Zinc hydrometallurgy production process
A production process, a technology of hydrometallurgy, applied in the field of hydrometallurgy, can solve the problems of high production cost, low zinc leaching rate, unfavorable environmental protection, etc., and achieve the effects of low production cost, high iron removal rate and small zinc loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
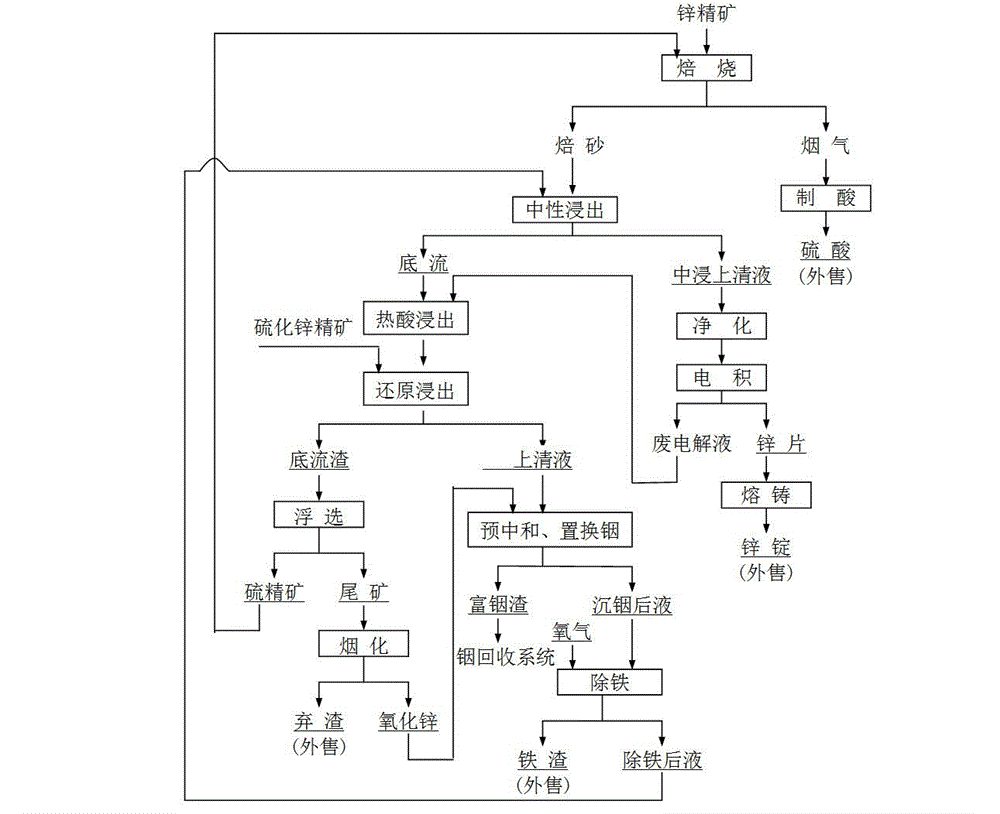
[0019] Example 1 The zinc concentrate is roasted to obtain calcined sand and flue gas, and the calcined sand is subjected to neutral leaching, the temperature is controlled at 40°C, and the pH at the end point is 4.8. After separation, the middle leaching supernatant and the middle leaching underflow are obtained. The clear liquid is leaching the zinc sulfate solution. Hot acid leaching is carried out on the middle leaching bottom flow, and waste electrolyte is added to further leach insoluble zinc with zinc ferrite as the main form under high temperature and high acid, and then reduction leaching is carried out, and excessive zinc sulfide concentrate is added to make the Fe in the solution 3+ reduced to Fe 2+ , the temperature is controlled at 85°C, and the final acid is 45g / l. After separation, the reduction leaching supernatant and underflow slag are obtained. The underflow slag is sent to flotation to obtain sulfur concentrate and tailings. Sulfur concentrate and zinc conc...
Embodiment 2
[0020] Example 2 The zinc concentrate is roasted to obtain calcined sand and flue gas. The calcined sand is subjected to neutral leaching, the temperature is controlled at 45°C, and the pH at the end point is 4.9. The clear liquid is leaching the zinc sulfate solution. Hot acid leaching is carried out on the middle leaching bottom flow, and waste electrolyte is added to further leach insoluble zinc with zinc ferrite as the main form under high temperature and high acid, and then reduction leaching is carried out, and excessive zinc sulfide concentrate is added to make the Fe in the solution 3+ reduced to Fe 2+ , the temperature is controlled at 87°C, and the final acid is 48g / l. After separation, the reduction leaching supernatant and underflow slag are obtained. The underflow slag is sent to flotation to obtain sulfur concentrate and tailings. Sulfur concentrate and zinc concentrate are roasted together to obtain roasted Sand and calcined sand are used for neutral leaching, ...
Embodiment 3
[0021] Example 3 The zinc concentrate is roasted to obtain calcined sand and flue gas. The calcined sand is subjected to neutral leaching, the temperature is controlled at 48°C, and the pH at the end point is 5.0. The clear liquid is leaching the zinc sulfate solution. Hot acid leaching is carried out on the middle leaching bottom flow, and waste electrolyte is added to further leach insoluble zinc with zinc ferrite as the main form under high temperature and high acid, and then reduction leaching is carried out, and excessive zinc sulfide concentrate is added to make the Fe in the solution 3+reduced to Fe 2+ , the temperature is controlled at 90°C, and the final acid is 50g / l. After separation, the reduction leaching supernatant and underflow slag are obtained. The underflow slag is sent to flotation to obtain sulfur concentrate and tailings. Sulfur concentrate and zinc concentrate are roasted together to obtain roasted Sand and calcined sand are used for neutral leaching, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com