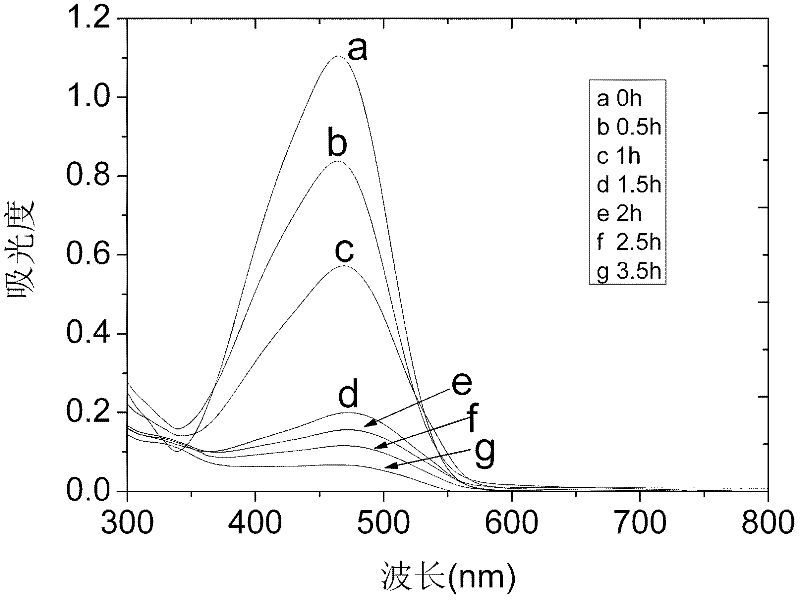
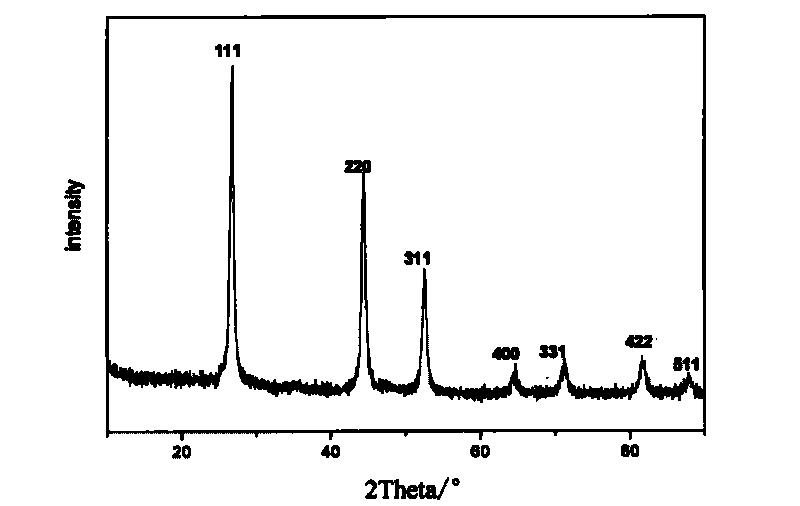
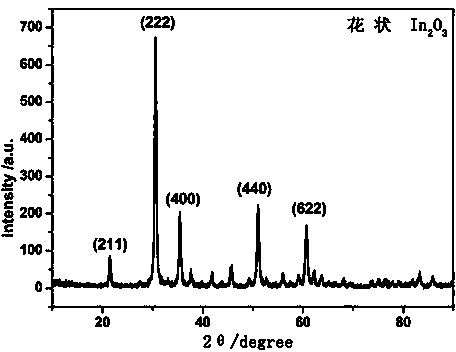
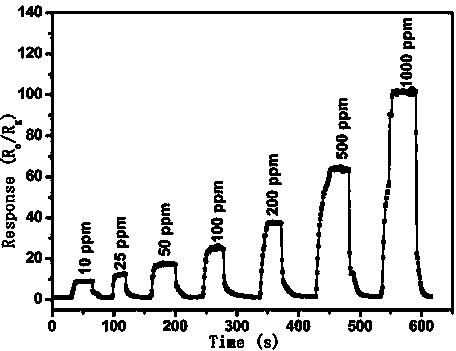
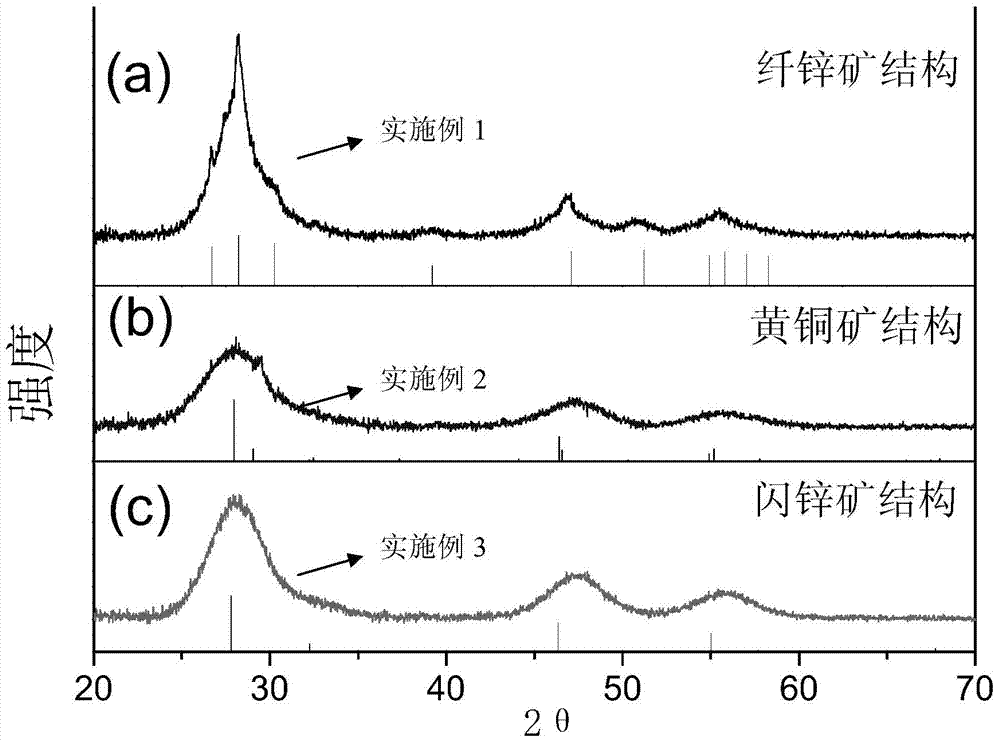
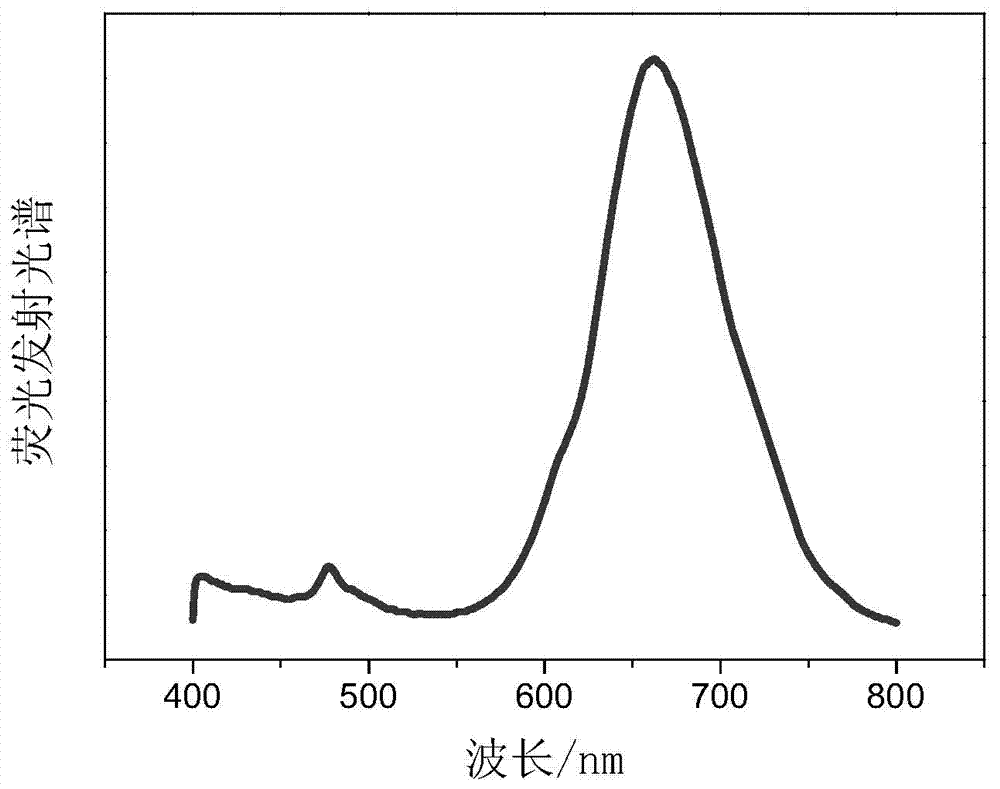
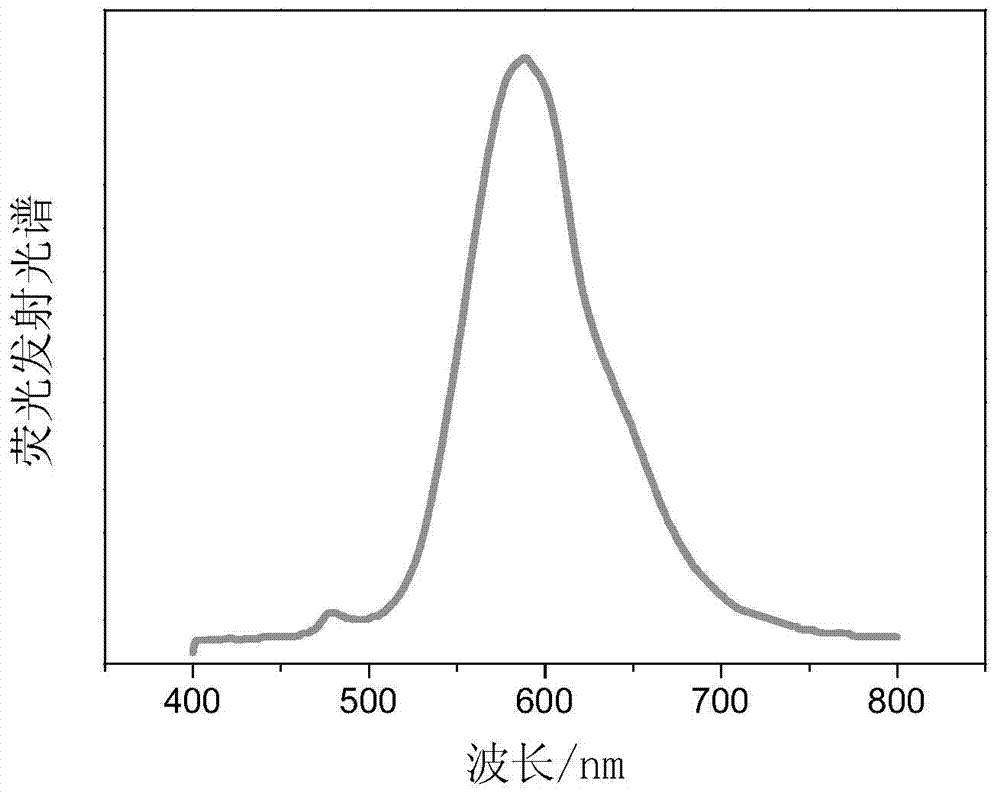
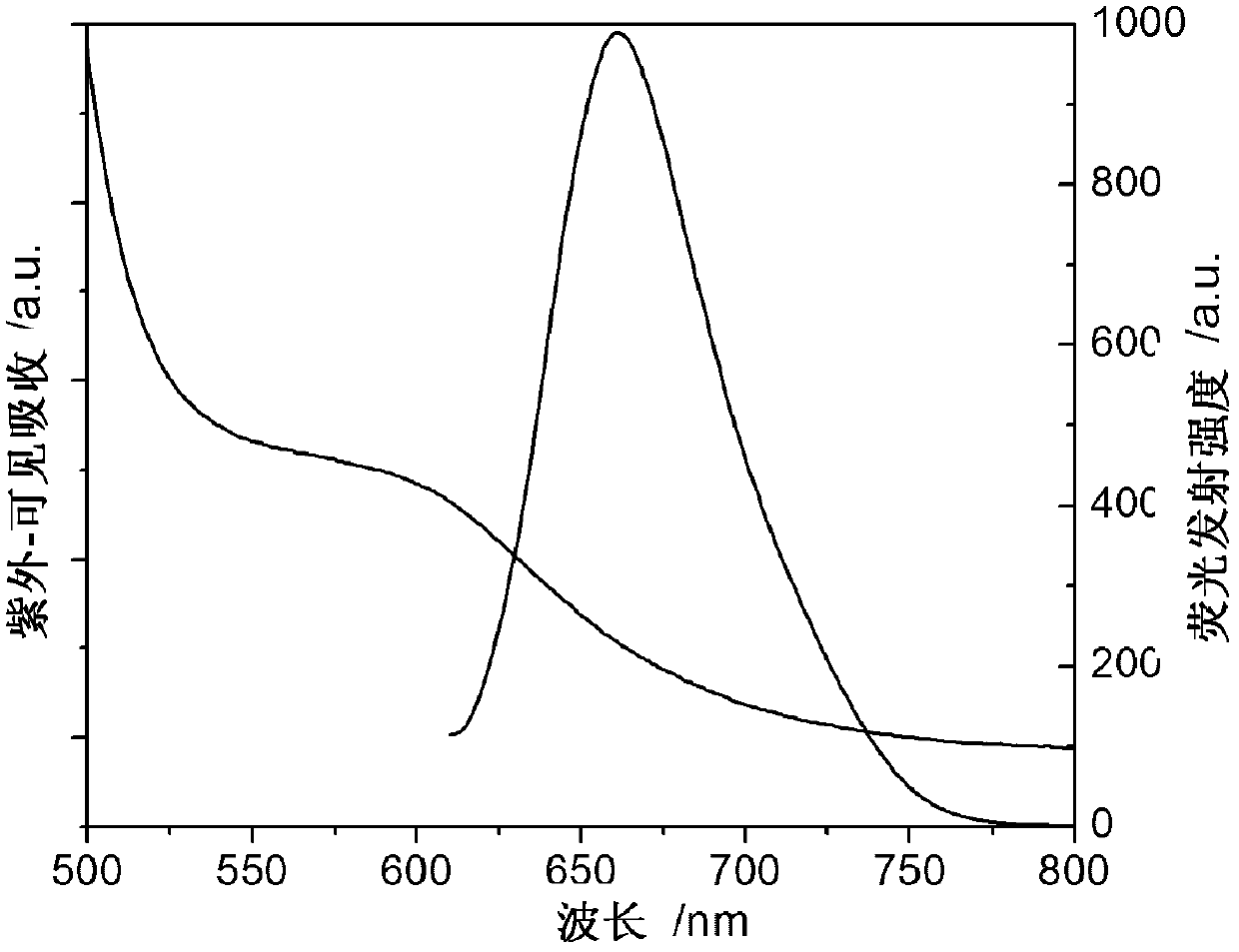
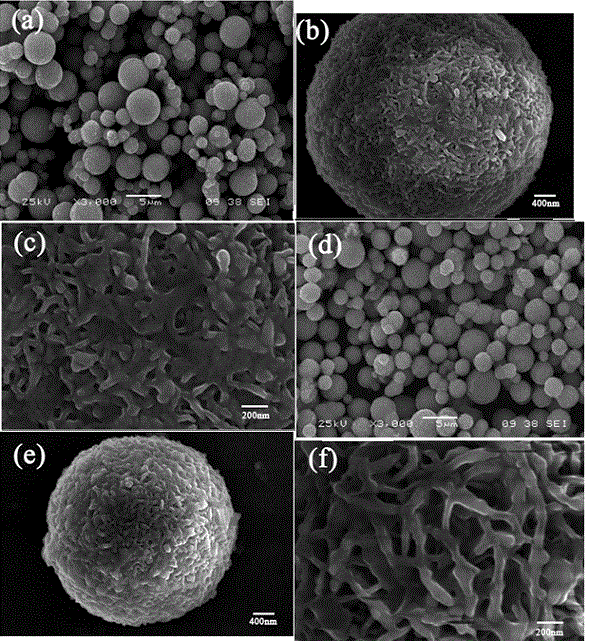
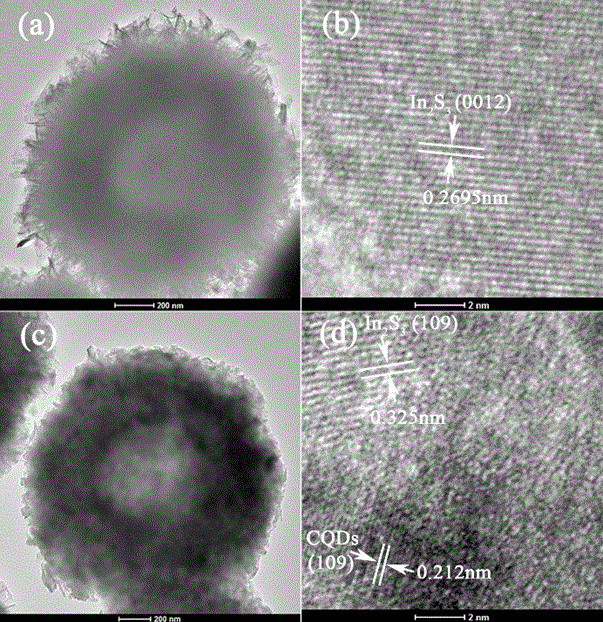
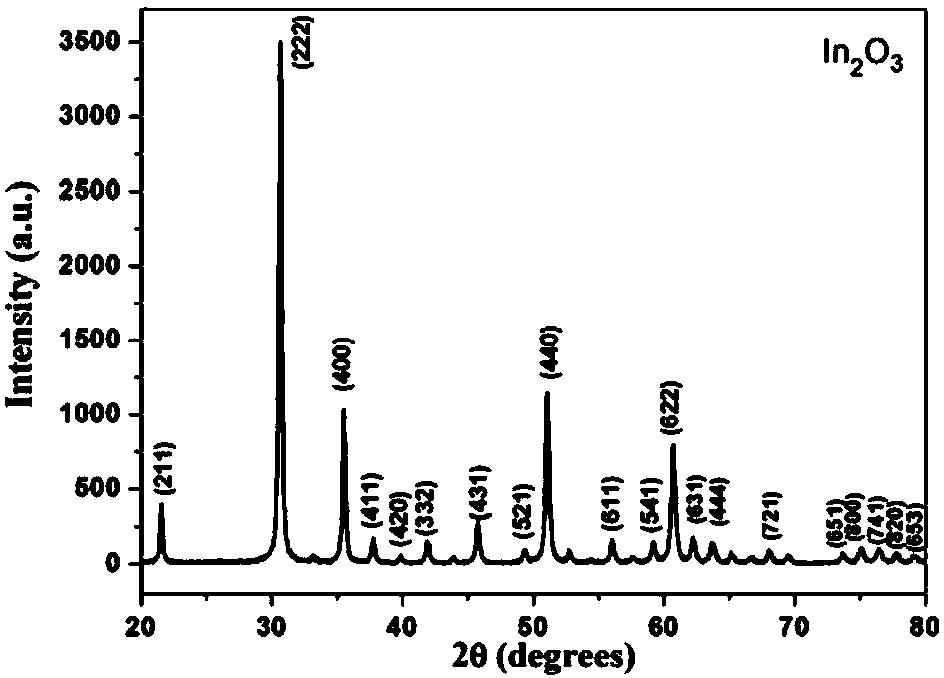
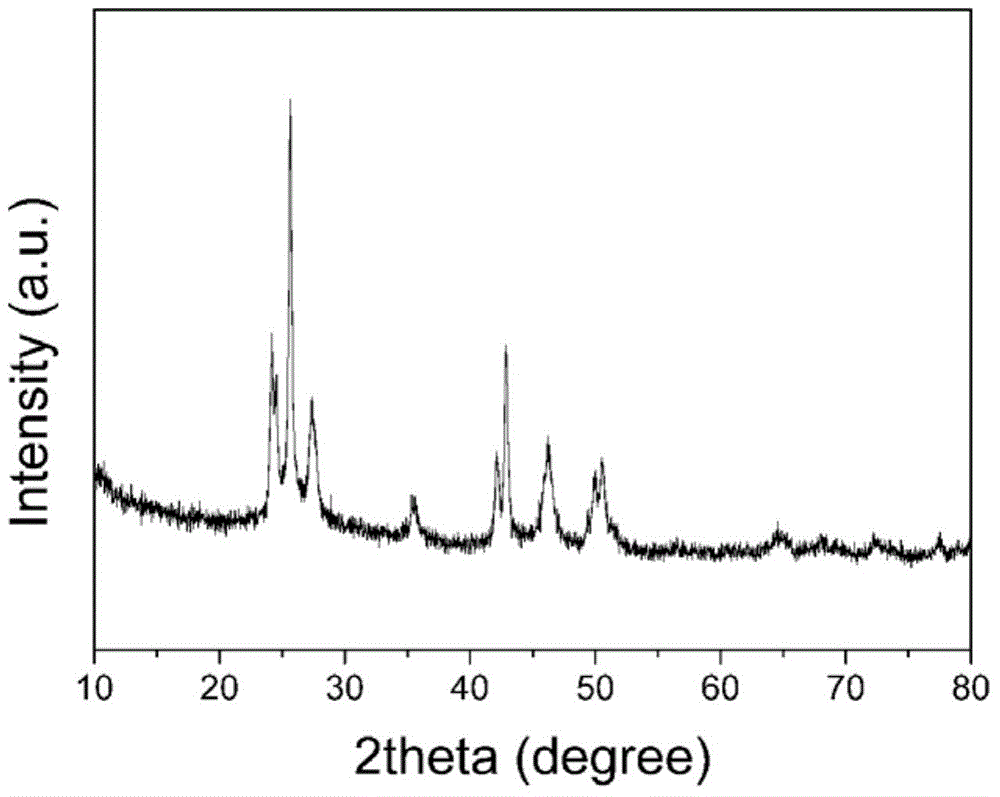
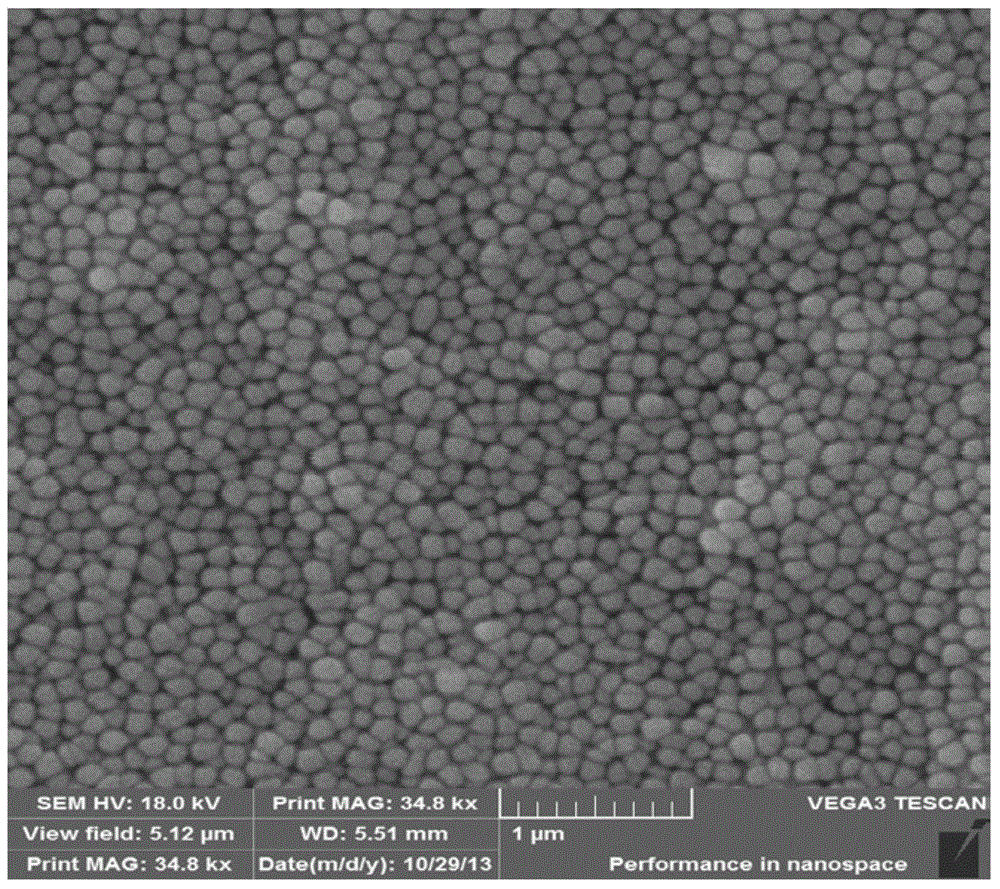
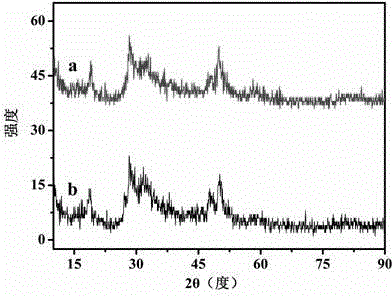
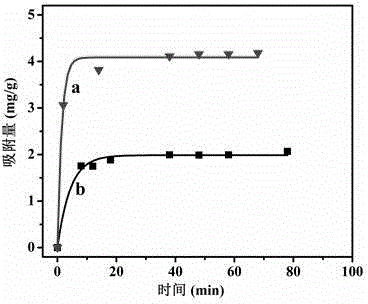
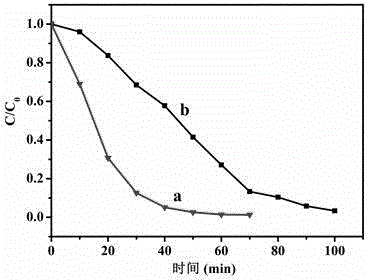
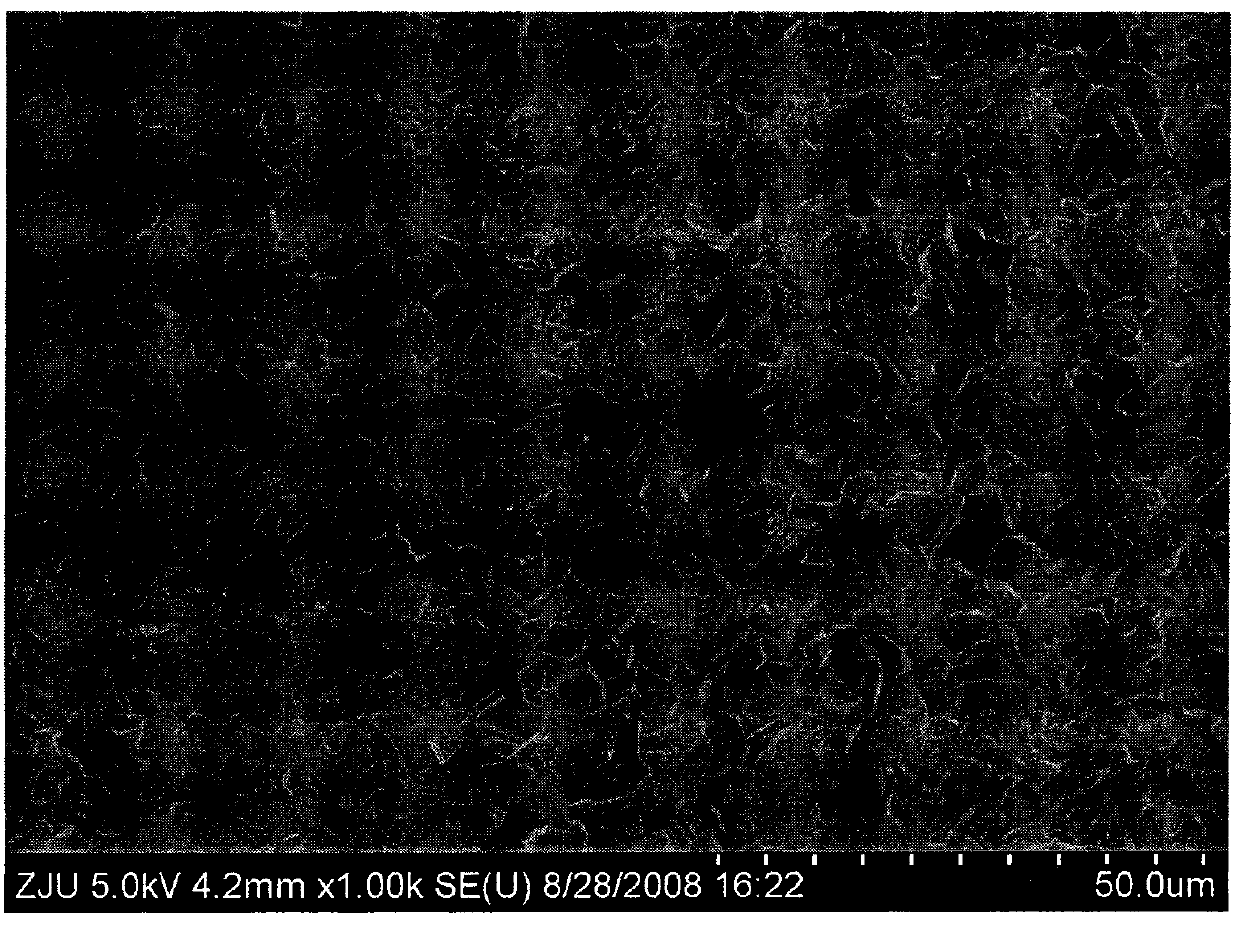
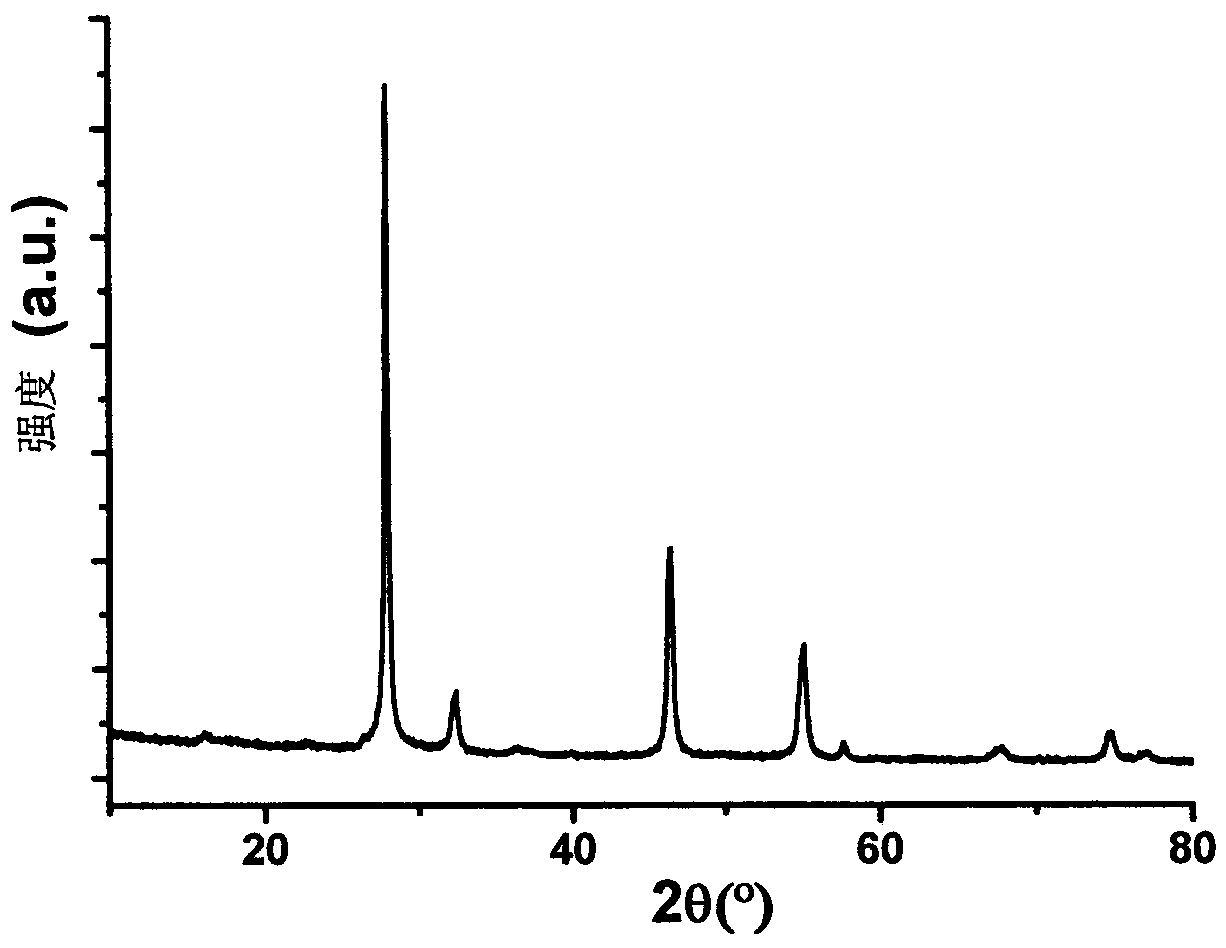
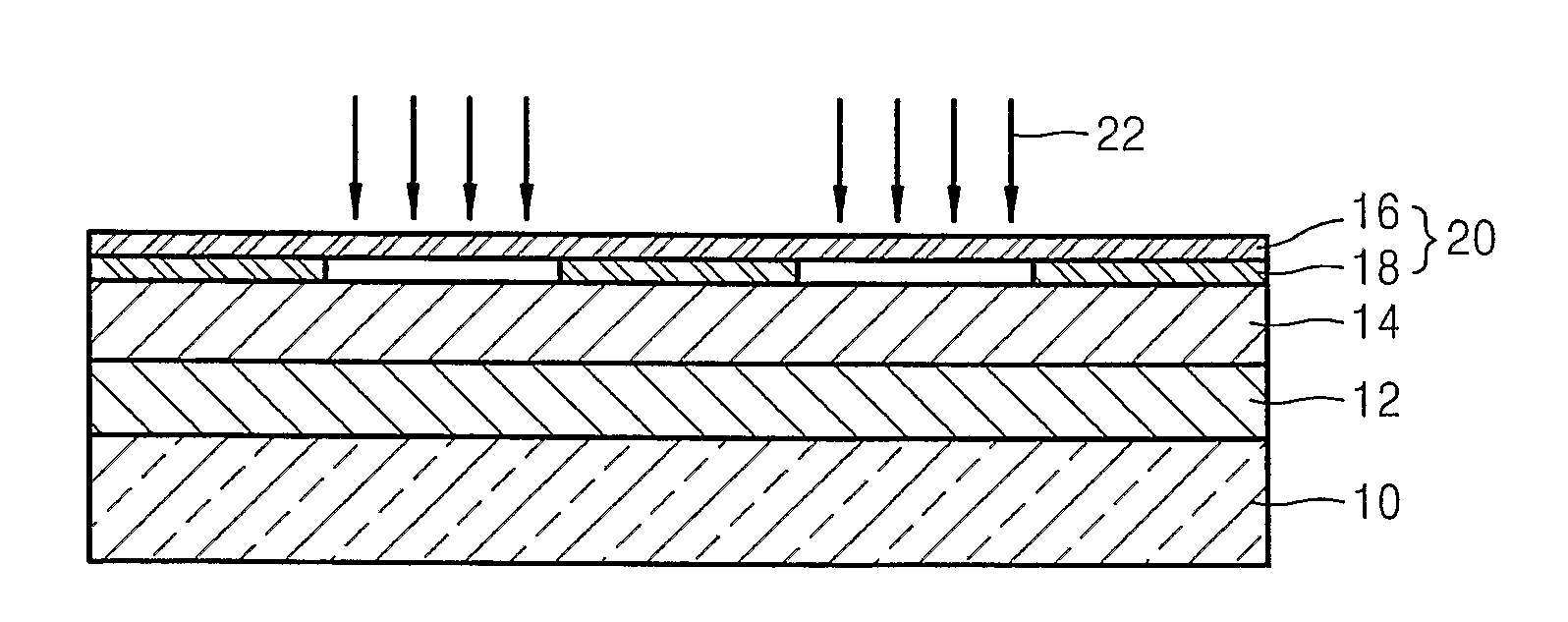
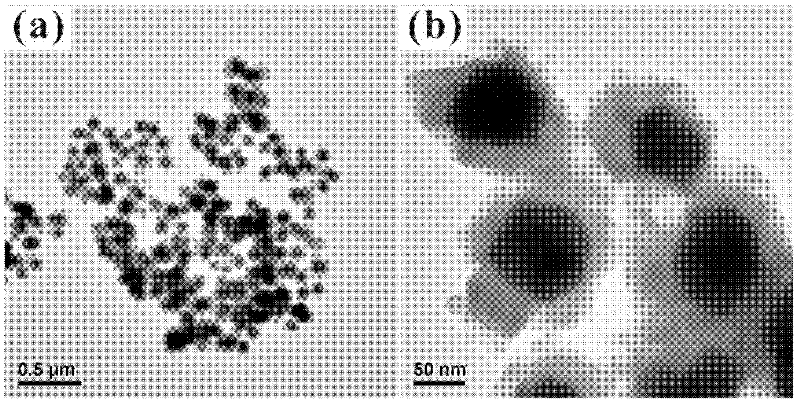
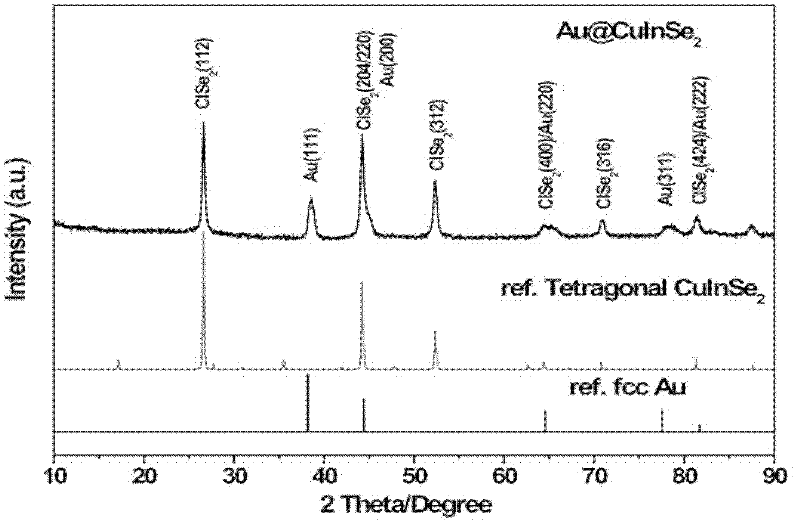
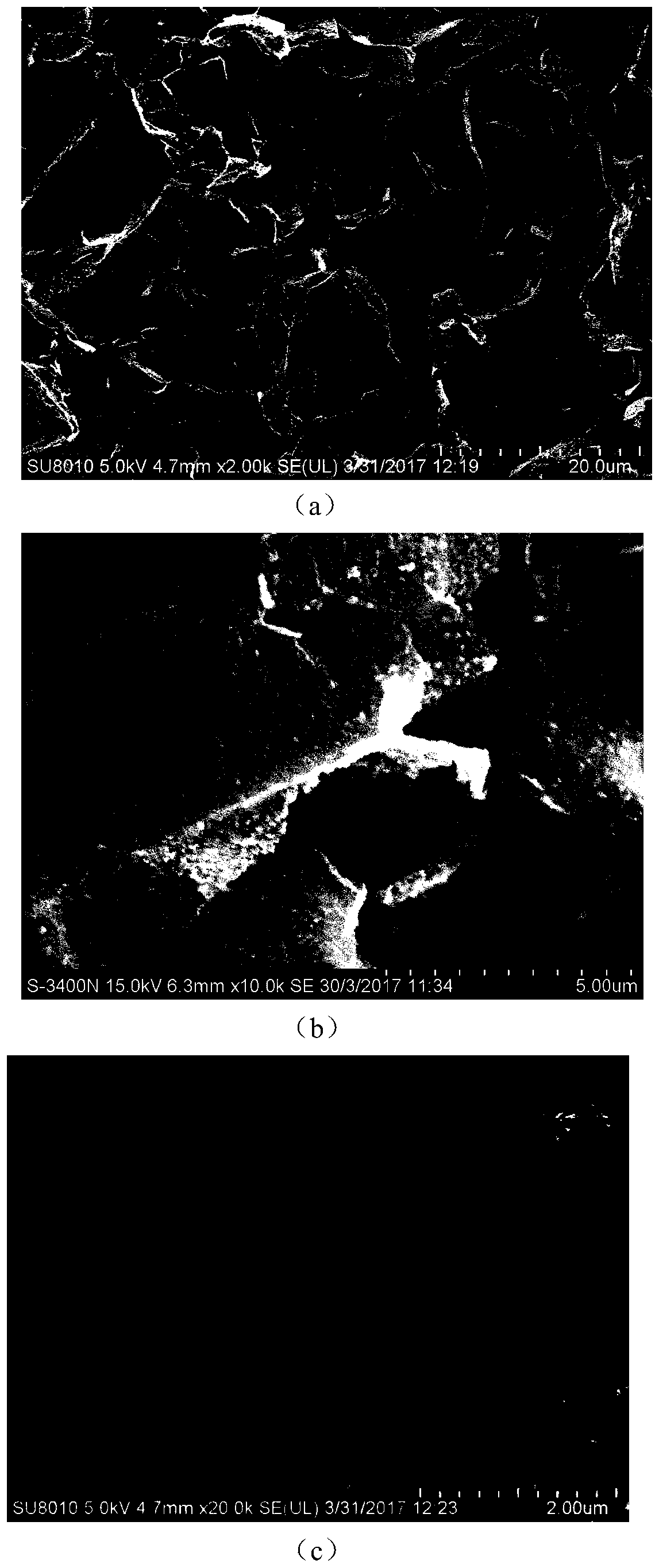
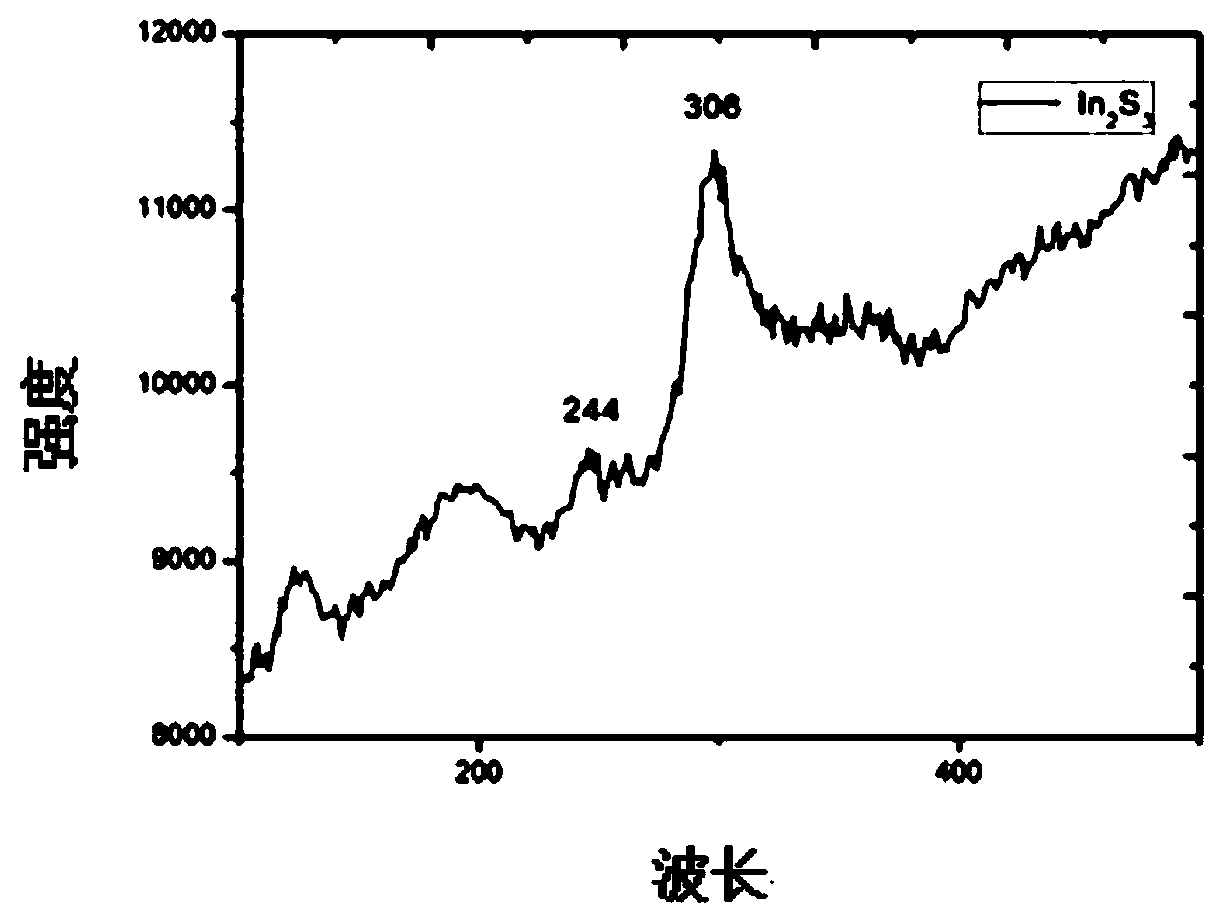
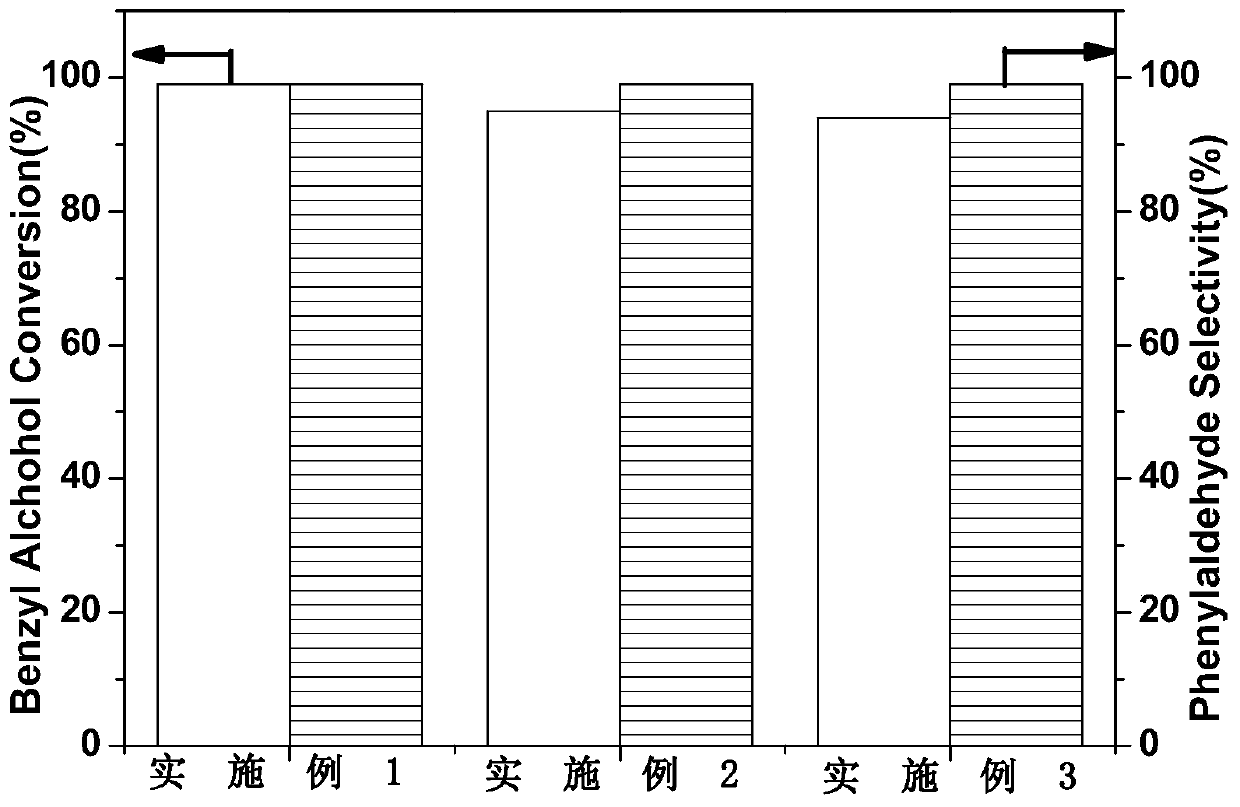
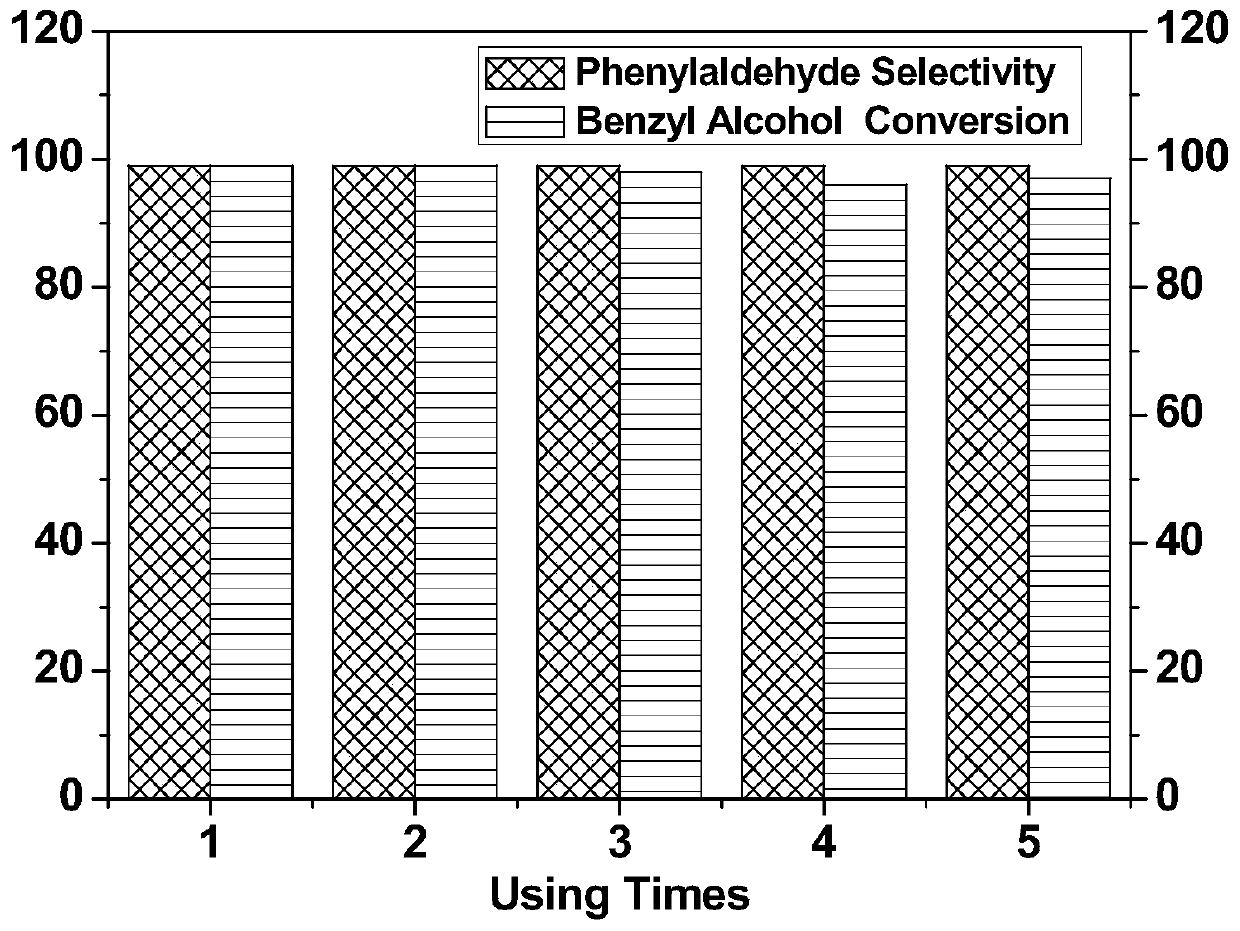
Patents
Literature
262 results about "Indium chloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Indium(III) chloride is the chemical compound with the formula InCl3. This colorless salt finds some use in organic synthesis as a Lewis acid. It is also the most available soluble derivative of indium.
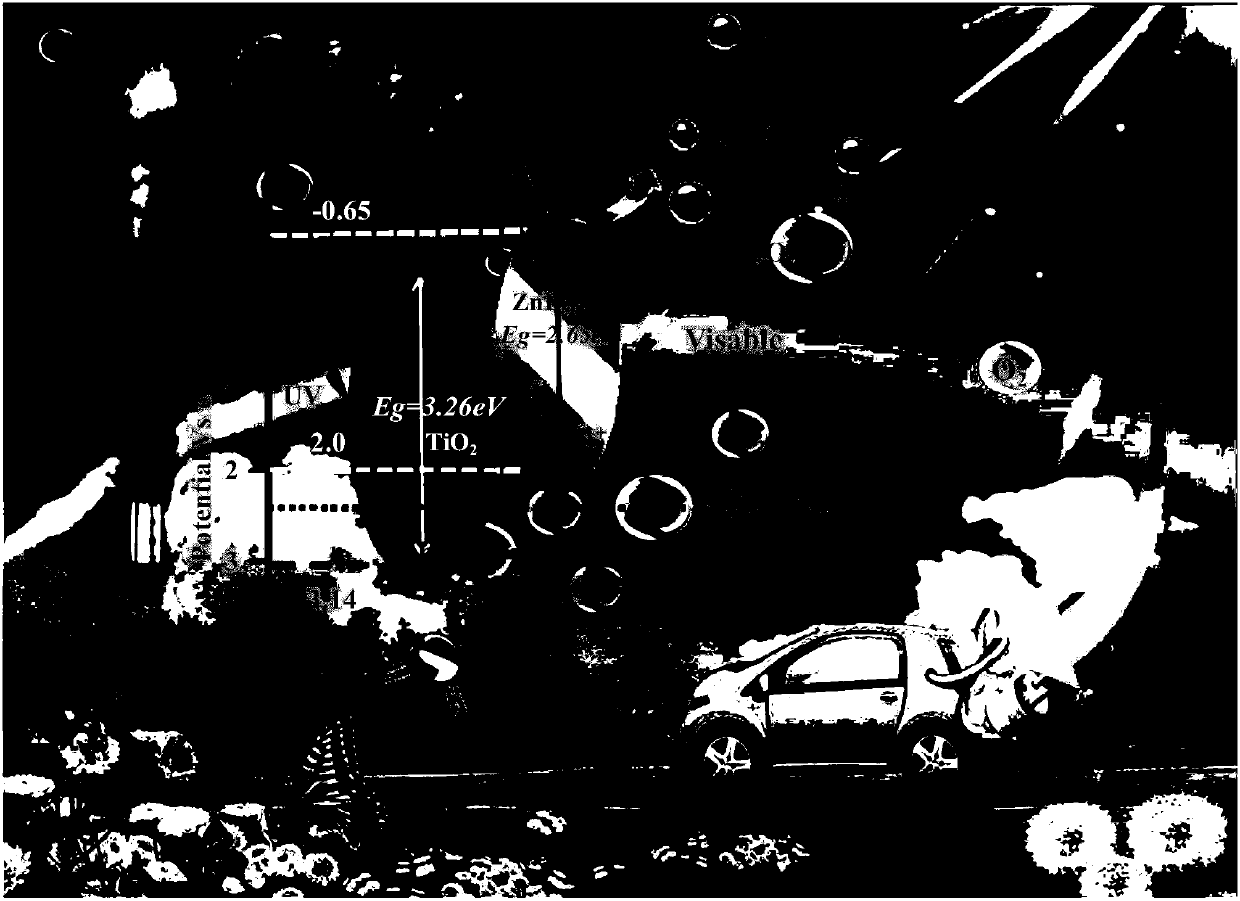
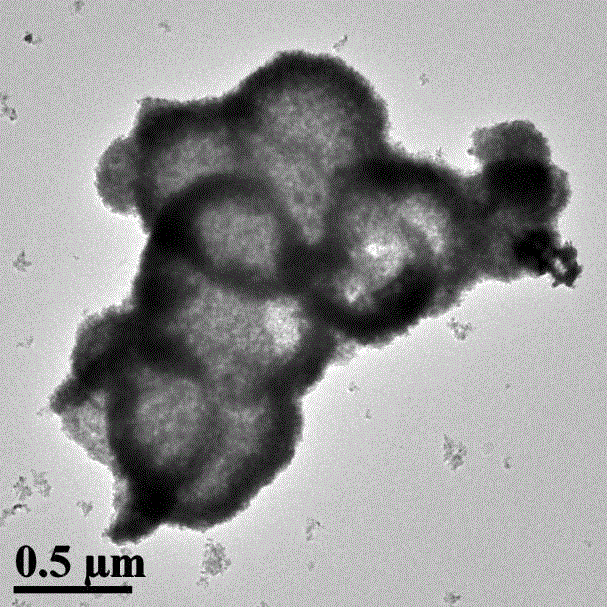
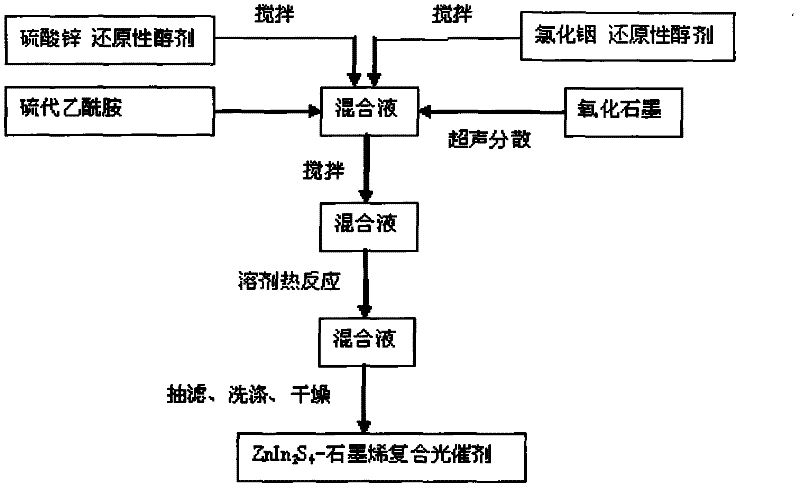
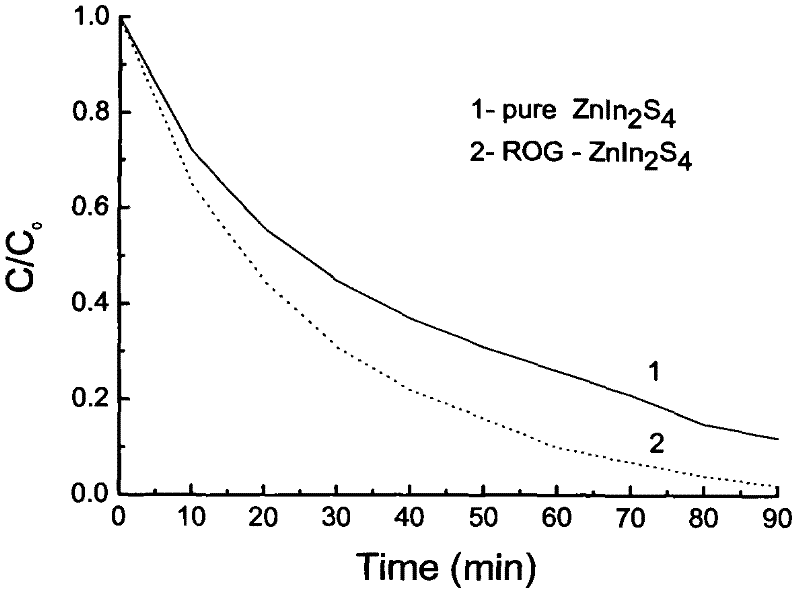
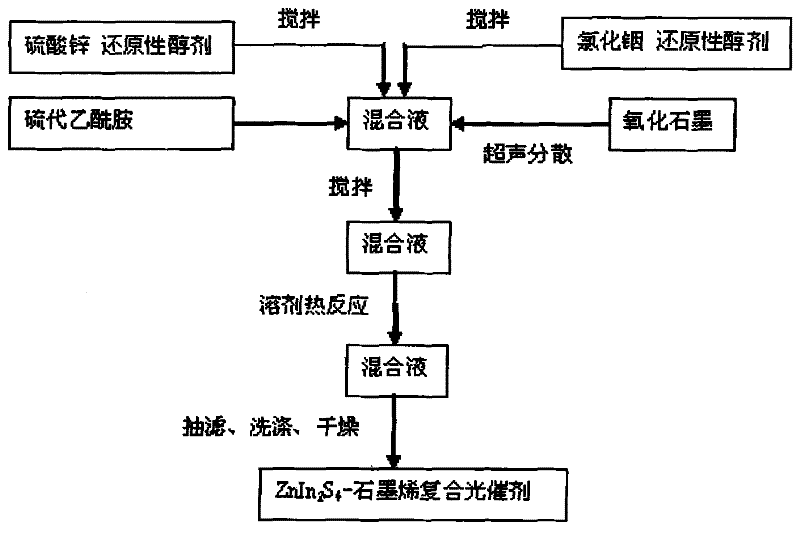
Preparation method and application of ZnIn2S4-graphene composited photochemical catalyst
InactiveCN102407147AReduce the chance of reunionLarge specific surface areaPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationFiltrationAlcohol agent
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a ZnIn2S4-graphene composited photochemical catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: placing graphite oxide into a reducibility alcohol agent for ultrasonic dispersion; adding zinc sulfate and indium chloride into the reducibility alcohol agent, stirring and dissolving; adding thioacetamide into two systems after the two systems are mixed; transferring the mixed systems into a hydrothermal kettle for a reaction; and after the reaction is finished, carrying out vacuum filtration on the obtained product, washing, vacuumizing and grinding to obtain a nano ZnIn2S4-graphene composited photochemical catalyst. In the invention, grapheme is taken as a supporting material, and a solvothermal synthesis method is adopted to further prepare the nano ZnIn2S4-graphene composited photochemical catalyst. The catalyst prepared by using the method in the invention has the advantages of wide visible light responding range and high photocatalysis activity, can be used for transformation and use of solar energy and comprehensive ecological improvement, such as air purification, sewage disposal, hydrogen production through photodegradation, preparation of alcohol or hydrocarbon chemical fuels and the like by the photocatalysis and reduction of CO2.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
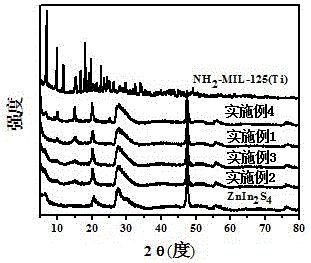
ZnIn2S4/NH2-MIL-125(Ti) composite visible-light catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105964305AOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsN dimethylformamideUltrasonic dispersion
The invention relates to a novel ZnIn2S4 / NH2-MIL-125(Ti) composite visible-light catalyst and belongs to the technical field of photocatalysis. The novel ZnIn2S4 / NH2-MIL-125(Ti) composite visible-light catalyst is characterized in that ZnIn2S4 is nanosheet-shaped and is uniformly distributed on the surface of lumpy NH2-MIL-125(Ti), and the mass percent of the NH2-MIL-125(Ti) is 20.0% to 6.0%. A preparation method comprises the steps: (1) dissolving a certain amount of tetrabutyl titanate and 2-amino terephthalic acid in a mixture solution of N,N-dimethylformamide and methanol, and carrying out a crystallizing reaction for 48 hours in an autoclave at the temperature of 150 DEG C, so as to obtain the NH2-MIL-125(Ti); (2) dispersing the synthesized NH2-MIL-125(Ti) into a certain volume of ethanol in an ultrasonic dispersion manner, then, sequentially adding a certain amount of propanetriol, indium chloride, zinc chloride and thioacetamide into the dispersion while carrying out stirring, carrying out a crystallizing reaction for 10 hours in an autoclave at the temperature of 180 DEG C to 200 DEG C so as to obtain a solid product, and subjecting the obtained solid product to filtrating, washing and drying, thereby obtaining the ZnIn2S4 / NH2-MIL-125(Ti) composite visible-light catalyst. The preparation method of the composite visible-light catalyst is environmentally-friendly and is simple in process. The prepared composite catalyst has very high visible-light catalytic activity and has a potential application value in photocatalytic hydrogen production using solar energy.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
High-active ZnIn2S4/TiO2 Z system catalyst material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107866234AIncrease profitSave raw materialsGas treatmentPhysical/chemical process catalystsPtru catalystThio-
The invention relates to a new preparation method of a ZnIn2S4 / TiO2Z system composite photocatalyst. The new preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) taking commercial P25 and sodium hydroxide solution as raw materials, performing hydrothermal treatment at 180DEG C for 48h, and performing replacement with H+ to obtain a H2Ti3O7 nanobelt, performing hydrothermal treatment through dilute sulfuric acid at 100DEG C, and performing high temperature calcination at 600DCG C to obtain a TiO2 nanobelt with rough surface; and (2) weighing zinc chloride, indium chloride, and thioacetamide according to a 1:2:4 molar ratio of Zn, In and S, and dissolving the zinc chloride, indium chloride, and thioacetamide into ethylene glycol to obtain a mixture, then dispersing the obtained TiO2 nanobelt into the mixture ultrasonically, performing treatment at 120DEG C for 2h, performing centrifugation and separation on the obtained mixture, and then performing oven-drying for 10h to obtain the ZnIn2S4 / TiO2Z system composite photocatalyst. According to the new preparation method, the obtained novel composite photocatalyst has an excellent performance on catalytic reduction of CO2 under a simulated sunlight condition; and the raw materials are inexpensive, and the technology is simple, so that the product cost is effectively reduced, a light absorption range is broadened, and utilization ratio of sunlight is improved, and the composite photocatalyst has a very high practical value and an application prospect.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Preparation method for indium oxide nanometer material
InactiveCN102826593AUniform particle size distributionHigh purityMaterial nanotechnologyGallium/indium/thallium compoundsDispersityFlat panel display
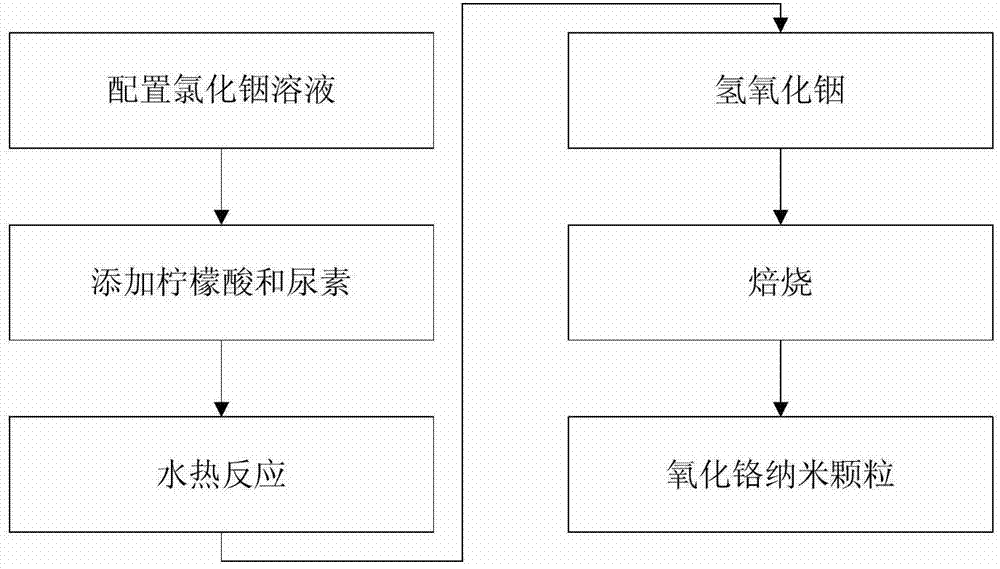
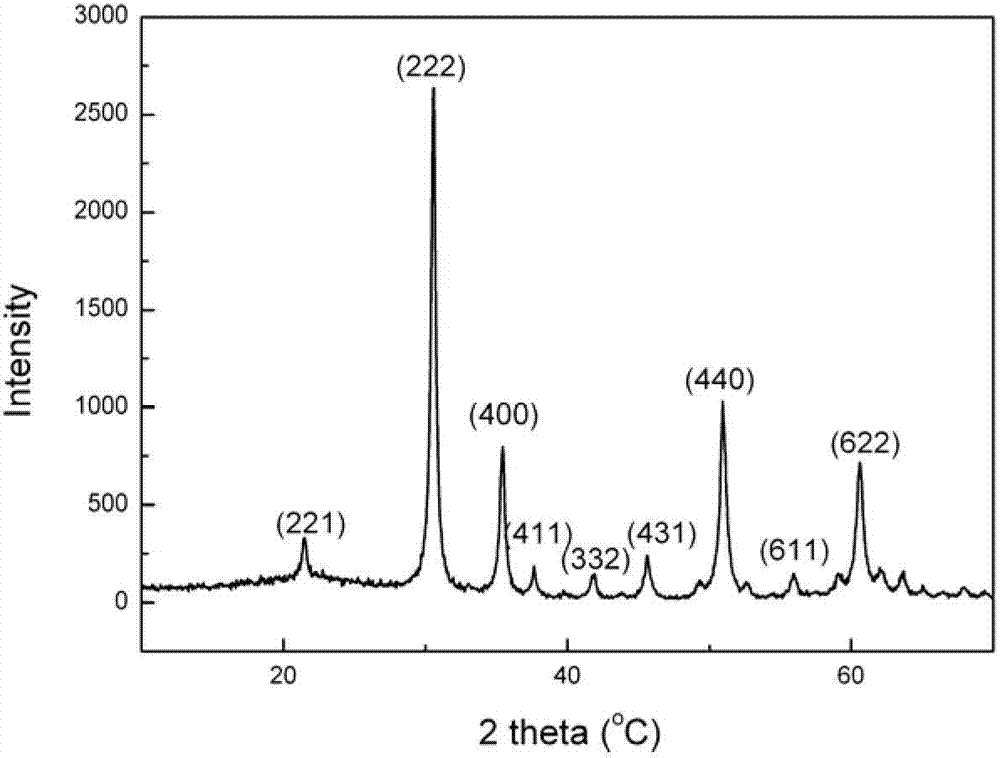
The invention relates to a preparation method for an indium oxide (In2O3) nanometer material, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of inorganic materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out a hydrothermal reaction on indium chloride to prepare indium hydroxide (In(OH)3) nanometer particles under the condition of taking lemon acid and urea as additives; and then carrying out a thermal calcination treatment to obtain the spherical In2O3 nanometer material. The method has the advantages of low cost, simplicity in production process, and easiness in industrial large-scale production. The prepared nanometer chromium oxide is a spherical particle with the diameter of about 30nm, and has the advantages of uniform particle distribution, high purity, good dispersity and large specific surface area. Therefore, the prepared nanometer chromium oxide is suitable for the fields of solar batteries, gas sensitive elements, flat-panel displays, electric light regulators, sensors and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Synthesis method of novel visible-light photocatalyst indium sulfide
InactiveCN102335616APromote degradationSimple processPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic dyeSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a synthesis method of a novel visible-light photocatalyst indium sulfide, belonging to the technical field of preparation of photocatalysts. The method comprises the following steps: weighing indium chloride tetrahydrate, dissolving the indium chloride tetrahydrate in deionized water, adding acetic acid to regulate the pH value to 1-3, and adding thioacetamide solution, wherein the concentration of indium ions is 0.025 mol / L, and the In / S mol ratio is 1:4-1:10; heating the obtained mixed solution to constant temperature so as to carry out hydrothermal reaction for 4-8 hours while regulating the temperature to 80 DEG C, and cooling at room temperature; and carrying out vacuum filtration under reduced pressure, washing, and drying to obtain the orange indium sulfide powder. The indium sulfide prepared by the method provided by the invention is in a ball-flower shape, and has the advantages of large specific area and uniform size; and the indium sulfide powder is in a cubic structure. The indium sulfide can be used as a visible-light photocatalyst, and has good degradation effect on organic dyes (such as methyl orange).
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for comprehensively recovering copper and indium from lead matte
ActiveCN104357661AAchieving selective leachingAchieve separationProcess efficiency improvementOxygenBall mill
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recovering copper and indium from lead matte. The method comprises the following steps: A, crushing lead matte block materials and then ball-milling to obtain lead matte powder; B, leaching the lead matte powder obtained by ball-milling in an autoclave by using sulfuric acid and continuously introducing oxygen in the leaching process; C, after leaching, carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain leaching residues and leachates containing copper ions and indium ions; D, selectively extracting the copper ions in the leachates by using ZJ988, obtaining copper sulfate enrichment liquid by using a sulfuric acid-copper sulfate solution to perform reverse extraction on loaded organic phase, taking the copper sulfate enrichment liquid as an electrolyte of electro-deposit copper and obtaining cathode copper through a copper sulfate electro-deposition process; E, selectively extracting the indium ions by using P204, then obtaining indium chloride enrichment liquid by using a hydrochloric acid solution to perform reverse extraction on the loaded organic phase and replacing the indium chloride enrichment liquid by using a zinc plate or an aluminum plate to obtain sponge indium. The method has the benefits that the complete separation of the copper from the indium in the lead matte is realized, recovery rate of the valuable metal is high, and the environmental friendliness is realized.
Owner:YUNNAN COPPER CO LTD +1
Method for synthesizing copper-indium-selenium nanocrystalline
InactiveCN101698472ANo pollution in the processImprove reaction efficiencySelenium/tellurium compundsNitrogen gasSolvent
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing copper-indium-selenium nanocrystalline and relates to a solar cell material. The invention provides a method for synthesizing copper-indium-selenium nanocrystalline with simple technological steps. The method comprises the following steps: mixing dodecyl mercaptan and oleyl amine to obtain a mixed solvent; adding an elementary substance selenium, and dispersing to obtain an evenly dispersed elementary substance solution; adding cuprous chloride and indium chloride into an oleic acid-octadecylene mixed solvent, heating while stirring, vacuumizing, so that the vacuum degree of the system is lower than -0.1 MPa, and introducing nitrogen to obtain an oleic acid-octadecylene composition of cupric salts and indium salts in the nitrogen atmosphere, wherein the oleic acid-octadecylene composition of cupric salts and indium salts is a light-brown transparent solution; and injecting the prepared selenium solution into the oleic acid-octadecylene composition of cupric salts and indium salts, heating to carry out the reaction, centrifugating to obtain a precipitate, and respectively washing the precipitate with methenyl chloride and ethanol at least once to obtain the copper-indium-selenium nanocrystalline.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Preparation method of flower type indium oxide gas-sensitive material with hierarchical structure
InactiveCN104229871ALow costImprove protectionGallium/indium/thallium compoundsPetalPhysical chemistry
The invention provides a method of preparing a flower type indium oxide gas-sensitive material with a hierarchical structure by adopting a solvothermal method. The preparation method concretely comprises the following steps: respectively adding a certain amount of indium oxide and a certain amount of sodium citrate into a dimethylformamide and deionized water mixed solution of certain mole ratio, fully mixing, then adding a certain amount of urea as a precipitator, evenly dispersing, sealing the mixed solution into an autoclave, performing hydrothermal reaction for certain time at specific temperature, centrifugally separating, washing and drying, placing the dried product in the air in a muffle furnace for calcinating, and thus obtaining the flower type indium oxide gas-sensitive material with the hierarchical structure. The method is simple in production technology, high in yield, low in cost and pollution-free, and mass production can be conducted. The prepared flower type indium oxide gas-sensitive material with the hierarchical structure is regular in shape, obvious in hierarchical structure of flower petals, smooth in surfaces of flower petals, large in specific surface, and mainly applied in the field of gas sensors.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Preparation method of Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dot luminescent thin film
ActiveCN103589427AEasy to operateSynthetic temperature is mildLuminescent compositionsFluorescence spectraAdhesive
The invention discloses a preparation method of a Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dot luminescent thin film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) adding cuprous chloride, indium chloride, zinc salt, a capping agent and a surface coating agent to a non-polar high boiling point organic solvent so as to obtain a Cu, In and Zn mixed precursor solution, stirring and heating under the atmosphere of nitrogen or inert gas so as to form a clear transparent solution; (2) adding an oleylamine solution of sulfur to the clear transparent solution obtained in the step (1), and heating for reacting so as to prepare a Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dot solution; (3) separating so as to obtain Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dots; (4) mixing the prepared Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dots with a component A of an LED (Light Emitting Diode) pouring sealant; (5) uniformly mixing a component B of the LED pouring sealant with a mixture obtained in the step (4), removing air bubbles, then coating a product on a glass substrate, and curing at a room temperature so as to obtain the Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dot luminescent thin film. The fluorescence spectra of the Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dot luminescent thin film prepared by the method can be adjusted. The Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dot luminescent thin film has the excellent fluorescence property of the Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dots and the good machining property of an organic silicon adhesive AB.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Hydro-thermal preparation method for novel near infrared water-soluble copper-indium-sulfur three-element quantum dots
InactiveCN102517003ALower requirementExcellent fluorescence propertiesLuminescent compositionsCarboxylic acidCadmium Cation
The invention belongs to the technical field of quantum dot preparation, and specifically to a method for preparing copper-indium-sulfur (CuInS2) three-element quantum dots under a hydro-thermal condition. According to the method, common metal salt compounds such as copper chloride and indium chloride, and a sulfhydryl-containing carboxylic acid such as mercaptopropionic acid and mercaptosuccinic acid are adopted to synthesize copper-indium-sulfur (CuInS2) nanoparticles with the particle size of 2-4 nm and emission wavelength in the near infrared region under the hydro-thermal condition. Compared to other organic phase synthesis of the near infrared quantum dots, the method of the present invention has characteristics of less variety of the raw materials, cheap price, simple method, easy operation, good repeatability, and low requirements on equipment. Compared to the traditional quantum dots, the synthesized water-soluble quantum dots of the present invention have the following advantages that: the synthesized water-soluble quantum dots do not contain mercury, cadmium and other toxic metal elements, the emission peak is located in the near infrared region, the synthesized water-soluble quantum dots provide strong penetrabilities for cells and other biological tissues, and the synthesized water-soluble quantum dots can be widely used in immunological assays, nucleic acid hybridizations, gene analysis, cell classification and imaging and other fields.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for preparing monodisperse indium oxide nanometer porous microsphere
InactiveCN103183374ALow costImprove protectionGallium/indium/thallium compoundsNanotechnologyManufacturing technologyDisplay device
The invention provides a method for preparing a monodisperse indium oxide nanometer porous microsphere, and belongs to the technical field of function materials. The preparation method particularly comprises the following steps: adding citric acid with a certain molar ratio in indium chloride aqueous solution, mixing intensively, adding moderate urea as a precipitant, and dispersing uniformly; sealing the mixed solution in an autoclave and conducting water thermal reaction for a period of time, and then centrifugalizating, washing and drying; calcining in a muffle furnace in air to obtain the monodisperse indium oxide nanometer porous microsphere. The method provided by the invention has low cost, simple manufacturing technology, high productivity, and is easy to realize industrialization and mass production. The indium oxide nanometer microsphere produced by the method has a neat appearance, uniform disperse, has a porous structure and a larger specific surface area, and can be applied in the field of solar cells, FPDs (Flat Panel Display), photo-electron devices, gas sensors and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Method for preparing graphene structure-like copper-indium-sulfur nanosheet array membrane
InactiveCN103819099AAbundant raw materialsLow priceMetallic material coating processesThioureaNew energy
The invention relates to a method for preparing a graphene structure-like copper-indium-sulfur nanosheet array membrane, belonging to the technical field of preparation of nano materials. According to the method, the copper resource is a monovalent copper salt, the indium resource is indium chloride, the sulfur resource is powdered sulfur and thiourea, and a regular nano membrane is prepared by an in situ solvothermal method. The method comprises steps of dissolving the copper resource and the indium resource in a solution of triethanolamine, acetone and sodium citrate, adding ammonia water for regulating pH value, adding the sulfur resource in which the molar ratio of powdered sulfur to thiourea is 2:1, adding hydrazine hydrate solution, finally adding a mixed solvent of water and ethylene glycol which are in a volume ratio of 1:1, so as to obtain the precursor reaction liquid of CuInS2; adding the reaction liquid into a reaction kettle, then inserting a glass sheet for in situ solvothermal reaction, so as to obtain the regular nanosheet array membrane. The method is simple and is low in cost, the array is uniform, the nanosheet is 2-8nm thick, and an efficient method for application of the copper, indium and sulfur to new energy fields like solar batteries and photocatalysis is provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
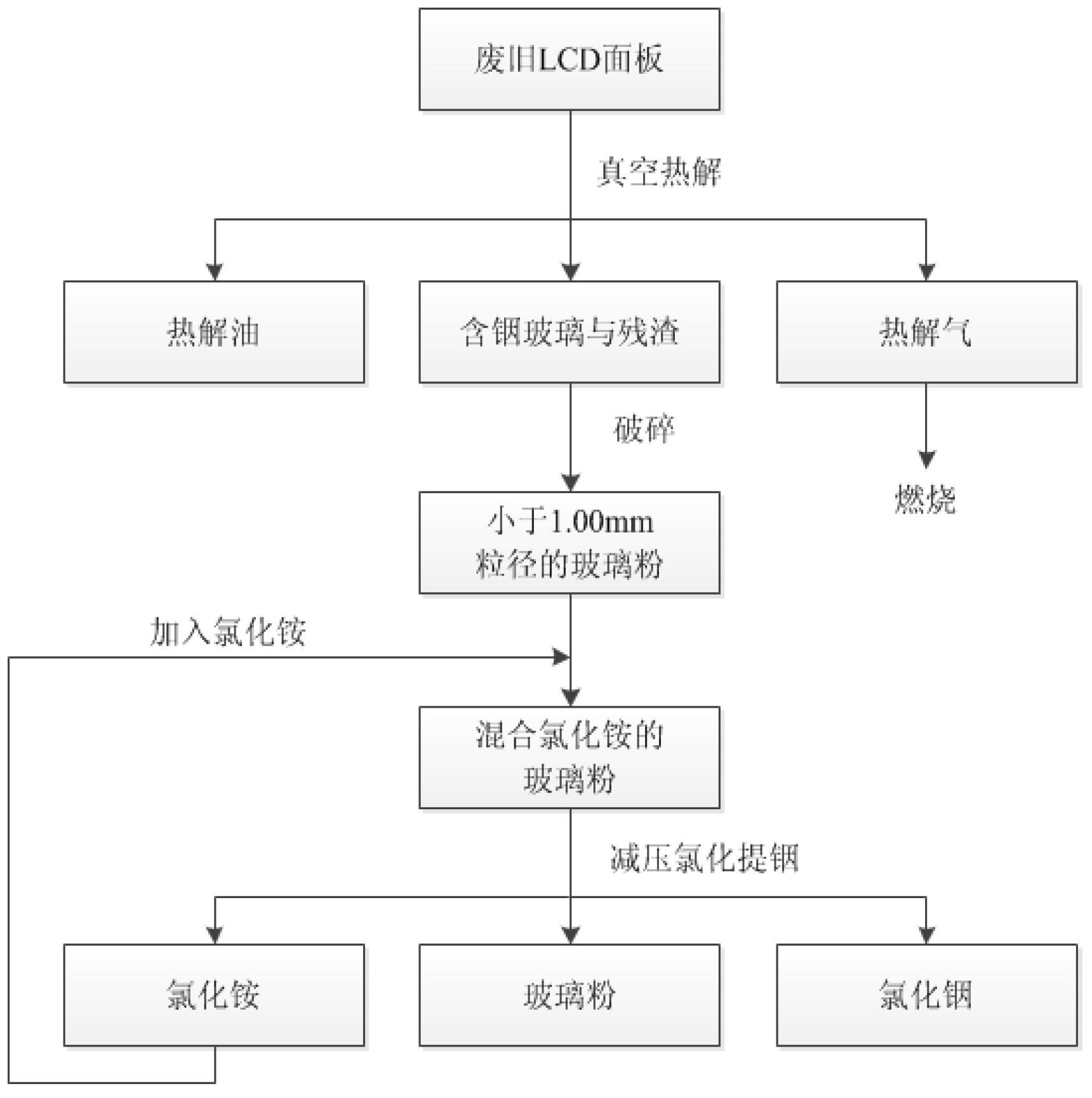
Waste liquid crystal display panel treatment and resource recycling method
InactiveCN102671921ASuitable for large-scale industrial applicationsHigh resource utilization rateSolid waste disposalLiquid-crystal displayHazardous substance
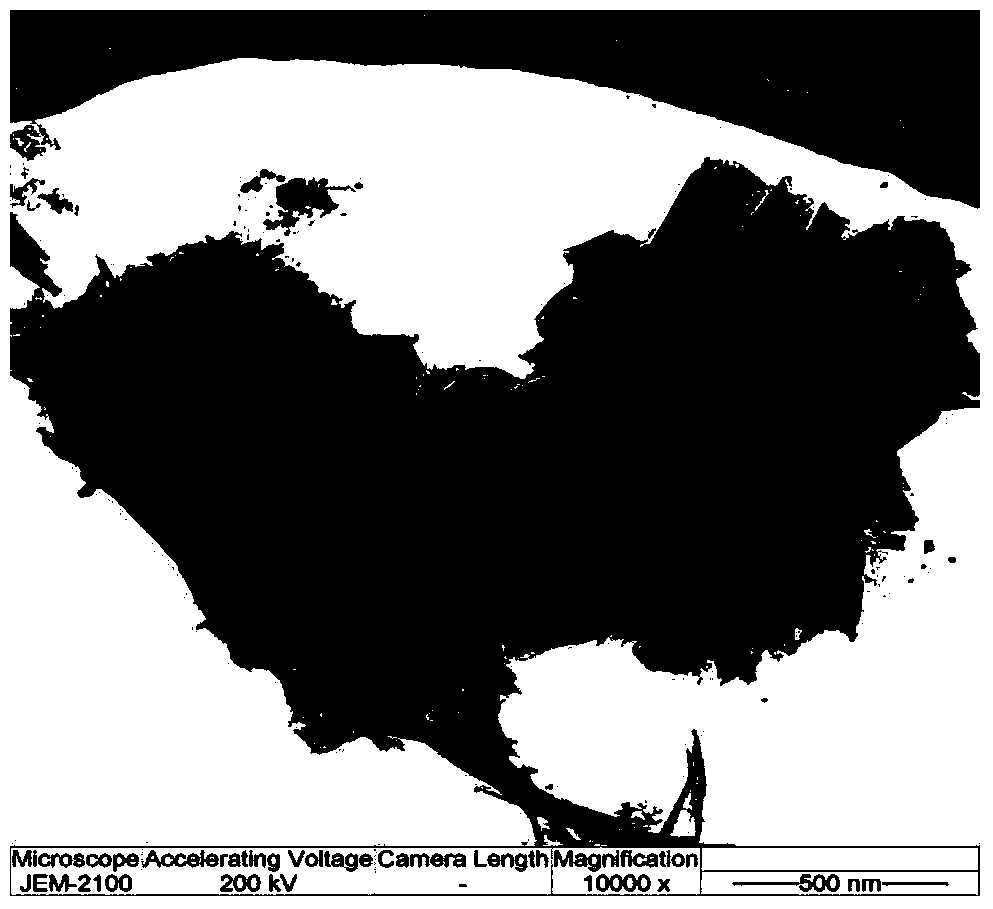
A waste liquid crystal display panel treatment and resource recycling method includes recycling organic ingredients of waste liquid crystal display panels in a vacuum pyrolysis furnace in a vacuum pyrolysis manner at first so as to obtain pyrolysis oil, pyrolysis gas and glass plates containing vacuum pyrolysis residues; then crushing the glass plates into particles with the sizes smaller than 1.00mm; and adding ammonium chloride accounting for 50% of glass powder by weight at least, reducing pressure, chloridizing and extracting indium so as to obtain indium chloride with the purity higher than 99%. Indium recycling rate is higher than 90%. The waste liquid crystal display panel treatment and resource recycling method has the advantages of high efficiency, zero pollution, high resource recycling rate, simplicity in operation and the like, and is suitable for large-scale industrial application in environment-friendly and resource recycling type enterprises, a treatment process is clean, any toxic and harmful substances are not discharged to environments, and organic matters, rare metal indium and glass in the waste liquid crystal display panels are almost recycled completely.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
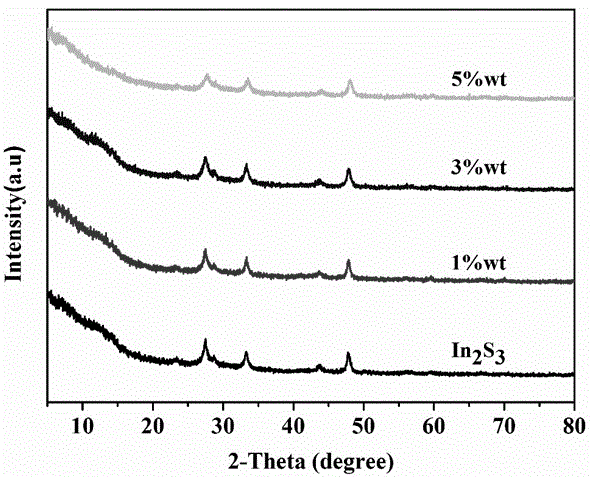
Indium-sulfide mesoporous hollow microsphere photocatalyst, and preparation method and uses thereof
ActiveCN105478142ASimple processImprove photocatalytic activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMicrosphereMethyl orange
The invention belongs to the technical field of nanometer material synthesis, and a carbon-quantum-dot-modified indium-sulfide (beta-In2S3) mesoporous hollow microsphere photocatalyst is synthesized in one step by utilizing a simple rapid hydrothermal method. The method comprises: dissolving indium chloride and L-cysteine in distilled water, and stirring to obtain a solution D; adding carbon quantum dot into the solution D, and stirring to obtain a solution E; transferring the solution E to a reaction kettle with a teflon inner liner, putting in a baking oven, and reacting at 150 DEG C for 24 h; and naturally cooling to room temperature, centrifuging to obtain a dark-red solid, washing and drying in vacuum, so as to obtain a sample. The indium-sulfide mesoporous hollow microsphere photocatalyst is applicable to degrade methyl orange dye under visible light.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparing method of nano-rod-shaped indium oxide gas-sensitive material
ActiveCN108455659AGood sensor detection performanceLower working temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyGallium/indium/thallium compoundsIndium TrichlorideWorking temperature
The invention relates to a preparing method of a nano-rod-shaped indium oxide (In2O3) gas-sensitive material, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of inorganic nanometer functional materials. The preparing method comprises the steps of with indium(III) chloride tetrahydrate being an indium source, by adopting hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide as surface active agent, conducting a hydrothermal reaction under the alkaline condition of sodium hydroxide to prepare indium hydroxide and finally, conducting thermal roasting to obtain the indium oxide gas-sensitive material of a nano-rod-shaped structure. Finally prepared indium oxide is In2O3 with the cubic phase and of the nano-rod-shaped structure, has very good performance of sensing and detecting both nitrogen dioxide gas andhydrogen sulfide gas and is insensitive to other gases (carbon monoxide, ethyl alcohol, ammonia, hydrogen, formaldehyde and the like); the indium oxide also has low working temperature, a quick response and restoration, very high sensitivity, a low detection limit, high selectivity and high stability. Besides, the indium oxide gas-sensitive material can also be used in the fields of catalyst, battery materials, photoelectric materials and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
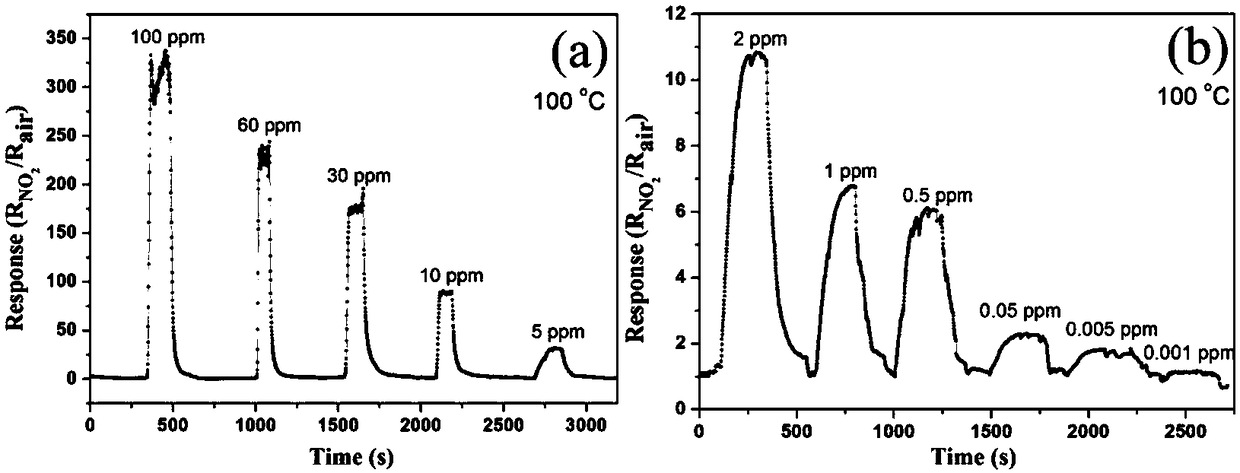
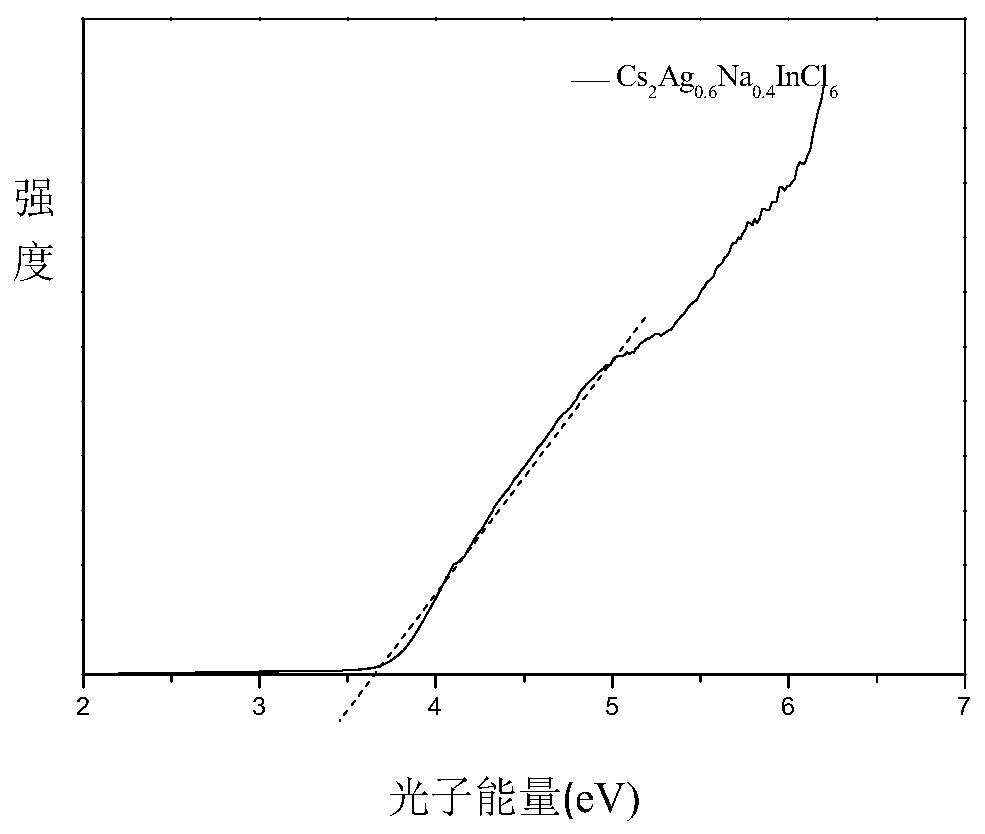
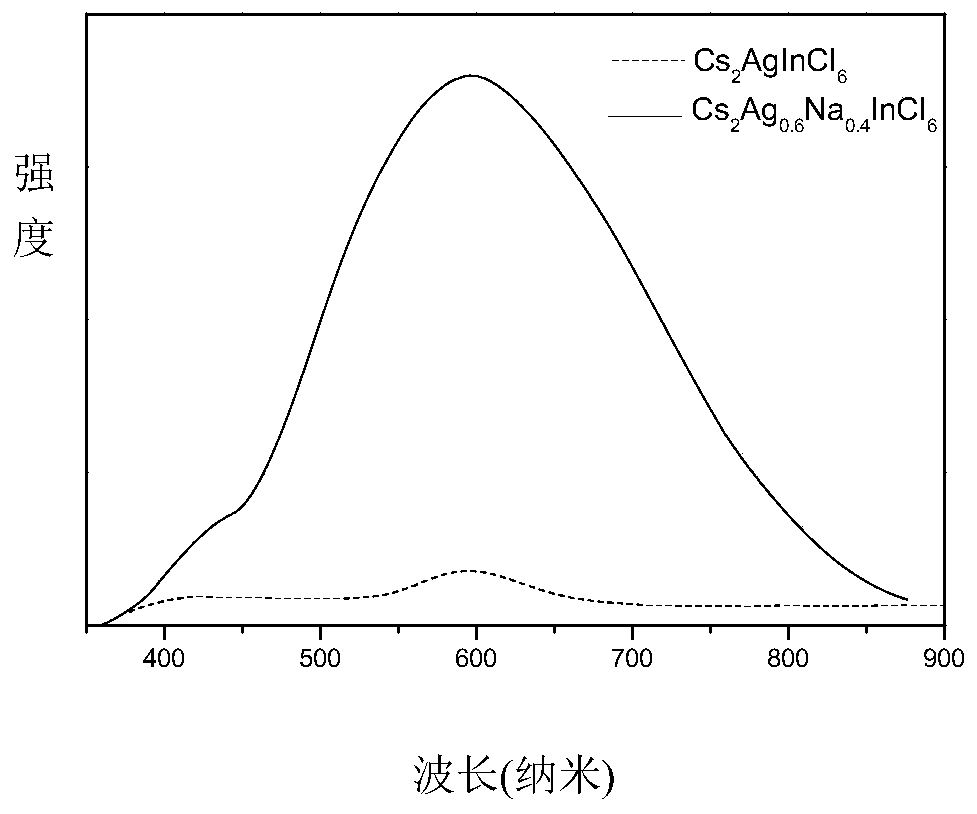
Preparation method of high fluorescence efficiency Cs2AgxNa1-xInncl6 dual-layer perovskite
InactiveCN109777403AHigh fluorescence yieldEasy to operateMaterial nanotechnologyLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceEthanol
The invention relates to a preparation method of high fluorescence efficiency Cs2AgxNa1-xInncl6 dual-layer perovskite and belongs to the technical field of semiconductor nanomaterial preparation. Themethod comprises the steps that firstly, caesium chloride, sodium chloride, silver chloride and indium chloride are mixed and ground, the mixture is gradually hardened from fluffy white powder and isattached to a container wall, and then the powder is softened and continues to be ground until the mixture becomes fluffy white powder again; then, bismuth chloride is added for continuous grinding, and the obtained product is cleaned through ethyl alcohol and dried for 2 hours at the vacuum condition of 60-350 DEG C so as to obtain the high fluorescence efficiency Cs2AgxNa1-xInncl6 dual-layer perovskite. According to the method, Na+ alloying and Bi3+ trace doping of Cs2AgInC16 are achieved through mechanical grinding, and the fluorescence yield of the perovskite is greatly increased; meanwhile, the method has the advantages that the operation is simple, the method is simple, and industrial production is easily achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for manufacturing ZnO/CuInS<2> nanorod film with core-shell structure
InactiveCN103000381ASimple processEasy to implementMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolytic capacitorsWater bathsCopper nitrate
The invention belongs to the technical field of manufacture of films, and particularly discloses a method and relevant technological parameters for manufacturing a ZnO / CuInS<2> nanorod film with a core-shell structure. The method for manufacturing the ZnO / CuInS<2> nanorod film is a medium template conversion method, and includes growing a ZnO nanorod on ITO (indium tin oxide) conducting glass by a hydrothermal process by means of using zinc nitrate [Zn(NO<3>)<2>] / hexamethylene tetramine (HMT) aqueous solution as a growth system; then performing water bath by using thioacetamide (TAA) as a reagent to obtain a ZnO / ZnS nanorod film with a core-shell structure; allowing the obtained sample to stand in triethylene glycol (TEG) solution of copper nitrate [Cu(NO<3>)<2>] for a period of time to obtain a medium template of the ZnO / CuS nanorod film with the core-shell structure; and placing the obtained sample in TEG solution of indium chloride (InCl<3>), and enabling the obtained sample to be subjected to high-temperature hydrothermal reaction in a hydrothermal kettle so as to obtain the ZnO / CuInS<2> nanorod film with the core-shell structure on the surface of the ITO conducting glass. Influence of the technological parameters such as the concentration of the TAA, the concentration of the [Cu(NO<3>)<2>] and the hydrothermal reaction time to the structure and the performance of the film is discussed, and the optimal technological parameters for manufacturing the high-performance ZnO / CuInS<2> nanorod film with the core-shell structure are obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN CHENGJIAN UNIV
Preparation method of indium oxide air-sensitive material having loaded gold nanoparticles in hollow and hierarchical structure
InactiveCN105084308AHigh yieldHigh sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureSurface-active agentsMaterials science
The invention provides a preparation method of indium oxide air-sensitive material having loaded gold nanoparticles in a hollow and hierarchical structure.The preparation method concretely comprises following steps: obtaining hollow indium oxide in a hierarchical structure in that indium chloride and L-cysteine as raw material and trisodium citrate as a surface active agent undergo a hydrothermal reaction and are subjected to calcination treatment; and finally obtaining indium oxide air-sensitive material having loaded gold nanoparticles in the hollow and hierarchical structure by using chloroauric acid as raw material, sodium borohydride as a reductant, L-lysine as an additive and loading the surface with precious metal gold nanoparticles. The preparation method of indium oxide air-sensitive material having loaded gold nanoparticles in the hollow and hierarchical structure has a simple production process; and indium oxide air-sensitive material has the hollow and hierarchical structure and is loaded with precious metal gold nanoparticles so that novel air-sensitive material with high sensitivity is acquired.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Preparation method and application of non-noble metal copper indium sulphide/zinc indium sulphide compound photocatalyst
ActiveCN109248694AEasy transferInhibitory recombination ratePhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionSynthesis methodsLight driven
The invention belongs to the field of photocatalytic materials, and provides a non-noble metal copper indium sulphide / zinc indium sulphide compound photocatalyst with a wide visible-light response range, high photocatalytic activity and stability and a preparation method and application in visible-light response photocatalysis hydrogen production thereof. Firstly, a mixed aqueous solution of zincchloride, indium chloride and thioacetamide is subjected to high-temperature hydrothermal reaction to prepare zinc indium sulphide powder; then the zinc indium sulphide powder is dispersed in water through ultrasound, a mixture, indium chloride, cuprous chloride and thioacetamide are mixed, and through high-temperature hydrothermal reaction, the copper indium sulphide / zinc indium sulphide compoundphotocatalyst is prepared. The photocatalyst does not contain noble metal, the cost is lower, and the synthesis method is simple, so that the photocatalyst has wide application prospects in the fieldof visible-light drive photocatalysis.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
AgInSe2 nanocrystalline and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104445098AEffective use of coordinationRaw materials are simple and cheapMaterial nanotechnologySelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsSpace groupHigh pressure
The invention discloses AgInSe2 nanocrystalline and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing and uniformly stirring silver nitrate, indium chloride and / or indium chloride tetrahydrate, selenium dioxide, polyvinylpyrrolidone and dimethyl formamide to obtain a precursor liquid; allowing the precursor liquid to have a constant-temperature reaction in a high-pressure kettle at the temperature of 160-220 DEG C for 3-20 hours to obtain the AgInSe2 nanocrystalline, wherein the AgInSe2 nanocrystalline is a metastable orthorhombic crystal system of which the space group is Pna21 and is soluble in water. The preparation method disclosed by the invention adopts simple and cheap raw materials and is simple in process, short in synthesis period, good in repeatability and environment-friendly; and the prepared AgInSe2 nanocrystalline can be well dispersed in a water phase and has application advantages in the fields such as biomedicines and water-phase optical catalysis.
Owner:INST OF CHEM MATERIAL CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
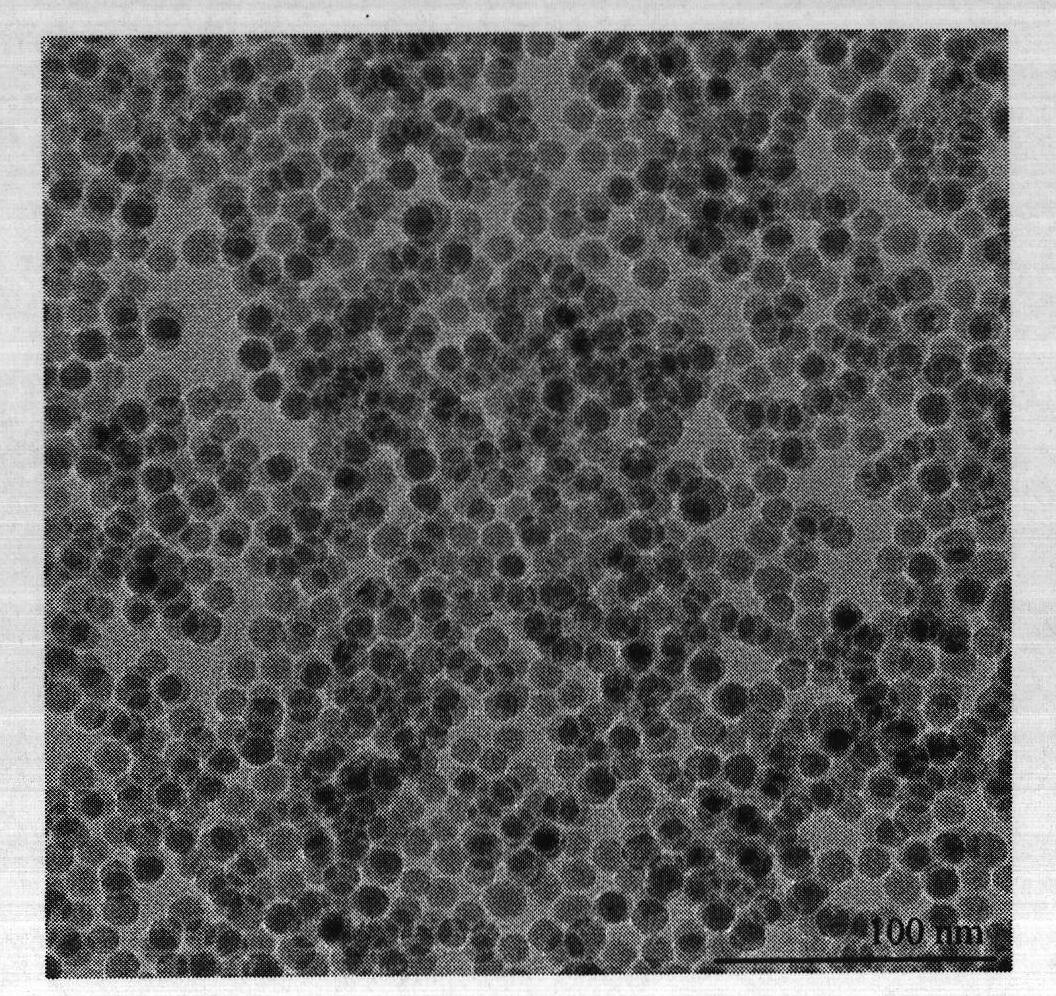
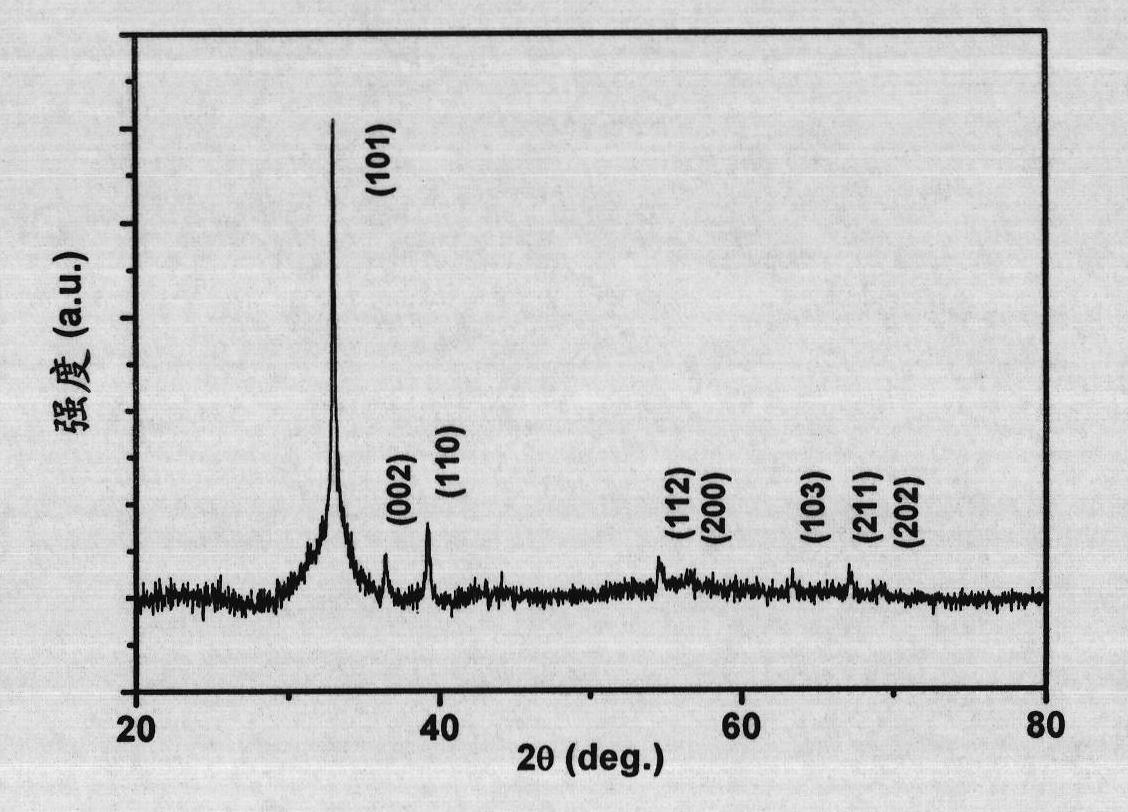
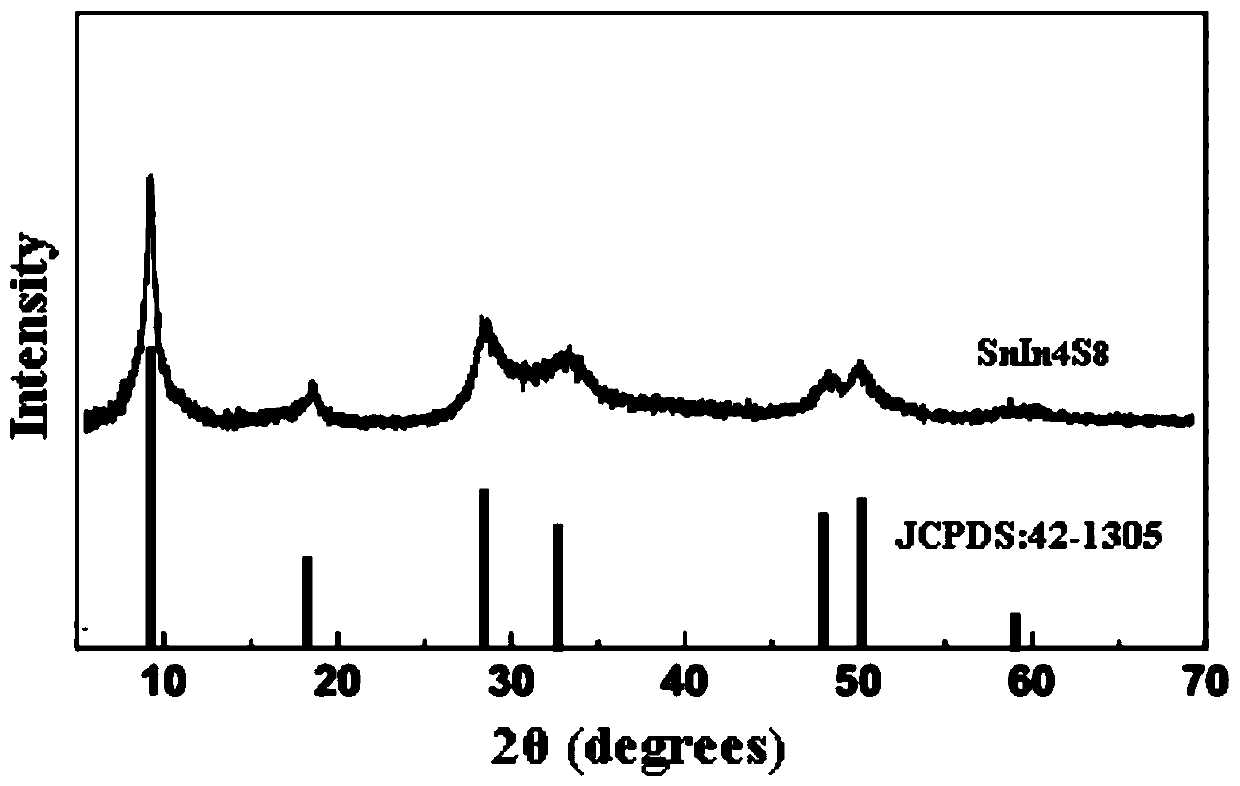
Method for preparing graphene-SnIn4S8 nano composite photocatalyst at low temperature by adopting coprecipitation method
InactiveCN104667950AReduce the temperatureShort preparation timeMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsReaction temperatureElectron
The invention relates to a method for preparing a graphene-SnIn4S8 nano composite photocatalyst at low temperature by adopting a coprecipitation method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: preparing graphene oxide by utilizing a modified Hummers method, and reducing the graphene oxide by utilizing 80% hydrazine hydrate to obtain reduced graphene oxide; dissolving raw materials such as tin chloride, indium chloride and thioacetamide in an organic alcohol solution, mixing the reduced graphene oxide which is prepared in advance, and preparing the graphene-SnIn4S8 nano composite photocatalyst bonded in chemical bonds by utilizing a low-temperature co-precipitation method. The method has characteristics that the reaction temperature is low, the reaction time is short, the prepared graphene-SnIn4S8 nano composite photocatalyst is relatively large in specific surface area and narrow in energy gap, photo-generated electrons can be effectively separated from electron holes, the stability is high, the regeneration performance is good, and the light absorption activity and the light catalytic activity are relatively strong under the visible light.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of copper and indium alloy ink and application thereof
InactiveCN101733409APromote sinteringNo obvious impurityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSolventSe element
The invention discloses a preparation method of a copper and indium alloy ink, comprising the following steps: (1) dissolving copper chloride and indium chloride in ethylene glycol at 80-200 DEG C, then slowing dropwise adding ethylene glycol solution of sodium borohydride for reaction; carrying out centrifuge, washing and drying to obtain copper and indium alloy nanoparticles; (2) preparing solution according to volume ratio: ethylene glycol: methanol: ethylene glycol methyl ether=2-8: 1:2-6; (2) dispersing the copper and indium alloy nanoparticles obtained in step (1) according to mass ratio: copper and indium alloy nanoparticles : solvent=1 : 2-8 and evenly dispersing the mixture by ultrasonic waves to obtain the copper indium alloy ink. The invention also discloses an application method of the copper and indium alloy ink in preparing sulphur indium copper film or selenium indium copper film. In the invention, a low-cost chemical method is adopted to synthesize copper and indium alloy nanoparticles, the prepared film features compact and smooth surface and large film crystallite dimension after sintering and no obvious film miscellaneous phase.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method of synthesizing ITO electron-beam resist and method of forming ITO pattern using the same
ActiveUS20100035179A1Eliminate the problemHigh light transmittanceTin compoundsPhotosensitive materialsAtomic physicsElectron beam resist
Provided is a method of synthesizing an ITO electron beam resist and a method of forming an ITO pattern. The ITO electron beam resist is synthesized by dissolving indium chloride tetrahydrate and tin chloride dihydrate in 2-ethoxy ethanol. The method of forming an ITO pattern includes: forming an ITO electron beam resist film on a substrate, forming an ITO electron beam resist pattern by patterning the ITO electron beam resist film, and forming an ITO pattern by annealing the ITO electron beam resist pattern.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method for preparing low-melting-point alloy-coated ceramic-phase reinforced body/aluminum-matrix composite materials
InactiveCN101698913ASimple processShorten the production cycleLead nitrateAluminum matrix composites
The invention provides a method for preparing low-melting-point alloy-coated ceramic-phase reinforced bodies / aluminum-matrix composite materials, which relates to a method for coating ceramic-phase reinforced bodies. The invention solves the problem that a sol-gel method is complex in the process of coating the surfaces of reinforced bodies with coatings. The method comprises the following steps: adding two or more than two of bismuth nitrate aqueous solution, lead nitrate aqueous solution, indium chloride aqueous solution and stannic chloride aqueous solution to dilute nitric acid solution and adding the obtained liquid mixture and ammonia solution dropwise to reinforced-body solution till the pH is between 6 and 14; preparing reinforced bodies into prefabticated pieces and preserving heat at a temperature between 350 and 1,100 DEG C; obtaining the ceramic-phase reinforced bodies coated with metal oxide; and preparing the composite materials by utilizing a squeeze casting method. The method is simple in process and shortens the production cycle of the composite materials. The damping value of the aluminum-matrix composite materials obtained by applying the method is 0.016 to 0.018 at 25 DEG C on a frequency of 70 Hz.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Core shell nanometer crystal of gold and copper-indium-diselenide and preparation method of core shell nanometer crystal
InactiveCN102500758AImprove photoelectric conversion performanceNovel methodCoatingsTriphenylphosphine gold chlorideNitrogen gas
The invention provides a core shell nanometer crystal of gold and copper-indium-diselenide and a preparation method of the core shell nanometer crystal, and relates to a core shell nanometer material. The core shell nanometer crystal of the gold and copper-indium-diselenide is in a core shell structure, wherein a core is a gold nano particle and a shell layer is a copper-indium-diselenide CuISe2 shell layer. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: mixing triphenylphosphine gold chloride with oleyl amine; heating and vacuumizing; introducing nitrogen gas and raising the temperature to react to obtain an oleyl amine solution of colloid nano gold; adding selenium powder into the oleyl amine; heating and vacuumizing; introducing the nitrogen gas and raising the temperature toreact to obtain the oleyl amine solution of the selenium; adding cuprous chloride and indium chloride into an oleyl amine solvent; heating and vacuumizing; introducing the nitrogen gas and raising the temperature to react to obtain an oleyl amine compound of a copper salt and an indium salt; injecting the oleyl amine solution of the colloid nano gold into the oleyl amine solution of the selenium;keeping heating and agitating to obtain a turbid solution; injecting the turbid solution into the oleyl amine compound of the copper salt and the indium salt; keeping heating to react and centrifuging; and washing sediment with trichloromethane and ethanol at least once to obtain the core shell nanometer crystal of the gold and copper-indium-diselenide.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Indium sulfide/graphene composite film, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109830549AUniform phasePromote crystallizationPhysical/chemical process catalystsCell electrodesComposite filmThiourea
The invention belongs to the technical field of composite semiconductor thin films and discloses an indium sulfide (In2S3) / graphene composite film, and a preparation method and application thereof. The In2S3 / graphene composite film is prepared by adding indium chloride, thiourea and polyvinylpyrrolidone to ethylene glycol to form a reaction precursor liquid, and subjecting a FTO conductive glass substrate spin-coated with graphene paste to a microwave hydrothermal reaction in a microwave oven at the power of 700 to 900W and at the temperature of 180 to 220 degrees centigrade. The In2S3 / graphene composite film has a uniform phase, good crystallization and high purity. The method uses a microwave assisted solution for synthesizing the nanometer In2S and graphene composite film, just requiressimple equipment and preparation processes, is low in cost and fast in speed, shortens the reaction time, and uses non-toxic and safe preparation reagents.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method and application of metallic indium nanometer particle ink
The invention discloses a preparation method for preparing metallic indium nanometer particle ink, which comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving indium chloride in polyalcohol, and adding stabilizing agents; (2) dissolving sodium-containing reducing agents in a polyalcohol solution to be prepared to a reducing agent solution; (3) fast injecting the reducing agent solution obtained in the second step into the solution prepared in the first step for reaction when the reducing agent solution is still hot, and obtaining metallic indium nanometer particles through centrifugation, washing and drying; and (4) dissolving the metallic indium nanometer particles in a special solvent for preparing the nanometer particle ink. The invention also discloses an application method of the metallic indium nanometer particle ink to the preparation of copper-indium sulfide films. The invention has the advantages of simple reaction, easy implementation of the reaction reaction, low cost, high yield and the like, and prepared films have compact and smooth surfaces, crystal grains have large dimension, and the films do not have obvious impure phases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of indium tin sulfide visible-light-induced photocatalyst and visible-light-induced catalytic performance application of indium tin sulfide visible-light-induced photocatalyst
PendingCN111250109ASimple processImprove stabilityTin compoundsPhysical/chemical process catalystsIndium TrichlorideThiourea
The invention relates to the technical field of material preparation and photocatalysis. The technical scheme comprises that a preparation method of an indium tin sulfide visible-light-induced photocatalyst comprises the following steps: (1) weighing stannic chloride pentahydrate and indium trichloride, dissolving stannic chloride pentahydrate and indium trichloride in a proper amount of deionizedwater, then weighing any one reactant of three sulfur sources, namely thioacetamide, thiourea or L-cysteine, adding the reactant into the uniformly stirred aqueous solution, adjusting the pH value to1-13, and continuously stirring for 2 h, wherein the molar ratio of tin tetrachloride pentahydrate to indium trichloride to the reactant is 1.5:4:8; (2) transferring the uniformly stirred solution into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, and carrying out a reaction for 10-12 h in an oven at the temperature of 140-180 DEG C; and naturally cooling to room temperature to obtain precipitates, respectively washing the precipitates with deionized water and absolute ethyl alcohol for multiple times, and carrying out vacuum drying at the temperature of 60 DEG C for 10 h to obtain an orange powder sample.The preparation method is simple in steps and low in cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHUREN UNIV
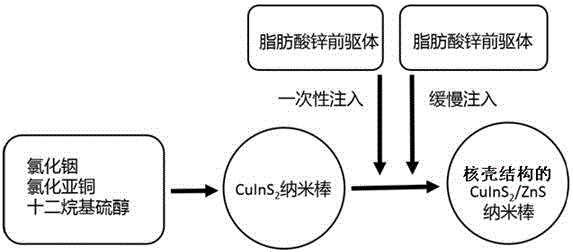
Core-shell structured CuInS2/ZnS nanorod and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106544003AAbsorbentLarge polarized emissionNanoopticsLuminescent compositionsLight energyDissolution
The invention discloses a core-shell structured CuInS2 / ZnS nanorod and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of mixing indium chloride, cuprous chloride and lauryl mercaptan to obtain a CuInS2 nanorod; mixing and heating zinc fatty acid, lauryl mercaptan and 1-octadecene to obtain zinc fatty acid precursor; rapidly filling the obtained zinc fatty acid precursor into CuInS2 nanorod solution then slowly filling in the rest of the zinc fatty acid precursor for reaction; performing repeated dissolution and precipitation on reaction products and then performing centrifugal purification to obtain the core-shell structured CuInS2 / ZnS nanorod. The core-shell structured CuInS2 / ZnS nanorod obtains a large light energy absorbing section for linear polarized absorption and polarized emission and meanwhile can inhibit Auger non-radiative recombination and achieves relatively high illumination efficiency. Meanwhile, the high-quality core-shell structured CuInS2 / ZnS nanorod can be applied to lighting and display.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Method for preparing indium oxide nanoparticle of porous structure
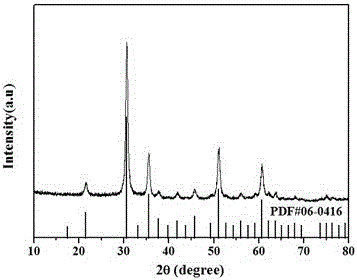
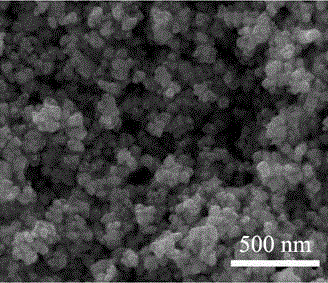
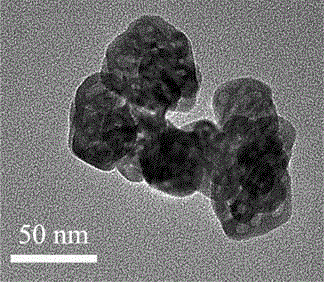
InactiveCN106167274ANo pollution in the processHigh sensitivityGallium/indium/thallium compoundsNanotechnologyNanoparticleIndium(III) chloride
The invention provides a method for preparing indium oxide nanoparticles of porous structures. The method specifically comprises the following steps: by taking indium chloride and dodecylamine as raw materials, performing a hydrothermal reaction, and performing calcination treatment, thereby obtaining the indium oxide nanoparticles of the porous structures. The method is simple in production process, free of expensive surfactant and relatively low in cost, and the prepared indium oxide can be used as a gas sensitive material, has good gas sensitivity on formaldehyde gases due to the porous structures, and thus has long-term application prospects in formaldehyde gas detection.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com