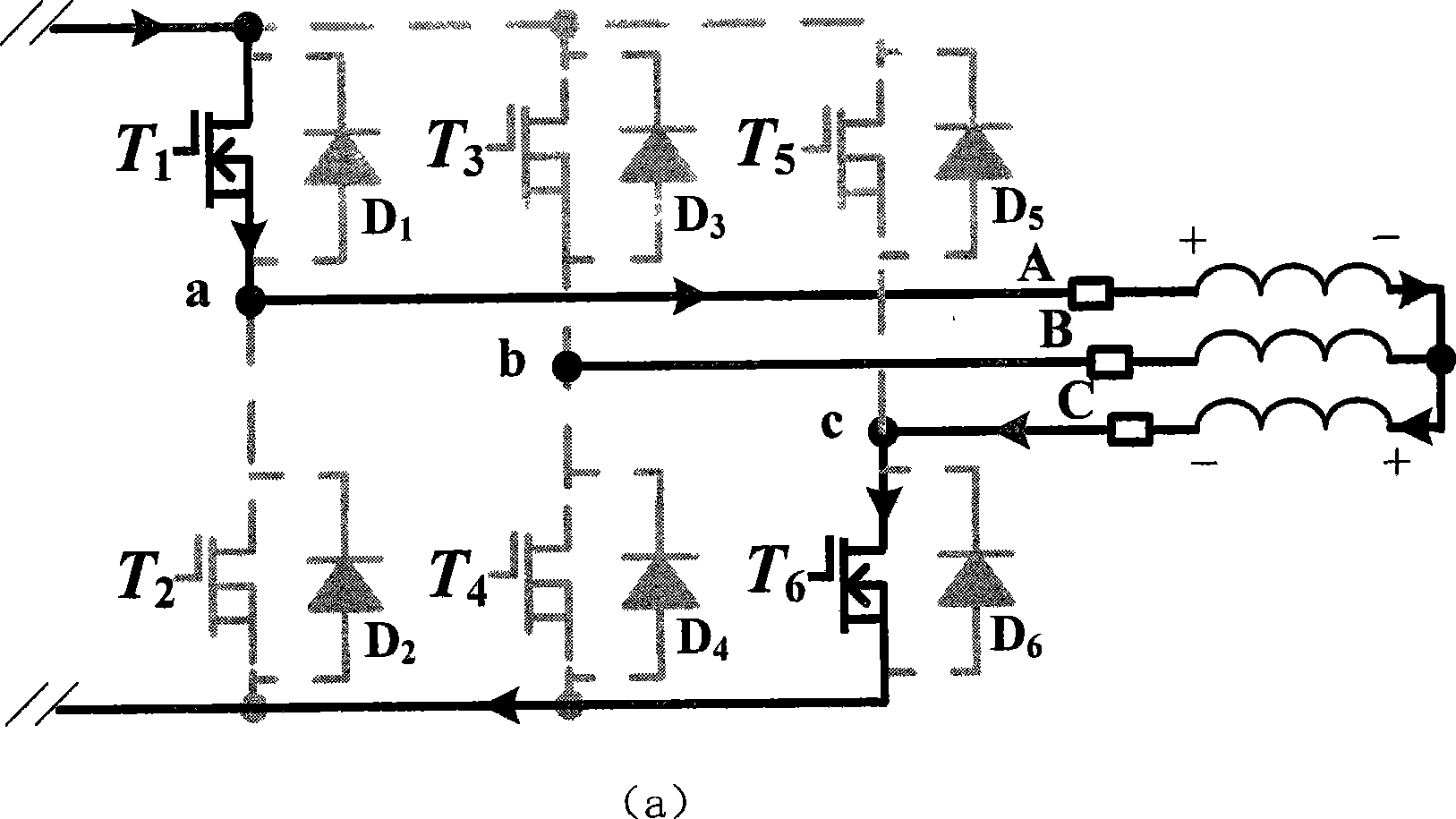
InactiveCN101078747AAvoid failureImprove reliabilityDynamo-electric machine testingCurrent sensorSystem failure
The invention relates to a diagnosis method for power transistor of doubly salient motor driver, belonging to the fault diagnosis method for power device in motor driving system. In the method three-phase current sensor is set on three-phase bridge arm; while three-phase current is measured the measurement for current signal of current reflowing is added; after current reflowing signal is treated digitally and driving signal of power transistor is combined on-line fault measurement and diagnosis for main power circuit are realized. The invention is provided with simple realization and good rapidity. Not only open fault of power transistor can be diagnosed quickly but also it can play a better protecting effect for bridge-arm direct phenomenon maybe generated by short circuit of power transistor. At the same time it provides a feasible method for fault diagnosis of motor driving system based on full-bridge converter.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Transformer-isolated switching converter
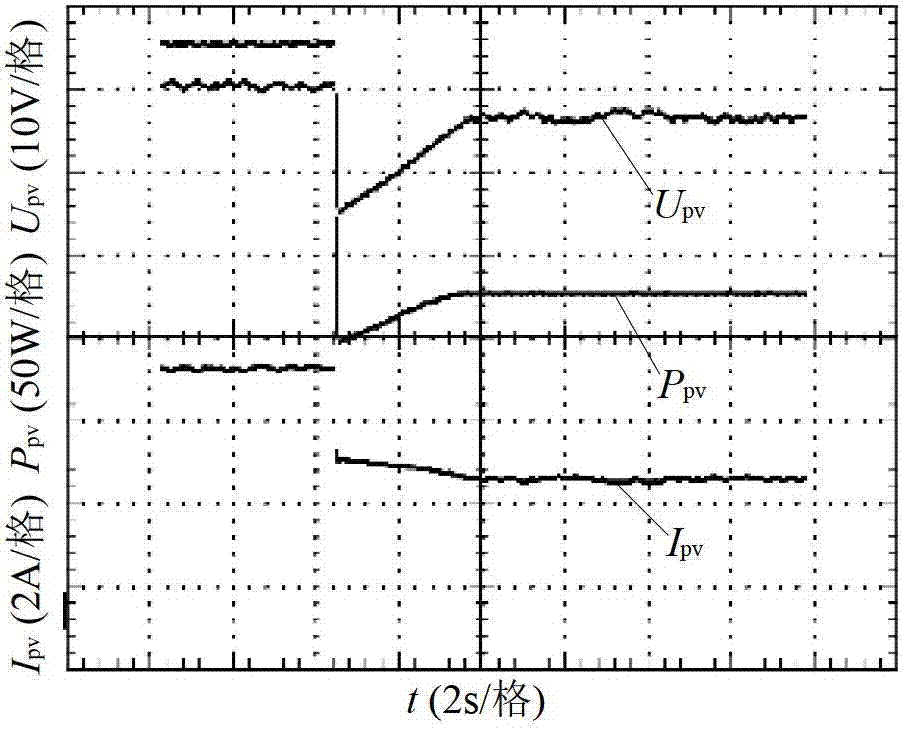
Exemplary systems and methods provide a transformer-isolated current-fed quadratic full-bridge converter topology. The optimal interfacing of a current source, such as a solar panel, can be implemented by using current-fed converters. The current-fed converter can operate within the whole range of a UI curve from short-circuit to open-circuit condition and its input voltage can be readily controlled. The quadratic behaviour between input and output in regard of a duty cycle allows large conversion ratios.
Owner:ABB OY
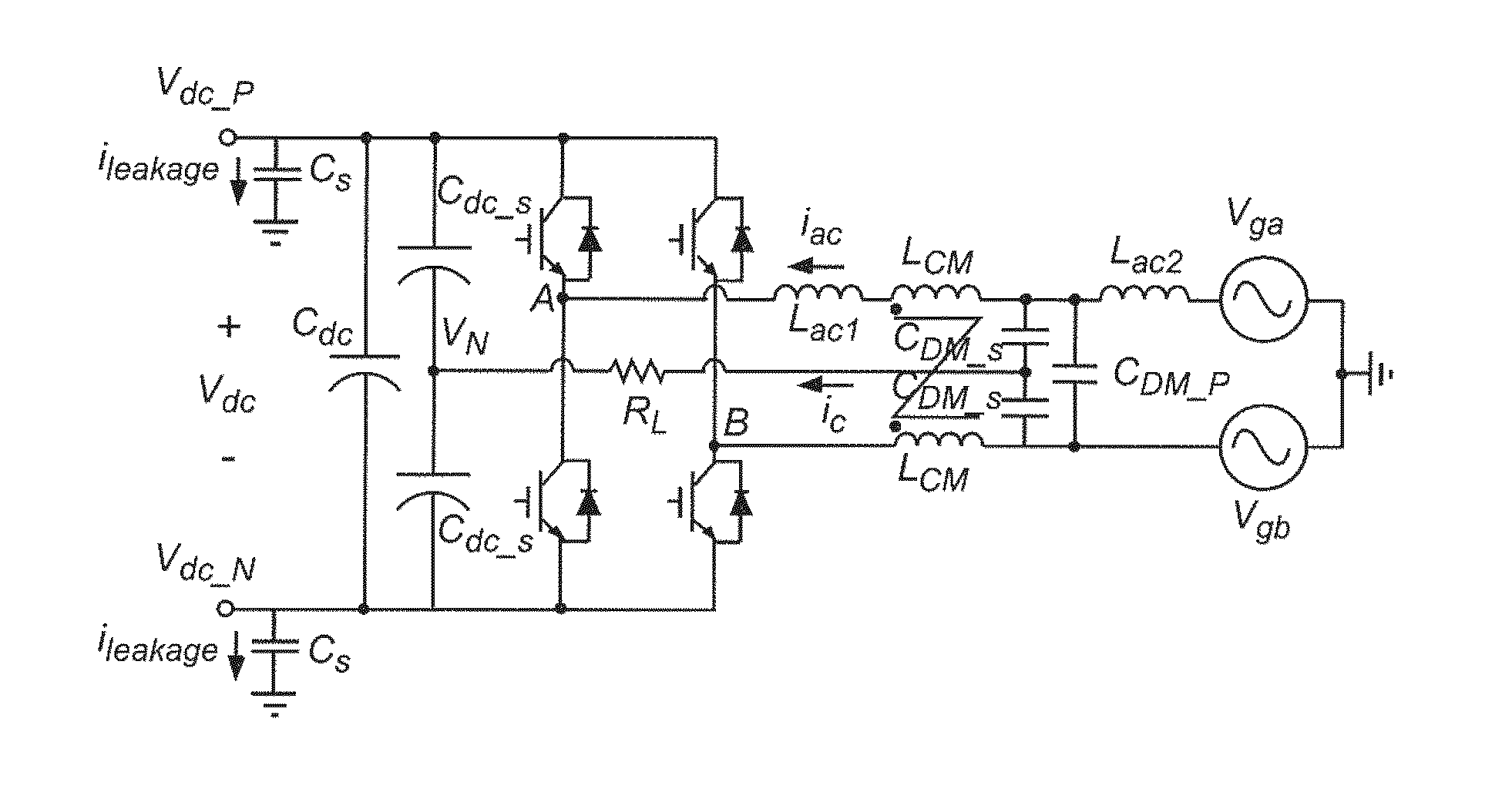
Dc-side leakage current reduction for single phase full-bridge power converter/inverter
ActiveUS20130235628A1Avoid it happening againReduce low frequency common mode noiseLine/current collector detailsAc-dc conversionFull bridgeSinusoidal modulation
Leakage current through stray or parasitic capacitance (which is particularly large in devices such as photovoltaic cell arrays and which are damaged by such leakage currents) due to common mode switching noise in a full bridge single phase power converter is reduced at high frequencies by magnetically coupling the two phase legs on the AC side of the power converter and connecting mid points of the AC and DC sides of the power converter and is reduced at low frequencies by use of a feedback arrangement that modifies sinusoidal modulation of the switches of the full bridge converter to function as an active filter. The magnetic coupling for the two phase legs is designed in a simple manner to avoid saturation based on volt-second considerations.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
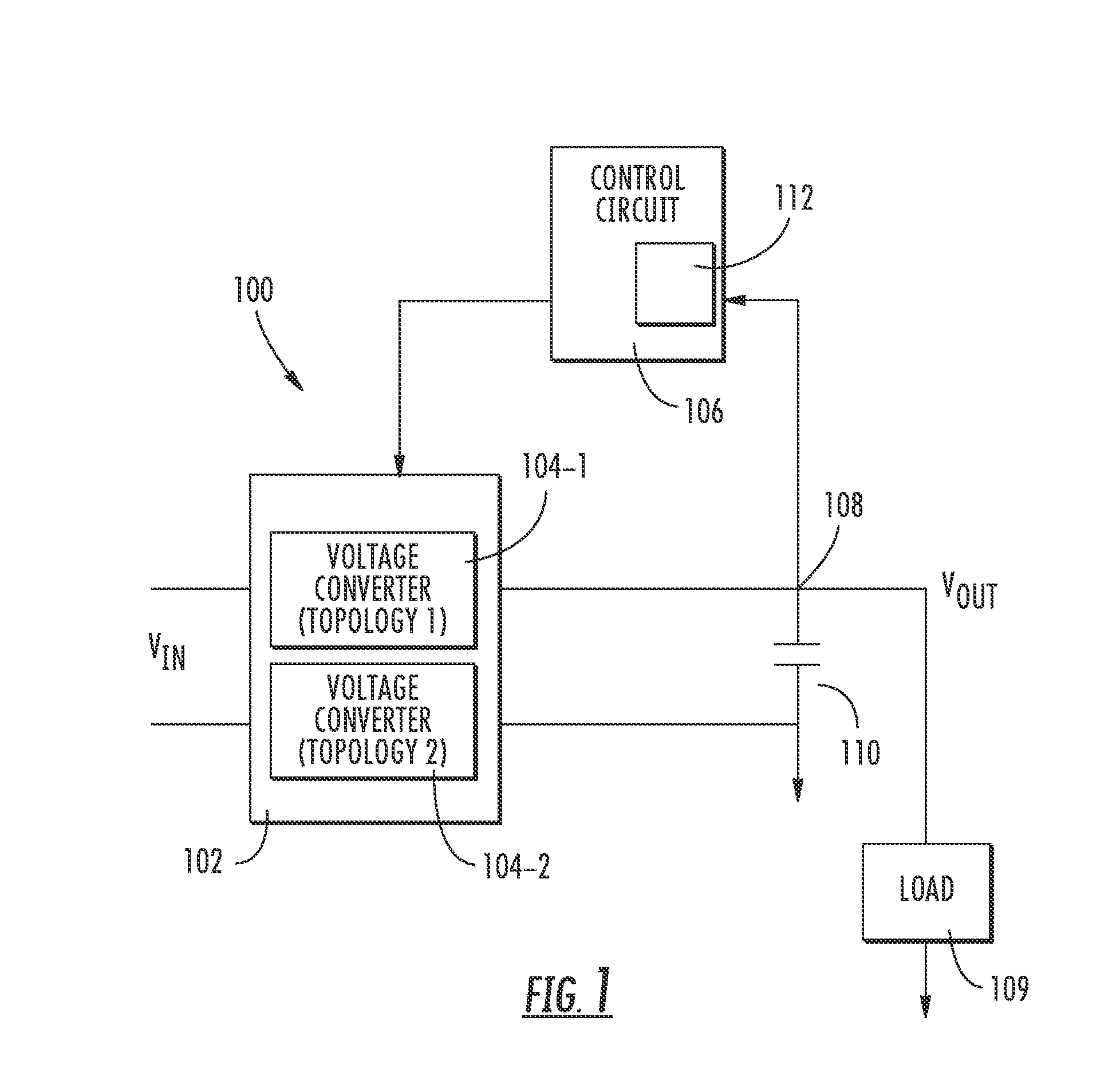
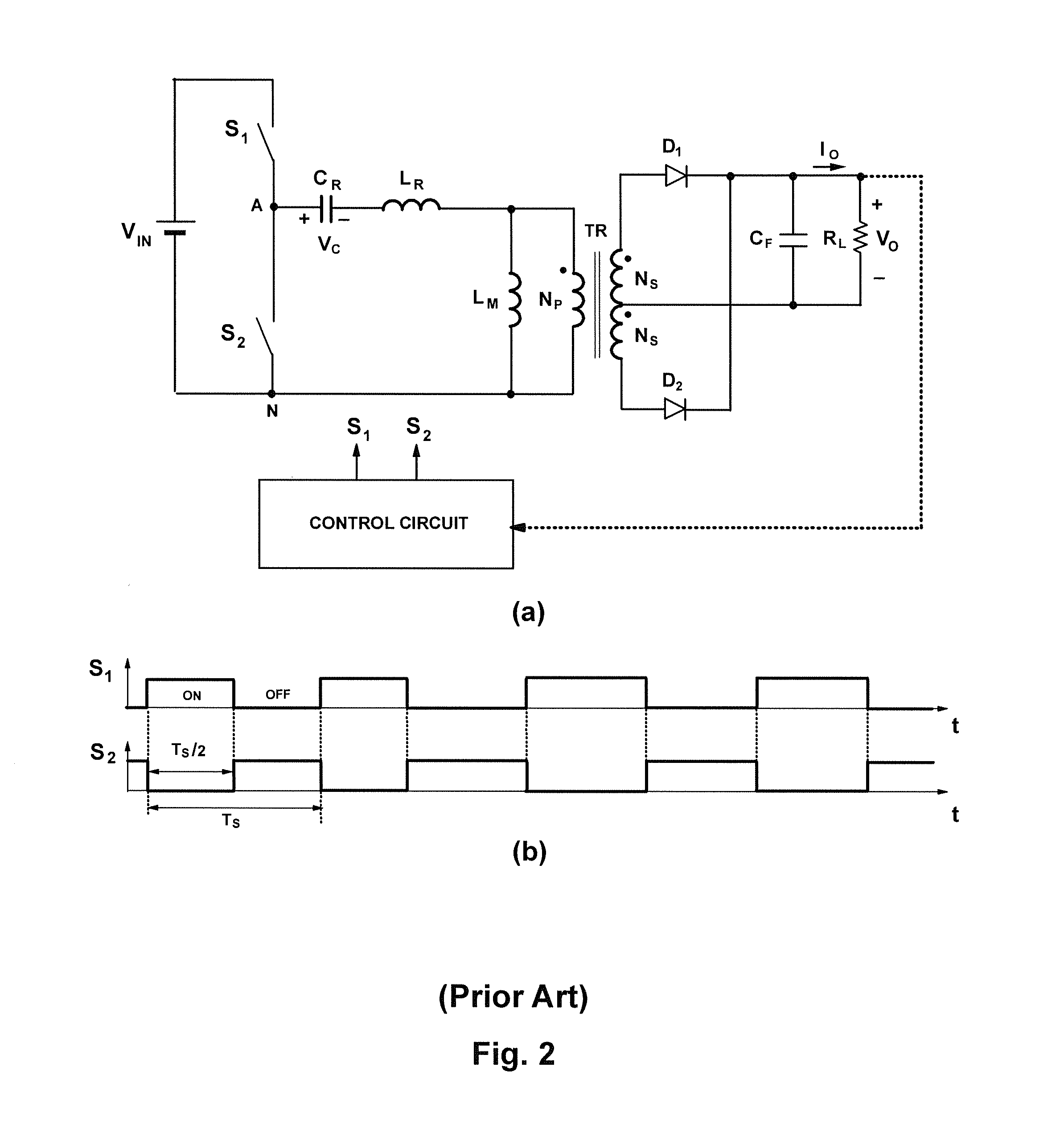
Dynamic converter topology
Methods and apparatus of dynamic topology power converters are provided. One method includes monitoring at least one variable of the power converter and based on the at least one monitored variable, using a converter topology selected between at least a full-bridge converter topology and a half-bridge converter topology to achieve an efficient operation at a then current operational load.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
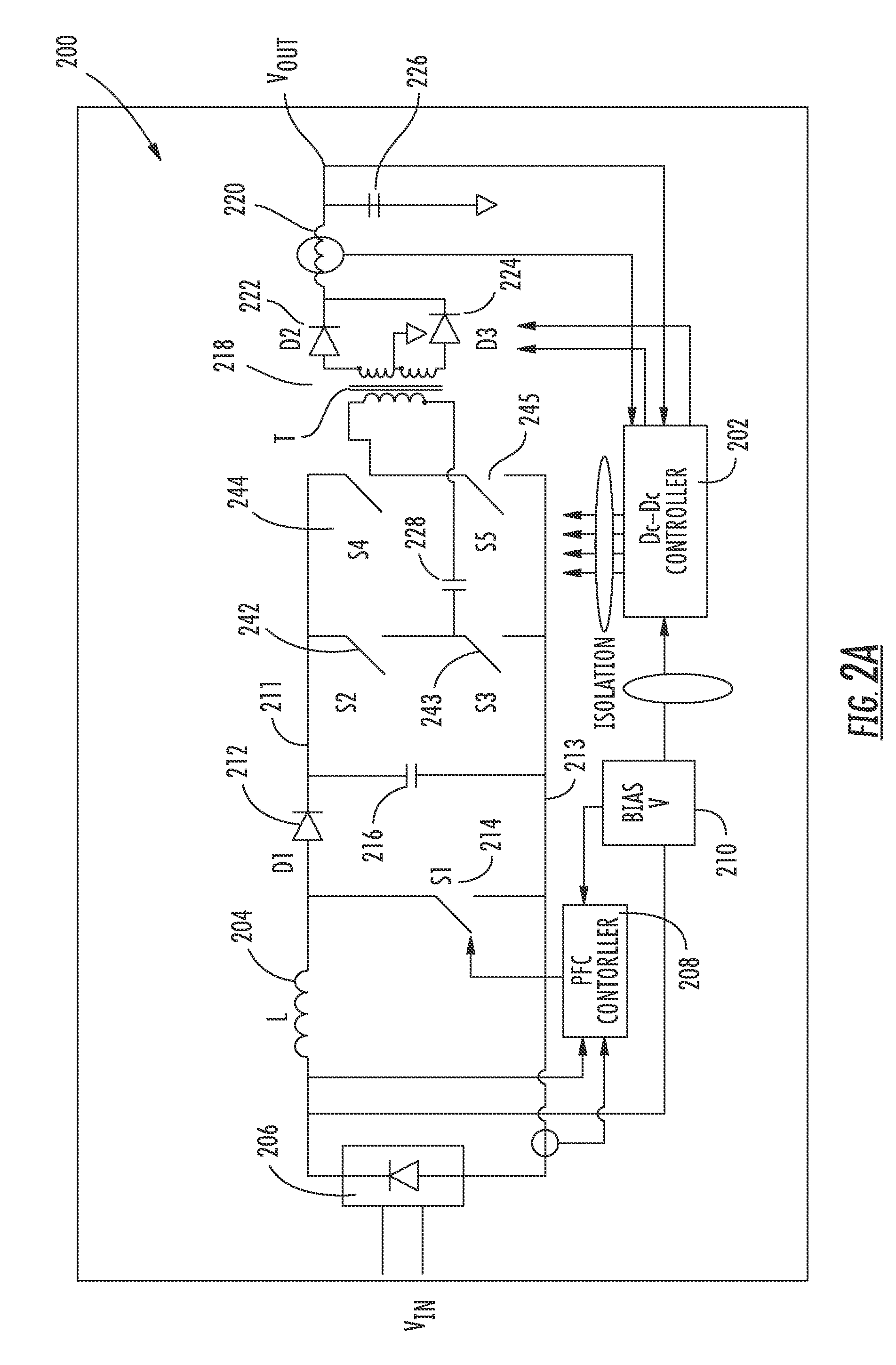
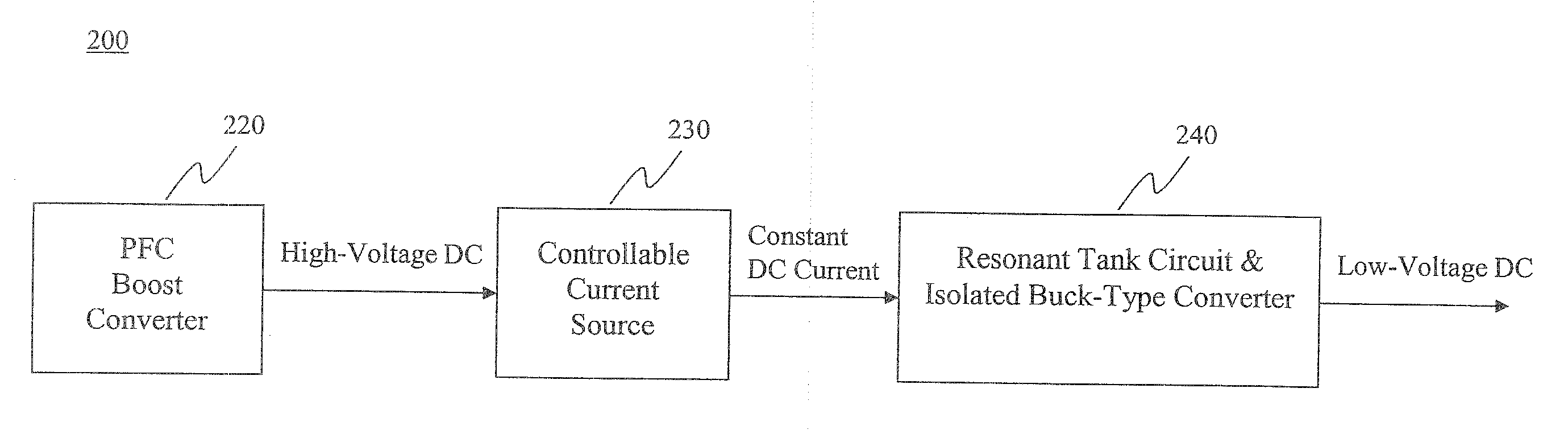
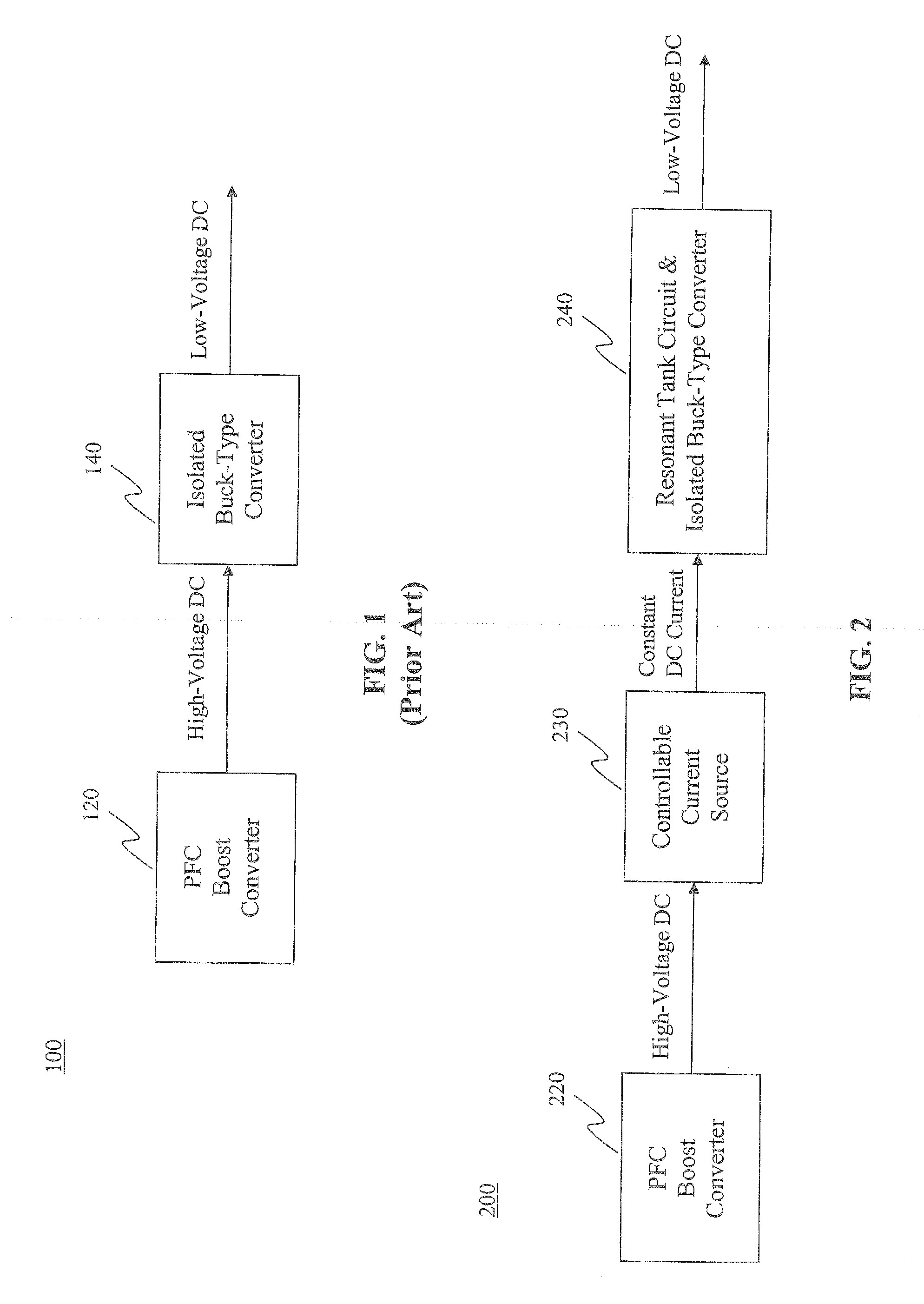
Two stage resonant converter
ActiveUS20110261590A1Efficient power electronics conversionEnergy industrySoft switchingResonant converter
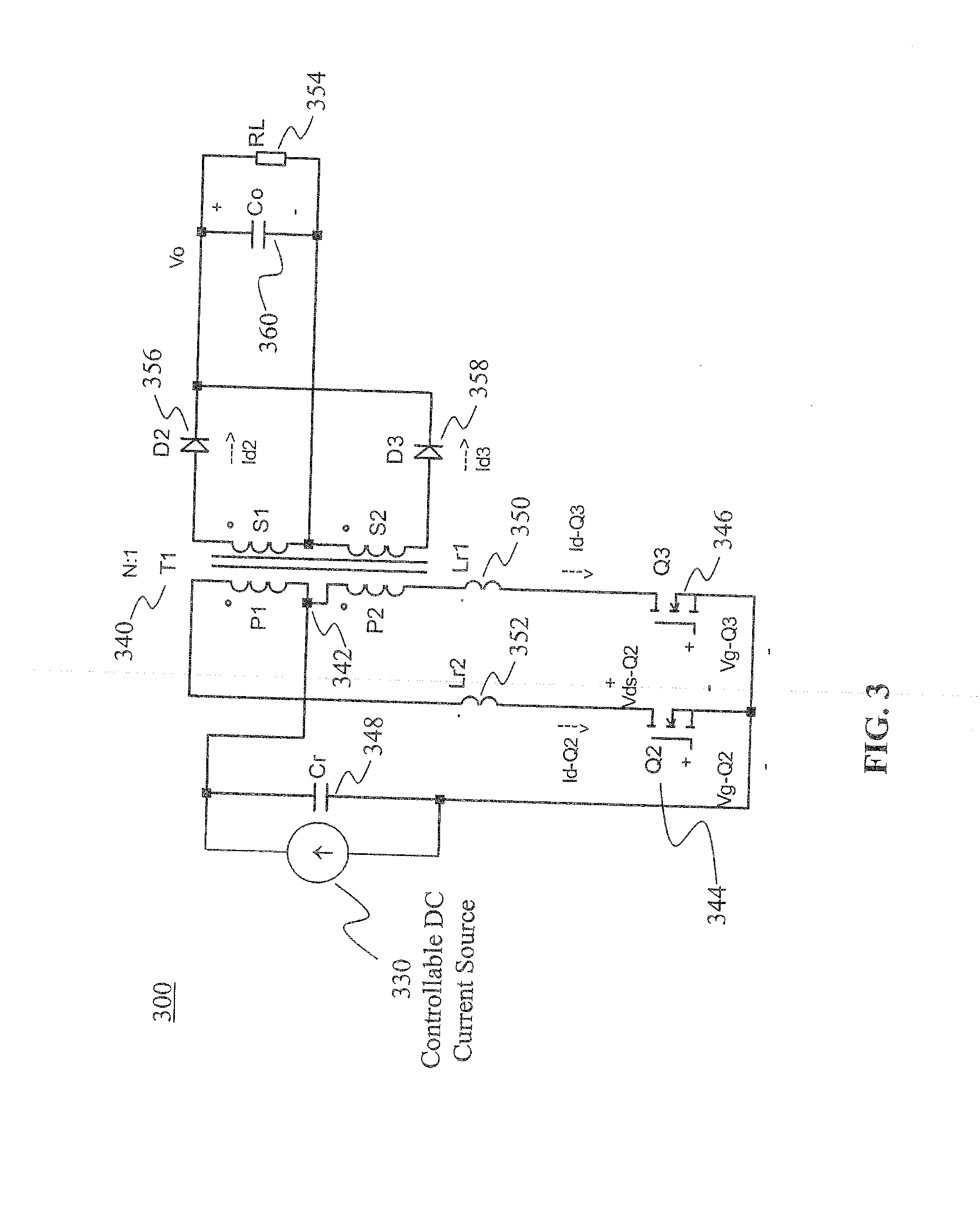
A resonant converter comprising: a controllable current source; a resonant tank circuit coupled to the current source; and an isolated buck-type converter coupled to the resonant tank circuit, the isolated buck-type converter having an output, wherein the resonant tank circuit enables switches in the isolated buck-type converter to switch under soft-switching conditions. In some embodiments, the controllable current source is a switch-mode-type current source. In some embodiments, the isolated buck-type converter comprises a half-bridge converter. In some embodiments, the isolated buck-type converter comprises a full-bridge converter. In some embodiments, the isolated buck-type converter comprises a push-pull converter.
Owner:FLEXTRONICS AP LLC
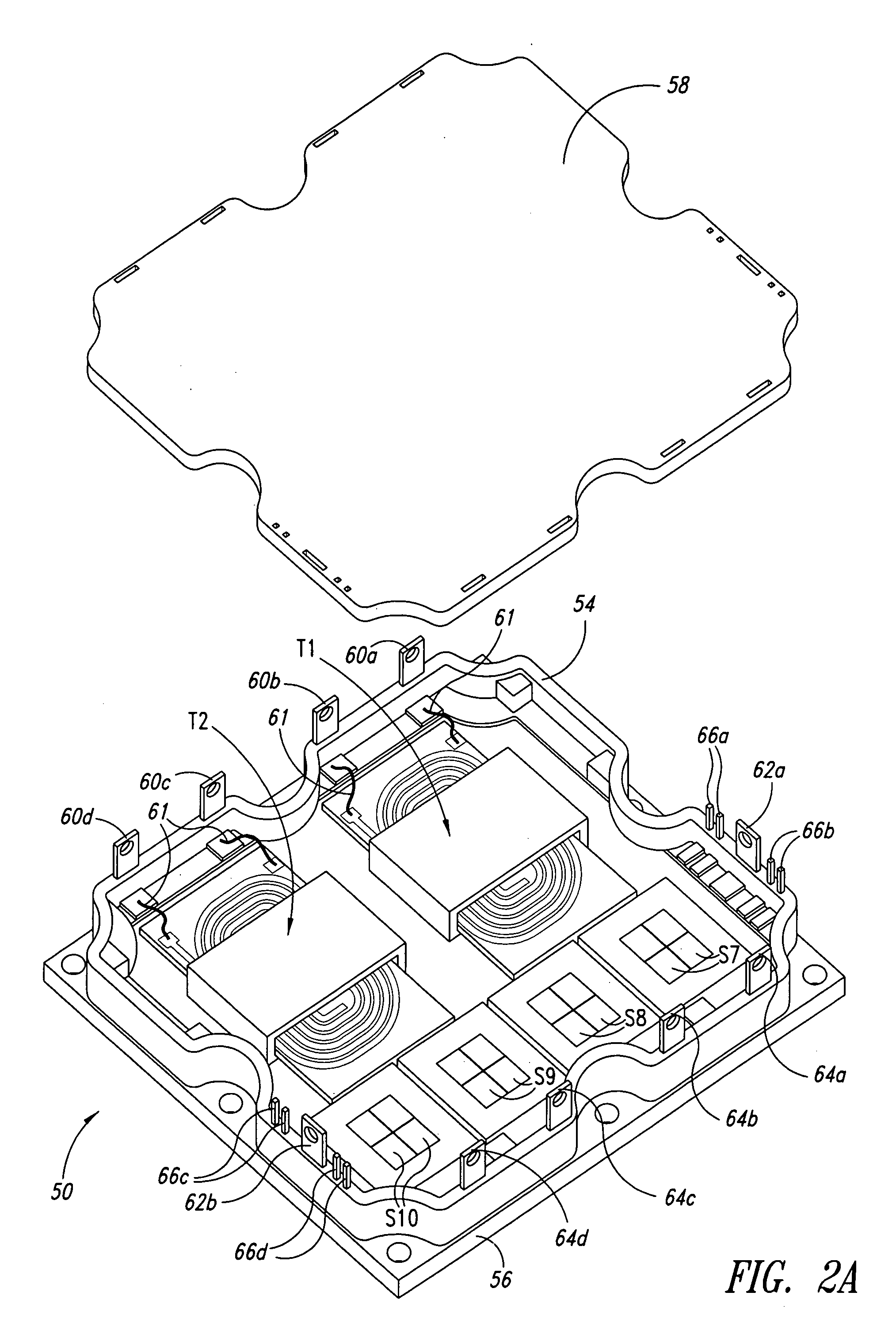
Soft switched zero voltage transition full bridge converter
InactiveUS7136294B2Reduce electromagnetic interferenceIncrease working frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionCapacitive voltage dividerConductor Coil
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
DC-DC converter with improved dynamic response
ActiveUS8054058B2Low implementation costNo longer be achievableMultiple-port networksDc network circuit arrangementsFull bridgePush pull
The invention relates to a control method and a controller for a DC-DC converter, such as a synchronous Buck converter, which exploits the principle of capacitor charge balance to allow the converter to recover from a positive and / or negative load current step in the shortest achievable time, with the lowest possible voltage undershoot / overshoot. The control method may be implemented by either an analog or a digital circuit. The controller may be integrated with existing controller schemes (such as voltage-mode controllers) to provide superior dynamic performance during large-signal transient conditions while providing stable operation during steady state conditions. The invention also relates to a method and a modification of a DC-DC converter topology that comprises connecting a controlled current source between an input terminal and an output terminal of the DC-DC converter; detecting a load current step to a new load current; modifying a duty cycle of the DC-DC converter; and modifying current through a parallel output capacitor of the DC-DC converter by controlling current of the current source. The methods and circuits provided herein are applicable to Buck converters and Buck-derived converters such as forward, push-pull, half-bridge, and full-bridge converters.
Owner:GANPOWER SEMICON FOSHAN LTD
DC power converter and method of operation for continuous conduction mode
InactiveUS20050195622A1Reduce demandImprove power densityAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionStored energyDc dc converter
A current-fed DC-DC converter has a topology that improves converter performance and operates an input inductor in continuous conduction mode. The configuration and operation of the converter produces reduced requirements for circuit component ratings and leads to faster transient response time than conventional current-fed DC-DC converters. The converter can operate as an apparent current-fed full bridge converter in one stage, and an apparent current-fed half bridge converter in another stage. The input inductor is configured and operated to release stored energy to the load in conjunction with other energy storage components to provide a continuous output current that significantly reduces output voltage ripple, leading to reduced rating requirements and output components. The converter topology permits a portion of the switching stage to operate with no deadtime to further improve circuit responsiveness and efficiency.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
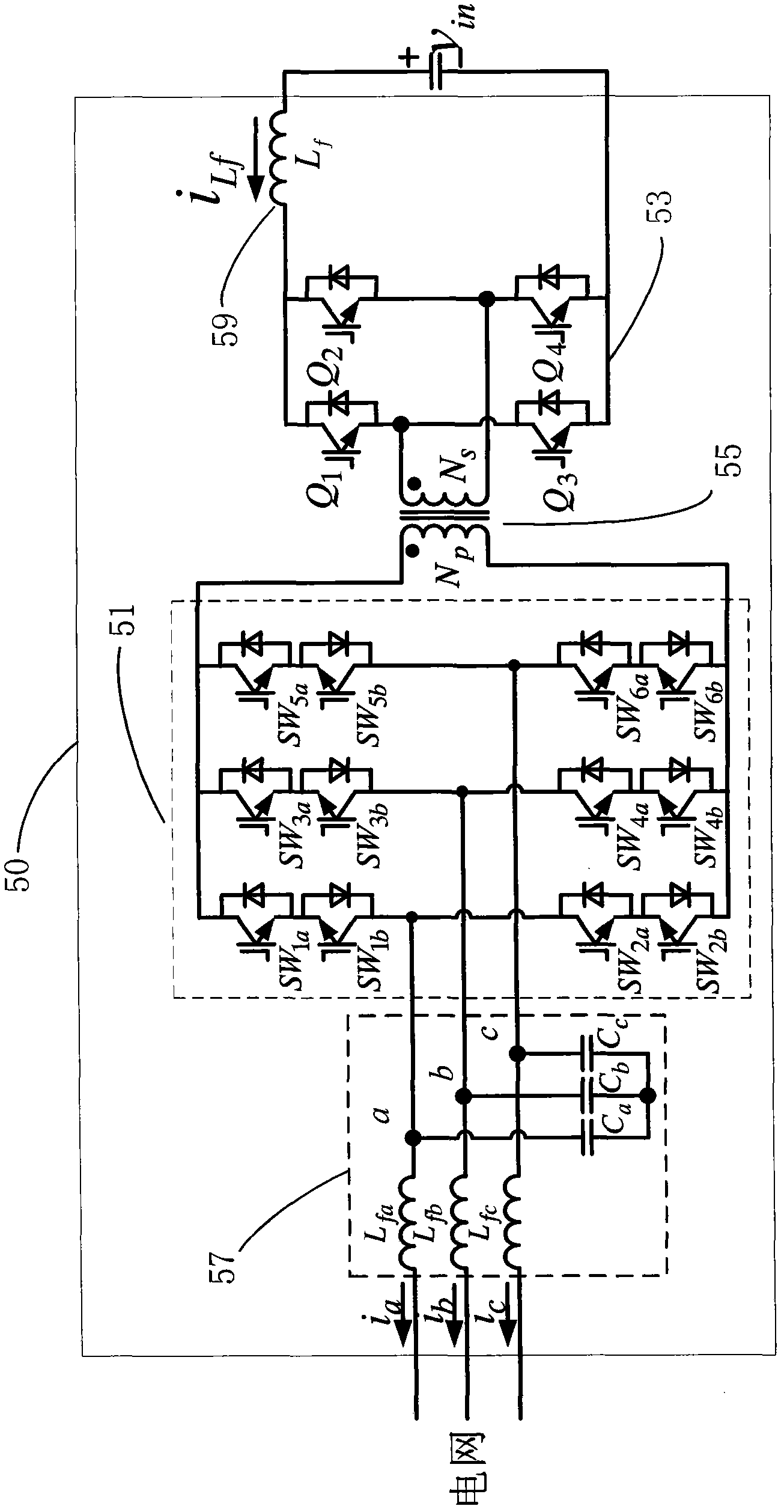
High-frequency isolated three-phase cycloconverter type two-way converter and control method thereof
InactiveCN102075109AImprove efficiencyCompact structureConversion with reversalCycloconverterElectron
The invention provides a high-frequency isolated three-phase cycloconverter type two-way converter and a control method thereof, which belongs to the three-phase high-frequency isolated converter in the field of power electronics and is suitable for charging and discharging a storage battery pack, a supercapcitor set and other energy storage devices. A main circuit is in a structure comprising an input filter, a three-phase cycloconverter, a high-frequency transformer, a full-bridge converter and an output direct current inductor, wherein a switch of the cycloconverter is in time-division drive to ensure the one-way flowing of the power and further realize the soft current conversion. The switching of two modes of rectification and inversion can be realized by changing the power flowing direction of the cycloconverter; the three-phase cycloconverter is modulated by digitalized alternating current space vector; and the alternating current adopts a control method of mixing a d-p decoupling, the proportional-integral (PI) and the repetition (RP). The two-way converter has the advantages of high power density, high efficiency, wide adjusting range of direct current side voltage and electrical isolation for input and output; and the input of unit power factors can be realized and the current harmonics can be effectively inhibited.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Modulation method with high efficiency in dual-active full-bridge converter full power range
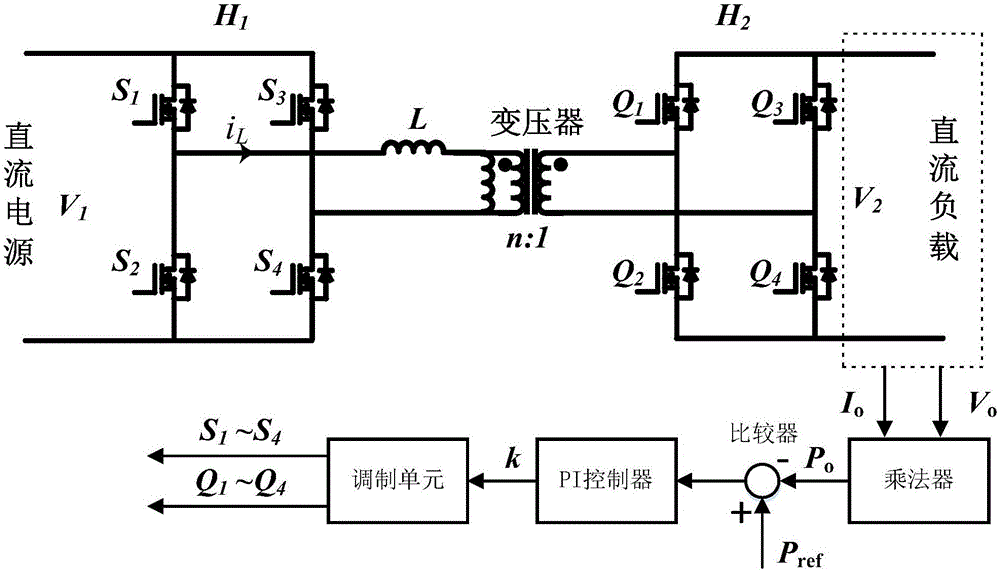
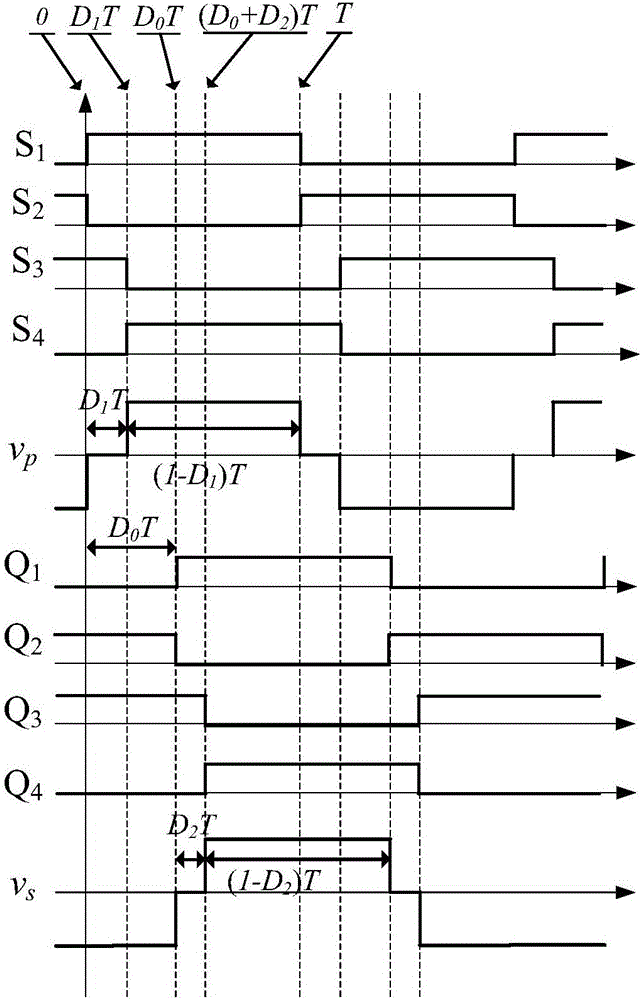
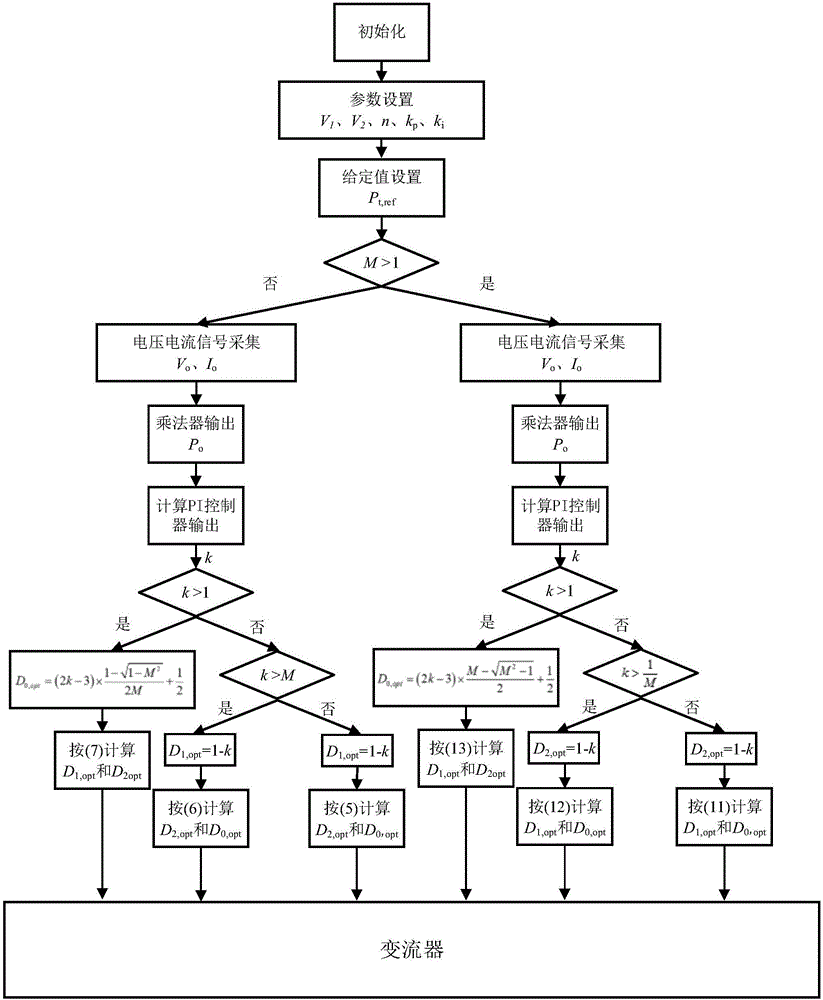
ActiveCN106685232AReduce current distortionImprove efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationPhase shiftedFull bridge
A modulation method with high efficiency in a dual-active full-bridge converter full power range is a modulation method through adoption of three controlled quantities consisting of a primary side full-bridge internal phase-shift ratio, a secondary full-bridge internal phase-shift ratio and a phase-shift ratio between primary secondary side of the dual-active full-bridge converter to allow the dual-active full-bridge converter in the full power range to reduce the distortion currents to the lowest in the work of the convertor so as to reduce the stress of a switch device in the convertor and realize the improvement of the whole efficiency of the convertor. The modulation method with the high efficiency in dual-active full-bridge converter full power range provides an analytical expression among three control quantities, and is simple in computing process and easy to realize.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Bidirectional full-bridge converter-based wide-output voltage range control method for soft switching
InactiveCN105634286AEasy to realize wide range adjustmentReduced loop currentEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionSoft switchingEngineering
The invention discloses a bidirectional full-bridge converter-based wide-output voltage range control method for soft switching. The method comprises the following steps: setting working frequencies of all switch tubes of a bidirectional full-bridge converter to be the same, and setting dead time of upper and lower switch tubes of a same bridge arm; determining a power phase-shift angle and a modulating phase-shift angle to be adjustable variables; obtaining conditions of a primary bridge of the bidirectional full-bridge converter for achieving soft switching according to the power phase-shift angle and current constraint conditions of an half cycle, and determining the range of the power phase-shift angle; and determining the relationship between the power phase-shift angle and the modulating phase-shift angle under the maximum power condition and changing a synchronous timing sequence according to the obtained calculation result. The advantages of achieving soft switching within a full-power range and easily achieving wide-range adjustment of the output voltage by the full-bridge converter can be achieved; and zero-voltage switching of all power tubes on a primary side and a secondary side is achieved within the wide-voltage output range from an idle load to a full load.
Owner:STATE GRID INTELLIGENCE TECH CO LTD
Power converter and method for controlling the same
ActiveUS20140119060A1Complex and difficult designImprove conversion efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationFull bridgeEngineering
A power converter includes a full-bridge converter circuit and a regulation circuit. The full-bridge converter circuit includes a full-bridge circuit having a first and a second input terminals and a first and a second output terminals. The regulation circuit is bridged across the first and the second input terminals of the full-bridge circuit and connected to the first output terminal of the full-bridge circuit. The regulation circuit is configured for operatively regulating an output voltage across the first and the second output terminals of the full-bridge circuit by cooperating with the full-bridge converter circuit, such that the output voltage across the first and the second output terminals of the full-bridge circuit has more than three voltage levels. A method for controlling a power converter is also disclosed herein.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
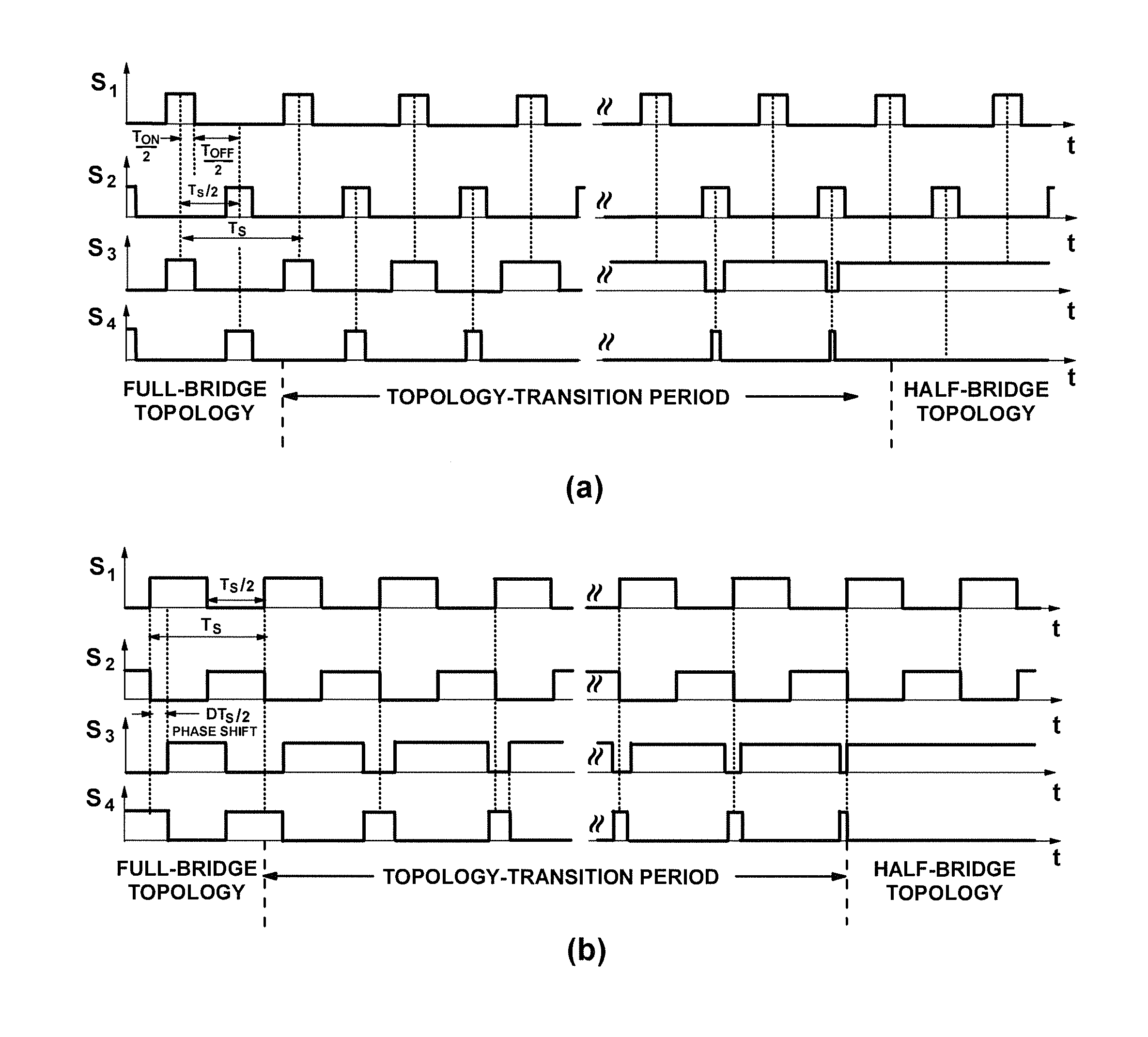
Power converters for wide input or output voltage range and control methods thereof
ActiveUS20150078036A1Improve efficiencyWide inputEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionFull bridgeControl signal
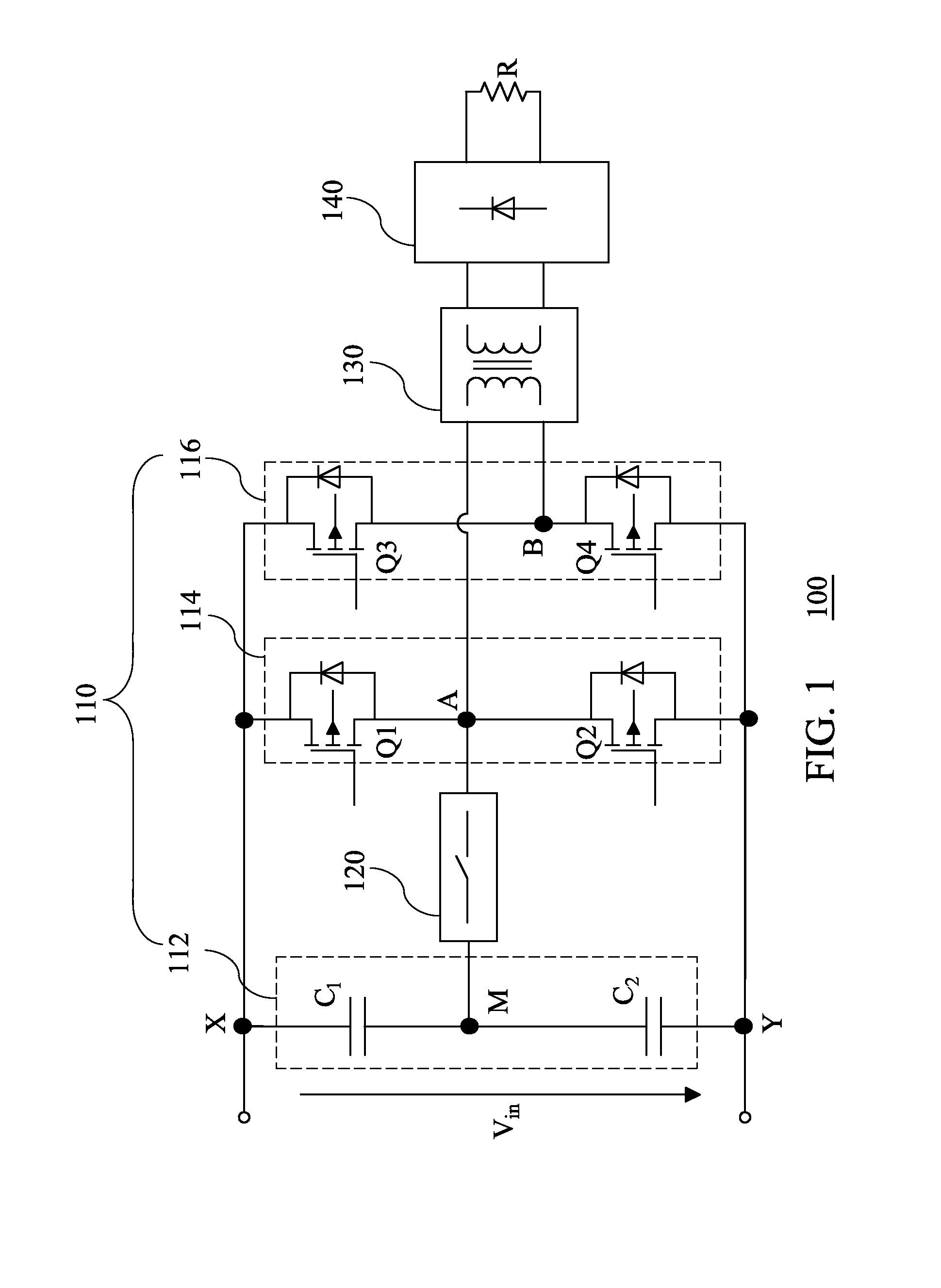
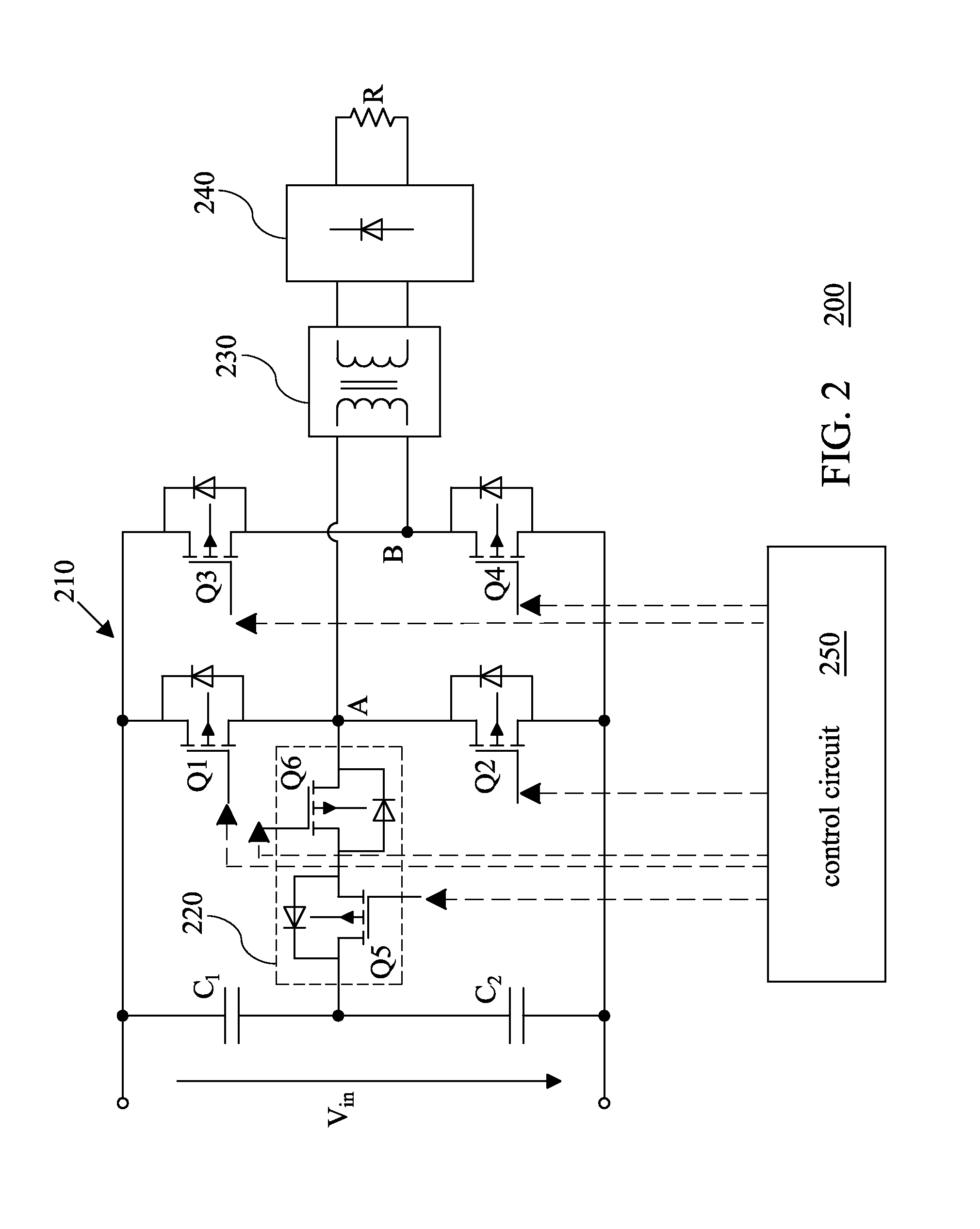
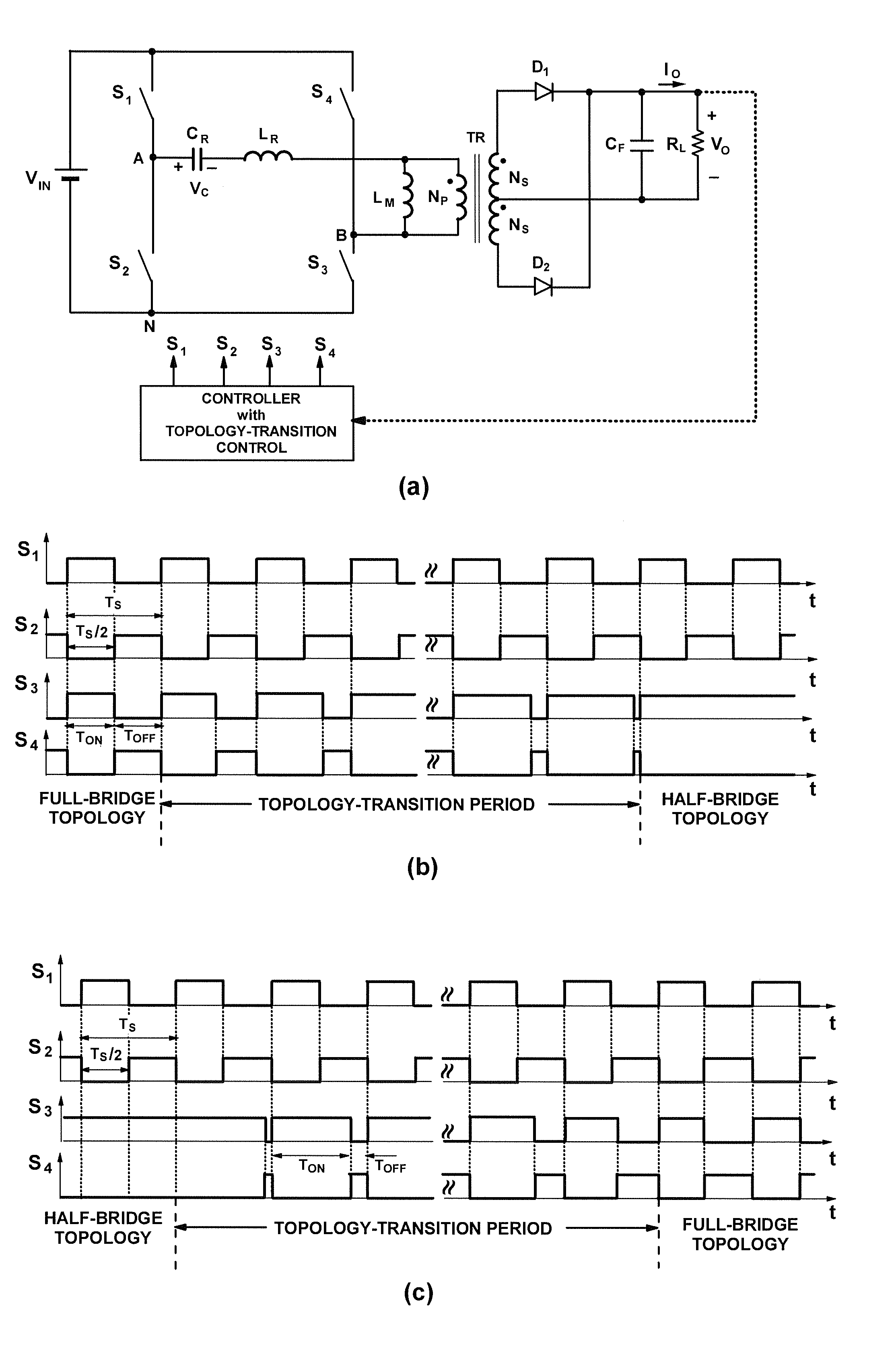
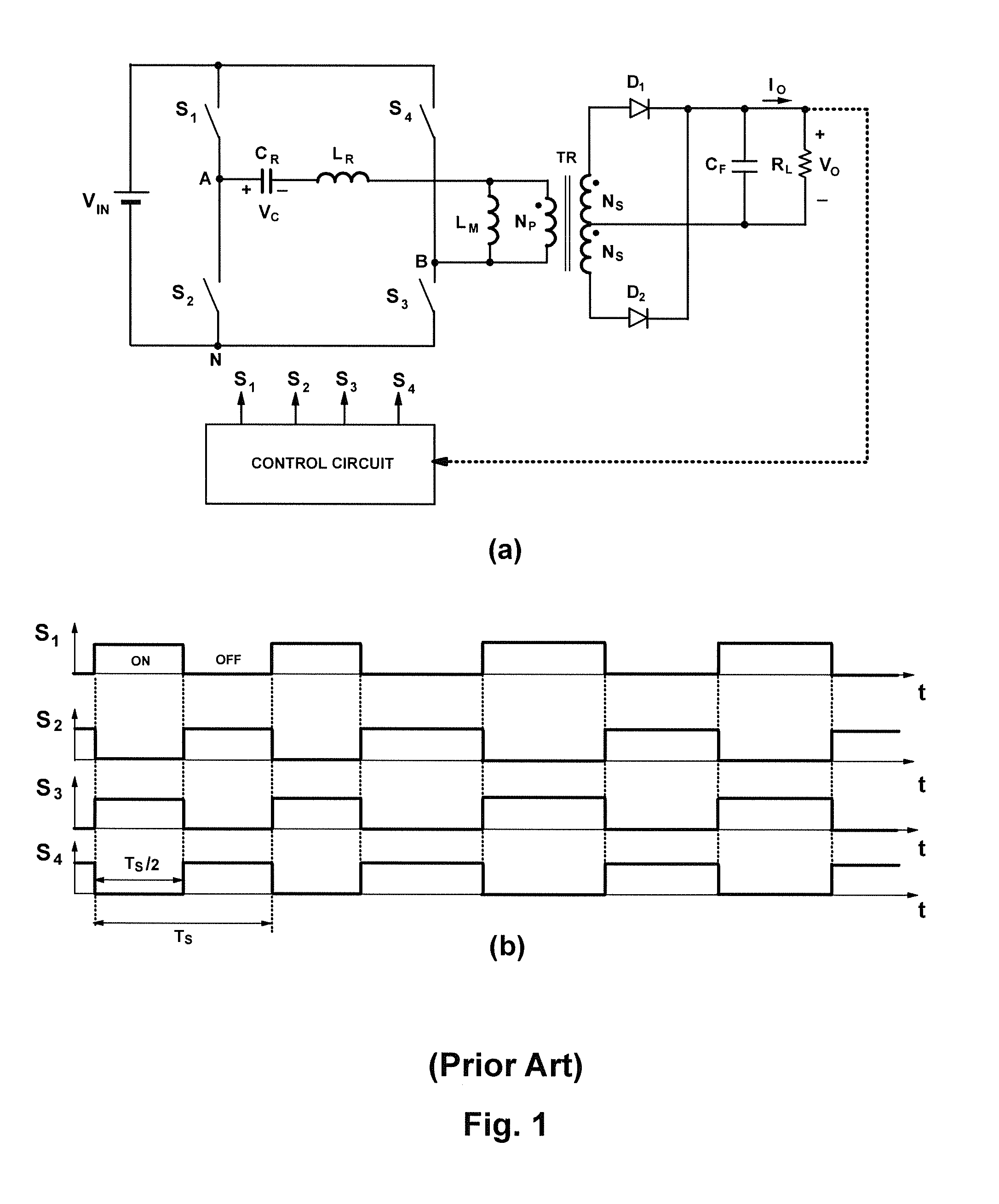
A power converter topology is adapted for efficiency according to input voltage, output voltage or output current conditions. Topology adaptation is achieved by control responsive to the input and output operating conditions, or to one or more external control signals. Transition between any two topologies is implemented by pulse width modulation in the two switches in one of two bridge legs of a full bridge converter. When transitioning from full-bridge to half-bridge topology, the duty ratio of one switch in one leg of the full bridge is increased, while simultaneously the duty ratio of the other switch in the same leg is reduced until one switch is continuously on, while the other switch is continuously off. The transition from the half-bridge to the full-bridge topology is accomplished by modulating the same switches such that, at the end of the transition, both switches operate with substantially the same duty cycle.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
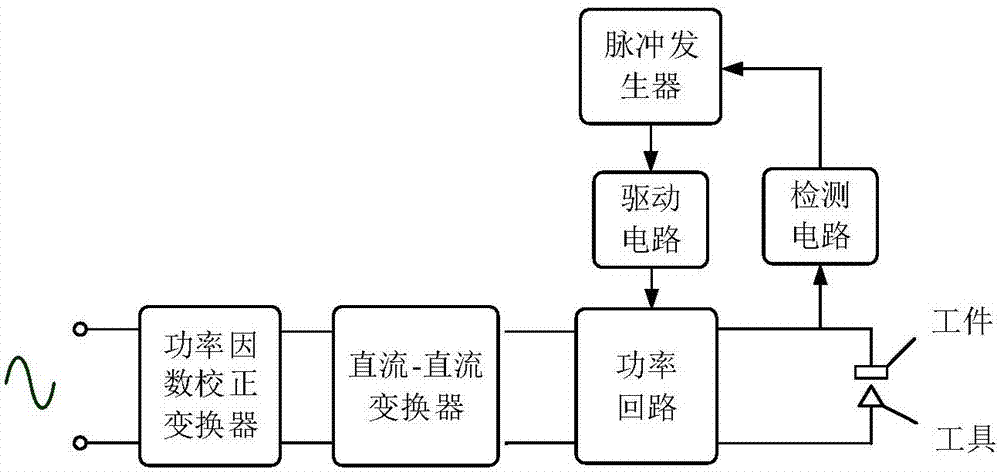
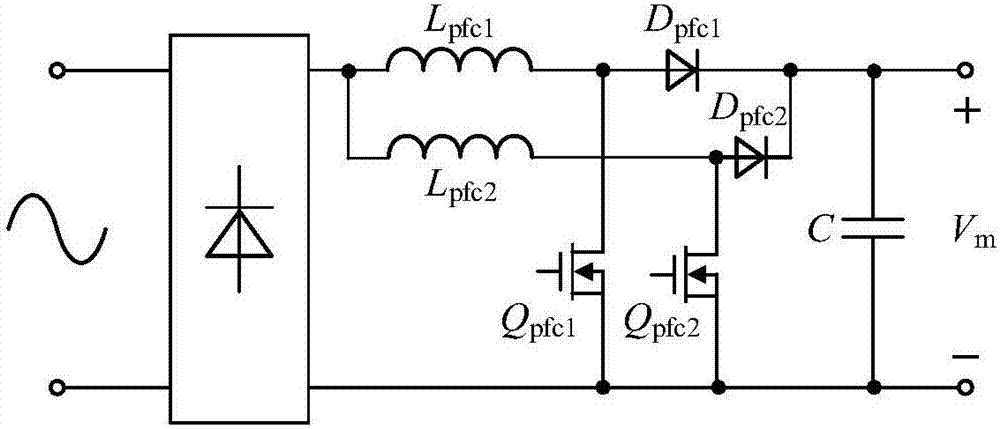
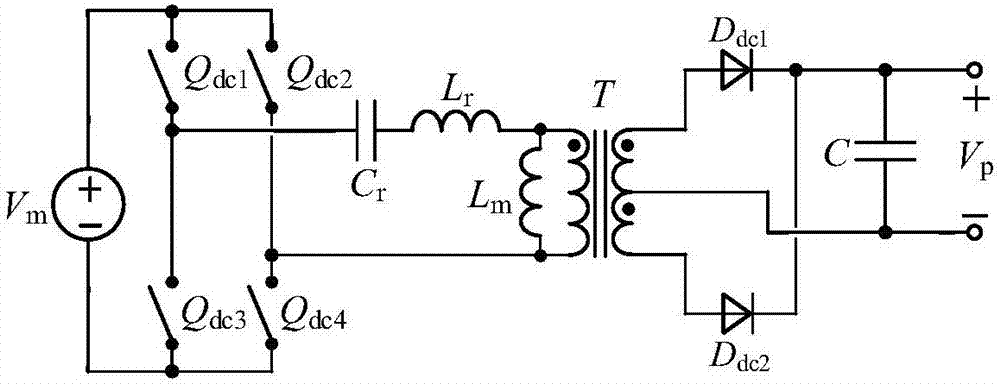
Micro electrical discharge pulse power source and segmental control method based on micro electrical discharge pulse power source
ActiveCN107276405ASimple topologyReduce volumeDc-dc conversionElectric circuitsDriver circuitDc dc converter
The invention discloses a micro electrical discharge pulse power source. The micro electrical discharge pulse power source comprises a power factor correction converter, a DC-DC converter, a power loop, a driving circuit, a pulse generator and a detection circuit, wherein the power loop comprises 6 switch tubes Qp, Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4 and Qoff and one inductor Llimit, the four switch tubes Q1-Q4 are connected in a bridge structure, the switch tube Qp is connected with an output side of the DC-DC converter and an input side of a full-bridge converter, after the switch tube Qoff is in parallel connection with a gap, one end of the switch tube Qoff is connected with a center point of a bridge arm through the inductor Llimit, and the other end is directly connected with a center point of another bridge arm. The invention further comprises a segmental control method based on the micro electrical discharge pulse power source. The micro electrical discharge pulse power source is advantaged in that only one power loop is comprised, the structure is simple, the volume is small, switching of voltage control and current control is carried out in a set of power loop through the corresponding segmental control method, voltage control and current control are mutually independent, and fast switching and precise and stable control can be realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Power converters for wide input or output voltage range and control methods thereof
ActiveUS9263960B2Improve efficiencyWide inputEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionFull bridgeControl signal
A power converter topology is adapted for efficiency according to input voltage, output voltage or output current conditions. Topology adaptation is achieved by control responsive to the input and output operating conditions, or to one or more external control signals. Transition between any two topologies is implemented by pulse width modulation in the two switches in one of two bridge legs of a full bridge converter. When transitioning from full-bridge to half-bridge topology, the duty ratio of one switch in one leg of the full bridge is increased, while simultaneously the duty ratio of the other switch in the same leg is reduced until one switch is continuously on, while the other switch is continuously off. The transition from the half-bridge to the full-bridge topology is accomplished by modulating the same switches such that, at the end of the transition, both switches operate with substantially the same duty cycle.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
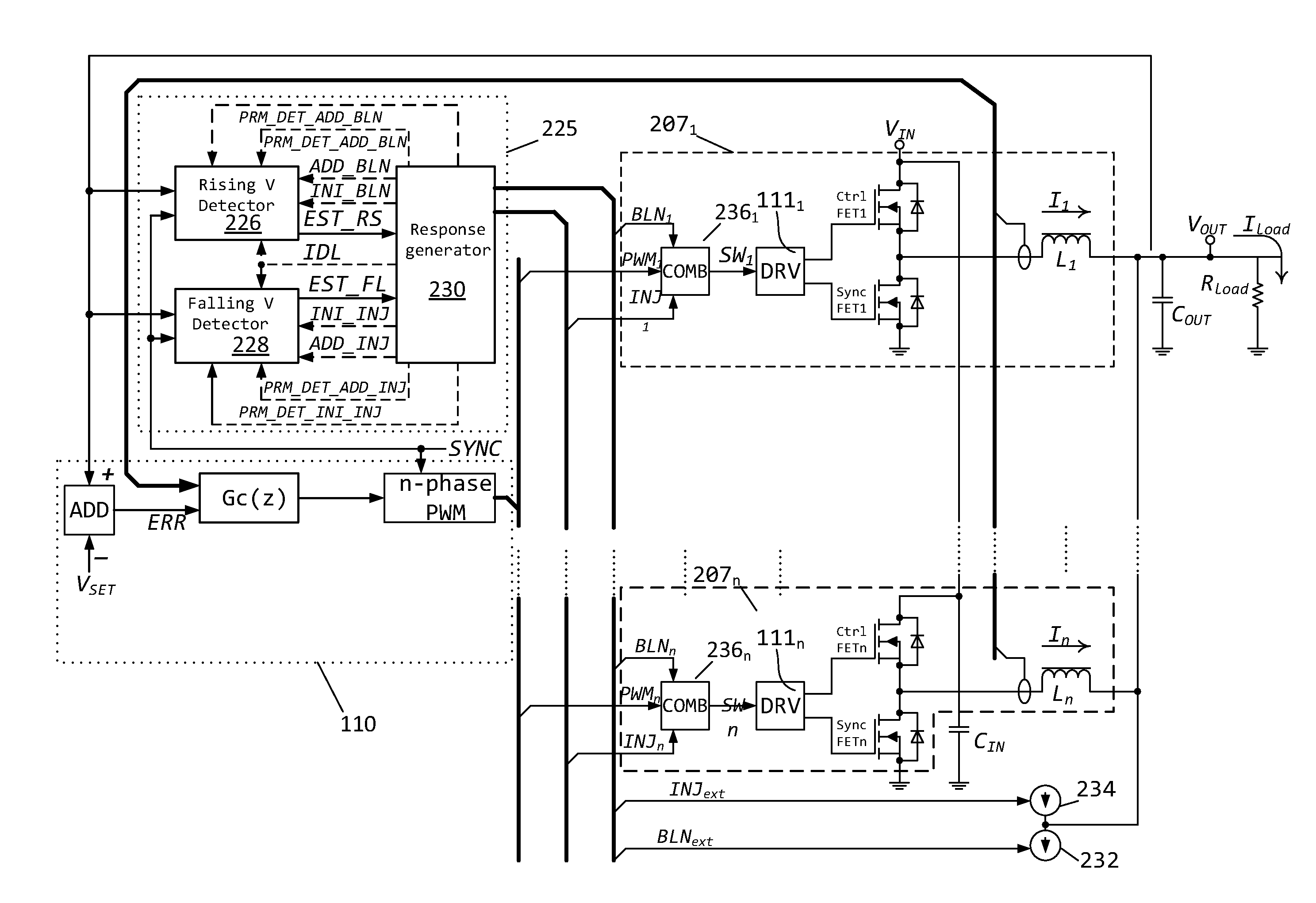
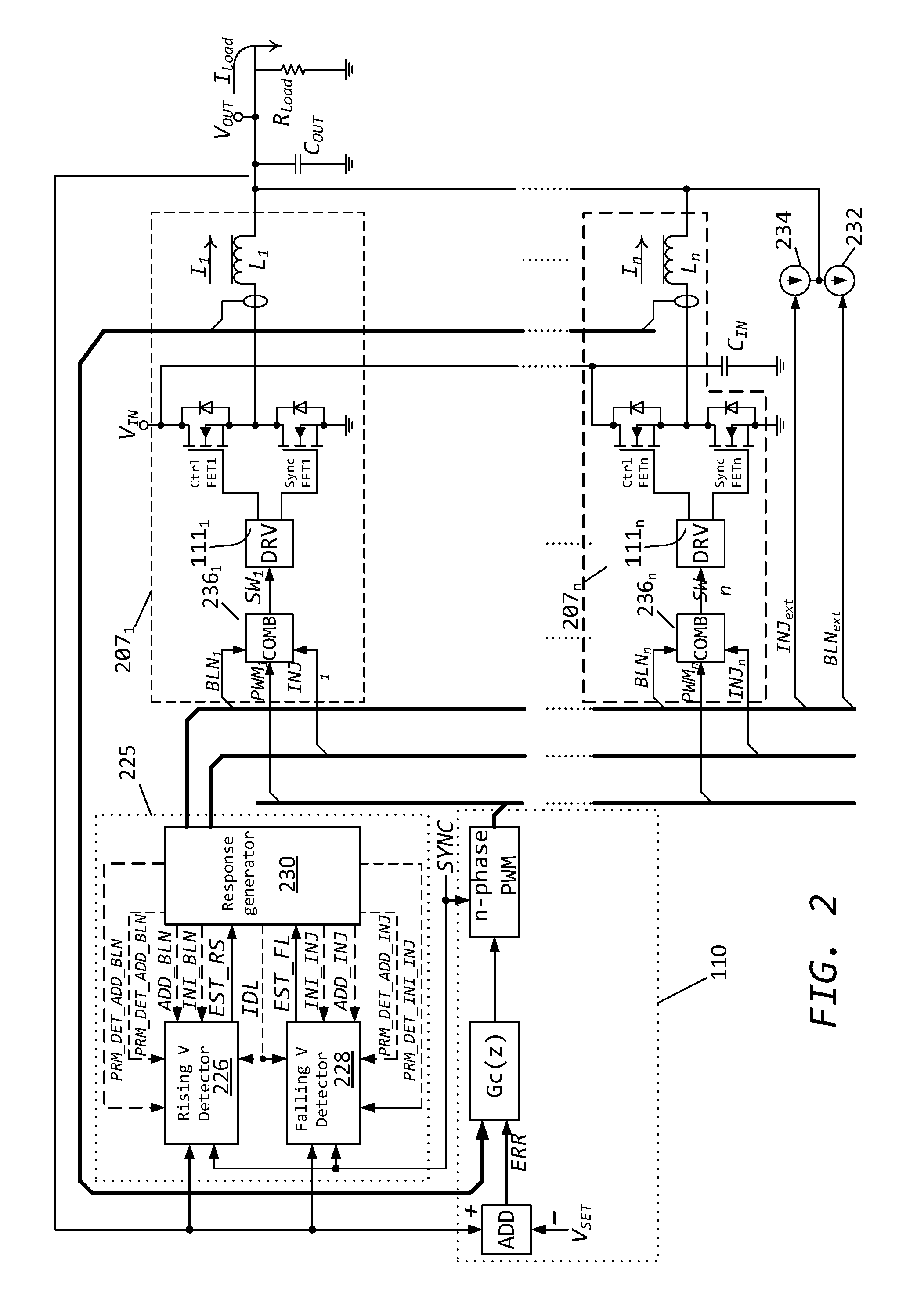
Method for controlling a dc-to-dc converter
ActiveUS20150326120A1Minimizing voltage deviationShorten total active timeDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationFull bridgePush pull
Methods and circuits for power supply arrangement and control are disclosed herein. More specifically the application relates to a control method and a controller for a DC-to-DC converter, such as a synchronous Buck converter, which implements a transient detection scheme together with response generation to allow the converter to recover from a positive and / or negative load current step in the robust way, with low undershoot / overshoot at the output voltage. The control method may be implemented by either an analog or a digital circuit. The controller may be integrated with existing controller schemes (such as voltage-mode controllers) to provide superior dynamic performance during large-signal transient conditions while providing stable operation during steady state conditions. The methods and circuits provided herein are applicable to Buck converters and Buck-derived converters such as forward, push-pull, half-bridge, and full-bridge converters.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
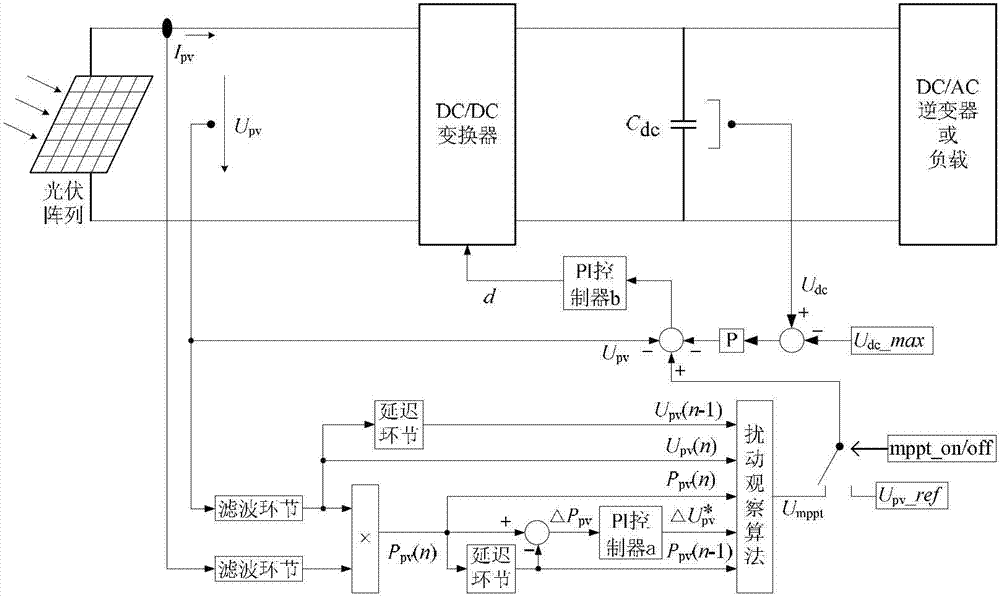
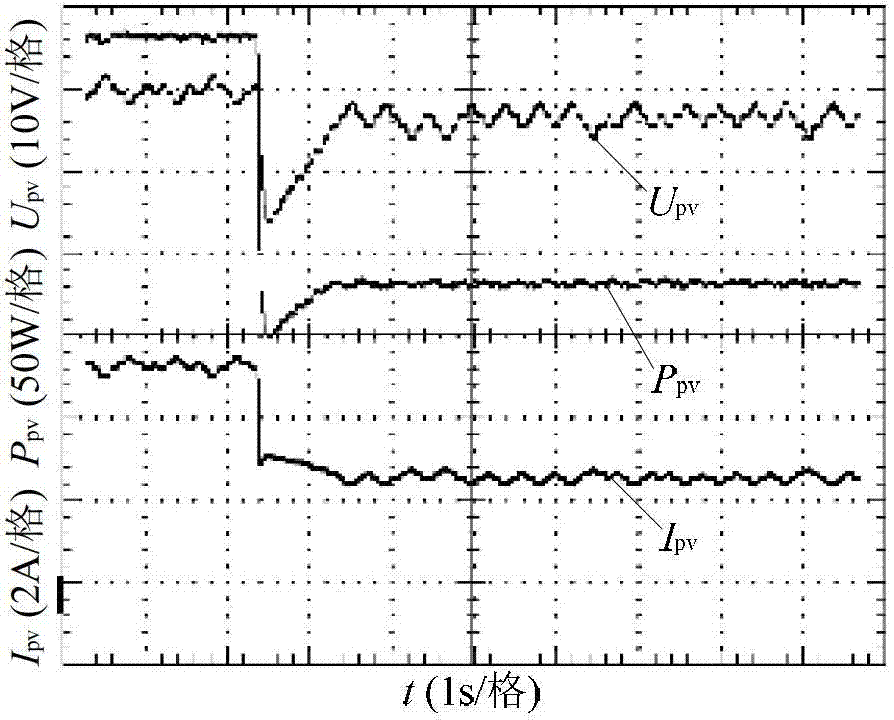
Maximum power point tracking method based on efficient adaptive perturbation and observation
ActiveCN102809980AImprove performanceIncreased speed of maximum power trackingPhotovoltaic energy generationElectric variable regulationPerturbation and observationEngineering
The invention provides a maximum power point tracking method based on efficient adaptive perturbation and observation. By the aid of the maximum power point tracking method, the problem that the step size used in a traditional perturbation and observation method in the photovoltaic-battery maximum power point tracking technology is difficult to balance, completely adaptive perturbation can be realized, and tracking speed, stability precision and universality of a system are high. The maximum power point tracking method with a basic principle includes that computing continuous output power values of a photovoltaic array according to filtered voltage and current signals; generating error signals according to changes among power signals; generating adaptive perturbation voltage values via a PI (proportional plus integral) controller; and finally generating a reference value of voltage of the photovoltaic array according to the basic principle of perturbation and observation. An error signal of an actual value and the reference value of the voltage of the photovoltaic signal is computed, and a duty cycle signal d required by a DC / DC converter is generated by another PI controller, so that on and off time of each power switch tube of a phase-shift full-bridge converter is controlled, power outputted by the photovoltaic array is adjusted, and the maximum power output point of the photovoltaic array can be tracked.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
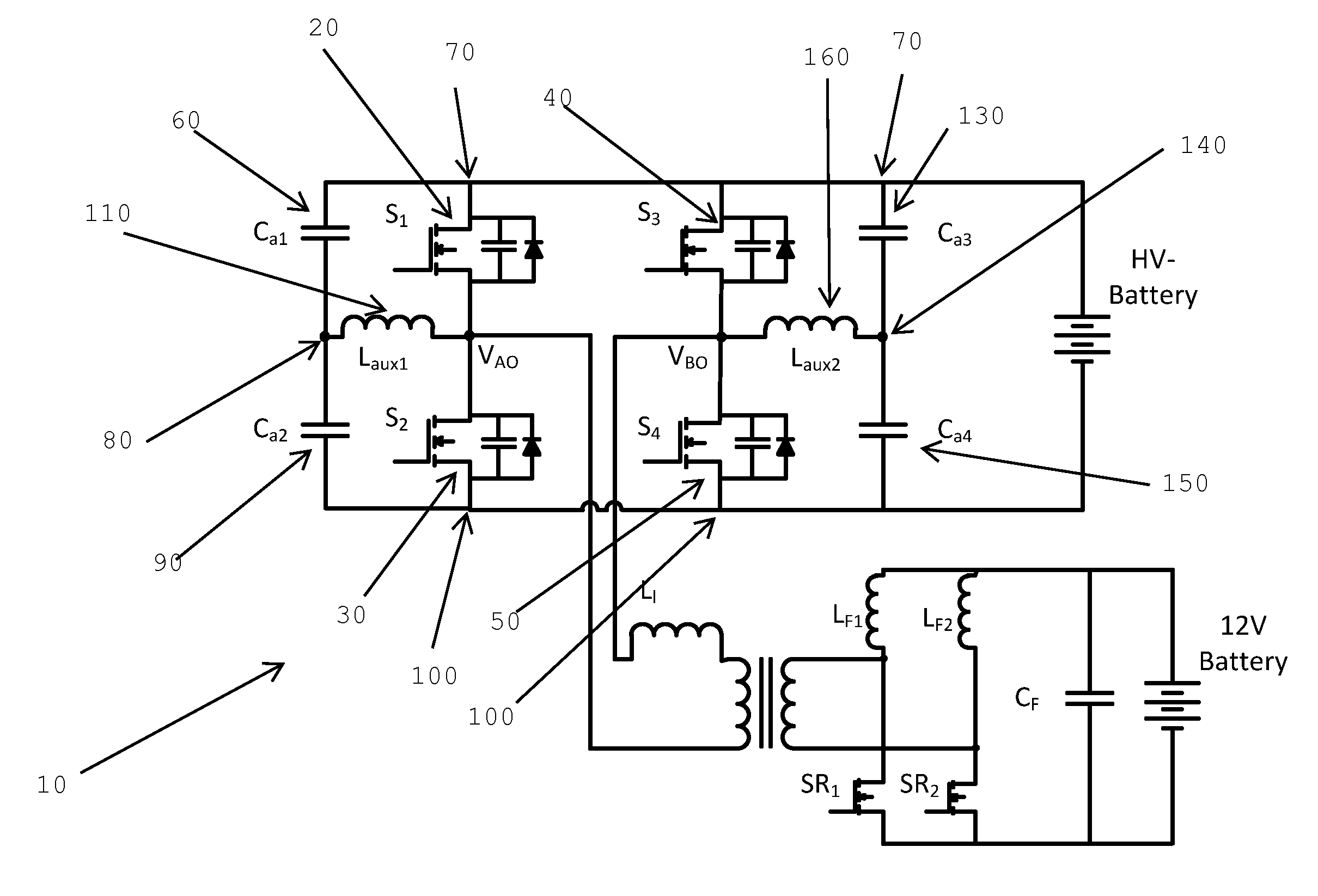
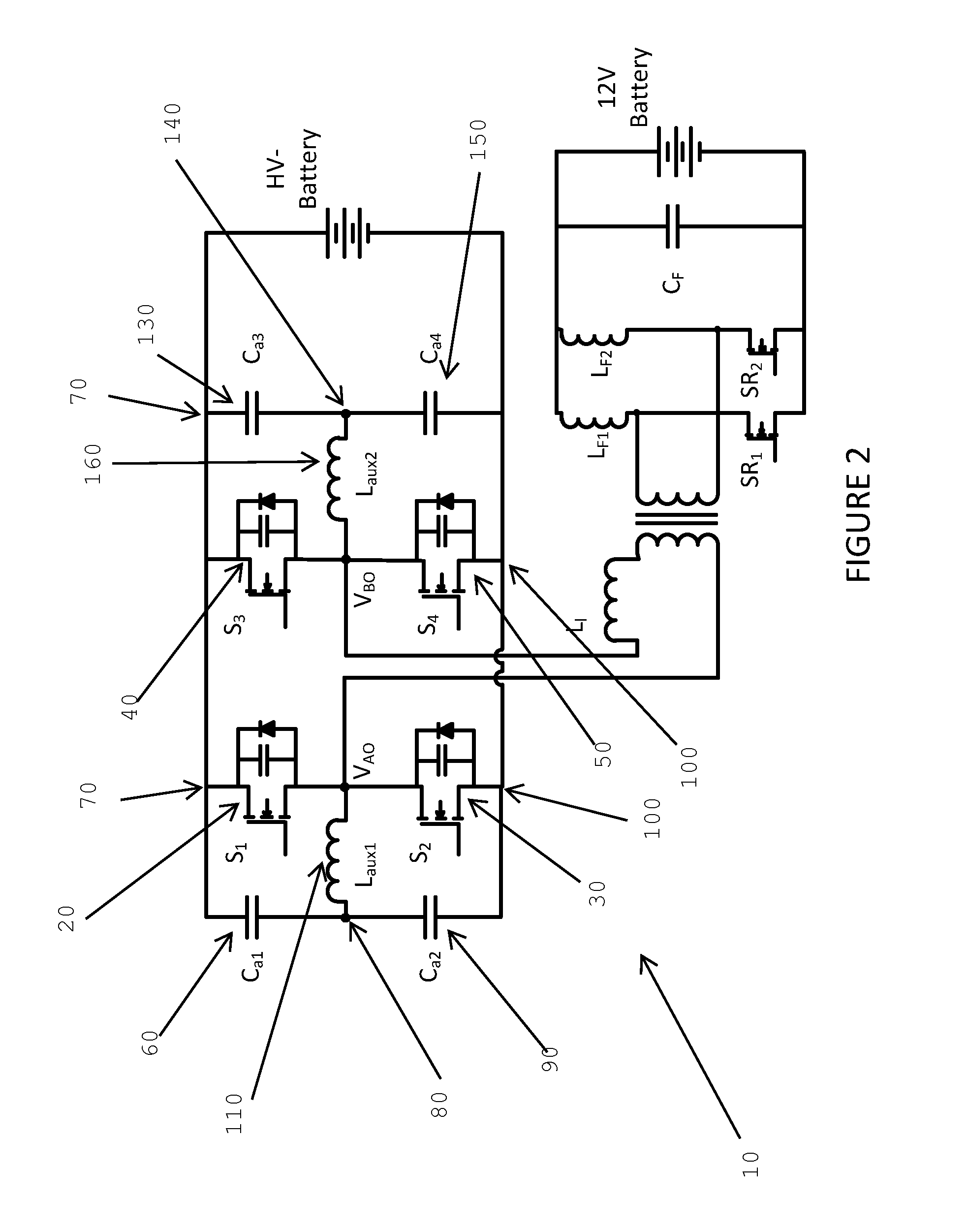
Load adaptive variable frequency phase-shift full-bridge dc/dc converter
Systems, methods, and circuits for providing zero voltage switching conditions across all load conditions in a full-bridge DC / DC converter. An asymmetric auxiliary circuit is provided and the reactive current due to the auxiliary circuit is controlled across various load conditions. This is done by adaptively adjusting the switching frequency of the converter as well as the phase shift of the rising edges of the waveforms for activating the gates in the leading and lagging legs of the full bridge converter.
Owner:SPARQ SYST INC
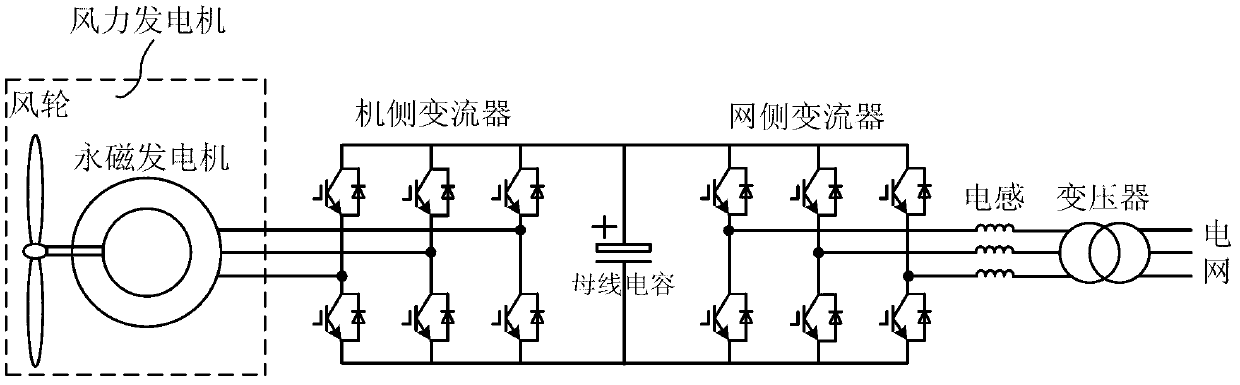
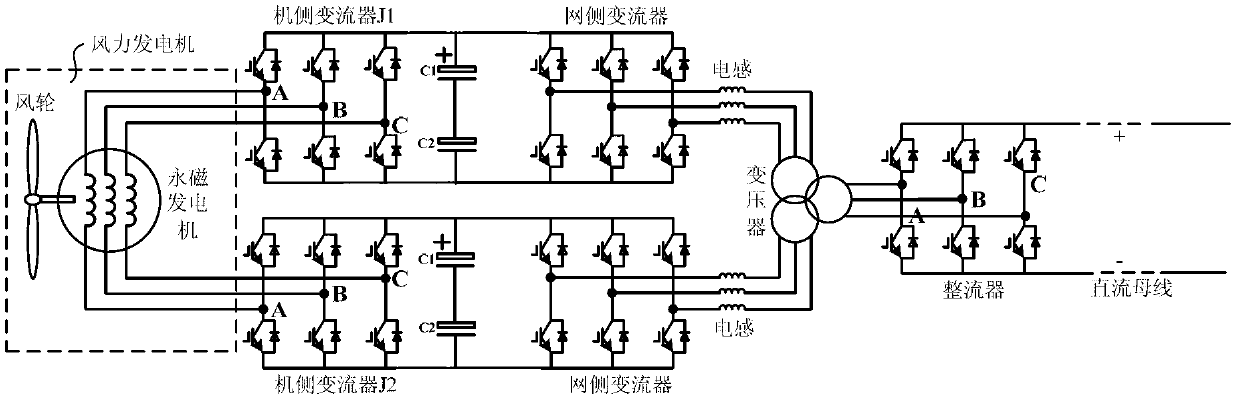
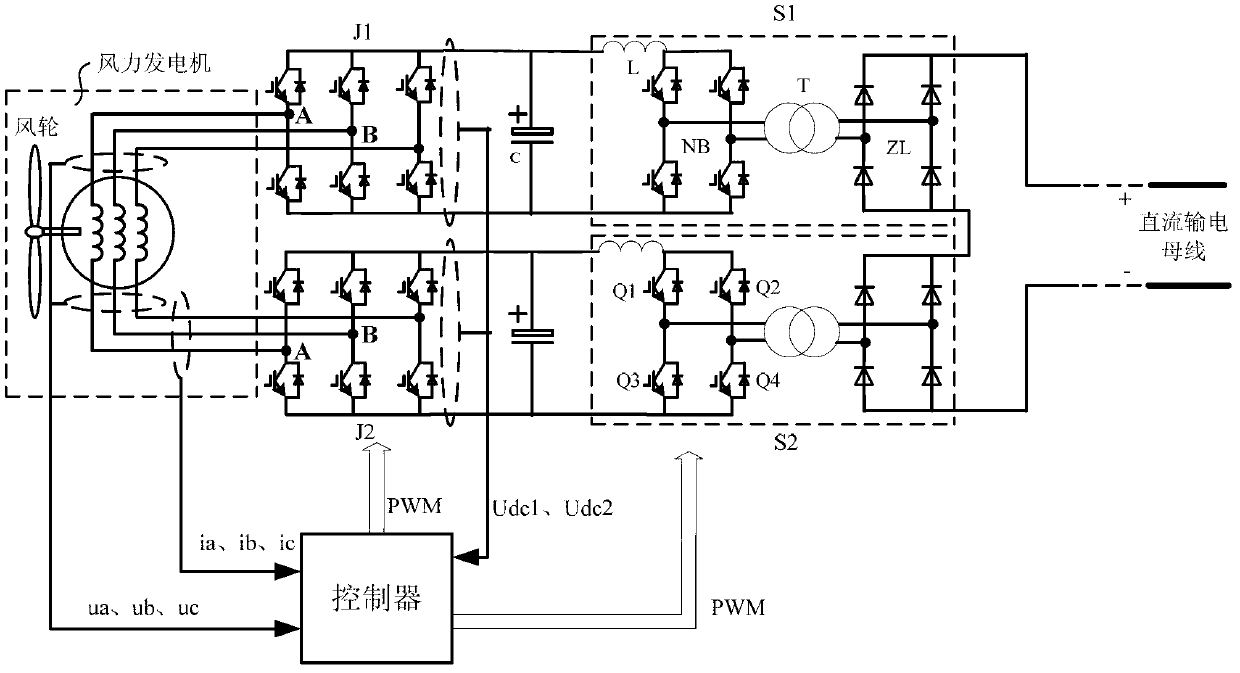
Wind power generation high-voltage direct current grid-connected system based on open coil structure and control method thereof
ActiveCN103280838AReduce current harmonic contentGuaranteed uptimeSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationWind drivenThree level
The invention discloses a wind power generation high-voltage direct current grid-connected system based on an open coil structure. The wind power generation high-voltage direct current grid-connected system comprises a permanent magnetism synchronous wind driven generator, two generator side converters, two direct current boosters and a controller, wherein the permanent magnetism synchronous wind driven generator is of the open coil structure, and each direct current booster is composed of an electric reactor, an inverter, a transformer and a rectifier in a sequentially connected mode. According to the wind power generation high-voltage direct current grid-connected system based on the open coil structure, the open coil permanent magnetism synchronous wind driven generator is used, the two double-level three-phase controllable full-bridge converters are used for controlling the permanent magnetism synchronous wind driven generator, three-level modulation is achieved, voltage stress of converter capacity and voltage stress of switching elements are reduced, and system cost can be reduced. The wind power generation high-voltage direct current grid-connected system based on the open coil structure is simple in structure, low in cost and high in operational efficiency. The invention further discloses a method for controlling the system. According to the method, the better PWM technology of the vector control strategy is used, therefore, current harmonic contents inside the generator can be reduced, and the generator can better operate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
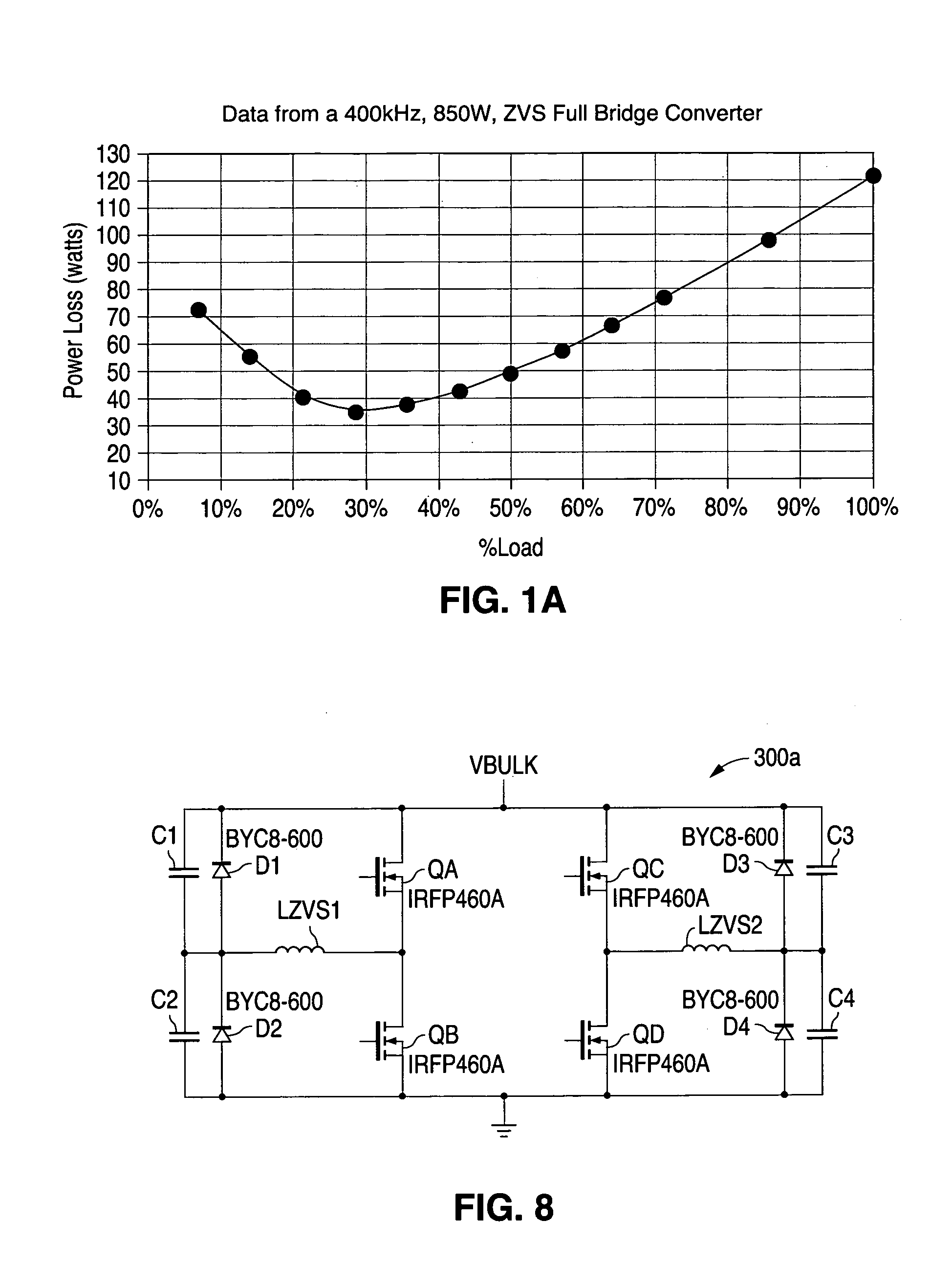
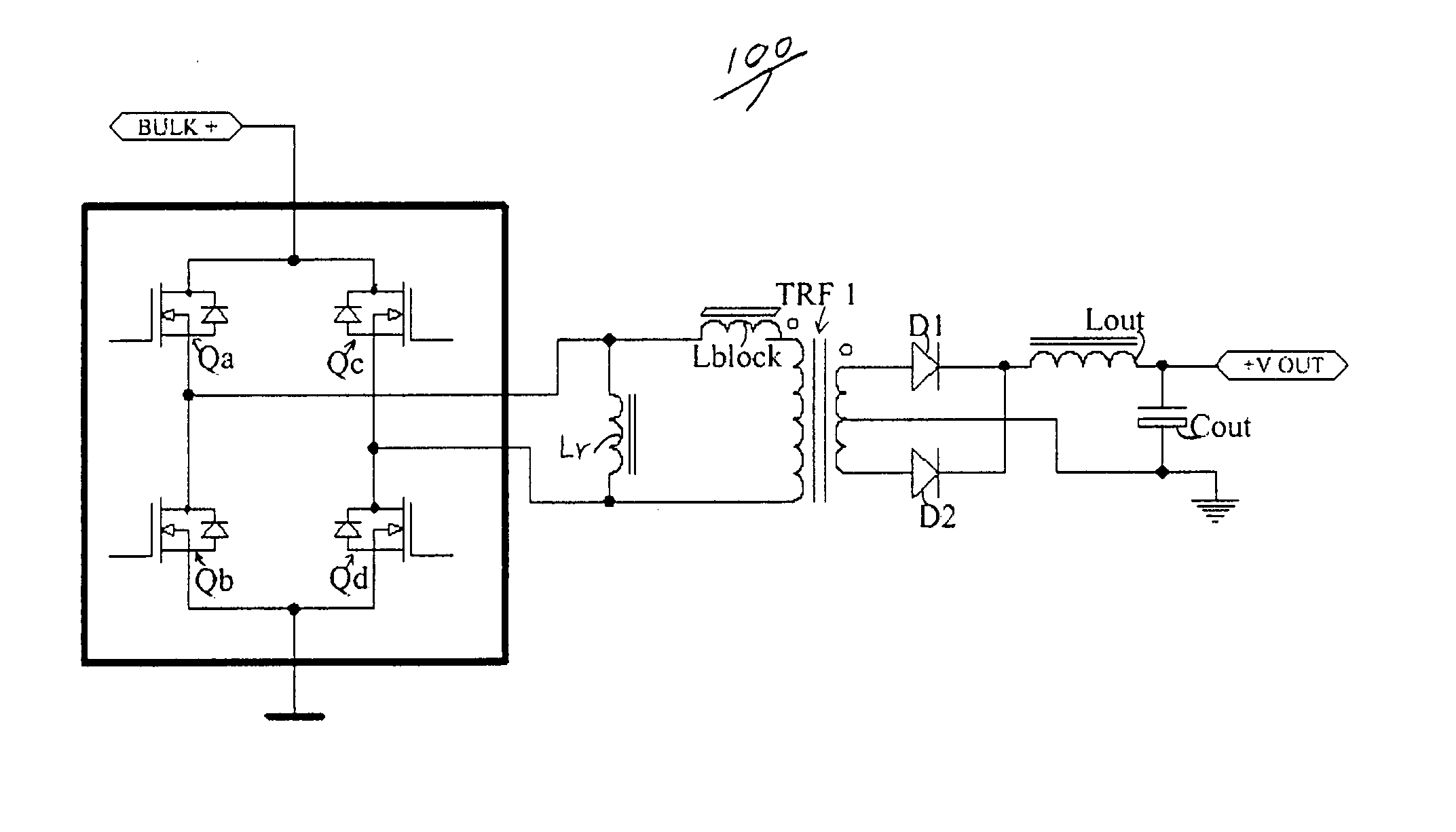
Circuit for reducing losses at light load in a soft switching full bridge converter
InactiveUS20050030767A1Overall design flexibilityLower component costsEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionSoft switchingFull bridge
A circuit for reducing the internal power losses of a soft switching full bridge converter at light loads and enables very high frequency operation without using a cold plate approach. In a preferred embodiment, the circuit includes a resonant inductor and blocking inductor on the primary side of the converter arranged so as to provide the reduced losses for zero voltage switching bridge converter. The circuit provides the above benefits even for converters having a power transformer with very low leakage inductance. The circuit is not dependent on the presence of a high leakage inductance for the power transformer. The circuit can be used in soft switched half bridge or full bridge converters. The inventive circuit can also be used in a hard switching full bridge or half bridge converter for achieving zero voltage switching at reduced cost with reduced losses at light load, if the operating duty cycle of the converter is set near fifty percent.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
Dynamic load fast response circuit
ActiveCN104638885AQuick responseReduce deviationDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceSignal processing circuits
The invention relates to a circuit for realizing fast dynamic load response by a Buck type DC / DC (direct current / direct current) converter. The load current change can be fast responded, and the output voltage deviation amplitude is reduced, so that the total required capacity of an outer capacitor is reduced. The circuit consists of a current sampling circuit, a signal processing circuit and a signal injection circuit, wherein the current sampling circuit consists of a sampling resistor or a resistance and capacitance series circuit connected with an output inductor in parallel, and for the second scheme, the other end of a capacitor is connected to the output voltage end. Voltage signals at two ends of the capacitor and the load current form the direct proportion, the signal processing circuit carries out amplification on direct current components and suppression on alternating current components in the voltage signals, the output of the signal processing circuit is injected into the negative feedback input end of a PWM (pulse width modulation) controller in an alternating current coupling mode by the signal injection circuit, the output duty ratio is forced to be fast regulated, the goals of fast response and small deviation oscillation amplitude are achieved, and the stability of the system steady work is not influenced. The circuit is also applicable to converters such as multi-phase Buck converters, normal shock converters, half-bridge converters and full-bridge converters.
Owner:上海英联电子系统有限公司 +1
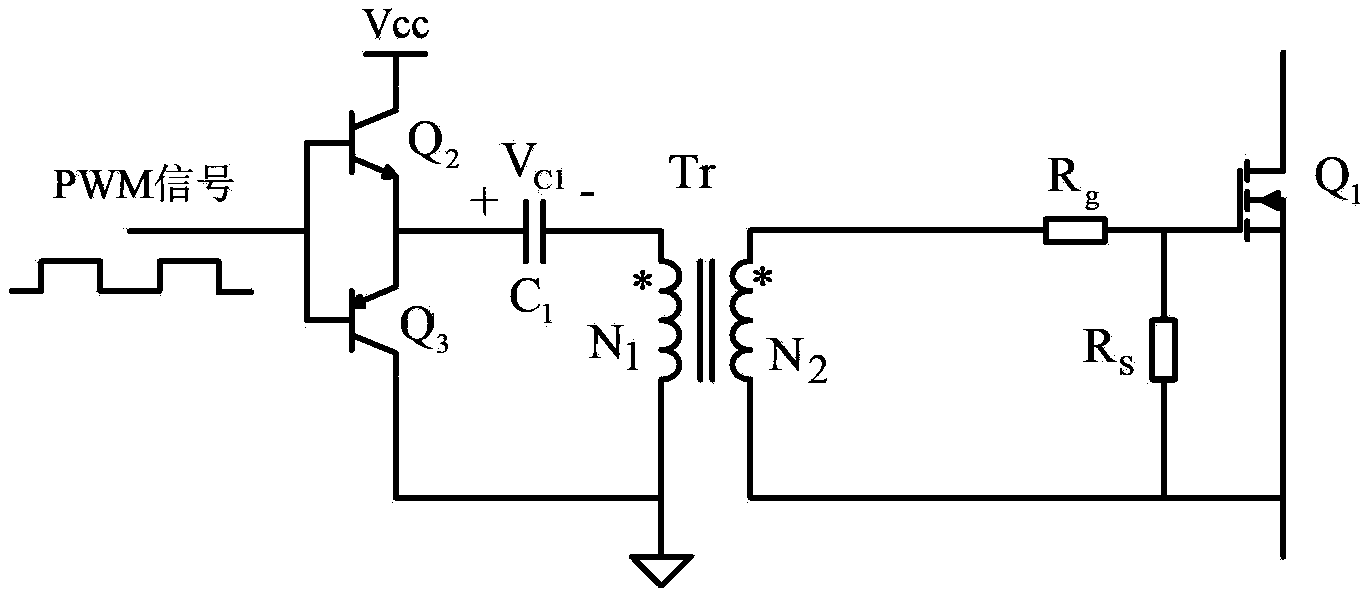
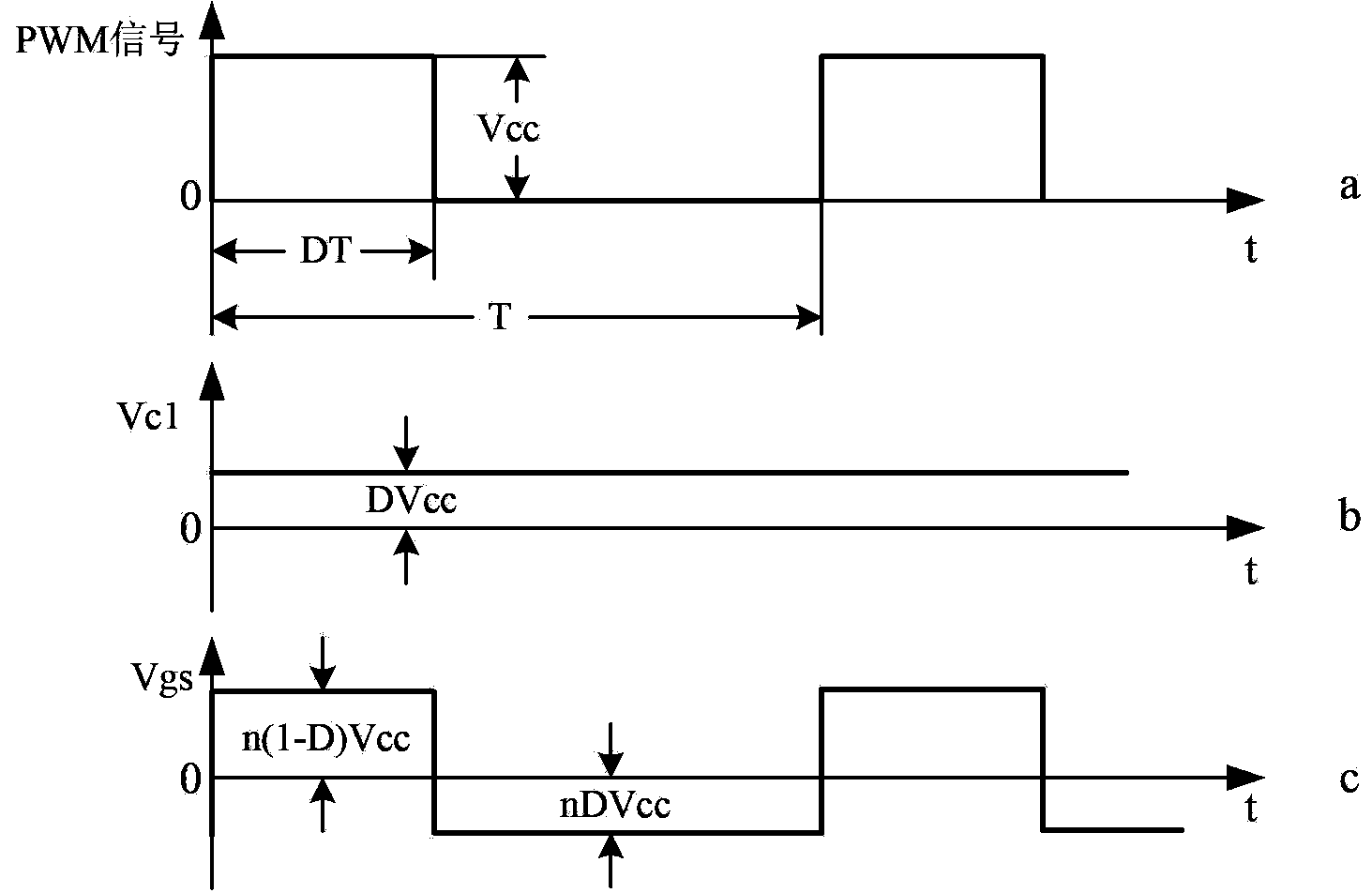
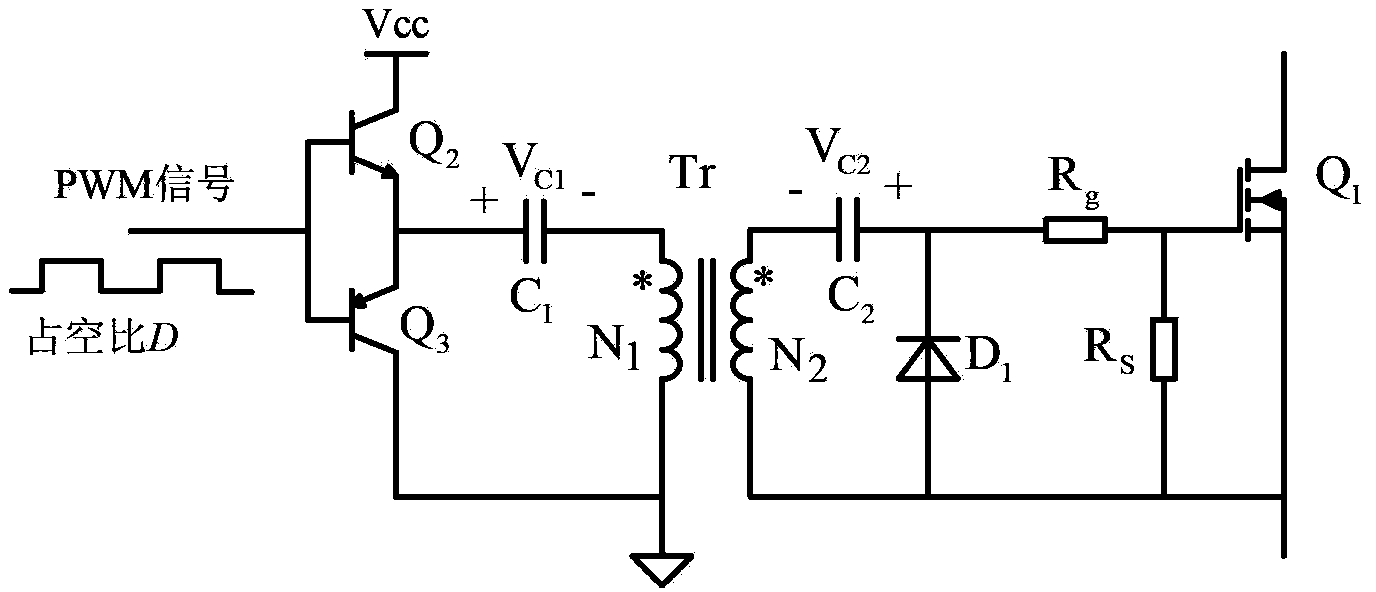
Power switch device pulse transformer isolation driving circuit
InactiveCN103414354AImprove noise immunityImprove reliabilityConversion without intermediate conversion to dcBuck converterFull bridge converter
The invention discloses a power switch device pulse transformer isolation driving circuit. The power switch device pulse transformer isolation driving circuit comprises a primary-side circuit, a pulse transformer Tr and a secondary-side circuit, wherein the primary-side circuit comprises an NPN transistor Q2, a PNP transistor Q3 and a blocking capacitor C1, and the secondary-side circuit comprises a power switch device Q1, a driving resistor Rg, a gate discharge resistor Rs, a diode D1, a compensation capacitor C2, a voltage-regulator tube Z1 and a negative pressure holding capacitor C3. The power switch device pulse transformer isolation driving circuit of the invention can be applied to all switching converters such as a boost converter, a buck converter, a forward converter, a flyback converter, a half-bridge switching converter, a half-bridge converter, a full-bridge converter and a push-pull converter, and can effectively improve the reliability of the switching converters.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Method of controlling phase-shift full-bridge converter in light load operation
ActiveUS20150098250A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionSoft switchingPhase shifted
A method of controlling a phase-shift full-bridge (PSFB) converter in a light load operation is provided to switch control modes of the PSFB converter by detecting magnetizing current of a transformer thereof. The method includes following steps: First, the PSFB converter is operated in an extended PSFB control mode when the magnetizing current is larger. Afterward, the PSFB converter is operated in a modified PSFB control mode when the magnetizing current is gradually reduced and electric charges transported by the residual magnetizing current near to or less than a half of the DC input voltage. Finally, the optimal degree of soft switching of the PSFB converter is implemented when the PSFB converter is operated at the modified PSFB control mode. Accordingly, it is to improve overall efficiency, reduce switching losses, and achieve electromagnetic compatibility.
Owner:CHICONY POWER TECH CO LTD
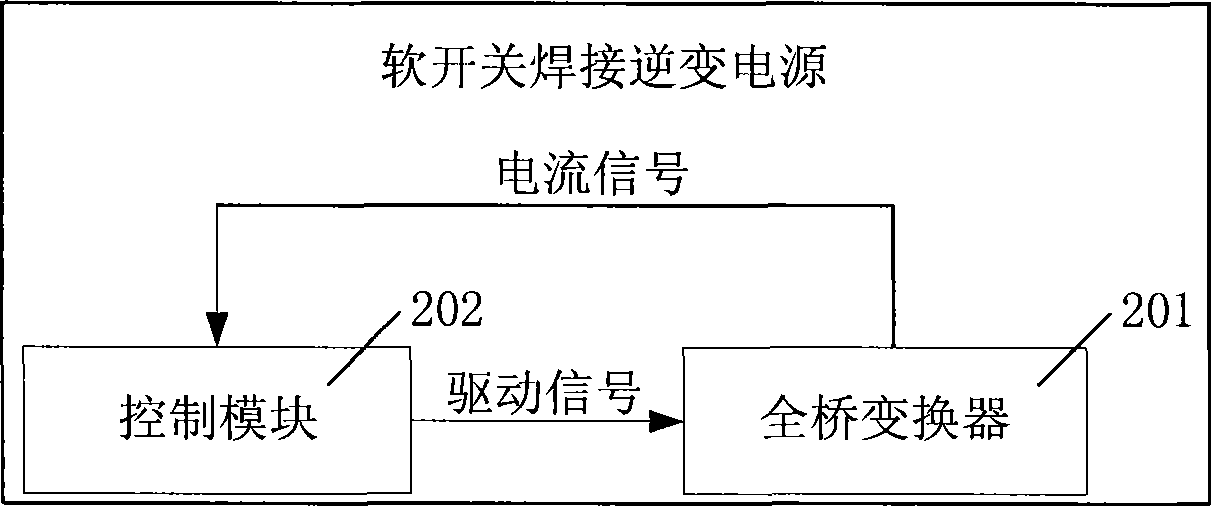
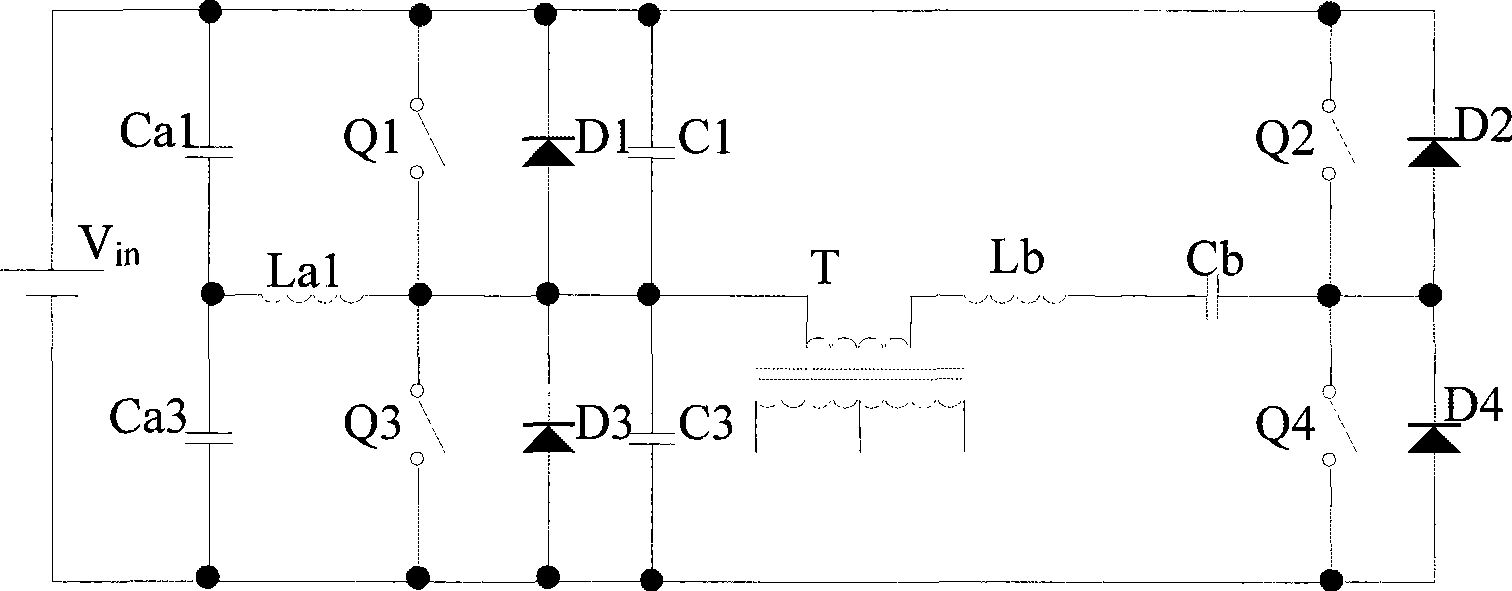
Soft switch welding inverter, phase-shifting control method and soft switching method
InactiveCN101478256AGuaranteed uptimeImprove reliable operationEfficient power electronics conversionArc welding apparatusSoft switchingEngineering
The invention discloses a soft-switching welding inverter power supply, a phase-shifting control method and a soft-switching method which belong to the electronic circuit field. The soft-switching welding inverter power supply comprises a full-bridge converter and a control module; the phase-shifting control method is applied to the power supply, and comprises the steps as follows: the control module receives current signals of the full-bridge converter, and adjusts dead-zone time of phase-shifting signals based upon the current signals; the soft-switching method is applied to the power supply, and comprises the steps as follows: an auxiliary resonant network is connected with a bridge leg of the power supply in parallel so as to provide subsidiary energy to the zero voltage turning-on of a switching element; before the switching element of a lagging leg on the full-bridge converter is turned off, main power loop current flowing through the switching element is weakened, and the reversion of the main power loop current is restrained; and an absorption capacitor is connected with the switching element in parallel, and the borne rate of voltage rise is slows down when the switching element is turned off. The soft-switching welding inverter power supply, the phase-shifting control method and the soft-switching method realize the zero-voltage zero-current soft-switching in full range of loads including idle load and short circuit.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com