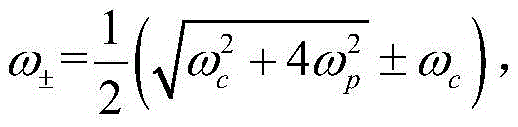Patents
Literature
105 results about "Indium antimonide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Indium antimonide (InSb) is a crystalline compound made from the elements indium (In) and antimony (Sb). It is a narrow-gap semiconductor material from the III-V group used in infrared detectors, including thermal imaging cameras, FLIR systems, infrared homing missile guidance systems, and in infrared astronomy. The indium antimonide detectors are sensitive between 1–5 µm wavelengths.
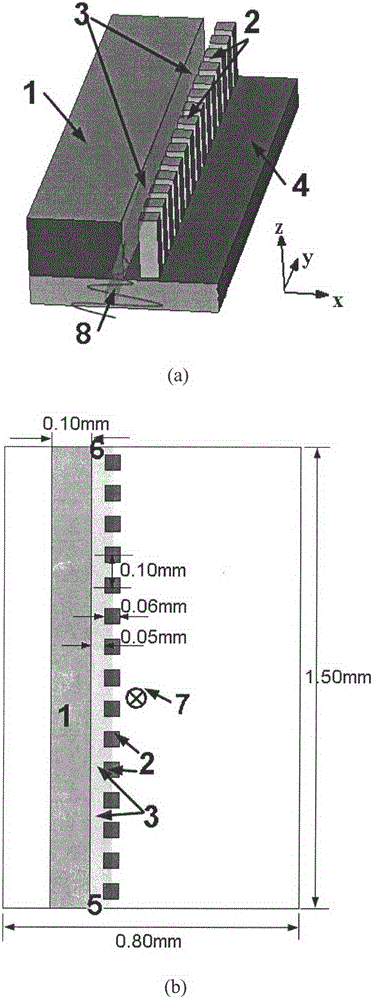
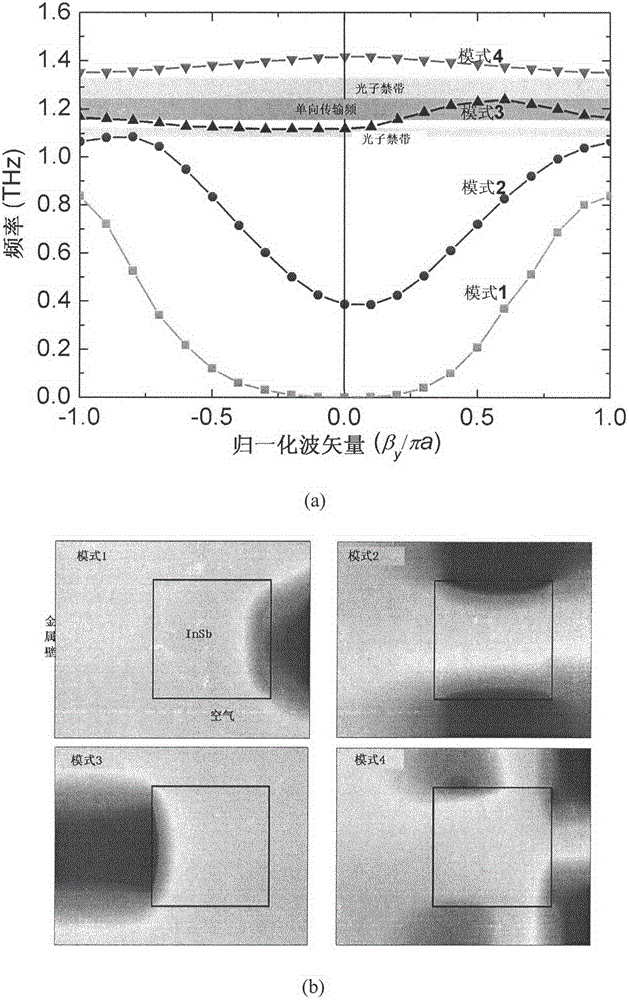
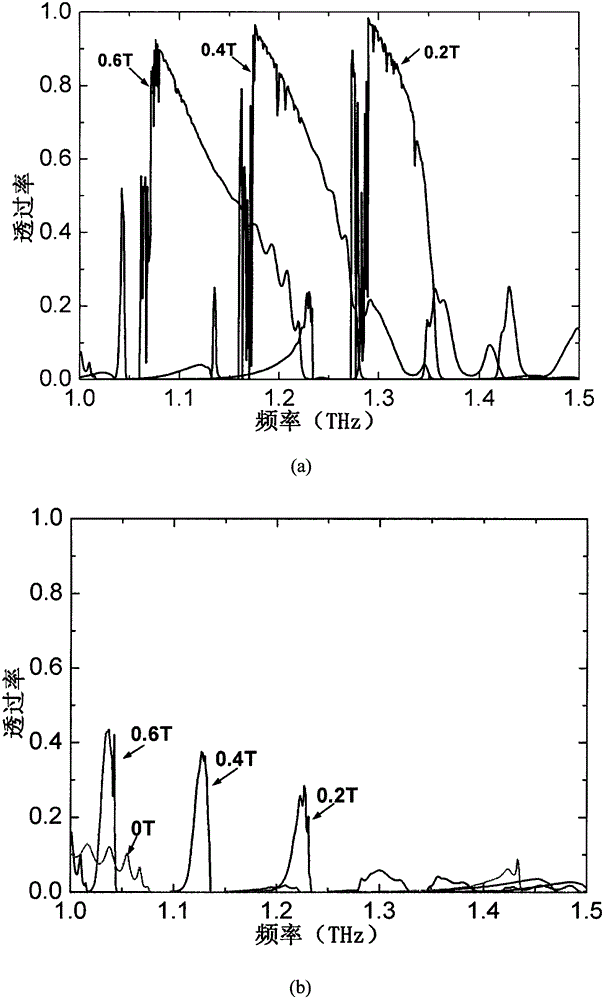
Terahertz isolator of magnetic surface plasma waveguide
InactiveCN102916238AEnhanced one-way transmission performanceImprove isolationWaveguide type devicesWaveguideTransmission quality
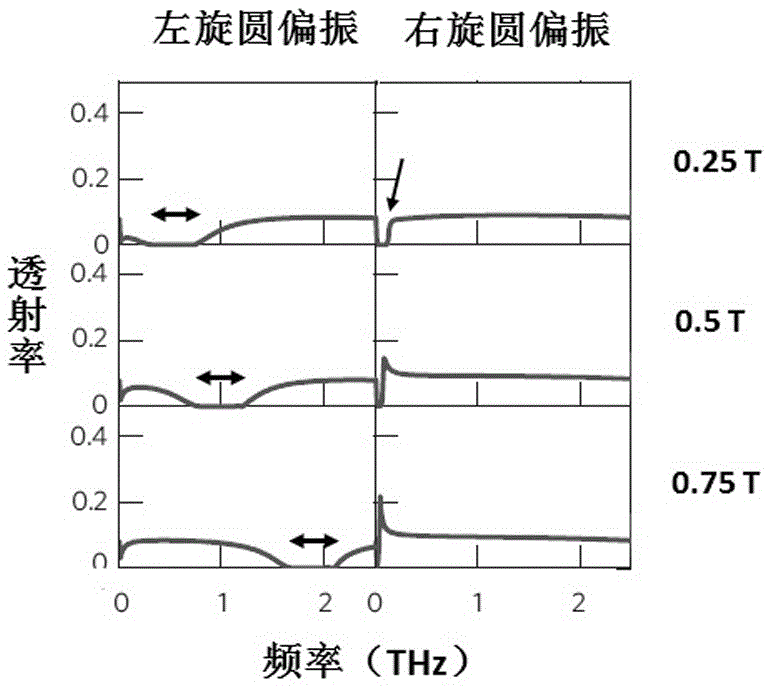
The invention discloses a terahertz isolator device of a magnetic surface plasma waveguide and a control method thereof. The asymmetric and periodic surface plasma waveguide is formed by a metal wall and a semiconductor indium antimonide pillar array. By exerting an external magnetic field under low temperature, the indium antimonide shows the revolving electrical property, and the structure can generate a magnetic surface plasma mode, so that the function of unidirectional isolation transmission of the terahertz wave can be achieved. The unidirectional transmission working frequency range is higher than 1THz, the bandwidth is larger than 80 GHz, the isolation reaches 90dB, the insertion loss is lower than 0.25dB, and tuning on the working frequency range can be performed by controlling the external magnetic field strength. Under the temperature of 186K, the frequency of the external magnetic field can be adjusted to 0.7T from 0.1T, and the central working frequency of a unidirectional transmission frequency band of the device can be tuned to 1THz from 1.42THz. The terahertz isolator is low in loss, high in isolation, tunable in broadband and capable of reducing echo and scattered noises in a terahertz application system and improving transmission quality of the terahertz beam.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
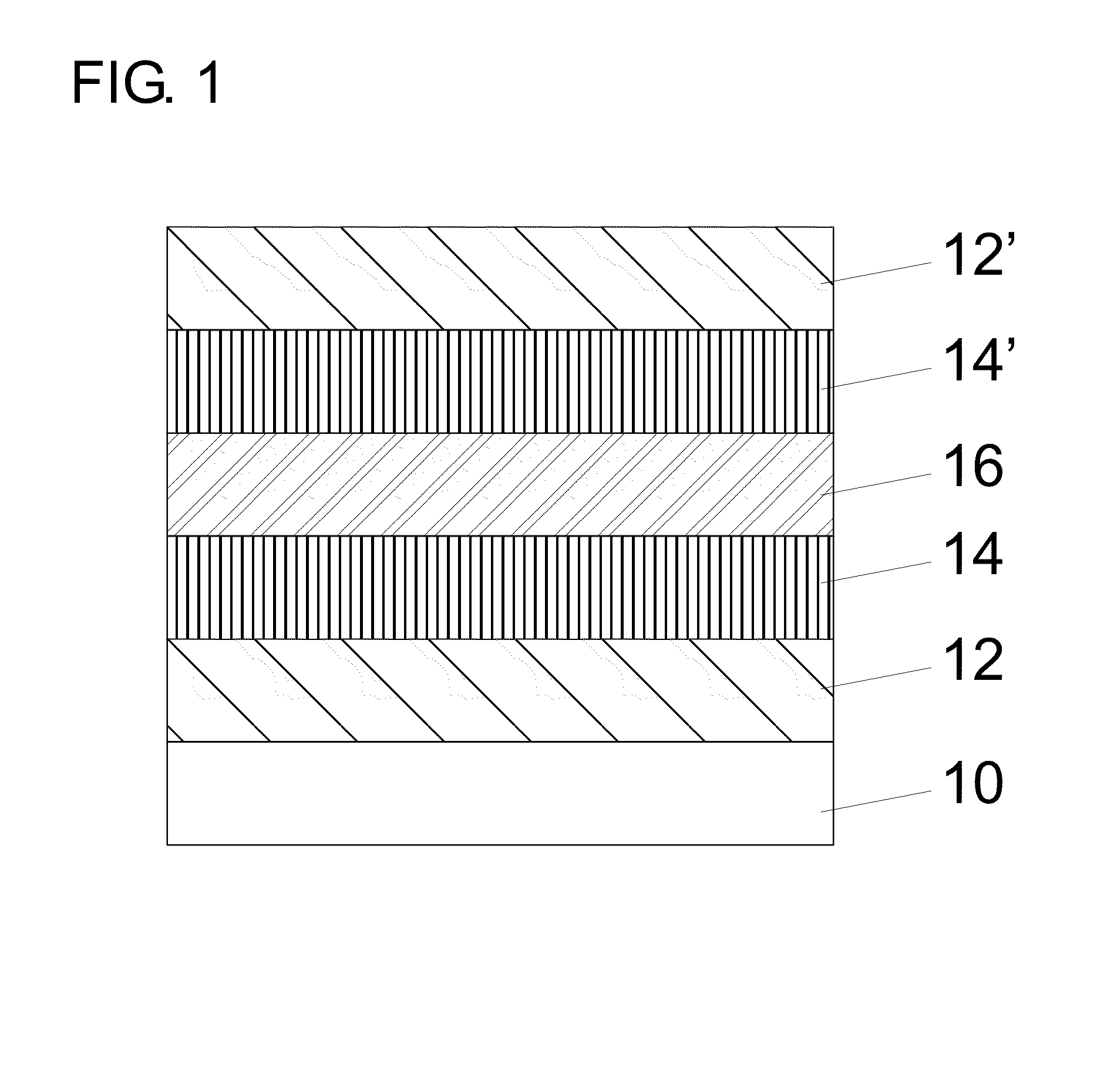
Long Wavelength Infrared Superlattice
InactiveUS20130043458A1Quality lossOvercome lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsGallium antimonideIndium arsenide
An embodiment of the present invention improves the fabrication and operational characteristics of a type-II superlattice material. Layers of indium arsenide and gallium antimonide comprise the bulk of the superlattice structure. One or more layers of indium antimonide are added to unit cells of the superlattice to provide a further degree of freedom in the design for adjusting the effective bandgap energy of the superlattice. One or more layers of gallium arsenide antimonide are added to unit cells of the superlattice to counterbalance the crystal lattice strain forces introduced by the aforementioned indium antimonide layers.
Owner:SVT ASSOCS
Long Wavelength Infrared Superlattice
InactiveUS20130043459A1Extend the cutoff wavelengthQuality lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsGallium antimonideIndium arsenide
An embodiment of the present invention improves the fabrication and operational characteristics of a type-II superlattice material. Layers of indium arsenide and gallium antimonide comprise the bulk of the superlattice structure. One or more layers of indium antimonide are added to unit cells of the superlattice to provide a further degree of freedom in the design for adjusting the effective bandgap energy of the superlattice. One or more layers of gallium arsenide antimonide are added to unit cells of the superlattice to counterbalance the crystal lattice strain forces introduced by the aforementioned indium antimonide layers.
Owner:SVT ASSOCS
Graphene mid-infrared light detector based on plasmon enhancement and preparation method
InactiveCN111554757APromote absorptionHigh resonance factorFinal product manufactureNanotechnologyHigh energyMaterials science
The invention discloses a graphene mid-infrared light detector based on plasmon enhancement, and belongs to the technical field of mid-infrared light detection. The graphene mid-infrared light detector comprises a silicon substrate, a silicon dioxide layer, a graphene micro-nano array and a dielectric layer which are sequentially stacked from bottom to top, wherein the graphene micro-nano array and the dielectric layer are positioned in the middle of the silicon dioxide layer; the surfaces of the silicon dioxide layer and the dielectric layer are covered with a graphene layer; and a first electrode and a second electrode are arranged on the two sides of the graphene layer respectively. According to the infrared detector manufactured by using the structure, the photoelectric conversion efficiency is greatly improved, the preparation method is simple, the infrared detector is compatible with the existing silicon process, the problems of continuous low-temperature refrigeration, high energy consumption, weak signal and the like of the traditional infrared detector using mercury cadmium telluride, indium antimonide and the like are solved, and the operation cost performance is greatlyimproved.
Owner:深圳激子科技有限公司
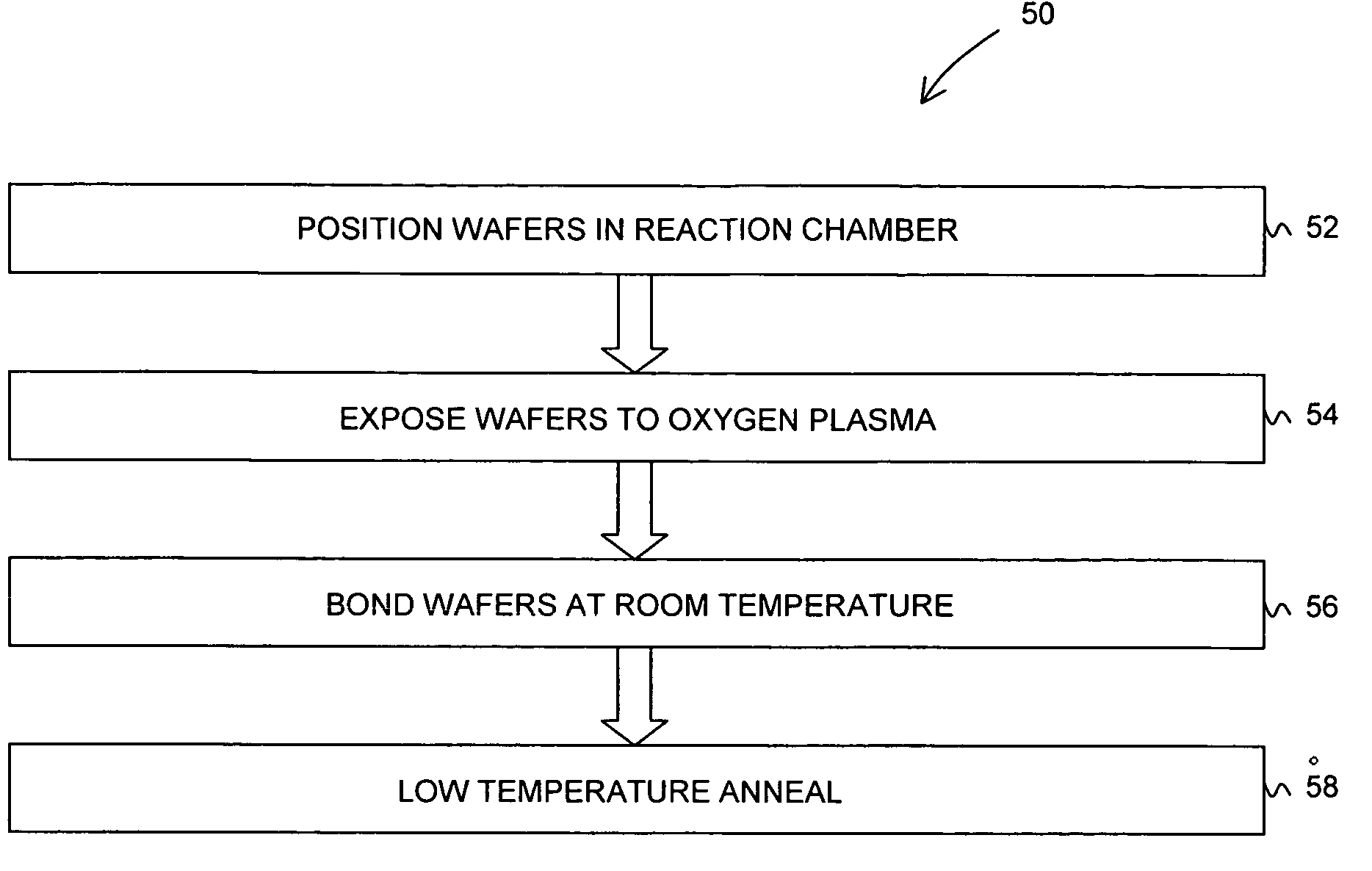
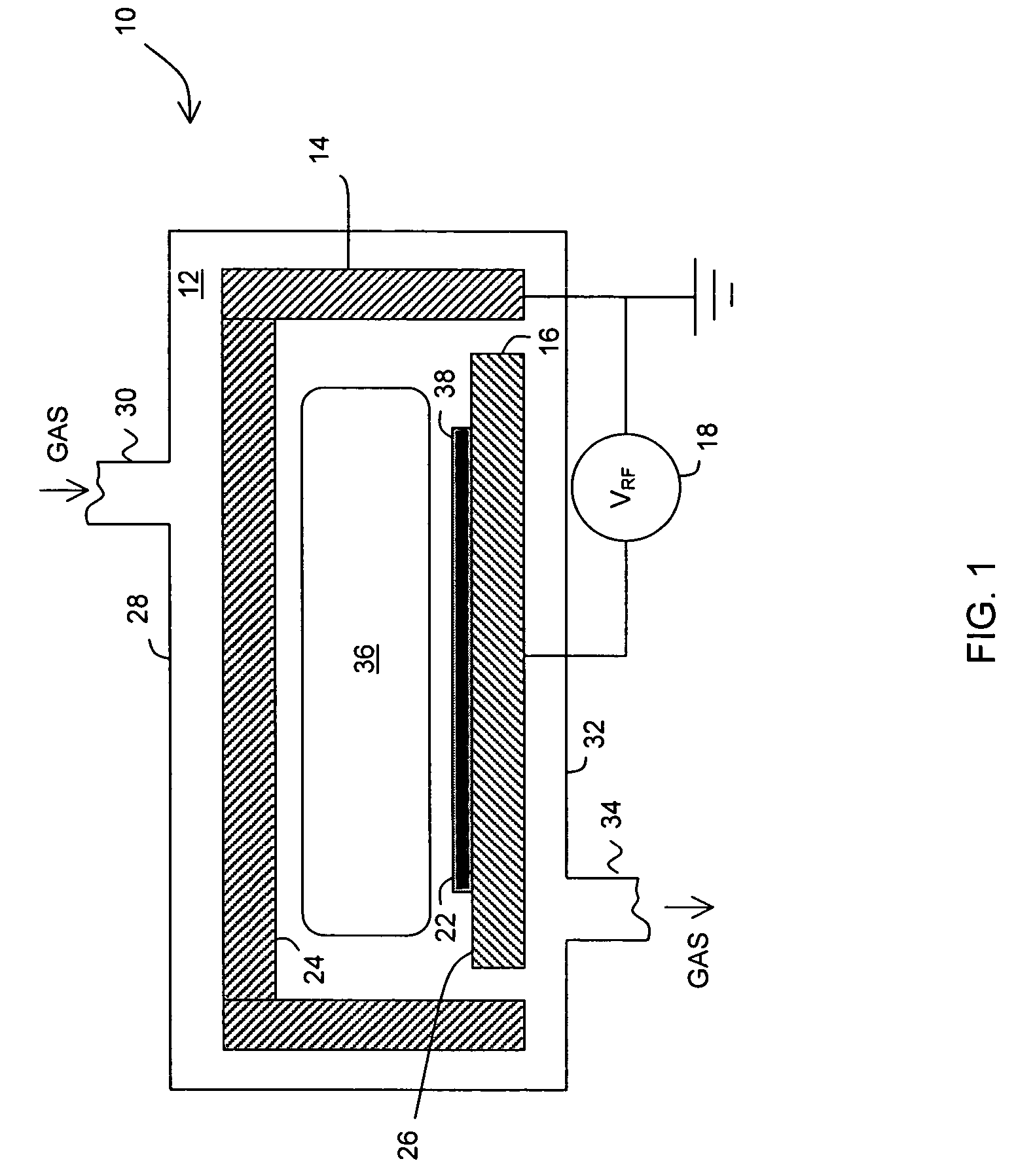
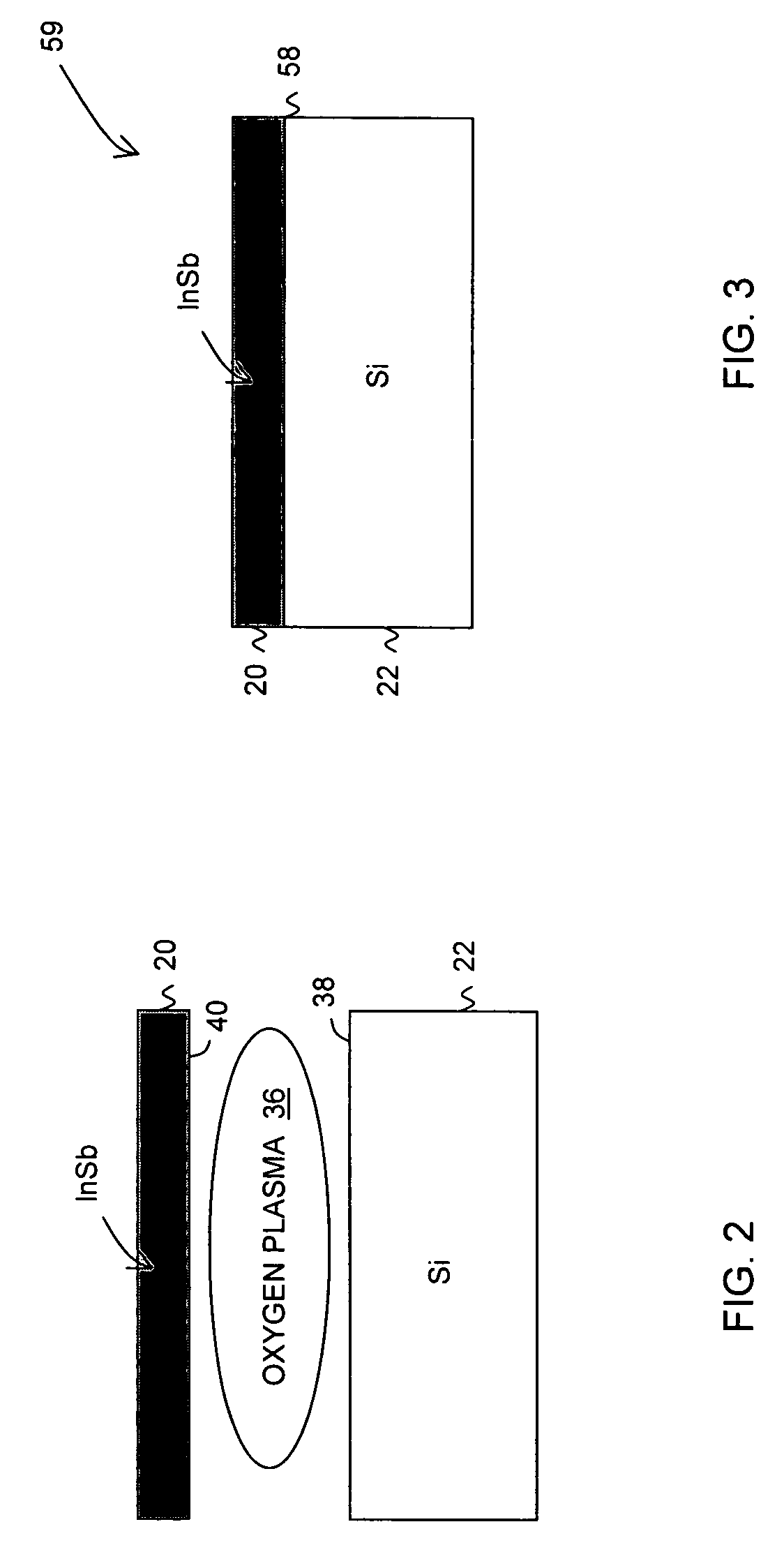
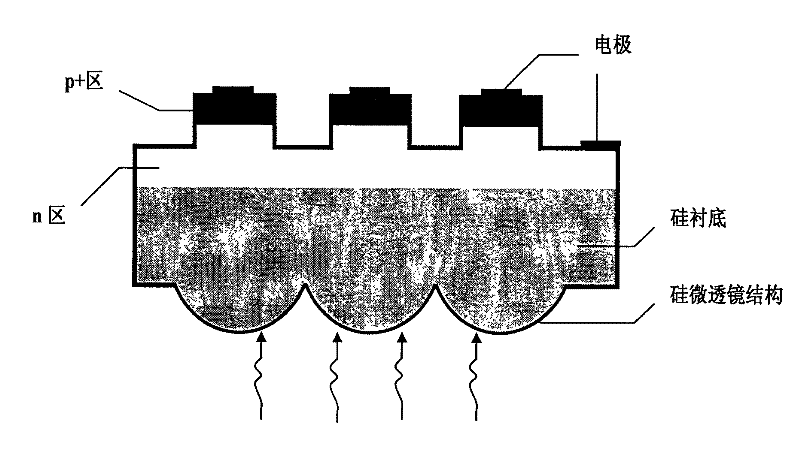
Bonding of substrates
InactiveUS20060043483A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygen plasmaSilicon dioxide
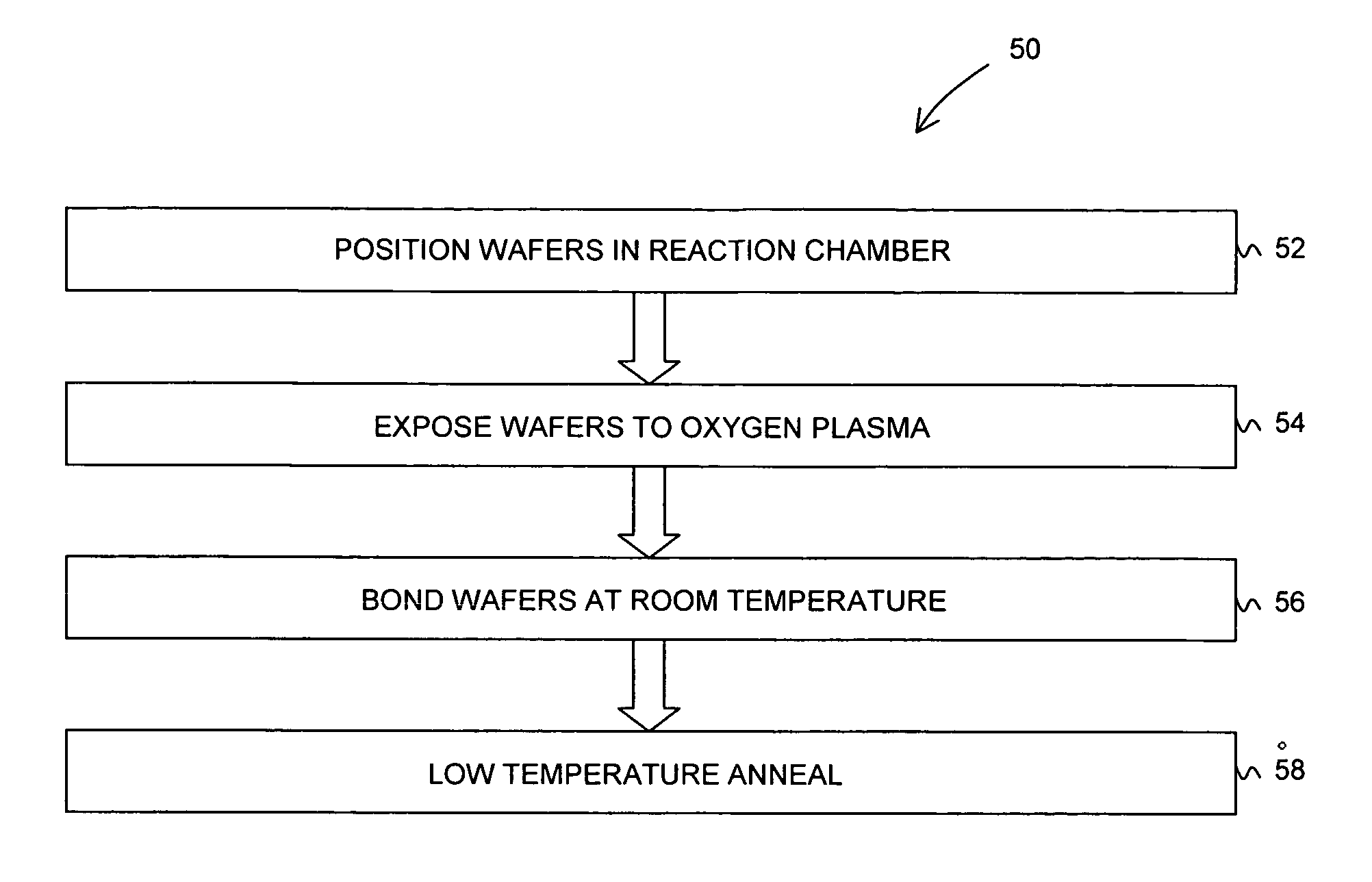
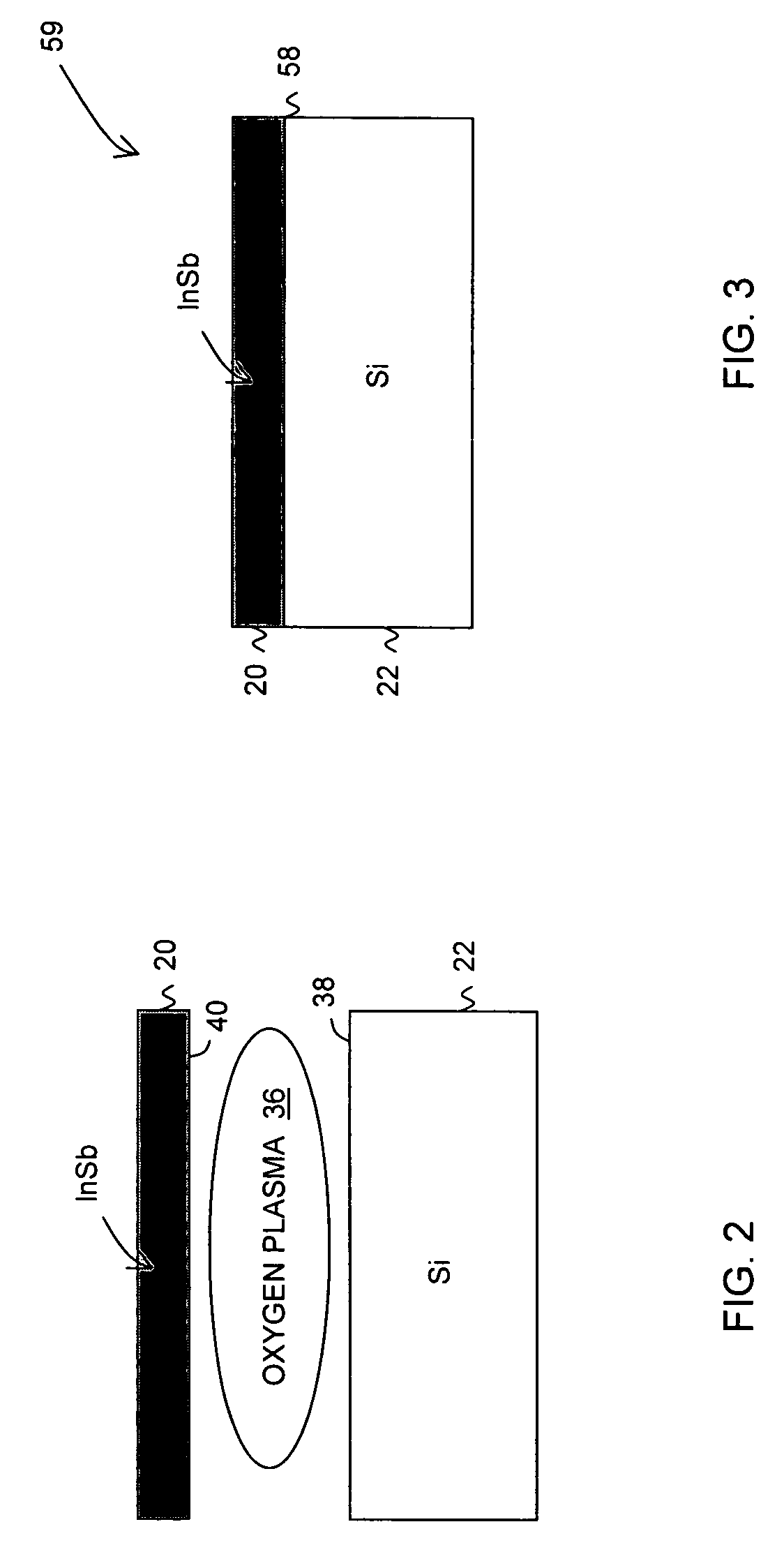
In one embodiment, a method comprises placing a first and a second substrate into a reaction chamber, the first substrate being made of an indium antimonide material and having a first surface and the second substrate being made of a silicon or a silicon dioxide material and having a second surface; exposing the first and second surfaces to an oxygen plasma; forming a bond between the first and the second substrates by placing the first surface in contact with the second surface; and annealing the first and the second substrates to strengthen the bond.
Owner:INTEL CORP
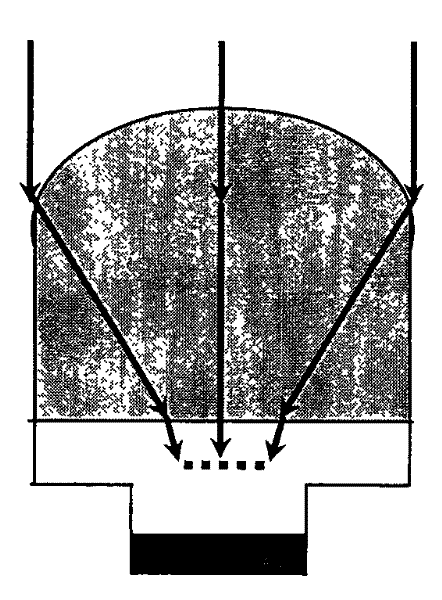
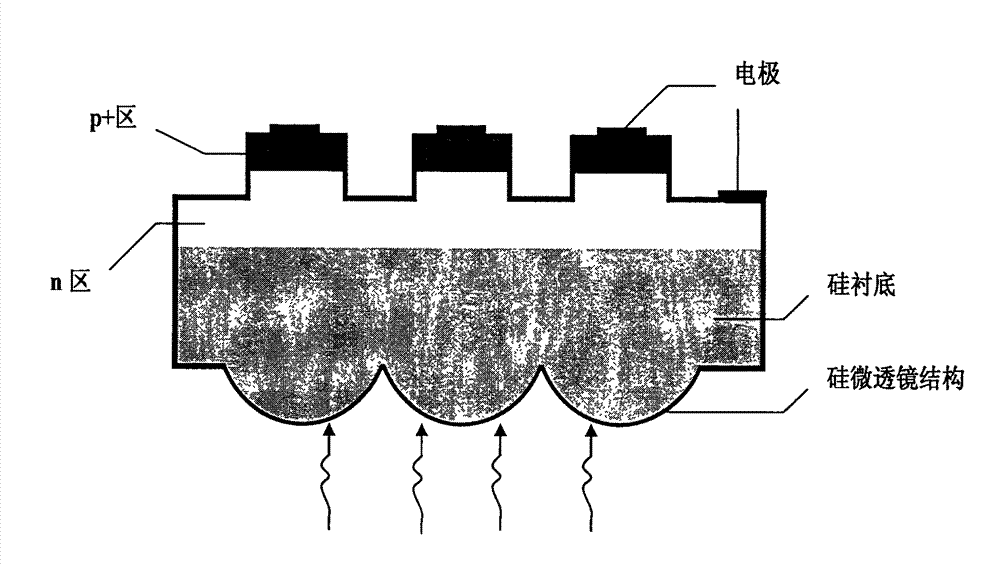
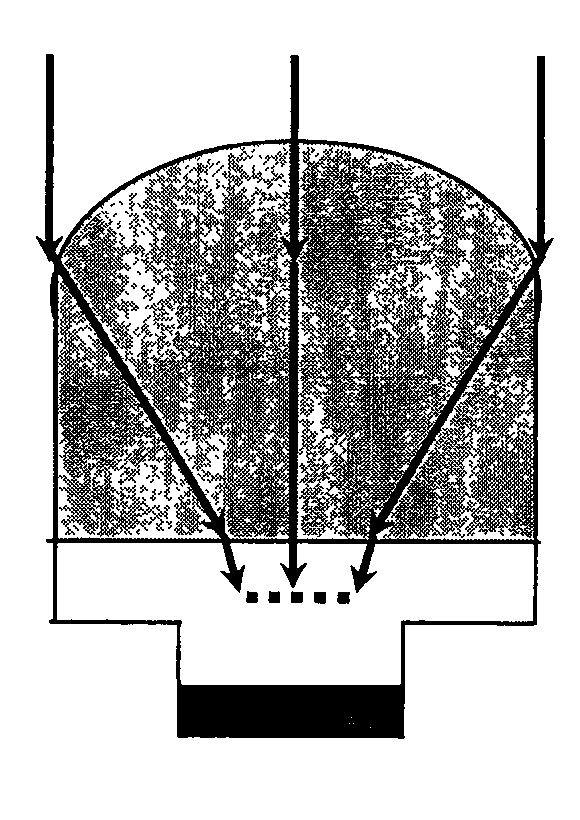
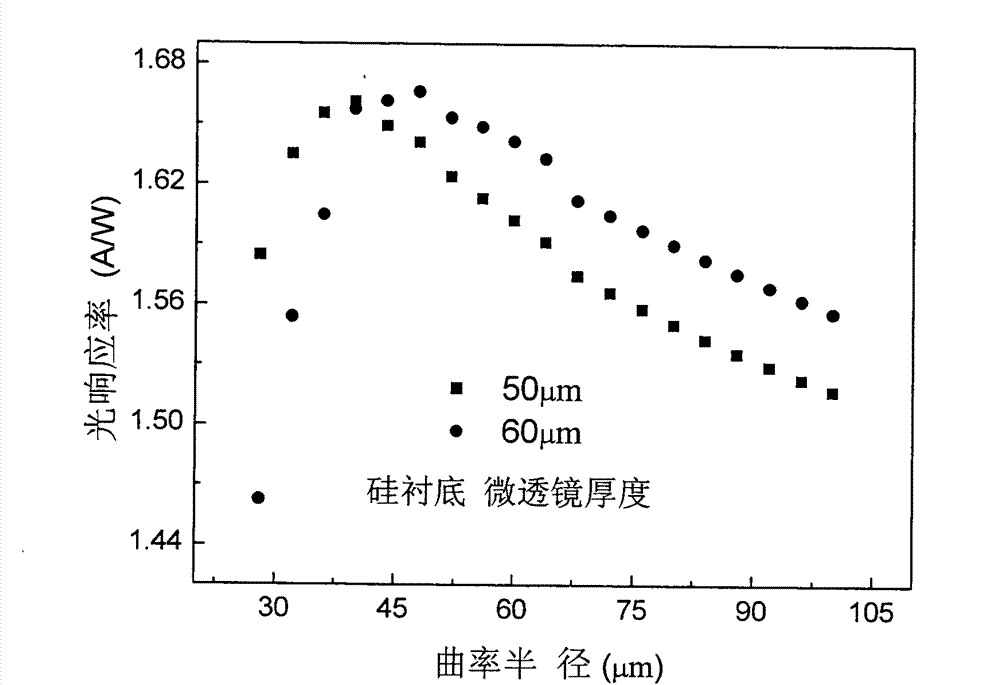
Method for optimizing light gathering ability of micro-lens array of back-illuminated infrared detector
InactiveCN102201487AHighly integratedImprove reliabilityFinal product manufactureLensDevice simulationMicro lens array
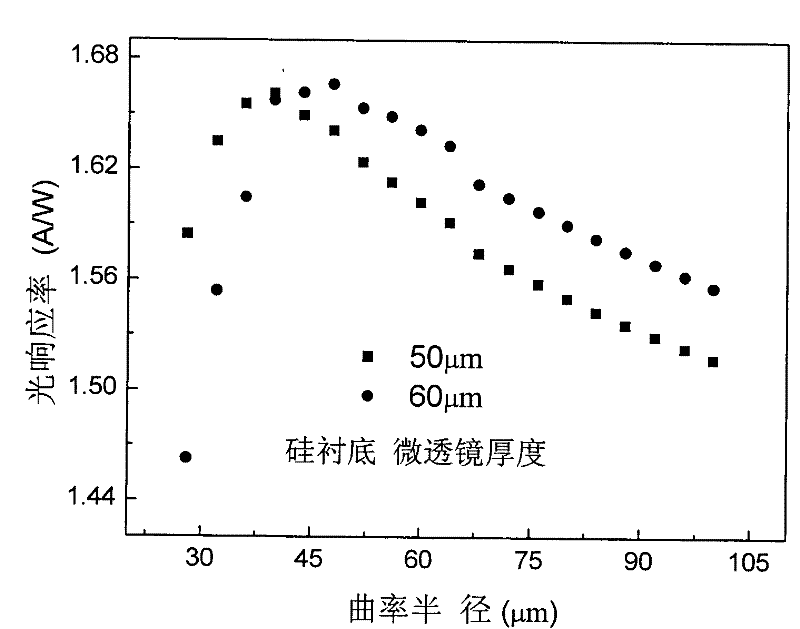
The invention discloses a method for optimizing the light gathering capability of a back-integrated micro-lens array of an InSb infrared focal plane detector. Through device simulation and theoretical calculation, the method finds that the device performance can be well improved by focusing light on a position 2.75 times of absorption distance away from an InSb-Si interface, and a micro-lens can be directly etched on a back substrate of the InSb infrared focal plane detector according to the result, thereby providing the basis for optimizing the light gathering ability of the back-integrated micro-lens array of the InSb IR focal plane detector. The method provided by the invention has important meanings for improving the device performance and optimizing the device design.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bonding of substrates
InactiveUS7148122B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygen plasmaSilicon dioxide
In one embodiment, a method comprises placing a first and a second substrate into a reaction chamber, the first substrate being made of an indium antimonide material and having a first surface and the second substrate being made of a silicon or a silicon dioxide material and having a second surface; exposing the first and second surfaces to an oxygen plasma; forming a bond between the first and the second substrates by placing the first surface in contact with the second surface; and annealing the first and the second substrates to strengthen the bond.
Owner:INTEL CORP
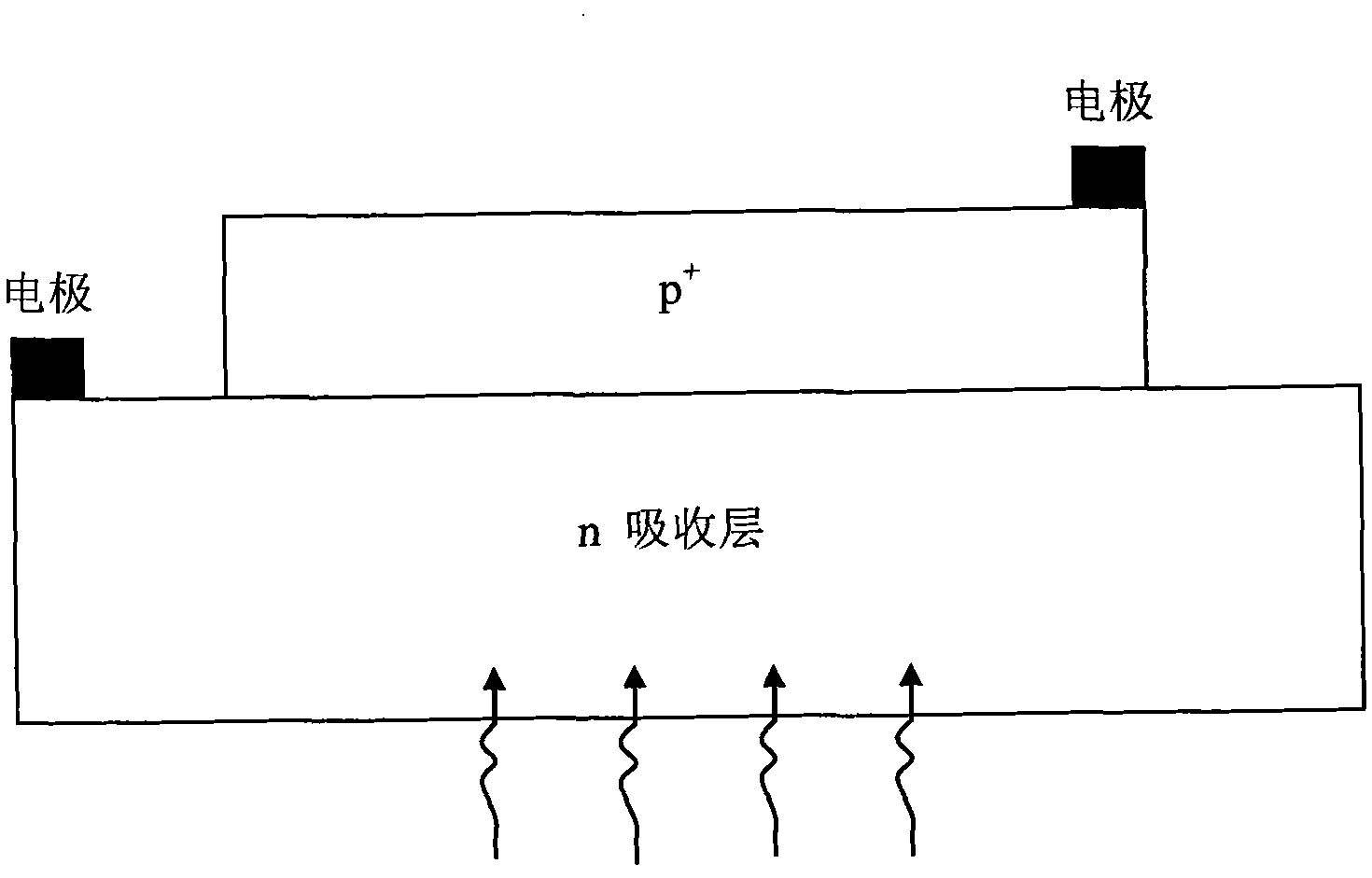
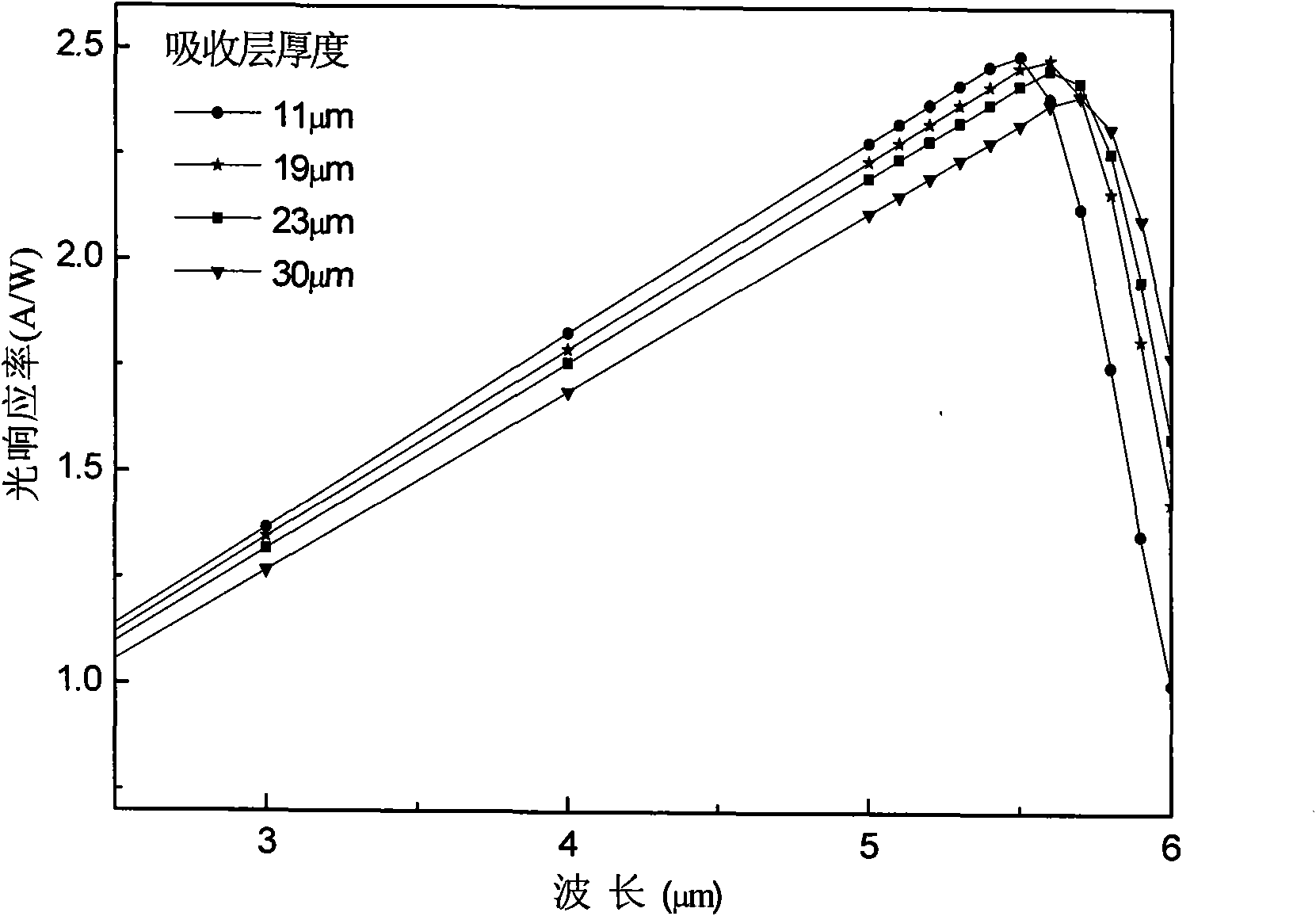
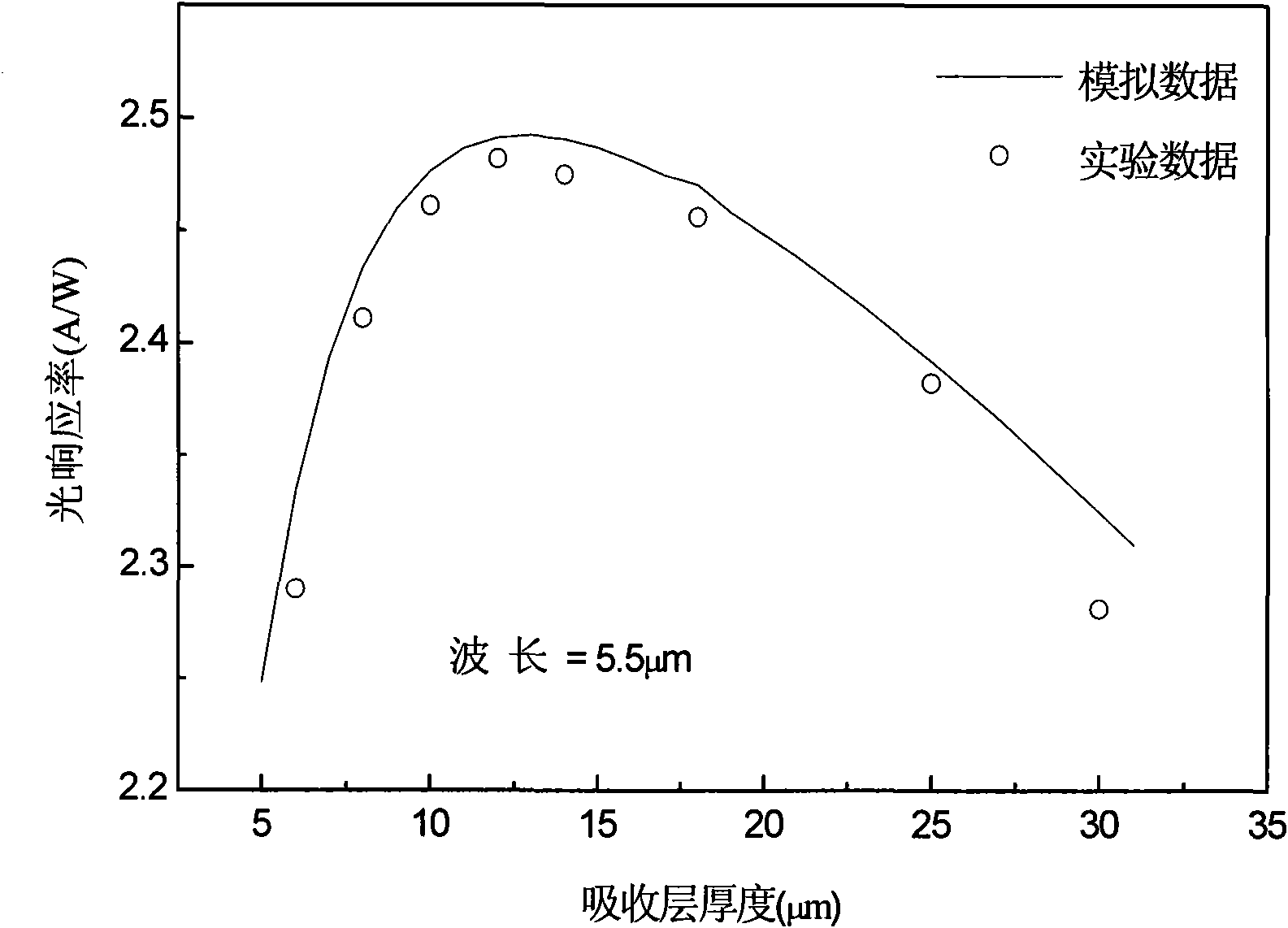
Method for optimizing thickness of absorbing layer of indium antimonide photovoltaic detection device
InactiveCN101794839AImprove performanceSimple designFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSpectral responseDevice simulation
The invention discloses a method for optimizing the thickness of the absorbing layer of an indium antimonide photovoltaic detection device. The method is that a spectral response curve under different thickness of the absorbing layer when light is irradiated in an absorbing area is obtained through device simulation, the obtained thickness of the absorbing layer corresponding to the maximum spectral response value is the optimum thickness of the absorbing layer through comparing with the spectral response data measured by experiments, and basis is further provided for the optimization of the thickness of the absorbing layer of the indium antimonide photovoltaic detection device. The invention has very great significance to the improvement of the device performance and the optimization of the device design.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of low dislocation indium antimonide (111) direction single crystal
InactiveCN109280978AImprove performanceReduce dislocationPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltLarge sizeDislocation
The invention relates to a preparation method of a low dislocation indium antimonide (111) direction single crystal, and belongs to the technical field of photoelectric materials. According to the preparation method, the temperature, the seed crystal lifting pulling speed and the shouldering angle in the crystal pulling process are mainly regulated, growth of an indium antimonide (111) direction single crystal is realized by the vertical pulling method, and the formed indium antimonide (111) direction single crystal is annealed in situ after the crystal pulling process is finished, so that thedislocation of the prepared indium antimonide (111) direction single crystal can be greatly reduced, and the dislocation density of a large size indium antimonide (111) direction single crystal witha diameter of about 50 mm is lower than 30 / cm<2>. The performance of an infrared detector prepared from the low dislocation indium antimonide (111) direction single crystal is relatively stable. The method greatly broadens the application of the indium antimonide (111) direction single crystal in infrared detectors.
Owner:云南昆物新跃光电科技有限公司
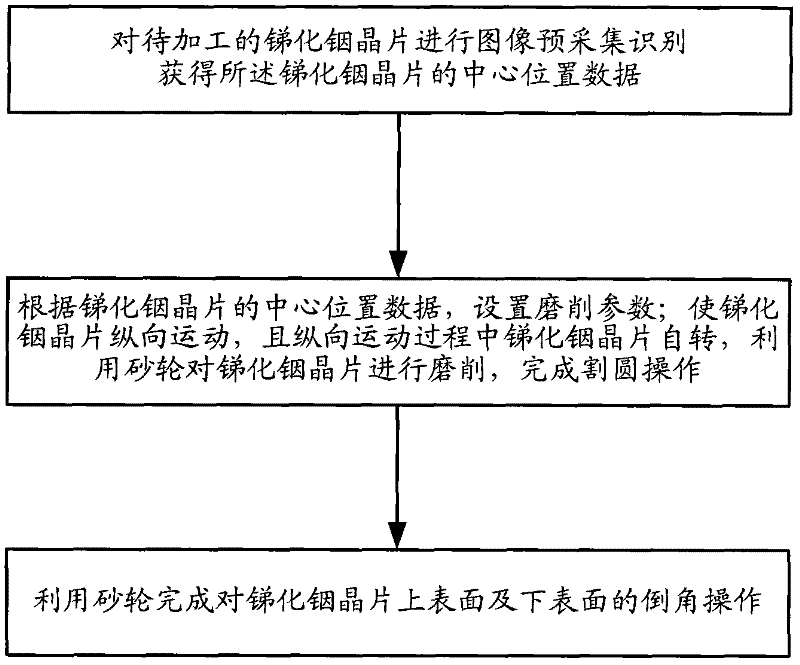
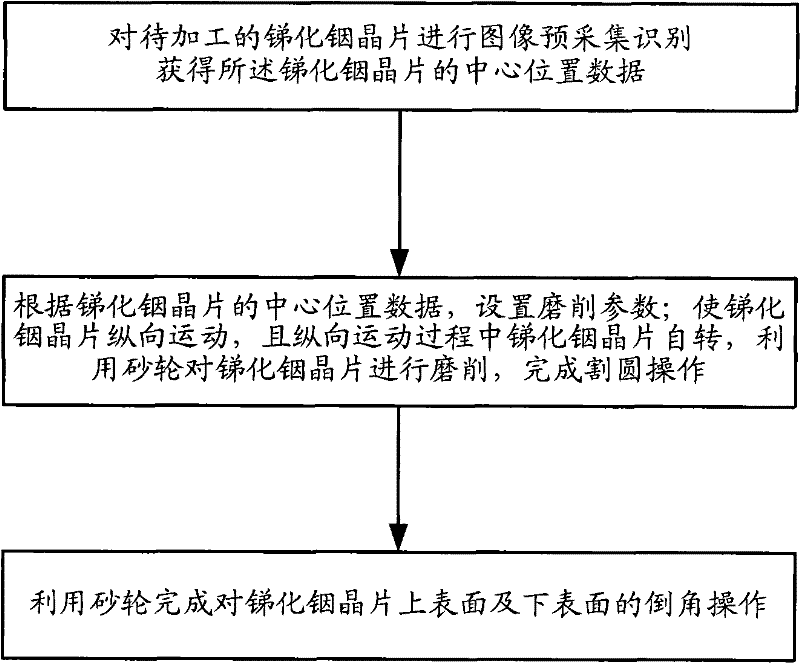
Method for grinding indium antimonide wafer
ActiveCN102172857AImprove consistencyReduce chippingEdge grinding machinesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndium antimonideEngineering
The invention discloses a method for grinding an indium antimonide wafer. The method comprises the following steps of: performing image pre-acquisition and identification on the indium antimonide wafer to be processed to acquire central position data of the indium antimonide wafer; setting grinding parameters according to the central position data of the indium antimonide wafer; making the indium antimonide wafer move longitudinally and rotate during longitudinal movement, and grinding the indium antimonide wafer by using a grinding wheel to finish circle cutting operation; and finishing chamfering operation on the upper surface and the lower surface of the indium antimonide wafer by using the grinding wheel. By the method, the positions of the center and the reference surface of the wafer are accurately positioned, and circle cutting treatment and chamfering treatment are performed during grinding after wafer identification to achieve the multi-step and accurate grinding effects. Edge breakage in the chamfering process is effectively reduced, repeatability of process conditions is ensured, the consistency of wafer appearance is improved, and the yield is improved.
Owner:11TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Four-band terahertz absorber with independent and continuously adjustable amplitude and frequency
InactiveCN111817024AWide working frequency bandPracticalAntennasOptical elementsDielectric substrateEngineering
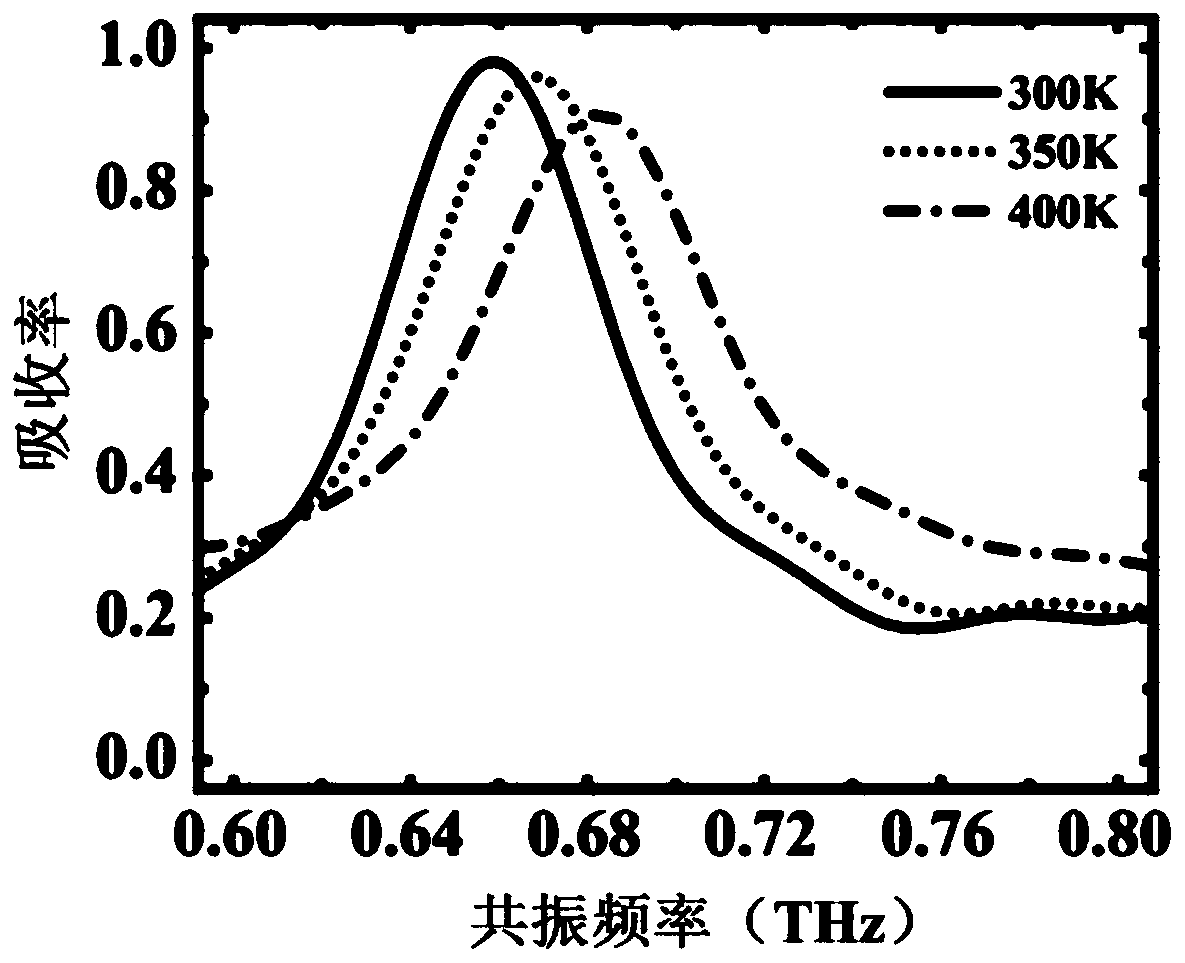
The invention provides a four-band terahertz absorber with independently and continuously adjustable amplitude and frequency. The device relates to the technical field of metamaterial and terahertz wave application. The main structure of the device comprises a dielectric substrate, a metal reflecting plate in the upper surface of the dielectric substrate, a dielectric substrate in the upper surface of the metal reflecting plate, and a composite resonance structure array in the upper surface of the dielectric substrate. Tunable materials of indium antimonide and photosensitive silicon are used,and the frequencies of four absorption frequency points are tuned by controlling the external temperature; the intensity of an external pump light source is controlled, the amplitudes of the four absorption frequency points are regulated and controlled, the effect that the amplitude and the frequency of an absorption peak are independently and continuously adjustable is achieved, and the workingfrequency band of the terahertz absorber is broadened. The four-band terahertz absorber has the advantages of strong functionality, insensitive polarization, simple structural design, strong practicability and the like.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Two-color infrared detector material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103208565AReduce detection limitHigh-resolutionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesLength waveWavelength range
The invention discloses a two-color infrared detector material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps of pre-treating an indium antimonide (InSb) crystal to obtain an epitaxial-level InSb substrate; and setting a parameter of an aluminium (Al) component in indium aluminium antimonide (InAlSb) according to a response wavelength range, and growing a lower electrode layer, an absorption layer, a barrier layer, a middle electrode layer, an absorption layer and an upper electrode layer of the InAlSb on the epitaxial-level InSb substrate sequentially, wherein the growth temperature is within a range of 400-450 DEG C, and the Sb / (In+Al) beam ratio is within a range of 1.2-10. By the aid of the two-color infrared detector material, two different wavelength ranges can be detected simultaneously, detection limits of environments on a two-color infrared detector are greatly reduced, and the detection effect is improved.
Owner:11TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
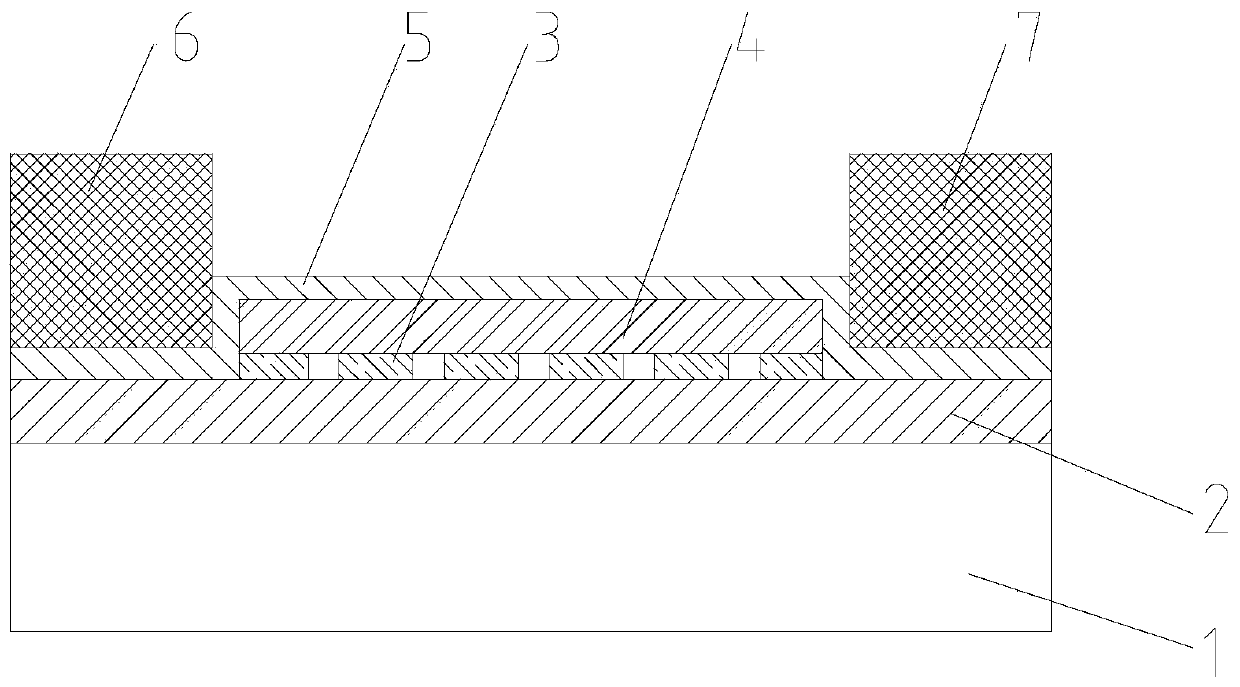
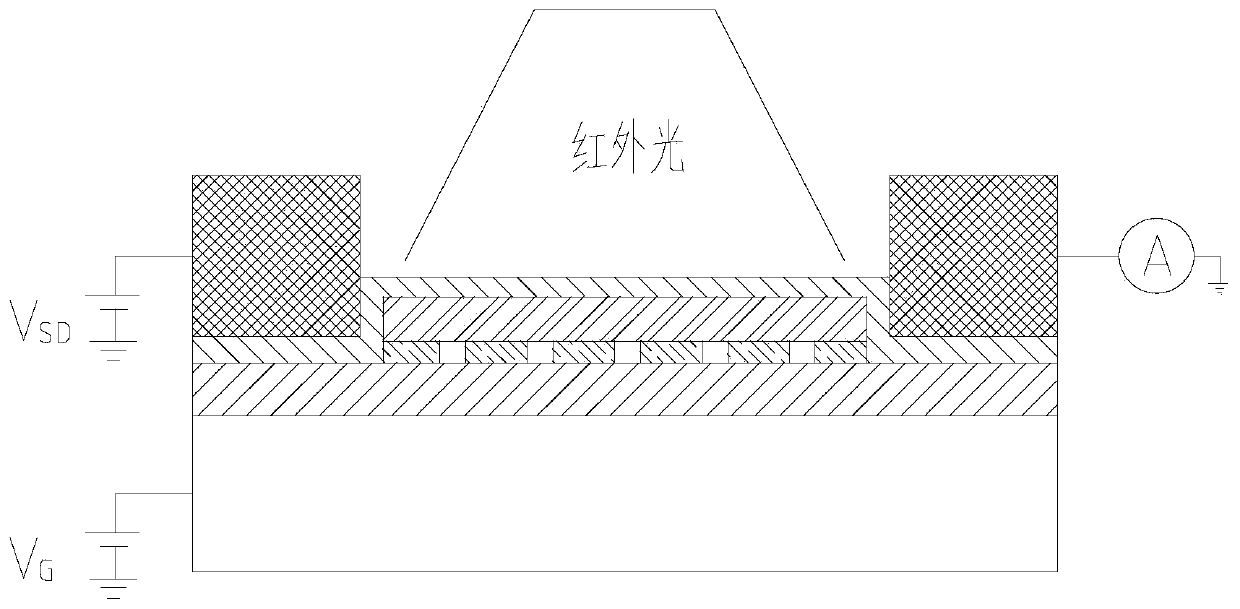
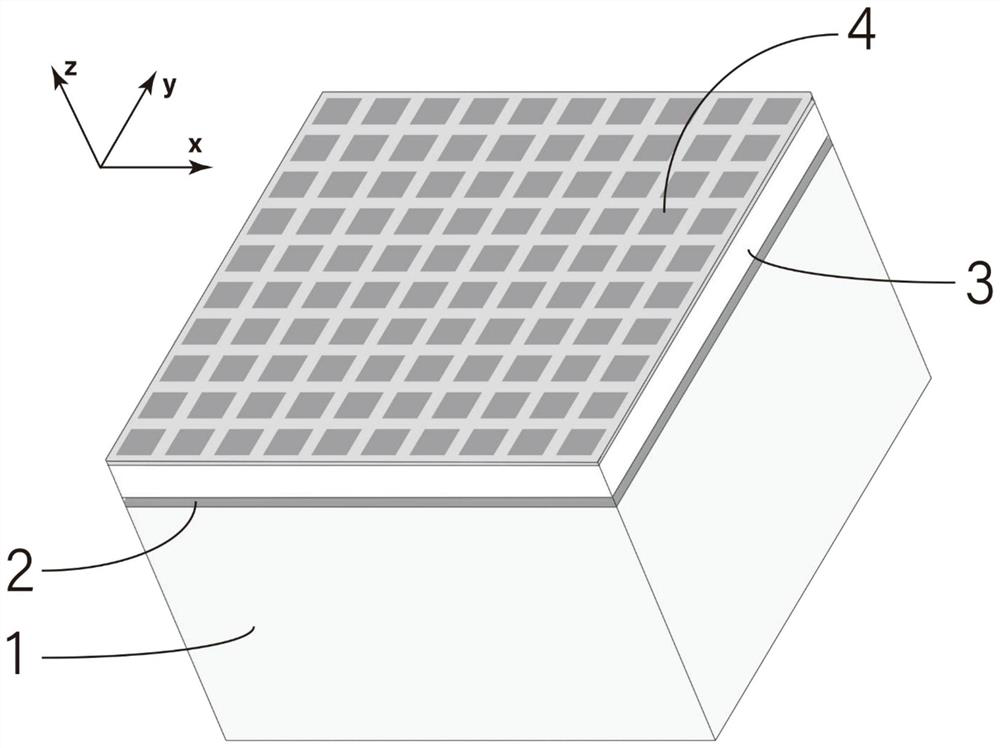
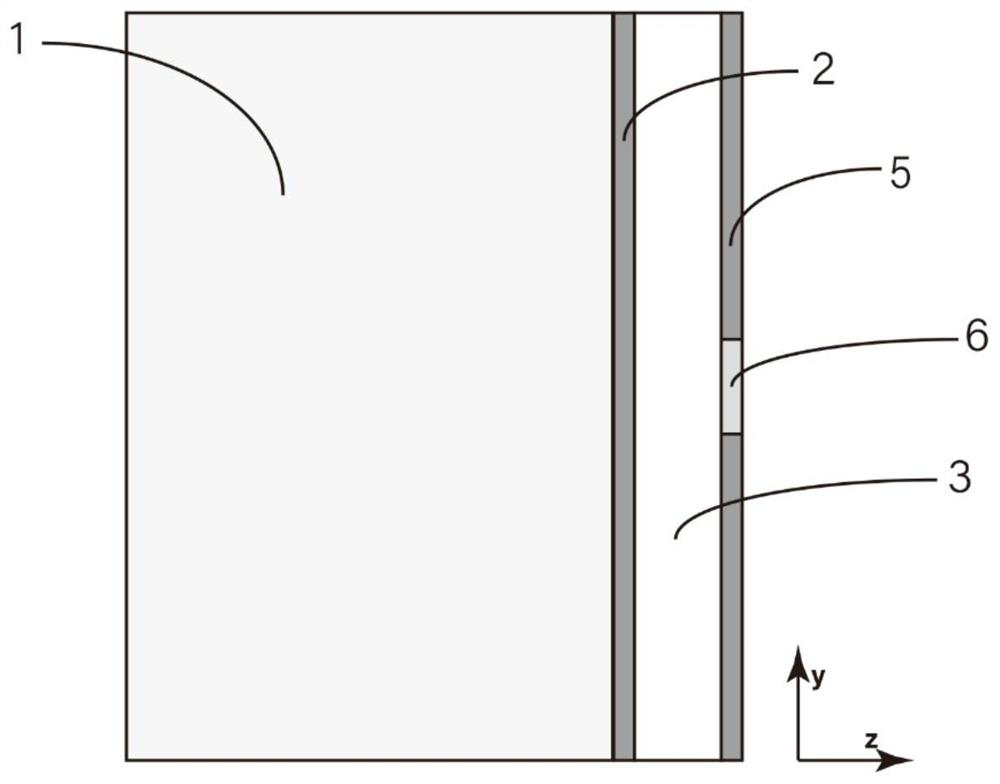
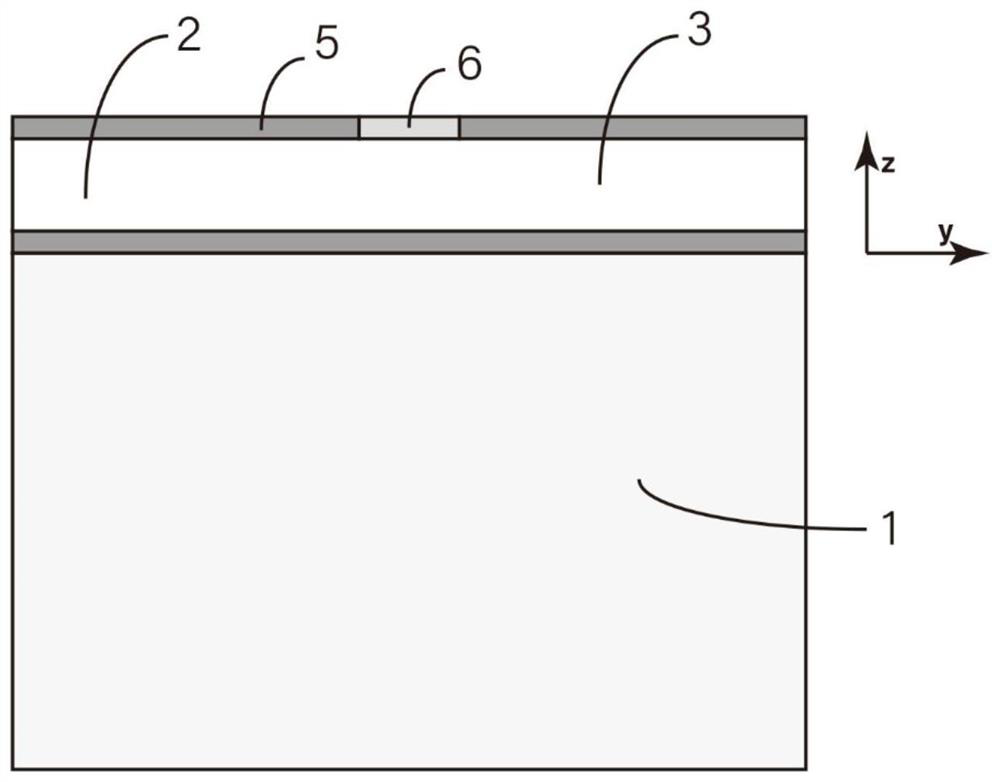
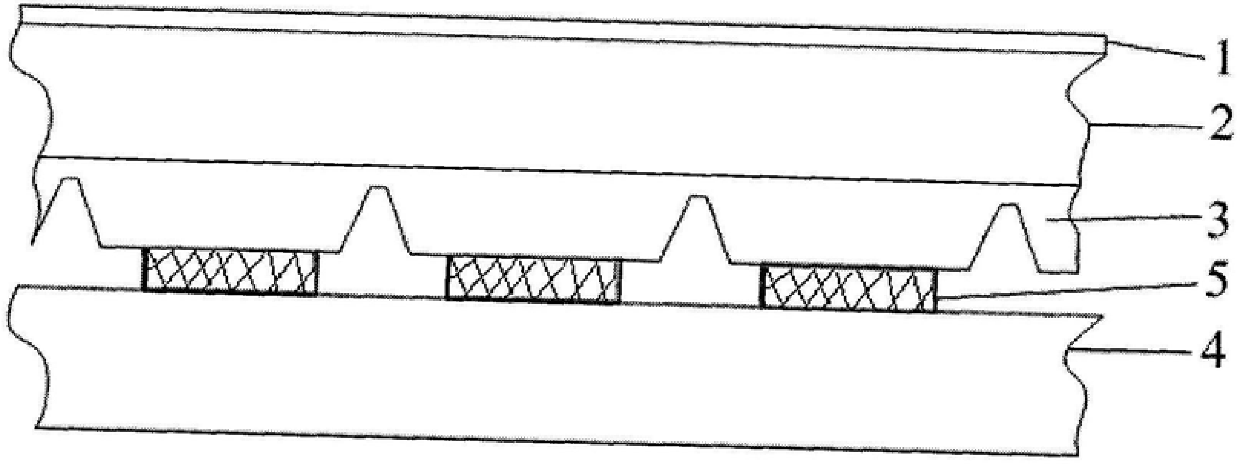
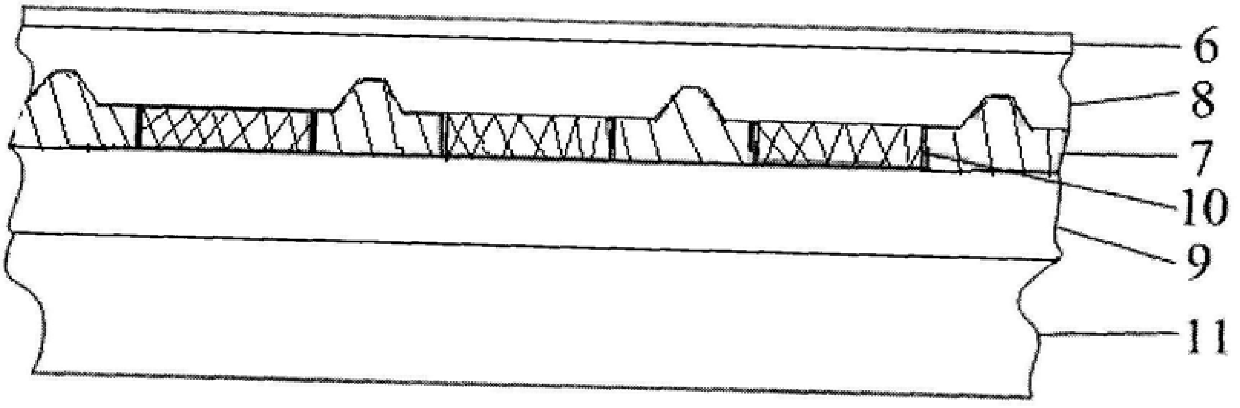
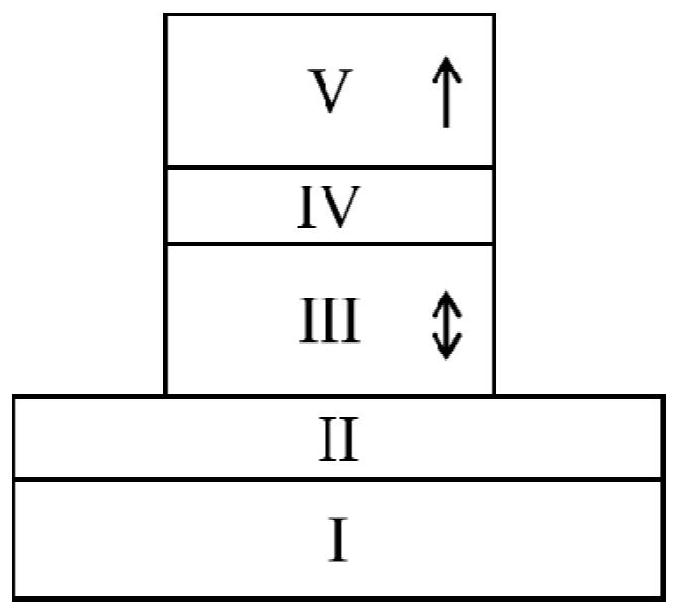
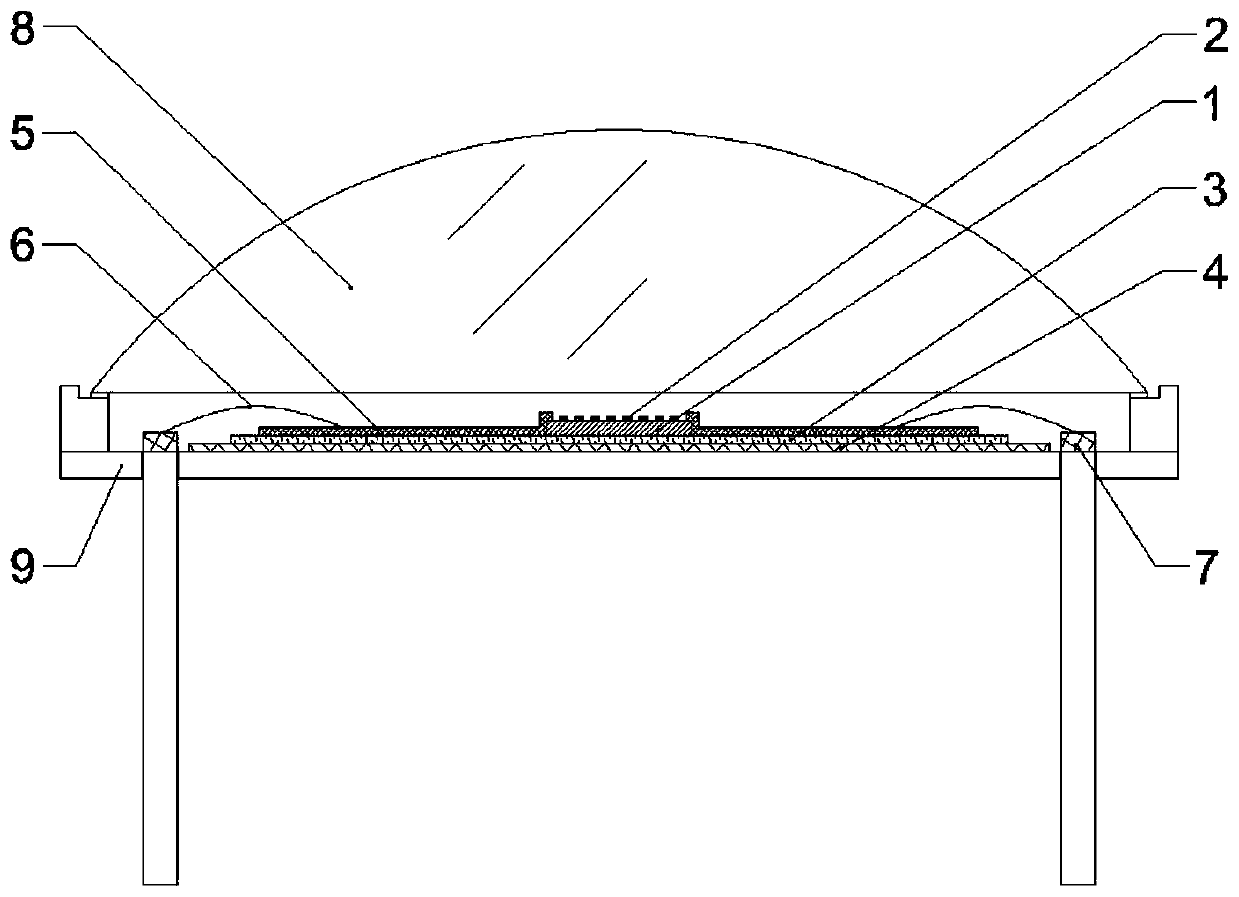
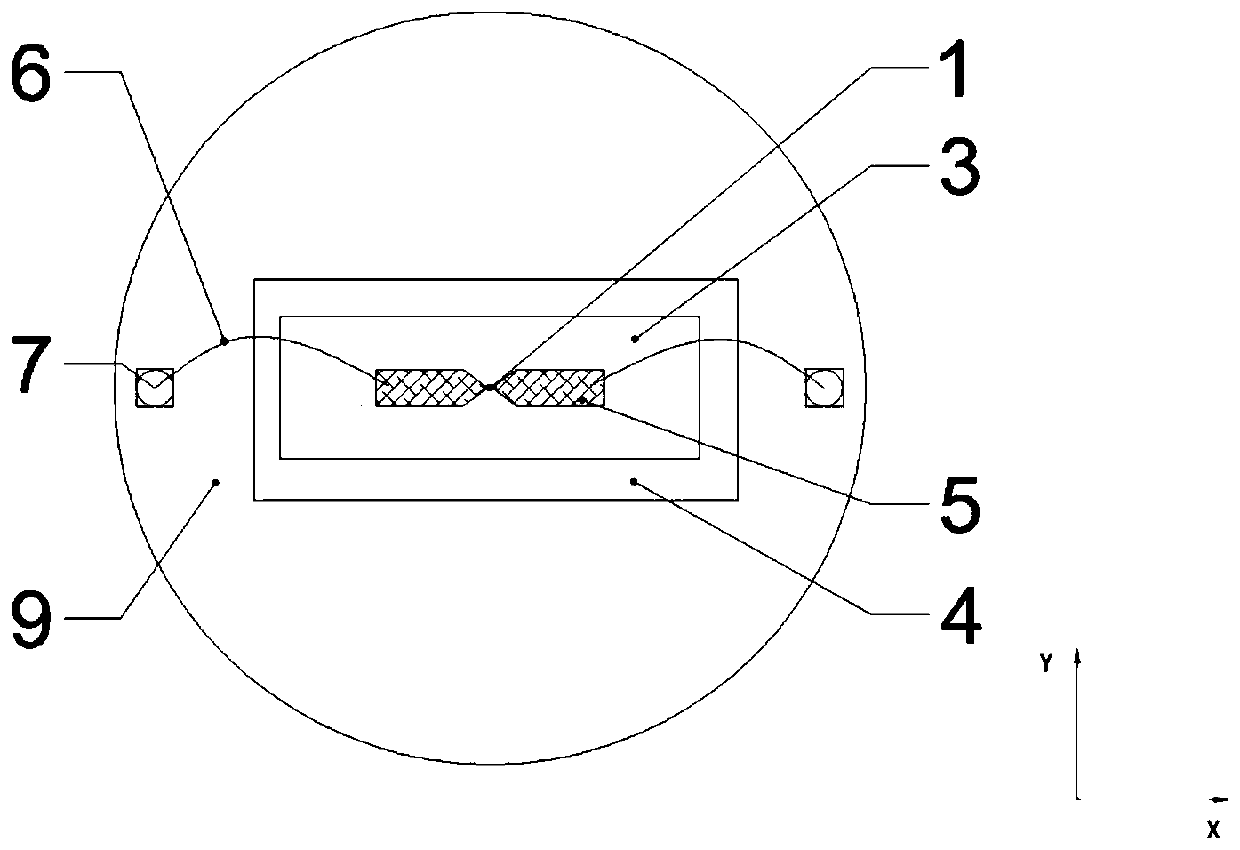
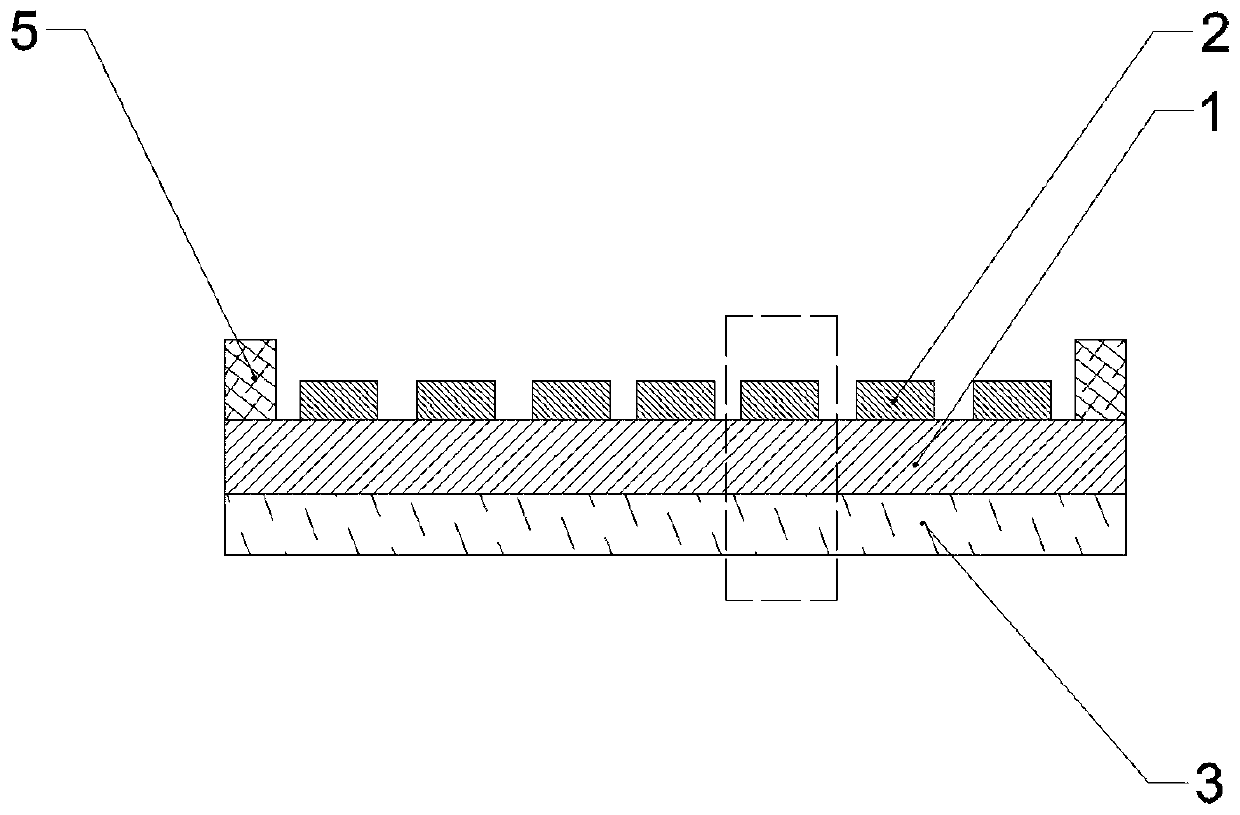
Indium antimonide infrared focal plane array detector chip and manufacturing method thereof
An indium antimonide infrared focal plane array detector chip, which includes an antireflection film [6], a low-temperature glue [7], an indium antimonide photosensitive array [8], a silicon readout circuit [9], and an indium column [10] , InSb substrate [11]. Wherein, the indium antimonide photosensitive array [8] is provided with an antireflection film [6] on the back, and an indium pillar [10] is provided on the front. The other end of the indium column [10] is connected to the silicon readout circuit [9], and the backside of the silicon readout circuit [9] is provided with an indium antimonide substrate [11], and the indium antimonide photosensitive array [8], the silicon A low-temperature glue [7] is arranged in the gap between the readout circuit [9] and the indium column [10]. The indium antimonide infrared focal plane array detector chip of the invention achieves thermal matching with the indium antimonide photosensitive array and the silicon readout circuit, reduces strain, and makes the indium antimonide infrared focal plane array detector have higher reliability. In addition, the invention provides a method for manufacturing the indium antimonide infrared focal plane array detector chip.
Owner:CHINA AIR TO AIR MISSILE INST
Sensor for identifying magnetism of medium
InactiveCN102721938AHigh sensitivityImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic property measurementsHigh volume manufacturingHall element
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
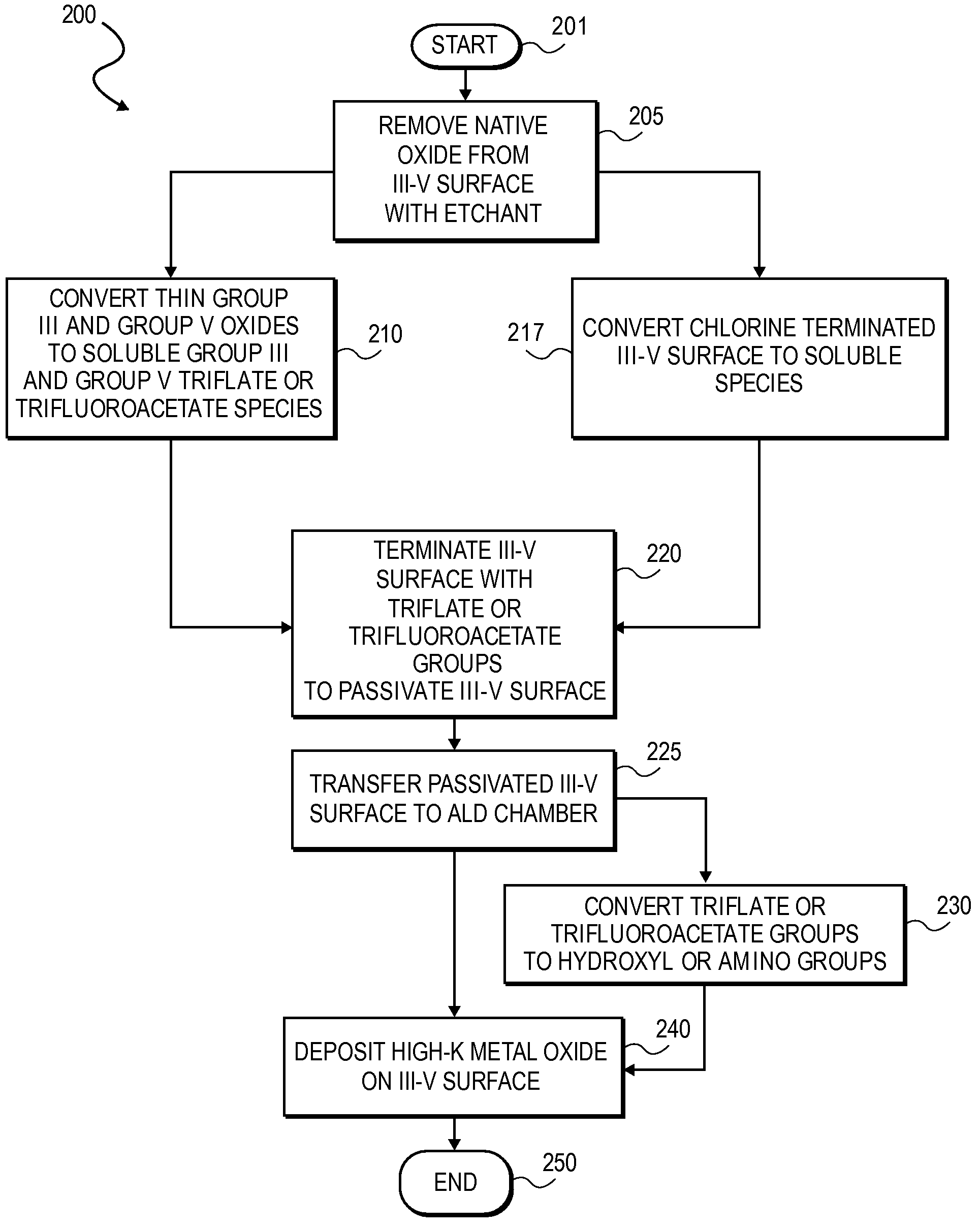
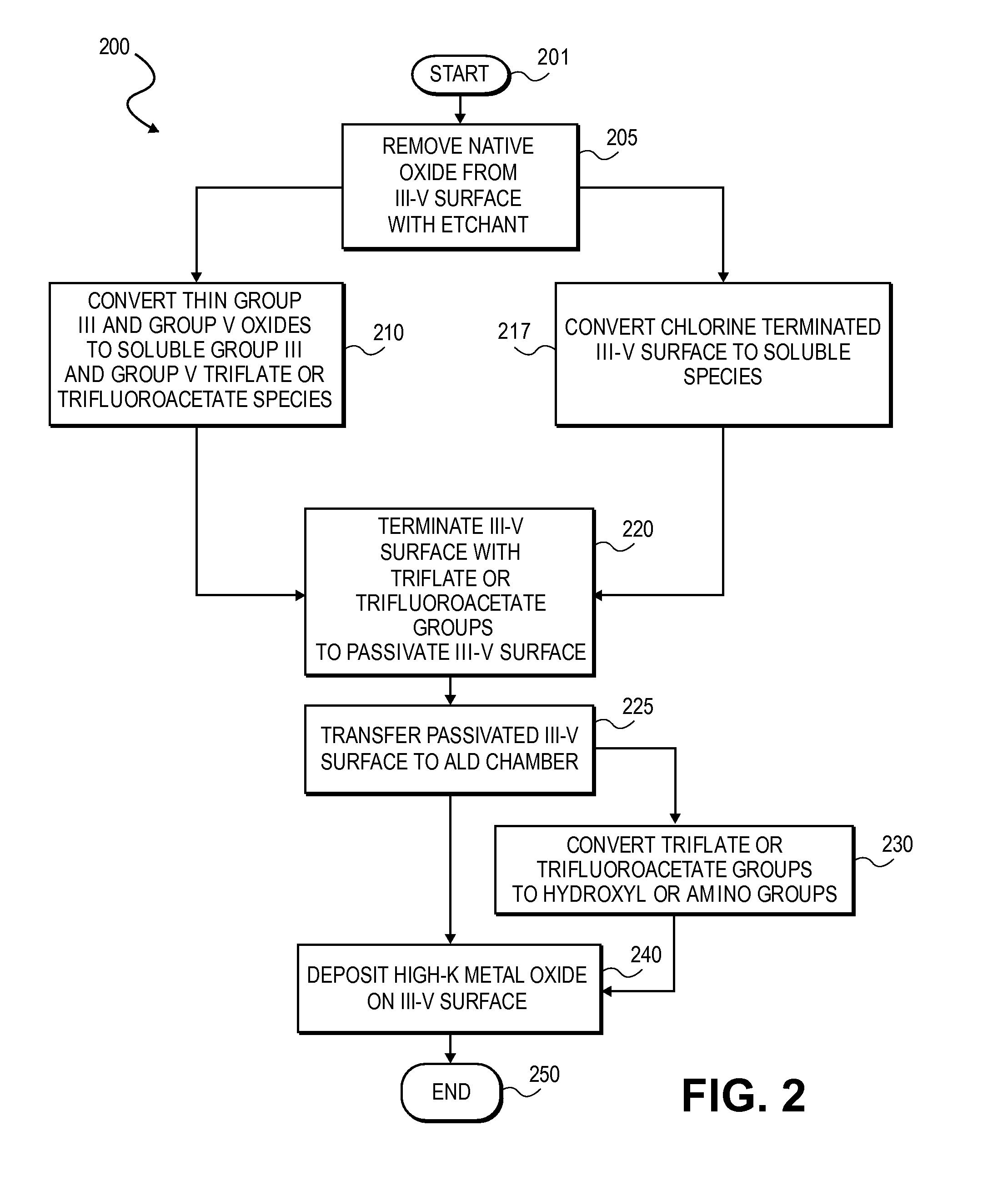
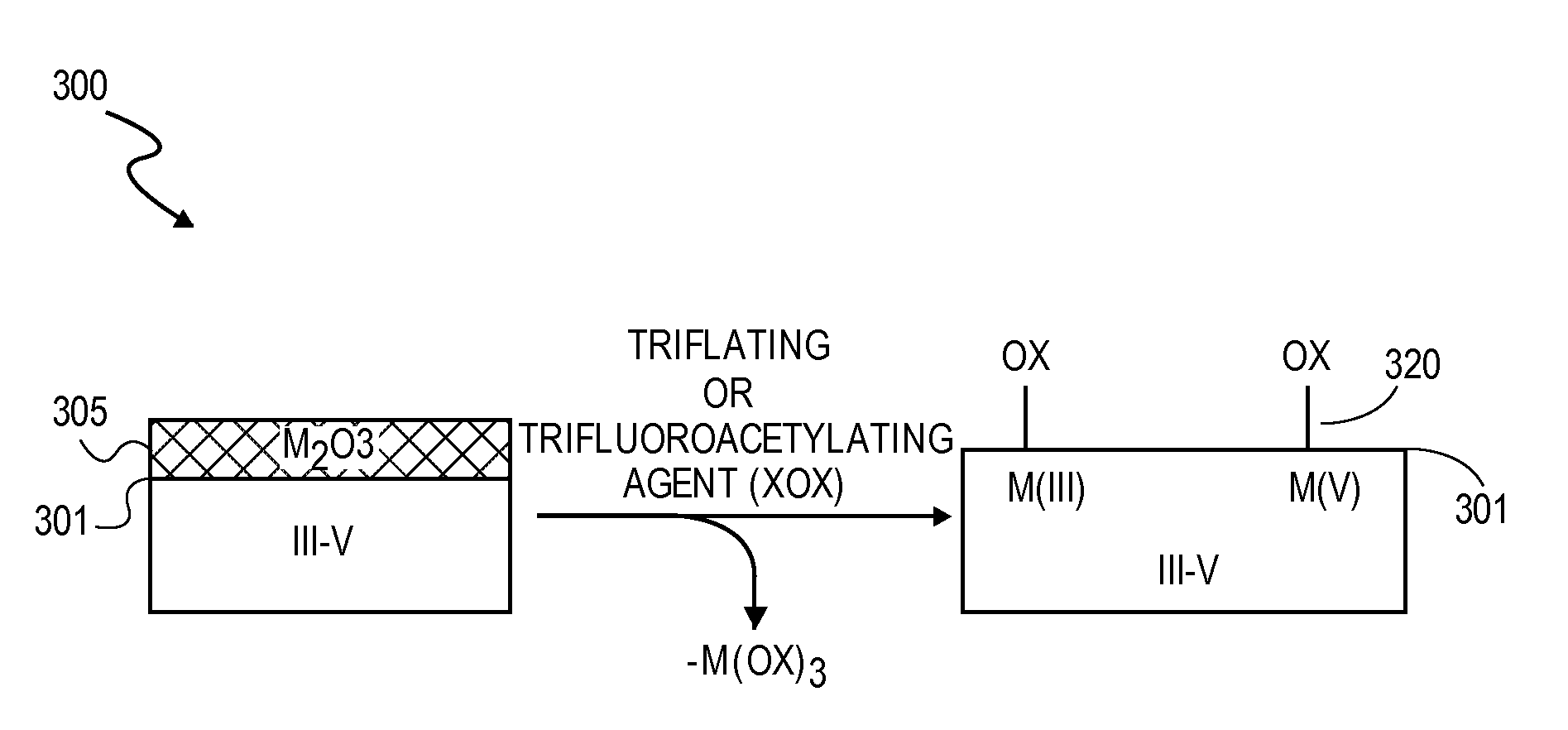
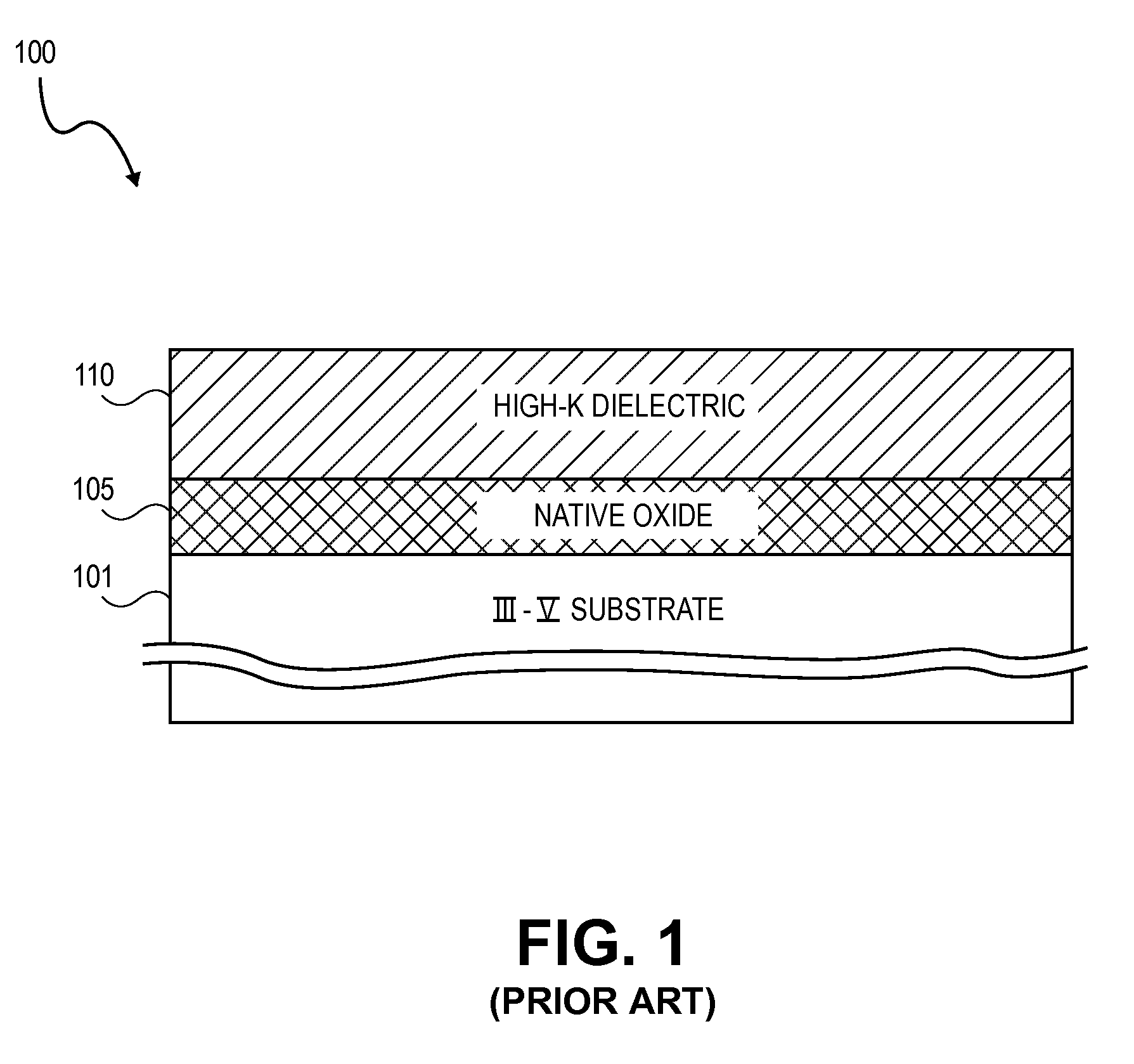
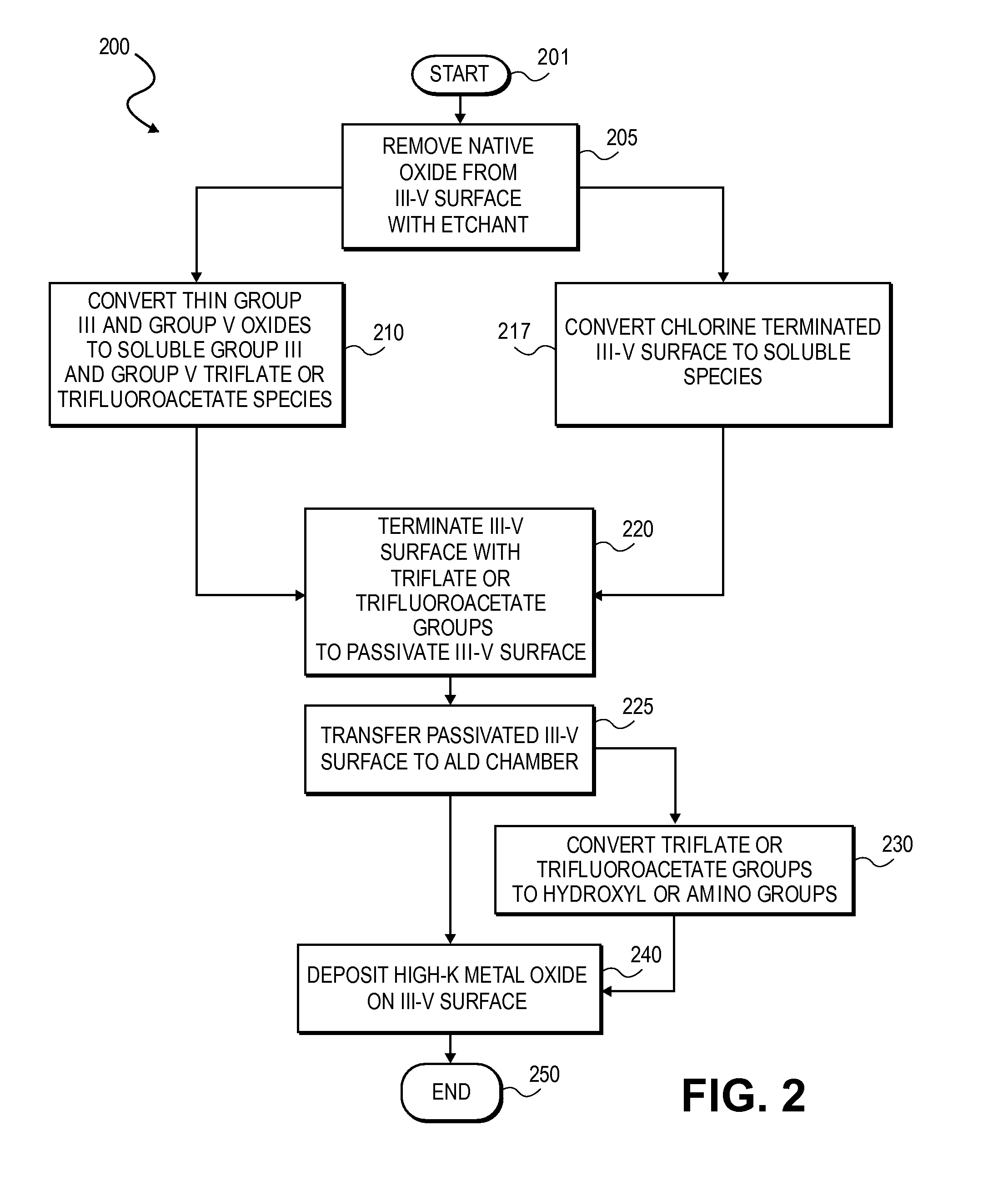
High K dielectric growth on metal triflate or trifluoroacetate terminated III-V semiconductor surfaces
InactiveUS7763317B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrifluoromethanesulfonic anhydrideTriflic acid
Surface preparation of a compound semiconductor surface, such as indium antimonide (InSb), with a triflating agent, such as triflic anhydride or a trifluoroacetylating agent, such as trifluoroacetic anhydride is described. In one embodiment, the triflating or trifluoroacetylating passivates the compound semiconductor surface by terminating the surface with triflate trifluoroacetate groups. In a further embodiment, a triflating agent or trifluoroacetylating agent is employed to first convert a thin native oxide present on a compound semiconductor surface to a soluble species. In another embodiment, the passivated compound semiconductor surface is activated in an ALD chamber by reacting the triflate or trifluoroacetate protecting groups with a protic source, such as water (H2O). Metalorganic precursors are then introduced in the ALD chamber to form a good quality interfacial layer, such as aluminum oxide (Al2O3), on the compound semiconductor surface.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Chemical and mechanical polishing liquid for semiconductor indium antimonide
InactiveCN1858136ASolve the scratching problemNo viscosityPolishing compositionsSurface roughnessSemiconductor
The present invention discloses a kind of chemical and mechanical polishing liquid for polishing semiconductor indium antimonide, and the polishing liquid has organic alkali to replace inorganic alkali, increased chelating agent and activator to result in less scoring and high flatness of indium antimonide surface. The polishing liquid of the present invention consists of silica sol of SiO2 concentration 30-50% in 50-98 vol%, amine alkali 0.1-1.5 vol%, chelating agent 0.1-0.5 vol%, surfactant 0.5-2 vol%, oxidant 0.5-2 vol% and deionized water for the rest. The present invention has less scoring in the surface of indium antimonide, lowered surface roughness of indium antimonide and simple post cleaning.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
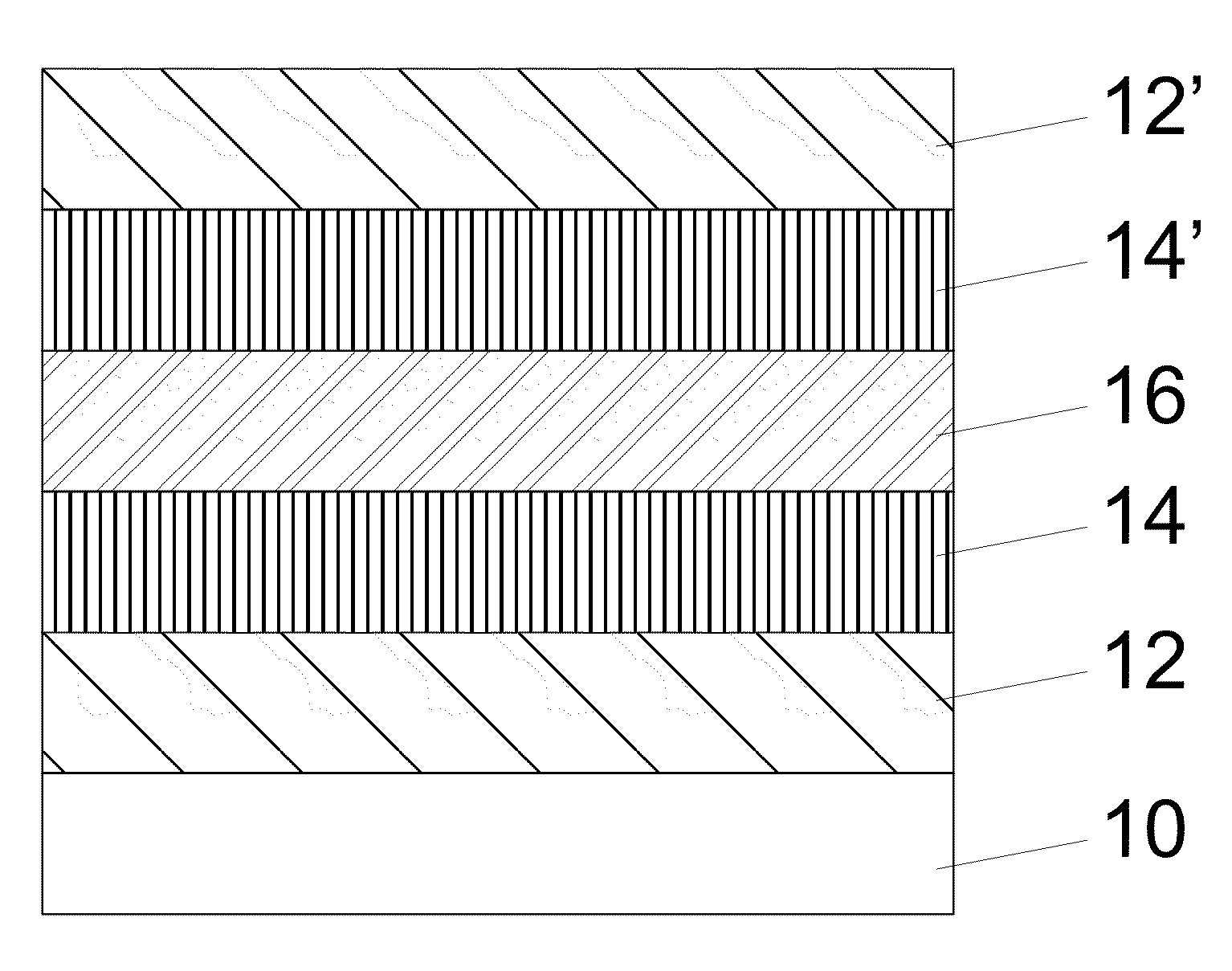
Long wavelength infrared superlattice
ActiveUS8426845B2Extend the cutoff wavelengthTotal current dropNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGallium antimonideIndium arsenide
An embodiment of the present invention improves the fabrication and operational characteristics of a type-II superlattice material. Layers of indium arsenide and gallium antimonide comprise the bulk of the superlattice structure. One or more layers of indium antimonide are added to unit cells of the superlattice to provide a further degree of freedom in the design for adjusting the effective bandgap energy of the superlattice. One or more layers of gallium arsenide are added to unit cells of the superlattice to counterbalance the crystal lattice strain forces introduced by the aforementioned indium antimonide layers.
Owner:SVT ASSOCS
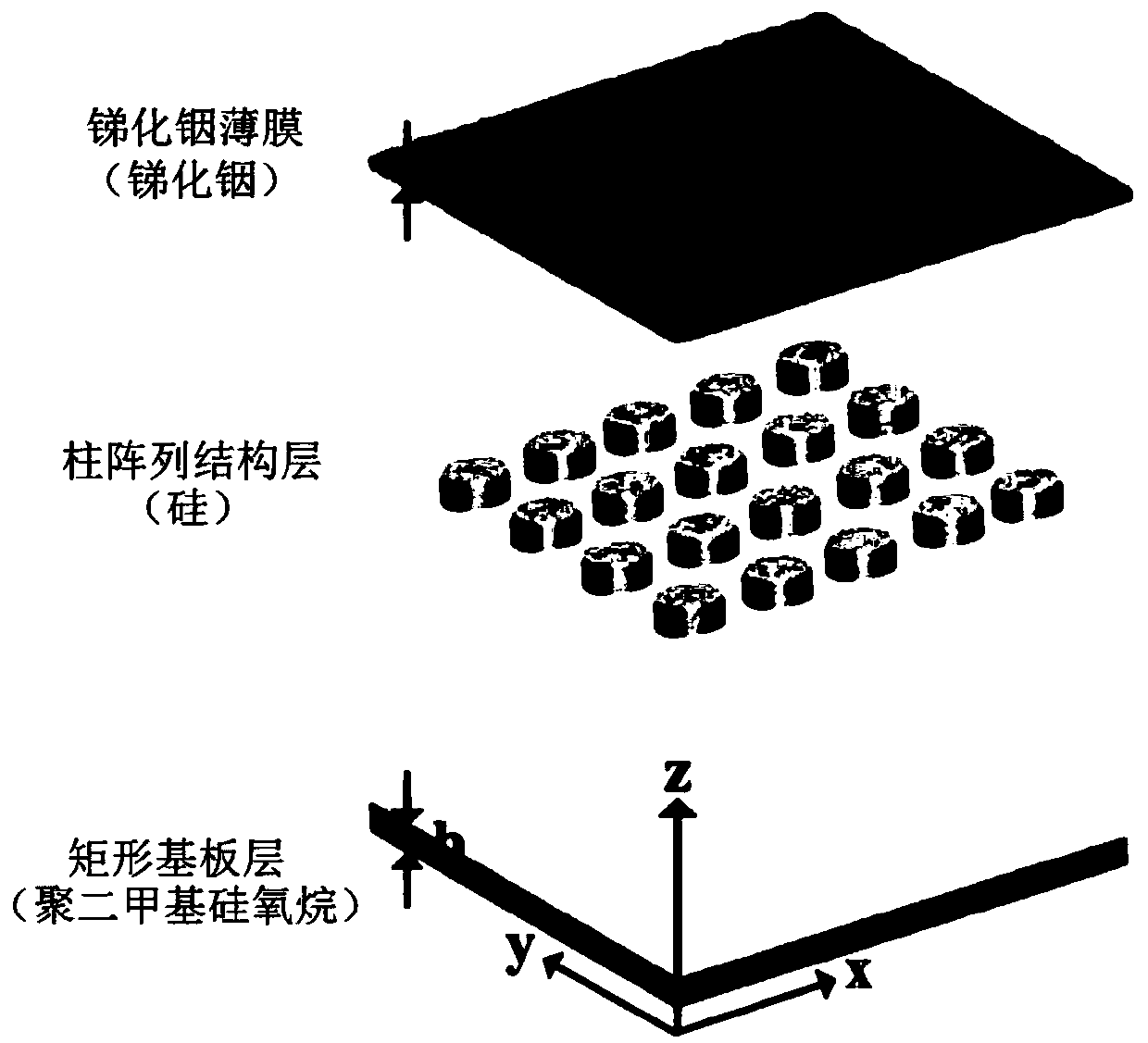
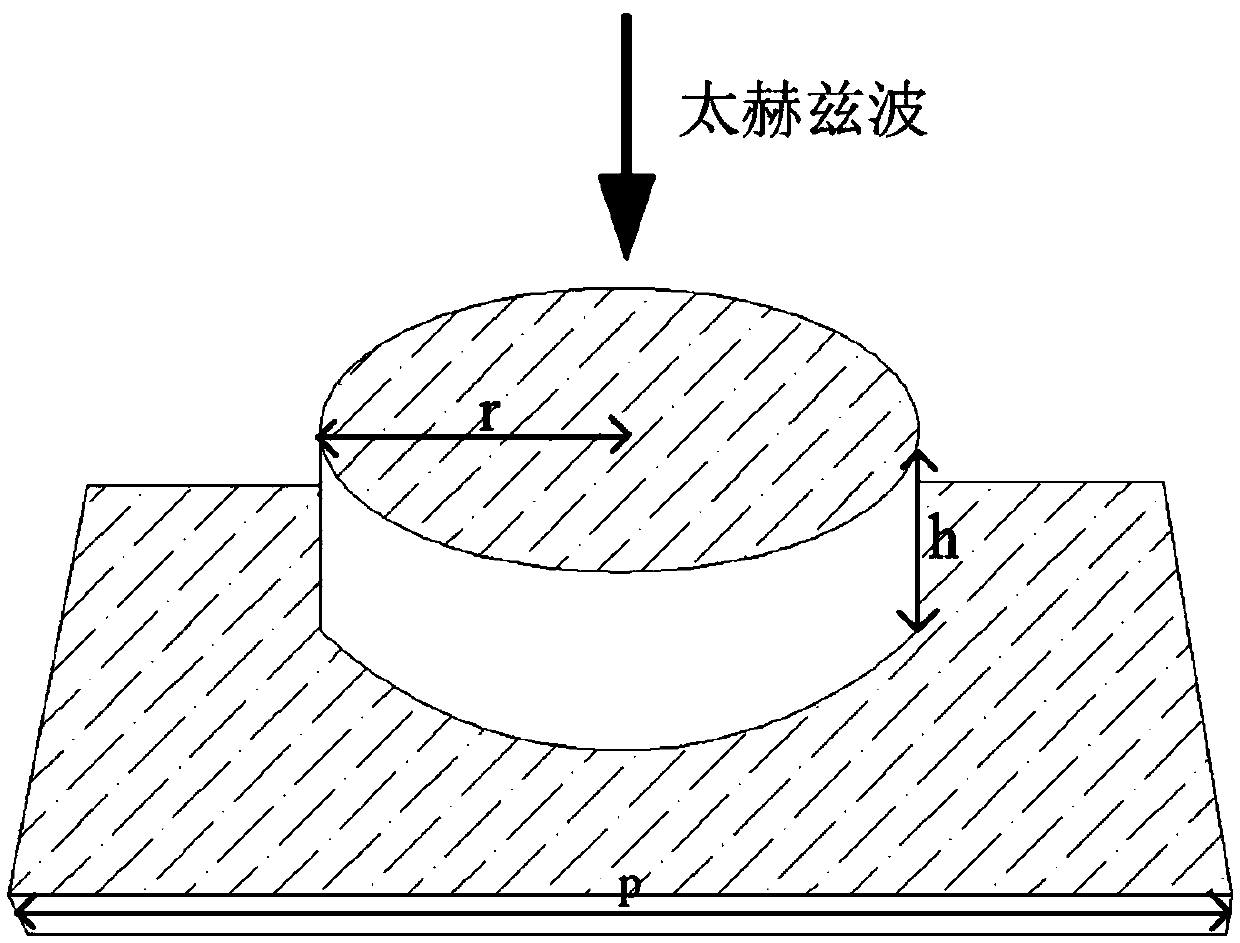
Indium antimonide thin film terahertz metasurface and thermal tuning method and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109683213ATuning method is simpleLarge tuning rangeNon-linear opticsOptical elementsWave resonanceMaterials science
The embodiment of the invention provides an indium antimonide thin film terahertz metasurface and a thermal tuning method and preparation method thereof. The terahertz metasurface is arranged to be ofa three-layer structure comprising a rectangular substrate layer, a column array structure layer and an indium antimonide thin film so that the dielectric constant of the indium antimonide thin filmcan be changed along with temperature change, and the resonance frequency of the terahertz metasurface is changed. Therefore, the terahertz metasurface can change the resonance frequency by changing the temperature, and meanwhile, the tuning range of the terahertz wave resonance frequency is enlarged. The terahertz metasurface is simple in preparation method and suitable for being widely applied to the field of photoelectric manufacturing, so that the application range of the terahertz metasurface is widened.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Preparation method of indium antimonide (211) direction single crystal
InactiveCN108166060AReduce dislocationImprove performancePolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsGallium antimonideDislocation
Belonging to the technical field of photoelectric materials, the invention relates to a preparation method of an indium antimonide (211) direction single crystal. The method mainly regulates the temperature, the seed crystal pulling speed and the shouldering angle of the crystal pulling process, and successfully realizes preparation of the indium antimonide (211) direction single crystal. Moreover, through in-situ annealing treatment on the crystal pulled indium antimonide (211) direction single crystal, the dislocation density of the prepared indium antimonide (211) direction single crystal is greatly reduced. Compared with an indium antimonide (111) direction single crystal, an infrared detector prepared from the indium antimonide (211) direction single crystal provided by the inventionhas more stable performance. The invention provides a technical scheme for successful preparation of the indium antimonide (211) direction single crystal, and greatly broadens application of the indium antimonide (211) direction single crystal to infrared detectors.
Owner:云南昆物新跃光电科技有限公司
High k dielectric growth on metal triflate or trifluoroacetate terminated iii-v semiconductor surfaces
InactiveUS20080241423A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrifluoromethanesulfonic anhydrideTrifluoroacetic acid
Surface preparation of a compound semiconductor surface, such as indium antimonide (InSb), with a triflating agent, such as triflic anhydride or a trifluoroacetylating agent, such as trifluoroacetic anhydride is described. In one embodiment, the triflating or trifluoroacetylating passivates the compound semiconductor surface by terminating the surface with triflate trifluoroacetate groups. In a further embodiment, a triflating agent or trifluoroacetylating agent is employed to first convert a thin native oxide present on a compound semiconductor surface to a soluble species. In another embodiment, the passivated compound semiconductor surface is activated in an ALD chamber by reacting the triflate or trifluoroacetate protecting groups with a protic source, such as water (H2O). Metalorganic precursors are then introduced in the ALD chamber to form a good quality interfacial layer, such as aluminum oxide (Al2O3), on the compound semiconductor surface.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method for optimizing light gathering ability of micro-lens array of back-illuminated infrared detector
InactiveCN102201487BHighly integratedImprove reliabilityFinal product manufactureLensDevice simulationMicro lens array
The invention discloses a method for optimizing the light gathering capability of a back-integrated micro-lens array of an InSb infrared focal plane detector. Through device simulation and theoretical calculation, the method finds that the device performance can be well improved by focusing light on a position 2.75 times of absorption distance away from an InSb-Si interface, and a micro-lens can be directly etched on a back substrate of the InSb infrared focal plane detector according to the result, thereby providing the basis for optimizing the light gathering ability of the back-integrated micro-lens array of the InSb IR focal plane detector. The method provided by the invention has important meanings for improving the device performance and optimizing the device design.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
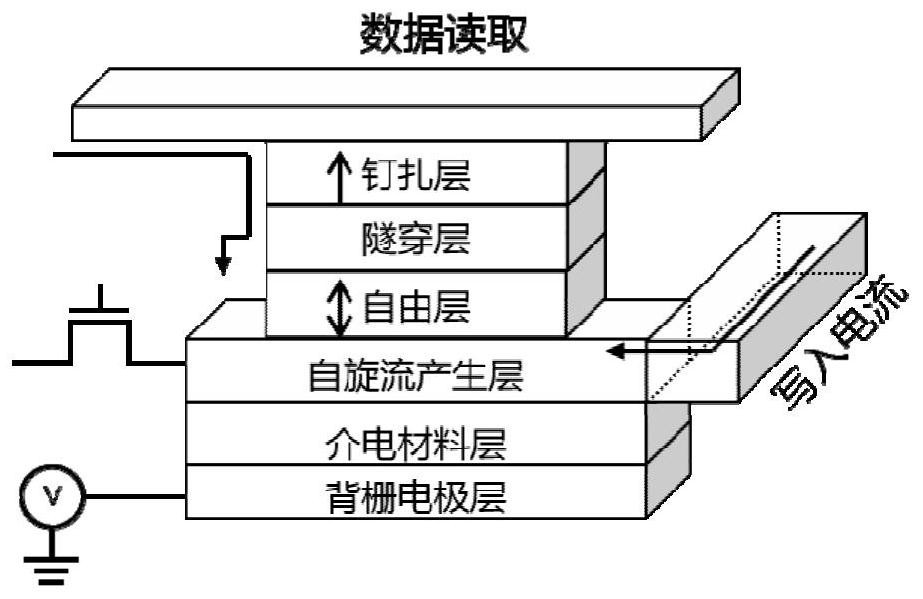
Magnetic random access memory based on III-V group narrow bandgap semiconductor
ActiveCN112054116AReduce power consumptionIncrease power consumptionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsIndium
The invention relates to a magnetic random access memory based on an III-V group narrow bandgap semiconductor, the magnetic random access memory is characterized by sequentially comprising a substratewafer, a dielectric layer, a spin orbit torque acting layer and an MTJ structure layer from bottom to top, and the dielectric layer is made of a cadmium telluride CdTe or zinc telluride ZnTe material; and the spin orbit torque acting layer is made of a III-V group narrow bandgap semiconductor indium antimonide InSb or indium arsenide InAs with high mobility. The structure based on the III-V semiconductor material not only can be matched with an existing semiconductor CMOS process, but also can provide spin orbit coupling strength higher than that of a traditional heavy metal SOT material, andtherefore the problem of power consumption of device write-in current is effectively solved. In addition, the spin orbit coupling strength can be regulated and controlled by applying the back gate voltage, so that the power consumption of the device is further improved. And through electric field control, the programmable and storage integrated capability of the modified device array can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECH UNIV
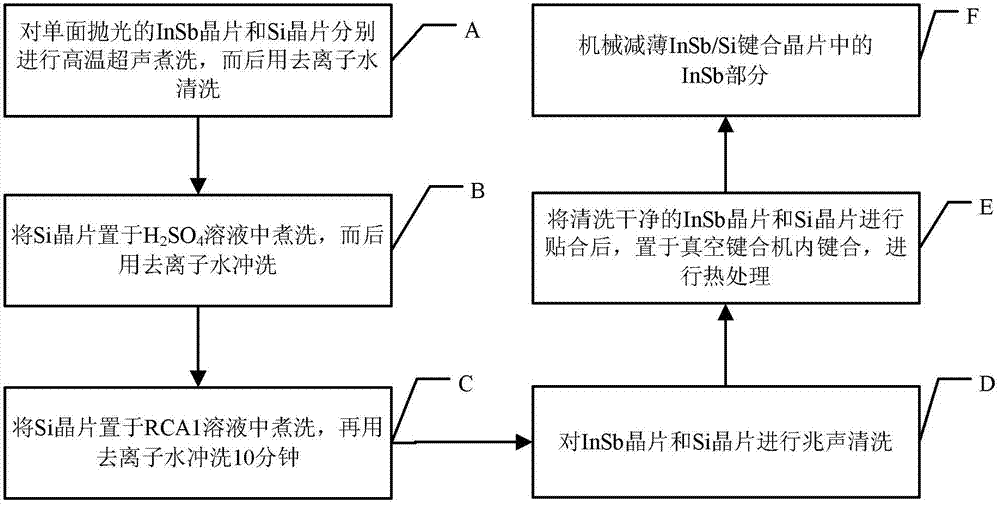
Indium antimonide (InSb) wafer and silicon (Si) wafer bonding method
InactiveCN103199156ASimple processPracticalFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesOrganic solventWafering
The invention provides an indium antimonide (InSb) wafer and silicon (Si) wafer bonding method. The method includes a first step of carrying out high-temperature ultrasonic boiling and washing in organic solvent on an InSb wafer and a Si wafer which are respectively polished on at least one side and then using deionized water to wash the InSb wafer and the Si wafer, a second step of placing the Si wafer into acid solution for boiling and washing and then using the deionized water to wash, a third step of placing the Si wafer into alkali solution for boiling and washing and then using the deionized water to wash, and a fourth step of enabling the polished surface of the InSb wafer and the polished surface of the Si wafer to face inwards, carrying out laminating, then placing the two laminated wafers into a vacuum bonding machine and carrying out heat treatment to complete bonding of the InSb wafer and the Si wafer. The InSb wafer and Si wafer bonding method is simple in process and has strong practicality.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ultra-thin multi-channel terahertz filter having temperature regulation
InactiveCN101504997AImprove transmittanceDifficult to controlWaveguide type devicesTransmittanceTotal thickness
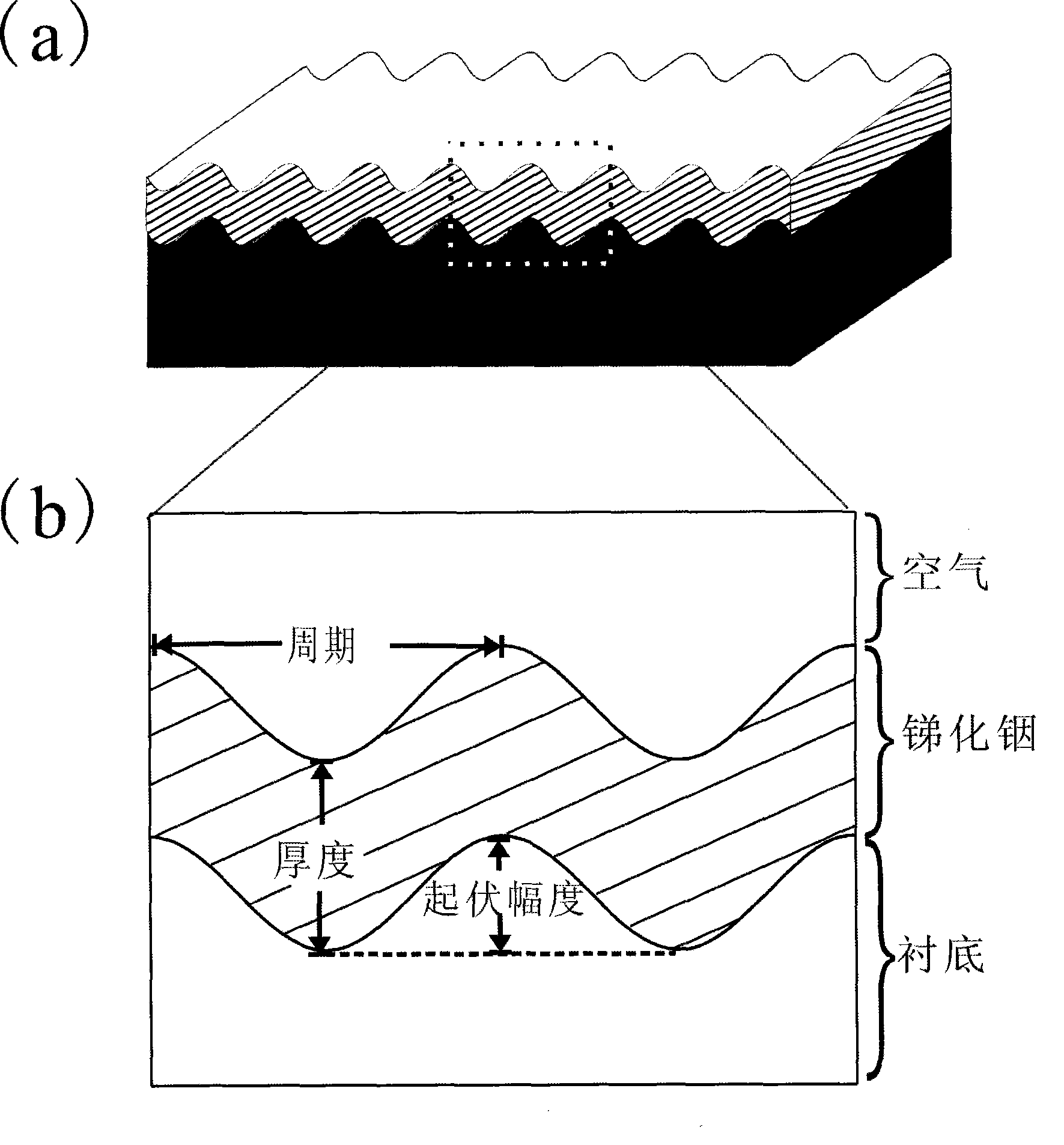
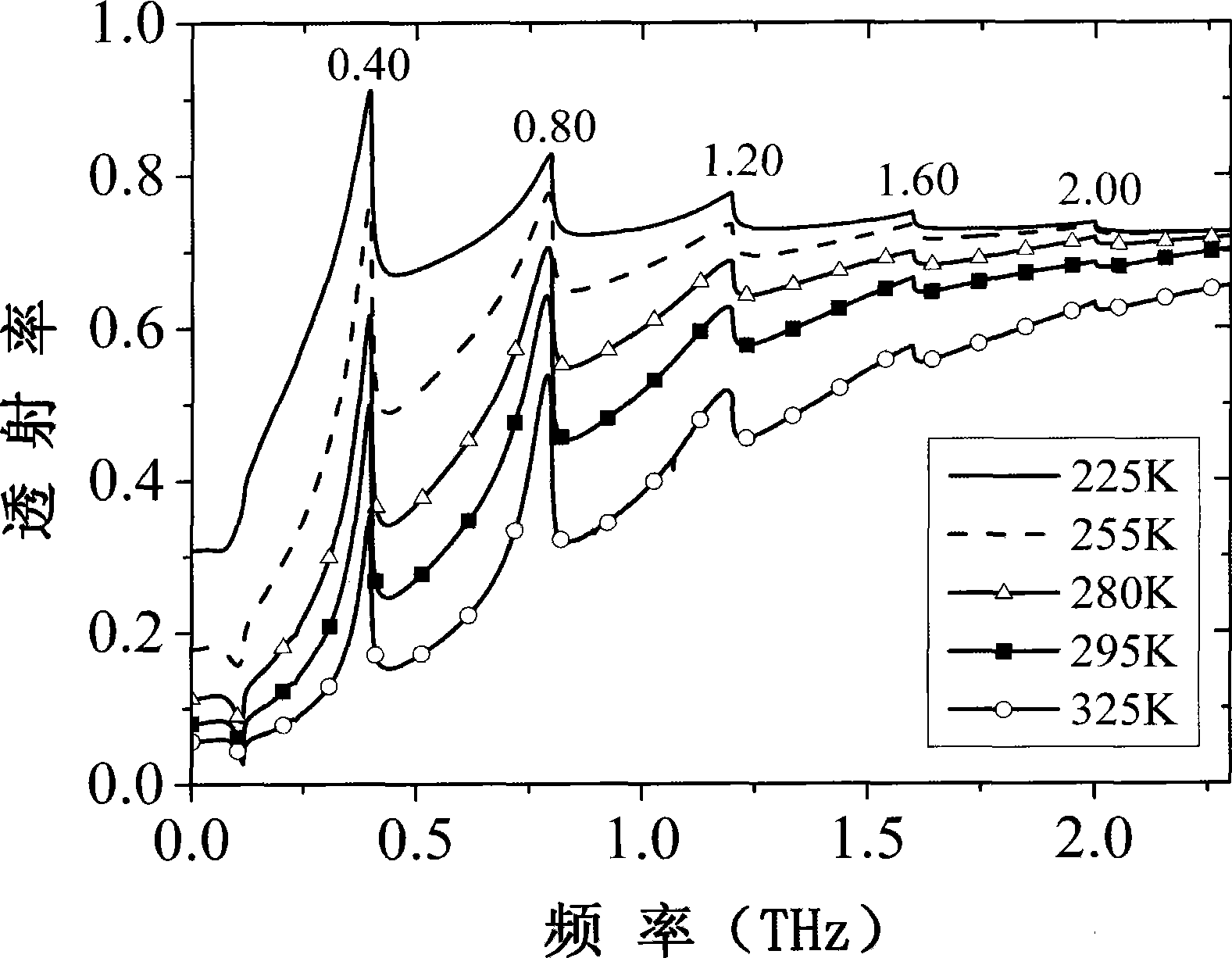
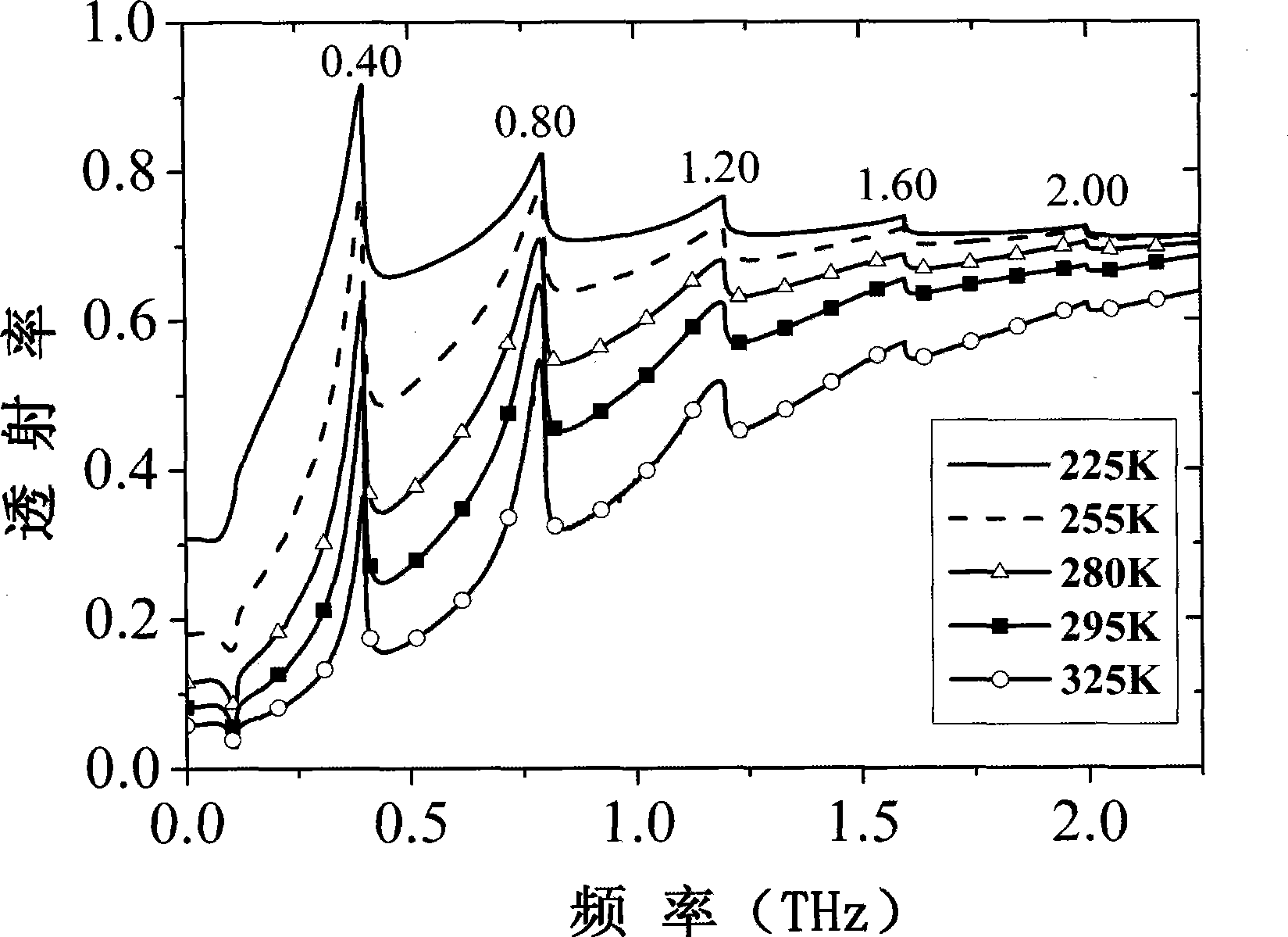
The invention discloses an ultrathin multichannel terahertz wave filter with temperature regulation; in the wave filter, a curved surface is constructed on the surface of a high-impedance monocrystalline silicon or a gallium arsenide underlay; then, a layer of an indium antimonide film grows on the curved surface of the underlay; the thickness of the film material is ultrathin (the total thickness does not exceed 2.15 microns); the multichannel terahertz wave filter obtains five resonant transmission peaks within the frequency range between 0.1 and 3 terahertz; the resonant transmission frequency is not changed along the temperature basically; the transmissivity of five resonant modes is increased along the temperature fall; and the transmissivity reaches as high as 90 to 93 percent.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
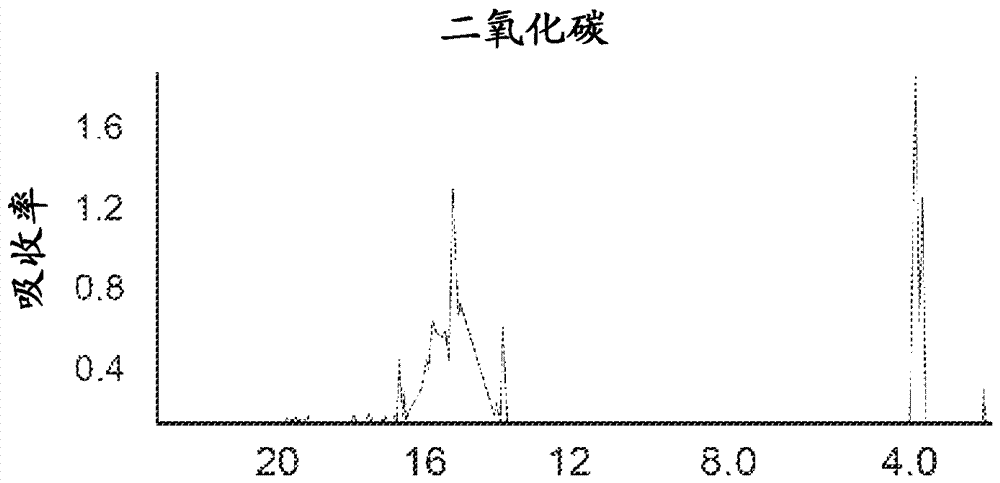
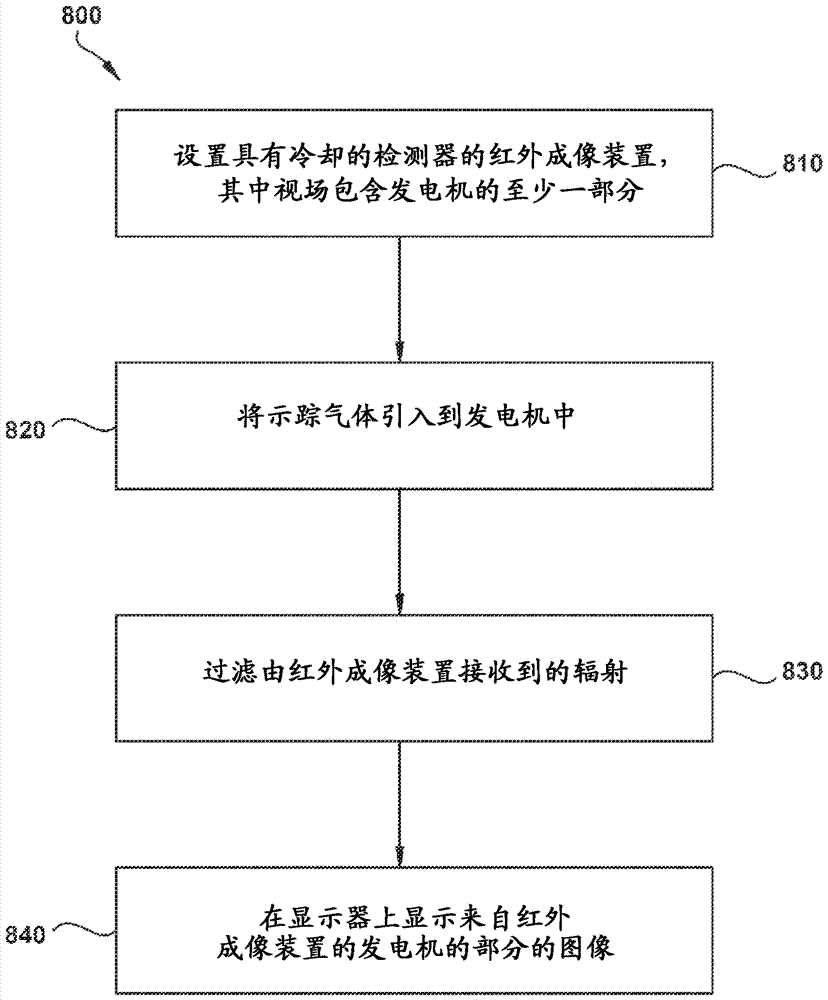
System and method for detecting leaks in generators
InactiveCN107024322ADetection of fluid at leakage pointMaterial analysis by optical meansSpectral responseMercury cadmium telluride
A system for detecting a gas leak in a machine includes a source of a non-corrosive tracer gas, and a subsystem for introducing the non-corrosive tracer gas into the machine. An infrared imaging device is adapted to communicate with a notification device to display an image of at least a portion of the machine. The infrared imaging device has a cooled detector and a filter with a spectral response between about 3 [mu]m and about 5 [mu]m. At least one of the detector and the filter is cooled. The infrared imaging device includes one of a mercury cadmium telluride (MCT) photodetector, an indium antimonide (InSb) photodetector or a mid-wavelength quantum well infrared photodetector (QWIP). The notification device is adapted to indicate the gas leak.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Long Wavelength Infrared Superlattice
ActiveUS20110272672A1Extend the cutoff wavelengthTotal current dropNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGallium antimonideIndium arsenide
An embodiment of the present invention improves the fabrication and operational characteristics of a type-II superlattice material. Layers of indium arsenide and gallium antimonide comprise the bulk of the superlattice structure. One or more layers of indium antimonide are added to unit cells of the superlattice to provide a further degree of freedom in the design for adjusting the effective bandgap energy of the superlattice. One or more layers of gallium arsenide are added to unit cells of the superlattice to counterbalance the crystal lattice strain forces introduced by the aforementioned indium antimonide layers.
Owner:SVT ASSOCS
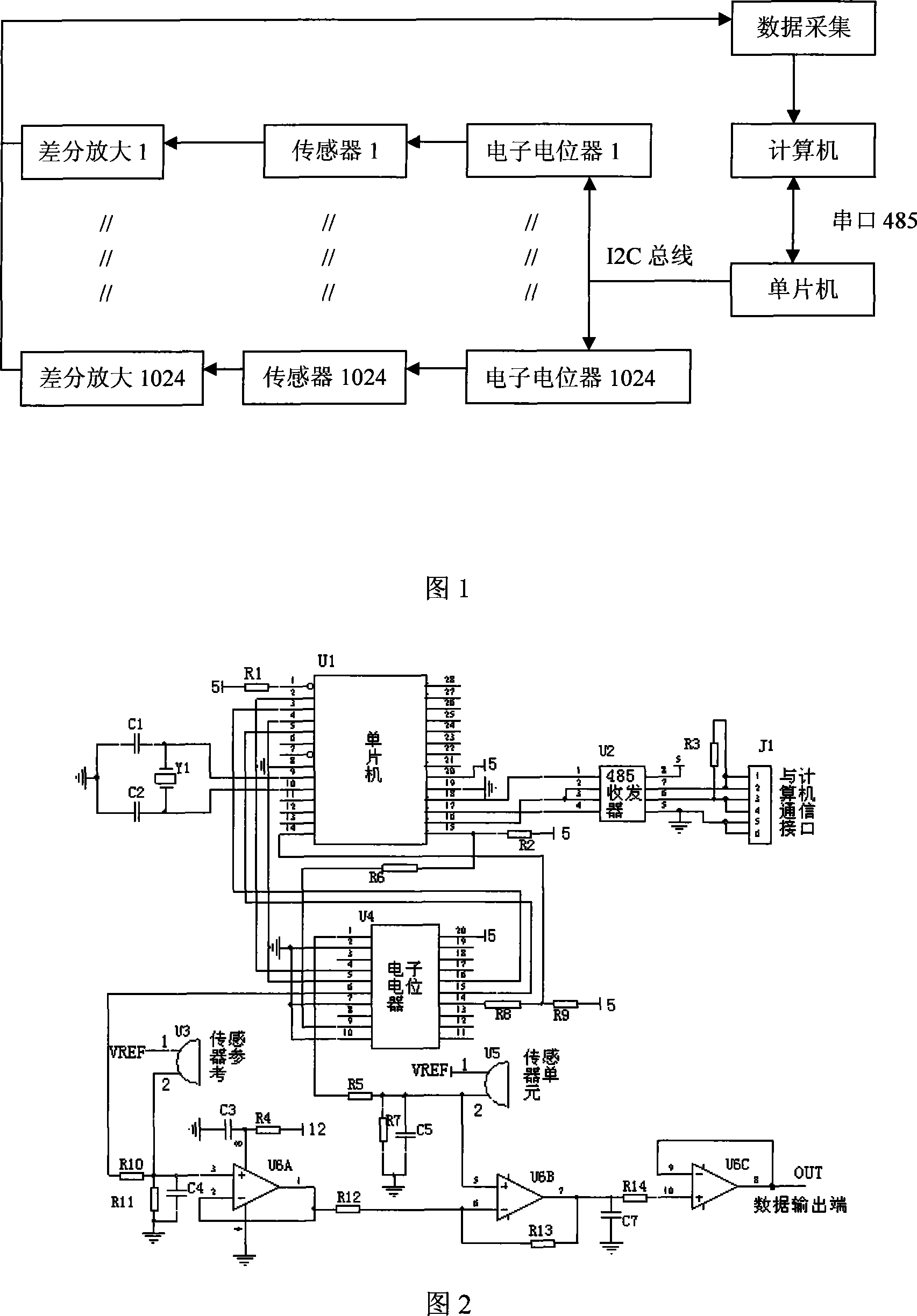
Lndium antimonide opto-electronic sensor array quiescent operating point auto-calibration device
InactiveCN101183028AImprove practicalityPyrometry using electric radation detectorsPhotometry electrical circuitsSensor arrayOperating point
The invention discloses an automatic adjusting device for the quiescent operation point of an indium antimonide photoelectric sensor array and comprises an indium antimonide photoelectric sensor array. The invention is characterized in that the each indium antimonide photoelectric sensor in the indium antimonide photoelectric sensor array switches in an adjusting branch circuit and the structure of each adjusting branch circuit is as follows that after the standard voltage VREF is outputted through a reference sensor, one way switches to an electric potentiometer through a voltage division circuit and the other way is outputted to a first voltage follower. An address line, a communication clock line and a communication data line are connected between the electric potentiometer and a single chip; the communication connection is established between a collection card and a computer; the communication connection is established between the computer and the single chip. With the automatic adjusting device for quiescent operation point, the sensor array can work naturally in the environment with the temperature range of 30 DEG C below zero to 40 DEG C and the practicality is improved greatly.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
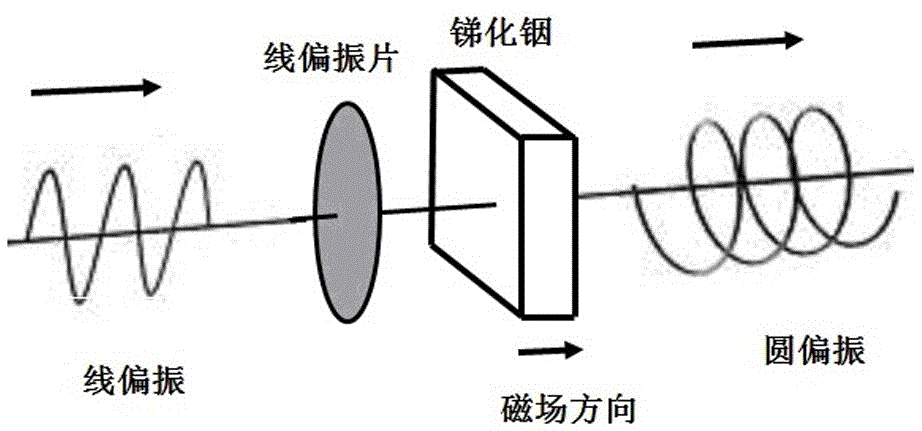
Terahertz circularly polarized light generating method based on narrow-band semiconductor indium antimonide
InactiveCN105549230AWide modulation frequencyNon-linear opticsOptical elementsDegree of polarizationOptical polarization
The invention relates to a terahertz circularly polarized light generating method based on narrow-band semiconductor indium antimonide. An indium antimonide sample wafer is placed in a cryostat, incident ray polarization terahertz waves pass through a linear polarizing film to make the degree of polarization increased after temperature becomes stable, incident rays irradiate on the surface of the indium antimonide sample wafer after focusing, and an adjustable and stable magnetic field is perpendicularly loaded on the indium antimonide sample wafer. Terahertz circularly polarized light is obtained according to the frequency of incident terahertz by adjusting the incidence loading direction and intensity of the magnetic field. The method has the advantages that modulation frequency is wide, circular polarization output is prefect and a polarizing device is tunable.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
System and method for detecting leaks in generators
InactiveUS20170138813A1Avoid healthAvoid environmentDetection of fluid at leakage pointMaterial analysis by optical meansSpectral responsePhotovoltaic detectors
A system for detecting a gas leak in a machine includes a source of a non-corrosive tracer gas, and a subsystem for introducing the non-corrosive tracer gas into the machine. An infrared imaging device is adapted to communicate with a notification device to display an image of at least a portion of the machine. The infrared imaging device has a cooled detector and a filter with a spectral response between about 3 μm and about 5 μm. At least one of the detector and the filter is cooled. The infrared imaging device includes one of a mercury cadmium telluride (MCT) photodetector, an indium antimonide (InSb) photodetector or a mid-wavelength quantum well infrared photodetector (QWIP). The notification device is adapted to indicate the gas leak.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Temperature-sensitive-type terahertz detector based on phase change material and preparation method
ActiveCN110617882AEasy to integrateSimple preparation processFinal product manufactureThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsVanadium dioxideGrating
The invention discloses a temperature-sensitive-type terahertz detector based on phase change material and a preparation method. The detector is composed of an alumina substrate, an indium antimonide-sensitive element, a vanadium dioxide grating structure layer, a half-wave antenna and a device socket. According to the temperature-sensitive-type terahertz detector prepared according to the invention, the vanadium dioxide grating structure layer is introduced on the basis of a traditional metal-semiconductor-metal structure, the phase change transition characteristic of vanadium dioxide at an ambient temperature of 68 DEG C is used, thus a drastic change of conductivity of the grating structure layer is caused, then field enhancement effects caused by local plasmons of the whole device areenabled to be different, and a modulation purpose of terahertz wave detection is achieved; and a new function of sensing the ambient temperature is added while fast highly-sensitive response of a widewave band of 0.01- 3THZ is realized. The detector has very important significance for both device structure design optimization and device function perfection, and can play important roles in the fields of science, technology and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com