Patents
Literature
45results about How to "Data Retention Time Enhancement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
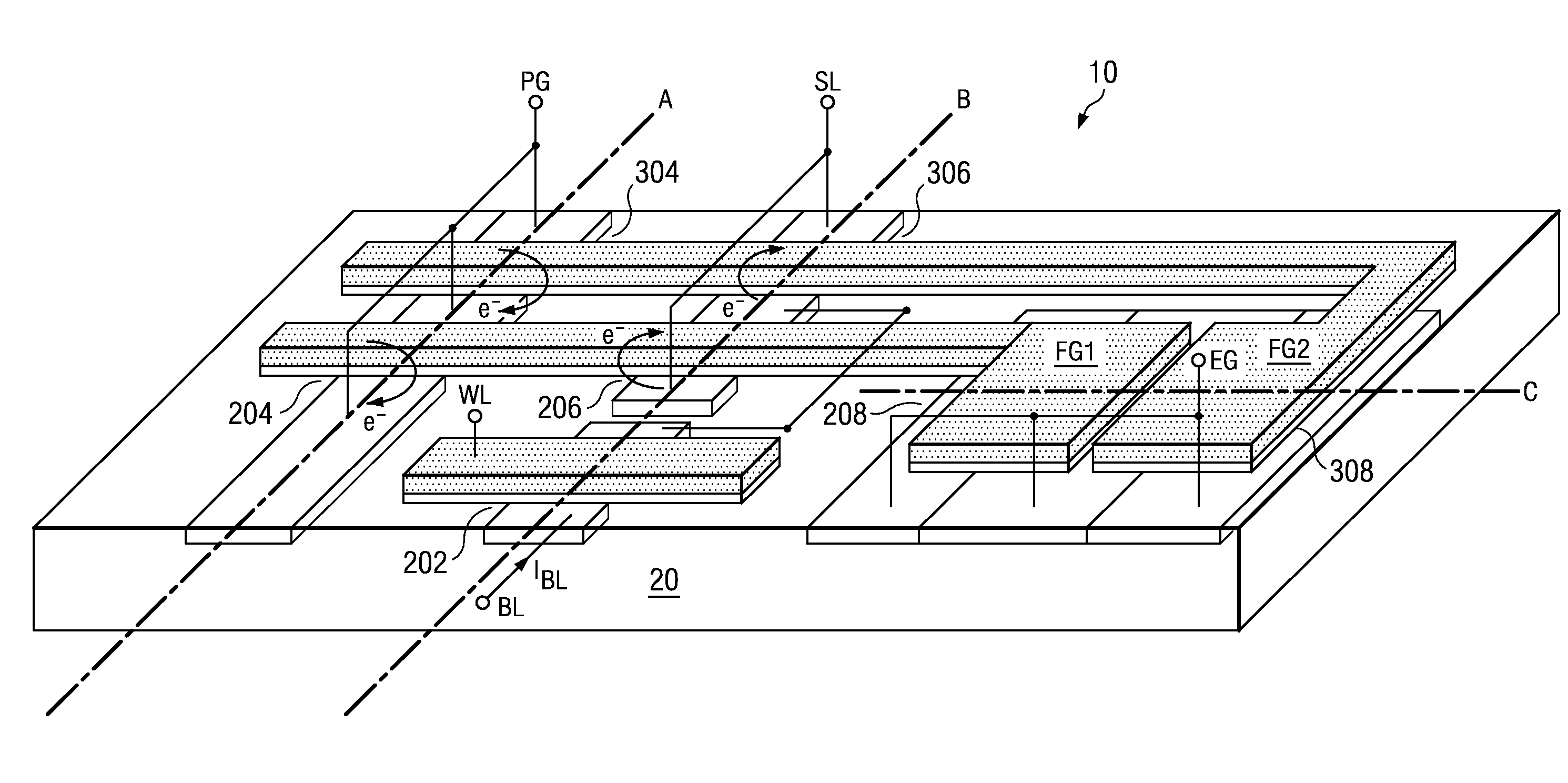
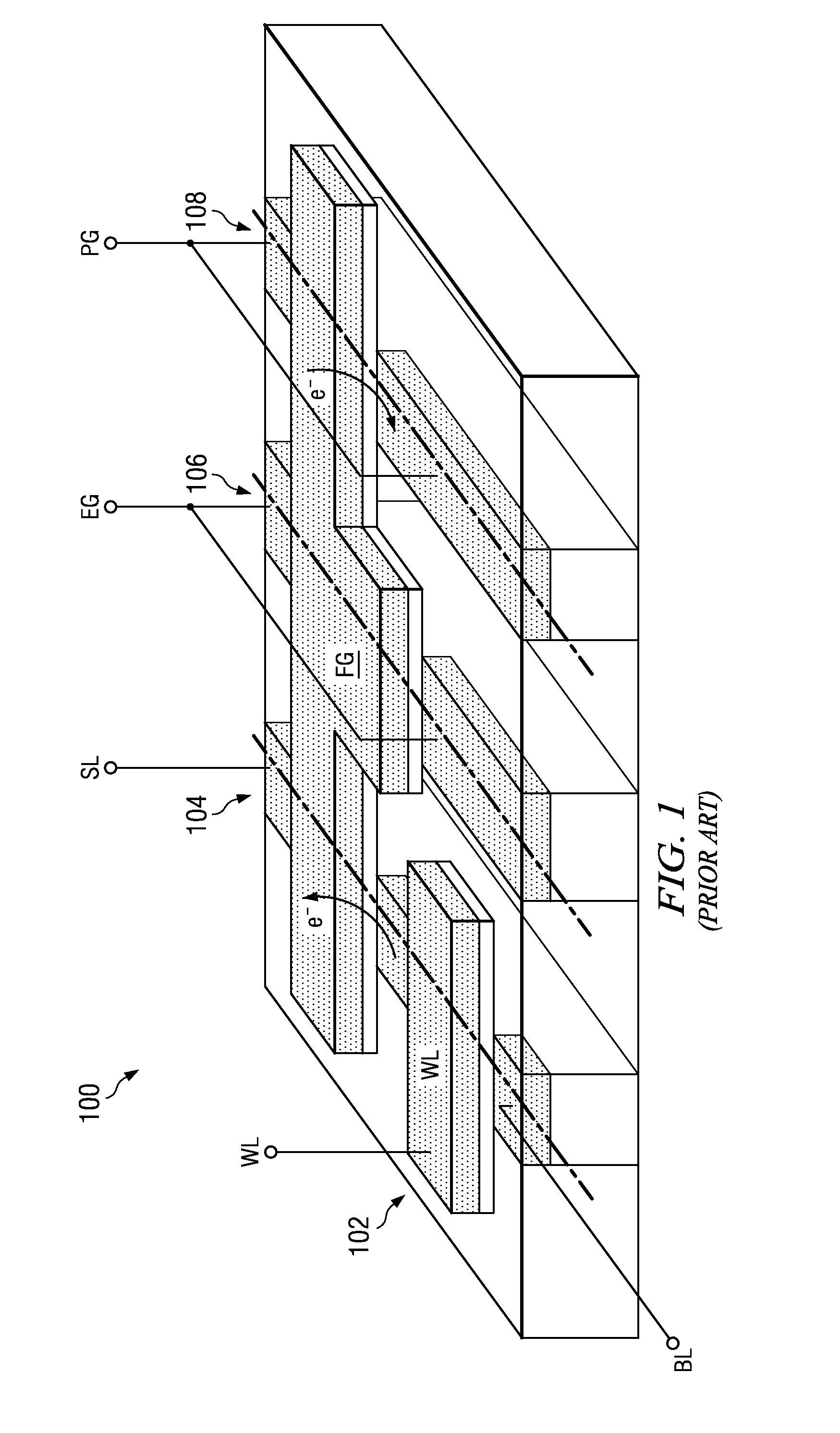
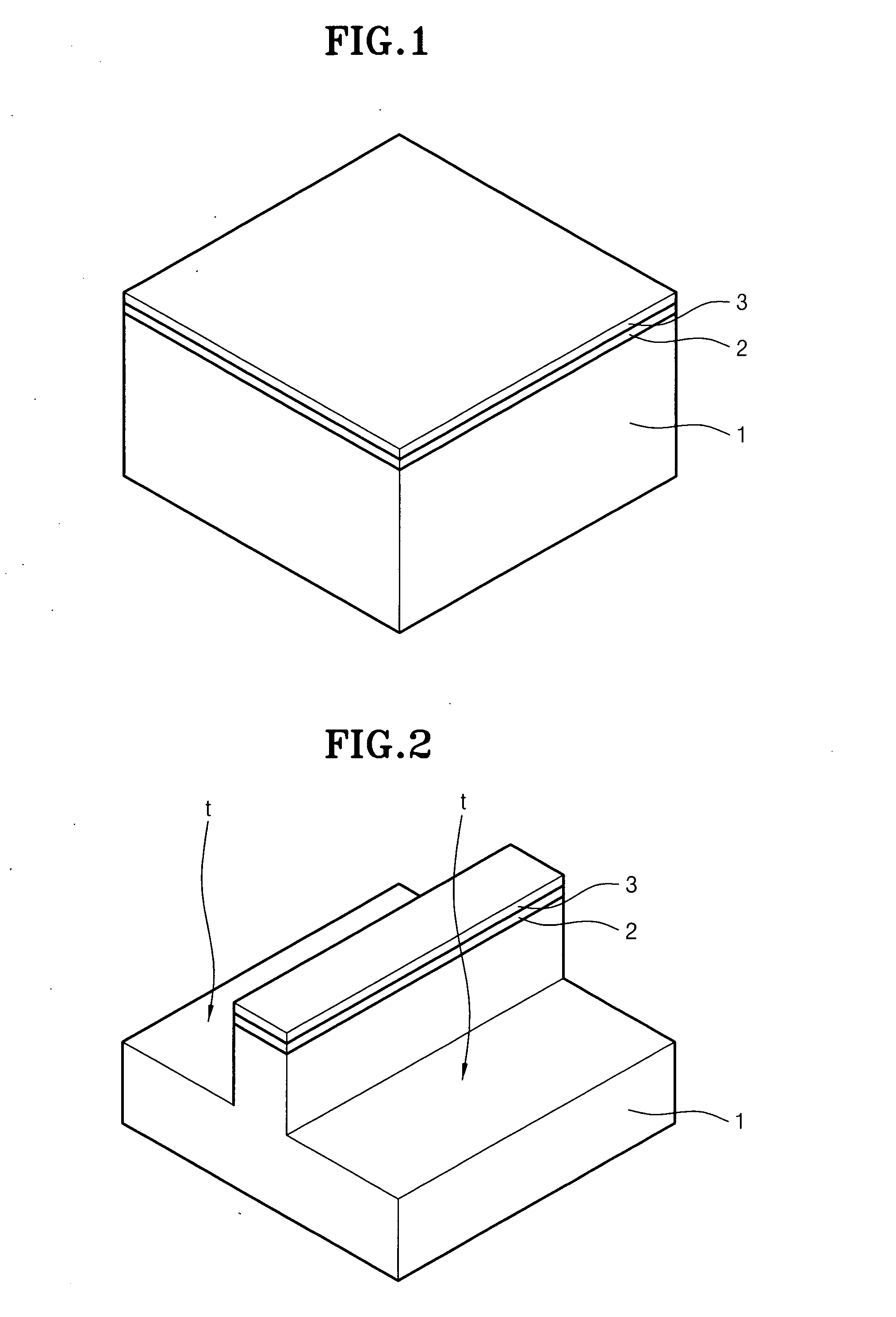
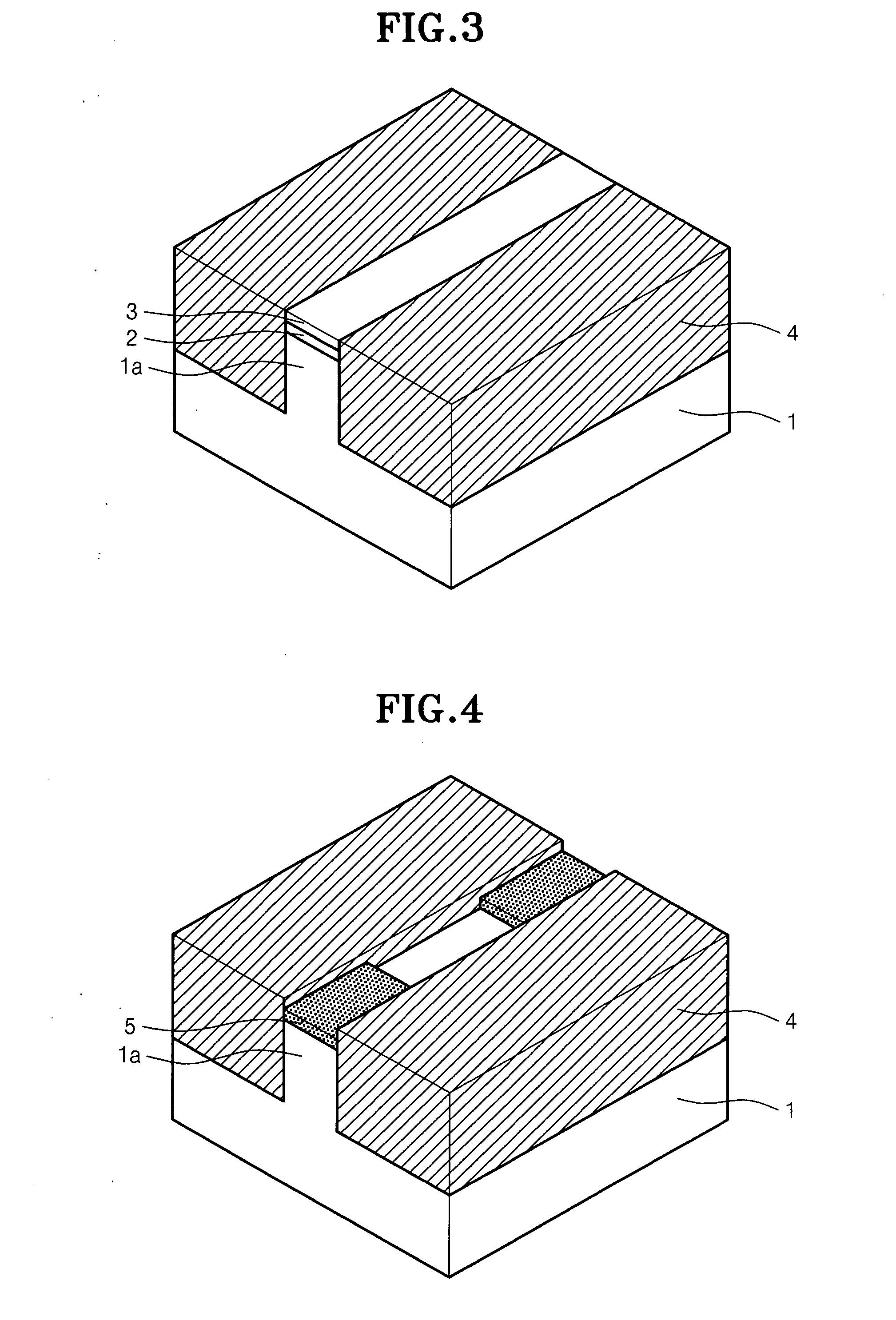
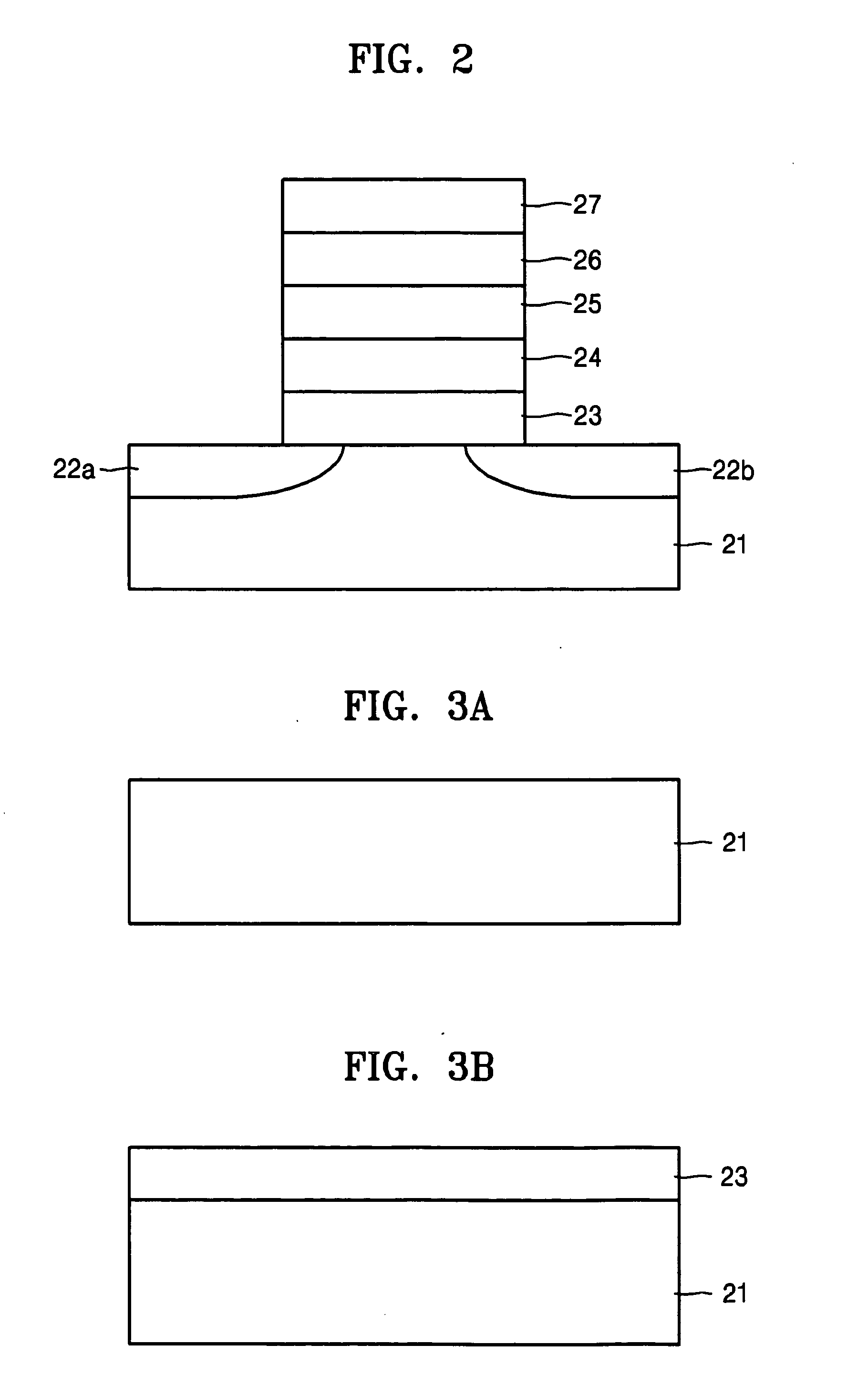
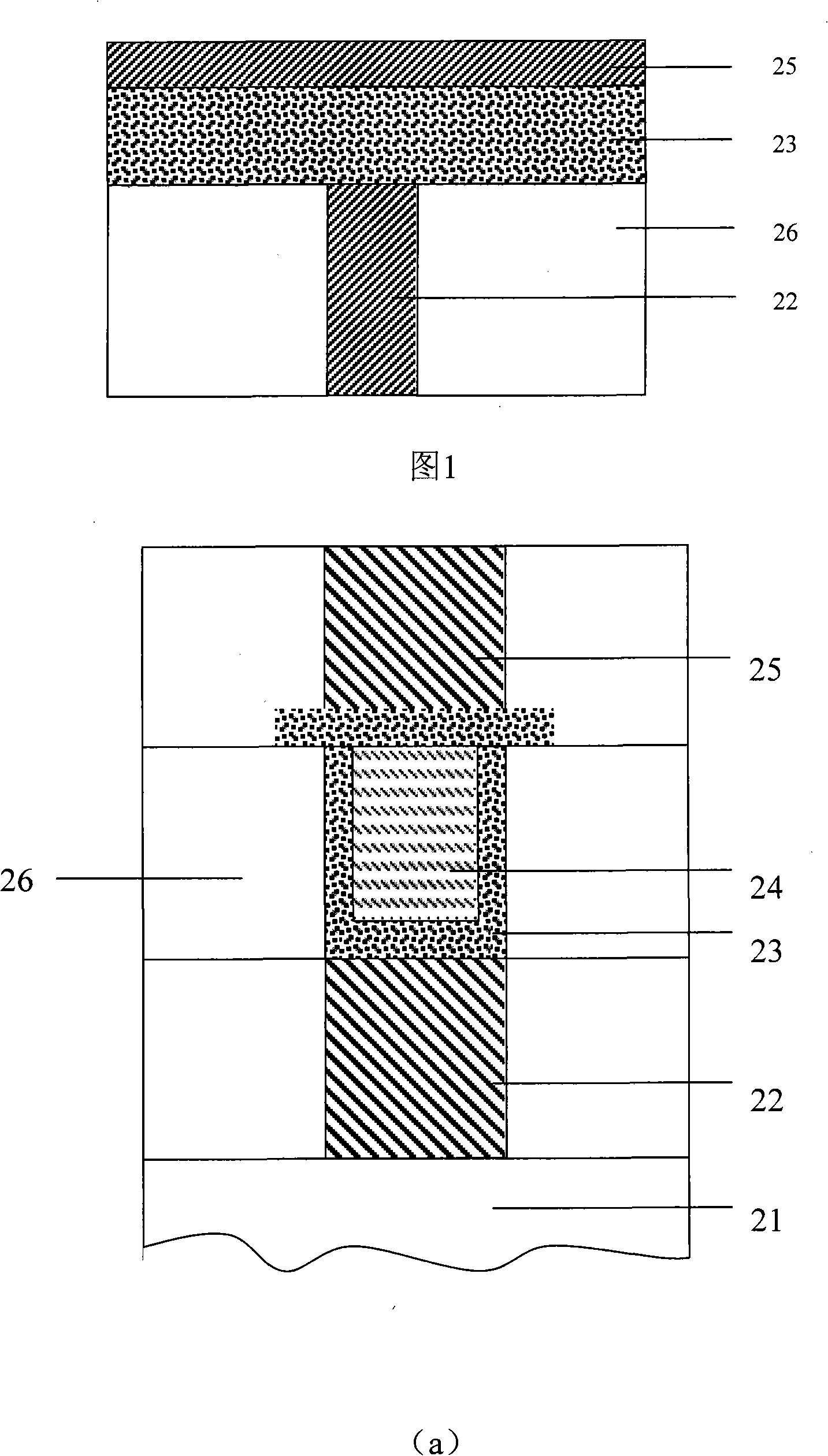
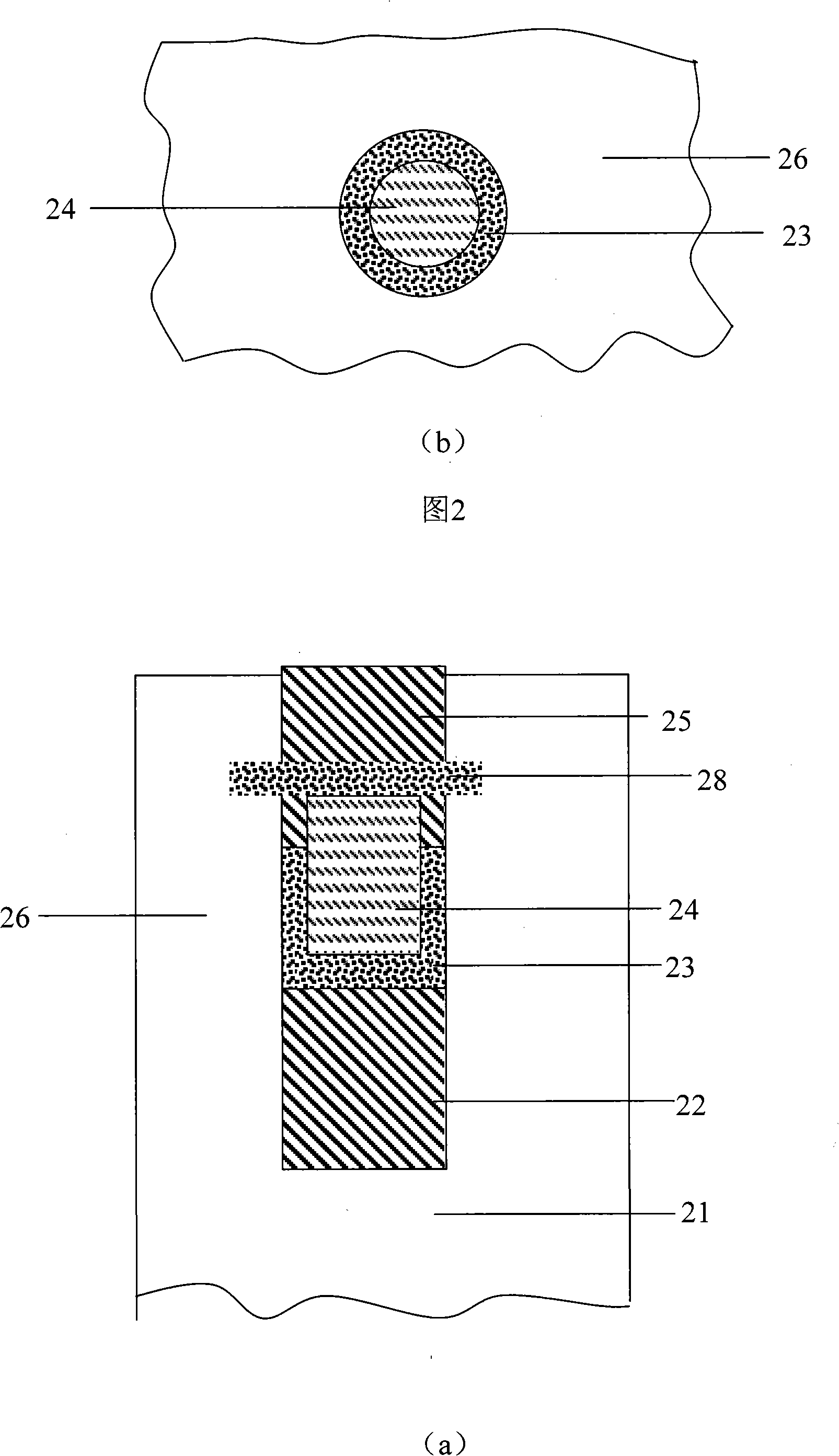
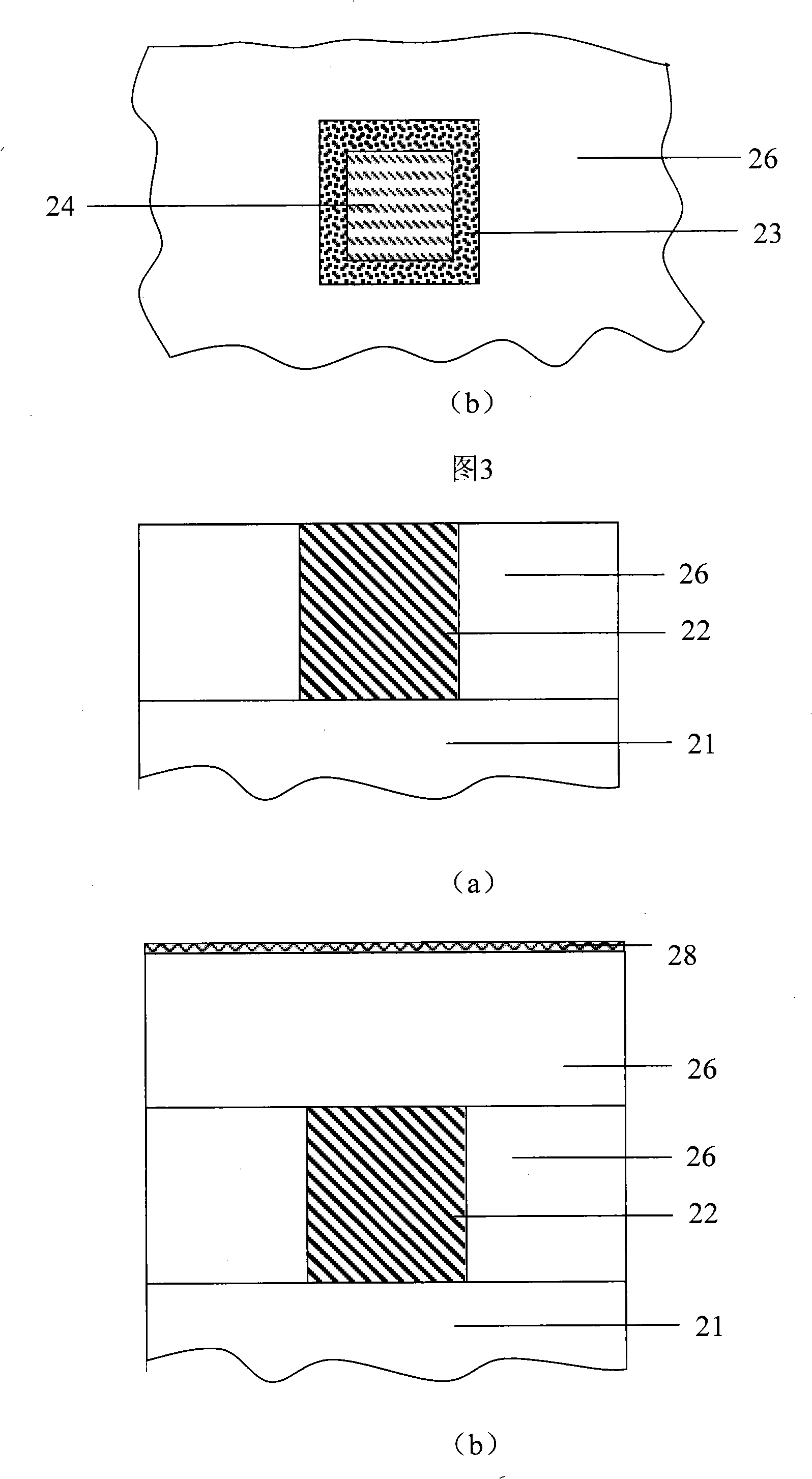
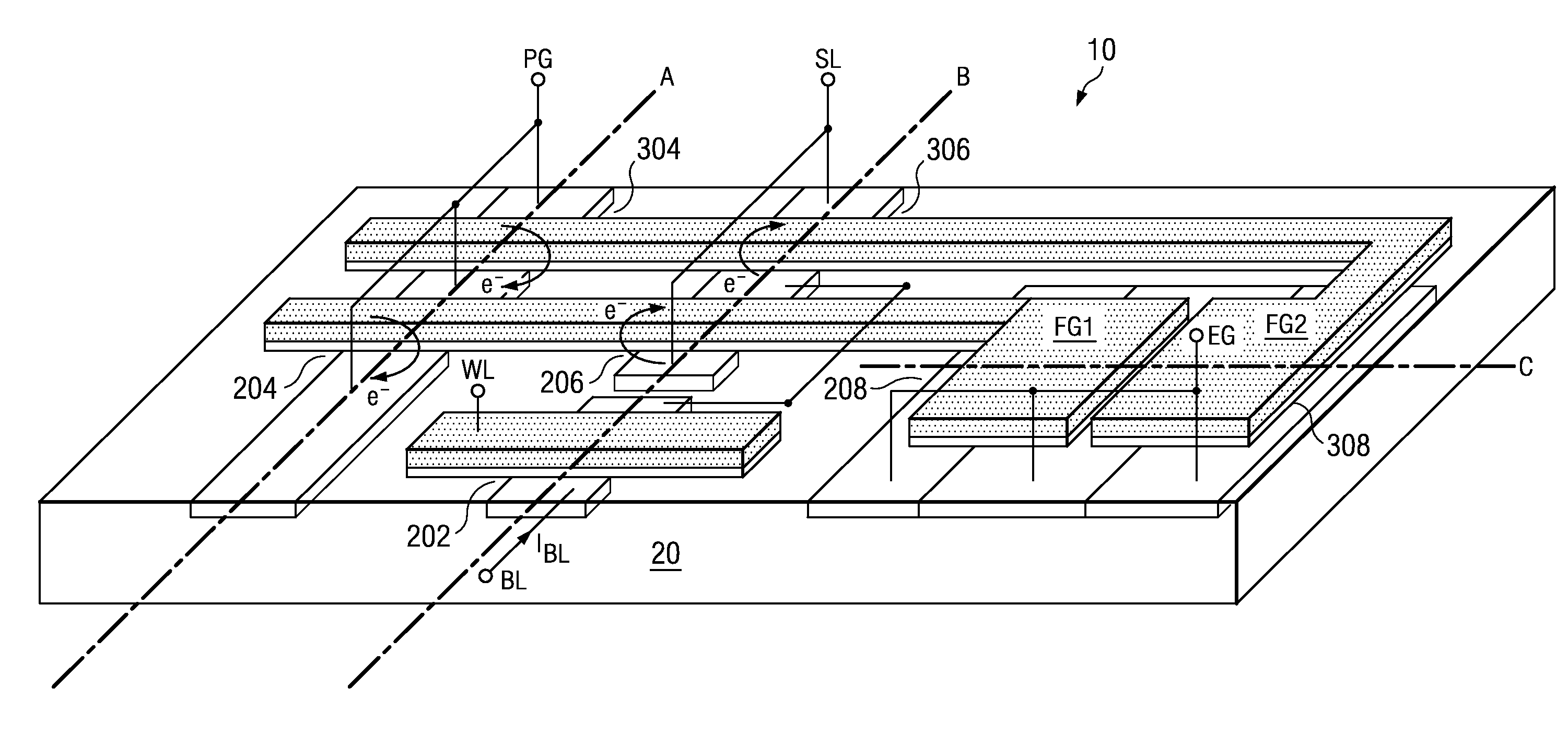
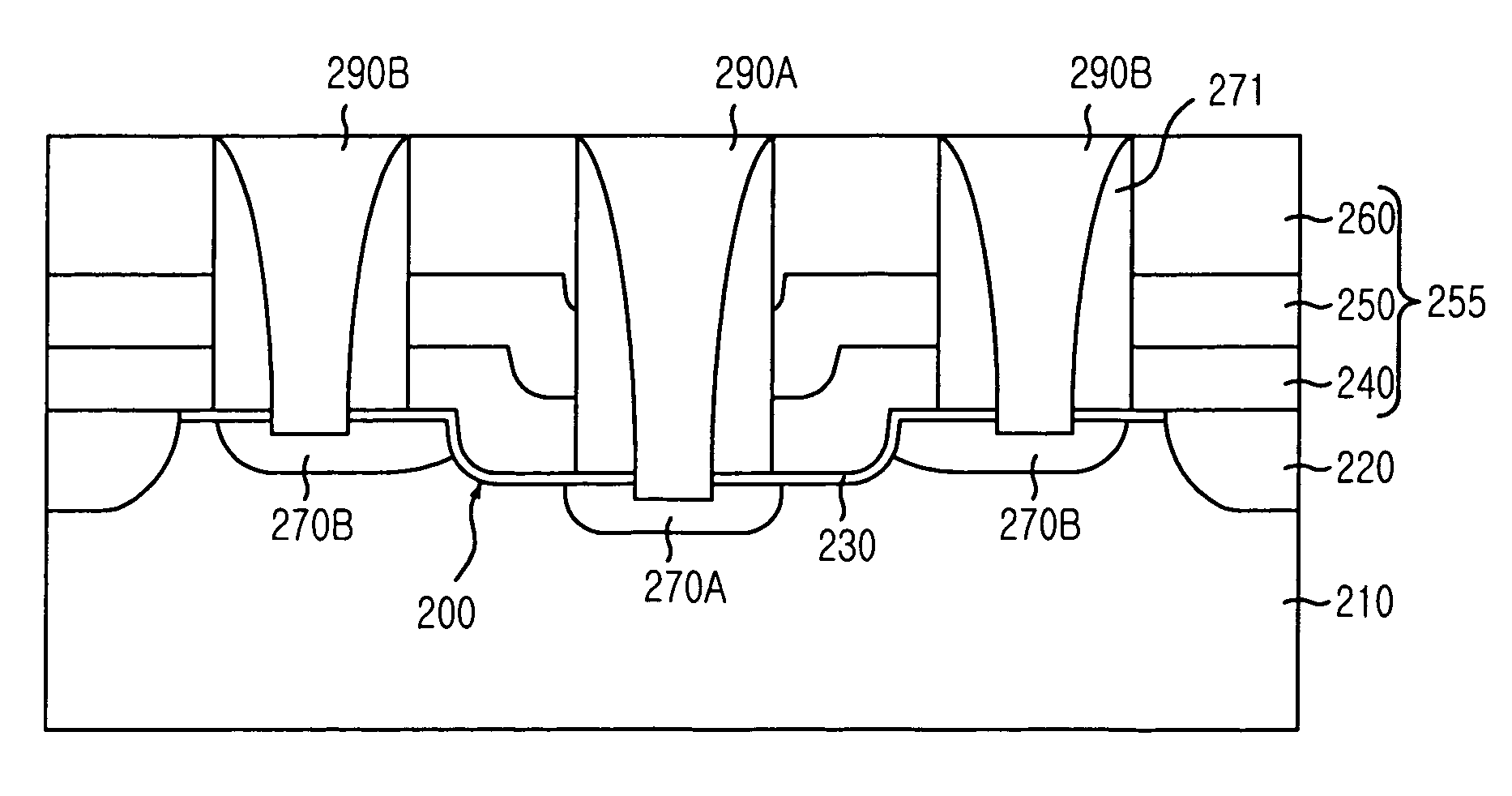
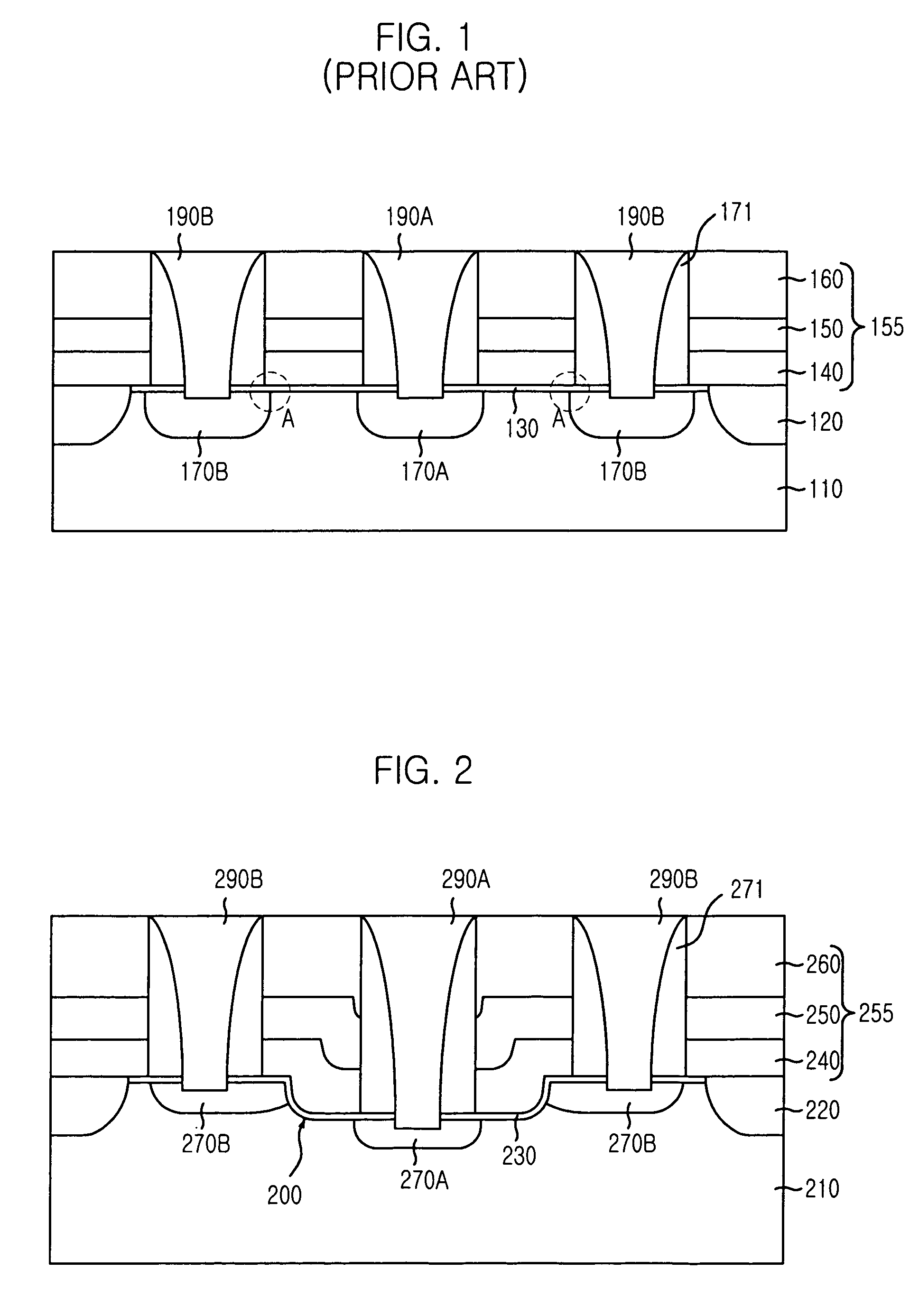
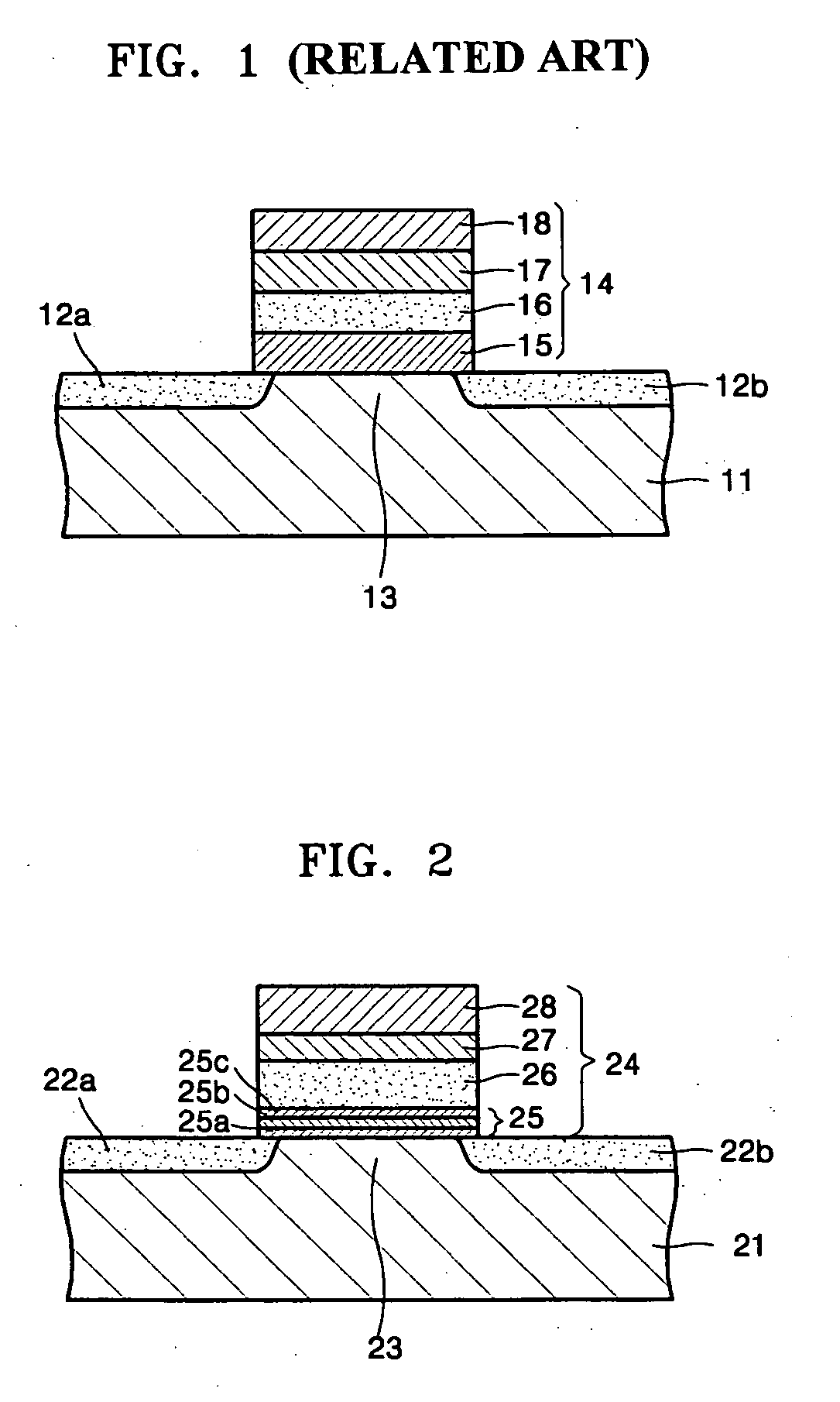
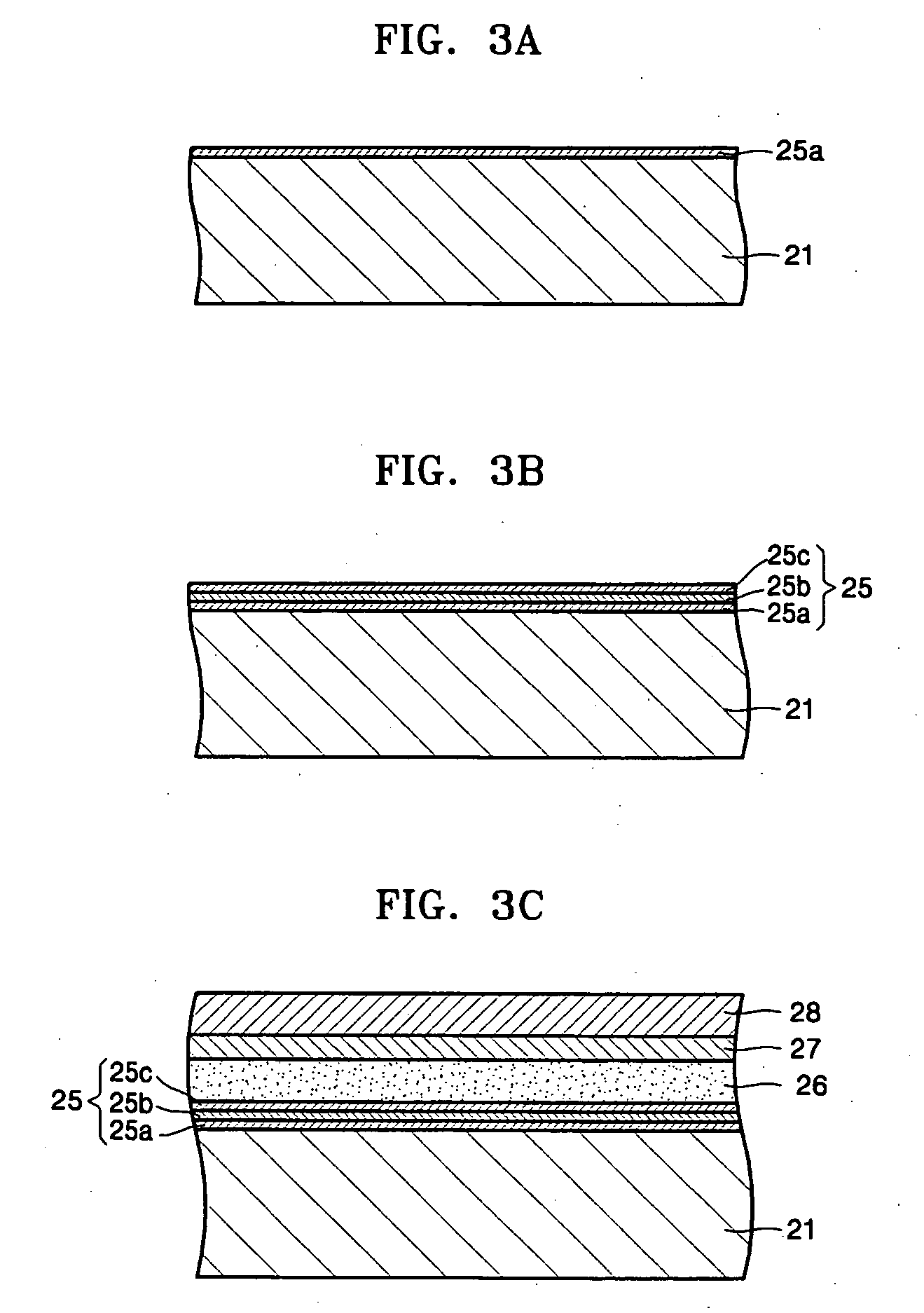
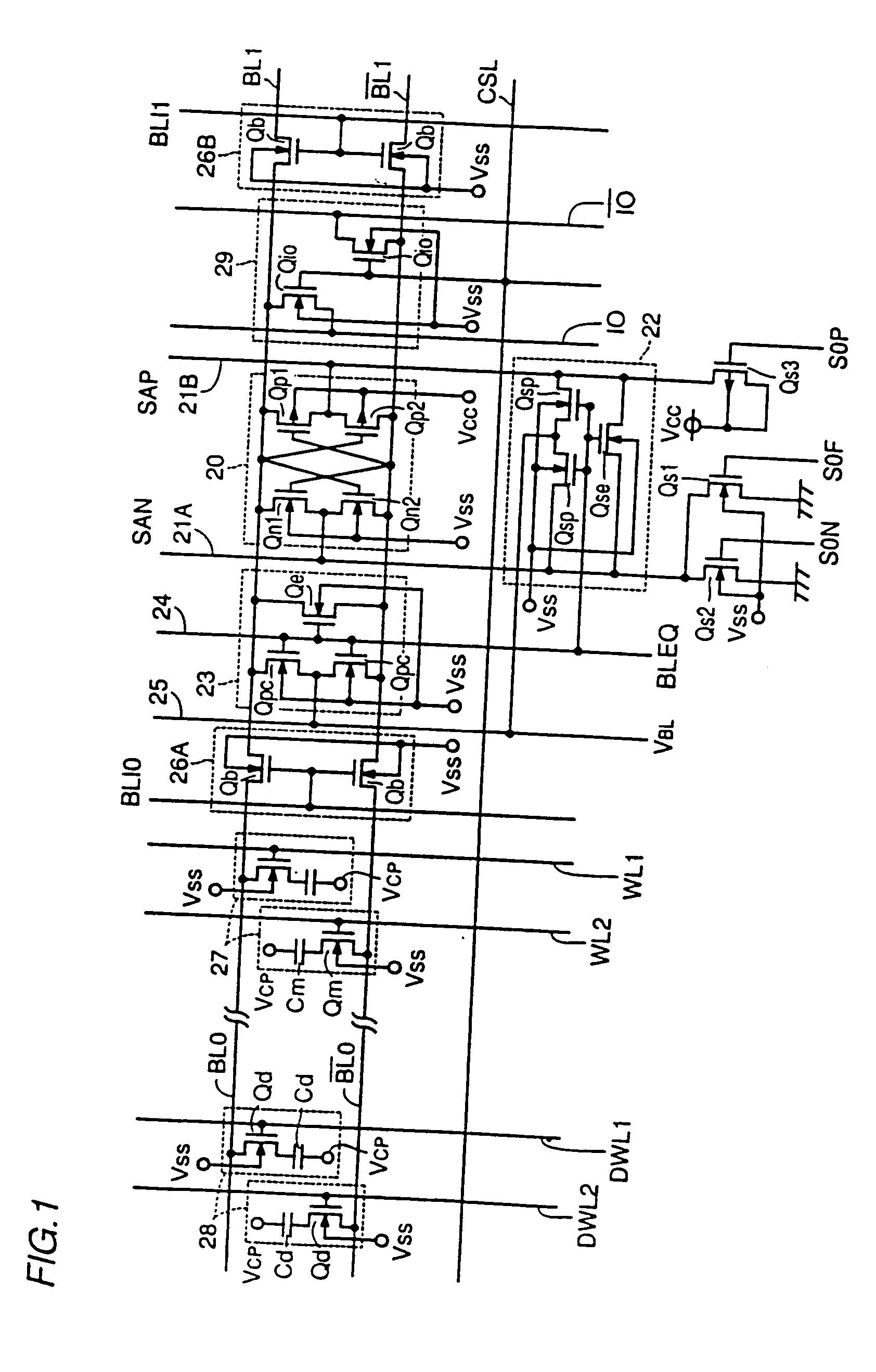
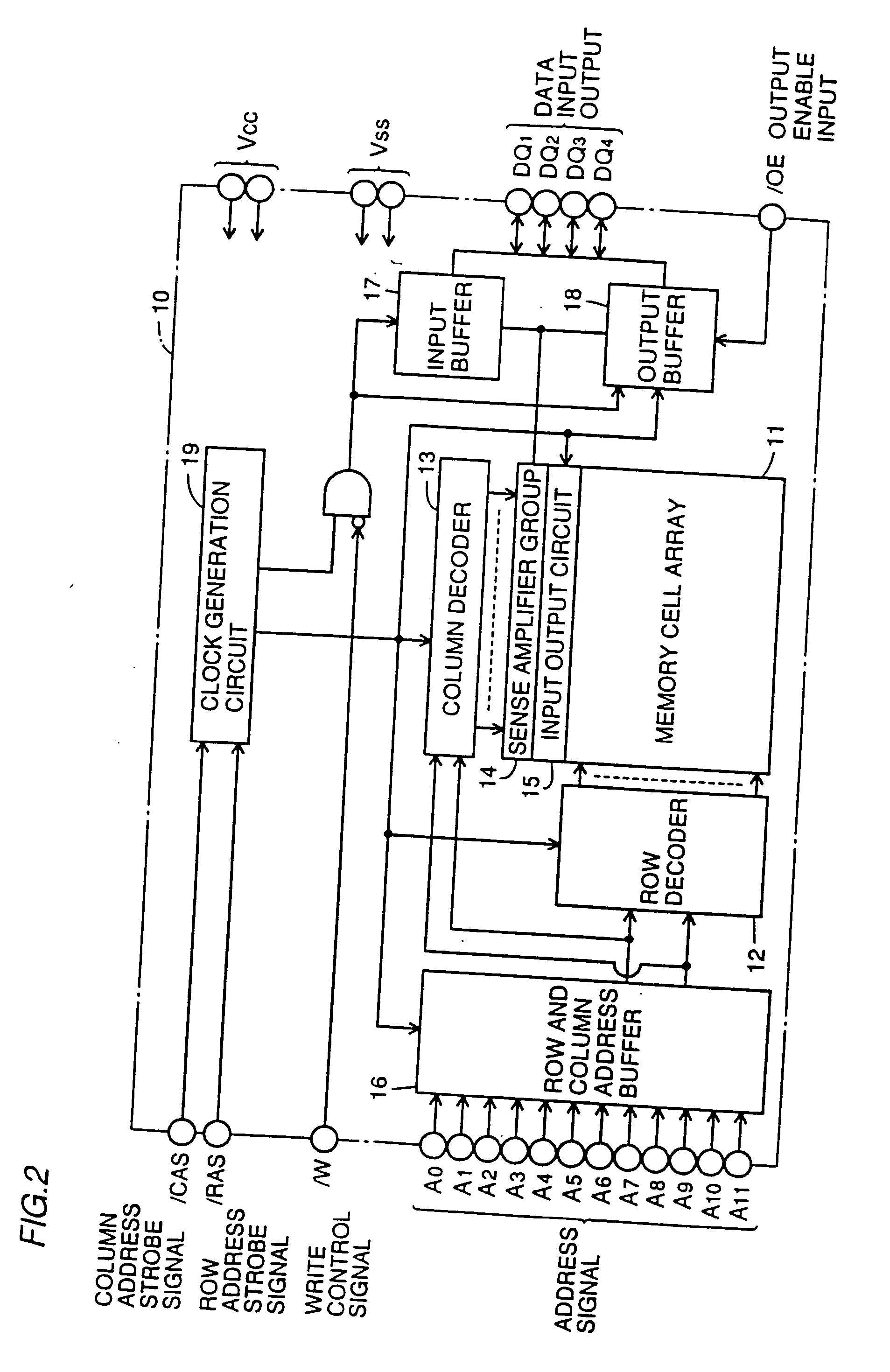
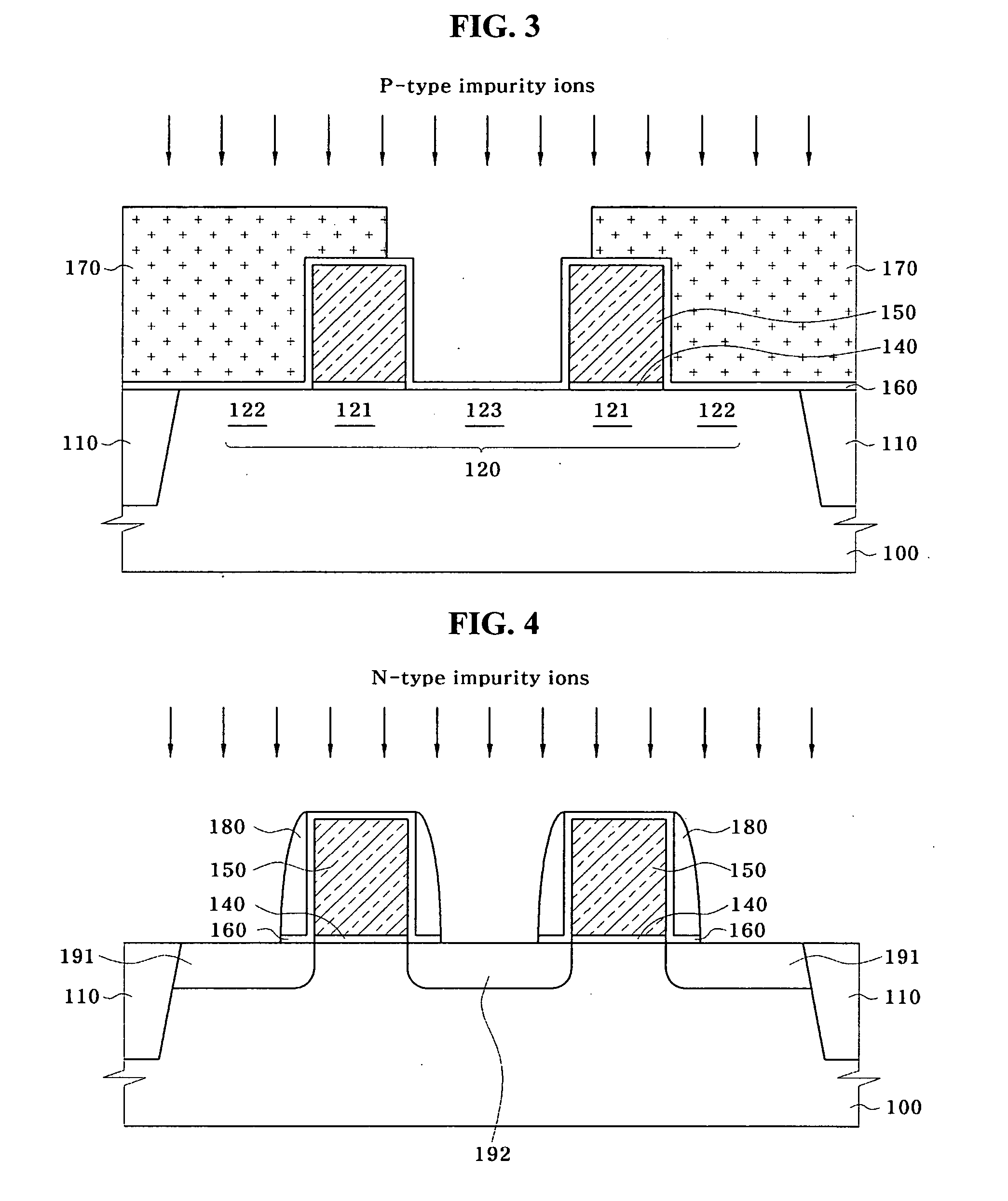
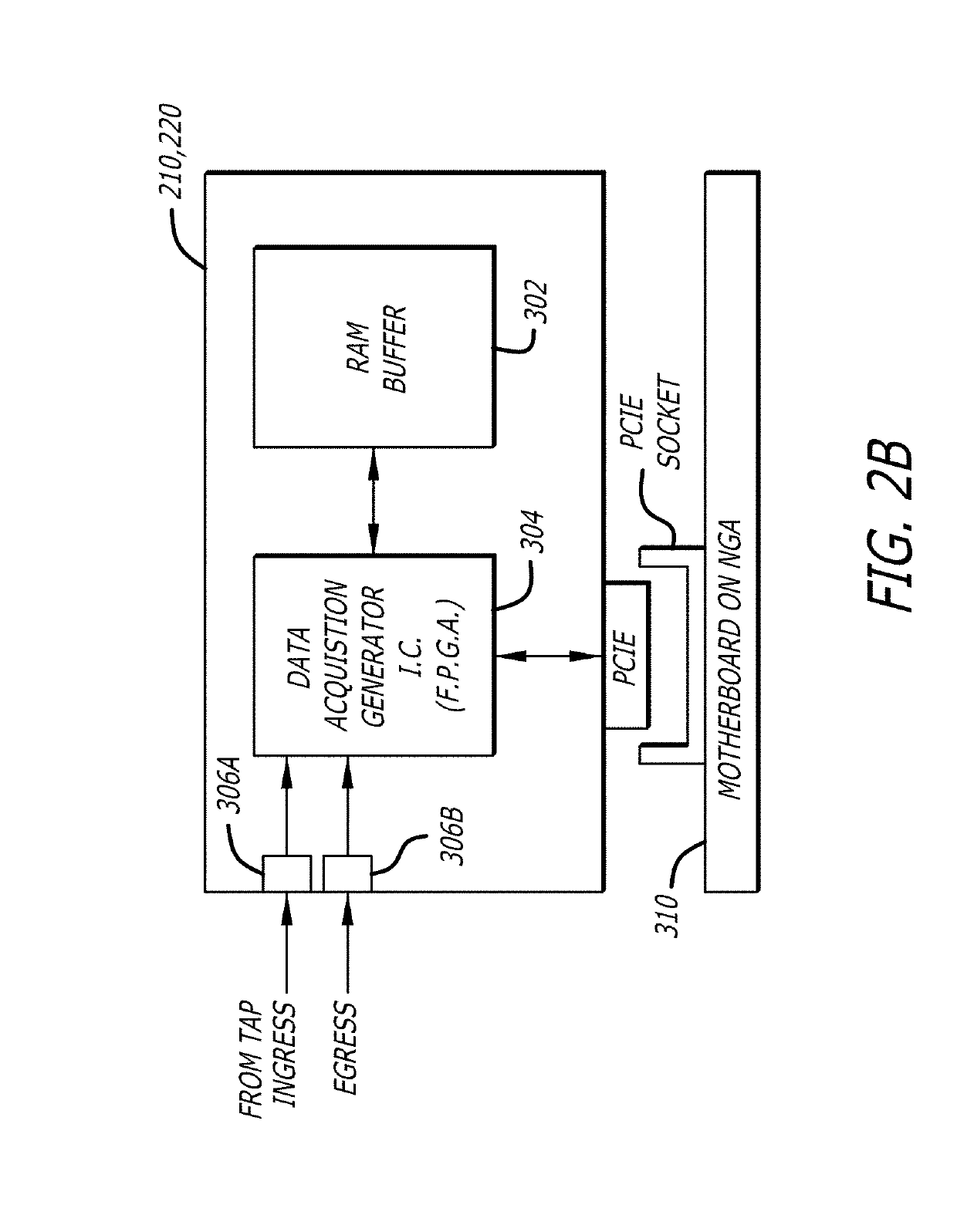
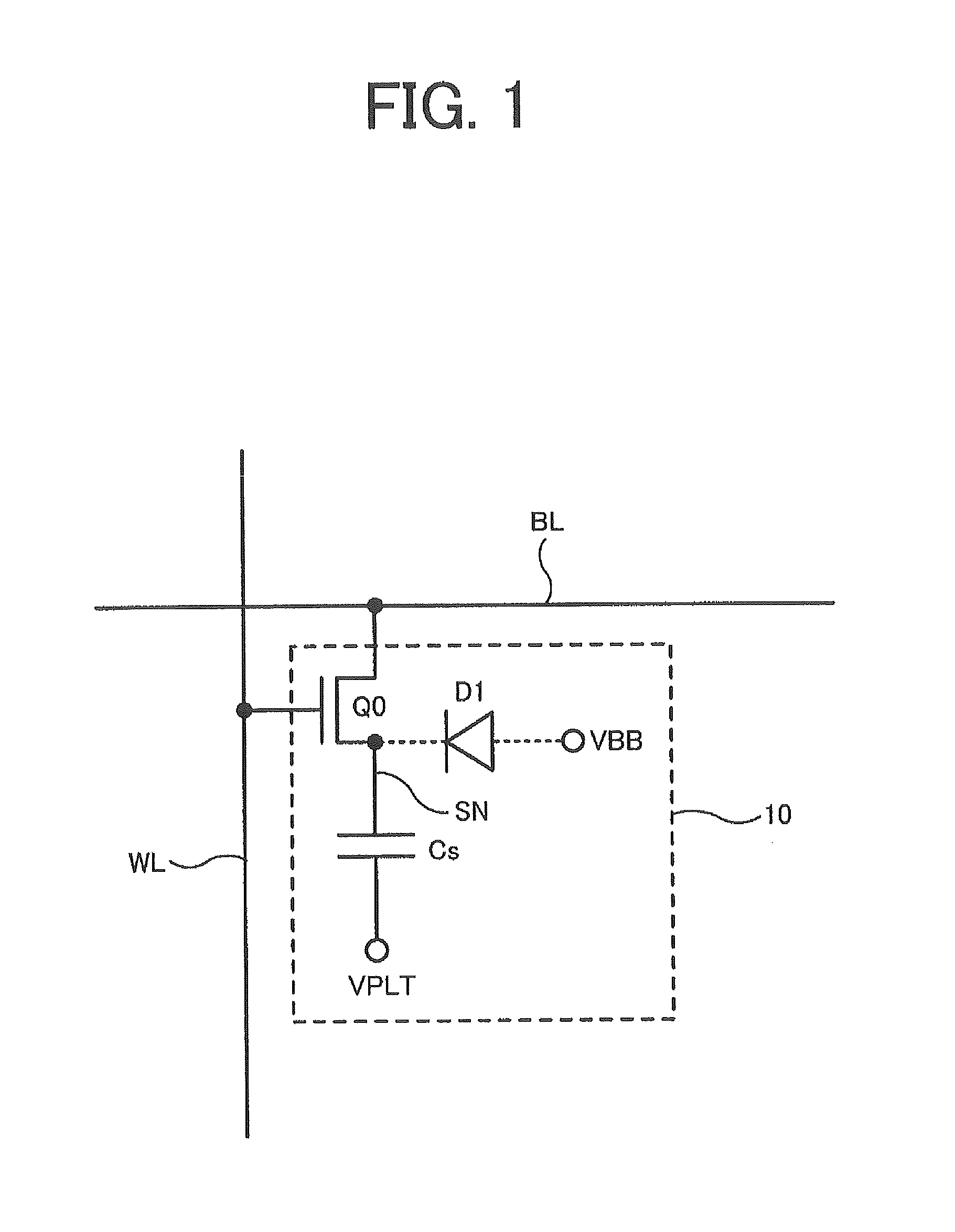
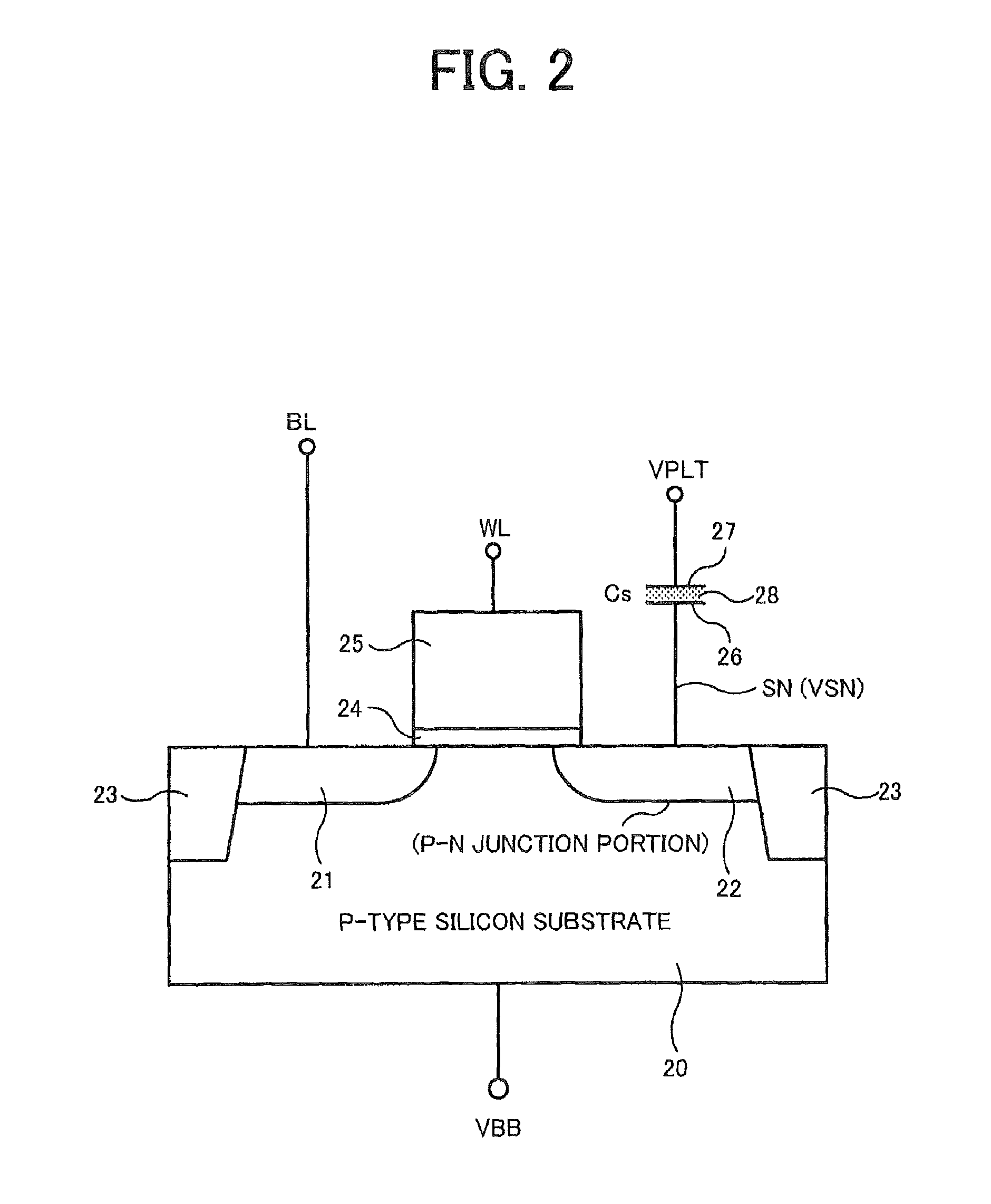
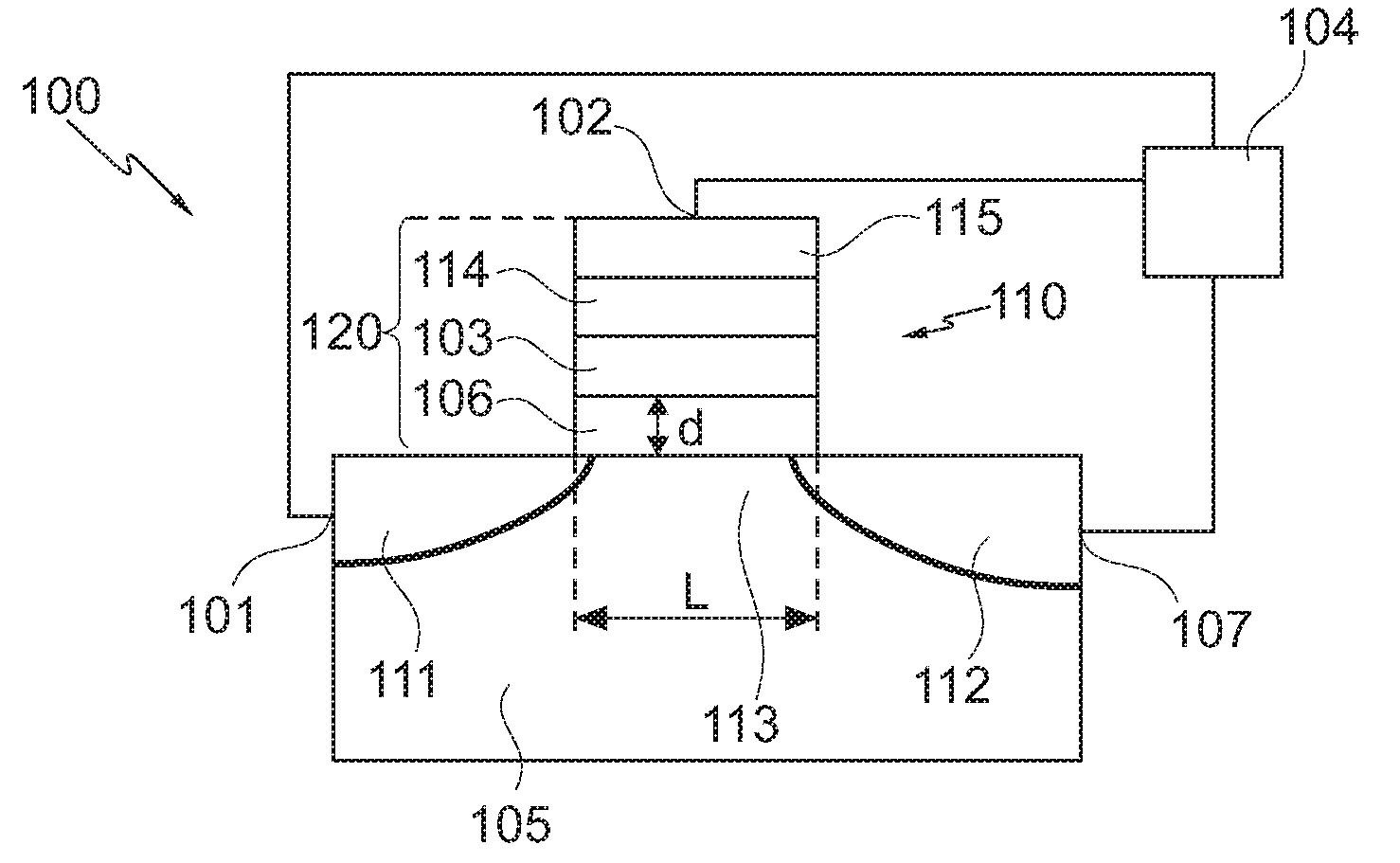
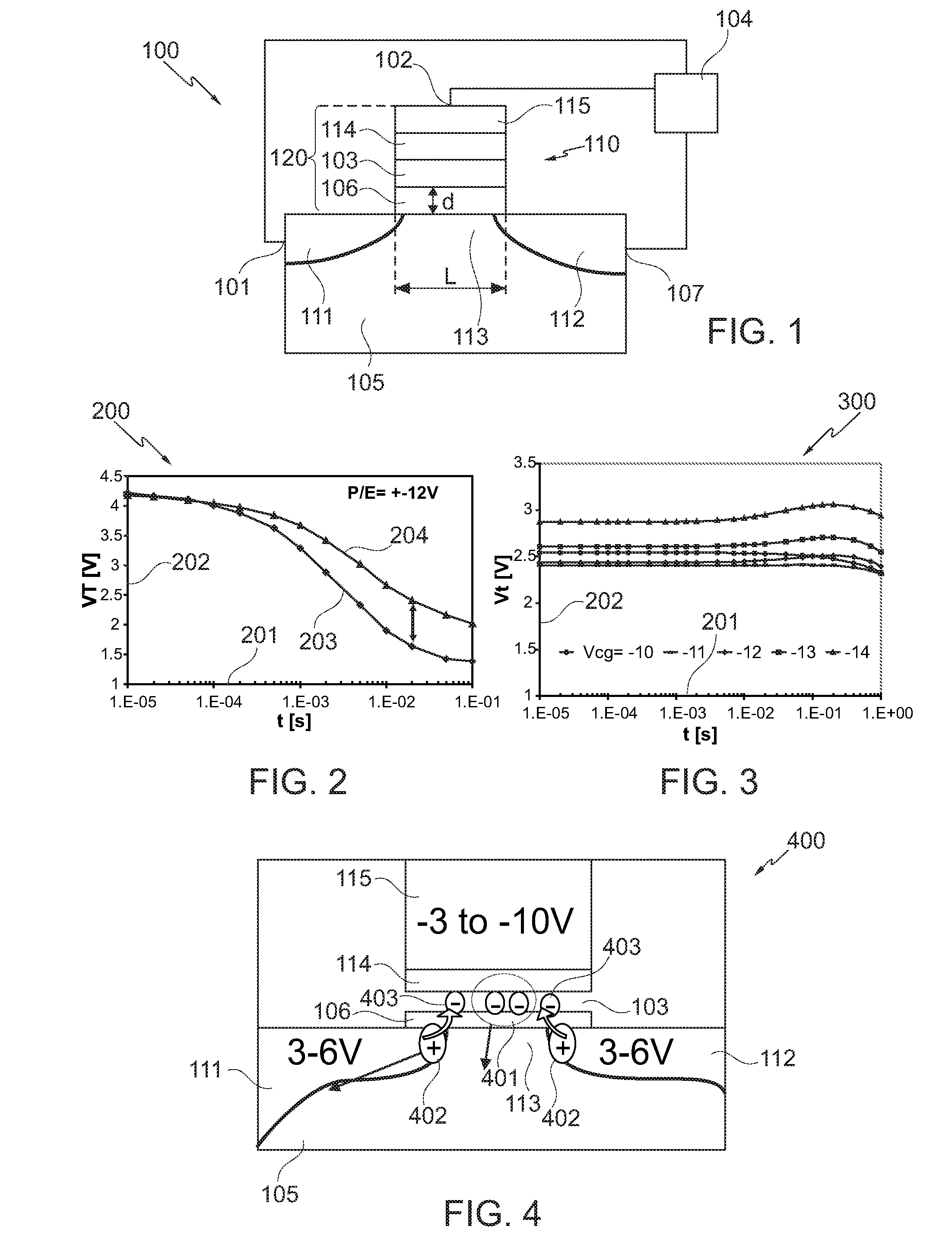
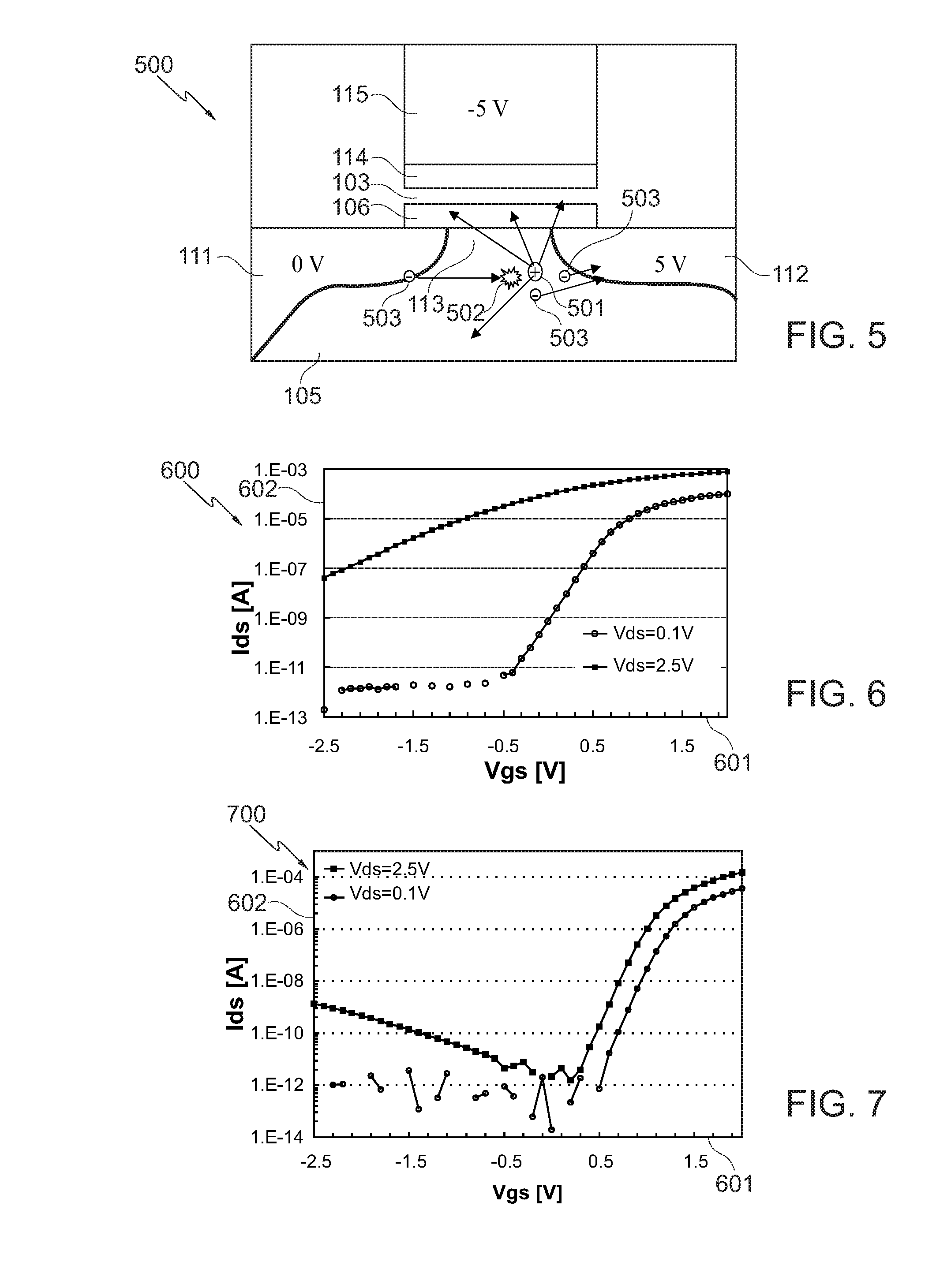
Logic Non-Volatile Memory Cell with Improved Data Retention Ability
InactiveUS20090159946A1Improve reliabilityData Retention Time EnhancementTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricSemiconductor
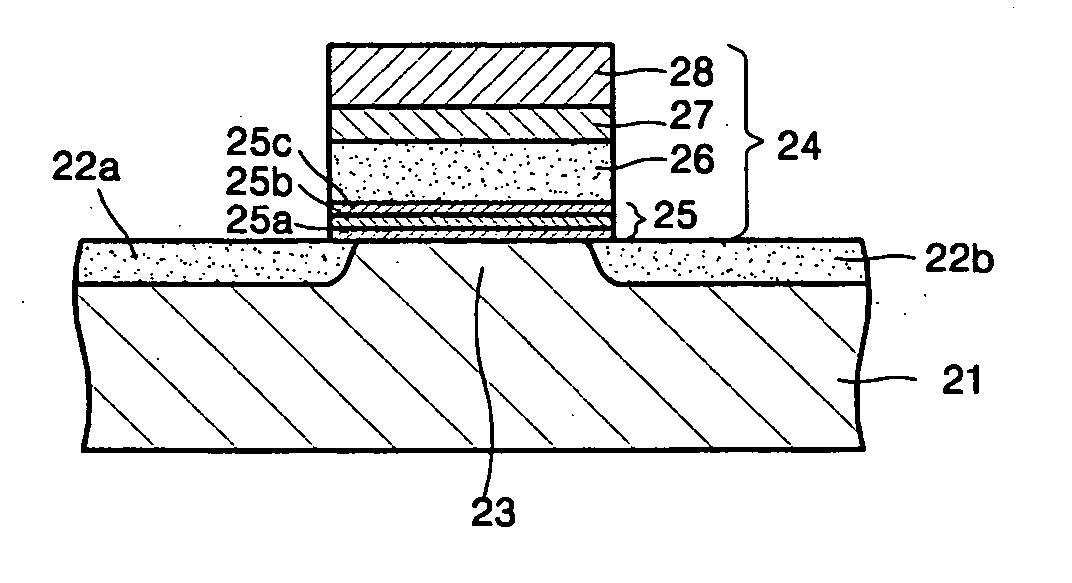
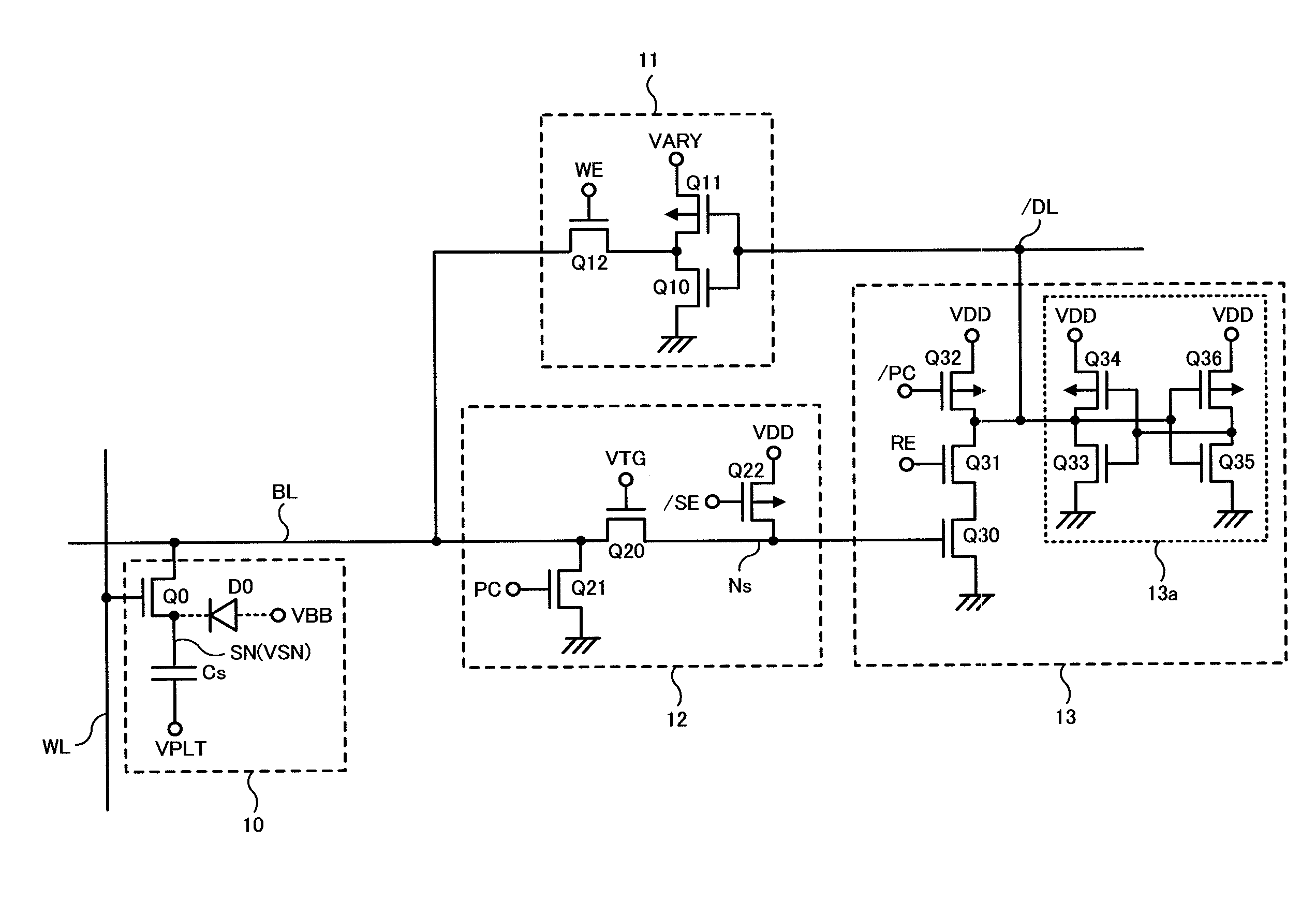
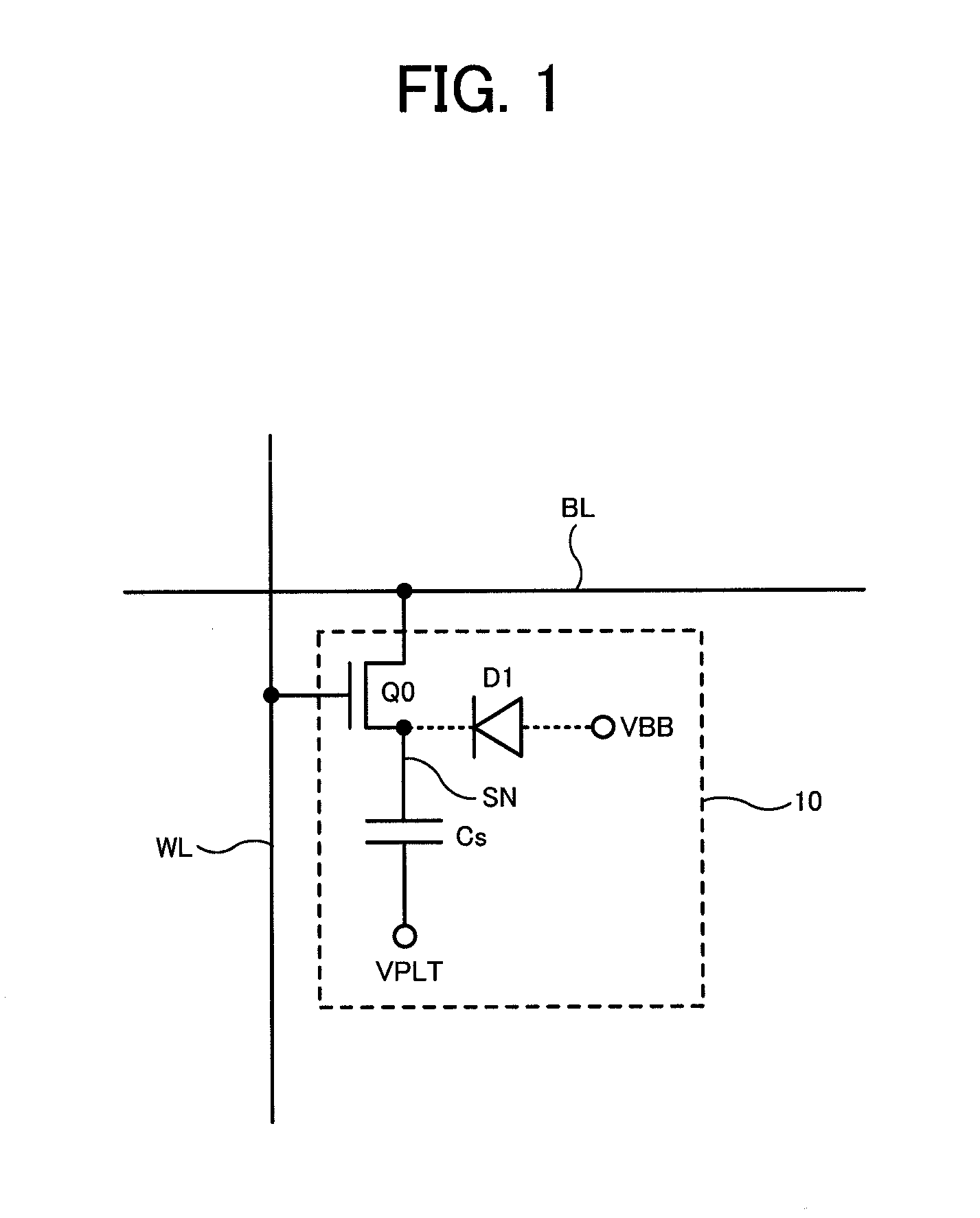
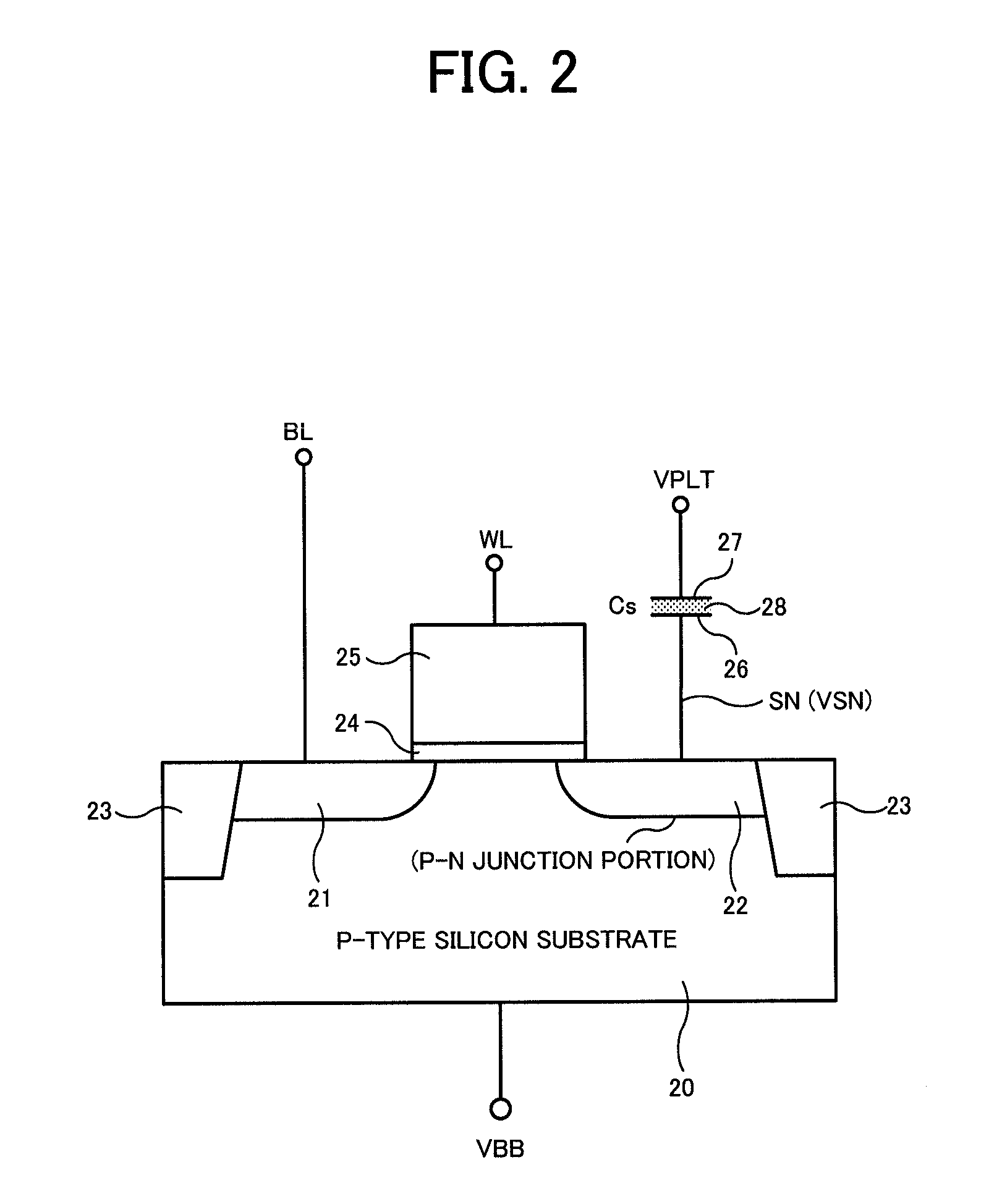
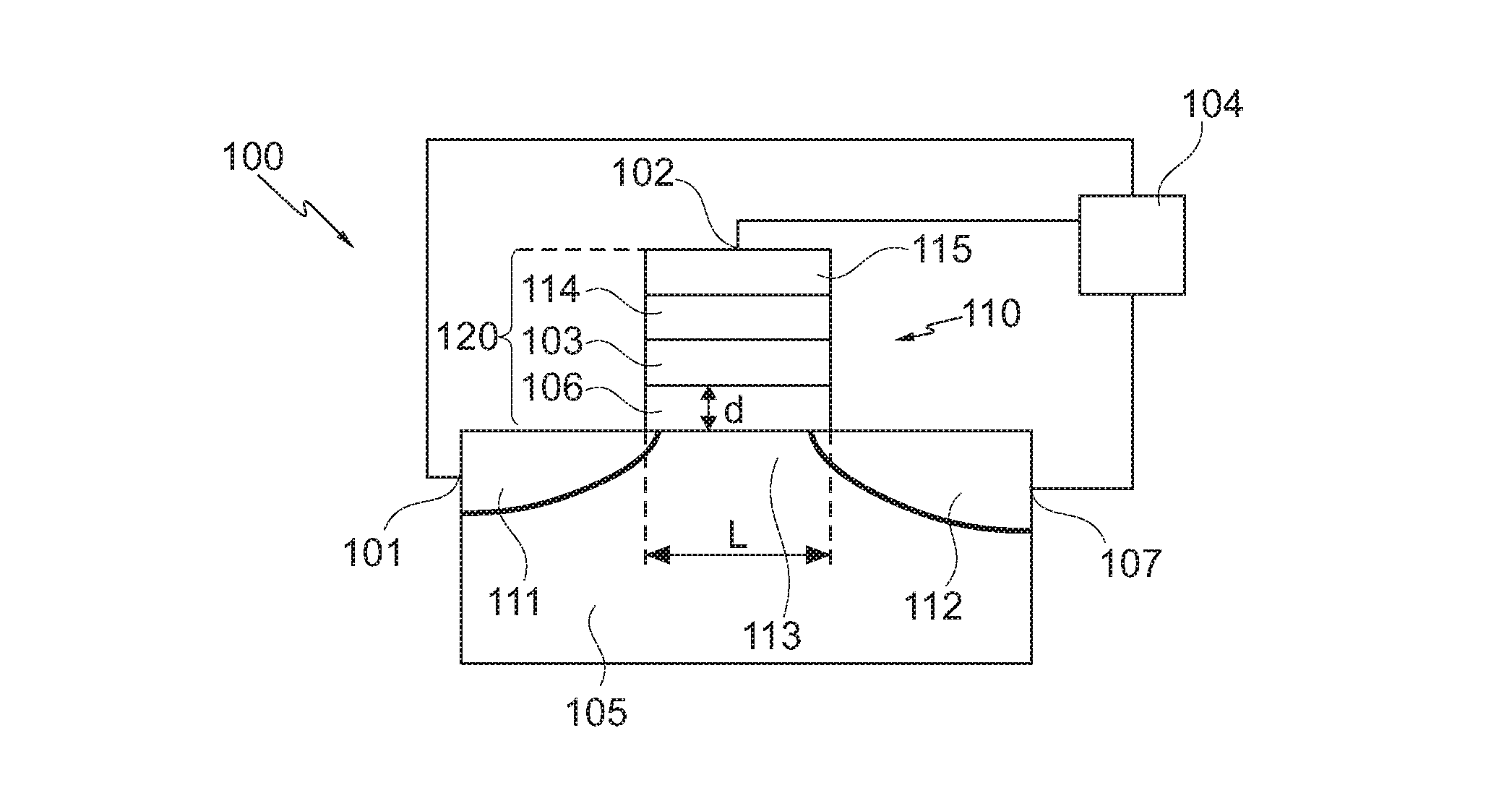
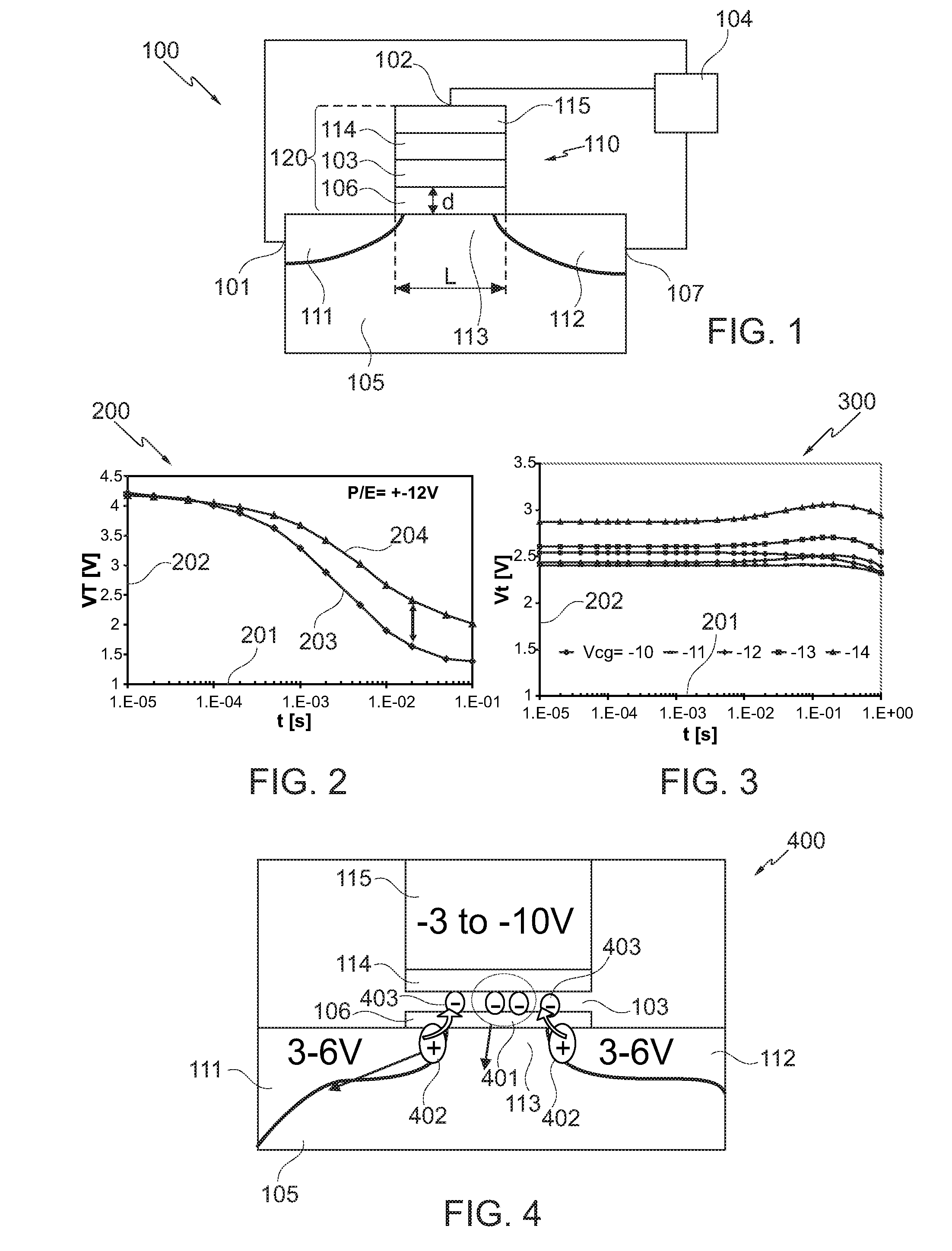
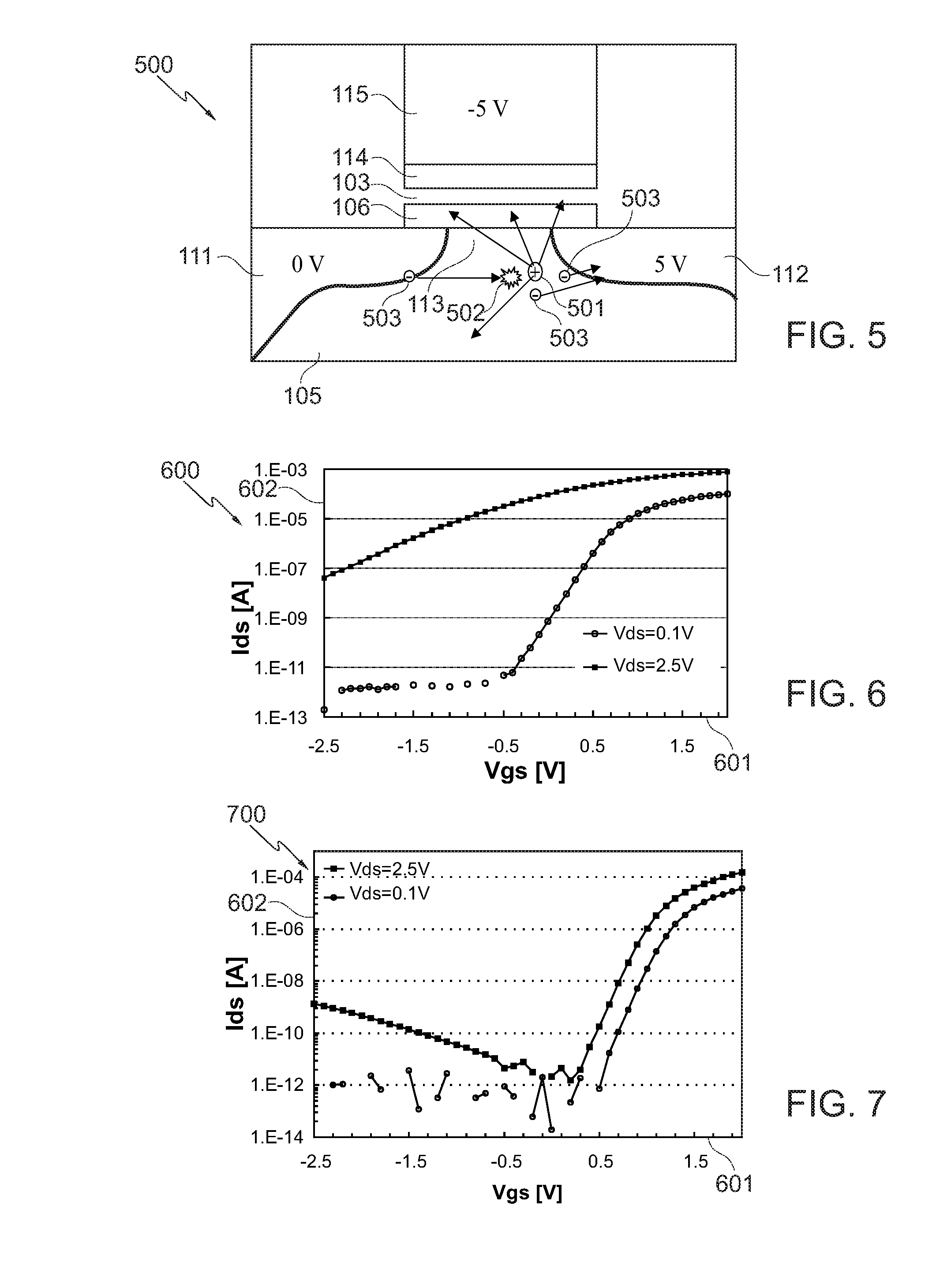
A memory cell includes a semiconductor substrate; and a first, a second, and a third transistor. The first transistor includes a first dielectric over the semiconductor substrate; and a first floating gate over the first dielectric. The second transistor is electrically coupled to the first transistor and includes a second dielectric over the semiconductor substrate; and a second floating gate over the second dielectric. The first and the second floating gates are electrically disconnected. The memory cell further includes a first capacitor; a second capacitor electrically coupled to the first capacitor; a third capacitor; a fourth capacitor electrically coupled to the third capacitor, wherein each of the first, the second, the third and the fourth capacitors includes the semiconductor substrate as one of the capacitor plates. The third transistor is a selector of the memory cell and is electrically coupled to the first and the second transistors.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Transistor for memory device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20060273415A1Data retention time be improveData Retention Time EnhancementTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringData retention
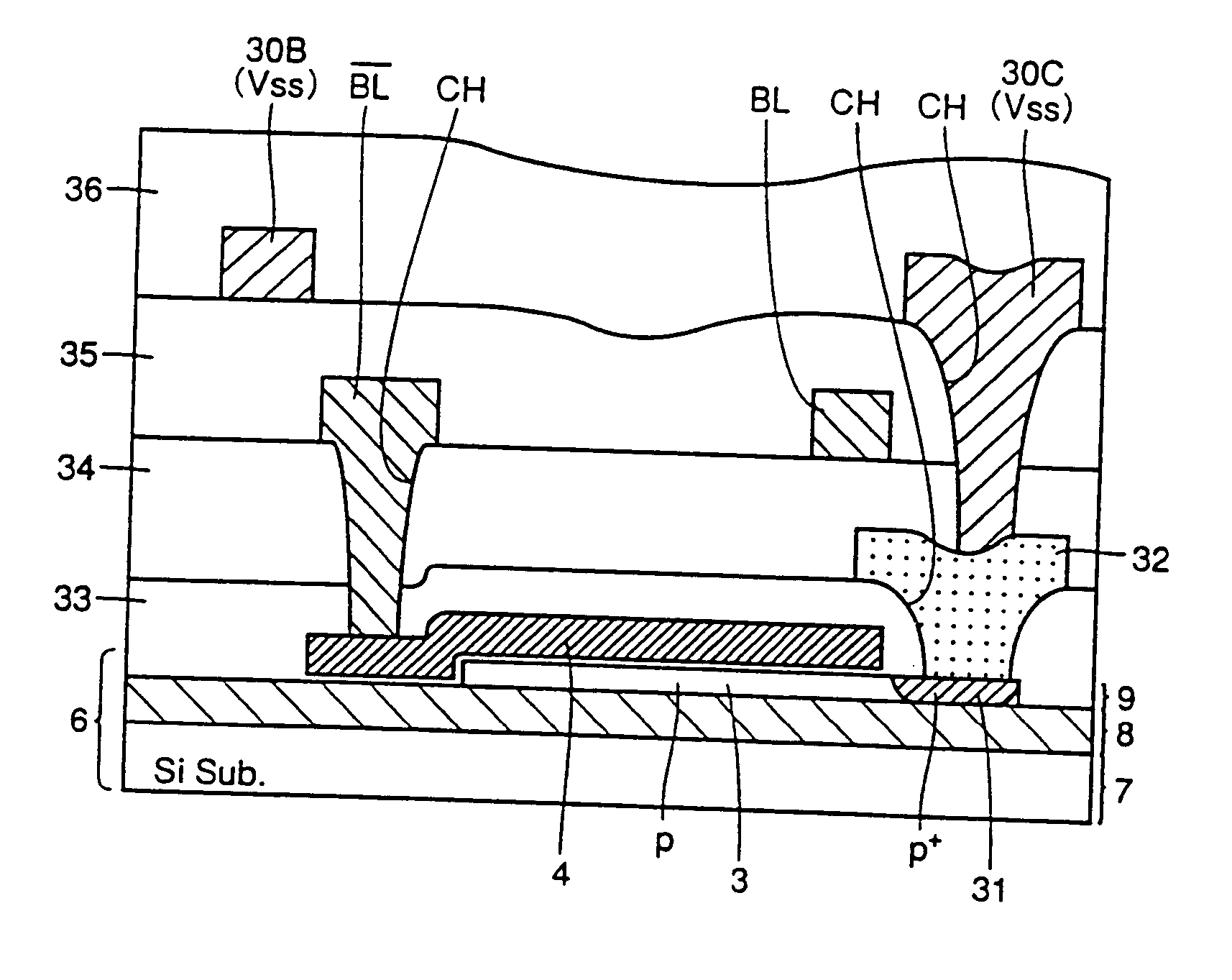
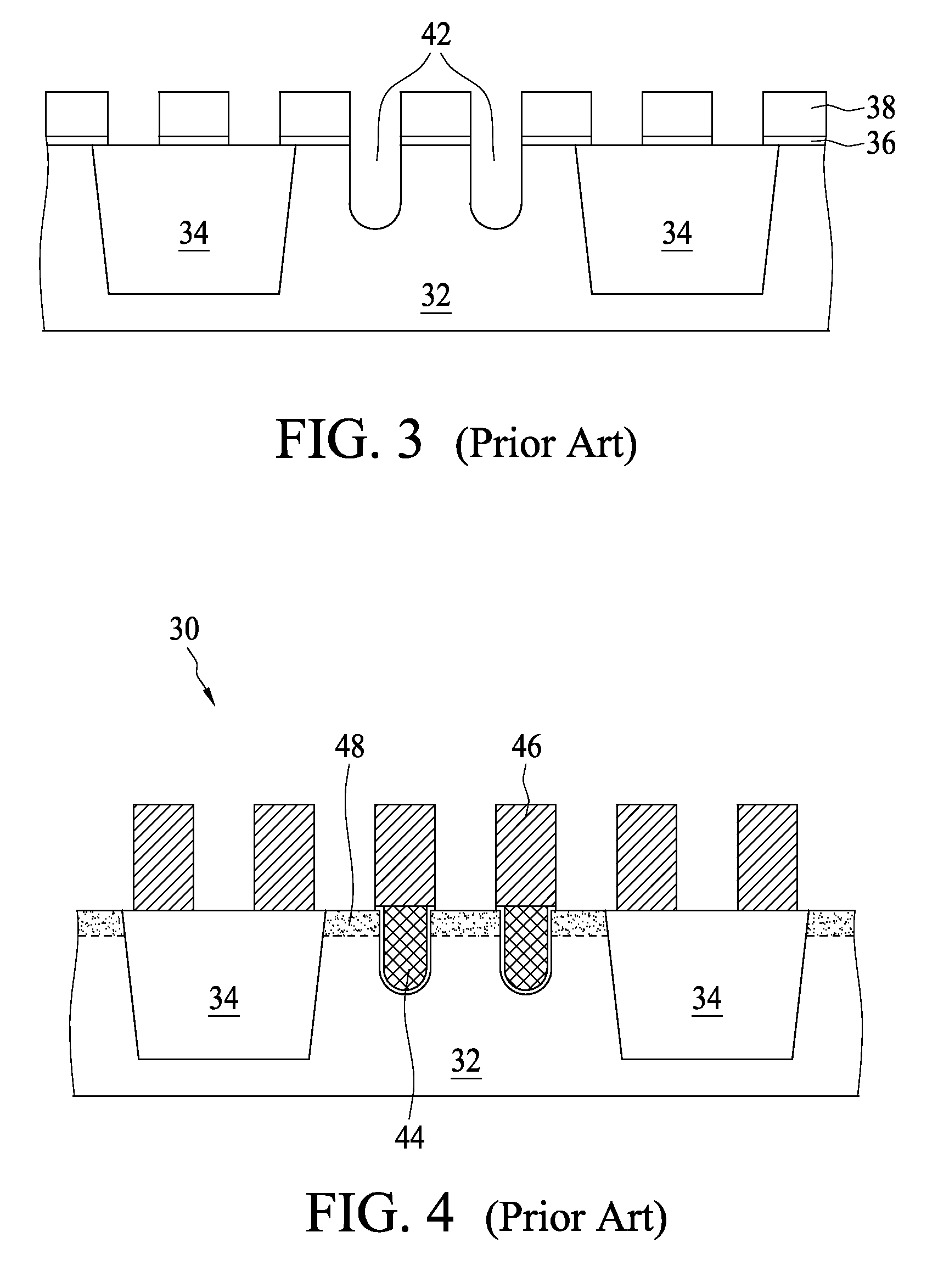
Disclosed is a transistor for a memory device realizing both a step-gated asymmetry transistor and a fin transistor in a cell and a method for manufacturing the same. The transistor has an active region protruding from a predetermined region of a substrate and a groove formed in the active region. A field oxide layer is formed on the substrate around the active region in such a manner that it has a surface lower than the upper surface of the active region including the groove. A pair of gates are placed along one and the other ends of groove across the upper surface of the active region while overlapping the stepped portion of the active region. The transistor has the structure of a step-gated asymmetry transistor when seen in a sectional view taken in a first direction, as well as that of a fin transistor when seen in a sectional view taken in a second direction, which is perpendicular to the first direction. The transistor having such a structure can secure improved data retention time of the step-gated asymmetry transistor and excellent current driving properties of the fin transistor and is applicable not only to a logic device, but also to a memory device (for example, DRAM) requiring low-power and high-speed properties.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Memory device including a dielectric multilayer structure and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20050247970A1Simple structureEnhancing data writingTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectric layerSemiconductor
In a memory device including a dielectric multilayer structure, and a method of fabricating the same, the memory device includes a semiconductor substrate, a first impurity region and a second impurity region spaced apart from each other in the semiconductor substrate, and a gate structure formed on the semiconductor substrate and contacting the first impurity region and the second impurity region, the gate structure including a tunneling oxide layer on the semiconductor substrate, a charge storage layer on the tunneling oxide layer, an insulating layer on the charge storage layer, the insulating layer including at least two dielectric layers, and a gate electrode layer on the insulating layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
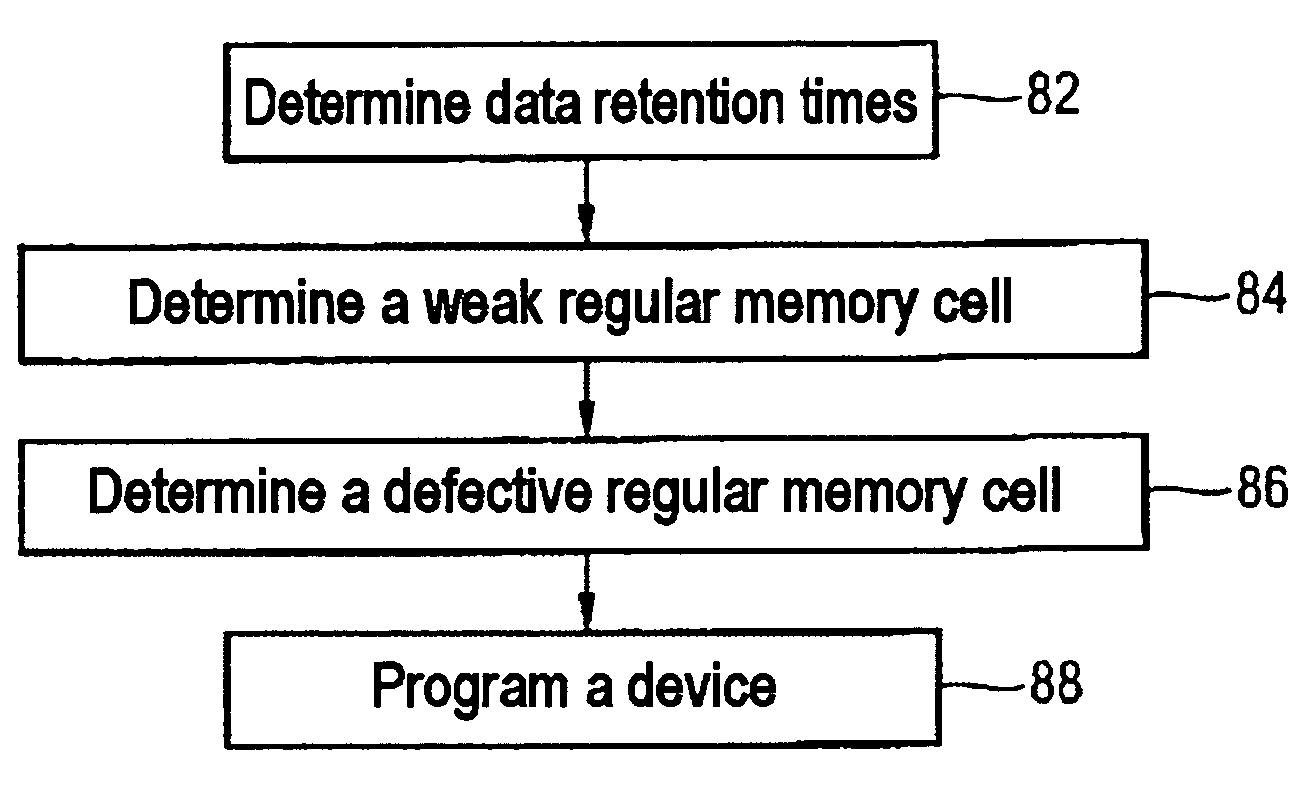
Methods for repairing and for operating a memory component
In a method for repairing a memory component, data retention times of regular memory cells are determined. Weak regular memory cells having a data retention time that is shorter than a predetermined limit value are determined. A device is programmed in such a manner that a write or read access to the weak regular memory cell is simultaneously also effected for a redundant memory cell in order to jointly read from, or write to, the weak regular memory cell and the redundant memory cell.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
A tube phase change memory unit structure and its making method
ActiveCN101267017AImprove utilization efficiencyData retention time is longSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesElectrical resistance and conductancePhase-change memory
The invention relates to a tube-like phase-change memory single structure and making method, the phase-change memory single structure comprises a top electrode, a bottom electrode and a memory part. The single structure has basic characters that: phase-change material distributes at lateral wall of a hole, the phase-change is implemented in the hole in reading and writing operation through heating own by using small sectional area and big resistance of the phase-change material, and tubular is formed at two ends of ring phase-change material through adding phase-change material insulating layer as closure, thus improving use efficiency of heat in the reading and writing operation, the memory part is a tubular structure enclosed by the phase-change material up and down, and is filled with metal, insulation materials or high resistivity material. The memory structure of the invention can reduce operating current, and has small-power, high heat utilization ratio and good data retention performance, and the invention can improve the consistency of resistance value of device of chip.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
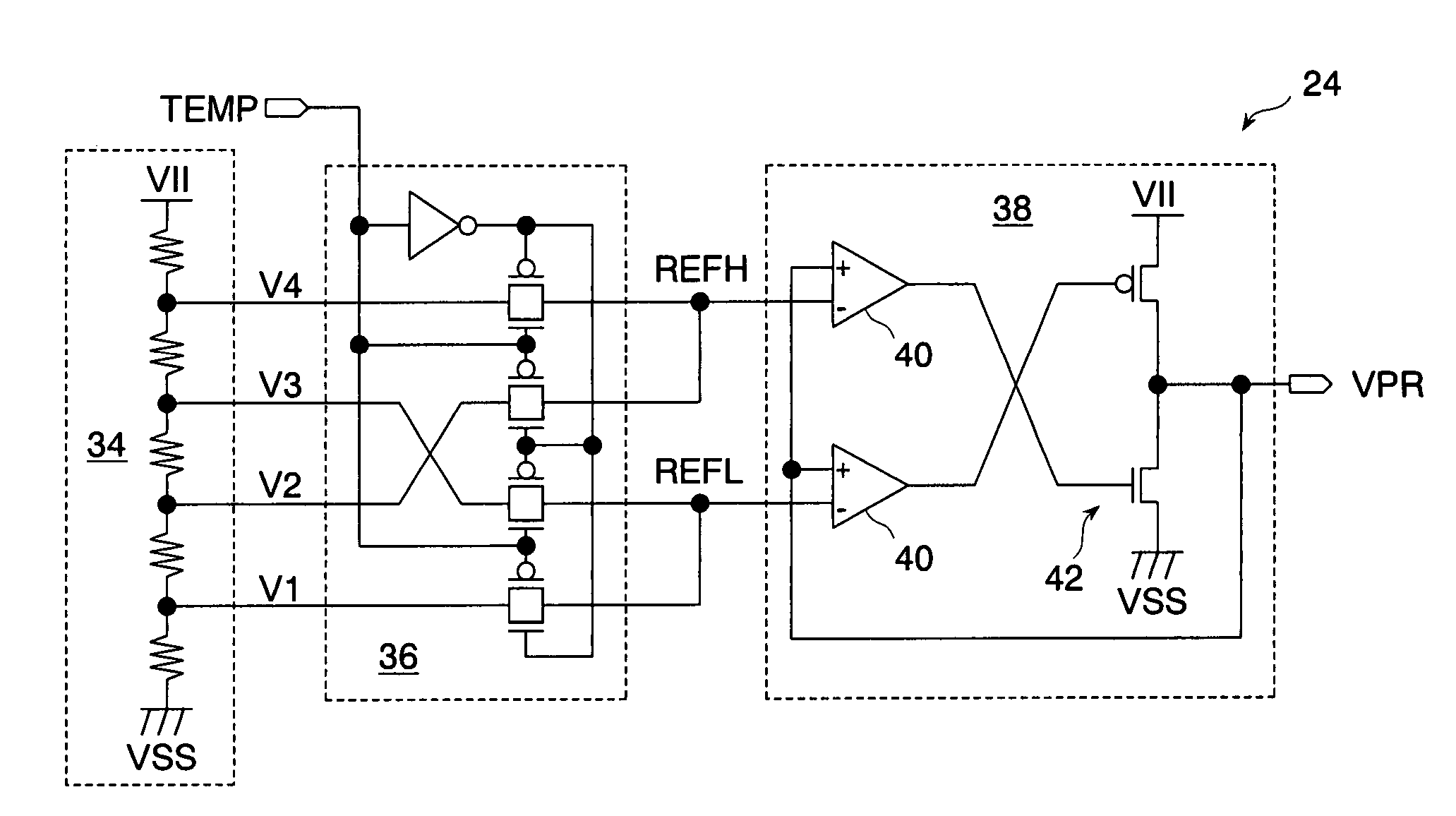
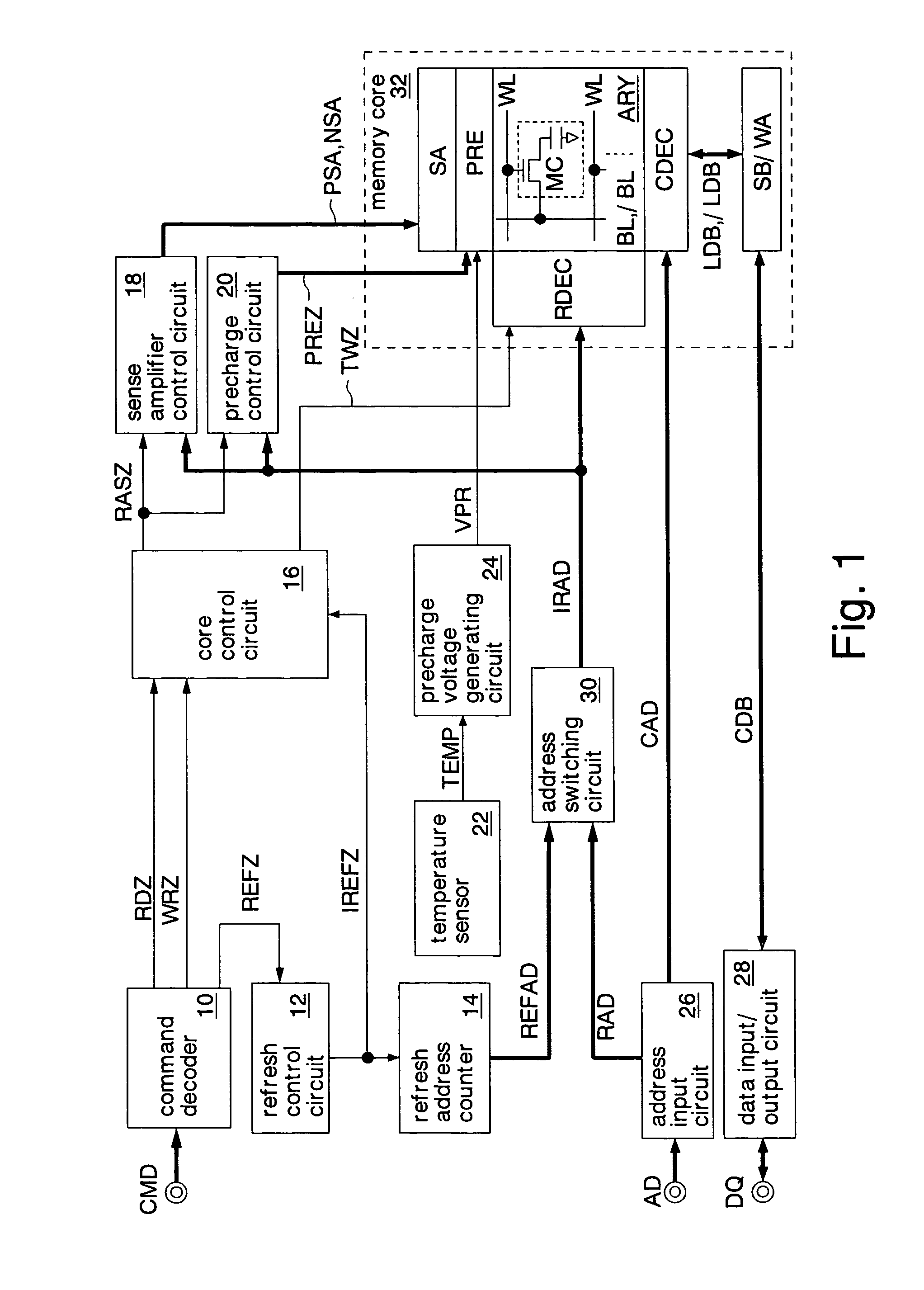
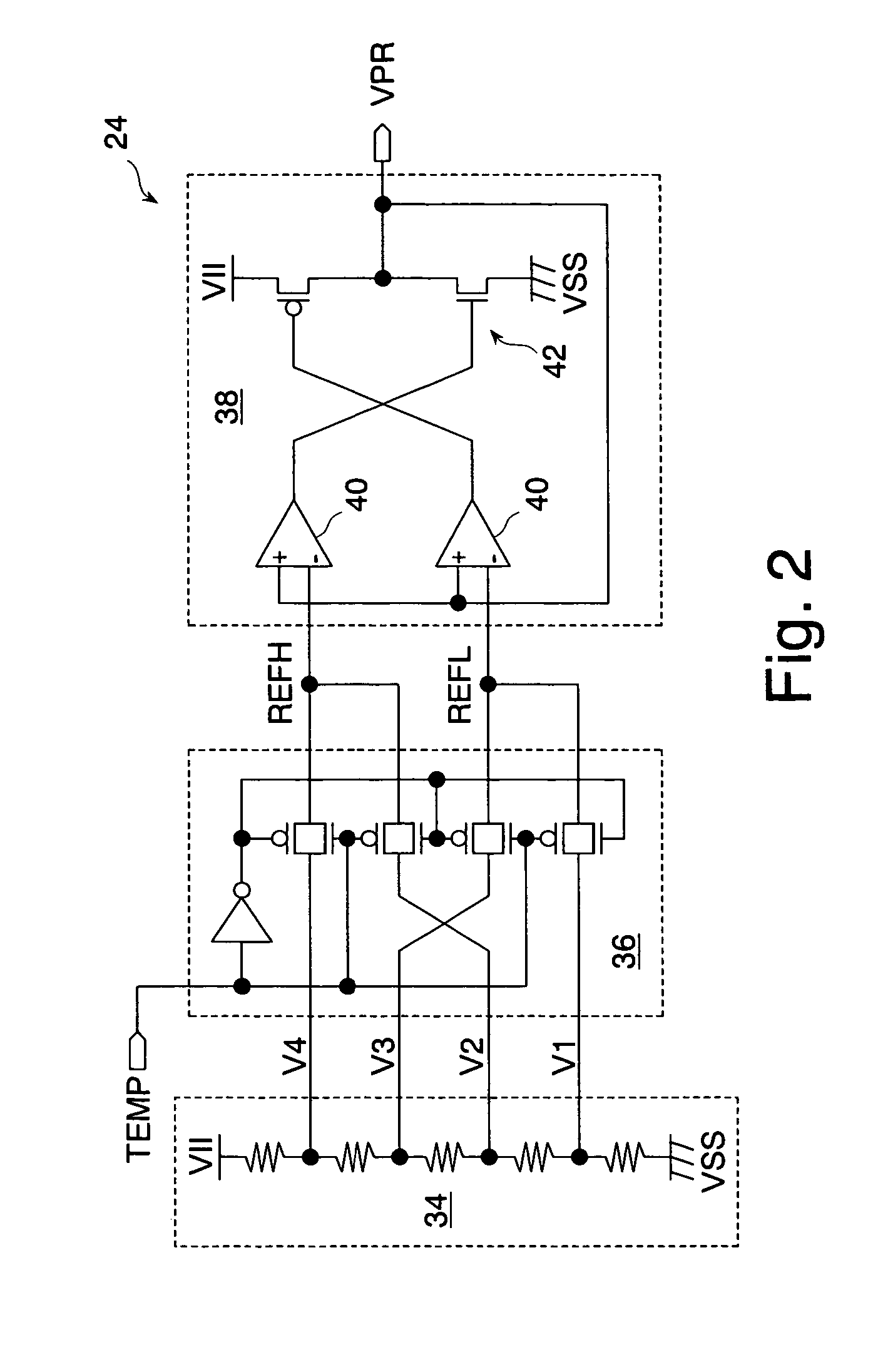
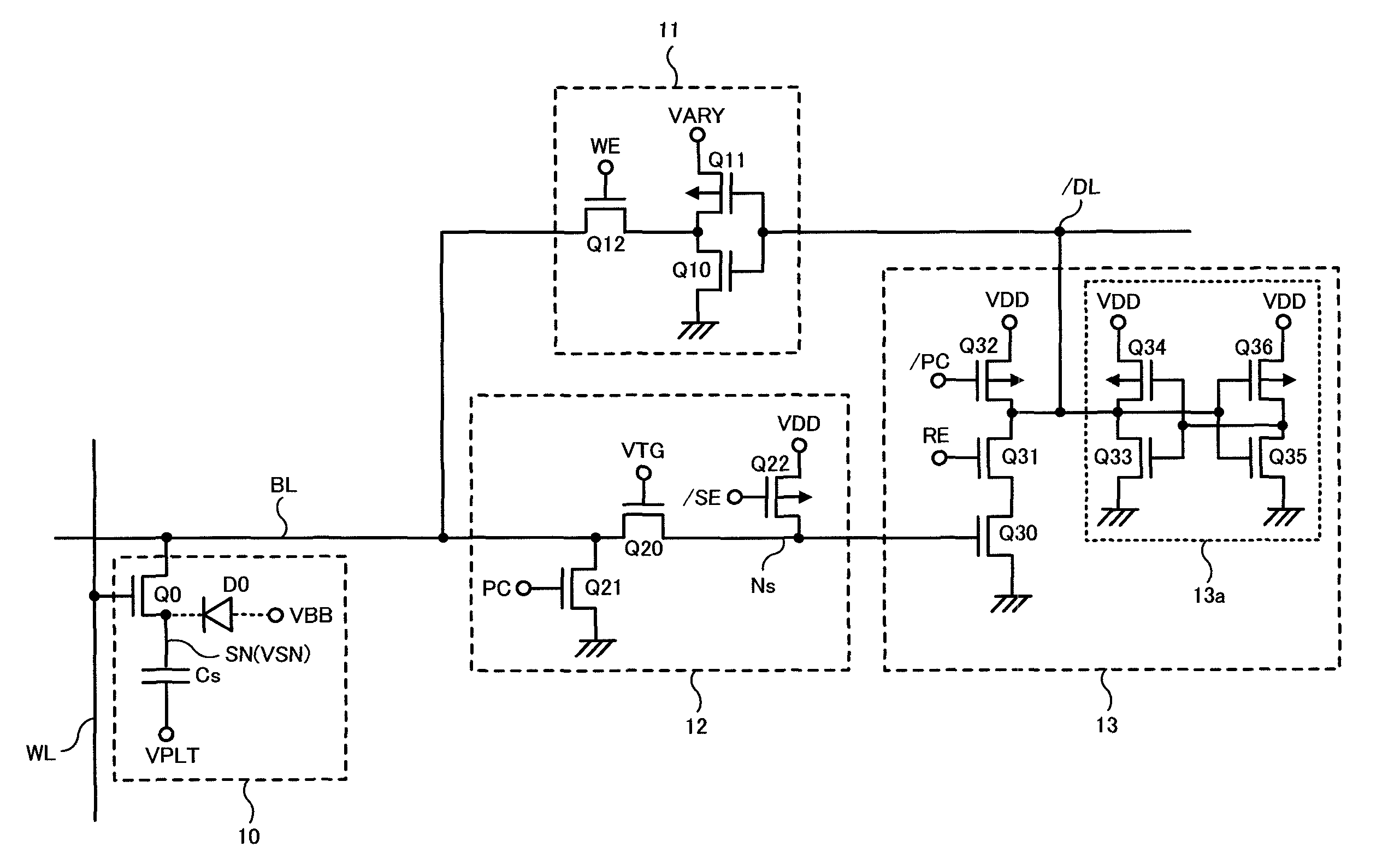
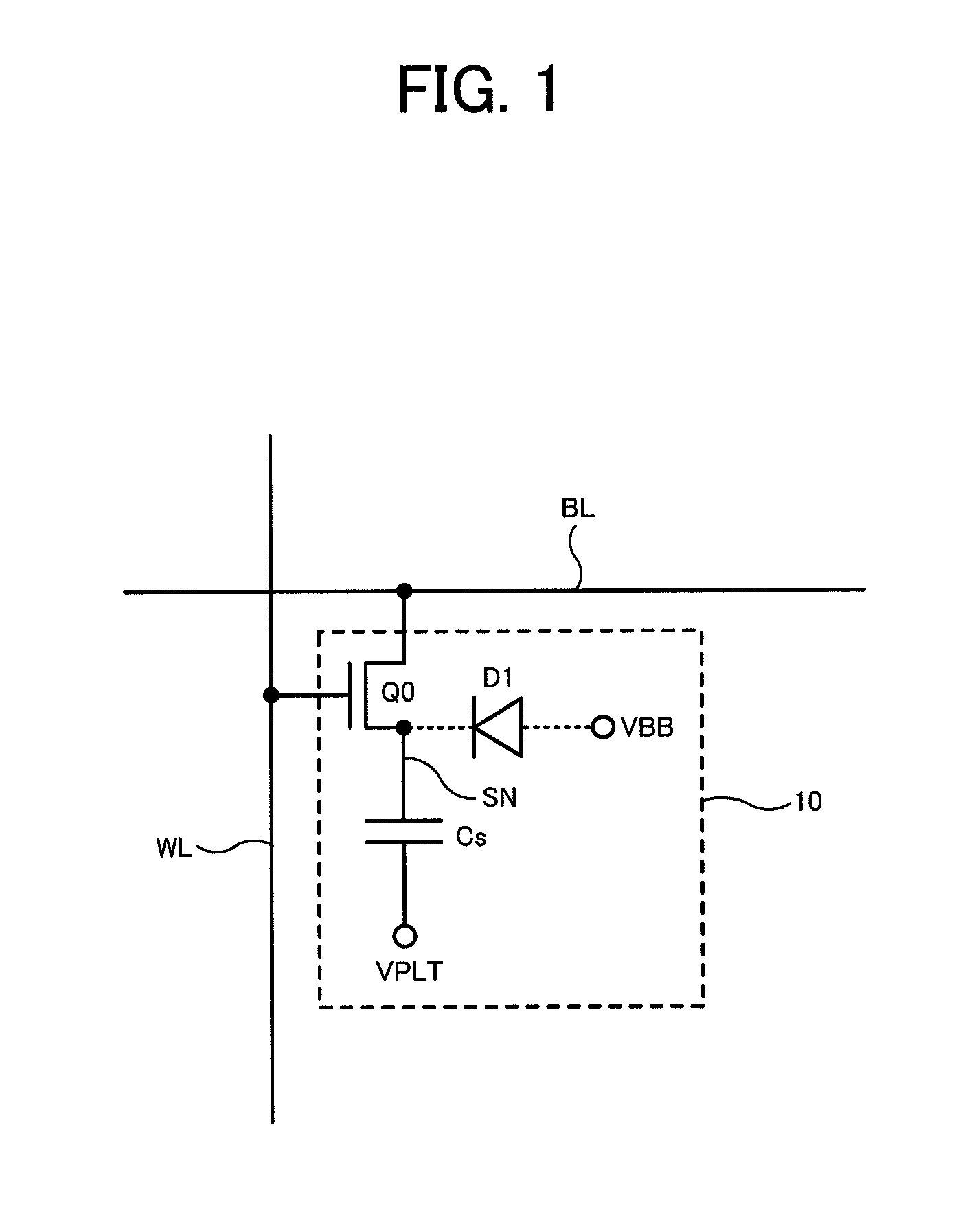
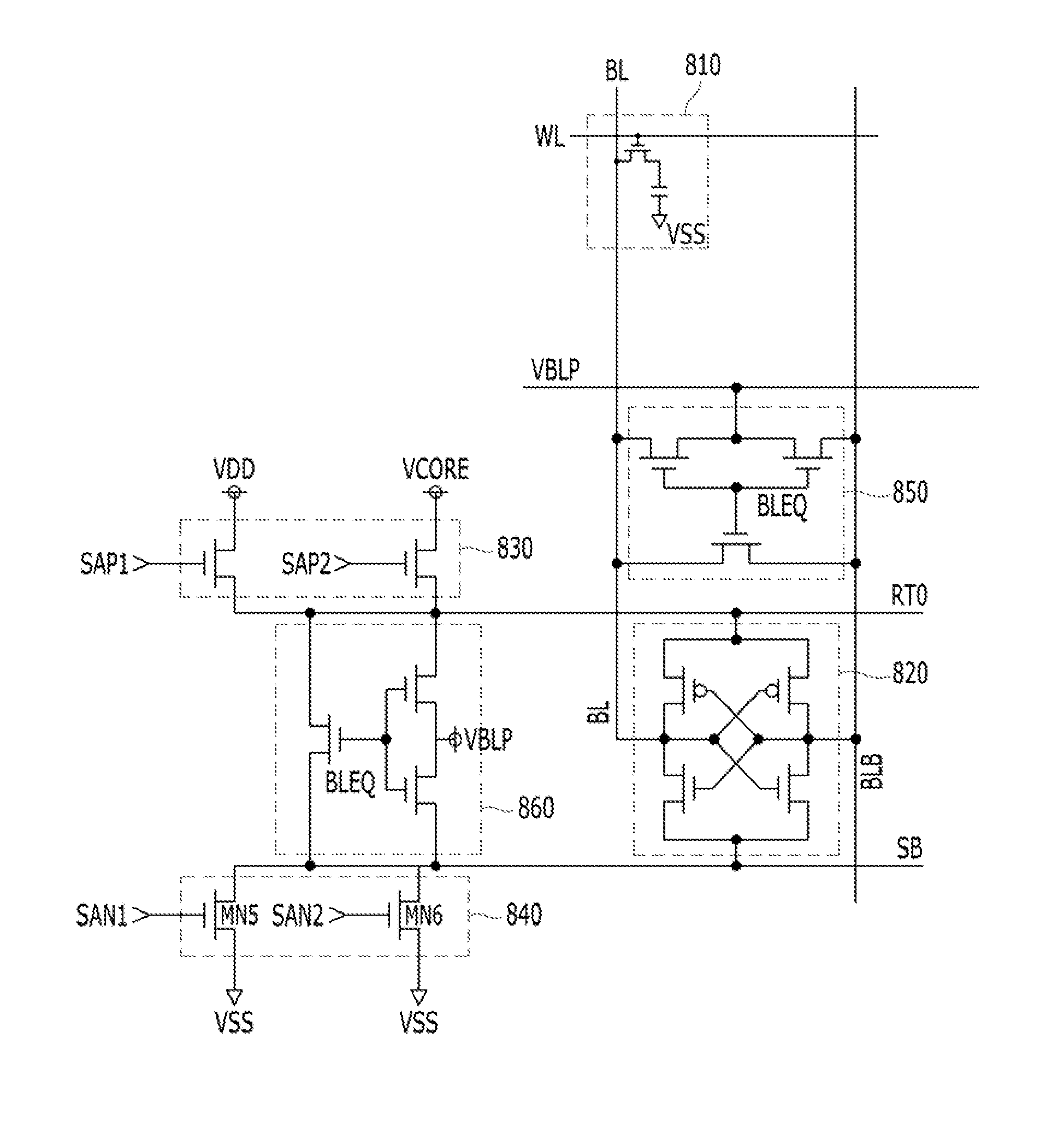
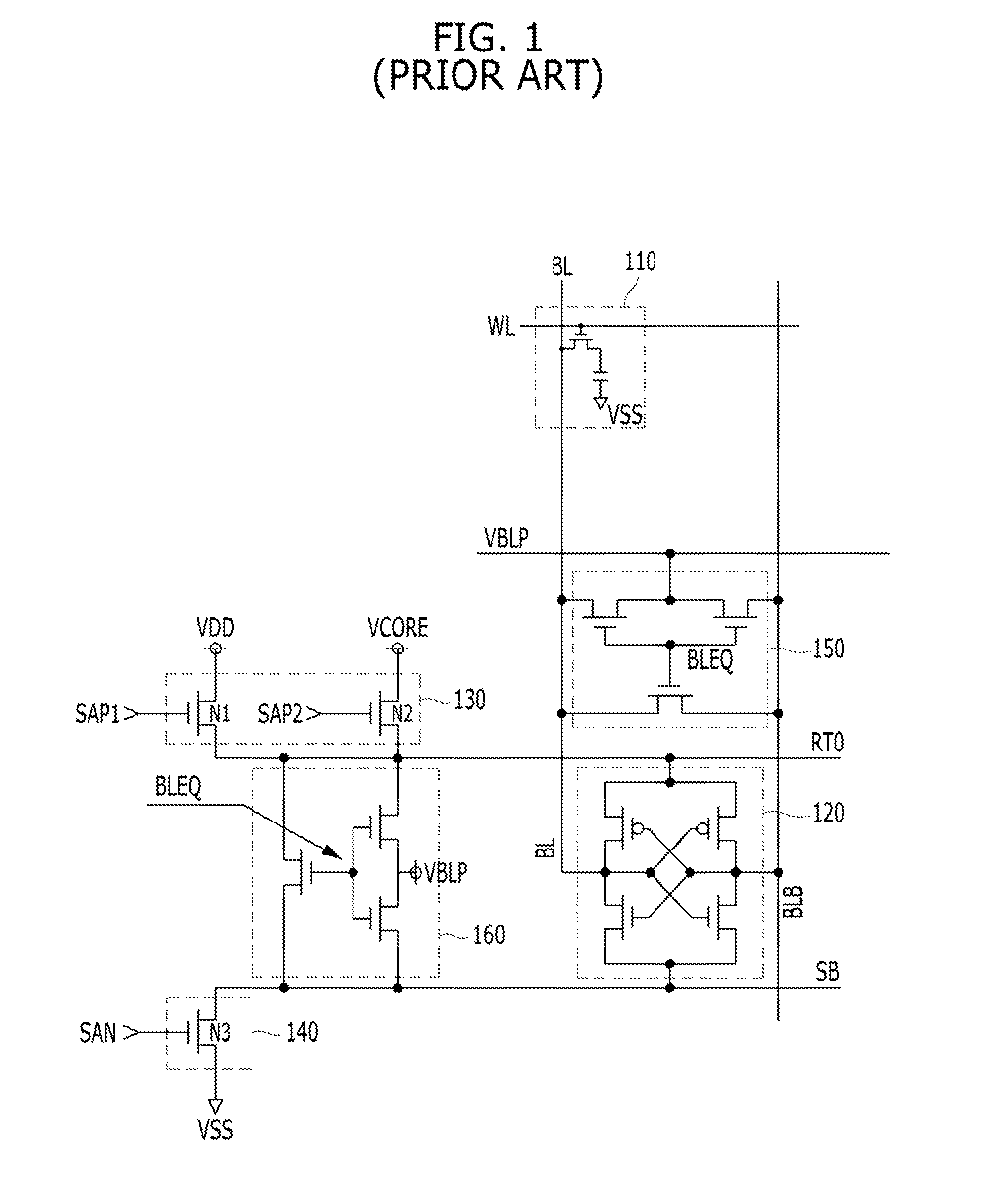
Semiconductor memory having a precharge voltage generation circuit for reducing power consumption
ActiveUS7580303B2Reduce power consumptionData Retention Time EnhancementDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
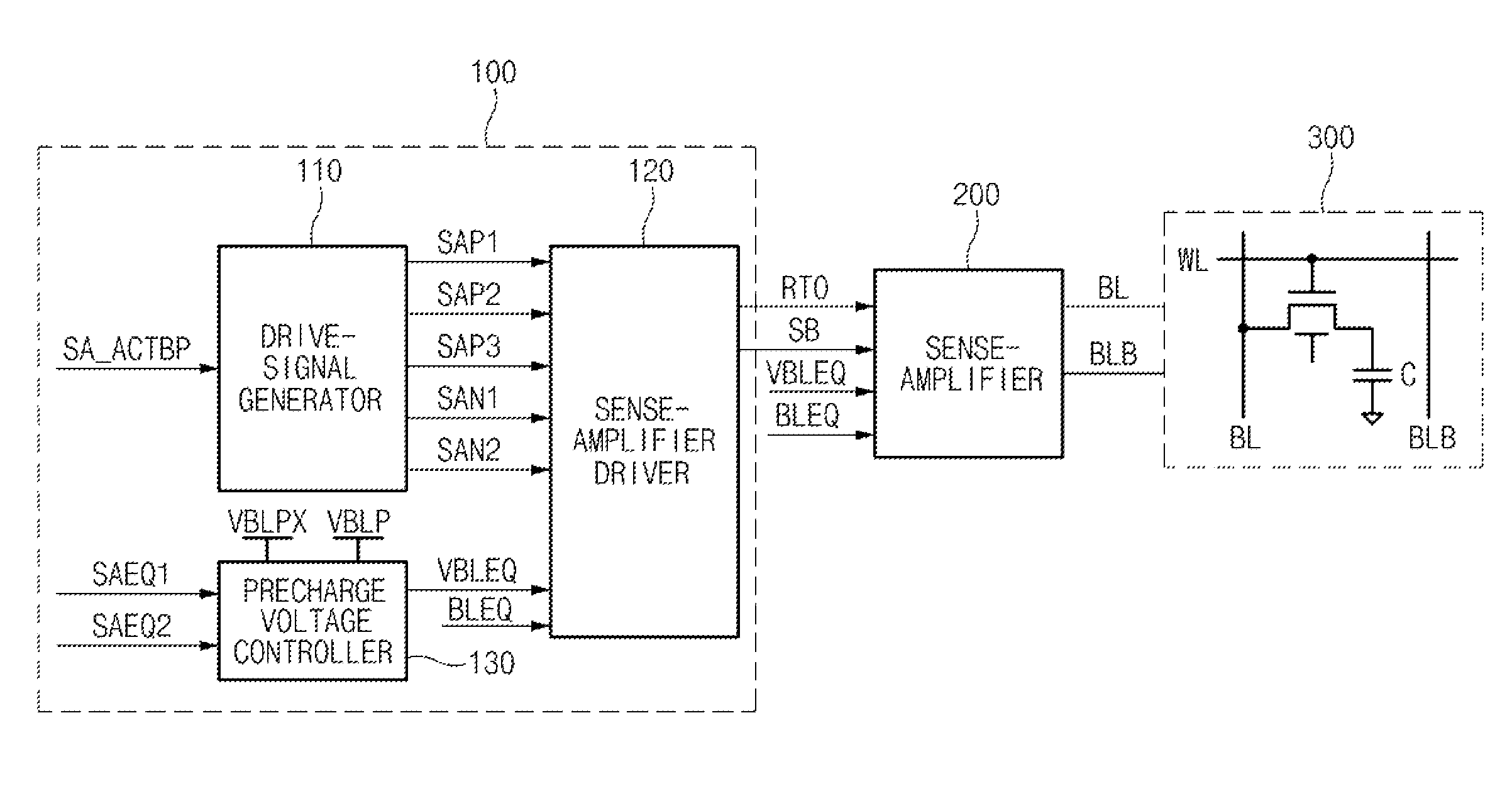
A precharge voltage generating circuit outputs any of a plurality of kinds of precharge voltages in accordance with an ambient temperature. A precharge circuit supplies the precharge voltage to a bit line during the nonaccess of a dynamic memory cell. A sense amplifier amplifies a difference between the voltage of a data signal read from the dynamic memory cell onto the bit line and the supplied precharge voltage. The precharge voltage is altered in accordance with the ambient temperature, whereby the read margin of the sense amplifier can be changed, and the worst value of the data retaining time of the memory cell can be improved. As a result, the frequency of refreshing of the memory cell can be lowered, reducing power consumption and a standby current.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
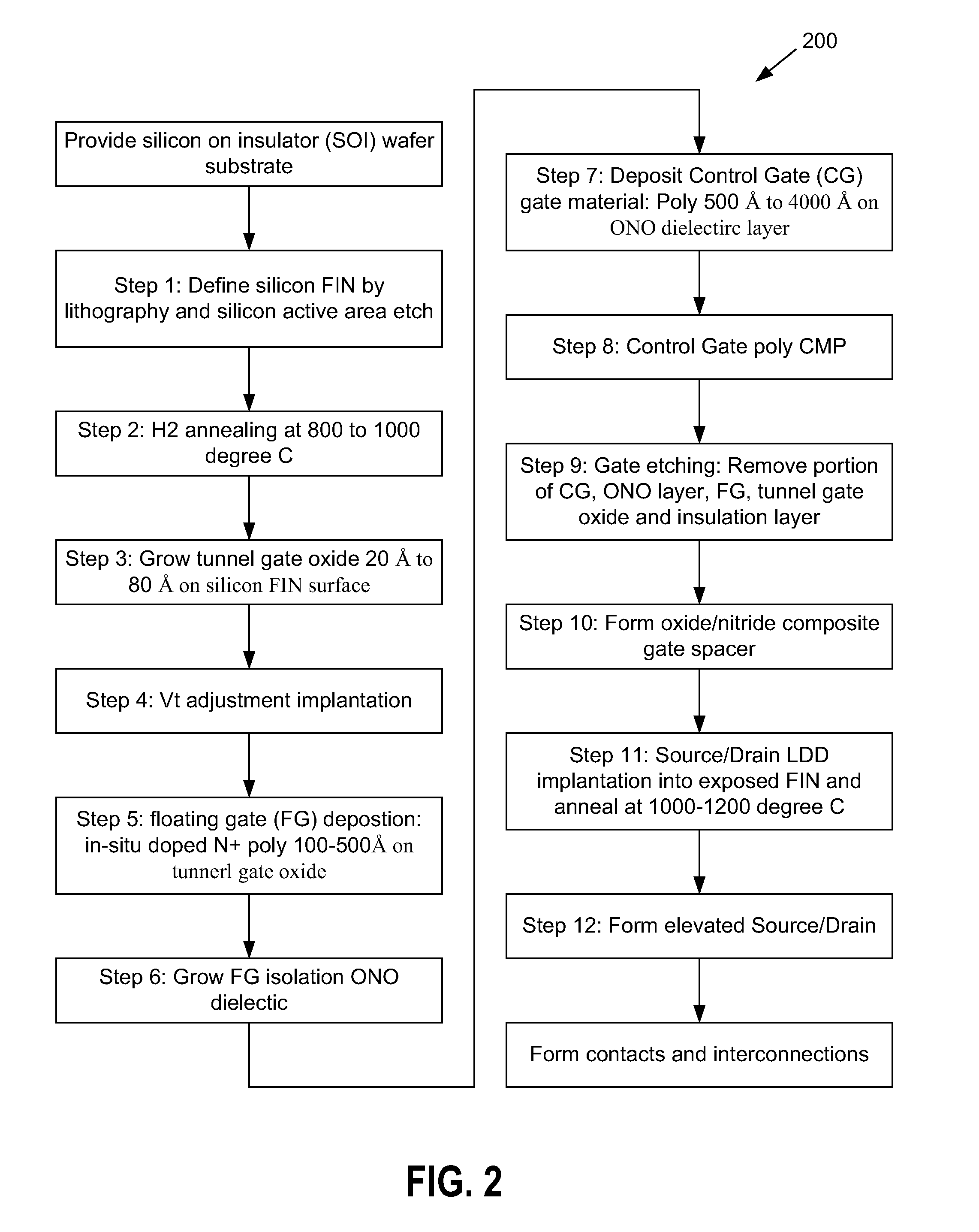
Surrounding stacked gate multi-gate fet structure nonvolatile memory device
ActiveUS20110163369A1Suppression of short channel effectsLower average currentTransistorSolid-state devicesPower flowNitride
Nonvolatile memory devices having a low off state leakage current and an excellent data retention time characteristics. The present invention provides a surrounding stacked gate fin field effect transistor nonvolatile memory structure comprising a silicon-on-insulator substrate of a first conductivity type and a fin active region projecting from an upper surface of the insulator. The structure further includes a tunnel oxide layer formed on the fin active region and a first gate electrode disposed on the tunnel oxide layer and upper surface of the insulator. Additionally, the structure includes an oxide / nitride / oxide (ONO) composite layer formed on the first gate electrode, a second gate electrode formed on the ONO composite layer and patterned so as to define a predetermined area of the ONO composite layer. The structure further includes a dielectric spacer formed on a sidewall of the second gate electrode and source / drain regions formed in the fin active region on both sides of the second gate electrode.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Logic non-volatile memory cell with improved data retention ability
InactiveUS7968926B2Improve reliabilityData Retention Time EnhancementTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricEngineering
A memory cell includes a semiconductor substrate; and a first, a second, and a third transistor. The first transistor includes a first dielectric over the semiconductor substrate; and a first floating gate over the first dielectric. The second transistor is electrically coupled to the first transistor and includes a second dielectric over the semiconductor substrate; and a second floating gate over the second dielectric. The first and the second floating gates are electrically disconnected. The memory cell further includes a first capacitor; a second capacitor electrically coupled to the first capacitor; a third capacitor; a fourth capacitor electrically coupled to the third capacitor, wherein each of the first, the second, the third and the fourth capacitors includes the semiconductor substrate as one of the capacitor plates. The third transistor is a selector of the memory cell and is electrically coupled to the first and the second transistors.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Memory device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS7045846B2Data Retention Time EnhancementReduce leakage currentTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineCell region
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor memory device
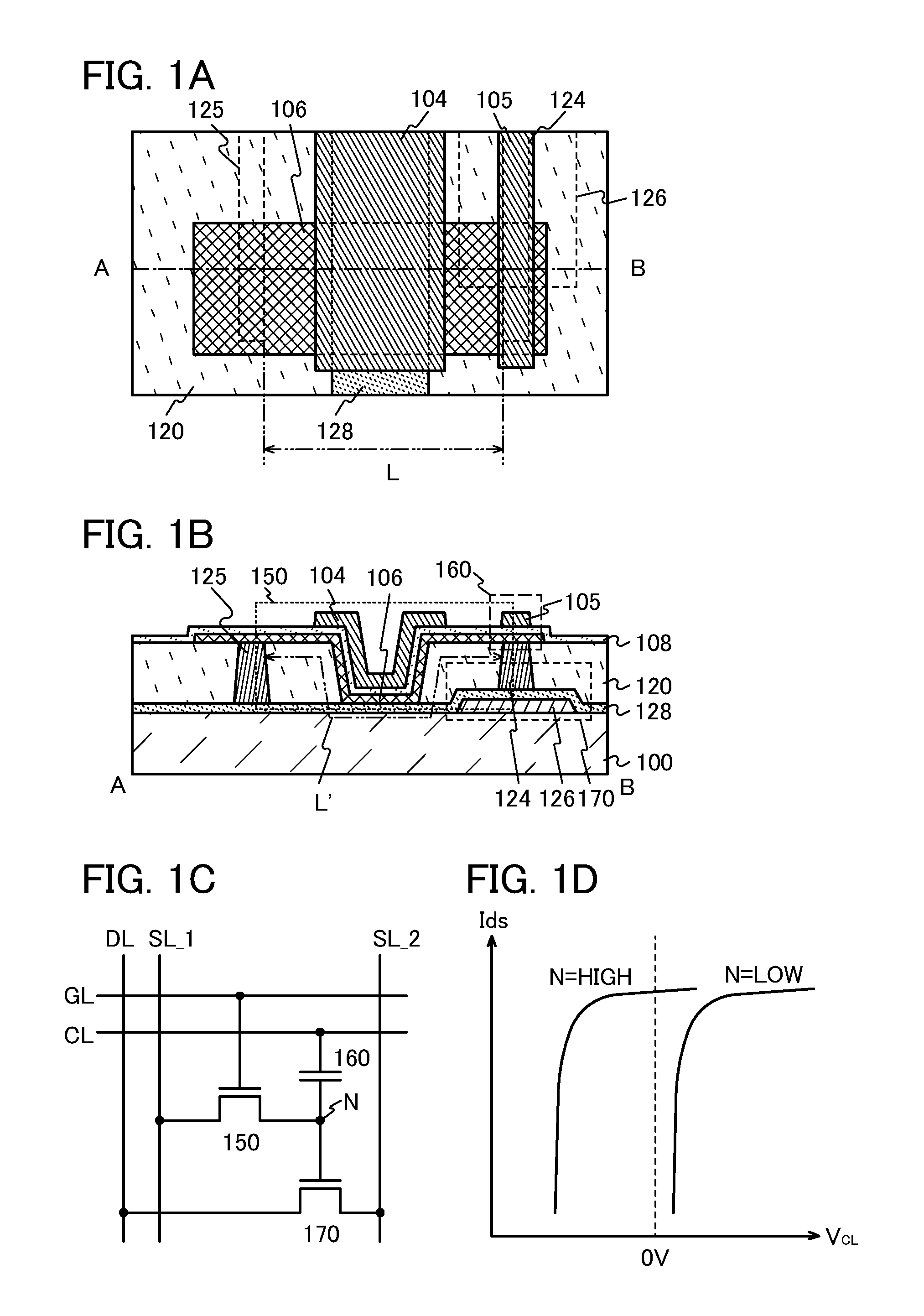
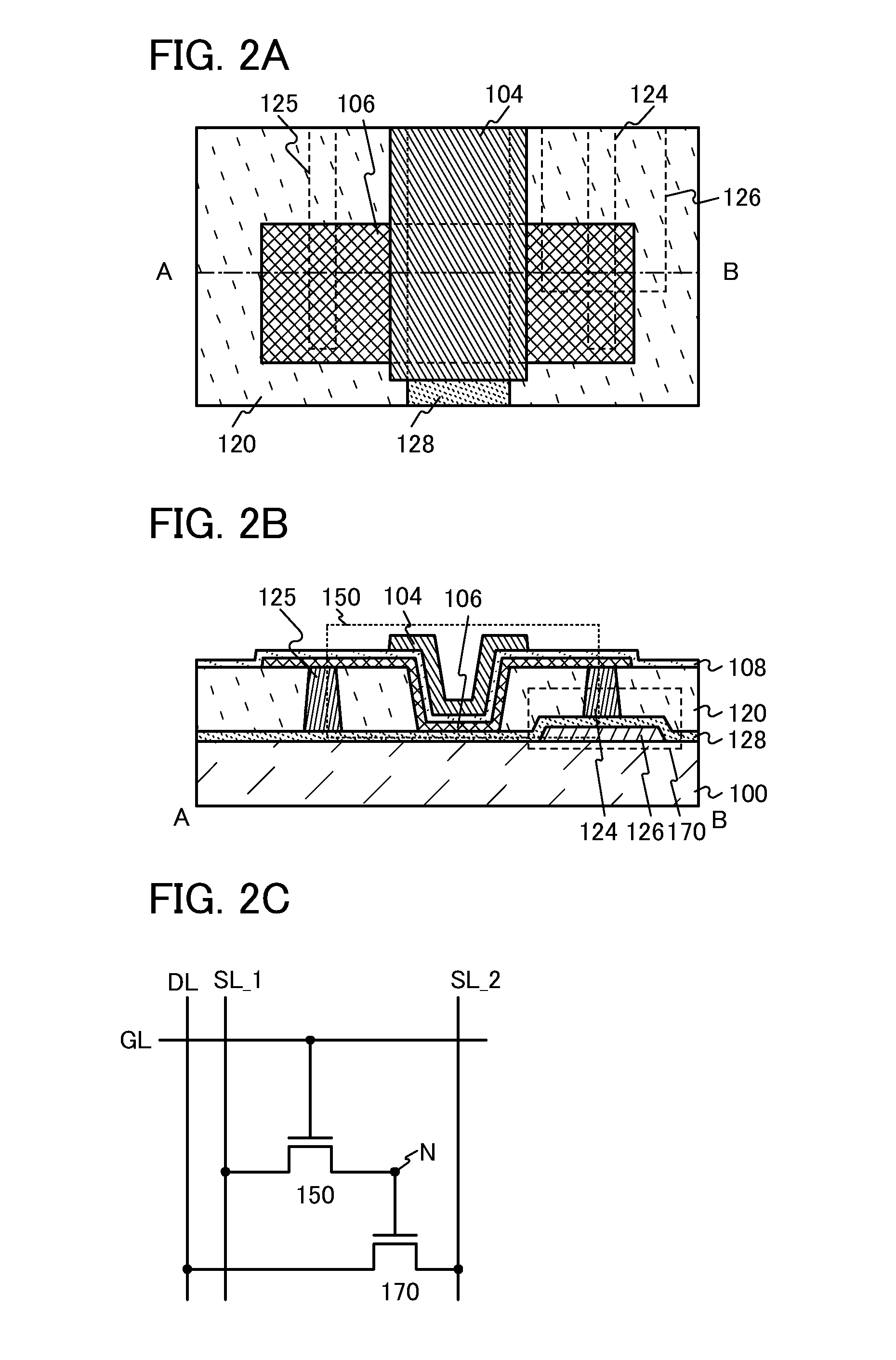
InactiveUS8772849B2Highly integratedData Retention Time EnhancementTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorSemiconductor device
A semiconductor memory device includes a semiconductor film; a first gate insulating film covering the semiconductor film; a first gate electrode provided over the semiconductor film with the first gate insulating film interposed therebetween; a first conductive film which is provided over the first gate insulating film; an insulating film which is provided over the first gate insulating film, exposes top surfaces of the first gate electrode and the first conductive film, and has a groove portion between the first gate electrode and the first conductive film; an oxide semiconductor film which is provided over the insulating film and is in contact with the first gate electrode, the first conductive film, and the groove portion; a second gate insulating film covering the oxide semiconductor film; and a second gate electrode provided over the oxide semiconductor film and the groove portion with the second gate insulating film interposed therebetween.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
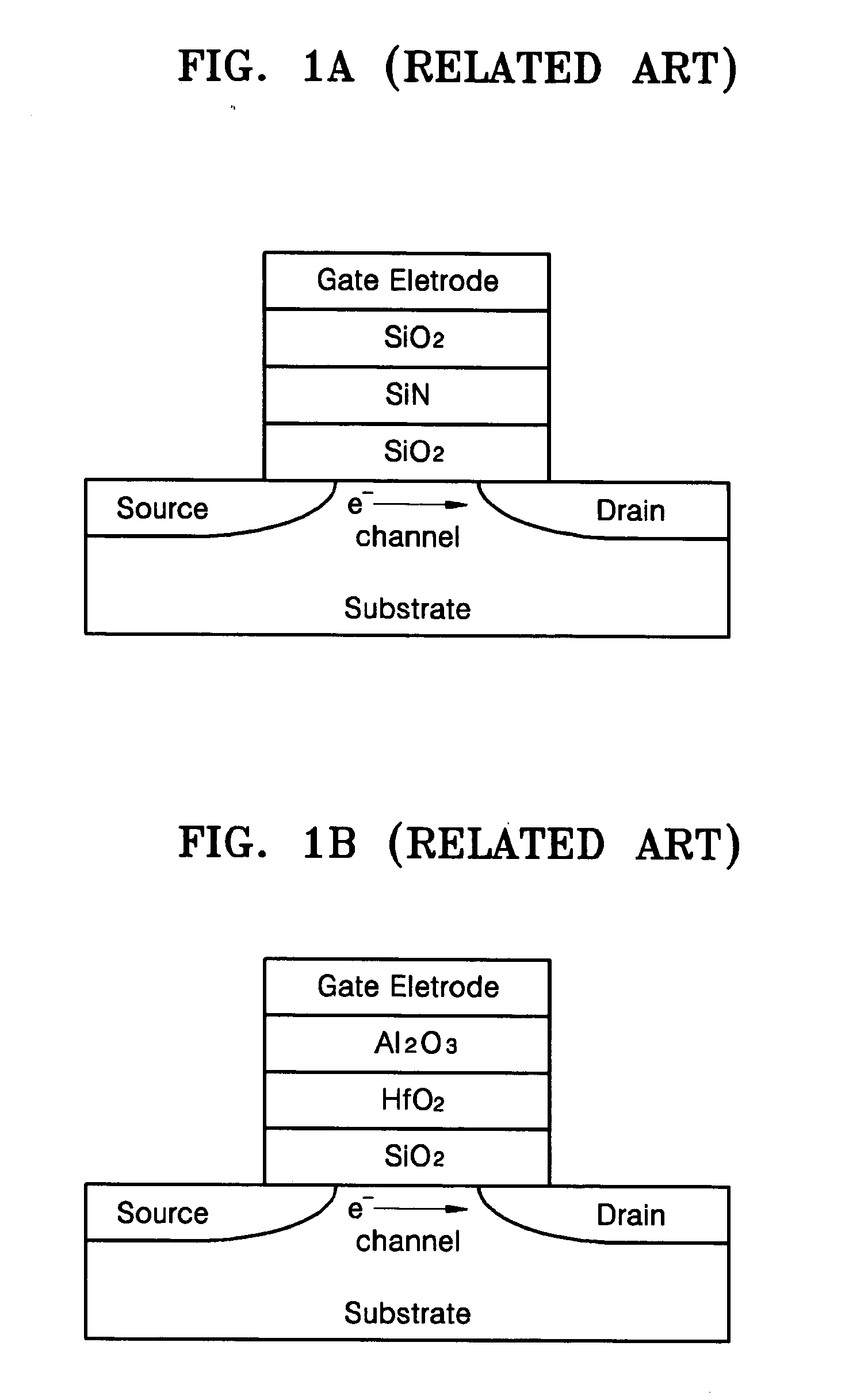
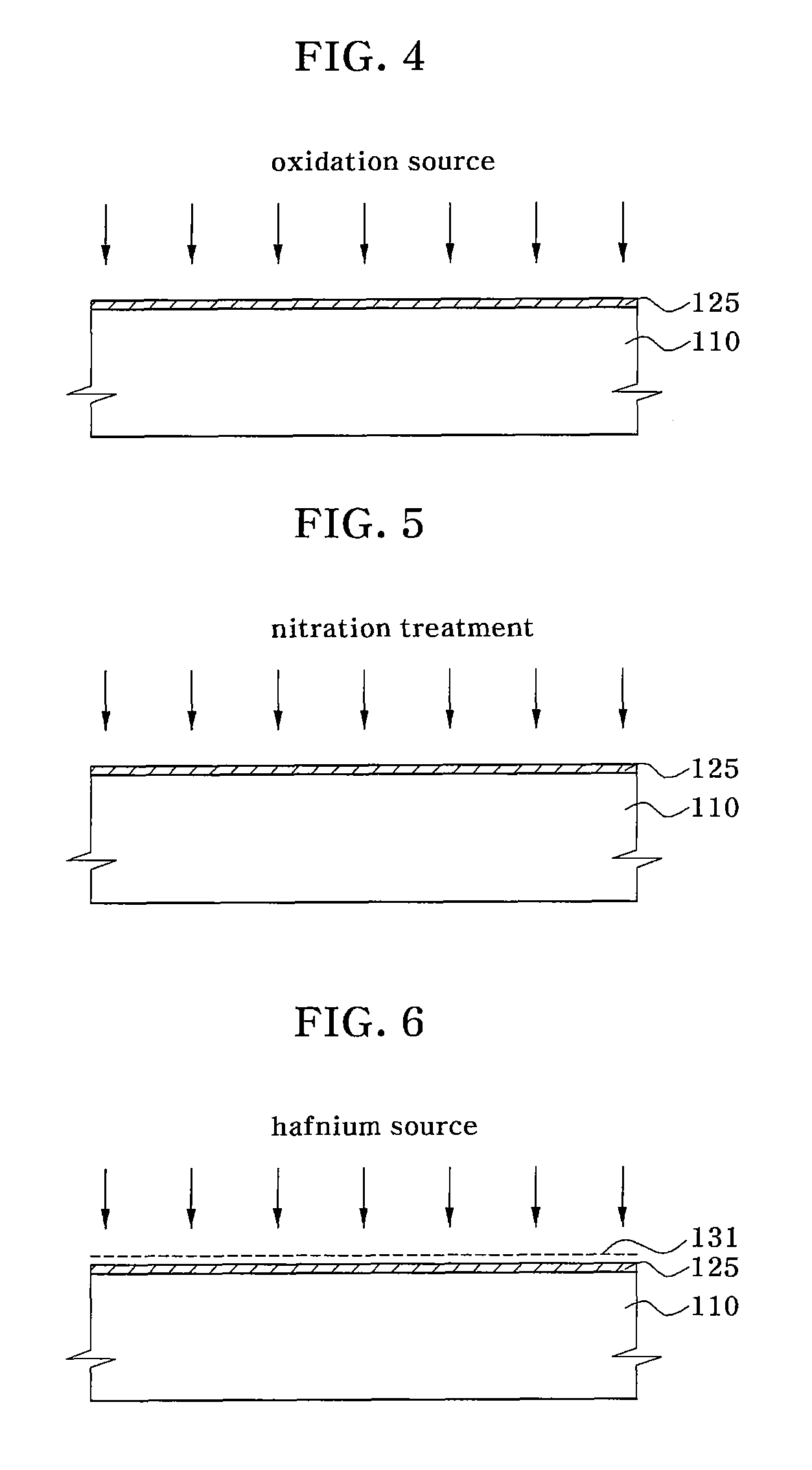
Non-volatile memory device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS7851285B2Data Retention Time EnhancementFast processingTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTrappingHafnium
A method for fabricating a non-volatile memory device includes forming a charge tunneling layer composed of a hafnium silicate (HfSixOyNz) layer on a semiconductor substrate. A charge trapping layer composed of a hafnium oxide nitride (HfOxNy) layer is formed on the charge tunneling layer. A charge blocking layer composed of a hafnium oxide layer is formed on the charge trapping layer. A gate layer is formed on the charge blocking layer. A non-volatile memory device fabricated by the method is also disclosed.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Memory device and method of storing data
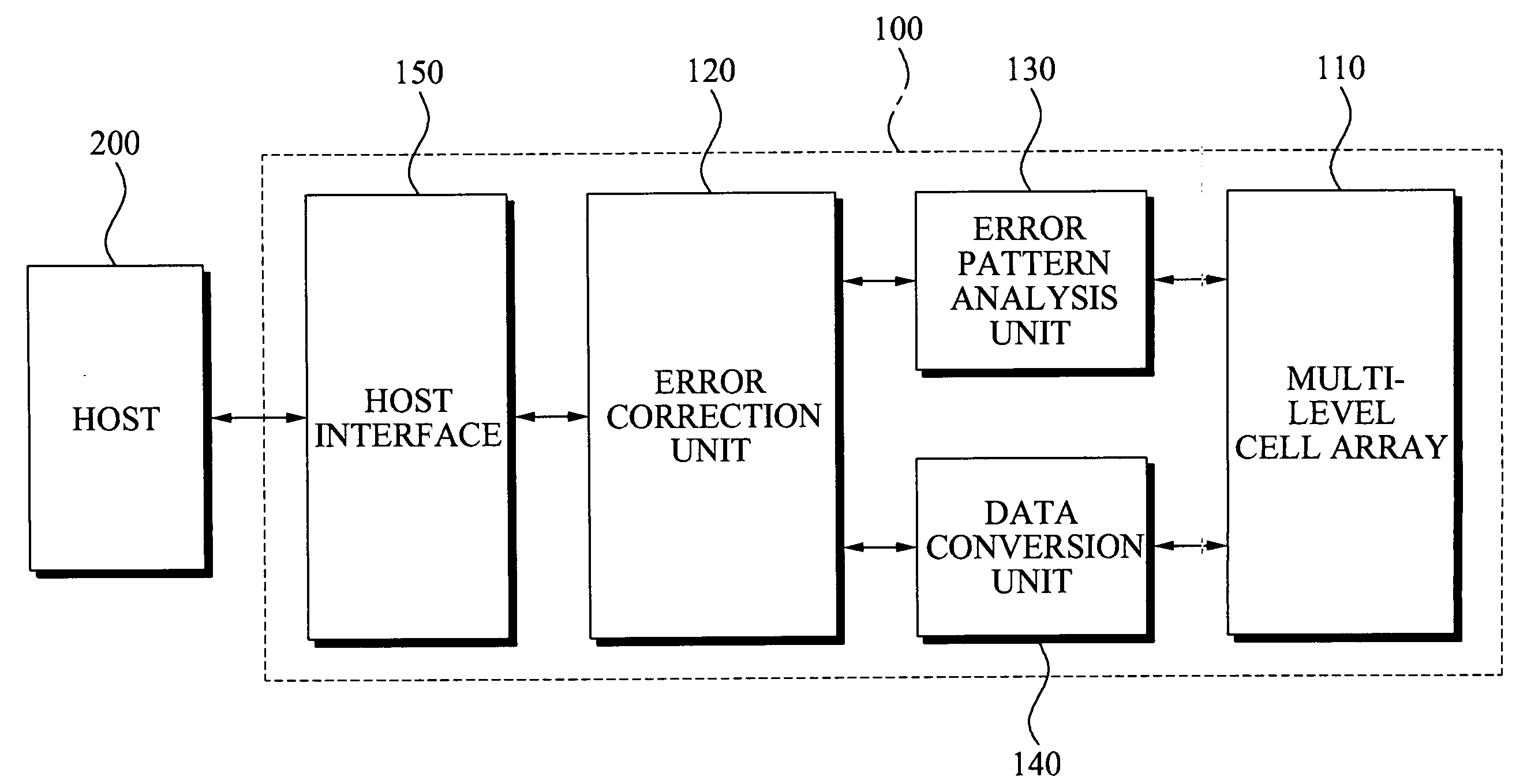
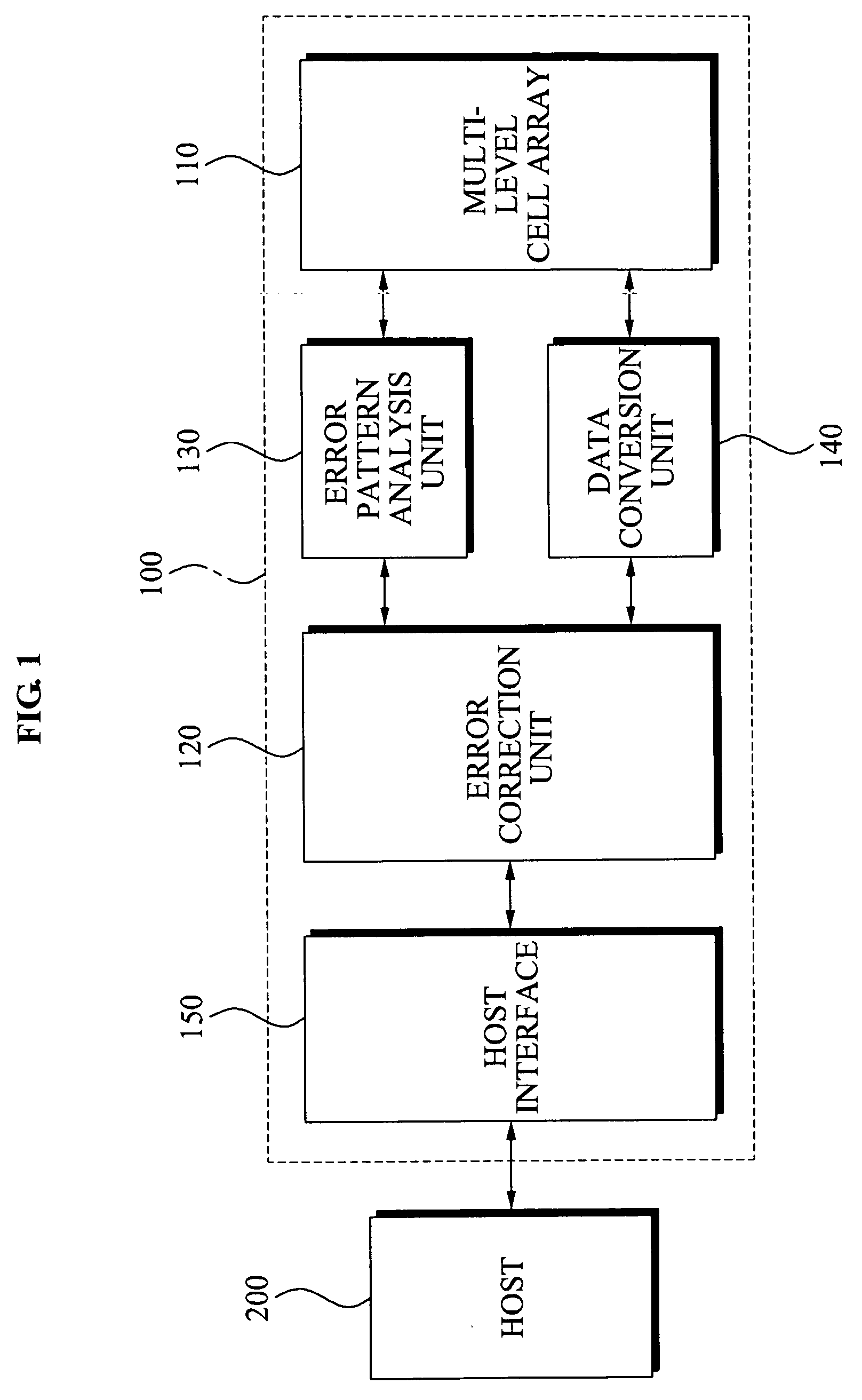
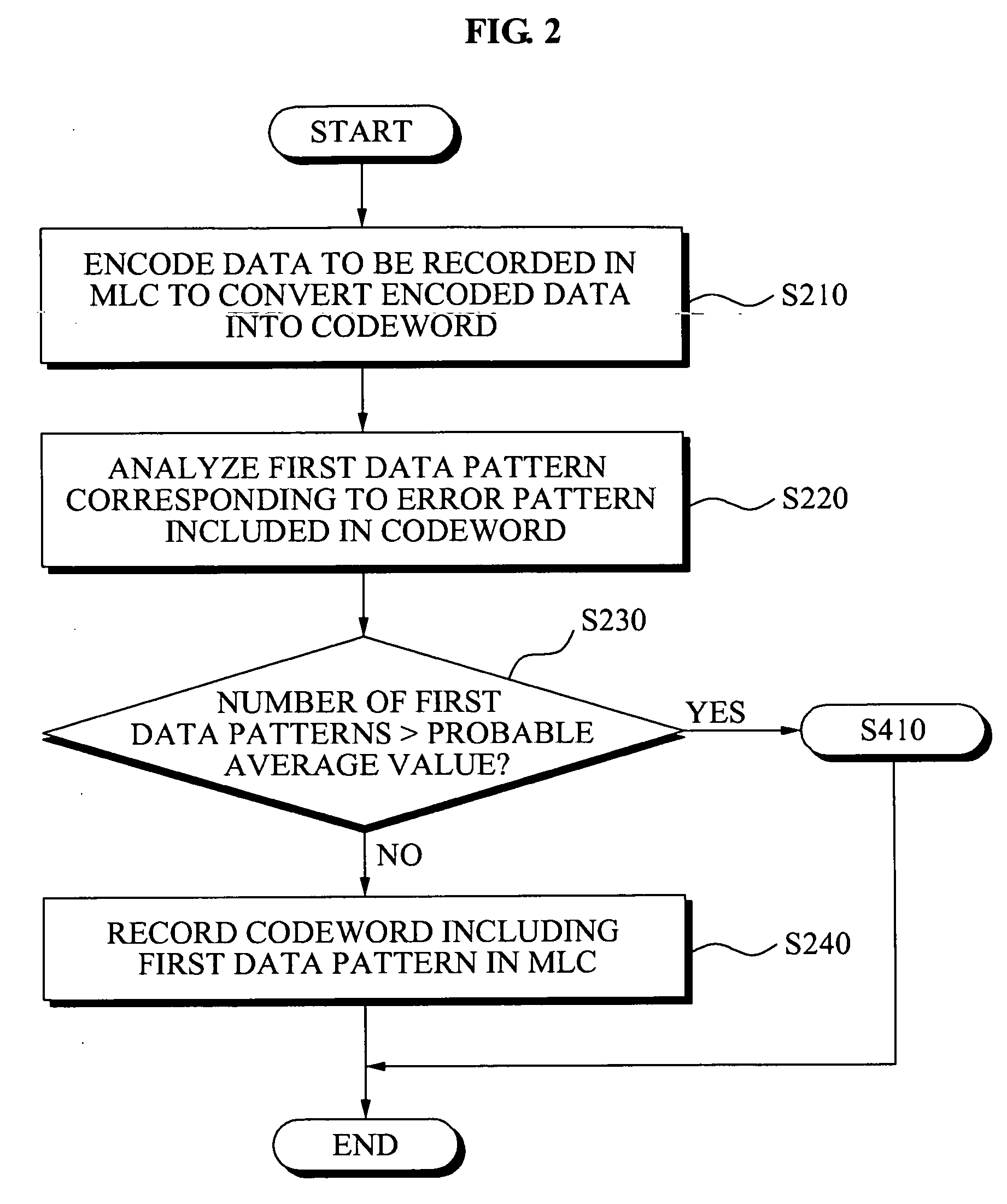
InactiveUS20090292973A1Reduce data errorsImprove reliabilityOther error detection/correction/protectionRead-only memoriesData memoryData error
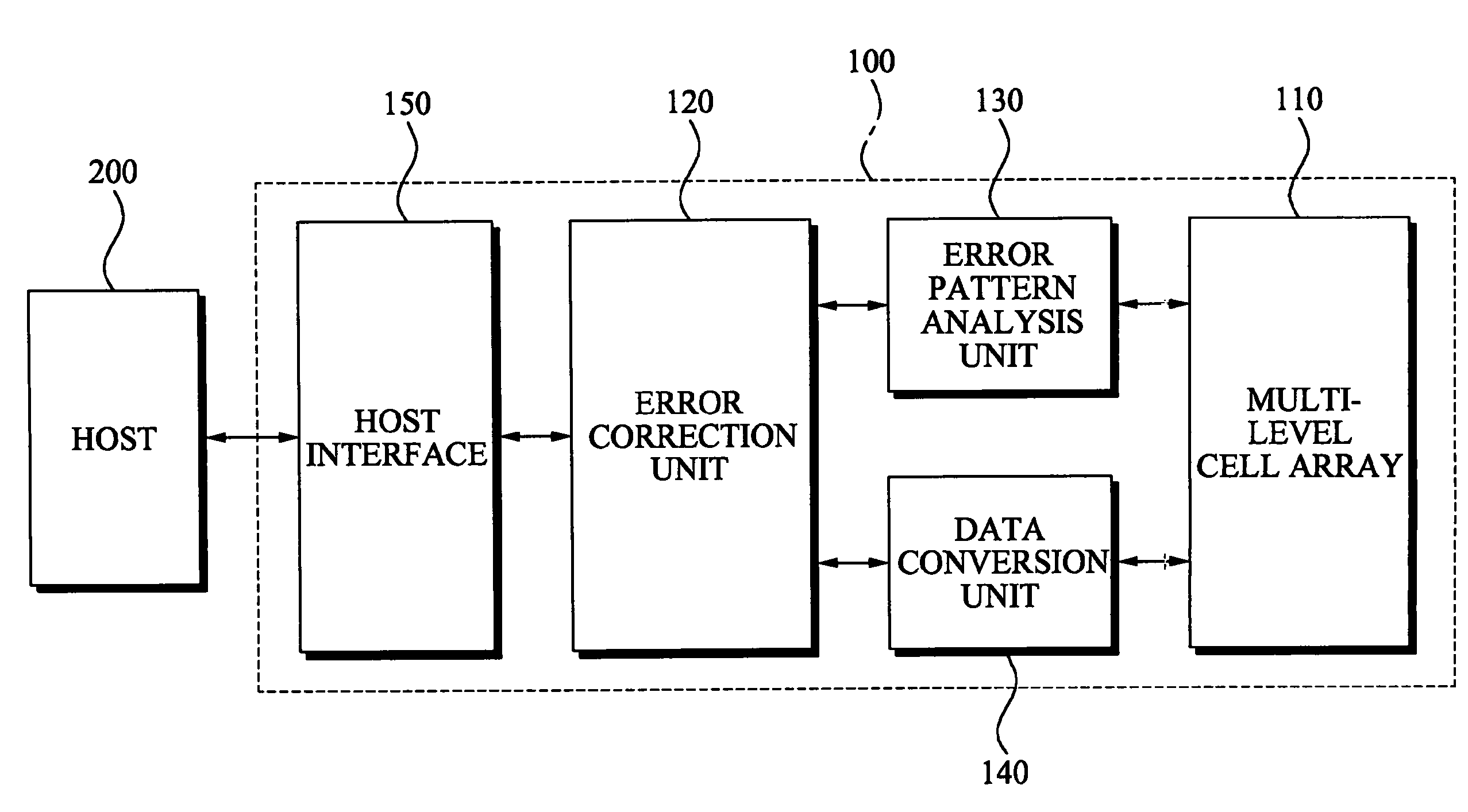
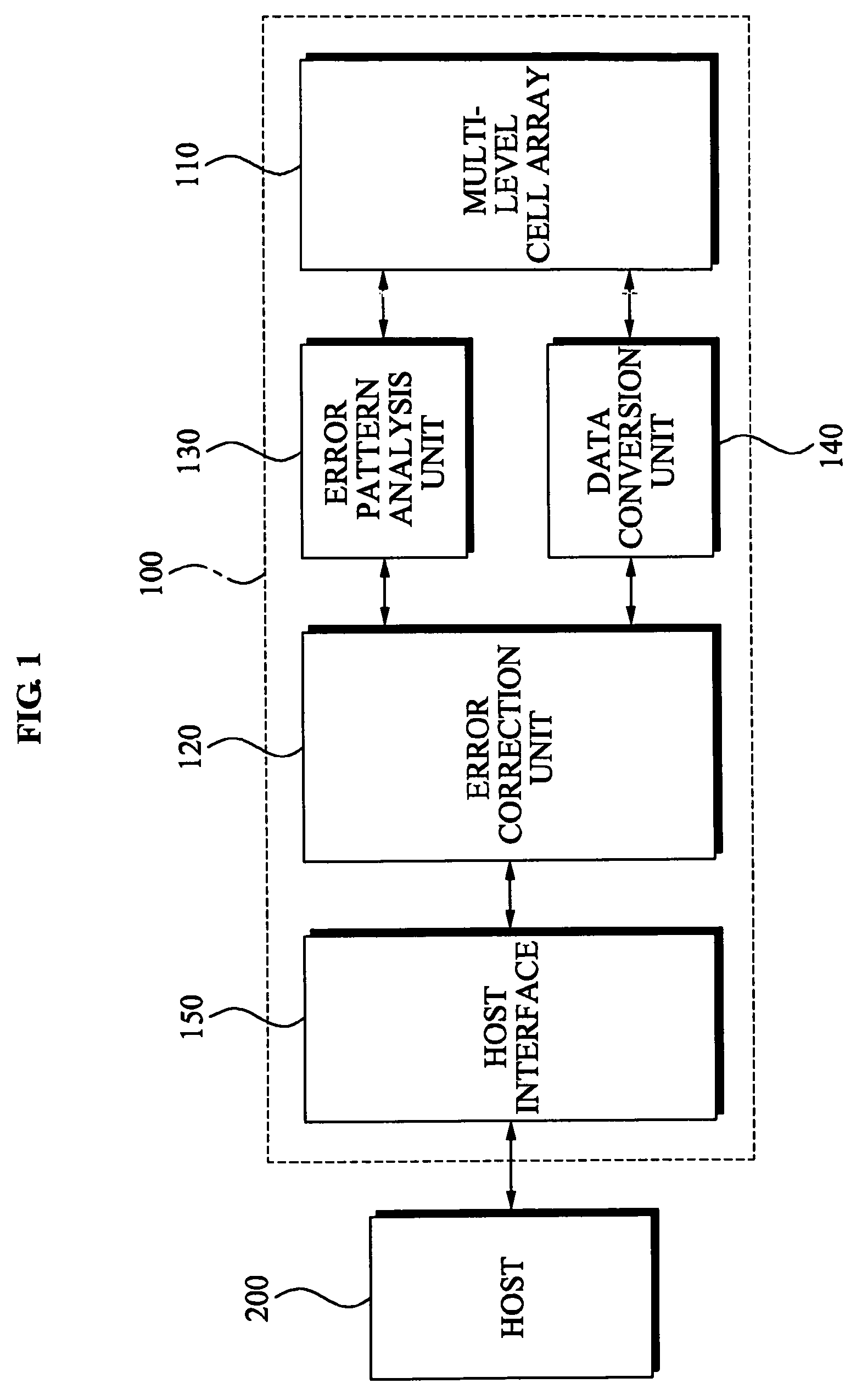
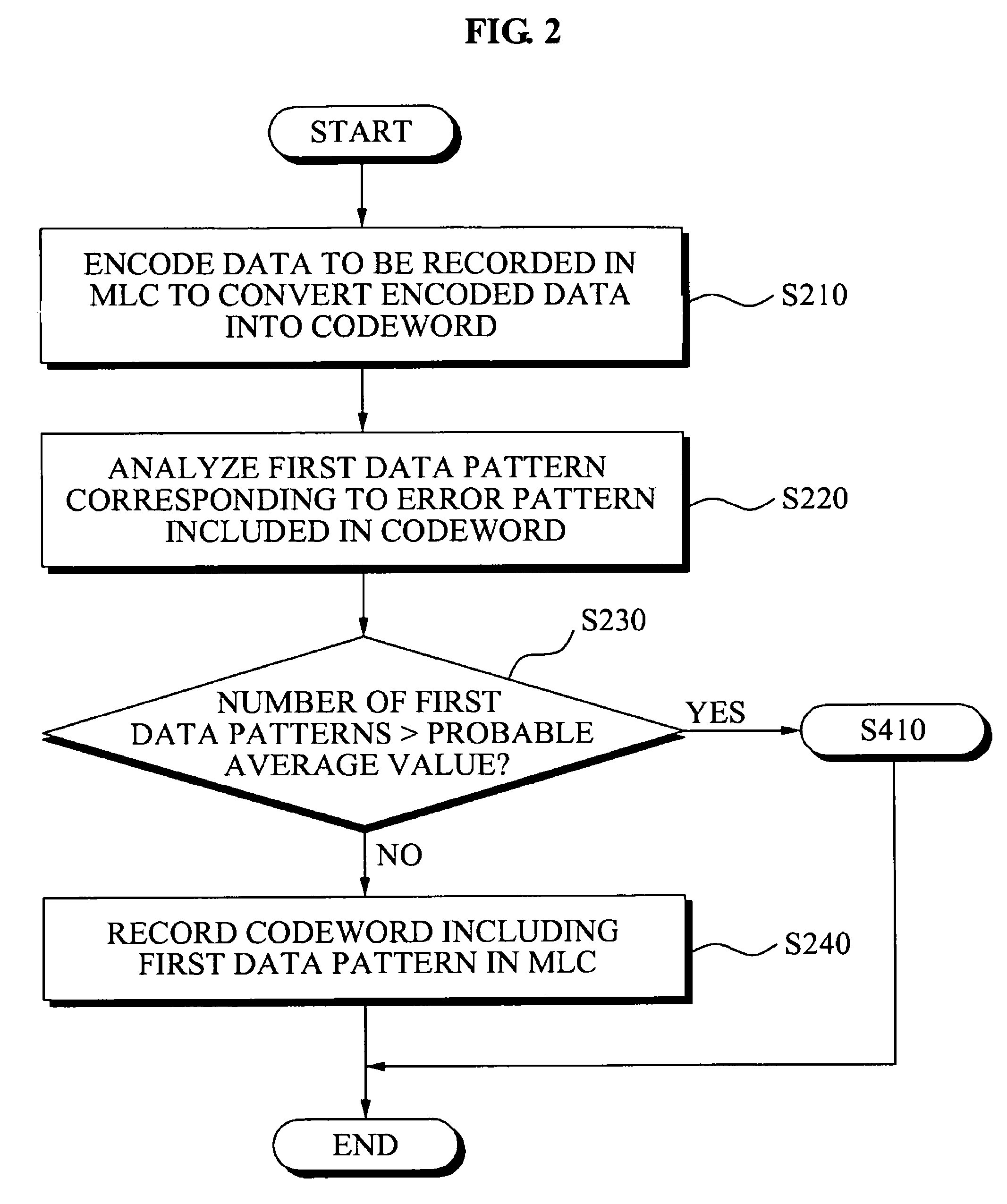
Memory devices and / or methods of storing memory data bits may be provided. A memory device may include a multi-level cell (MLC) array including a plurality of MLCs, an error correction unit configured to encode data to be recorded in an MLC, where the encoded data is converted to convert the encoded data into a codeword, an error pattern analysis unit configured to analyze a first data pattern included in the codeword corresponding to an error pattern included in the codeword and a data conversion unit configured to convert the analyzed first data pattern into a second data pattern. According to the above memory devices and / or methods, it may be possible to efficiently reduce a data error that occurs when the data is stored for a relatively long period of time, thereby improving reliability.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Reading memory cells using multiple thresholds
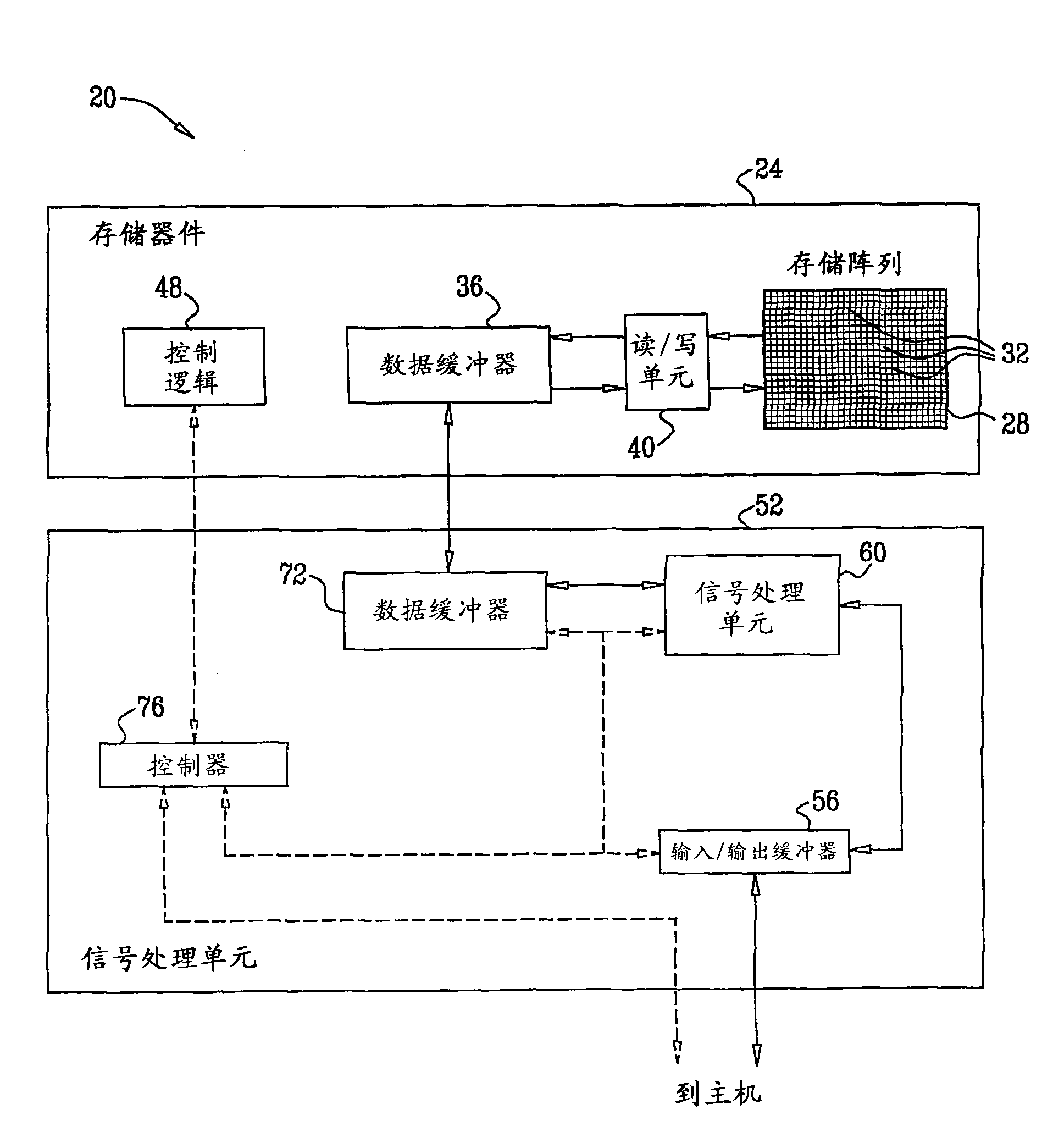
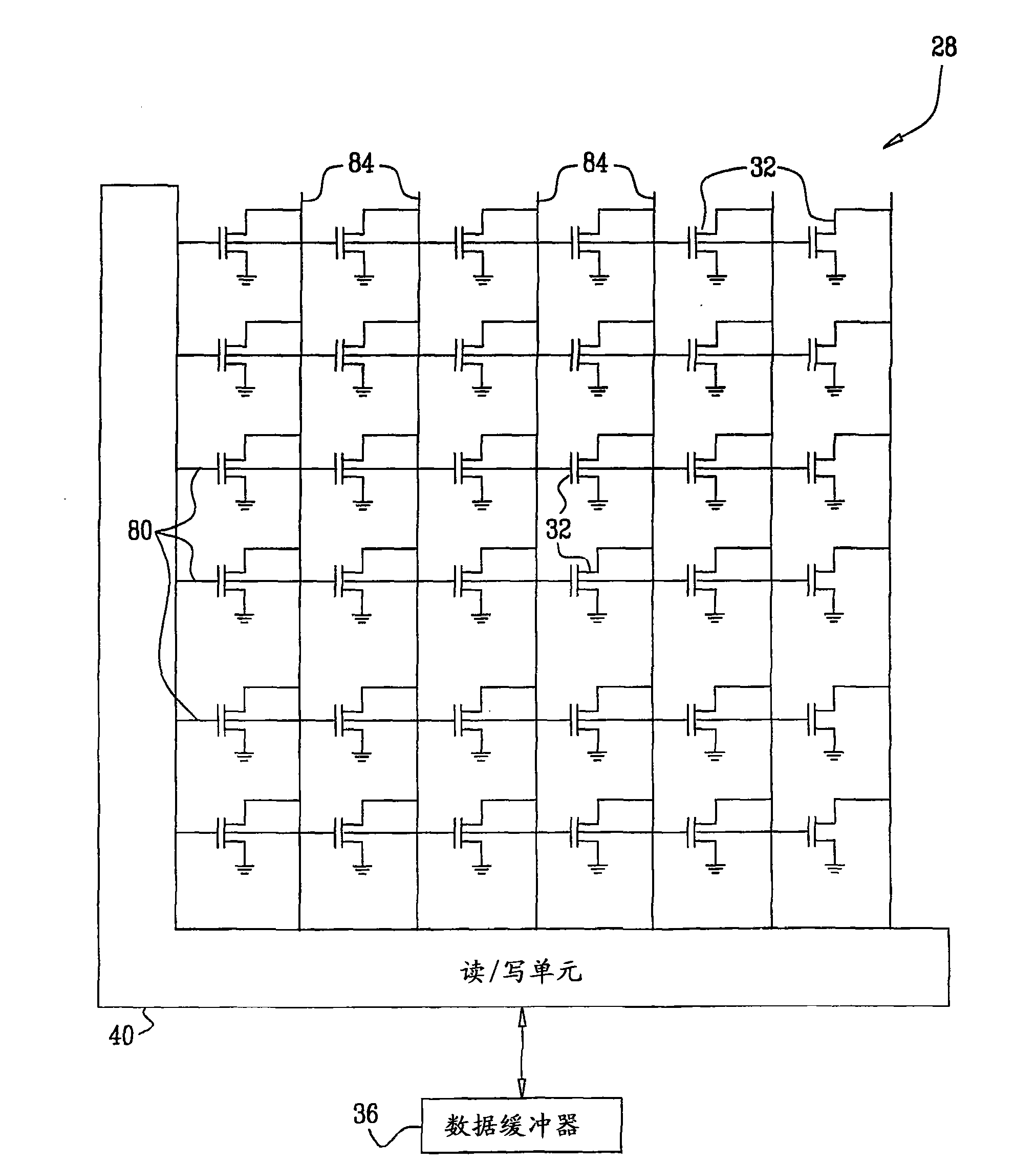
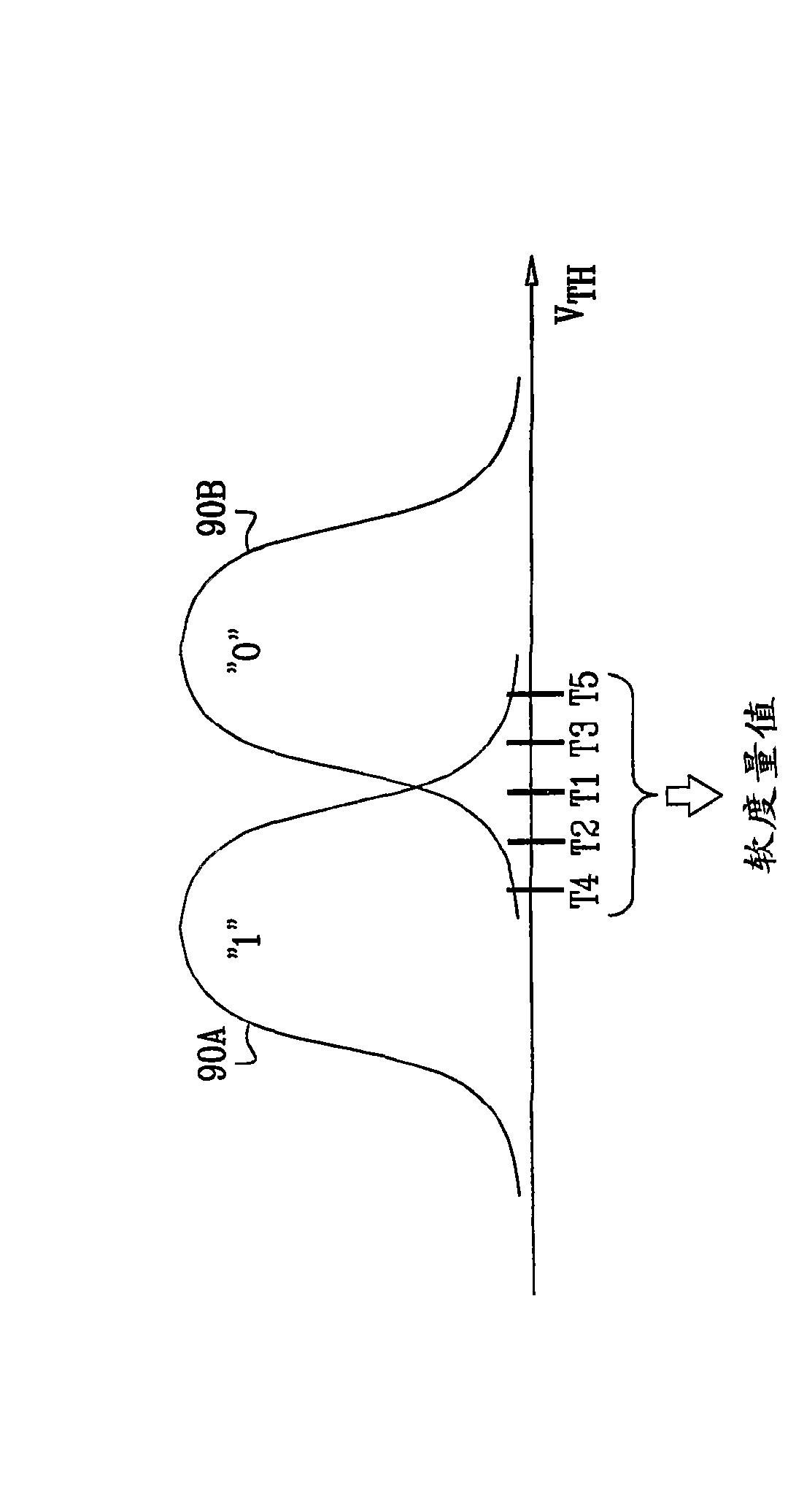
ActiveCN101601094AHigh precisionImprove decoding performanceElectric analogue storesRead-only memoriesData storingData store
A method for operating a memory (28) includes storing data, which is encoded with an Error Correction Code (ECC), in analog memory cells (32) of the memory by writing respective analog input values selected from a set of nominal values to the analog memory cells. The stored data is read by performing multiple read operations that compare analog output values of the analog memory cells to different, respective read thresholds so as to produce multiple comparison results for each of the analog memory cells. At least two of the read thresholds are positioned between a pair of the nominal values that are adjacent to one another in the set of the nominal values. Soft metrics are computed responsively to the multiple comparison results. The ECC is decoded using the soft metrics, so as to extract the data stored in the analog memory cells.
Owner:APPLE INC
Memory devices including barrier layers and methods of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20060077743A1Data Retention Time EnhancementEnhance data data writing/erasing speedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Memory devices and methods of manufacturing the same are provided. Memory devices may include a substrate, a source region and a drain region and a gate structure. The gate structure may be in contact with the source and drain regions, and may include a barrier layer. The barrier layer may be formed of at least two layers. The at least two layers may have different bandgap energies.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device, semiconductor memory device and data processing system comprising semiconductor system
ActiveUS8199559B2Excellent operating marginLower write voltageDigital storageData processing systemBit line
A semiconductor device comprises a memory cell, a bit line, a sense amplifier operating between a first voltage and a second voltage higher than the first voltage, a transfer control circuit including a transfer transistor, and a write circuit writing data into the memory cell through the bit line based on the first voltage and a third voltage. The sense amplifier receives and amplifiers the signal voltage at a sense node when the transfer transistor controls the connection between the bit line and the sense node in response to a transfer control voltage. The third voltage is set to a voltage lower than the second voltage and higher than the transfer control voltage, and the sense node is set to a voltage higher than the transfer control voltage in an initial period of a read operation before the data of the memory cell is read out to the bit line.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
Semiconductor memory device including an SOI
InactiveUS20060118849A1Data Retention Time EnhancementOperation moreTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringBody region
A semiconductor memory device includes a plurality of N and P channel MOS transistors. The plurality of MOS transistors are formed on an SOI (Silicon On Insulator) substrate. Each MOS transistor includes a source region, a drain region, and a body region located between the source region and the drain region. The body region of at least one N channel MOS transistor is electrically fixed. The body region of at least one P channel MOS transistor is rendered floating.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device, semiconductor memory device and data processing system comprising semiconductor system
ActiveUS20110063891A1Excellent operating marginRun at high speedDigital storageData processing systemBit line
A semiconductor device comprises a memory cell, a bit line, a sense amplifier operating between a first voltage and a second voltage higher than the first voltage, a transfer control circuit including a transfer transistor, and a write circuit writing data into the memory cell through the bit line based on the first voltage and a third voltage. The sense amplifier receives and amplifiers the signal voltage at a sense node when the transfer transistor controls the connection between the bit line and the sense node in response to a transfer control voltage. The third voltage is set to a voltage lower than the second voltage and higher than the transfer control voltage, and the sense node is set to a voltage higher than the transfer control voltage in an initial period of a read operation before the data of the memory cell is read out to the bit line.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
Semiconductor memory device including an SOI substrate
InactiveUS20050001254A1Data Retention Time EnhancementOperation moreTransistorSolid-state devicesSoi substrateBody region
A semiconductor memory device includes a plurality of N and P channel MOS transistors. The plurality of MOS transistors are formed on an SOI (Silicon On Insulator) substrate. Each MOS transistor includes a source region, a drain region, and a body region located between the source region and the drain region. The body region of at least one N channel MOS transistor is electrically fixed. The body region of at least one P channel MOS transistor is rendered floating.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method for manufacturing semiconductor memory device using asymmetric junction ion implantation
InactiveUS20070065999A1Improve featuresData Retention Time EnhancementSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBit lineGate stack
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor memory device using asymmetric junction ion implantation, including performing ion implantation for adjusting a threshold voltage to a semiconductor substrate, forming a gate stack on the semiconductor substrate to define a storage node junction region and a bit line junction region, implanting a first conductive impurity ion and a second conductive impurity ion using a mask layer pattern covering the storage node junction region while exposing the bit line junction region, forming a gate spacer layer at both sides of the gate stack, and implanting the first conductive impurity ion using the gate stack and the gate spacer layer as an ion implantation mask layer to form a storage node junction region and a bit line junction region having different impurity concentrations, and different junction depths from each other.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
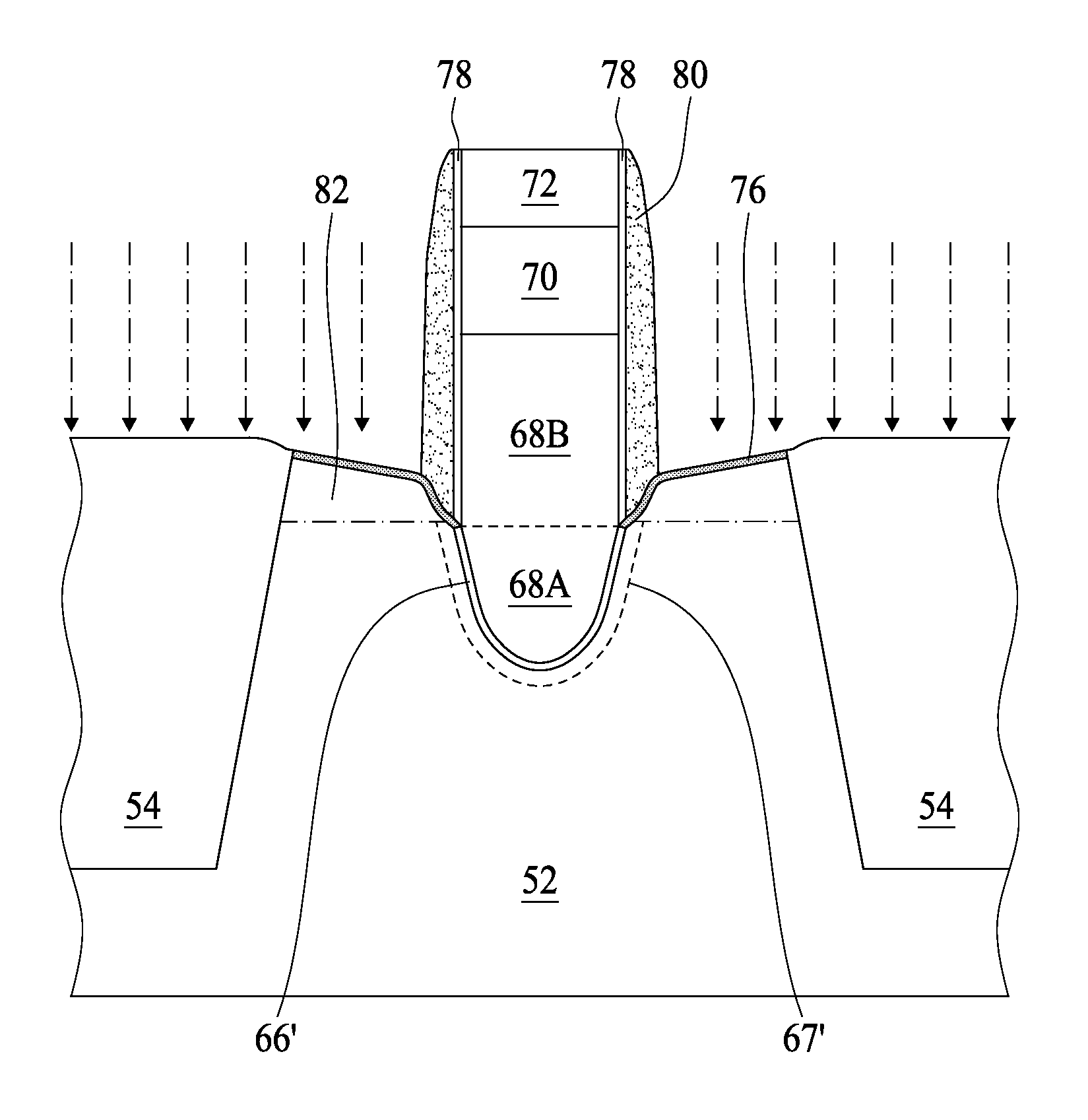
Recessed channel transistor and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20100013004A1Reduce leakage currentData Retention Time EnhancementTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
A recessed channel transistor comprises a semiconductor substrate having a trench isolation structure, a gate structure having a lower block in the semiconductor substrate and an upper block on the semiconductor substrate, two doped regions positioned at two sides of the upper block and above the lower block, and an insulation spacer positioned at a sidewall of the upper block and having a bottom end sandwiched between the upper block and the doped regions. In particular, the two doped regions serves as the source and drain regions, respectively, and the lower block of the gate structure serves as the recessed gate of the recessed channel transistor.
Owner:PROMOS TECH INC
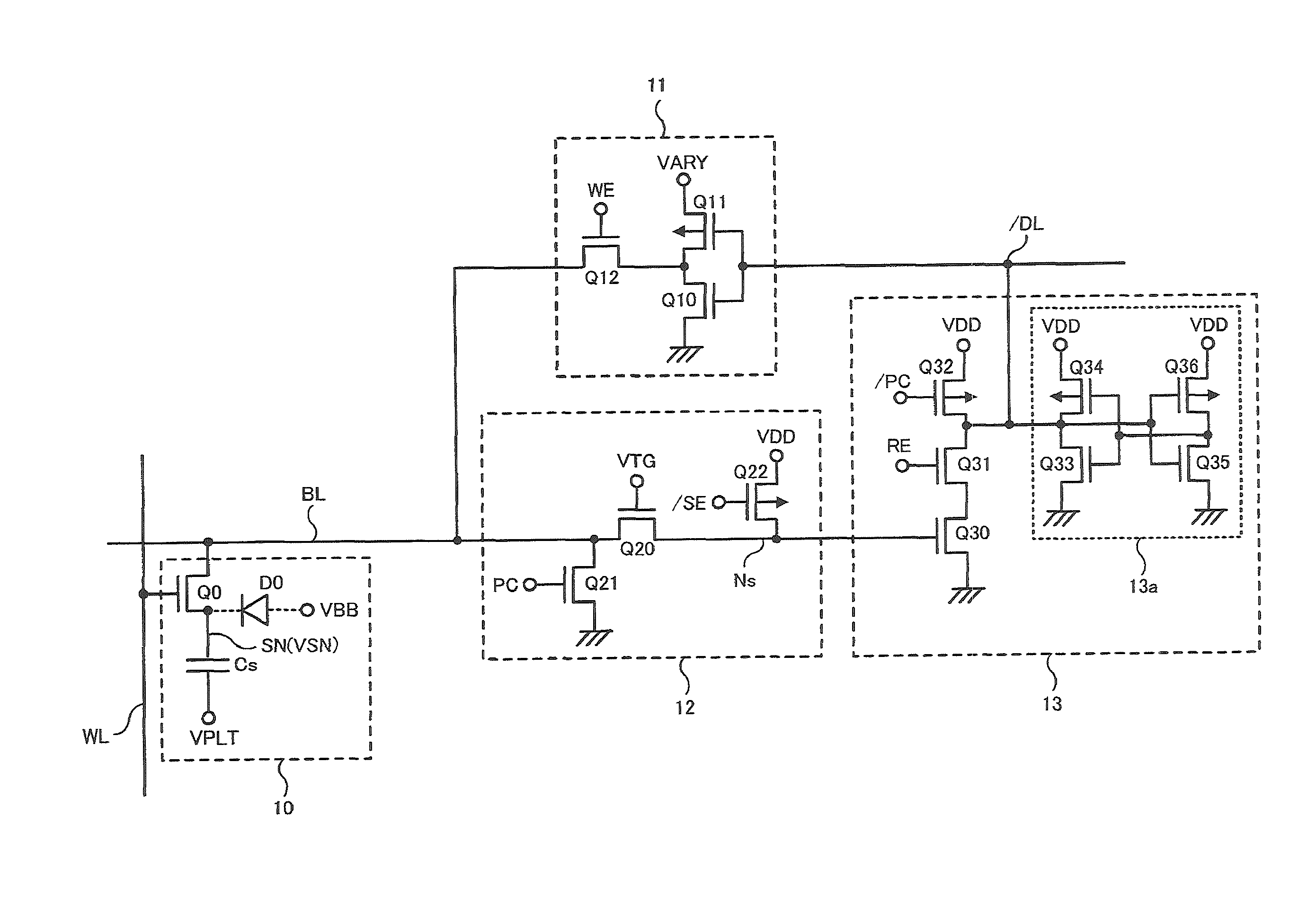
Memory cell, a memory array and a method of programming a memory cell
InactiveUS8320192B2Data Retention Time EnhancementFast and efficient mass erasureRead-only memoriesDigital storageElectricityTrapping
A method of programming a memory cell (100), the method comprising applying a first electric potential to a first electric terminal (101) of the memory cell (100) to accelerate first charge carriers of a first type of conductivity to thereby generate second charge carriers of a second type of conductivity by impact ionisation of the accelerated first charge carriers, and applying a second electric potential to a second electric terminal (102) of the memory cell (100) to accelerate the second charge carriers to thereby inject the second charge carriers in a charge trapping structure (103) of the memory cell (100).
Owner:NXP BV
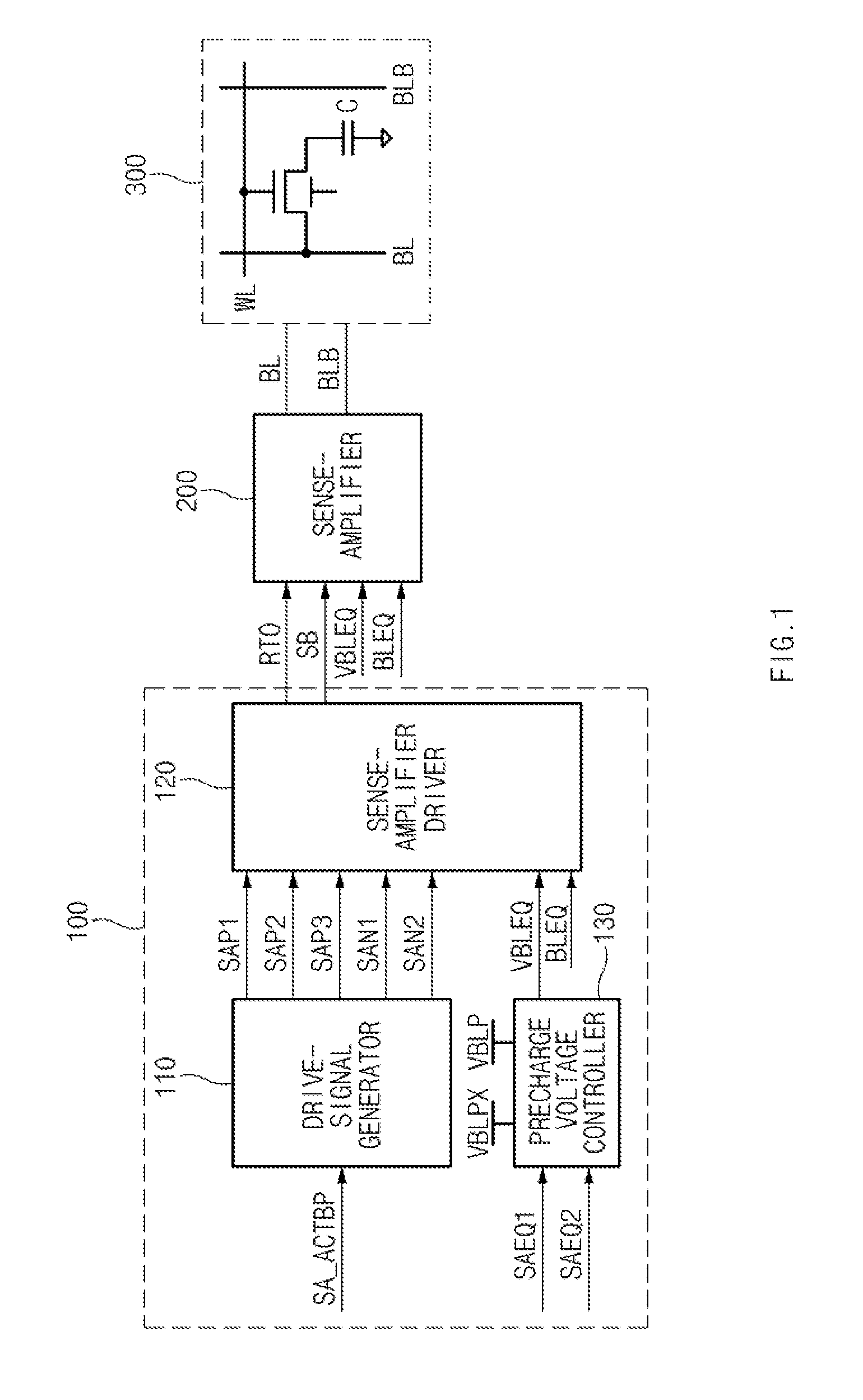
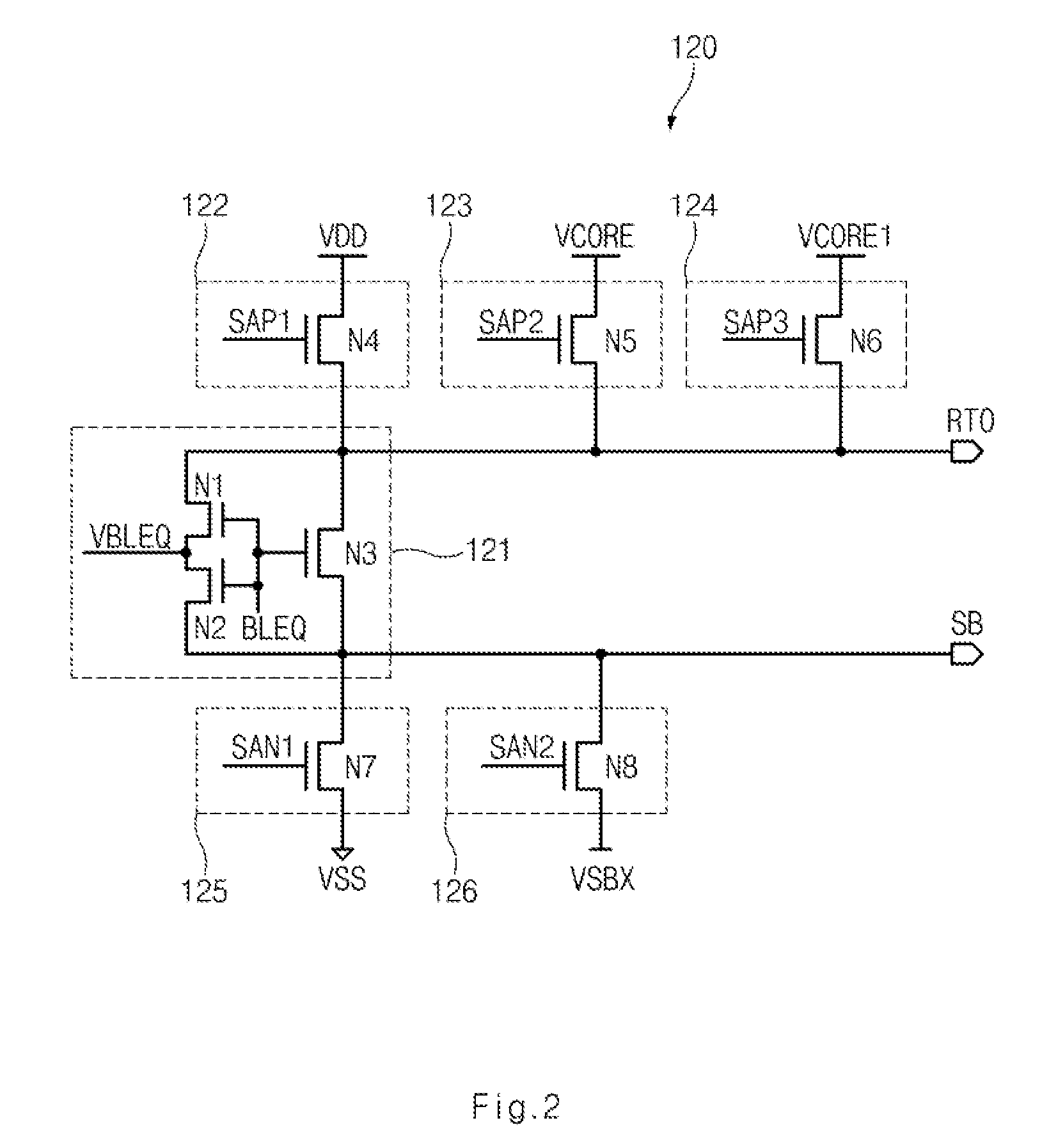
Sense-amplifier driving device and semiconductor device including the same
ActiveUS9117545B1Improve featuresData Retention Time EnhancementDigital storageAmplififers with field-effect devicesPower semiconductor deviceAudio power amplifier
A semiconductor device includes a sense-amplifier driving device. The sense-amplifier driving device includes a sense-amplifier driver configured to provide a first pull-up voltage and a first pull-down voltage to a pull-up power line and a pull-down power line, respectively, during a first over-driving time period, provide the second pull-up voltage and the first pull-down voltage to the pull-up power line and the pull-down power line, respectively, during an active time period, and provide a third pull-up voltage and a second pull-down voltage to the pull-up power line and the pull-down power line, respectively, during a second over-driving time period, and a drive-signal generator configured to generate a plurality of drive signals, which is selectively activated during the first over-driving time period, the active time period, and the second over-driving time period, to control an operation of the sense-amplifier driver.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Network recorders with entropy and value based packet truncation
ActiveUS20190158635A1Use less storage spaceData Retention Time EnhancementCode conversionData switching networksNetwork packetReal-time computing
In one embodiment, a computer-implemented method of conserving storage space in a network recorder includes receiving a computer packet including a header and payload data; estimating entropy of the payload data in the computer packet; determining if storage of the computer packet is of value or not based on the header of the computer packet; and storing all or a portion of the computer packet into a storage device based on the estimated entropy and the value determination.
Owner:ENDACE TECH
Methods for repairing and for operating a memory component
InactiveUS20060126407A1Maximizing refresh timeRepair operationDigital storageLimit valueComputer science
In a method for repairing a memory component, data retention times of regular memory cells are determined. Weak regular memory cells having a data retention time that is shorter than a predetermined limit value are determined. A device is programmed in such a manner that a write or read access to the weak regular memory cell is simultaneously also effected for a redundant memory cell in order to jointly read from, or write to, the weak regular memory cell and the redundant memory cell.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS20160163364A1Data Retention Time EnhancementImprove data retentionDigital storageAudio power amplifierSemiconductor
Disclosed is a semiconductor memory device including: a sense amplifier capable of sensing and amplifying data loaded on a data-line pair based on a pull-up driving voltage and a pull-down driving voltage; a pull-up driving unit capable of supplying a first voltage as the pull-up driving voltage for first and third active sections of an active mode, and supplying a second voltage having a voltage level lower than the first voltage as the pull-up driving voltage for a second active section of the active mode, between the first and third active sections of the active mode; and a pull-down driving unit capable of supplying a third voltage as the pull-down driving voltage for the first to third active sections of the active mode and for an initial section of a precharge mode after the active mode.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor device, semiconductor memory device and data processing system comprising semiconductor system
ActiveUSRE45819E1Excellent operating marginLower write voltageDigital storageData processing systemPower semiconductor device
A semiconductor device comprises a memory cell, a bit line, a sense amplifier operating between a first voltage and a second voltage higher than the first voltage, a transfer control circuit including a transfer transistor, and a write circuit writing data into the memory cell through the bit line based on the first voltage and a third voltage. The sense amplifier receives and amplifiers the signal voltage at a sense node when the transfer transistor controls the connection between the bit line and the sense node in response to a transfer control voltage. The third voltage is set to a voltage lower than the second voltage and higher than the transfer control voltage, and the sense node is set to a voltage higher than the transfer control voltage in an initial period of a read operation before the data of the memory cell is read out to the bit line.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Recessed channel transistor and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS7781830B2Reduce leakage currentTotal current dropTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorTransistor
A recessed channel transistor comprises a semiconductor substrate having a trench isolation structure, a gate structure having a lower block in the semiconductor substrate and an upper block on the semiconductor substrate, two doped regions positioned at two sides of the upper block and above the lower block, and an insulation spacer positioned at a sidewall of the upper block and having a bottom end sandwiched between the upper block and the doped regions. In particular, the two doped regions serves as the source and drain regions, respectively, and the lower block of the gate structure serves as the recessed gate of the recessed channel transistor.
Owner:PROMOS TECH INC
Memory device and method of storing data with error correction using codewords
InactiveUS8301978B2Improve reliabilityReduce data errorsError detection/correctionOther error detection/correction/protectionData errorMulti-level cell
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Memory cell, a memory array and a method of programming a memory cell
InactiveUS20100128536A1Fast and efficient mass erasureData Retention Time EnhancementRead-only memoriesDigital storageTrappingCharge carrier
A method of programming a memory cell (100), the method comprising applying a first electric potential to a first electric terminal (101) of the memory cell (100) to accelerate first charge carriers of a first type of conductivity to thereby generate second charge carriers of a second type of conductivity by impact ionisation of the accelerated first charge carriers, and applying a second electric potential to a second electric terminal (102) of the memory cell (100) to accelerate the second charge carriers to thereby inject the second charge carriers in a charge trapping structure (103) of the memory cell (100).
Owner:NXP BV
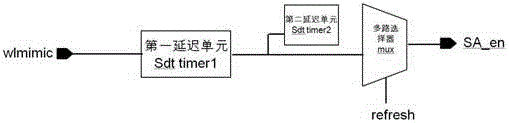
Signal establishing time control circuit and dynamic storage based on same
The invention relates to a signal establishing time control circuit and a dynamic storage based on the same. The signal establishing time control circuit comprises a first delay unit, a second delay unit and a multiplexer, wherein a selected word line signal wlmimic is divided into two paths by virtue of the first delay unit, the first path directly outputs a signal SA_en1, the second path outputs a signal SA_en2 by virtue of the second delay unit, the multiplexer outputs sense amplifier enabling signals by selecting the signal SA_en1 and the signal SA_en2, and the gating of the multiplexer is controlled by virtue of signal refresh. According to the signal establishing time control circuit, the technical problem of short storage retention time when same signal establishing time is adopted during activation operation and refresh operation of an existing dynamic storage is solved, and the data retention time of the dynamic storage is effectively prolonged.
Owner:XI AN UNIIC SEMICON CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com