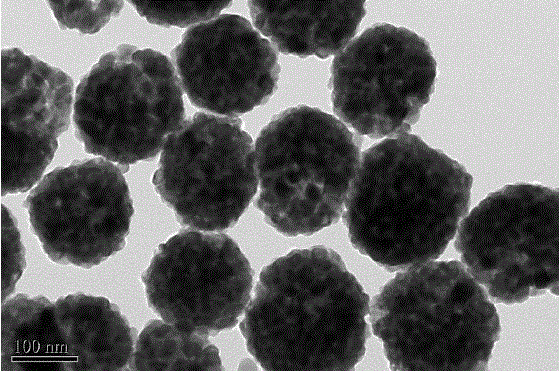
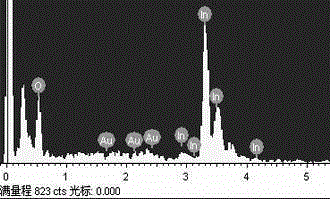
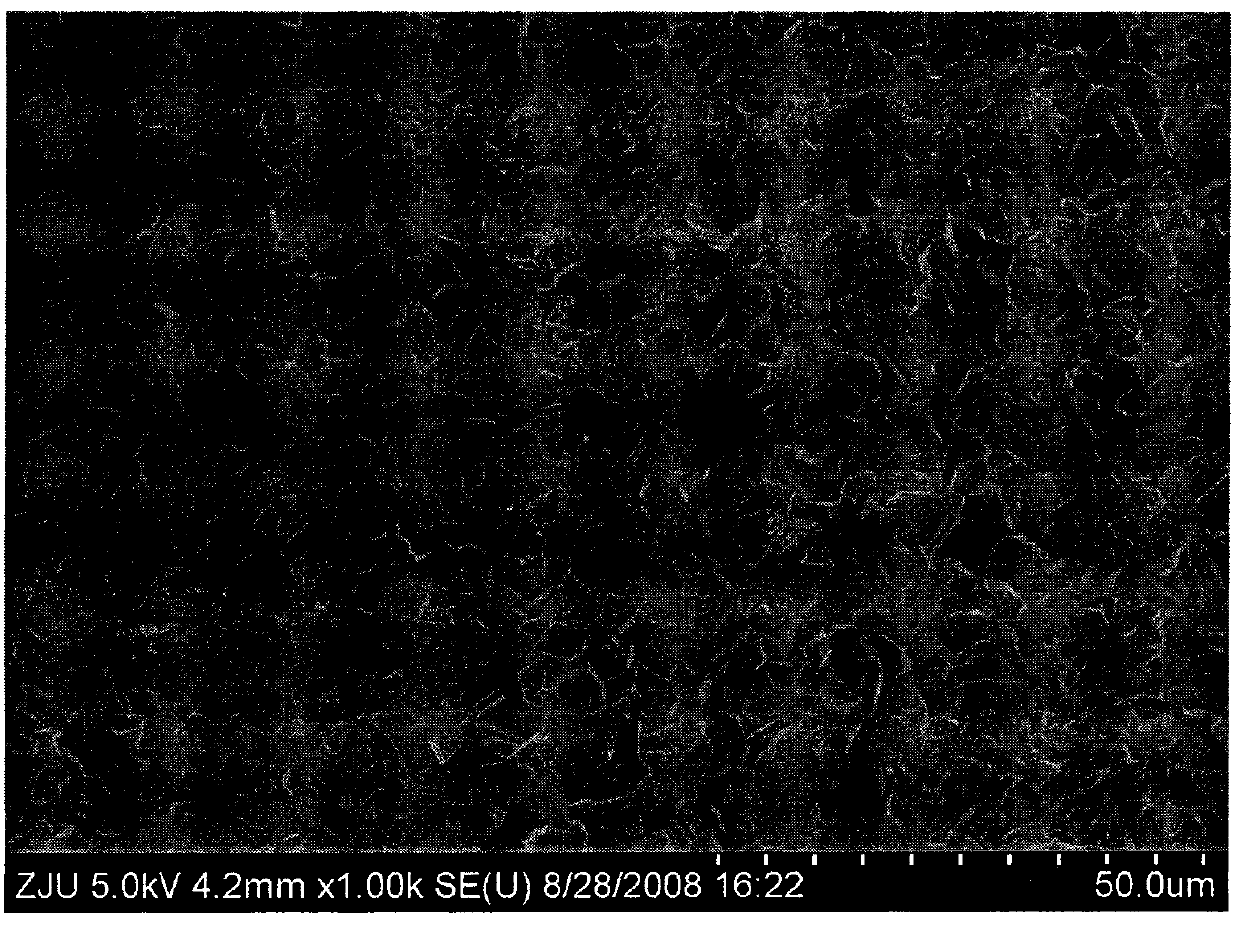
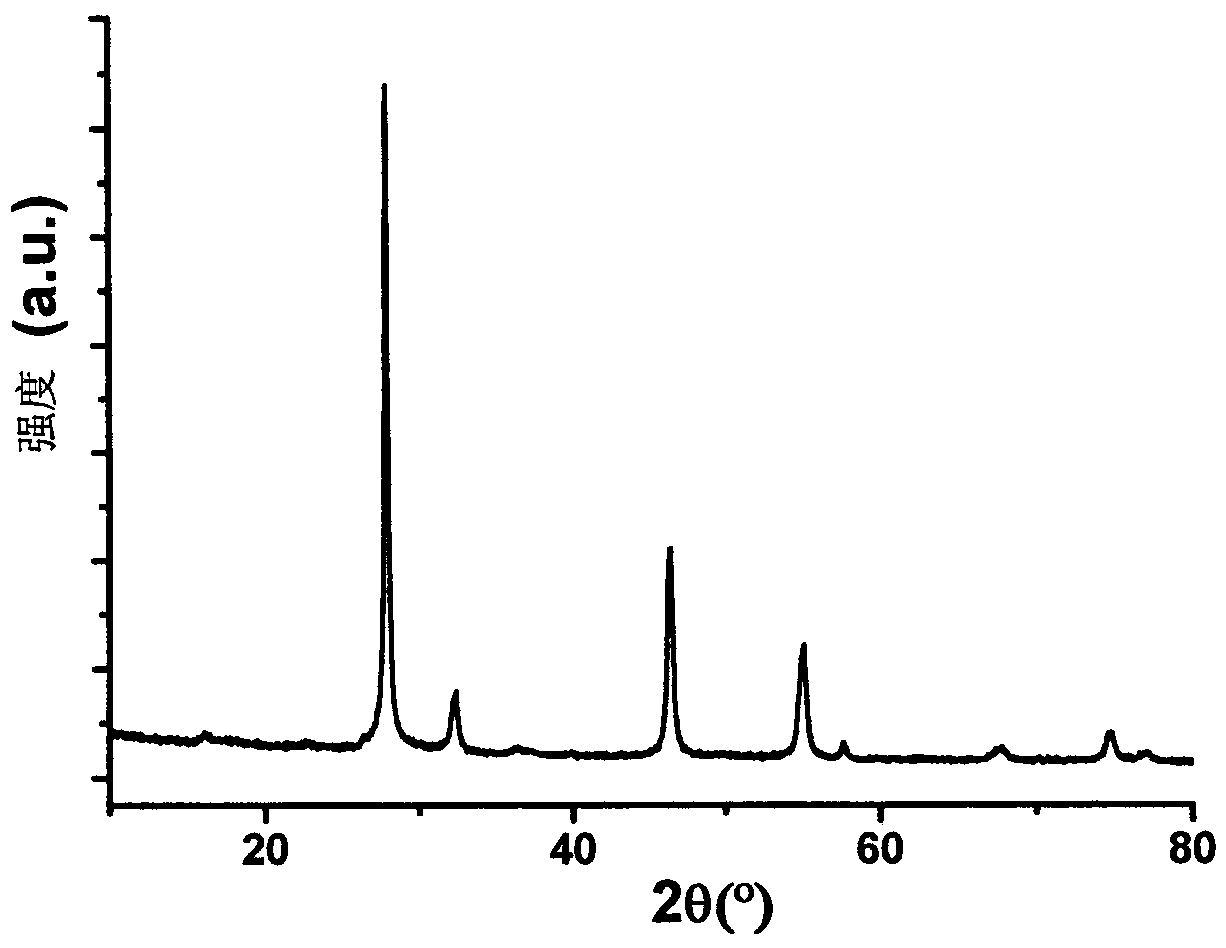
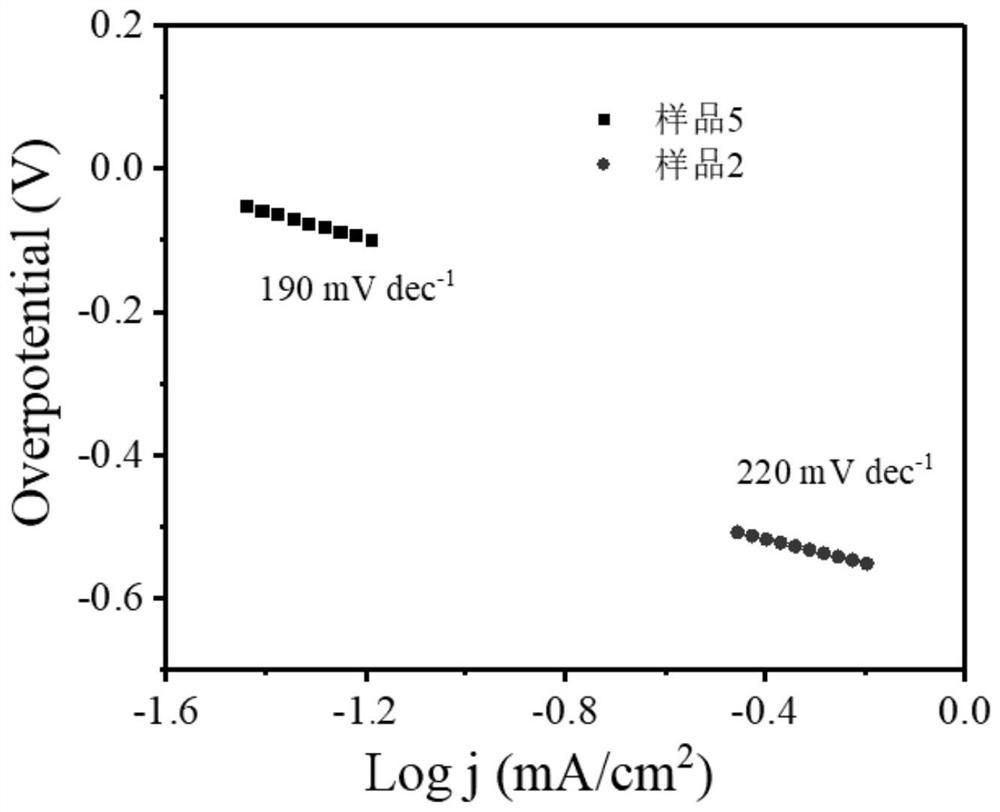
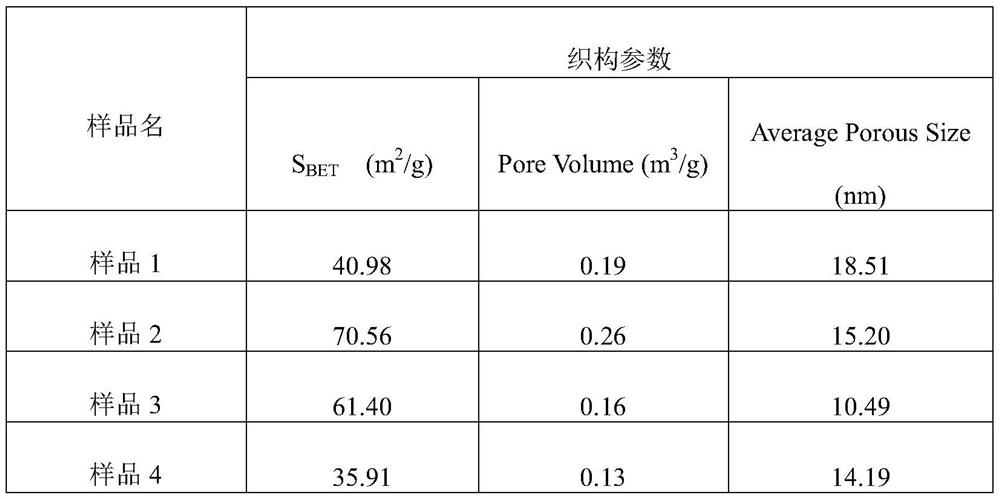
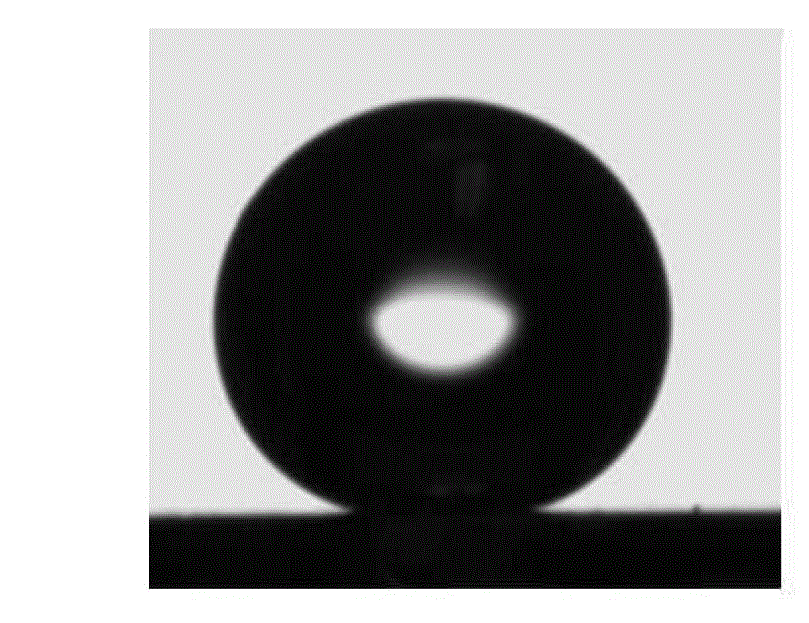
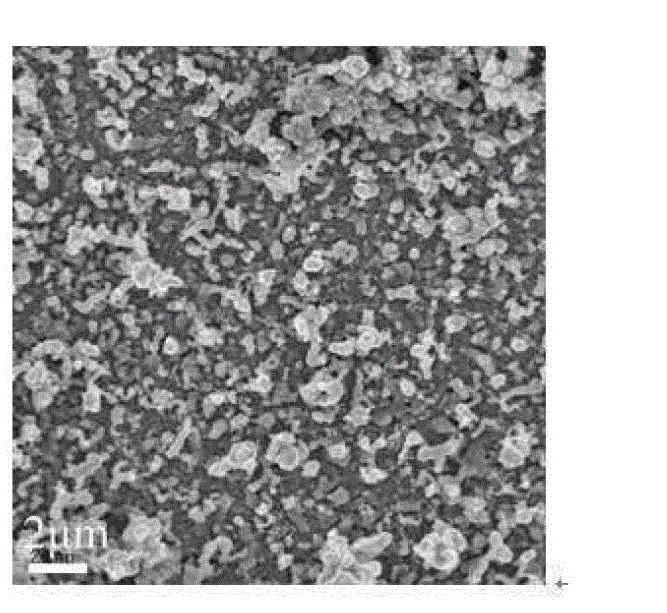
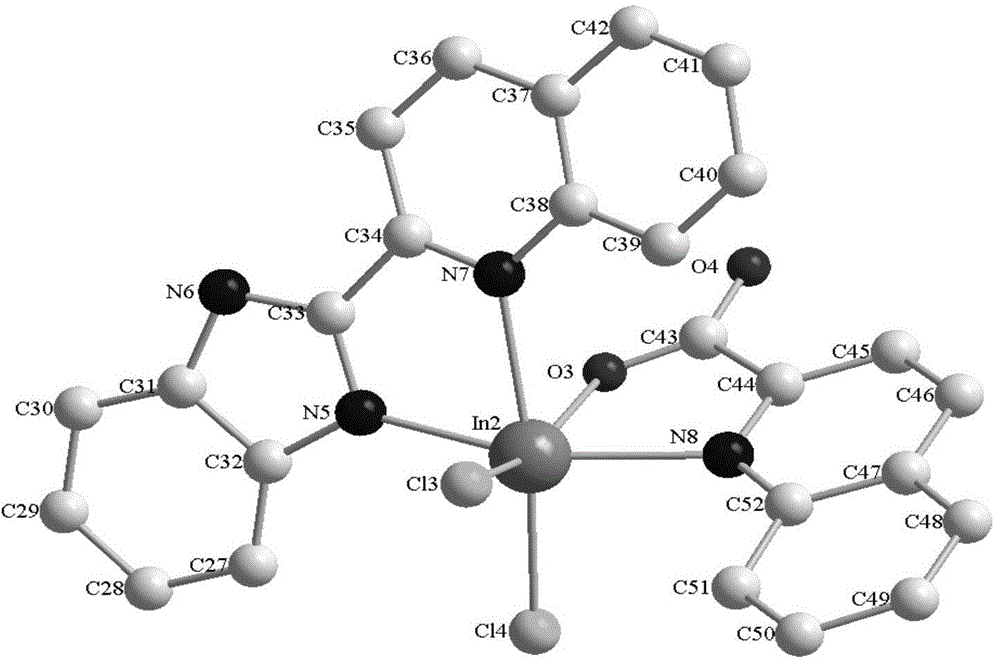
Patents
Literature
58 results about "Indium(III) chloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Indium(III) chloride is the chemical compound with the formula InCl₃. This salt is a white, flaky solid with applications in organic synthesis as a Lewis acid. It is also the most available soluble derivative of indium.
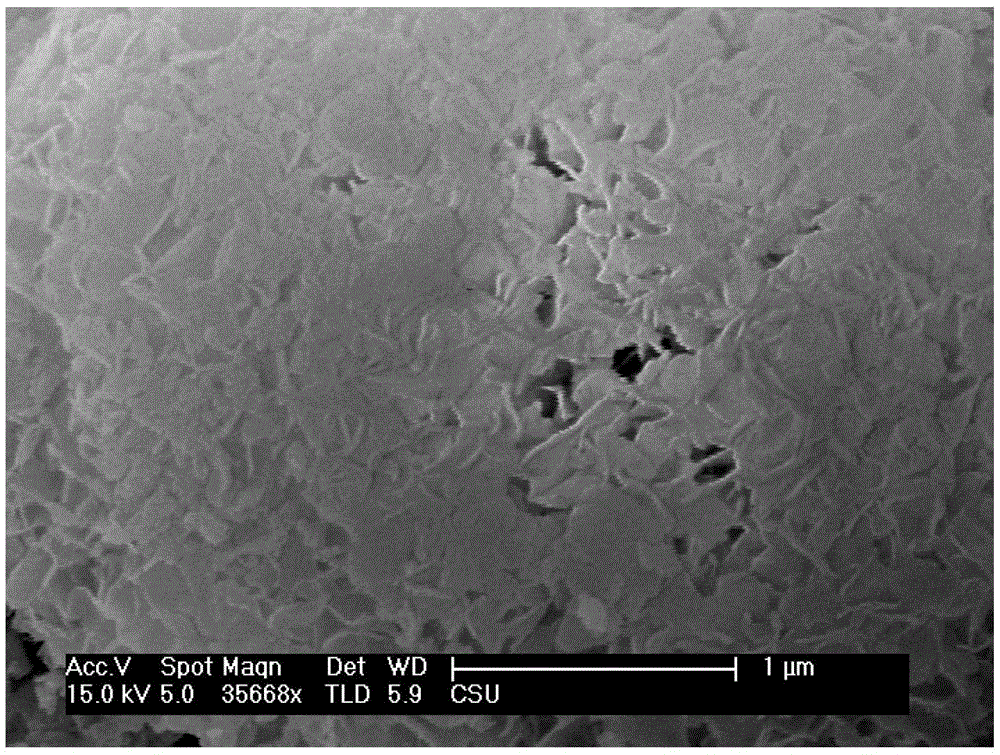
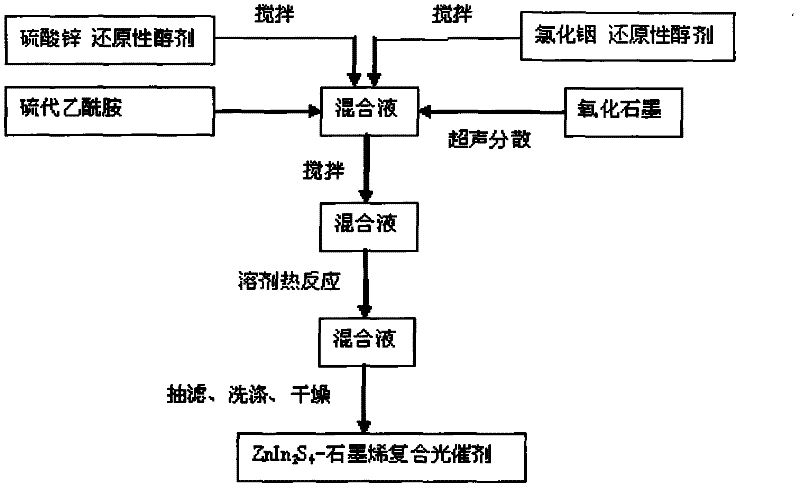
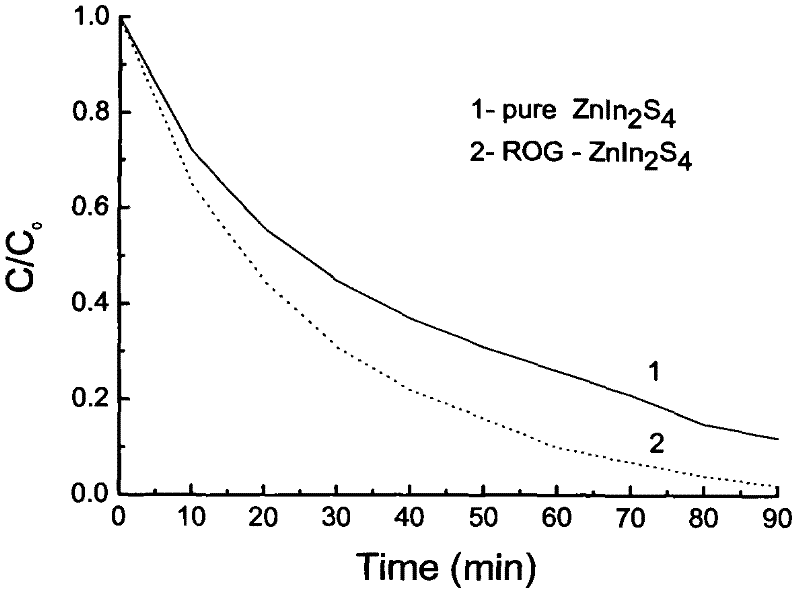
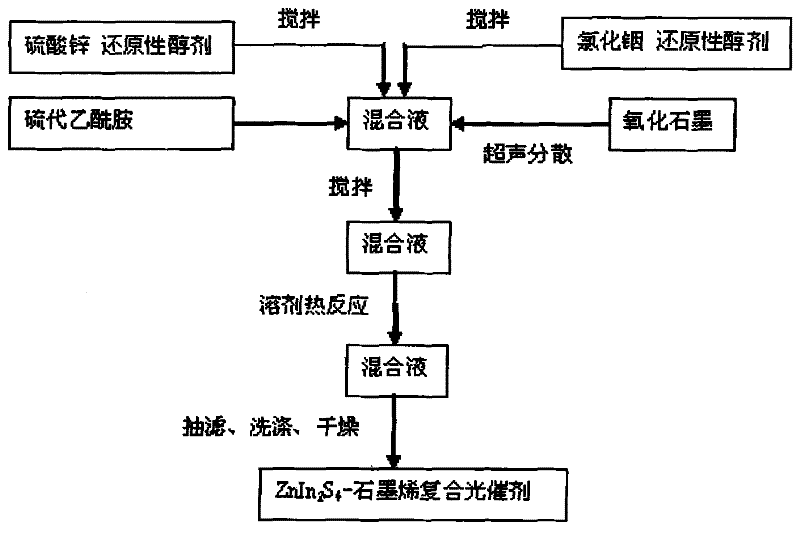
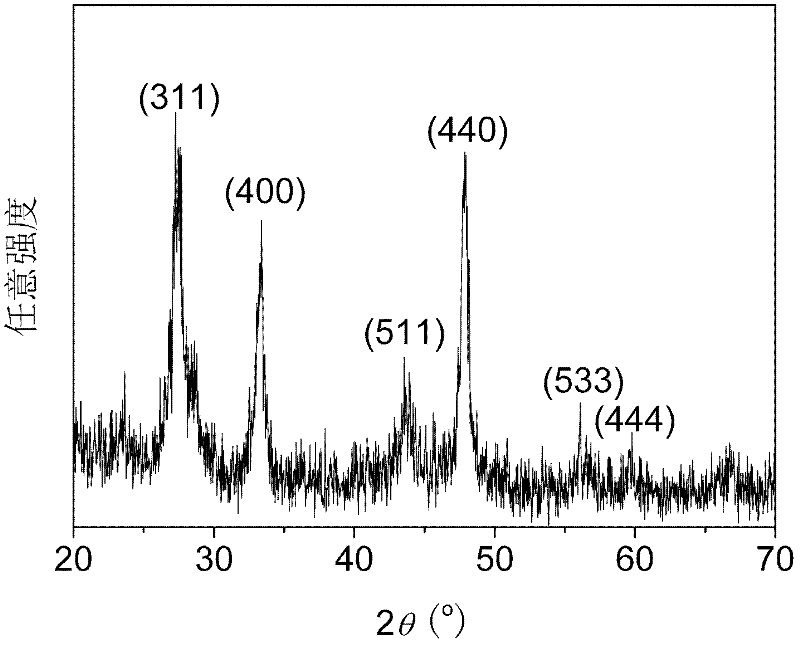
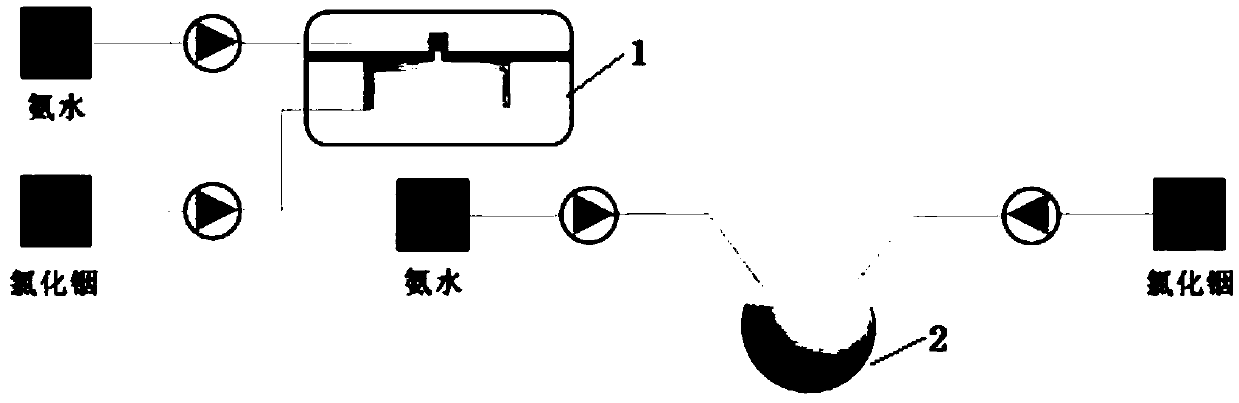
Preparation method and application of ZnIn2S4-graphene composited photochemical catalyst
InactiveCN102407147AReduce the chance of reunionLarge specific surface areaPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationFiltrationAlcohol agent
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a ZnIn2S4-graphene composited photochemical catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: placing graphite oxide into a reducibility alcohol agent for ultrasonic dispersion; adding zinc sulfate and indium chloride into the reducibility alcohol agent, stirring and dissolving; adding thioacetamide into two systems after the two systems are mixed; transferring the mixed systems into a hydrothermal kettle for a reaction; and after the reaction is finished, carrying out vacuum filtration on the obtained product, washing, vacuumizing and grinding to obtain a nano ZnIn2S4-graphene composited photochemical catalyst. In the invention, grapheme is taken as a supporting material, and a solvothermal synthesis method is adopted to further prepare the nano ZnIn2S4-graphene composited photochemical catalyst. The catalyst prepared by using the method in the invention has the advantages of wide visible light responding range and high photocatalysis activity, can be used for transformation and use of solar energy and comprehensive ecological improvement, such as air purification, sewage disposal, hydrogen production through photodegradation, preparation of alcohol or hydrocarbon chemical fuels and the like by the photocatalysis and reduction of CO2.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Synthesis method of novel visible-light photocatalyst indium sulfide
InactiveCN102335616APromote degradationSimple processPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic dyeSynthesis methods
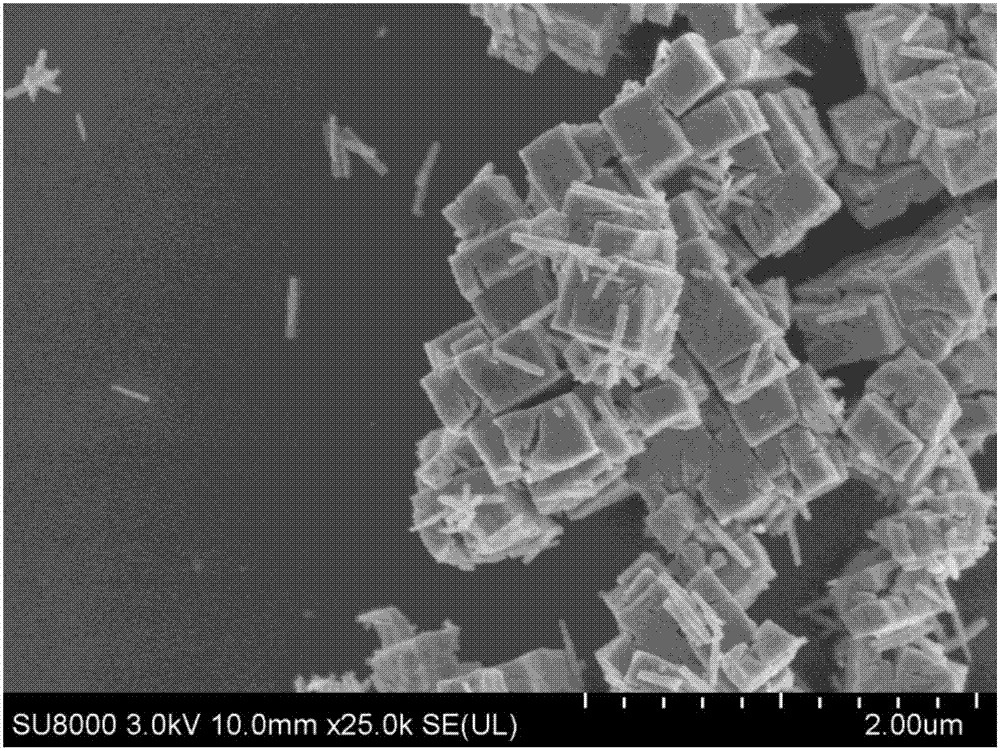
The invention relates to a synthesis method of a novel visible-light photocatalyst indium sulfide, belonging to the technical field of preparation of photocatalysts. The method comprises the following steps: weighing indium chloride tetrahydrate, dissolving the indium chloride tetrahydrate in deionized water, adding acetic acid to regulate the pH value to 1-3, and adding thioacetamide solution, wherein the concentration of indium ions is 0.025 mol / L, and the In / S mol ratio is 1:4-1:10; heating the obtained mixed solution to constant temperature so as to carry out hydrothermal reaction for 4-8 hours while regulating the temperature to 80 DEG C, and cooling at room temperature; and carrying out vacuum filtration under reduced pressure, washing, and drying to obtain the orange indium sulfide powder. The indium sulfide prepared by the method provided by the invention is in a ball-flower shape, and has the advantages of large specific area and uniform size; and the indium sulfide powder is in a cubic structure. The indium sulfide can be used as a visible-light photocatalyst, and has good degradation effect on organic dyes (such as methyl orange).
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for synthesizing copper-indium-selenium nanocrystalline
InactiveCN101698472ANo pollution in the processImprove reaction efficiencySelenium/tellurium compundsNitrogen gasSolvent
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing copper-indium-selenium nanocrystalline and relates to a solar cell material. The invention provides a method for synthesizing copper-indium-selenium nanocrystalline with simple technological steps. The method comprises the following steps: mixing dodecyl mercaptan and oleyl amine to obtain a mixed solvent; adding an elementary substance selenium, and dispersing to obtain an evenly dispersed elementary substance solution; adding cuprous chloride and indium chloride into an oleic acid-octadecylene mixed solvent, heating while stirring, vacuumizing, so that the vacuum degree of the system is lower than -0.1 MPa, and introducing nitrogen to obtain an oleic acid-octadecylene composition of cupric salts and indium salts in the nitrogen atmosphere, wherein the oleic acid-octadecylene composition of cupric salts and indium salts is a light-brown transparent solution; and injecting the prepared selenium solution into the oleic acid-octadecylene composition of cupric salts and indium salts, heating to carry out the reaction, centrifugating to obtain a precipitate, and respectively washing the precipitate with methenyl chloride and ethanol at least once to obtain the copper-indium-selenium nanocrystalline.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for preparing monodisperse indium oxide nanometer porous microsphere
InactiveCN103183374ALow costImprove protectionGallium/indium/thallium compoundsNanotechnologyManufacturing technologyDisplay device
The invention provides a method for preparing a monodisperse indium oxide nanometer porous microsphere, and belongs to the technical field of function materials. The preparation method particularly comprises the following steps: adding citric acid with a certain molar ratio in indium chloride aqueous solution, mixing intensively, adding moderate urea as a precipitant, and dispersing uniformly; sealing the mixed solution in an autoclave and conducting water thermal reaction for a period of time, and then centrifugalizating, washing and drying; calcining in a muffle furnace in air to obtain the monodisperse indium oxide nanometer porous microsphere. The method provided by the invention has low cost, simple manufacturing technology, high productivity, and is easy to realize industrialization and mass production. The indium oxide nanometer microsphere produced by the method has a neat appearance, uniform disperse, has a porous structure and a larger specific surface area, and can be applied in the field of solar cells, FPDs (Flat Panel Display), photo-electron devices, gas sensors and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Preparation method of indium oxide air-sensitive material having loaded gold nanoparticles in hollow and hierarchical structure
InactiveCN105084308AHigh yieldHigh sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureSurface-active agentsMaterials science
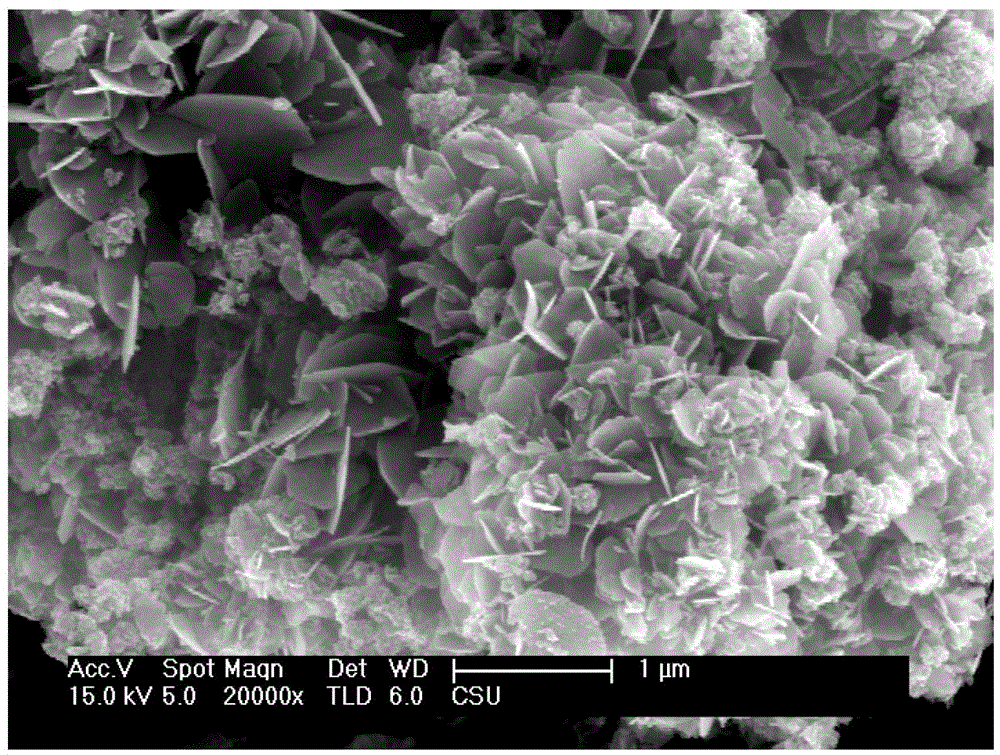
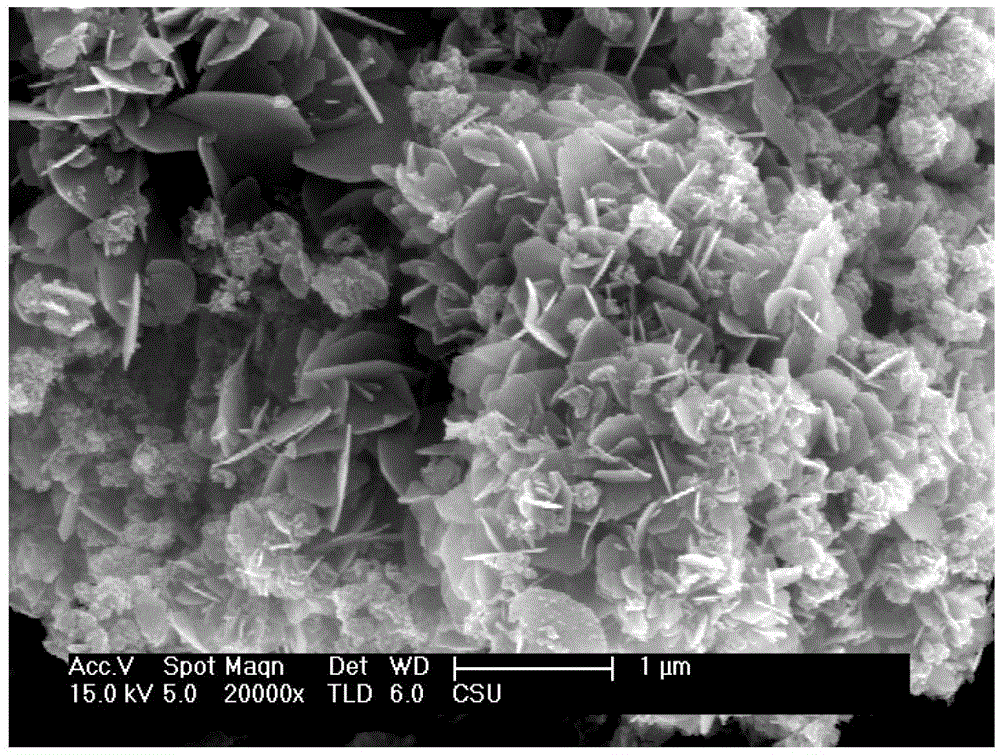
The invention provides a preparation method of indium oxide air-sensitive material having loaded gold nanoparticles in a hollow and hierarchical structure.The preparation method concretely comprises following steps: obtaining hollow indium oxide in a hierarchical structure in that indium chloride and L-cysteine as raw material and trisodium citrate as a surface active agent undergo a hydrothermal reaction and are subjected to calcination treatment; and finally obtaining indium oxide air-sensitive material having loaded gold nanoparticles in the hollow and hierarchical structure by using chloroauric acid as raw material, sodium borohydride as a reductant, L-lysine as an additive and loading the surface with precious metal gold nanoparticles. The preparation method of indium oxide air-sensitive material having loaded gold nanoparticles in the hollow and hierarchical structure has a simple production process; and indium oxide air-sensitive material has the hollow and hierarchical structure and is loaded with precious metal gold nanoparticles so that novel air-sensitive material with high sensitivity is acquired.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Preparation method of copper and indium alloy ink and application thereof
InactiveCN101733409APromote sinteringNo obvious impurityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSolventSe element
The invention discloses a preparation method of a copper and indium alloy ink, comprising the following steps: (1) dissolving copper chloride and indium chloride in ethylene glycol at 80-200 DEG C, then slowing dropwise adding ethylene glycol solution of sodium borohydride for reaction; carrying out centrifuge, washing and drying to obtain copper and indium alloy nanoparticles; (2) preparing solution according to volume ratio: ethylene glycol: methanol: ethylene glycol methyl ether=2-8: 1:2-6; (2) dispersing the copper and indium alloy nanoparticles obtained in step (1) according to mass ratio: copper and indium alloy nanoparticles : solvent=1 : 2-8 and evenly dispersing the mixture by ultrasonic waves to obtain the copper indium alloy ink. The invention also discloses an application method of the copper and indium alloy ink in preparing sulphur indium copper film or selenium indium copper film. In the invention, a low-cost chemical method is adopted to synthesize copper and indium alloy nanoparticles, the prepared film features compact and smooth surface and large film crystallite dimension after sintering and no obvious film miscellaneous phase.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Core shell nanometer crystal of gold and copper-indium-diselenide and preparation method of core shell nanometer crystal
InactiveCN102500758AImprove photoelectric conversion performanceNovel methodCoatingsTriphenylphosphine gold chlorideNitrogen gas
The invention provides a core shell nanometer crystal of gold and copper-indium-diselenide and a preparation method of the core shell nanometer crystal, and relates to a core shell nanometer material. The core shell nanometer crystal of the gold and copper-indium-diselenide is in a core shell structure, wherein a core is a gold nano particle and a shell layer is a copper-indium-diselenide CuISe2 shell layer. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: mixing triphenylphosphine gold chloride with oleyl amine; heating and vacuumizing; introducing nitrogen gas and raising the temperature to react to obtain an oleyl amine solution of colloid nano gold; adding selenium powder into the oleyl amine; heating and vacuumizing; introducing the nitrogen gas and raising the temperature toreact to obtain the oleyl amine solution of the selenium; adding cuprous chloride and indium chloride into an oleyl amine solvent; heating and vacuumizing; introducing the nitrogen gas and raising the temperature to react to obtain an oleyl amine compound of a copper salt and an indium salt; injecting the oleyl amine solution of the colloid nano gold into the oleyl amine solution of the selenium;keeping heating and agitating to obtain a turbid solution; injecting the turbid solution into the oleyl amine compound of the copper salt and the indium salt; keeping heating to react and centrifuging; and washing sediment with trichloromethane and ethanol at least once to obtain the core shell nanometer crystal of the gold and copper-indium-diselenide.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Preparation method and application of metallic indium nanometer particle ink
The invention discloses a preparation method for preparing metallic indium nanometer particle ink, which comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving indium chloride in polyalcohol, and adding stabilizing agents; (2) dissolving sodium-containing reducing agents in a polyalcohol solution to be prepared to a reducing agent solution; (3) fast injecting the reducing agent solution obtained in the second step into the solution prepared in the first step for reaction when the reducing agent solution is still hot, and obtaining metallic indium nanometer particles through centrifugation, washing and drying; and (4) dissolving the metallic indium nanometer particles in a special solvent for preparing the nanometer particle ink. The invention also discloses an application method of the metallic indium nanometer particle ink to the preparation of copper-indium sulfide films. The invention has the advantages of simple reaction, easy implementation of the reaction reaction, low cost, high yield and the like, and prepared films have compact and smooth surfaces, crystal grains have large dimension, and the films do not have obvious impure phases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing indium oxide nanoparticle of porous structure
InactiveCN106167274ANo pollution in the processHigh sensitivityGallium/indium/thallium compoundsNanotechnologyNanoparticleIndium(III) chloride
The invention provides a method for preparing indium oxide nanoparticles of porous structures. The method specifically comprises the following steps: by taking indium chloride and dodecylamine as raw materials, performing a hydrothermal reaction, and performing calcination treatment, thereby obtaining the indium oxide nanoparticles of the porous structures. The method is simple in production process, free of expensive surfactant and relatively low in cost, and the prepared indium oxide can be used as a gas sensitive material, has good gas sensitivity on formaldehyde gases due to the porous structures, and thus has long-term application prospects in formaldehyde gas detection.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Appearance-controllable indium oxide powder and low-temperature hydrothermal synthesis method thereof
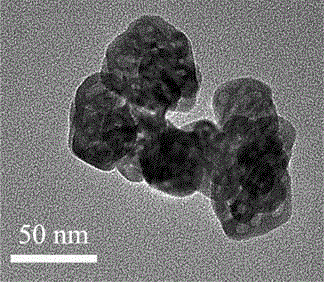
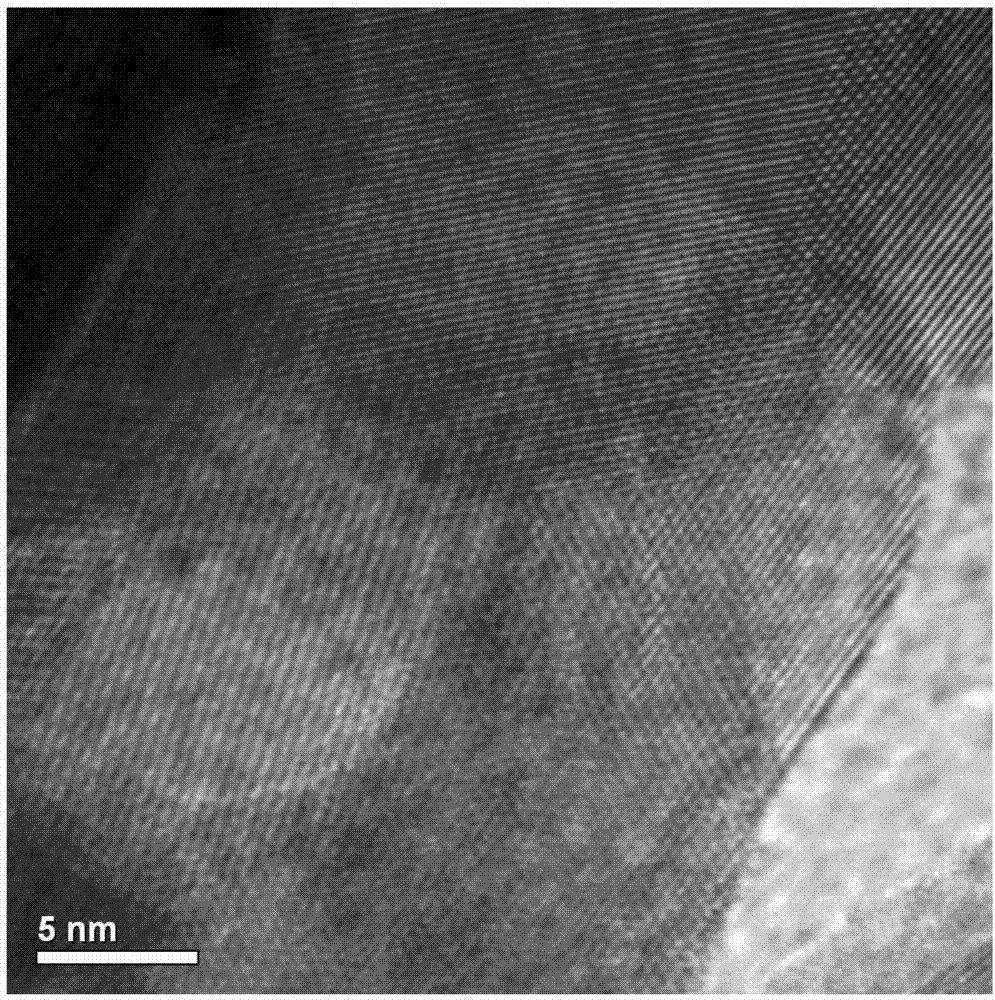
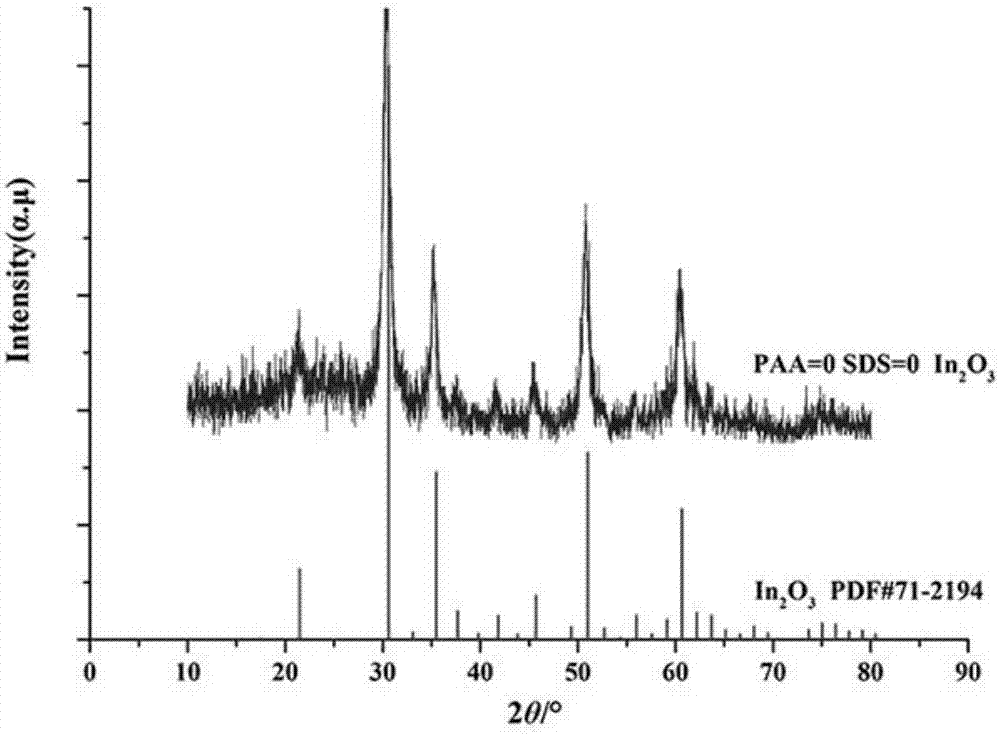
The invention relates to an appearance-controllable indium oxide powder and a low-temperature hydrothermal synthesis method thereof and belongs to the technical field of inorganic chemical synthesis. The low-temperature hydrothermal synthesis method comprises the following steps: taking indium nitrate or indium chloride as an indium source, urea as an alkaline source, nitric acid or hydrochloric acid as a hydrolysis inhibitor and polyacrylic acid (PAA) and sodium dodecyl sulfonate (SDS) as a double template agent, and reacting for 8-12 hours under a hydrothermal condition at 80-95 DEG C; performing suction filtration and washing a product, and roasting to obtain In2O3 power. Cubic, flower-shaped, spherical and hollow spherical products formed by primary particles as In2O3 single crystals can be obtained by regulation and control of PAA and SDS consumption; the obtained In2O3 power belongs to a cubic crystal system. The obtained products are made into a side heat type gas sensor element for gas sensitive performance detection; when the working temperature of a device made of the cubic In2O3 power is 100 DEG C, the gas-sensitive property of 100-ppm nitromethane is good, a sensitivity value is higher than 500, the response time is about 1-2 s, and the quick detection on flammable and explosive nitromethane gas at a relatively low temperature can be realized.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Preparation method of nanometer composite N-doped graphene-ZnIn2S4 material
InactiveCN104785284AThe process is simple and convenientGood for mass manufacturingMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsDoped grapheneSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nanometer composite N-doped graphene-ZnIn2S4 material responded by visible light. The preparation method comprises the following steps: placing graphite oxide and urea in a reducing alcohol agent for ultrasonic dispersion, then transferring the graphite oxide and the urea after the ultrasonic dispersion to a hydrothermal reaction kettle for reaction, performing vacuum filtration, washing and vacuum drying on a product so as to obtain N-doped graphene, adding the N-doped graphene to the reducing alcohol agent for the ultrasonic dispersion, adding zinc sulfate and indium chloride to the reducing alcohol agent to be stirred and dissolved, then mixing two kinds of systems, adding thioacetamide, then transferring the mixture of the systems and the thioacetamide to the hydrothermal reaction kettle for reaction, and performing vacuum filtration, washing and vacuum drying on the product so as to obtain nanometer composite N-doped grapene-ZnIn2S4 material. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the N-doped graphene is used as a carrier material, and the nanometer composite N-doped graphene-ZnIn2S4 material is prepared by using a solvent thermal synthesis method in two steps.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method and device for extracting metal indium in LCD by virtue of chloridizing volatilization with PVC as a chloridizing agent
ActiveCN104911360ASimple structureSimple processing methodProcess efficiency improvementIndium(III) chlorideQuartz
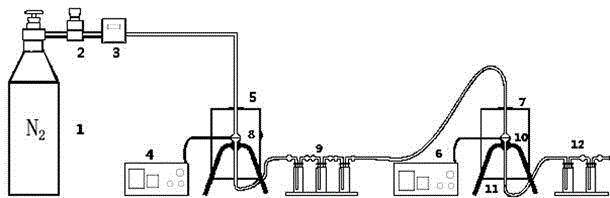
The invention discloses a method and a device for extracting metal indium in LCD by virtue of chloridizing volatilization with PVC as a chloridizing agent. The method comprises the steps of (1) putting PVC powder into the first quartz reactor of a first electric furnace and putting desiliconized LCD glass substrate powder into the second quartz reactor of a second electric furnace, (2) introducing N2, firstly increasing the temperature of the second electric furnace to the range of 500+ / -100 DEG C, after the temperature is stable, starting increasing the temperature of the first electric furnace to the range of 400+ / -100 DEG C, next, continuing reacting for 20-40 minutes, volatilizing and condensing the indium chloride generated through the reaction to the lower end of the second quartz reactor, and trapping and collecting silica wool. The method is capable of realizing the recovery of the indium from the LCD glass substrate powder; as a result, a new way for effectively treating the waste LCD and the PVC can be developed.
Owner:SHANGHAI SECOND POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
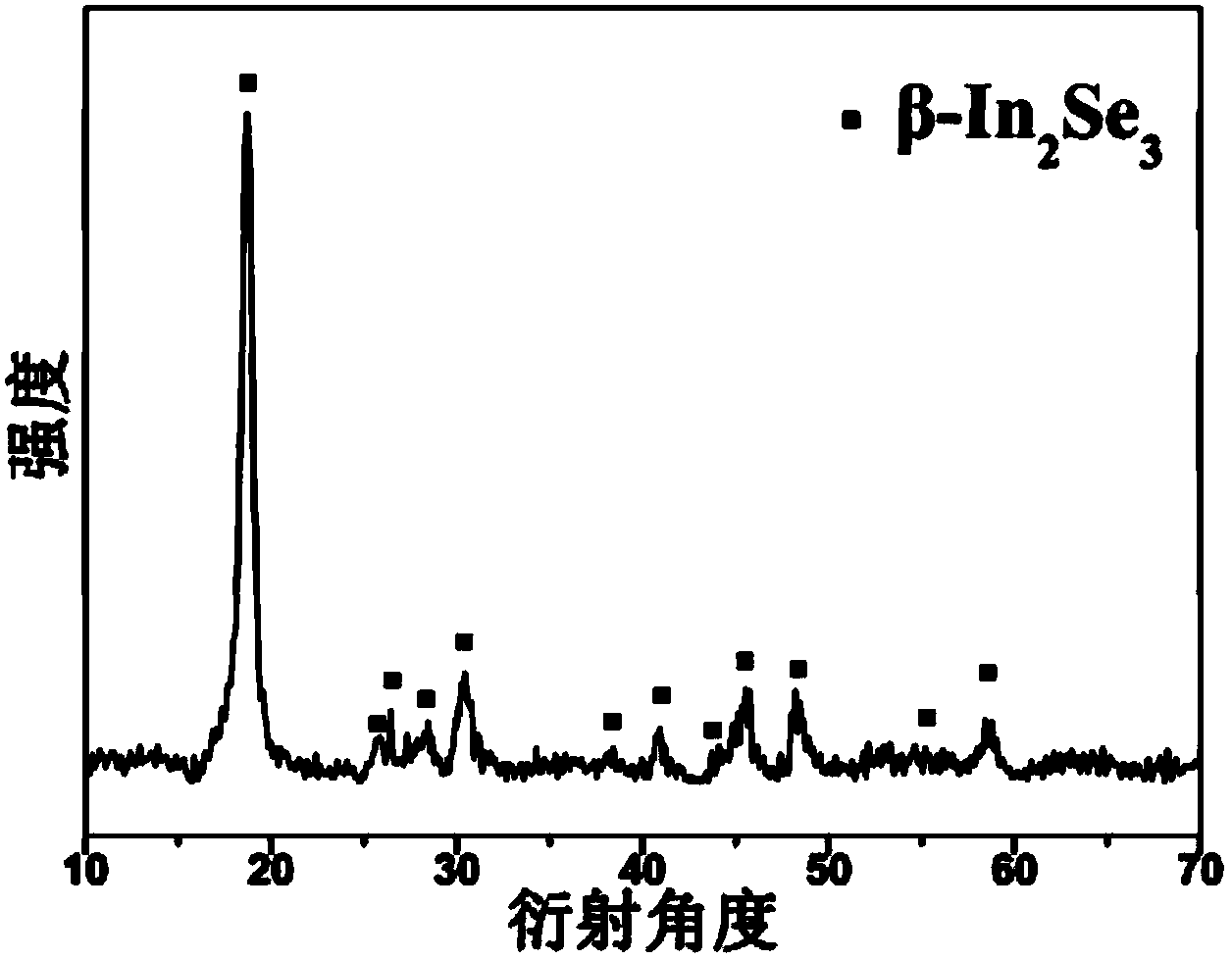
Method for synthesizing beta-phase indium selenide flaky nanocrystalline by using hydrazine hydrate-assisted polyhydric alcohol solution
InactiveCN104291278ASingle phaseMild reaction conditionsMaterial nanotechnologyBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsBottleNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing beta-phase indium selenide flaky nanocrystalline by using a hydrazine hydrate-assisted polyhydric alcohol solution. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, weighing 0.1mol of tetrahydrate indium chloride and dissolving into 10ml of triethylene glycol to obtain a cationic precursor solution; additionally, adding 40ml of triethylene glycol to a three-necked round-bottomed flask; adding 0.15mmol of selenium powder, adding 0.1ml of hydrazine hydrate and introducing nitrogen to obtain an anionic source reaction base fluid; putting the three-neck bottle into a thermal reaction reflux device, introducing nitrogen, slowly heating the anionic source reaction base fluid, quickly injecting the cationic precursor solution until the injection temperature / reflux temperature ranges from 250 / 250 DEG C to 270 / 270 DEG C, so as to obtain a reaction solution containing indium selenide nanocrystalline; and centrifugally separating and purifying the reaction solution to prepare In2Se3 nanocrystalline. The entire reaction of the method is mild in condition, safe, low in toxicity, simple and convenient to operate and low in cost; the product is single and stable in phase and relatively good in repeatability, and the stoichiometric ratio accords with the standard ratio.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method of hierarchical structured indium oxide hollow tubular gas-sensitive material
InactiveCN105271370AHigh sensitivityNo pollution in the processGallium/indium/thallium compoundsFiberIndium(III) chloride
The invention provides a preparation method of a hierarchical structured indium oxide hollow tubular gas-sensitive material. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps: indium chloride and L-cysteine which are used as raw materials and C-fiber used as a template undergo hydrothermal reaction and calcinations treatment to obtain the hierarchical structured hollow tubular indium oxide. The method has a simple production process. The obtained indium oxide gas-sensitive material has a hollow and hierarchical structure and is a novel gas-sensitive material with high sensitivity.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
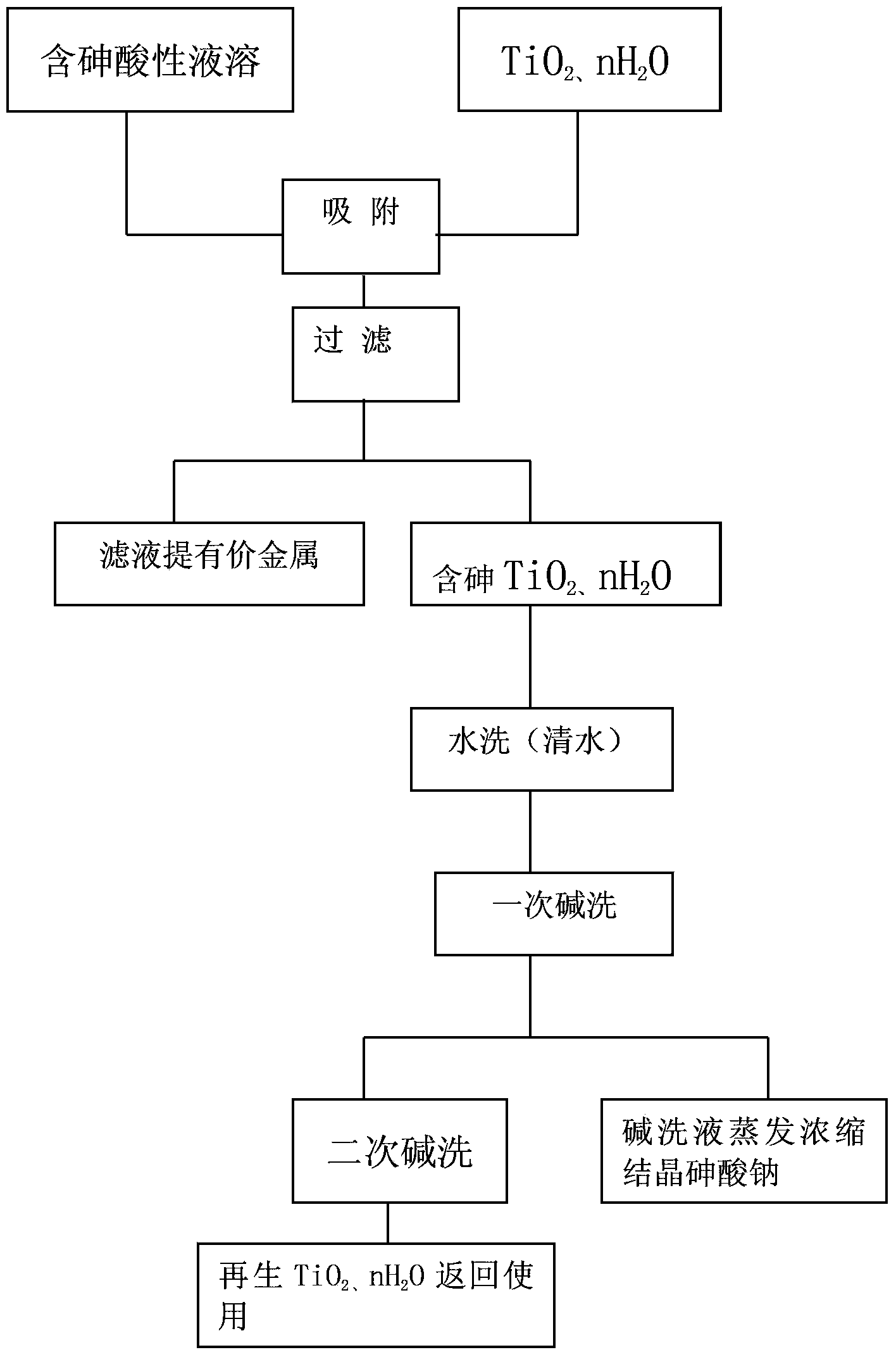
Method for removing arsenic from acid solution
InactiveCN103409625AEfficient recyclingAvoid secondary pollutionProcess efficiency improvementFiltrationIon exchange
The present invention discloses a method for removing arsenic from an acid solution, and relates to the technical field of hydrometallurgy, wherein TiO2 and nH2O can be adopted to carry out absorption removal of trivalent arsenic and pentavalent arsenic from a H2SO4 solution containing 10 mg / L-30 g / L of arsenic and a HCl solution containing 10 mg / L-30 g / L of arsenic, and acidity of an acid solution is 0.5-150 g / L. The adopted removal method can comprises: carrying out nature infiltration through an ion exchange column, carry out vacuum filtration, stirring according to a liquid-solid ratio, and carrying out pressure filtration with a pressure filter, wherein a 10-20% NaOH solution is adopted to wash and regenerate TiO2 absorbing arsenic and nH2O absorbing arsenic, an arsenic absorption effect is not reduced, the alkali washing solution is treated to obtain a sodium arsenate crystal containing more than 50% of arsenic, Zn<2+> and In<3+> are not be absorbed during arsenic removal processes of a zinc sulfate solution and an indium chloride solution, and arsenic and germanium are absorbed in a Ge-containing solution. With the method, arsenic can be effectively recovered, the problem of secondary pollution of arsenic in other methods is solved, and a certain economic value is produced.
Owner:GUIZHOU HONGDA ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for preparing ITO powder by spray thermolysis method
The invention relates to the technical field of a functional material, in particular to a method for preparing ITO powder by a spray thermolysis method. Required InCl3.4H2O and SnCl2.2H2O are calculated according to the conversion mixture ratio of m(In2O3):m(SnO2) being 9:1 in the final ITO product; indium chloride and stannous chloride are weighed and are dissolved into deionized water, so that the two kinds of metal salts can be uniformly mixed in the molecular range to be prepared into a precursor solution; in the process, little hydrochloric acid at a proportion of 1:1 is dripped for preventing hydrolysis; the precursor solution is added into an ultrasonic sprayer for spray making; the air is used as carrier gas; atomized liquid drips are introduced into a microwave wave tubular heating furnace; the carrier gas feeds spray drips into a microwave heating cavity to be heated through a catheter; the spray drips are subjected to evaporation, pyrolysis, drying, crystallization and nucleation; finally, thermolysis is performed to produce the ITO powder. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the ultrasonic wave spraying is used for being combined with the microwave pyrolysis one-step method; the prepared ITO powder has good dispersibility, high purity and small and uniform dimension distribution.
Owner:SHAANXI SHENGMAI PETROLEUM
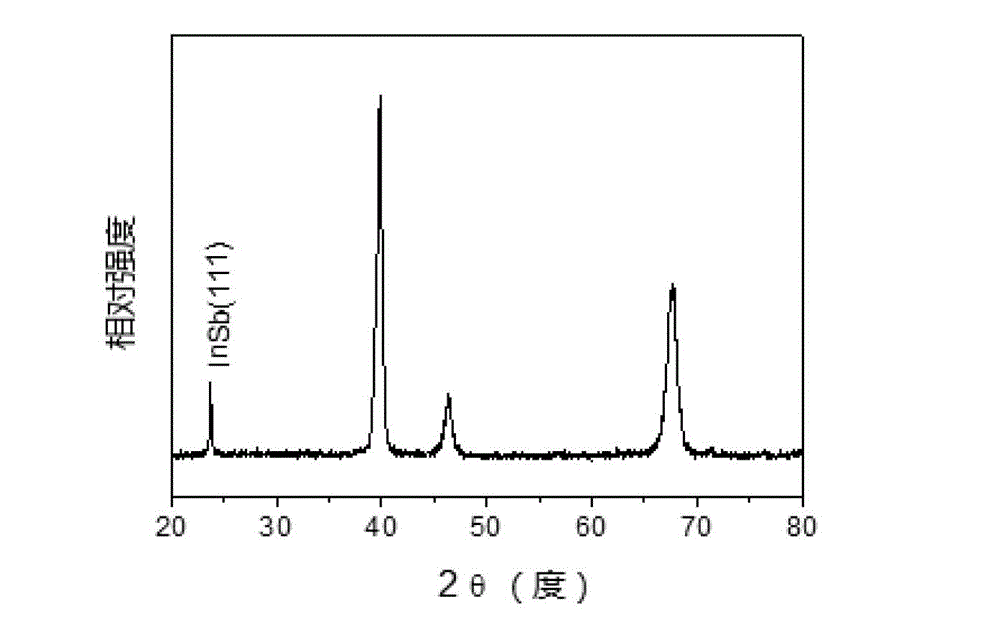
Method for preparing super-hydrophobic indium antimonide film by deposition in ionic liquid
The invention relates to a method for preparing a super-hydrophobic indium antimonide film by deposition in ionic liquid in the field of micro / nano technology. The method comprises the following steps of: putting a substrate into 1-methyl-3-ethylimidazole bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide salt solution containing indium chloride and antimony chloride and performing electrochemical deposition to obtain a film; and performing surface chemical modification on the film to obtain the super-hydrophobic indium antimonide film. The contact angle of water drops of the deposited indium antimonide film subjected to surface chemical modification is more than 150 degrees, and the rolling angle is less than 20 degrees. The method is simple and practicable and can be suitable for the surfaces of various conductive substrates.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method and application of TiN-In2S3 nano-composite photocatalyst
ActiveCN108607589AGood nano sizeLarge specific surface areaPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionRefluxAnhydrous ethanol
The invention discloses a preparation method of a TiN-In2S3 nano-composite photocatalyst, which includes the steps of: adding titanium nitride nanospheres to anhydrous ethanol, performing ultrasonic dispersion, adding cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide with stirring, adding indium chloride tetrahydrate and thioacetamide with uniform stirring, and performing constant temperature condensing reflux at95 DEG C to obtain a turbid liquid; centrifugally separating the turbid liquid, and drying a separated solid substance to prepare the TiN-In2S3 nano-composite photocatalyst. The preparation method forthe nano flower-like spherical composite photocatalyst, which is adjustable in appearance and nano-diameter, has universality.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Anhydrous indium chloride synthesizing method
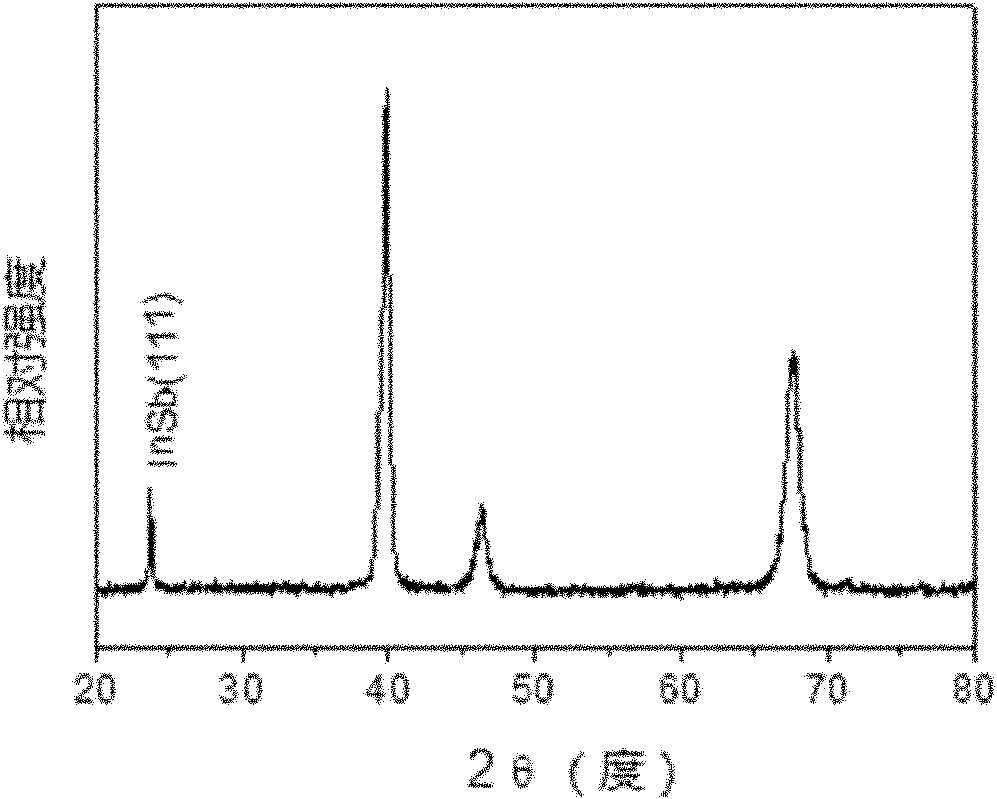
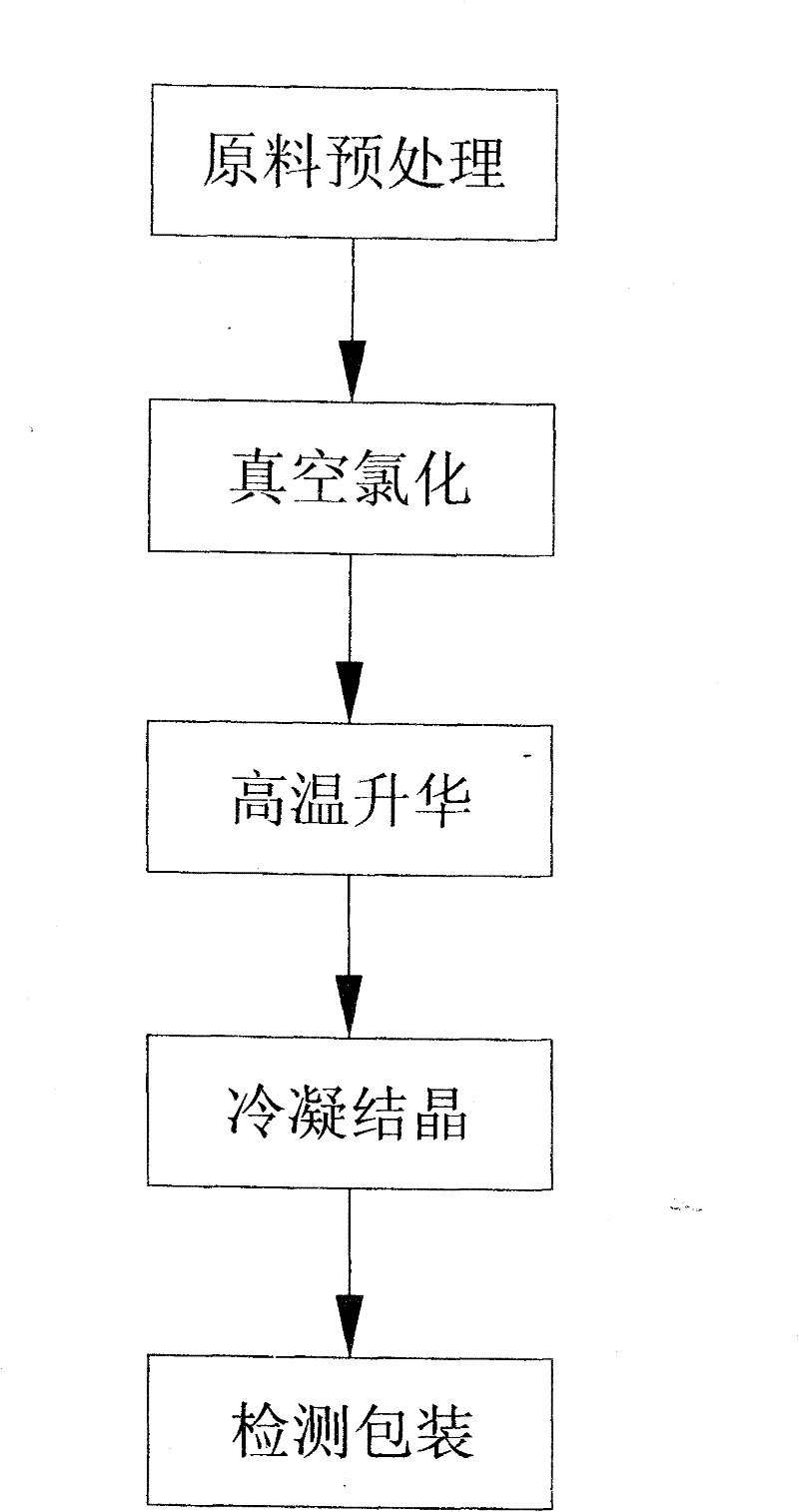
ActiveCN101792174BHigh purityIncrease productionChloride preparationGallium/indium/thallium compoundsVacuum sublimationIndium(III) chloride
The invention relates to an anhydrous indium chloride synthesizing method. The method adopts the following process steps: pre-treatment, vacuum chlorination, sublimation and purification, and formation of a finished anhydrous indium chloride product. According to the method, the high-purity anhydrous indium chloride is synthesized by adopting totally nontoxic agents and raw materials by using vacuum high-temperature chlorination and distilled purification technology; the product has high purity, high yield and no toxicity; by detecting the synthesized high-purity anhydrous indium chloride product, the impurity content is below 5ppm, and the purity reaches above 99.995 percent; and the trace impurity produced in the synthesizing process is blown out in a form of dust and then is hydrolyzedand absorbed under the sealed condition, the liquid enters an indium metal reclaiming link, the process flow avoids toxic agents, and the product is further purified by the unique vacuum sublimation technology.
Owner:SHAOGUAN JINYUAN INDAL
Method for synthesizing indium gallium selenide nanocrystal and film thereof from polyalcohol solution
InactiveCN104891451AGood dispersionReact SafeMaterial nanotechnologyBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsEthylenediamineDissolution
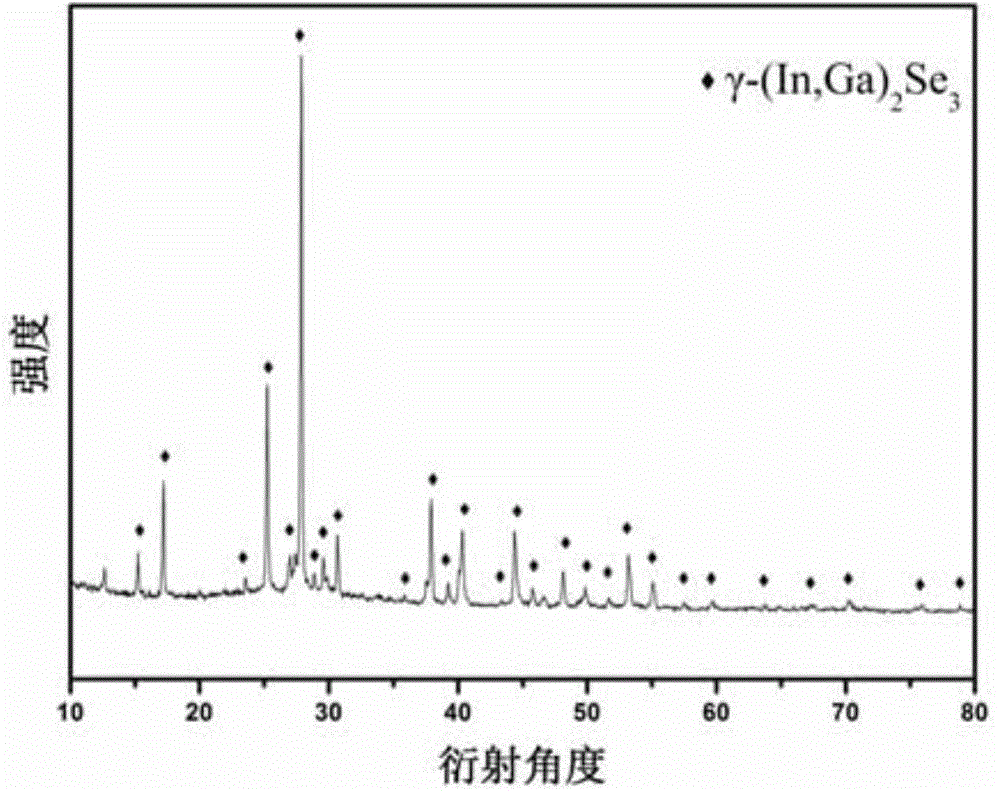
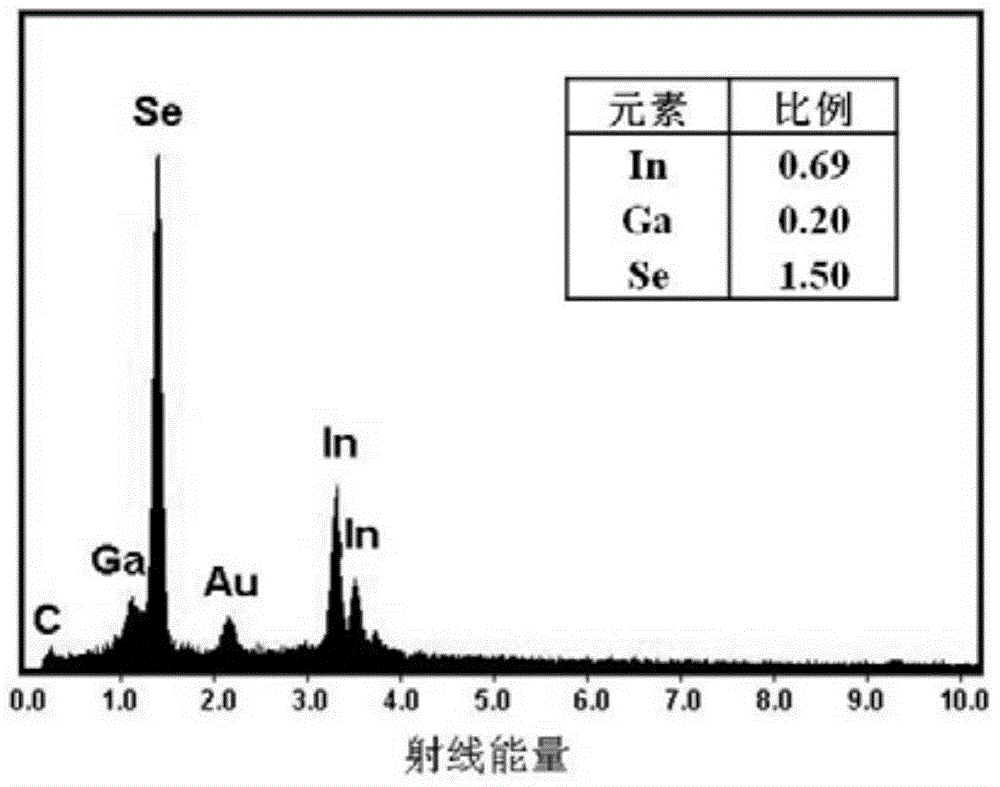
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing indium gallium selenide nanocrystal and a film thereof from a polyalcohol solution. The method comprises the following steps: putting 40ml of triethylene glycol into a three-neck flask, adding 0.45mmol Se powder, and magnetically stirring; adding nitrogen and 25-100mu L of dodecyl mercaptan and 0.1-1.2ml of ethylenediamine solution to obtain an anion precursor solution; putting 10ml of triethylene glycol into the flask, adding indium chloride tetrahydrate and 0.1mmol / mL gallium chloride solution, and performing ultrasonic dissolution to obtain a cation precursor solution; slowly heating the anion solution in the three-neck flask to 220-260 DEG C; quickly injecting the cation precursor solution; keeping the temperature at 200-240 DEG C and performing reflux for 30min; cooling to room temperature to obtain a solution of (In(1-x)Gax)2Se3 nanocrystal; and performing purification and extraction to obtain a solid-state film of indium gallium selenide nanocrystal. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the reaction process is safe and reliable, the cost is low, the method is easy to operate, the product is stable, the stoichiometric ratio of In, Ga and Se is adjustable, and the repeatability is relatively good.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method of nano indium phosphate photocatalyst
InactiveCN107308966AImprove dispersionImprove stabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationDistilled waterIndium(III) chloride
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nano indium phosphate photocatalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dropwise adding an ammonium phosphate solution into an indium chloride solution during stirring at a rotating speed of 200 to 400 r / s, then continuously stirring the solutions at the same rotating speed for 55 to 65 minutes after dropwise adding is completed, thus forming colloid, centrifugally separating the colloid, washing the colloid with distilled water for 3 to 5 times, and drying, thus obtaining the nano indium phosphate photocatalyst. The catalyst is high in dispersivity, high in stability and excellent in photocatalysis performance; the visible photocatalysis efficiency is substantially improved when compared with that of a conventional catalyst such as TiO2.
Owner:柳州若思纳米材料科技有限公司
Preparation method of halloysite loaded indium phosphate catalyst
InactiveCN107308964AImprove surface roughnessIncrease roughnessPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationHalloysiteNanoparticle
The invention discloses a preparation method of a halloysite loaded indium phosphate catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: acidizing halloysite, dissolving an aluminum oxide structure of halloysite to be favorable for loading; adding the processed halloysite into an indium chloride solution, adding an ammonium phosphate solution dropwise so as to cover a colloid on the surface of the halloysite, finally centrifuging, separating, washing and drying to obtain the halloysite loaded indium phosphate catalyst. The adsorption action between the uneven surface of the halloysite and an indium phosphate colloid particle is utilized, an indium phosphate nanoparticle is loaded on the surface of the halloysite, and the fixing of the catalyst is promoted.
Owner:柳州若思纳米材料科技有限公司
Preparation method and application of copper-indium composite catalyst
InactiveCN113151859ASimple preparation conditionsReduce energy consumptionElectrolytic organic productionElectrodesHydration reactionIndium(III) hydroxide
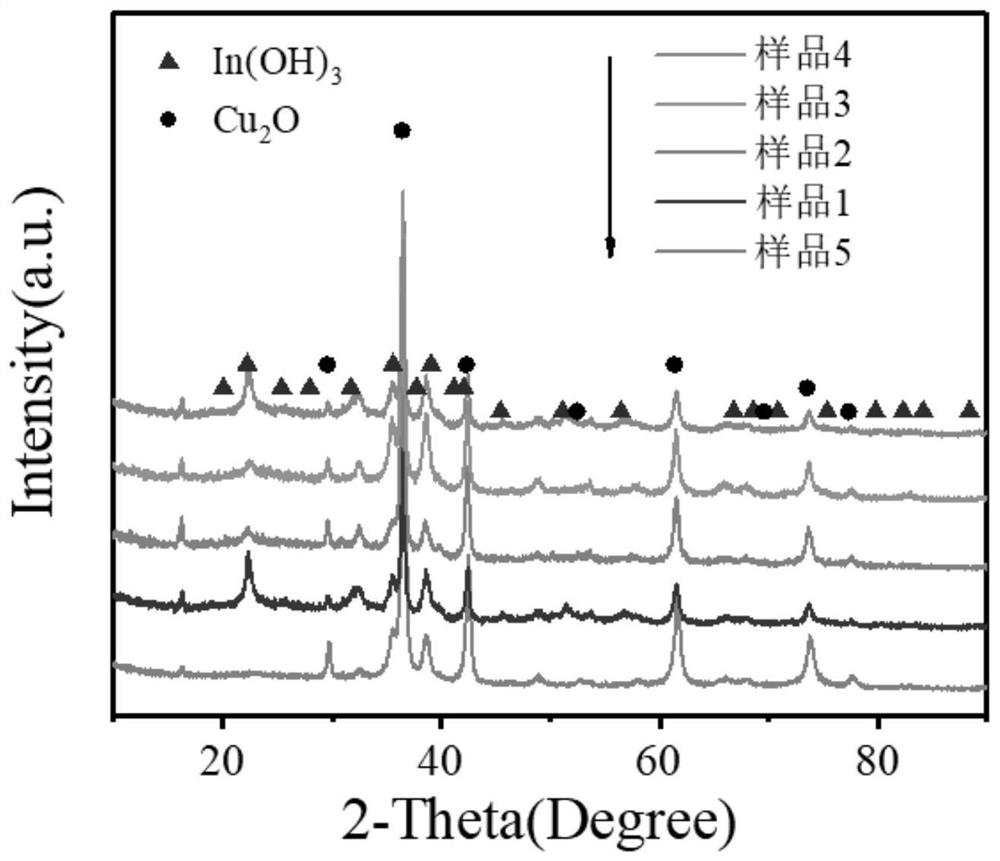
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a copper-indium composite catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of material preparation and electro-catalysis. The composite cuprous oxide and indium hydroxide electrocatalyst is prepared by taking cupric chloride dihydrate CuCl2. 2H2O, anhydrous indium chloride InCl3, stronger ammonia water, sodium hydroxide and hydrazine solution N2H4 as raw materials, feeding in batches, co-precipitating under a normal temperature condition, introducing an In-based material into a pure cuprous oxide Cu2O material, and developing the high-performance composite cuprous oxide and indium hydroxide electrocatalyst for electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide for the first time. The prepared electrocatalyst has the advantages of being large in specific surface area and good in electrocatalytic performance. The preparation process is simple and convenient, the energy consumption is low, the cost is low, and the application potential is great.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for depositing and preparing super-hydrophobic indium antimonide thin film from ionic liquid
The invention relates to a method for depositing and preparing a super-hydrophobic indium antimonide thin film, belonging to the field of micro-nano technologies. The method comprises the steps: placing a substrate in 1-methyl-3-ethyl imidazolium bis(trifluoromethyl sulfonyl) imide solution containing indium chloride and antimonic chloride to carry out electrochemical deposition to obtain a thin film, and carrying out surface chemical modification on the thin film to obtain the super-hydrophobic indium antimonide thin film. After surface chemical modification of the indium antimonide thin film obtained by deposition, the contact angle of water drop is more than 150 degrees and the roll angle is smaller than 20 degrees. The method is simple and feasible, and is suitable for various conductive substrate surfaces.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for preparing copper indium selenium sulfur powder or thin film used in thin-film solar cell
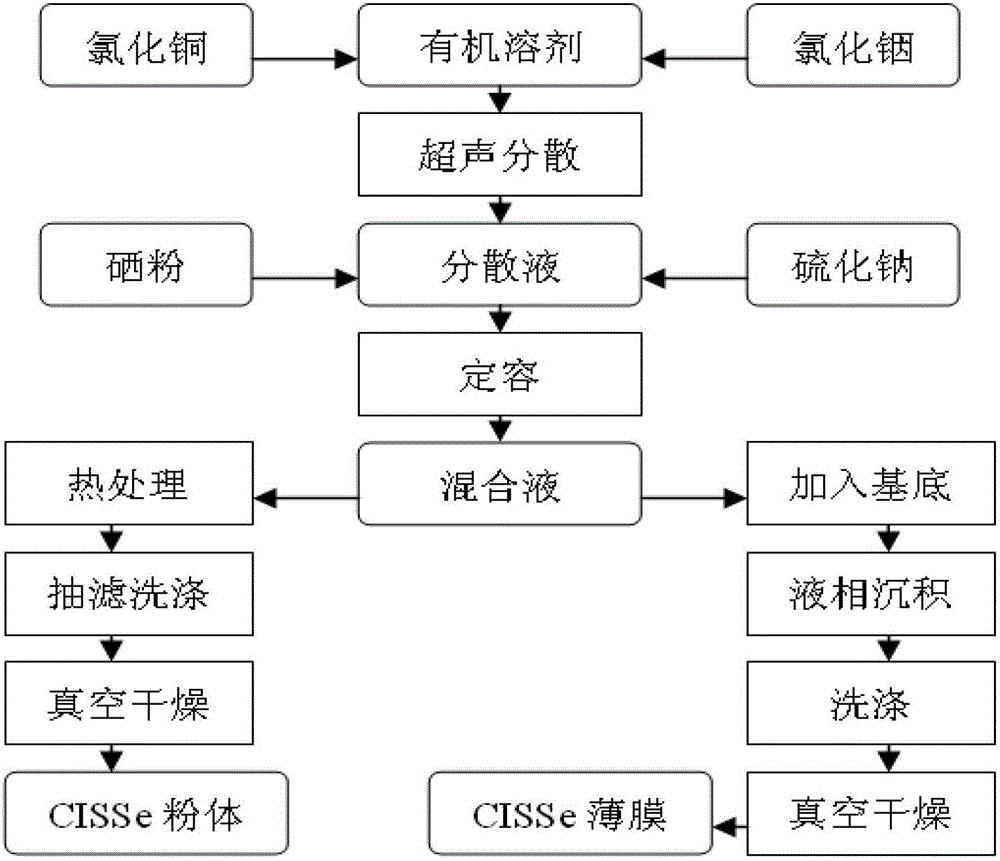
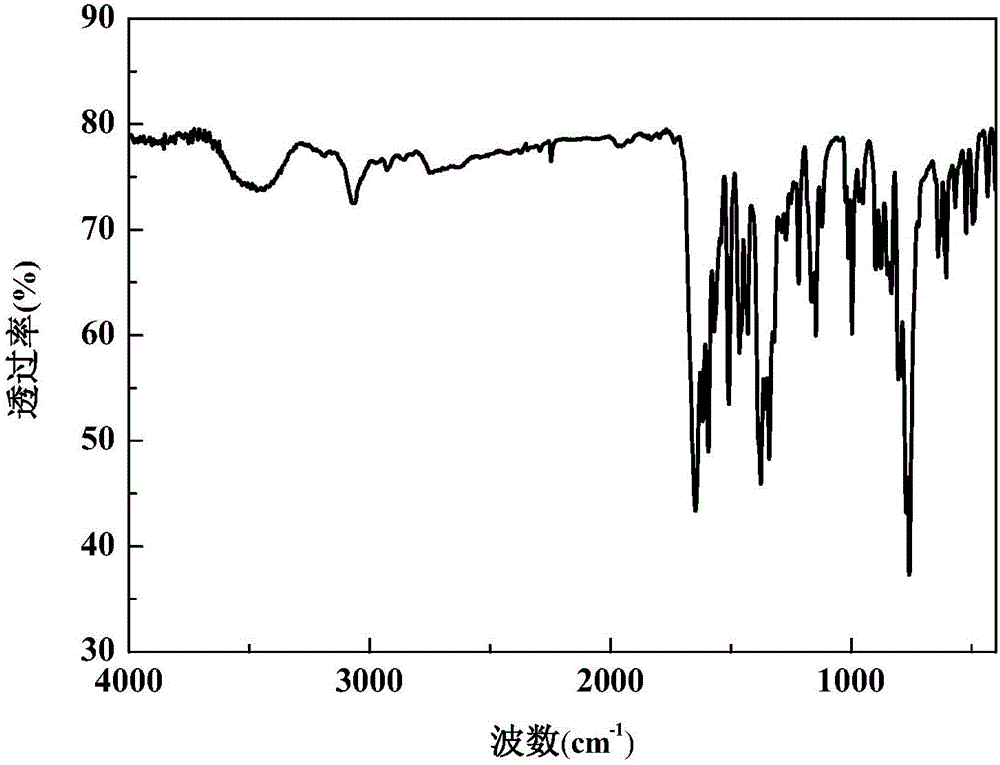
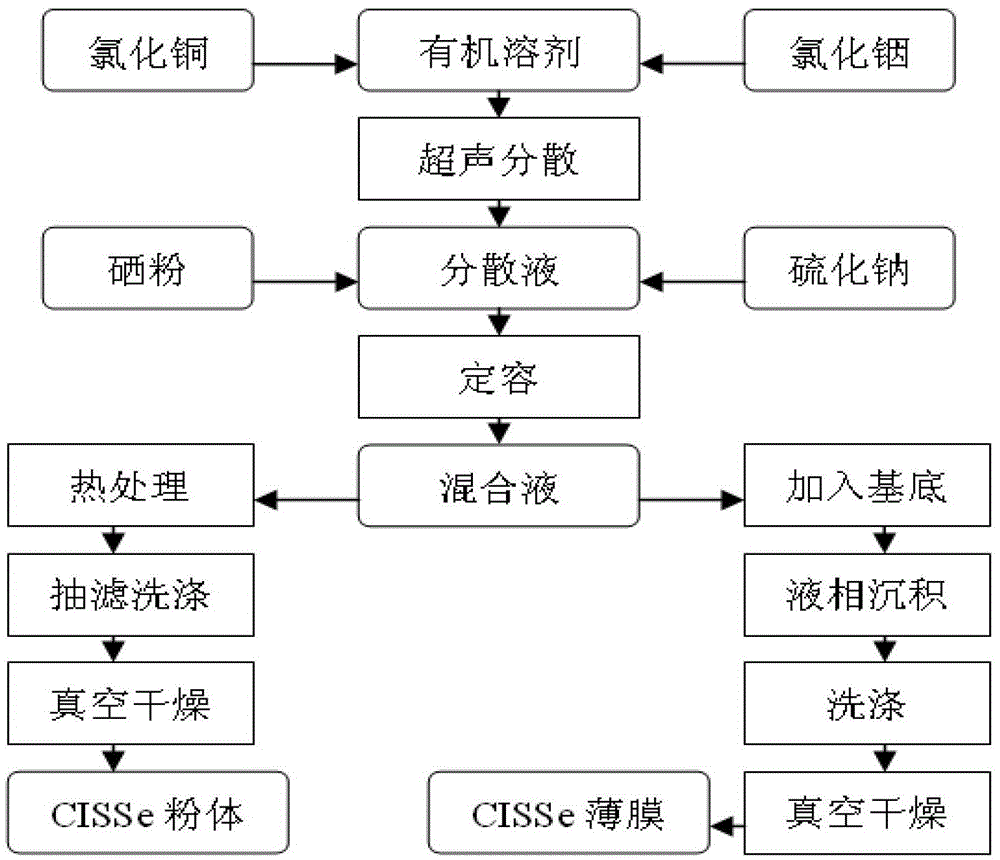
ActiveCN103337555ALow costNo pollution in the processFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesFiltrationUltrasonic dispersion
The invention discloses a method for preparing copper indium selenium sulfur powder or thin film used in a thin-film solar cell. The method comprises the following steps: firstly copper chloride and indium chloride are dispersed in an organic solvent and subjected to ultrasonic dispersion to obtain dispersion liquid; after being added with sodium sulfide and selenium powder, the dispersion liquid is stirred to be uniform to obtain a mixed solution; then the mixed solution is transferred to a reactor to perform reaction after completion of the constant volume and the sealing, after the reaction is completed, suction filtration is performed, residue is washed by deionized water and anhydrous ethyl alcohol sequentially, then is dried in volume to obtain CuIn (S, Se)2 powder; or the mixed solution is transferred to the reactor, then a glass substrate is added into, liquid phase deposition is performed after the completion of the constant volume and the sealing, the deposited glass substrate is washed by deionized water and anhydrous ethyl alcohol sequentially, and then is dried in volume to obtain CuIn (S, Se)2 thin film. According to the method, adopted devices are simple, the prepared CuIn (S, Se)2 powder or thin film is excellent in performance, and good in stability; the industrial production can be realized; a band gap of the CuIn (S, Se) 2 can be continuously adjustable within the range of 1.21-1.45 eV by controlling the content of an S element.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
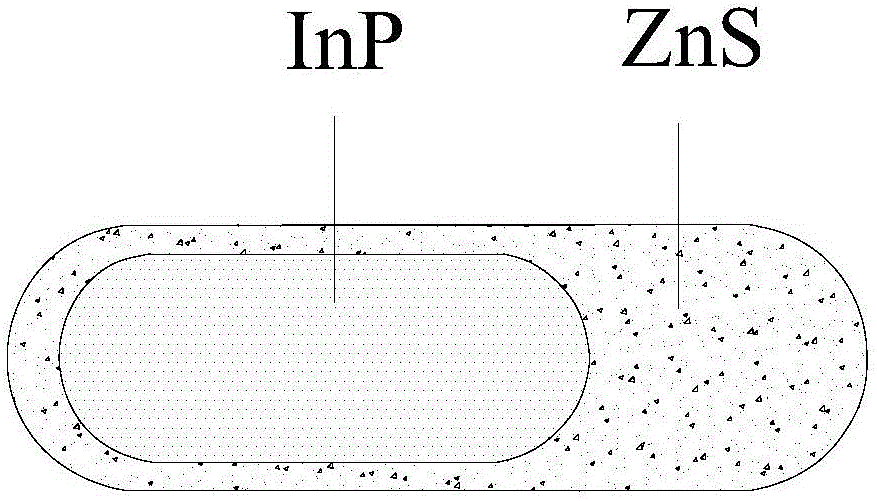
Preparation method of core-shell InP/ZnS nanorods
ActiveCN106433613AAdjustable aspect ratioImprove luminous efficiencyNanoopticsLuminescent compositions1-dodecanethiolTrioctylphosphine
The invention provides a preparation method of core-shell InP / ZnS nanorods, comprising: in inert atmosphere, mixing indium chloride or indium oxide, trioctyl phosphine oxide, dodecylamine and tri-n-octylphosphine to obtain mixed liquid, heating and degassing in vacuum, heating in the inert atmosphere to form transparent indium precursor solution; in inert atmosphere, preparing tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphine precursor with tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphine, diphenyl ether and biphenyl; in inert atmosphere, heating the indium precursor solution to 290-320 DEG C, injecting the tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphine precursor into the indium precursor solution, adjusting the temperature to 295-305 DEG C, and reacting to obtain an InP nanorods; in inert atmosphere, injecting zinc fatty acid and 1-dodecanethiol into InP nanorod solution under heating to prepare the core-shell InP / ZnS nanorods.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Preparation method of large-particle-size indium oxide
ActiveCN109607598APromote growthExpand the particle size control rangeGallium/indium/thallium compoundsNanotechnologyMicroreactorSlurry
The invention provides a preparation method of a large-particle-size indium oxide, which comprises the following steps of: respectively flowing an indium chloride solution and an ammonia aqueous solution into a membrane microreactor for coprecipitation reaction, and dripping the obtained seed crystal solution into the indium chloride solution and the ammonia aqueous solution in parallel flow underthe heating condition, so as to obtain a reaction solution; then centrifuging, washing and drying the reaction solution in sequence to obtain a precursor powder, and roasting to obtain the large-particle-size indium oxide. According to the preparation method of a large-particle-size indium oxide, a precipitation method is used for preparing slurry as seed crystal liquid, indium chloride and the ammonia aqueous solution are dripped in parallel subsequently to promote the growth process of particles, the large-particle-size indium oxide particles are prepared through a seed crystal induction method, and the particle size regulation and control range of the indium oxide particles is expanded; Compared with the prior method for greatly improving the roasting temperature to obtain the particles with larger particle size, the preparation method of a large-particle-size indium oxide simplifies the process flow, saves energy, which is more convenient to operate and easy to amplify, and can prepare the indium oxide with the particle size of more than or equal to 30nm at the roasting temperature of 300-500 DEG C.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A kind of preparation method of indium oxide nanoparticles with porous structure
InactiveCN106167274BNo pollution in the processHigh sensitivityGallium/indium/thallium compoundsNanotechnologyNanoparticleIndium(III) chloride
The invention provides a method for preparing indium oxide nanoparticles of porous structures. The method specifically comprises the following steps: by taking indium chloride and dodecylamine as raw materials, performing a hydrothermal reaction, and performing calcination treatment, thereby obtaining the indium oxide nanoparticles of the porous structures. The method is simple in production process, free of expensive surfactant and relatively low in cost, and the prepared indium oxide can be used as a gas sensitive material, has good gas sensitivity on formaldehyde gases due to the porous structures, and thus has long-term application prospects in formaldehyde gas detection.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Organic blue light-emitting material benzimidazole derivative-indium metal complex and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104910199ALong luminous lifeImprove luminous efficiencyGroup 3/13 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesLuminescent compositionsBenzimidazole derivativeFiltration
The invention relates to a light-emitting material and a preparation method thereof, and concretely relates to an organic blue light-emitting material benzimidazole derivative-indium metal complex and a preparation method thereof. The technical problems of low luminescence efficiency, poor monochromaticity and short life of present organic blue light-emitting materials are solved in the invention. The molecular formula of the organic blue light-emitting material benzimidazole derivative-indium metal complex is C26H17Cl2N4O2In, the structural formula is shown in the specification. The preparation method of the complex comprises the following steps: 1, dissolving 2-quinolinecarbaldehyde and o-phenylenediamine in acetonitrile under the protection of nitrogen, stirring at room temperature under a stirring speed of 400-600r / min for 5-8h, and carrying out pumping filtration to obtain a deep yellow solid; and 2, placing the deep yellow solid and indium chloride in acetonitrile, and carrying out a hydrothermal reaction to obtain the organic blue light-emitting material benzimidazole derivative-indium metal complex. The organic blue light-emitting material benzimidazole derivative-indium metal complex can be obtained in the invention.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
A preparation method of copper indium sulfide selenide powder or film for thin film solar cells
ActiveCN103337555BLow costNo pollution in the processFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesFiltrationUltrasonic dispersion
The invention discloses a method for preparing copper indium selenium sulfur powder or thin film used in a thin-film solar cell. The method comprises the following steps: firstly copper chloride and indium chloride are dispersed in an organic solvent and subjected to ultrasonic dispersion to obtain dispersion liquid; after being added with sodium sulfide and selenium powder, the dispersion liquid is stirred to be uniform to obtain a mixed solution; then the mixed solution is transferred to a reactor to perform reaction after completion of the constant volume and the sealing, after the reaction is completed, suction filtration is performed, residue is washed by deionized water and anhydrous ethyl alcohol sequentially, then is dried in volume to obtain CuIn (S, Se)2 powder; or the mixed solution is transferred to the reactor, then a glass substrate is added into, liquid phase deposition is performed after the completion of the constant volume and the sealing, the deposited glass substrate is washed by deionized water and anhydrous ethyl alcohol sequentially, and then is dried in volume to obtain CuIn (S, Se)2 thin film. According to the method, adopted devices are simple, the prepared CuIn (S, Se)2 powder or thin film is excellent in performance, and good in stability; the industrial production can be realized; a band gap of the CuIn (S, Se) 2 can be continuously adjustable within the range of 1.21-1.45 eV by controlling the content of an S element.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com