Patents
Literature
79results about How to "Compensation is simple" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optical transceivers for use in fiber optic communication networks
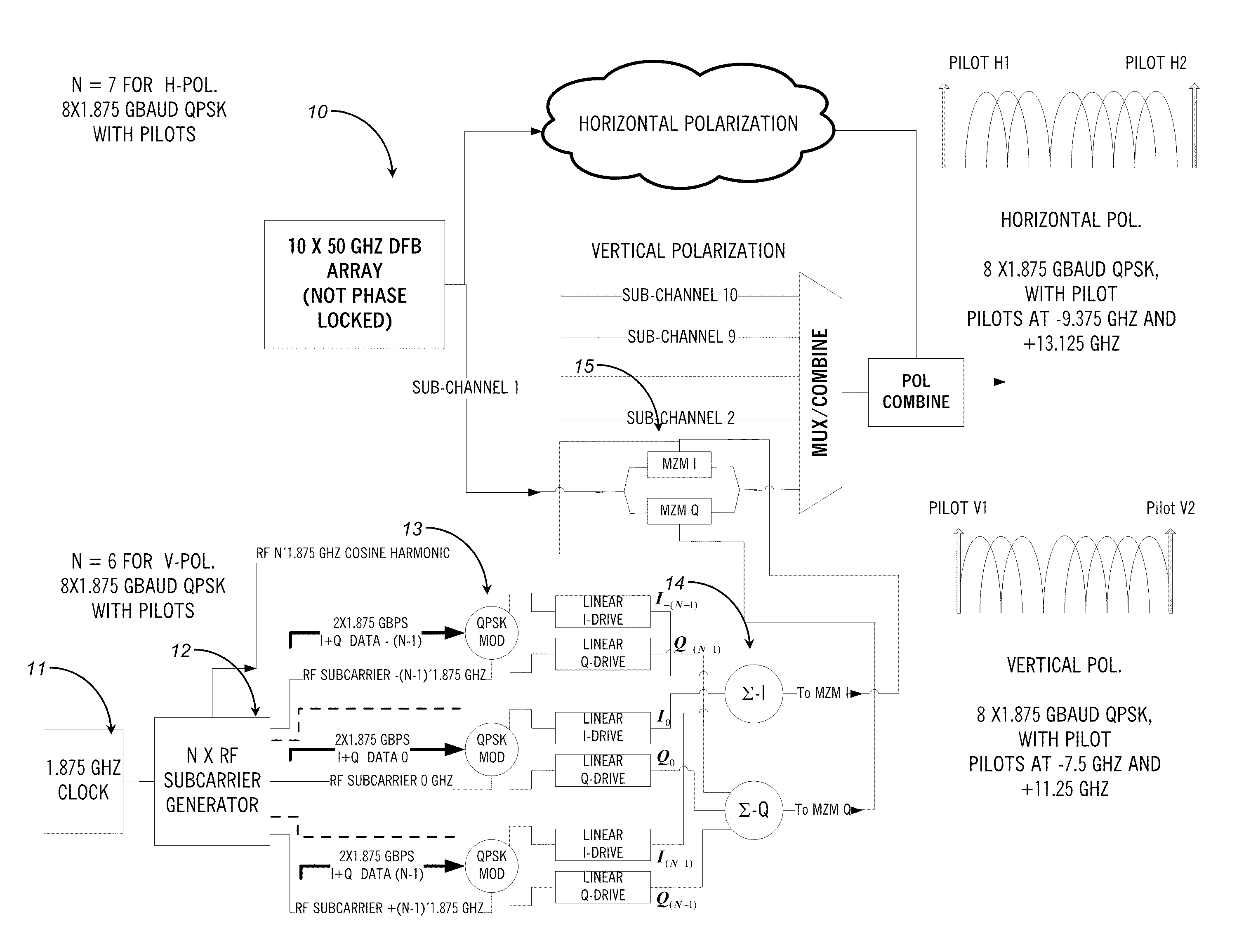
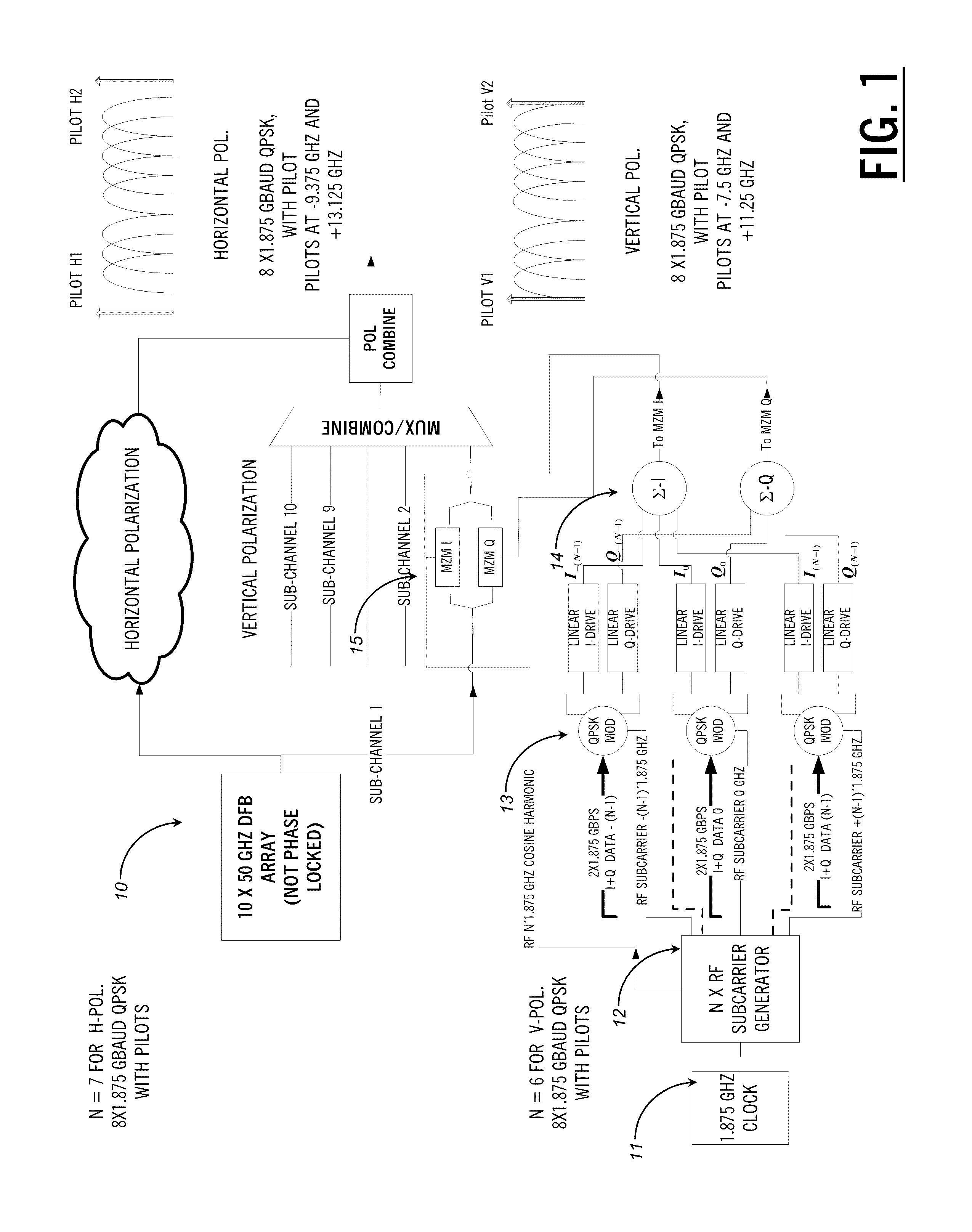
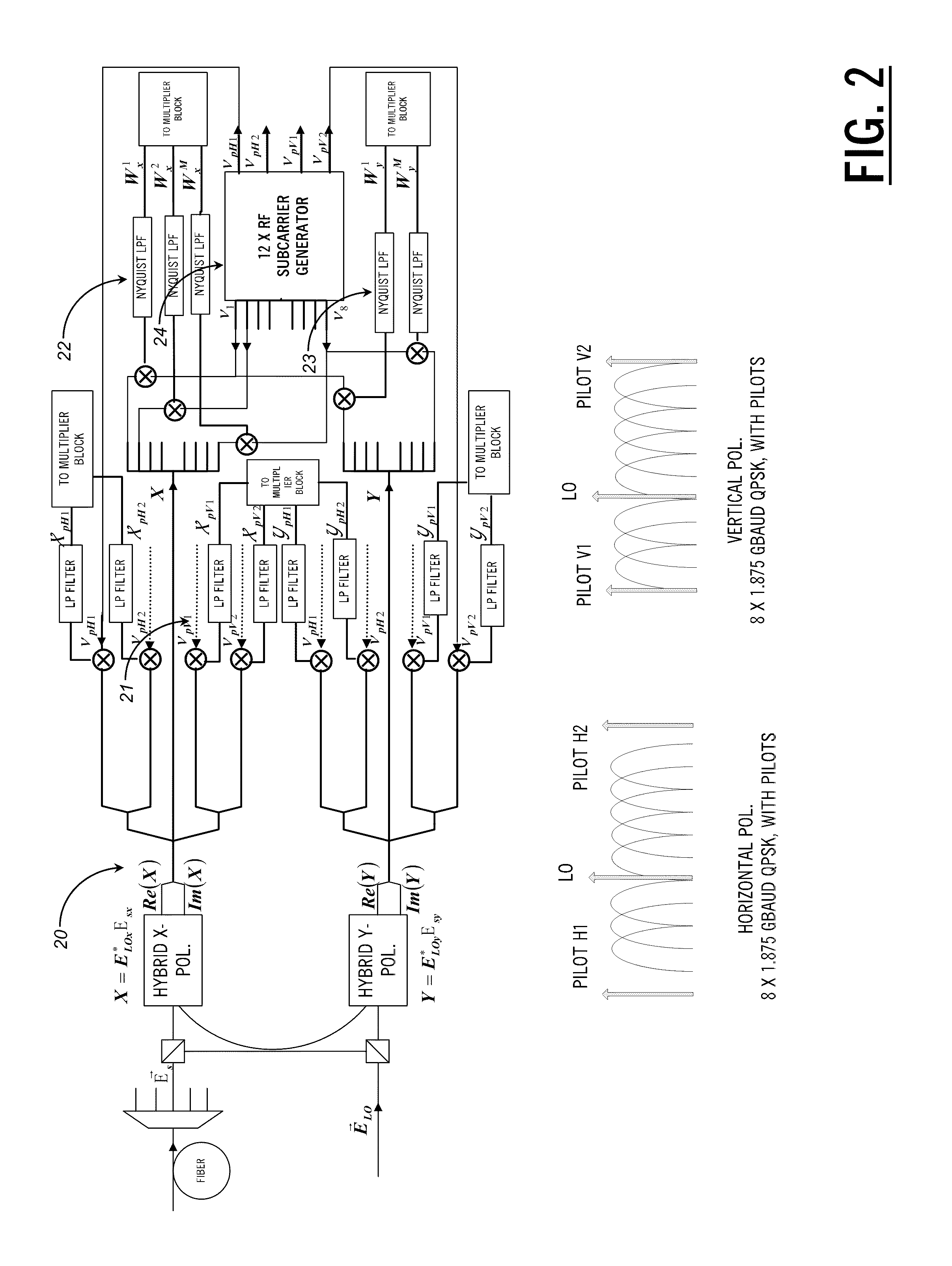
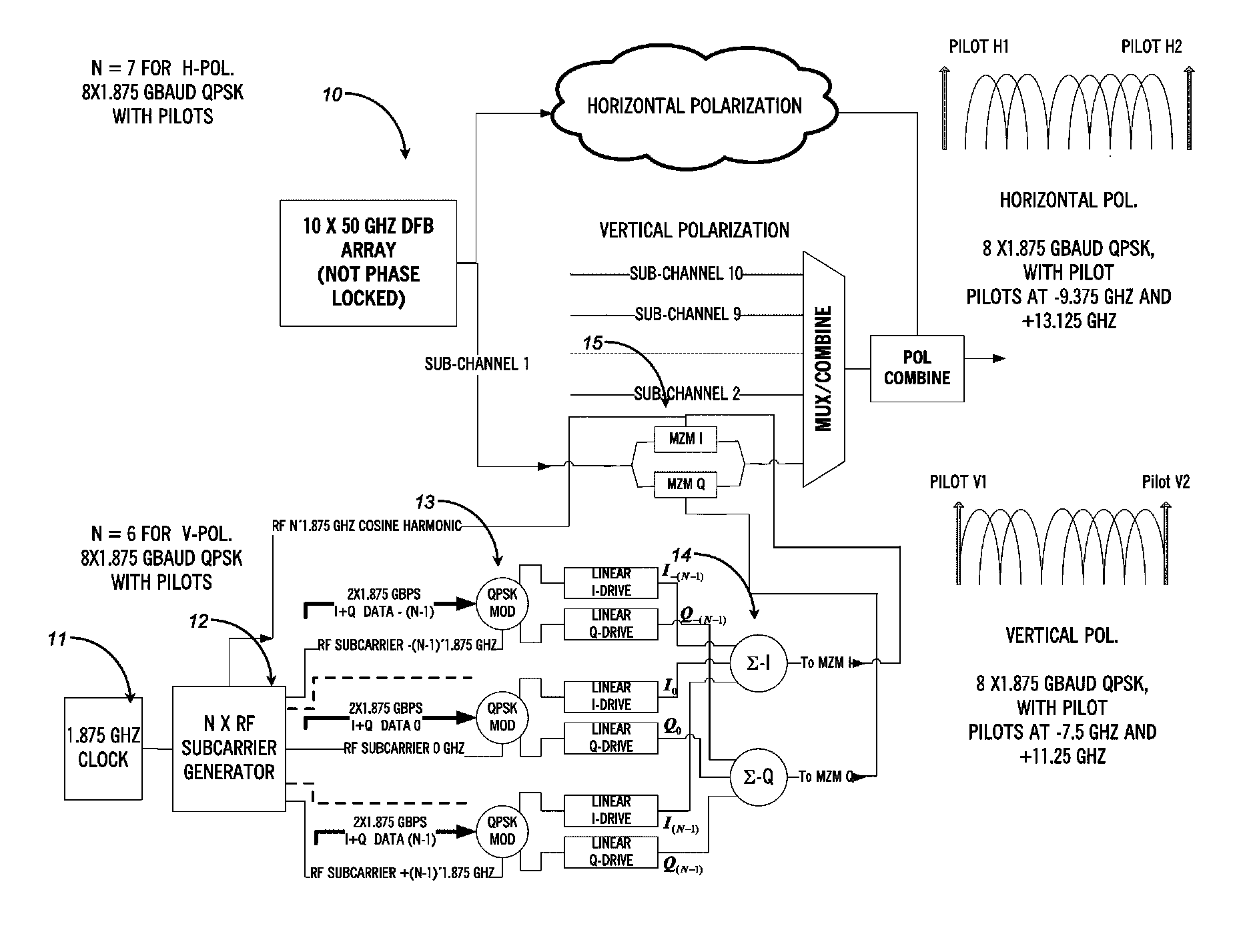
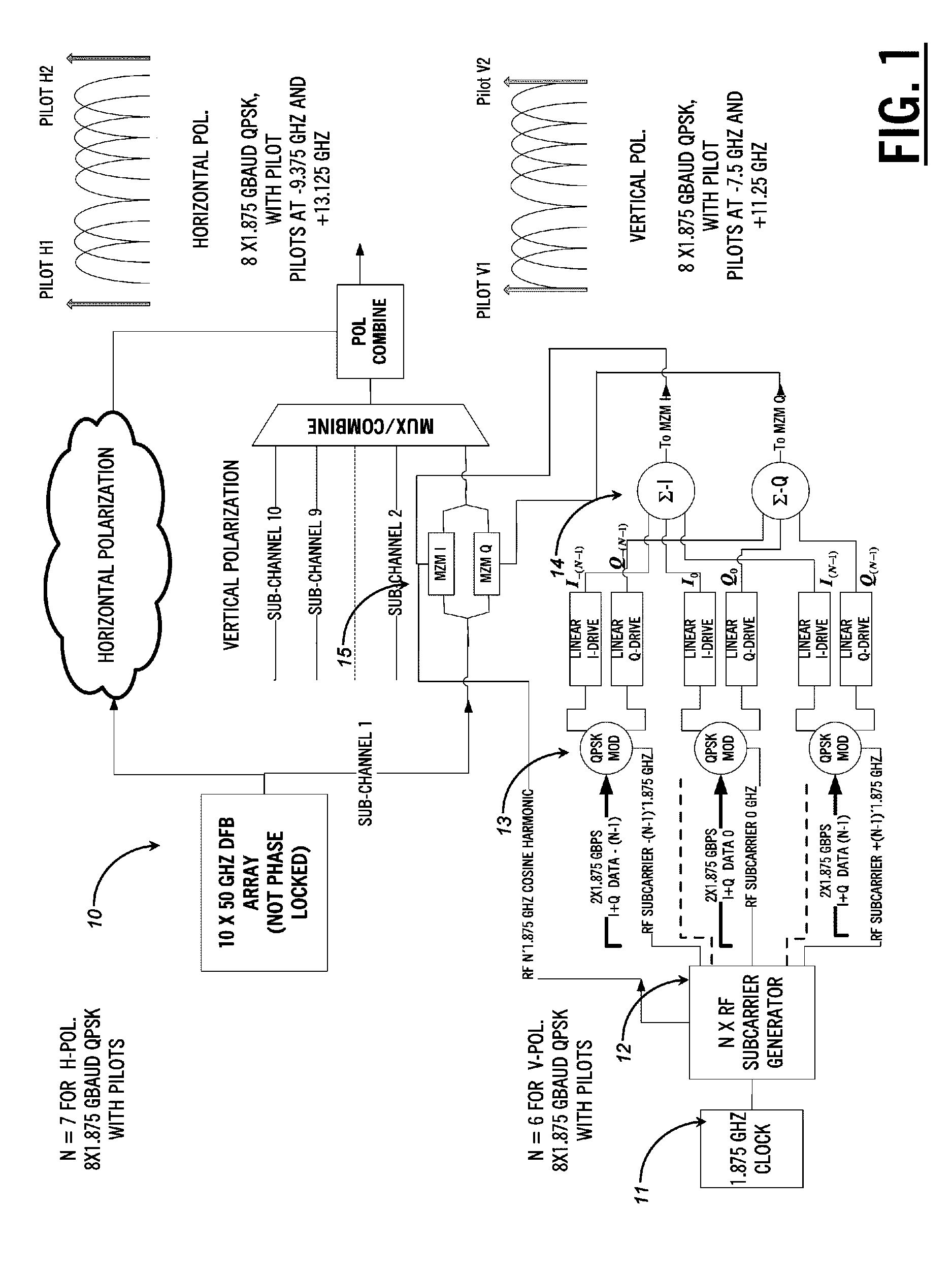
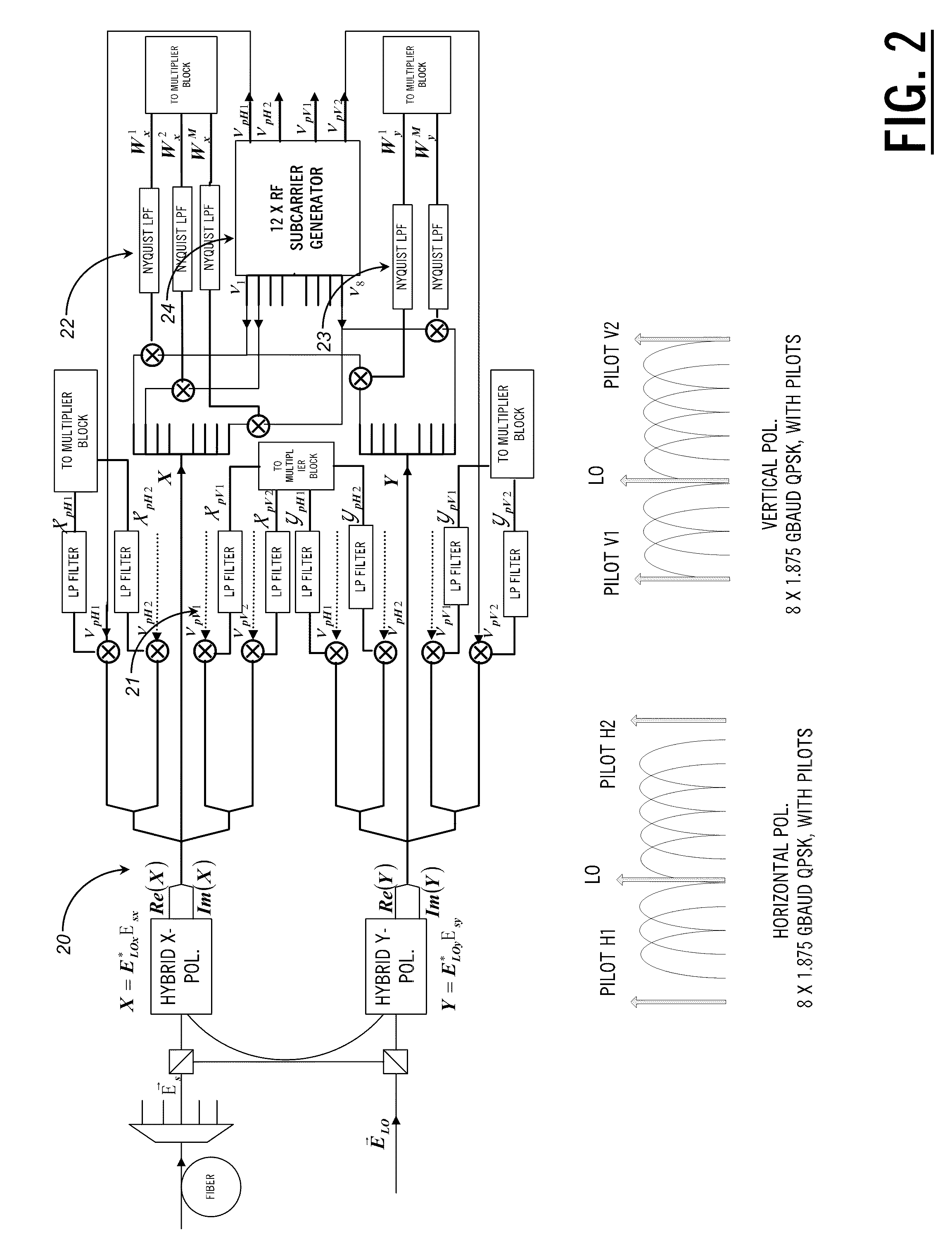
ActiveUS20110255870A1Simplify channel impairment compensation algorithmMinimizes sizeModulated-carrier systemsPolarisation multiplex systemsTransceiverFrequency spectrum
The present disclosure provides a polarization multiplexed transceiver, including: a transmitter; a receiver; circuitry within the transmitter configured to insert pilot tones as a reference state of polarization for a polarization multiplexed signal; and circuitry within the receiver configured to de-multiplex the polarization multiplexed signal using the pilot tones. The transmitted signal is constructed in such a manner as to facilitate the division of the receiver processing between the analog and digital domains such that the implementation may be simultaneously both highly spectrally efficient and power efficient.
Owner:CIENA
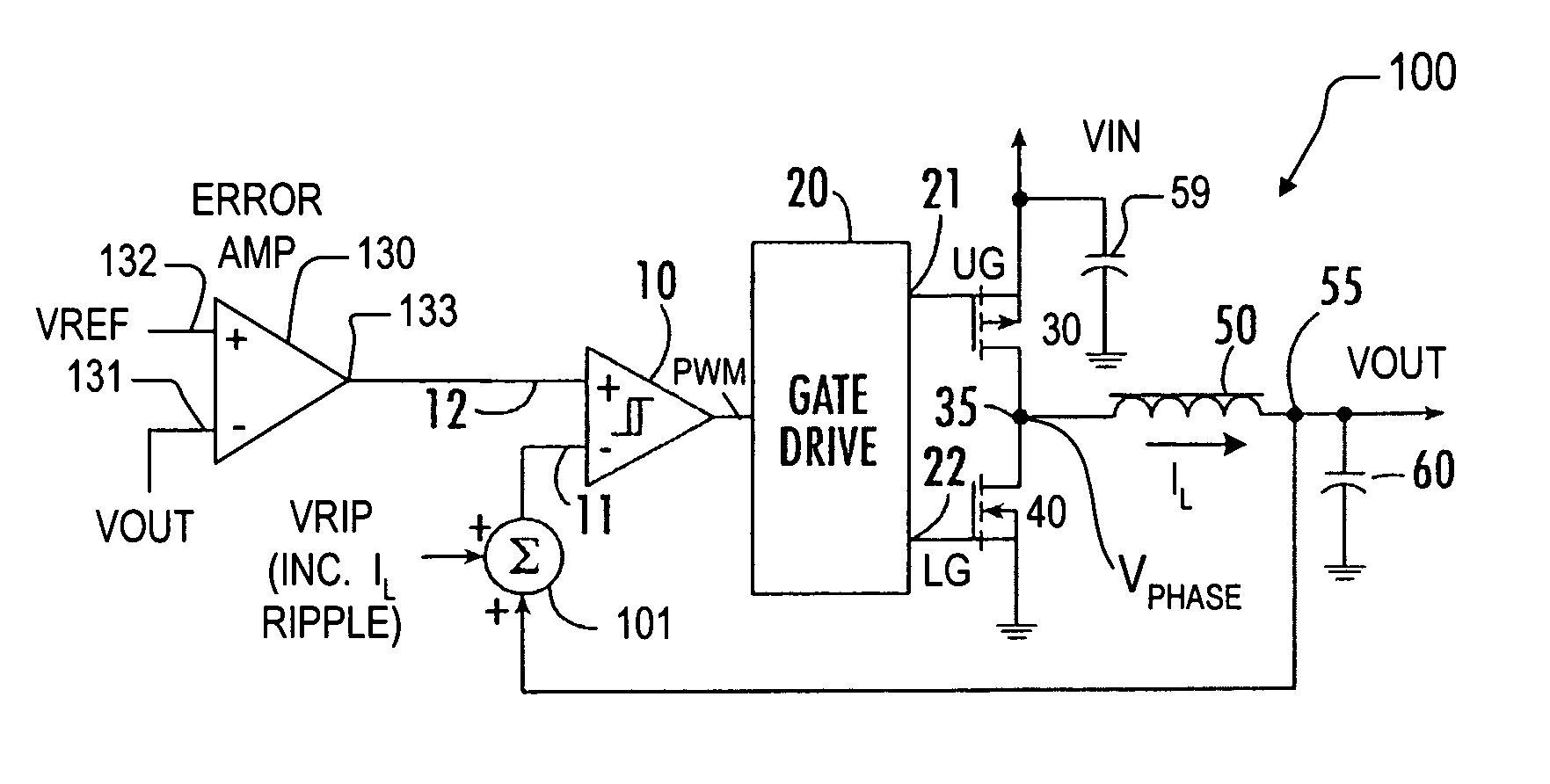
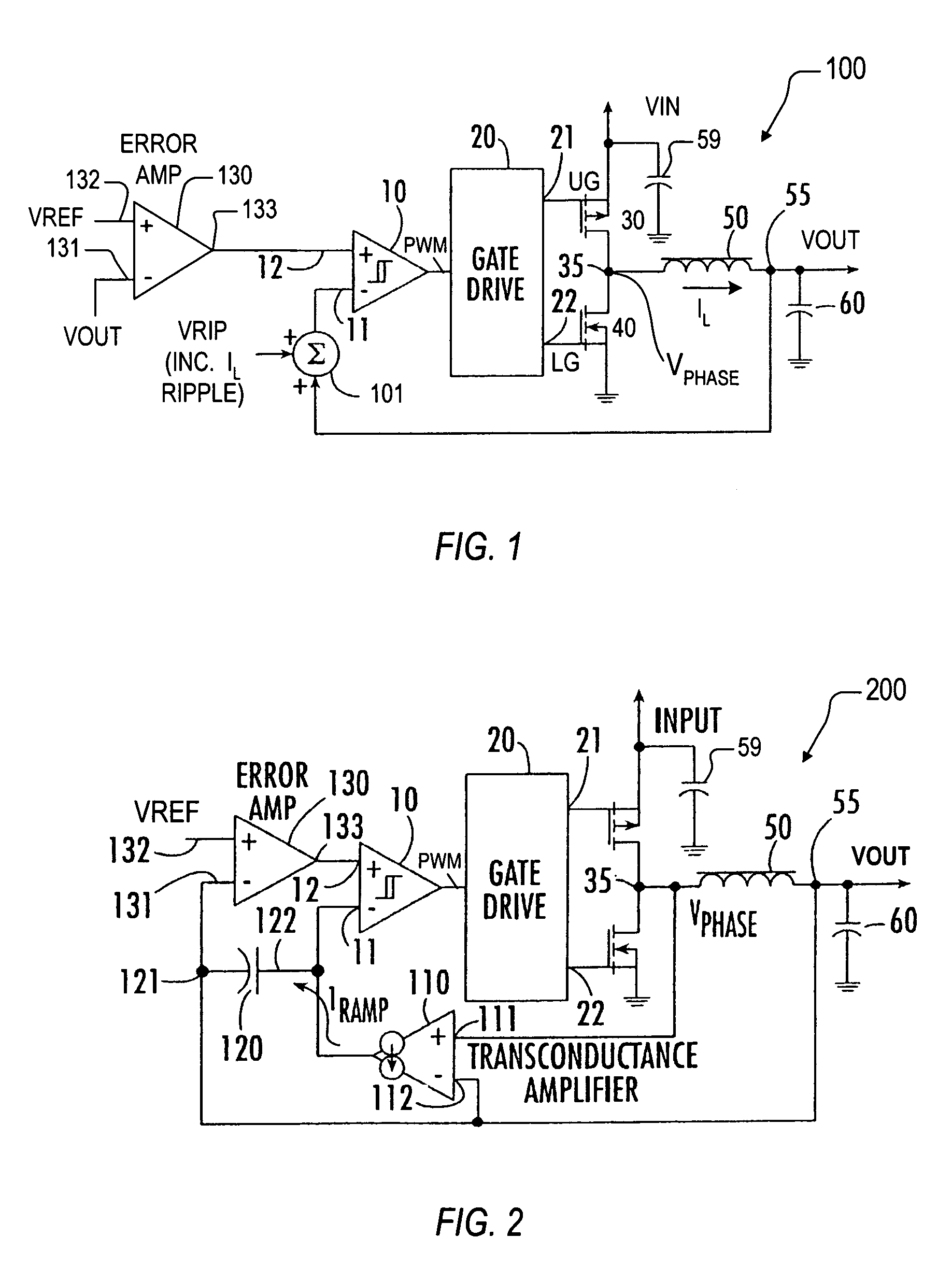
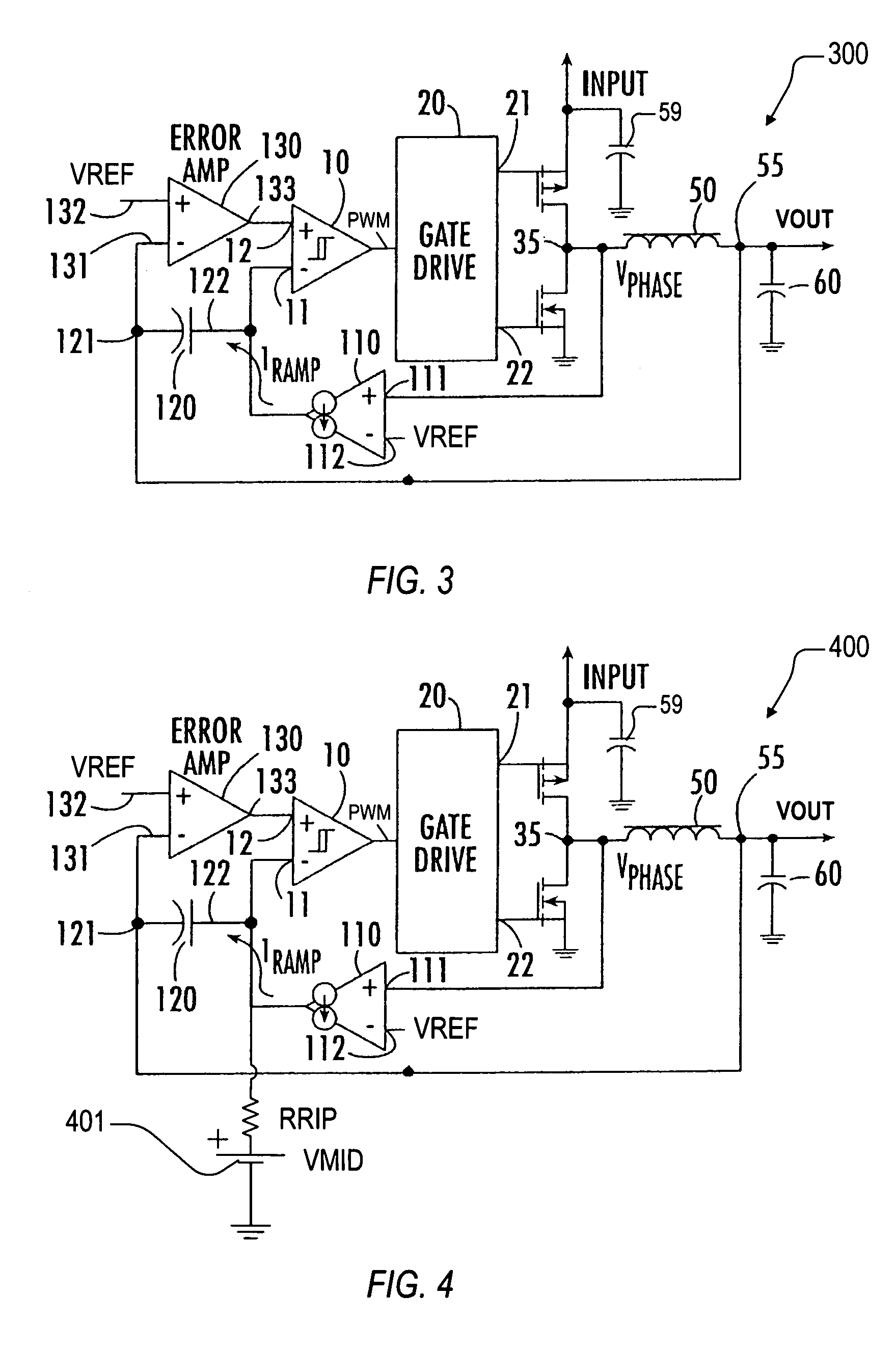
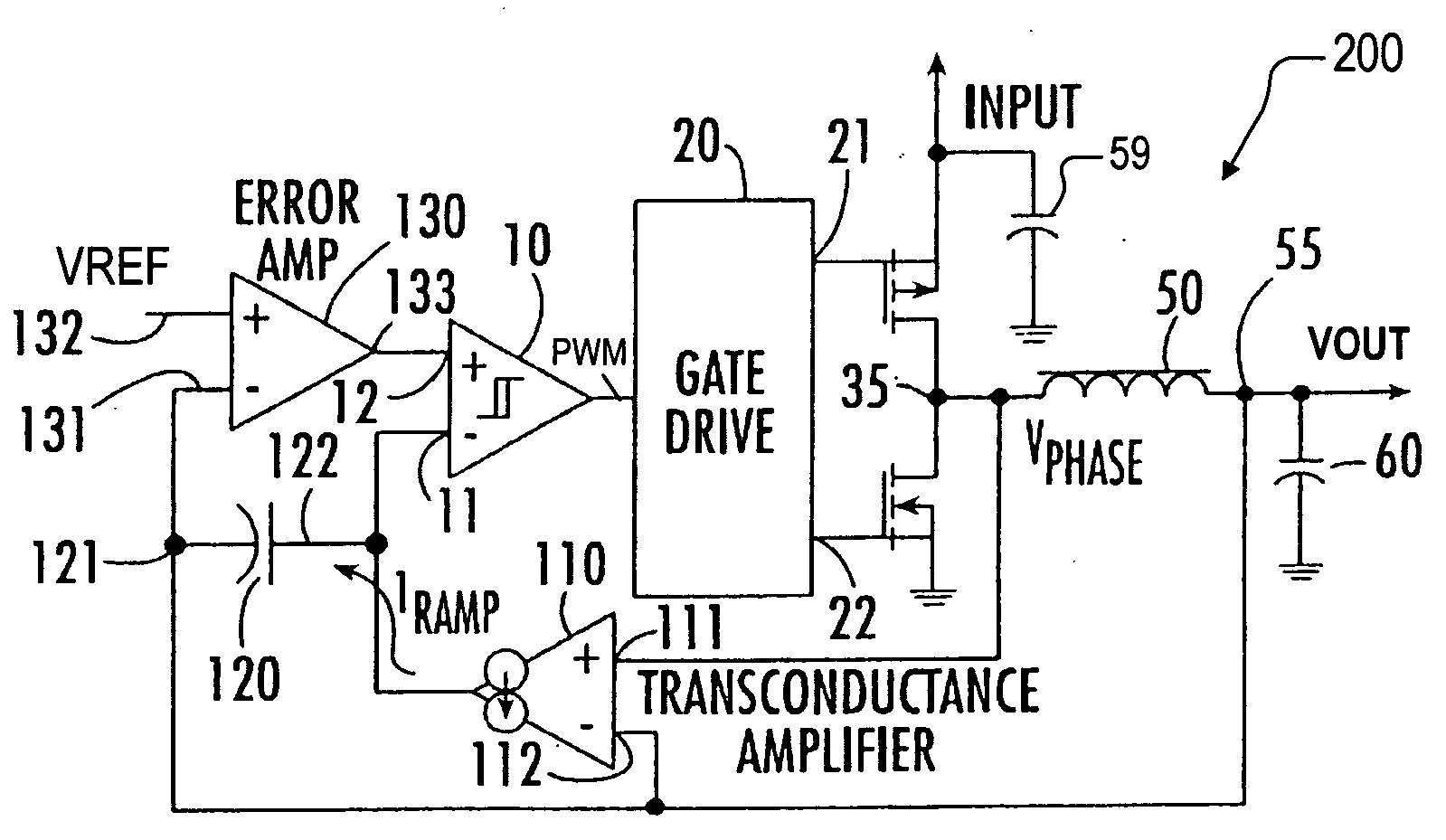
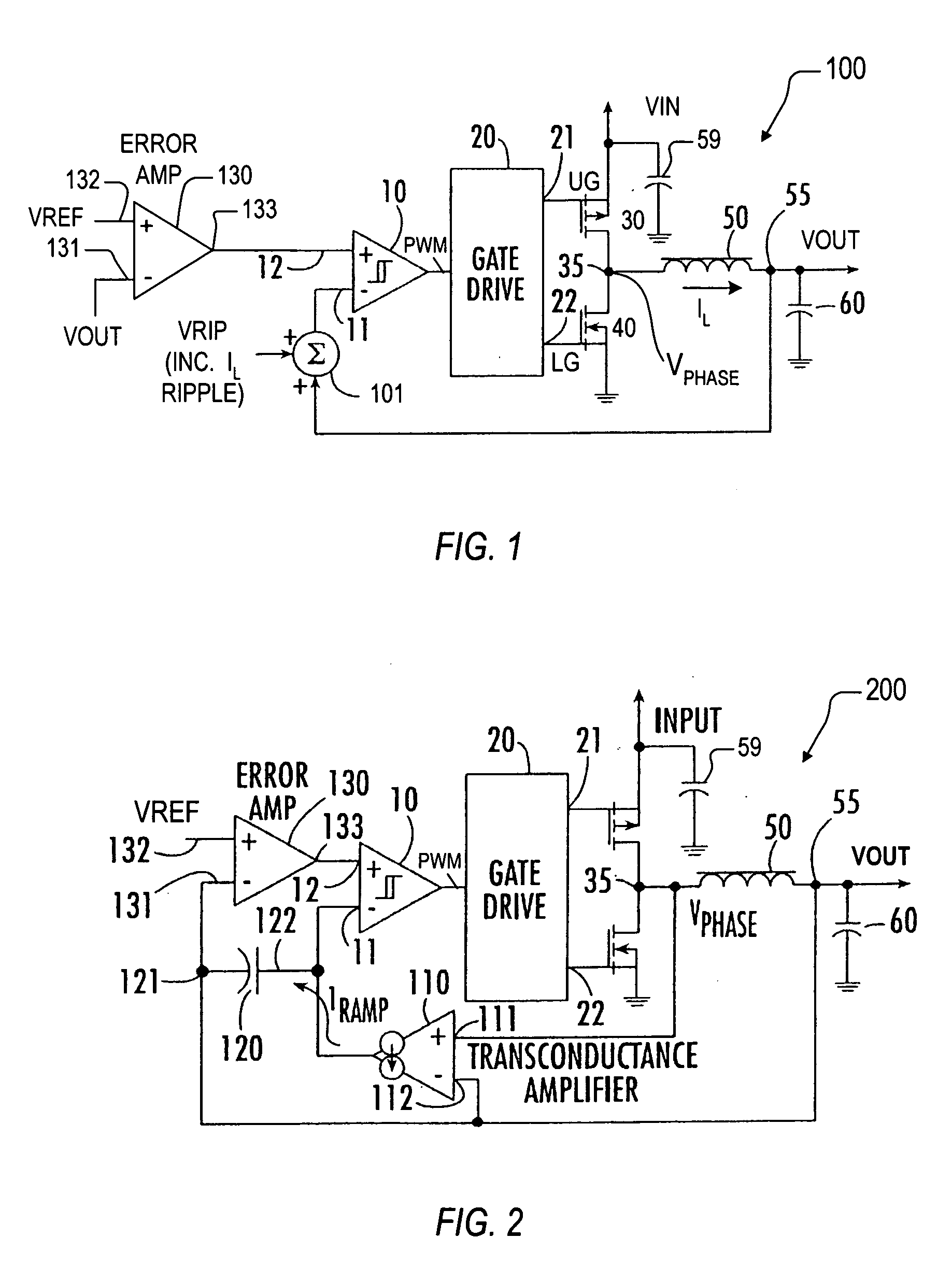
Synthetic ripple regulator
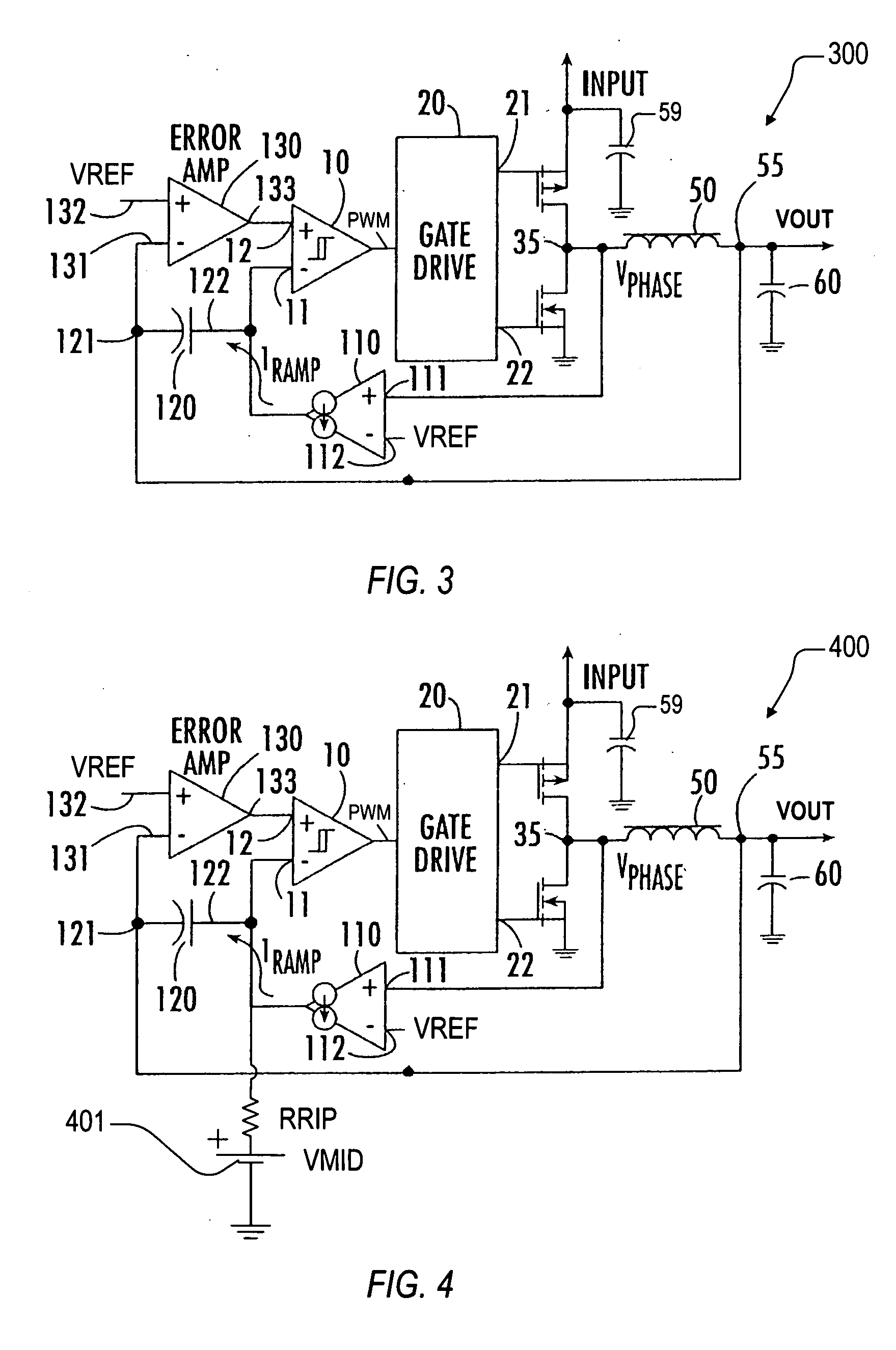
InactiveUS7132820B2Low output rippleCompensation is simpleDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationVoltage generatorInductor
A synthetic ripple regulator including a synthetic ripple voltage generator that generates a synthetic ripple voltage indicative of the ripple current through an output inductor. The regulator uses the synthetically generated ripple voltage to control toggling of a hysteretic comparator for developing the pulse width modulation (PWM) signal that controls switching of the regulator. In a non-limiting implementation, a transconductance amplifier monitors the phase node voltage of the inductor and supplies an inductor voltage-representative current to a ripple capacitor, which produces the synthetic ripple voltage. Using the replicated inductor current for ripple regulation results in low output ripple, input voltage feed forward, and simplified compensation.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Synthetic ripple regulator
InactiveUS20050017703A1Low output rippleCompensation is simpleDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationTransconductanceInductor
A synthetic ripple regulator including a synthetic ripple voltage generator that generates a synthetic ripple voltage indicative of the ripple current through an output inductor. The regulator uses the synthetically generated ripple voltage to control toggling of a hysteretic comparator for developing the pulse width modulation (PWM) signal that controls switching of the regulator. In a non-limiting implementation, a transconductance amplifier monitors the phase node voltage of the inductor and supplies an inductor voltage-representative current to a ripple capacitor, which produces the synthetic ripple voltage. Using the replicated inductor current for ripple regulation results in low output ripple, input voltage feed forward, and simplified compensation.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Error compensation model and algorithm implementation of high-precision pressure sensor
ActiveCN101201284AAchieve correctionReal-time correctionFluid pressure measurementMathematical modelSignal conditioning
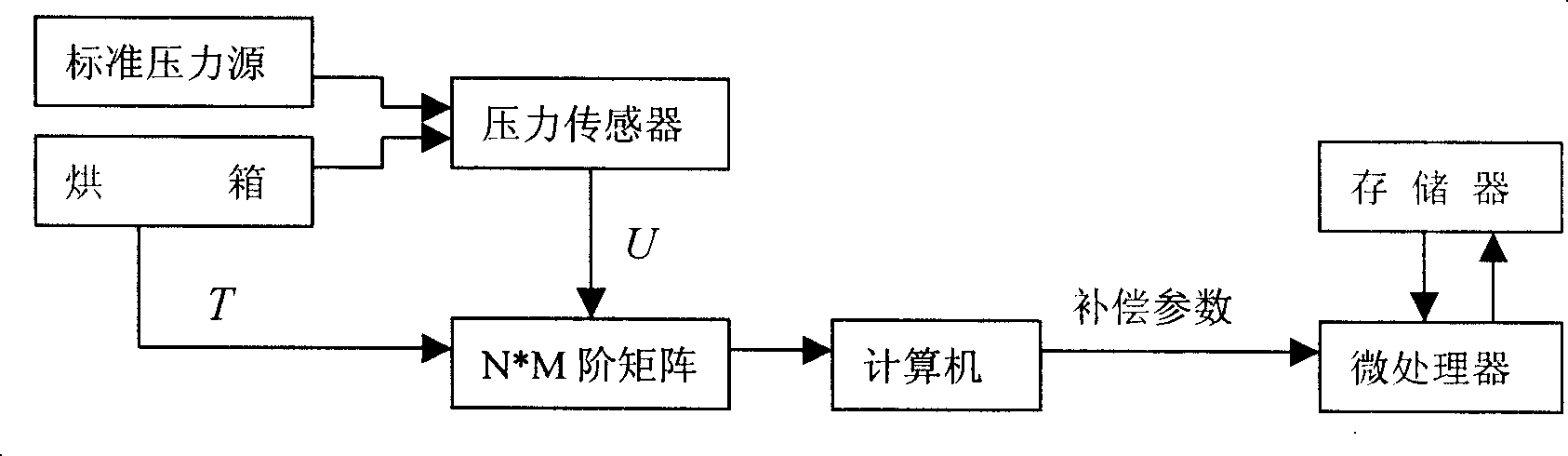
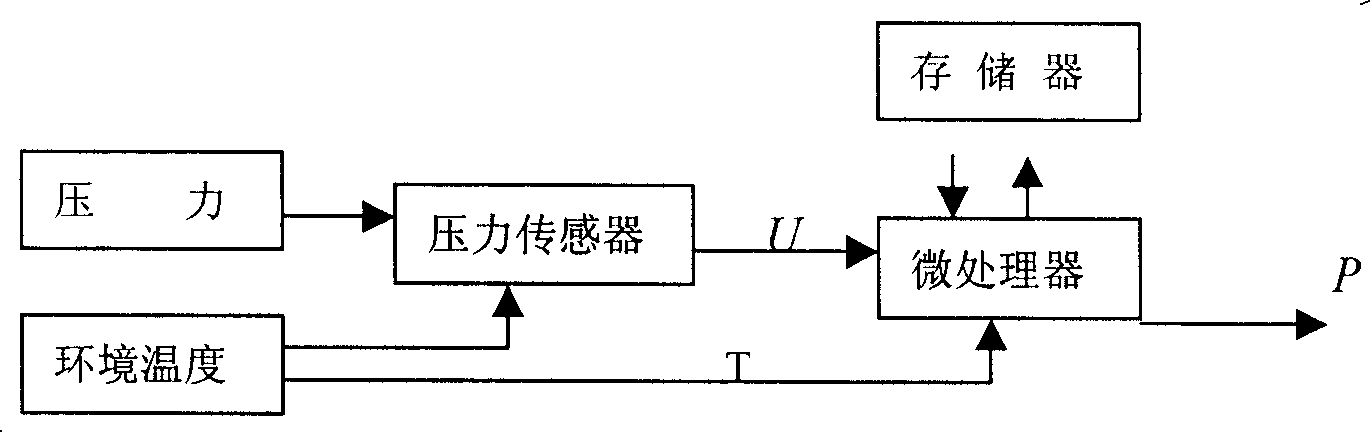
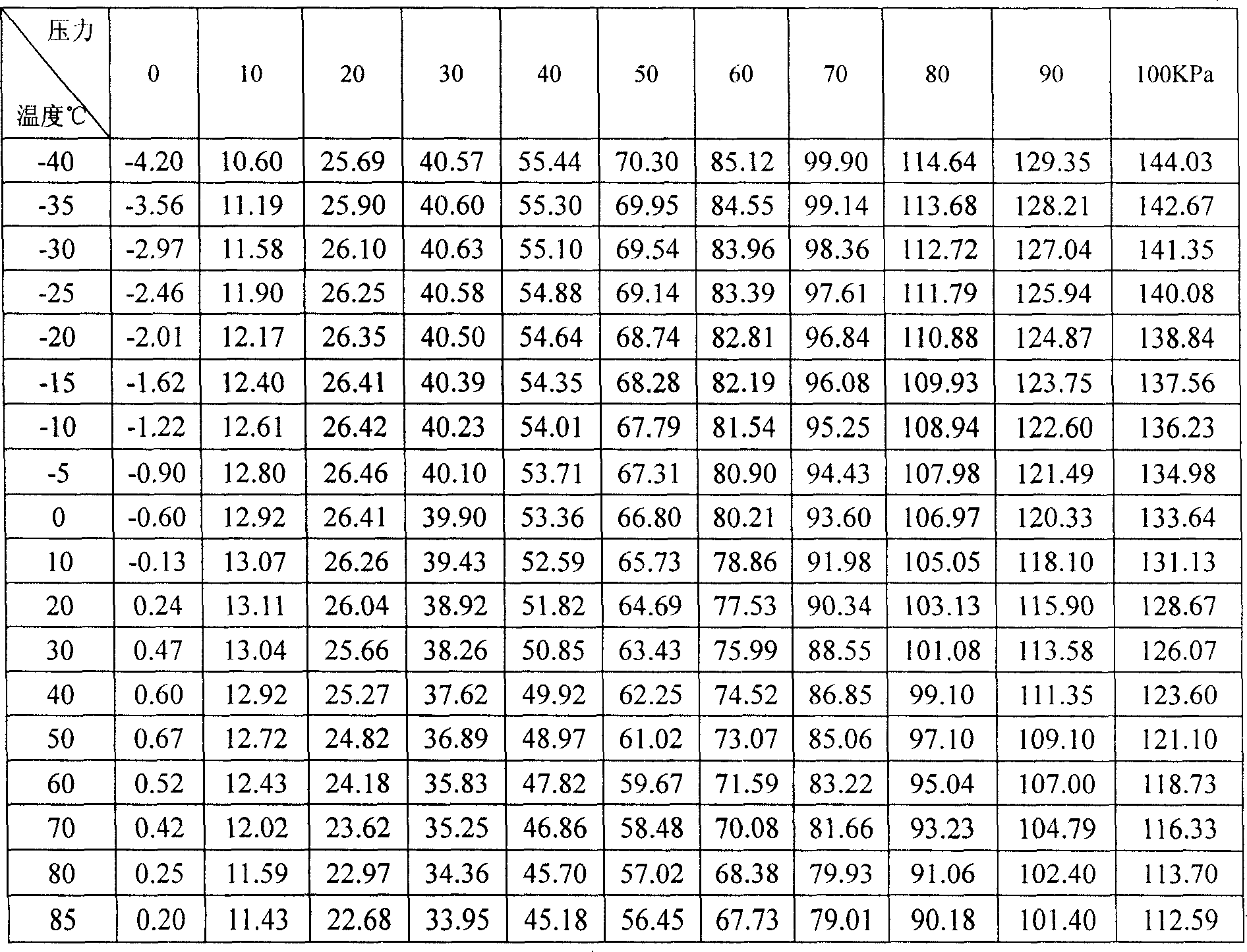
The invention provides an error compensation model and an algorithm of a high precision pressure transducer. The invention uses an oven and a standard pressure source to collect the output data of the transducer under N temperature spots and M pressure spots to constitute an N*M matrix; a sensor output mathematical model is established, and the thermal compensation coefficients a(T), b(T), c(T) of the sensor output function, and the electrical null of the sensor under different temperatures are fit according to the collected data: U0(T)=f(T), and the parameters are written into a microprocessor; when the invention is used, the electrical null U0 of the restoration record transducer is clicked at the time point of zero pressure, and U0(T) is calculated through the information of the collected temperatures (T), and the time shift of the sensor within the use and compensation intervals is calculated out: delta=U0-U0(T); the microprocessor calculates the conditioner microprocessor output by collecting the information of the output signal (U) of the temperature transducer (T) and the pressure transducer according to the compensation formula: P=a(T)(U-delta)<2>+b(T)(U-delta)+c(T). The invention combines the design and production technologies of pressure sensors, the signal conditioning technology and the computer technology to achieve rectification of the pressure transducer in the wide temperature range. The pressure signal characteristic and effect is excellent.
Owner:SHANGHAI WENXIANG AUTOMOTIVE SENSORS
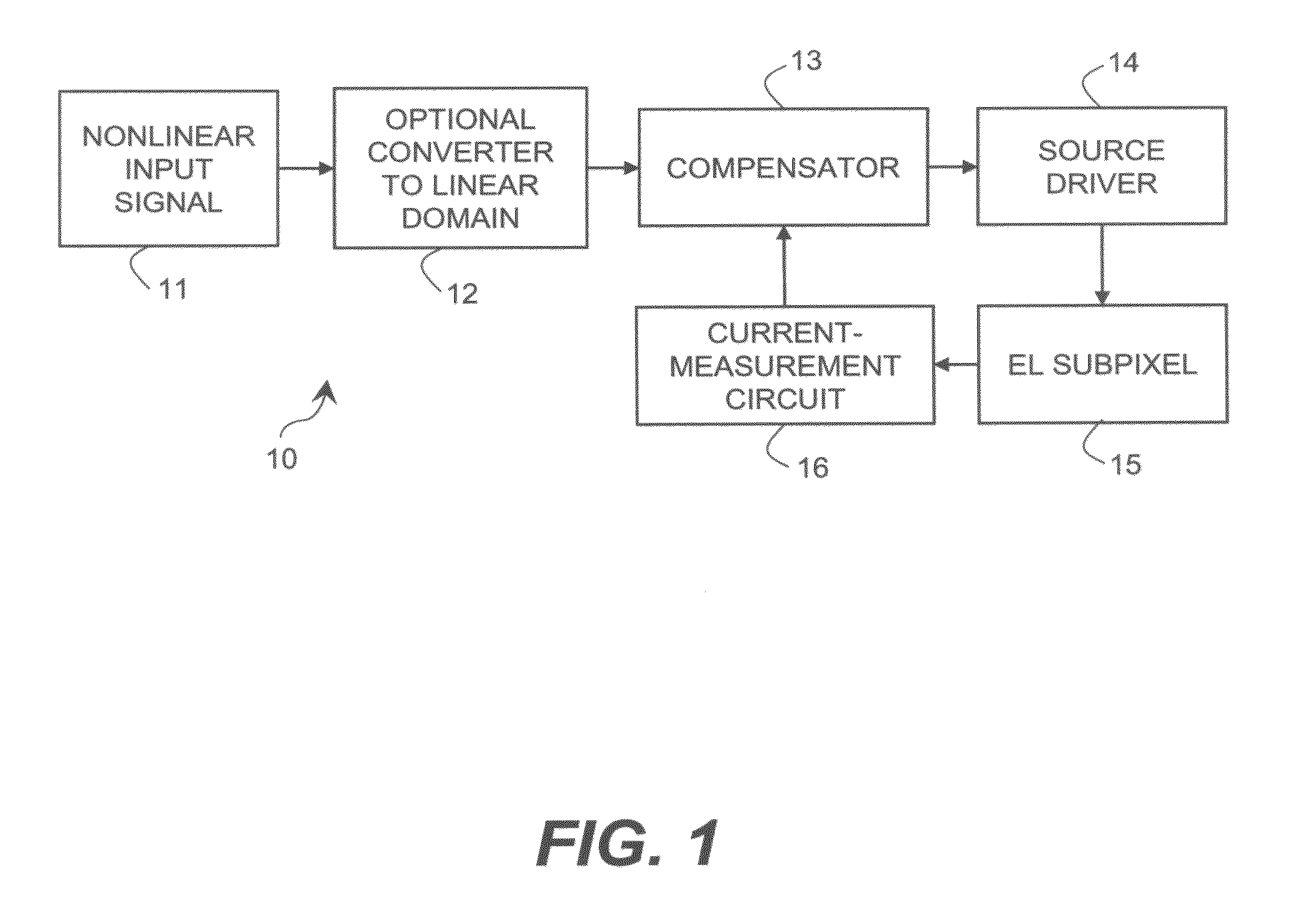
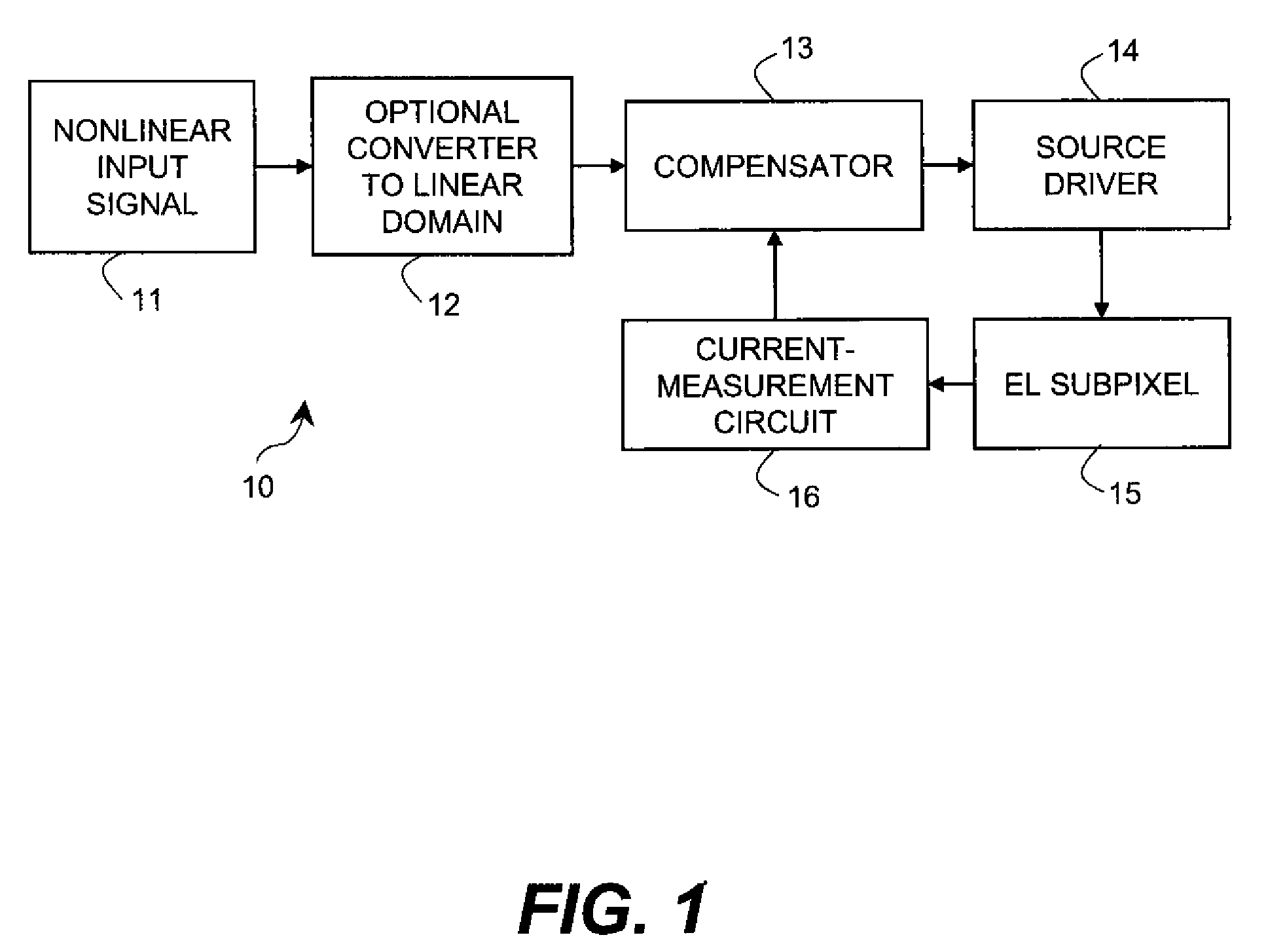
Electroluminescent display compensated analog transistor drive signal
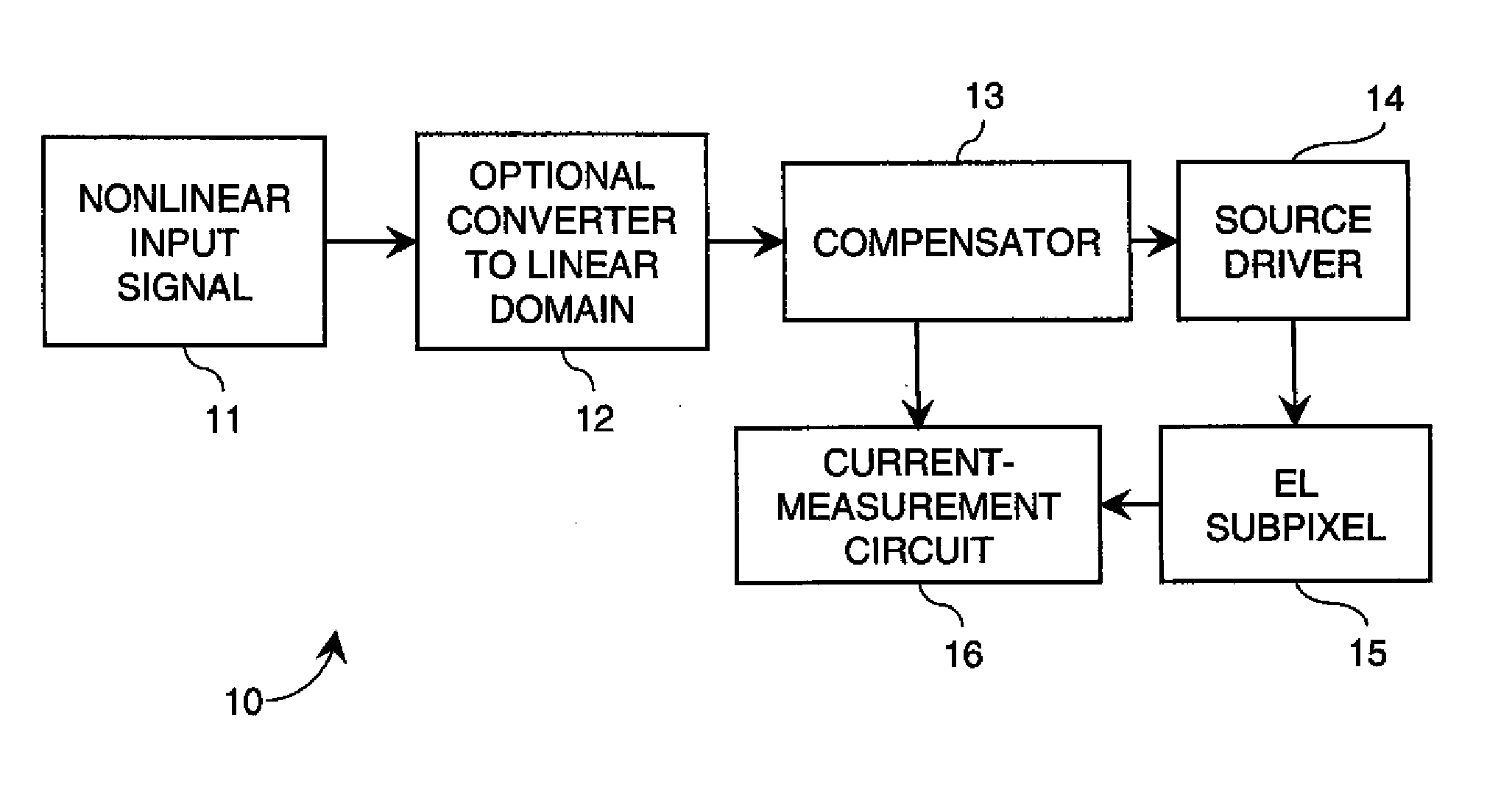
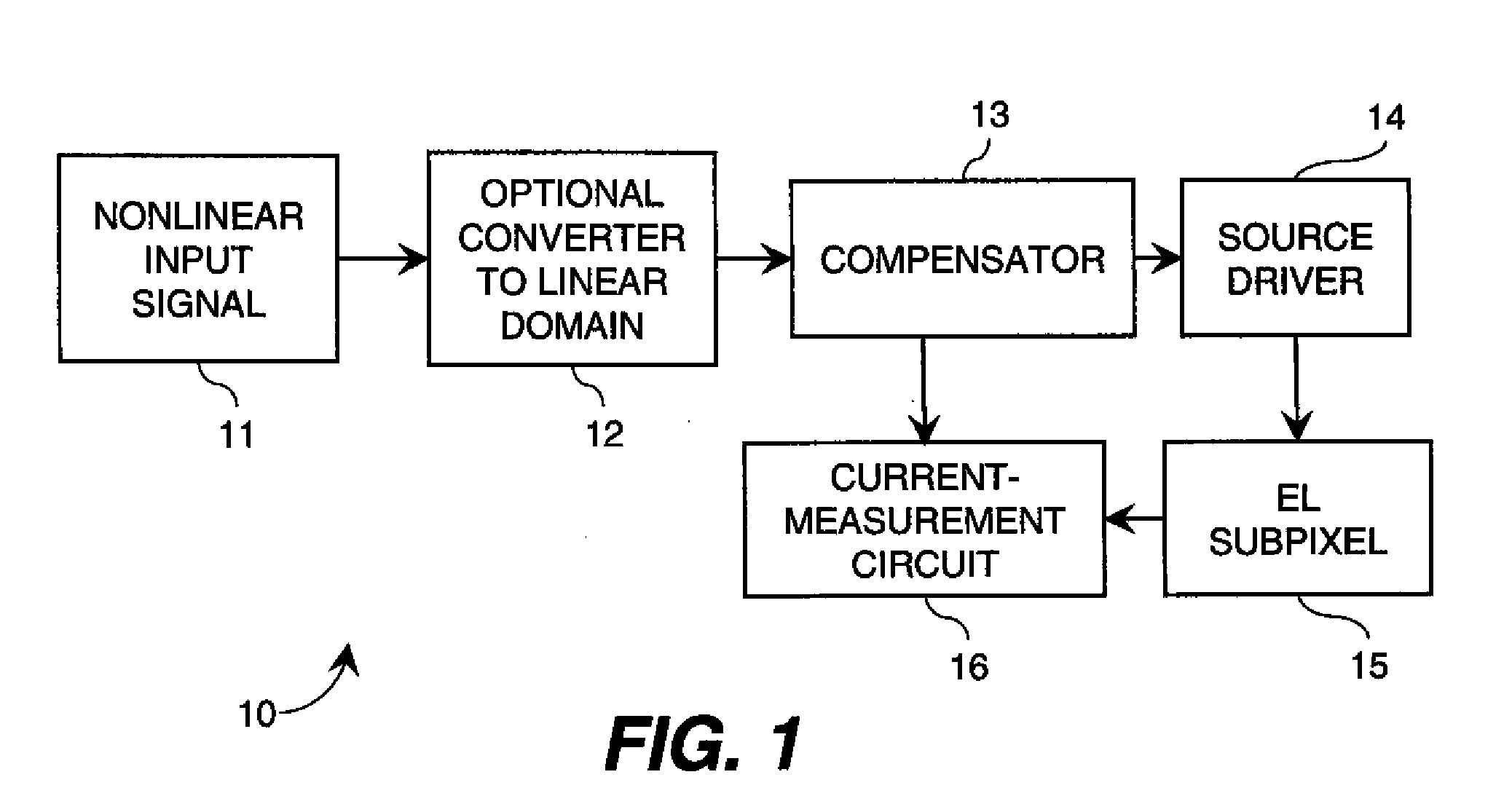
ActiveUS20090160740A1Raise the ratioSimple control signalStatic indicating devicesDriver circuitControl signal
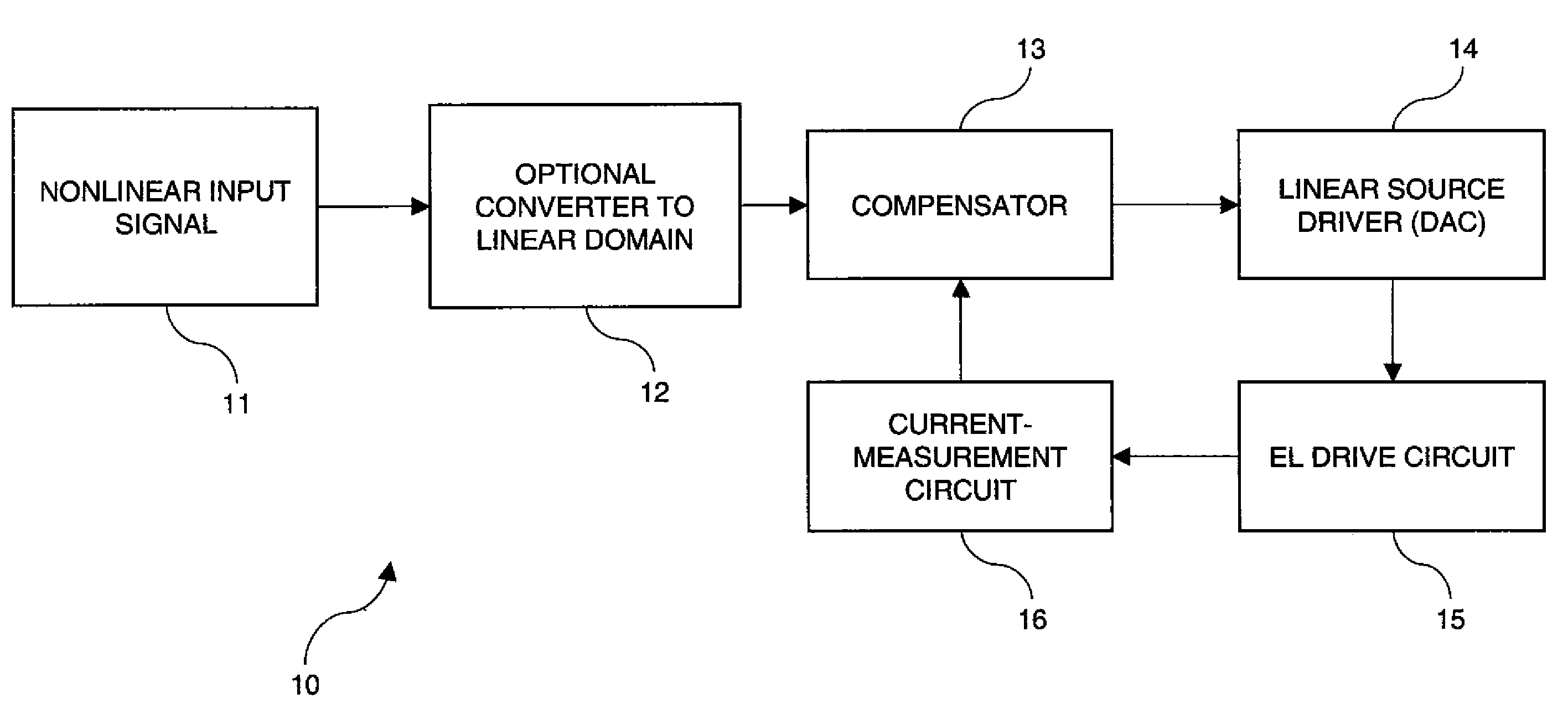
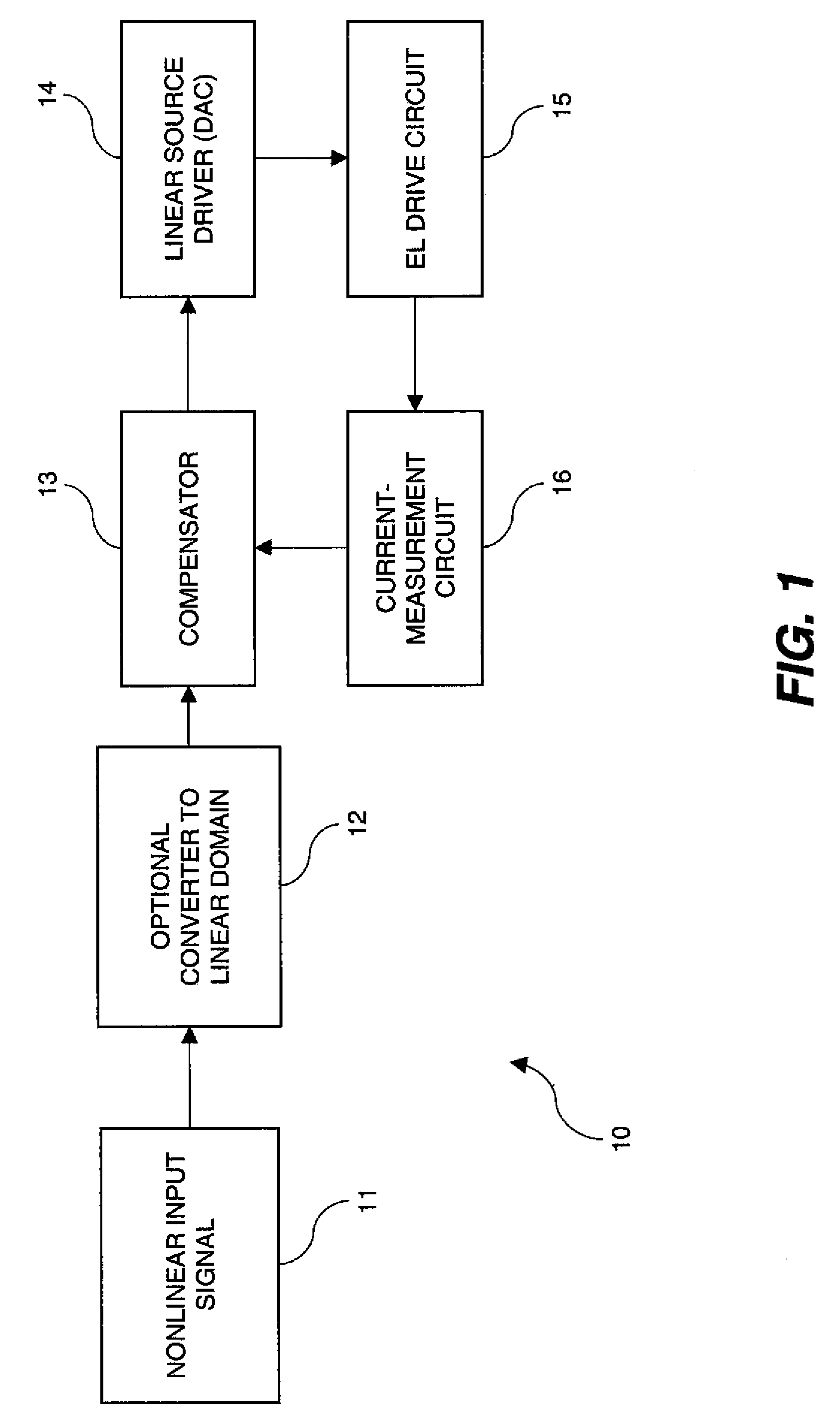
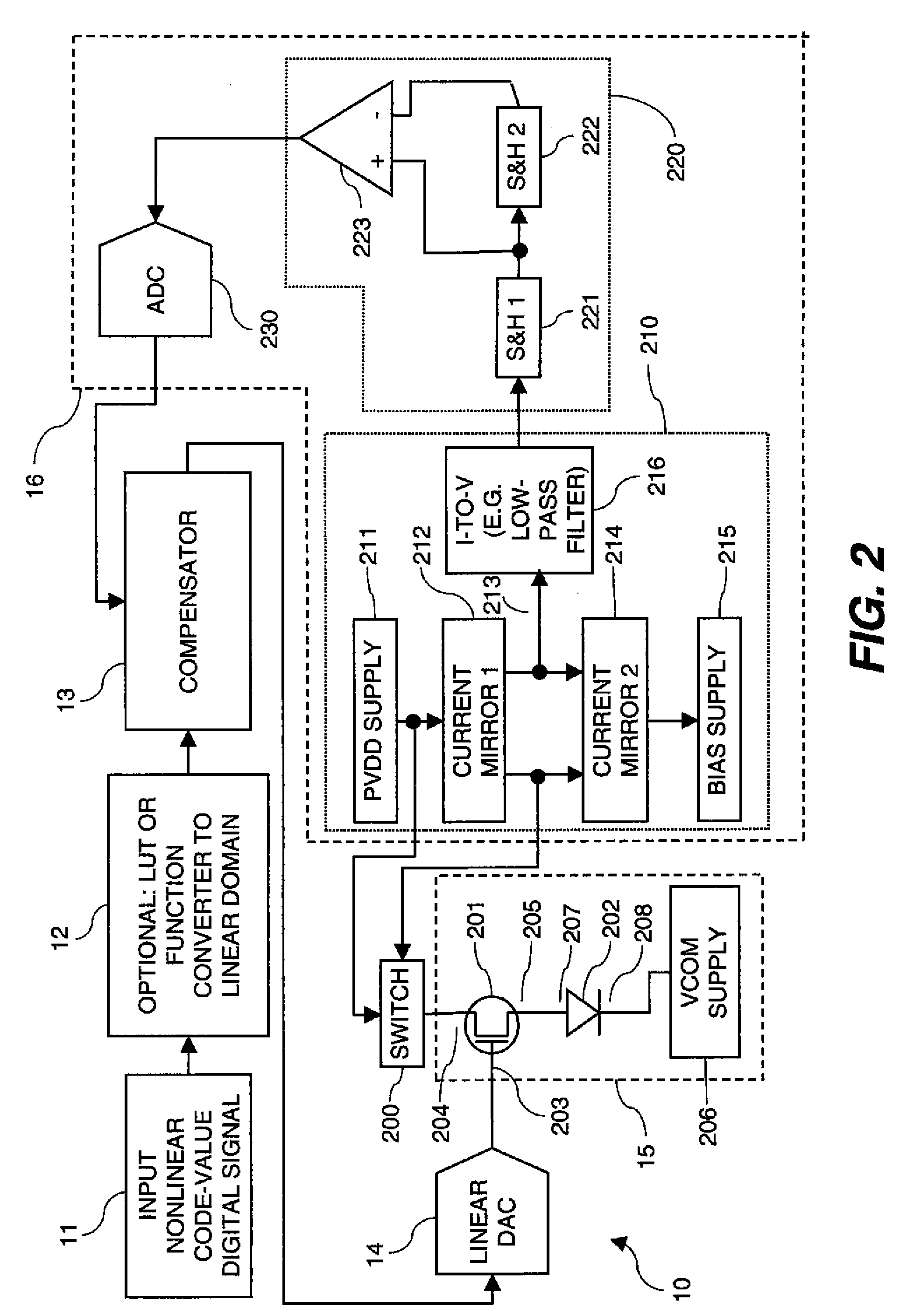
Apparatus for providing an analog drive transistor control signal to the gate electrode of a drive transistor in a drive circuit that applies current to an EL device, the drive circuit including a first supply electrode of the drive transistor and the EL device connected to a second supply electrode of the drive transistor, comprising a measuring circuit for measuring the current passing through the supply electrodes at different times to provide an aging signal representing variations in the characteristics of the drive transistor and EL device caused by operation of the drive transistor and EL device over time; a compensator for changing a linear code value in response to the aging signal to compensate for the variations in the characteristics of the drive transistor and EL device; and a linear source driver for producing the analog drive transistor control signal in response to the changed linear code value.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
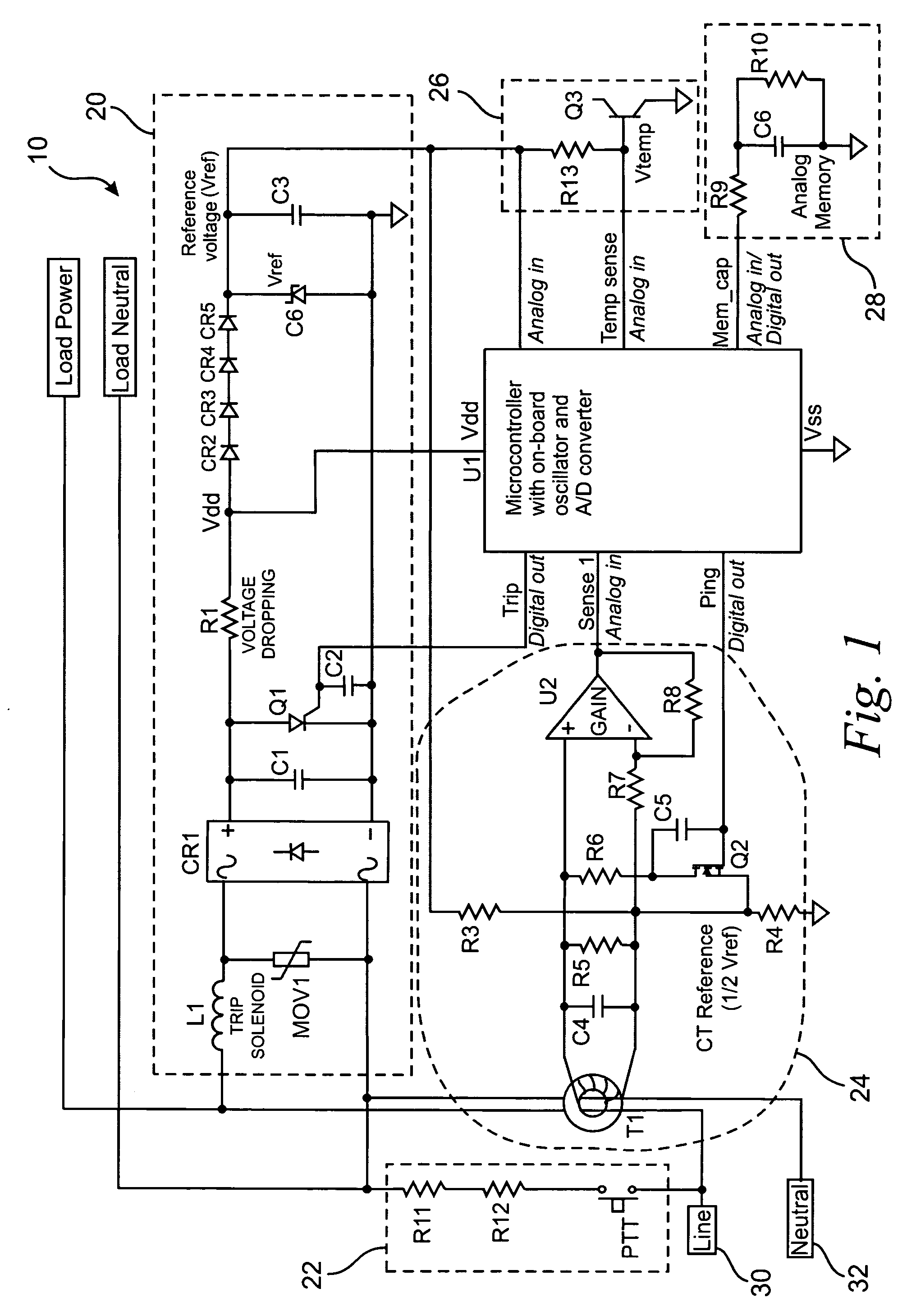
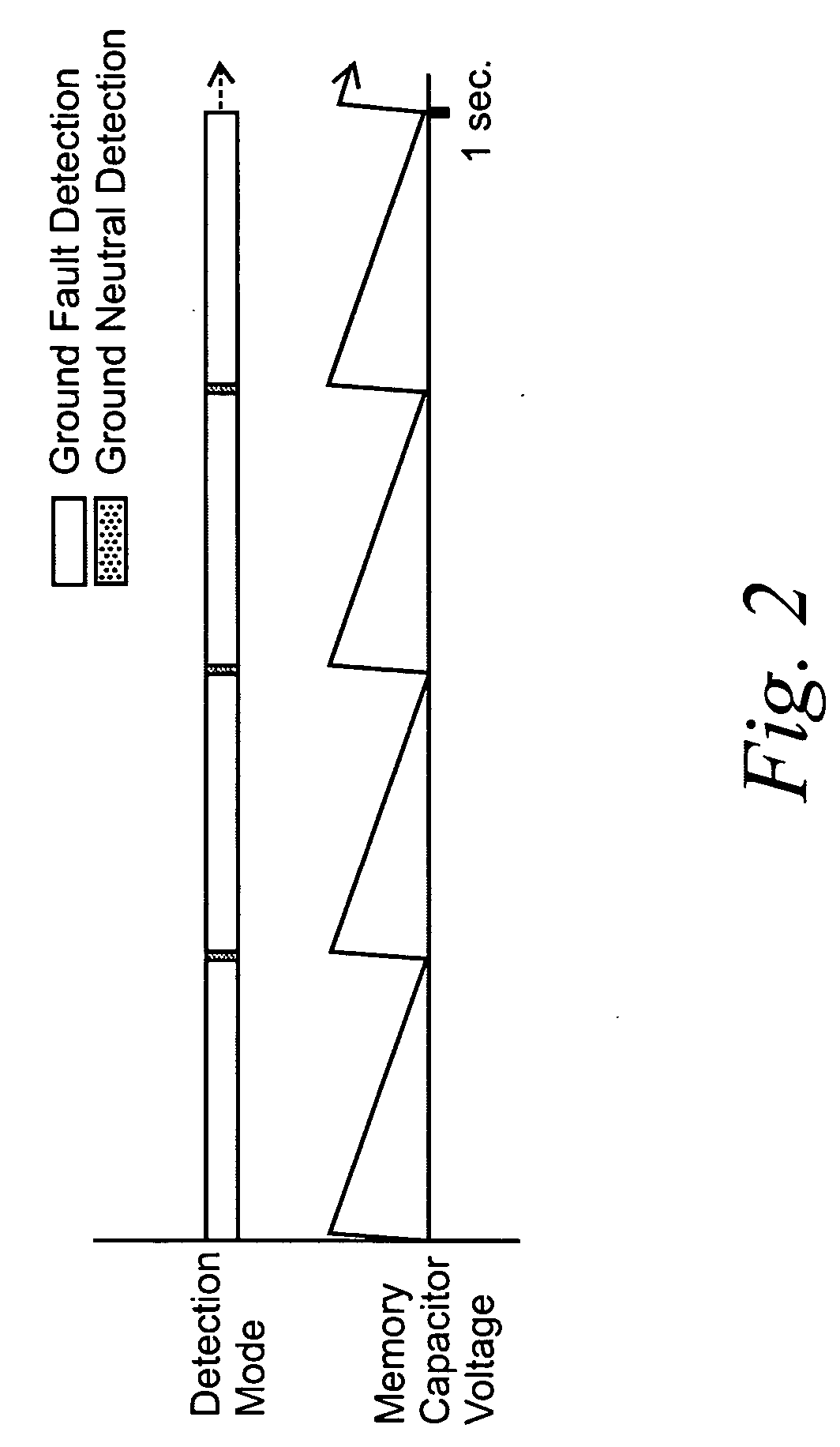
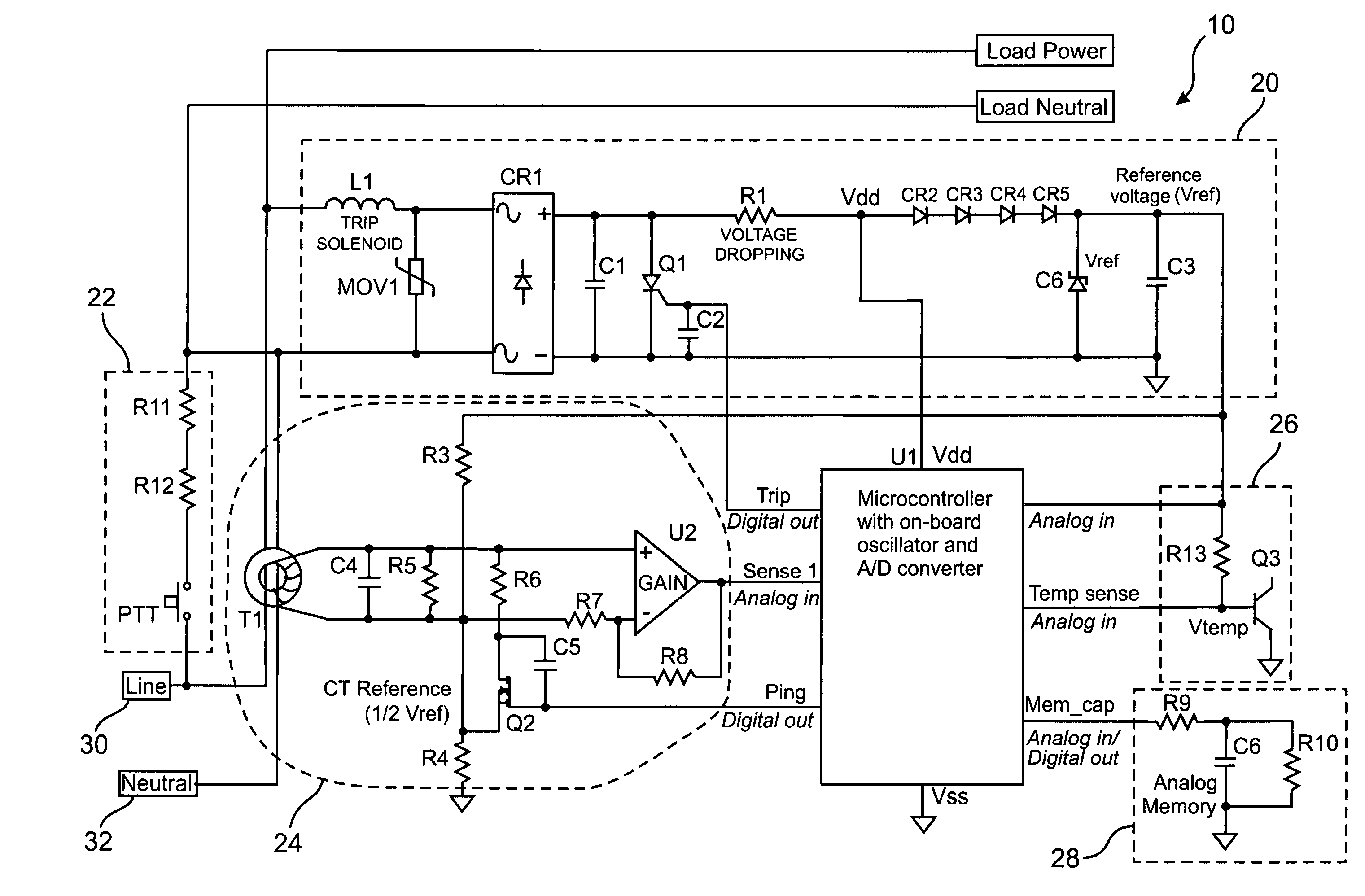
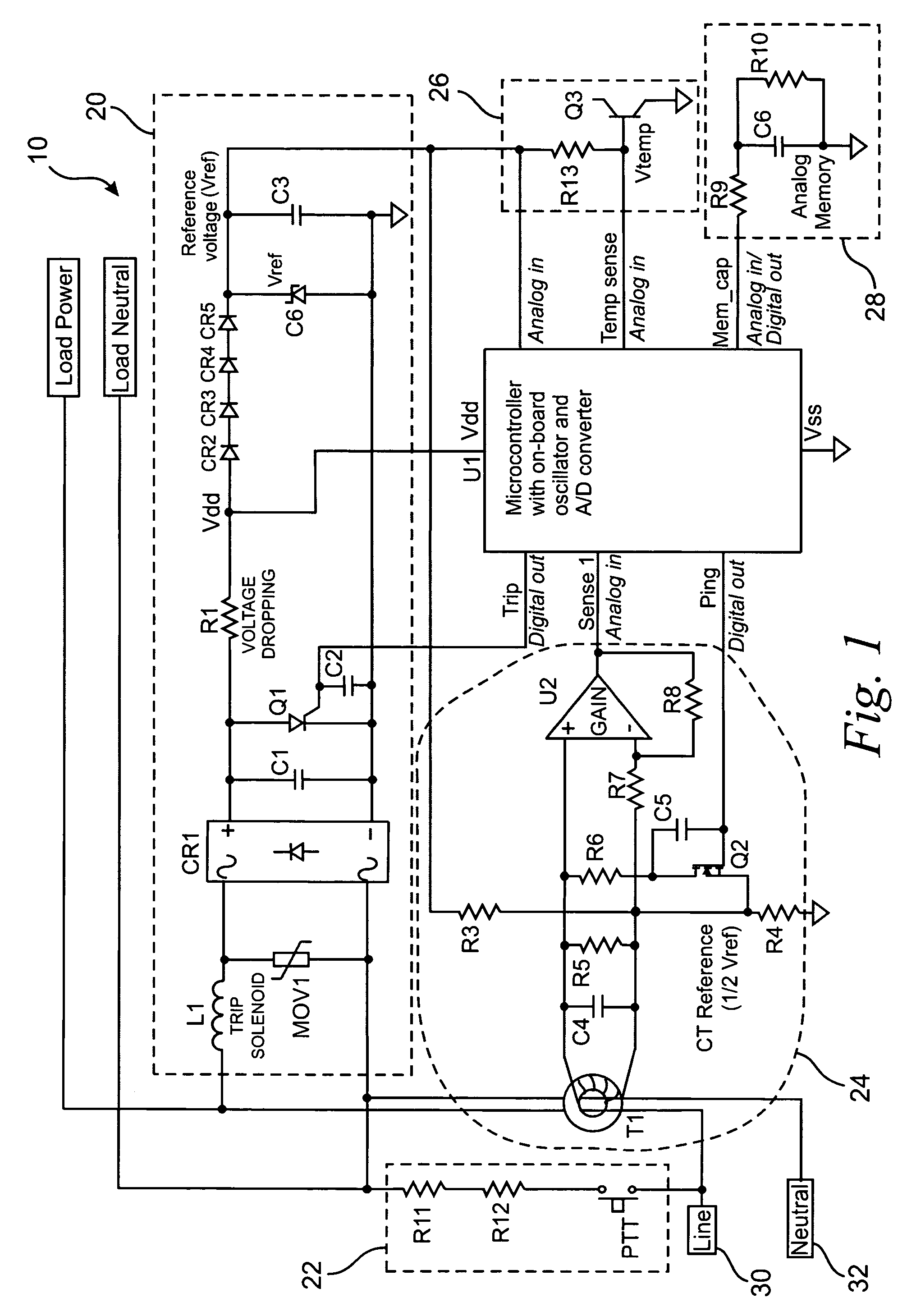
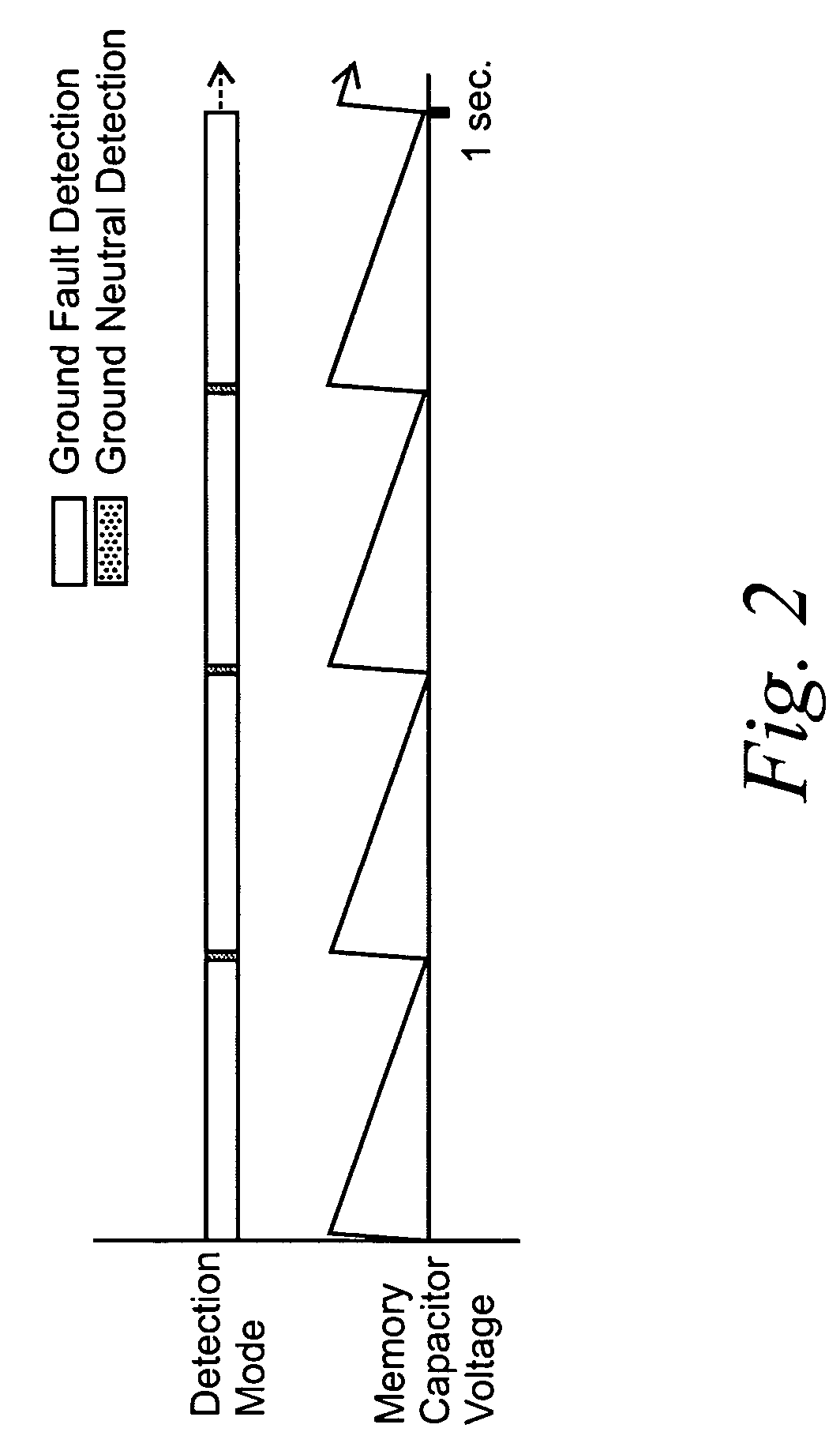
Single-sensor microcontroller-based approach for ground fault circuit interrupters
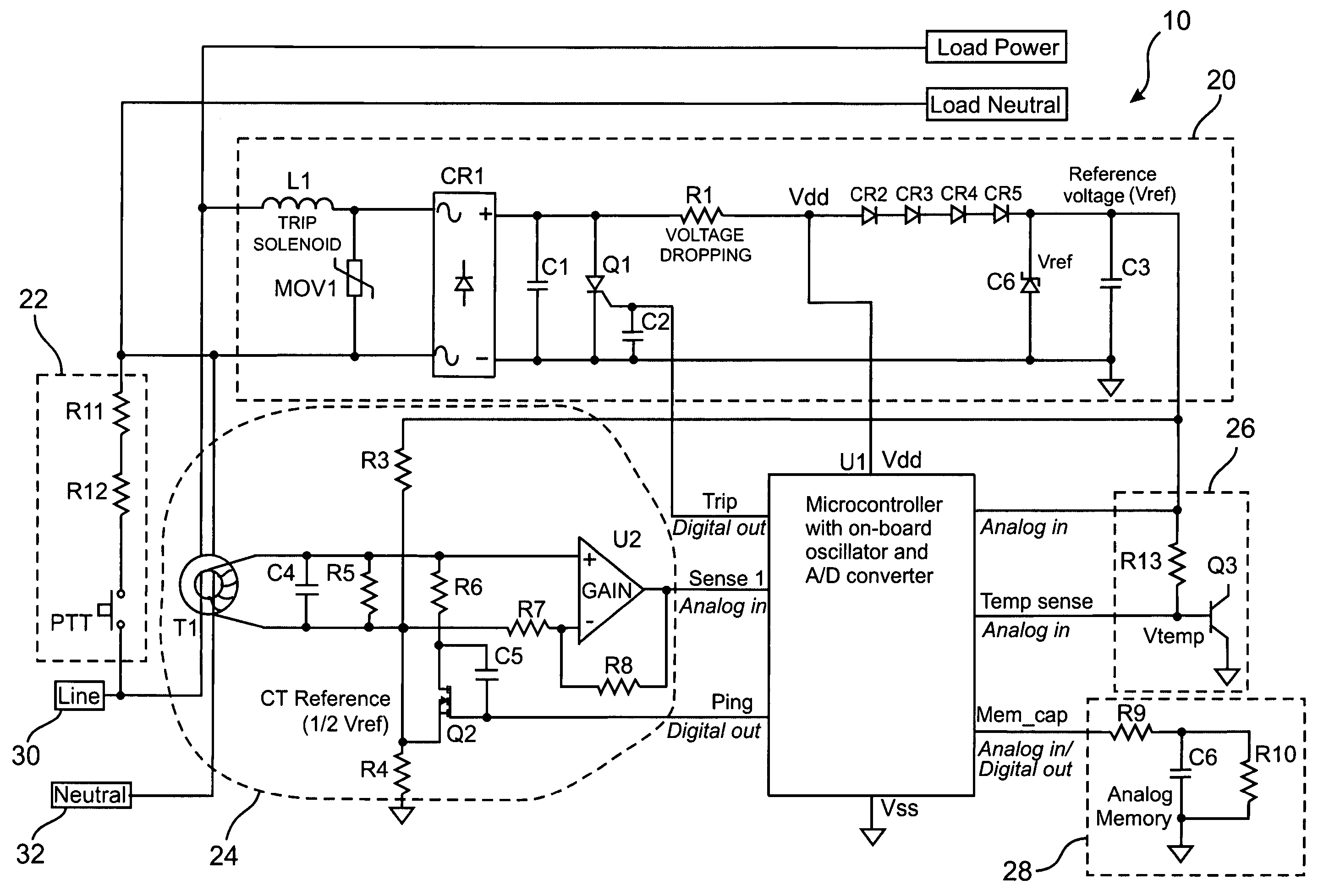
ActiveUS20050083616A1Low costSimple manufacturing processResistance/reactance/impedenceEmergency protective arrangement detailsMicrocontrollerFull wave
A microcontroller-based temperature compensated circuit for ground-fault circuit interrupter to meet the requirements of UL 943 using a single sensor to detect both ground-fault and grounded-neutral fault conditions in both full-wave and half-wave AC power supplies as part of a ground-fault circuit breaker or a receptacle device.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC USA INC
Single-sensor microcontroller-based approach for ground fault circuit interrupters
ActiveUS7193827B2Low costCompensation is simpleResistance/reactance/impedenceEmergency protective arrangement detailsMicrocontrollerFull wave
A microcontroller-based temperature compensated circuit for ground-fault circuit interrupter to meet the requirements of UL 943 using a single sensor to detect both ground-fault and grounded-neutral fault conditions in both full-wave and half-wave AC power supplies as part of a ground-fault circuit breaker or a receptacle device.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC USA INC
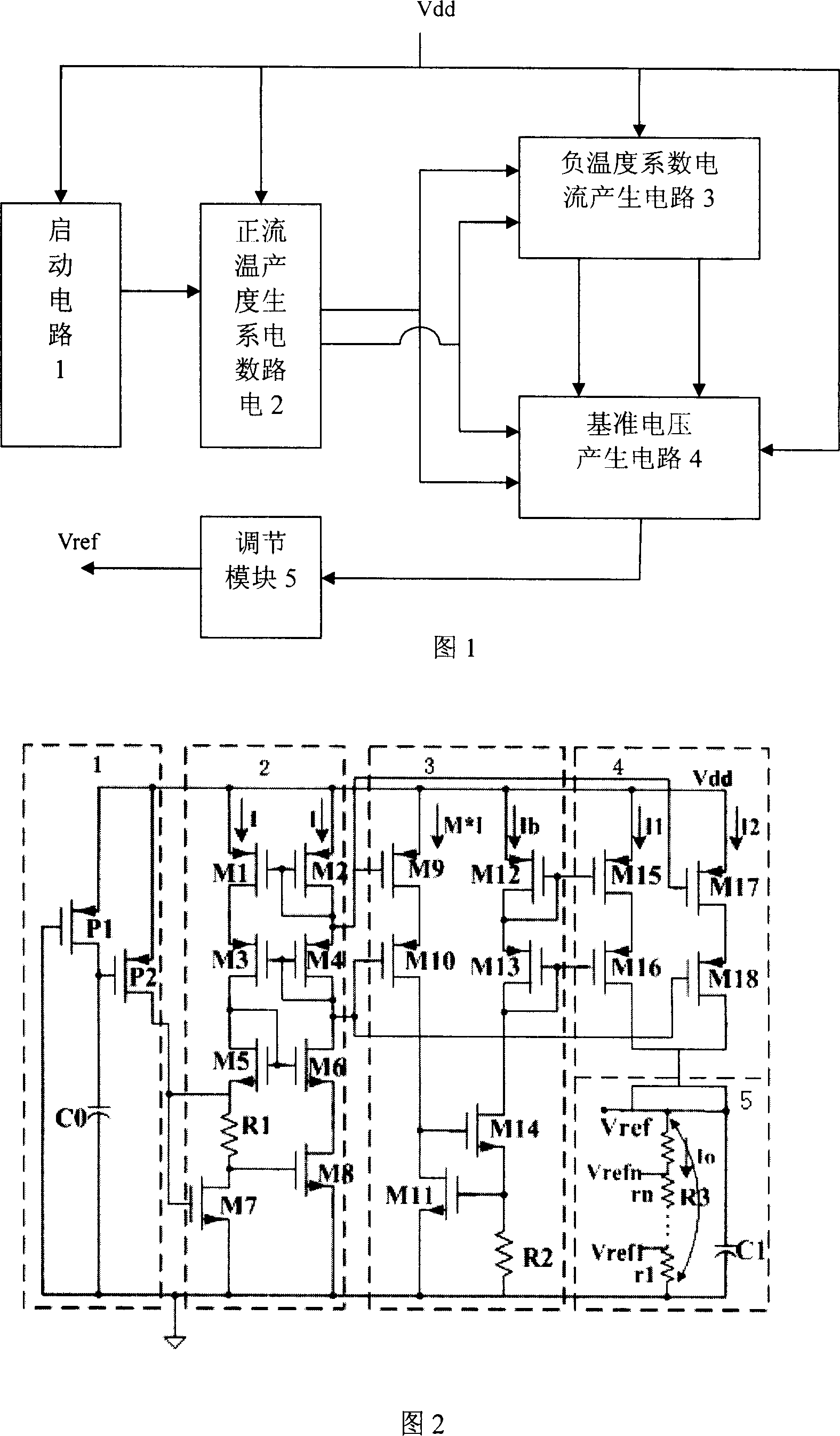
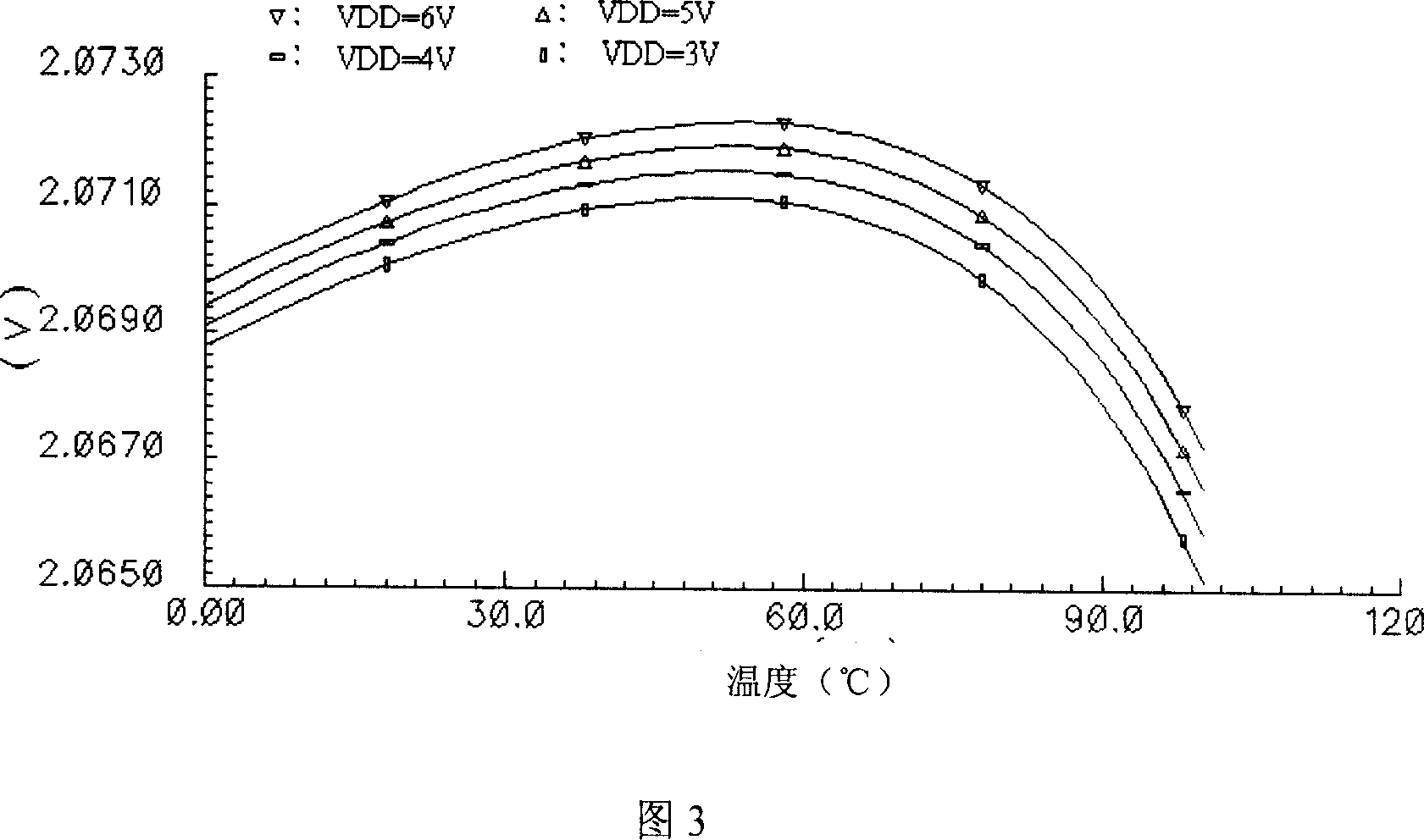
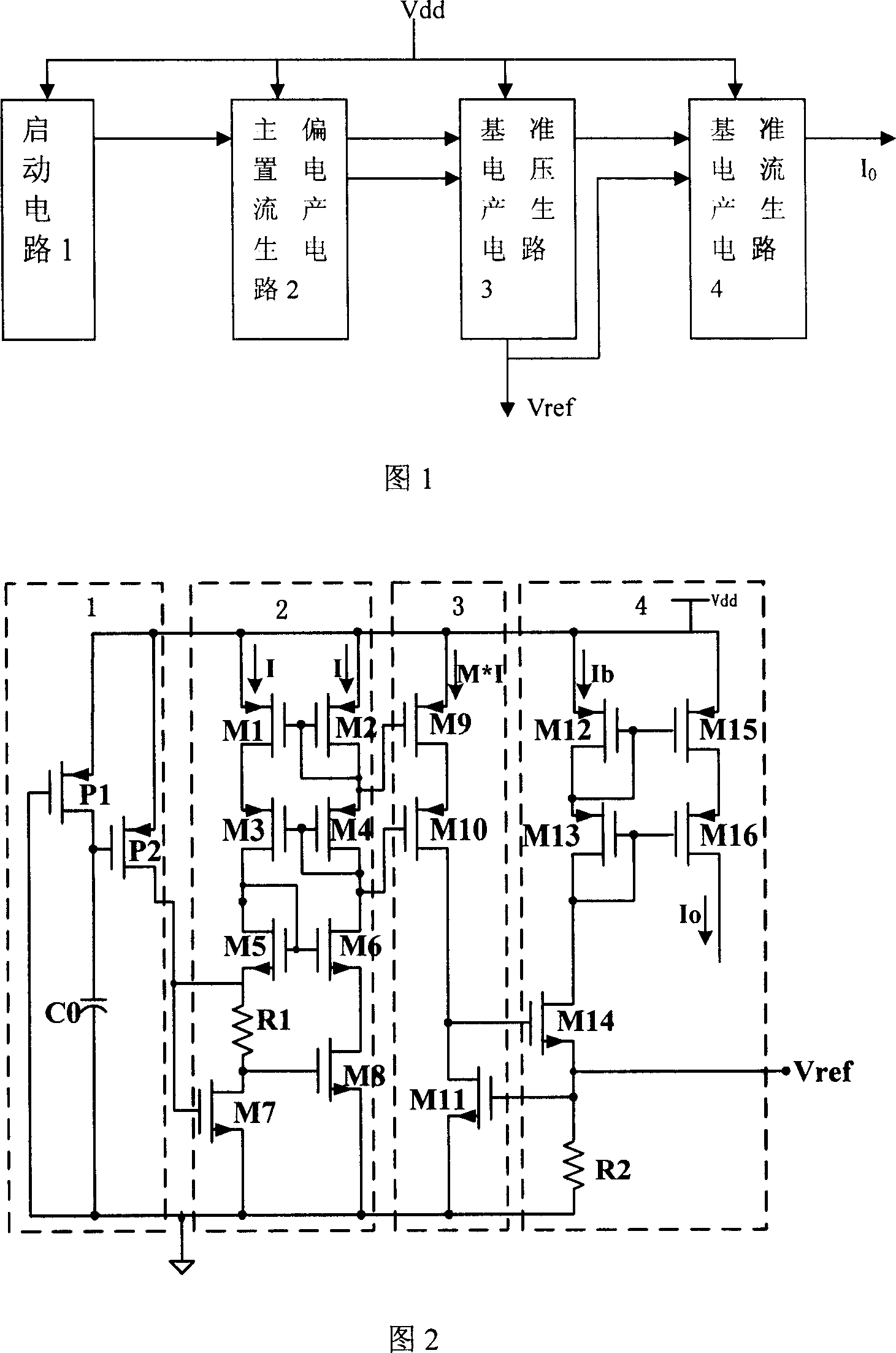
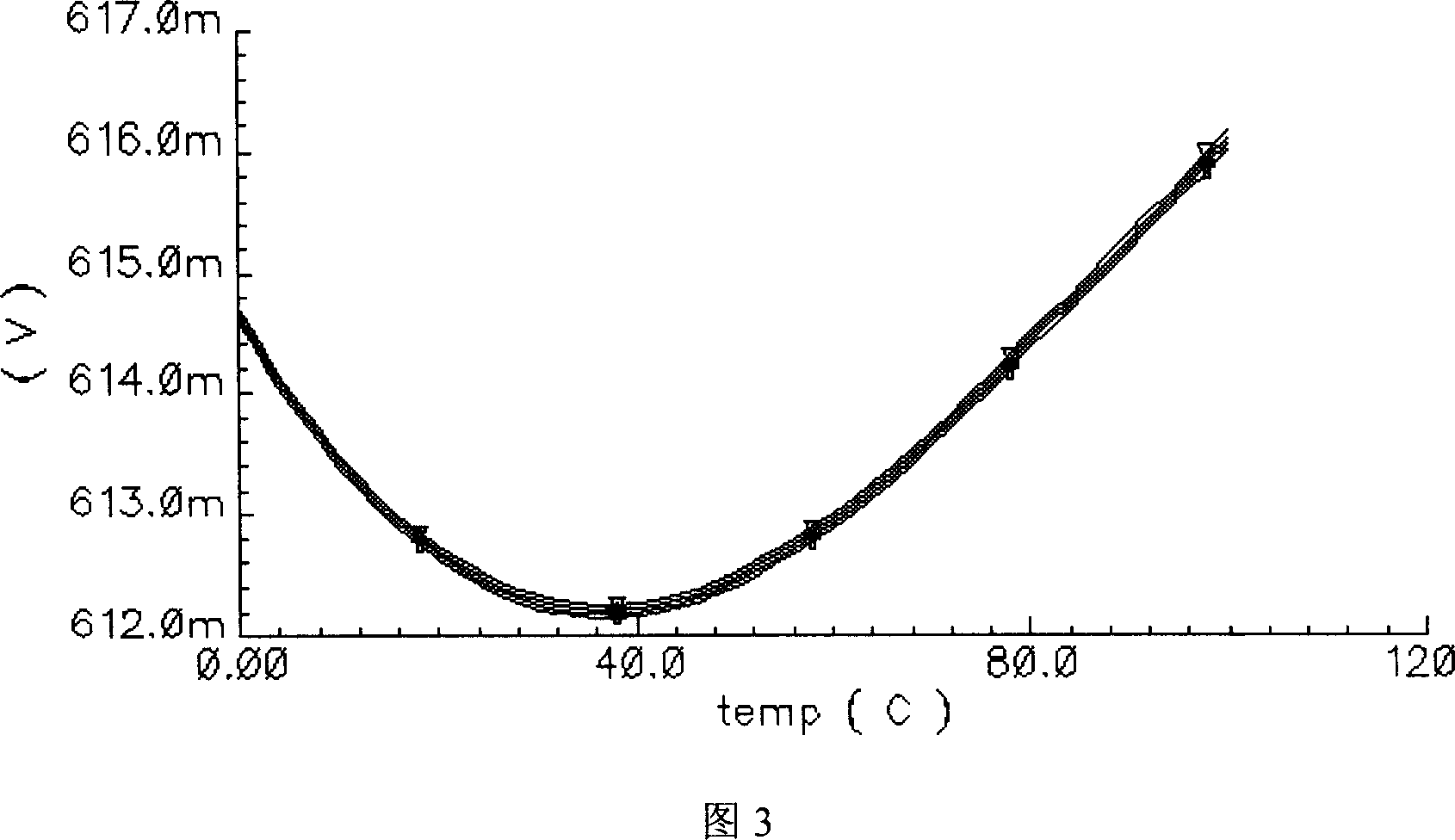
CMOS reference voltage source with adjustable output voltage
InactiveCN101013331ASmall temperature coefficientFast switching speedElectric variable regulationNegative temperatureEngineering
The invention provides an output voltage adjustable CMOS reference voltage source to facilitate the realization of the standard CMOS process, which includes the start circuit, the positive temperature coefficient current generating circuit, the negative temperature coefficient current generating circuit, and the reference voltage generating circuit; the output of the start circuit connecting with the input of the positive temperature coefficient current generating circuit, the first output of the positive temperature coefficient current generating circuit respectively connecting with the first input of the negative temperature coefficient current generating circuit and the third input of the reference voltage generating circuit, the second output of the positive temperature coefficient current generating circuit respectively connecting with the second input of the negative temperature coefficient current generating circuit and the fourth input of the reference voltage generating circuit, the first and second outputs of the negative temperature coefficient current generating circuit respectively corresponding connecting with the first and second inputs of the reference voltage generating circuit, and the reference voltage generating circuit has the reference voltage output to output reference voltage.
Owner:南通金石工贸有限公司 +1
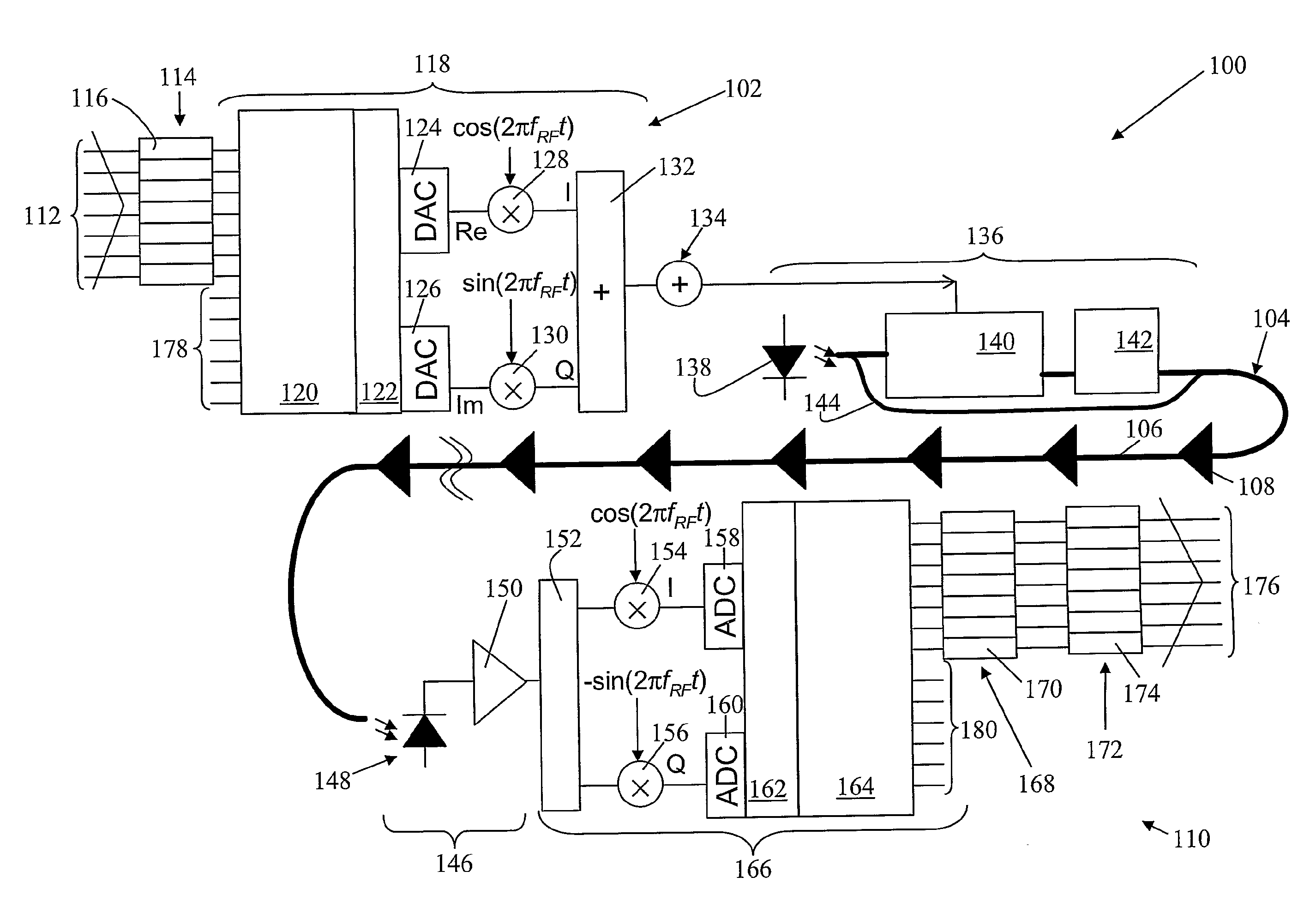
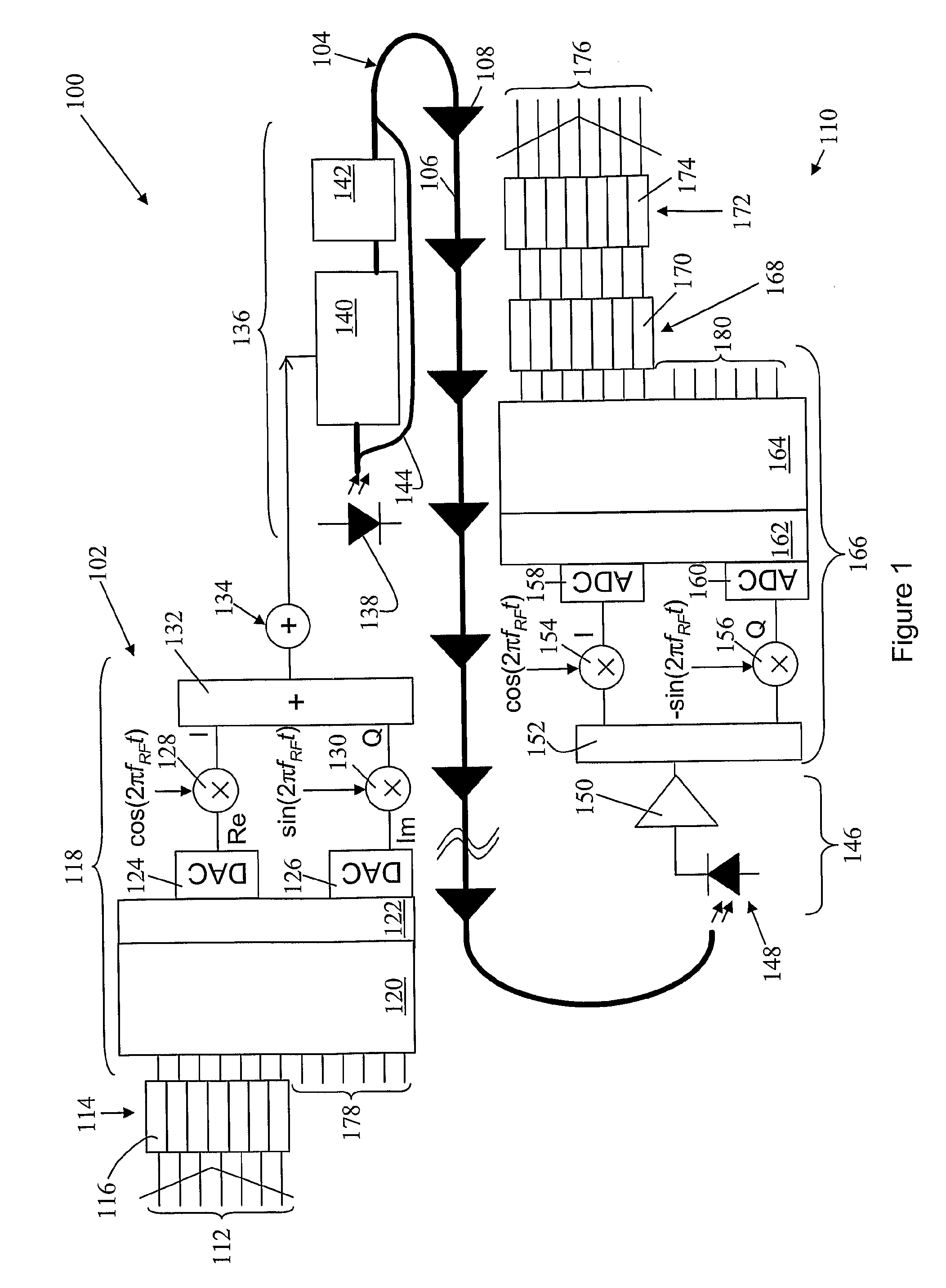
Methods and apparatus for optical transmission of digital signals
ActiveUS20090169213A1Mitigate effect of chromatic dispersionImprove scalabilityTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringSignal generator
A system (100) for transmitting digital information includes a transmitting apparatus (102) for generating an optical signal bearing digital information, a dispersive optical channel (104), and a receiving apparatus (110) for receiving the optical signal. The dispersive optical channel (104) is disposed to convey the optical signal from the transmitting apparatus (102) to the receiving apparatus (110). The transmitting apparatus includes an encoder (114) for encoding digital information into a series of blocks, each including a plurality of data symbols corresponding with one or more bits of digital information. A signal generator (118) generates a time-varying signal corresponding with each of said blocks. An optical transmitter (136) is arranged to apply the time-varying signal to an optical source (138) to produce an optical signal which includes an optical carrier and substantially only a single information bearing optical sideband in an optical frequency domain, the sideband corresponding with the time-varying signal. The receiving apparatus (110) includes an optical detector (146) for detecting the optical signal to produce a corresponding received time-varying electrical signal. The receiver further includes means (166) for generating a series of received data blocks from the time-varying electrical signal. An equaliser (168) performs an equalisation of received data symbols included in each data block to mitigate the effect of dispersion of the optical channel, thereby enabling the transmitted data symbols to be recovered.
Owner:MONASH UNIV
CMOS reference source circuit
InactiveCN101004618ASimple structureEasy to implementElectric variable regulationCMOSReference current
A circuit of CMOS reference source is prepared for connecting DC input end of start-up circuit, master offset current generating circuit, reference voltage generating circuit and reference current generating circuit separately to DC source, connecting master offset current generating circuit to start-up circuit and to reference voltage generating circuit being connected with reference current generating circuit, outputting reference voltage by reference voltage output end being connected to reference current generating circuit and outputting reference current by reference current generating circuit.
Owner:海安江理工技术转移中心有限公司 +1
Optical transceivers for use in fiber optic communication networks
ActiveUS8699880B2Simplifies aboveCompensation is simplePolarisation multiplex systemsModulated-carrier systemsPower efficientTransceiver
The present disclosure provides a polarization multiplexed transceiver, including: a transmitter; a receiver; circuitry within the transmitter configured to insert pilot tones as a reference state of polarization for a polarization multiplexed signal; and circuitry within the receiver configured to de-multiplex the polarization multiplexed signal using the pilot tones. The transmitted signal is constructed in such a manner as to facilitate the division of the receiver processing between the analog and digital domains such that the implementation may be simultaneously both highly spectrally efficient and power efficient.
Owner:CIENA
Apparatus for moving a pair of opposing surfaces in response to an electrical activation
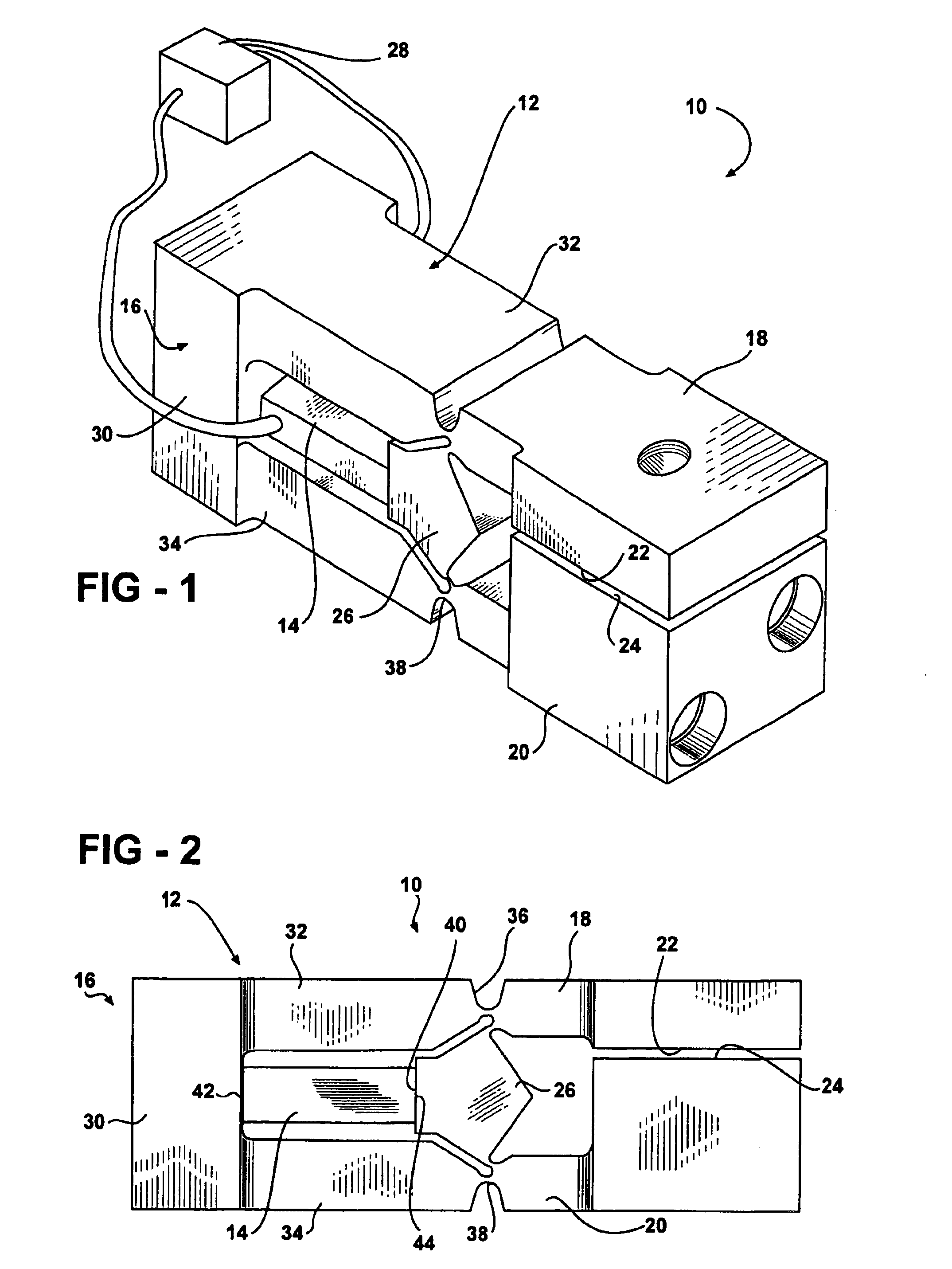
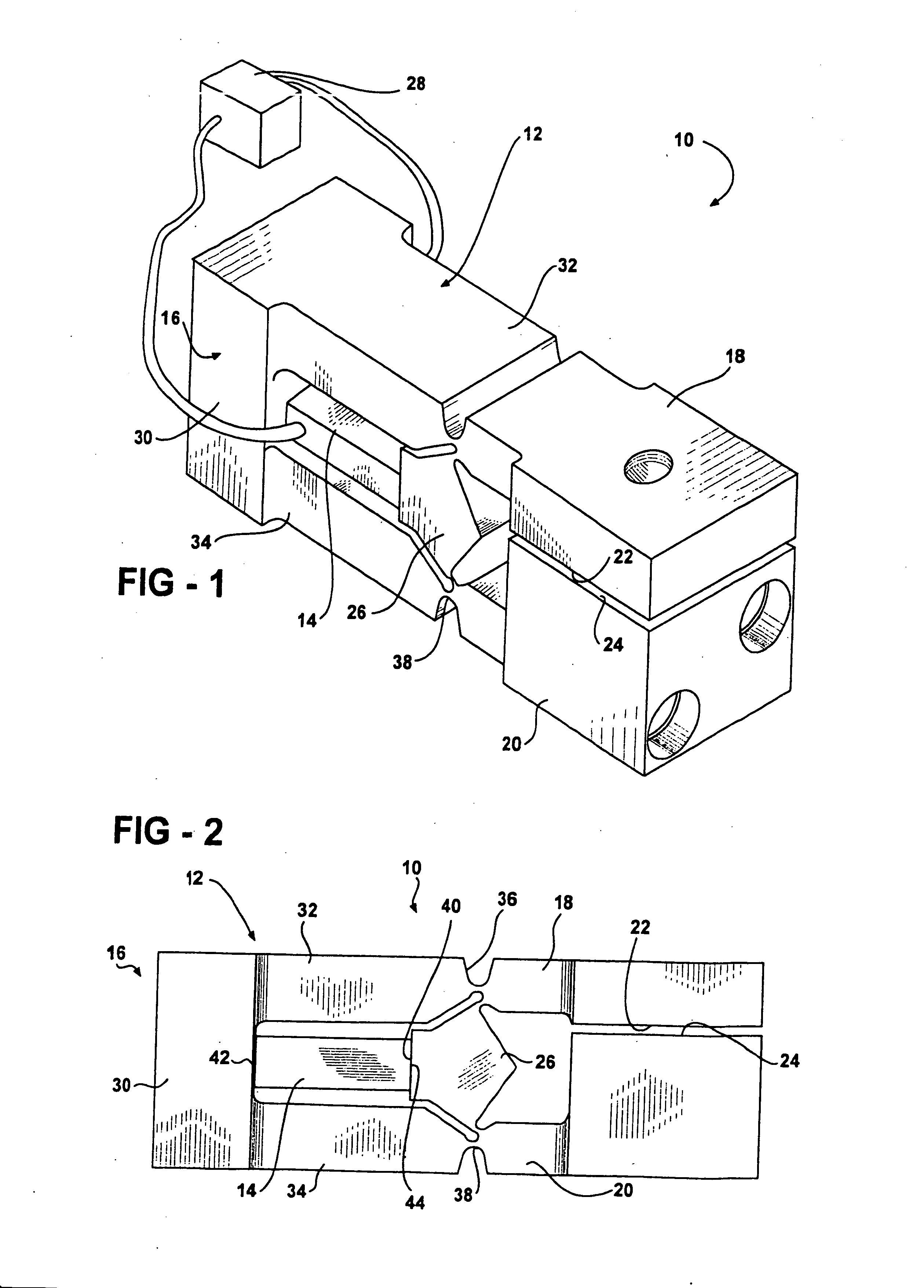
InactiveUS6870305B2Reduce the amount requiredReduces effective lifePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPivotal connectionsElectricityEngineering
An apparatus for moving a pair of opposing surfaces in response to an electrical activation having a support including a rigid non-flexing portion, at least one pivotable arm portion extending from the rigid non-flexing portion, a pair of opposing surfaces with one opposing surface on the at least one pivotable arm portion for movement relative to one another, and a force transfer member operably positioned for driving the at least one pivotable arm portion in rotational movement. An actuator is operably engaged between the rigid portion and the force transfer member to drive the force transfer member in movement relative to the rigid portion to pivot the at least one pivotable arm portion with a loss of motion of less than 40% in response to an electrical activation of the actuator.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
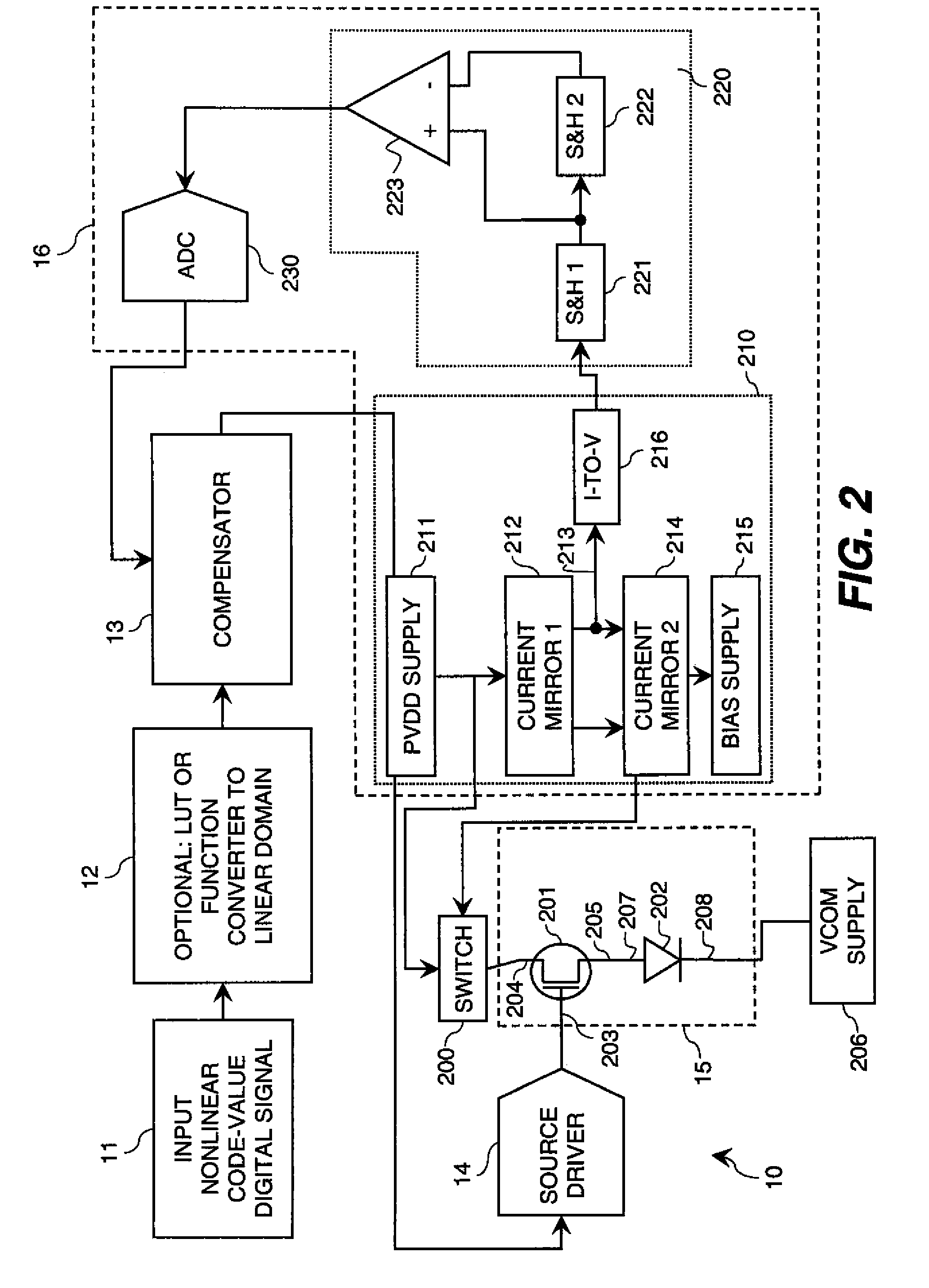
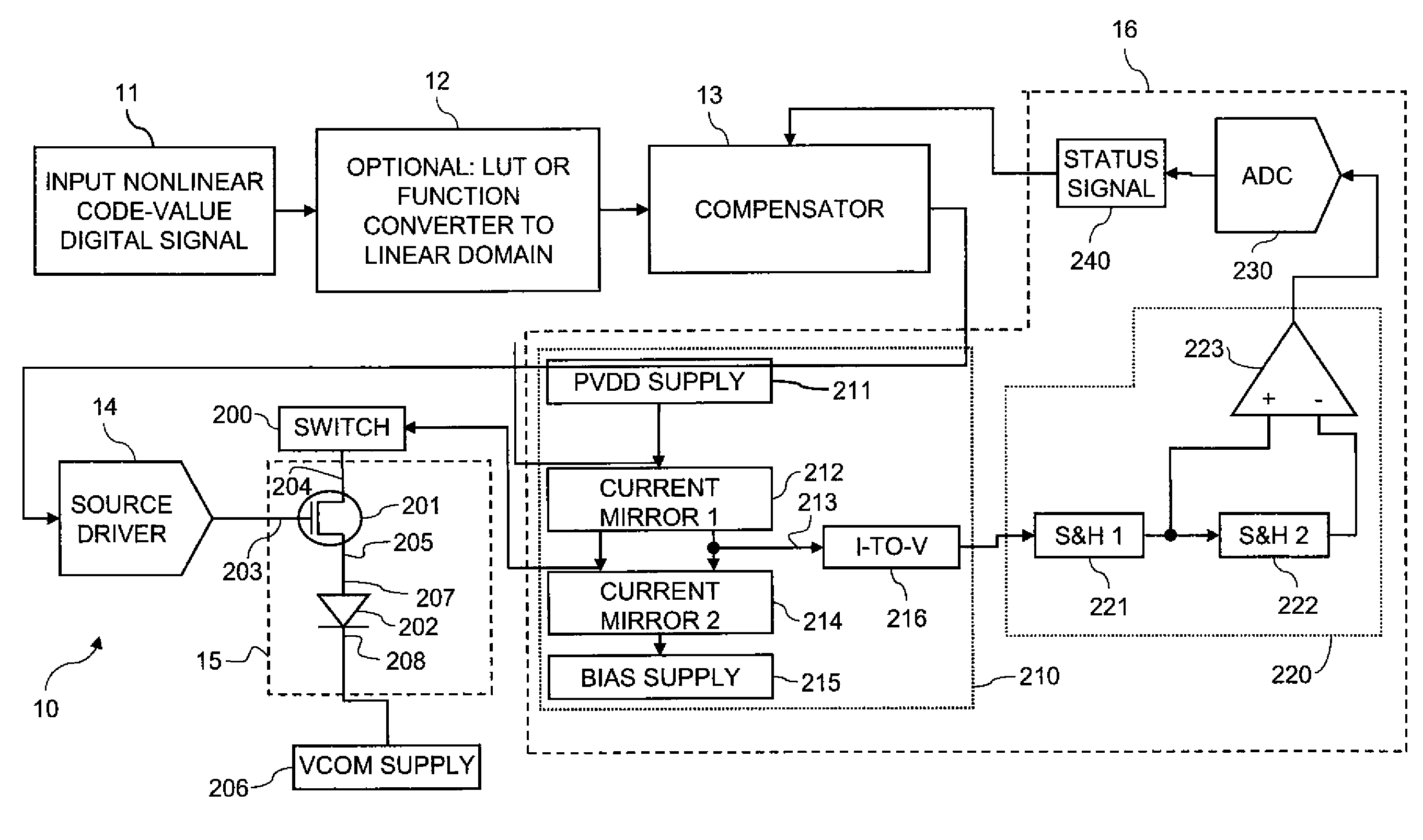
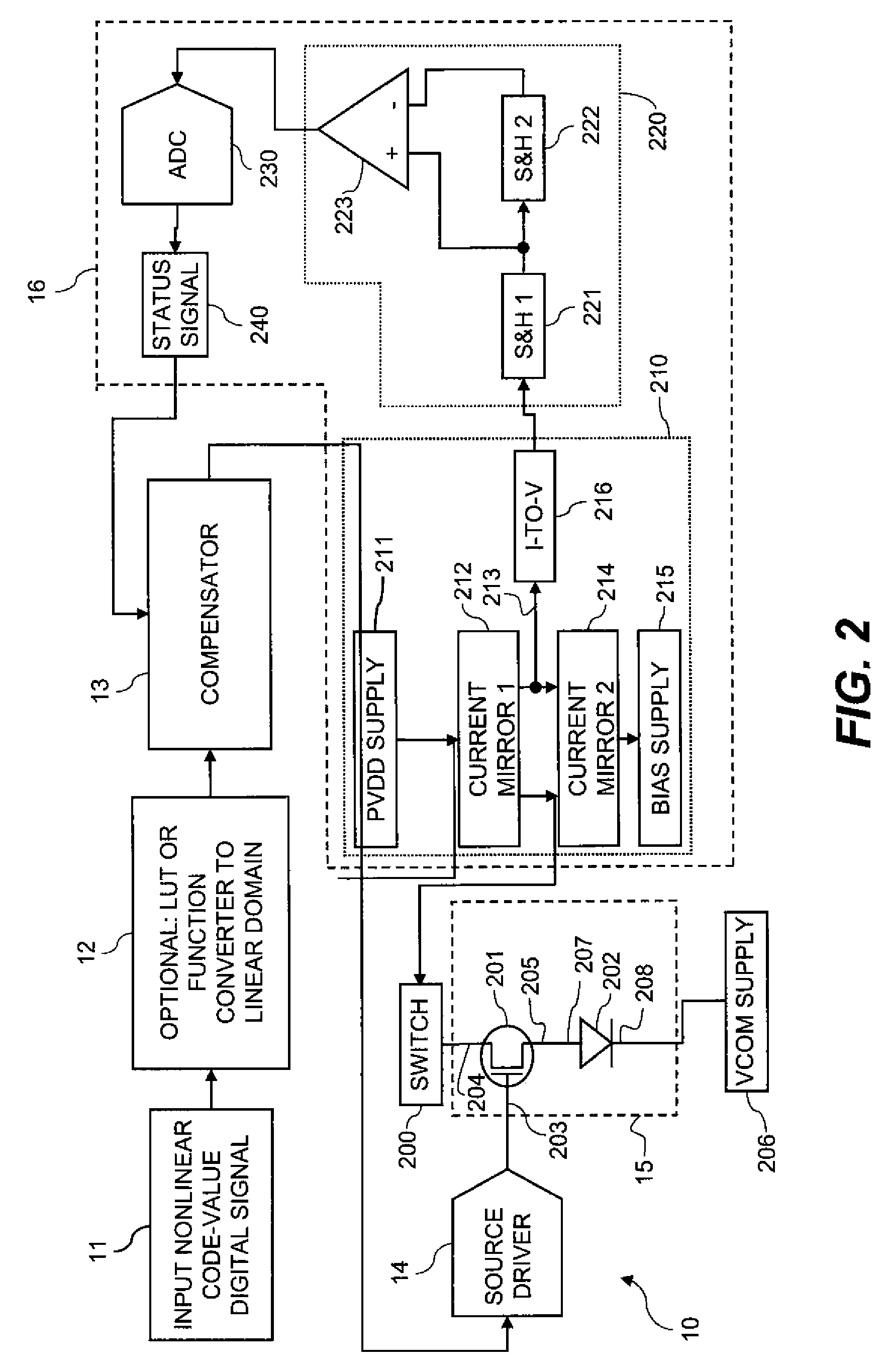
Electroluminescent display initial-nonuniformity-compensated drive signal
ActiveUS20100123699A1Increase the aperture ratioIncrease productionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringLinear code
An electroluminescent (EL) panel with 2T1C subpixels is compensated for initial nonuniformity (“mura”). The current of each subpixel is measured at a selected time to provide a status signal representing the characteristics of the subpixel. A compensator receives a linear code value and changes it according to the status signals. A linear source driver drives the panel with the changed code values.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
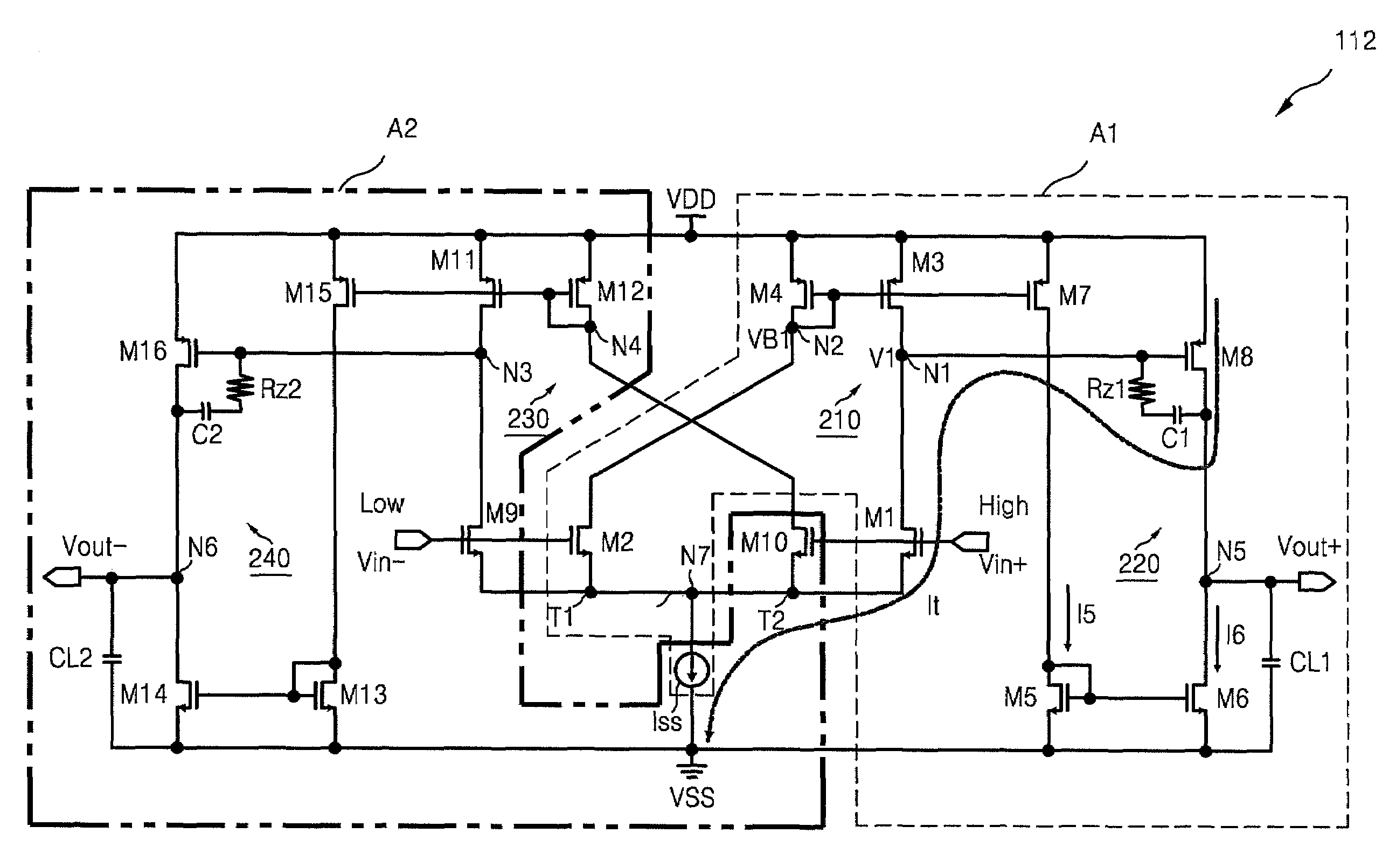
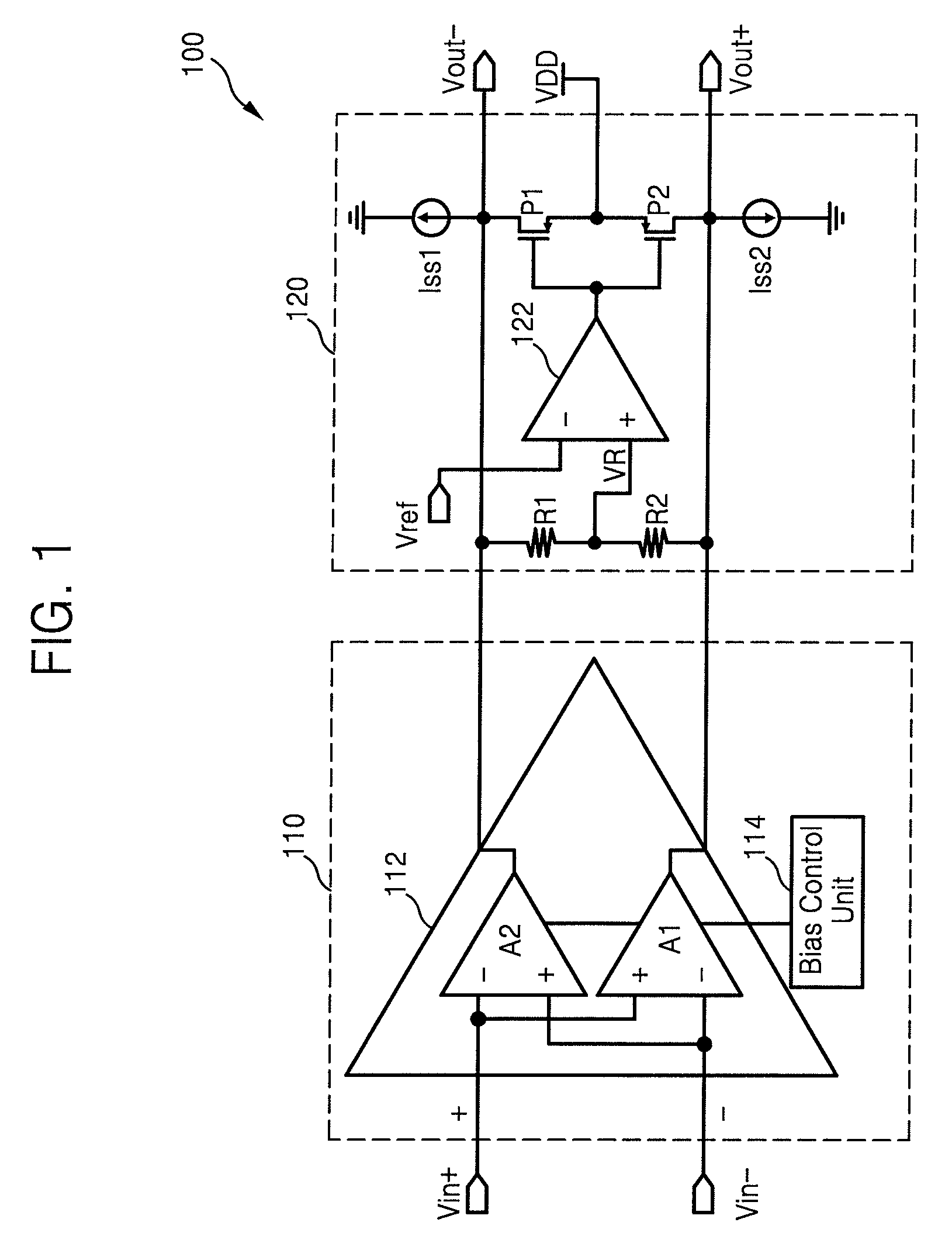
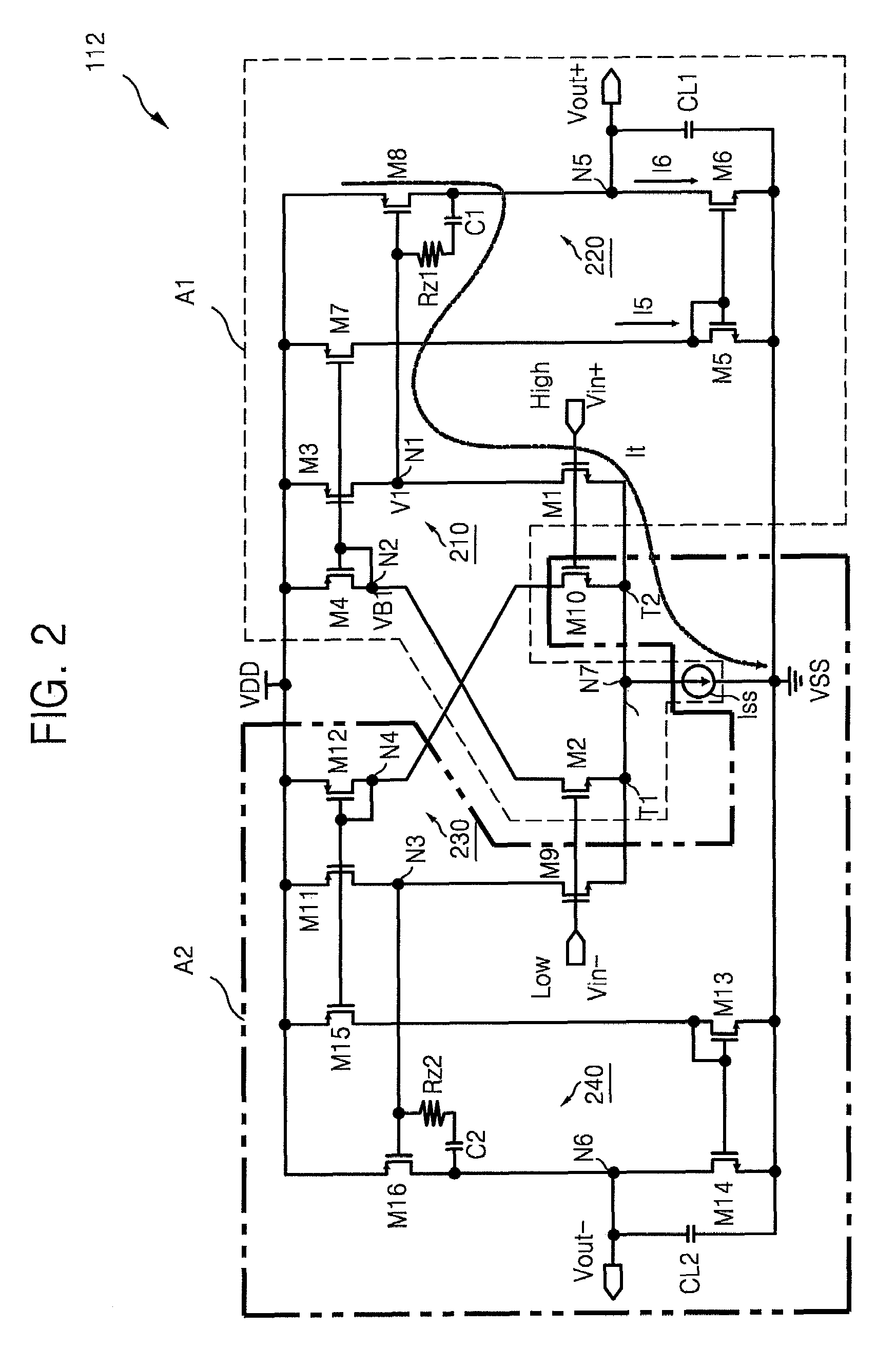
Fully differential class AB amplifier and amplifying method using single-ended, two-stage amplifier
InactiveUS7586373B2High gainReduce voltageDifferential amplifiersSingle-ended push-pull amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
A fully differential amplifier includes a first single-ended current mirror type fully differential amplifier outputting a first output signal by two stage amplifying a difference between a first input signal and a second input signal and a second single-ended current mirror type fully differential amplifier outputting a second output signal by two stage amplifying a difference between the first input signal and the second input signal. A first tail of the first single-ended current mirror type fully differential amplifier and a second tail of the second single-ended current mirror type fully differential amplifier are connected to each other and the first output signal and the second output signal are differential signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
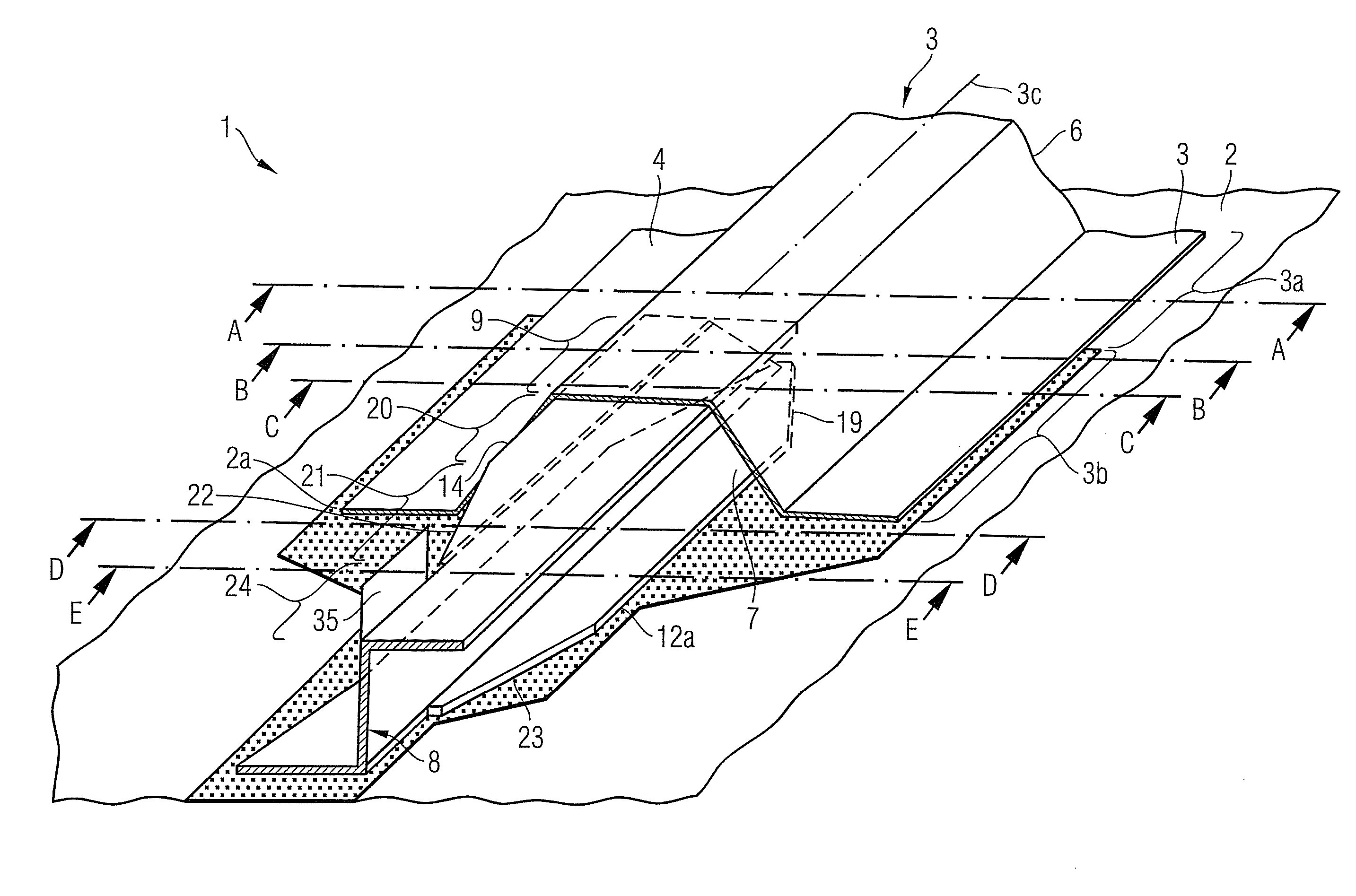
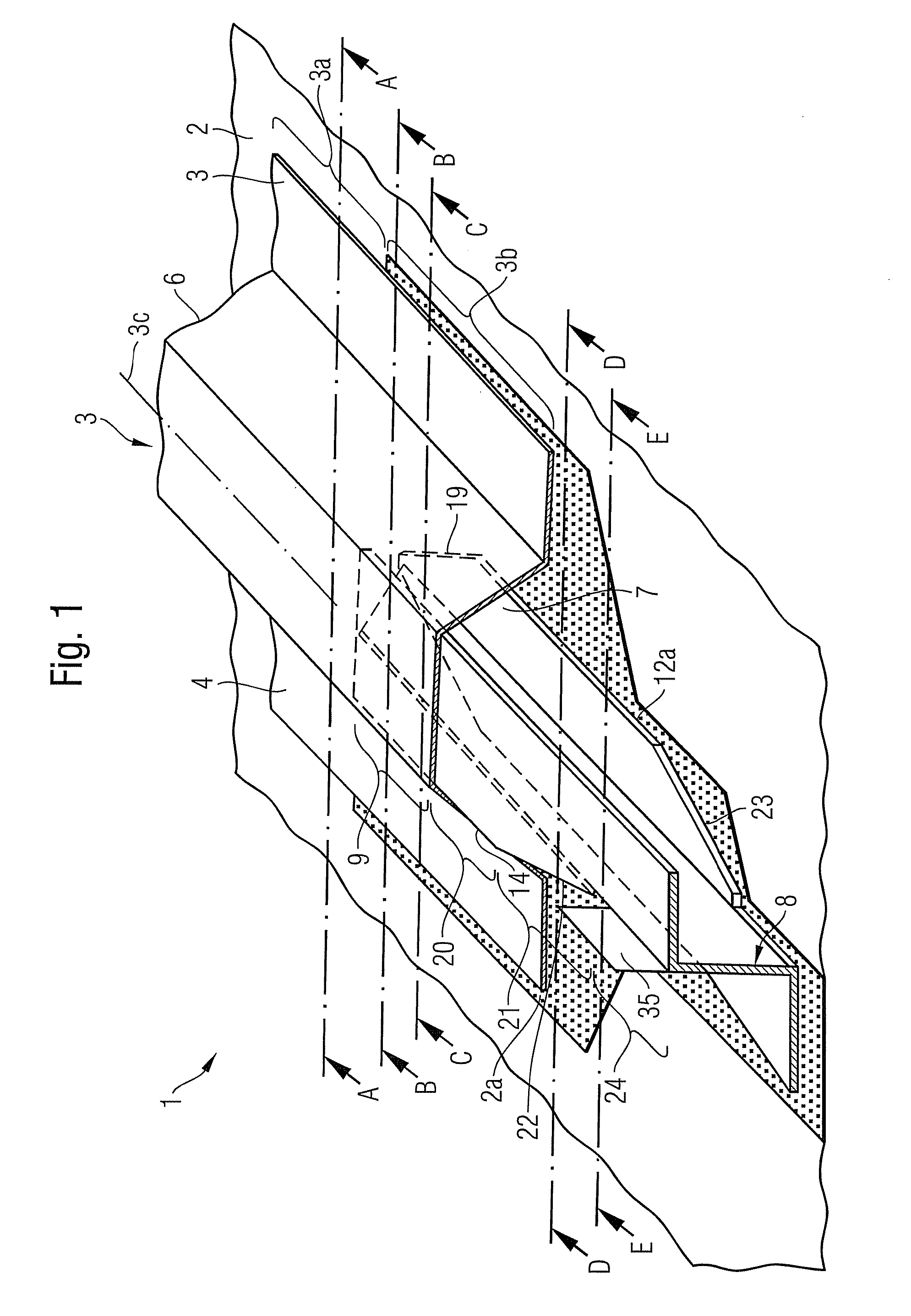
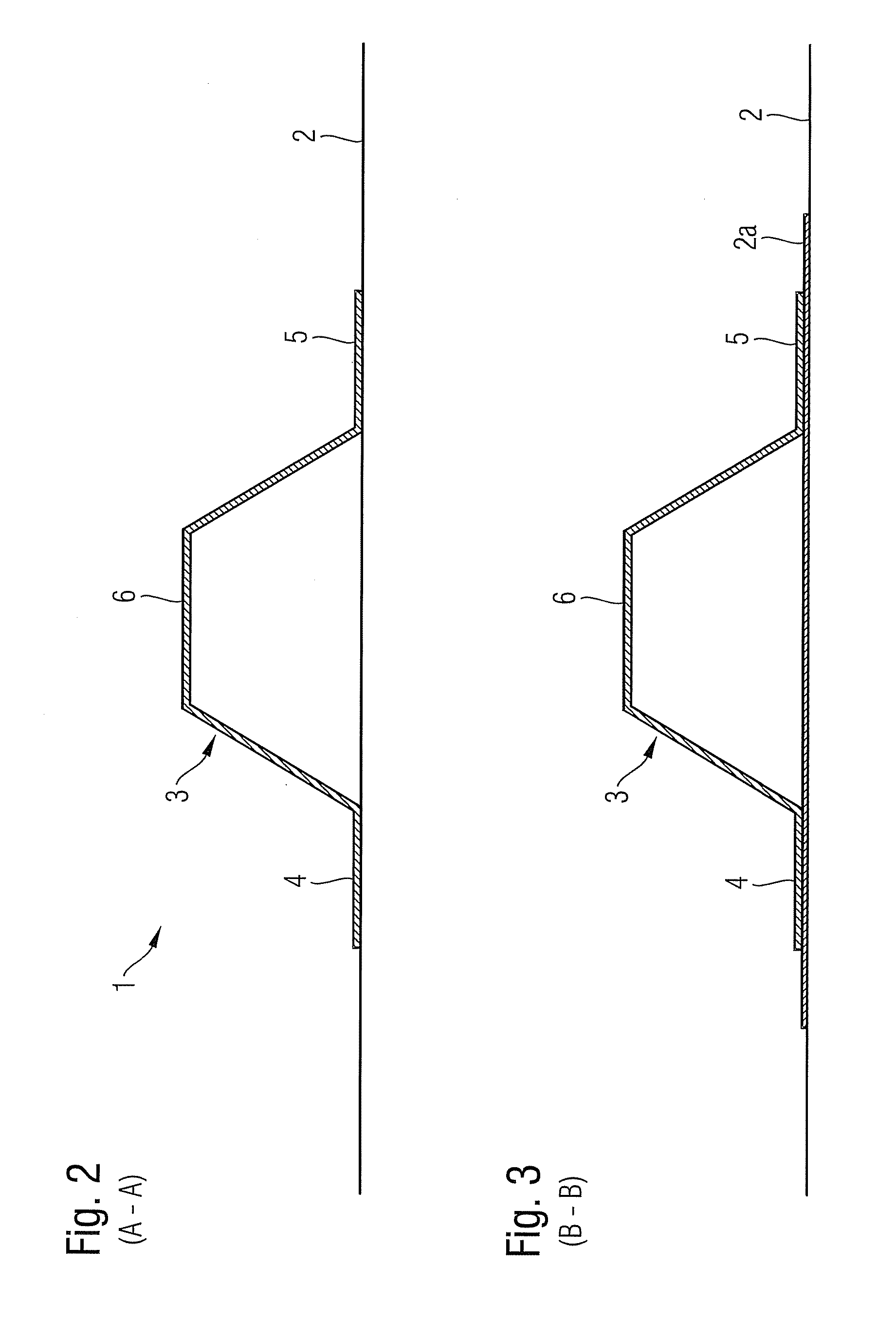
Composite and structure, particularly in the aerospace sector
InactiveUS20110095130A1Raise the possibilityImprove usabilityFuselage framesAircraft stabilisationAviationCoupling
The present invention provides a composite, in particular in the field of aviation and aerospace, comprising an omega-stringer that comprises a comb portion, and a connecting member that is connected at one end to the comb portion of the omega-stringer and can be connected at its other end to a standard coupling member. The idea underlying the present invention consists in forming omega-stringers with a connection zone that, on the one hand, is coupled to the comb portion of the omega-stringer and therefore makes it possible to transfer comparatively high loads and, on the other hand, can be connected to a standard coupling member so as to utilise the advantages of standard coupling members of this type when connecting omega-stringers to other stringers, for example T-stringers or other omega-stringers.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
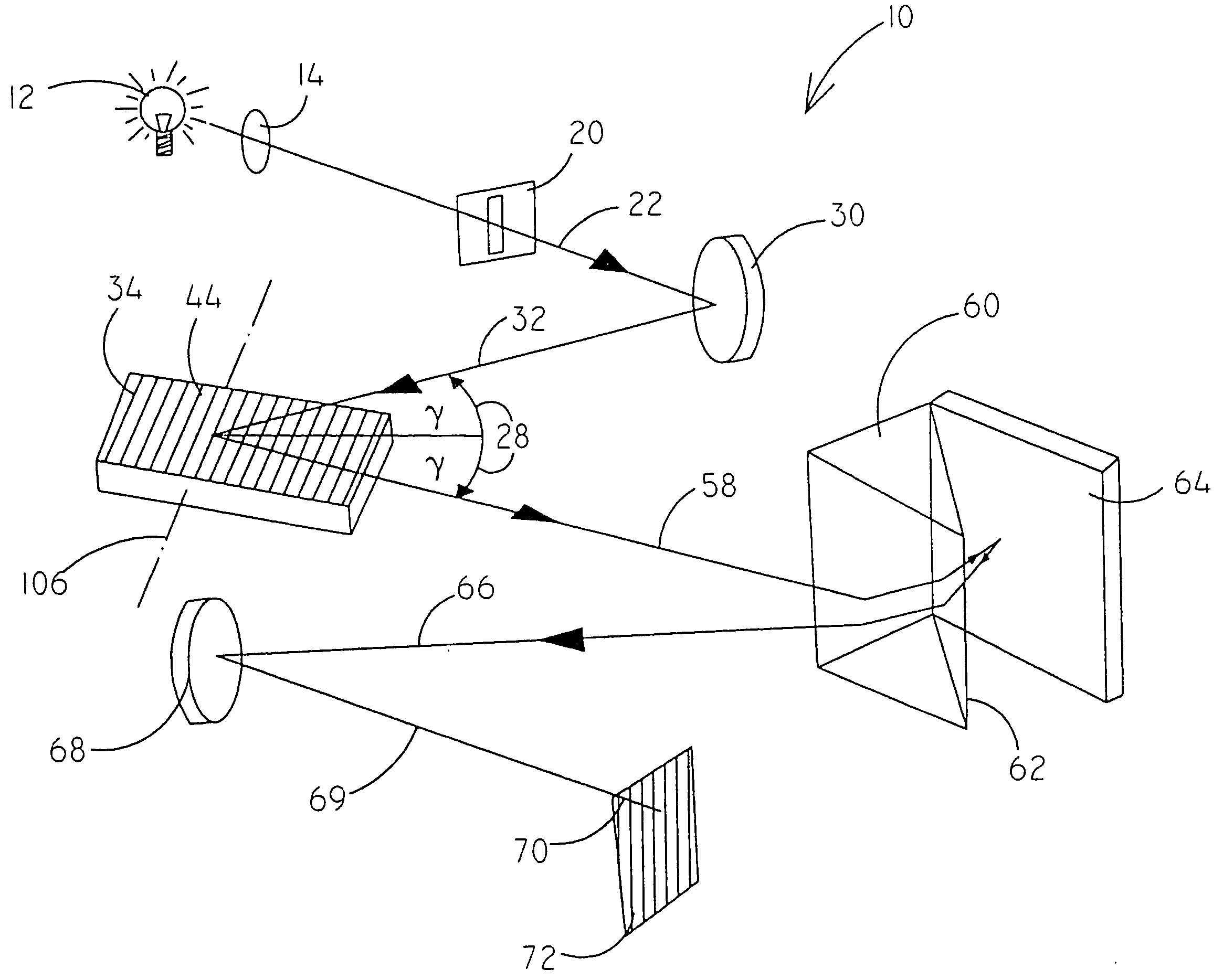
Method for the analysis of echelle spectra
InactiveUS20040114139A1Prone to driftEasy to adjustRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationPeak valueWavelength calibration
A method for the wavelength calibration of echelle spectra, in which the wavelengths are distributed across number of orders is characterised by the steps: recording of a line-rich reference spectrum with known wavelengths for a number of the lines, determination of the position of a number of peaks of the reference spectrum in the recorded spectrum, selection of at least two first lines of known order, position and wavelength, determination of a wavelength scale for the order in which the known lines lie, by means of a fit function gammam(x), determination of a provisional wavelength scale gamma?m 1<custom-character file="US20040114139A1-20040617-P00900.TIF" wi="20" he="20" id="custom-character-00001" / >(x) for at least one neighbouring order m 1, by means of addition / subtraction of a wavelength difference gammaFSR which corresponds to a free spectral region, according to gamma<custom-character file="US20040114139A1-20040617-P00900.TIF" wi="20" he="20" id="custom-character-00002" / >m 1 ?(x)=0gammam(x)gammaFSR with gammaFSR=gamma<custom-character file="US20040114139A1-20040617-P00900.TIF" wi="20" he="20" id="custom-character-00003" / >m(x) / m, determination of the wavelengths of lines in said neighbouring order m 1, by means of the provisional wavelength scale gamma 1(x), replacement of the provisional wavelength of at least two lines by the reference wavelength for said lines as obtained in step (a) and repeat of steps (d) to (g) for at least one further neighbouring order.
Owner:LEIBNIZ INSTITUT FUR ANALYTISCHE WISSENSCHAFTEN - ISAS -
Manually activated roll-up window shade
InactiveUS20080073035A1Low production costPositive synchronizationScreensWindowsMechanical engineering
A roll-up sunroof shade is provided that has two guide rails in addition to the tensioned shade element. A push element runs in each guide rail. Each push element is driven with a positive fit via a separate drive gear. For manual activation of the shade element, the rotational movement of the wind-up shade is transferred to the drive gears, and thus to the push elements, via a gear arrangement. In contrast, during retraction, the force acts from the push elements onto the wind-up shaft via the drive gears in order to generate the necessary rotational movement of the wind-up shaft.
Owner:BOS
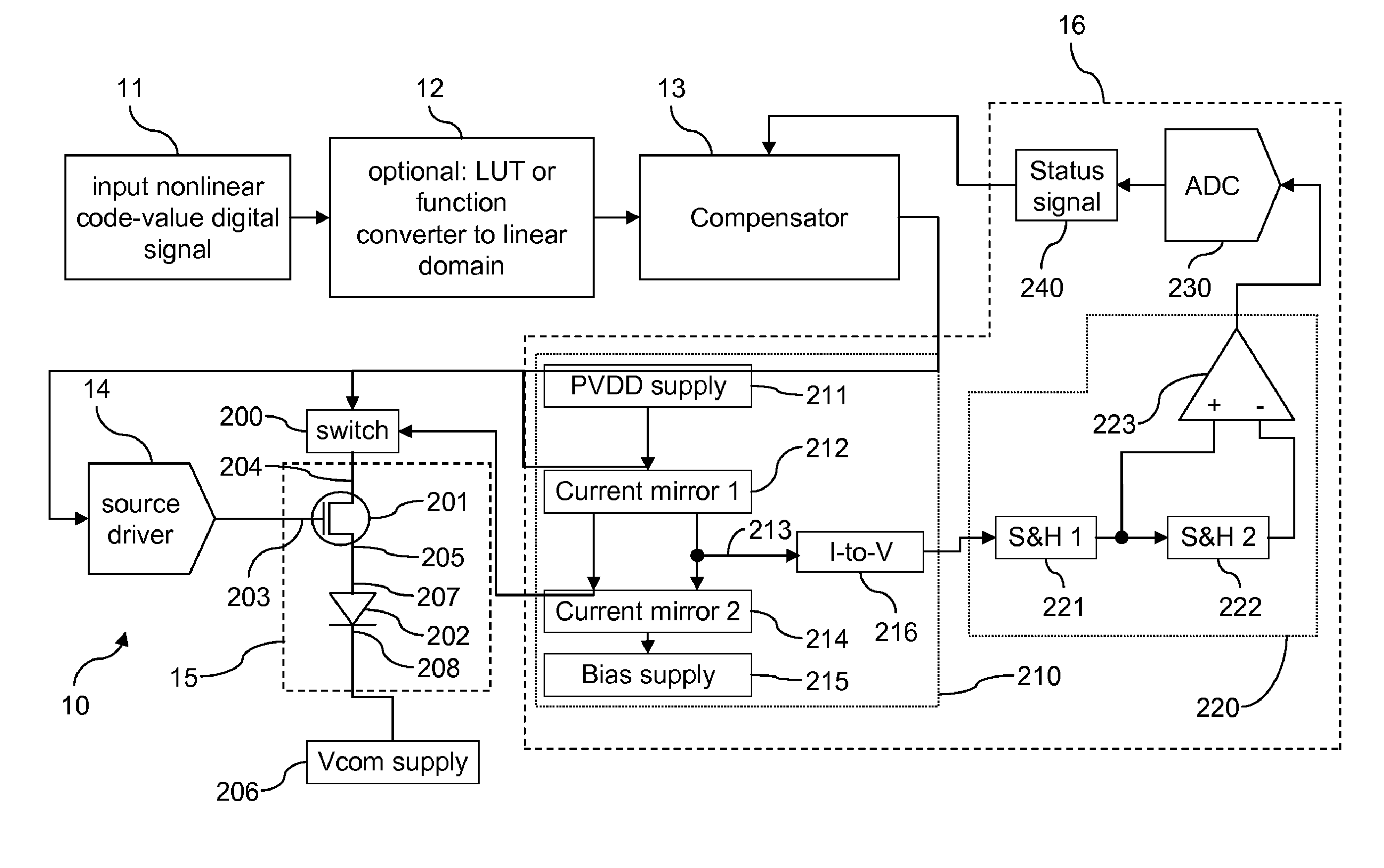
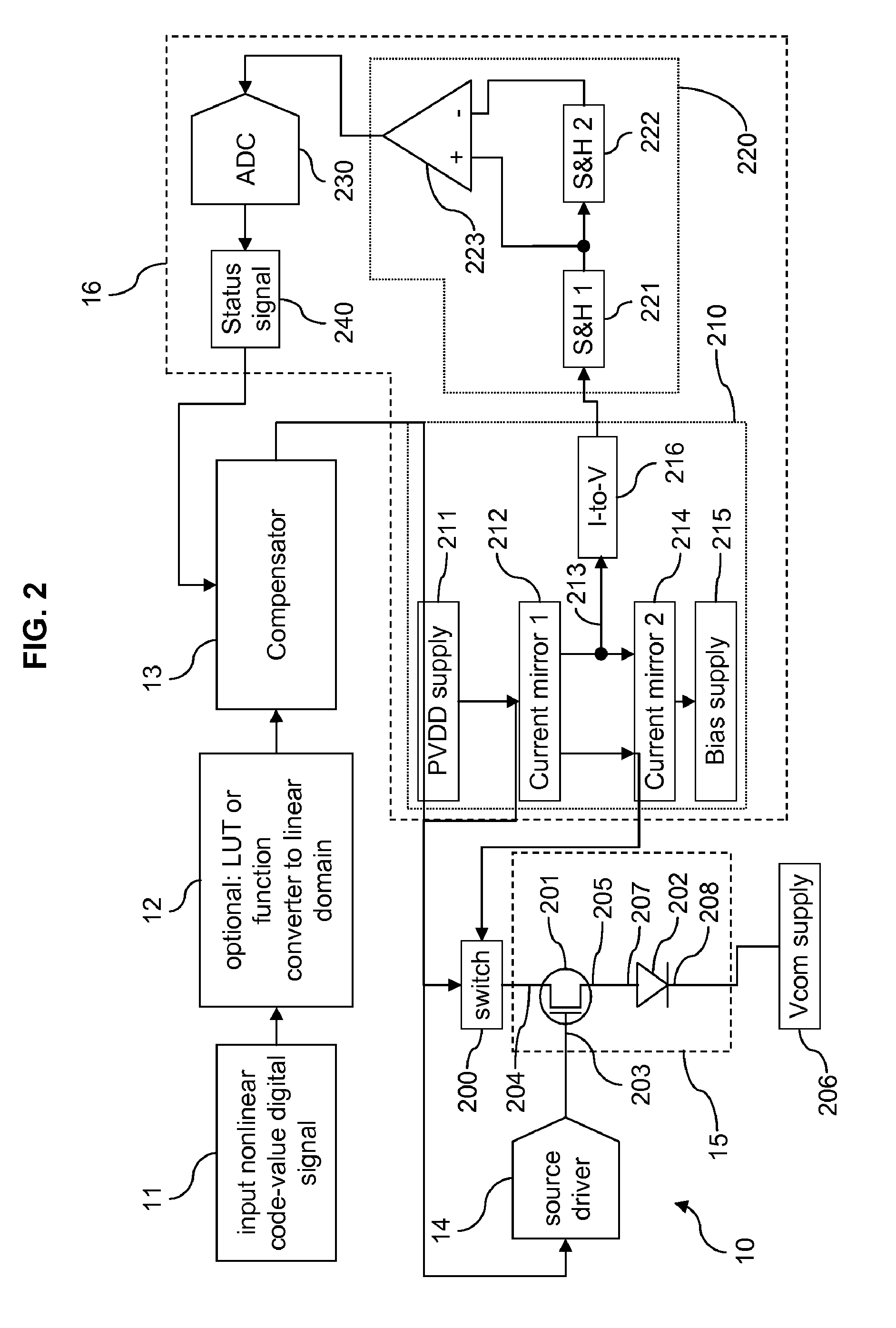
Electroluminescent display compensated drive signal
ActiveUS8194063B2Raise the ratioIncrease productionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingChannel length modulationDriving current
Subpixels on an electroluminescent (EL) display panel, such as an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) panel, are compensated for initial nonuniformity (“mura”) and for aging effects such as threshold voltage Vth shift, EL voltage Voled shift, and OLED efficiency loss. The drive current of each subpixel is measured at one or more measurement reference gate voltages to form status signals representing the characteristics of the drive transistor and EL emitter of those subpixels. Current measurements are taken in the linear region of drive transistor operation to improve signal-to-noise ratio in systems such as modern LTPS PMOS OLED displays, which have relatively small Voled shift over their lifetimes and thus relatively small current change due to channel-length modulation. Various sources of noise are also suppressed to further increase signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Device for influencing the movement of furniture parts which can be moved with respect to one another, and piece of furniture
Owner:GRASS GMBH
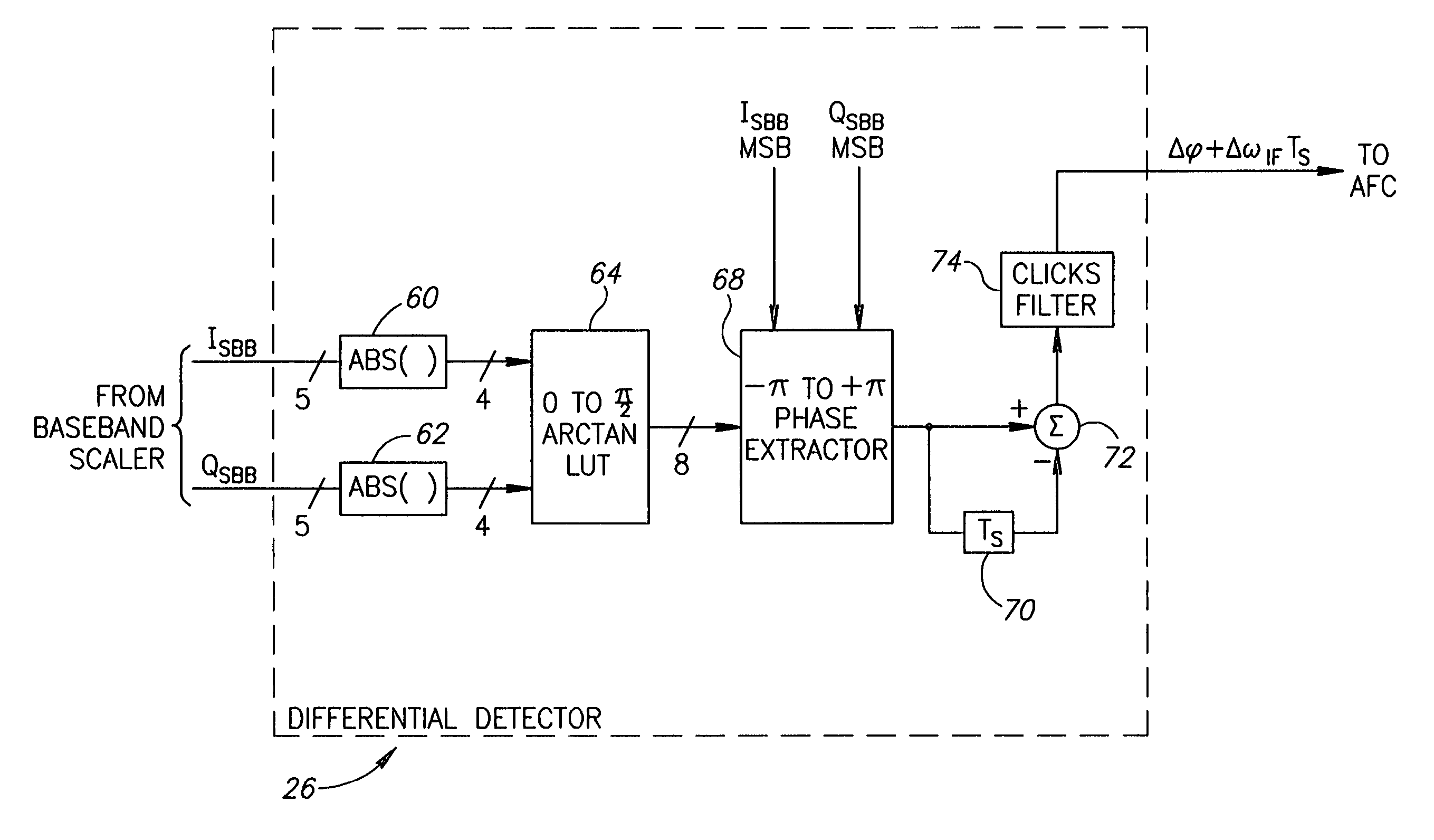
Gaussian frequency shift keying digital demodulator
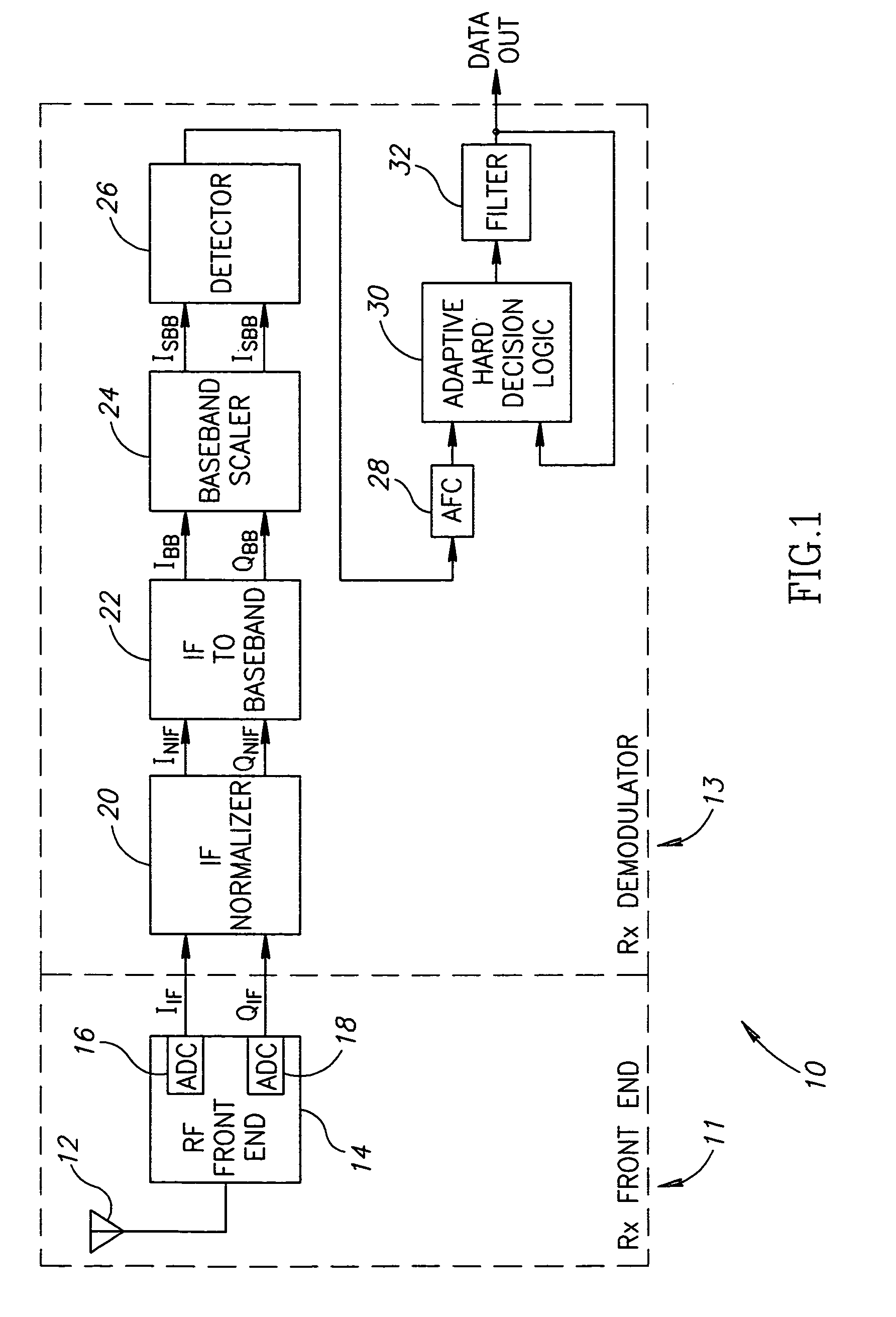
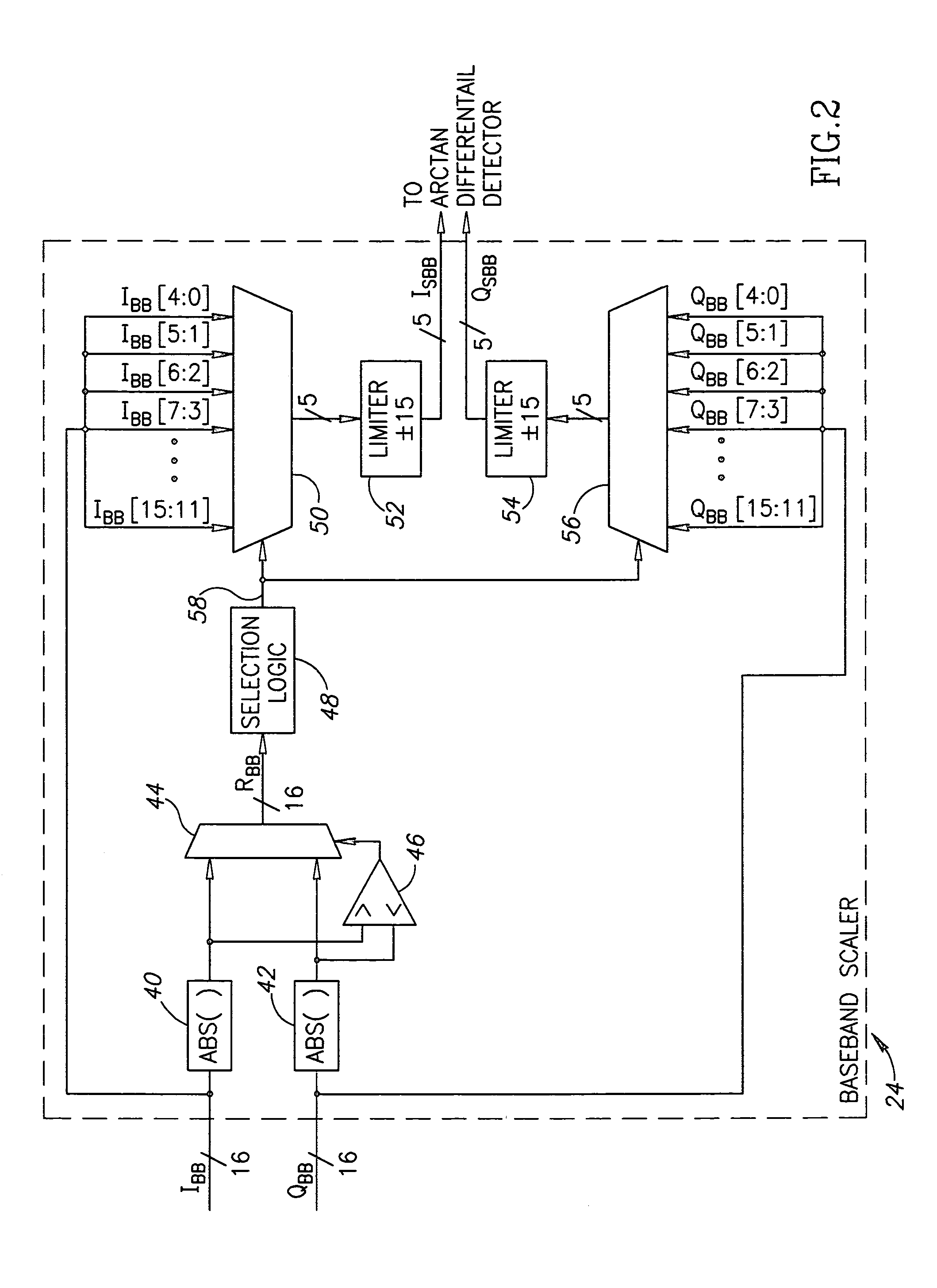
ActiveUS7110477B2Small sizeLow costFrequency-modulated carrier systemsPhase-modulated carrier systemsPhase differenceReduced size
A digital demodulator employing a digital differential detection mechanism based on extracting phase differences directly from the I and Q signals after downconversion to zero-IF and image rejection are performed. The phase of the input I and Q signals is determined using the principle that the phase is equivalent to arctan(QI).A lookup table stores the values of the arctan function preferably in a reduced size format. The size of the lookup table can be reduced significantly by storing arctan values for the first quadrant only (i.e. 0 to 90°) and taking advantage of the fact that the phase values for the other three quadrants can be derived from those of the first with some correction applied depending on the signs of the I and Q input samples. Phase extraction logic is provided that is operative to map the phase into the entire 0 to 360° range of phase values (i.e. −π to +π radians) based on the signs of the I and Q signals. The phase difference between a current phase value and the previous phase value is then calculated. It is these phase differences that reflect the frequency deviations present in the transmitted signal which represent the original modulating signal. A ‘click’ removal filter circuit is provided to remove the discontinuities in the phase difference output that occur when the 2π radians value is crossed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method, apparatus, and medium for removing shading of image
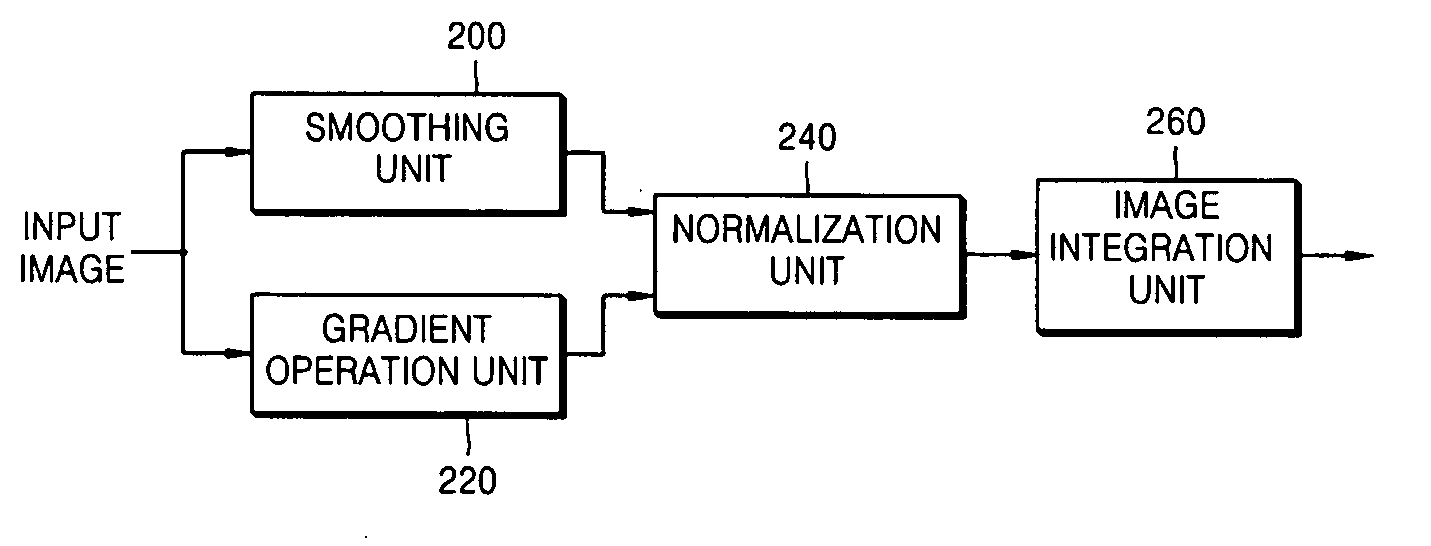
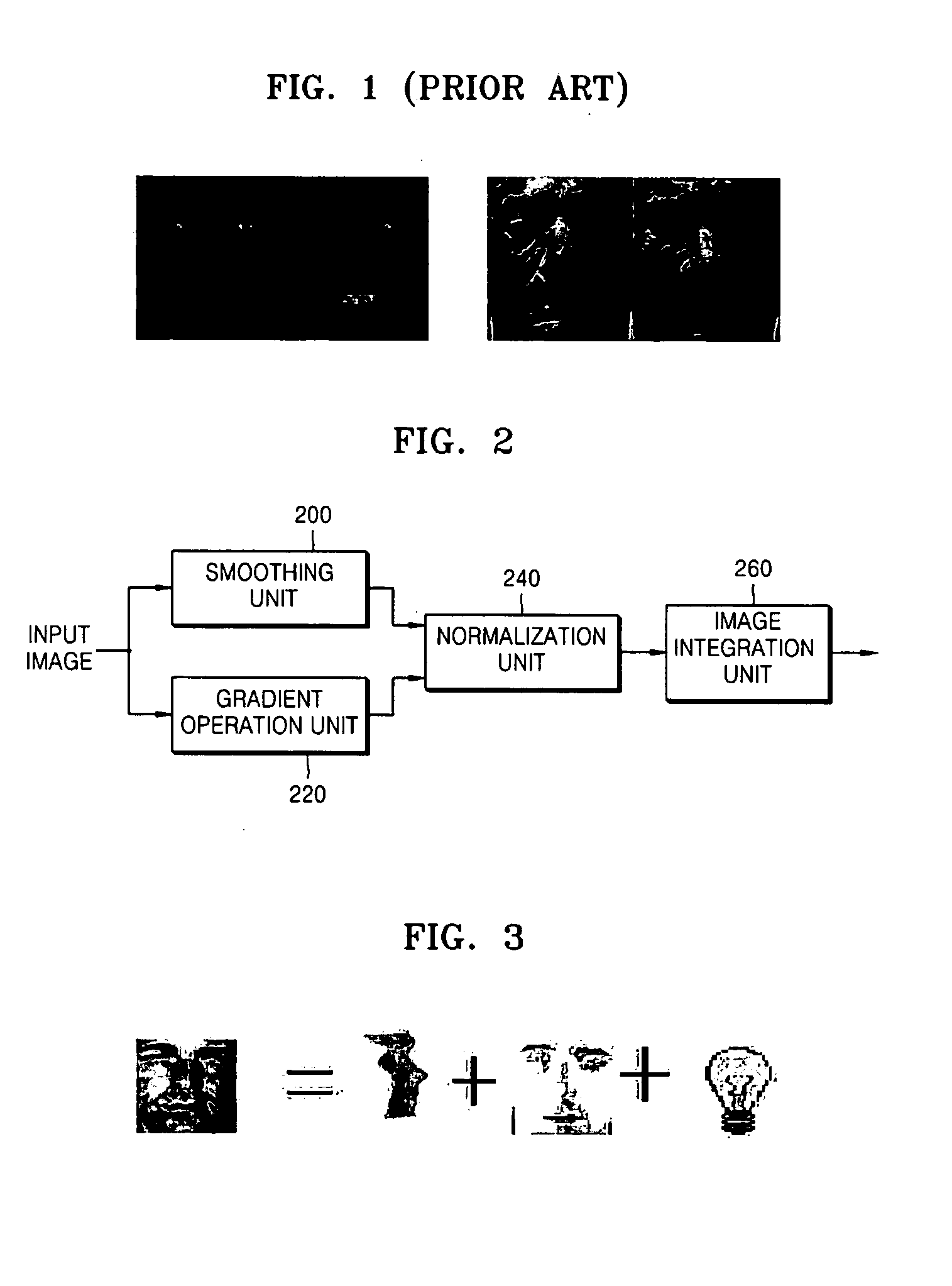
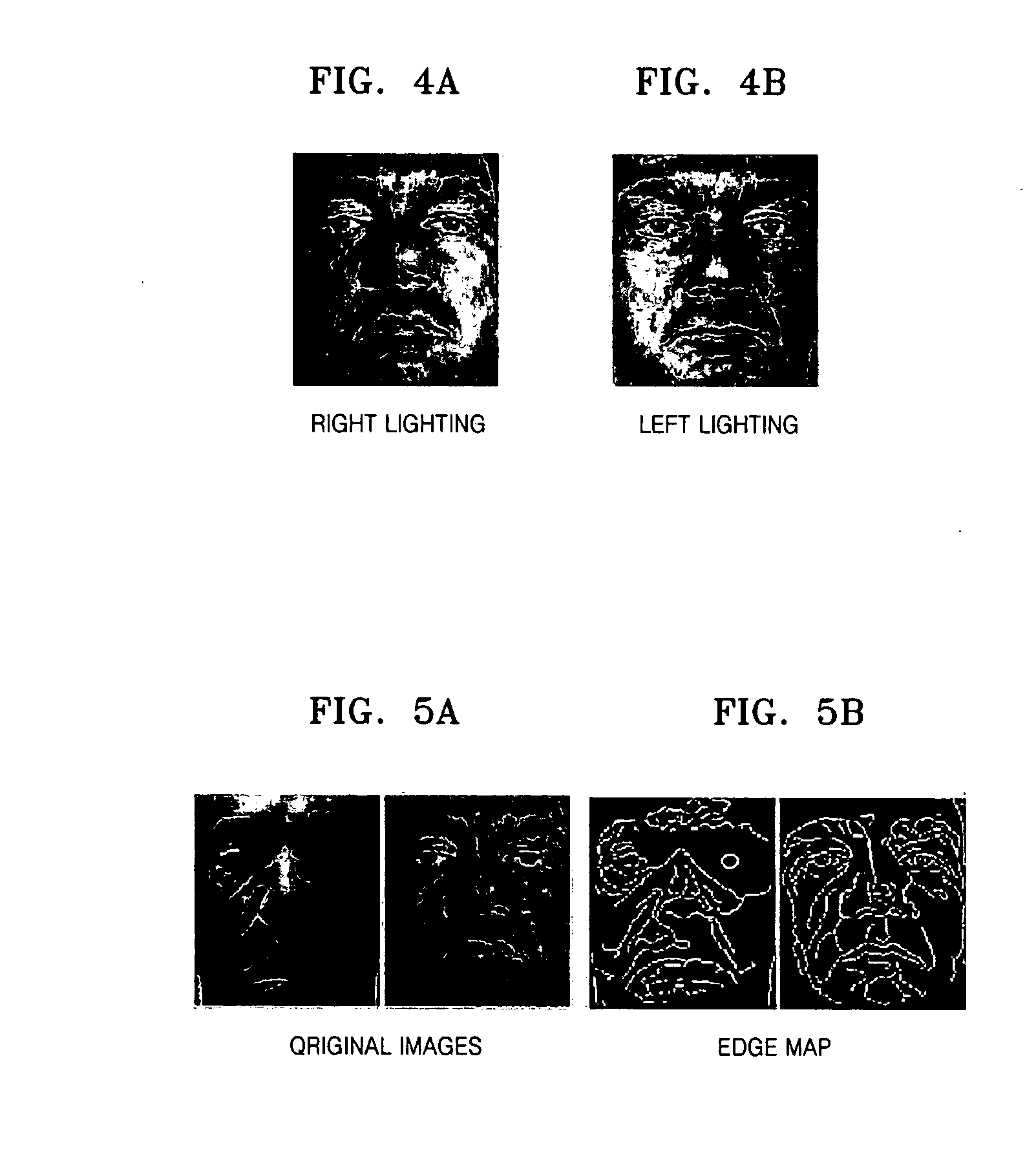
InactiveUS20060285769A1Improve performanceCompensation is simpleImage enhancementImage analysisGradient operatorsSmoothing kernel
A method, apparatus, and medium for removing shading of an image are provided. The method of removing shading of an image includes: smoothing an input image; performing a gradient operation for the input image; performing normalization using the smoothed image and the images for which the gradient operation is performed; and integrating the normalized images. The apparatus for removing shading of an image includes: a smoothing unit smoothing an input image using a predetermined smoothing kernel; a gradient operation unit performing a gradient operation for the input image using a predetermined gradient operator; a normalization unit performing normalization using the smoothed image and the images for which the gradient operation is performed; and an image integration unit integrating the normalized images. According to the method, apparatus, and medium, by defining a face image model analysis and intrinsic and extrinsic factors and setting up a rational assumption, an integral normalized gradient image not sensitive to illumination is provided. Also, by employing an anisotropic diffusion method, a moire phenomenon in an edge region of an image can be avoided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electronic field device with a sensor unit for capacitive level measurement in a container
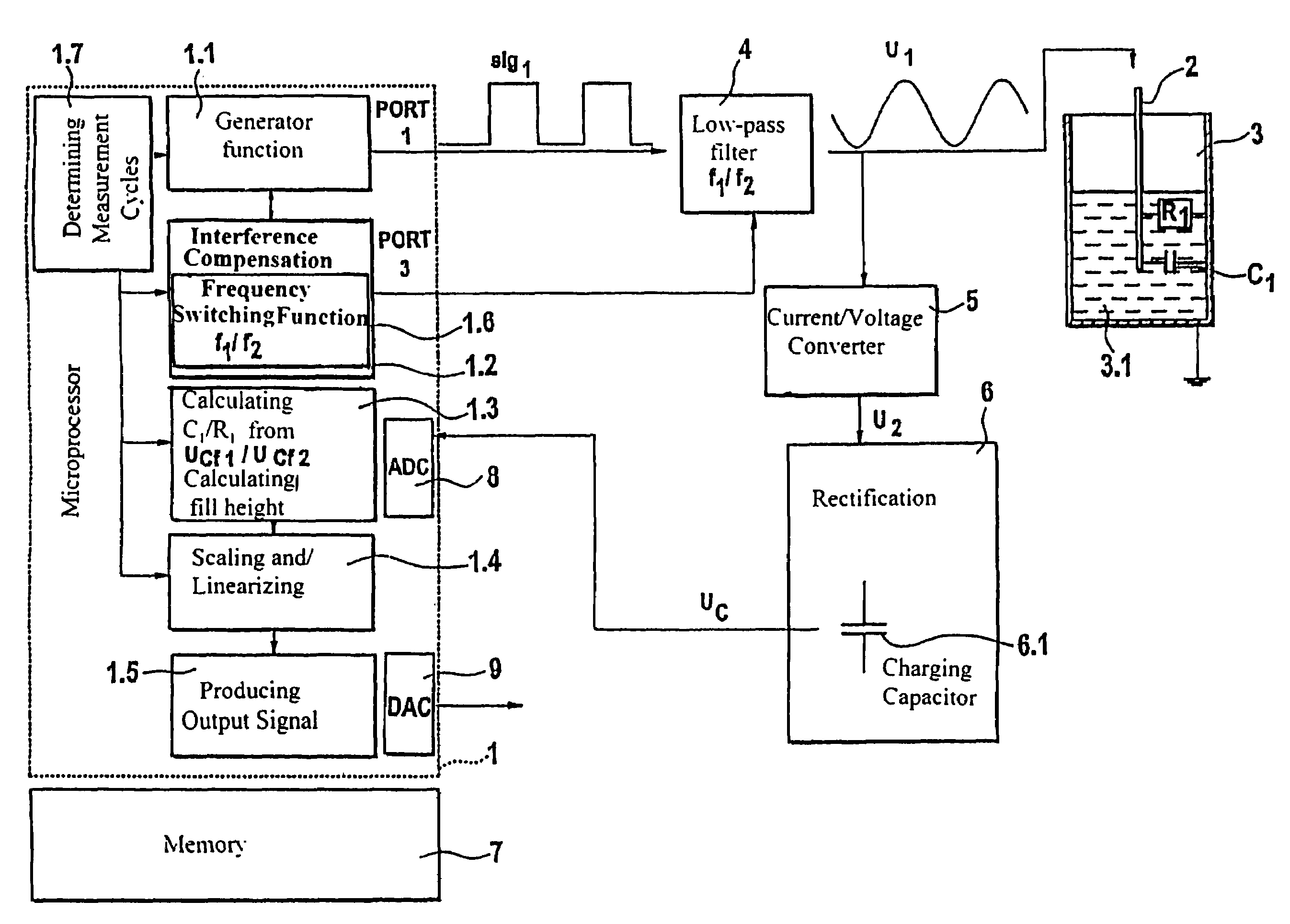
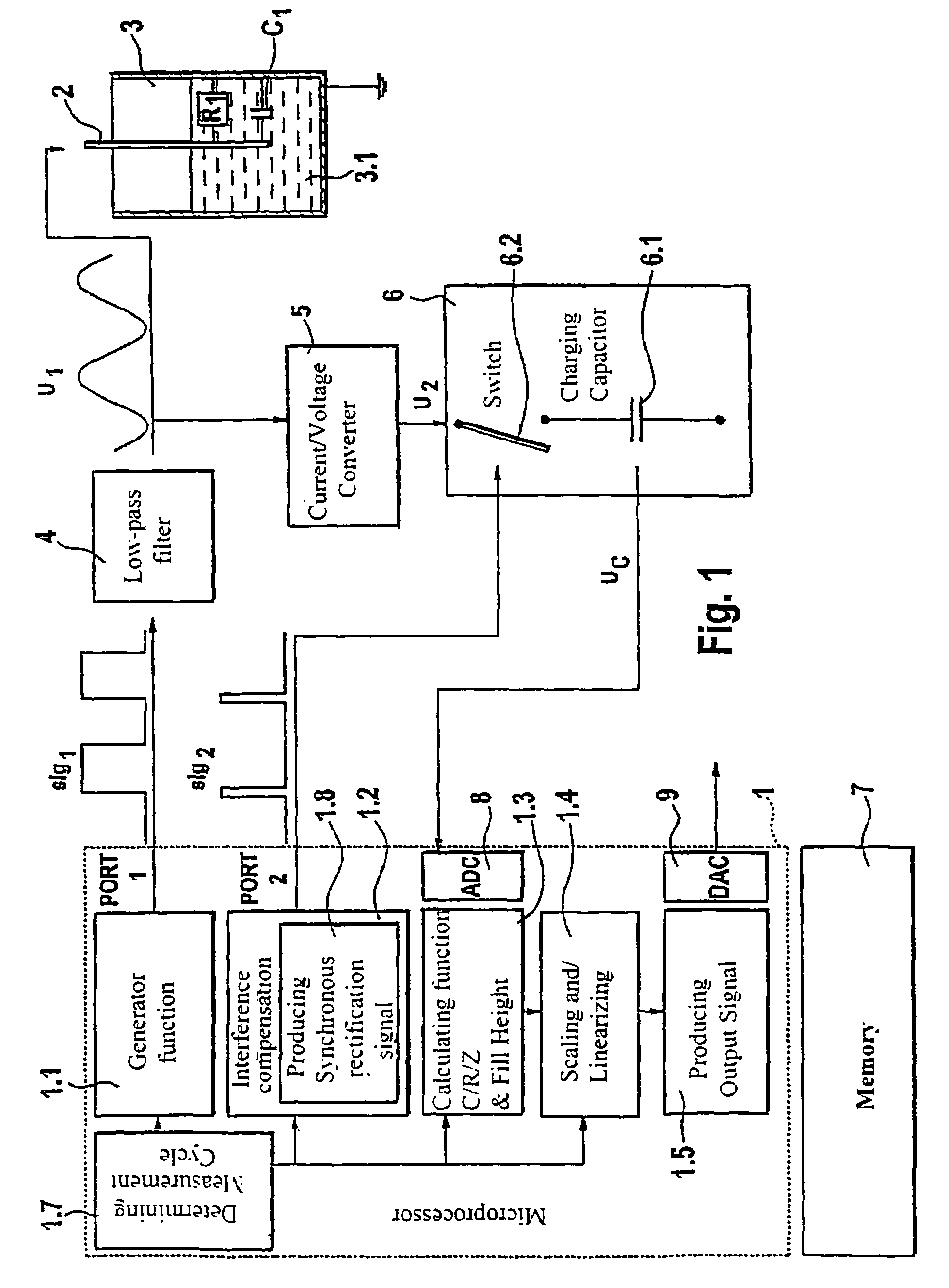
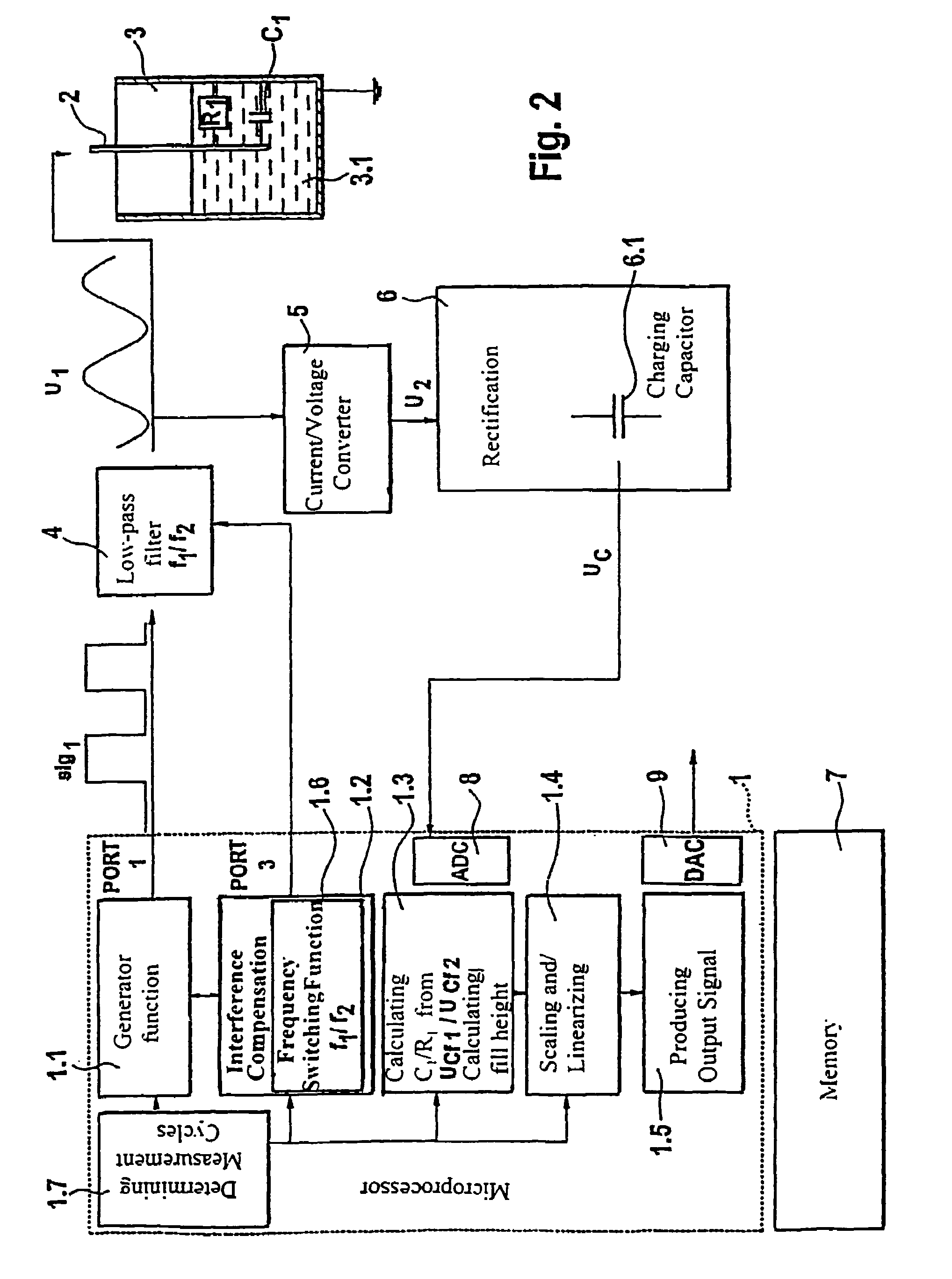
InactiveUS7415366B2Easy to adaptCompensation is simpleResistance/reactance/impedenceCurrent/voltage measurementCapacitanceEngineering
A field device electronics with a sensor unit for capacitive fill level measurements in a container, wherein the field device electronics is connected over appropriate signal paths with the sensor unit, wherein the field device electronics produces a voltage signal for driving the sensor unit and receives and evaluates a measurement current from the sensor unit. According to the invention, an analog / digital converter digitizing the analog measurement current, a microprocessor and a memory unit are present, wherein the microprocessor utilizes predetermined program routines to perform the production of the voltage signal and the evaluation of the measurement current and a compensation of interference parameters and a determination of the parameters of the sensor-container arrangement which are to be determined, with the associated programs being stored in the memory unit.
Owner:EHNDRESS KHAUZER GMBKH KO KG
Electroluminescent subpixel compensated drive signal
ActiveUS8217928B2Raise the ratioSimple control signalCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringGate voltage
An electroluminescent (EL) subpixel, such as an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) subpixel, is compensated for aging effects such as threshold voltage Vth shift, EL voltage Voled shift, and OLED efficiency loss. The drive current of the subpixel is measured at one or more measurement reference gate voltages to form a status signal representing the characteristics of the drive transistor and EL emitter of the subpixel. Current measurements are taken in the linear region of drive transistor operation to improve signal-to-noise ratio in systems such as modern LTPS PMOS OLED displays, which have relatively small Voled shift over their lifetimes and thus relatively small current change due to channel-length modulation. Various sources of noise are also suppressed to further increase signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Apparatus for moving a pair of opposing surfaces in response to an electrical activation
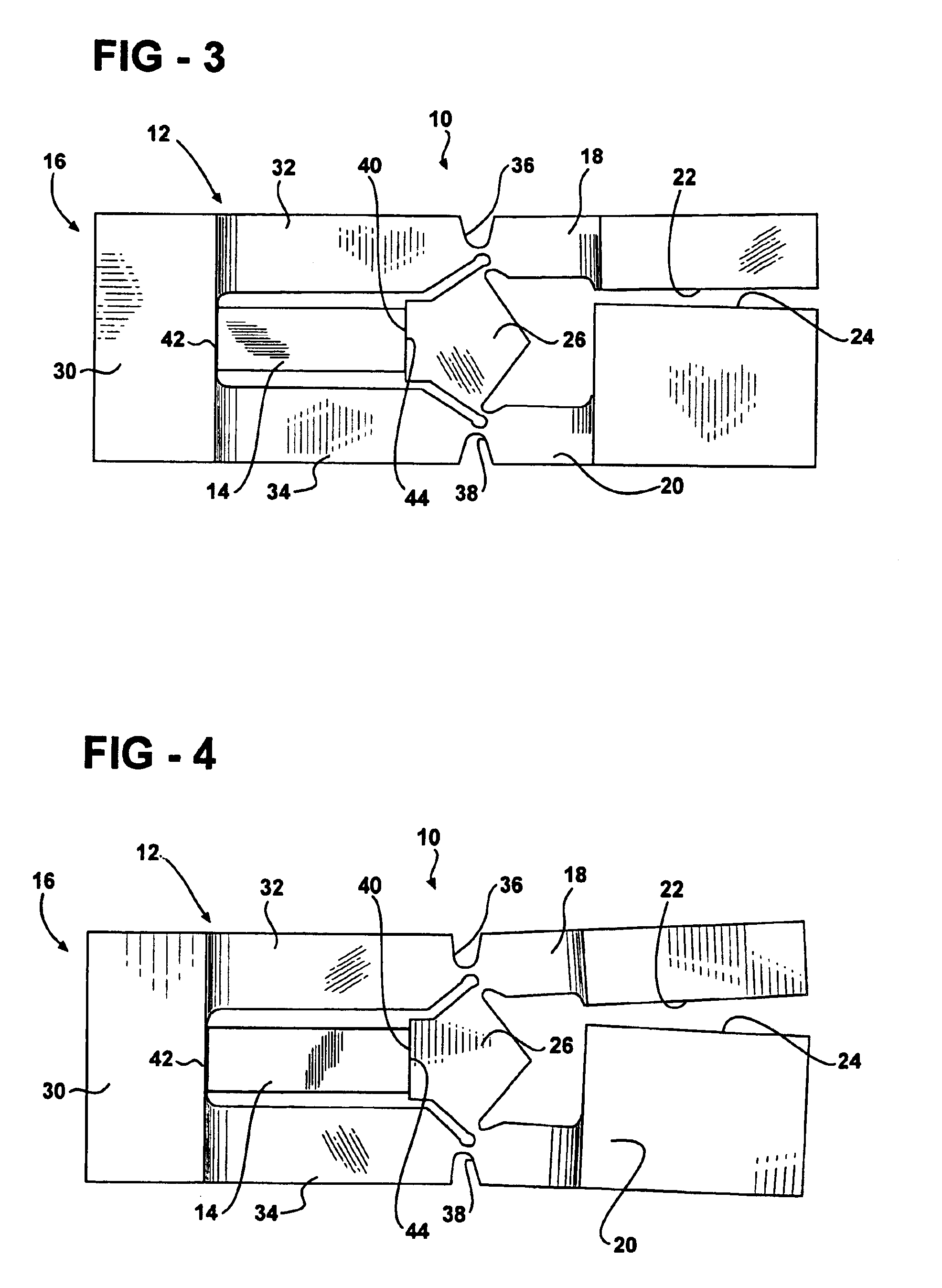
InactiveUS20050073220A1Reduce the amount requiredShort lifePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionElectricityEngineering
An apparatus for moving a pair of opposing surfaces in response to an electrical activation having a support including a rigid non-flexing portion, at least one pivotable arm portion extending from the rigid non-flexing portion, a pair of opposing surfaces with one opposing surface on the at least one pivotable arm portion for movement relative to one another, and a force transfer member operably positioned for driving the at least one pivotable arm portion in rotational movement. An actuator is operably engaged between the rigid portion and the force transfer member to drive the force transfer member in movement relative to the rigid portion to pivot the at least one pivotable arm portion with a loss of motion of less than 40% in response to an electrical activation of the actuator.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
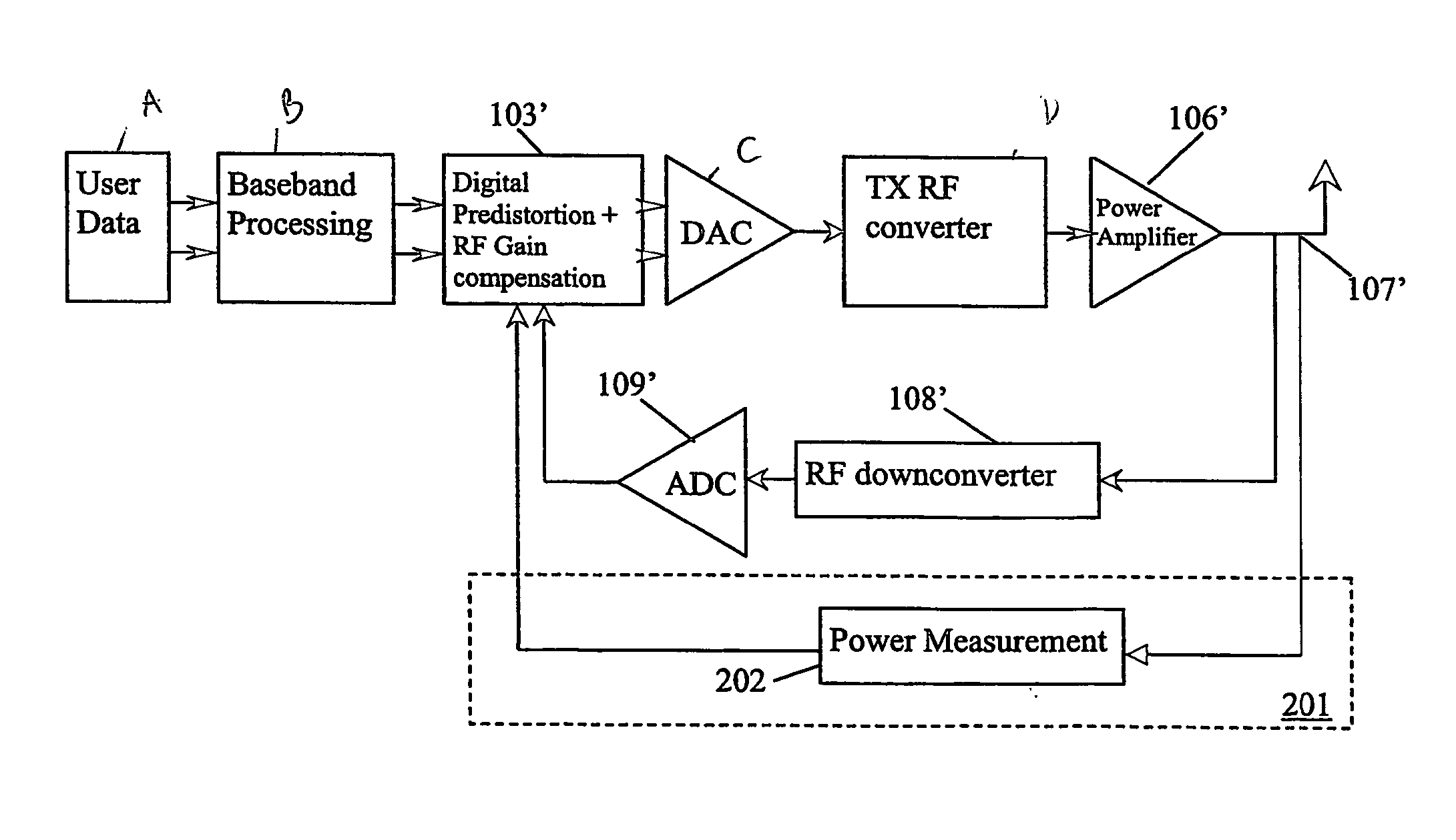
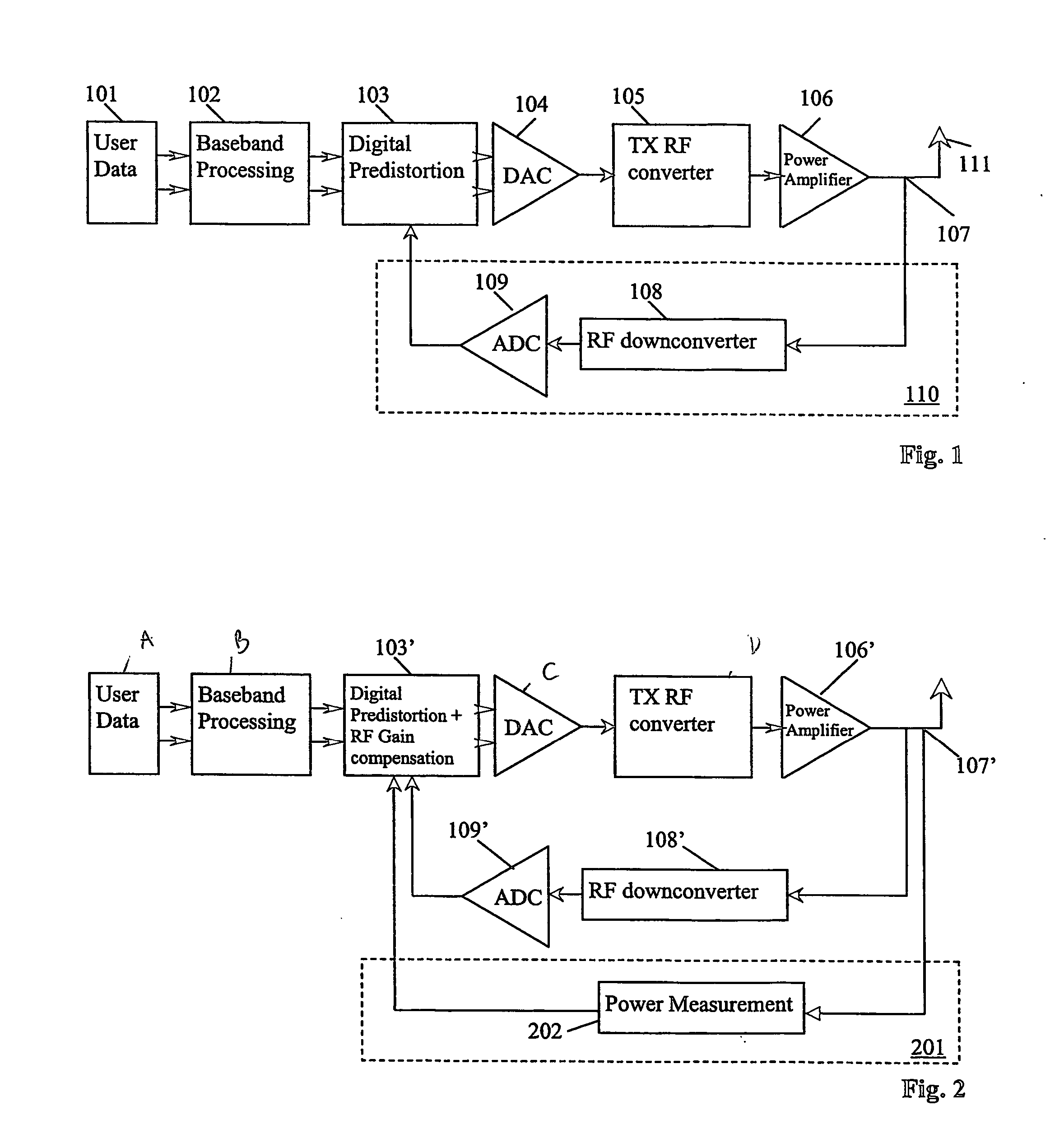
Method and device for power amplifier with high accuracy of an ouput signal
InactiveUS20060270365A1High output signal accuracyEasy to measureAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierPredistortion
The invention relates to a method for improving the output signal accuracy of a transmitter with a forward branch for converting an input signal into a signal for transmission. The forward branch comprises an adaptation unit (103) for applying a predistortion to the input signal and a power amplifier (106). The transmitter has a first feedback branch (110), the first feedback branch (110) generating a feedback signal from the signal for transmission, said feedback signal being fed back to the adaptation unit (103), and the predistortion applied to the input signal is determined according to the feedback signal. The method comprises the steps of: measuring the output power of said signal for transmission in a second feedback branch (201) and adjusting the predistortion according to said measurement of the output power. A transmitter and a computer program product adapted to the method are also described.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method for monitoring wavelength of tunable laser on user end by optical line terminal on local end
ActiveUS20170170898A1Reduced control accuracySimplify requirement on positioning accuracyWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionOptical line terminationLength wave
Disclosed is a method for monitoring the wavelength of a tunable laser device of user by local OLT. The method is applied to a wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network framework. The framework comprises an ONU, a first athermal array waveguide grating, a transmission optical fiber, a second athermal array waveguide grating and the OLT, which are sequentially connected. ONU comprises tunable wavelength optical transmitters. The method comprises: starting handshaking is carried out between the OLT and the ONU; and the OLT carries out wavelength drifting monitoring during operation of the ONU. Wavelength adjustment can be carried out on the multi-channel tunable laser device in an external auxiliary monitoring environment, thus channel wavelengths of the multi-channel tunable laser device can be accurately controlled, and the requirement for calibration accuracy of channels of the tunable laser device at the ONU is greatly reduced.
Owner:ACCELINK TECHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Method and system for obfuscating a cryptographic function
ActiveUS20090122978A1Improve protectionCompensation is simpleEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationTheoretical computer science
In a system 300, a server 310 provides a cryptographic function F to an execution device in an obfuscated form. The function F composes output of a plurality of the mapping tables Ti(0≦i≦n; n≧1) using an Abelian group operator . A processor 312 chooses tables O and C such that C[x]O[x]=0, ∀x±Di and creates tables T′i, 0≦i≦m; n≦m≦n+1, where for 0≦i≦n, each Table T′i represents the respective corresponding table T,j and at least one table T′o1, 0≦01, ≦n, being formed through an Abelian composition of To1 and O, and at least one table T′c10≦c1,≦m, c1#oj, being formed through an Abelian composition that includes C. Means 314 are used for providing the tables T′i, to the executing device. The executing device 320 includes means 324 for receiving the tables and a processor 322 for forming a function F′ that is functionally equivalent to the cryptographic function F by an Abelian composition of the tables T′i.
Owner:IRDETO ACCESS
Method and system for obfuscating a cryptographic function
ActiveUS7881466B2Improve protectionCompensation is simpleEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationCryptographic hash functionTheoretical computer science
Embodiments include a system, wherein a server provides a cryptographic function F to an execution device in an obfuscated form. The function F composes output of a plurality of the mapping tables Ti (0≦i≦n; n≧1) using an Abelian group operator. A processor chooses tables O and C such that C[x] O[x]=0, x Di and creates tables T′i, 0≦i≦m; n≦m≦n+1, where for 0≦i≦n, each Table T′i represents the respective corresponding table Ti and at least one table T′o1, 0≦o1≦n, being formed through an Abelian composition of To1 and O, and at least one table T′c1, 0≦c1≦m, c1≠oj; being formed through an Abelian composition that includes C.
Owner:IRDETO ACCESS
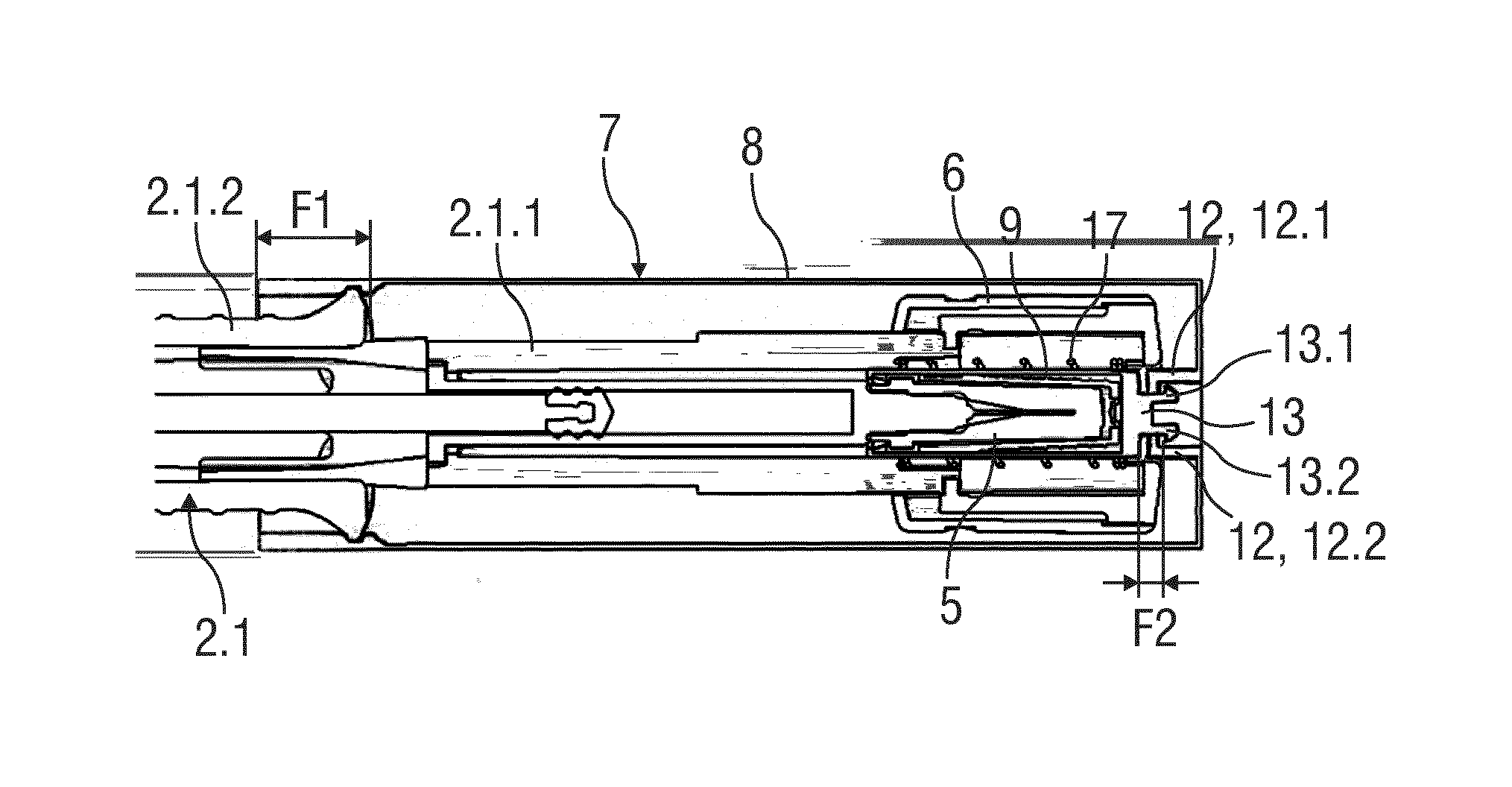
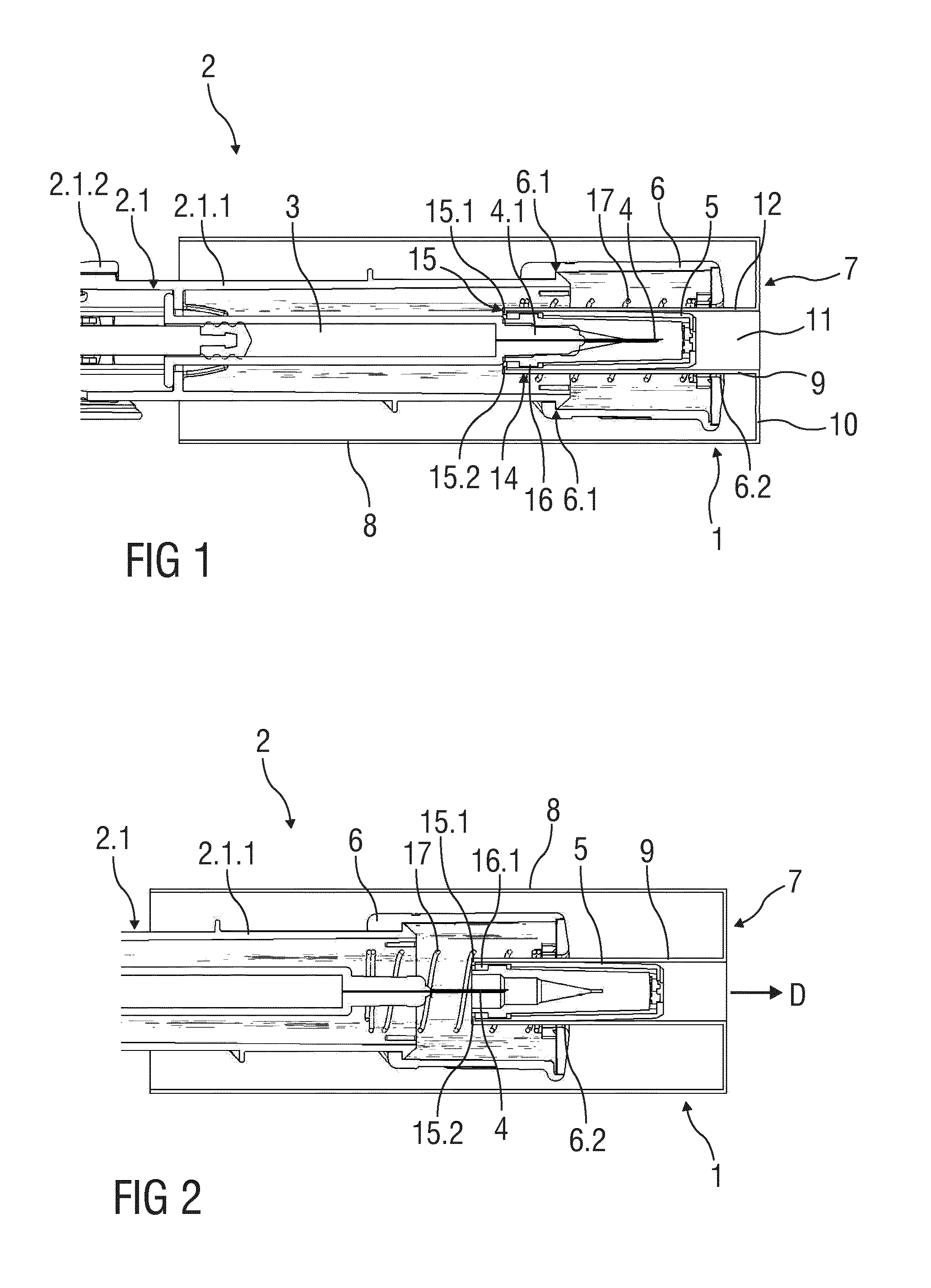
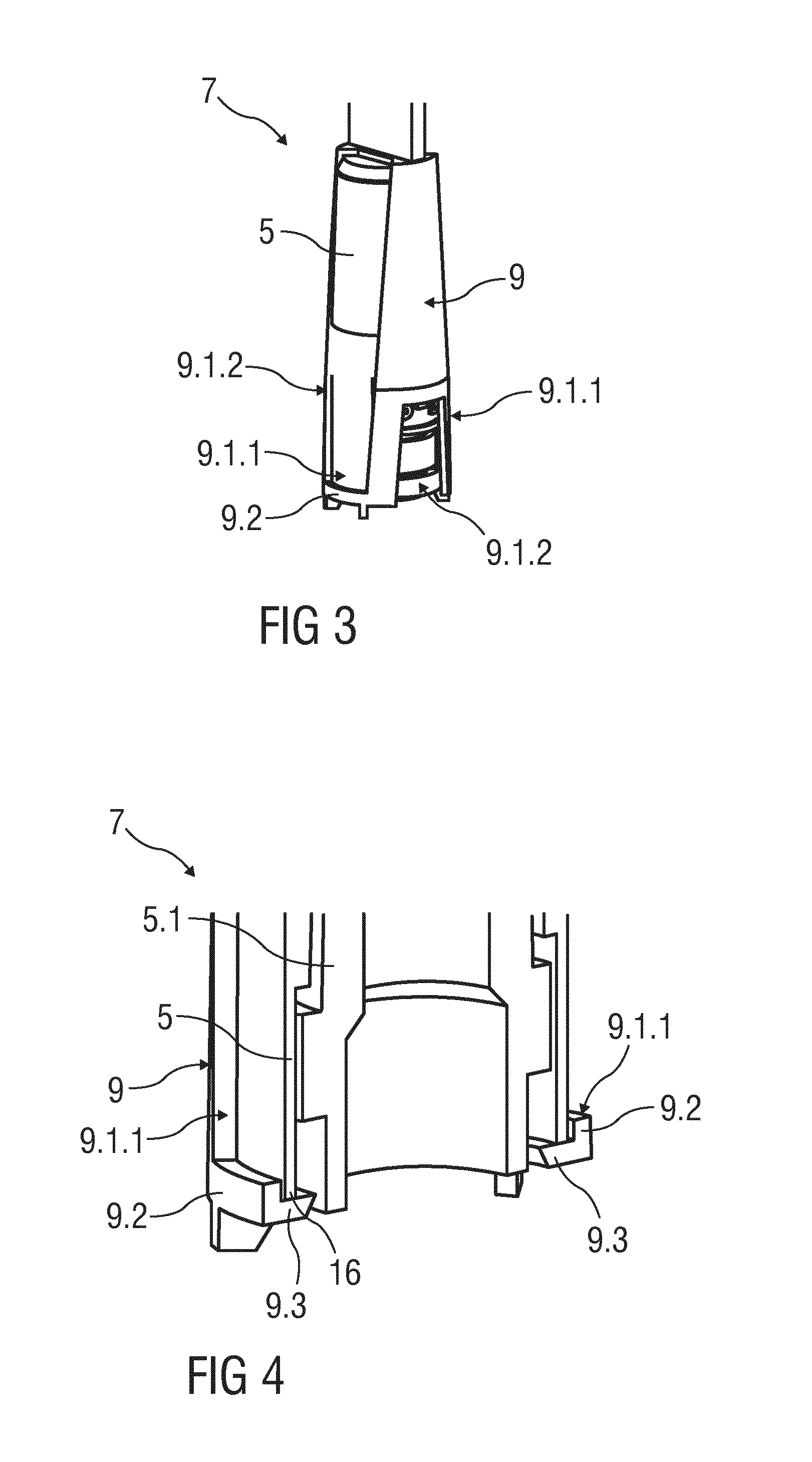
Drug Delivery Device
InactiveUS20160325051A1Reduce riskSimple to useAutomatic syringesInfusion needlesBiomedical engineeringDrug delivery
The invention refers to a drug delivery device (2) comprising a housing (2.1) capable of receiving and containing a container (syringe 3) and a needle safety device (1). The needle safety device (1) comprises a needle cap (5.1) arranged to cover and protect a needle (4), a needle shield (6) relatively movable with respect to the housing (2.1) to cover and protect the needle (4) and a needle cap remover (7). The needle cap remover (7) has an outer part (8) adapted to be arranged to the housing (2.1) and to cover the needle shield (6) and partly the housing (2.1) and an inner part (9) adapted to be arranged to the needle cap (5.1).
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
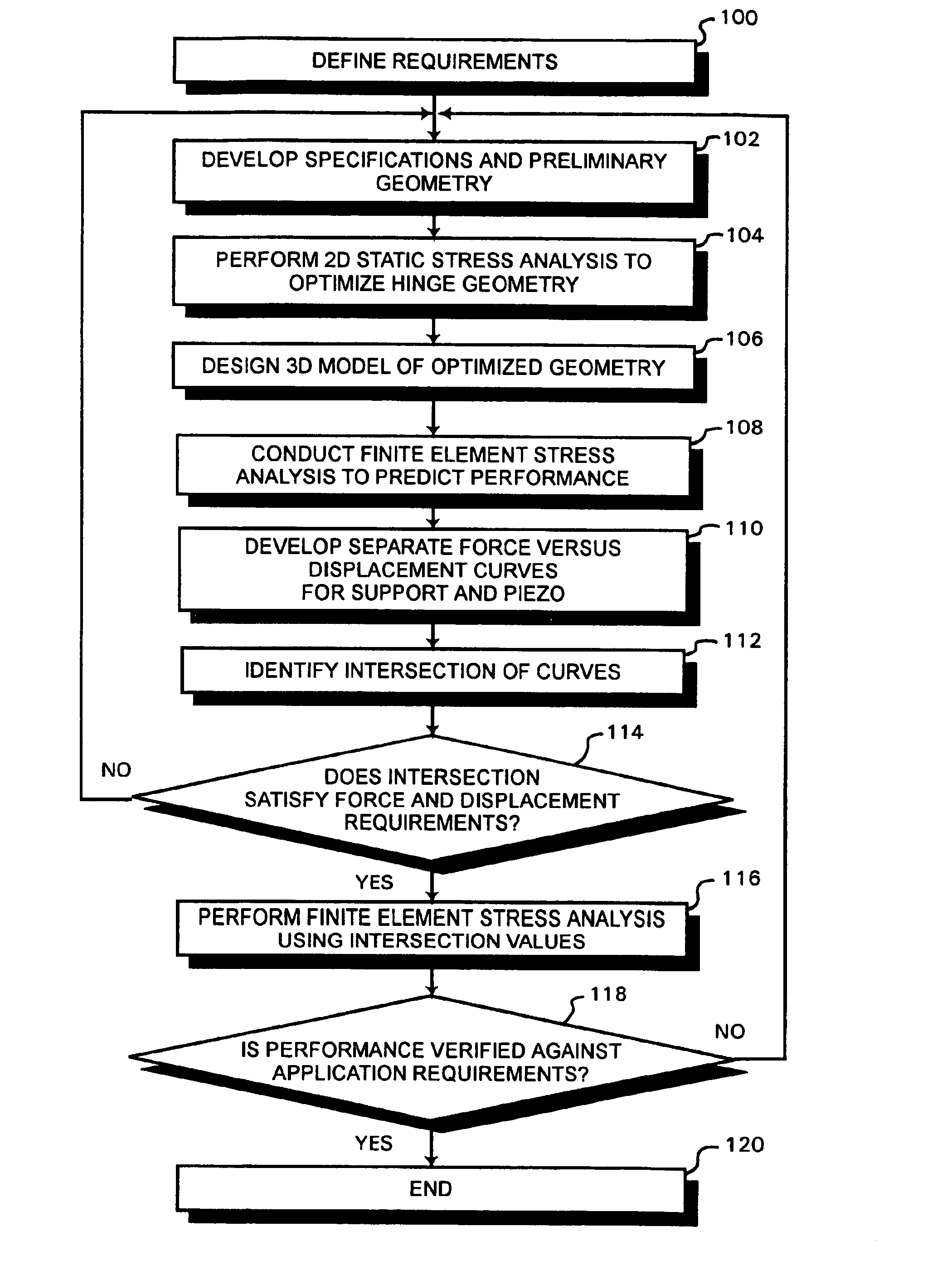
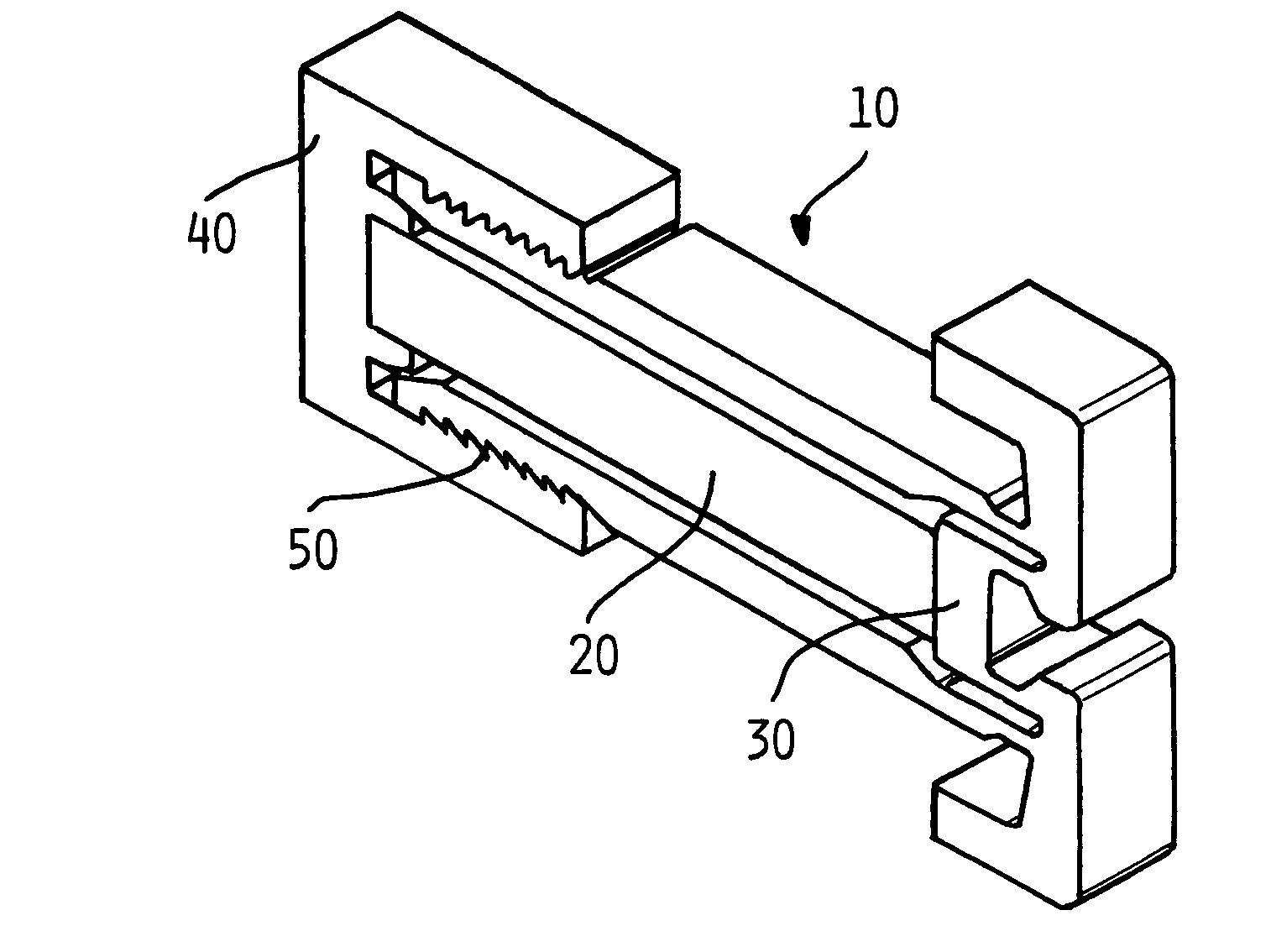
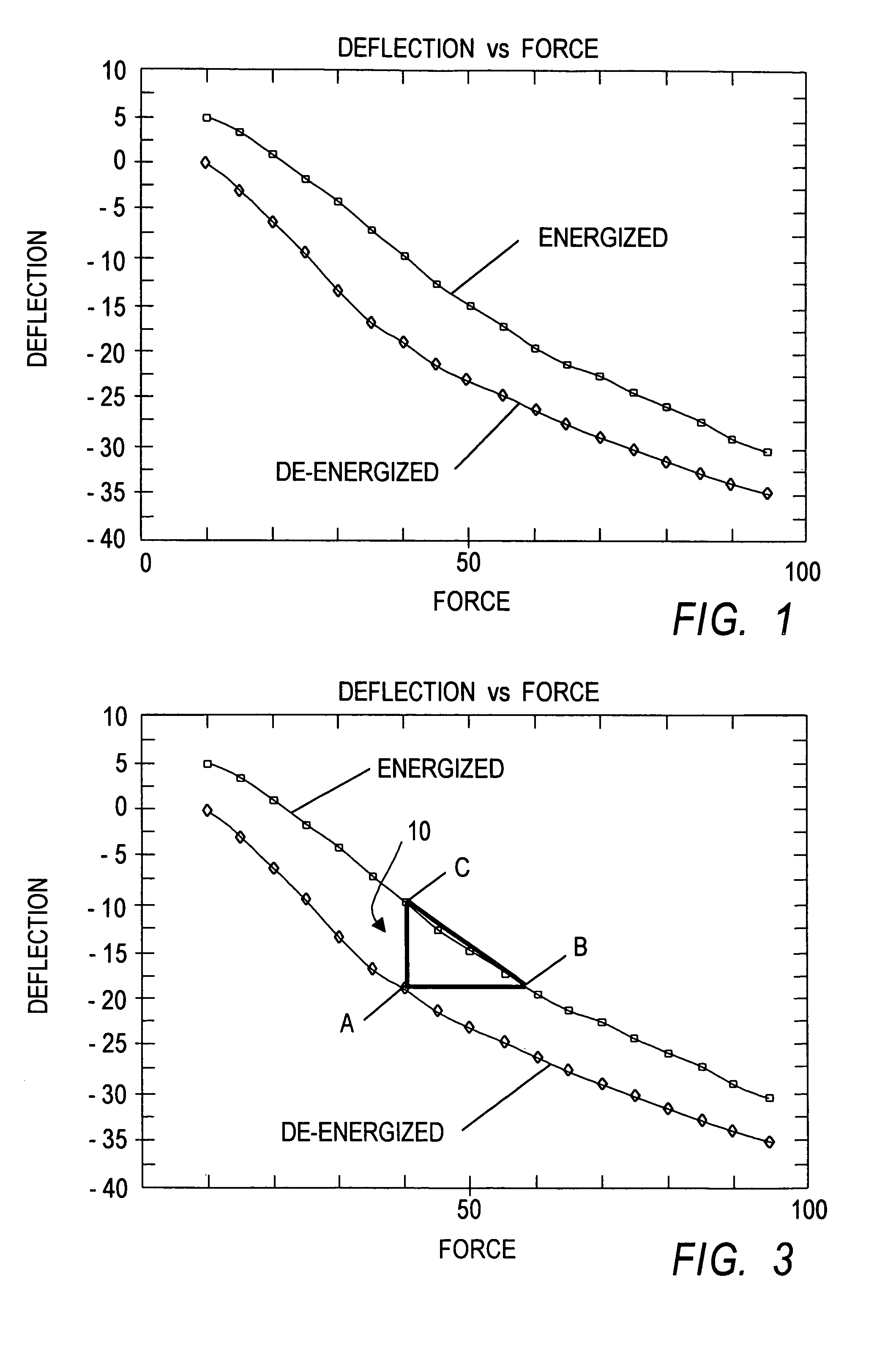
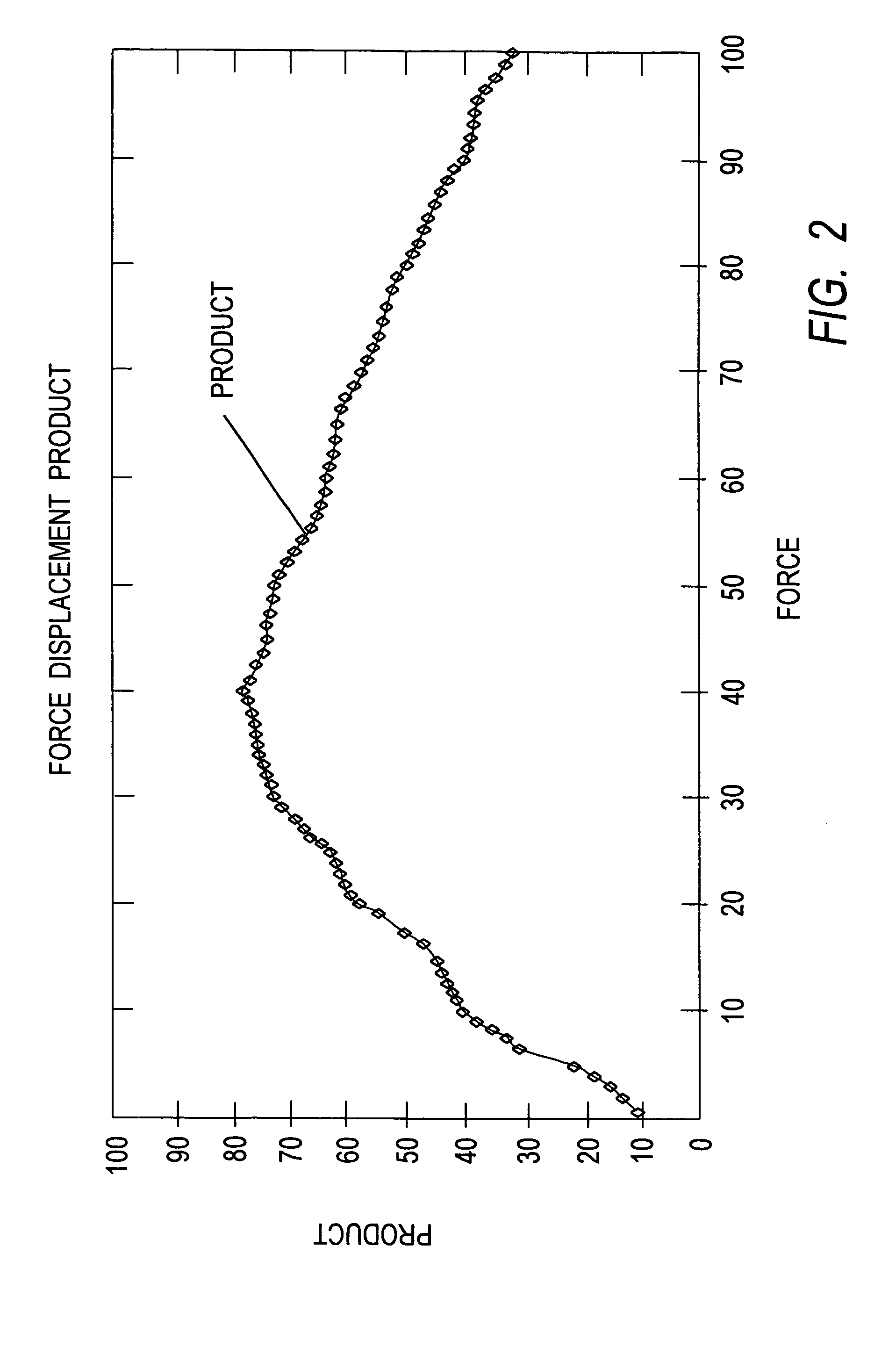
Apparatus and process for optimizing work from a smart material actuator product
InactiveUS7368856B2Improve Smart EffectsShort lifePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionElectricityHysteresis
An apparatus and process for pre-loading an electrically stimulated smart material actuator product to obtain maximum work from the actuator. When a smart material actuator is optimally pre-loaded certain desirable characteristics become apparent, such as work, operational frequency, hysteresis, repeatability, and overall accuracy. When used in conjunction with a mechanically leveraged actuator structure the smart material actuator can be used to its greatest potential. Since the mechanically leveraged actuator can be based on the maximum work provided by the smart material actuator, certain attributes such as the force, and displacement of total system can be adjusted without loss to system efficiency. Pre-loading methods and a determination of the optimal pre-load force are disclosed. Each smart material actuator type has a unique work curve. In the design of an actuator assembly, the process of optimizing uses the unique work curve to optimize the design for the requirements of the particular application. The unique work curve is used by finding the place where the smart material actuator is capable of providing the most work in order to set the optimum pre-load point accordingly. Different mechanical pre-load techniques are provided.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com