Patents
Literature
87 results about "Gallium antimonide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
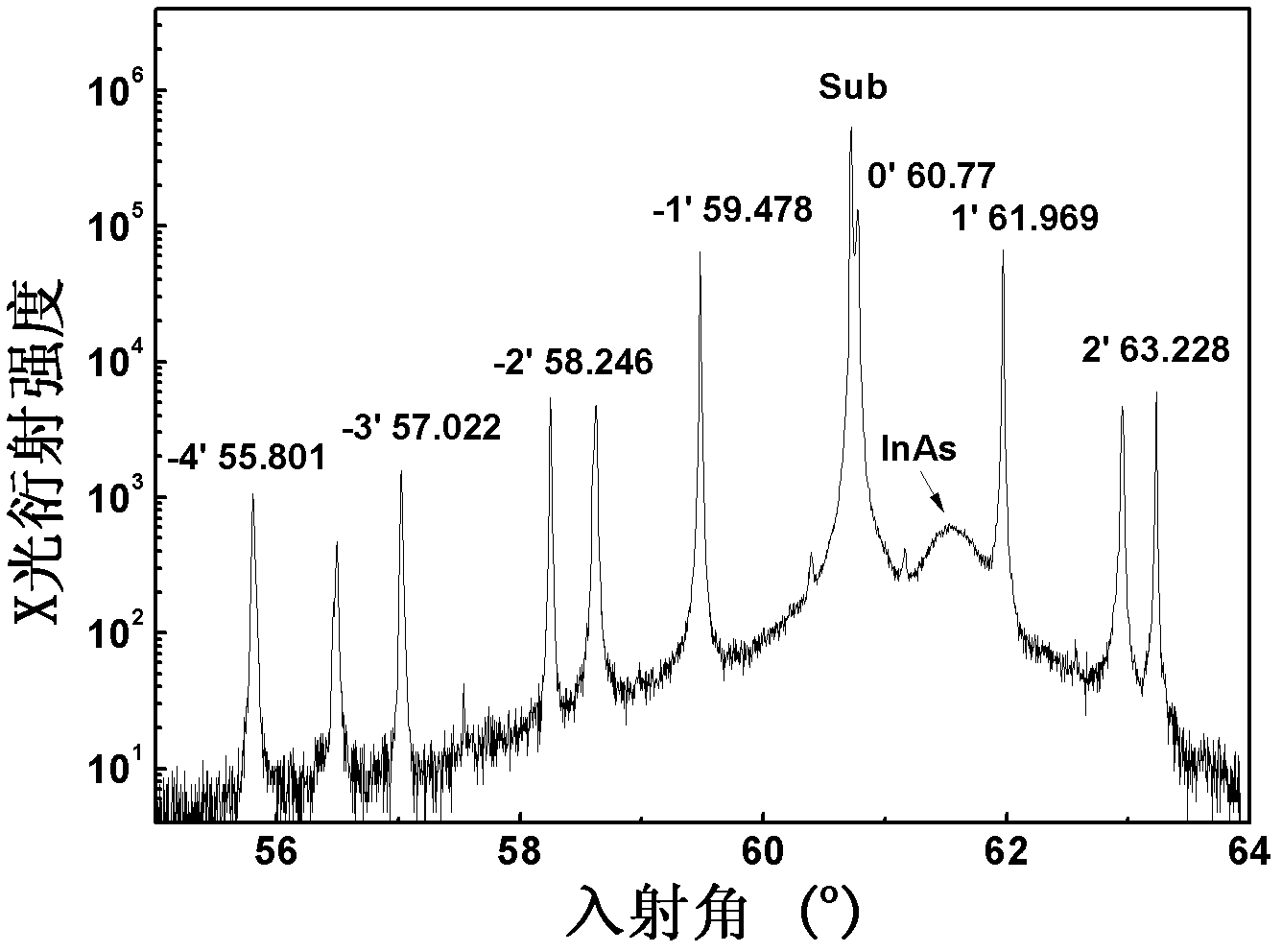
Gallium antimonide (GaSb) is a semiconducting compound of gallium and antimony of the III-V family. It has a lattice constant of about 0.61 nm. It has a band gap of 0.67 eV.
Long Wavelength Infrared Superlattice
InactiveUS20130043458A1Quality lossOvercome lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsGallium antimonideIndium arsenide
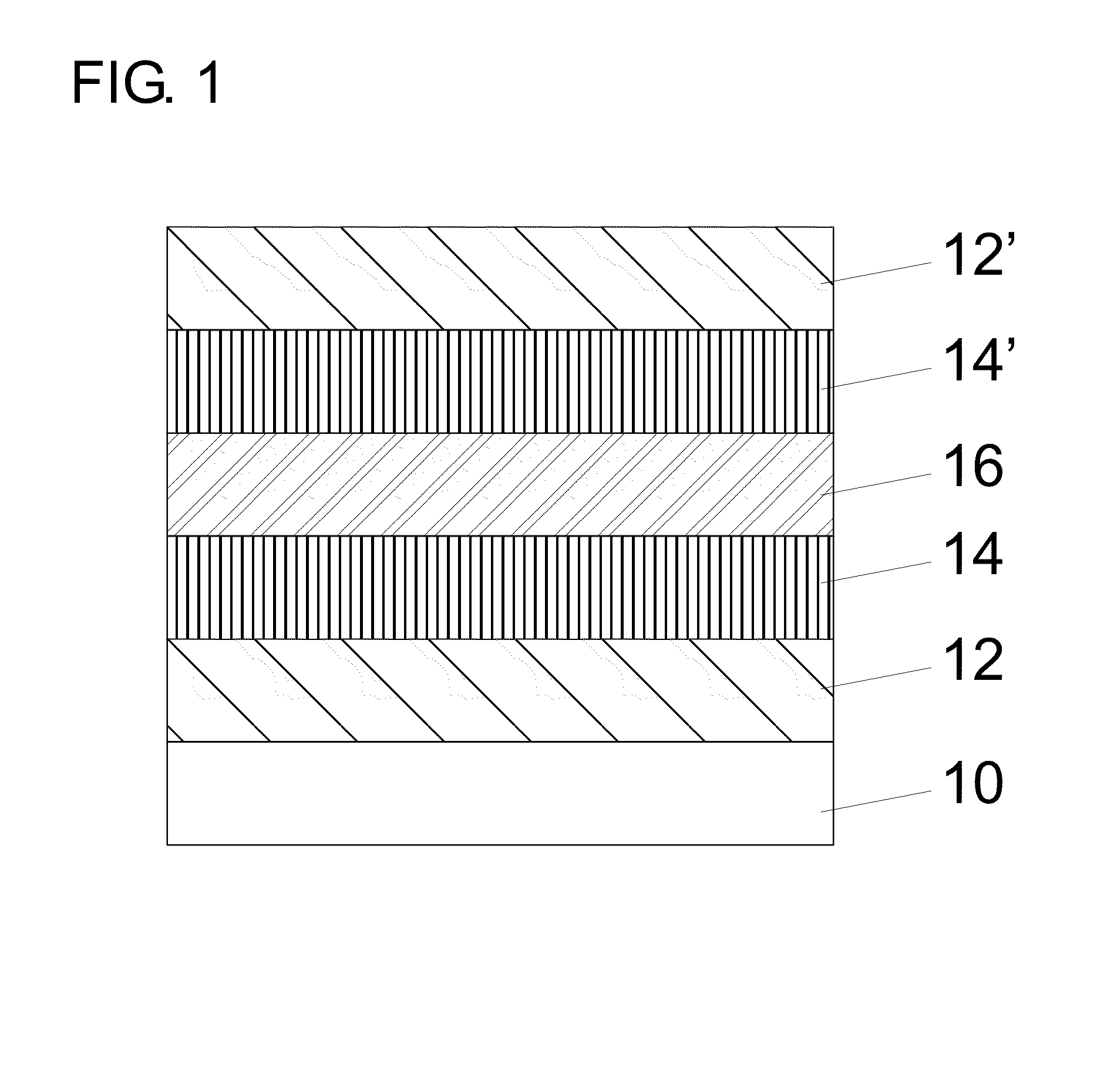
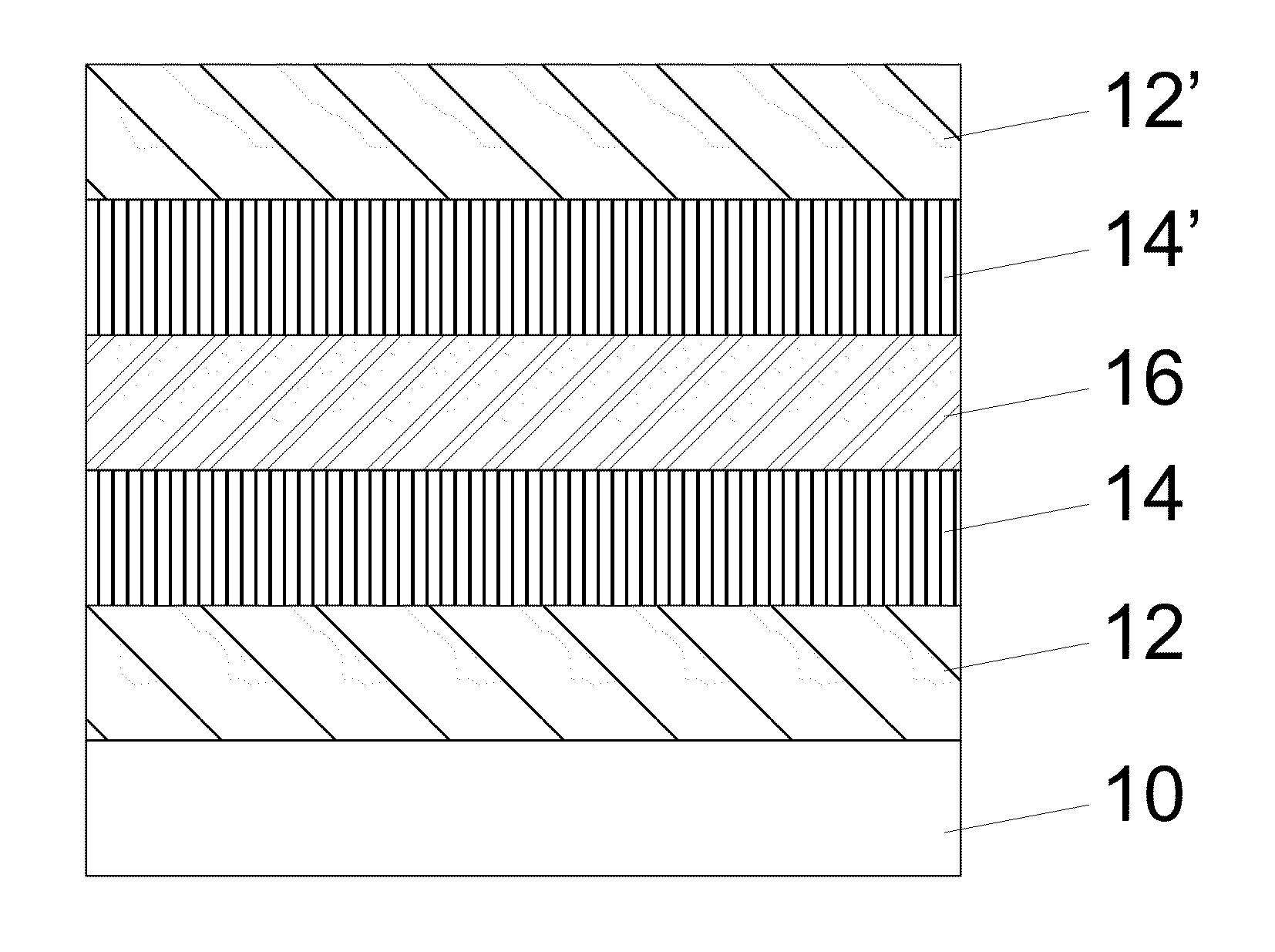
An embodiment of the present invention improves the fabrication and operational characteristics of a type-II superlattice material. Layers of indium arsenide and gallium antimonide comprise the bulk of the superlattice structure. One or more layers of indium antimonide are added to unit cells of the superlattice to provide a further degree of freedom in the design for adjusting the effective bandgap energy of the superlattice. One or more layers of gallium arsenide antimonide are added to unit cells of the superlattice to counterbalance the crystal lattice strain forces introduced by the aforementioned indium antimonide layers.
Owner:SVT ASSOCS
Long Wavelength Infrared Superlattice
InactiveUS20130043459A1Extend the cutoff wavelengthQuality lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsGallium antimonideIndium arsenide
An embodiment of the present invention improves the fabrication and operational characteristics of a type-II superlattice material. Layers of indium arsenide and gallium antimonide comprise the bulk of the superlattice structure. One or more layers of indium antimonide are added to unit cells of the superlattice to provide a further degree of freedom in the design for adjusting the effective bandgap energy of the superlattice. One or more layers of gallium arsenide antimonide are added to unit cells of the superlattice to counterbalance the crystal lattice strain forces introduced by the aforementioned indium antimonide layers.
Owner:SVT ASSOCS
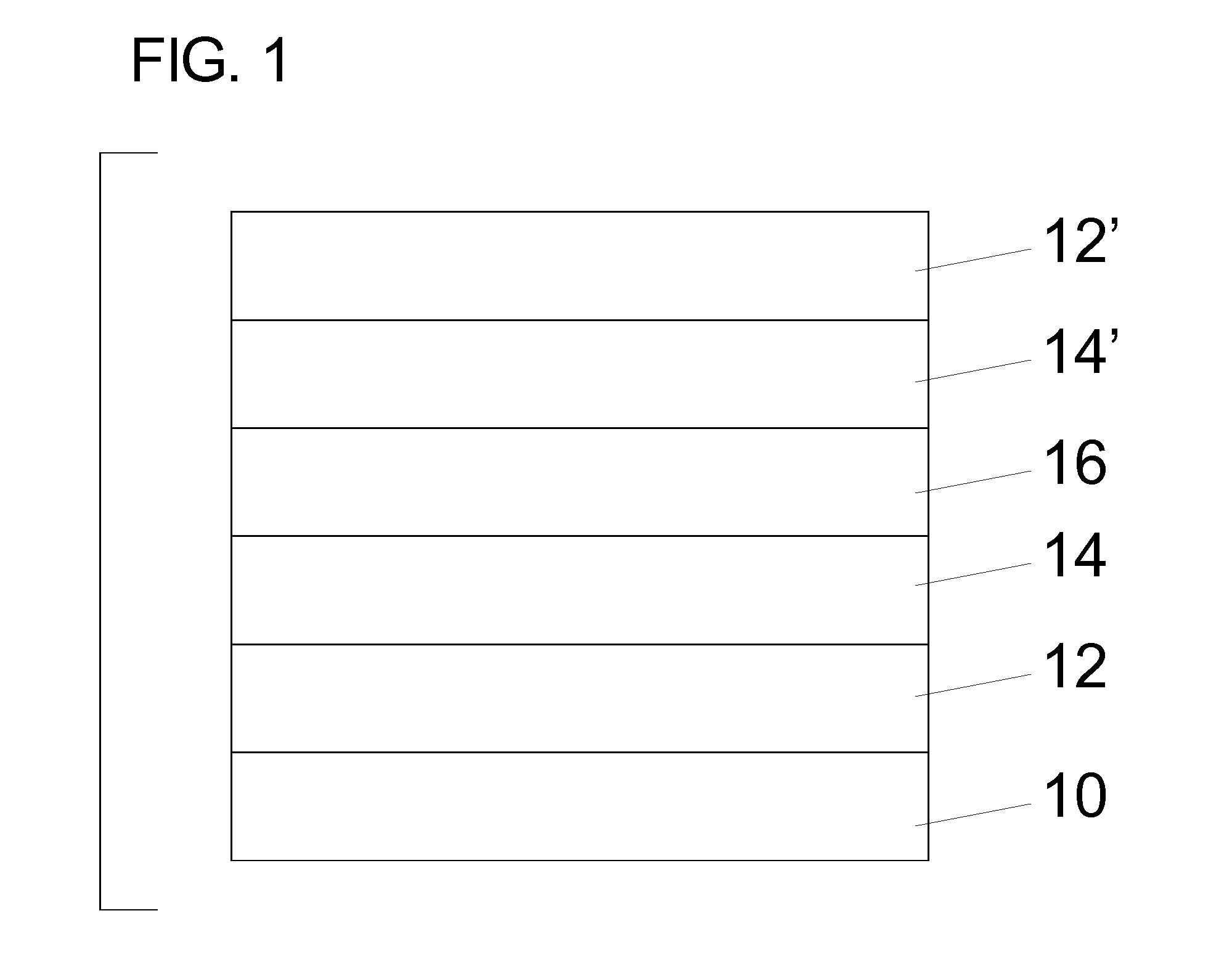
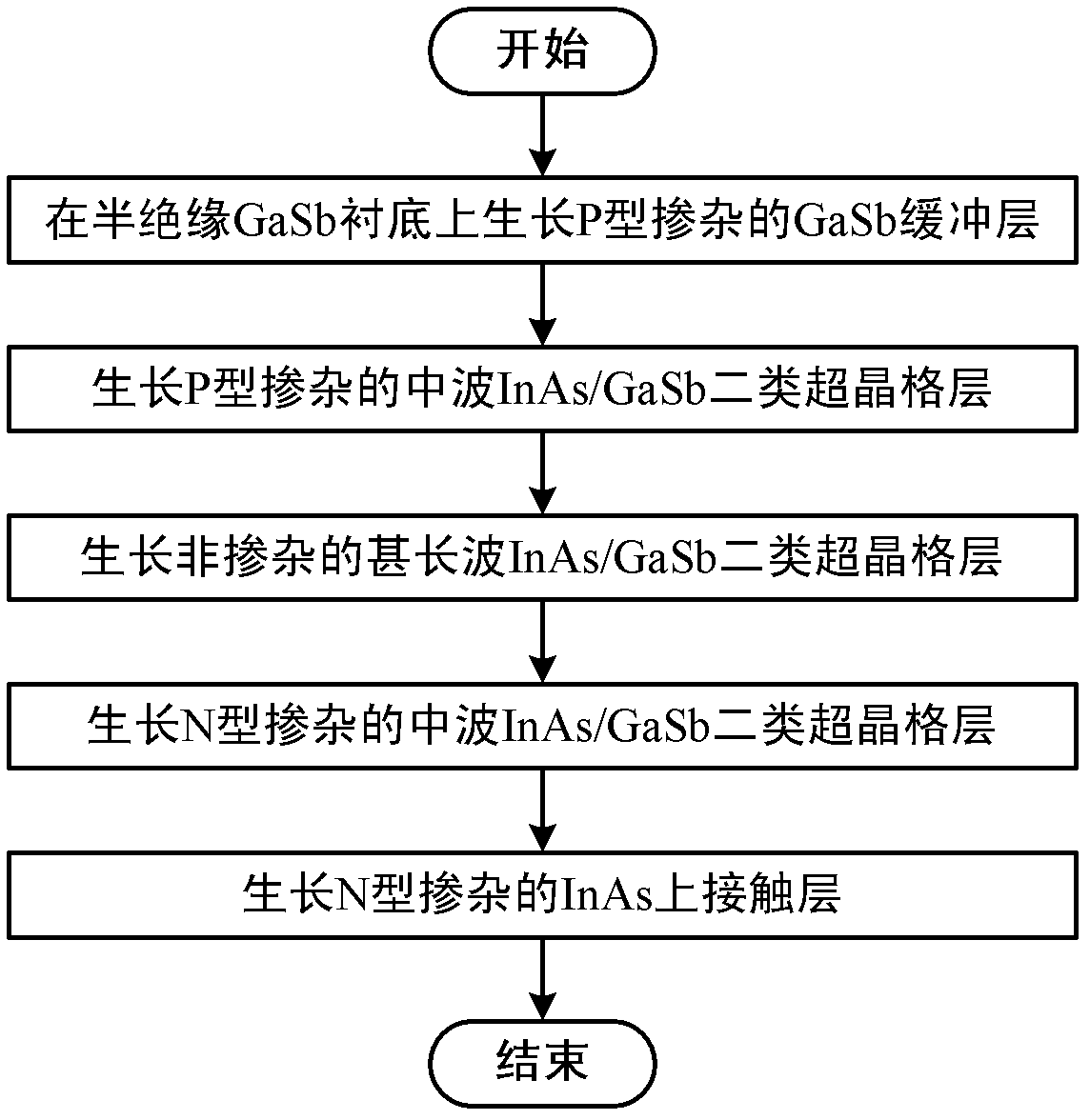
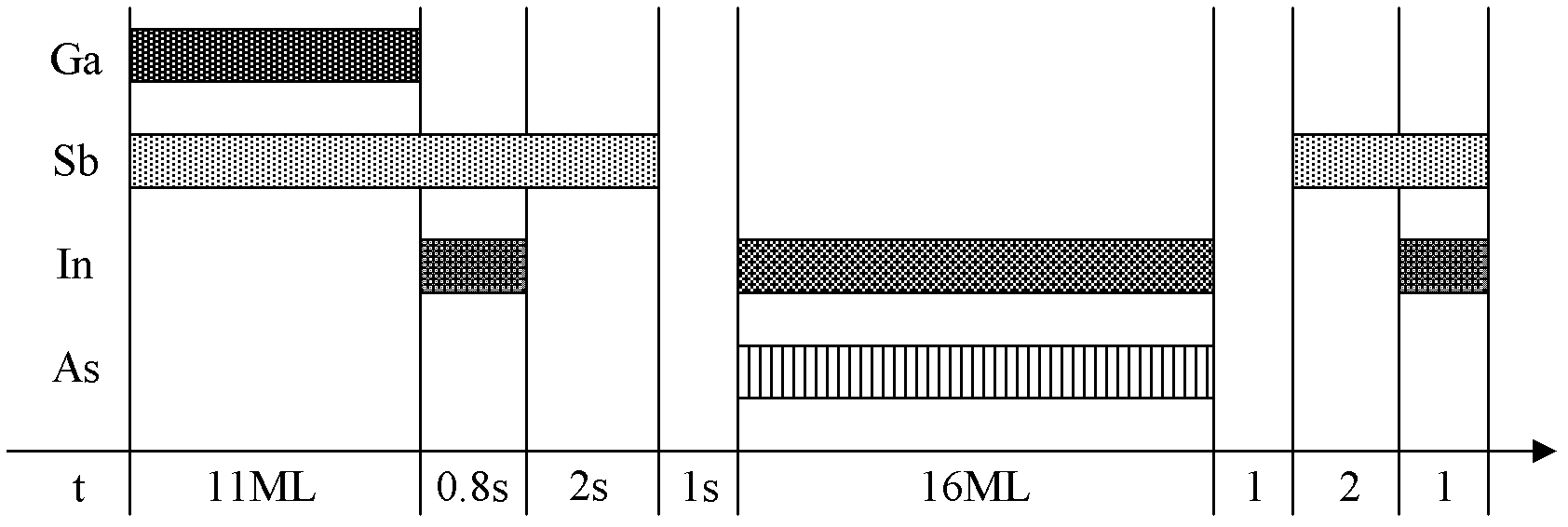
Method for producing very-long wave indium arsenide (InAs)/gallium antimonide (GaSb) second class superlattice infrared detector material
InactiveCN102544229AReduce dark currentExcellent optical propertiesFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesGallium antimonideInterface design
The invention discloses a method for producing a very-long wave indium arsenide (InAs) / gallium antimonide (GaSb) second class superlattice infrared detector material, which comprises the step that: a P type doped GaSb buffer layer, a P type doped medium wave InAs / GaSb second class superlattice layer, a non-doped very-long wave InAs / GaSb second class superlattice layer, a N type doped medium wave InAs / GaSb second class superlattice layer and an N type doped InAs upper contact layer are sequentially grown on a semi-insulating GaSb substrate, so the very-long wave InAs / GaSb second class superlattice infrared detector material is obtained. After the method is utilized, because 'Sb-soak' and 'grow interruption' which are well designed are added in an interface design, the quality of the superlattice material is further improved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polishing method for gallium antimonide single crystal wafer
ActiveCN106064326AReduce surface damageEasy to cleanLapping machinesGallium antimonideSurface roughness
The invention discloses a polishing method for a gallium antimonide single crystal wafer. For coarse polishing, a cerium oxide polishing pad is adopted, and polishing liquid contains aluminum oxide abrasives with the particle size of W1, at the pressure of 100 to 200 g / cm<2>, the rotating speed of 10 to 40 r / min and the flow of 10 to 50 mL / min; for medium polishing, a black polyurethane polishing pad is adopted, and the polishing liquid contains silicon dioxide nano abrasives with the particle size of 60 to 100 nm and an oxidant, i.e., sodium hypochlorite, at the pressure of 80 to 150 g / cm<2>, the rotating speed of 60 to 100 r / min and the flow of 10 to 30 mL / min; for fine polishing, a black synthesized leather polishing cloth is adopted, and the polishing liquid is abrasive-free polishing liquid, at the pressure of 30 to 100 g / cm<2>, the rotating speed of 20 to 60 r / min and the flow of 5 to 10 mL / min. The polishing process is simple and easy to operate; the gallium antimonide single crystal wafer is low in surface damage and easy to clean, and the surface roughness is 0.3 nm.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 46 RES INST
Double-surface polishing method for gallium antimonide wafer
InactiveCN102554750ARelieve oxidationSimple methodPolishing machinesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGallium antimonideWafering
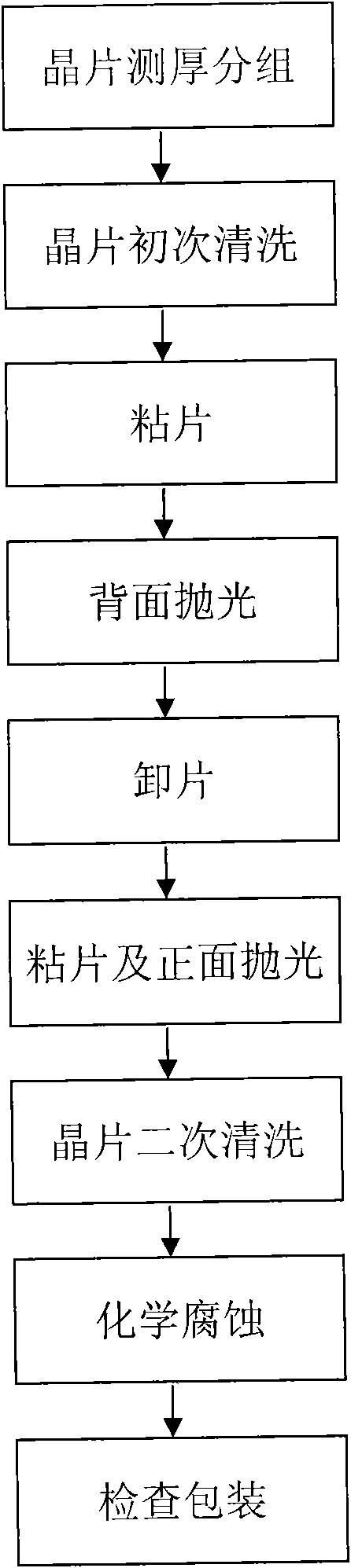
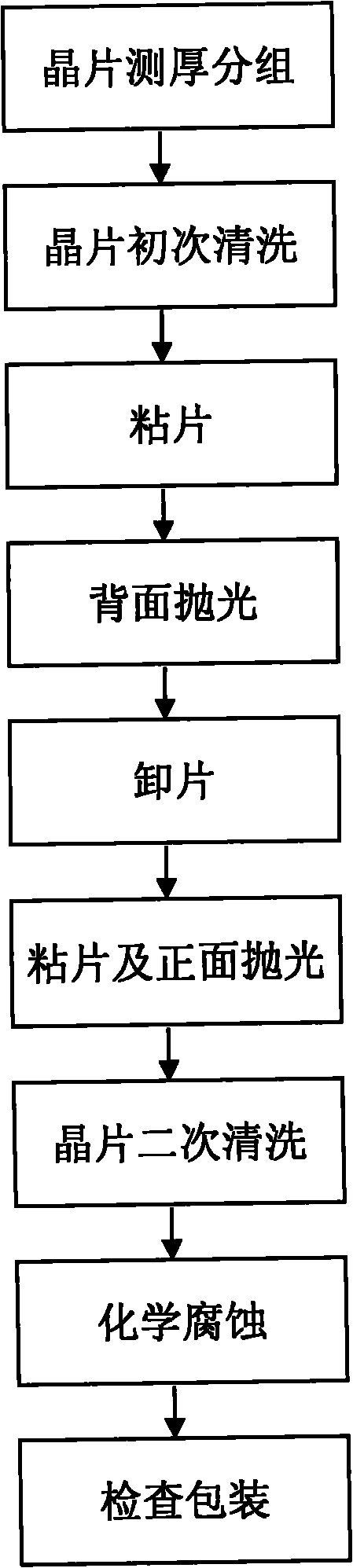
The invention relates to a double-surface polishing method for a gallium antimonide wafer. The double-surface polishing method comprises the following steps of: grouping wafer thickness measurement; initially cleaning a wafer; adhering the wafer; polishing a back surface; dismantling the wafer; adhering the wafer and polishing a positive surface; secondly cleaning the wafer; placing the wafer with polished double surfaces in a solution prepared from cleaning liquid and purified water in volume ratio of 1:(3-10) for ultrasonic cleaning at 50-100 DEG for 10-30min, washing by using the purified water; corroding chemically: preparing corrosion liquid according to a proportion of CH3COOH, H2O and HF in volume ratio of (10-30):(5-15):1; and checking and packing. According to the double-surface polishing method for the gallium antimonide wafer, disclosed by the invention, the gallium antimonide (100) wafer with polished double surfaces can be machined in batch, the method is simple and practical, the maneuverability is strong, and the polished yield is up to 90%; simultaneously, a problem of oxidation of the polished gallium antimonide wafer is released. The gallium antimonide wafer polished by the double-surface polishing method disclosed by the invention is not larger than 20 microns in warping degree, not larger than 4 microns in wafer surface flatness, 0.1-0.2 micron in surface roughness and not larger than 5 microns in total thickness of the wafer, and the defects of the polished wafer, such as dirt, fog, scratch, particles, cracking, orange peel and crow claw, are not detected.
Owner:GRINM ELECTRO OPTIC MATERIALS
Semiconductor material polishing method and polishing solution for polishing gallium antimonide substrate
PendingCN112701037AImprove surface roughnessGuaranteed stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolishing compositions with abrasivesGallium antimonideOrganic acid
In order to overcome the defects that when a soft semiconductor material such as gallium antimonide is polished by adopting a CMP (Chemical Mechanical Polishing) process in the prior art, metal ions and the like contained in a polishing abrasive and a polishing solution are easily attached to the surface of a polished object, scratches are generated on the surface of the polished object, and the service life of the polishing solution is short, the invention provides a semiconductor material polishing method and a polishing solution for polishing a gallium antimonide substrate. According to the method, a semiconductor material with the Mohs hardness of 1.5-6 is polished. A first step is rough polishing, and a polishing solution containing a hard abrasive is adopted to conduct mechanical polishing on a semiconductor material substrate slice. A second step is medium polishing, and a medium polishing solution comprises a soft polishing abrasive, a weak acid oxidizing agent, organic acid, a hydrophilic nonionic surfactant and deionized water. A third step is fine polishing, and a fine polishing solution comprises a weak acid oxidizing agent, organic acid and deionized water. When the polishing method is adopted for polishing a semiconductor material, corrosion pits and scratches are eliminated, pits are reduced, and a material with good surface roughness is obtained.
Owner:SUZHOU KUNYUAN OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
Light emitting material, light emitting element, light emitting device and electronic device
InactiveUS20070215880A1Reduce power consumptionLow costElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesLow voltageInorganic compound
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for epitaxial generation of gallium antimonide on gallium arsenide substrate
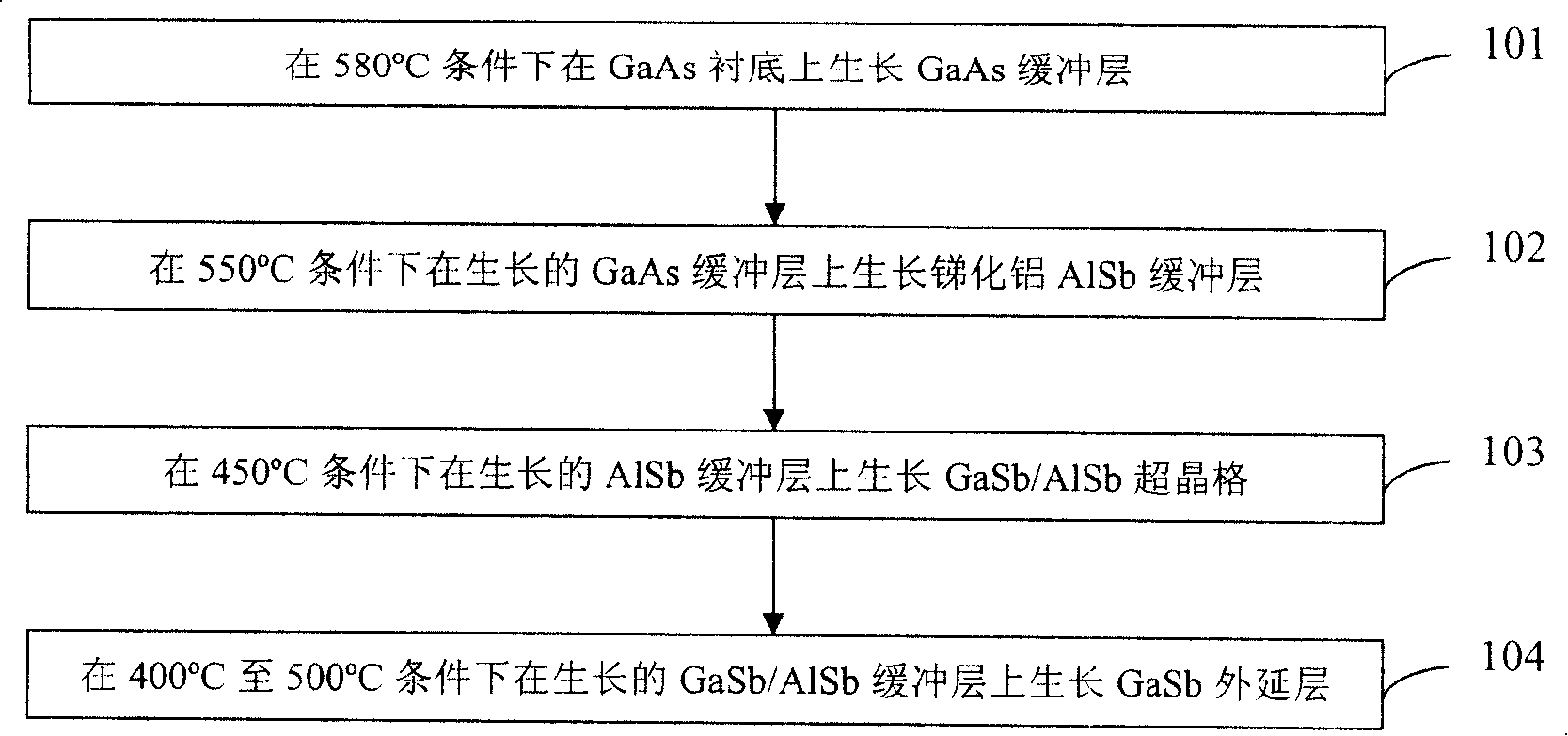
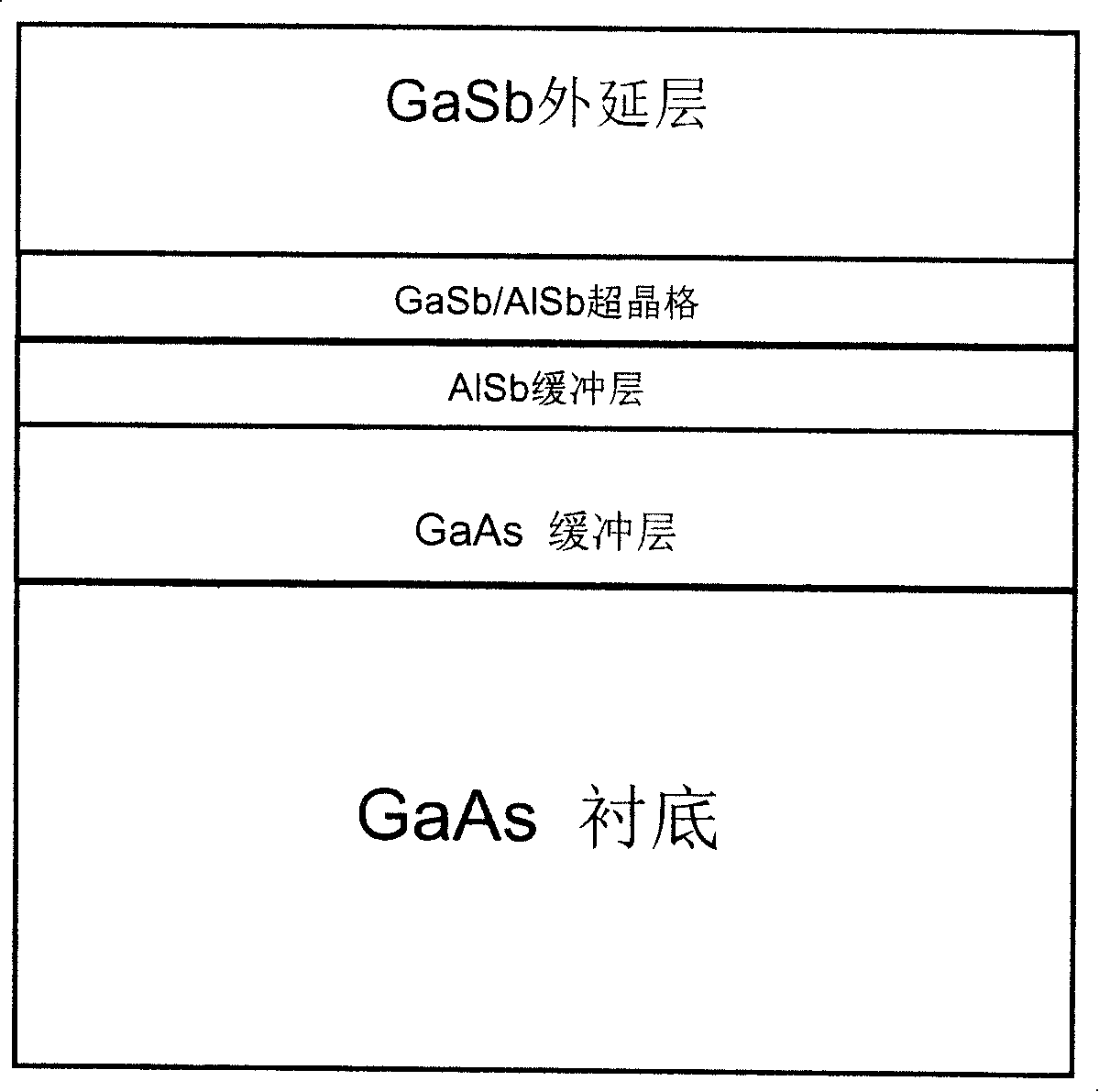
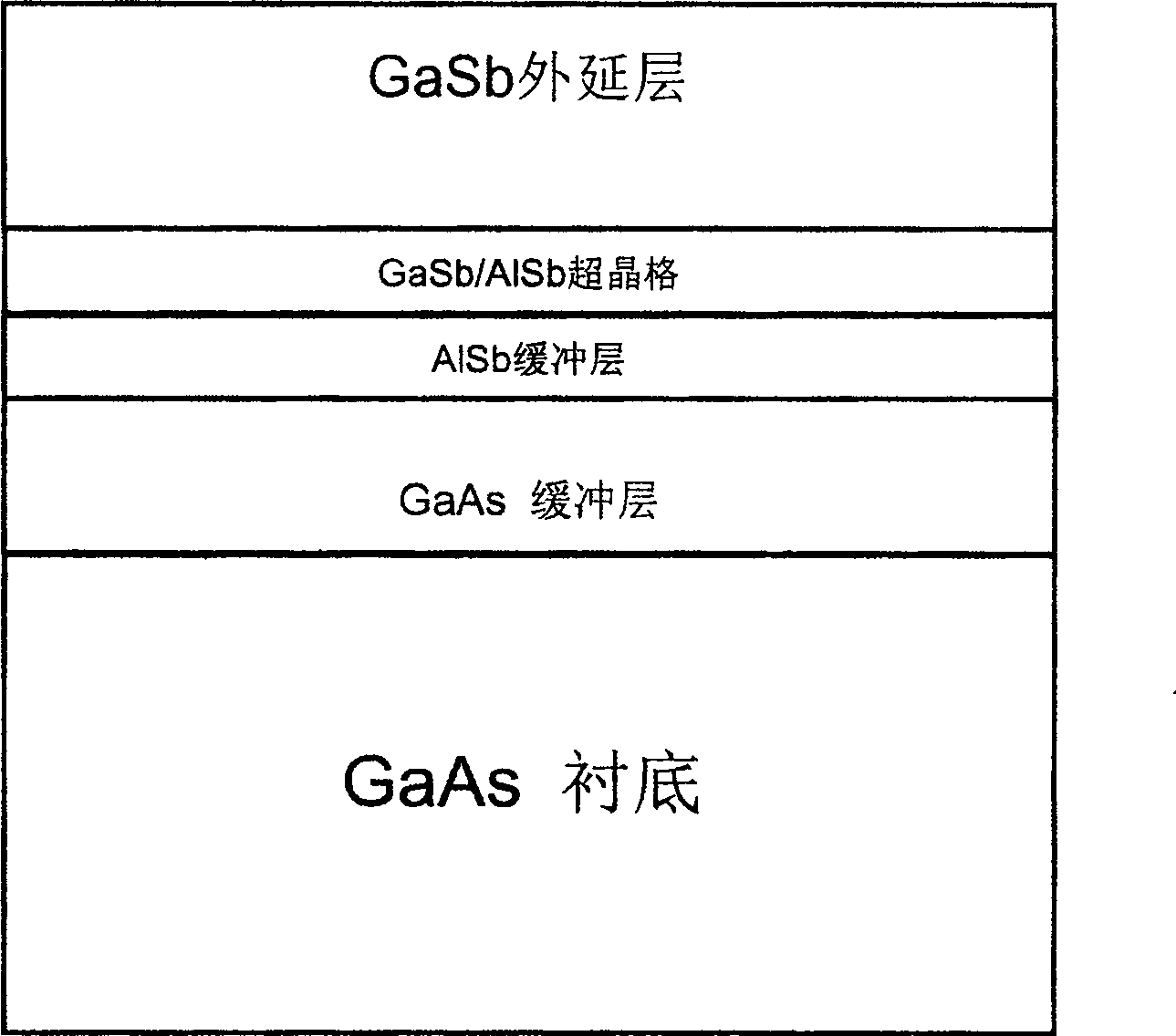
InactiveCN101207022AReduce defectsBlock vertical growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGallium antimonideGallium arsenide
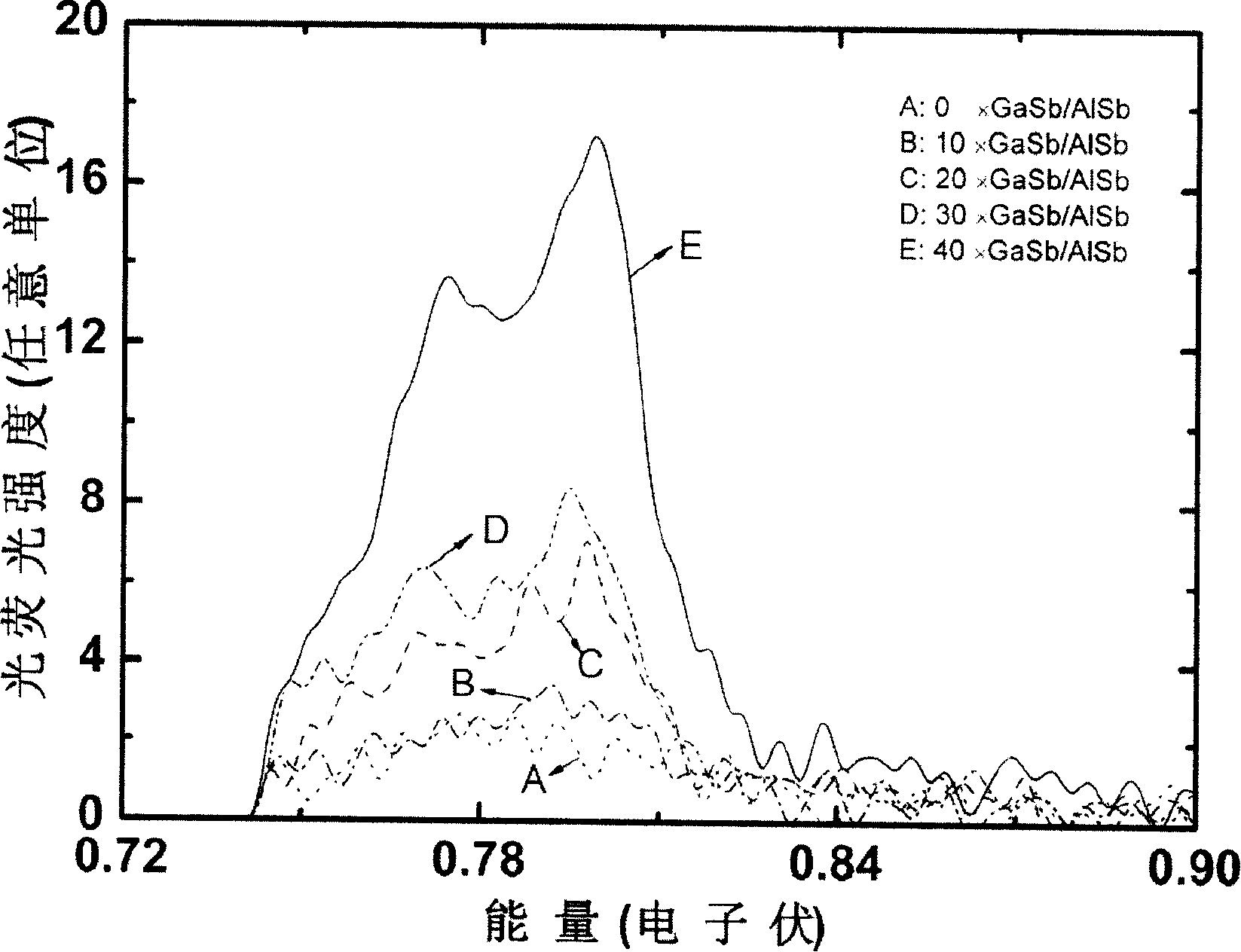
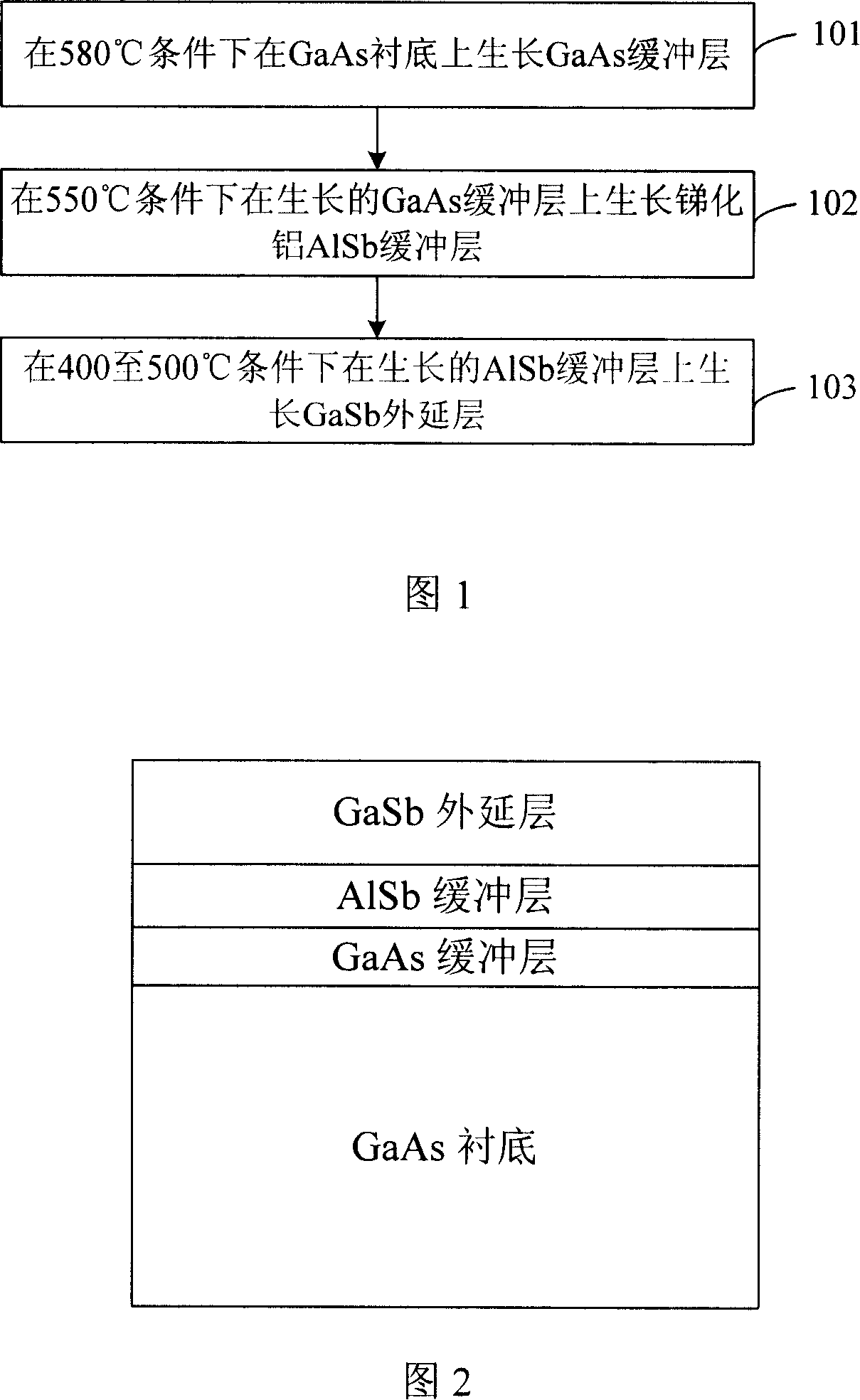
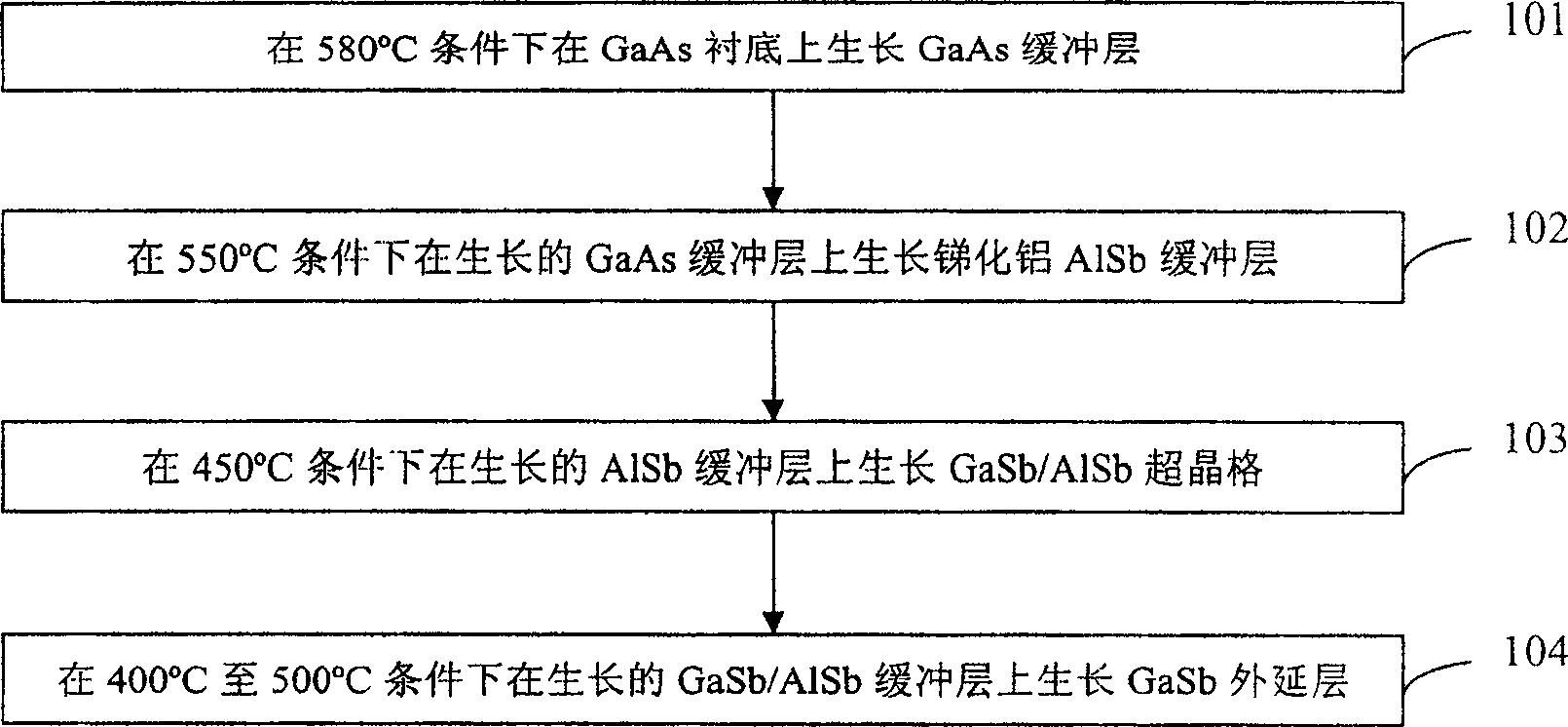
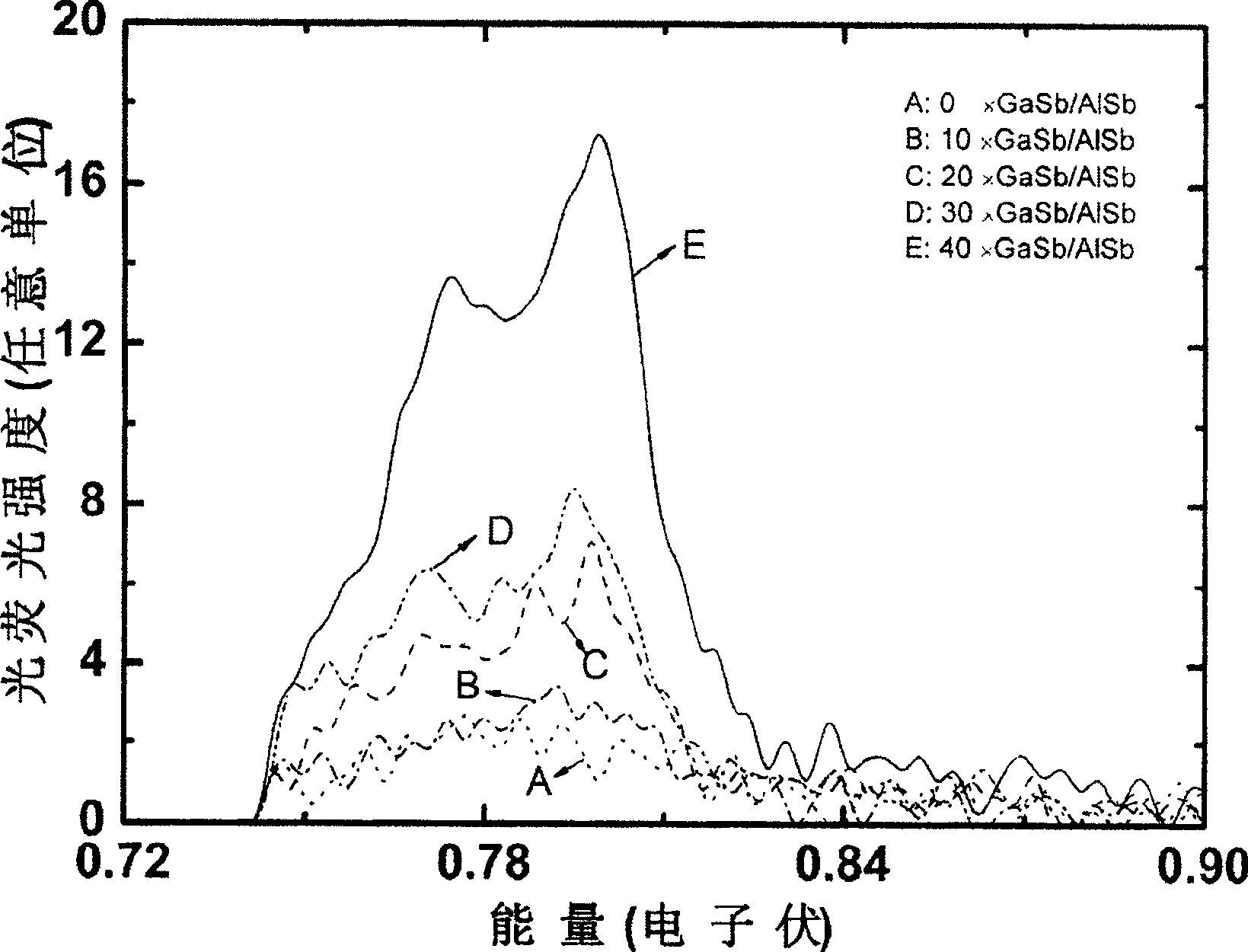
The invention discloses a method of the epitaxial growth GaSb on a gallium arsenide substrate. A three buffer layers growth process is adopted in the method. The method specifically comprises the following steps: firstly, a GaAs buffer layer grows on a GaAs substrate under the condition of 580 DEG C; secondly, an AlSb buffer layer grows on the grown GaAs buffer layer under the condition of 550 DEG C; thirdly, a GaSb / AlSb super crystal lattice buffer layer grows on the AlSb buffer layer under the condition of 450 DEG C; fourthly, a GaSb epitaxial layer grows on the GaSb / AlSb super crystal lattice buffer layer under the condition of 400 to 500 DEG C. By utilizing the invention, a doublebuffer layer process is changed into a three-buffer layer process, firstly the GaAs buffer layer grows on the GaAs substrate, then the AlSb buffer layer grows on the grown GaAs buffer layer, the GaSb / AlSb super crystal lattice buffer layer grows on the AlSb buffer layer, finally the GaSb epitaxial layer grows on the GaSb / AlSb super crystal lattice buffer layer, and the perforating dislocation is reduced effectively, thereby the optical quality of the GaSb epitaxial layer is enhanced.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cleaning method of gallium antimonide polished monocrystal wafer
ActiveCN105405746AEfficient removalIncrease roughnessAfter-treatment detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGallium antimonideWafering
The invention discloses a cleaning method of a gallium antimonide polished monocrystal wafer. The cleaning method comprises the following steps: (1) embathing the gallium antimonide polished monocrystal wafer with an organic solvent; (2) washing the gallium antimonide polished monocrystal wafer with deionized water; (3) putting the gallium antimonide polished monocrystal wafer into a chemical corrosion solution, and corroding the wafer surface at 10-40 DEG C; (4) washing the gallium antimonide polished monocrystal wafer corroded in the step (4) with the deionized water; and (5) drying the gallium antimonide polished monocrystal wafer. According to the used cleaning technology and corrosion solution, impurities and particles left on the wafer surface in the processing process can be effectively eliminated to obtain a clean surface; meanwhile, the surface roughness of the wafer is improved to reach the condition of Rq=0.5-0.3 microns; and the requirements of epitaxial growth are met.
Owner:BEIJING HUAJINCHUANGWEI ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Epitaxy growth method for gallium antimonide on gallium arsenide substrate
InactiveCN101148776AImprove crystal qualityImprove flatnessPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesGallium antimonideComputational physics
The process of epitaxially growing GaSb on GaAs substrate is one double buffering layer growing process including the following steps: 1. growing a buffering GaAs layer on GaAs substrate at 580 deg.c; 2. growing a buffering AlSb layer on the buffering GaAs layer at 550 deg.c; and 3. growing an epitaxial GaSb layer on the buffering AlSb layer at 400-500 deg.c. The double buffering layer growing process can promote the 2D growth of the epitaxial GaSb layer, and raise the crystal quality and surface smoothness of the epitaxial GaSb layer effectively.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Long wavelength infrared superlattice
ActiveUS8426845B2Extend the cutoff wavelengthTotal current dropNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGallium antimonideIndium arsenide
An embodiment of the present invention improves the fabrication and operational characteristics of a type-II superlattice material. Layers of indium arsenide and gallium antimonide comprise the bulk of the superlattice structure. One or more layers of indium antimonide are added to unit cells of the superlattice to provide a further degree of freedom in the design for adjusting the effective bandgap energy of the superlattice. One or more layers of gallium arsenide are added to unit cells of the superlattice to counterbalance the crystal lattice strain forces introduced by the aforementioned indium antimonide layers.
Owner:SVT ASSOCS
Polishing method for gallium antimonide monocrystal wafer
ActiveCN112077691ARealize one-step moldingImprove surface qualityLapping machinesPolishing compositions with abrasivesGallium antimonidePolishing
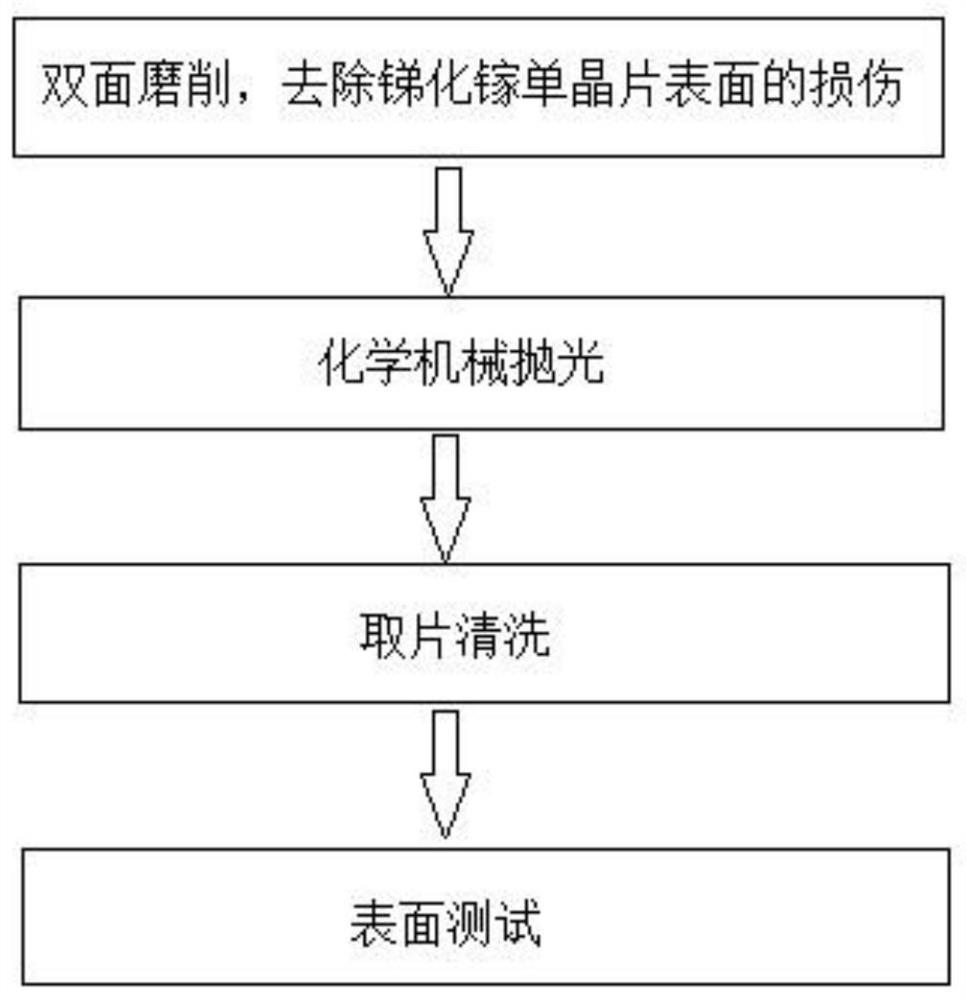
The invention provides a polishing method for a gallium antimonide monocrystal wafer. The polishing method comprises the following step (1) of grinding both sides of the gallium antimonide monocrystalwafer to remove damage from the surface of the gallium antimonide monocrystal wafer; the step (2) of chemically and mechanically polishing the ground gallium antimonide monocrystal wafer by using polishing cloth coordinated with polishing solutions; and the step (3) of taking and cleaning the gallium antimonide monocrystal wafer after chemical mechanical polishing. According to the polishing method, through selection and optimization of the components and content of the polishing solutions, and the polishing cloth coordinated with the polishing solutions, one-step forming of polishing of thegallium antimonide monocrystal wafer is achieved, and three steps of rough polishing, medium polishing and fine polishing are not required; the process is simple, and the stability is high; the surface quality of the polished gallium antimonide monocrystal wafer is high, and the defects of scratches and fogging are avoided; the surface roughness is low; and the roughness value Ra can be less than0.15 nm.
Owner:WUHAN GAOXIN TECH
Thin film material used for terahertz and infrared light polarization modulation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107065058AEasy to integrateImprove continuityPolarising elementsGallium antimonideSemiconductor materials
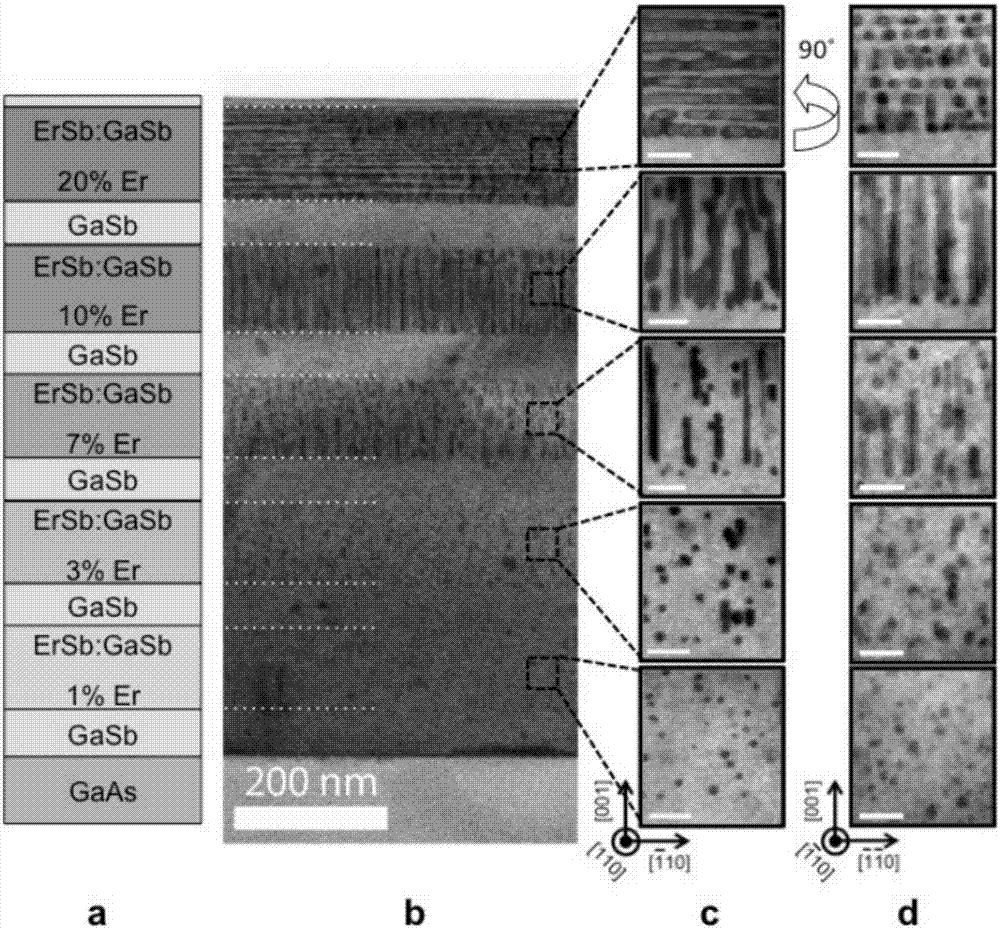
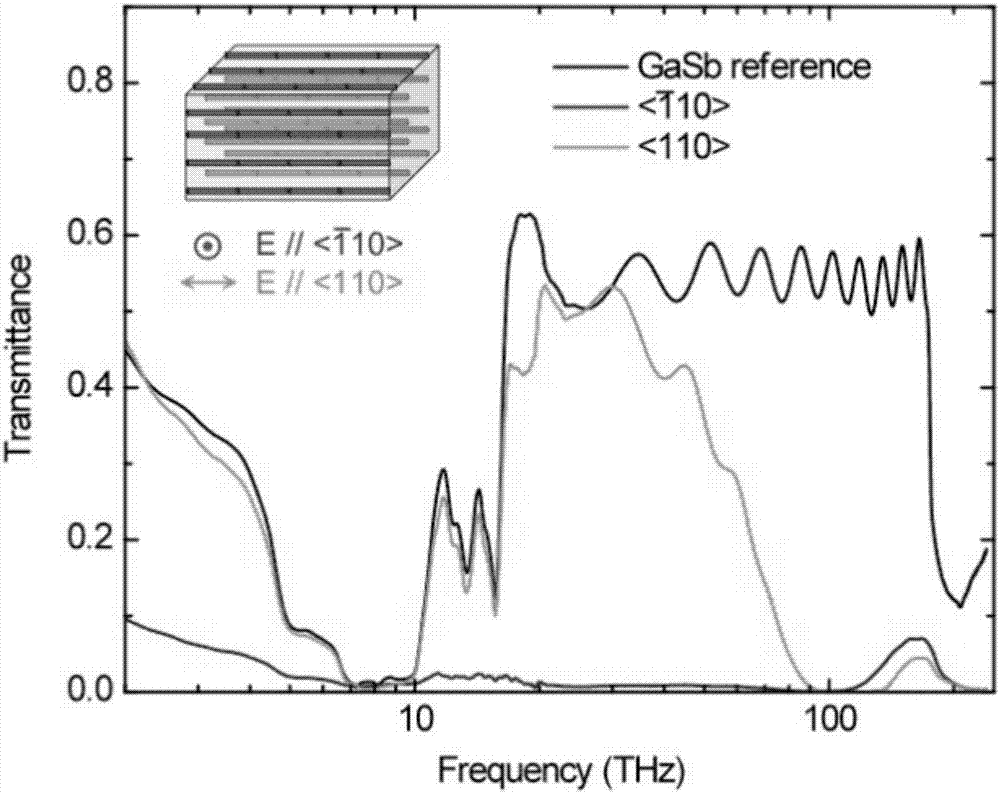
The invention discloses a thin film material used for terahertz and infrared light polarization modulation and a preparation method thereof. According to the thin film material, particularly, an ErSb nanowire array is embedded in a GaSb substrate, the direction of the nanowire array is vertical to or parallel with the surface of the substrate, and when the volume by volume concentration of the ErSb is 10%, the direction of the nanowire array is vertical to the surface of the substrate; and when the volume by volume concentration of the GaSb is 15 to 25%, the direction of the nanowire array is parallel with t the surface of the substrate. Through a molecular beam epitaxy method, a composite material of embedding the nanowire structure with a semi metallic property in a semiconductor material is acquired, the material can be used for a broadband terahertz and infrared polarizer and can be integrated with a terahertz and infrared optoelectronic device based on III-V semiconductor materials.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Rheotaxial preparation method of gallium antimonide quantum dot
InactiveCN102347221AAchieve growthSimple preparation processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGallium antimonideLattice mismatch
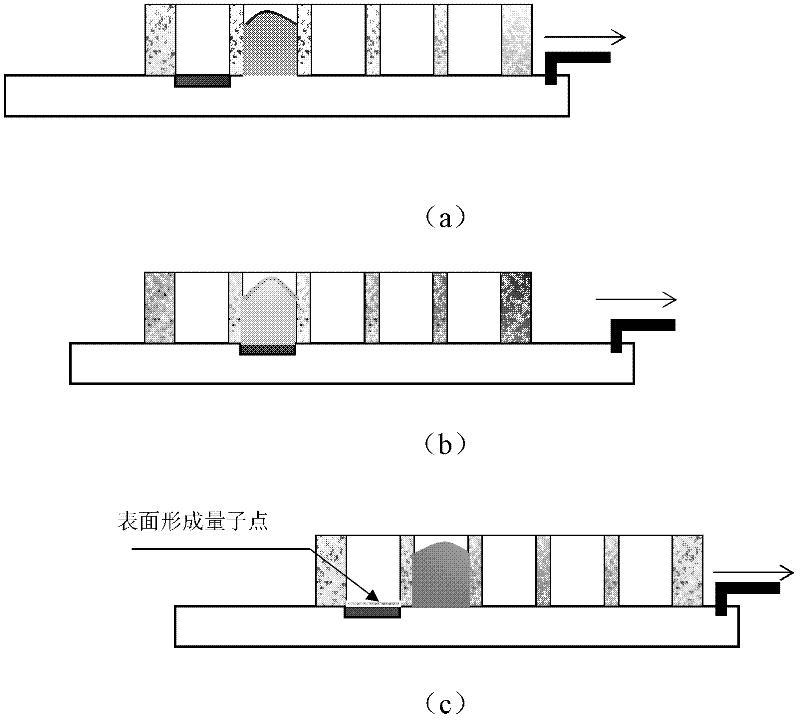
The invention discloses a rheotaxial preparation method of a gallium antimonide quantum dot. The method comprises the steps of rapidly pushing a growth source with an overcooling degree from the surface of a gallium arsenide substrate through a drive motor; and consequently forming a material structure of the gallium antimonide quantum dot on the surface of the substrate due to the lattice mismatch between the material of the quantum dot and the surface of the substrate. The preparation method provided by the invention is simpler and lower in cost, and the problems in high cost and high toxicity in the prior art are solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of indium antimonide (211) direction single crystal
InactiveCN108166060AReduce dislocationImprove performancePolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsGallium antimonideDislocation
Belonging to the technical field of photoelectric materials, the invention relates to a preparation method of an indium antimonide (211) direction single crystal. The method mainly regulates the temperature, the seed crystal pulling speed and the shouldering angle of the crystal pulling process, and successfully realizes preparation of the indium antimonide (211) direction single crystal. Moreover, through in-situ annealing treatment on the crystal pulled indium antimonide (211) direction single crystal, the dislocation density of the prepared indium antimonide (211) direction single crystal is greatly reduced. Compared with an indium antimonide (111) direction single crystal, an infrared detector prepared from the indium antimonide (211) direction single crystal provided by the inventionhas more stable performance. The invention provides a technical scheme for successful preparation of the indium antimonide (211) direction single crystal, and greatly broadens application of the indium antimonide (211) direction single crystal to infrared detectors.
Owner:云南昆物新跃光电科技有限公司
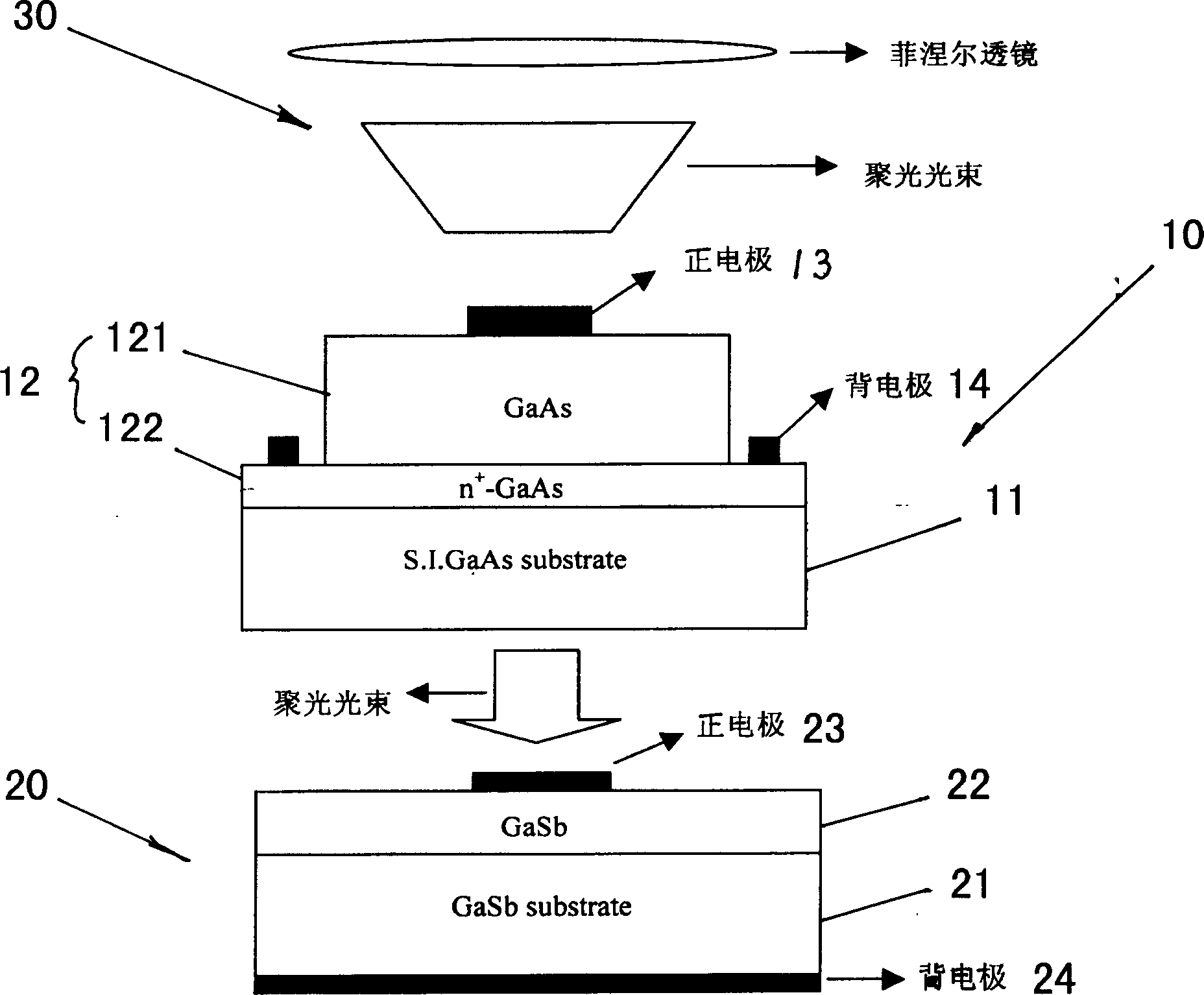
Method for making gallium arsenide/gallium stibide laminated focusing solar battery
InactiveCN1905217AImprove solar utilizationLess investmentFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesGas phaseEngineering
The invention is a method for making a gallium arsenide / gallium antimonide laminated light-collecting solar battery, comprising the steps of: a top battery uses semi-insulating gallium arsenide single crystal plate as substrate; growing an epitaxial plate by organometallic compound gas phase precipitation, molecular beam epitaxial growth technique and liquid phase epitaxial growth technique; making positive electrode on the gallium arsenide layer of the epitaxial plate of the top battery; making back electrode of the top battery on the heavy-doped n-type gallium arsenide layer on the bottom layer of the epitaxial plate; a bottom battery uses gallium antimonide single crystal plate as substrate; making positive electrode on an epitaxial plate of the bottom battery and making back electrode on the bottom surface of the substrate; making the top and bottom batteries into a mechanically laminated solar battery in a mechanical cascade mode, and then packing; using a bracket to equip light collector and solar tracker on the right side of the battery, and equip cooler on the back of the battery.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
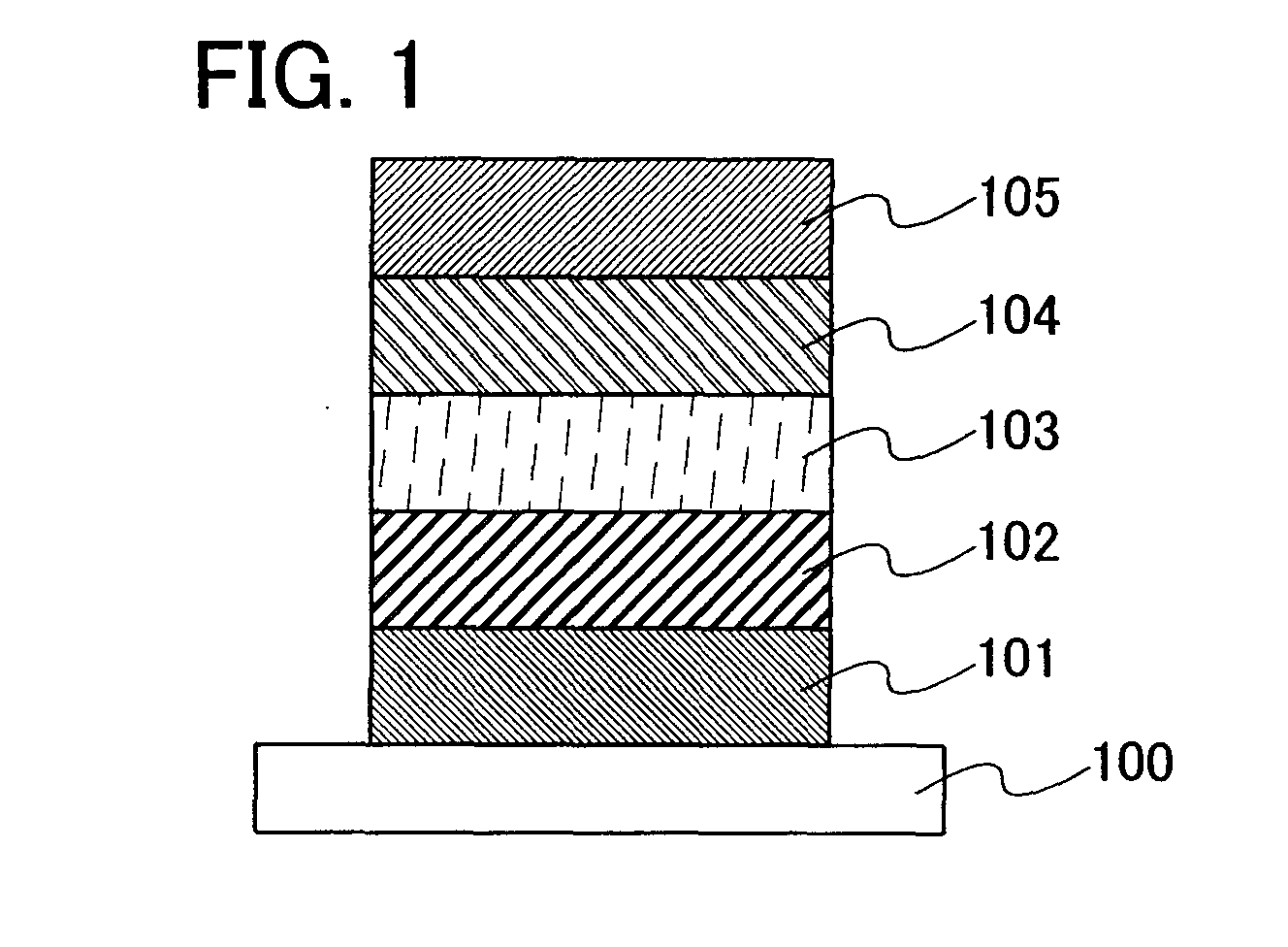
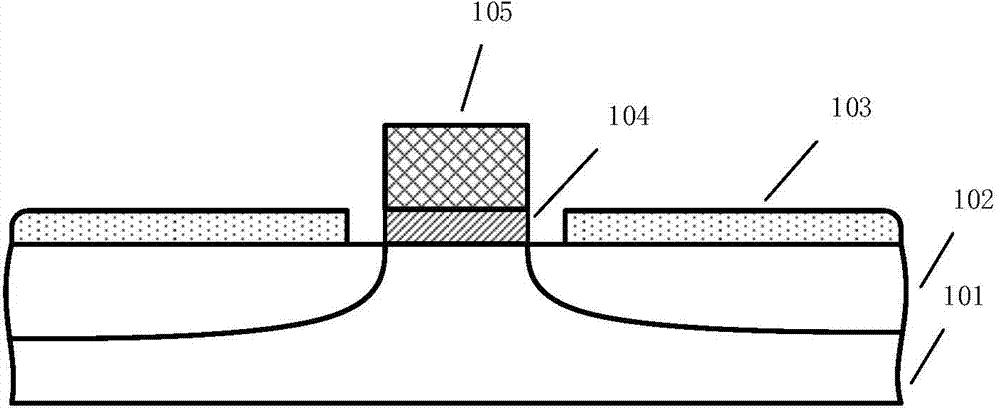
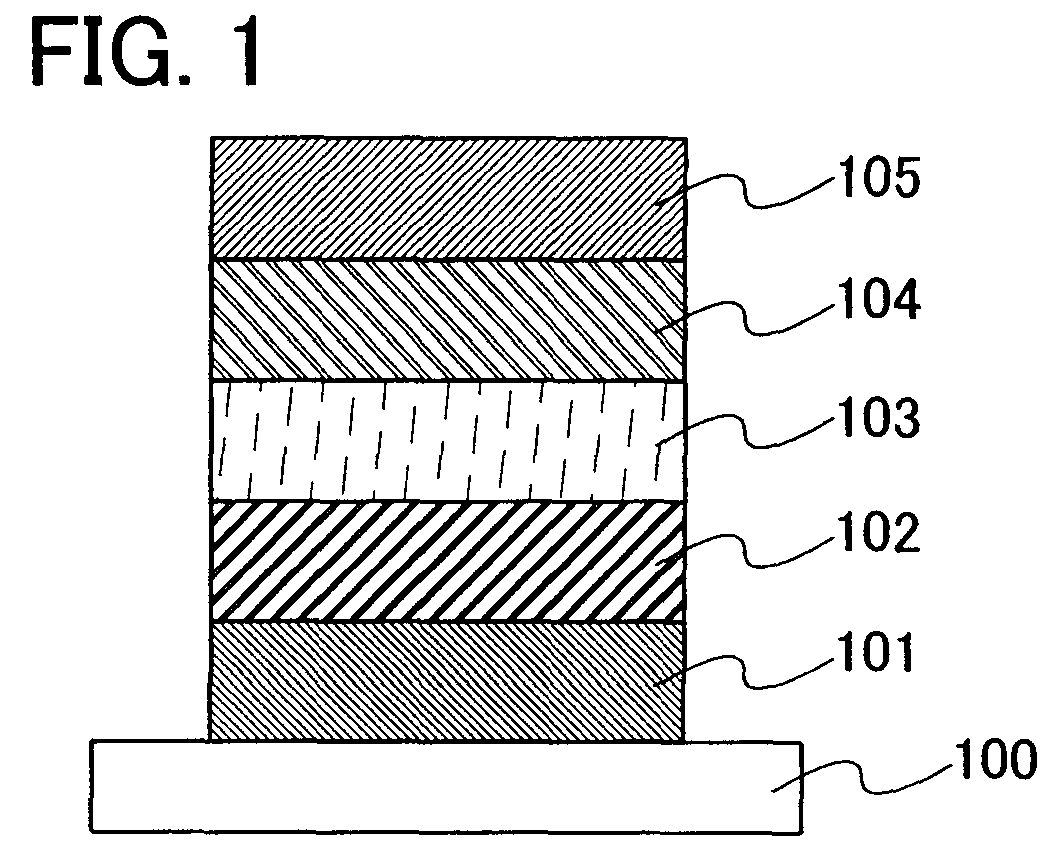
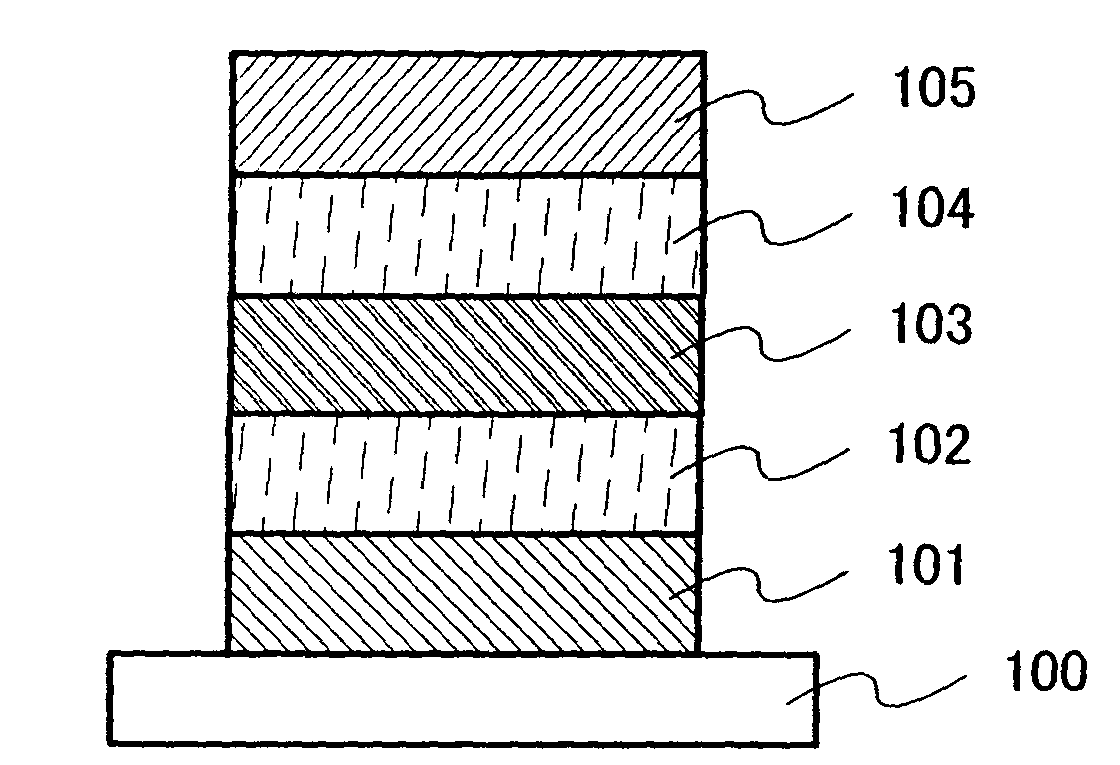
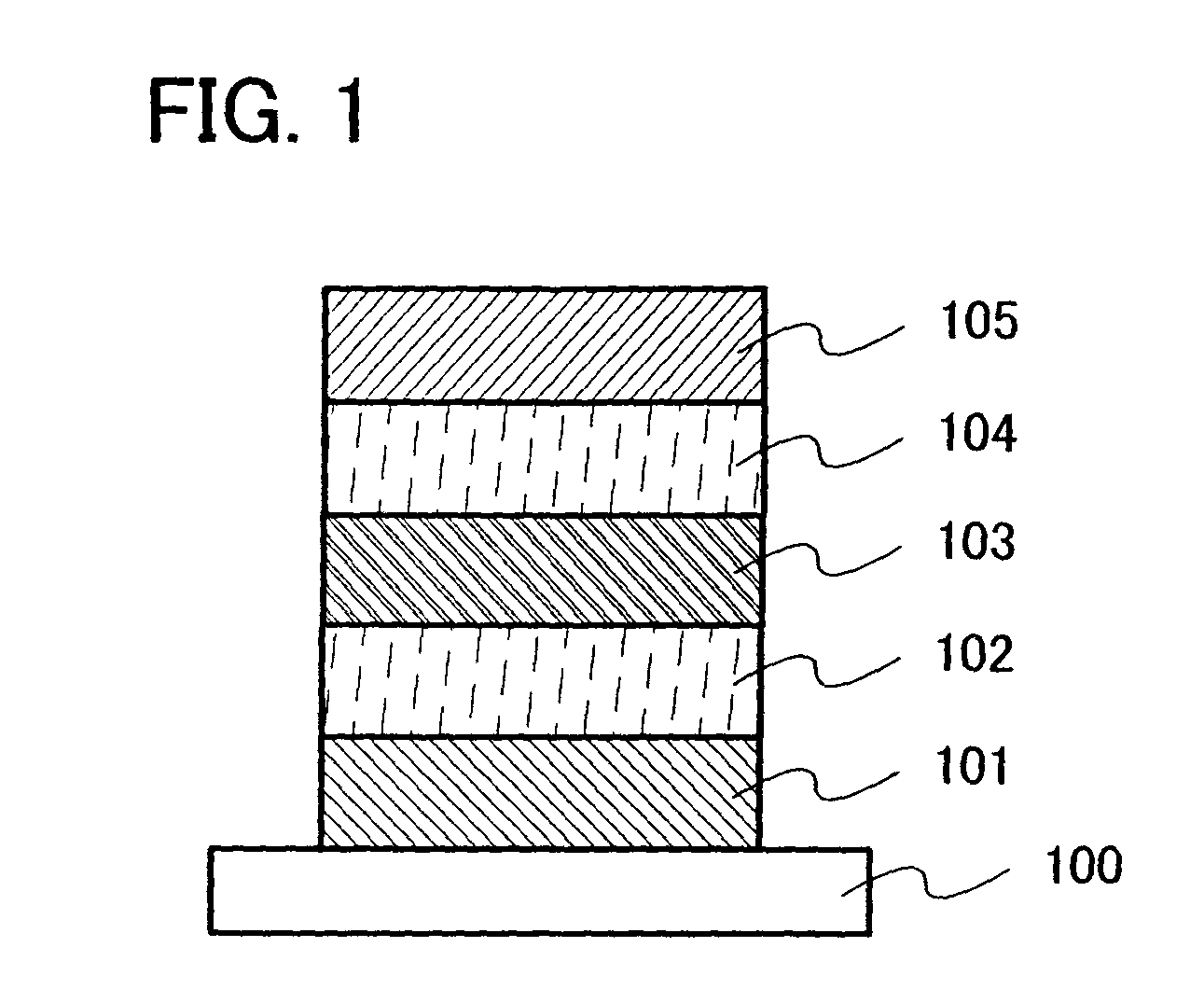
Gallium-antimonide-based semiconductor device provided with interface passivation layer and preparation method thereof
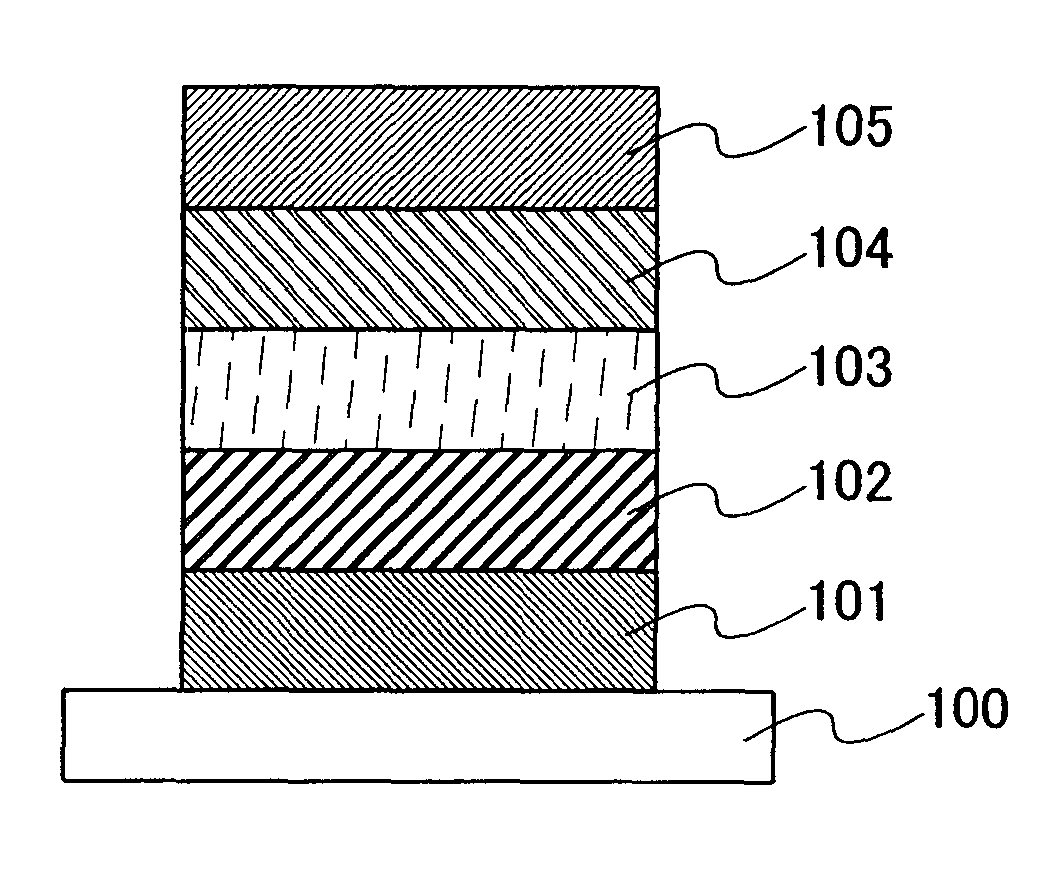
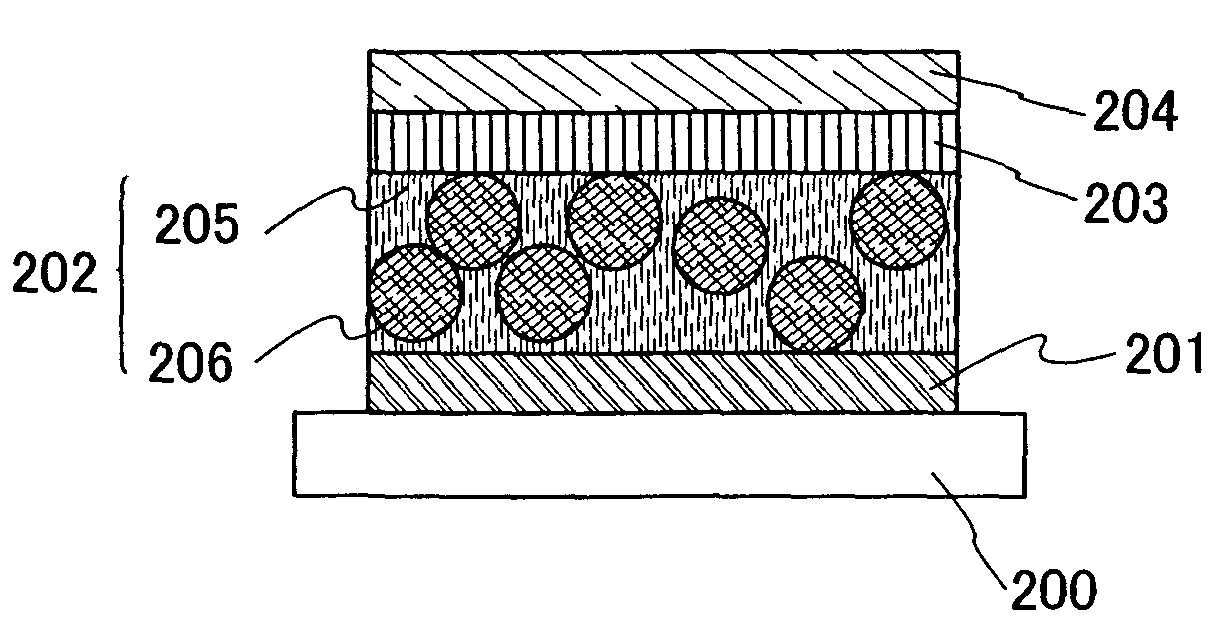
InactiveCN104716189AImprove electrical performanceReduce defect densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGallium antimonideInterface layer
The invention discloses a gallium-antimonide-based semiconductor device provided with an interface passivation layer and a preparation method thereof. The gallium-antimonide-based semiconductor device provided with the interface passivation layer comprises a first conductive type impurity gallium antimonide substrate (101), a second conductive type impurity injection layer (102), a source electrode and drain electrode layer (103), a passivated gate medium (104) and a grid electrode (105) which are sequentially arranged from bottom to top. When the gallium-antimonide-based semiconductor device is prepared, an interface of the gallium antimonide semiconductor device is passivated by introducing plasma containing the fluorine element, and therefore a plurality of fluorine passivation interface layers are formed. Stable metal-fluorine keys are formed through fluorine passivation treatment, and volume defects in the gate medium and gate medium / gallium antimonide interface traps are obviously reduced. The metal-fluorine keys are reflected onto the gallium-antimonide-based semiconductor device, so gate leakage and interface-state density are reduced, and the stability and electrical properties of the device are further greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Long Wavelength Infrared Superlattice
ActiveUS20110272672A1Extend the cutoff wavelengthTotal current dropNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGallium antimonideIndium arsenide
An embodiment of the present invention improves the fabrication and operational characteristics of a type-II superlattice material. Layers of indium arsenide and gallium antimonide comprise the bulk of the superlattice structure. One or more layers of indium antimonide are added to unit cells of the superlattice to provide a further degree of freedom in the design for adjusting the effective bandgap energy of the superlattice. One or more layers of gallium arsenide are added to unit cells of the superlattice to counterbalance the crystal lattice strain forces introduced by the aforementioned indium antimonide layers.
Owner:SVT ASSOCS
Light emitting material, light emitting element, light emitting device and electronic device
InactiveUS7622744B2Reduce power consumptionLow-voltage drivingElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesLow voltageInorganic compound
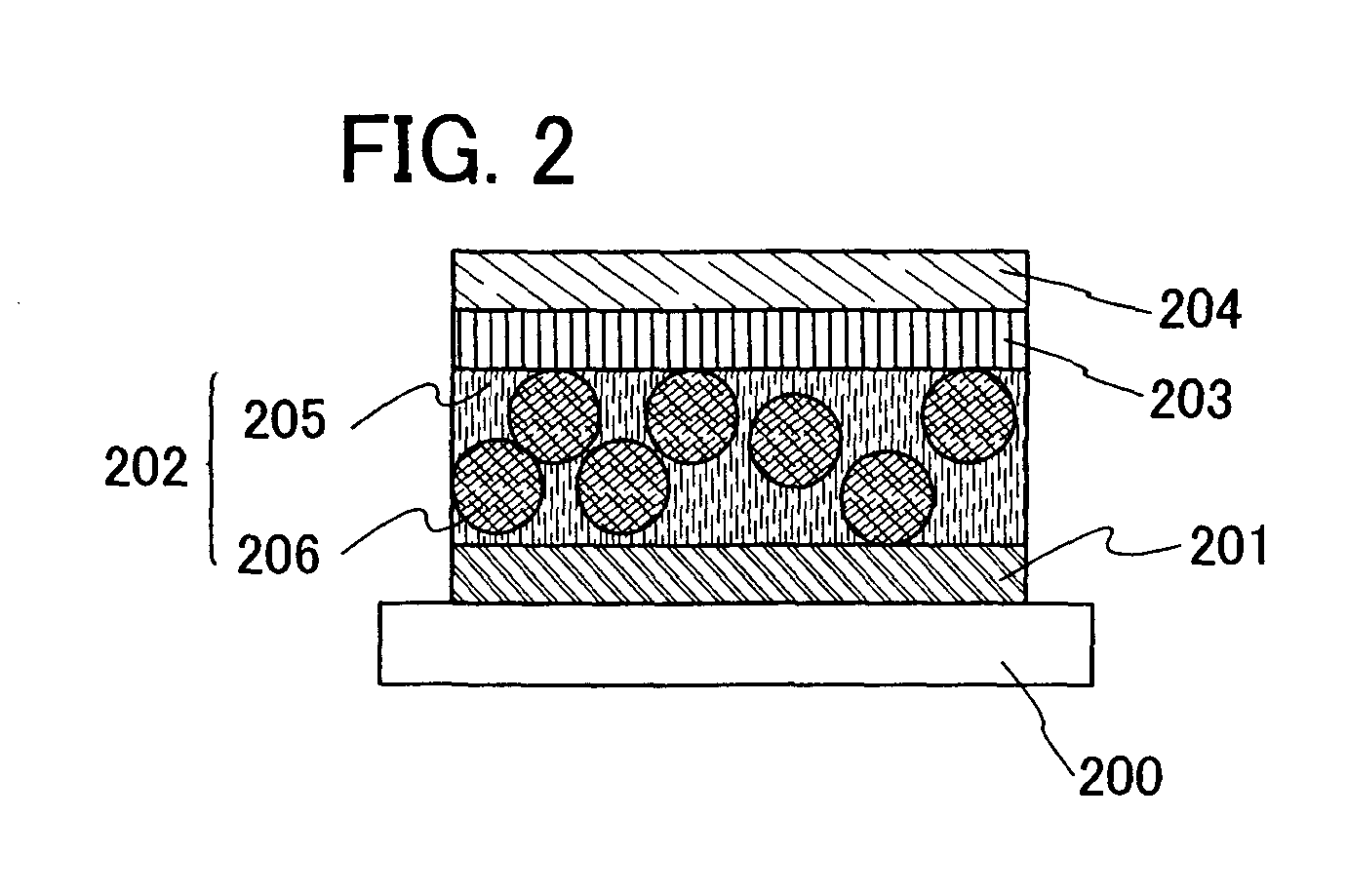
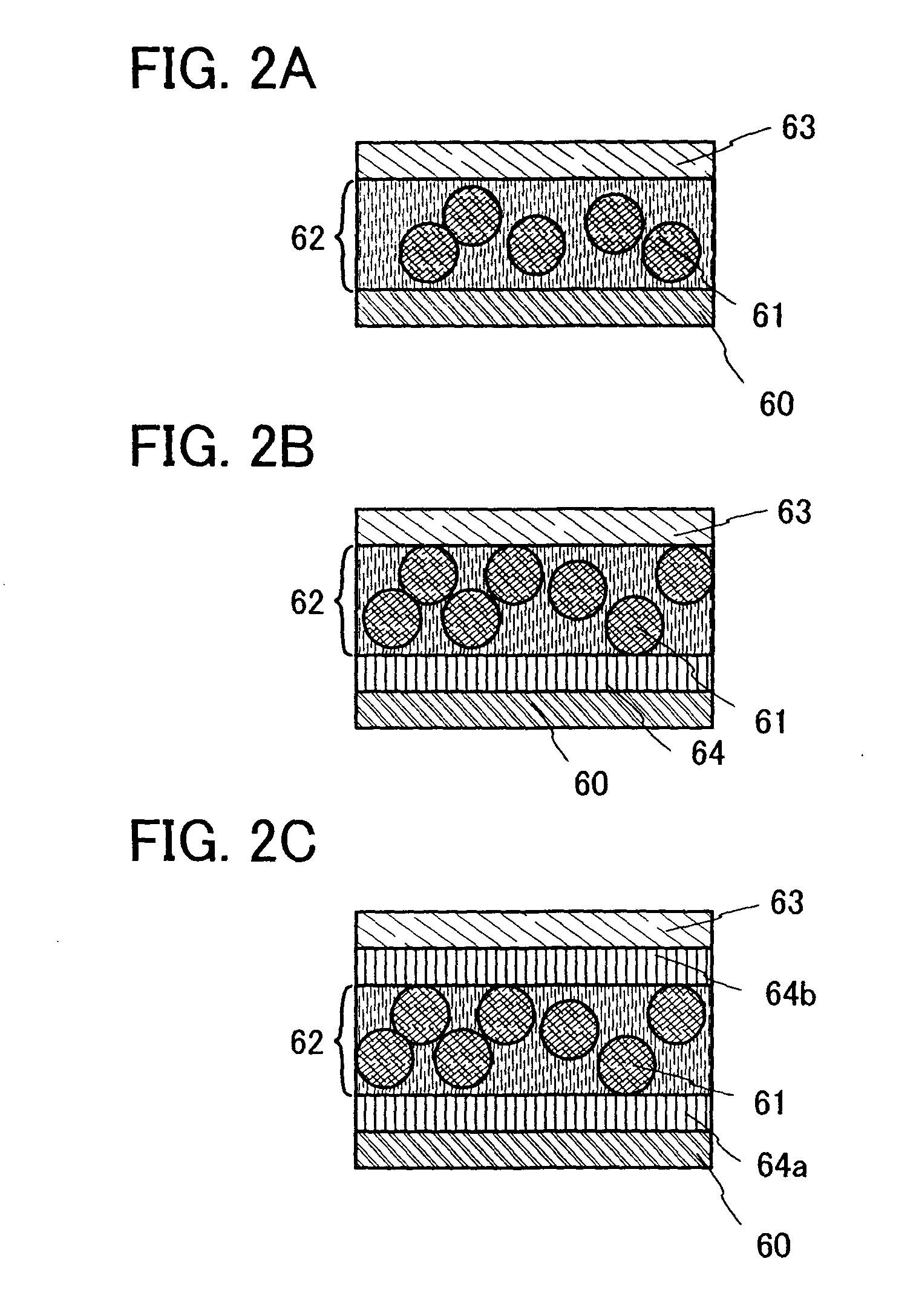
The present invention provides a light emitting material having high electric conductivity, and further a light emitting element which can be driven at low voltage. Light emitting devices and electronic devices with reduced power consumption can also be provided. A light emitting element including a light emitting material is provided in which a first electrode 101, a first insulating layer 102, a light emitting layer 103, a second insulating layer 104 and a second electrode 105 are provided over a first electrode 101, the light emitting layer 103 includes an inorganic compound that is any of a sulfide, a nitride and an oxide as a base material; at least one element selected from the group consisting of copper, silver, aluminum, fluorine and chlorine, as a luminescent center material; manganese; and either gallium phosphide or gallium antimonide.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light-emitting material, light emitting-element, light-emitting device, electronic device, and method for manufacturing thereof
InactiveUS20090009058A1Increase brightnessImprove conductivityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesGallium antimonideManganese
It is an object to provide a light-emitting material with higher emission luminance than conventional one in terms of a crystalline structure of the light-emitting material, as a light-emitting material using an inorganic compound. First baking is performed after mixing gallium arsenide, gallium phosphide, or gallium antimonide with manganese to form a first baked product, second baking is performed after mixing a base material with an element for forming a luminescent center material or a compound including the element to form a second baked product, and third baking is performed after mixing the first baked product with the second baked product, so that a light-emitting material is manufactured.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Chemical corrosion method of manganese doped gallium antimonide monocrystalline
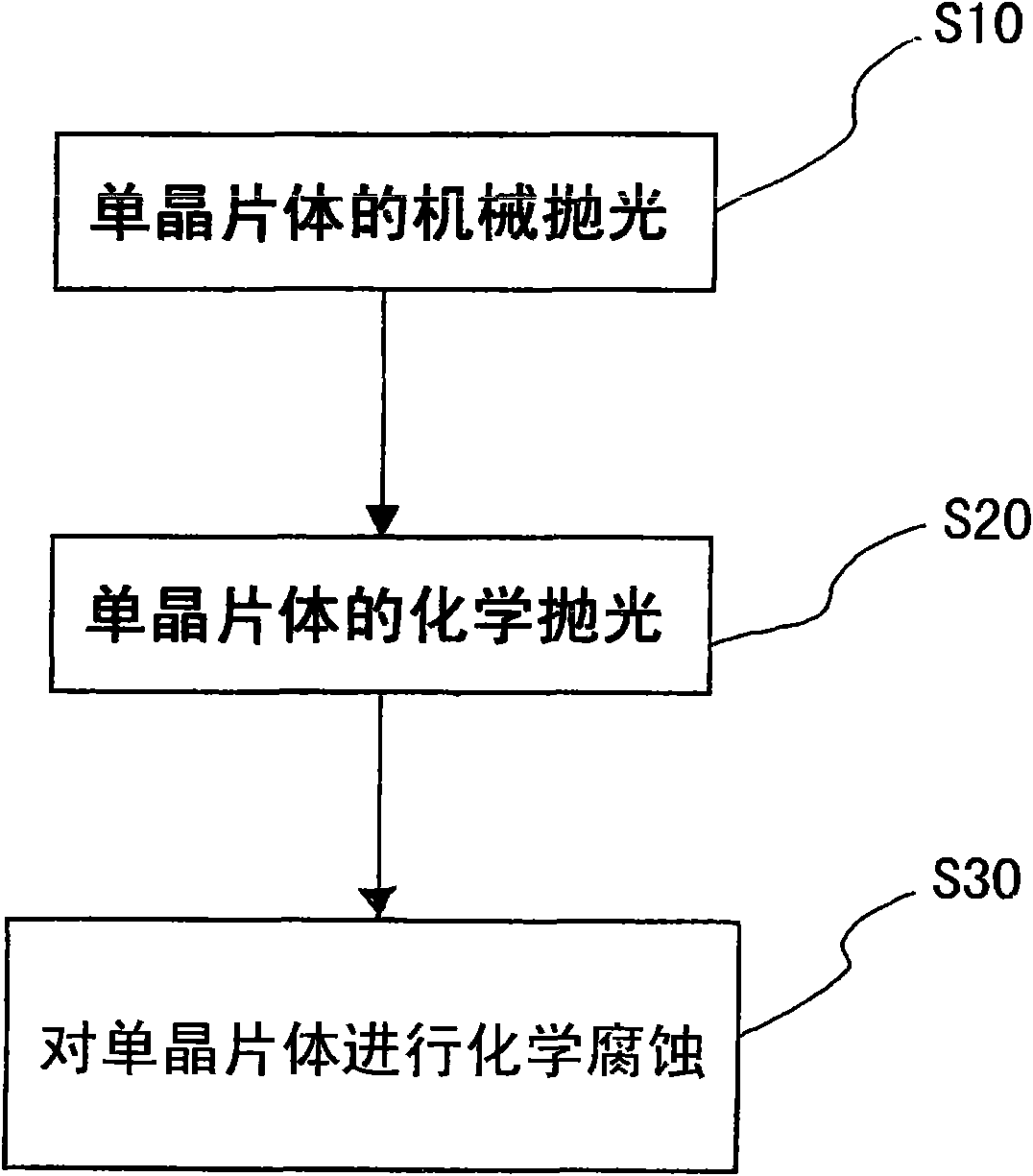
InactiveCN101858836ASimple and quick displayGood repeatabilityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsGallium antimonideSingle crystal
The invention provides a chemical corrosion method of manganese doped gallium antimonide monocrystalline, comprising the following steps: step one, taking a monocrystalline sheet, and performing mechanical polishing on the monocrystalline sheet by polishing powder; step two, performing chemical polishing on the monocrystalline sheet after mechanical polishing by a reagent; and step three, preforming chemical corrosion on the monocrystalline sheet after mechanical polishing and chemical polishing.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
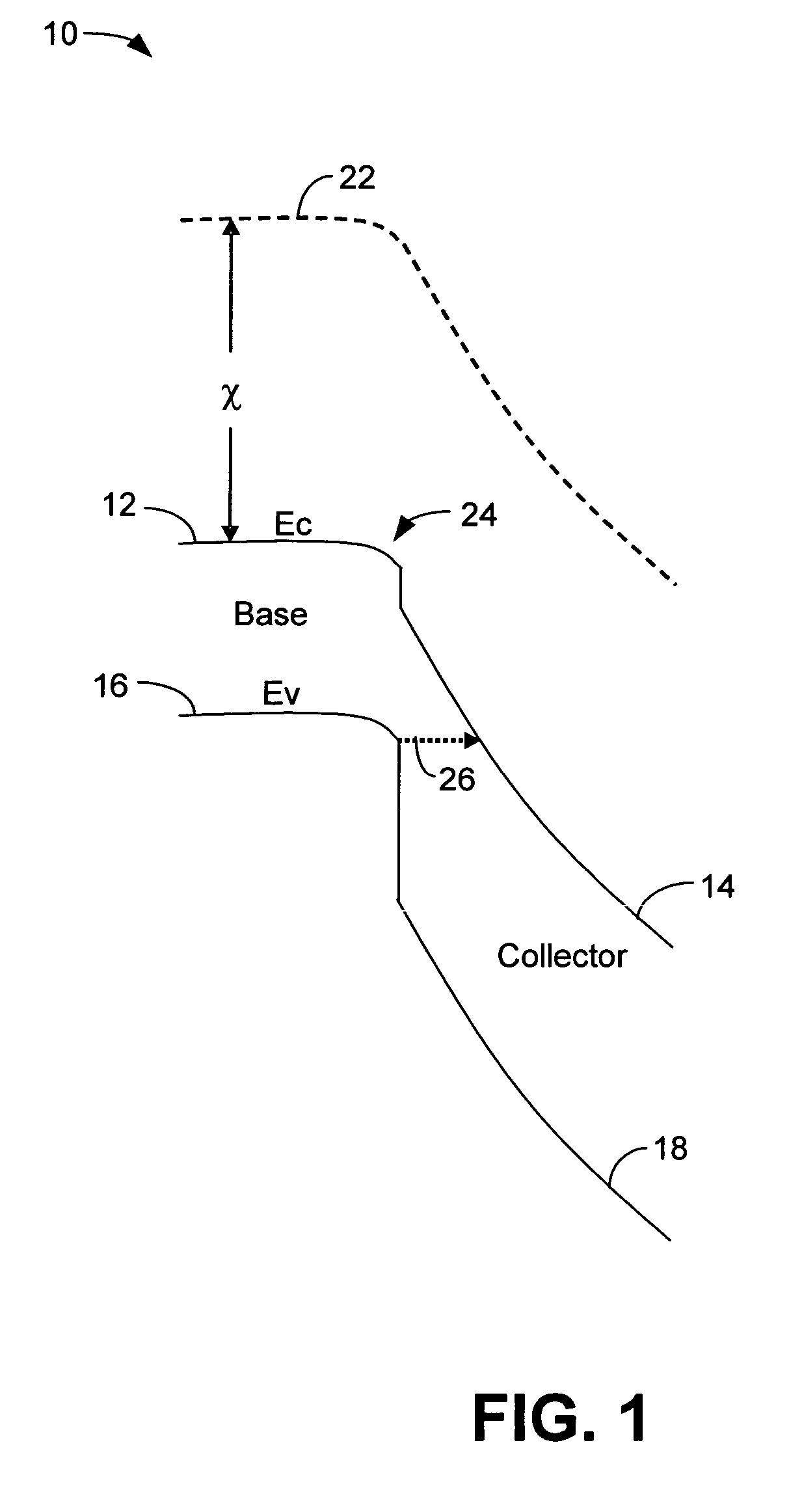
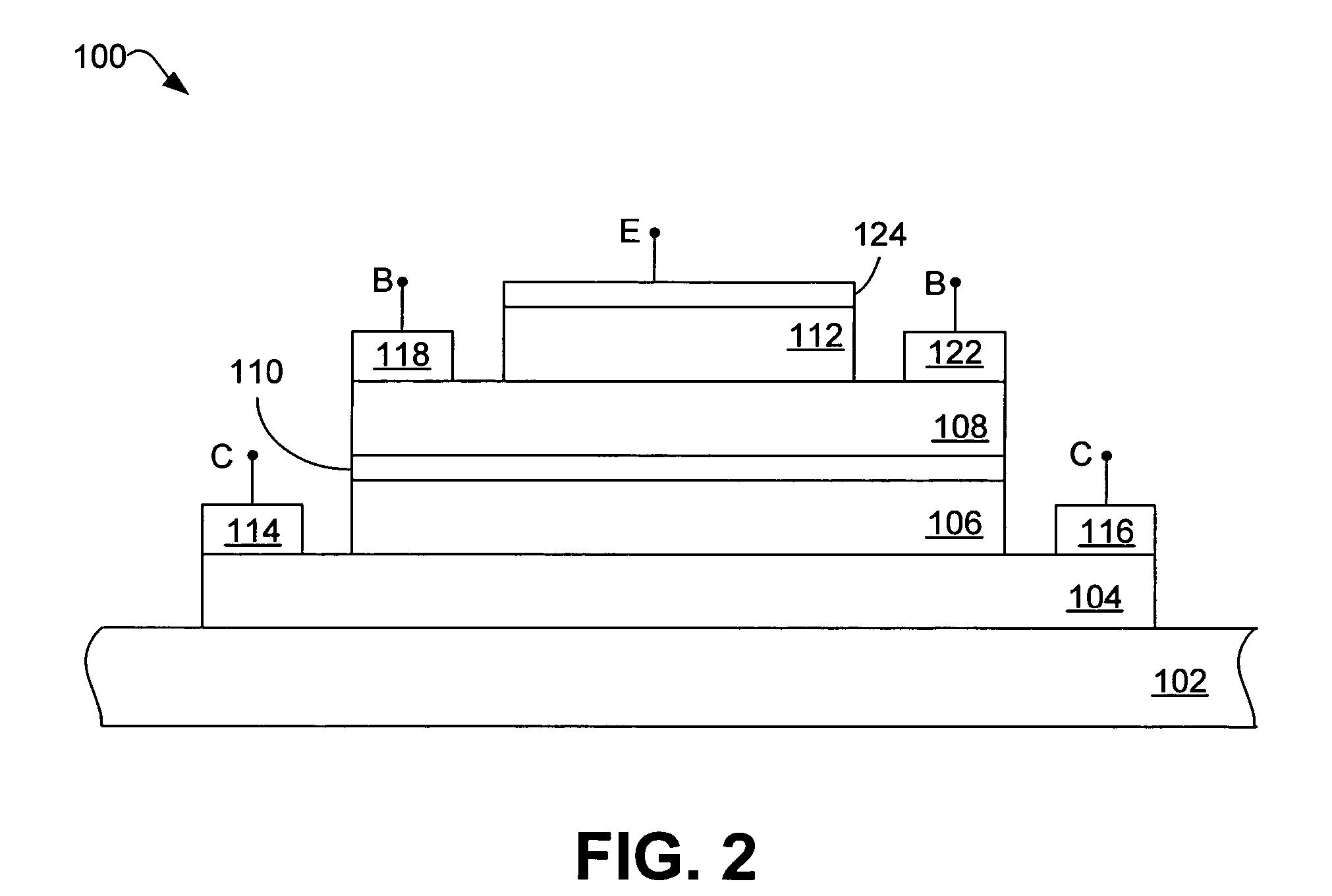
Gallium arsenide antimonide (GaAsSB)/indium phosphide (InP) heterojunction bipolar transistor (HBT) having reduced tunneling probability
InactiveUS6992337B2Improve breakdown voltageReduce probabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGallium antimonideElectron affinity
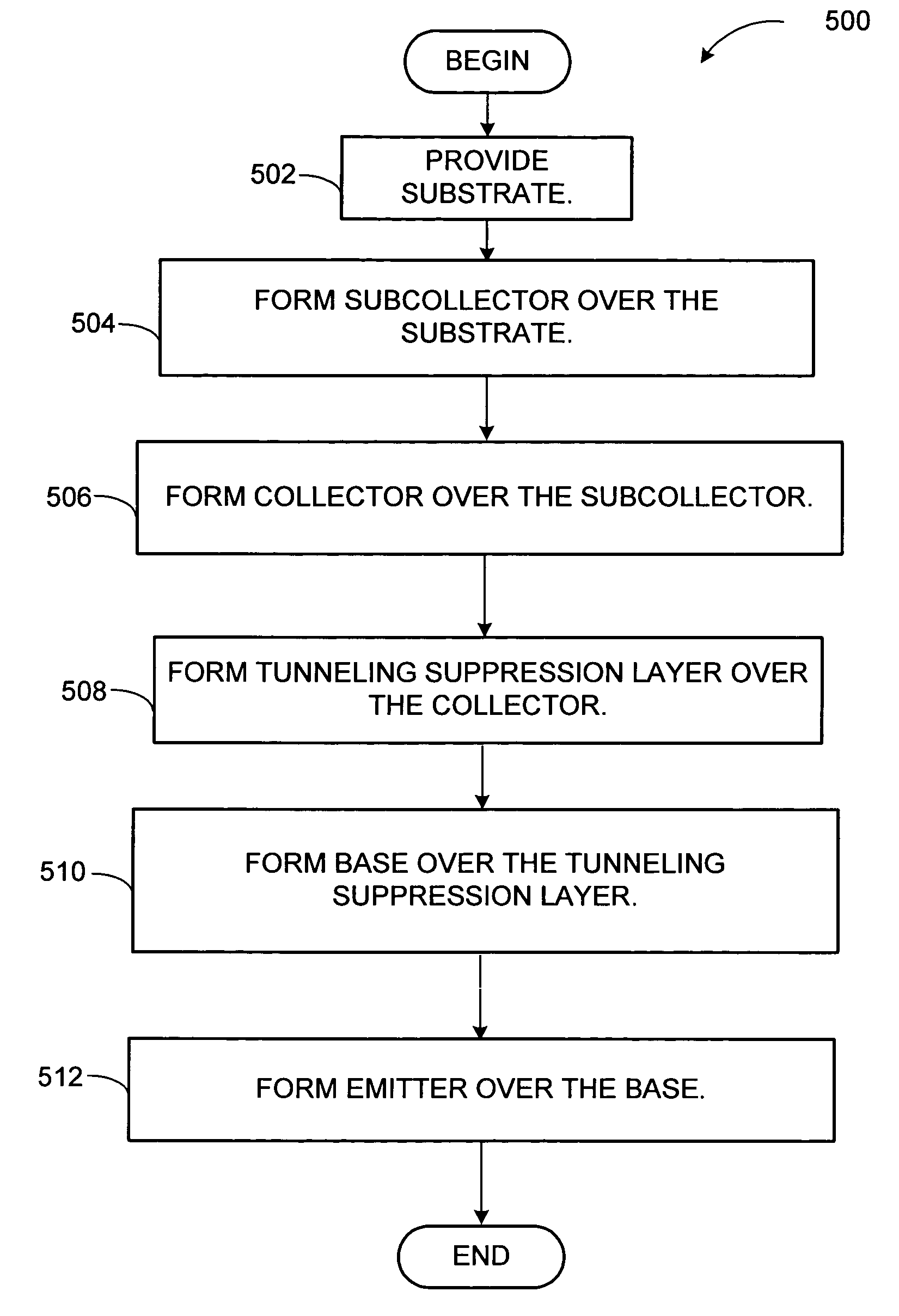
A heterojunction bipolar transistor (HBT), comprises a collector formed over a substrate, a base formed over the collector, an emitter formed over the base, and a tunneling suppression layer between the collector and the base, the tunneling suppression layer fabricated from a material that is different from a material of the base and that has an electron affinity equal to or greater than an electron affinity of the material of the base.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
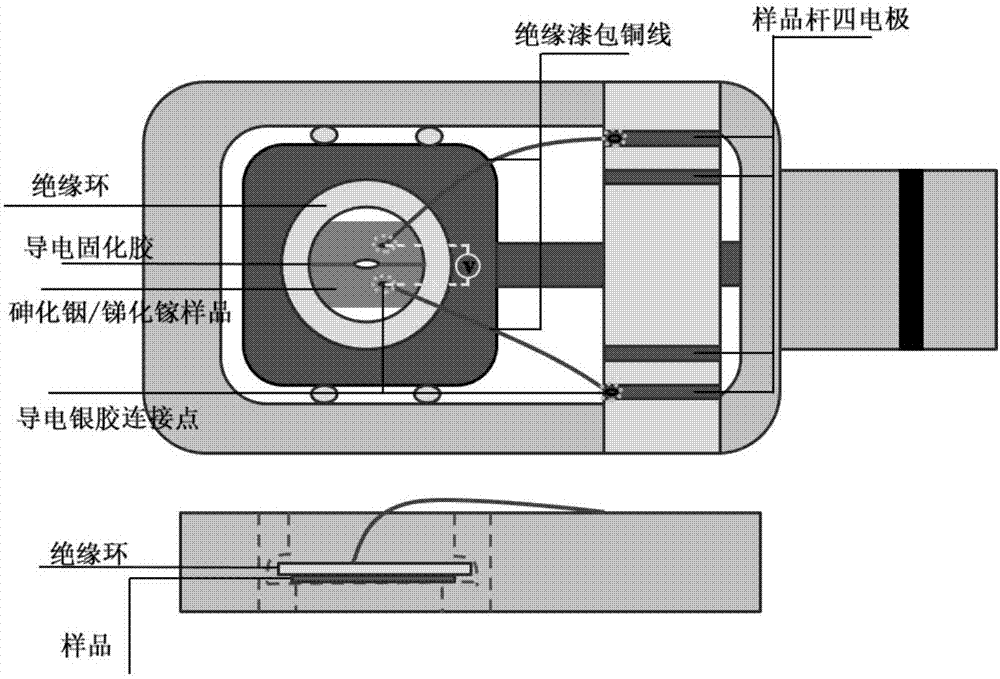
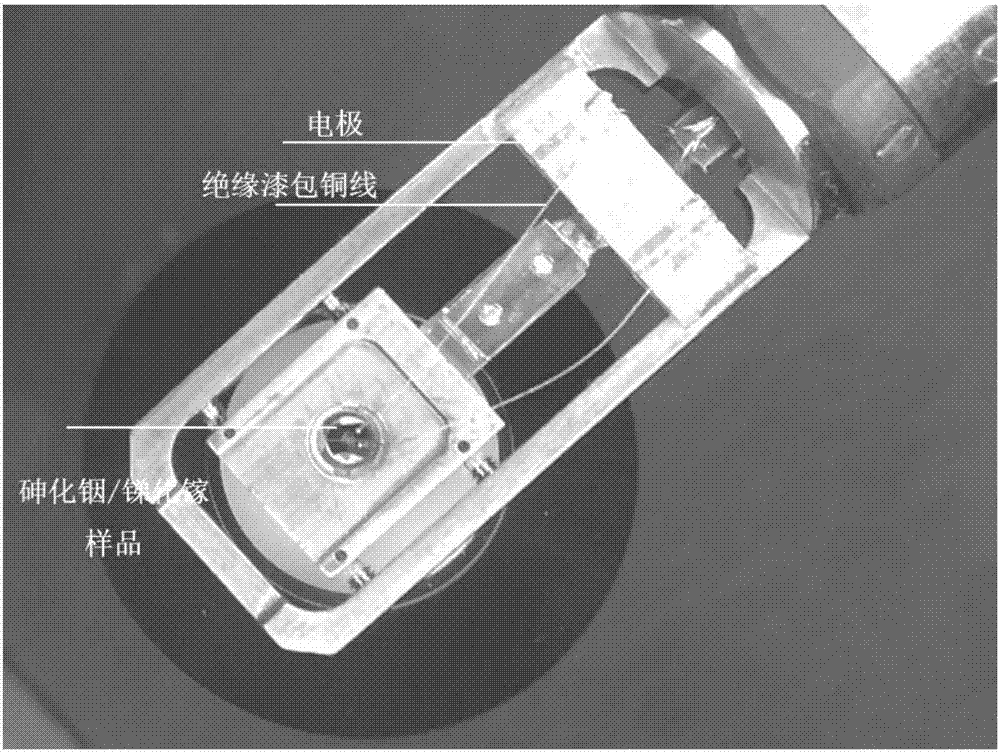
Preparation method of in-situ electrifying type indium arsenide/gallium antimonide superlattice semiconductor sample of transmission electron microscope
ActiveCN107576541AUniversalGreat application potentialPreparing sample for investigationAdhesiveCharacterization test
The invention belongs to the technical field of nanometer functional materials, and specifically relates to a preparation method of an of in-situ electrifying type indium arsenide / gallium antimonidesuperlattice semiconductor sample of a transmission electron microscope. The preparation method comprises three steps of preparing high-temperature conductive adhesive, preparing a superlattice material transmission sample, and preparing an in-situ electrode, wherein the indium arsenide / gallium antimonide superlattice semiconductor sample suitable for the characterization test of the transmissionelectron microscope can be prepared by oppositely adhering the conductive adhesive, and mechanically thinning and other processes, and then the sample is connected to a four-electrode transmission electron microscope sample stand through an enamel insulated wire, therefore, the in-situ electrifying test of the transmission electron microscope can be carried out. According to the preparation method, an arsenide / gallium antimonide superlattice semiconductor is a classic and practical infrared photoelectric detecting device for researching the physical mechanism between a microstructure and current carrier property and the conveying mechanism of a current carrier in an electrifying working state, and the arsenide / gallium antimonide superlattice semiconductor assists the design of photoelectric devices such as an infrared detector and a quantum cascade laser.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
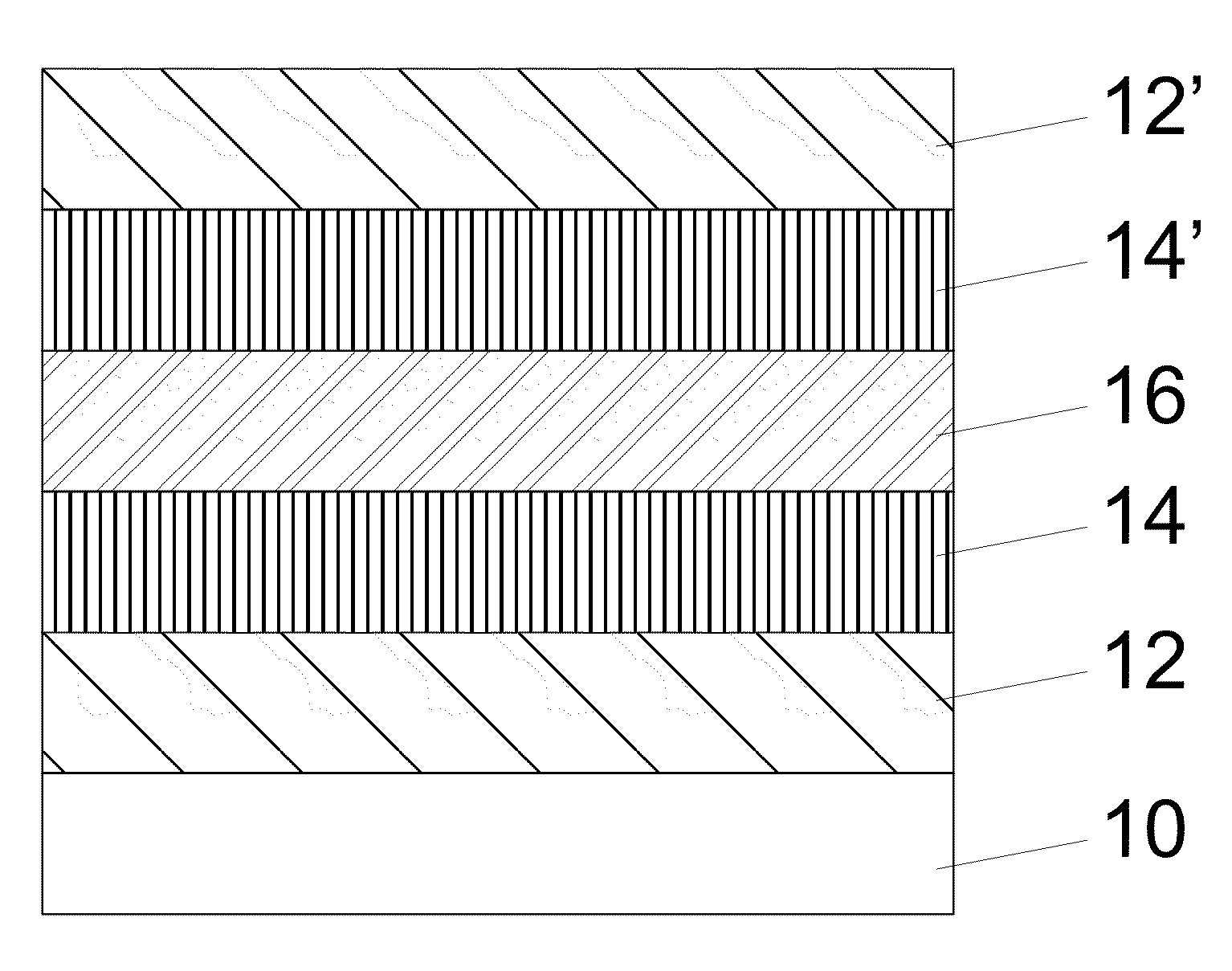
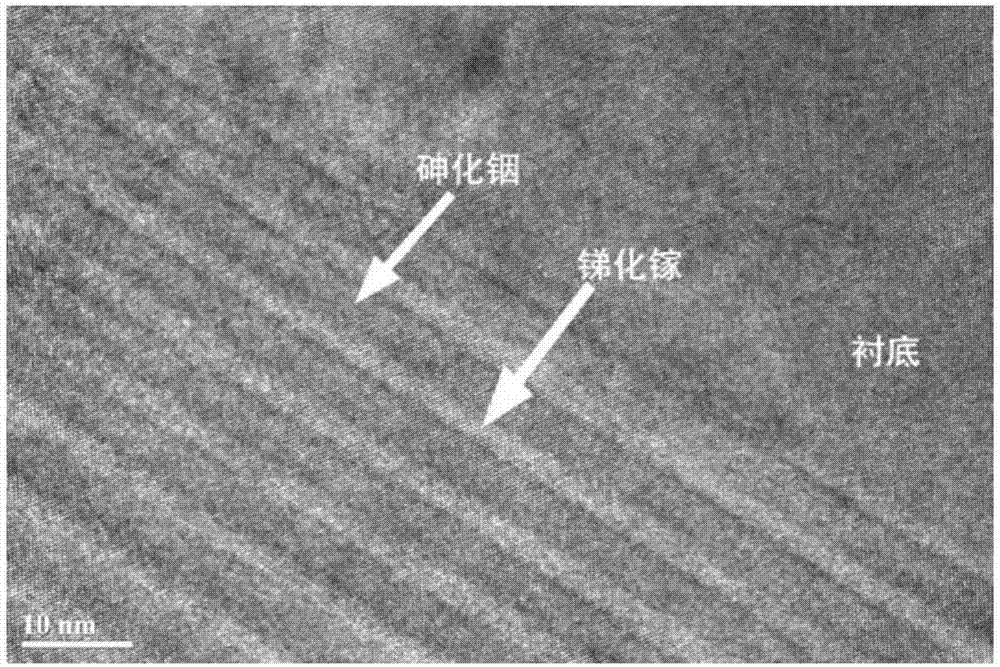
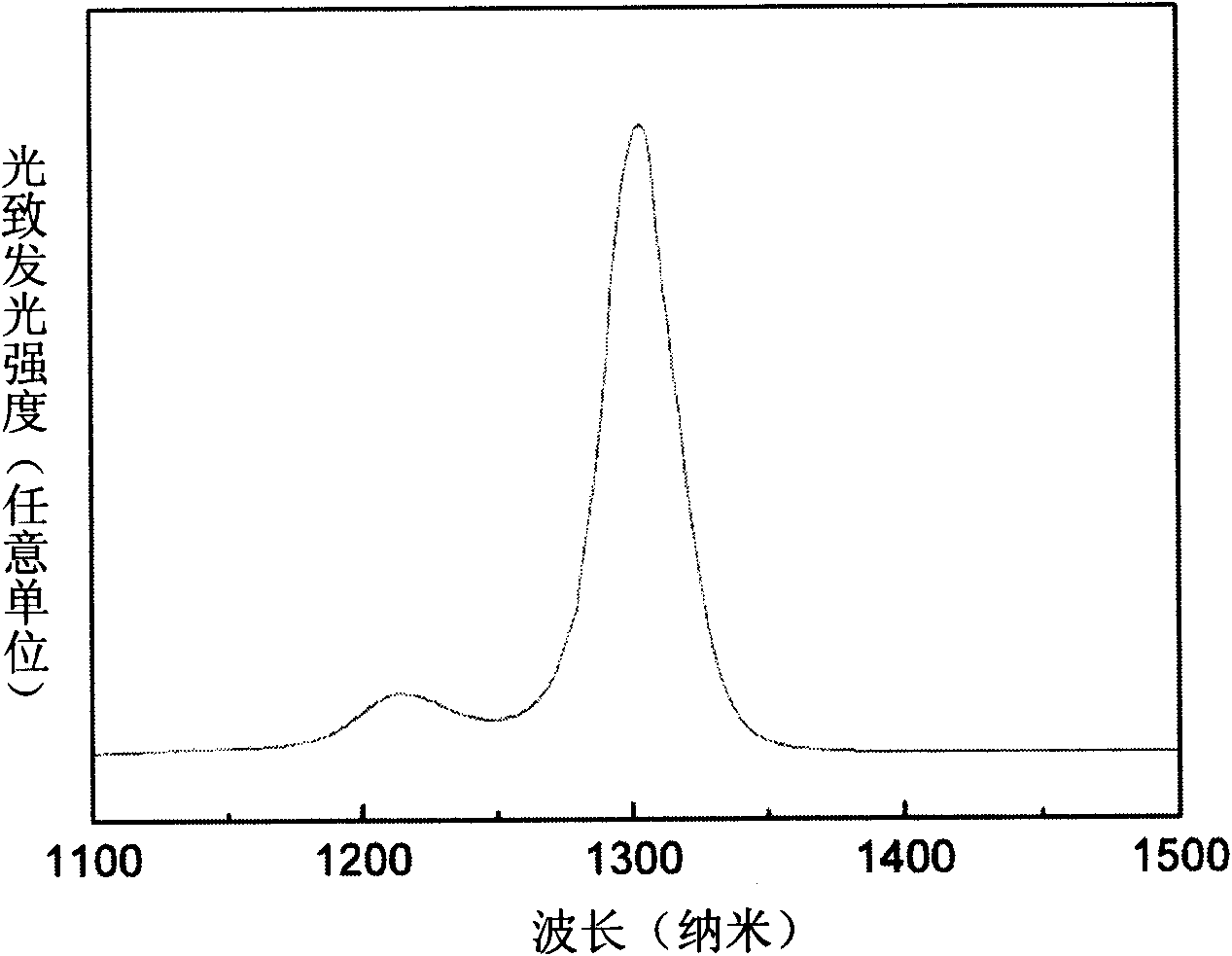
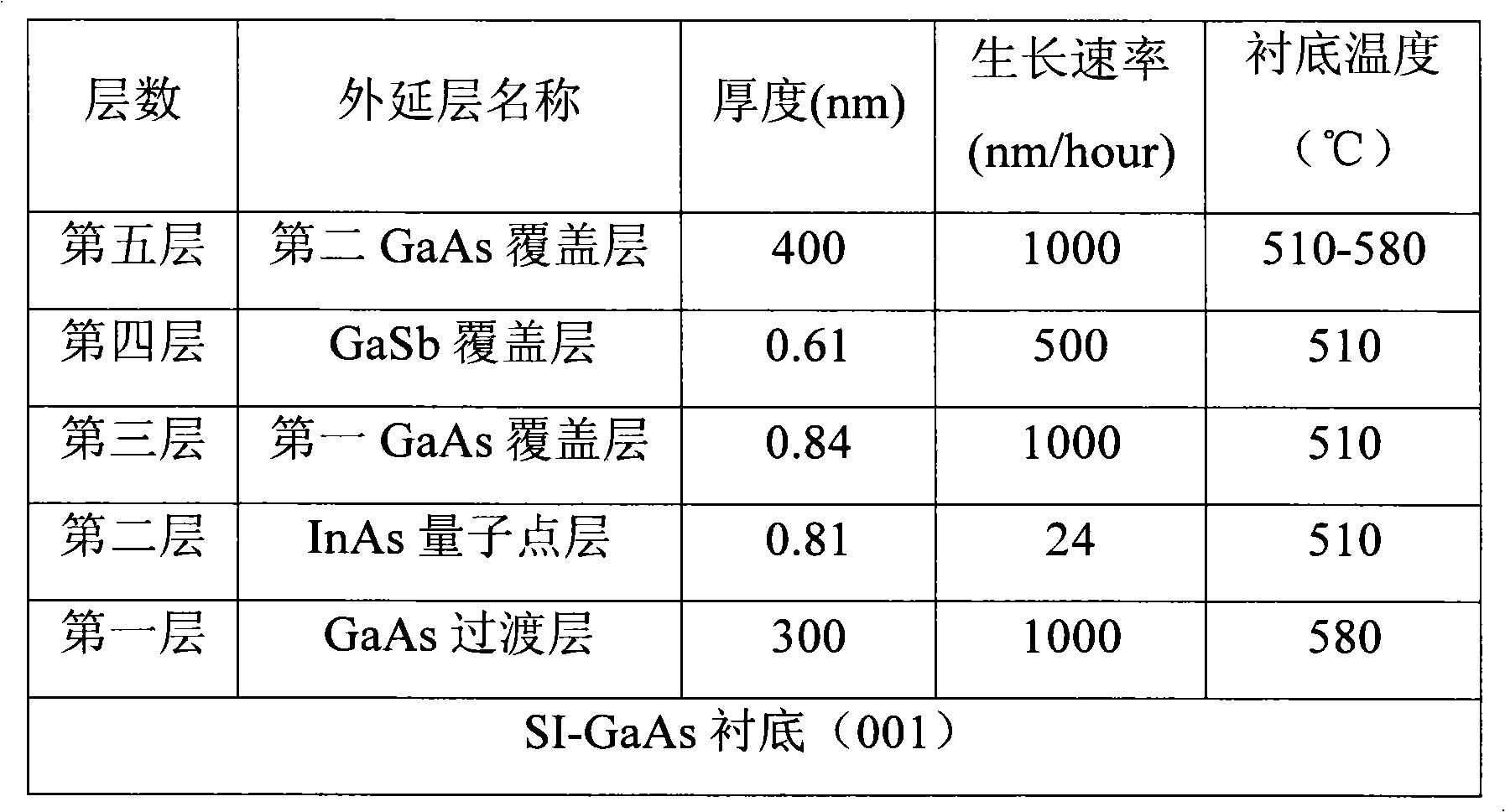
Indium arsenide (InAs) quantum dot material modulated by covering layers of gallium arsenide (GaAs) and gallium antimonide (GaSb) and growing method thereof
The invention provides an Indium arsenide (InAs) quantum dot structure modulated by covering layers of gallium arsenide (GaAs) and gallium antimonide (GaSb), comprising a GaAs buffer layer, an InAs self-assembled quantum dot layer, a first GaAs covering layer, a GaSb covering layer and a second GaAs covering layer, which are subjected to molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) on a substrate. Room temperature photoluminescence of the quantum dot obtained by the material structure can reach over 1.3mu m and half-peak breadth thereof is only 20mev. The quantum dot has good dimensional homogeneity. In addition, the invention also discloses a manufacturing method of an epitaxial homogeneous quantum dot material structure with wavelength of 1.3mu m.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for epitaxial growth of gallium antimonide on gallium arsenide substrate
InactiveCN100495646CReduce defectsBlock vertical growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGallium antimonideGallium arsenide
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Surface cleaning method of gallium antimonide substrate and second-type antimonide-base superlattice material
InactiveCN107578985APromote growthAvoid damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGallium antimonideGeneration process
The invention relates to a surface cleaning method of a gallium antimonide substrate and a second-type antimonide-base superlattice material. The method includes the steps of packing a sample into a high-vacuum chamber, wherein the vacuum degree is higher than 1*10 <-6> Torr; raising the temperature of the sample to a target temperature value and maintaining the temperature of the sample; releasing a beam of an atomic hydrogen source to cover the sample continuously for 1-50 minutes till oxidative products on the surface of the sample are completely removed, wherein the vacuum degree is 1*10 <-6> - 1*10 <-5> Torr during the process; closing the atomic hydrogen source, and executing a subsequent material generation process in the same vacuum system. According to the surface cleaning method,at a low temperature, through assistance of the atomic hydrogen, an oxidation layer and other remaining impurities on the surface are removed, so that damage caused by high temperature to the material surface or each interface of the superlattice can be avoided; the surface roughness of the material is low after cleaning, the subsequent generation of the material is greatly facilitated, and higher interface quality can be achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU KUNYUAN OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
Polishing agent and method for polishing gallium antimonide wafer by employing polishing agent
ActiveCN106590439AHigh polishing removal rateNo chippingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolishing compositions with abrasivesGallium antimonideEngineering
The invention discloses a polishing agent and a method for polishing a gallium antimonide wafer by employing the polishing agent. The polishing agent is high in speed of polishing and removing a gallium antimonide material; the polished wafer surface is glabrous and smooth; edge breakage and scaling off do not exist; the polishing technology is simple, artificial control factors are relatively few, the availability ratio is greatly improved, and the polishing agent and the method are beneficial to cost reduction.
Owner:11TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Thermal coreduction preparation method of gallium antimonide nano-semiconductor solvent
InactiveCN1718544ASimple ingredientsAchieving Process Cleanliness GoalsGallium/indium/thallium compoundsAntimony compoundsGallium antimonideOrganic solvent
A process for preparing the nano-particles of GaSb semiconductor by solvent heat coreduction method includes such steps as reacting between CaCl3, SbCl3, reducer and solvent at 120-350 deg.C for 10-60 hr, cooling, filtering, washing and drying. Its advantages are less pollution and low reaction temp.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Indium gallium antimonide crystal growing furnace with traveling wave magnetic field
PendingCN108193279AReduce dislocationEvenly distributedPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsMelting tankIndium
The invention provides an indium gallium antimonide crystal growing furnace with a traveling wave magnetic field. The indium gallium antimonide crystal growing furnace comprises a magnetic field generation mechanism, a vertical lifting mechanism and a furnace body supporting mechanism. The magnetic field generation mechanism is composed of an iron core, a three-phase conduction insulated wire, andan insulated protective shell; the three-phase conduction insulated wire is connected to a power supply; the power supply generates electric current, and the electric current generates a travelling wave magnetic field in a horizontal coil. By applying a travelling wave magnetic field in the crystal growing furnace, when the direction of the lorentz force caused by the travelling wave magnetic field is downward, the melted material of indium gallium antimonide in a crucible is conveyed under the action of the lorentz force so that the convection process of the melted material can be accelerated and cold and hot area distribution in a furnace hearth can be more uniform. Meanwhile, a rectangular wave current generator is used for periodically controlling phase displacement signals of the three-phase current in the coil, so that uniform distribution of the melted material is facilitated, macrosegregation is obviously weakened, and indium gallium antimonide crystal ingots with lower dislocation and better crystal quality are obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
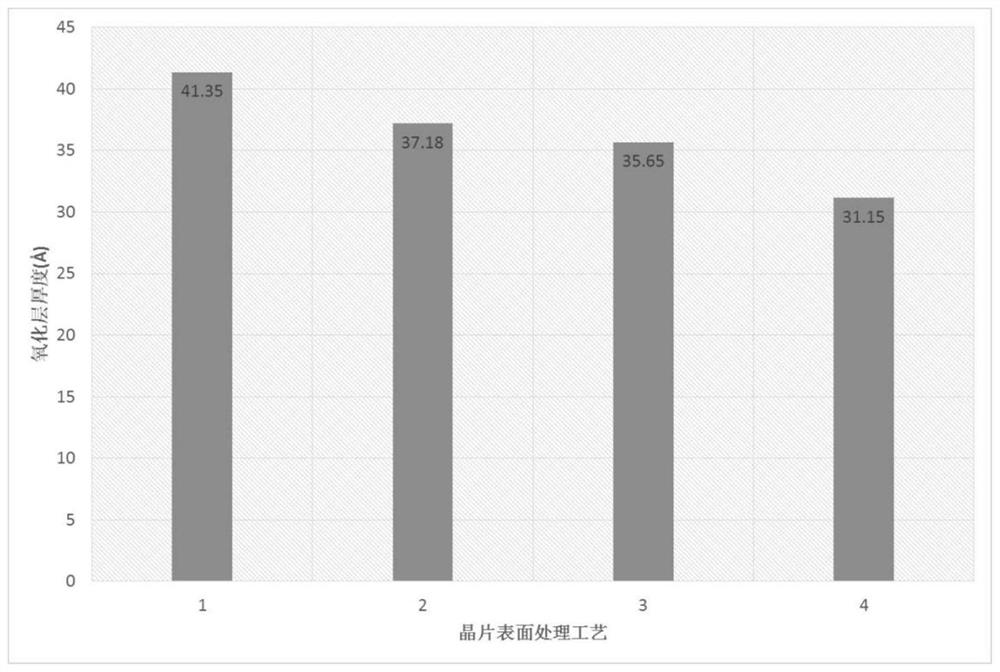
Method for controlling thickness of oxide layer on surface of gallium antimonide single crystal
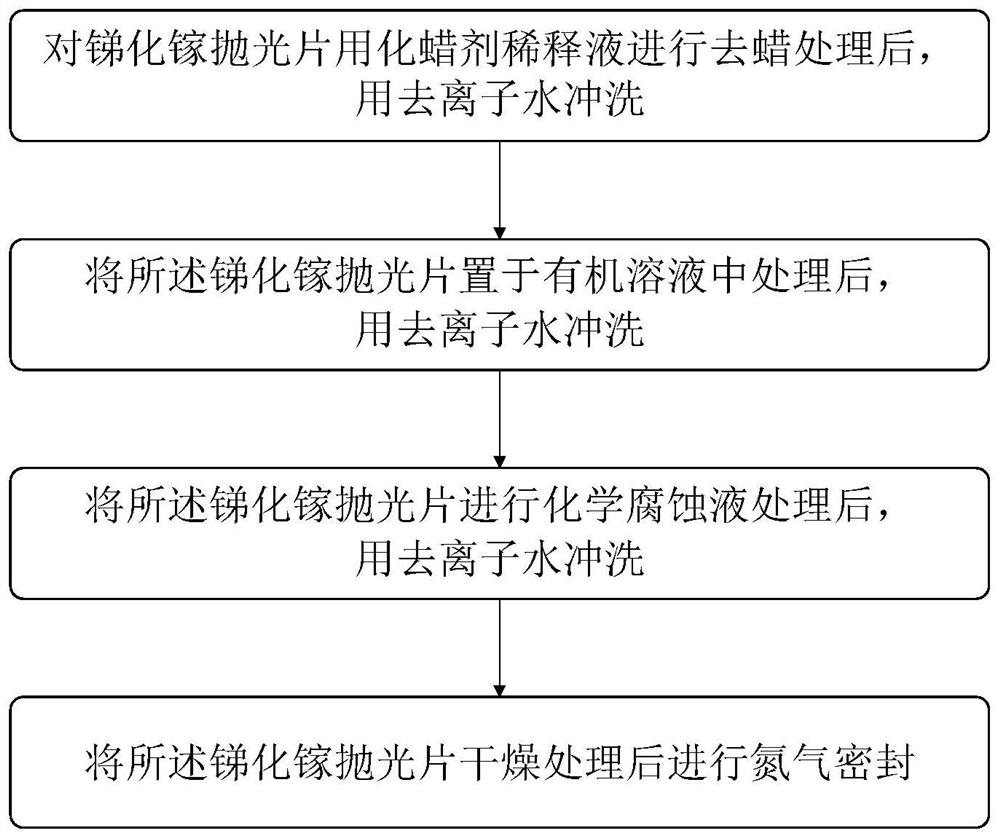
PendingCN114203526AImprove adsorption capacityControl thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning using liquidsGallium antimonideWax
The invention discloses a method for controlling the thickness of an oxide layer on the surface of a gallium antimonide single crystal, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the dewaxing treatment of a gallium antimonide polished wafer through a wax melting agent diluent, and then washing the dewaxed gallium antimonide polished wafer with deionized water; the gallium antimonide polished wafer is placed in an organic solution to be treated and then washed with deionized water; treating the gallium antimonide polished wafer with a chemical corrosive liquid, and then washing the gallium antimonide polished wafer with deionized water; and the gallium antimonide polished wafer is subjected to nitrogen sealing after being dried. The wax melting agent diluent, the organic solution and the chemical corrosive liquid are sequentially used for conducting surface wax melting process treatment on the gallium antimonide polished wafer, adsorption of surface particles can be improved, a natural oxide layer generated on the surface can be removed, the contact time of gallium antimonide single crystals and the external environment is shortened, and therefore the thickness of the oxide layer on the surface of gallium antimonide is effectively controlled, and the surface quality of the gallium antimonide polished wafer is improved. The use requirements of epitaxial materials are met.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com