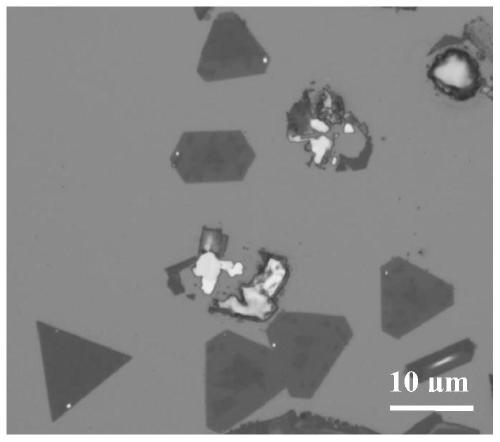
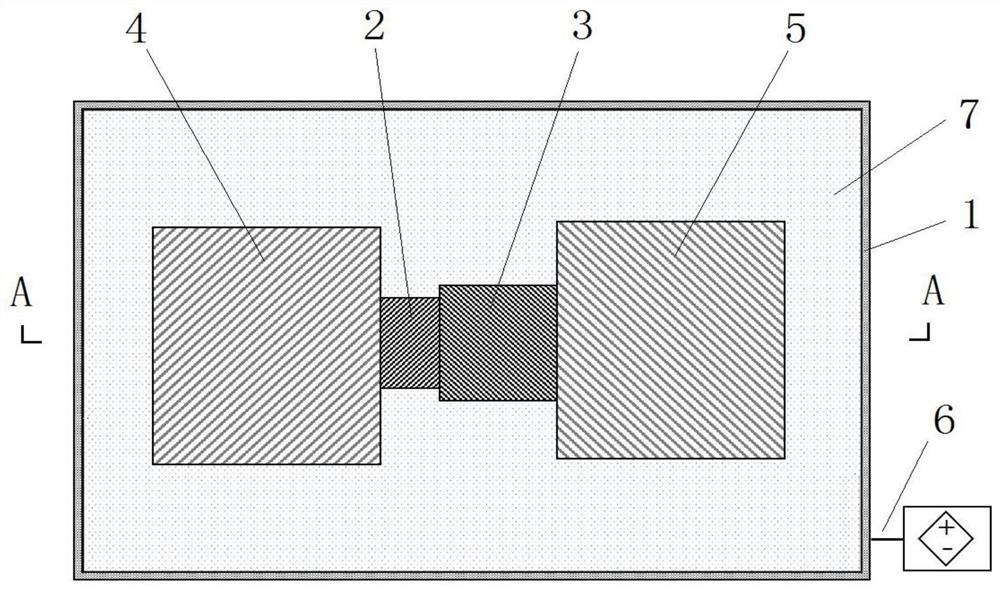
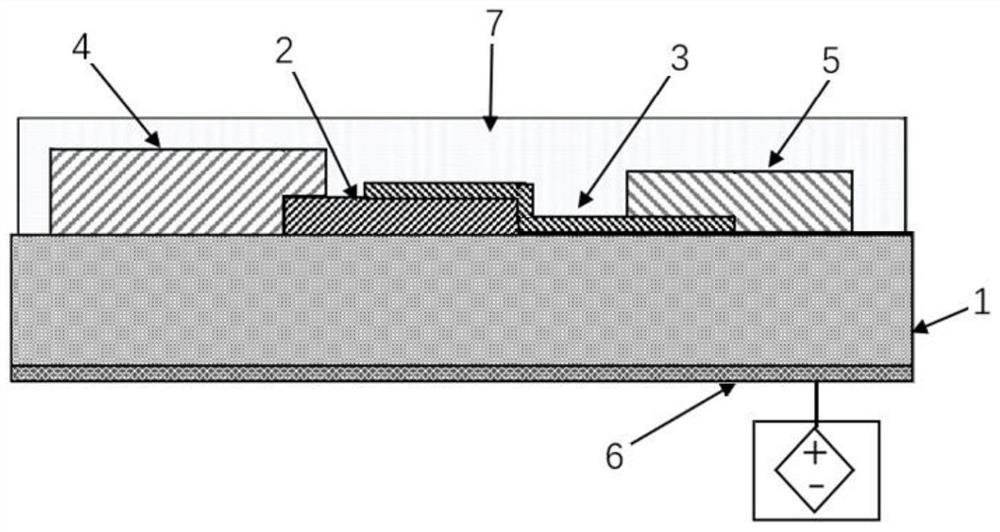
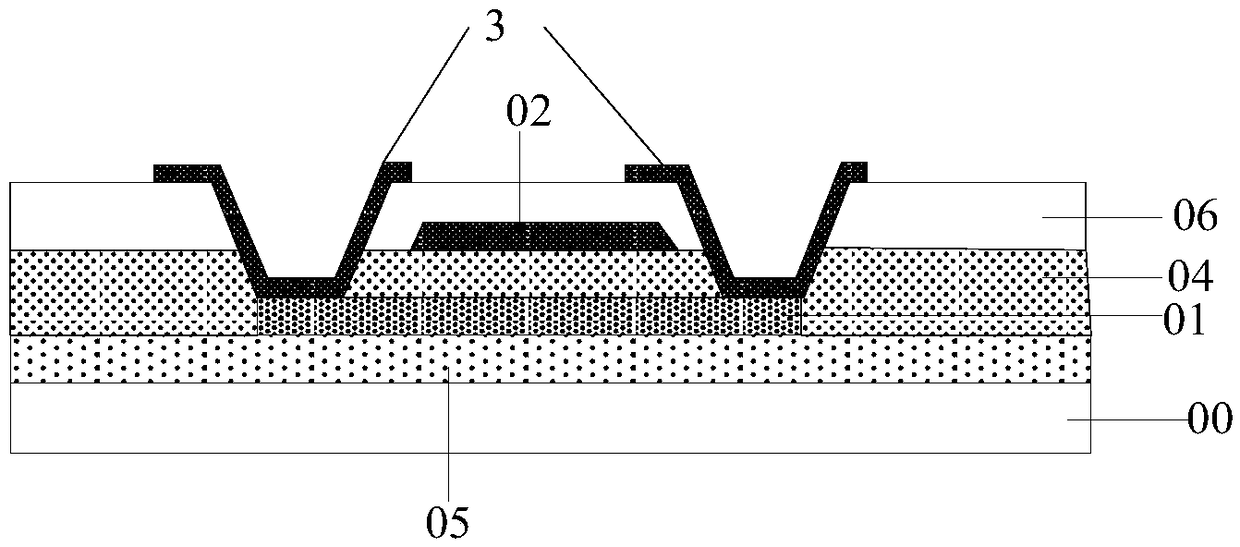
Patents
Literature
53 results about "Molybdenum telluride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
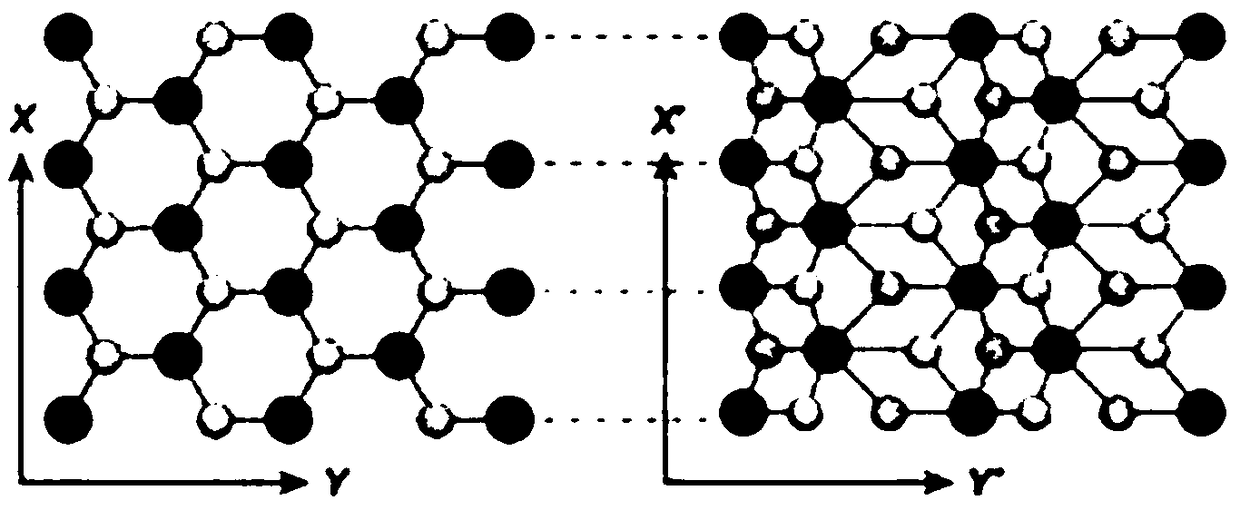
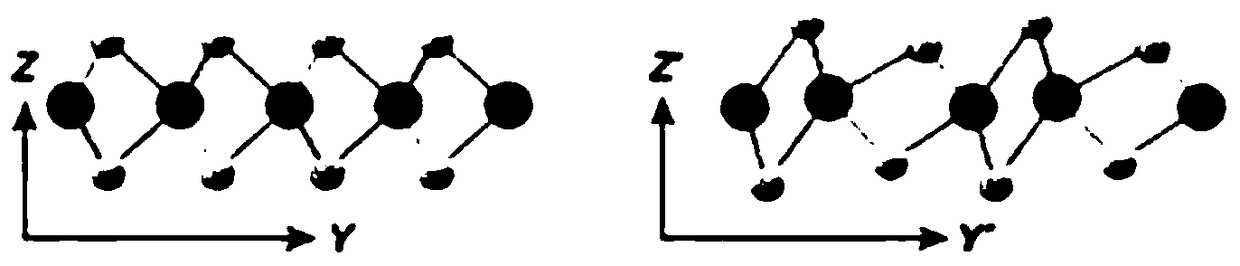
Molybdenum(IV) telluride, molybdenum ditelluride or just molybdenum telluride is a compound of molybdenum and tellurium with formula MoTe₂, corresponding to a mass percentage of 27.32% molybdenum and 72.68% tellurium. It can crystallise in two dimensional sheets which can be thinned down to monolayers that are flexible and almost transparent. It is a semiconductor, and can fluoresce. It is part of a class of materials called transition metal dichalcogenides. As a semiconductor the band gap lies in the infrared region. This raises the potential use as a semiconductor in electronics or an infrared detector.
One-dimensional conductive nanomaterial-based conductive film having the conductivity thereof enhanced by a two-dimensional nanomaterial
InactiveUS20140212672A1Improve conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyConductive layers on insulating-supportsMolybdenum tellurideNiobium
A one-dimensional conductive nanomaterial-based conductive film having the conductivity thereof enhanced by a two-dimensional nanomaterial in which the conductive film includes a substrate, a one-dimensional conductive nanomaterial layer formed on the substrate, and a two-dimensional nanomaterial layer formed on the one-dimensional conductive nanomaterial layer, wherein the one-dimensional conductive nanomaterial layer includes a one-dimensional conductive nanomaterial formed of at least one selected from a carbon nanotube, a metal nanowire, and a metal nanorod, and the two-dimensional nanomaterial layer includes a two-dimensional nanomaterial formed of at least one selected from graphene, boron nitride, tungsten oxide (WO3), molybdenum sulfide (MoS2), molybdenum telluride (MoTe2), niobium diselenide (NbSe2), tantalum diselenide (TaSe2), and manganese dioxide (MnO2). A two-dimensional nanomaterial, such as graphene may be stacked on a one-dimensional conductive nanomaterial such as a carbon nanotube or a metal nanowire to enhance the conductivity of the one-dimensional conductive nanomaterial film.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Asymmetric van der Waals heterojunction device, preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN109004016AIncrease the current switch ratioImprove responsivenessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionMolybdenum telluride
The invention provides an asymmetric van der Waals heterojunction device, comprising graphene nanosheets, hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets, molybdenum disulfide nanosheets and molybdenum telluride nanosheets sequentially arranged from bottom to top; The graphene nano sheet and the hexagonal boron nitride nano sheet, the molybdenum disulfide nano sheet and the molybdenum telluride nano sheet havean overlapping region; A surface area of that molybdenum disulfide nanosheet is lar than that of the molybdenum telluride nanosheet, and parts of the molybdenum disulfide nanosheet do not overlap with the molybdenum telluride nanosheet. The invention also provides the preparation and application of the asymmetric van der Waals heterojunction device. The asymmetric van der Waals heterojunction device of the invention can realize the organic unity of ultra high performance and multiple functions. When operating as a transistor, the device exhibits ultra-high current switching ratio, ultra-smallsubthreshold swing and obvious negative transconductance behavior. When operating as a rectifier, the device exhibits an ultra-high current rectification ratio. When operating as memory, the device exhibits an ultra-high erase / write current ratio and current rectification ratio.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
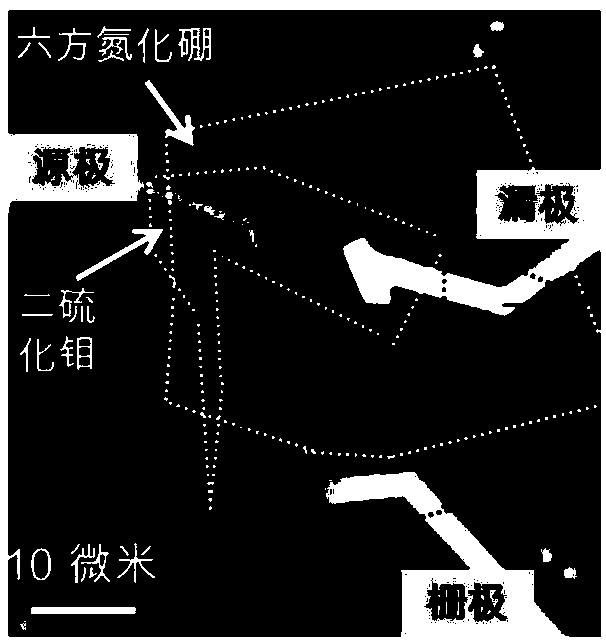
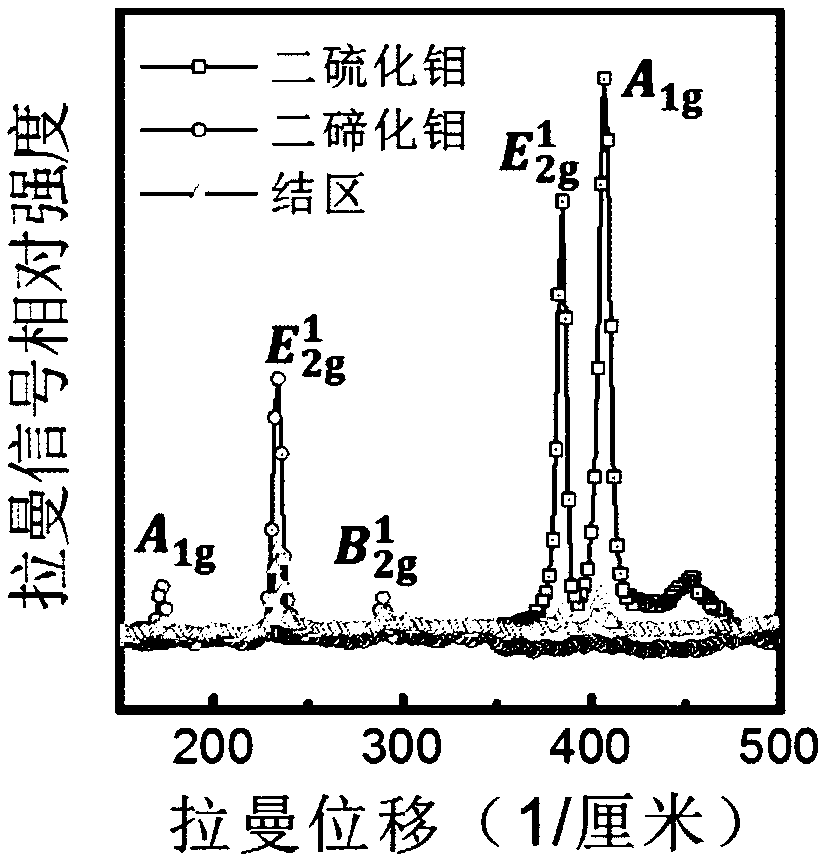
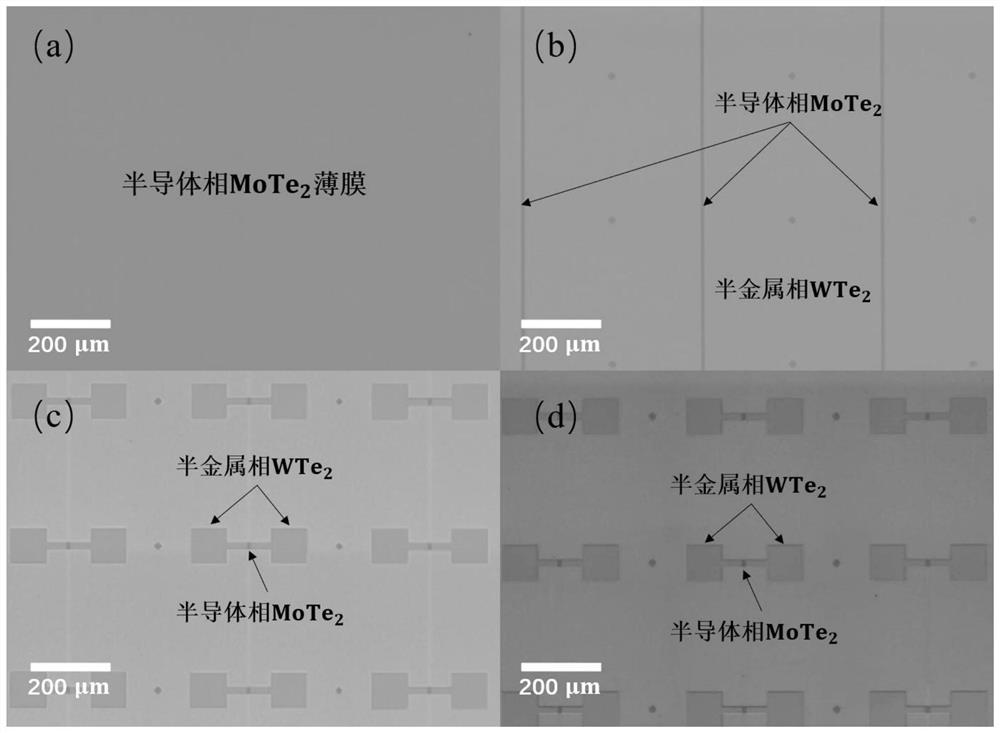
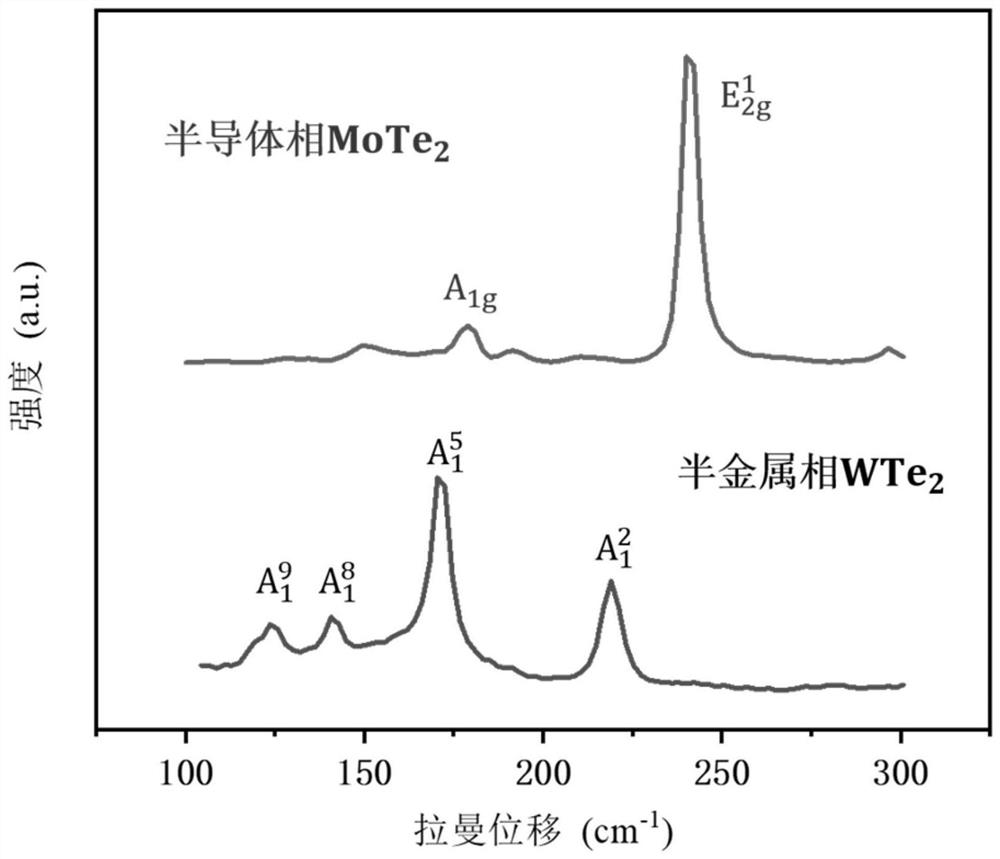
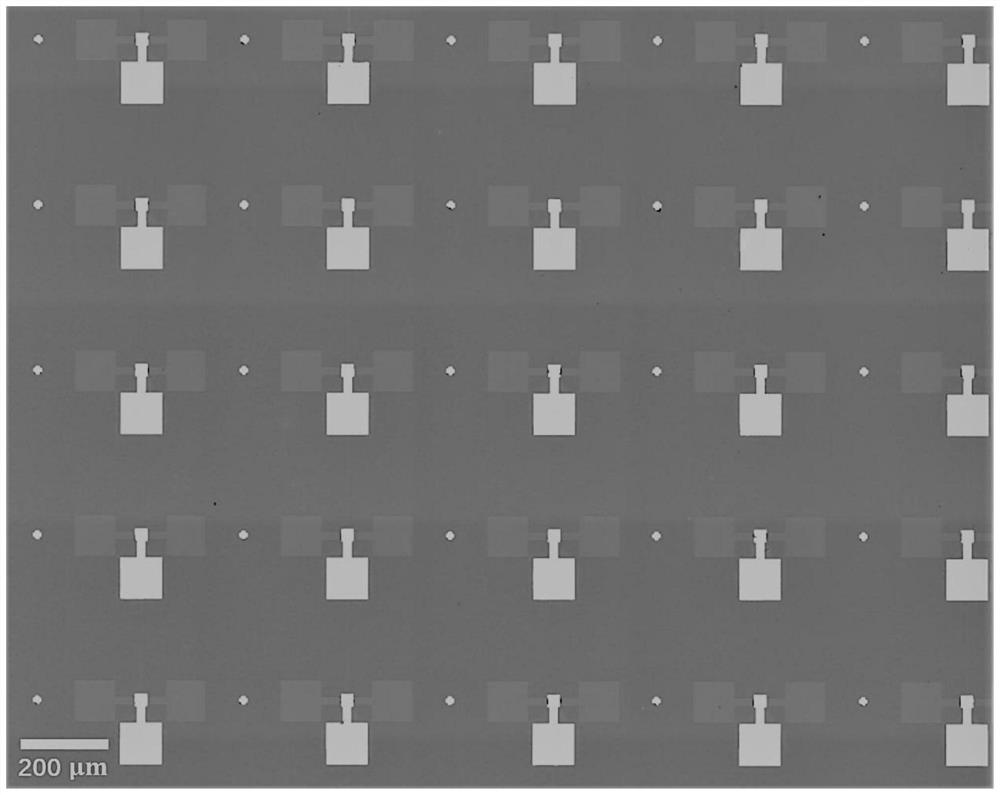
Method for large-area preparation of two-dimensional molybdenum telluride in-plane heterojunction with contact of metal phase and semiconductor phase and application thereof
ActiveCN109727846AReduce contact resistanceImprove injection efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesIn planeTransistor array
The invention discloses a method for large-area preparation of two-dimensional molybdenum telluride in-plane heterojunction with contact of a metal phase and a semiconductor phase and application thereof. The method comprises the steps of: growing a two-dimensional molybdenum thin film on a substrate, employing a chemical vapor deposition method to convert the two-dimensional molybdenum thin filmto a semiconductor phase molybdenum telluride thin film, performing photolithography and etching imaging of the semiconductor phase molybdenum telluride thin film, growing a molybdenum thin film, performing peeling to obtain a thin film with spaced apart metal phases and semiconductor phase molybdenum telluride, and further employing the chemical vapor deposition method to convert the metal molybdenum thin film to a metal phase molybdenum telluride thin film to obtain a two-dimensional molybdenum telluride in-plane heterojunction with contact of the metal phase and the semiconductor phase. Thefield effect transistor array of the two-dimensional molybdenum telluride in-plane heterojunction with contact of the metal phase and the semiconductor phase is low in contact resistance, improves the injection efficiency of the carrier, and improves the electrical properties of the device. The method provides basis for application of the two-dimensional semiconductor materials at the aspects ofintegration circuits and flexible devices.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
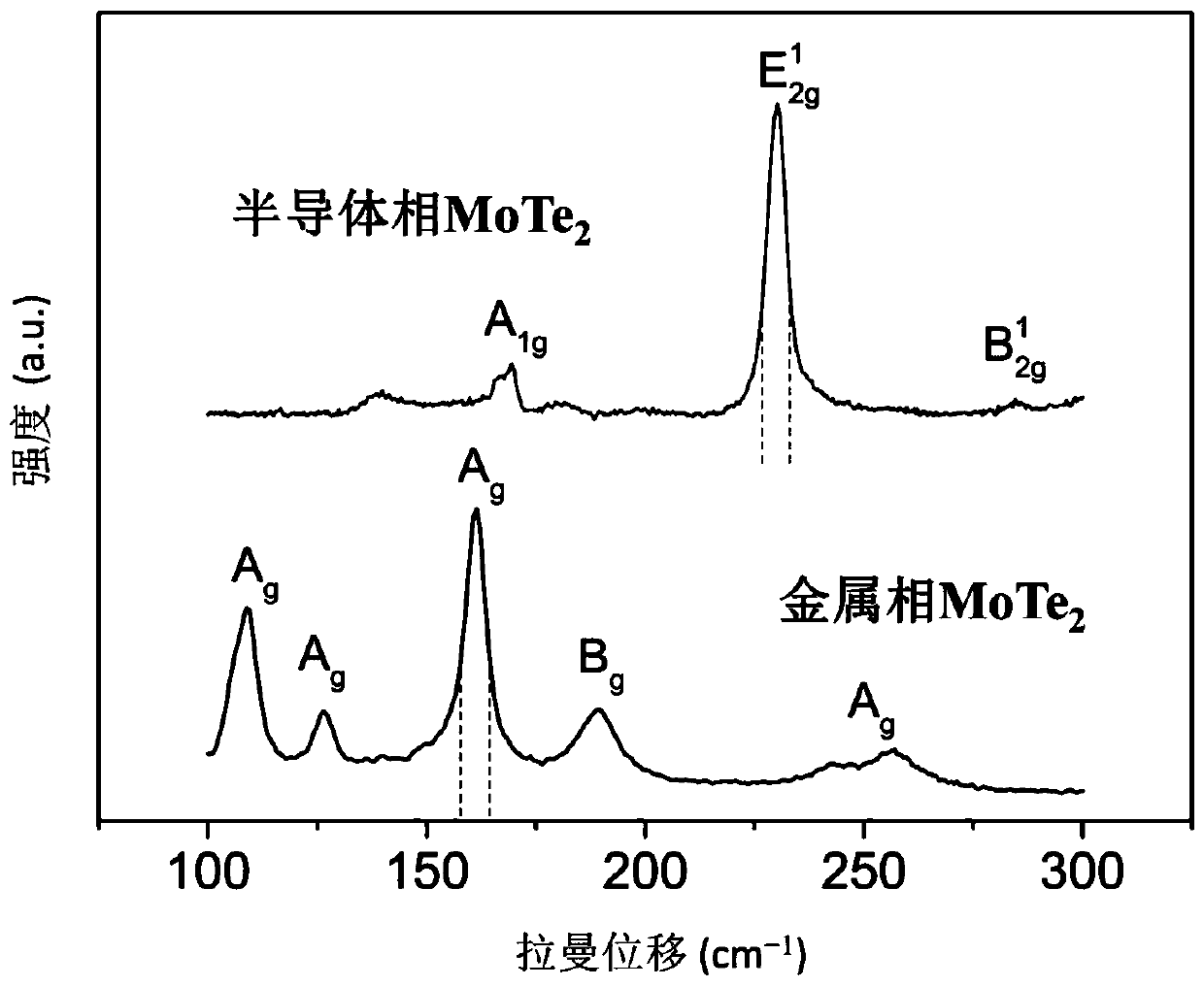
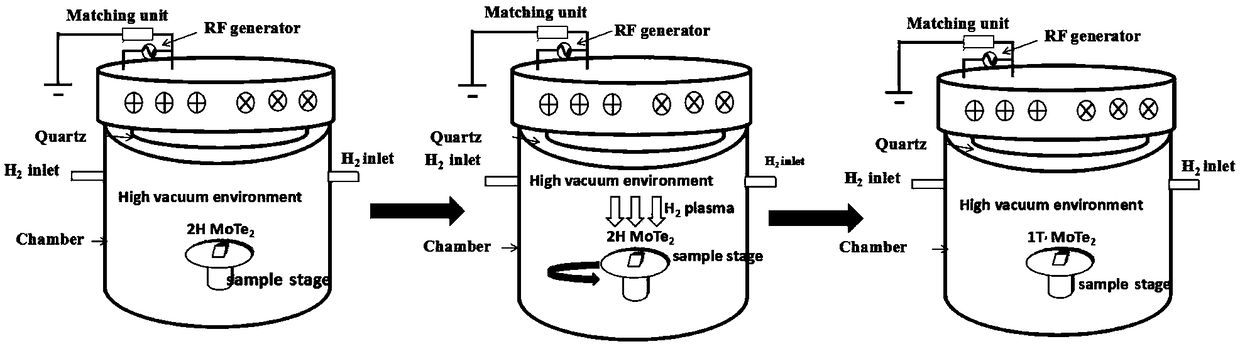
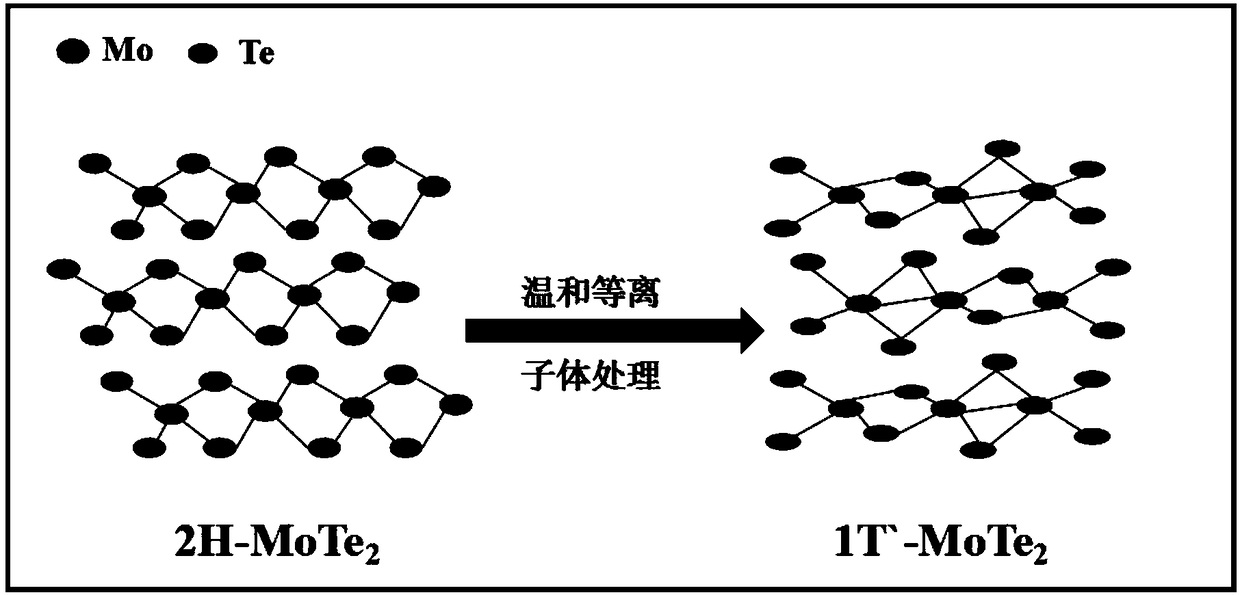
Preparation method of semimetal phase molybdenum telluride based on mild hydrogen plasma
ActiveCN108389779AObvious bombardmentReduce decreaseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceMolybdenum telluride
The invention relates to a preparation method of semimetal phase molybdenum telluride based on a mild hydrogen plasma. The preparation method comprises the following steps: placing a semiconductor phase molybdenum telluride thin layer sample in a plasma chamber; introducing H2 under a low pressure environment, and opening an inductive antenna radio-frequency power source to excite a capacitively coupled plasma; and carrying out plasma modification treatment on the semiconductor phase molybdenum telluride thin layer sample. According to the preparation method of the semimetal phase molybdenum telluride based on the mild hydrogen plasma provided by the method, the phase change degree of the MoTe2 is regulated and controlled at normal temperature, the reaction conditions are mild, the operation is simple, the controllability is strong, the phase change is uniform, the large-area phase change can be realized, and the practicability is high.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
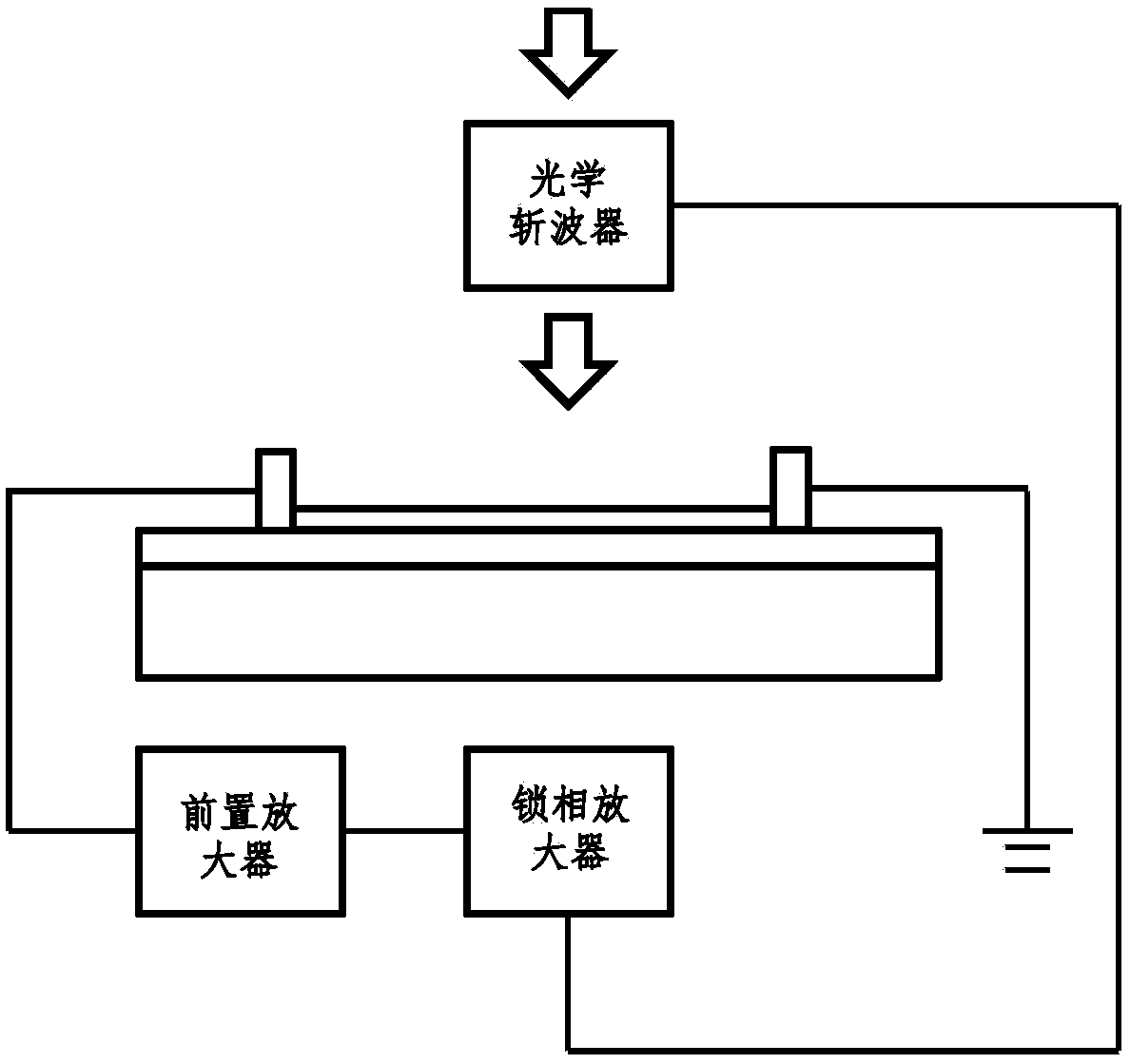
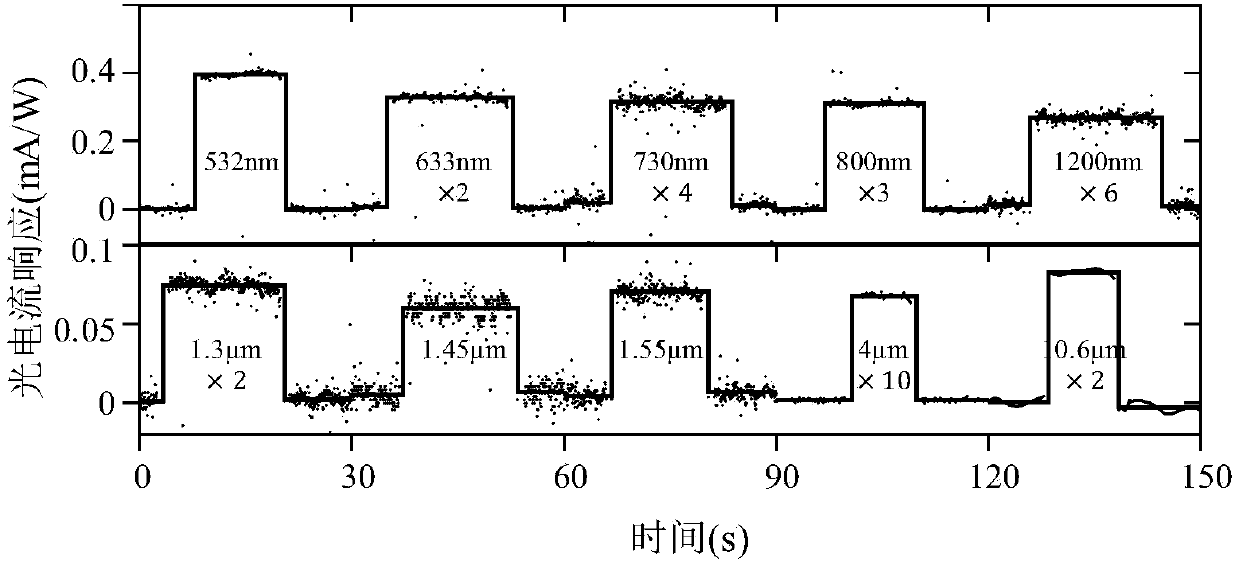
Optical detector based on second-class Weyl semimetal molybdenum ditelluride and detection method of optical detector
ActiveCN109870234AWide detection rangeSensitivitySpectrum investigationLight polarisation measurementMolybdenum tellurideOptical detector
The invention discloses an optical detector based on second-class Weyl semimetal molybdenum ditelluride and a detection method of the optical detector. According to the optical detector, a molybdenumditelluride nanosheet is adopted to serve as a light detection material, wherein the molybdenum ditelluride nanosheet is a zero-gap material and is wide in detection spectrum range, bias voltage doesnot need to be added and cannot be added, and the material has sensitive responsivity under room temperature; the detector is sensitive to a polarized light direction and can be used for polarizationdetection; the detector can be applied to the fields of infrared imaging, military reconnaissance, night vision goggles, etc. and has broad application prospects in terms of military equipment; besides, it is needed to be specially pointed out that the optical detector based on the material can make a rather high light current response without the need for providing bias voltage, and the dark current is quite low; and moreover, the bias voltage cannot be added to the optical detector, or otherwise a background current can be generated, it is not needed to provide a low-temperature environmentfor the optical detector based on the material, and therefore miniaturization and economy of the detector are benefited a lot.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
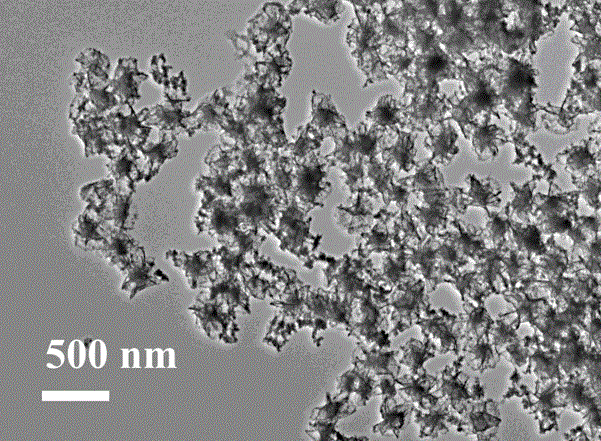
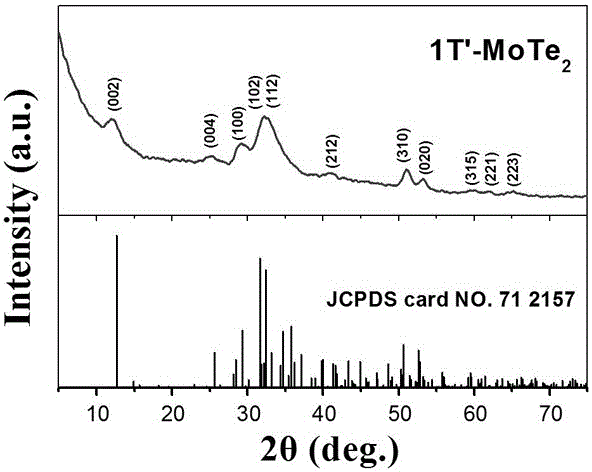
Molybdenum ditelluride electrochemical energy storage material, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106395765AImprove electrochemical energy storage performanceImprove electrochemical stabilityMetal selenides/telluridesBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsMolybdenum tellurideNew energy
The invention provides a molybdenum ditelluride electrochemical energy storage material which is molybdenum ditelluride (MoTe2) in a metastable state, a expression formula is 1T' MoTe2, and the morphology is a nano flower structure or nanosphere structure assembled by ultrathin nanosheets. The invention also provides a preparation method and application of the molybdenum ditelluride electrochemical energy storage material. The metastable-state hexagonal-phase molybdenum ditelluride nano flower structure or nanosphere structure with a uniform size and a regular shape is prepared by using oleylamine as a reducing agent and molybdenum hexacarbonyl or molybdenum pentachloride as a precursor matter, injecting a Te-trioctylphosphin precursor at certain temperature and controlling reaction temperature and reaction time. The material shows excellent super capacitor energy storage performance and is suitable for the new energy development field.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
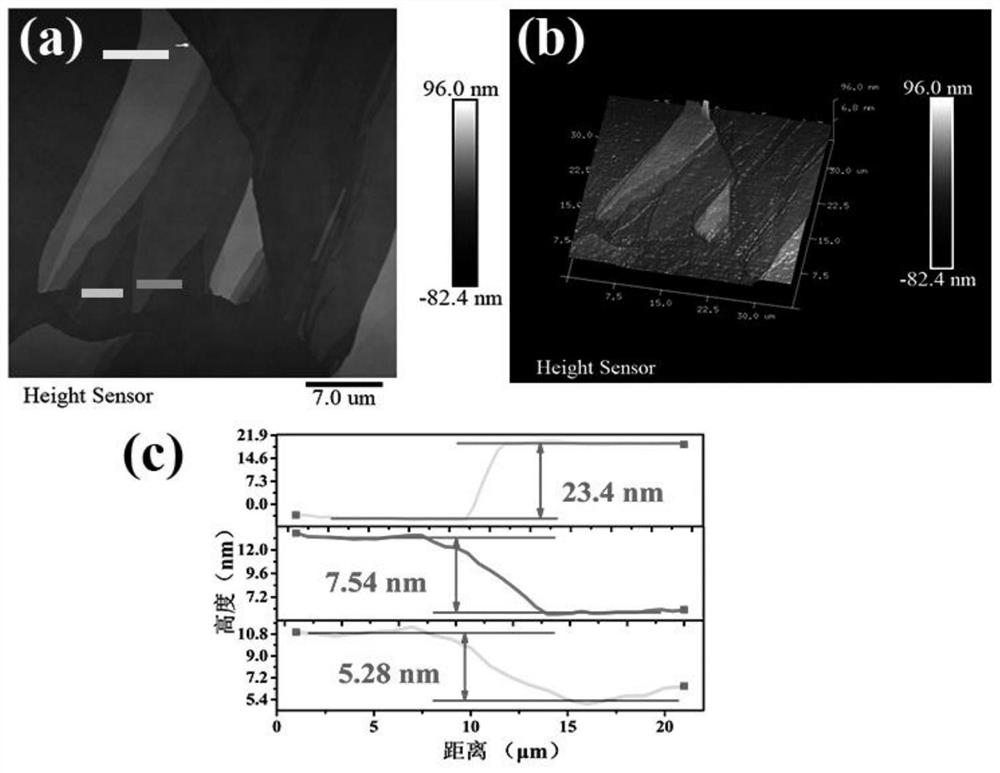
Preparation of molybdenum ditelluride nanowire material and molybdenum ditelluride nanowire material
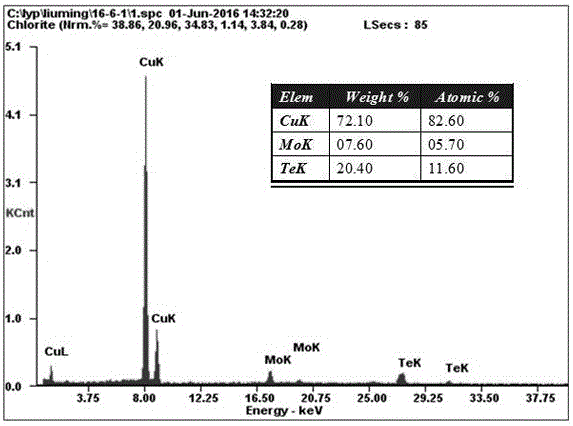
ActiveCN109336069AUniform sizeEasy to makeMaterial nanotechnologyMetal selenides/telluridesNanowireMolybdenum telluride
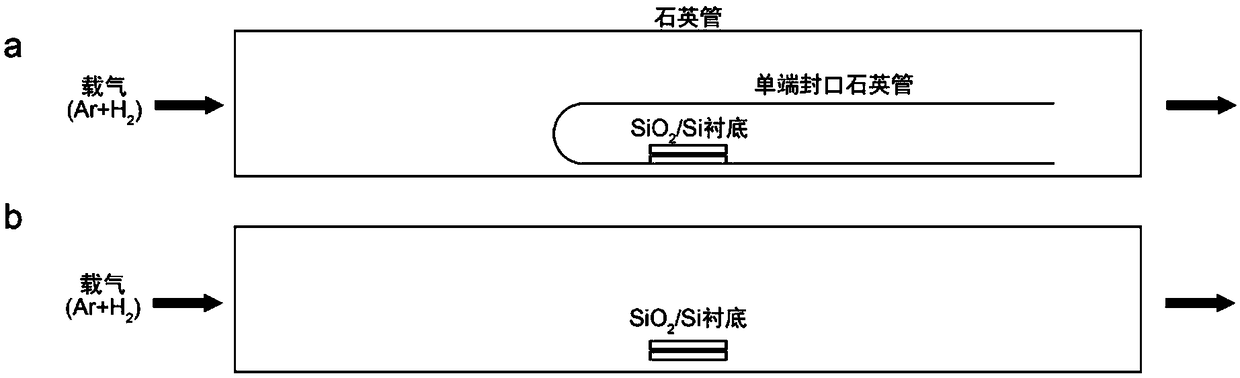
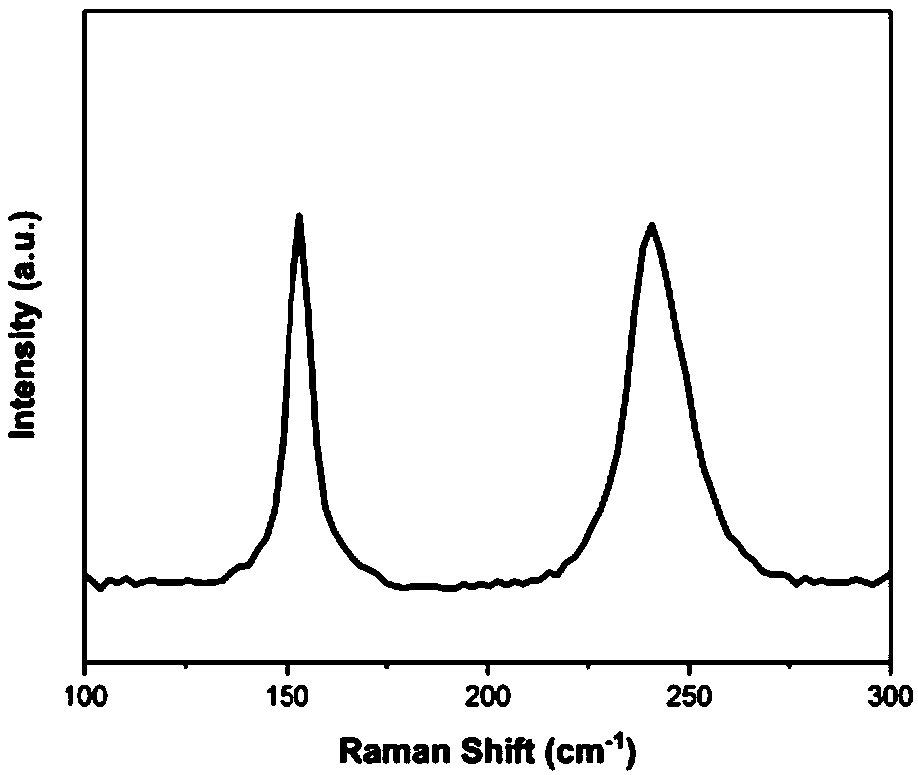
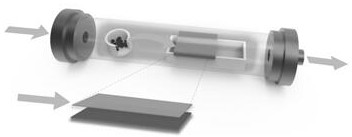
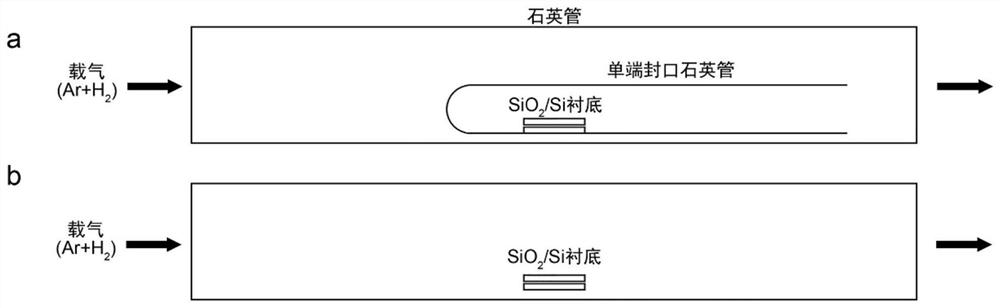
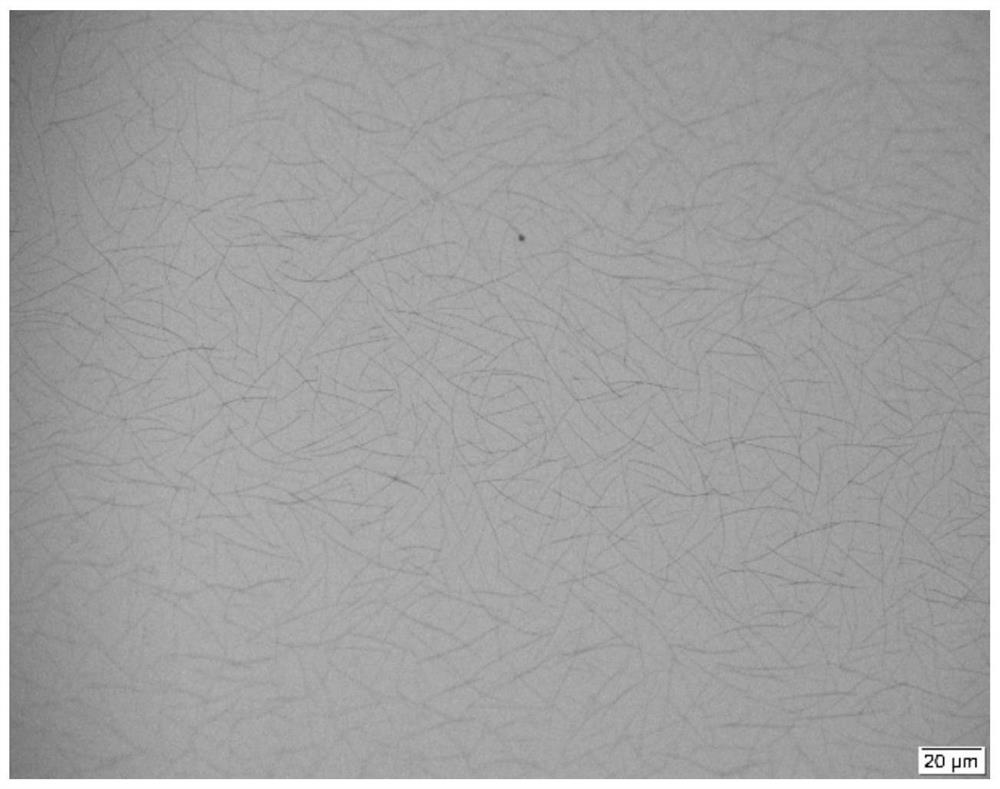
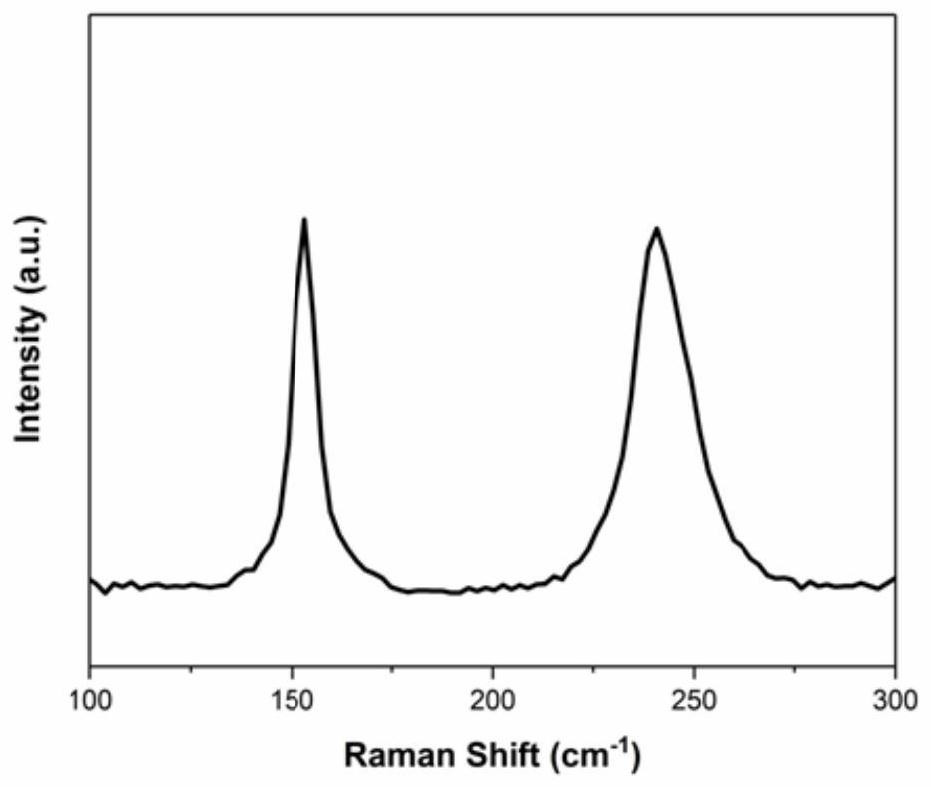
The invention discloses preparation of a molybdenum ditelluride nanowire material and the molybdenum ditelluride nanowire material. A silicon dioxide / silicon wafer is used as a substrate; molybdenum powder and tellurium powder are used as raw materials; molybdenum ditelluride nanowires are grown on a silica surface of the substrate by a chemical vapor deposition method; a growth container of the molybdenum ditelluride nanowires is a quartz tube; a mixed gas of argon and hydrogen is introduced into the quartz tube; a quartz test tube is further arranged in the quartz tube; a sealed end of the quartz test tube is opposite to a flowing direction of the mixed gas; the quartz test tube is used for placing the substrate for chemical vapor deposition; the flow rate of argon is 100 sccm; the flowrate of hydrogen is 5-30 sccm; and the reaction temperature of the chemical vapor deposition is 600-800 DEG C. The preparation provided by the invention is simple in process, low in cost and high in quality of molybdenum ditelluride nanowires.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
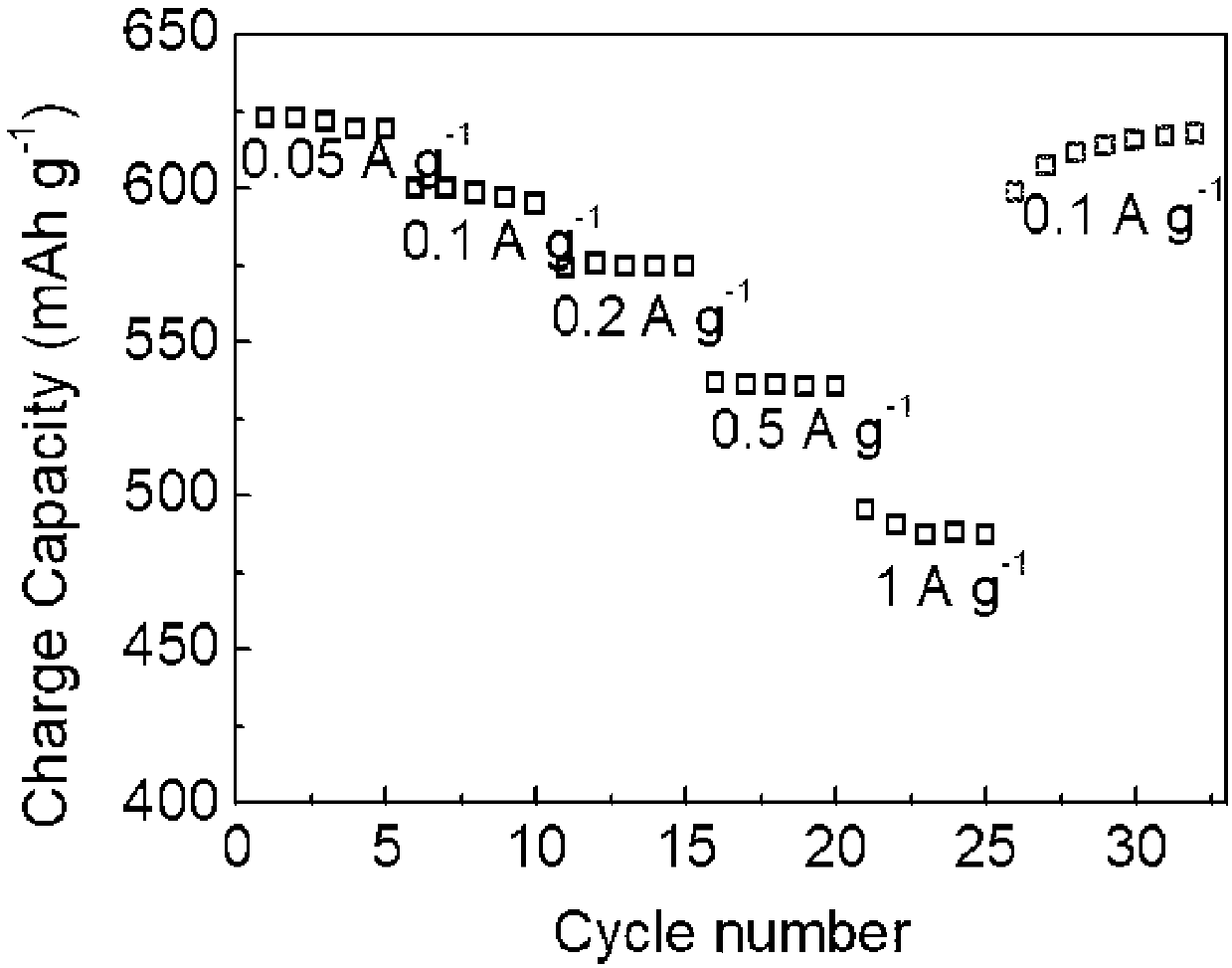
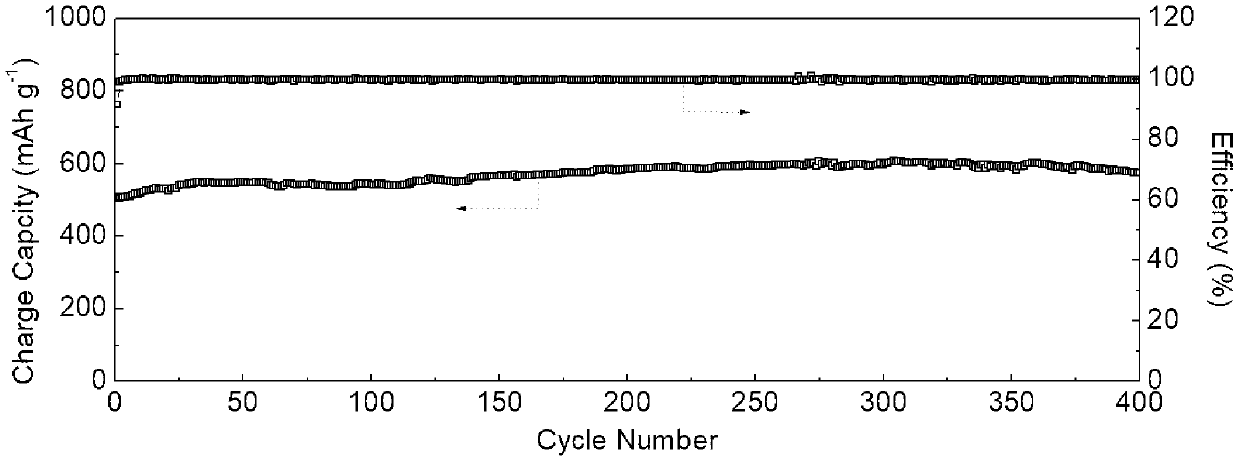
Molybdenum telluride positive electrode material for lithium-ion battery and preparation method of molybdenum telluride positive electrode material
ActiveCN107919464AImproved magnification performancePromote circulationMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesMolybdenum tellurideFully developed
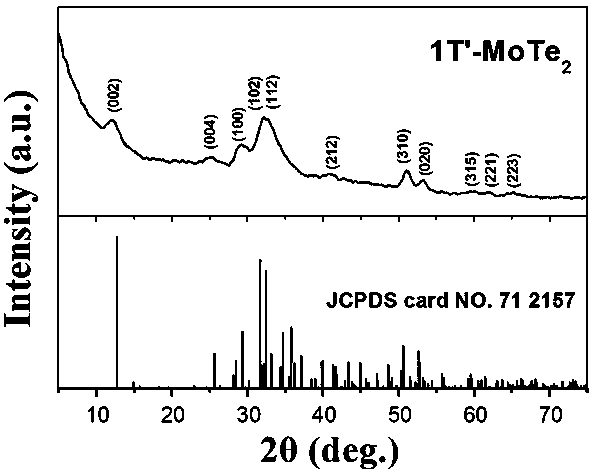
The invention provides a molybdenum telluride positive electrode material for a lithium-ion battery. The molybdenum telluride positive electrode material comprises 1T'-type molybdenum ditelluride crystal and a conductive material coating the outer surface of the 1T'-type molybdenum ditelluride crystal, and the mass percent of the conductive material in the molybdenum telluride positive electrode material is 5-15%. If the mass percent of the conductive material in the molybdenum telluride positive electrode material is smaller than 5%, reunion of the 1T'-type molybdenum ditelluride crystal is caused; if the mass percent of the conductive material in the molybdenum telluride positive electrode material is greater than 15%, the 1T'-type molybdenum ditelluride crystal cannot fully develop excellent electrochemical properties; and the conductive material coats the 1T'-type molybdenum ditelluride crystal and the mass percent of the conductive material in the molybdenum telluride positive electrode material is 5-15%, so that the molybdenum telluride positive electrode material for the lithium-ion battery has excellent rate capability and good cycle performance. The invention further provides a preparation method of the molybdenum telluride positive electrode material for the lithium-ion battery. The preparation method is simple in process, environment-friendly and efficient.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Two-dimensional molybdenum ditelluride vertical heterojunction and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111403475AIncrease contactLower Schottky BarrierSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionSchottky barrier
The invention belongs to the field of two-dimensional materials, and particularly discloses a two-dimensional molybdenum ditelluride vertical heterojunction and a preparation method and application thereof. The two-dimensional molybdenum ditelluride vertical heterojunction comprises a 1T'-MoTe<2> part and a 2H-MoTe<2> part, and the two parts are connected through interlayer Van der Waals' force; the preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, drying a mixed solution of ammonium tetramolybdate and sodium chloride, putting the dried mixed solution as a molybdenum source into a reactor,putting a growth substrate on the molybdenum source, putting tellurium powder as a tellurium source into the reactor, and putting the tellurium powder at the upstream of the molybdenum source; and S2, raising the temperature of the molybdenum source and the tellurium source to a reaction temperature, naturally cooling to room temperature, introducing carrier gas into the reactor to bring the tellurium source to the molybdenum source, introducing a reducing agent, and generating the two-dimensional molybdenum ditelluride vertical heterojunction on the growth substrate. The metal phase and semiconductor phase vertically stacked MoTe2 heterostructure prepared by the invention can effectively reduce the Schottky barrier of contact between a metal electrode and a material, and an important thought for improving metal-semiconductor contact is provided.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Gallium oxide-two-dimensional P-type Van der Waals tunneling transistor, dual-band photoelectric detector and preparation method
ActiveCN113972262AOn-state current reductionReduce leakage currentFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionMolybdenum telluride
The invention particularly relates to a gallium oxide-two-dimensional P-type Van der Waals tunneling transistor, a dual-band photoelectric detector and a preparation method, and solves the technical problem that PN junction deep ultraviolet-infrared dual-band detection of the tunneling transistor and gate voltage modulation cannot be realized simultaneously due to lack of P-type doping of Ga2O3 in preparation of an existing UWBG material transistor / photoelectric detector. The transistor and the photoelectric detector comprise a back gate electrode, a dielectric oxide layer, a gallium oxide layer, a gallium oxide electrode forming ohmic contact, a P-type two-dimensional material layer, a P-type two-dimensional material electrode forming ohmic contact, and a dielectric passivation layer. The gallium oxide layer and the P-type two-dimensional material layer are partially overlapped to form a heterojunction; the gallium oxide layer is an unintentionally doped or doped Ga2O3 quasi-two-dimensional crystal film; and the P-type two-dimensional material layer is black phosphorus or a beta-phase tellurium elementary substance or a 2H-phase molybdenum ditelluride or tungsten diselenide or platinum diselenide film. In addition, the invention also provides a preparation method of the transistor and the dual-band photoelectric detector.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for growing large-area single-layer or multi-layer molybdenum ditelluride structure through secondary reaction
InactiveCN110923663ARealize large area preparationImprove controllabilityChemical vapor deposition coatingMolybdenum telluridePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for growing a large-area single-layer or multi-layer molybdenum ditelluride structure through a secondary reaction. The method comprises the steps: a molybdenum telluride nano-film is deposited on a substrate in an atomic layer depositing mode firstly, then the substrate with the deposited molybdenum telluride nano-film is subjected to the high-temperature secondary reaction with elementary substance tellurium by taking inert gas or hydrogen as a carrier, and the large-area single-layer or multi-layer molybdenum ditelluride structure is obtained on the substrate. The method has the advantages that controllability is good, operation is easy, and large-area preparation of the single-layer or multi-layer molybdenum ditelluride can be achieved; and the preparedmolybdenum ditelluride has wide application prospects in the aspects of optical materials, storage materials, catalytic materials, semiconductor optoelectronic materials and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
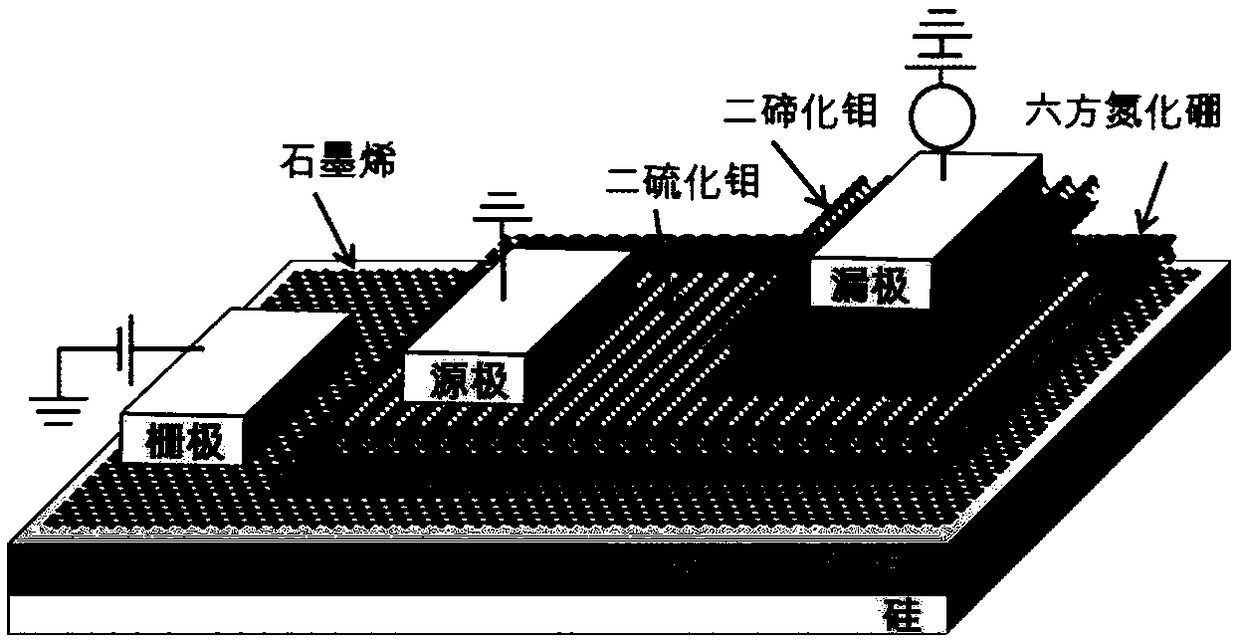
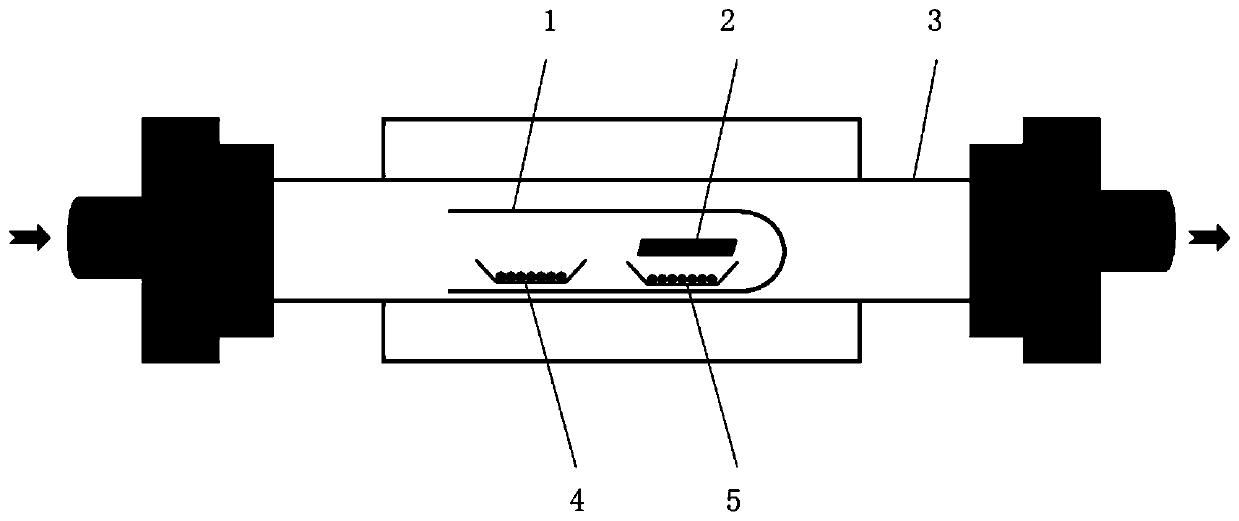
Thin film transistor, detecting device and method of detecting device for detecting pressure or illumination
ActiveCN108807551AIncrease photosensitivityGood pressure sensitivityTransistorFluid pressure measurement using piezo-electric devicesMolybdenum telluridePressure sense
The invention discloses a thin film transistor, a detecting device and method of the detecting device for detecting pressure or illumination, which are used for improving the photosensitive property and pressure sensing performance of the thin film transistor, thereby helping improve the accuracy of pressure or illumination detection. The thin film transistor provided by the invention of embodiment comprises a substrate, a semiconductor layer, a grid, and a source drain arranged on the substrate, and the materials of the semiconductor layer comprise molybdenum ditelluride.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
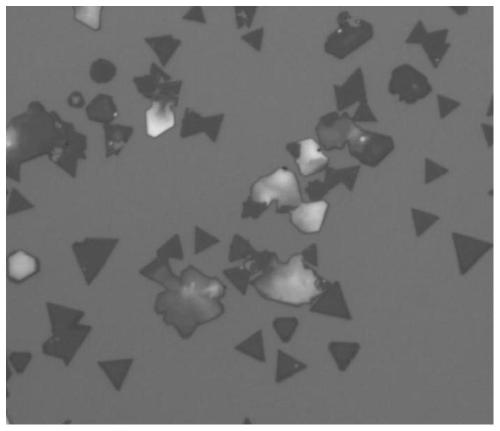
Confinement chemical vapor deposition preparation method of two-dimensional molybdenum ditelluride nano material
ActiveCN113428845AAvoid Spatial InhomogeneityLarge compositing windowNanotechnologyMetal selenides/telluridesMicron scaleSodium molybdate
The invention generally relates to the technical field of two-dimensional material preparation, and provides a confinement chemical vapor deposition preparation method of a two-dimensional molybdenum ditelluride (MoTe2) nano material, which comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing two substrates, and marking the substrates as a substrate A and a substrate B; and carrying out plasma surface treatment on the polished surface of the substrate A; (2) coating the surface of the treated substrate A with a sodium molybdate solution to form a sodium molybdate coating; (3) constructing a confinement growth environment: overlapping the sodium molybdate coating surface of the substrate A and the polished surface of the substrate B in a face-to-face manner, with the substrate B being on the top, to form a laminated substrate with a micron-order slit (1-30 microns); (4) enabling the tellurium powder to be firstly heated into tellurium steam through arrangement of the placement position, and then enabling the tellurium steam and a molybdenum source, rapidly introduced into the heating area, in the laminated substrate to react in a confinement and grow; and (5) sampling: after a quartz tube is cooled to room temperature, taking out the laminated substrate, and obtaining two-dimensional MoTe2 on the surface of the substrate B.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method for constructing electrochemical luminescence aptamer sensor for omethoate detection
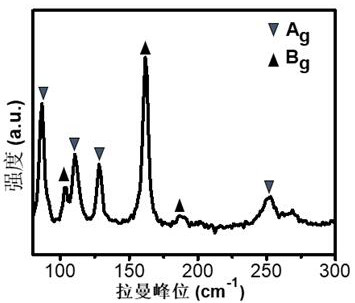
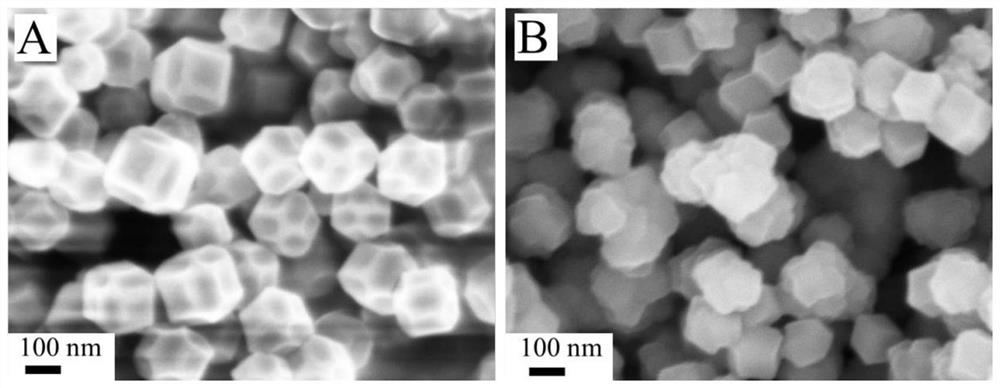
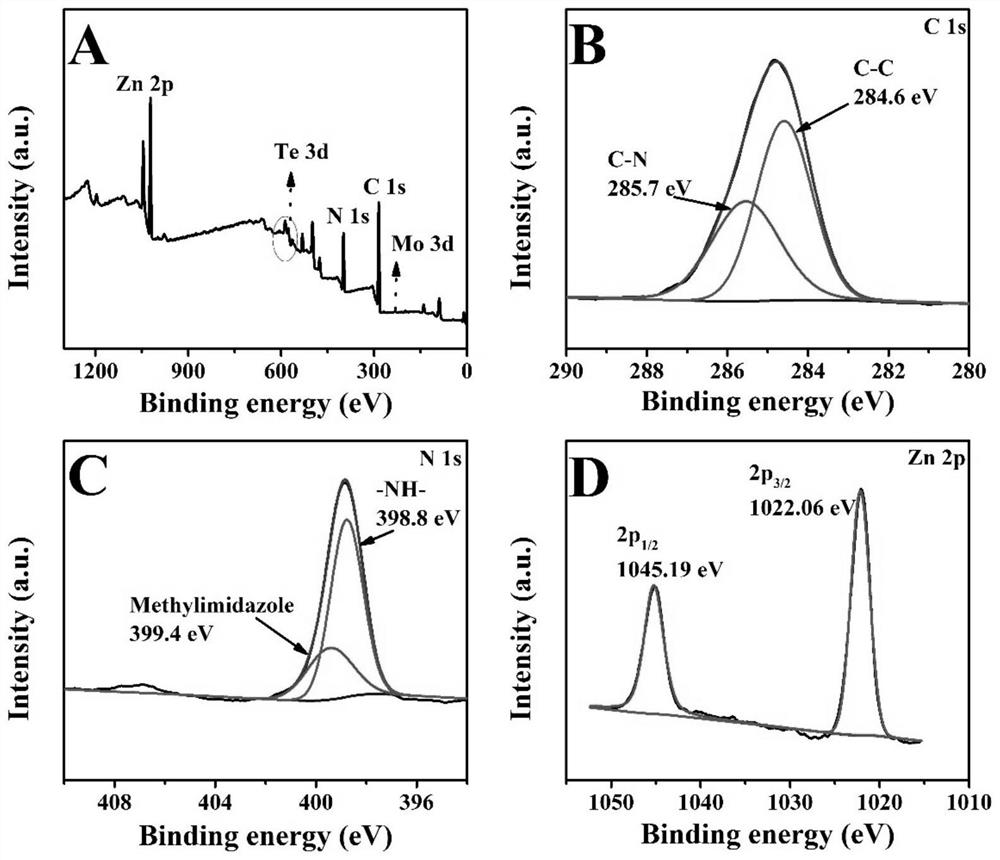
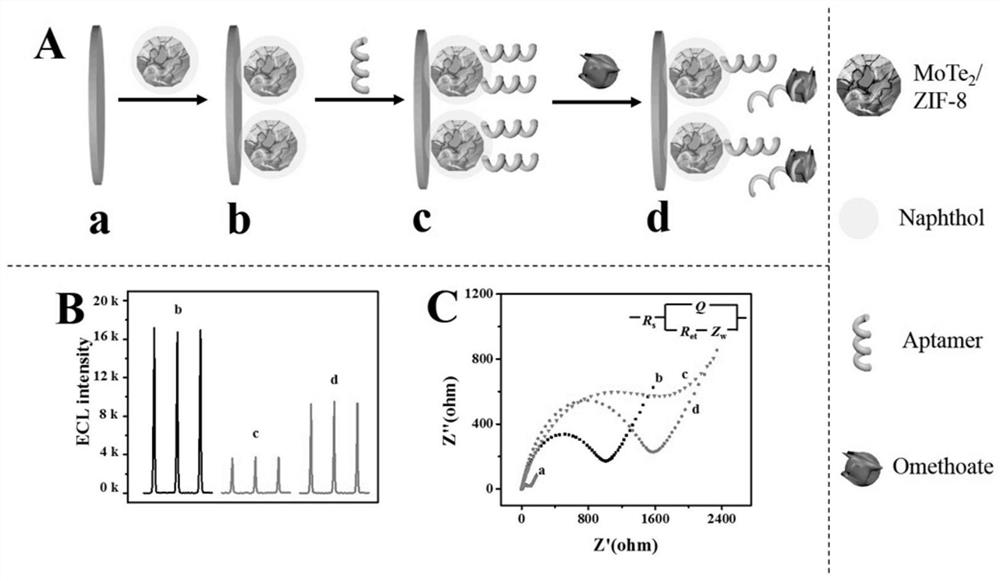
ActiveCN113109406AECL signal enhancementImprove catalytic performanceChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial electrochemical variablesDimethoateMolybdenum telluride
The invention provides a method for constructing an electrochemical luminescence aptamer sensor for sensitively detecting omethoate. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, preparing molybdenum telluride (MoTe2) quantum dots; step 2, preparing a molybdenum telluride / 2-methylimidazole zinc salt (MoTe2 / ZIF-8) nano compound; and step 3, constructing the electrochemical luminescence aptamer sensor for sensitively detecting omethoate. The electrode material of the sensor adopts ZIF-8 with defects caused by quantum dots, so that the excitation potential of the material is effectively reduced, and the sensitivity of the sensor is greatly improved. Based on the excellent ECL performance of MoTe2 / ZIF-8, an OMT aptamer with specific recognition is combined, and an ECL aptamer sensor is successfully prepared and used for OMT monitoring. Meanwhile, the electrochemical luminescence detection method of OMT provided by the invention has the characteristics of simplicity, convenience and flexibility in operation, simple instrument and equipment, wide detection range, low detection limit, low detection cost and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for preparing large-area high-performance n-type two-dimensional molybdenum telluride field effect transistor array
PendingCN114171392AImprove performanceImprove injection efficiencyVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingMolybdenum tellurideSemiconductor materials
The invention discloses a method for preparing a large-area high-performance n-type two-dimensional molybdenum telluride field effect transistor array. The method comprises the following steps: growing a semiconductor phase molybdenum telluride thin film on a substrate, patterning the semiconductor phase molybdenum telluride thin film and growing a tungsten thin film to obtain a thin film in which metal tungsten and semiconductor phase molybdenum telluride are alternated, and changing the tungsten thin film into a semimetal phase tungsten telluride thin film through a chemical vapor deposition method; patterning again to obtain a discrete device array which takes semiconductor phase molybdenum telluride as a channel and semi-metal phase tungsten telluride as an electrode; and finally, performing n-type doping on the device through atomic layer deposition of a hafnium oxide thin film, and preparing a patterned top gate metal electrode to obtain a large-area high-performance n-type two-dimensional molybdenum telluride field effect transistor array. According to the method, the n-type doping effect on the two-dimensional molybdenum telluride is ideal, the doping degree is adjustable, meanwhile, the contact resistance of the source electrode and the drain electrode of the prepared device is low, the performance of the device is improved, and a foundation is provided for application of two-dimensional semiconductor materials in the field of integrated circuits and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Topological insulator/molybdenum ditelluride heterojunction-based phototransistor, and production method and application thereof
PendingCN113964219ALow Bias RegulationImprove photoelectric performanceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionMolybdenum telluride
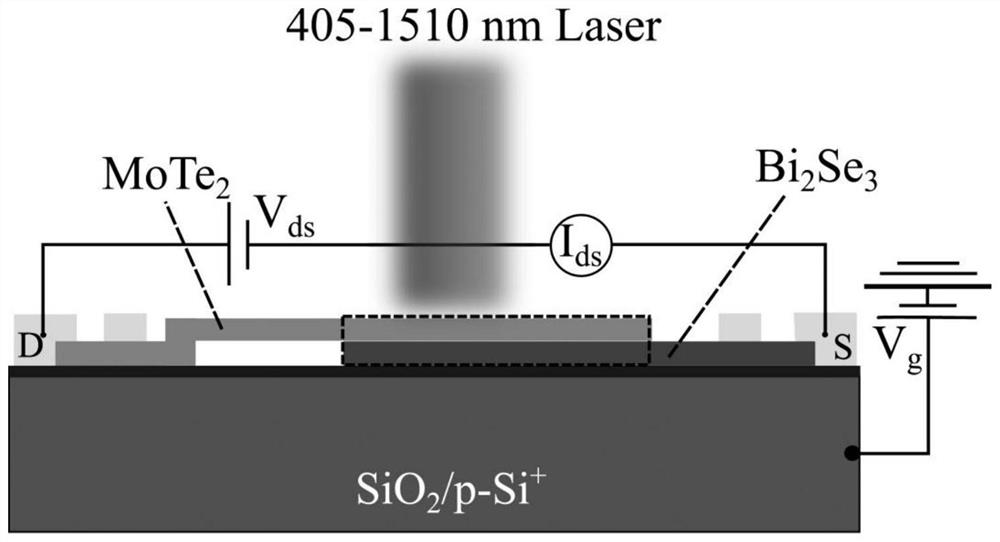
The invention belongs to the technical field of multifunctional phototransistors, and discloses a topological insulator / molybdenum ditelluride heterojunction-based phototransistor, and a production method and an application thereof. According to the heterojunction-based phototransistor, a prepared topological insulator nanosheet is transferred on a SiO2 / Si substrate, then a 2H-MoTe2 nanosheet is transferred to the topological insulator nanosheet, and a vertical Van der Waals heterojunction is formed at the overlapped part of the topological insulator nanosheet and the 2H-MoTe2 nanosheet. Metal bonding layers / Au electrodes are evaporated on the 2H-MoTe2 nanosheet and the topological insulator nanosheet respectively, and annealing treatment is carried out in protective gas at the temperature of 150-300 DEG C. The heterojunction provided by the invention realizes a unique carrier tunneling transport mechanism, and has good photoelectric response performance in a wide-spectrum wave band range of 405-1550nm. The method can be used in the field of logic loop devices or visible-near infrared light response photoelectric devices.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Molybdenum ditelluride electrochemical energy storage material, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106395765BAchieve synthesisMeets requirementsMetal selenides/telluridesBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsMolybdenum tellurideNew energy
The invention provides a molybdenum ditelluride electrochemical energy storage material, the material is metastable molybdenum ditelluride, and its expression is 1T'-MoTe 2 , the morphology is a nanoflower structure or a nanosphere structure assembled by ultrathin nanosheets. The invention also provides a preparation method and application of the material, using oleylamine as the reducing agent, molybdenum hexacarbonyl or molybdenum pentachloride as the precursor of molybdenum, injecting the tellurium-trioctylphosphine precursor at a certain temperature, and controlling the reaction temperature and reaction time, thereby preparing a metastable hexagonal phase molybdenum ditelluride nanoflower structure or nano spherical structure with uniform size and regular shape. This type of material exhibits excellent supercapacitor energy storage performance and is suitable for the field of new energy development.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method for preparing molybdenum ditelluride nanotubes
ActiveCN107934927AGood size controllabilityHigh crystallinityNanotechnologyMetal selenides/telluridesSingle substanceMolybdenum telluride
The invention discloses a method for preparing molybdenum ditelluride nanotubes. The method comprises the following steps: 1) laying molybdenum hexacarbonyl to the bottom of a ceramic crucible, layinga porous anodic aluminum oxide mold plate with an opening facing downwards on the molybdenum hexacarbonyl, sealing the ceramic crucible, putting into a tubular furnace, performing low-temperature sublimation deposition in the presence of a gas, and continuously performing heating pyrolysis; 2) cooling the vacuum tubular furnace to the room temperature, putting the mold plate with the opening facing downwards into a ceramic crucible with tellurium powder, sealing the ceramic crucible, heating in the presence of the gas, and enabling a single substance, namely tellurium, to react with a metal,namely molybdenum, directly; 3) removing the excessive aluminum oxide mold plate and excessive tellurium by using a diluted acid solution, performing suction filtration treatment, and drying, therebyobtaining a finished product. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in step, free of environment pollution and free of complex equipment, a molybdenum ditelluride nanotube powder material prepared by using the method is good in size controllability, good in crystallinity and uniform in nanotube wall and morphology, and thus the comprehensive properties of a finished product of the molybdenum ditelluride nanotube powder material are greatly improved. The method is wide in applicability and beneficial to large-scale industrial production.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
Heterogeneous integration method for monocrystalline two-dimensional semiconductor molybdenum telluride film and arbitrary lattice mismatched monocrystalline substrate
PendingCN114373828AImprove performanceImprove functionalityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMolybdenum tellurideSemiconductor materials
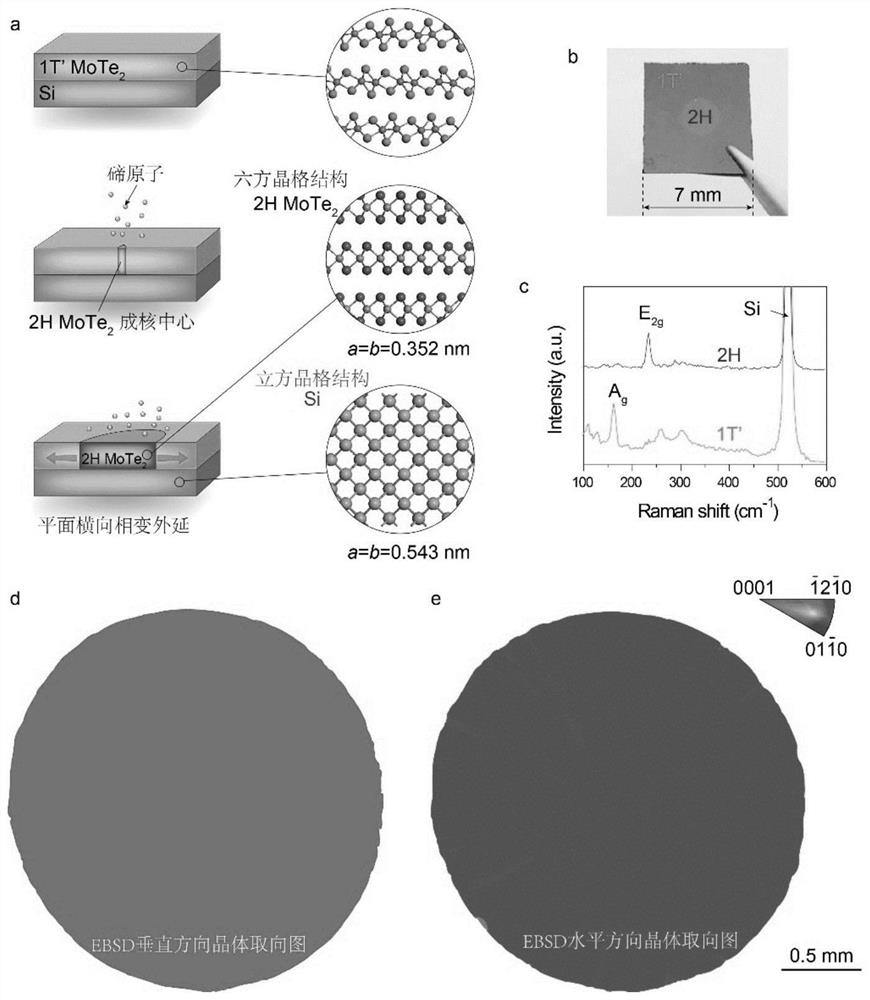
The invention discloses a method for heterogeneous integration of a monocrystal two-dimensional semiconductor molybdenum telluride film and an arbitrary lattice mismatched monocrystal substrate. According to the method, the necessary condition, namely lattice matching, of heterogeneous integration of different types of single crystal materials in the traditional epitaxial process is broken through, and the 2H-MoTe2 prepared by utilizing the chemical vapor deposition method has a special growth mechanism of transverse epitaxial phase change; the monocrystal two-dimensional semiconductor molybdenum telluride film can be directly grown and integrated with any monocrystal substrate by controlling the temperature and the time without being limited by lattice matching. According to the obtained heterogeneous integrated structure, the semiconductor characteristic of molybdenum telluride and the physical characteristic of the substrate can be utilized at the same time, the performance of the device is improved, and the functionalization of the device is enhanced. Moreover, the method is suitable for large-area preparation, the preparation of an integrated photoelectric device array can be realized, a basis is provided for realizing wafer-level and industrial chip manufacturing, and a basis is provided for the application of a two-dimensional semiconductor material in the aspects of integrated circuits and photoelectric chips.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Van der Waals heterojunction device, preparation method thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN109390388AIncrease the current switch ratioHigh current rectification ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionMolybdenum telluride
The invention provides a van der Waals heterojunction device which comprises a substrate, a molybdenum telluride nanosheet, a molybdenum disulfide nanosheet and a metal electrode arranged in order from the bottom to top, and the cross-sectional area of the molybdenum telluride nanosheet is larger than that of the molybdenum disulfide nanosheet. According to the van der Waals heterojunction device,the dynamic adjustment of conductive polarity can be achieved. Under different bias voltage conditions, a field effect transistor based on the van der Waals heterojunction device can realize double polarities and an N-type conductivity polarity, and an ultra-high current switching ratio (10<7>) and current rectification ratio (10<6>) and excellent photovoltaic performance are exhibited, and the device can be applied to a novel two-dimensional electronic and optoelectronic device.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
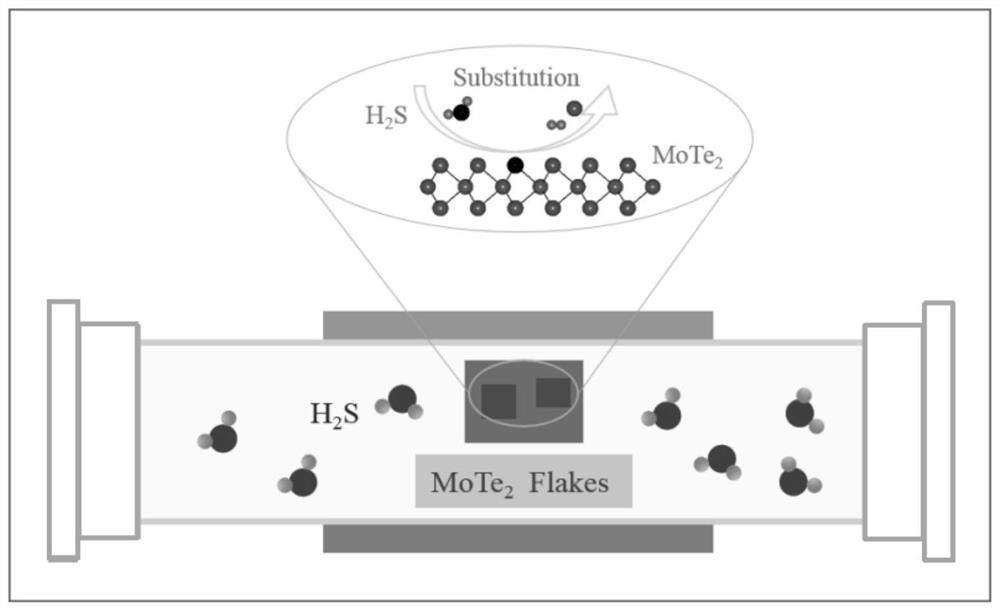
Uniform and high-strain two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111634947AHighly uniform strainSimple methodMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthMolybdenum tellurideReaction temperature
The invention belongs to the field of two-dimensional material preparation, and specifically discloses a uniform and high-strain two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide material and a preparation methodthereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking two-dimensional molybdenum ditelluride as a precursor at the reaction temperature of 600 DEG C or above, and performing controllable tellurium element and sulfur element replacement between the precursor and hydrogen sulfide so as to obtain uniform and high-strain two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide and finish the preparation of the two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide material. An element replacement method is adopted, two-dimensional molybdenum ditelluride is converted into two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide while the two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide is kept in a high-strain state, so the method is simple and high in controllability, large-scale preparation can be achieved, and the generated strain is uniform and adjustable in a large range; and the obtained two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide material has a huge application prospect in the fields of novel photoelectronic devices and catalysis, and the physical and chemical properties of the two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide material can be adjusted to a great extent by applying strain energy.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
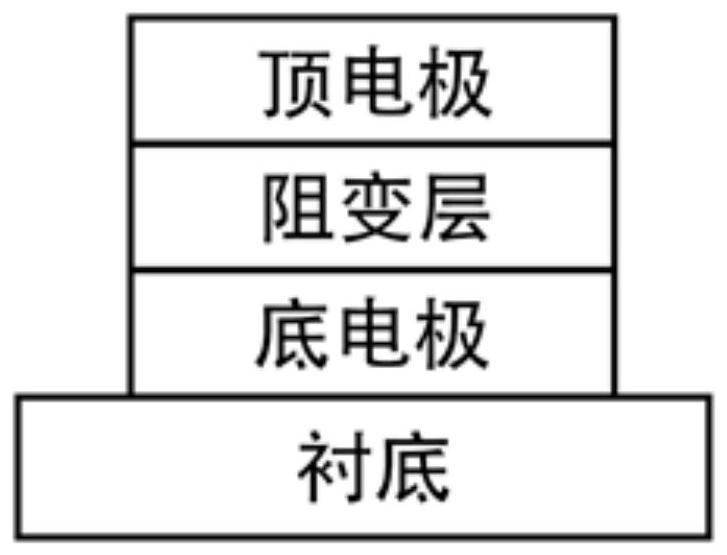
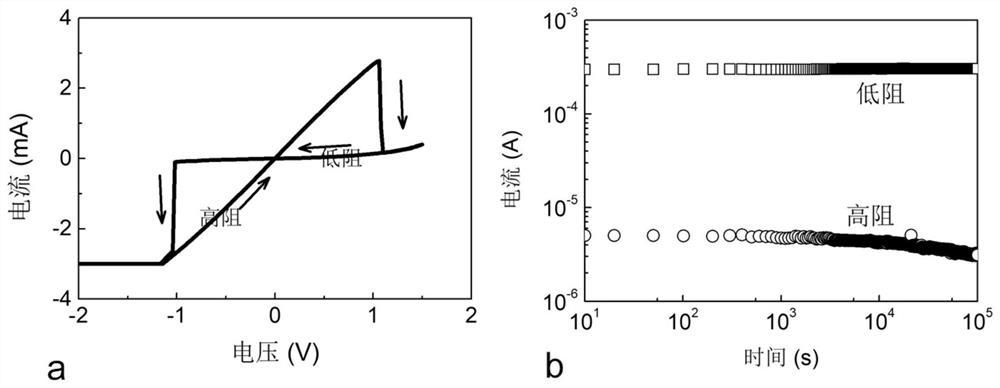
Molybdenum telluride-based memristor and preparation method thereof and nonvolatile memory
ActiveCN112331766AReduce operating voltageHigh speedElectrical apparatusEnergy efficient computingMolybdenum telluridePhysical chemistry
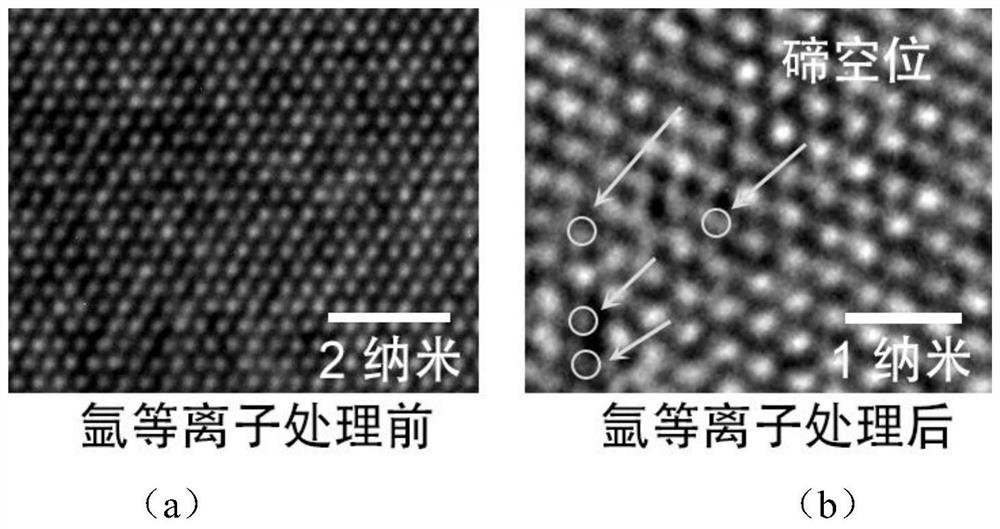
The invention belongs to the related technical field of semiconductor storage, and discloses a molybdenum telluride-based memristor and a preparation method thereof, and a nonvolatile memory, the memristor comprises a top electrode, a resistive layer and a bottom electrode which are arranged from top to bottom, the resistive layer is located between the top electrode and the bottom electrode, andthe resistive layer is a molybdenum telluride sheet which is a two-dimensional molybdenum telluride sheet subjected to argon plasma treatment; tellurium vacancies are introduced into the surface of the molybdenum telluride sheet through argon plasma treatment, so that the energy of phase transformation of molybdenum telluride from a 2H phase to a 1T' phase is reduced, and the phase transformationof molybdenum telluride from the 2H phase to the 1T' phase is easier to occur; and according to the invention, the phase transformation between the molybdenum telluride 2H and the molybdenum telluride1T' is easier to occur, the operation voltage of the phase transformation is reduced, the transformation speed is improved, and the cycle life is prolonged at the same time.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
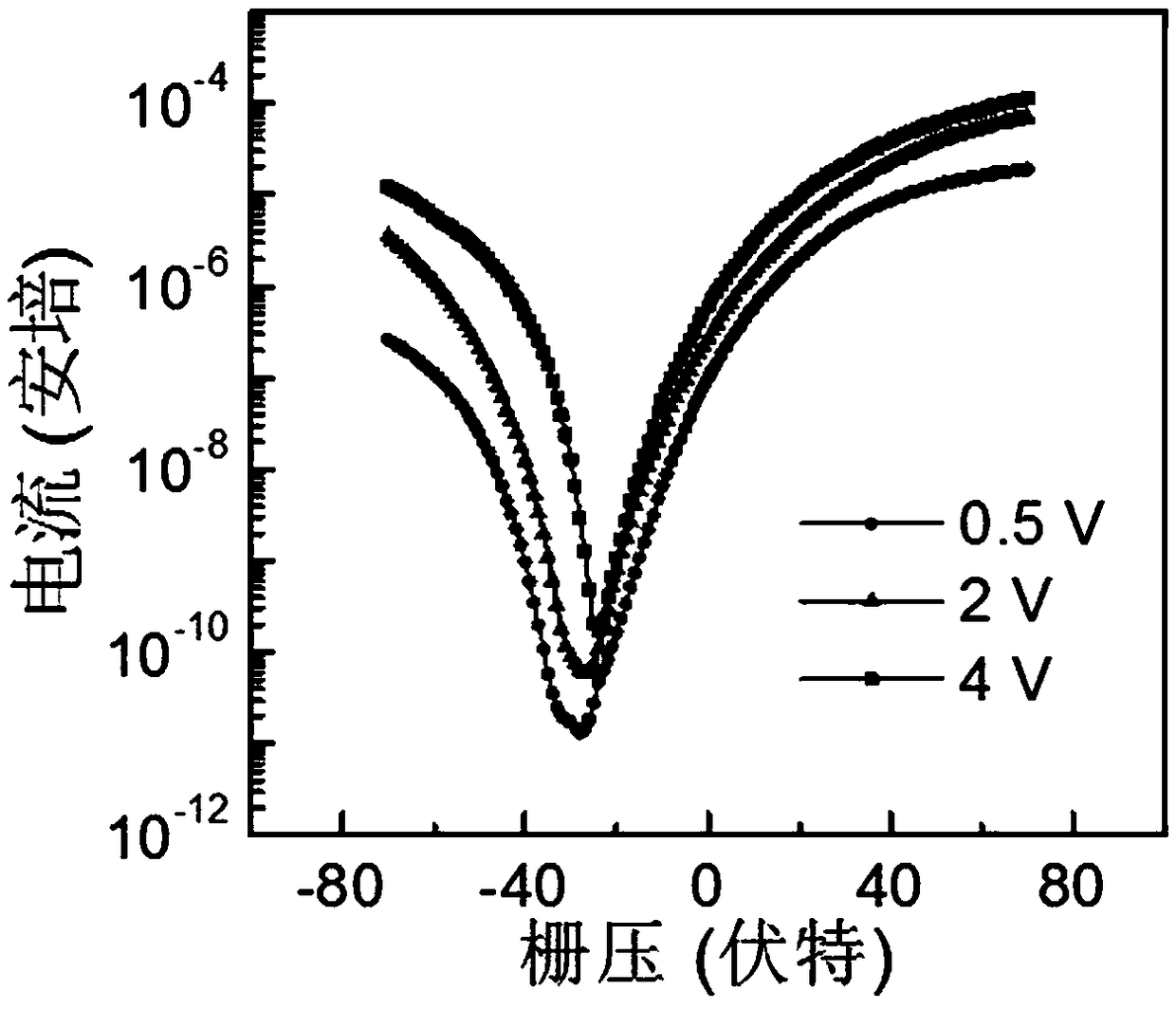
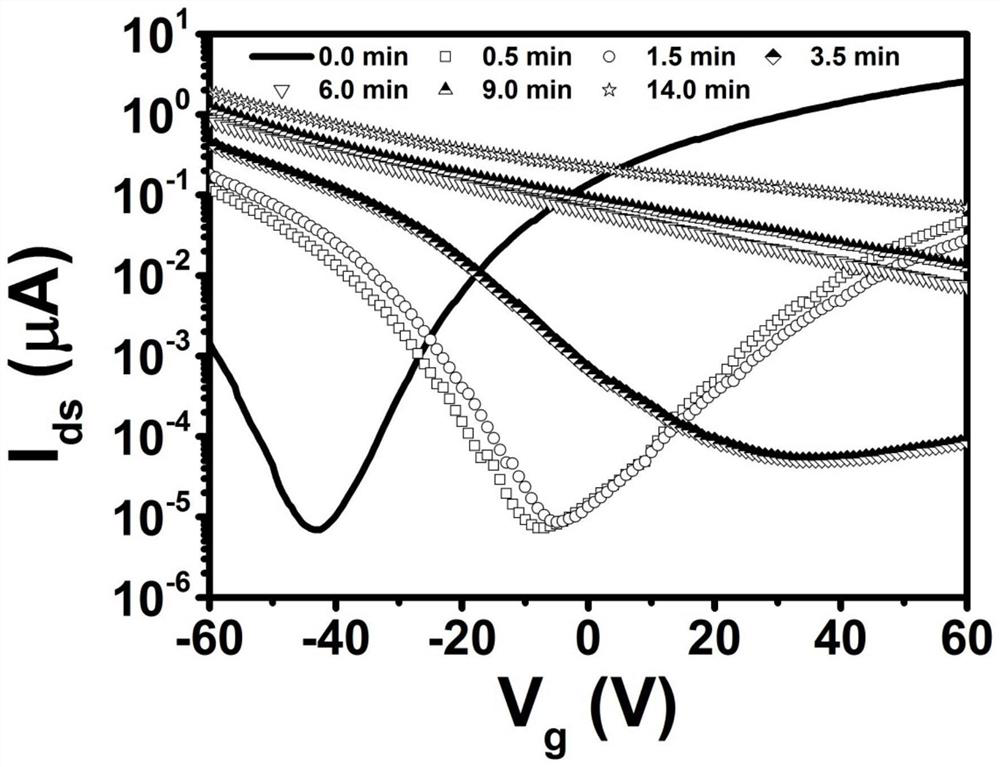
Electron-hole reversible doping method of multilayer molybdenum ditelluride field effect transistor
ActiveCN111627821ARealize electron-hole reversible doping methodThe process is simple and convenientSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMolybdenum tellurideScanning electron microscope
The invention discloses an electron-hole reversible doping method of a multilayer molybdenum telluride field effect transistor. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a MoTe2 field effect transistor device by using a mechanical stripping method; then heating the MoTe2 field effect transistor device in air at a proper temperature for a proper time to obtain a P-type doped MoTe2 field effect transistor device; and irradiating the surface of the MoTe2 field effect transistor by using a high-voltage electron beam in a scanning electron microscope cabin to obtain the N-type doped MoTe2 field effect transistor device. The P-type doping process and the N-type doping process can be repeated and controllable. The electron-hole reversible doping method of the multi-layer molybdenum ditelluride field effect transistor is realized, so that the electron transport polarity of a molybdenum ditelluride device can be controlled in a large range, and the method is simple, good in repeatability, good in measured molybdenum ditelluride performance, small in damage to materials, simple in required condition and environmentally friendly.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
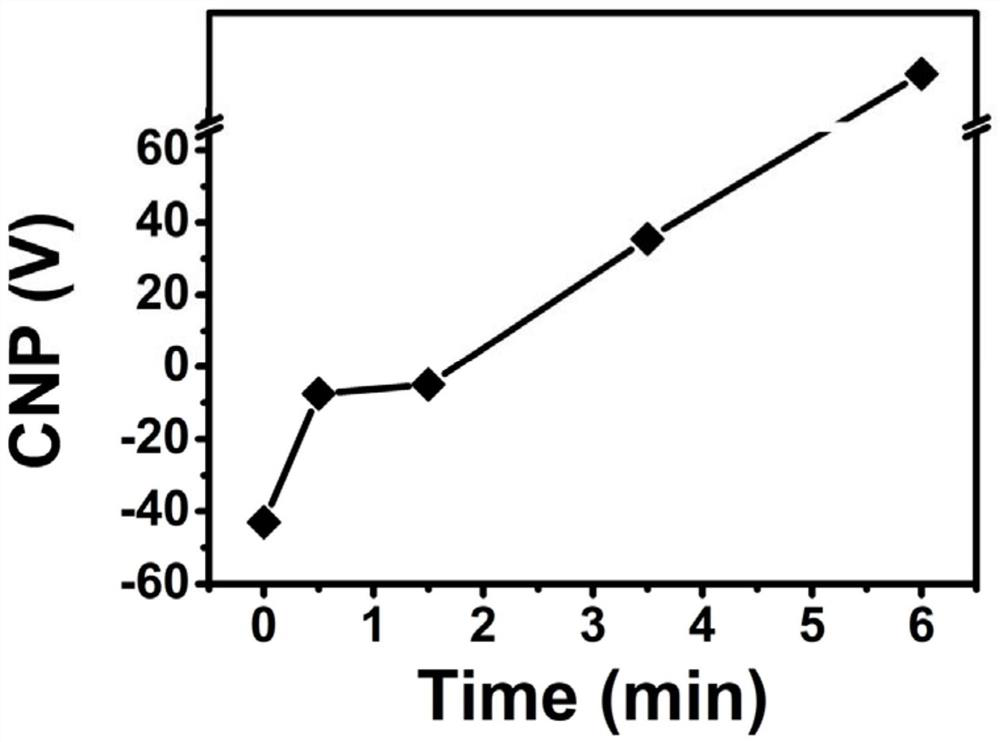
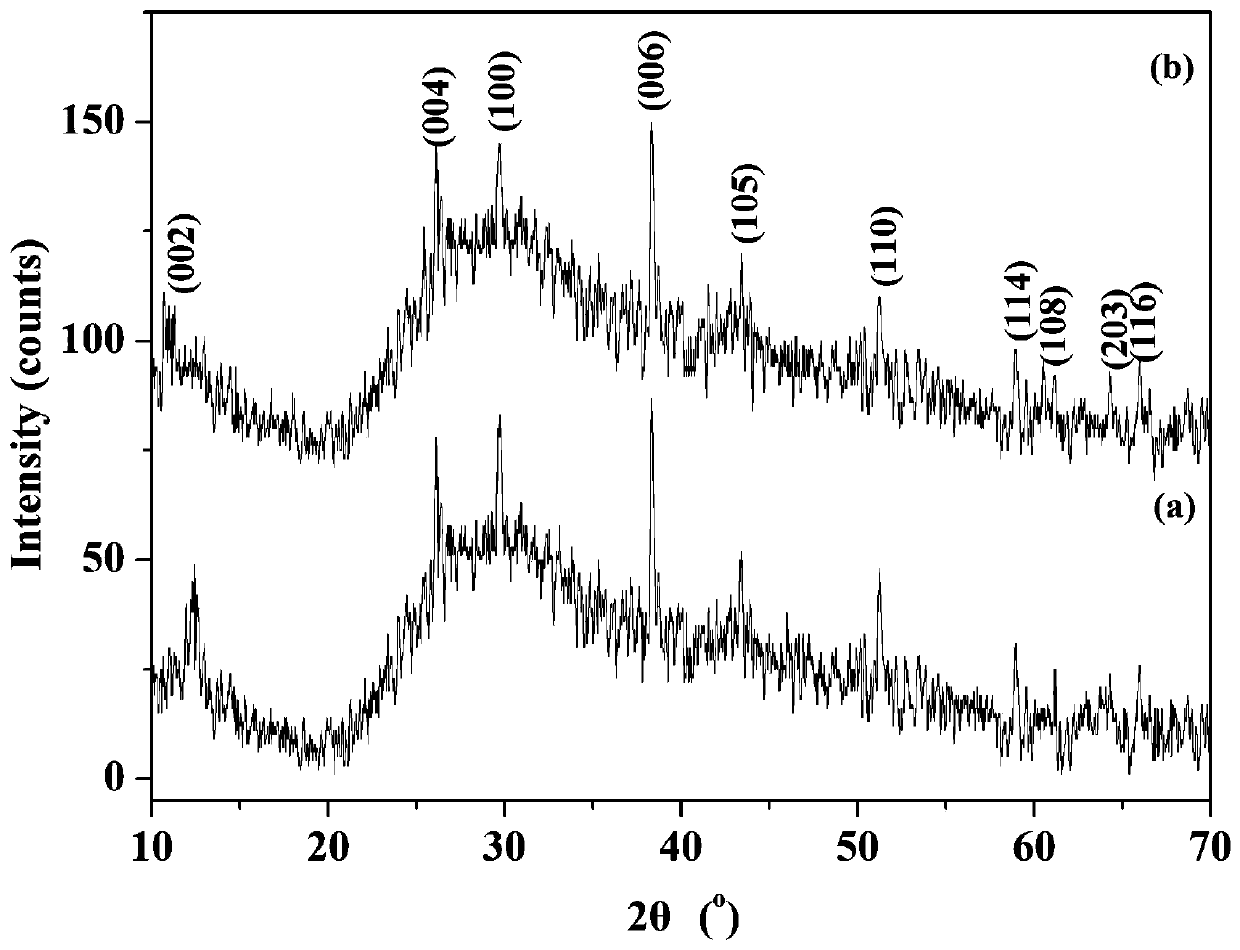
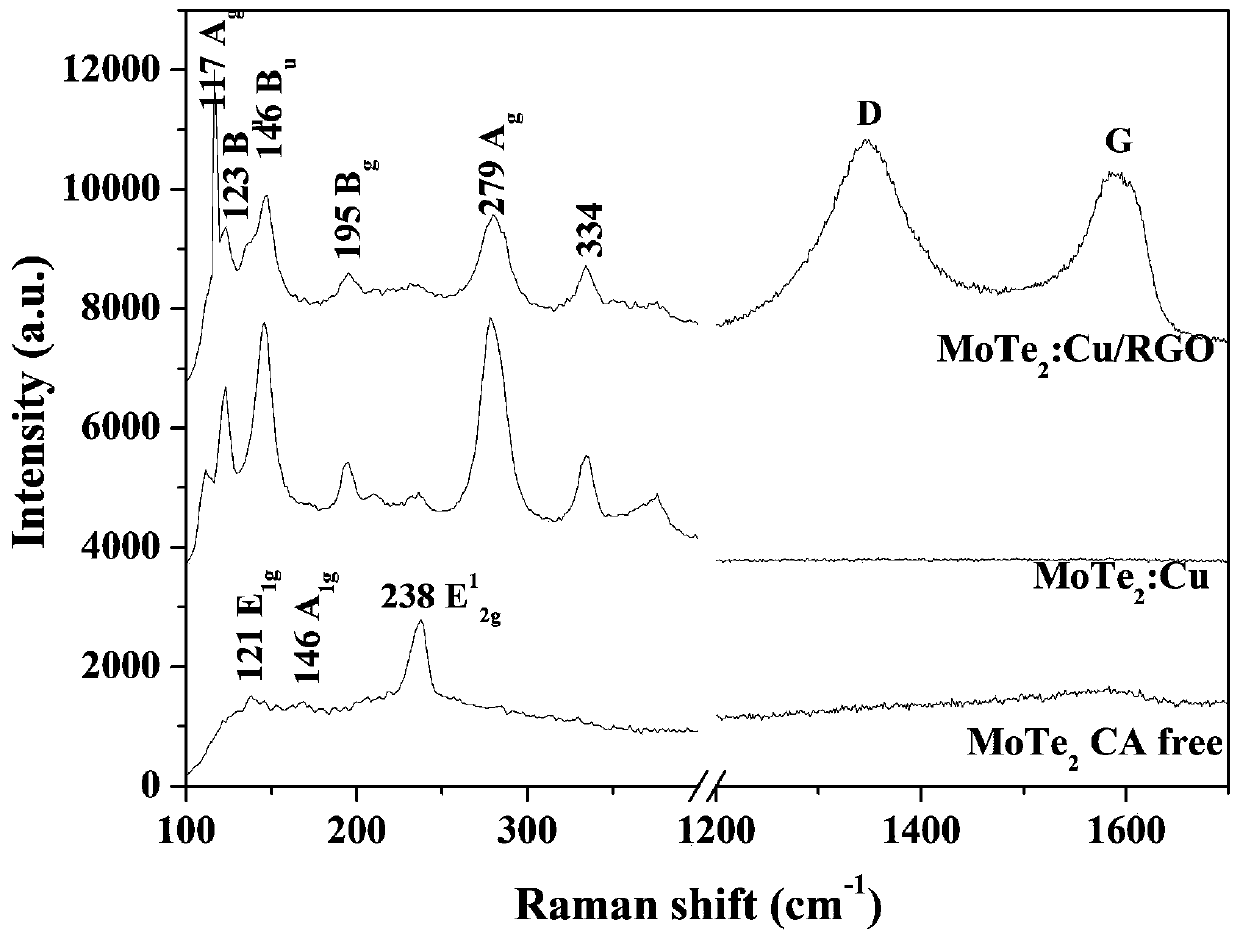
Preparation method of flaky semimetal MoTe2: Cu and flaky semimetal MoTe2: Cu/RGO
ActiveCN110560095AThe reaction process is simpleSimple processCatalyst activation/preparationElectrodesMolybdenum tellurideRoom temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method of flaky semimetal MoTe2: Cu and flaky semimetal MoTe2: Cu / RGO. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding tellurium powder and potassiumborohydride into deionized water, and carrying out a reaction in a sealed environment to obtain an aqueous Te2-precursor solution; adding ammonium paramolybdate and copper acetate into 10 ml of a solvent, carrying out dissolving, and adding citric acid to obtain a molybdenum ion source precursor solution; putting the aqueous Te2-precursor solution and the molybdenum ion source precursor solutioninto a reaction kettle, keeping the reaction kettle at room temperature, and then performing gradient heating to 155-165 DEG C for a hydrothermal reaction; and carrying out cooling to room temperature, performing filtering, cleaning a filtrate, and drying the filtrate to obtain Cu ion-doped flaky semimetal molybdenum ditelluride and a compound of the Cu ion-doped flaky semimetal molybdenum ditelluride and graphene. The preparation method can be directly used for preparation of metal molybdenum ditelluride of a semi-metal structure, and is simple in preparation process.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for growing single-layer telluride doping structure through impulse type injection of reactants
InactiveCN110863189APrecise and controllable growth conditionsEasy to operateChemical vapor deposition coatingMolybdenum tellurideReaction temperature
The invention discloses a method for growing a single-layer telluride doping structure through impulse type injection of reactants. According to the method, a plurality of transition metal organics and diethyl tellurium or molybdenum hexacarbonyl and a plurality of chalcogens are injected simultaneously to control the carrier gas flow to control the amount of telluride doping, the reaction temperature and the reaction time are controlled to control the area and the number of layers of telluride growth, and thus high-quality molybdenum ditelluride with the doping structure is obtained. The method has the advantages that growth conditions are precise and controllable, operation is easy and convenient, and the stable molybdenum ditelluride with the single-layer doping structure can be prepared. The prepared molybdenum ditelluride with the single-layer doping structure has broad application prospects in the fields of nano-electronical appliances, lubricating materials, photocatalysis and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation of a molybdenum ditelluride nanowire material and molybdenum ditelluride nanowire material
ActiveCN109336069BUniform sizeEasy to makeMaterial nanotechnologyMetal selenides/telluridesMolybdenum tellurideNanowire
The invention discloses a preparation of a molybdenum ditelluride nanowire material and a molybdenum ditelluride nanowire material. A silicon dioxide / silicon chip is used as a substrate, and molybdenum powder and tellurium powder are used as raw materials. Molybdenum ditelluride nanowires are grown on the silicon surface by chemical vapor deposition; the growth container of the molybdenum ditelluride nanowires is a quartz tube, and a mixed gas of argon and hydrogen is introduced into the quartz tube; A quartz test tube is also set, the sealed end of the quartz test tube is opposite to the flow direction of the mixed gas, and the quartz test tube is used to place the substrate for chemical vapor deposition; the flow rate of argon is 100 sccm; the flow rate of hydrogen is 5-30 sccm; the reaction of chemical vapor deposition The temperature is 600-800°C. The process is simple, the cost is low, and the molybdenum ditelluride nanowires are of high quality.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Asymmetric van der Waals heterojunction device, its preparation method and use
ActiveCN109004016BIncrease the current switch ratioImprove responsivenessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionMolybdenum telluride
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
A van der Waals heterojunction device and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN109390388BIncrease the current switch ratioHigh current rectification ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionMolybdenum telluride
The invention provides a van der Waals heterojunction device, comprising a base, a molybdenum ditelluride nanosheet, a molybdenum disulfide nanosheet and a metal electrode sequentially arranged from bottom to top, and the cross-sectional area of the molybdenum ditelluride nanosheet is larger than The cross-sectional area of the molybdenum disulfide nanosheets. The van der Waals heterojunction device of the invention can realize the dynamic adjustment of the conduction polarity. Under different bias conditions, field-effect transistors based on this van der Waals heterojunction device can achieve bipolar and N-type conduction polarity, respectively, and exhibit an ultrahigh current switching ratio (~10 7 ), current rectification ratio (~10 6 ) and excellent photovoltaic performance, which can be applied in new two-dimensional electronic and optoelectronic devices.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
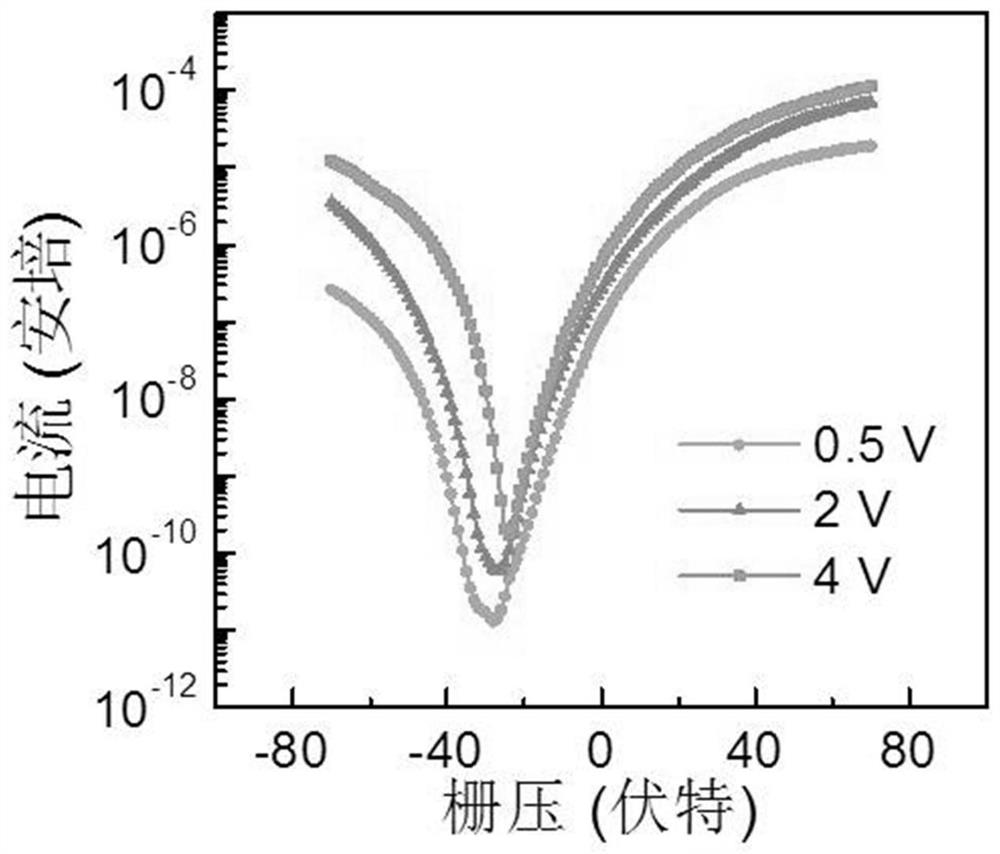
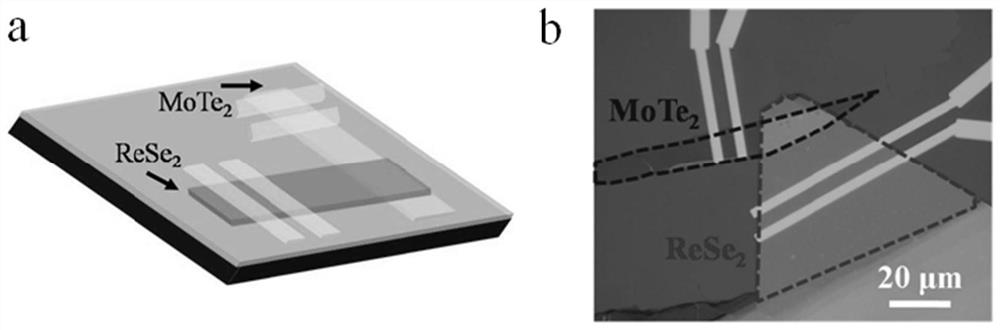
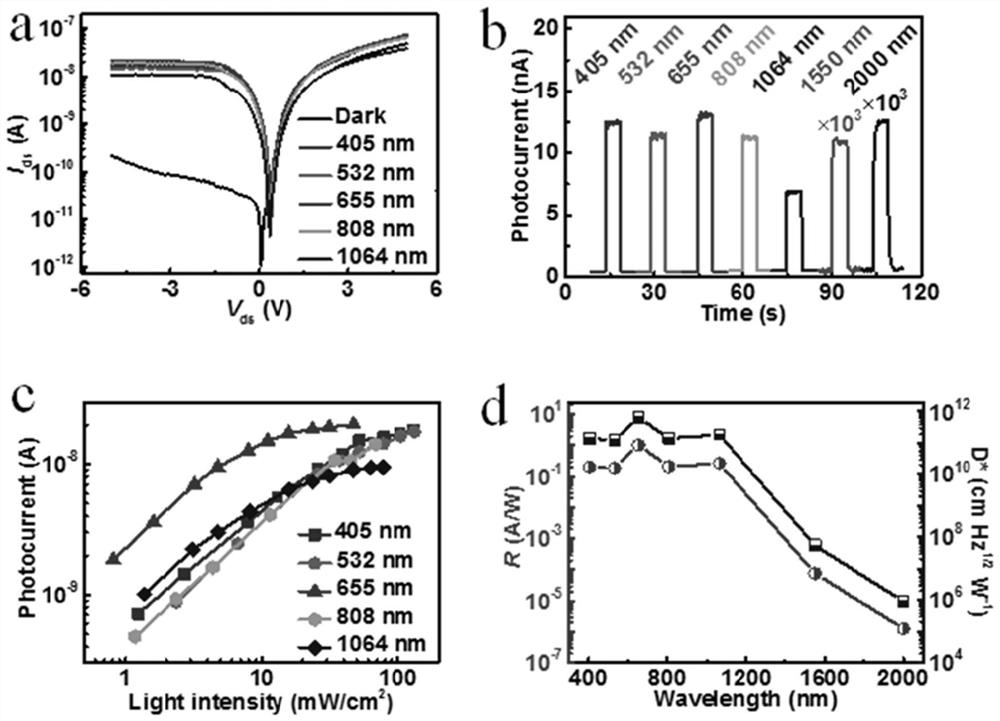
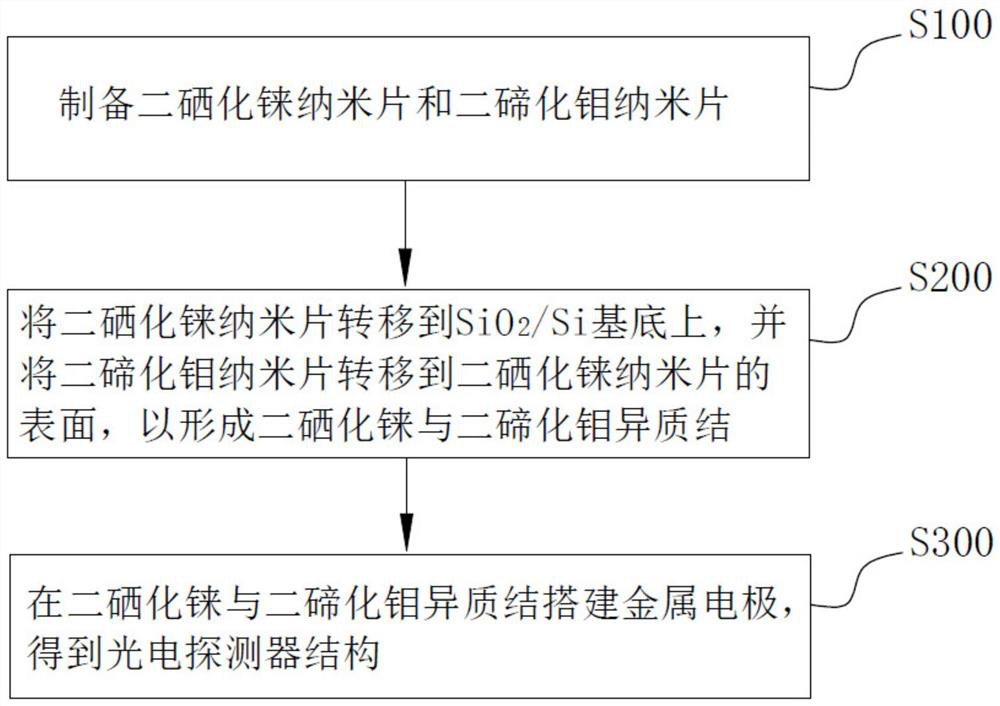
Photoelectric detector based on rhenium diselenide and molybdenum telluride heterojunction and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114759113AImprove photoelectric performanceSolve the problem of limited light absorption rangeSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionRhenium
The invention discloses a rhenium diselenide and molybdenum ditelluride heterojunction-based photoelectric detector and a preparation method thereof, the photoelectric detector comprises a SiO2 / Si substrate, a rhenium diselenide nanosheet, a molybdenum ditelluride nanosheet and a metal electrode, the rhenium diselenide nanosheet and the molybdenum ditelluride nanosheet are arranged on the surface of the SiO2 / Si substrate, and the metal electrode is arranged on the surface of the rhenium diselenide nanosheet and the molybdenum ditelluride nanosheet. The surface of the rhenium diselenide nanosheet and the surface of the molybdenum ditelluride nanosheet are partially overlapped to form a rhenium diselenide and molybdenum ditelluride heterojunction, and light current is generated when the heterojunction is illuminated, so that optical detection is realized, type-II type staggered energy band arrangement is met, interlayer transition excitation can be realized, and the detection sensitivity is improved. The rhenium diselenide photoelectric detector effectively solves the problem that the light absorption range of a single rhenium diselenide photoelectric detector is limited, so that the photoelectric property of the photoelectric detector is improved, wide-spectrum photoelectric detection from visible light to a short-wave infrared region can be realized, and the light response range is wider.
Owner:TAISHAN UNIV +1
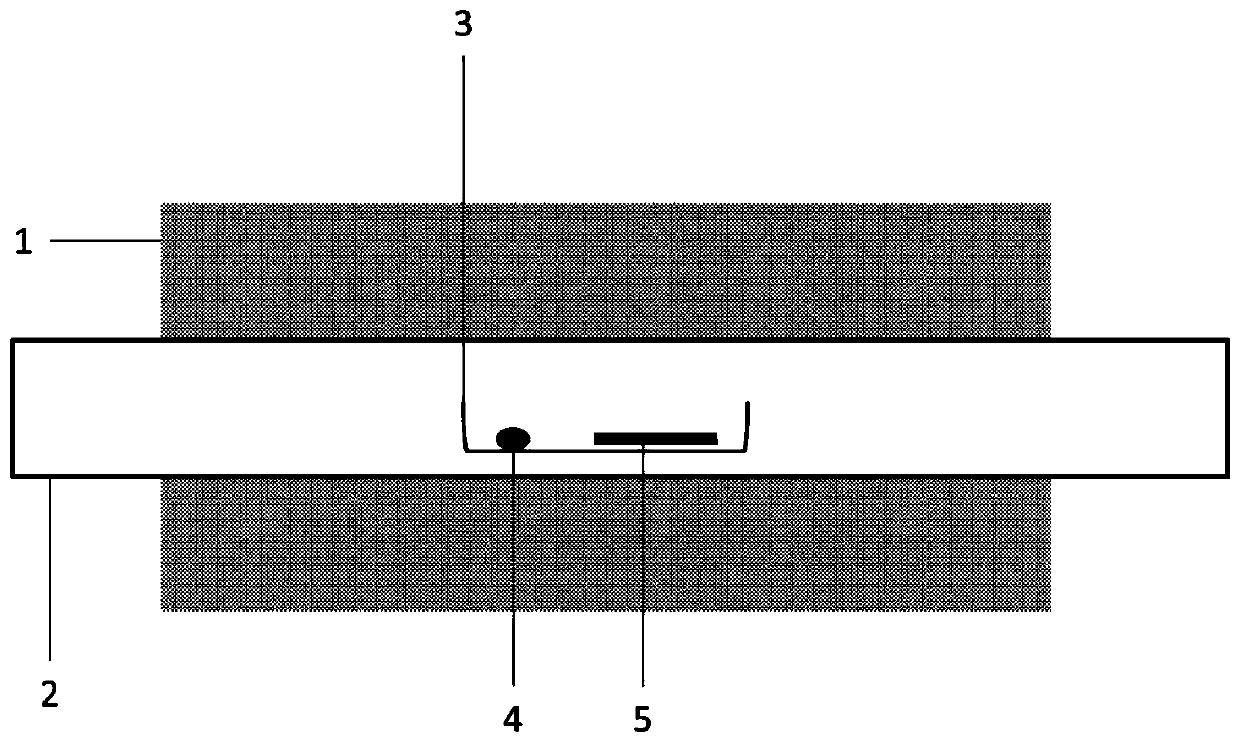
A self-driven two-dimensional molybdenum telluride homoheterojunction near-infrared photodetector and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105932091BSimple processMature and reliable technologyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionElectrical conductor
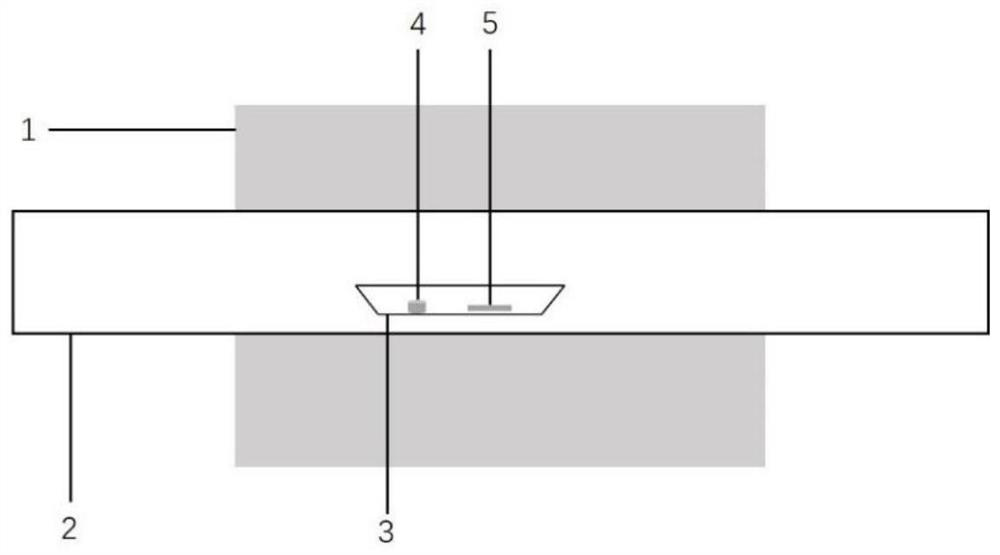
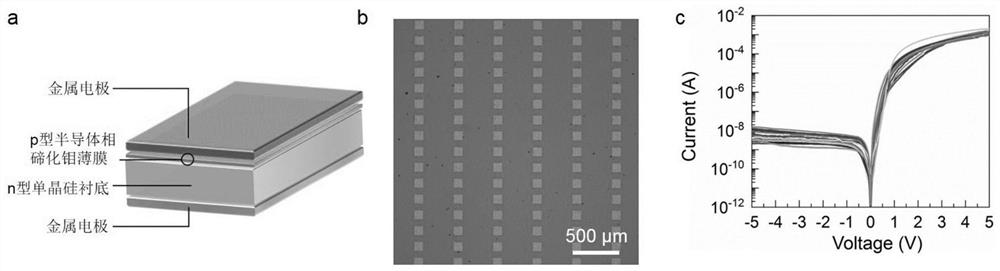
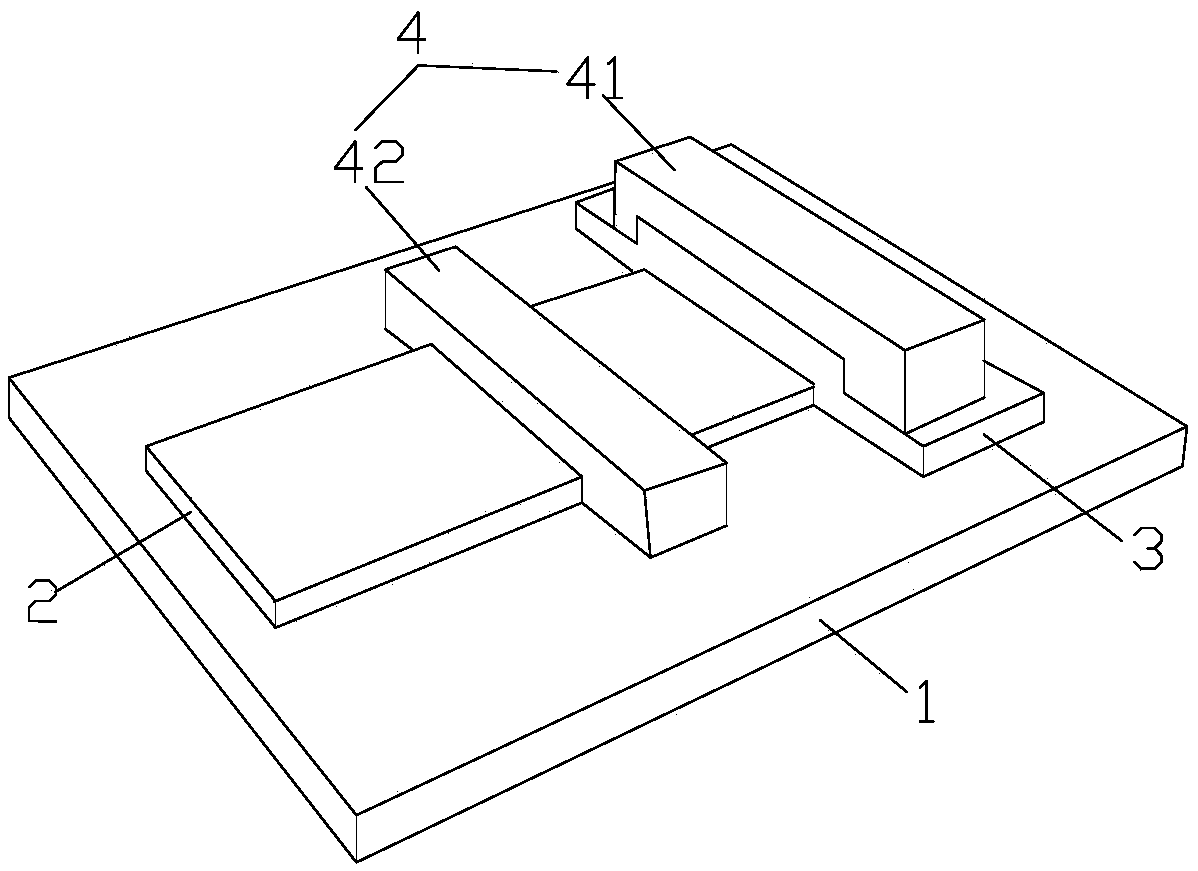
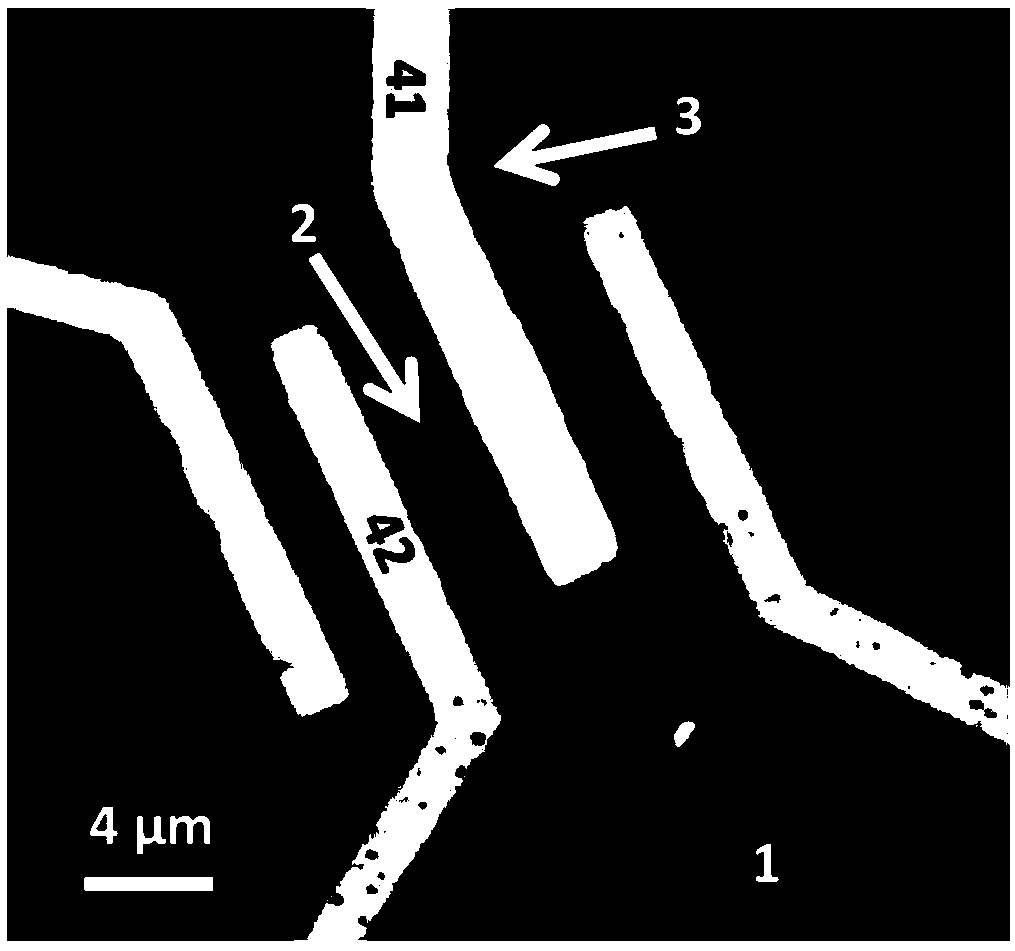
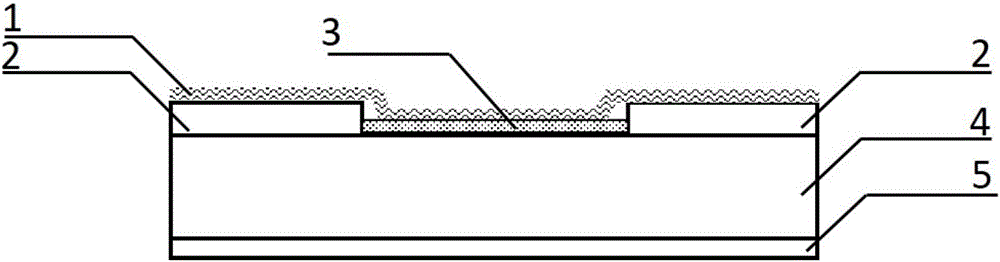
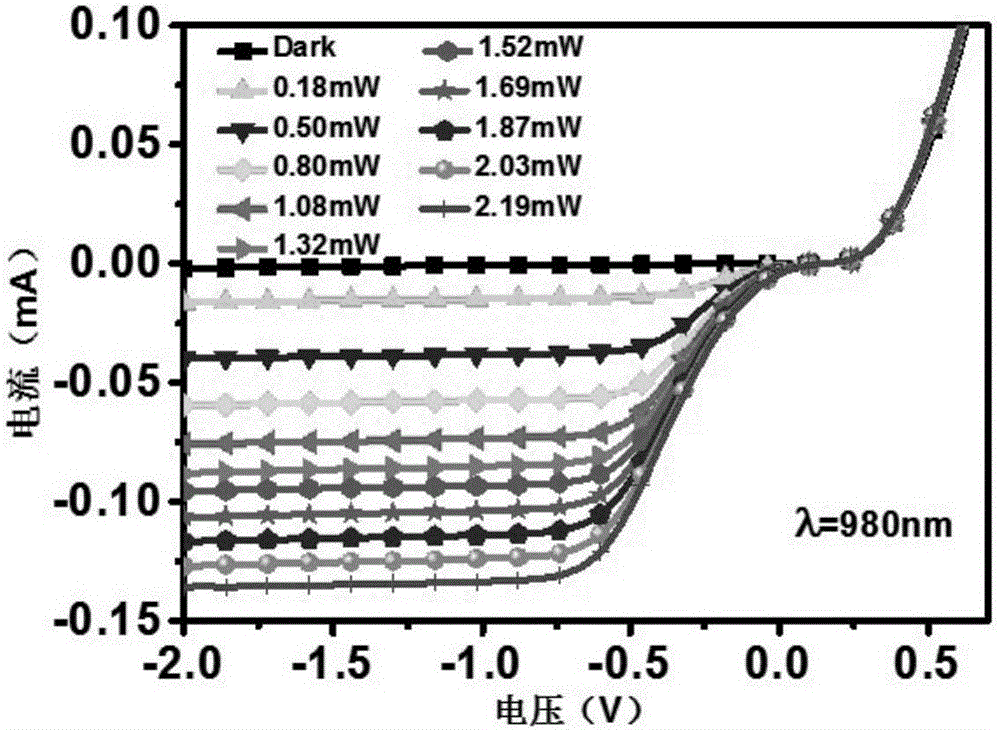
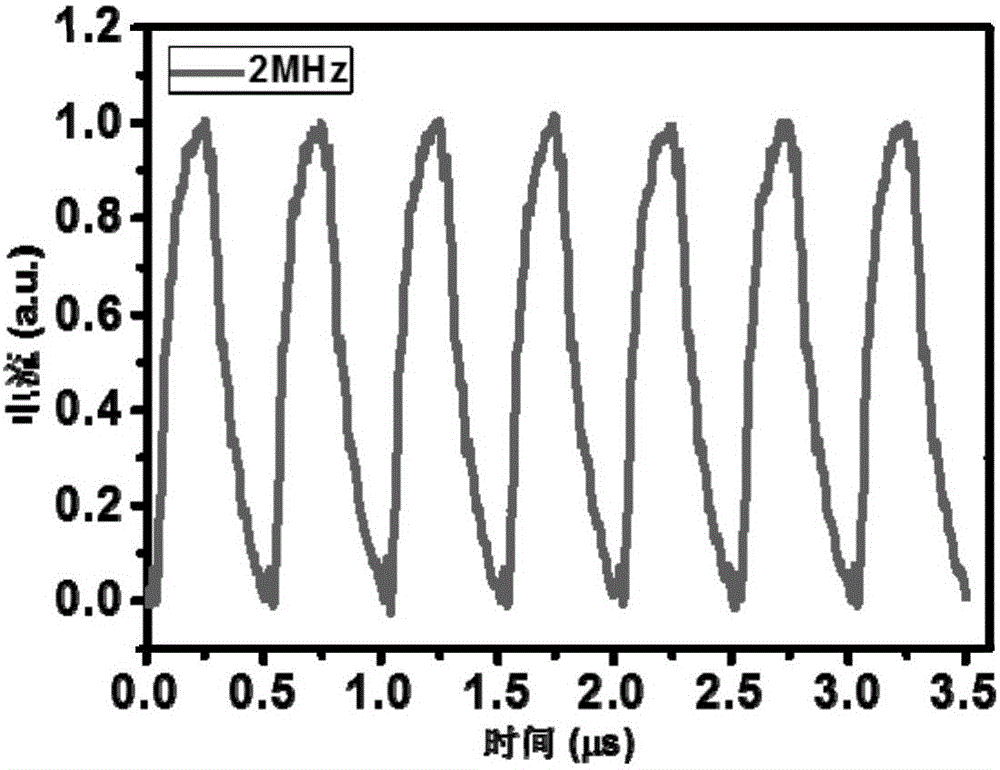
The invention discloses a self-driving two-dimensional molybdenum(IV) telluride homotype heterojunction near infrared electric detector and preparation method thereof. The detector is characterized in that a bottom electrode in ohmic contact with the N type semiconductor substrate is arranged on the lower surface of an N type semiconductor substrate, the upper surface is covered by a mask layer which is made of insulating materials, a through hole is reserved in the center of the mask layer, a two-dimensional molybdenum(IV) telluride film is deposited in the through hole and is contacted with the N type semiconductor substrate to form an N-N homotype heterojunction, and the upper surface of the molybdenum(IV) telluride film is provided with a top electrode in ohmic contact with the molybdenum(IV) telluride. The near infrared electric detector is simple in preparation process, mature and reliable in technology, easy to control, and the obtained device has excellent performances of high sensitivity, high speed, high detectability, and self-driving.
Owner:合肥庐阳科技创新集团有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com