Method and device for extracting metal indium in LCD by virtue of chloridizing volatilization with PVC as a chloridizing agent
A technology of chlorination volatilization and chlorination agent, applied in the direction of improvement of process efficiency, etc., can solve the problem of being unable to get rid of heat treatment, etc., and achieve the effect of ingenious design, simple process method and low operating cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
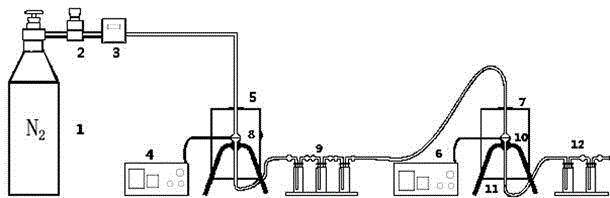
[0020] 1.25g of PVC powder was loaded into the first quartz reactor 8 of the first electric furnace 5, and 100g of desiliconized LCD glass substrate powder was loaded into the second quartz reactor 10 of the second electric furnace 7. At this time, Cl:In (molar ratio) was 11:1. Fill the second group of scrubbing bottles 12 with 1 mol / L sodium hydroxide solution. Feed N at a rate of 0.1L / min 2 After 5 minutes, the temperature of the second electric furnace 7 is first raised to 500°C. After the temperature stabilizes, the first electric furnace 5 begins to heat up to 400°C. From the first electric furnace 5 heating up, start timing 30min and the reaction finishes. The indium chloride produced by the reaction will volatilize and condense into the lower end of the second quartz reactor 10 and the quartz wool 11 . At this moment, the mass of recovered indium chloride was 0.46g, and the recovery rate of In was 97.50%.
Embodiment 2
[0022] 1.02g of PVC powder was loaded into the first quartz reactor 8 of the first electric furnace 5, and 100g of desiliconized LCD glass substrate powder was loaded into the second quartz reactor 10 of the second electric furnace 7. At this time, Cl:In (molar ratio) is 9:1. Fill the second group of scrubbing bottles 12 with 1 mol / L sodium hydroxide solution. Feed N at a rate of 0.1L / min 2 After 5 minutes, the temperature of the second electric furnace 7 is first raised to 500°C. After the temperature stabilizes, the first electric furnace 5 begins to heat up to 400°C. From the first electric furnace 5 heating up, start timing 30min and the reaction finishes. The indium chloride produced by the reaction will volatilize and condense into the lower end of the second quartz reactor 10 and the quartz wool 11 . Through detection and calculation, the mass of recovered indium chloride at this time is 0.36g, and the recovery rate of In is 74.20%.
Embodiment 3
[0024] 1.25g of PVC powder was loaded into the first quartz reactor 8 of the first electric furnace 5, and 100g of desiliconized LCD glass substrate powder was loaded into the second quartz reactor 10 of the second electric furnace 7. At this time, Cl:In (molar ratio) was 11:1. Fill the second group of scrubbing bottles 12 with 1 mol / L sodium hydroxide solution. Feed N at a rate of 0.1L / min 2 After 5 minutes, the temperature of the second electric furnace 7 is first raised to 600°C. After the temperature stabilizes, the first electric furnace 5 begins to heat up to 300°C. From the first electric furnace 5 heating up, start timing 30min and the reaction finishes. The indium chloride produced by the reaction will volatilize and condense into the lower end of the second quartz reactor 10 and the quartz wool 11 . At this time, the quality of indium chloride recovered was 0.38g, and the recovery rate of In was 80.54%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com