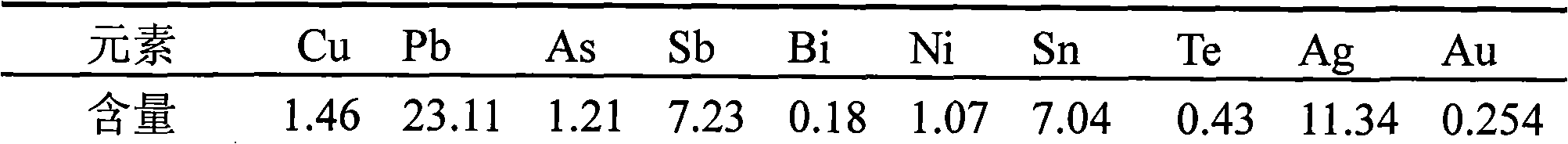Method for preprocessing anode sludge and recovering dissipated metal
A technology of scattered metals and anode slime, applied in non-metallic elements, chemical instruments and methods, and improvement of process efficiency. The effect of silver recovery rate and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Take 3kg of copper anode slime, the composition of which is shown in Table 1:
[0015] Table 1 Composition / % of copper anode slime
[0016]
[0017] When the amount of sulfuric acid is 1.5% of the amount of copper in the anode slime, the reaction temperature is 80°C, the reaction time is 1.5h, and the reaction liquid-solid ratio is 3:1, the copper leaching rate reaches 99%, and the selenium leaching rate is 10.4%. Tellurium leaching rate was 22.4%.
[0018] The sulfuric acid leaching solution is evaporated, cooled, and crystallized to recover copper sulfate. The contents of Se and Te in the mother liquor respectively reach 6.105g L -1 , 10g·L -1 . Sodium sulfite was added to the mother liquor according to 2.6 times of the amount of selenium substance, reacted at room temperature for 0.5h, filtered and dried to obtain 9.1g of crude selenium with a mass percentage of 85%. After reducing selenium, add sodium sulfite three times the amount of tellurium, and add appro...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Take 3kg of copper anode slime, the composition of which is shown in Table 1. The anode slime is leached under the conditions that the amount of sulfuric acid is 1.5% of the amount of copper in the anode slime, the reaction temperature is 80°C, the reaction time is 1.5h, and the reaction liquid-solid ratio is 3:1.
[0028] After sulfuric acid leaching to remove copper, sodium carbonate conversion to remove lead. The conditions for sodium carbonate conversion and deleading are: the ball milling time is 3 hours, the amount of sodium carbonate is 2.5 times the theoretical amount, the ball milling liquid-solid ratio is 2:1, and the ball-to-material ratio is 8:1. Sodium carbonate conversion deleading slag is leached with nitric acid, the liquid-solid ratio is 2:1, the leaching temperature is 23°C, the leaching time is 1.5h, and the amount of nitric acid is 6.0 times the amount of lead substance. The lead leaching rate reached 68.2%, and the composition of the deleaded anode...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com