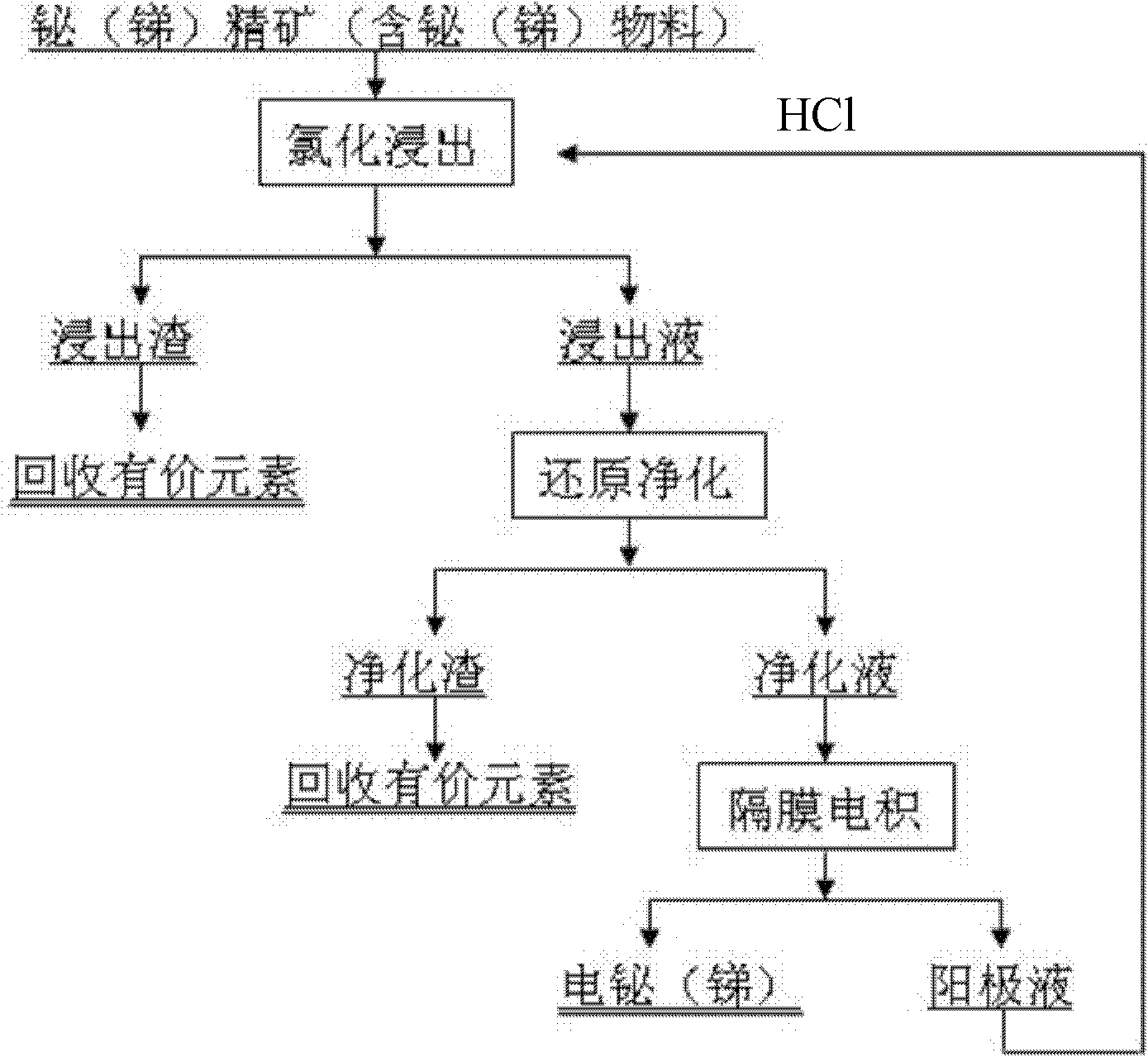
Clean metallurgical method for bismuth or stibium by wet method
A wet and clean technology, applied in the field of bismuth extraction, can solve the problems of large discharge of "three wastes", difficulty in liquid-solid separation, slow reduction speed, etc., achieve significant economic and social benefits, short process flow, and effective separation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] The composition of bismuth concentrate provided by a company in Hunan is: Bi25.02%, WO 3 0.43%, Mo 3.17%, Fe 20.68%, SiO 2 6.33%, Cu1.6%. S 26.5%.
[0044] Take 100g of the above-mentioned bismuth concentrate powder, and make it -1 , Oxidant NaClO 3 The amount of addition (by Bi 2 S 3 consumption) is 1.5 times of the theoretical amount, and the leaching temperature is 70°C for 3 hours, then filtered and separated, the washing liquid and the filtrate are combined, and the filter residue is dried and weighed. The content of bismuth in the filtrate and filter residue was analyzed, and the leaching rate of bismuth was 99.6% (liquid basis) / 99.1% (residue basis).
[0045] Analysis of impurity components and Fe in the filtrate 3+ , Cu 2+ , Ag + content, add 1.5 times the theoretical amount of bismuth powder to carry out reduction and purification agent to remove impurities, react at room temperature for 60 minutes, and then filter and separate.
[0046] In the reducti...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The composition of antimony concentrate provided by a company in Hunan is: Sb 37.31%, Fe 13.68%, SiO 2 6.33%, Cu 4.6%, S 26.5%.
[0050] Take 100g of the above-mentioned antimony concentrate powder, in the liquid-solid ratio of 5:1, the acidity of hydrochloric acid is 4.5mol L -1 , Oxidant SbCl 5 The amount of addition (as Sb 2 S 3 consumption) is twice the theoretical amount, and the leaching temperature is 60°C for 2 hours, then filtered and separated, the washing liquid and the filtrate are combined, and the filter residue is dried and weighed. The antimony content in the filtrate and filter residue was analyzed, and the antimony leaching rate was 98.9% (liquid basis) / 99.4% (residue basis).
[0051] Analyze the main impurity components and Fe in the filtrate 3+ , Cu 2+ content, adding 1.2 times the theoretical amount of antimony sponge powder and 1.4 times the theoretical amount (NH 4 ) 2 S is subjected to the reduction and purification agent to remove impuri...
Embodiment 3
[0055] A kind of bismuth-containing dust, bismuth with Bi 2 o 3 Morphology exists. The main components (%) are: Bi4.23, Pb 41.30, Sn 3.01, Zn 1.0, Cu 1.7, As 2.3, S 9.7, Cd 0.12, In 0.016, Ag 0.01, Ge 0.02.
[0056] Take 10000g of the above-mentioned bismuth soot powder, when the liquid-solid ratio is 4:1, and the acidity of hydrochloric acid is 4mol L -1 1. After leaching for 3 hours at a leaching temperature of 50°C, filter and separate, combine the lotion with the filtrate, dry and weigh the filter residue. The content of bismuth in the filtrate and filter residue was analyzed, and the leaching rate of bismuth was 96.2% (liquid basis) / 95.5% (residue basis).
[0057] Add 1.2 times of theoretical amount of sponge bismuth powder and 1.3 times of theoretical amount (NH 4 ) 2 S was used as a reduction and purification agent, and after reduction and purification at room temperature for 40 minutes, it was filtered and separated.
[0058] In the reduction purification solutio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com