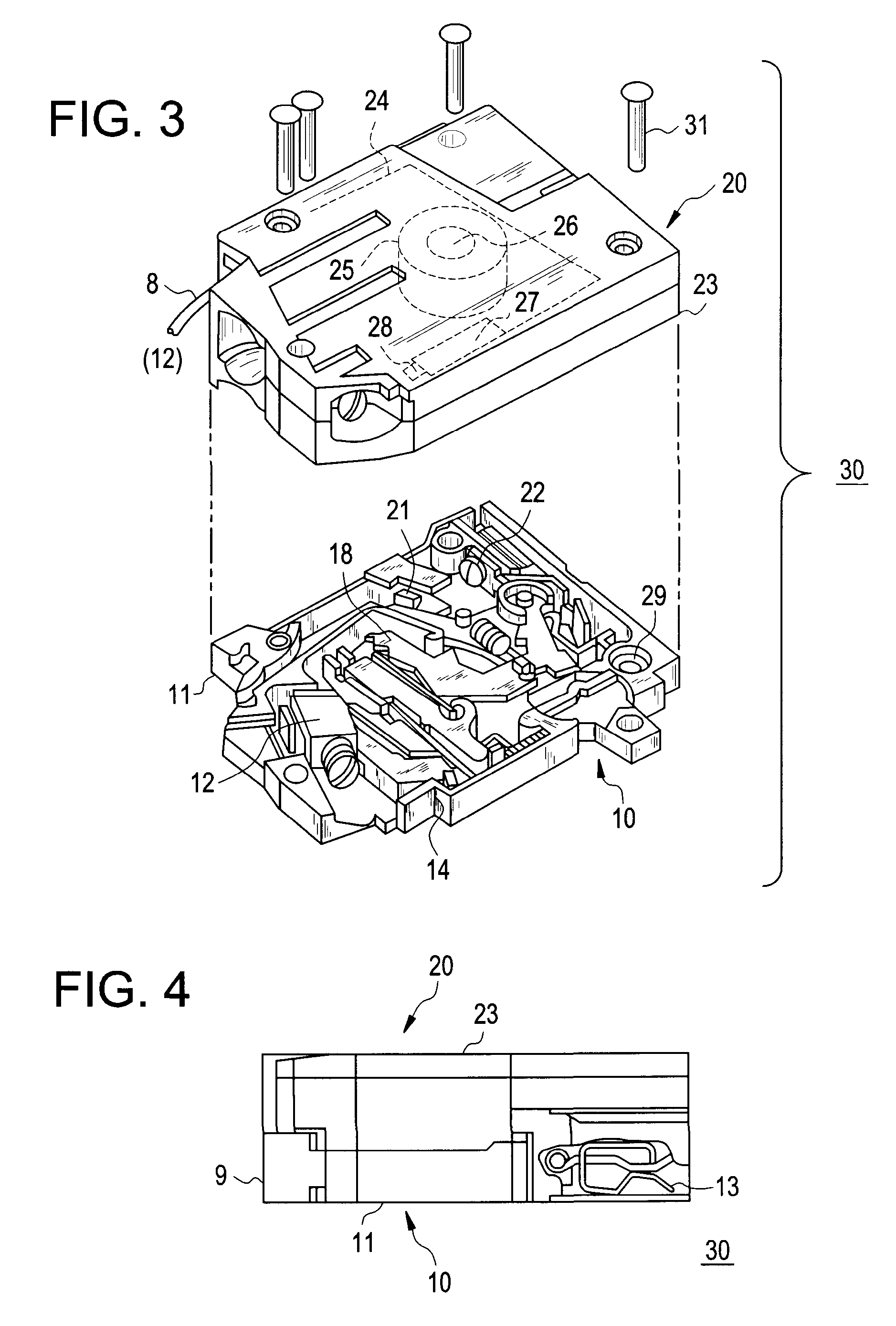
Patents
Literature
429 results about "Signal band" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
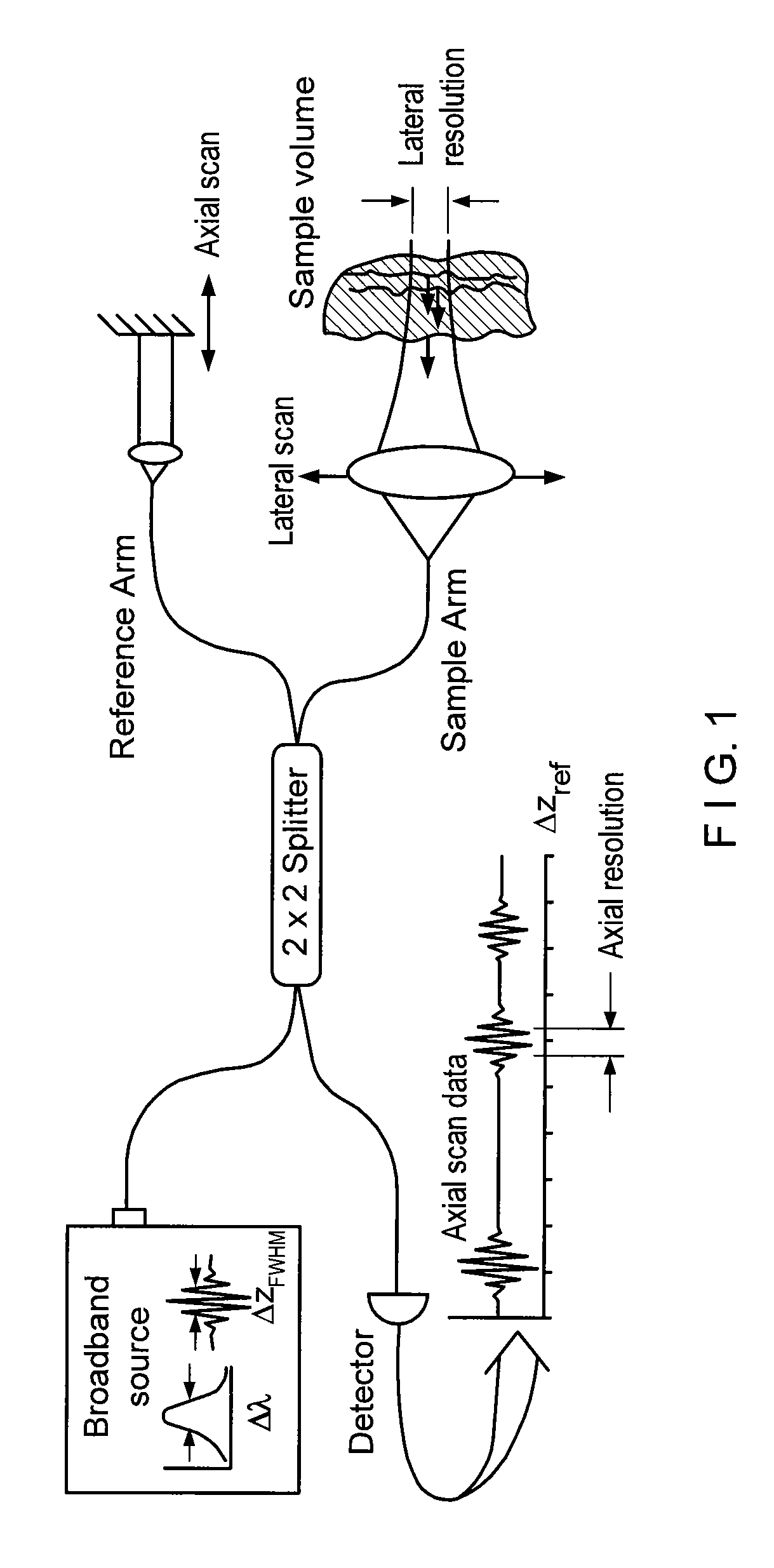
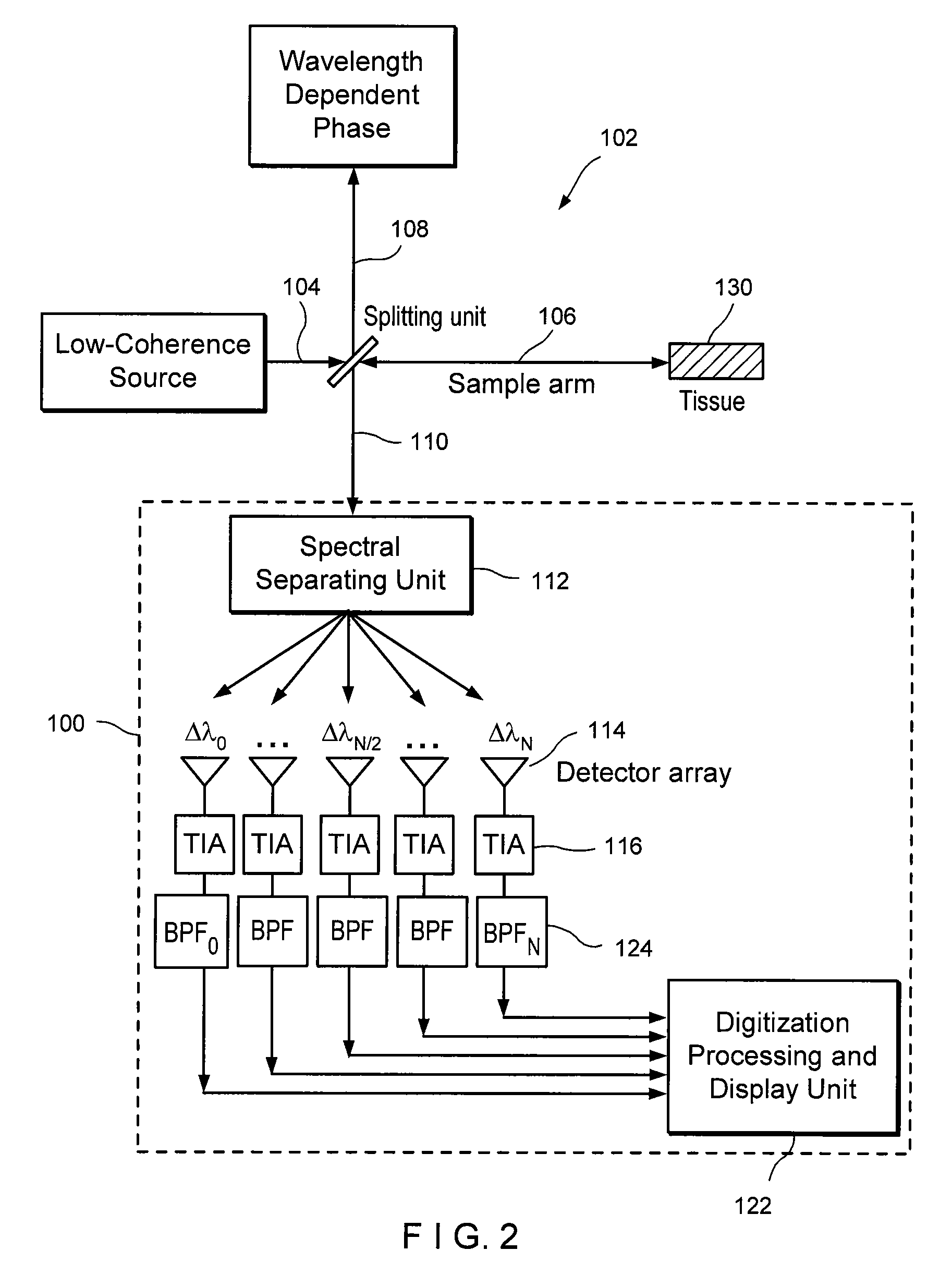
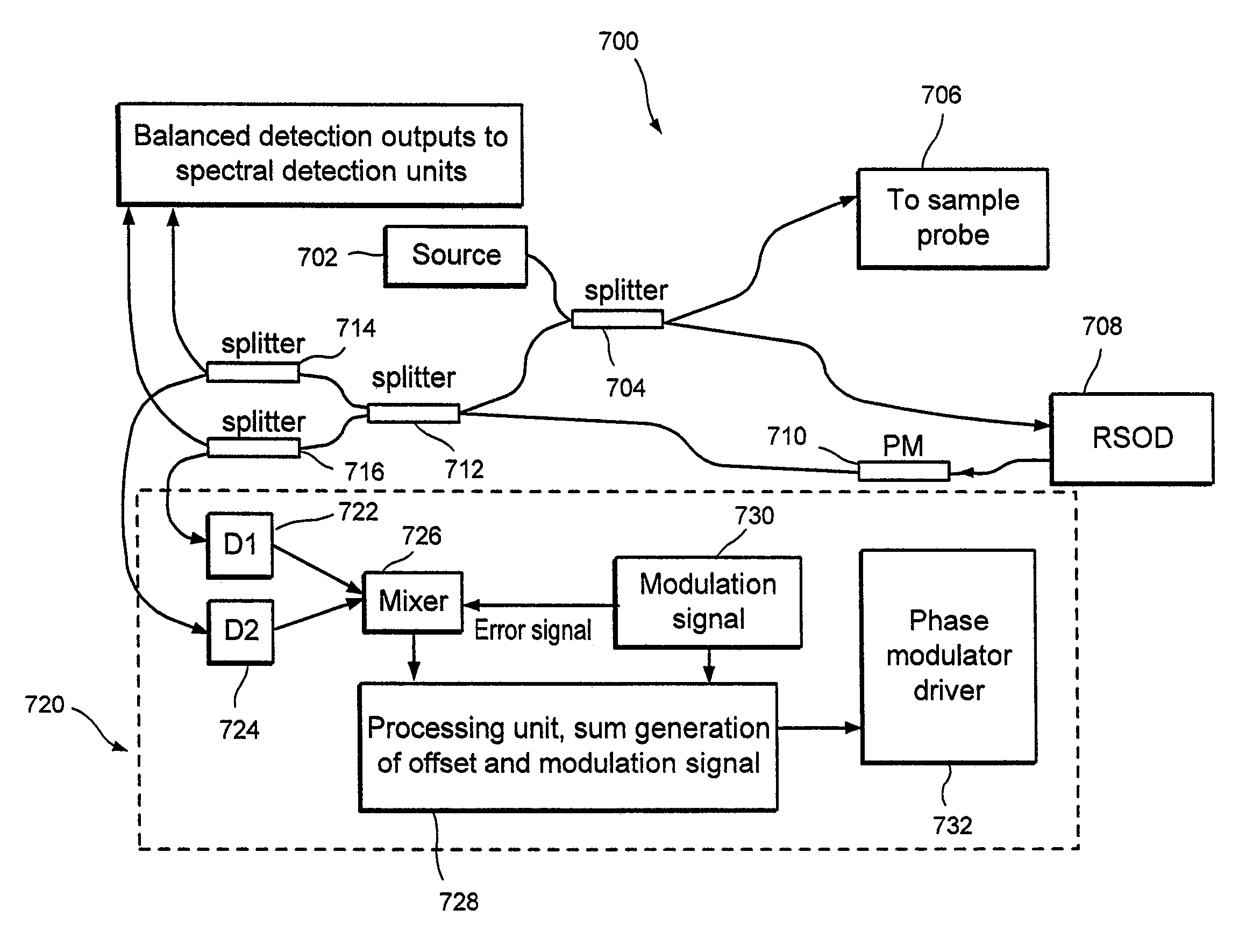
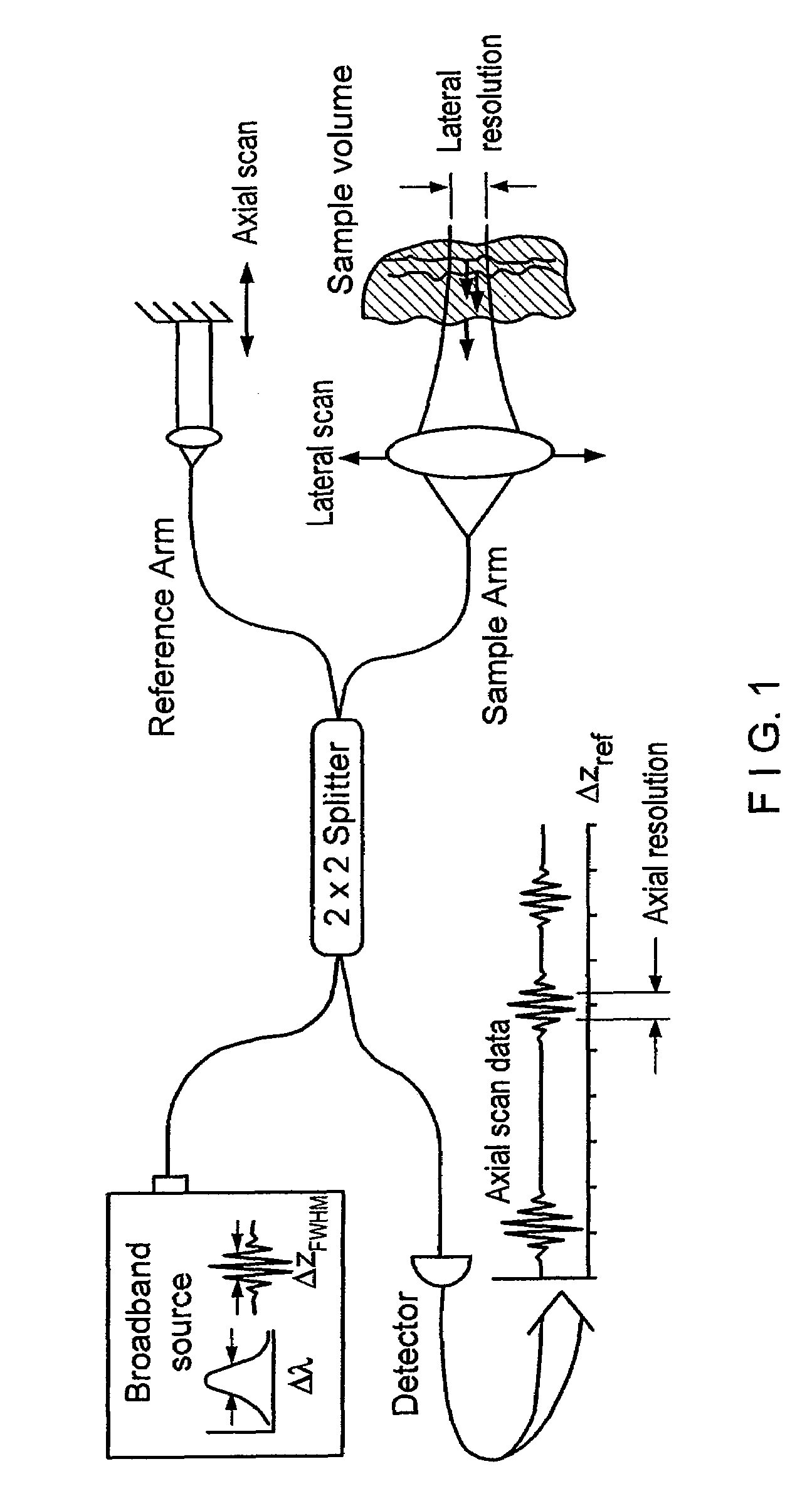
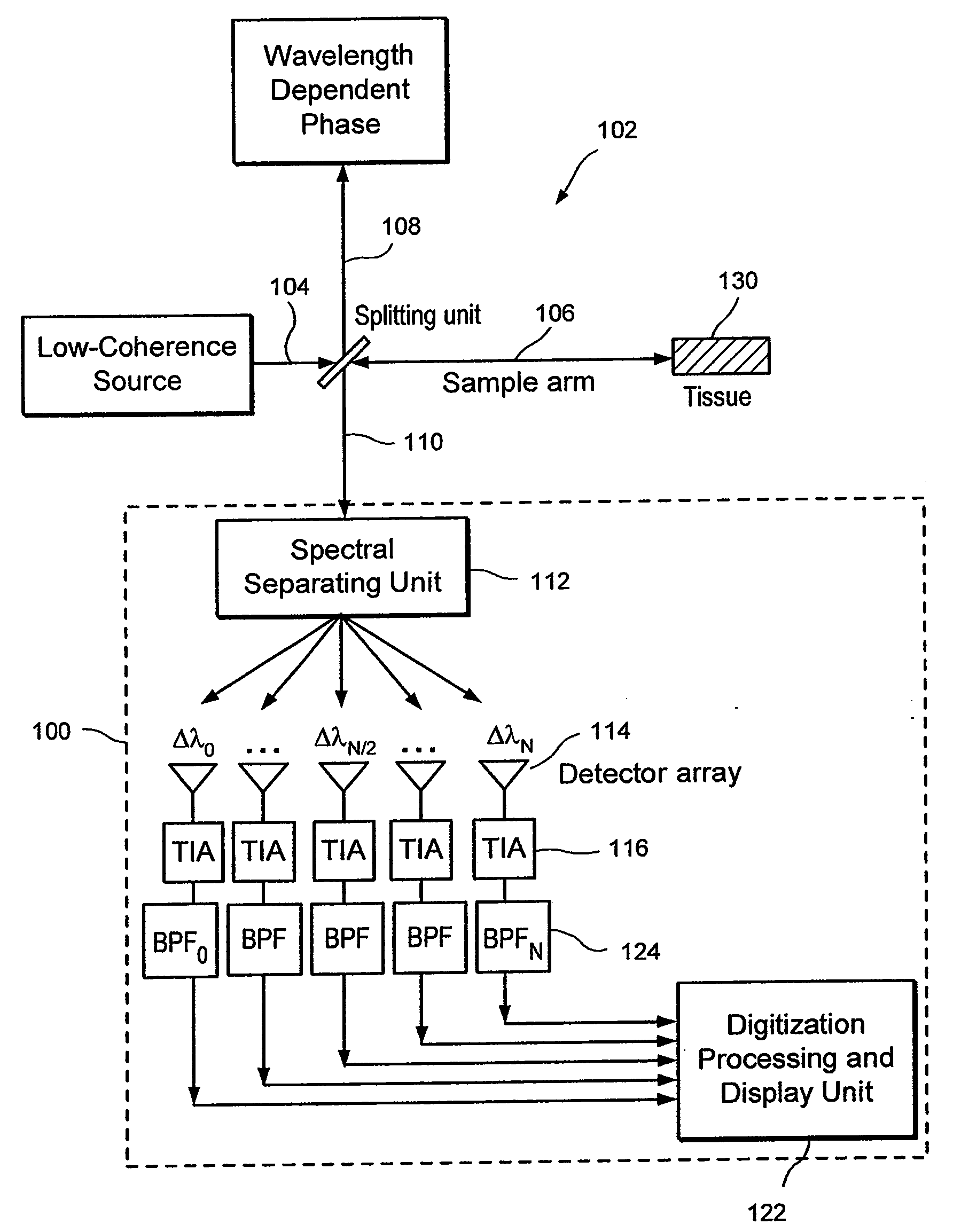
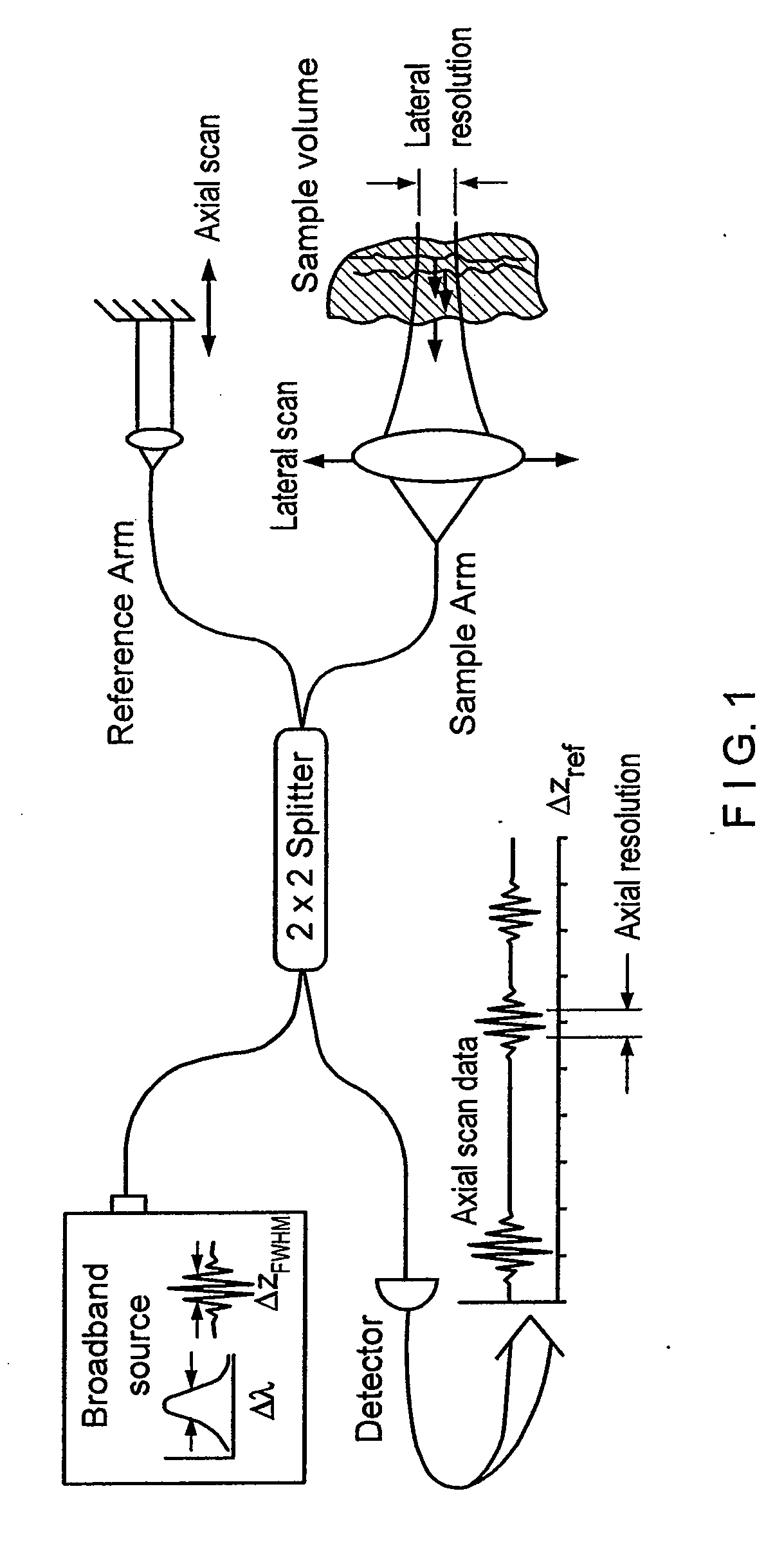
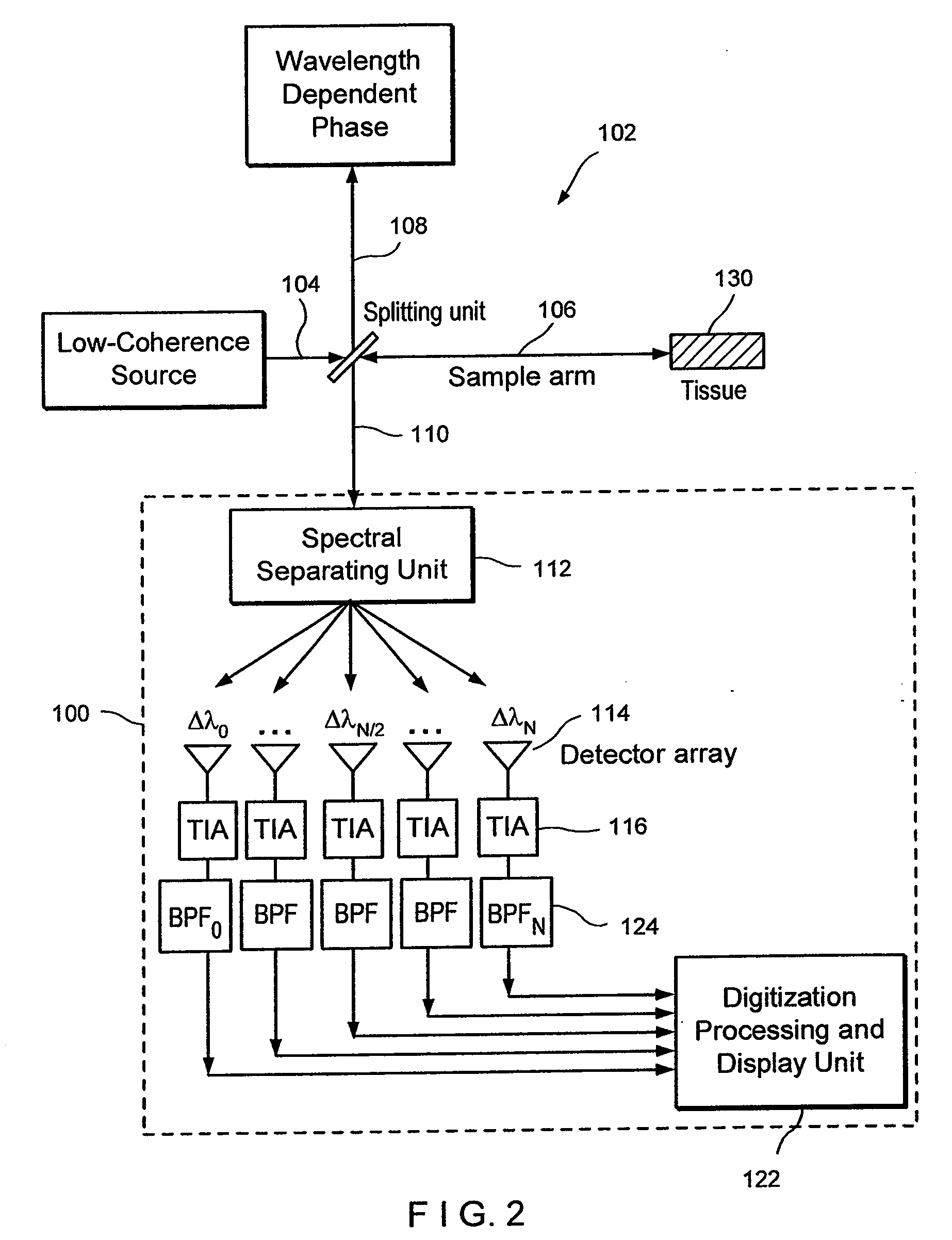
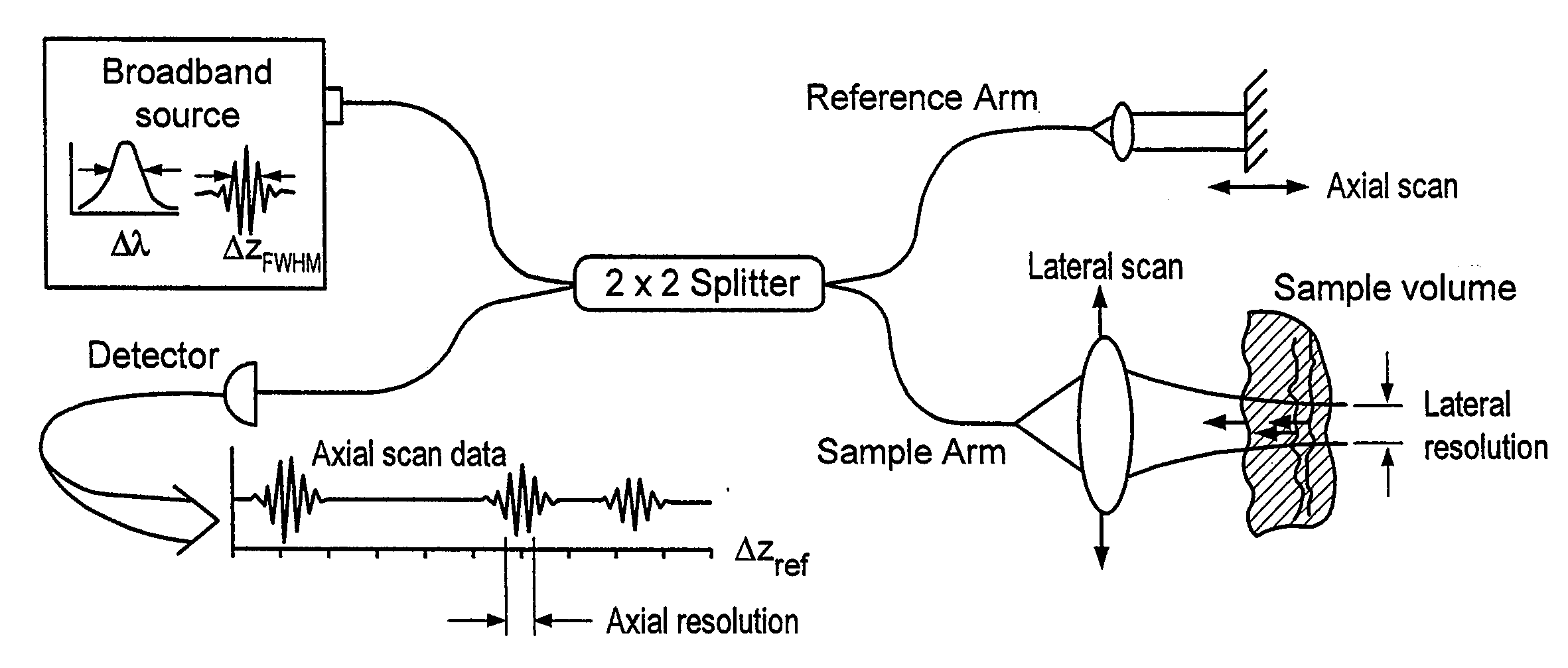
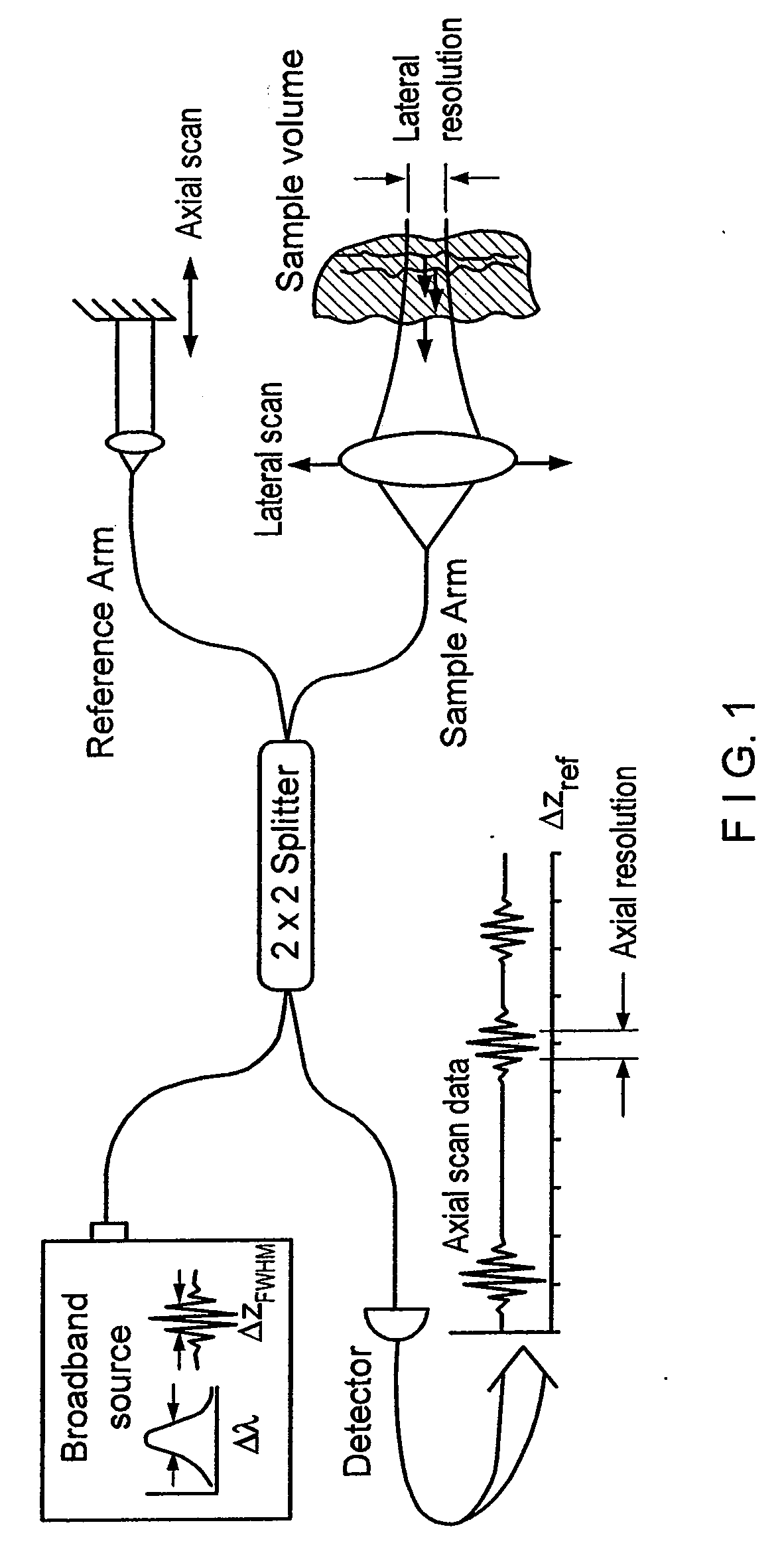
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry lci and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
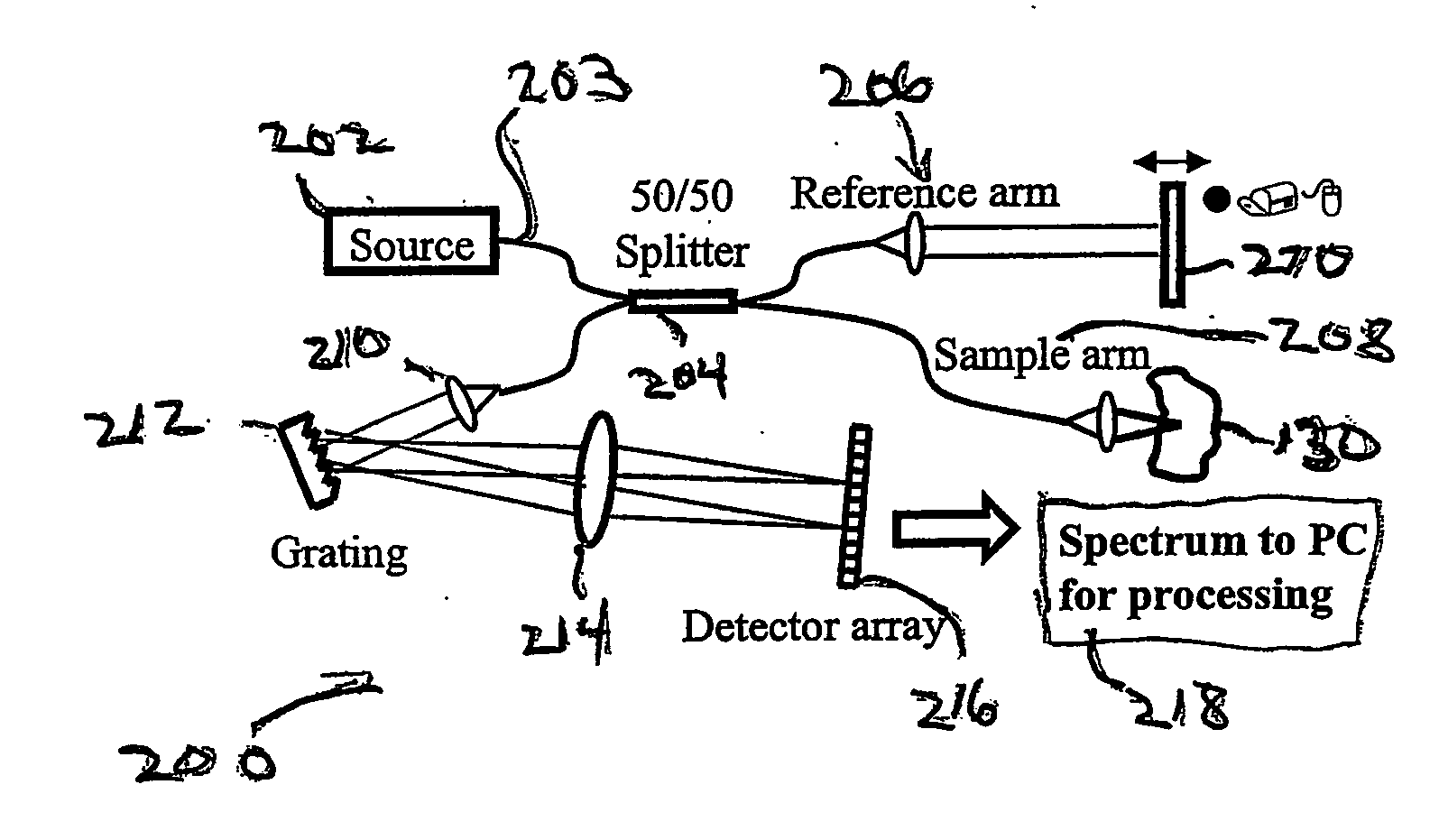
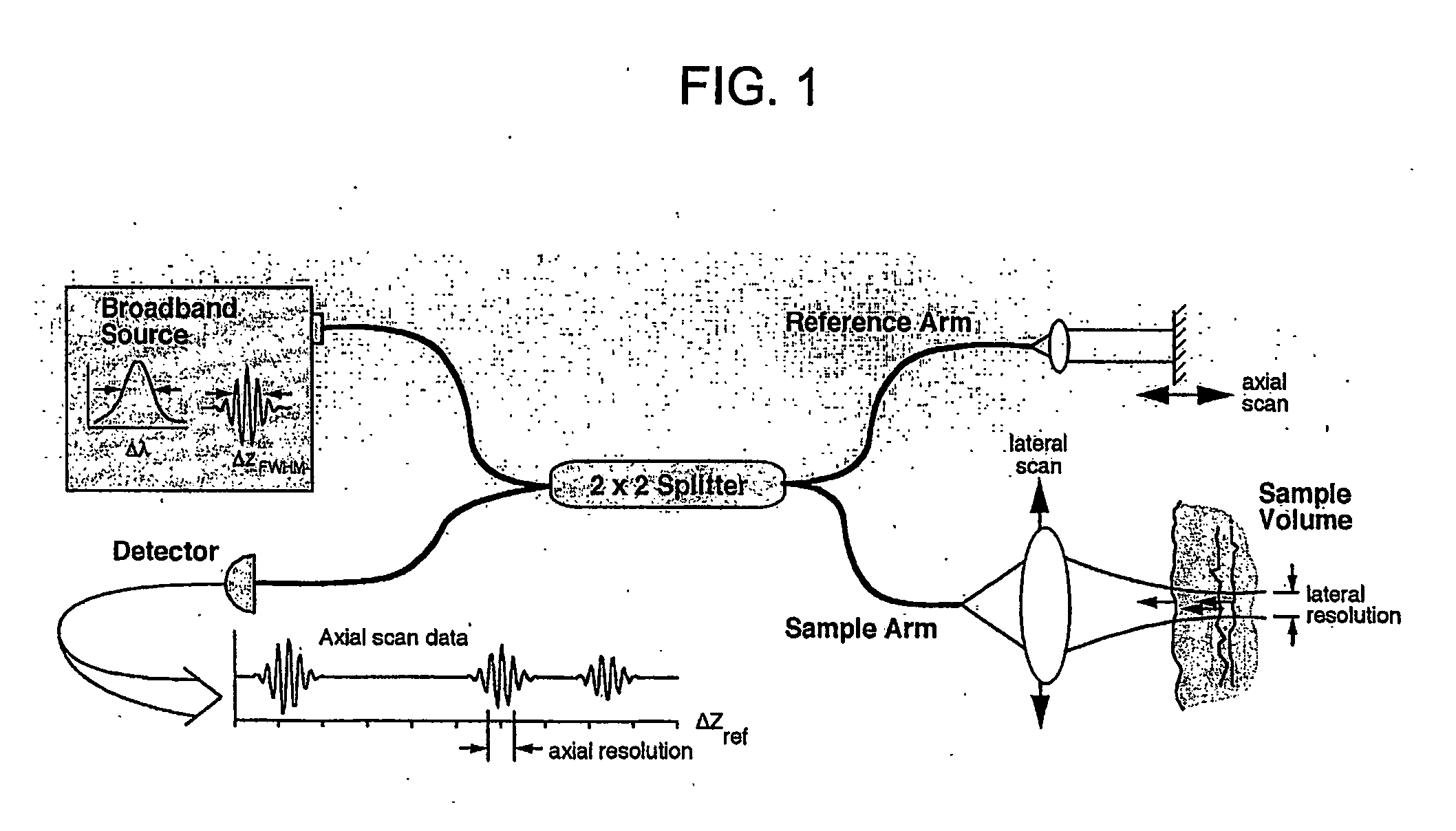
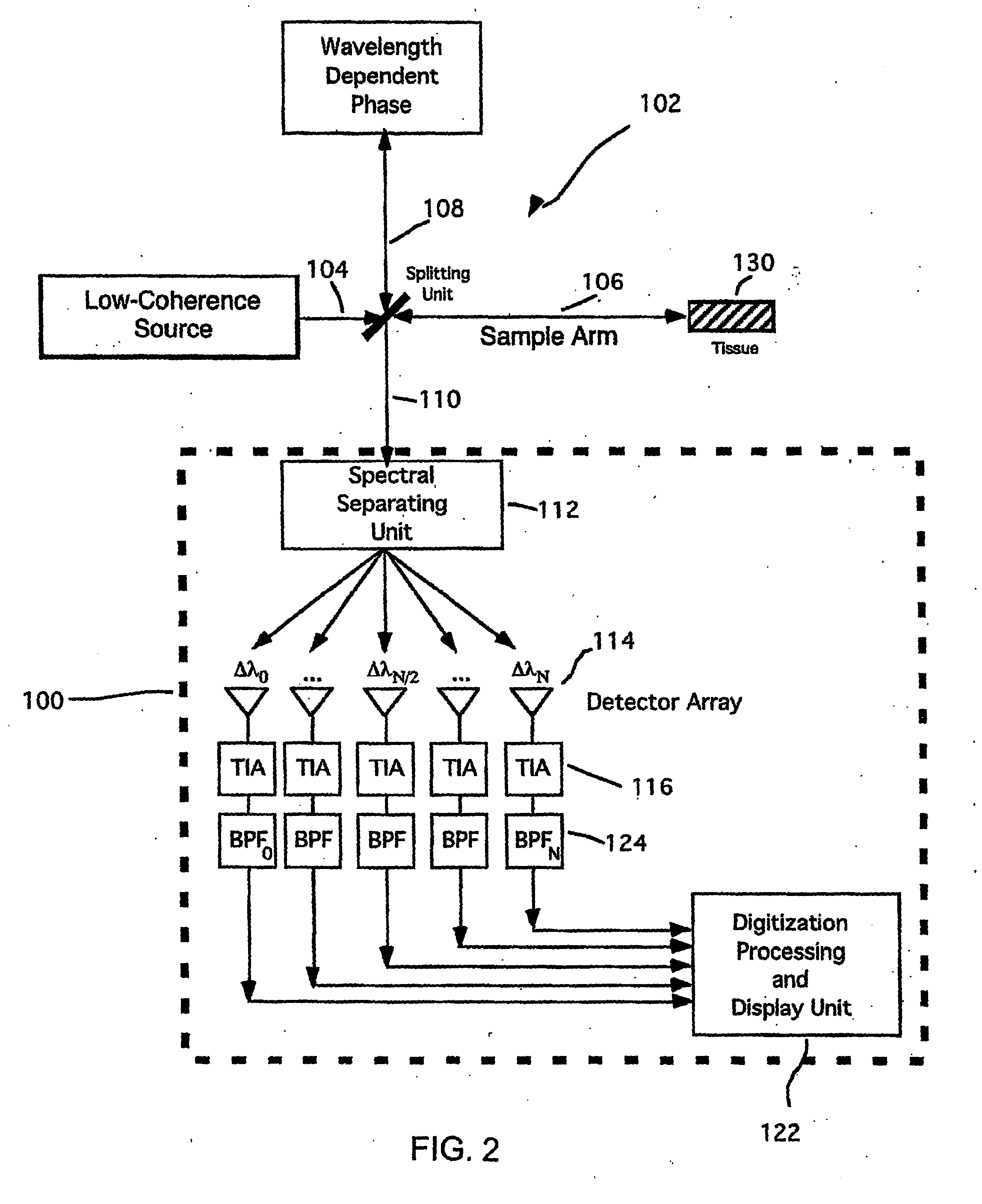
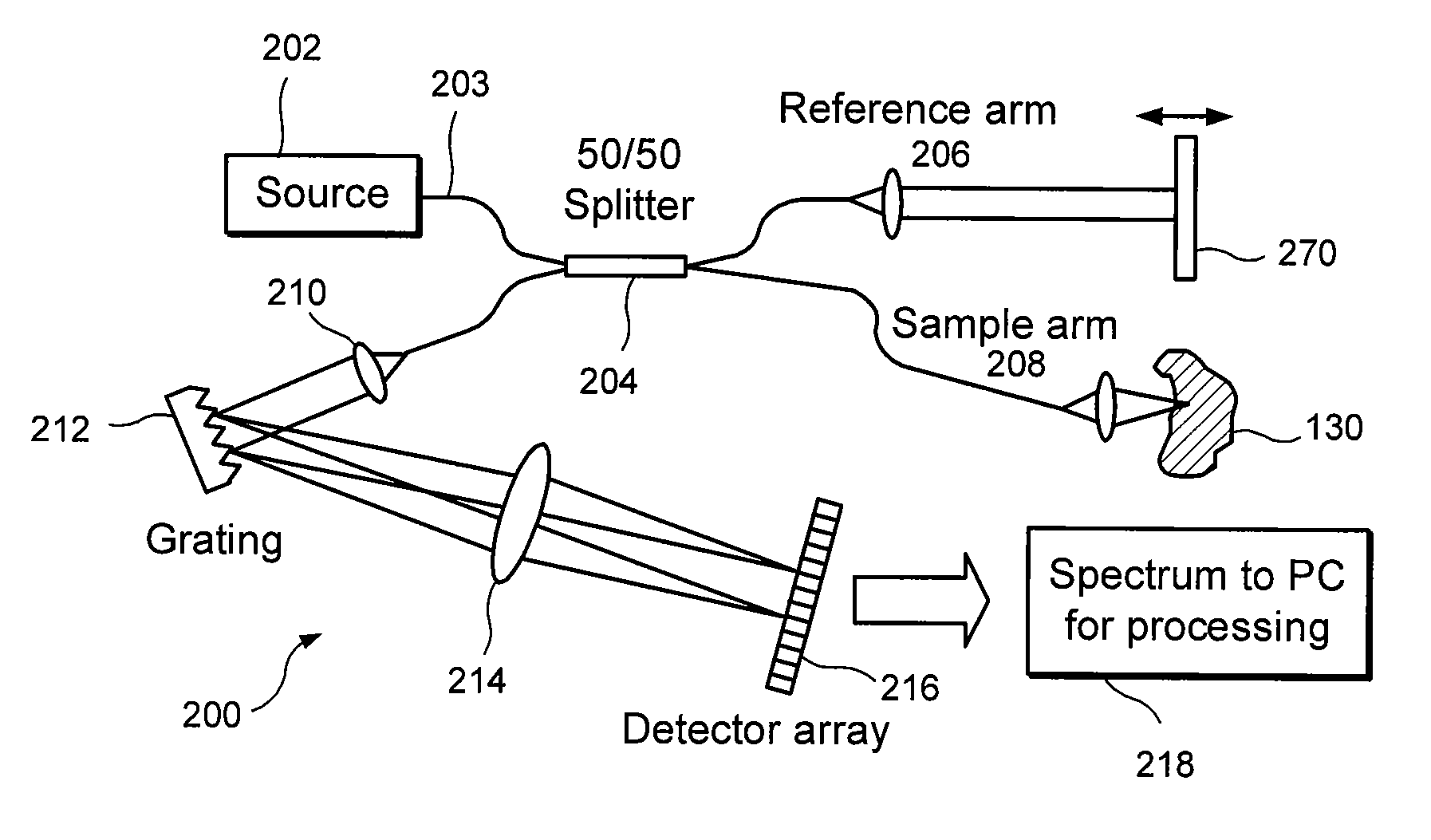
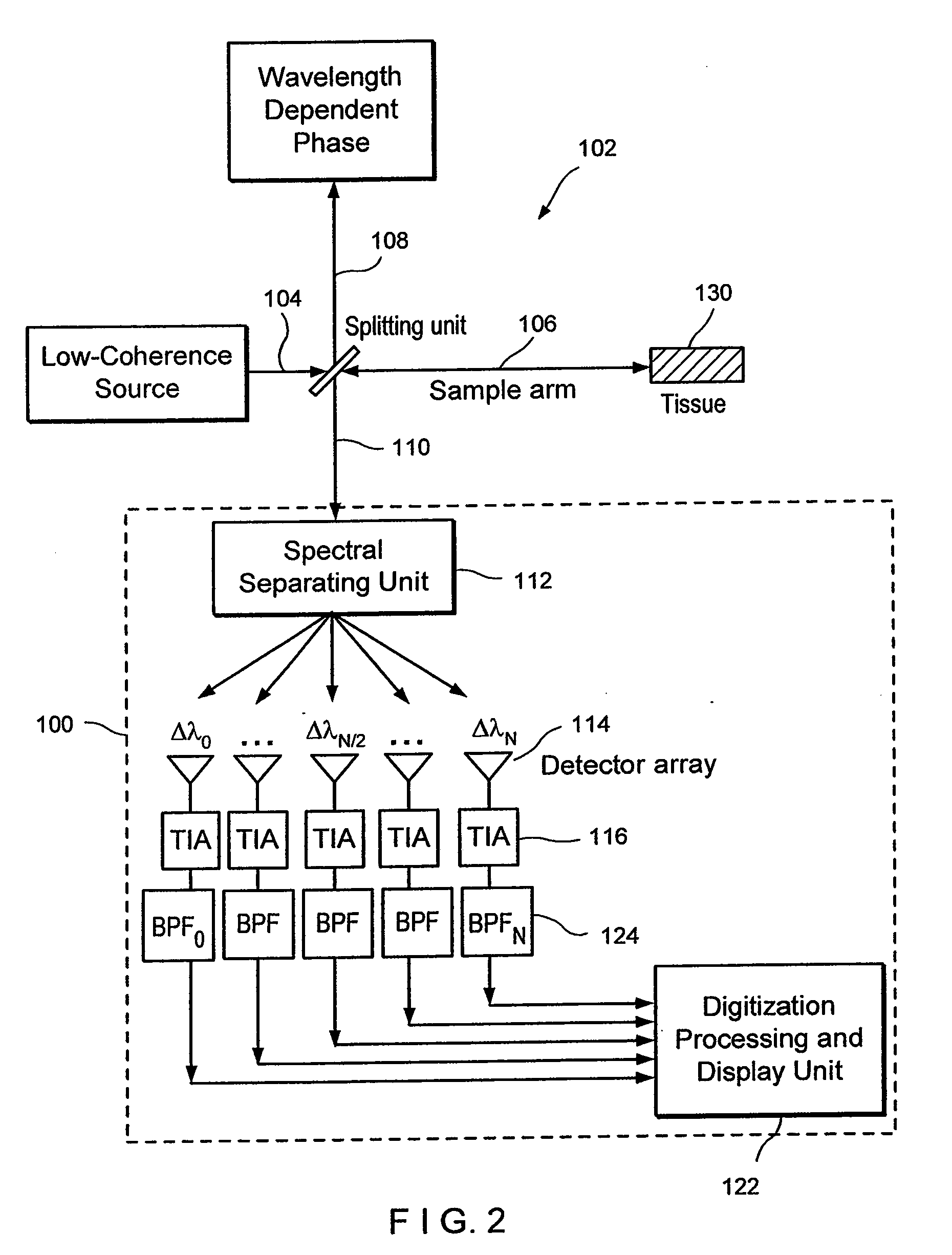
InactiveUS20050018201A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioImproves current data acquisition speed and availabilityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringSpectral bands
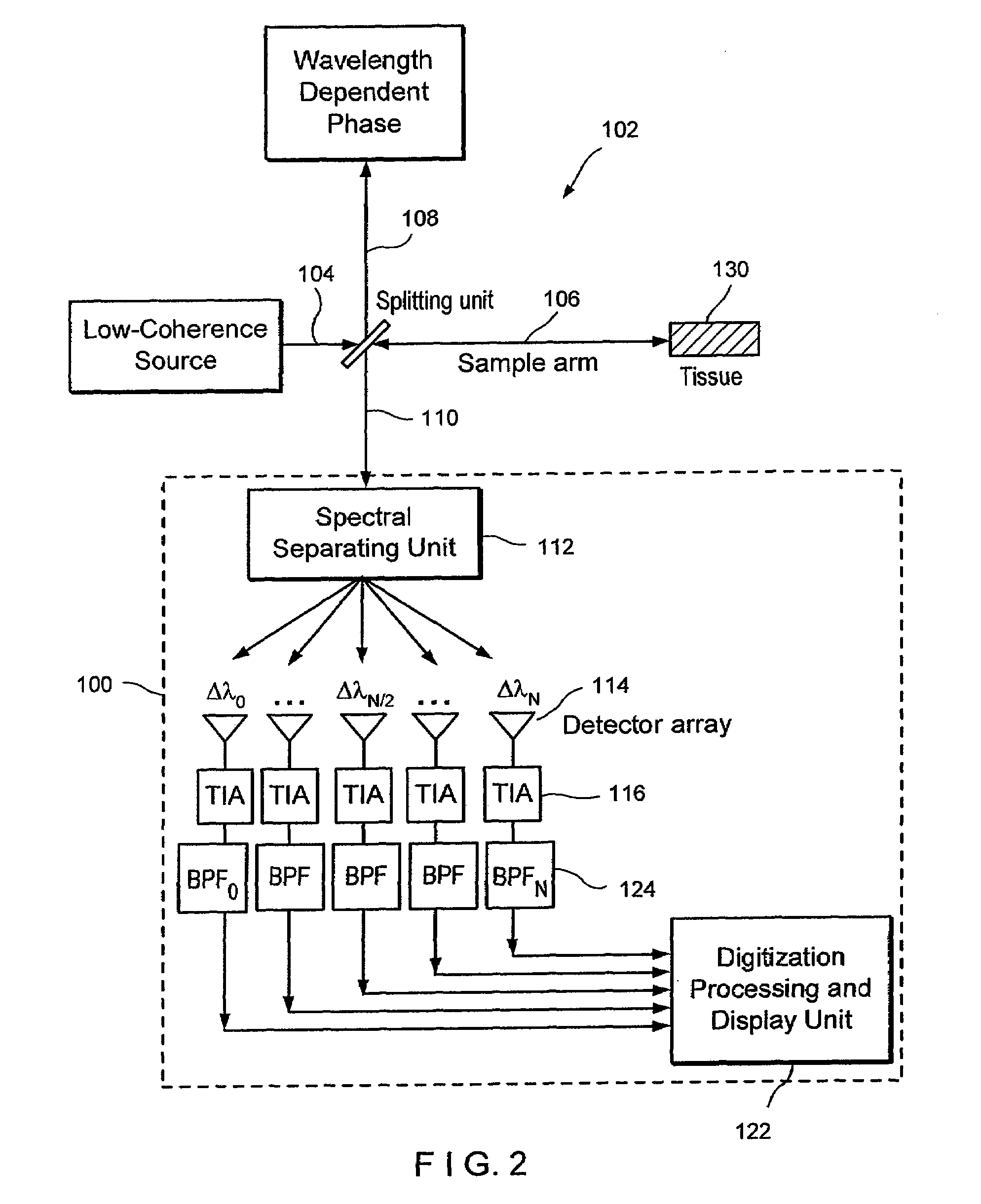
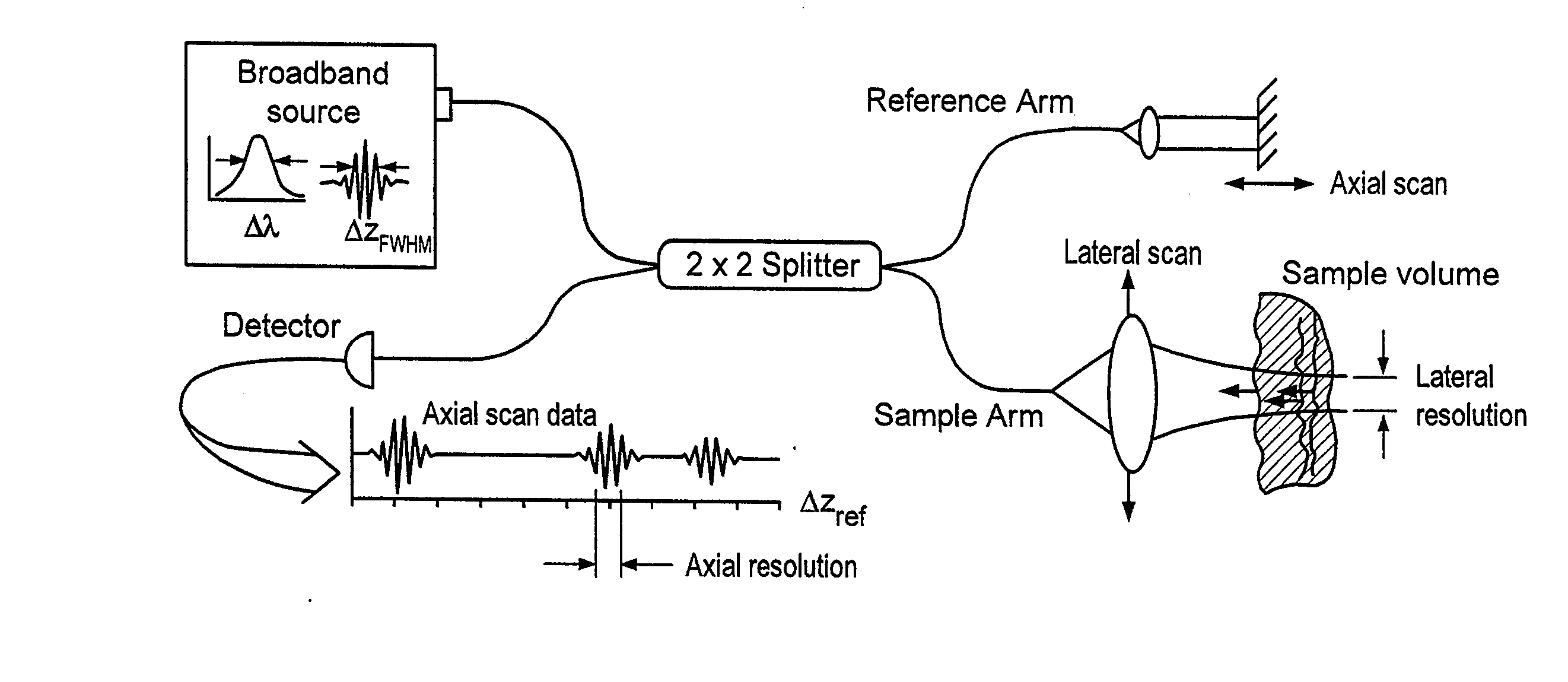
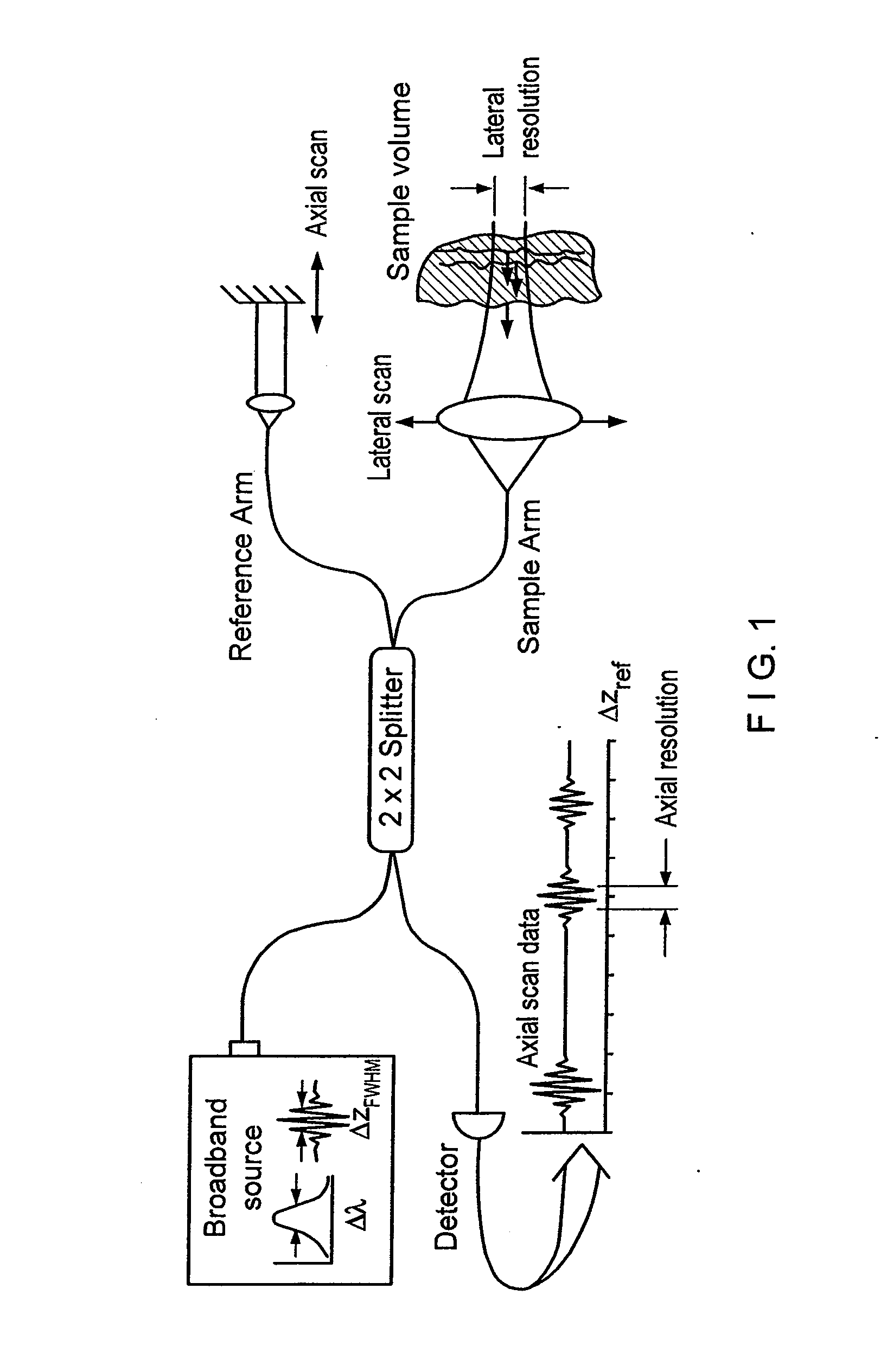
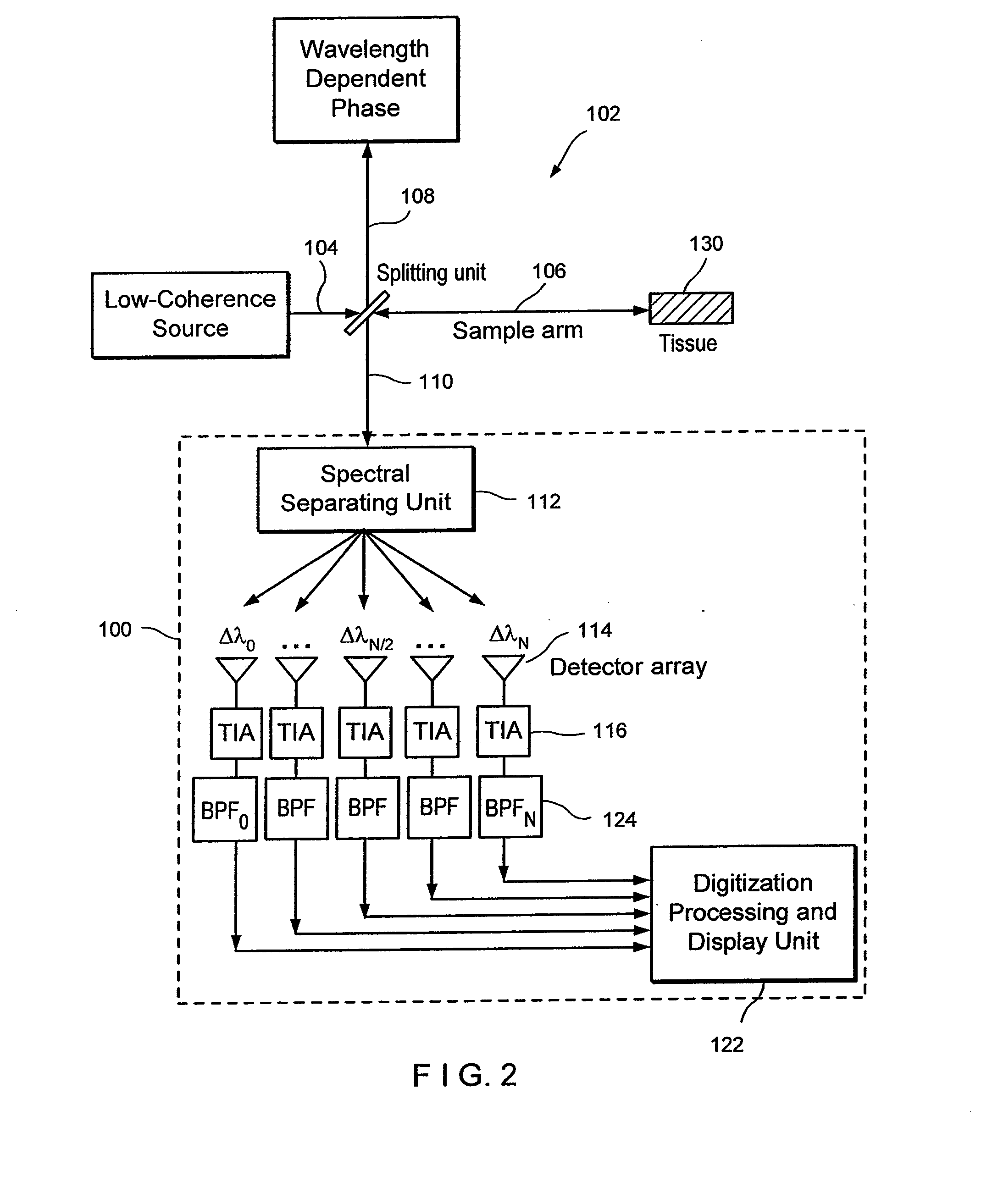
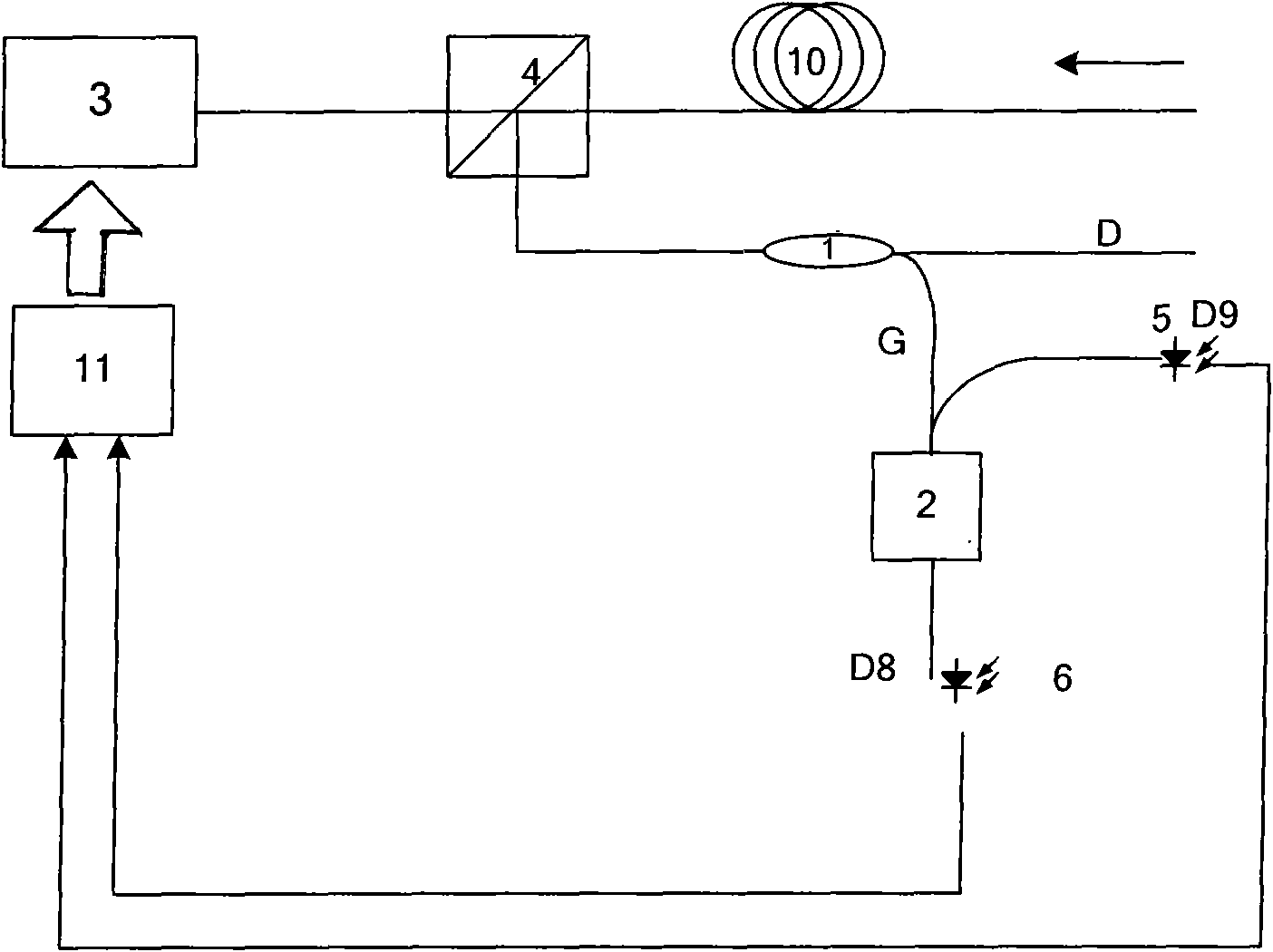
Apparatus, method, logic arrangement and storage medium are provided for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source can be split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands can be individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band may be detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band, the signal can be band p3 filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is likely reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands, while the signal amplitude can remain the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography OCT signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS7355716B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioImproves current data acquisition speed and availabilityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringSpectral bands
Apparatus, method, logic arrangement and storage medium are provided for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source can be split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands can be individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band may be detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band, the signal can be band p3 filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is likely reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands, while the signal amplitude can remain the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography OCT signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS7643153B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioImproves current data acquisition speed and availabilityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringSpectral bands
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS20080094637A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
Apparatus and method for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source is split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands are individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band is detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band the signal is band pass filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands. The signal remains the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
ActiveUS20080094613A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometryDiagnostics using lightBandpass filteringSpectral bands
Apparatus and method for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source is split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands are individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band is detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band the signal is band pass filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands. The signal remains the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
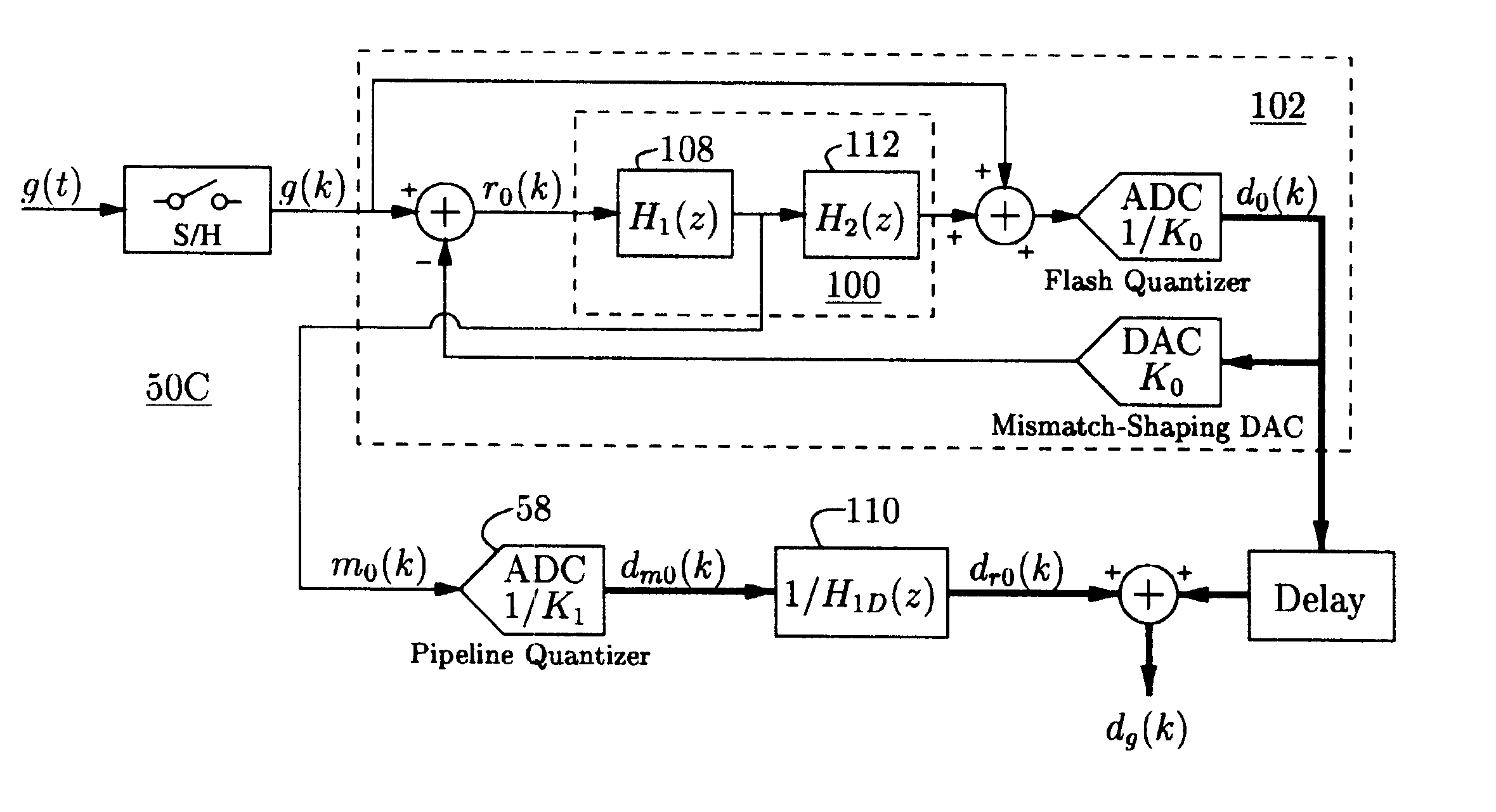
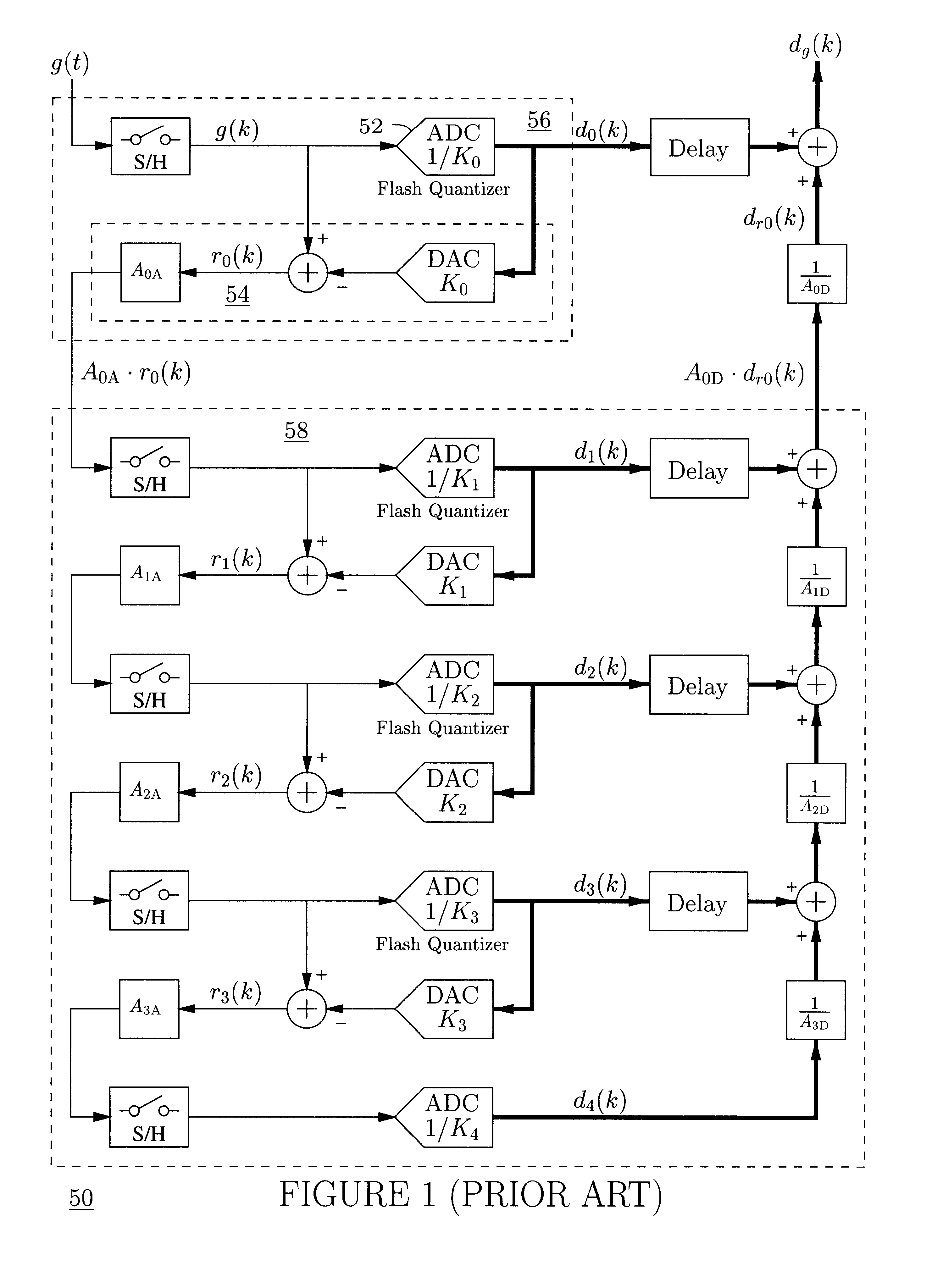
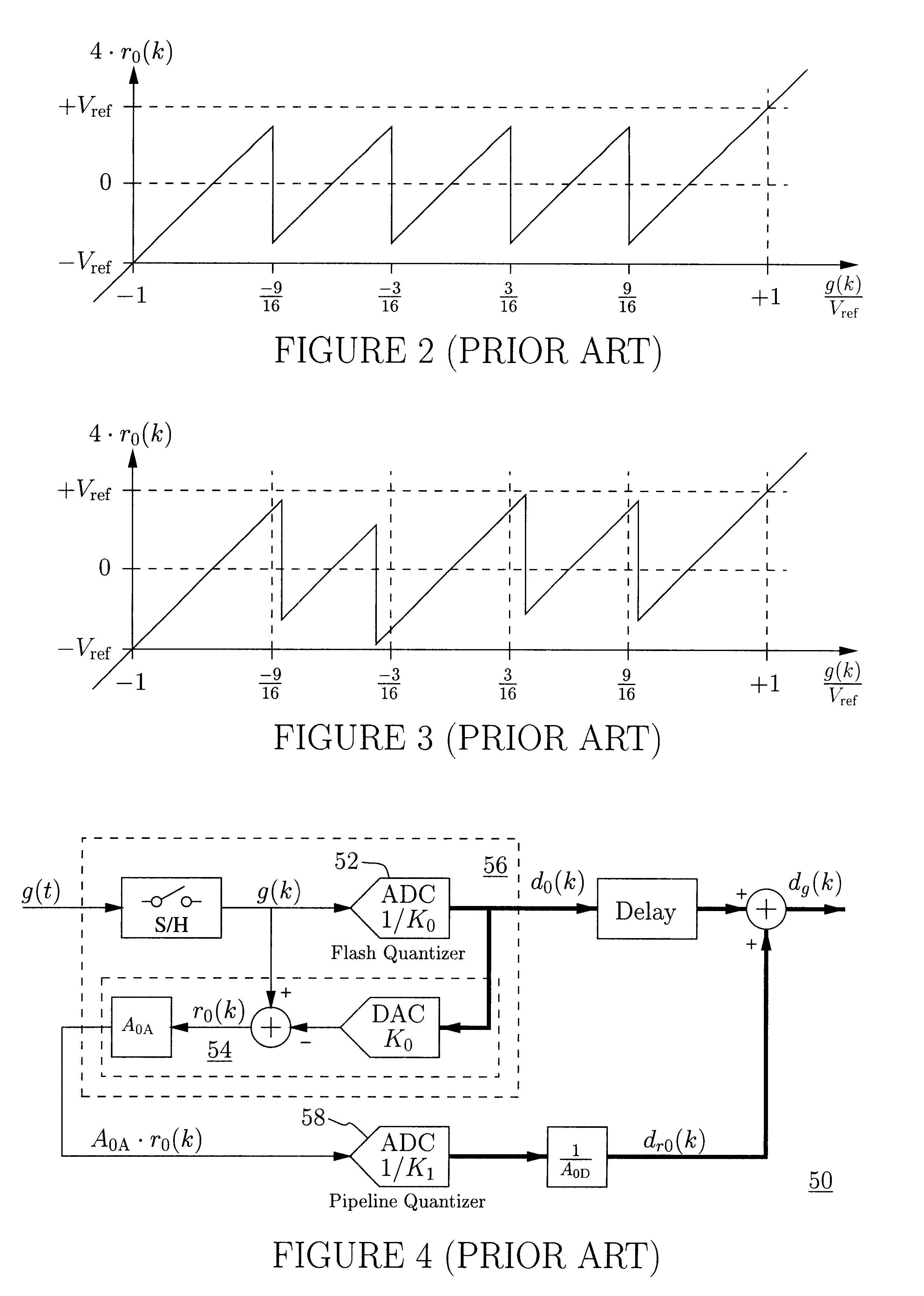
Residue-compensating A/D converter
InactiveUS6556158B2Low-cost highly-linearSuitable for useElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationModem deviceFrequency spectrum
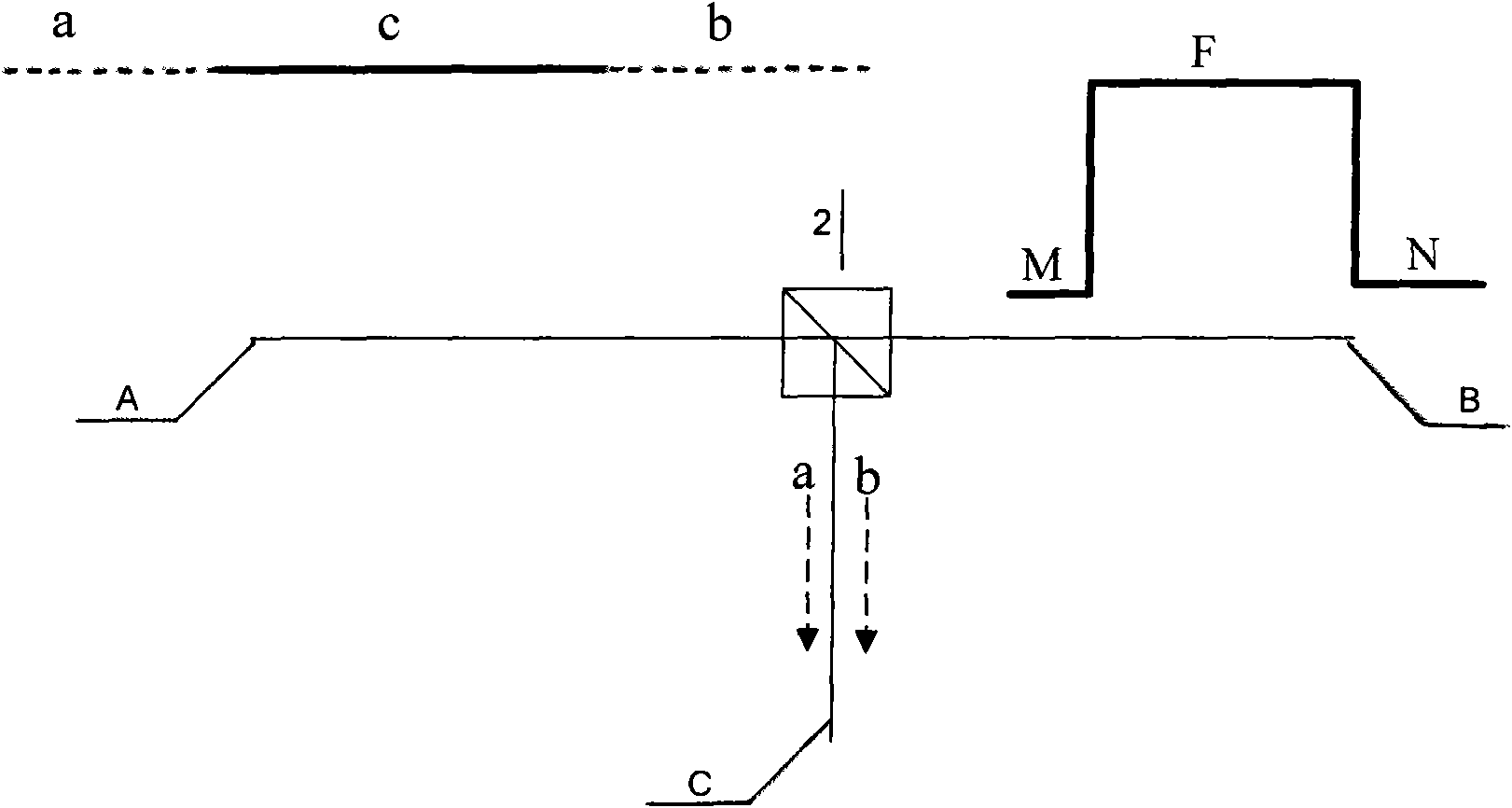
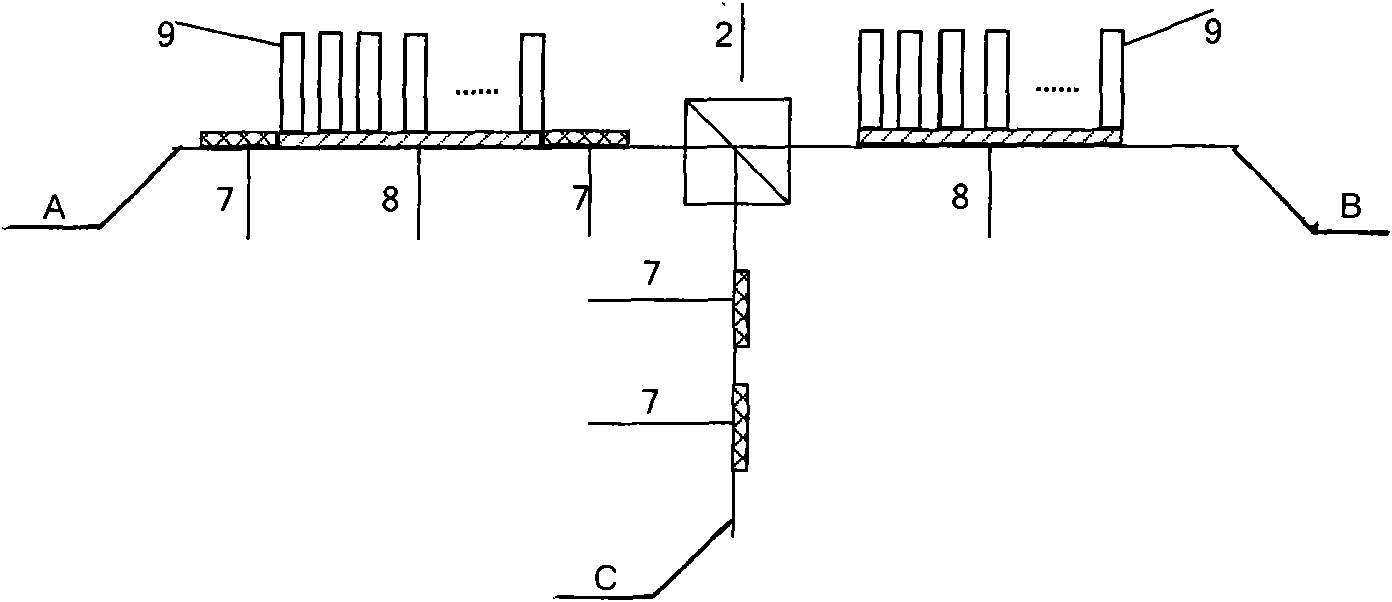
An analog-to-digital converter system [50D] processing an input signal, g, which can be either a discrete-time or a continuous-time signal. A first quantizer [154] generates a first digital signal, d0(k), representing the sum of the input signal, g, and a dithering signal, y0. A digital-to-analog converter [156] generates an analog feedback signal, alpha, representing accurately the first digital signal, d0(k). The DAC [156] may be linearized by the use of mismatch-shaping techniques. A filter [158] generates the dithering signal, y0, by selectively amplifying in the signal band the residue signal, r0, defined as the difference of the input signal, g, and the analog feedback signal, alpha. Optional signal paths [166][168] are used to minimize the closed-loop signal transfer function from g to y0, which ideally will be zero. An analog compensation signal, m0, which is described by a well-controlled relationship to the residue signal, r0, is extracted from the filter [158]. Ideally, the closed-loop signal transfer function from g to m0 will be zero, or at least small in the signal band. A second quantizer [160] converts the analog compensation signal, m0, into a second digital signal, dm0(k). The two digital signals, d0(k) and dm0(k), are filtered individually and then added to form the overall output signal, dg(k). The second digital filter [164] has a low signal-band gain, which implies that the sensitivity to signal-band errors caused by the second quantizer [160] will be low. The output signal, dg(k), is a highly-accurate high-resolution representation of the input signal, g. Circuit imperfections, such as mismatch, gain errors, and nonlinearities, will cause only noise-like errors having a very low spectral power density in the signal band.The invention facilitates the implementation of uncalibrated highly-linear high-resolution wide-bandwidth A / D converters [50D], e.g., for use in digital communication systems, such as xDSL modems and other demanding consumer-market products for which low cost is of the essence.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES BV
Apparatus and method for rangings and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry lci and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS20080097709A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivityDiagnostics using lightNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
Apparatus and method for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source is split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands are individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band is detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band the signal is band pass filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands. The signal remains the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Sampling system
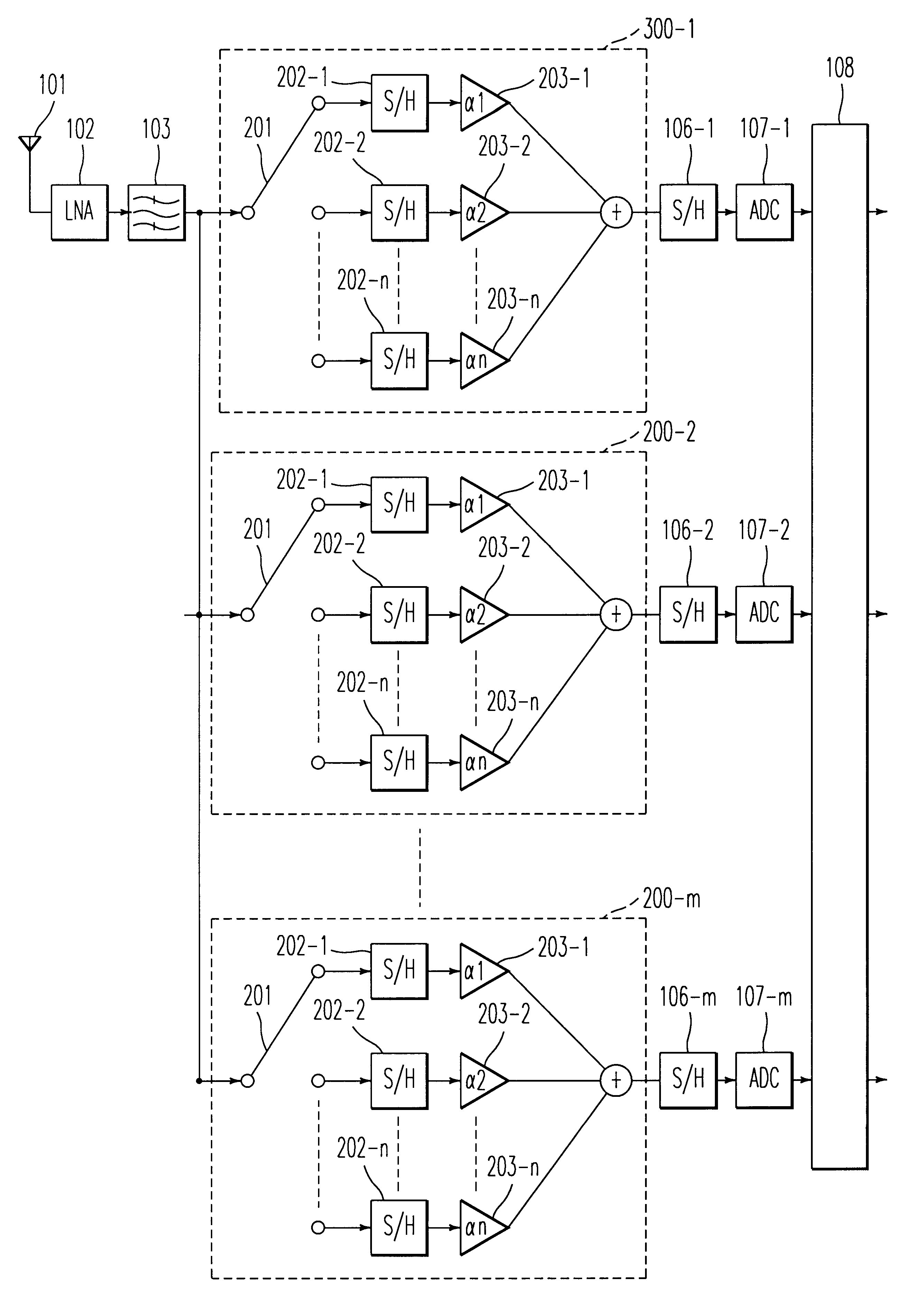
A sampling system arranged such that a modulated signal received by an antenna and input via a low noise amplifier and a band-pass filter is sampled at a sampling frequency higher than the signal band of the modulated signal by a first sample and hold circuit and is input to an analog decimation filter to remove a frequency component which may turn out to be aliasing noise. The output of the analog decimation filter is sampled with a sampling frequency lower than the sampling frequency of the first sample and hold circuit by a second sample and hold circuit and is digitized by an A / D converter to be demodulated by a demodulator. The sampling system which can convert the modulated signal into a low frequency without using the highly precision mixer circuit or a filter having sharp characteristics may be provided by constructing as described above.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Non-linear distortion detection method and distortion compensation amplifying device
InactiveUS20080187035A1Improve accuracyImprove convergence stabilityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionMultiple-port networksNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
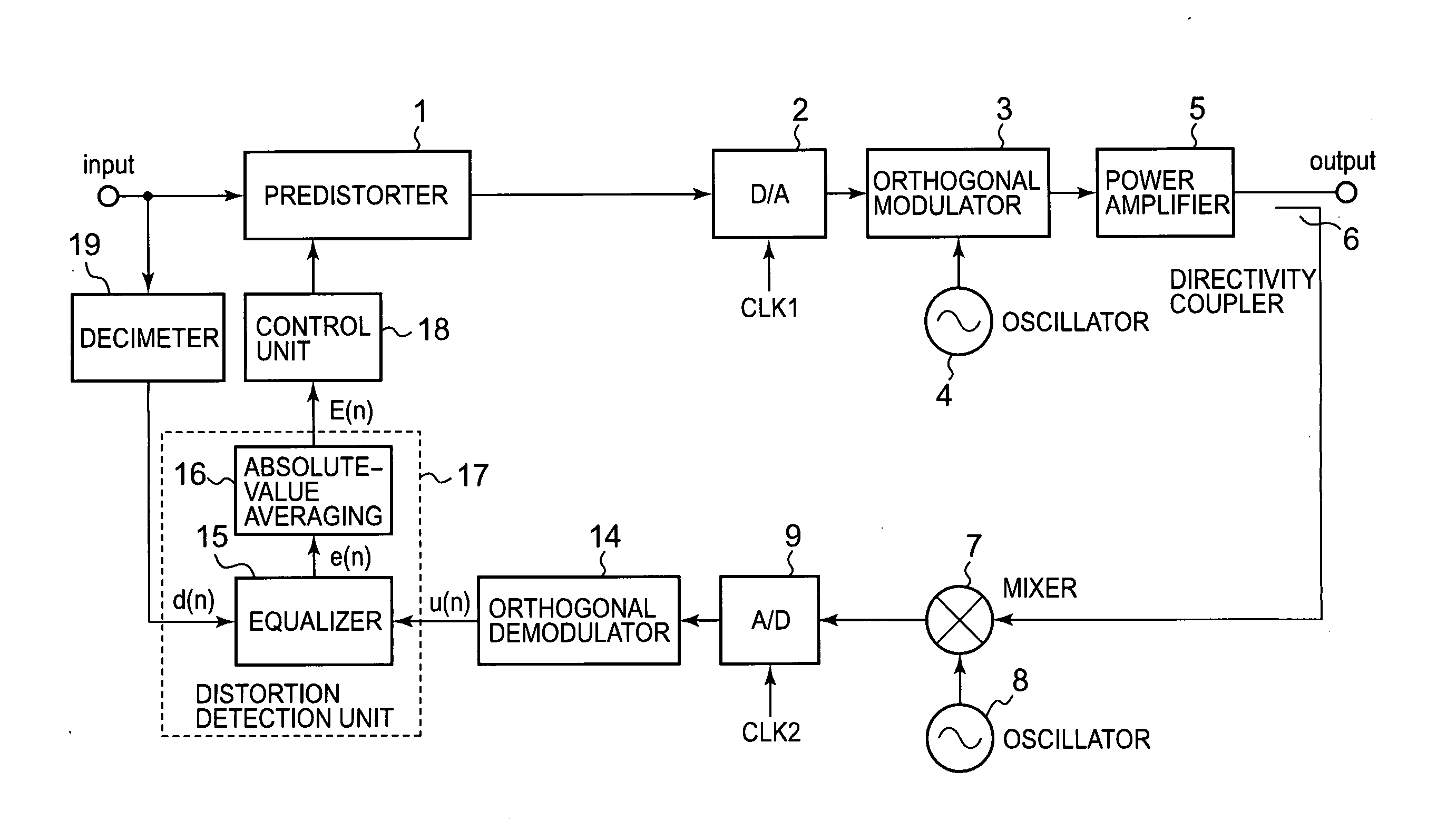
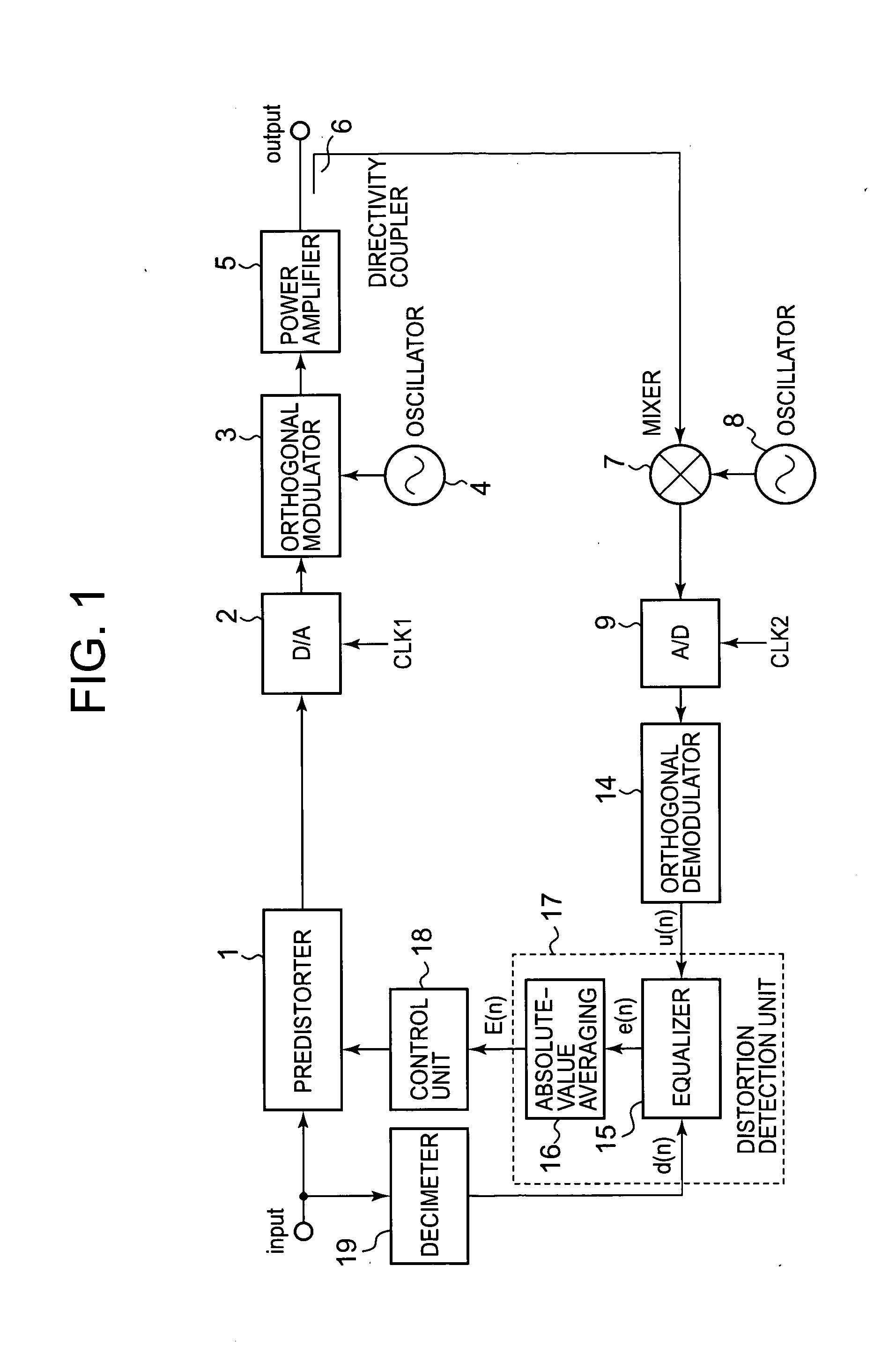
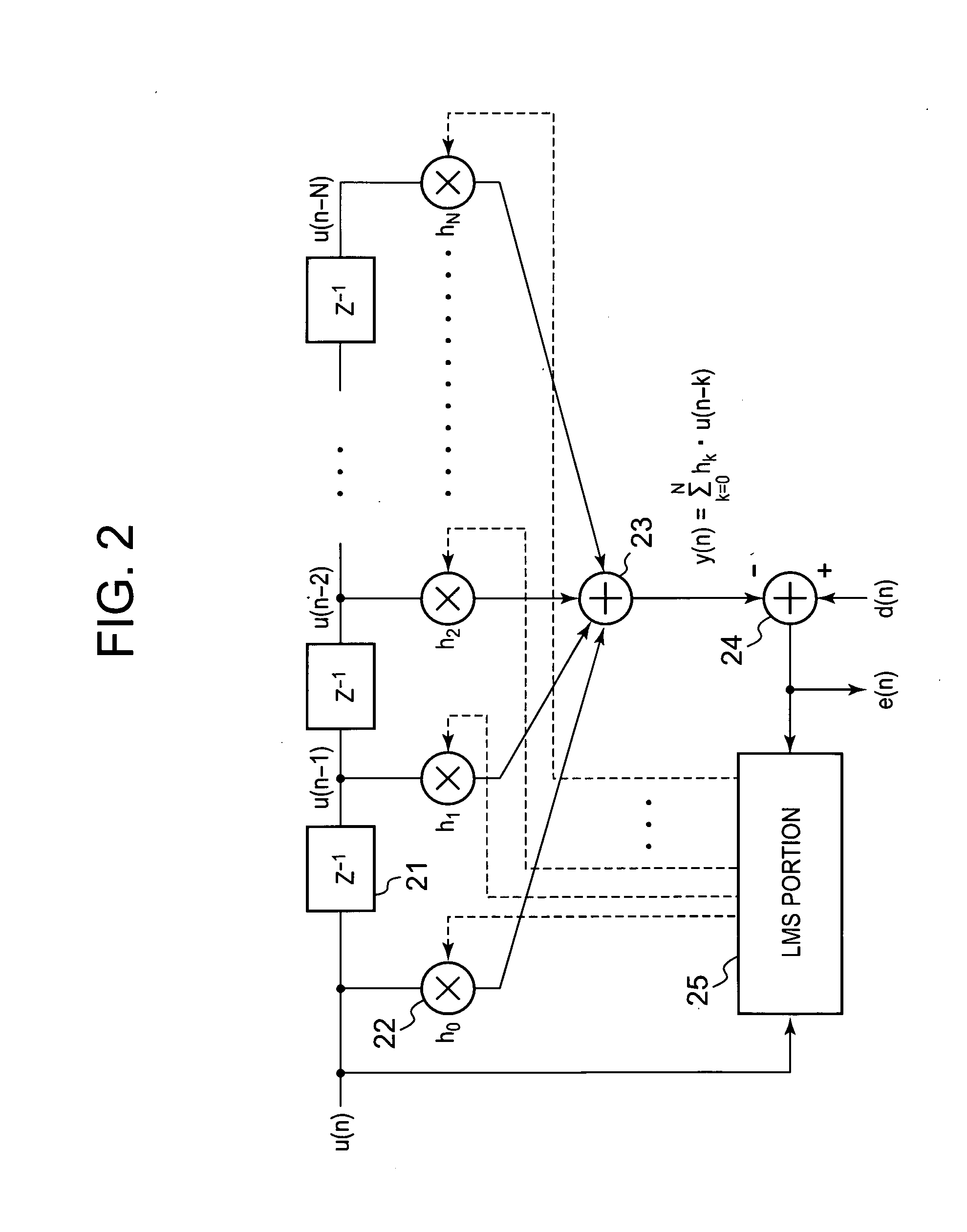
A conventional power amplifying device has a problem that when a signal band is widened, sampling frequency for distortion detection is increased and an FFT calculation amount of a distortion compensation unit is increased, which increase a circuit size and power consumption. The present invention provides a non-linear distortion detection method and a distortion compensation amplifying device capable of suppressing increase of the circuit size and the power consumption even if the signal band is widened. A signal obtained by feeding back an output of a power amplifier is sampled by an A / D converter. An equalizer of a distortion detection unit uses an input signal d(n) of a predistorter as a reference symbol to detect an equalization error e(n) of the orthogonal demodulation signal u(n). An absolute value averaging unit outputs an absolute value of the equalization error e(n) which has been temporally averaged to E(n) as a distortion value to a control unit. According to the distortion value, the control unit adaptively controls the predistorter to perform distortion compensation.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
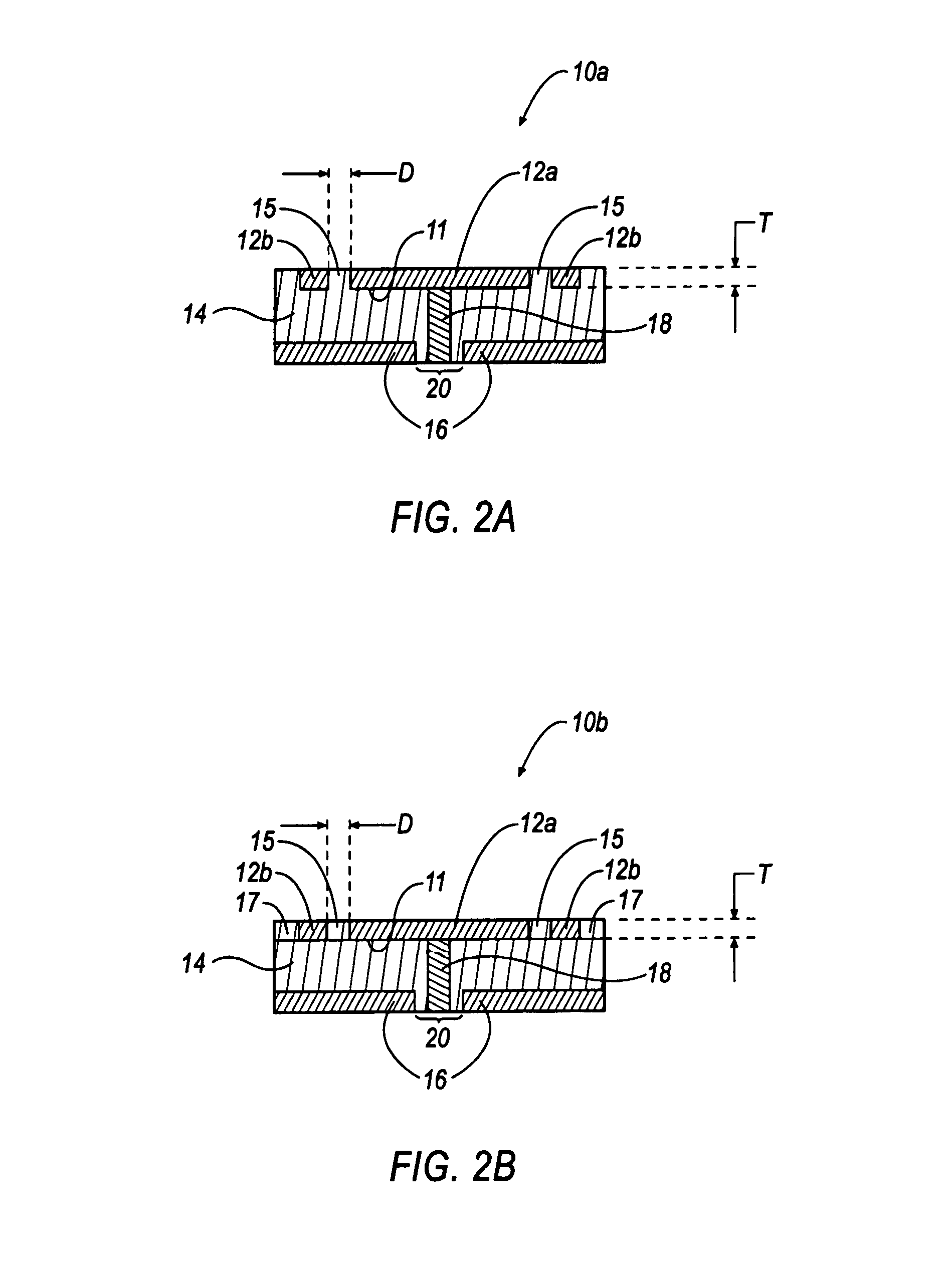
Compact via transmission line for printed circuit board and its designing method
ActiveUS20060255876A1Increased frequency rangeMultiple-port networksPrinted circuit aspectsElectrical conductorMiniaturization
A compact via transmission line for a printed circuit board having preferred characteristic impedance and capable of miniaturizing the printed circuit board including a multilayer printed circuit board, and extending the frequency range of a via transmission line mounted on the printed circuit board, and a design method of the same. The transmission line has a central conductor forming an inner conductor layer boundary make up a signal via hole, a plurality of via holes arranged around the central conductor form an outer conductor layer boundary, and a plurality of conductor plates formed of a printed circuit board conductor layer, is further provided with a constitutive parameter adjustment clearance hole between the inner and outer conductor layer boundaries of the compact via transmission line, and electrically isolates to prevent cross-talk of a signal propagating through a signal via hole with other signals in a high-frequency signal band.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +1
Integrated GPS and SDARS antenna
ActiveUS7253770B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesGlobal Positioning SystemAudio frequency
An integrated patch antenna is disclosed. The integrated patch antenna receives at least a first and second band of signals. The integrated patch antenna includes a bottom metallization and first and second upper metallizations disposed about a dielectric material to receive the first and second signal bands. The first and second signal bands may be, for example, a satellite digital audio radio systems (SDARS) band and a global positioning system (GPS) band.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
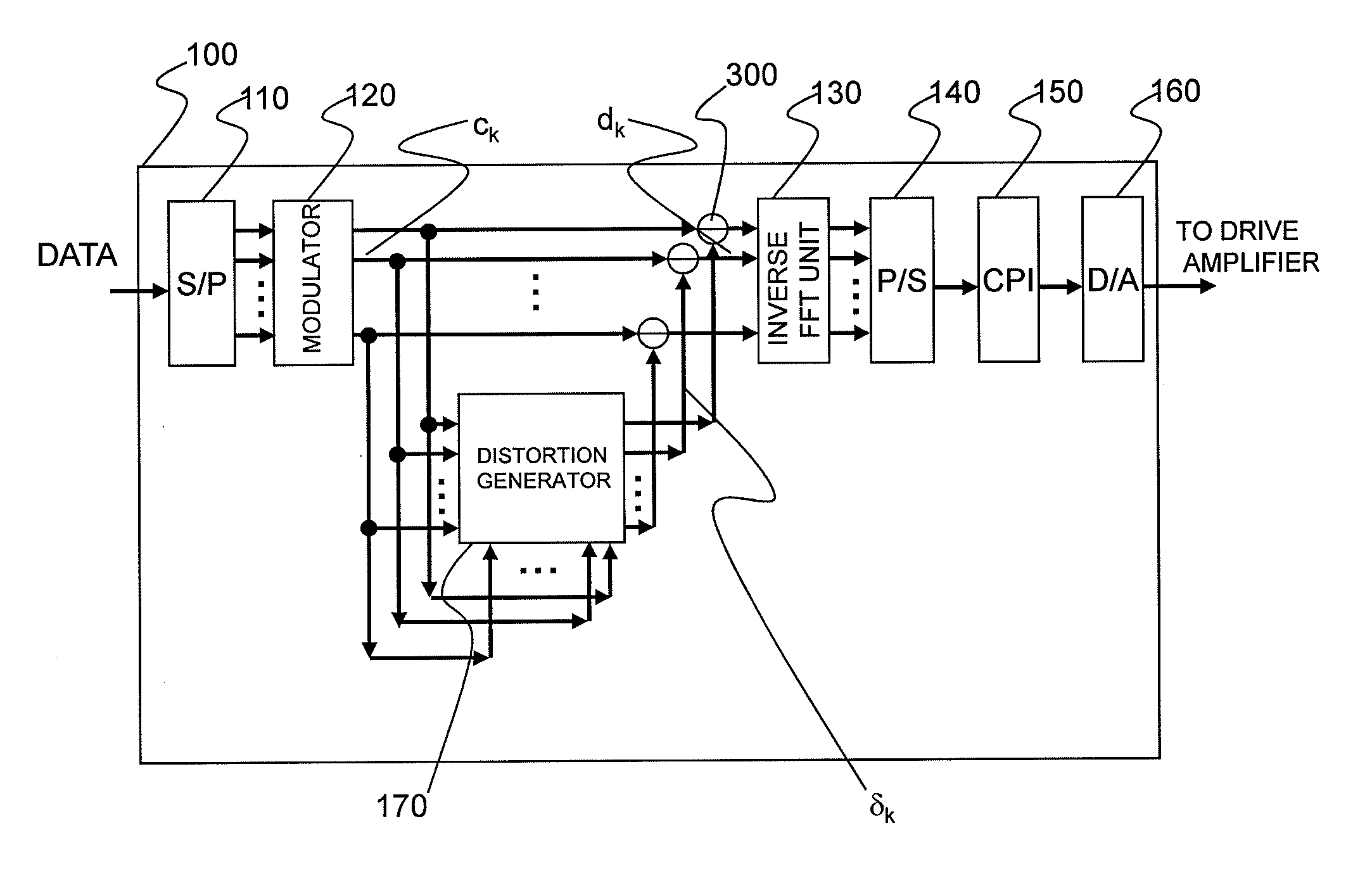
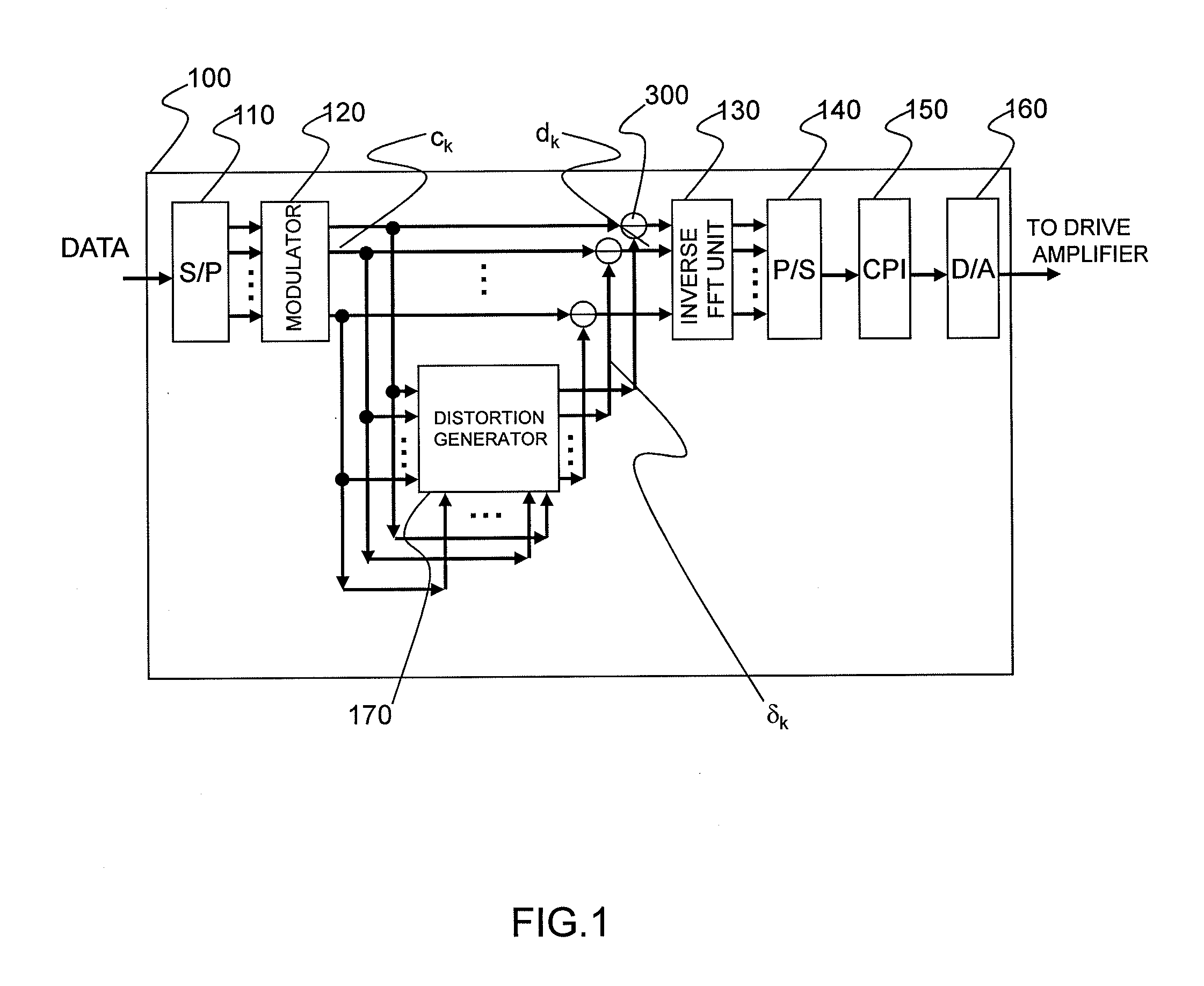
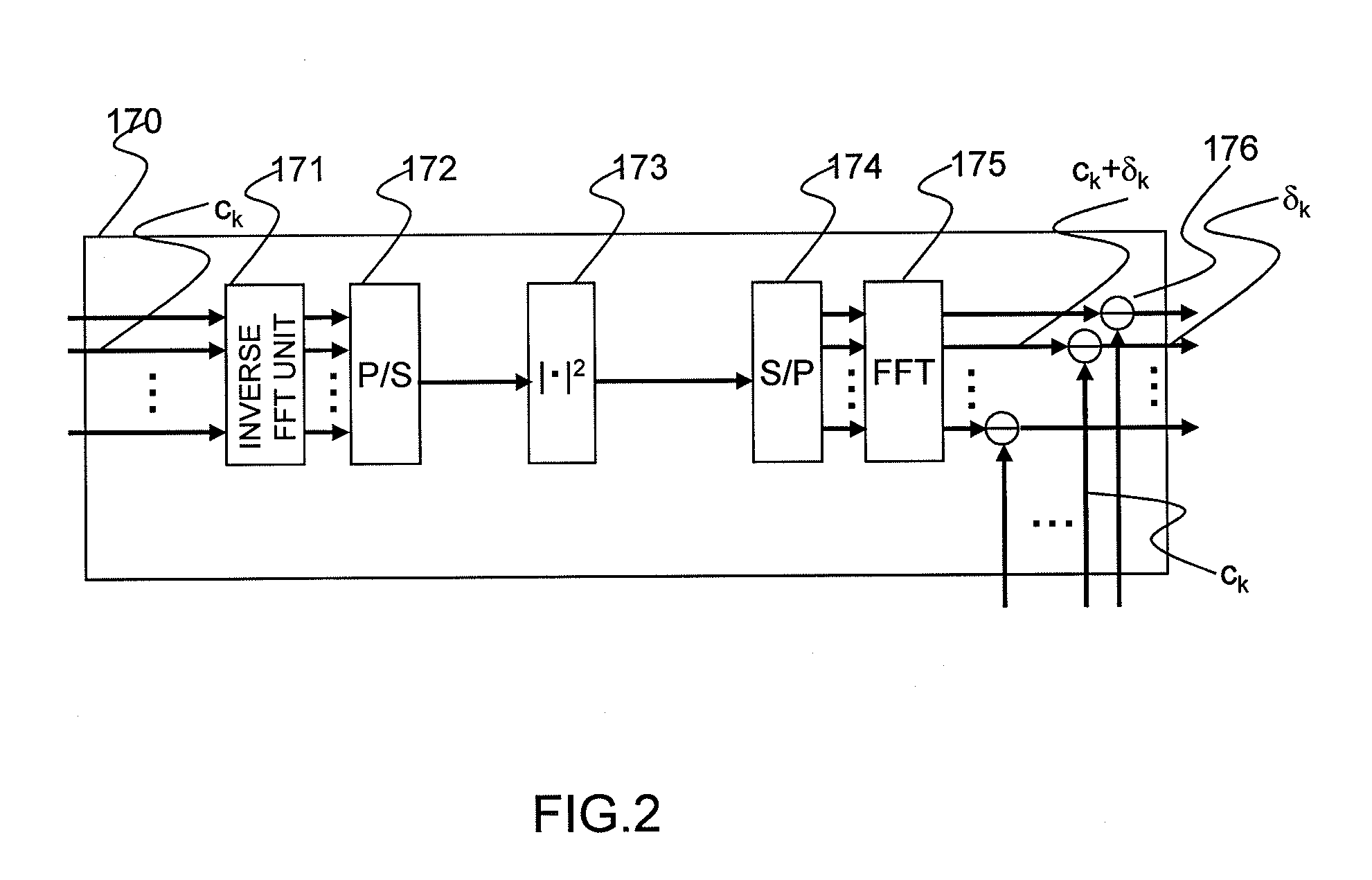
Optical Transmitter and Optical OFDM Communication System
InactiveUS20110249978A1Reduce signalingReduce impactModulated-carrier systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOriginal dataCarrier signal
Distortion of a reception signal which is attributable to interference between subcarriers during photoelectric conversion is reduced in an optical OFDM communication system without broadening the signal band. A transmission signal processing unit (100) in a transmitter is provided with a distortion generating circuit (distortion generating unit) (170). A subcarrier signal is utilized as an input signal for the circuit. The distortion generating circuit (170) generates a baseband OFDM signal by means of inverse FFT calculation using the input signal, computes the square of the absolute value of the signal, and restores the subcarrier signal by mean of FFT calculation. Because interference between subcarriers is also included in the signal, the distortion element generated by the interference between the subcarriers can be extracted when the difference from the input signal is found. The signal obtained by subtracting the distortion element from the subcarrier signal, which has been modulated using the original data to be communicated, is used as the transmission signal. The transmission signal is photoelectrically converted with a receiver. The interference between subcarriers generated at this time is smaller than when the aforementioned processing is not performed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
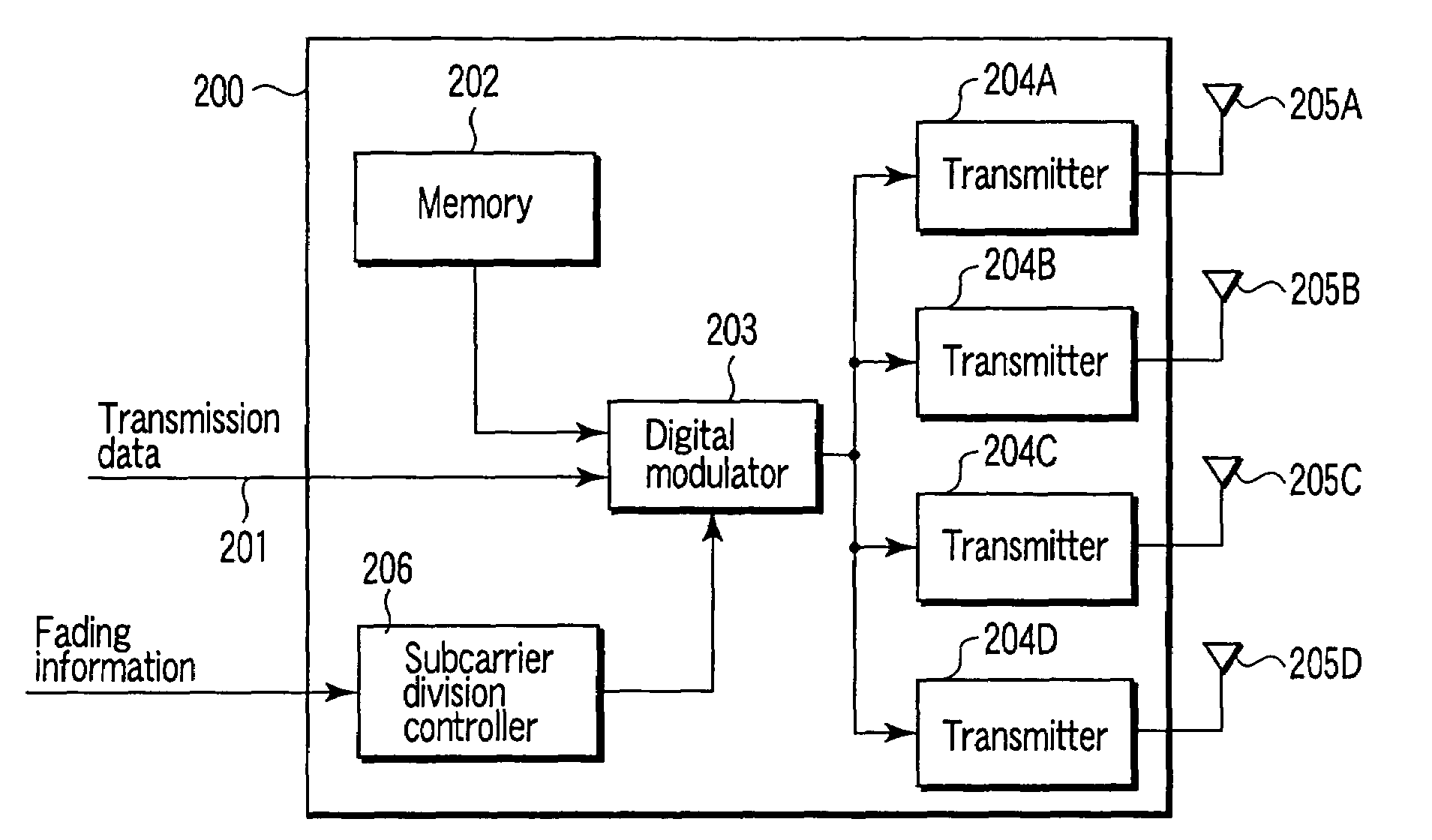
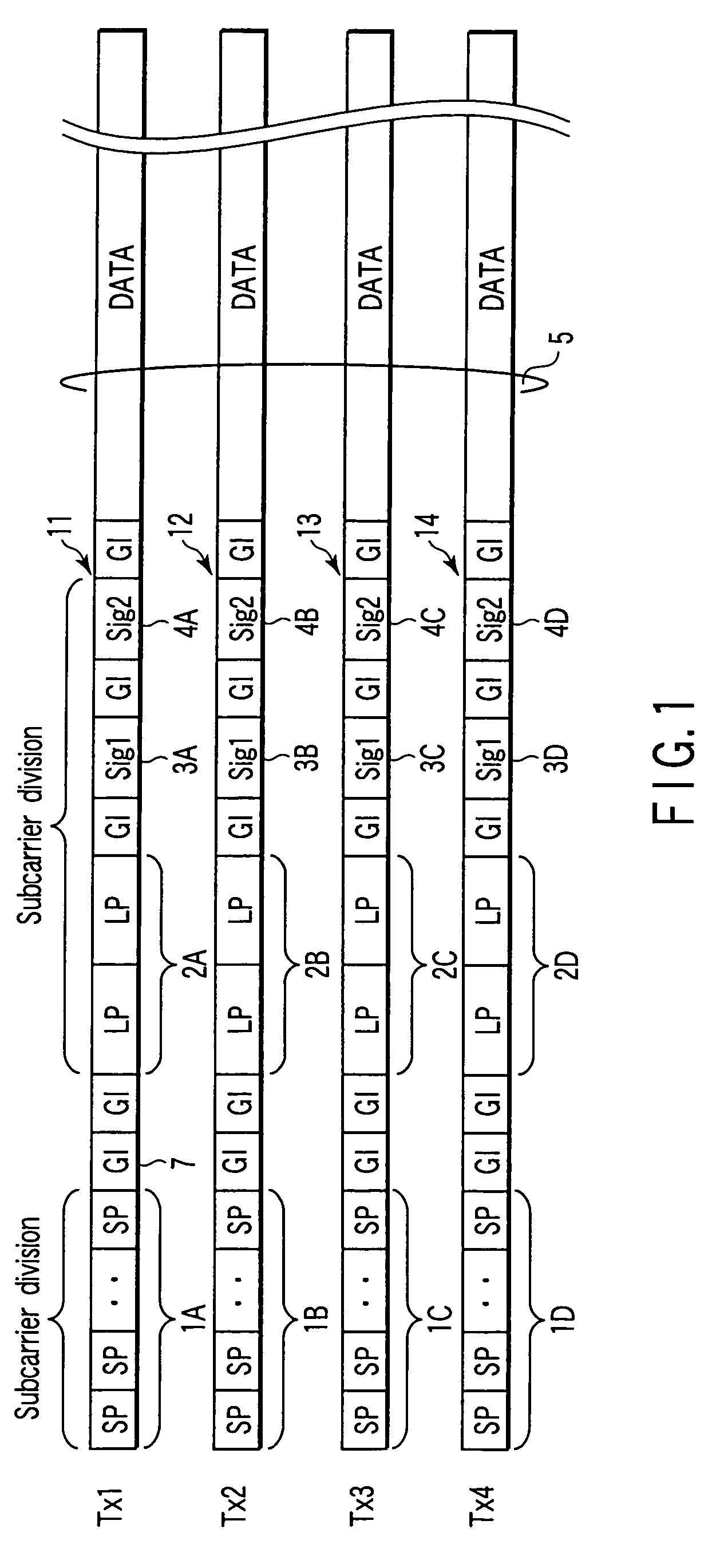
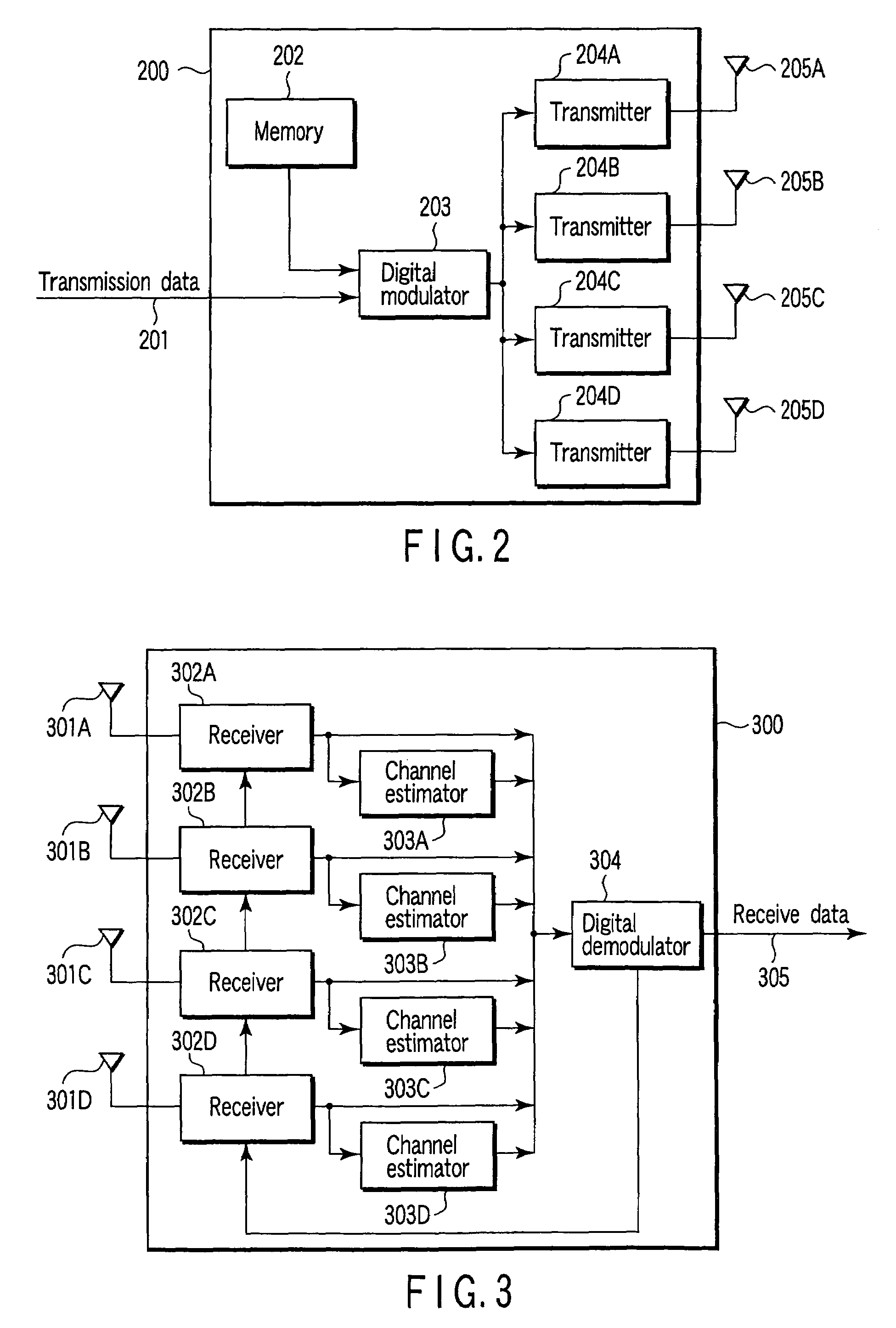
MIMO transmission and reception methods and devices
InactiveUS7415074B2Spatial transmit diversityMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsTelecommunicationsMimo transmission
In a wireless transmitting device which performs transmission by an OFDM using a plurality of subcarriers orthogonal to each other, a plurality of preambles to which a plurality of different subcarrier groups selected from a plurality of subcarriers within an OFDM signal band are allocated are transmitted by using a plurality of transmit antennas, and data is transmitted by using the antennas after the preambles are transmitted.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Integrated GPS and SDARS antenna
ActiveUS20060097924A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesEngineeringGlobal Positioning System
An integrated patch antenna is disclosed. The integrated patch antenna receives at least a first and second band of signals. The integrated patch antenna includes a bottom metallization and first and second upper metallizations disposed about a dielectric material to receive the first and second signal bands. The first and second signal bands may be, for example, a satellite digital audio radio systems (SDARS) band and a global positioning system (GPS) band.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
No-time-delay flat-frequency-spectrum broadband photon integrated chaos semiconductor laser
ActiveCN104158085ASpectrum flatFlat outputLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionFrequency spectrumTime delays
The invention relates to a semiconductor laser, in particular to a no-time-delay flat-frequency-spectrum broadband photon integrated chaos semiconductor laser which solves the problems that chaos lasers generated by an existing semiconductor laser have the time delay characteristic, the signal band width is small, and the frequency spectrum is not flat. The no-time-delay flat-frequency-spectrum broadband photon integrated chaos semiconductor laser comprises a chip substrate, an optical waveguide, an erbium-doped passive optical waveguide, a left distributed feedback semiconductor laser chip, a no-isolation two-way amplified semiconductor light amplification chip, a right distributed feedback semiconductor laser chip and a high-speed photoelectric detection chip. The no-time-delay flat-frequency-spectrum broadband photon integrated chaos semiconductor laser is suitable for the fields of synchronization of chaos, secrecy light communication, high-speed random number secret key generation, laser radar, optical fiber network fault detection, ultra broadband technology, distributed optical fiber sensing and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Encoding Device, Decoding Device, and Method Thereof
ActiveUS20080027733A1Improve subjective qualityEasy to adjustSpeech analysisCode conversionMultiplexingFrequency spectrum
There is disclosed an encoding device capable of appropriately adjusting the dynamic range of spectrum inserted according to the technique for replacing a spectrum of a certain band with a spectrum of another band. The device includes a spectrum modification unit (112) which modifies a first spectrum S1(k) of the band 0≦k<FL in various ways to change the dynamic range so that a way of modification for obtaining an appropriate dynamic range is checked. The information concerning the modification is encoded and given to a multiplexing unit (115). By using a second spectrum S2(k) having a valid signal band 0≦k.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
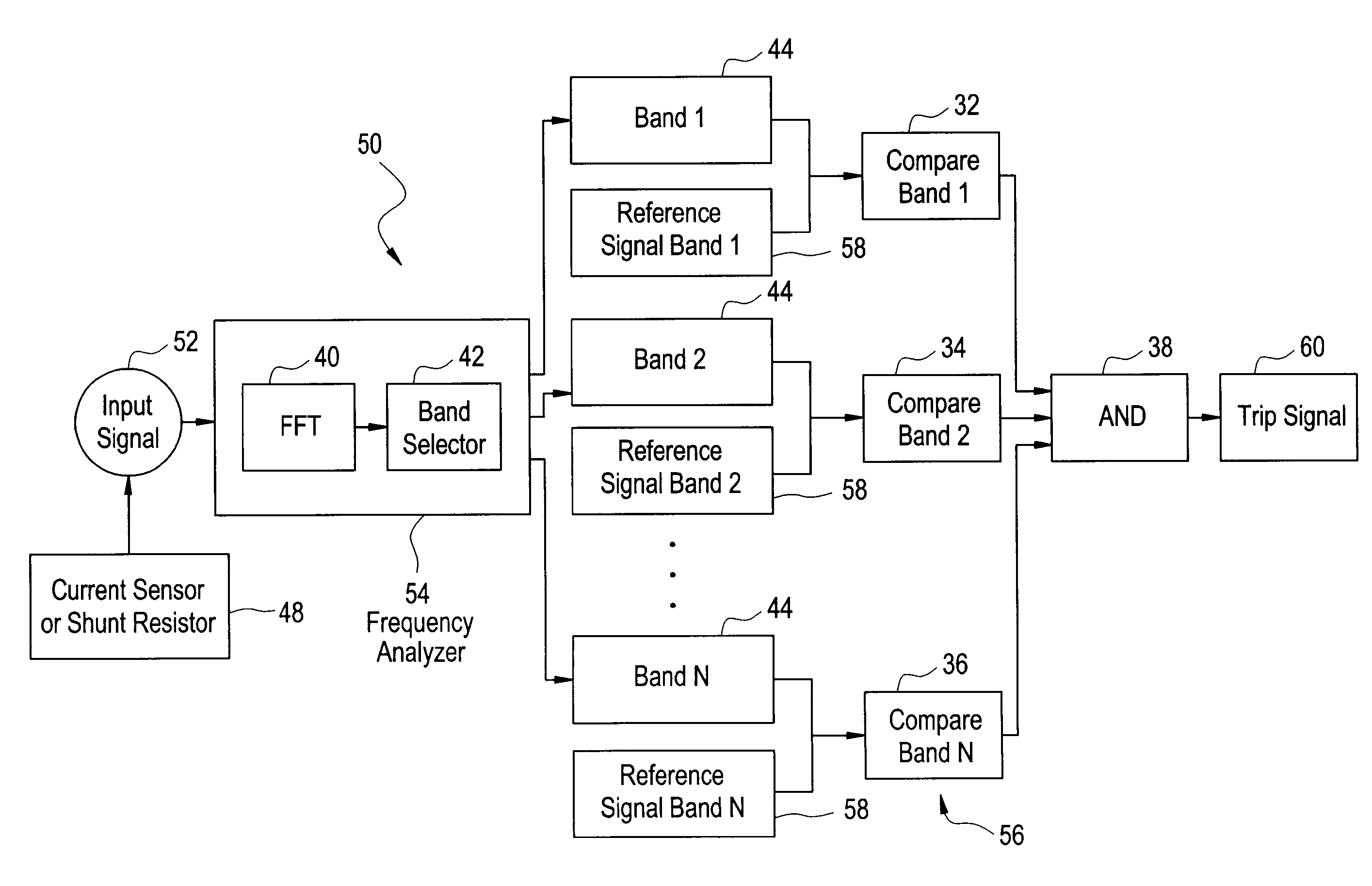
Series arc detection
ActiveUS7062388B2Spectral/fourier analysisCircuit-breaking switches for excess currentsHarmonicElectric power
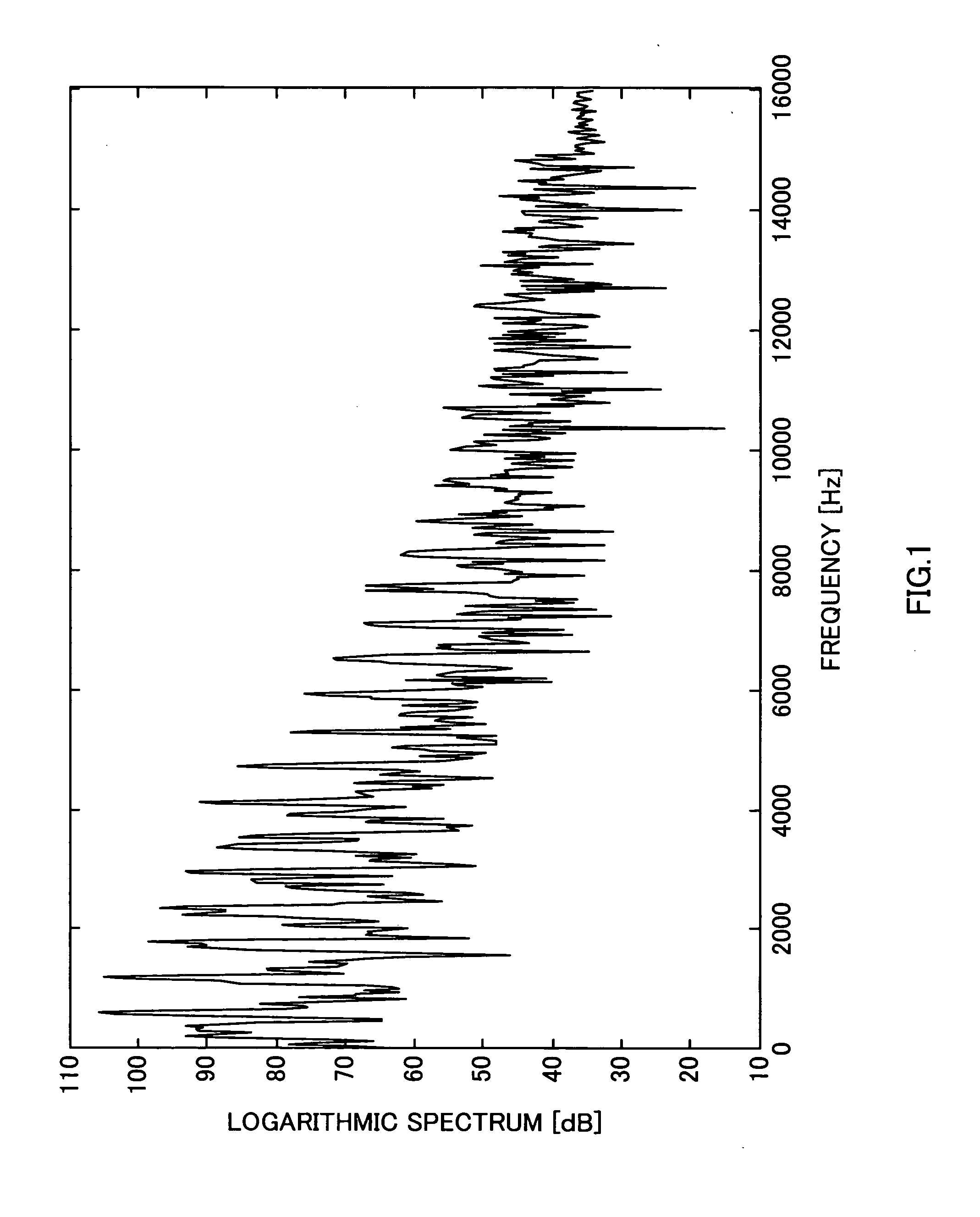
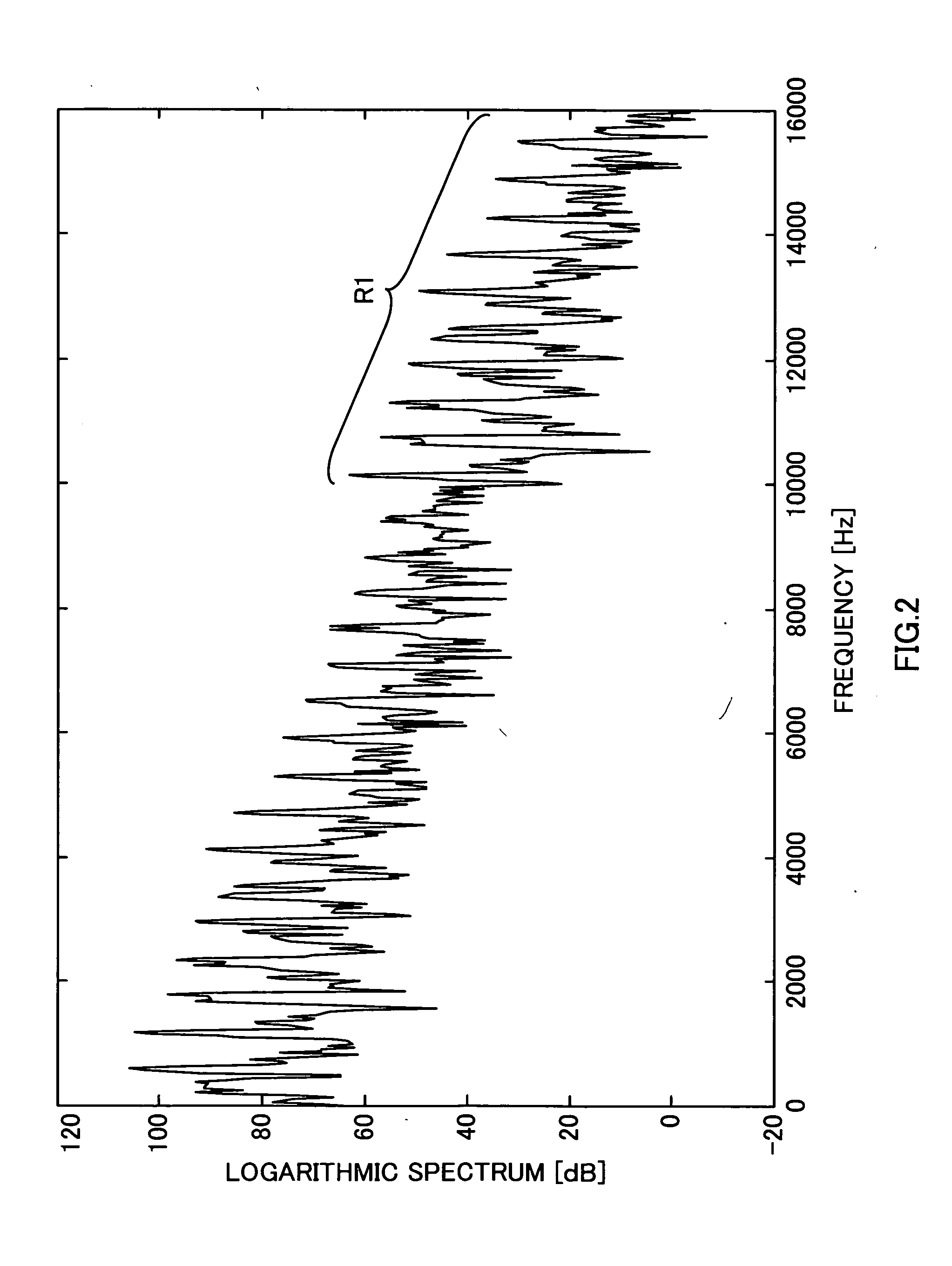
A frequency harmonic identifier for detecting series arcs on a power line includes a frequency analyzer for providing the harmonic content of a sensed current signal and a decision logic for comparing a tested signal to at least one reference signal band. The reference signal band or bands may represent a variety of common loads and if the tested signal does not match any of the sets of reference signal bands, then the logic determines the tested signal to be a series arc signal. The frequency harmonic identifier may be provided within a circuit interrupter and may issue a trip signal if the tested signal is determined to be a series arc signal. Also disclosed is a method for detecting series arcs, and a storage medium having instructions for causing a computer to implement the method.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
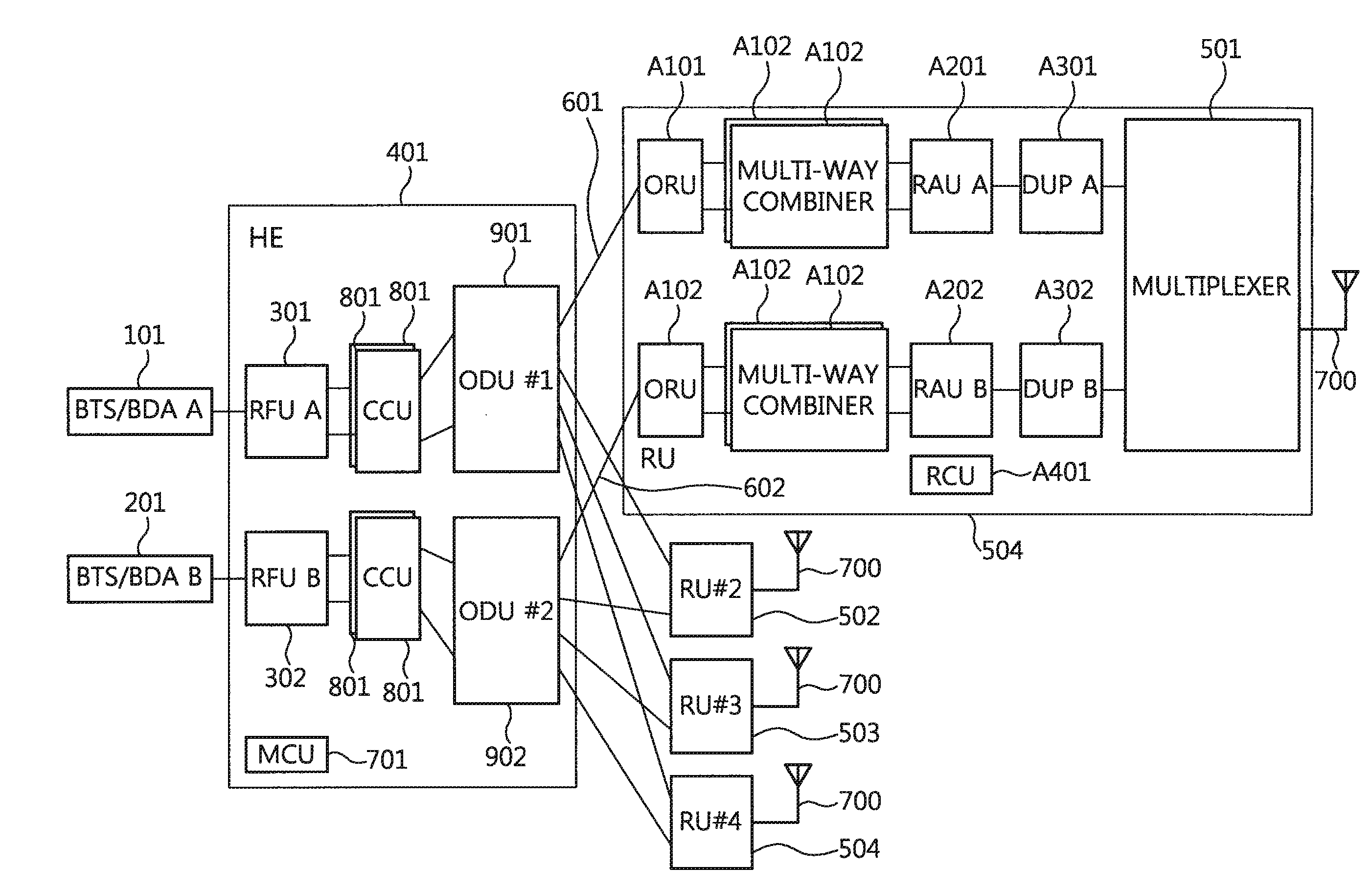
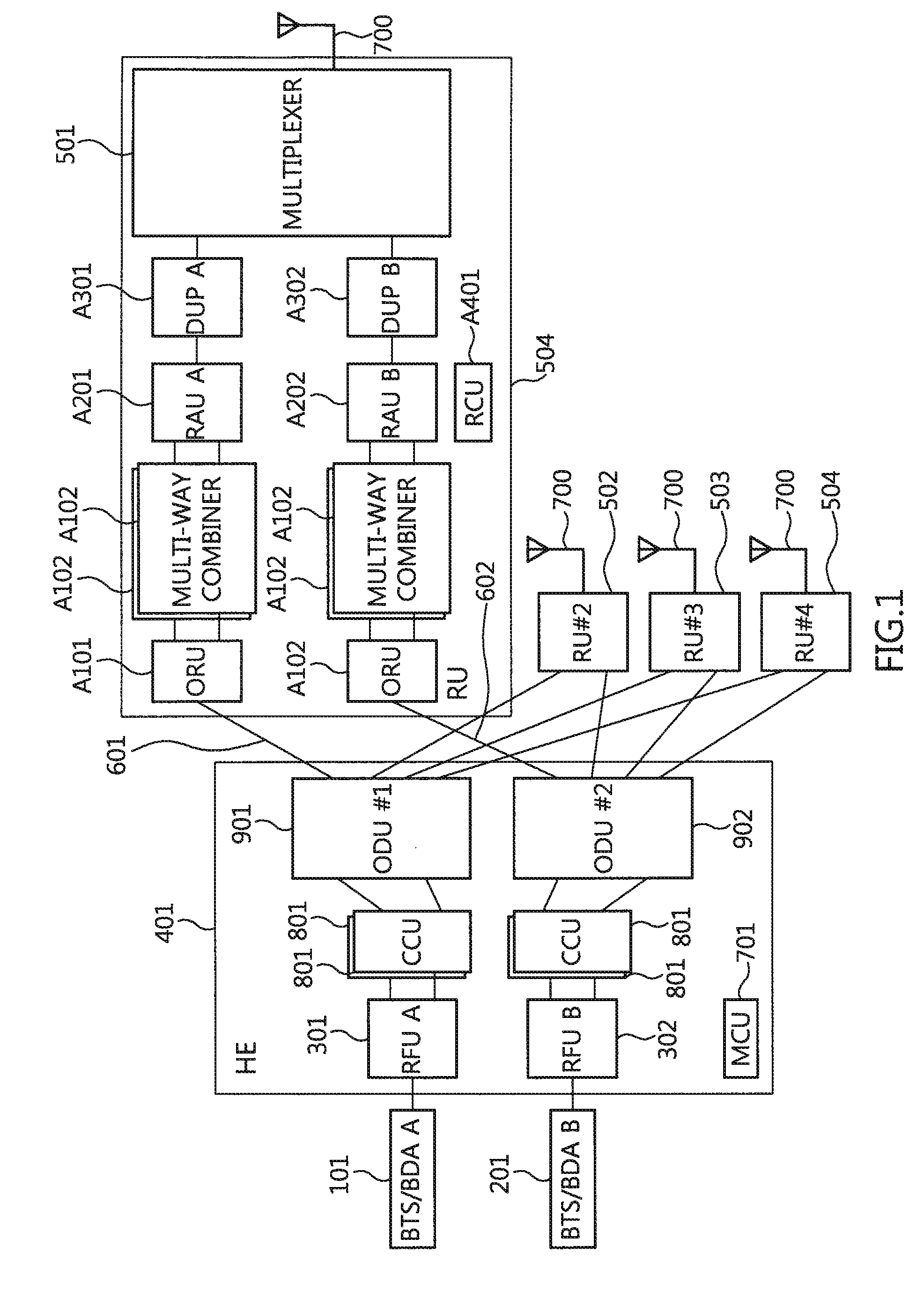
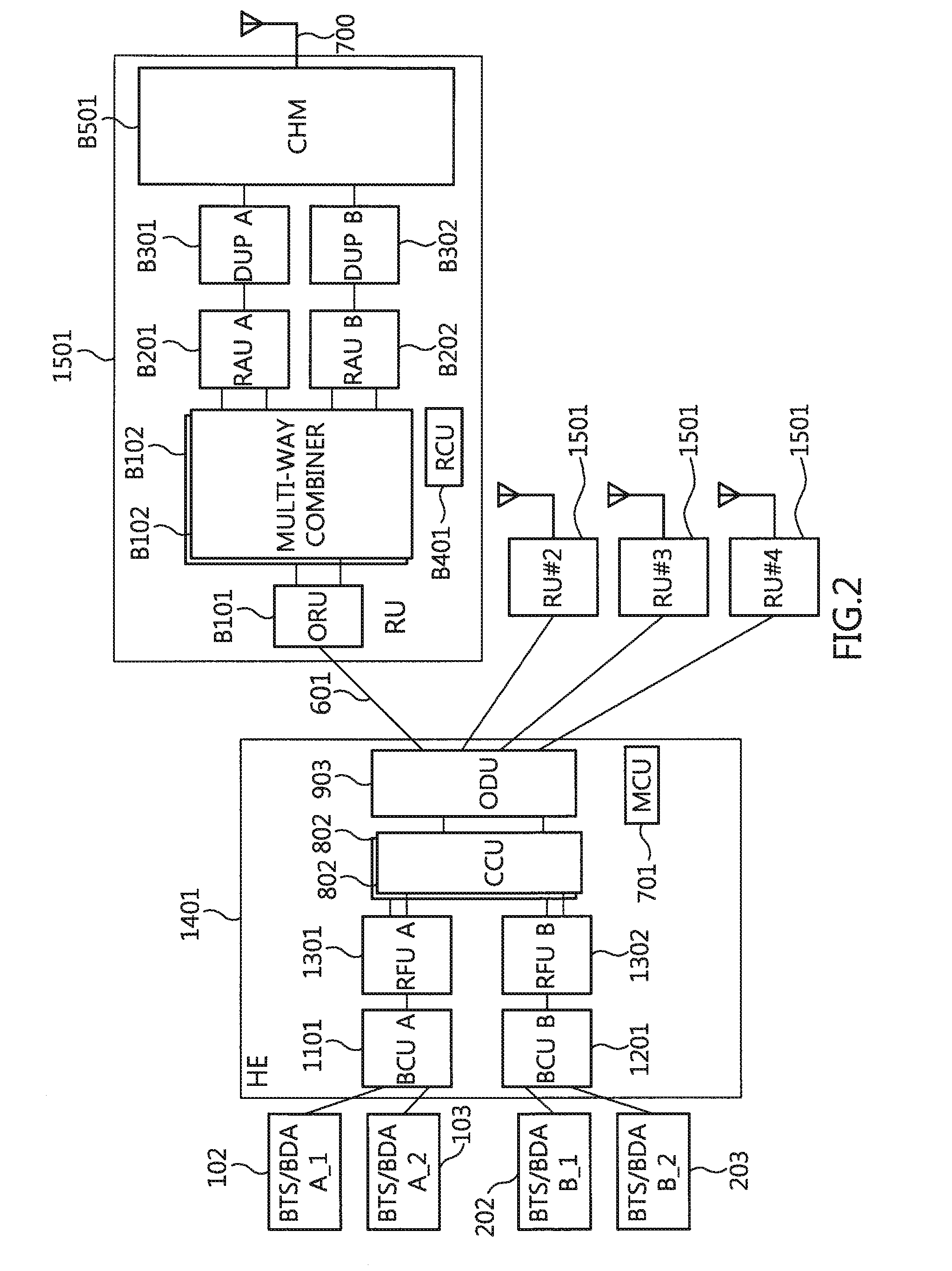
Optic distributed antenna system supporting multi-band multi-carrier service over a reduced number of optic core lines
An optic Distributed Antenna System includes a Head End (HE) configured to adjust a first signal for a first carrier at a first band to a first level, to adjust a second signal having at least a carrier different from the first carrier or a band different from the first band to a second level, to combine the first and second signals, to perform Electronic / Optic conversion on the combined signal, and to optic-distribute and send the combined optic signal, and a plurality of Remote Units (RUs) each connected to the HE over a corresponding single optic line, wherein each of the RUs is configured to perform Optic / Electronic conversion on the combined optic signal, to adjust the converted signal for each signal band, to perform high-power amplification on the adjusted signals, to multiplex the amplified signals, and to transmit the multiplexed signal to a Mobile station via at least one antenna.
Owner:ADVANCED RF TECH
Apparatus and method for front-end circuitry in radio-frequency apparatus
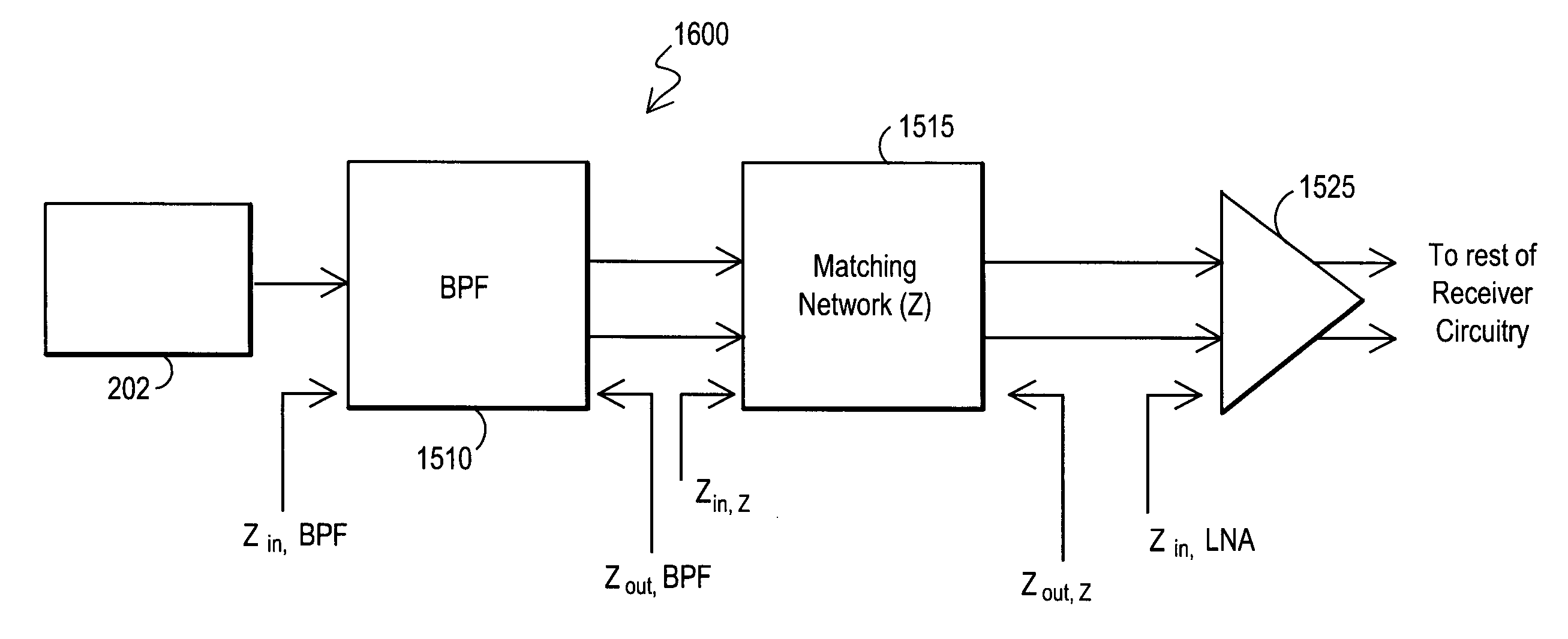
InactiveUS7035611B2Guaranteed interference effectReduce the impact of interferenceMultiple-port networksRadio transmissionSignal processing circuitsInput impedance
A radio-frequency (RF) apparatus includes front-end circuitry. The front-end circuitry includes a filter circuitry and an impedance matching circuitry. The filter circuitry has a differential output that has an output impedance. The filter circuitry filters signals outside a signal band of interest. The impedance matching network has a differential input coupled to the output of the filter circuitry. The impedance matching network also has a differential output coupled to a signal processing circuitry. The signal processing circuitry has an input impedance. The impedance matching network matches the input impedance of the signal processing circuitry to the output impedance of the filter circuitry.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Antenna System Monitor
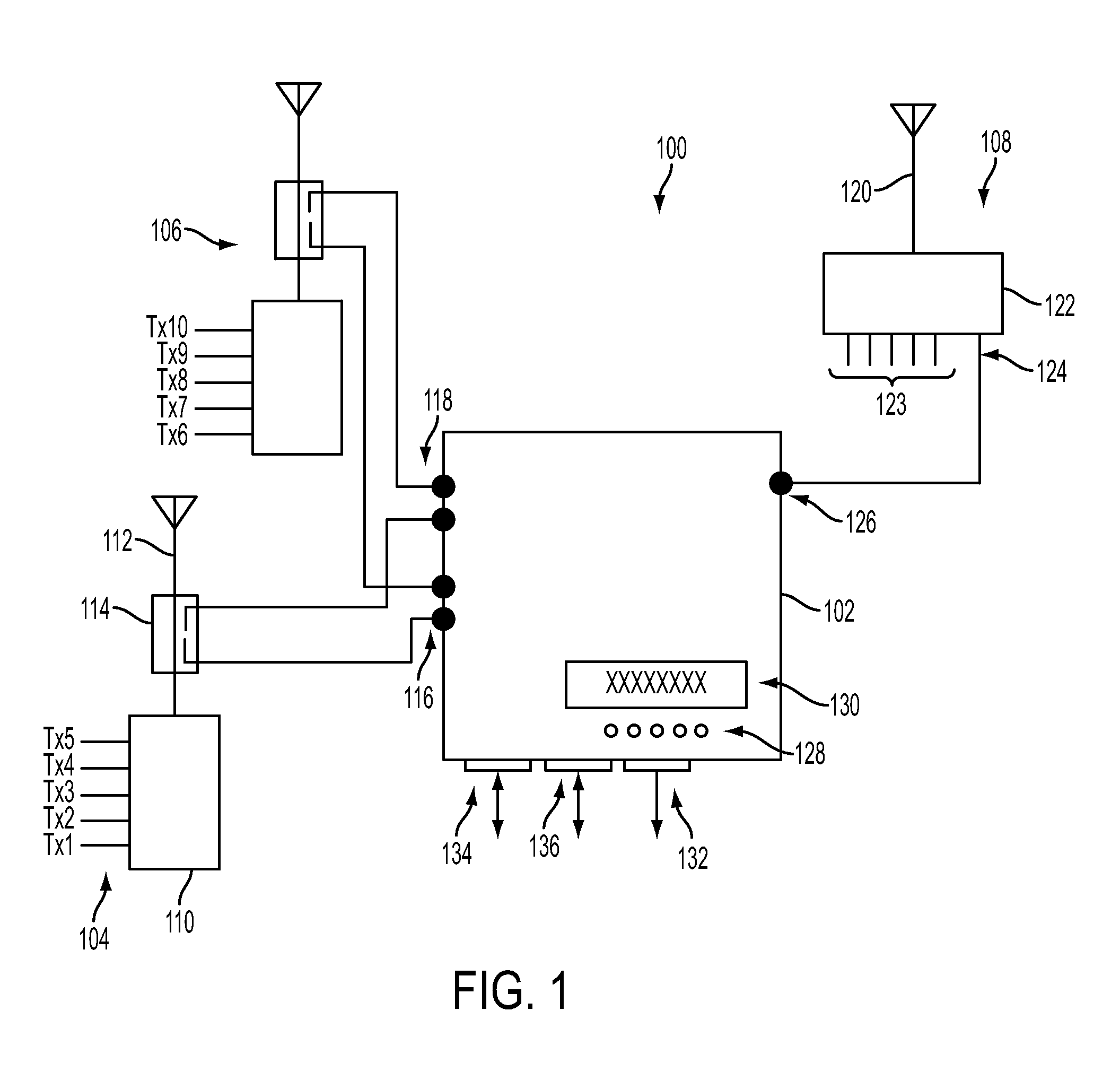
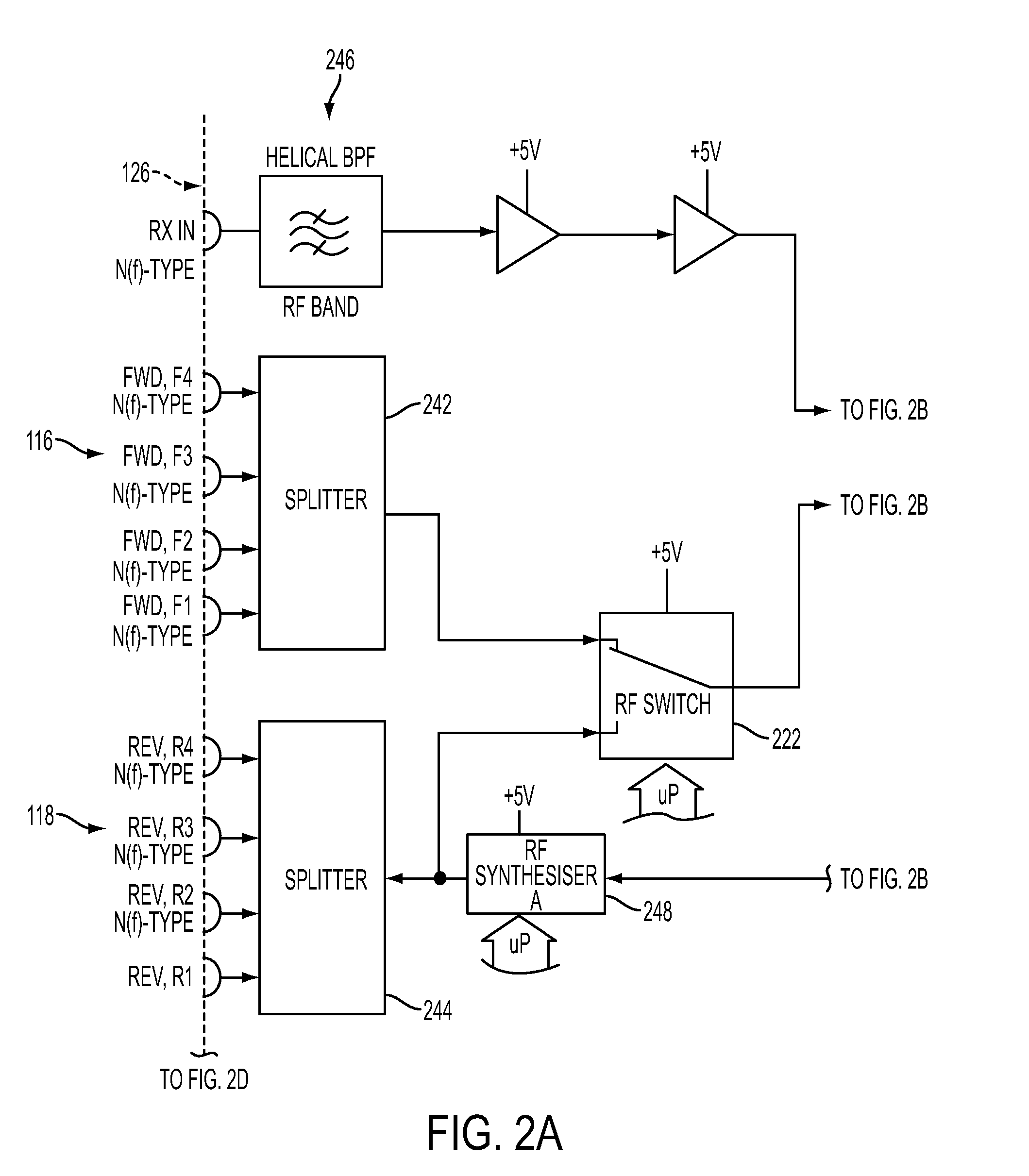
A system is disclosed for monitoring of individual frequency channels in an RF signal band by configuration of the electronic processor to operate the tunable filter to select desired channel sub bands. Measurement of forward and / or reverse-propagating fields within the selected sub-bands may be performed and corresponding power levels recorded. The records may be used to provide monitoring signals, such as measures of forward and reflected power, as well as VSWR, return loss. Indications or alarms may be activated if any of these quantities, associated with any one or more channels, falls outside a predetermined acceptable operating range.
Owner:RF IND
Optical amplifier and optical monitor circuit
InactiveUS20060024063A1Low costImprove accuracyLaser arrangementsFibre transmissionOptical reflectionSignal light
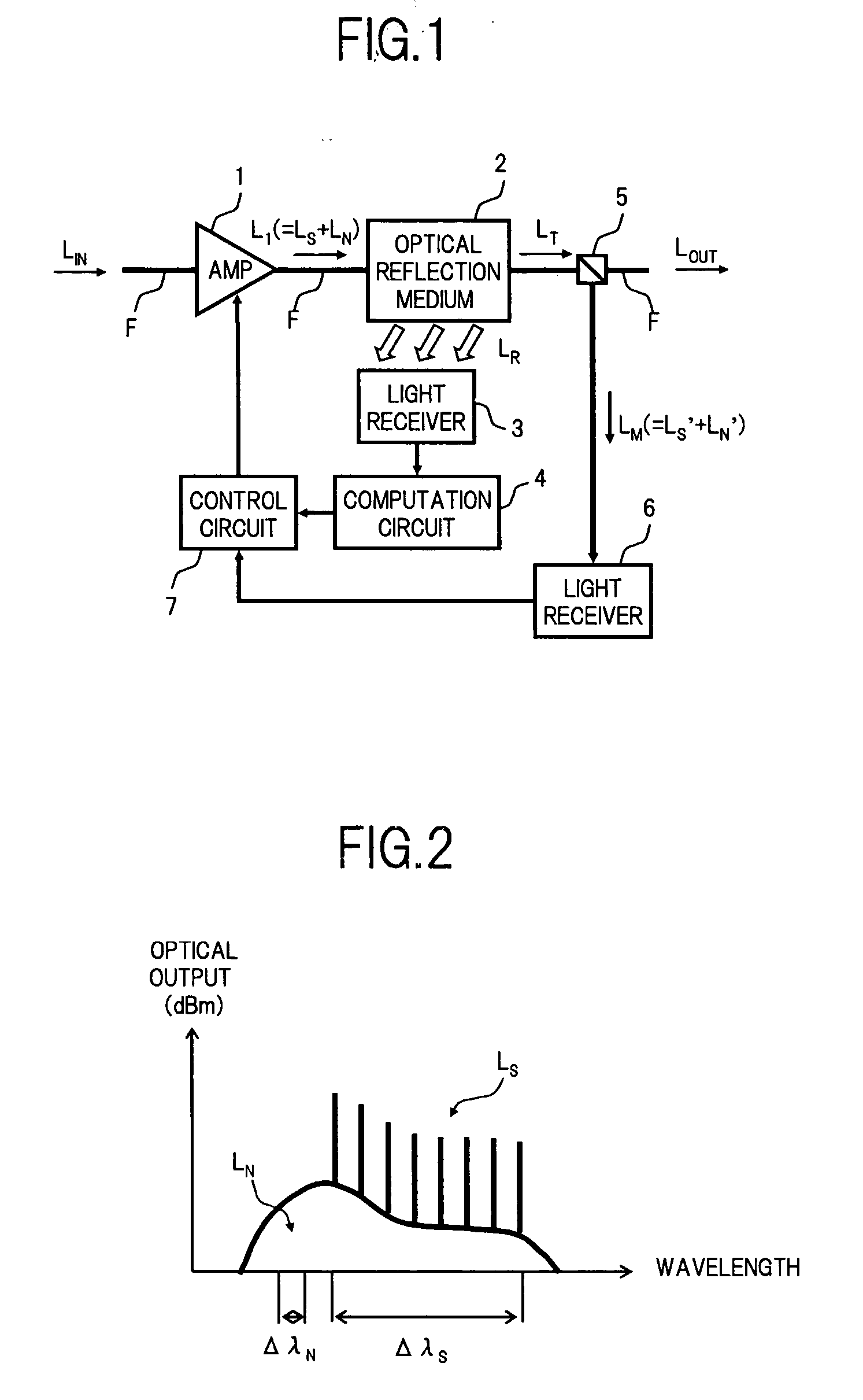
An optical amplifier of the present invention comprises: an optical amplifying circuit which amplifies a signal light; an optical reflection medium which is disposed on an optical fiber connected to the optical amplifying circuit and is capable of reflecting a noise light which exists in a predetermined wavelength range outside a signal band, among noise lights generated in said optical amplifying circuit, to radiate the reflected noise light to the outside of a core of the optical fiber; a light receiver which receives the noise light reflected to be radiated to the outside of the core of the optical fiber by the optical reflection medium, to detect the power of the noise light; and a computation circuit which computes the total power of the noise lights generated in the optical amplifying circuit based on the detection result of the light receiver. Thus, it is possible to provide at a low cost an optical amplifier provided with a monitoring function capable of detecting high accurately, with a simple optical circuit configuration, the noise light power and the like generated when the signal light is amplified.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical amplification method and device usable with bands other than the C-band
InactiveUS20020001124A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsFibre transmissionC bandingAudio power amplifier
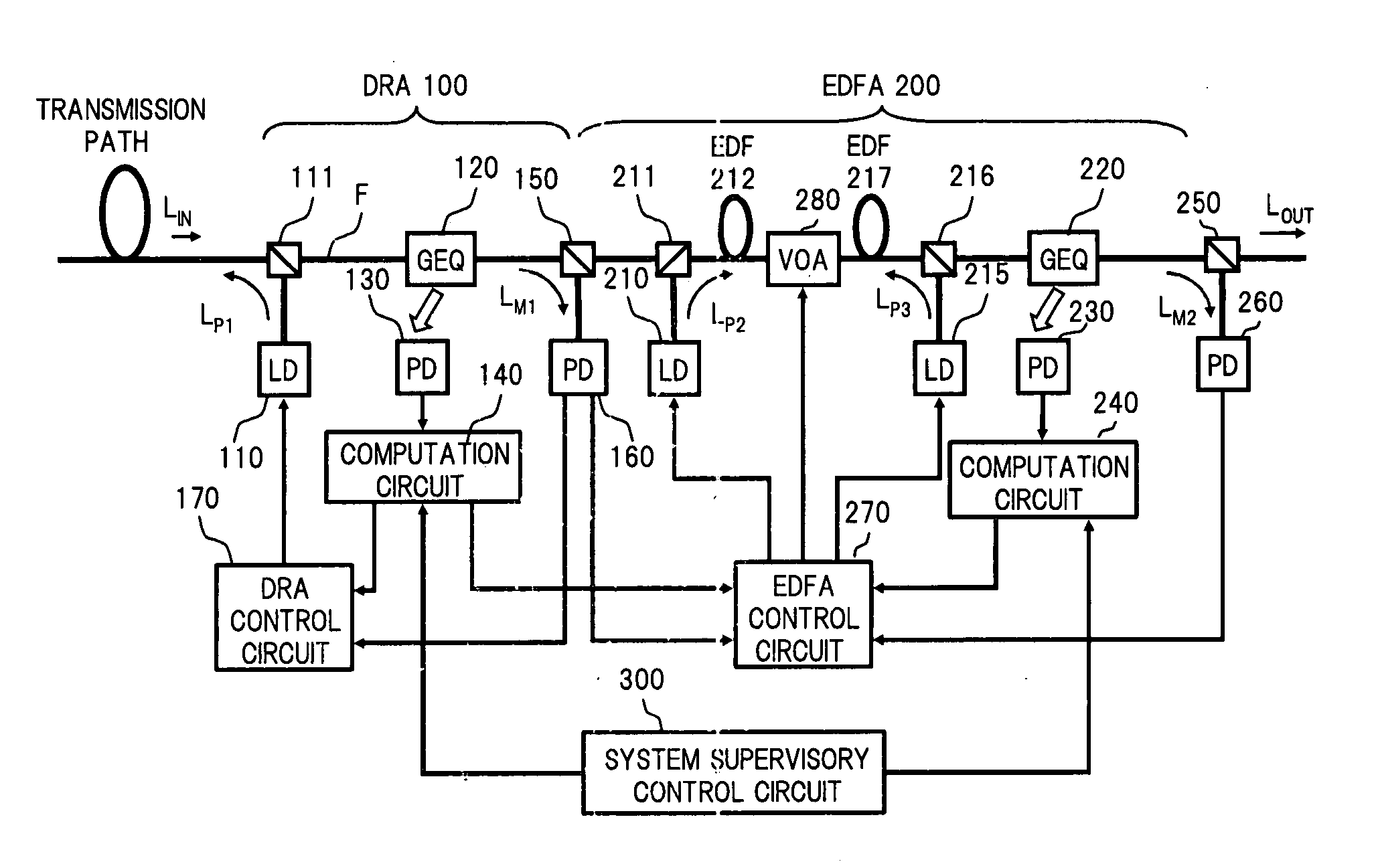
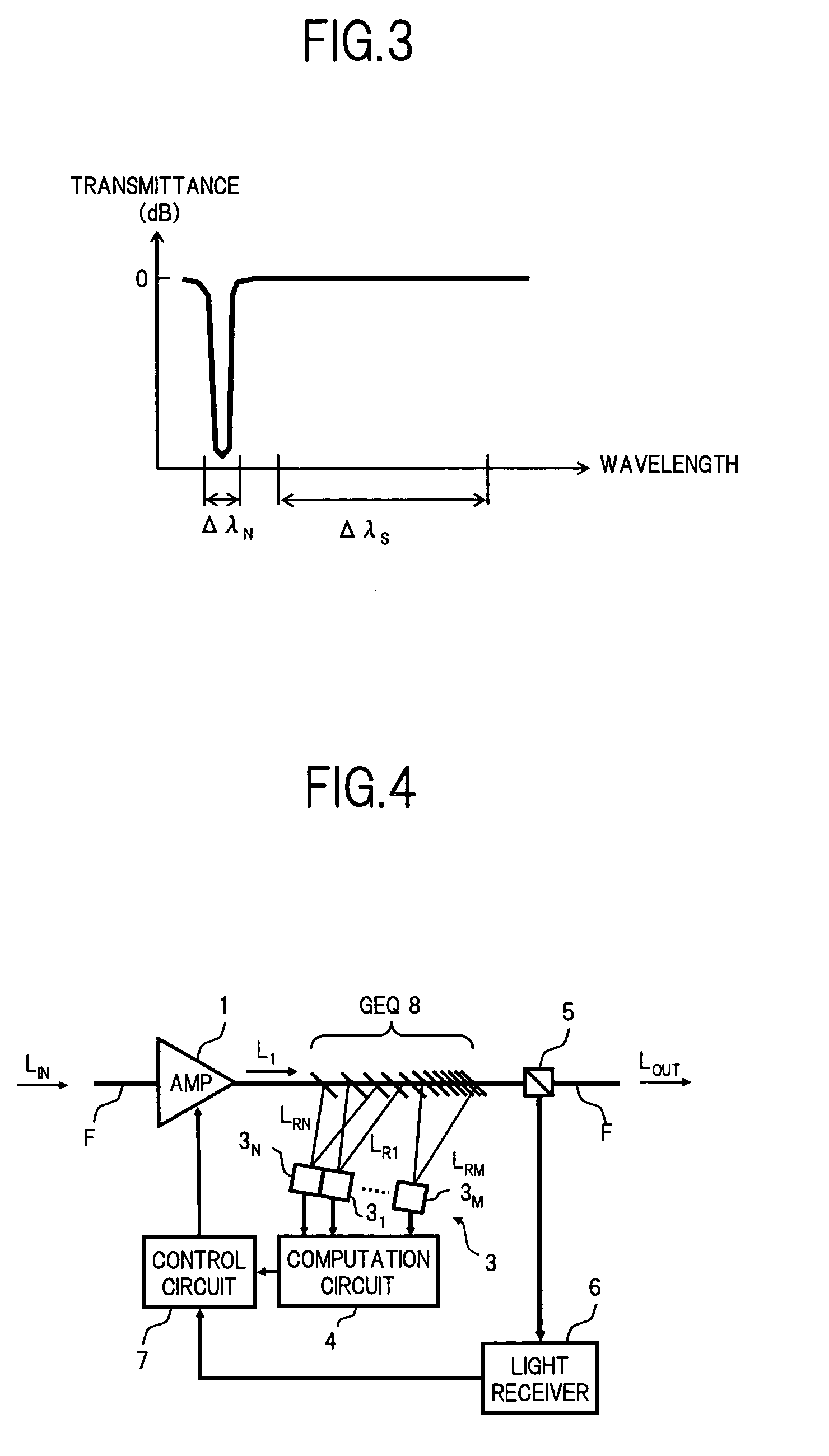
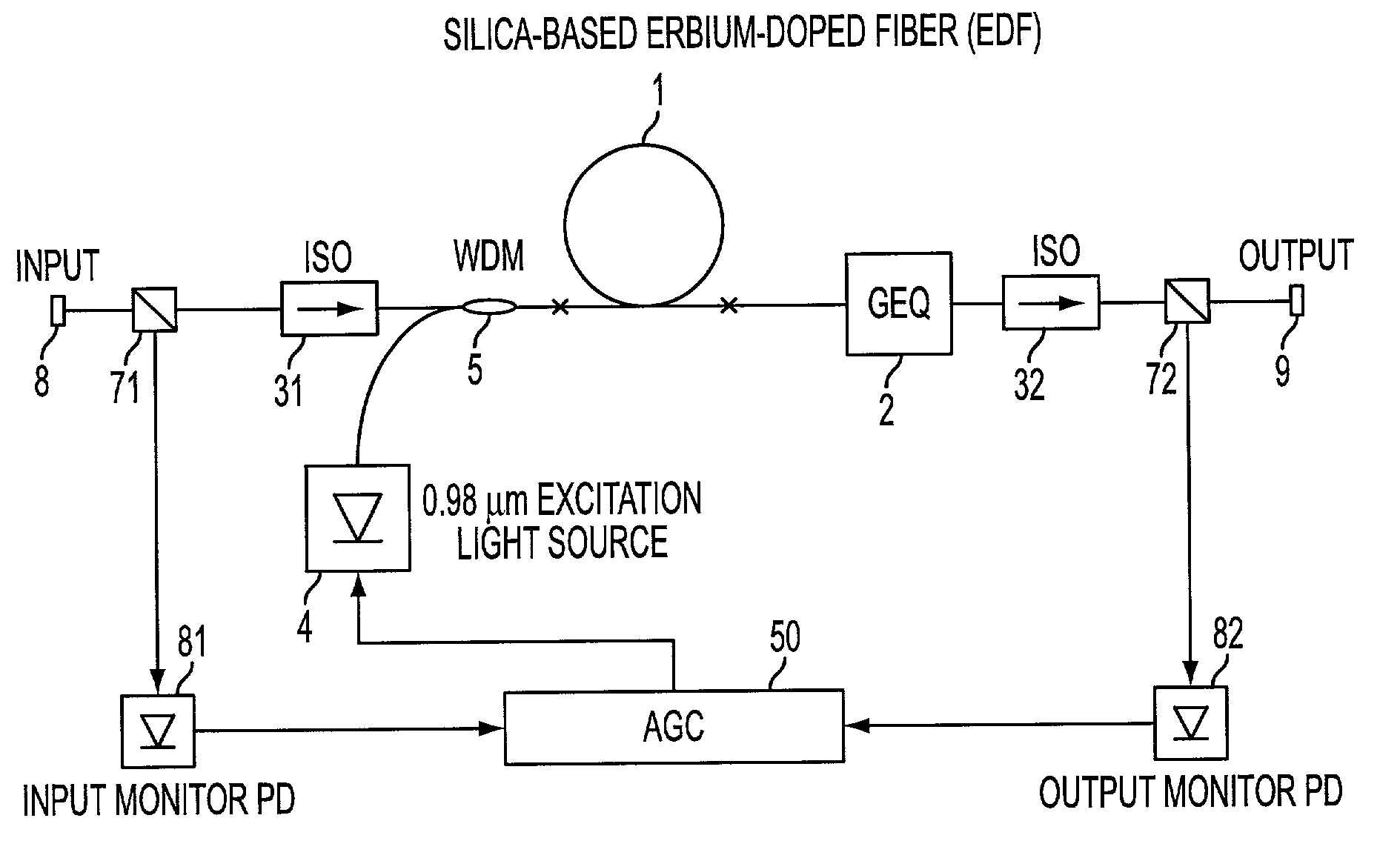
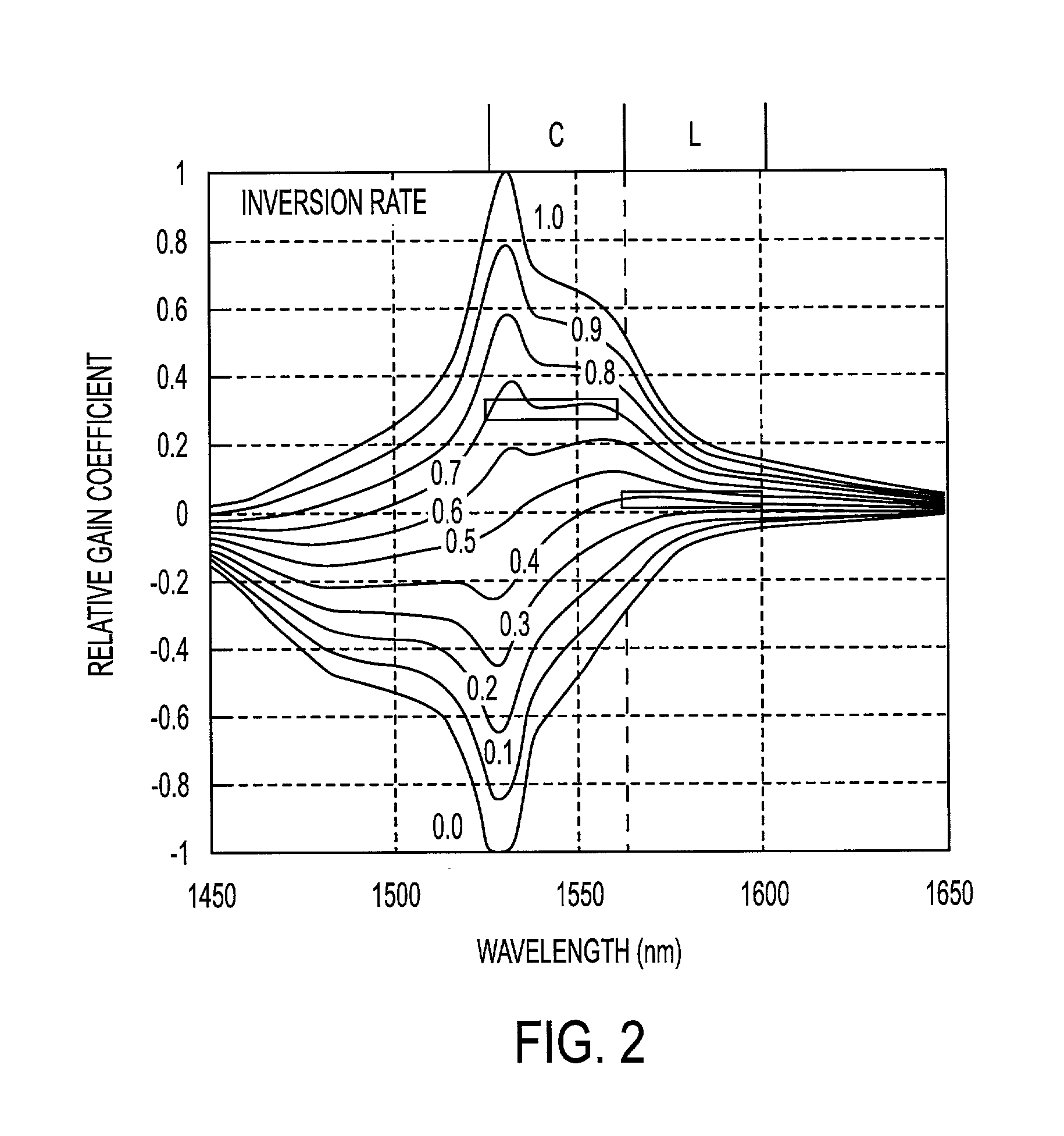
An optical amplifier includes an optical amplification medium, an excitation source to stimulate the amplification medium to output at least one wavelength gain peak, and a gain equalizer to equalize the output of the amplification medium such that gain is produced at wavelengths other than the wavelength gain peak. The gain equalizer may attenuate gain at the peak wavelength. The gain equalizer may equalize the output of the amplification medium such that gain is produced at wavelengths less than the wavelength gain peak. The optical amplifier may include both a gain equalizer and automatic level control circuitry to respectively maintain substantially uniform gain at wavelengths within an optical signal band and maintain constant output power.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Online matt Raman amplifier with automatic shutdown and starting and control method thereof
ActiveCN101552428AAccurate and real-time reportingWon't hurtLaser using scattering effectsAudio power amplifierRaman amplifiers
The invention relates to an online matt Raman amplifier with automatic shutdown and starting and a control method thereof. An output end of a pump laser unit group is connected with a pump end of a combiner, a public end of the combiner is connected with a transmission optical fiber, a signal end of the combiner is connected with an input end of a spectro-coupler, the big end of the spectro-coupler is a signal output end, the small end of the spectro-coupler is connected with the public end of a signal band-pass filter, a reflection end of the signal band-pass filter is connected with a detector of noise outside bandwidth, a transmission end is connected with a detector of signal plus the noise within the bandwidth, the signal output ends of the detector of the noise outside the bandwidth and the detector of the signal plus the noise within the bandwidth are respectively connected with a signal input end of a control unit, and the signal output end of the control unit is connected with the pump laser unit group. The method is to realize the signal power detection and the ASE compensation according to the method of detecting the ASE power of the Raman amplifier outside the working bandwidth and the total power of the ASE within the working bandwidth and the signal. The method can accurately detect the actual power of the signal and automatically shut down and start the amplifier according to the level of the signal power.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
Antenna and electronic device including the same
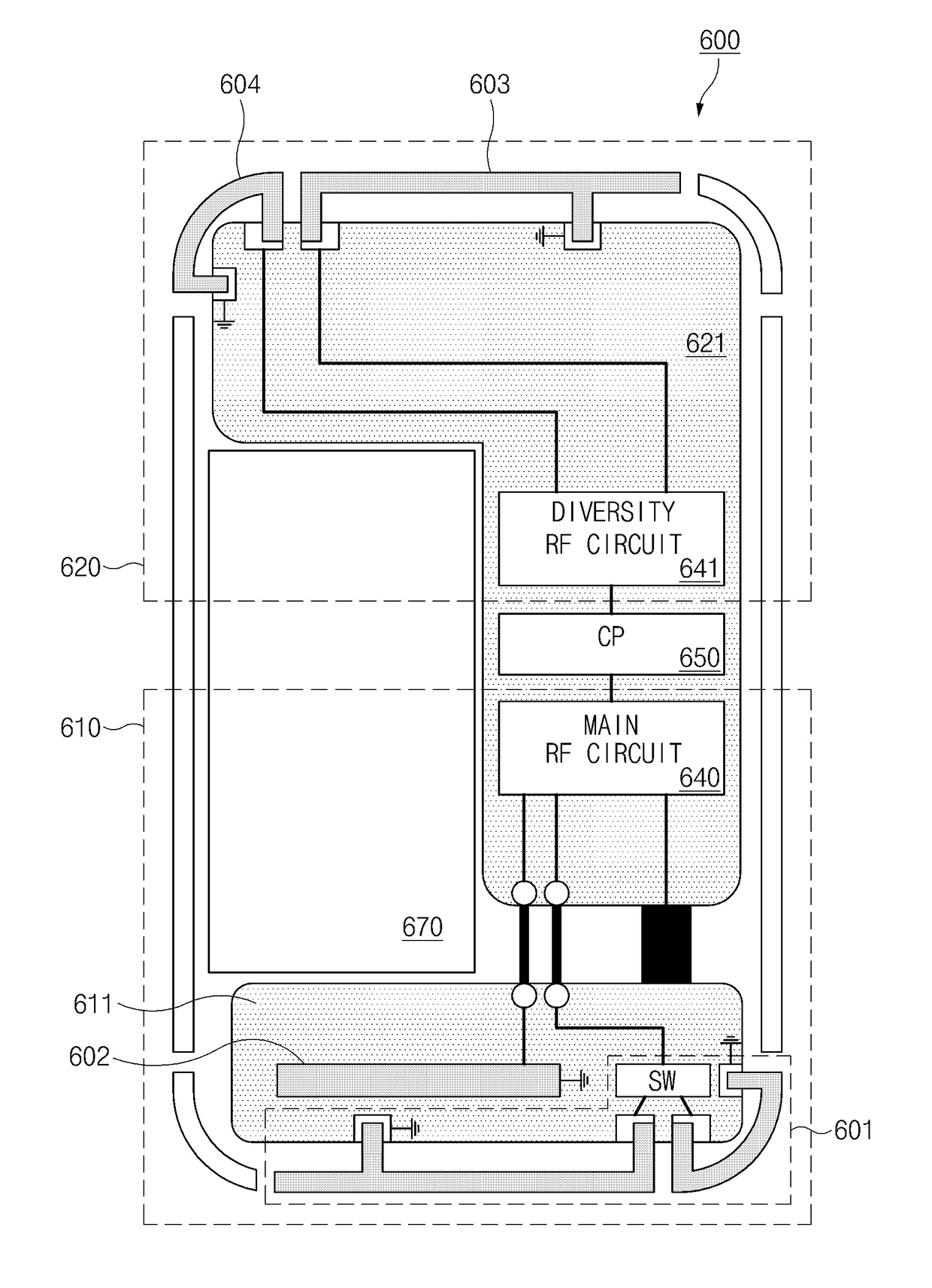
ActiveUS20170365914A1Spatial transmit diversitySimultaneous aerial operationsTransceiverCarrier signal
Disclosed is an electronic device including a first antenna element configured selectively to receive signals of a first frequency band and a second frequency band or of the first frequency band and a third frequency band, a second antenna element configured to receive a signal of the third frequency band, a transceiver configured to be electrically connected with the first antenna element and the second antenna element, and a processor configured to be electrically connected with the transceiver. The electronic device performs carrier aggregation using the second frequency band and the third frequency band.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for post filtering peak power reduction in communications systems
ActiveUS7170952B2Reduce output signalReduce decreaseAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationFrequency spectrumCommunications system
A system and method for post filtering signal peak reduction adapted for use in a communication system incorporating a source of a communication signal band limited in a manner corresponding to a spectral band to which the communication system is limited. A first signal path receives as an input the band limited communication signal. A second parallel signal path includes a peak reduction calculation unit for calculating a peak reduction correction signal and a filter providing a filtering operation on the peak reduction correction signal corresponding to the spectral band to which the communication system is limited. The filtered peak reduction correction signal and delayed input signal are combined to provide peak adjusted output signals without violating the band limits of the communication signal or the modulation scheme of the communication signal.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Surface emitting dfb laser structures for broadband communication systems and array of same
InactiveUS20050053112A1High yieldLow costLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsPeriodic alternatingActive layer
A surface emitting semiconductor laser (10) is shown having a semiconductor lasing structure having an active layer (22), opposed cladding layers contiguous to said active layer, a substrate (17), and electrodes (12,14) by which current can be injected into the semiconductor lasing structure. Also included is a second or higher order distributed diffraction grating (24) having periodically alternating elements, each of the elements being characterized as being either a high gain element (26) or a low gain element (28). Each of the elements has a length, the length of the high gain element and the length of the low gain element together defining a grating period, where the grating period is in the range required to produce an optical signal in the optical telecommunications signal band. The total length of the high gain elements is no more than the total the lengths of the low gain elements. A single laser structure may be provided or an array of side by side laser structures on a common substrate is also provided. In a further aspect a method of testing laser structures on wafer is provided.
Owner:PHOTONAMI INC
Tuner and demodulator for analog cable television
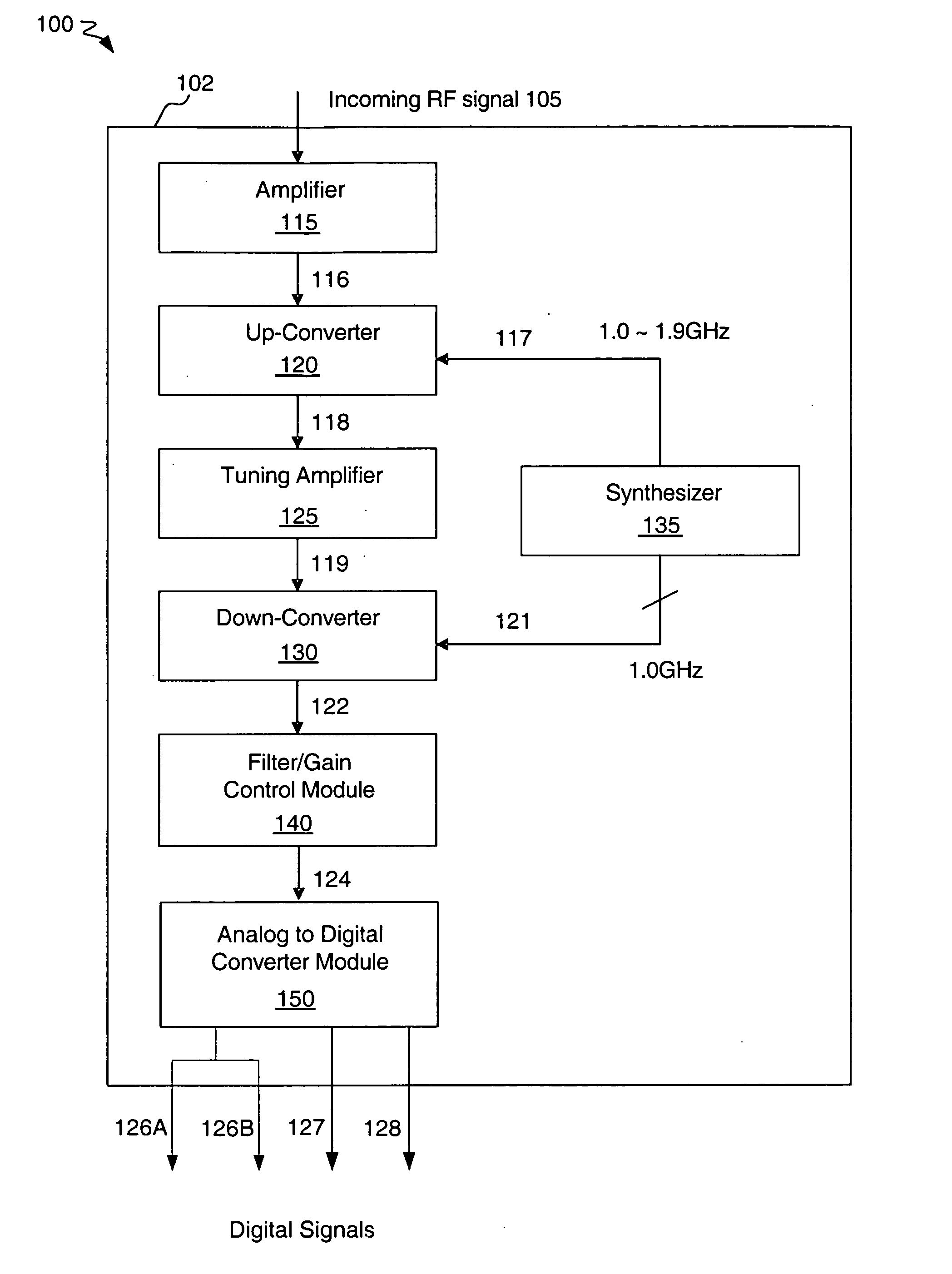
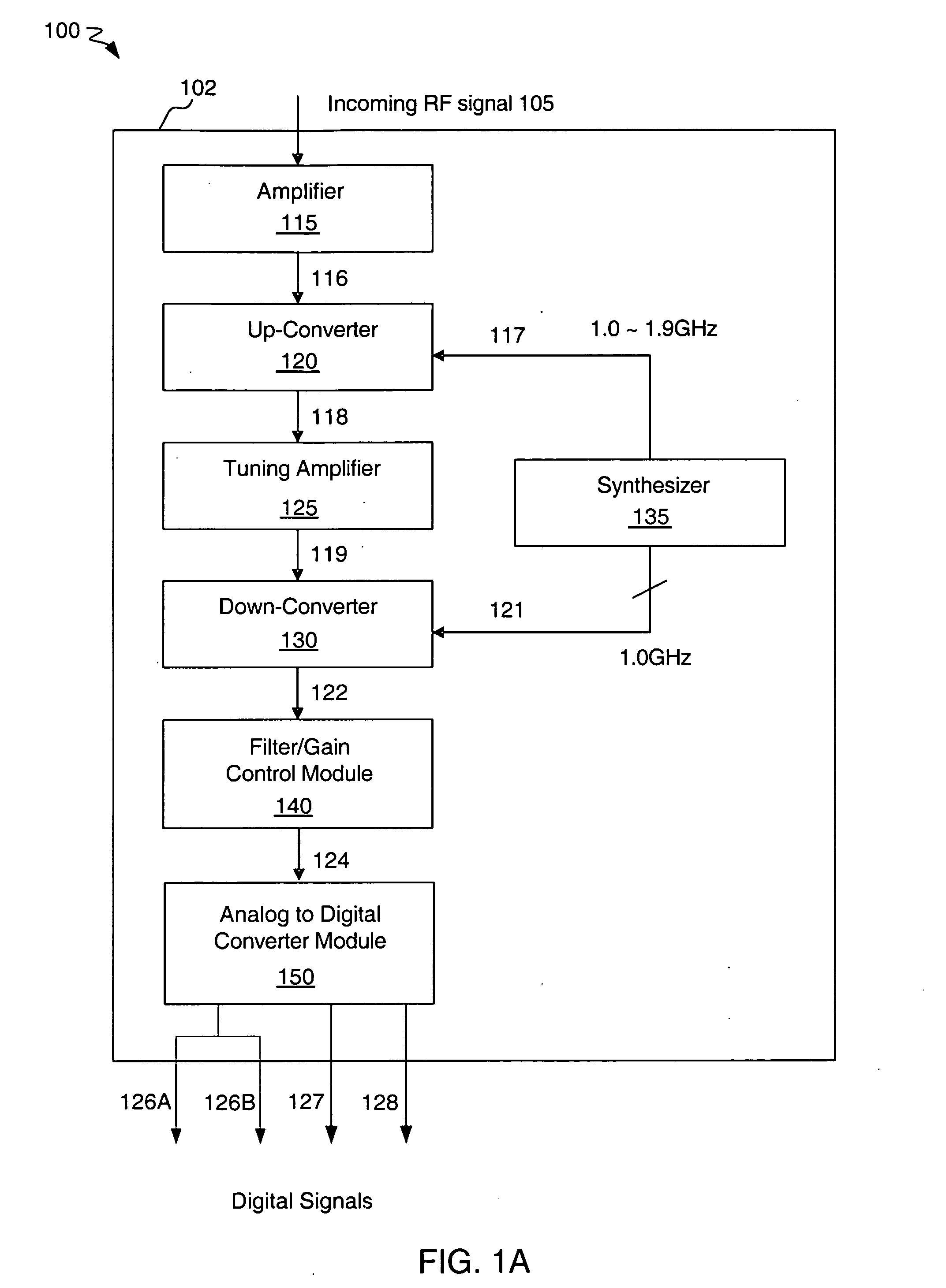
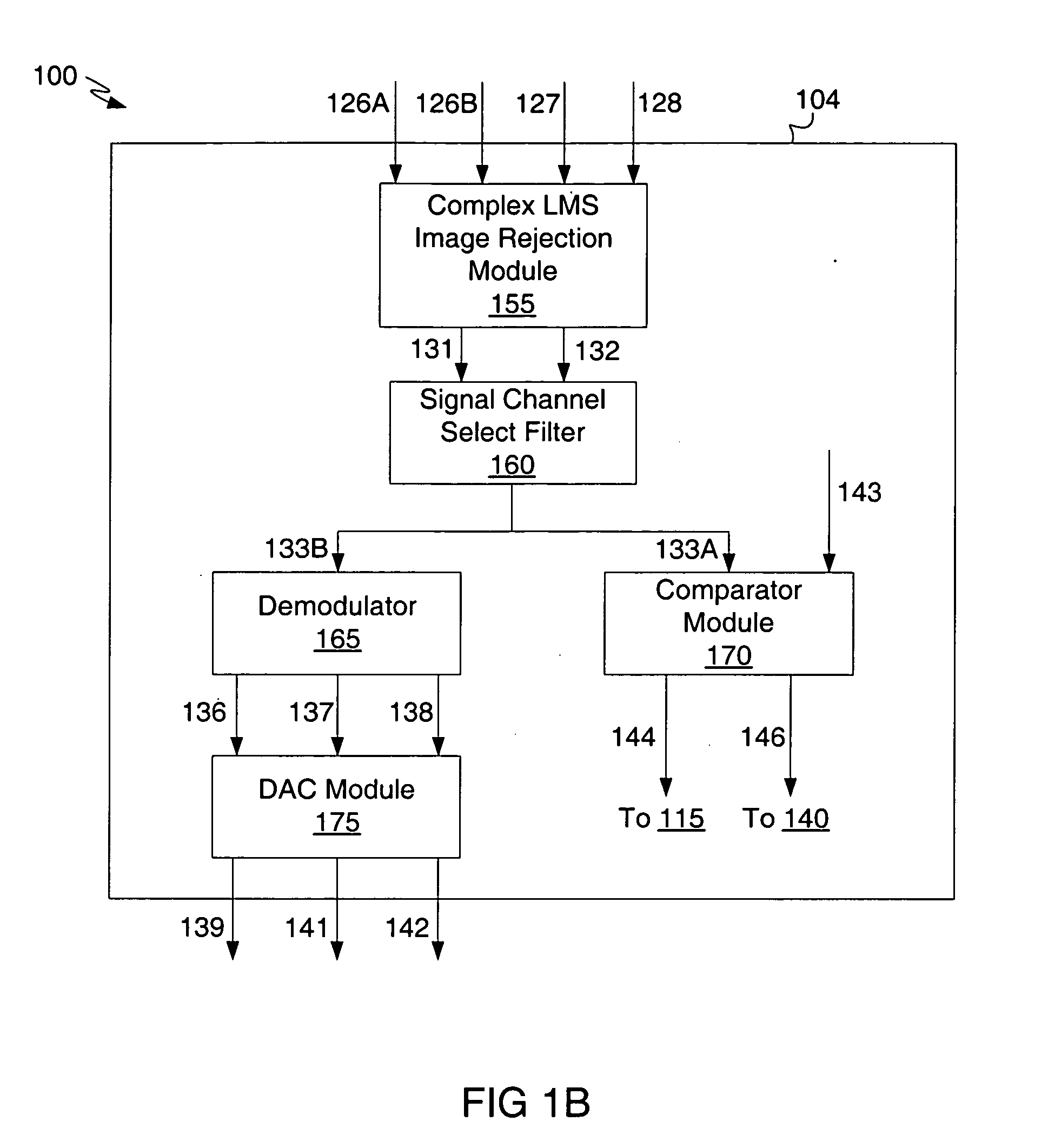
InactiveUS20050090213A1Reducing image leakageReduce leakageTelevision system detailsBroadcast transmission systemsTelevision systemIntermediate frequency
A tuner and demodulator performing image rejection in an analog cable television system. Various embodiments disclose a tuner including an analog RF section to generate a complex intermediate frequency digital signal, an image rejection module configured to perform image rejection on the complex intermediate frequency digital signal to generate an enhanced image rejection signal, a signal channel select filter configured to perform digital on-chip filtering on the enhanced image rejection signal to generate a filtered signal, and a demodulator configured to demodulate the filtered signal to generate digital output signals. In some embodiments, the tuner is substantially or fully monolithic. In some embodiments, the tuner performs image rejection by applying an algorithm to estimate a signal correlation between the signal band and the image band of the complex intermediate frequency digital signal, and providing adaptive filtering to reduce signal leakage and image leakage.
Owner:CHRONTEL
Series arc detection
ActiveUS20050207083A1Spectral/fourier analysisCircuit-breaking switches for excess currentsElectric powerPhysics
A frequency harmonic identifier for detecting series arcs on a power line includes a frequency analyzer for providing the harmonic content of a sensed current signal and a decision logic for comparing a tested signal to at least one reference signal band. The reference signal band or bands may represent a variety of common loads and if the tested signal does not match any of the sets of reference signal bands, then the logic determines the tested signal to be a series arc signal. The frequency harmonic identifier may be provided within a circuit interrupter and may issue a trip signal if the tested signal is determined to be a series arc signal. A method for detecting series arcs includes sensing current on a power line and providing a sensed current signal as an input signal to a frequency harmonic identifier, performing a Fast Fourier Transform on the input signal for providing a tested signal, accessing a storage area storing at least one reference signal band, comparing the tested signal to the at least one reference signal band and determining if the tested signal is a series arc signal through comparison and, if the test signal is a series arc signal, sending a trip signal. A storage medium may also be encoded with machine-readable computer program code for detecting series arcs on a power line, wherein the storage medium includes instructions for causing a computer to implement the method.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
System and Method for Communication over a Network with Extended Frequency Range
A communication system comprising a network having a legacy band and an extendable frequency band, a head end, and a user end, wherein said head end processes and splits source data into multiple signals and transmits said multiple signals over multiple physical channels over said extendable frequency band, and wherein said user end containing multiple receivers and a data reconstructor receives said multiple signals and recovers said source data. Another embodiment includes a communication system comprising a network having a legacy band and an extendable frequency band, a head end; and a user end, wherein said user end processes and splits source data into multiple signals and transmits said multiple signals over multiple physical channels over said extendable frequency band and wherein said head end receives said multiple signals and recovers said source data. Other embodiments include methods of communication over a network having a legacy band and an extendable frequency band.
Owner:MAEDA RYUJI
Method and apparatus for extending band of audio signal using noise signal generator
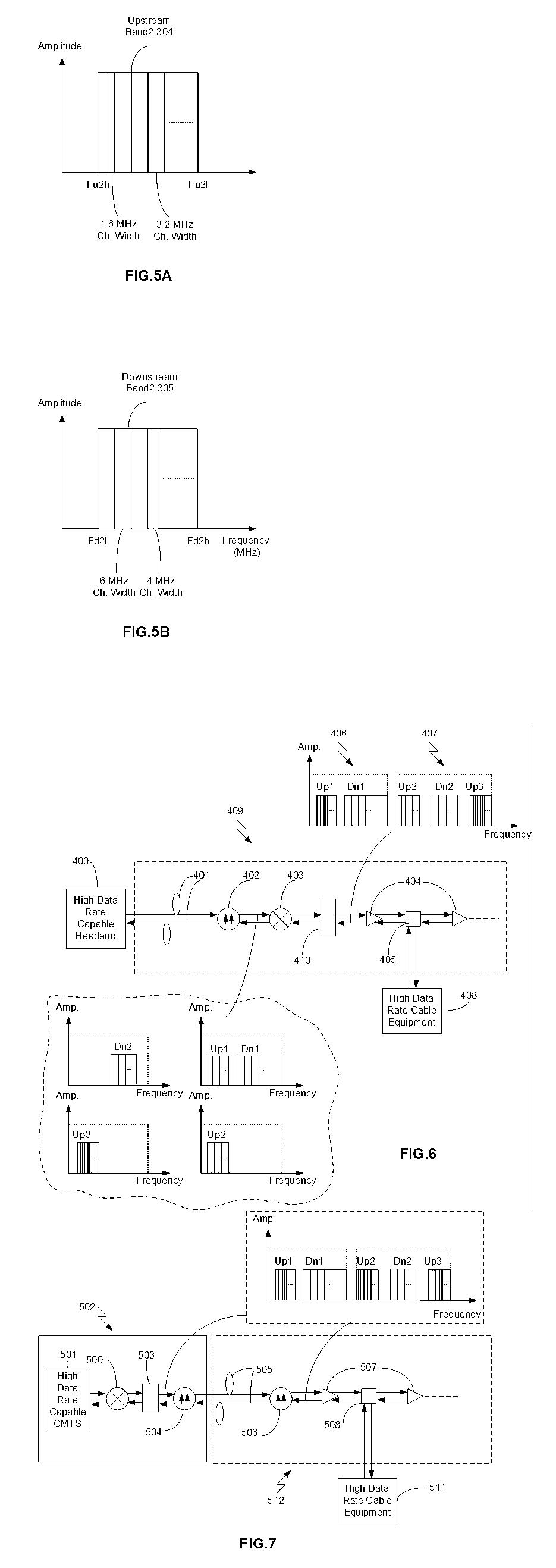
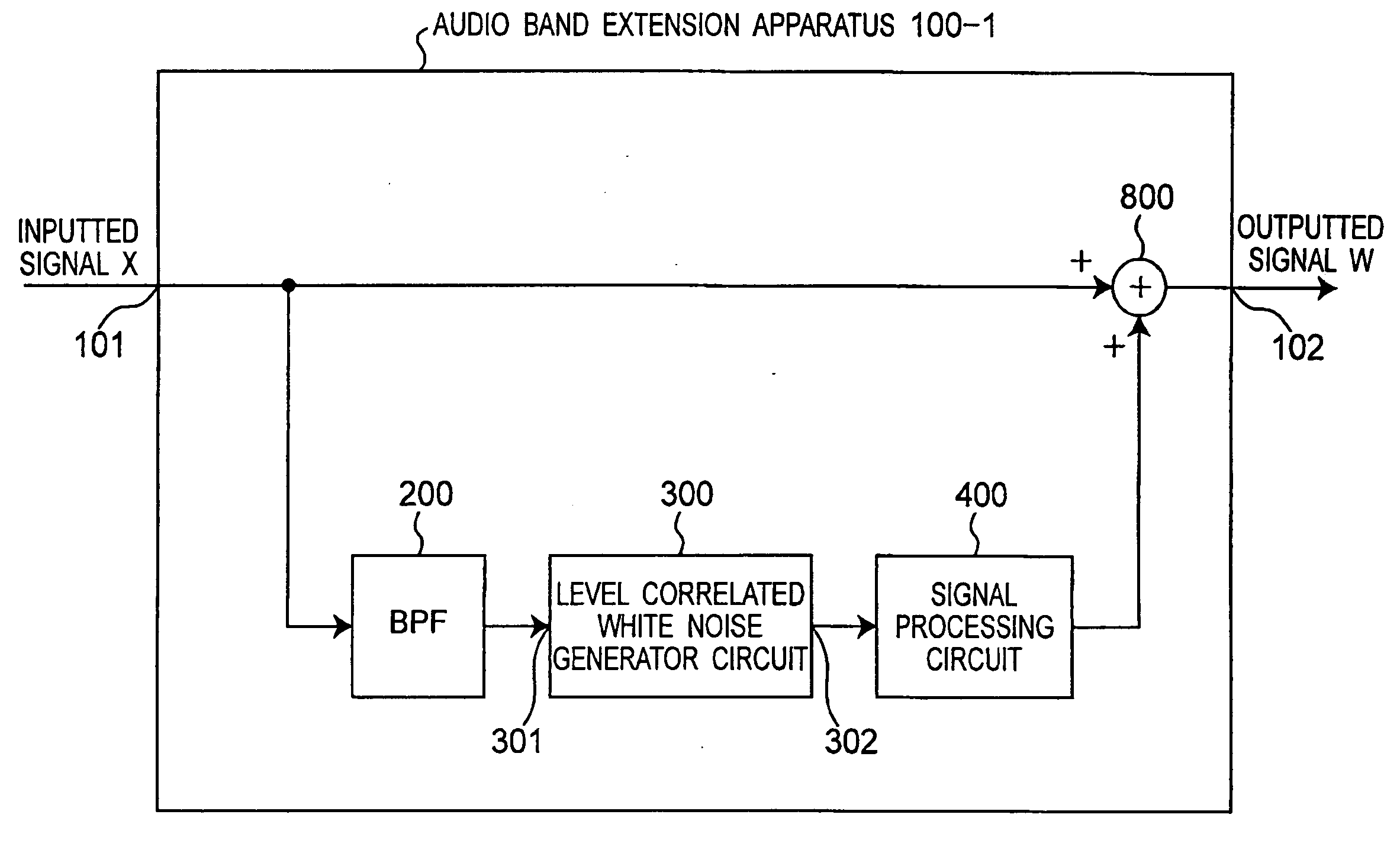
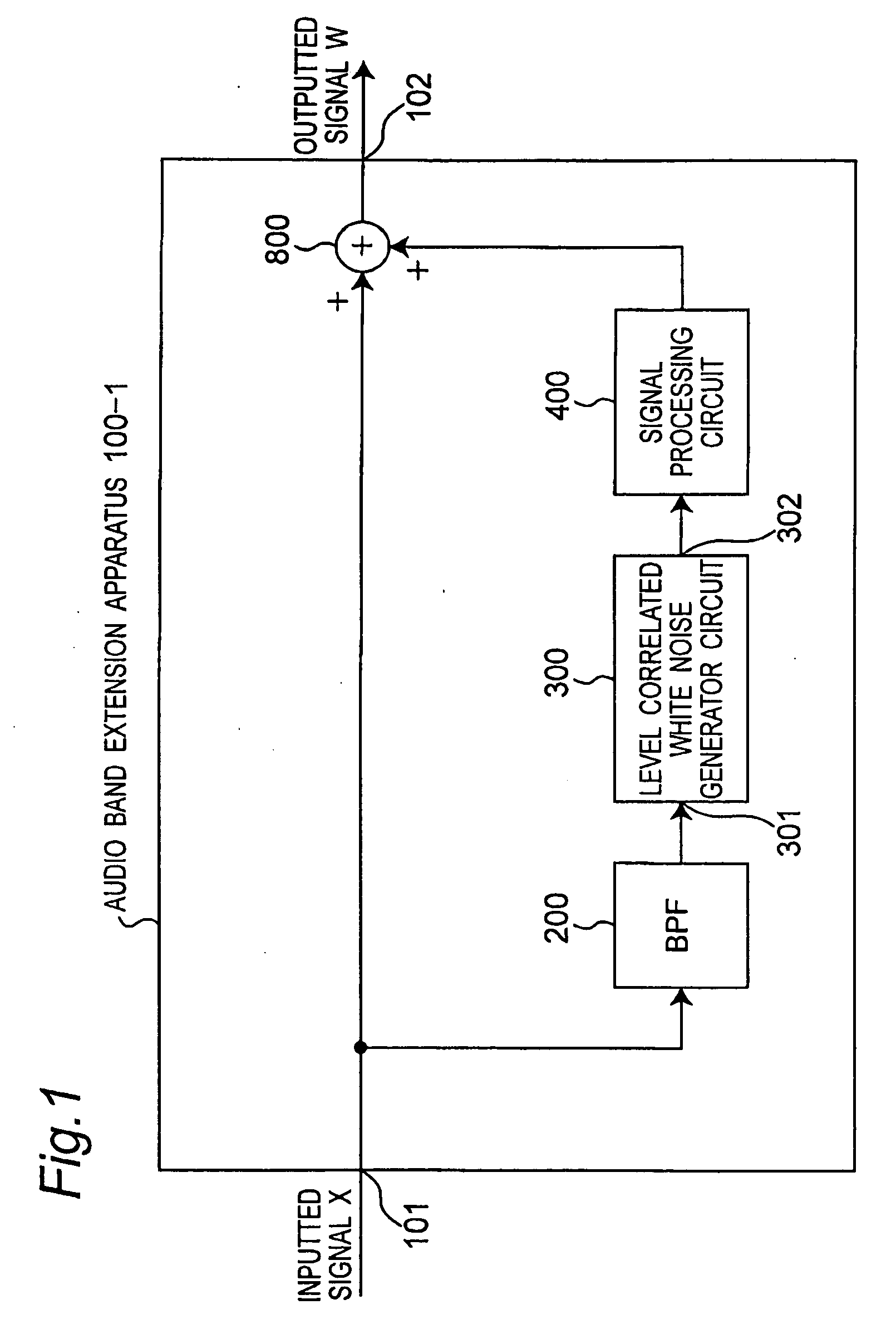
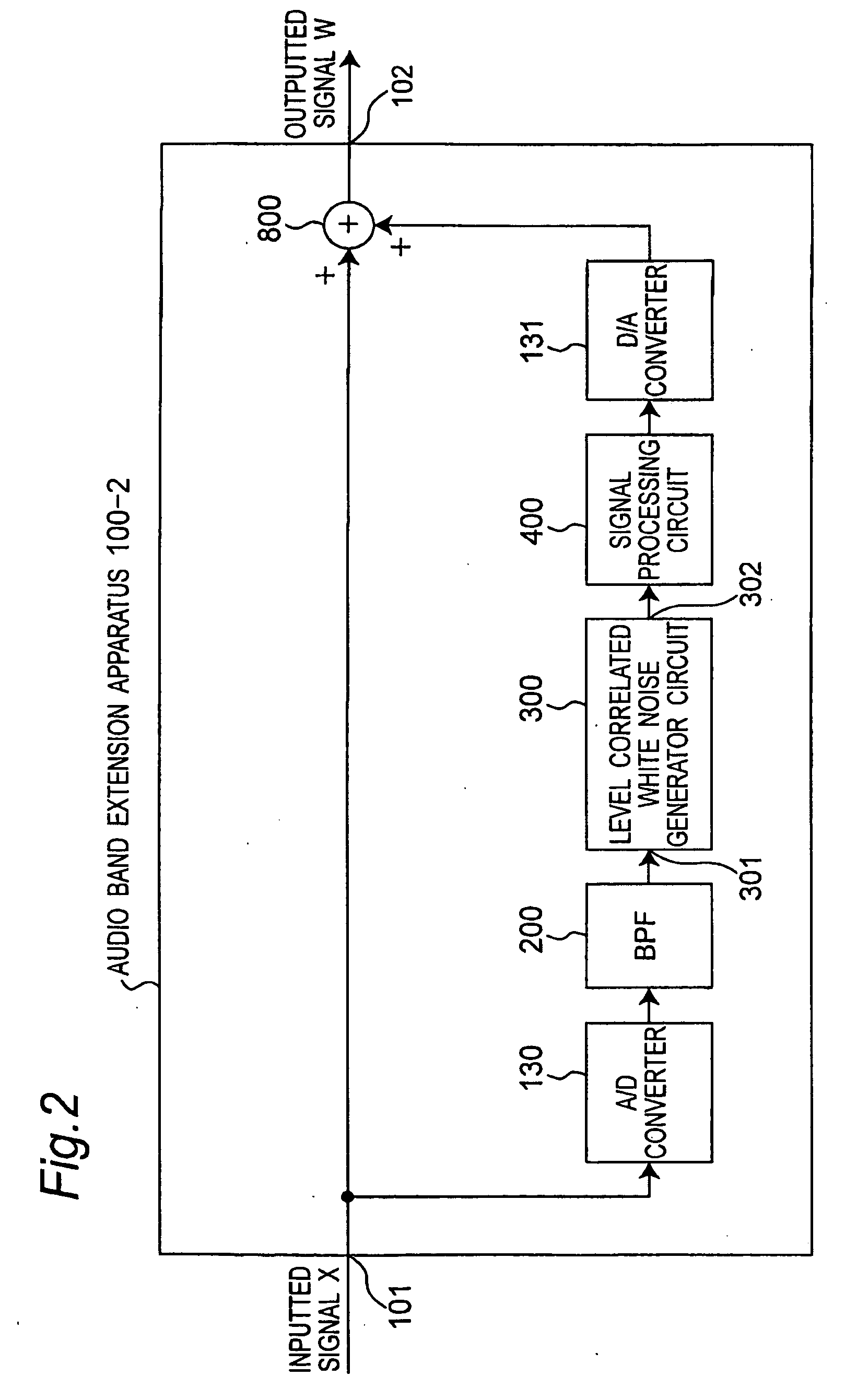
InactiveUS20060227018A1Easily signalMaintain continuitySpeech analysisCode conversionBandpass filteringSignal processing circuits
A bandpass filter bandpass-filters an inputted signal X to pass therethrough a partial band of a band of the inputted signal X, and a level correlated white noise generator circuit generates a white noise signal having a level changing according to a level of the inputted signal and correlated to the inputted signal. A signal processing circuit executes a signal processing that includes a predetermined bandpass filtering processing, an echo adding processing, and a level adjustment processing, and that multiplies the inputted white, noise signal by a predetermined transfer function, and outputs a processed white noise signal to an adder. The adder adds up the white noise signal from the signal processing circuit and the inputted signal X, and outputs a band-extended signal having an addition result, as an outputted signal.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com