Patents
Literature
37results about How to "Lower write voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
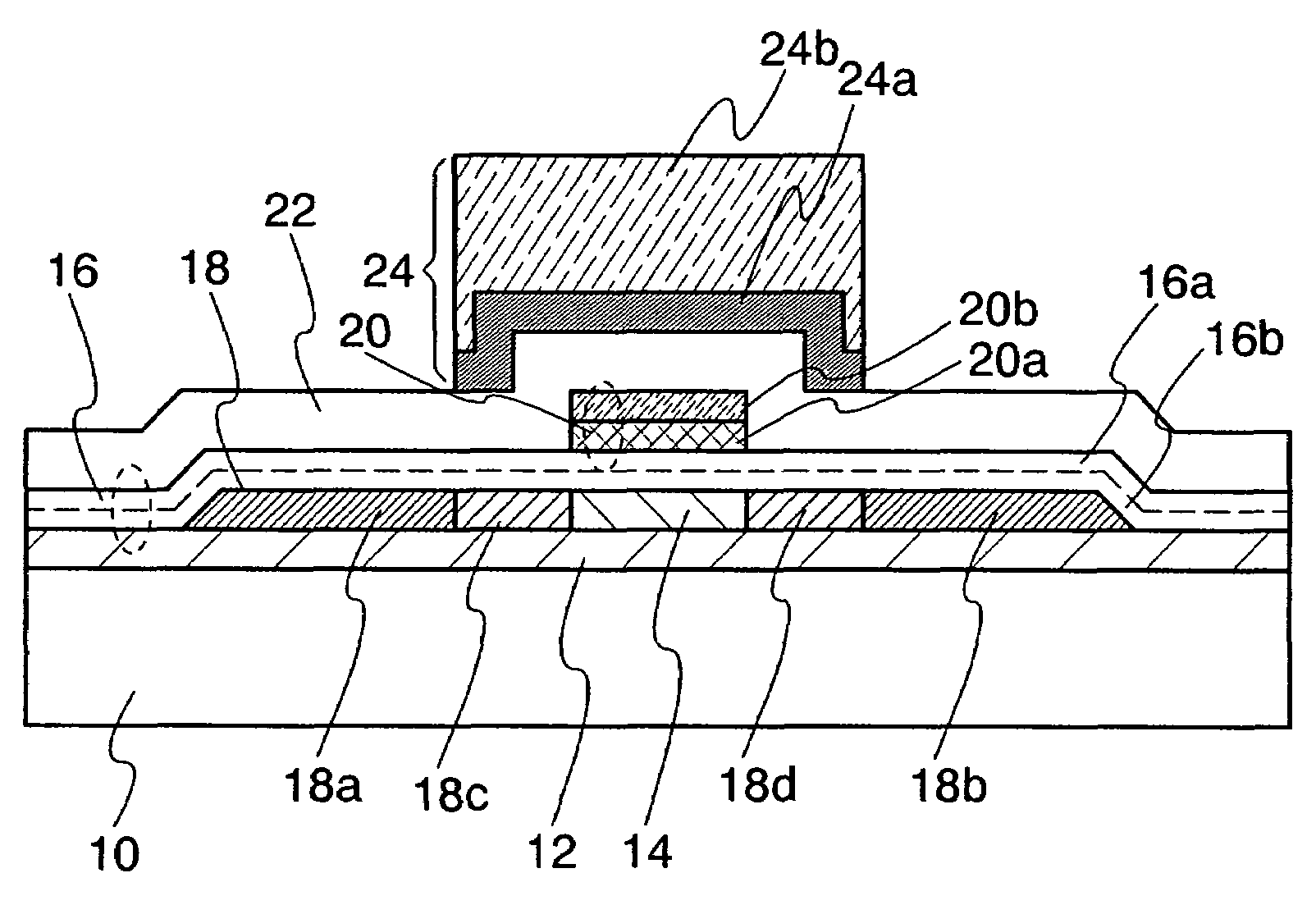
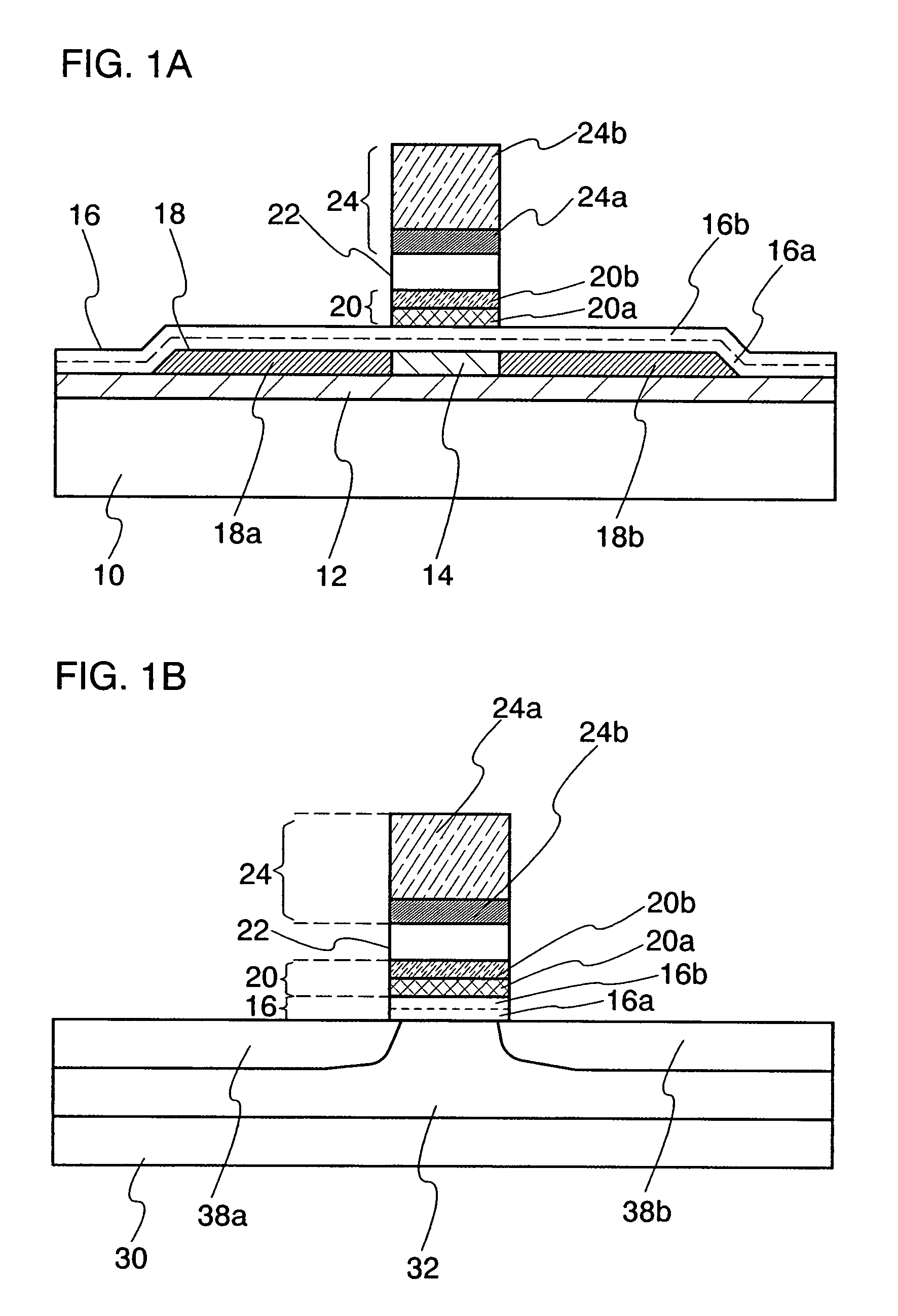
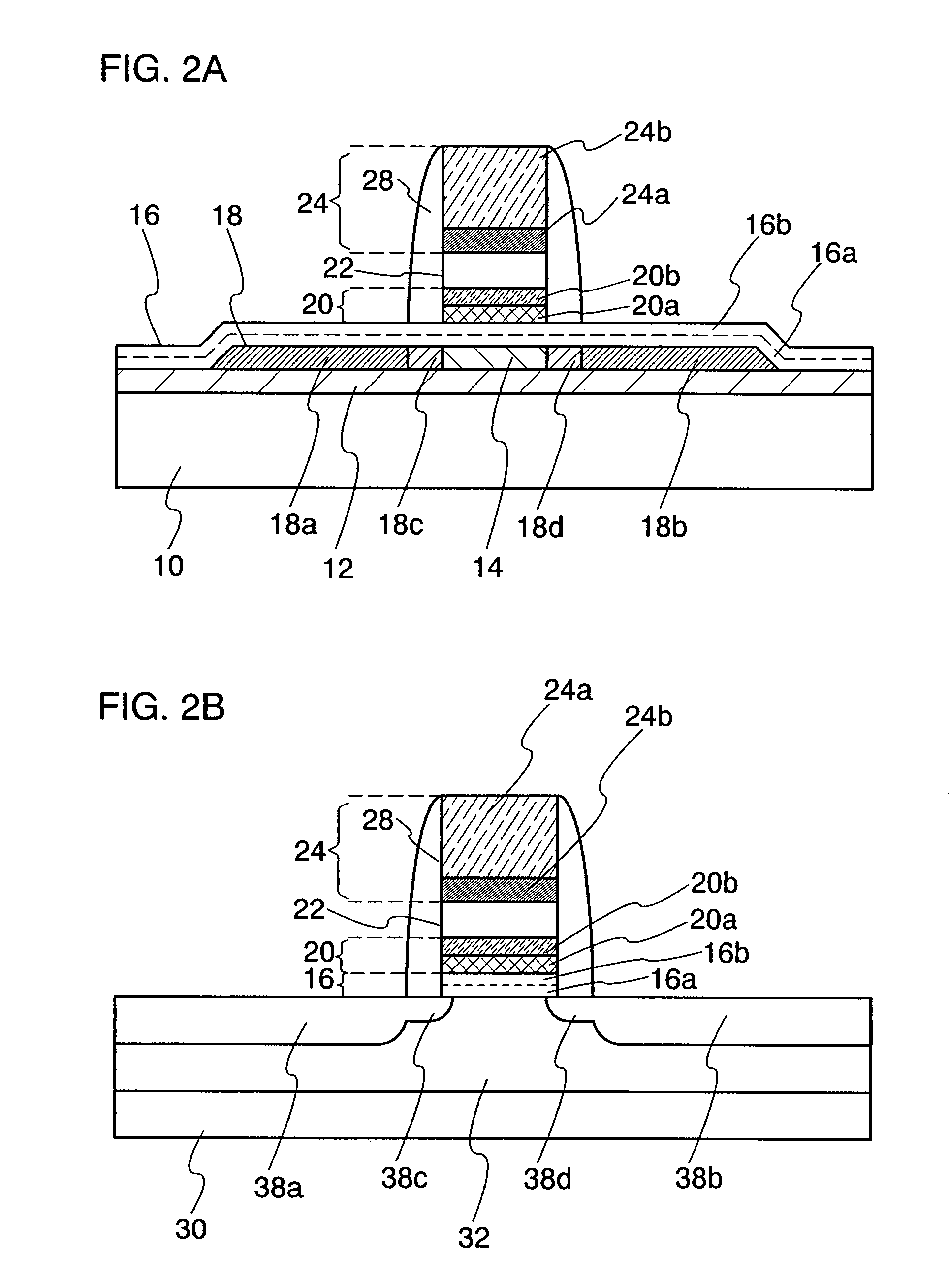
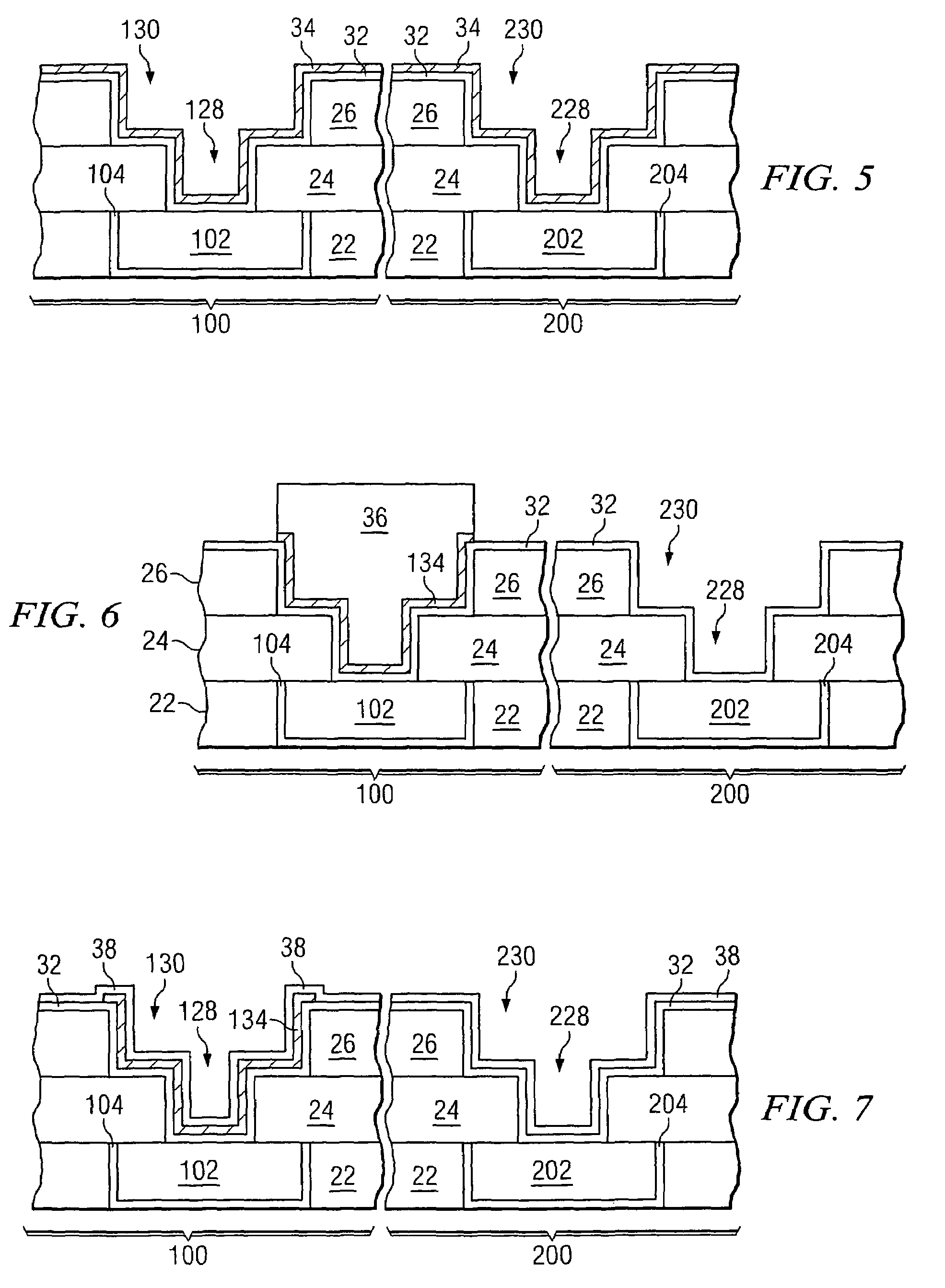
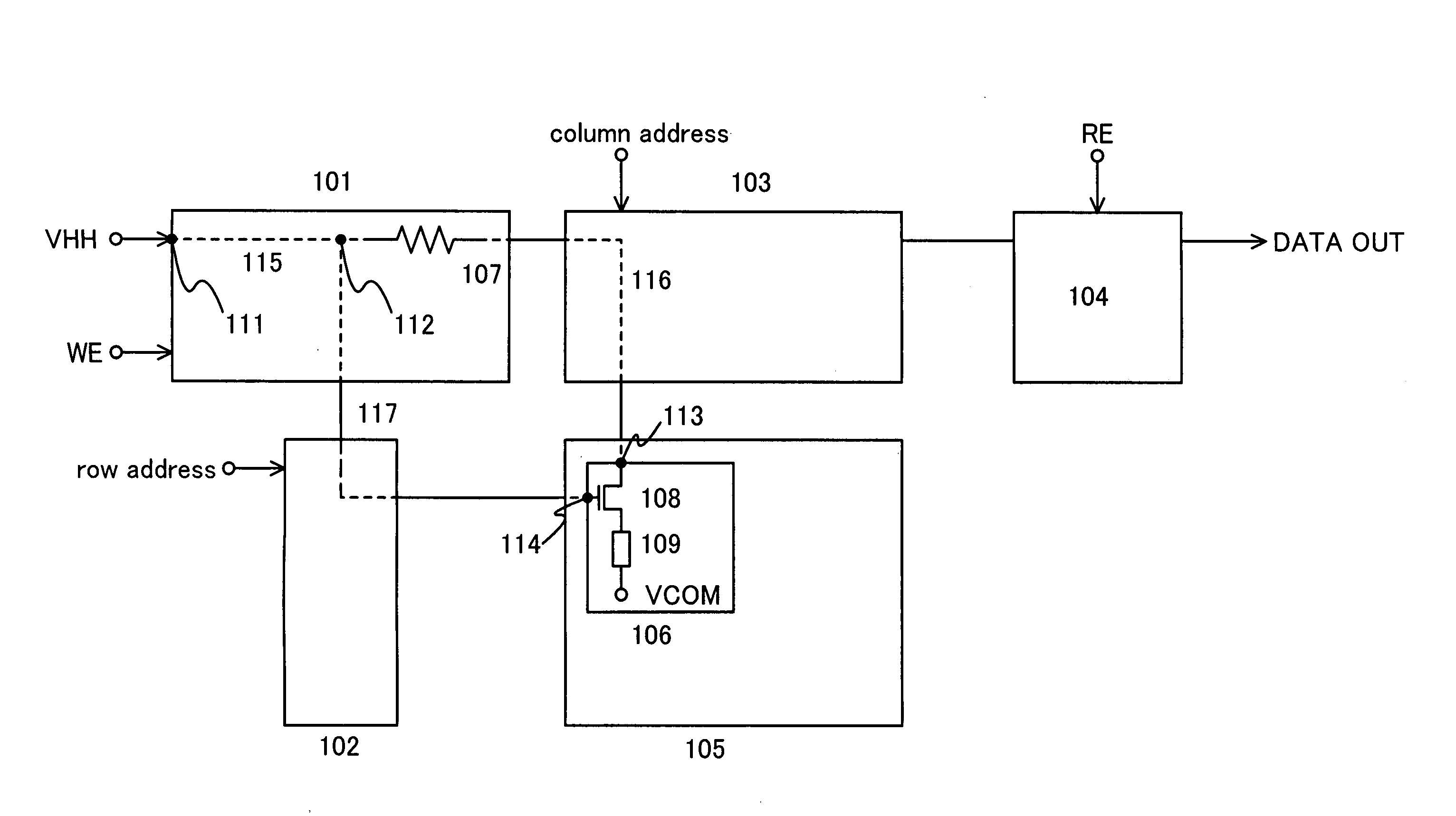
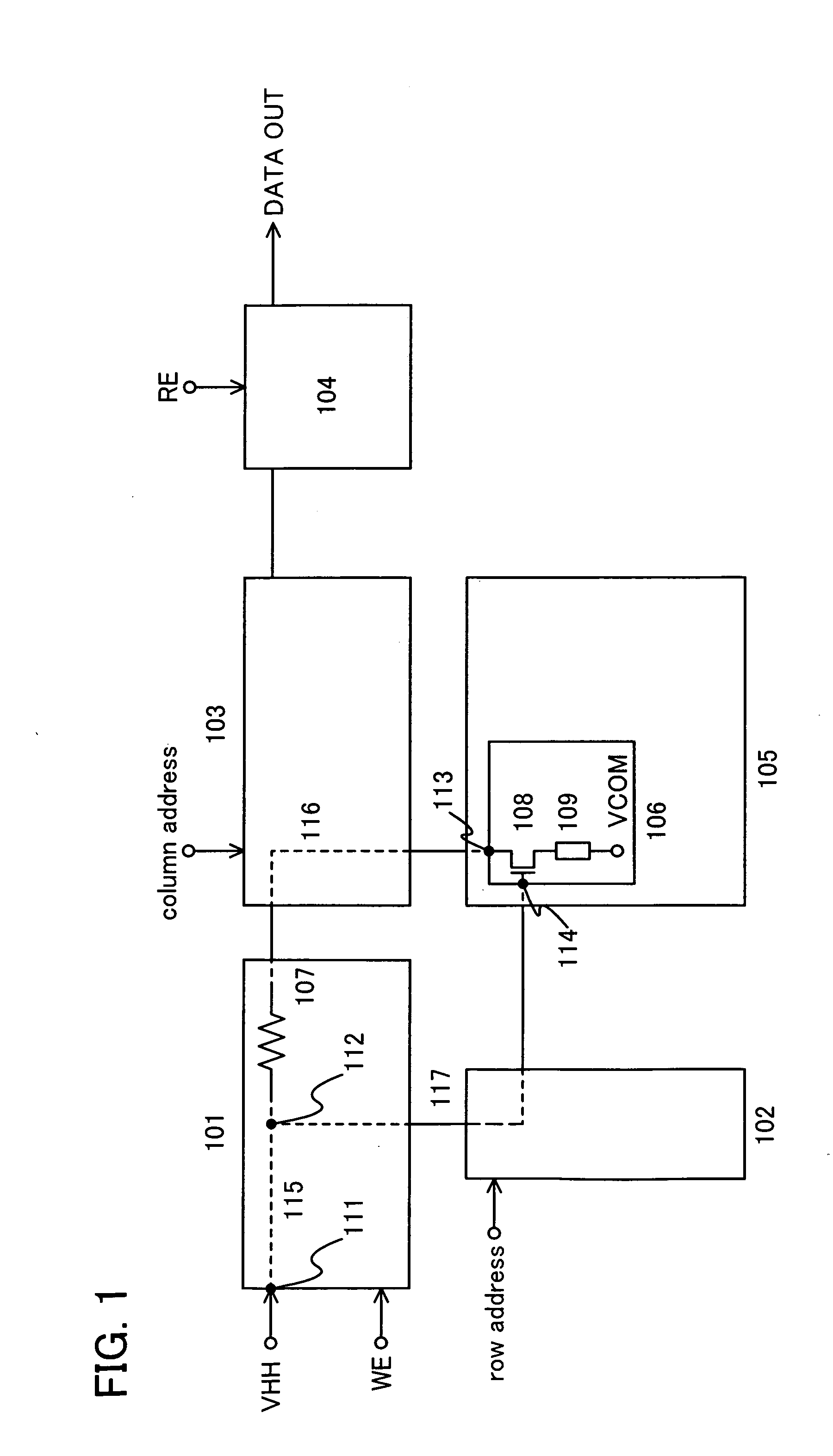
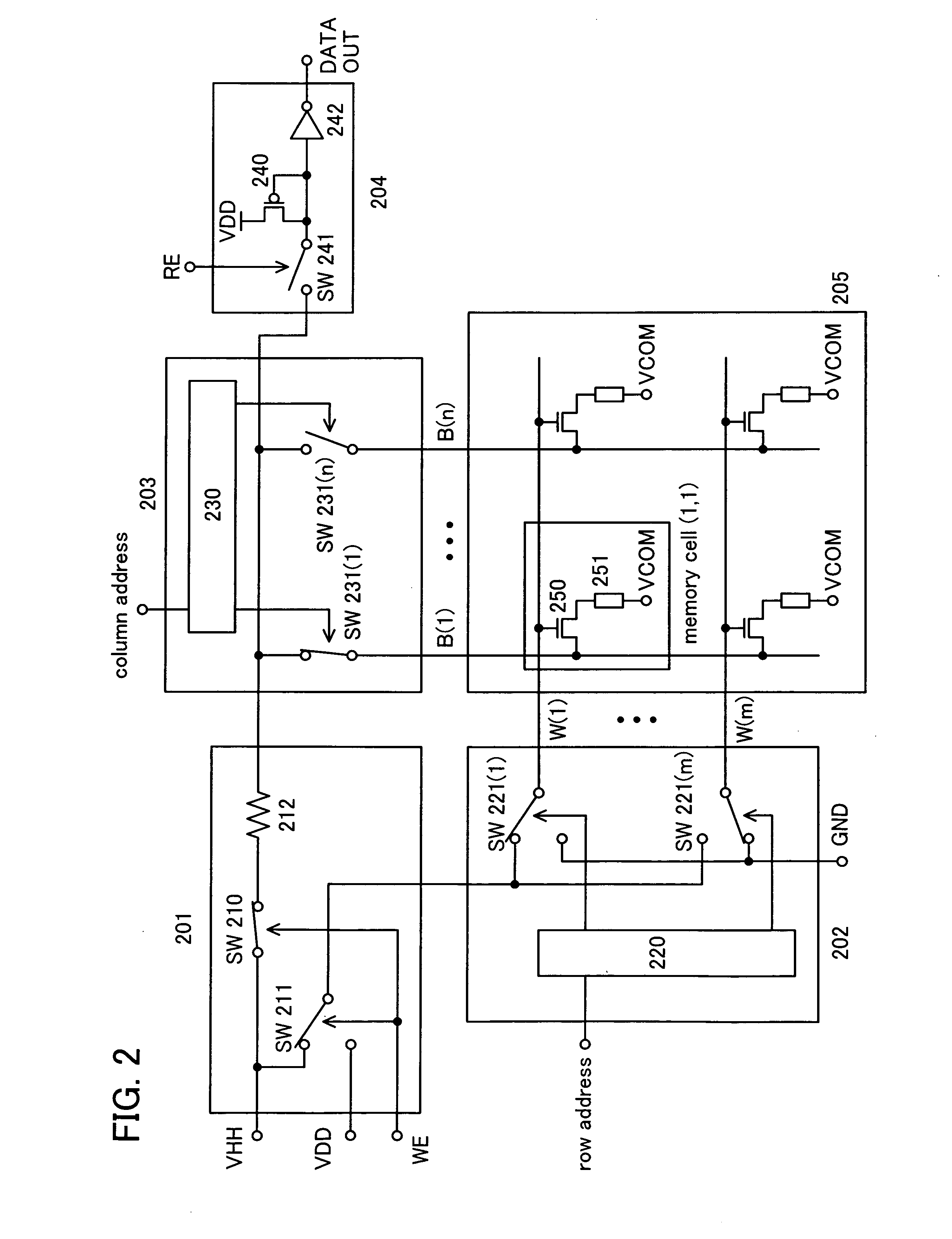
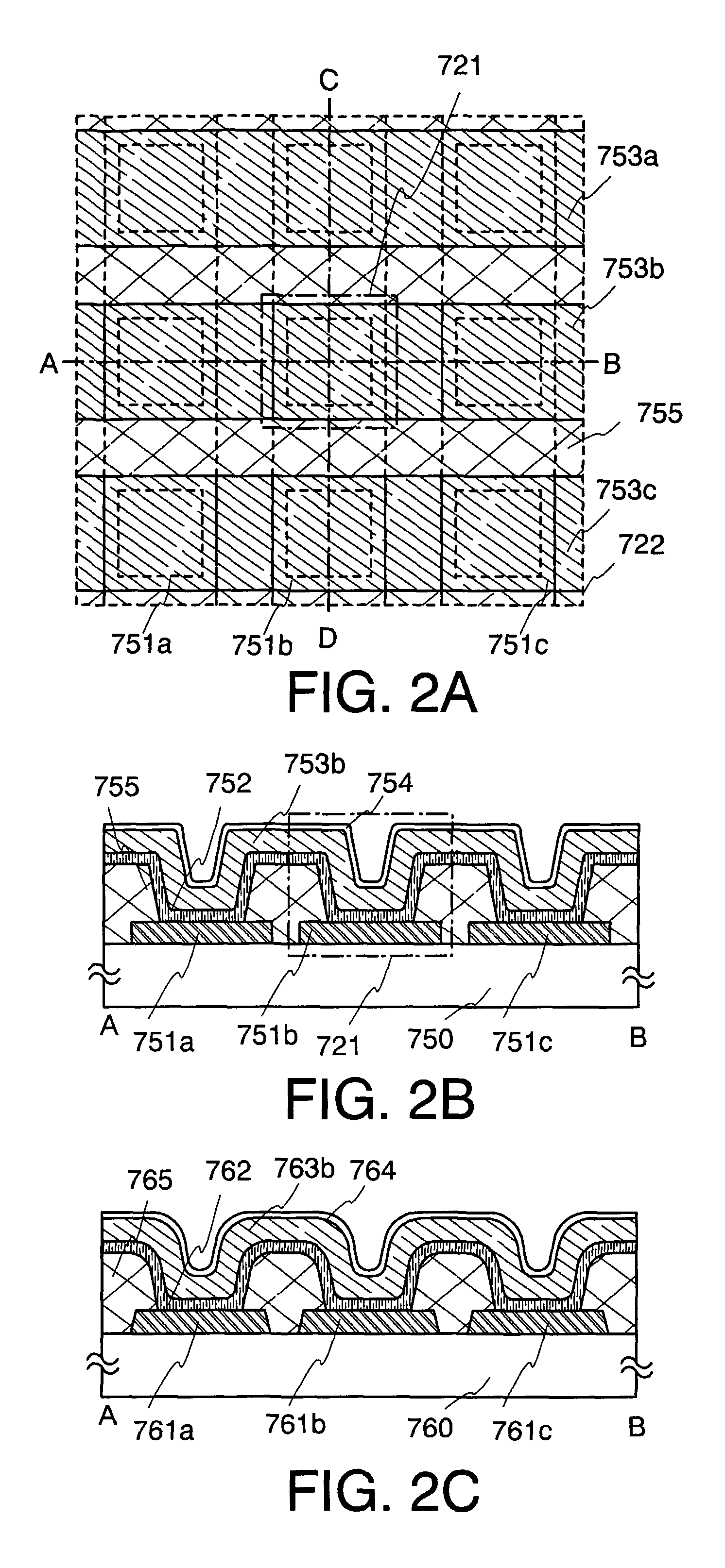
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20070278563A1Easy to keepReduce charge leakageSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCharge retentionSemiconductor package
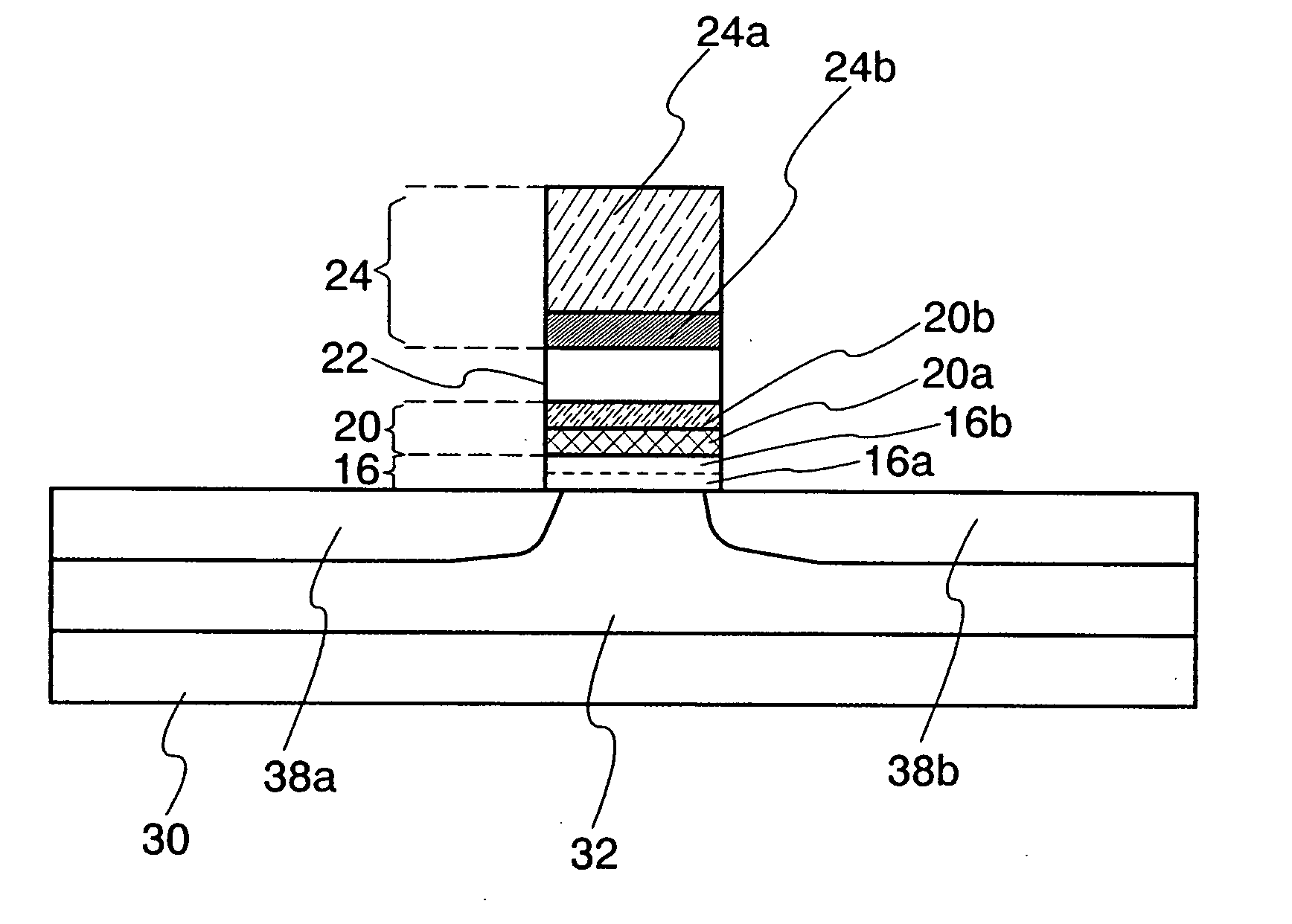
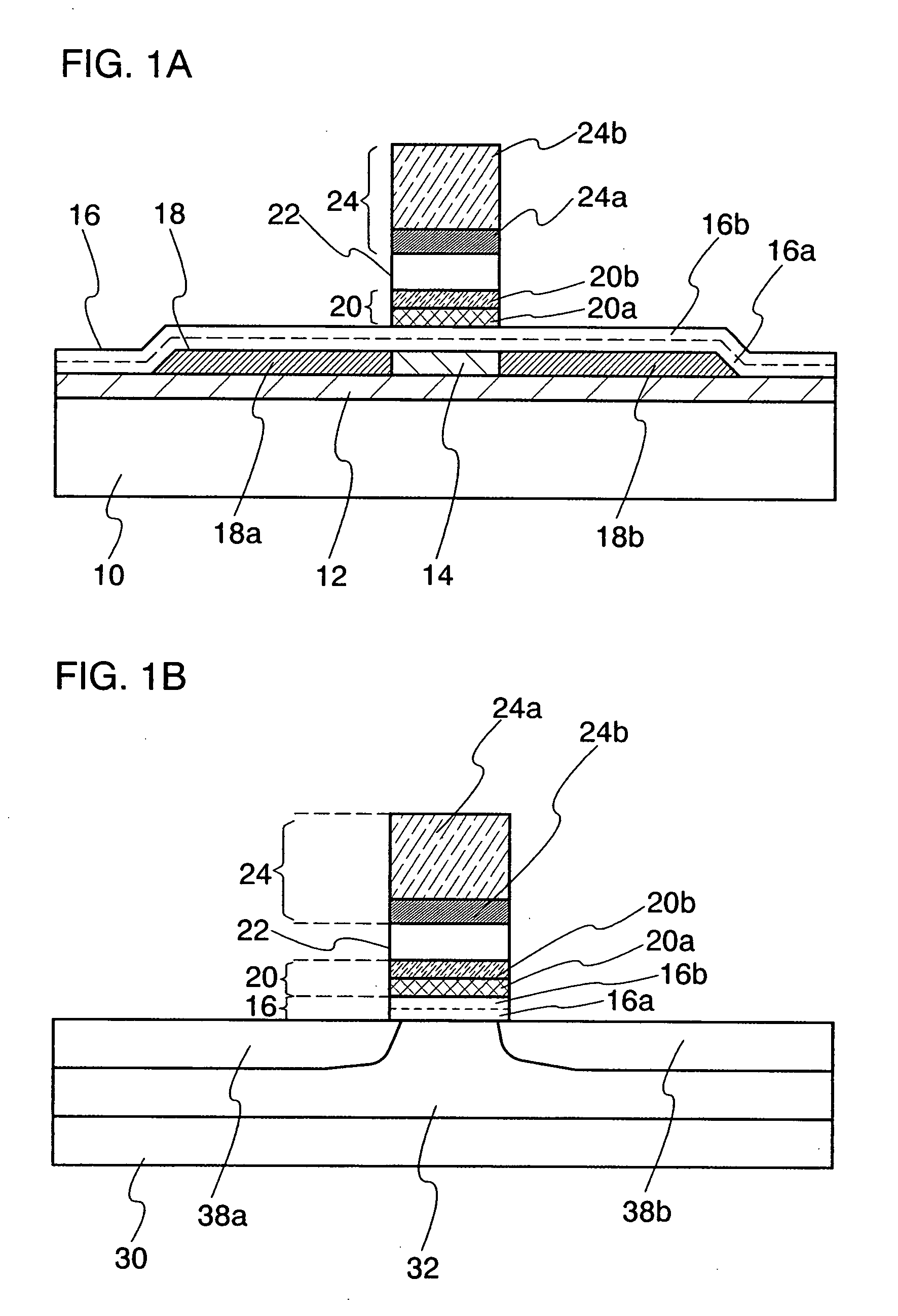
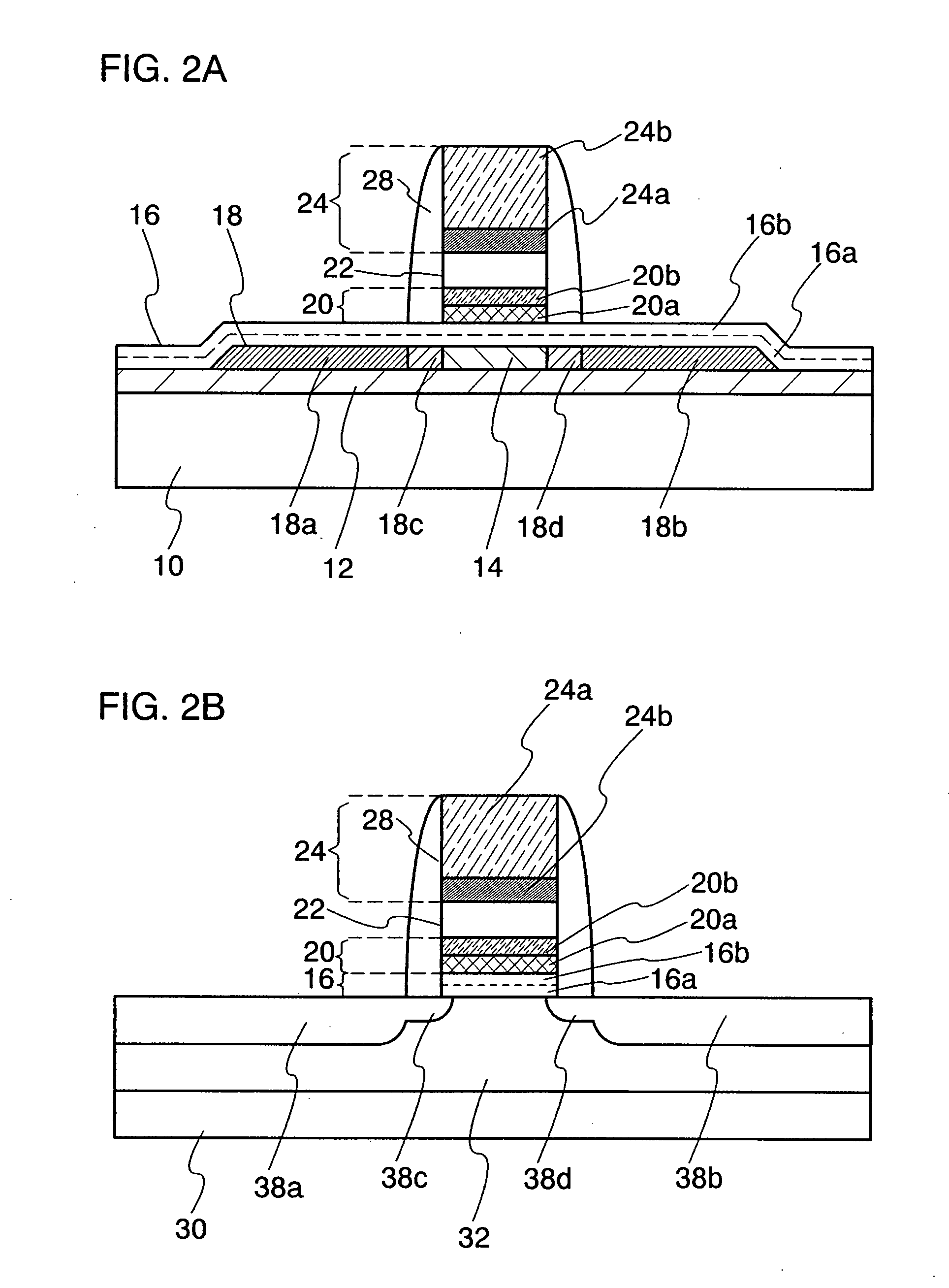
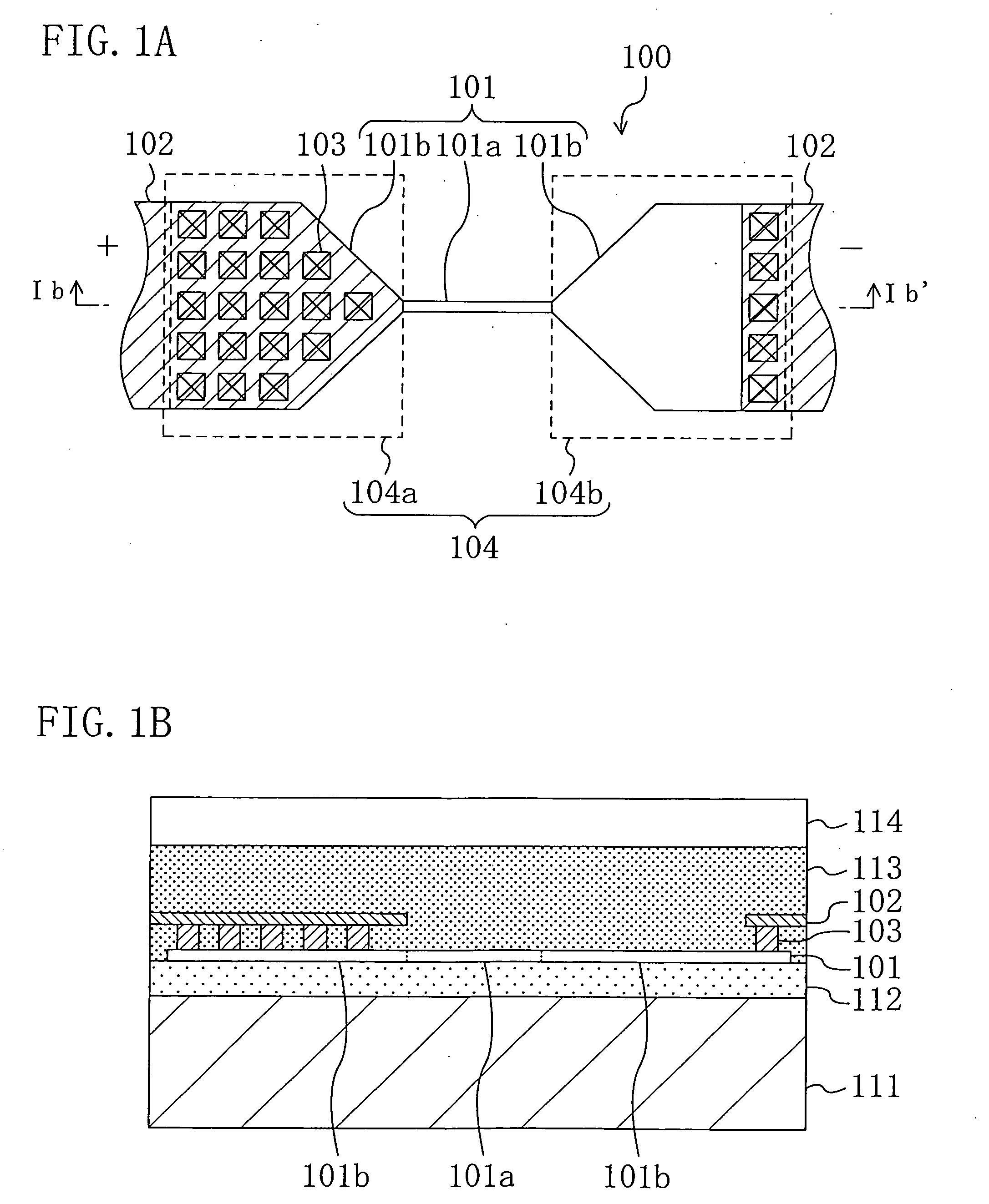
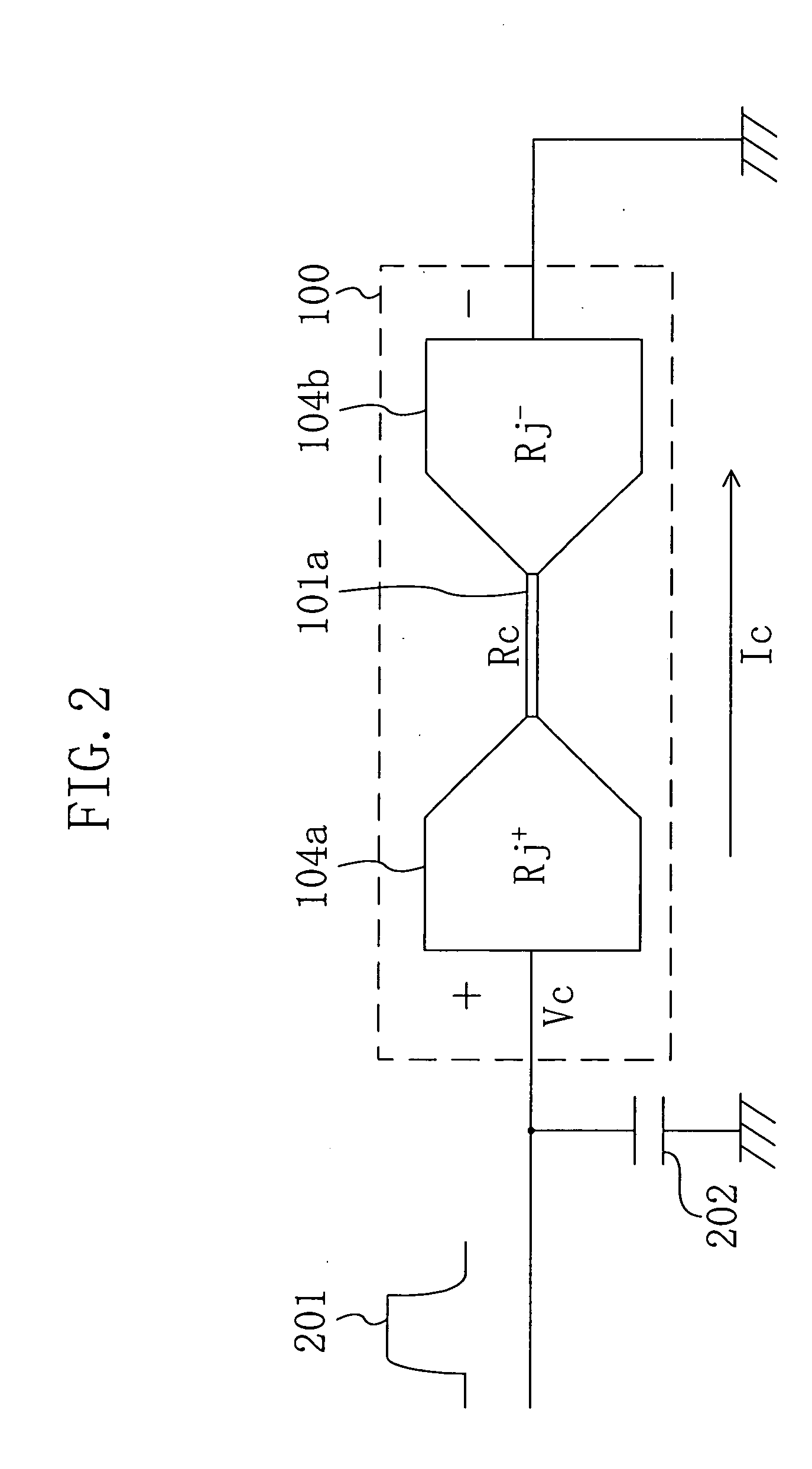
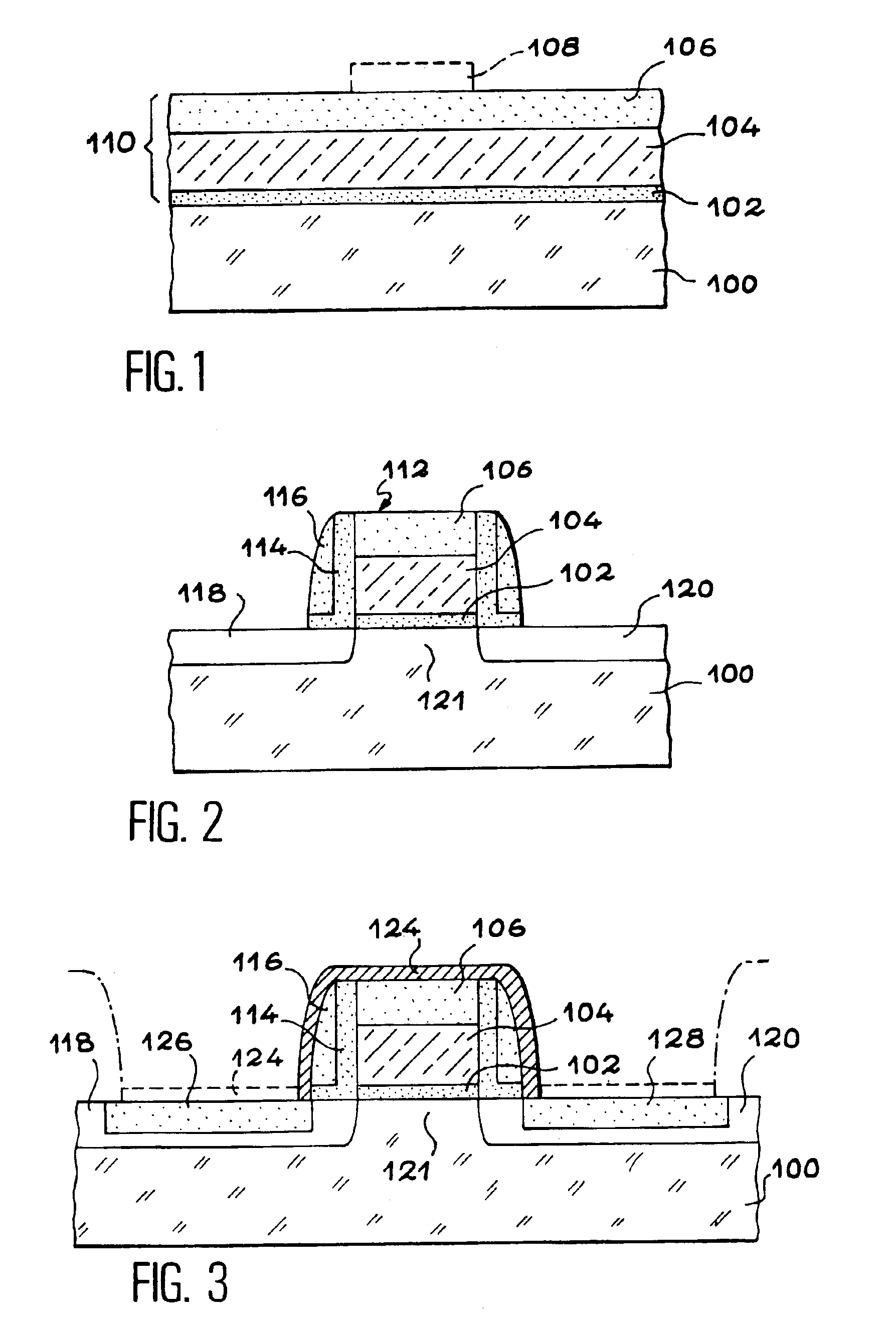
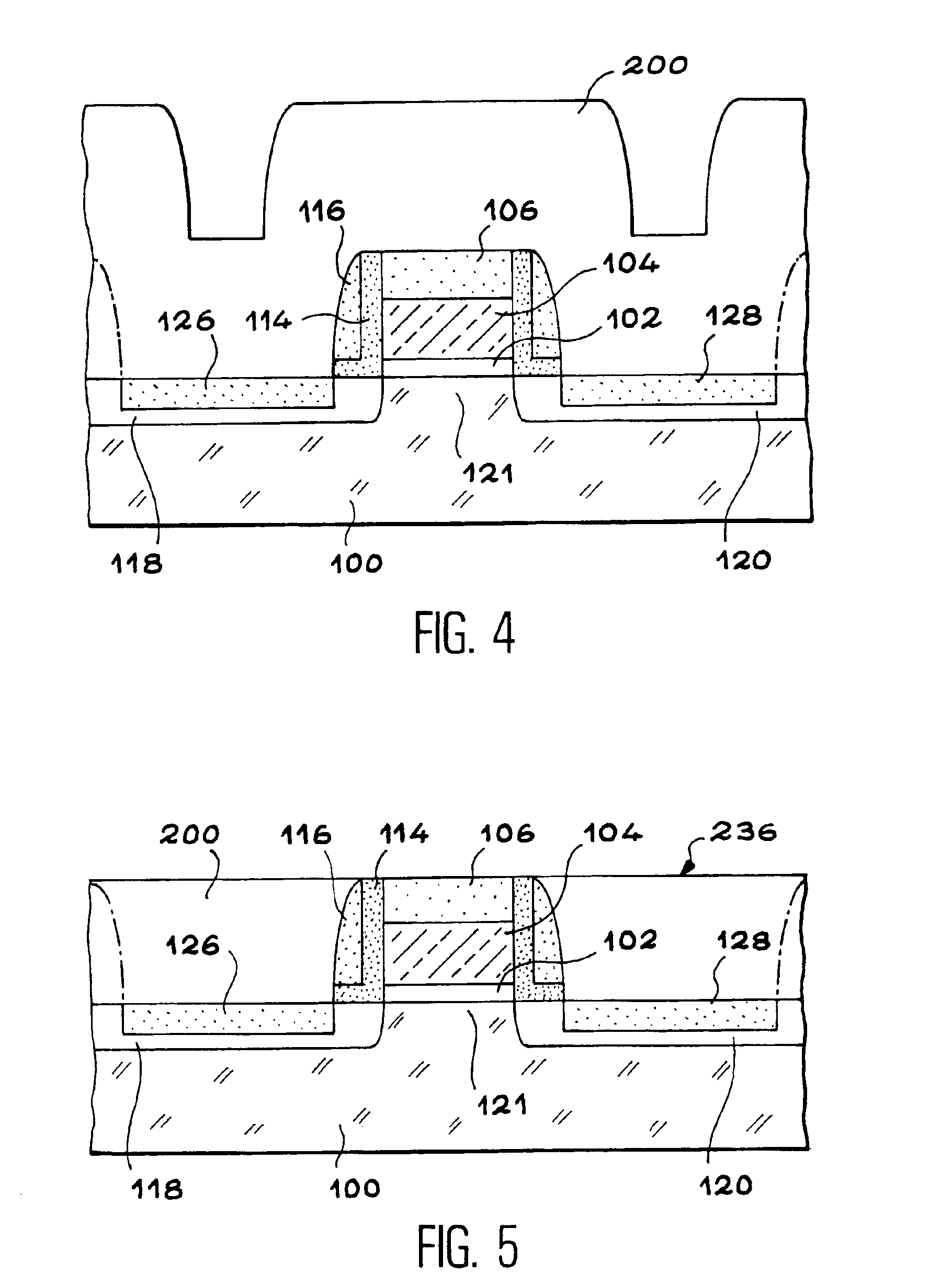
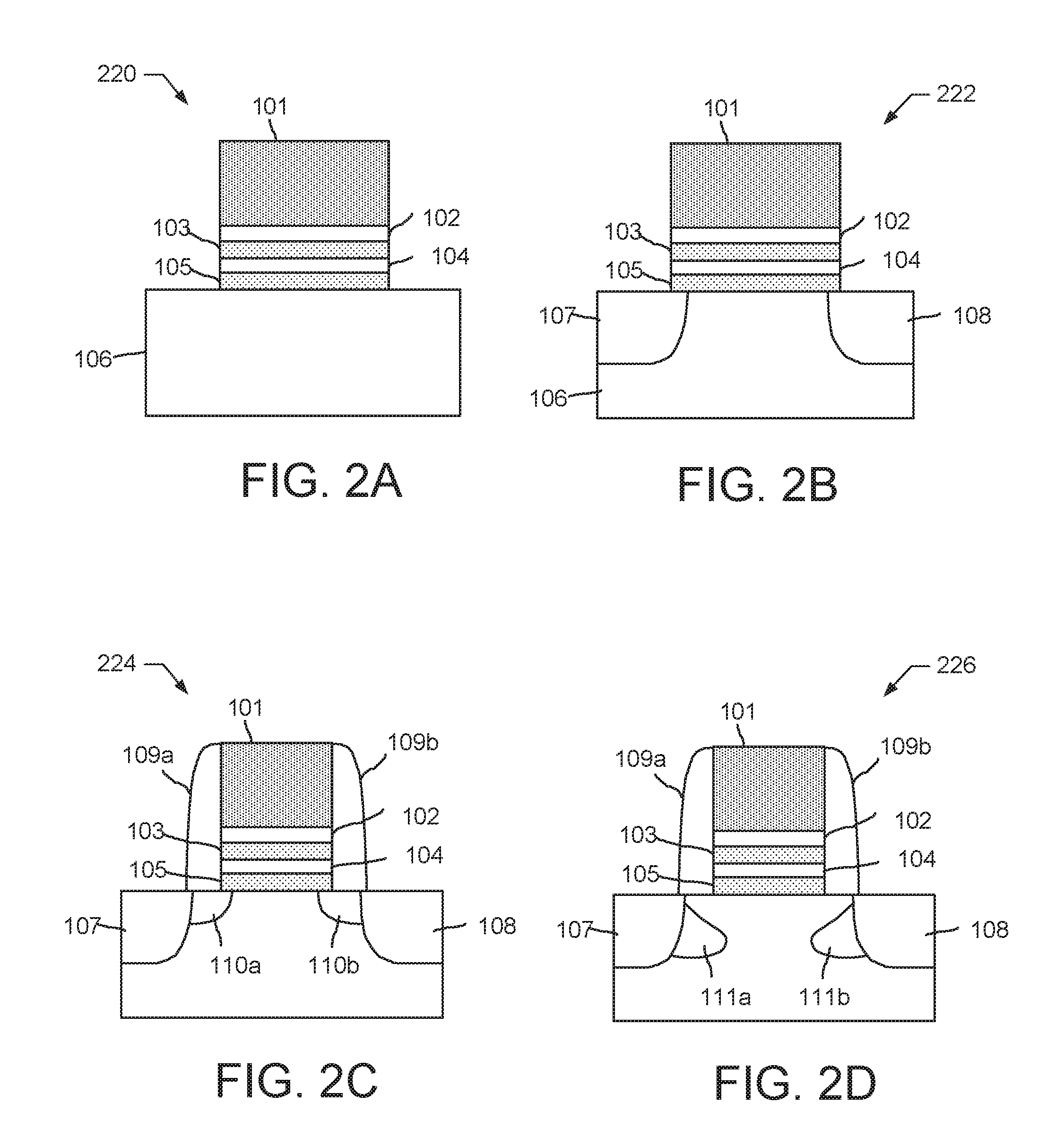
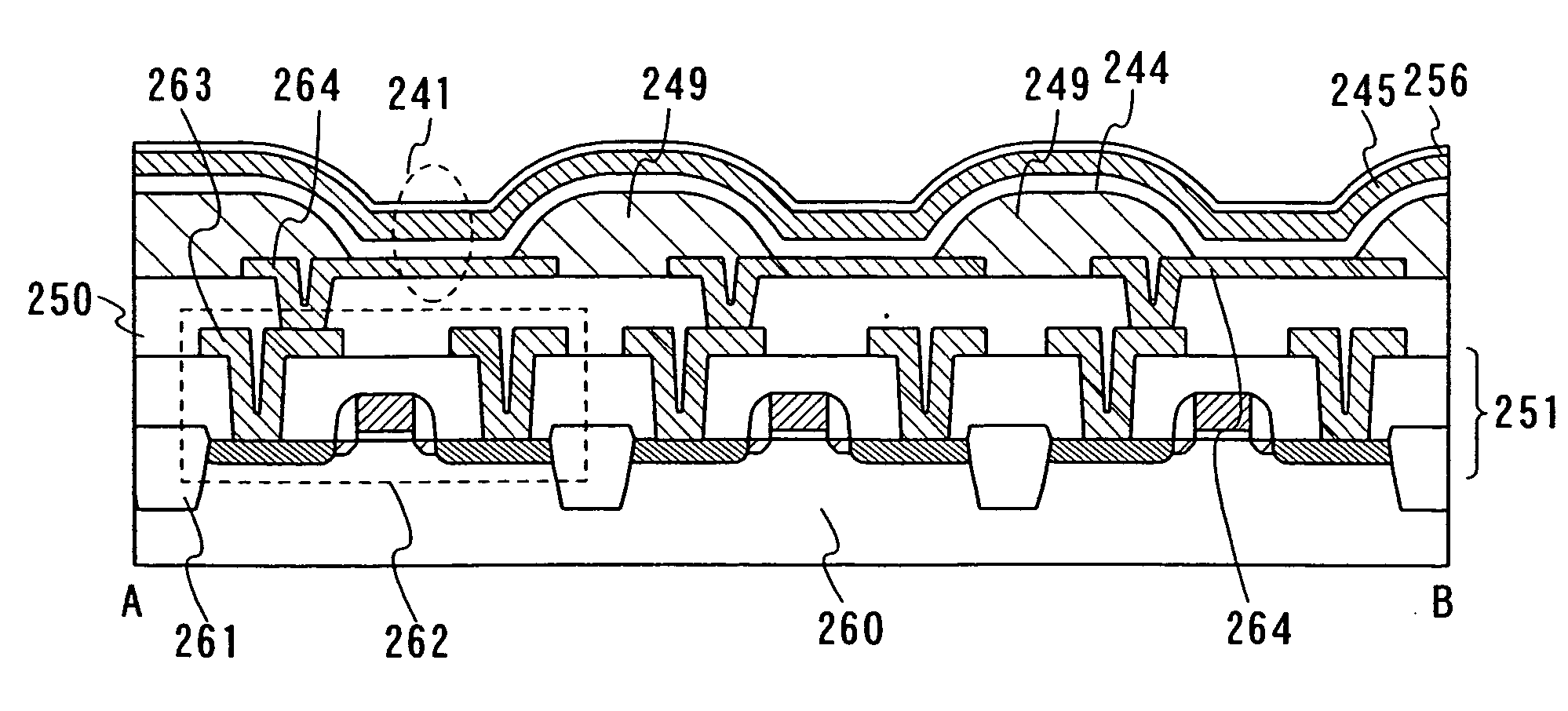
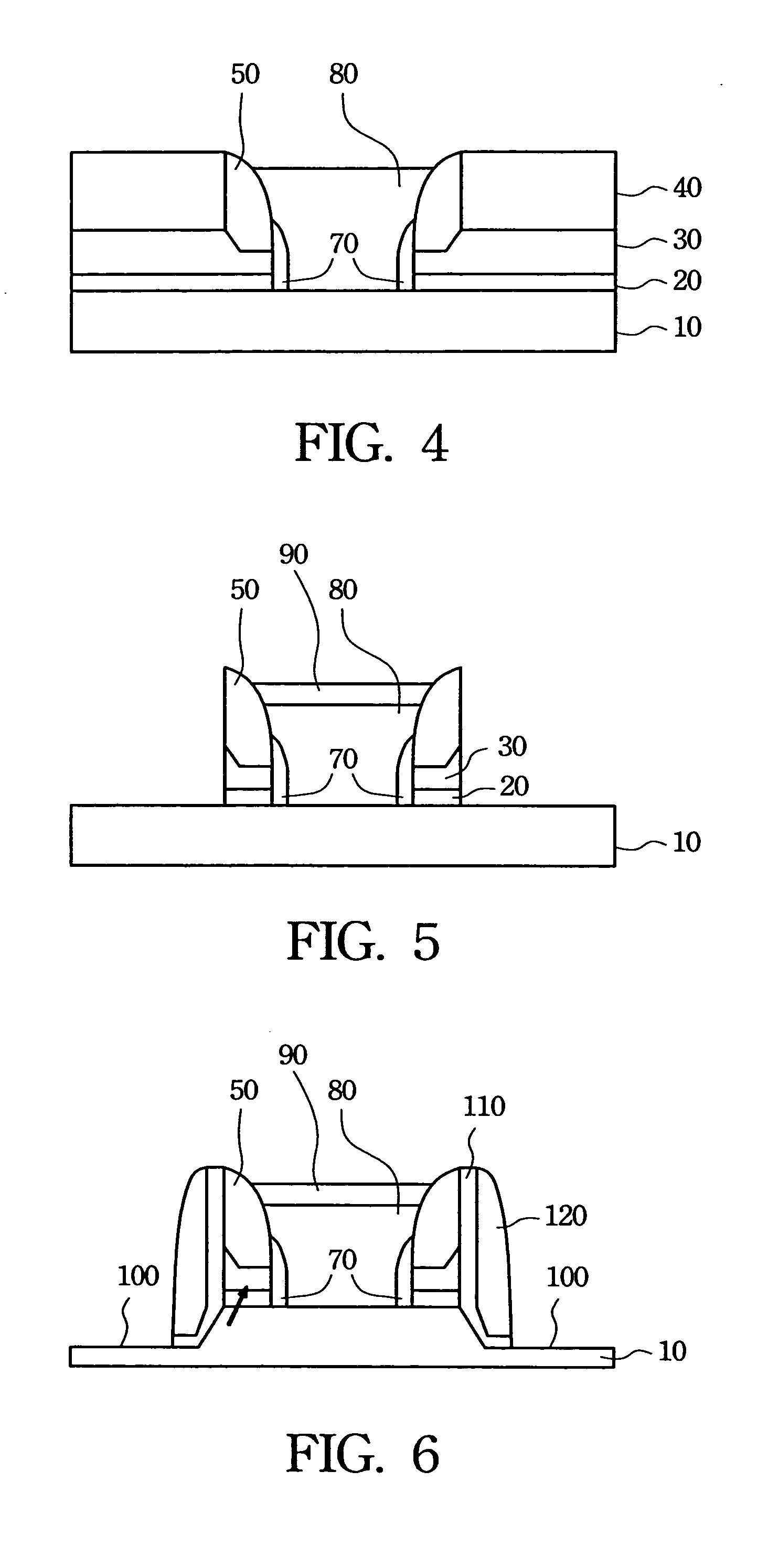
An object is to provide a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device which is excellent in a writing property and a charge retention property. In addition, another object is to provide a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device capable of reducing writing voltage. A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device includes a semiconductor layer or a semiconductor substrate including a channel formation region between a pair of impurity regions that are formed apart from each other, and a first insulating layer, a plurality of layers formed of different nitride compounds, a second insulating layer, and a control gate that are formed in a position which is over the semiconductor layer or the semiconductor substrate and overlaps with the channel formation region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
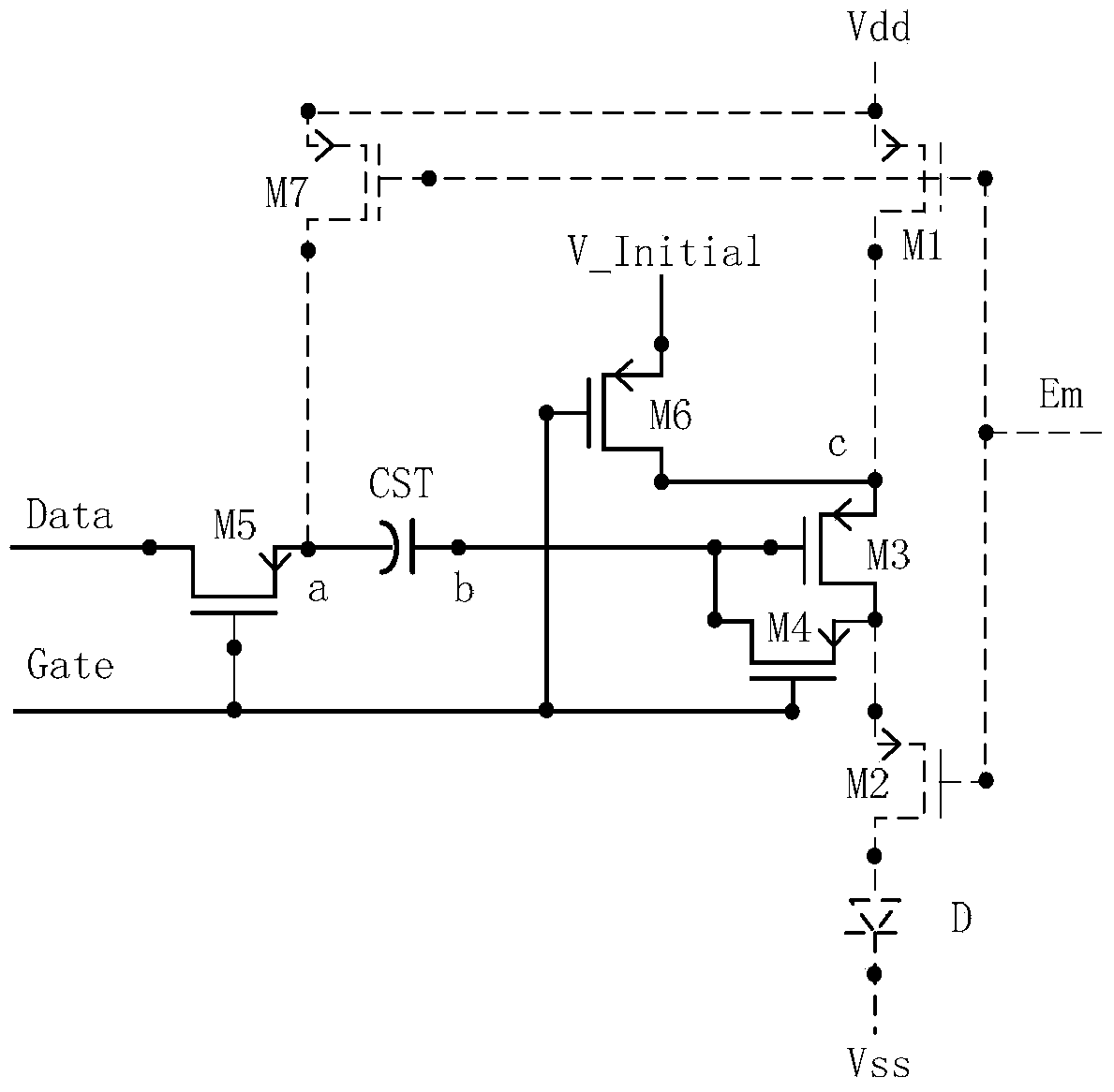
Pixel circuit of organic luminous display as well as drive method thereof
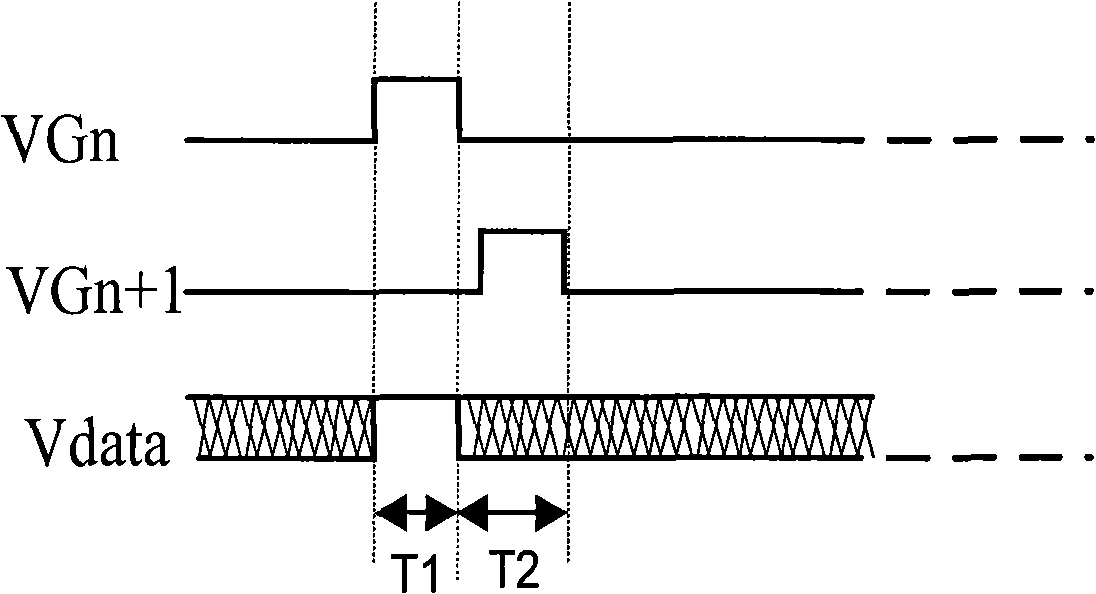
InactiveCN101281723ALower write voltageIncrease power consumptionStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceCoupling
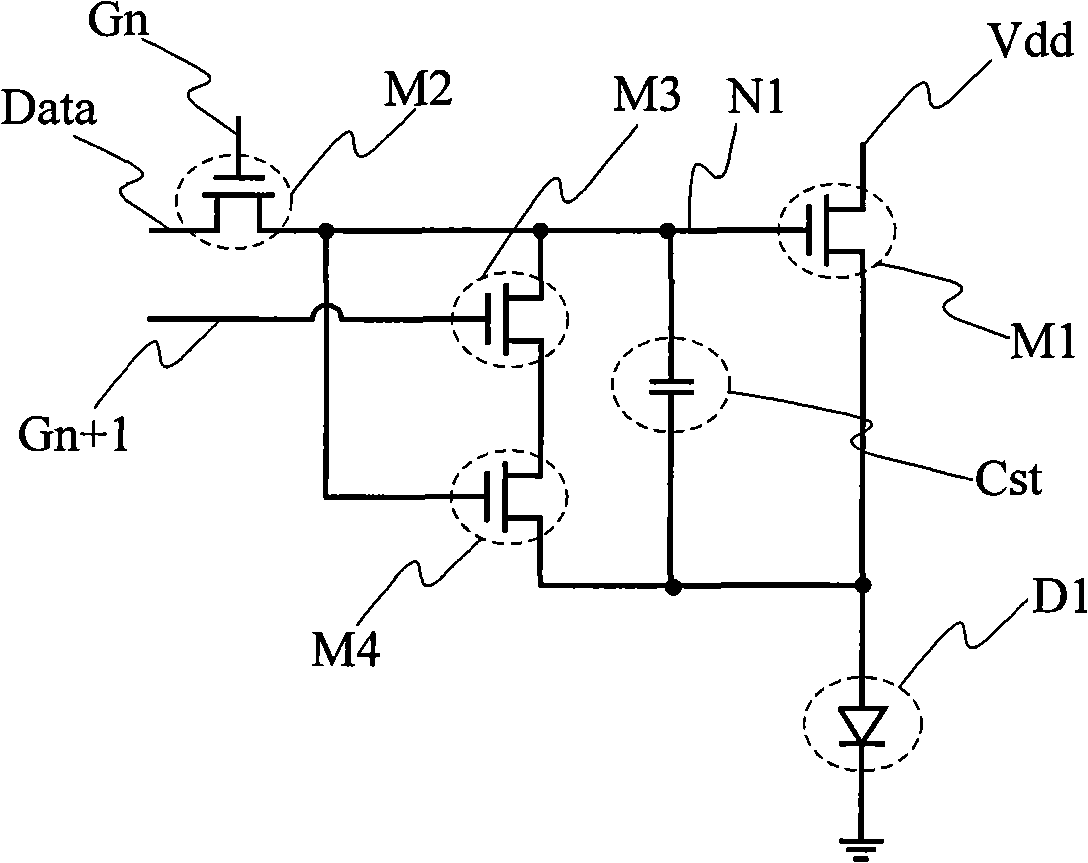
The present invention discloses a pixel circuit of an organic illuminated display device and a method for driving the pixel circuit; the pixel circuit comprises a first driving transistor, a second driving transistor, a storage capacitor, a coupling capacitor, and an organic light emitting diode (LED); the organic LED is driven by the first driving transistor. The method comprises the following steps: a. pre-charging: pre-charge the first drive transistor with pre-charge voltage, and holds the pre-charge voltage by means of the storage capacitor; b. storing a threshold voltage: the storage capacitor discharges the pre-charge voltage via the second drive transistor to the threshold voltage; c. writing grayscale data voltage: charge grayscale data voltage for the first drive transistor via the coupling capacitor, wherein, the grayscale data voltage is superimposed on the threshold voltage, and held by the storage capacitor. The pixel circuit and the driving method for the pixel circuit provided in the present invention can effectively suppress drifting of TFT property of the OLED unit in the organic illuminated display device, and thereby prolong the service life of the device.
Owner:NANJING CEC PANDA LCD TECH
Pixel circuit and driving method thereof, and display apparatus
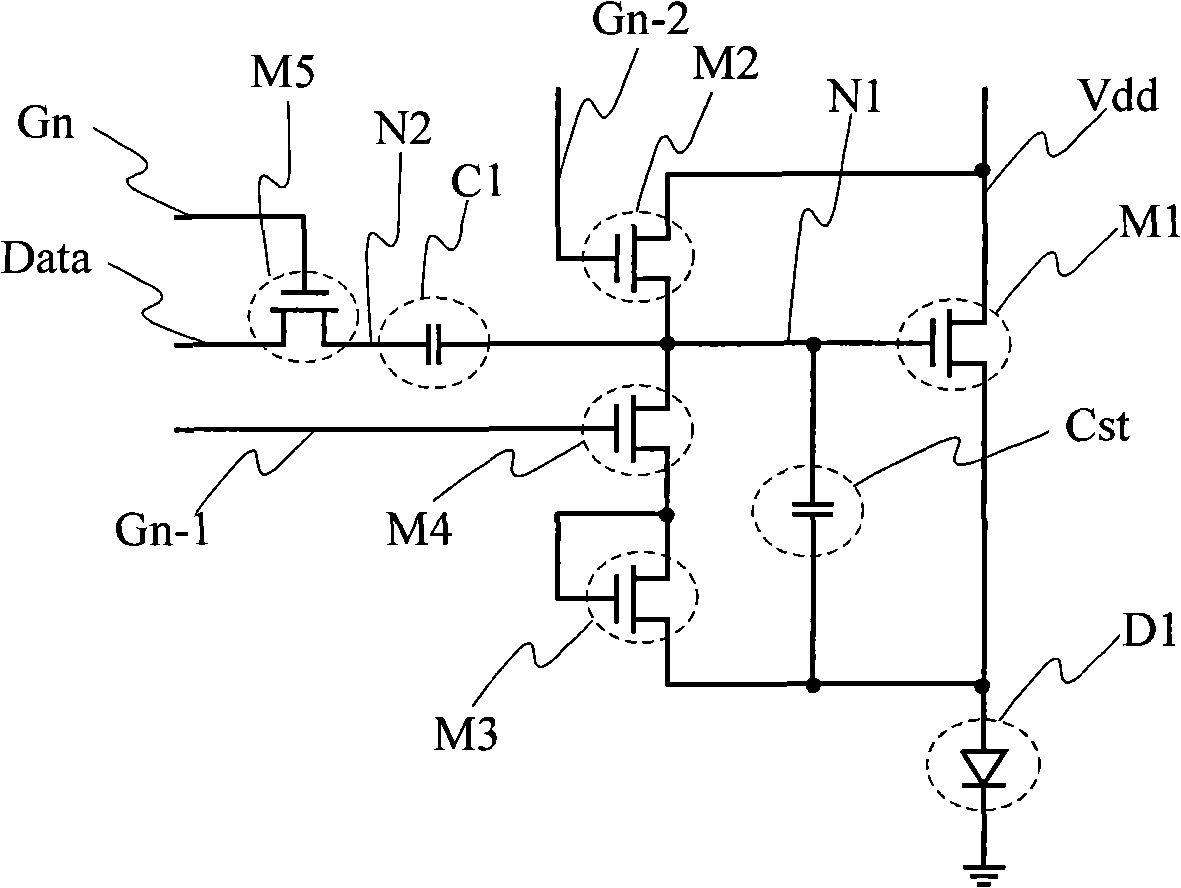
PendingCN104021757AImprove uniformityLower write voltageStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of display, is applied to manufacturing a display panel, and discloses a pixel circuit and a driving method thereof, and a display apparatus, for reducing a difference between output data and write-in data of an integrated circuit. The pixel circuit comprises a first transistor, a second transistor, a third transistor, a fourth transistor, a fifth transistor, a sixth transistor, a seventh transistor, a storage capacitor and a luminescent device.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS7709883B2High voltageReliability is ensuredTransistorSolid-state devicesCharge retentionSemiconductor package
An object is to provide a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device which is excellent in a writing property and a charge retention property. In addition, another object is to provide a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device capable of reducing writing voltage. A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device includes a semiconductor layer or a semiconductor substrate including a channel formation region between a pair of impurity regions that are formed apart from each other, and a first insulating layer, a plurality of layers formed of different nitride compounds, a second insulating layer, and a control gate that are formed in a position which is over the semiconductor layer or the semiconductor substrate and overlaps with the channel formation region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device and data processing device
InactiveUS20100265754A1Avoid adverse effectsUnnecessary currentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringData processing
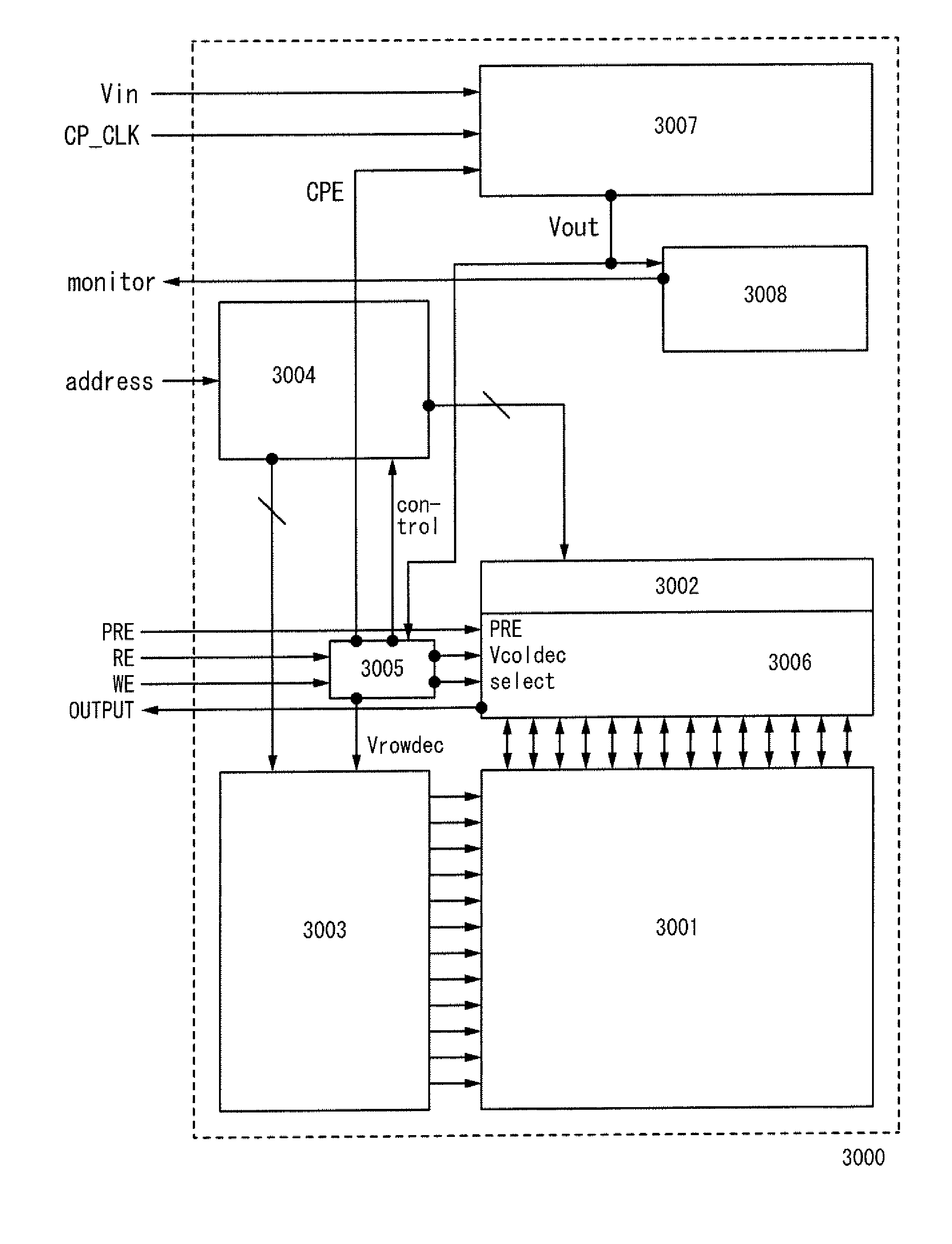
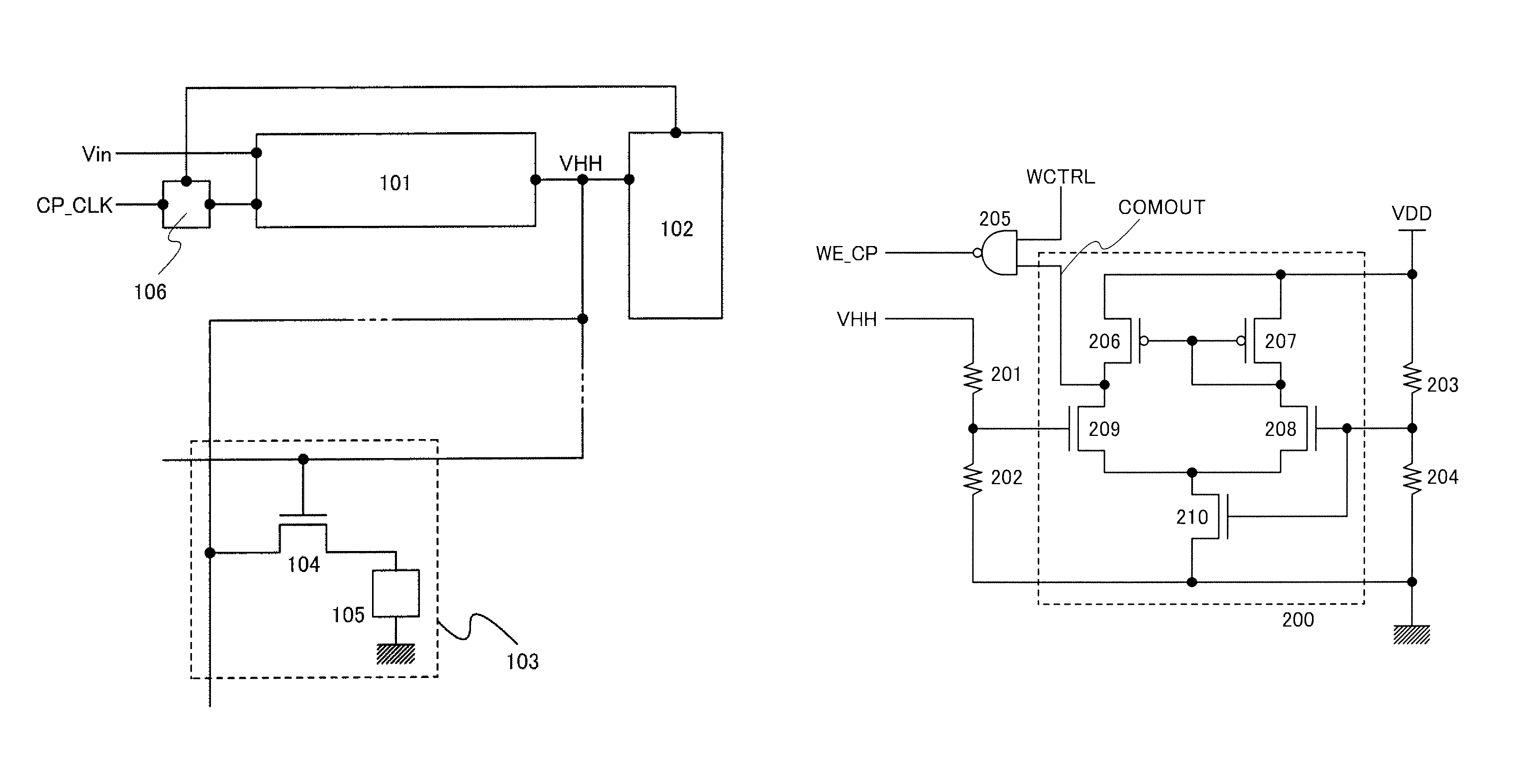
When writing into an antifuse memory element finishes, a value of resistance of the memory element rapidly decreases; accordingly, an output voltage of a boosting circuit which produces a writing voltage rapidly decreases. By detecting a change in the output voltage of the boosting circuit to control a writing command, the writing operation can be stopped immediately after the memory element is shorted. Thus, unnecessary current consumption caused by continuing a writing operation on the shorted memory element can be suppressed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Fuse and write method for fuse
InactiveUS20050274966A1Increase cell areaTotal current dropSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceCurrent limiting
A polysilicon fuse includes a fusing part to be fused through voltage application, a positive terminal side joint connected to one end of the fusing part and a negative terminal side joint connected to the other end of the fusing part. The positive terminal side joint that attains a high voltage through the voltage application has lower resistance and higher heat conductivity than the negative terminal side joint. Furthermore, a write operation is performed, with a current limiting resistance serially connected to a positive terminal side joint of a polysilicon fuse, by applying a voltage pulse to the polysilicon fuse through the current limiting resistance. Thus, a current flowing to the polysilicon fuse in fusing the fusing part is limited to a given range.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
One-time-programmable anti-fuse formed using damascene process
ActiveUS7968967B2Lower write voltageMeet compatibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInsulation layerSemiconductor structure
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
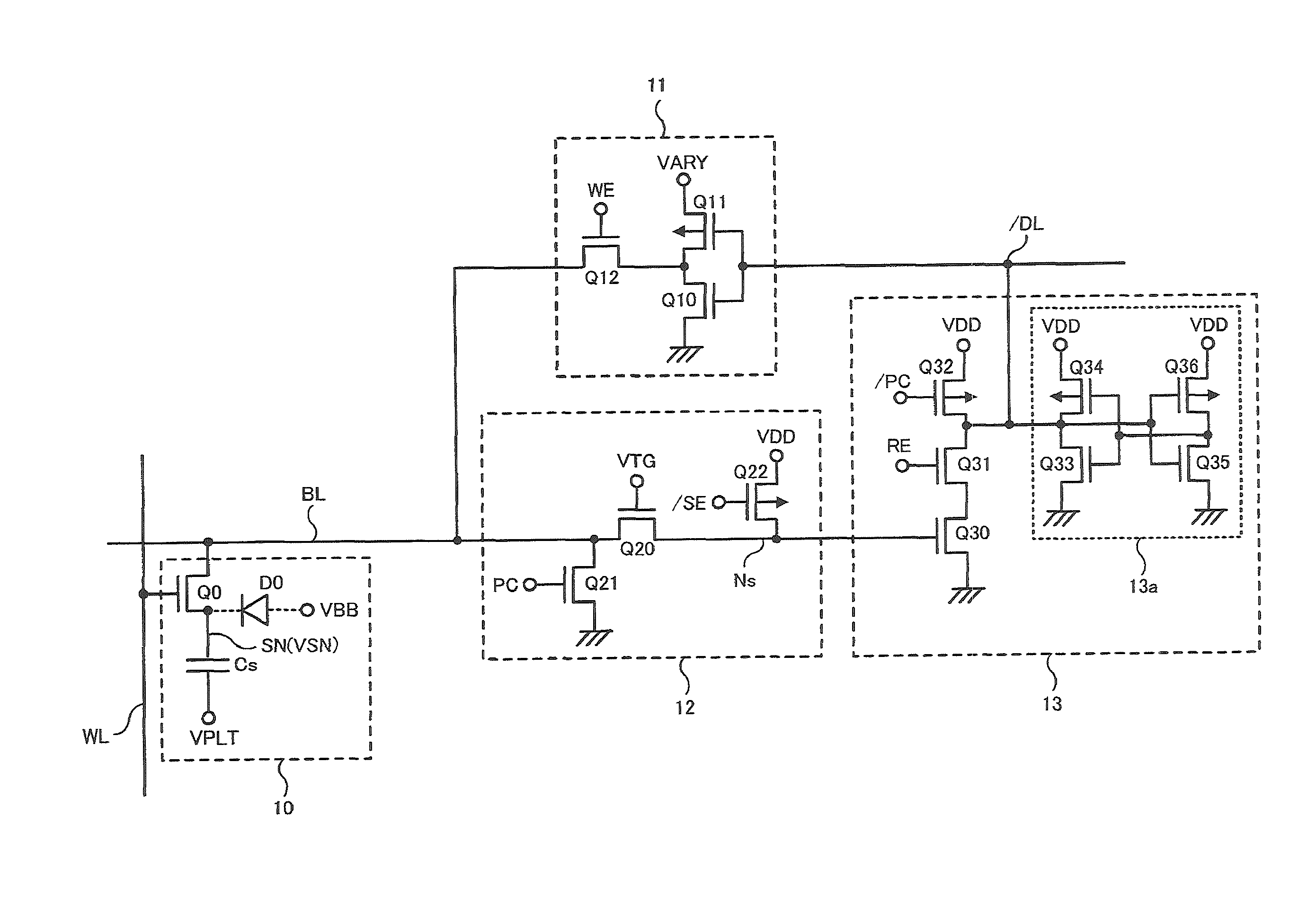
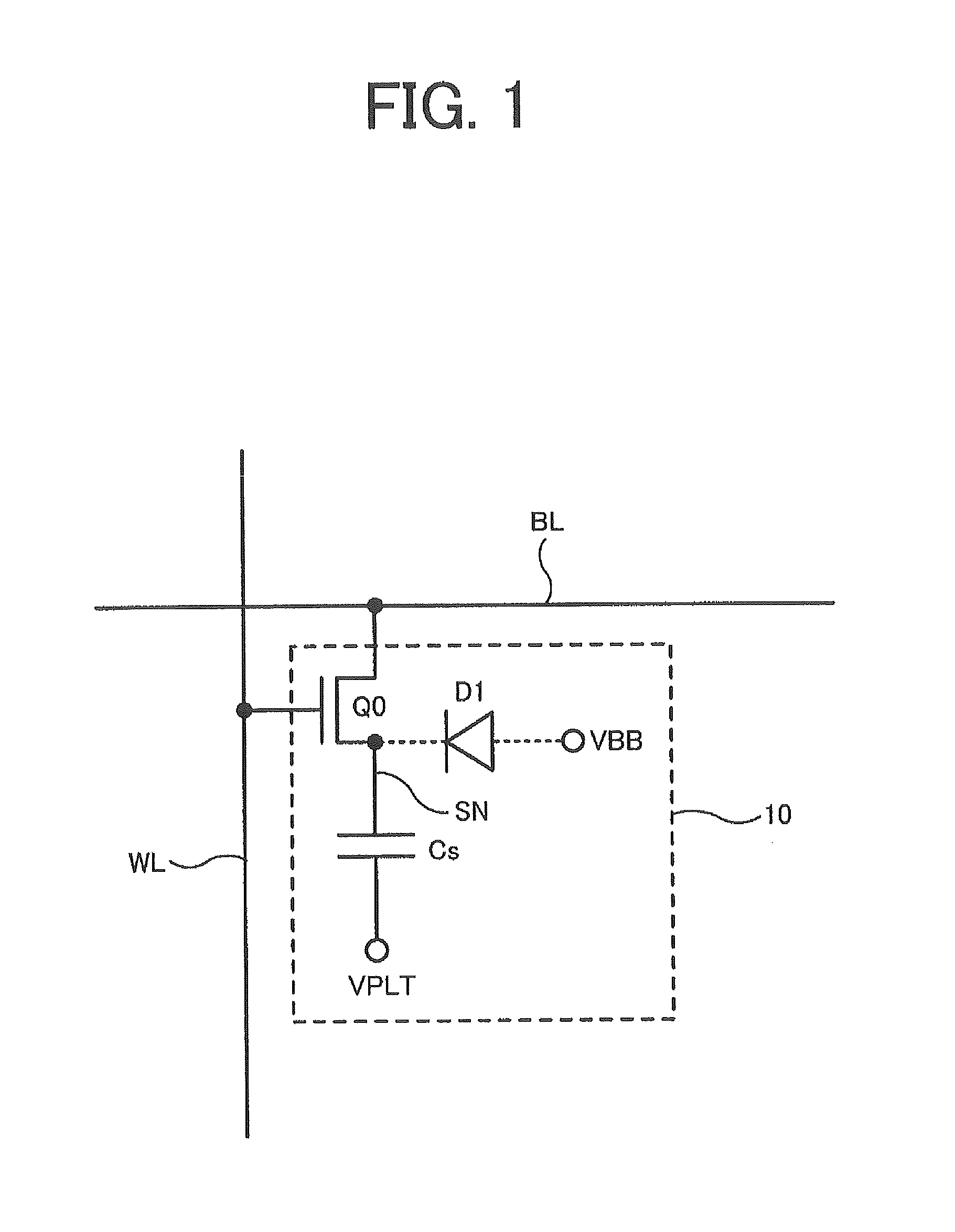
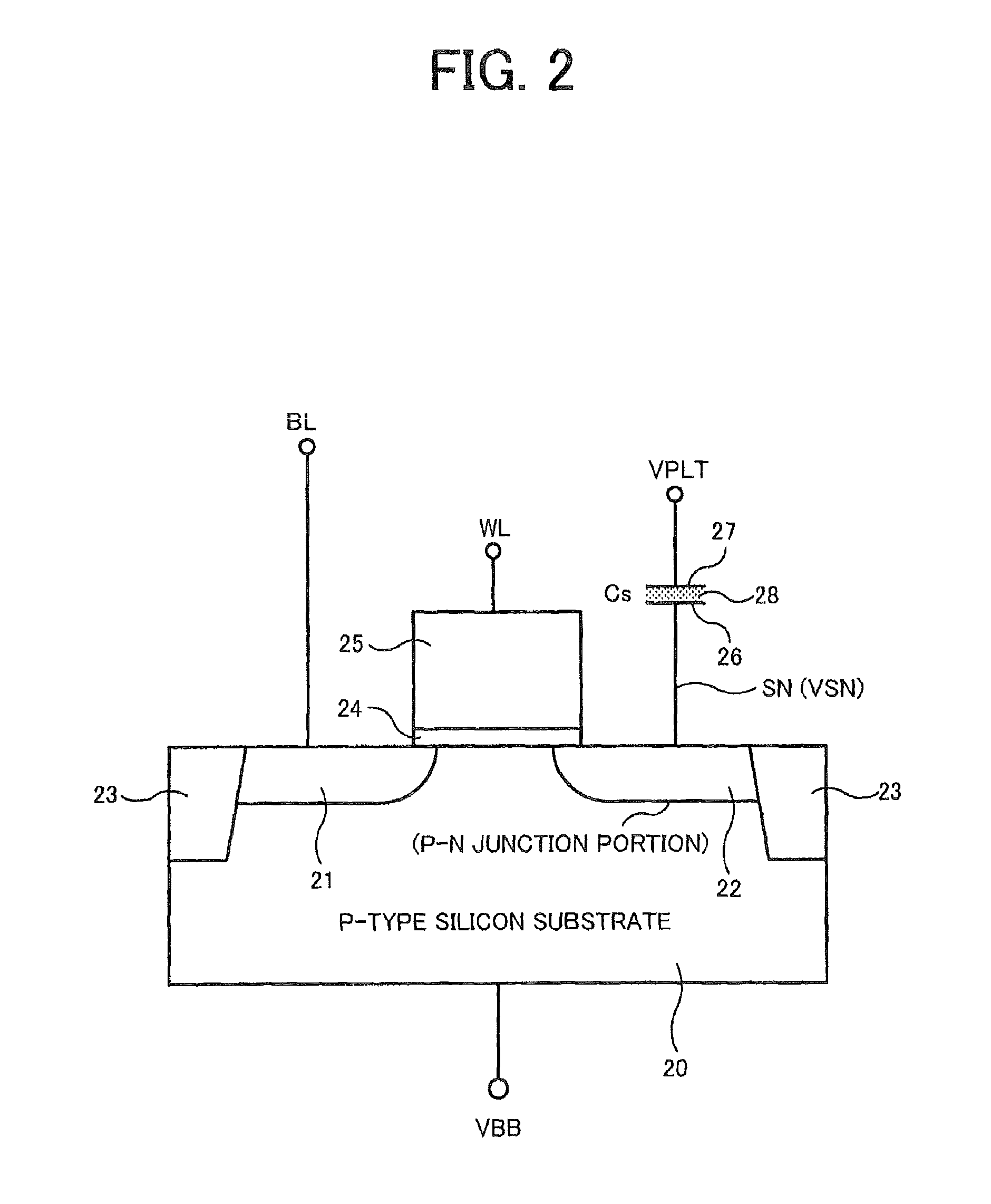
Semiconductor device, semiconductor memory device and data processing system comprising semiconductor system
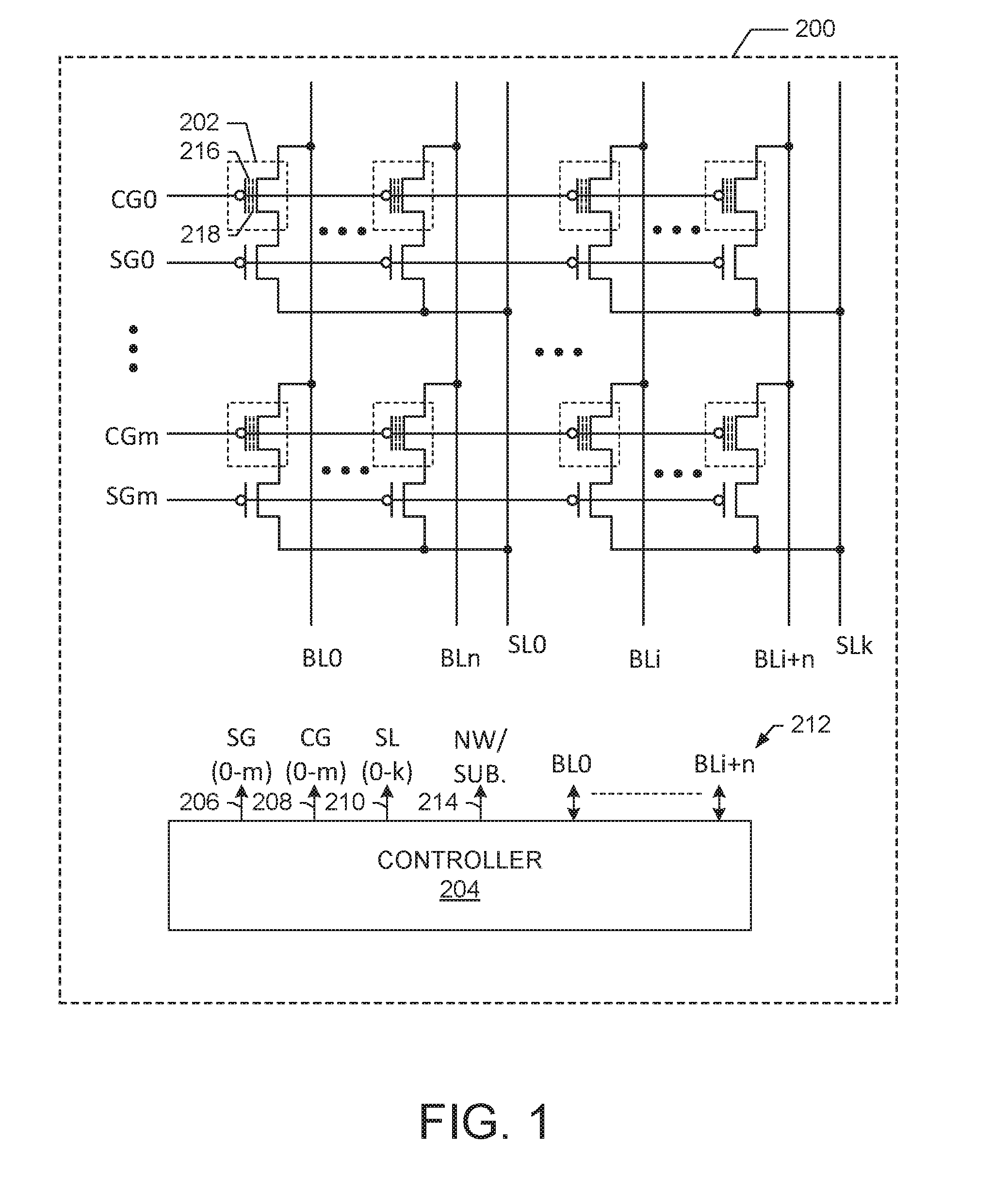
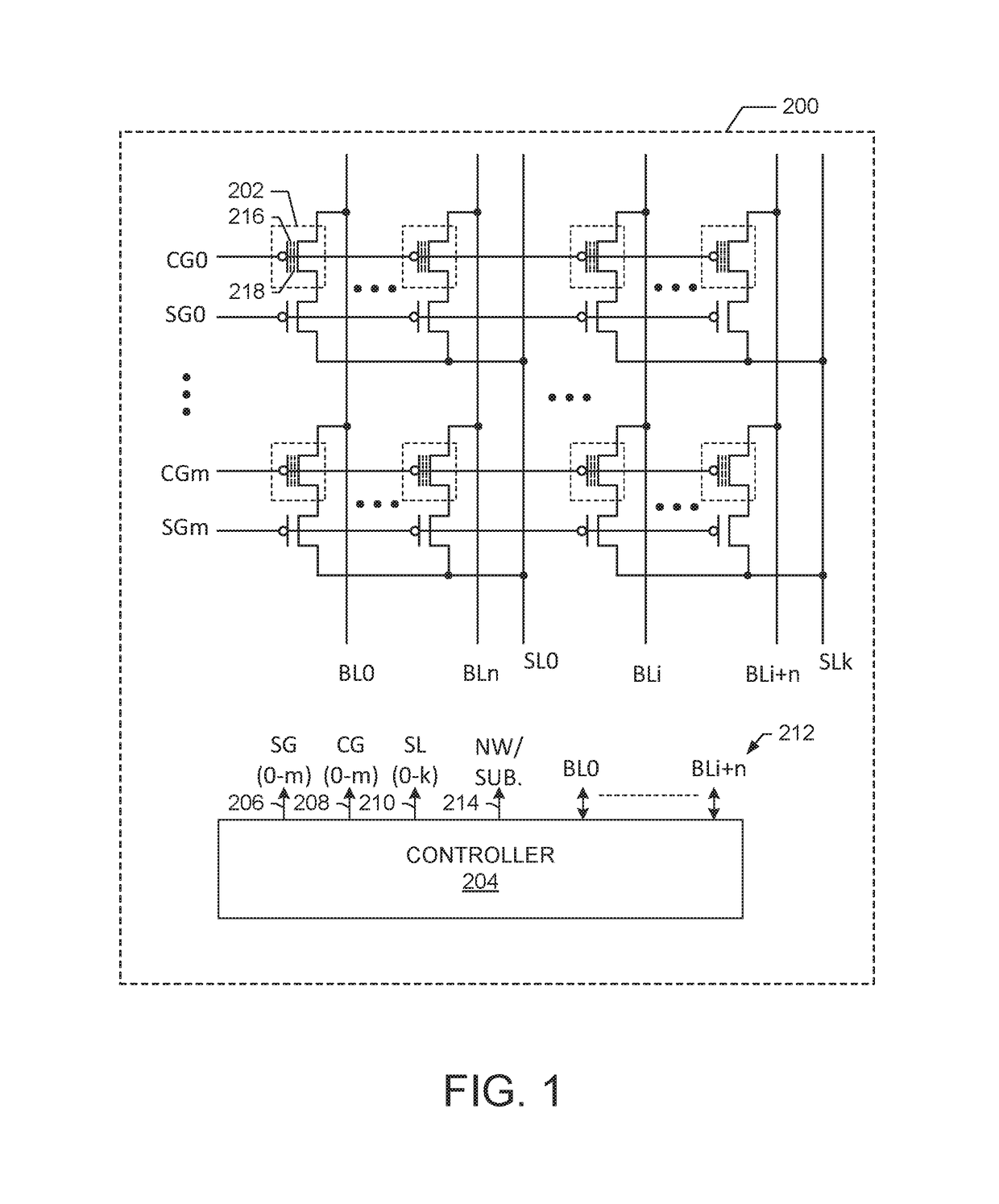
ActiveUS8199559B2Excellent operating marginLower write voltageDigital storageData processing systemBit line
A semiconductor device comprises a memory cell, a bit line, a sense amplifier operating between a first voltage and a second voltage higher than the first voltage, a transfer control circuit including a transfer transistor, and a write circuit writing data into the memory cell through the bit line based on the first voltage and a third voltage. The sense amplifier receives and amplifiers the signal voltage at a sense node when the transfer transistor controls the connection between the bit line and the sense node in response to a transfer control voltage. The third voltage is set to a voltage lower than the second voltage and higher than the transfer control voltage, and the sense node is set to a voltage higher than the transfer control voltage in an initial period of a read operation before the data of the memory cell is read out to the bit line.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
Semiconductor device, semiconductor memory device and data processing system comprising semiconductor system
ActiveUS20110063891A1Excellent operating marginRun at high speedDigital storageData processing systemBit line
A semiconductor device comprises a memory cell, a bit line, a sense amplifier operating between a first voltage and a second voltage higher than the first voltage, a transfer control circuit including a transfer transistor, and a write circuit writing data into the memory cell through the bit line based on the first voltage and a third voltage. The sense amplifier receives and amplifiers the signal voltage at a sense node when the transfer transistor controls the connection between the bit line and the sense node in response to a transfer control voltage. The third voltage is set to a voltage lower than the second voltage and higher than the transfer control voltage, and the sense node is set to a voltage higher than the transfer control voltage in an initial period of a read operation before the data of the memory cell is read out to the bit line.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
Damascene architecture electronic storage and method for making same
InactiveUS6955963B2Easy to integrateImproved floating gate-control gate capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringElectronic memory
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Dual Function Hybrid Memory Cell
ActiveUS20160314839A1Short timeLower write voltageSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesTrapping regionEngineering
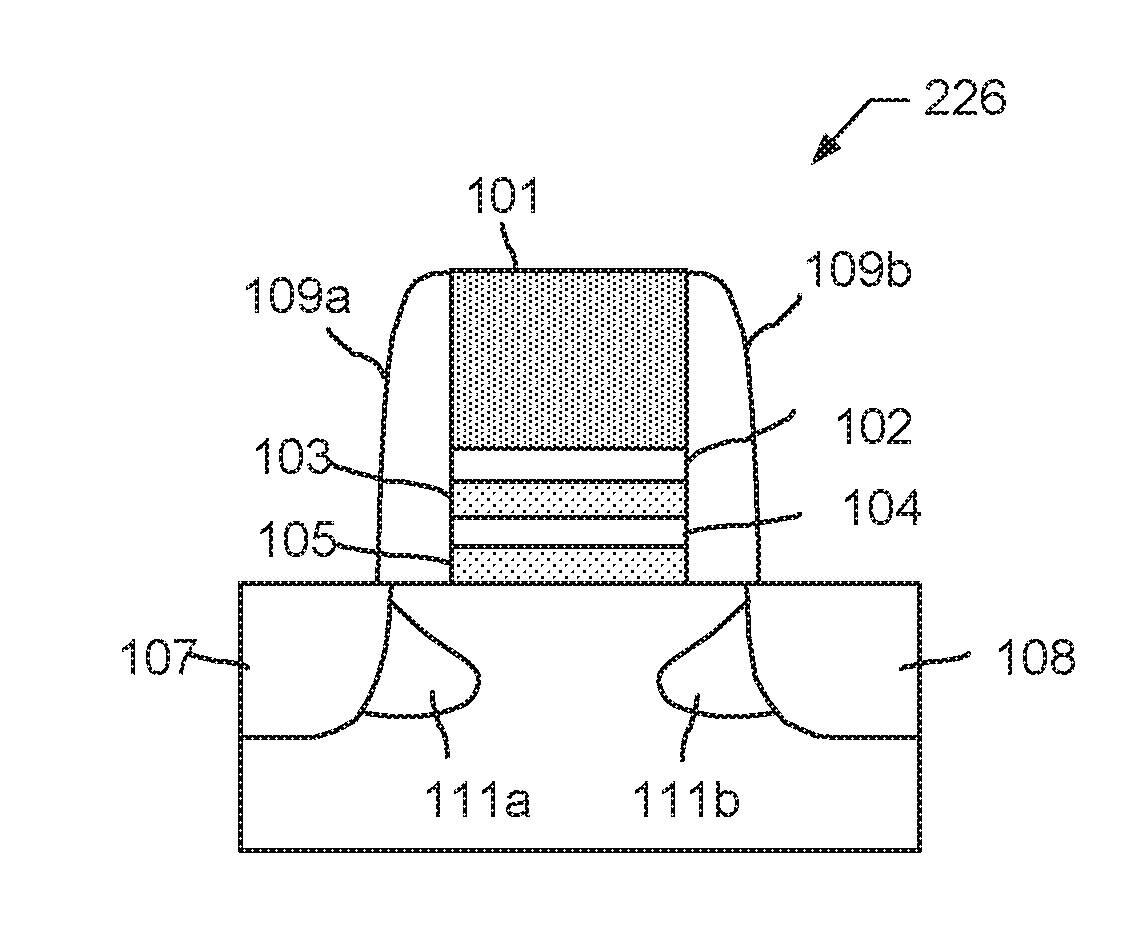
A dual function hybrid memory cell is disclosed. In one aspect, the memory cell includes a substrate, a bottom charge-trapping region formed on the substrate, a top charge-trapping region formed on the bottom charge-trapping region, and a gate layer formed on the top charge trapping region. In another aspect, a method for programming a memory cell having a substrate, a bottom charge-trapping layer, a top charge-trapping layer, and a gate layer is disclosed. The method includes biasing a channel region of the substrate, applying a first voltage differential between the gate layer and the channel region, injecting charge into the bottom charge-trapping layer from the channel region based on the first voltage differential. The method also includes applying a second voltage differential between the gate layer and the channel region and injecting charge from the bottom charge-trapping layer into the top charge-trapping layer based on the second voltage differential.
Owner:NEO SEMICON
Semiconductor memory device capable of optimizing an operation time of a boosting circuit during a writing period
InactiveUS8964489B2Increase currentPrevented from inefficiently consumedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringCurrent consumption
When writing into an antifuse memory element finishes, a value of resistance of the memory element rapidly decreases; accordingly, an output voltage of a boosting circuit which produces a writing voltage rapidly decreases. By detecting a change in the output voltage of the boosting circuit to control a writing command, the writing operation can be stopped immediately after the memory element is shorted. Thus, unnecessary current consumption caused by continuing a writing operation on the shorted memory element can be suppressed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Nonvolatile memory and semiconductor device including nonvolatile memory
InactiveUS20080151602A1Reduce power consumptionTotal current dropRead-only memoriesDigital storageHigh resistanceElectrical battery
An object is to provide a nonvolatile memory with reduced power consumption. The nonvolatile memory includes a memory element that has a low resistance state and a high resistance state, a writing circuit, a resistance element, a voltage source input terminal that inputs a writing voltage to the writing circuit, a bit line driver circuit that selects whether the memory element is connected to the writing circuit, and a word line driver circuit that selects whether or not writing is done in the memory element. With such as structure, power consumption during writing can be reduced, and a nonvolatile memory with low power consumption can be realized. Further, with such a nonvolatile memory, an active type wireless tag with a long lifetime of a battery or a passive type wireless tag with a wide communication range in which writing to a memory is possible, can be realized.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method of making the selection gate in a split-gate flash EEPROM cell and its structure
InactiveUS20050029575A1Reduce horizontal sizeReduce power consumptionTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectric layerSemiconductor
A method of making the selection gate in a split-gate flash EEPROM cell forms a selection gate on a trench sidewall of a semiconductor substrate to minimize the sidewise dimension of the selection gate and to maintain the channel length. The disclosed method includes the steps of: forming a trench on a semiconductor substrate on one side of a suspending gate structure; forming an inter polysilicon dielectric layer on the sidewall of the suspending gate structure and the trench; and forming a polysilicon spacer on the inter polysilicon dielectric layer as the selection gate. Such a split-gate flash EEPROM cell can produce ballistic hot electrons, improving the data writing efficiency and lowering the writing voltage.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor device with liquid repellant layer
InactiveUS8242486B2Higher-reliability memoryLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLiquid layerDevice material
An object is to provide technology for manufacturing a higher-reliability memory device and a semiconductor device that is equipped with the memory device at low cost. A semiconductor device of the present invention has a first conductive layer, a first insulating layer that is provided to be in contact with a side end portion of the first conductive layer, a second insulating layer that is provided over the first conductive layer and the first insulating layer, and a second conductive layer that is provided over the second insulating layer. The second insulating layer is formed of an insulating material, and wettability against a fluidized substance when the insulating material is fluidized, is higher for the first insulating layer than the first conductive layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device, semiconductor memory device and data processing system comprising semiconductor system
ActiveUSRE45819E1Excellent operating marginLower write voltageDigital storageData processing systemPower semiconductor device
A semiconductor device comprises a memory cell, a bit line, a sense amplifier operating between a first voltage and a second voltage higher than the first voltage, a transfer control circuit including a transfer transistor, and a write circuit writing data into the memory cell through the bit line based on the first voltage and a third voltage. The sense amplifier receives and amplifiers the signal voltage at a sense node when the transfer transistor controls the connection between the bit line and the sense node in response to a transfer control voltage. The third voltage is set to a voltage lower than the second voltage and higher than the transfer control voltage, and the sense node is set to a voltage higher than the transfer control voltage in an initial period of a read operation before the data of the memory cell is read out to the bit line.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Semiconductor device including memory cell
InactiveUS7700984B2Improve reliabilityForgery by rewriting or the like can be preventedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsOrganic compoundSemiconductor
It is an object of the present invention to provide a semiconductor device capable of additionally recording data at a time other than during manufacturing and preventing forgery due to rewriting and the like. Moreover, another object of the present invention is to provide an inexpensive, nonvolatile, and highly-reliable semiconductor device. A semiconductor device includes a first conductive layer, a second conductive layer, and an organic compound layer between the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer, wherein the organic compound layer can have the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer come into contact with each other when Coulomb force generated by applying potential to one or both of the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer is at or over a certain level.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Multi-value recording phase-change memory device, multi-value recording phase-change channel transistor, and memory cell array
ActiveUS7781753B2Improve reliabilityLarge marginSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase-change memoryAmorphous phase
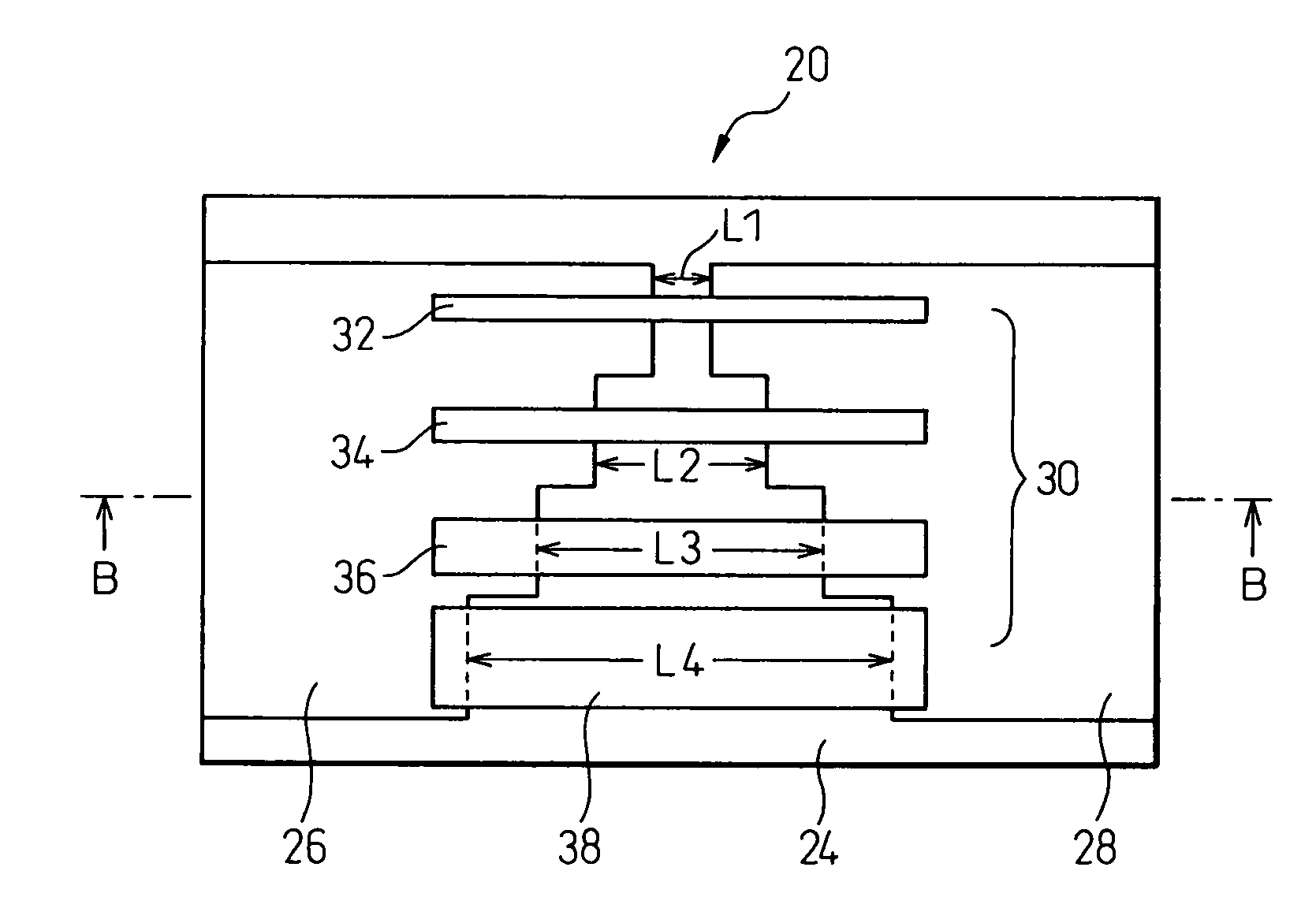
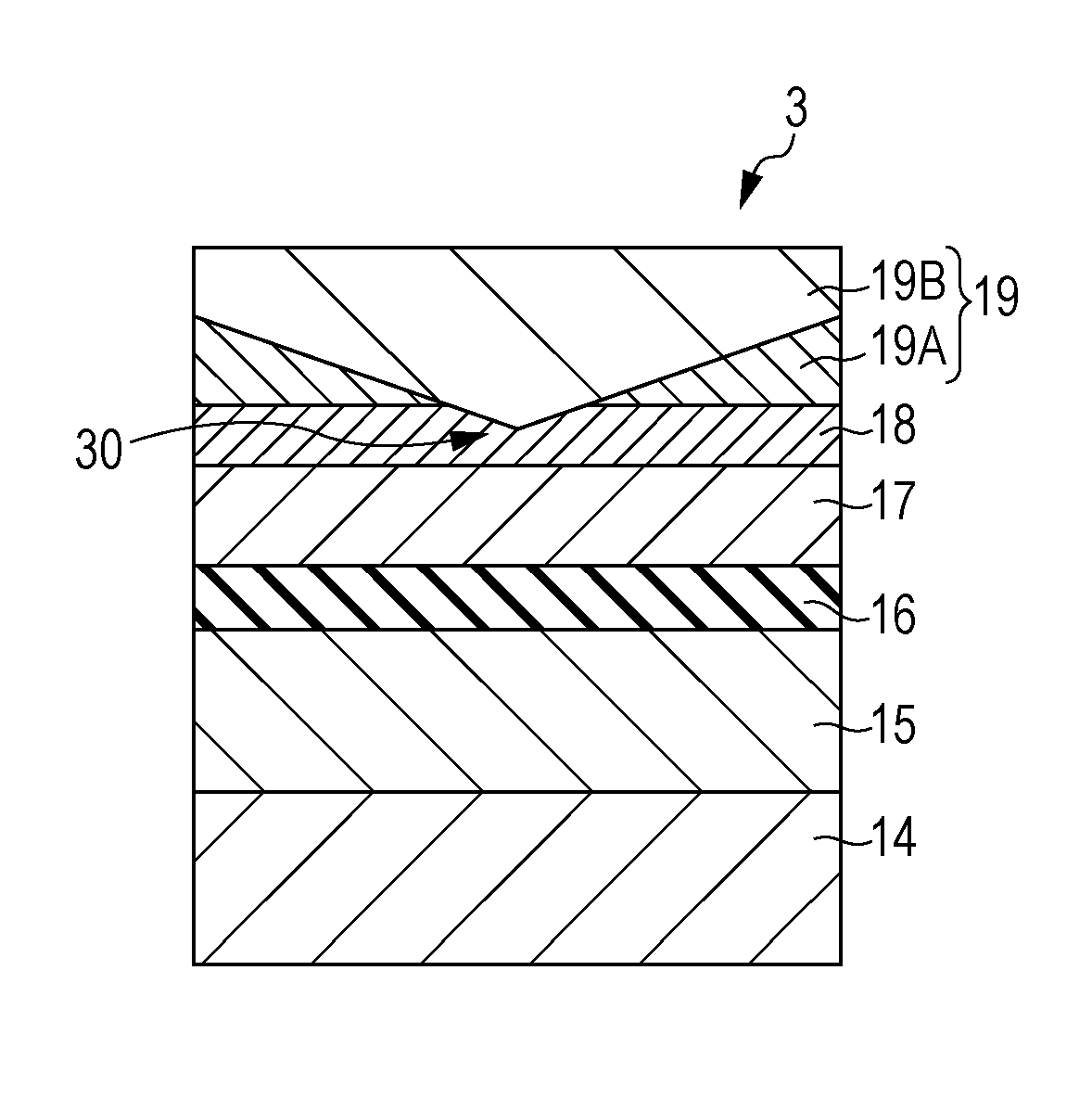
A multi-value recording phase-change memory device that can stably record multi-value information, and that can reproduce information with high reliability, comprises a first electrode layer 26, a second electrode layer 28, and a memory layer 30 provided between the first and second electrode layers 26 and 28 and containing a phase-change material layer formed from a phase-change material which is stable in either an amorphous phase or a crystalline phase at room temperature, wherein the memory layer 30 includes a plurality of mutually isolated sub-memory layers 32, 34, 36, and 38 between the first and second electrode layers 26 and 28.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Method of making the selection gate in a split-gate flash EEPROM cell its and structure
InactiveUS20050026368A1Reduce horizontal sizeReduce power consumptionTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectric layerSemiconductor
A method of making the selection gate in a split-gate flash EEPROM cell forms a selection gate on a trench sidewall of a semiconductor substrate to minimize the sidewise dimension of the selection gate and to maintain the channel length. The disclosed method includes the steps of: forming a trench on a semiconductor substrate on one side of a suspending gate structure; forming an inter polysilicon dielectric layer on the sidewall of the suspending gate structure and the trench; and forming a polysilicon spacer on the inter polysilicon dielectric layer as the selection gate. Such a split-gate flash EEPROM cell can produce ballistic hot electrons, improving the data writing efficiency and lowering the writing voltage.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Storage element, storage device, method of manufacturing storage element, and magnetic head
ActiveUS9397288B2Reduce resistanceEfficient workMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMagnetizationLow resistance
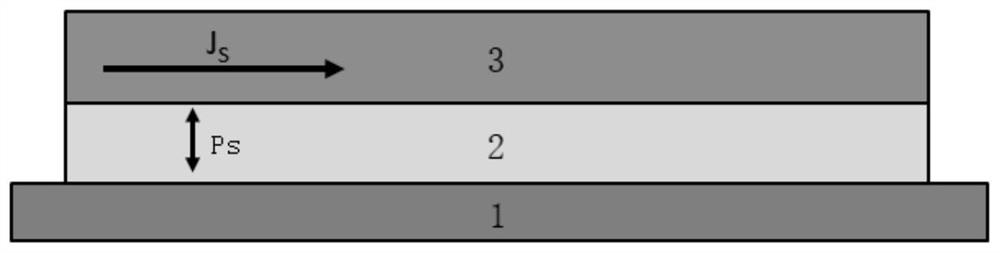
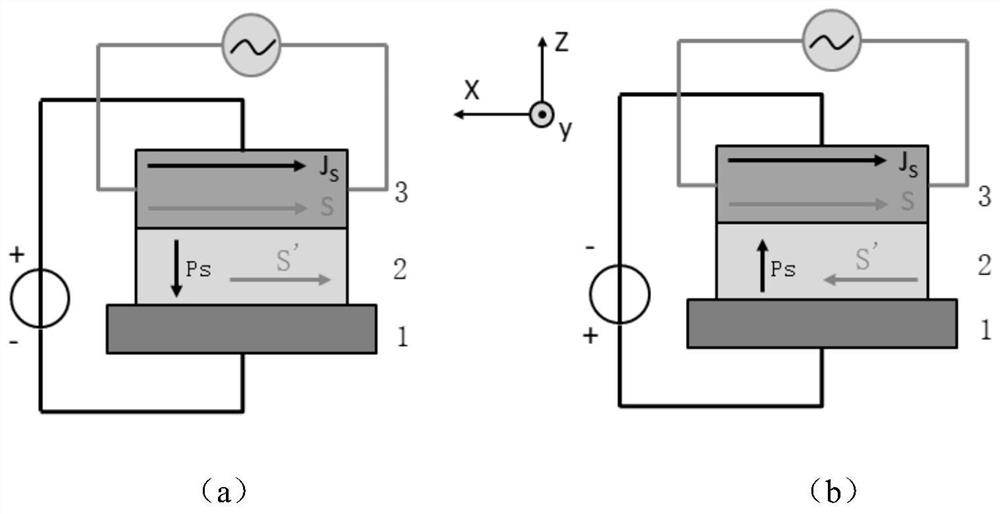
A storage element includes a layer structure, which includes a storage layer including magnetization perpendicular to the film surface, in which the magnetization direction is changed corresponding to information; a magnetization fixing layer including magnetization perpendicular to the film surface that becomes a reference for information stored on the storage layer; a tunnel barrier layer made from an oxide provided between the storage layer and the magnetization fixing layer; and a spin barrier layer made from an oxide provided contacting the surface of the opposite side of the storage layer to the surface contacting the tunnel barrier layer. A low resistance region is formed in a portion of the spin barrier layer formed with a predetermined set film thickness value and information storage on the storage layer is performed by changing the magnetization direction of the storage layer by current flowing in the stacking direction of the layer structure.
Owner:SONY CORP
Nonvolatile memory and semiconductor device including nonvolatile memory
InactiveUS7692999B2High power consumptionBattery shortRead-only memoriesDigital storageHigh resistanceHemt circuits
An object is to provide a nonvolatile memory with reduced power consumption. The nonvolatile memory includes a memory element that has a low resistance state and a high resistance state, a writing circuit, a resistance element, a voltage source input terminal that inputs a writing voltage to the writing circuit, a bit line driver circuit that selects whether the memory element is connected to the writing circuit, and a word line driver circuit that selects whether or not writing is done in the memory element. With such as structure, power consumption during writing can be reduced, and a nonvolatile memory with low power consumption can be realized. Further, with such a nonvolatile memory, an active type wireless tag with a long lifetime of a battery or a passive type wireless tag with a wide communication range in which writing to a memory is possible, can be realized.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Dual function hybrid memory cell
ActiveUS9715933B2Short timeLower write voltageSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesTrappingDual function
A dual function hybrid memory cell is disclosed. In one aspect, the memory cell includes a substrate, a bottom charge-trapping region formed on the substrate, a top charge-trapping region formed on the bottom charge-trapping region, and a gate layer formed on the top charge trapping region. In another aspect, a method for programming a memory cell having a substrate, a bottom charge-trapping layer, a top charge-trapping layer, and a gate layer is disclosed. The method includes biasing a channel region of the substrate, applying a first voltage differential between the gate layer and the channel region, injecting charge into the bottom charge-trapping layer from the channel region based on the first voltage differential. The method also includes applying a second voltage differential between the gate layer and the channel region and injecting charge from the bottom charge-trapping layer into the top charge-trapping layer based on the second voltage differential.
Owner:NEO SEMICON
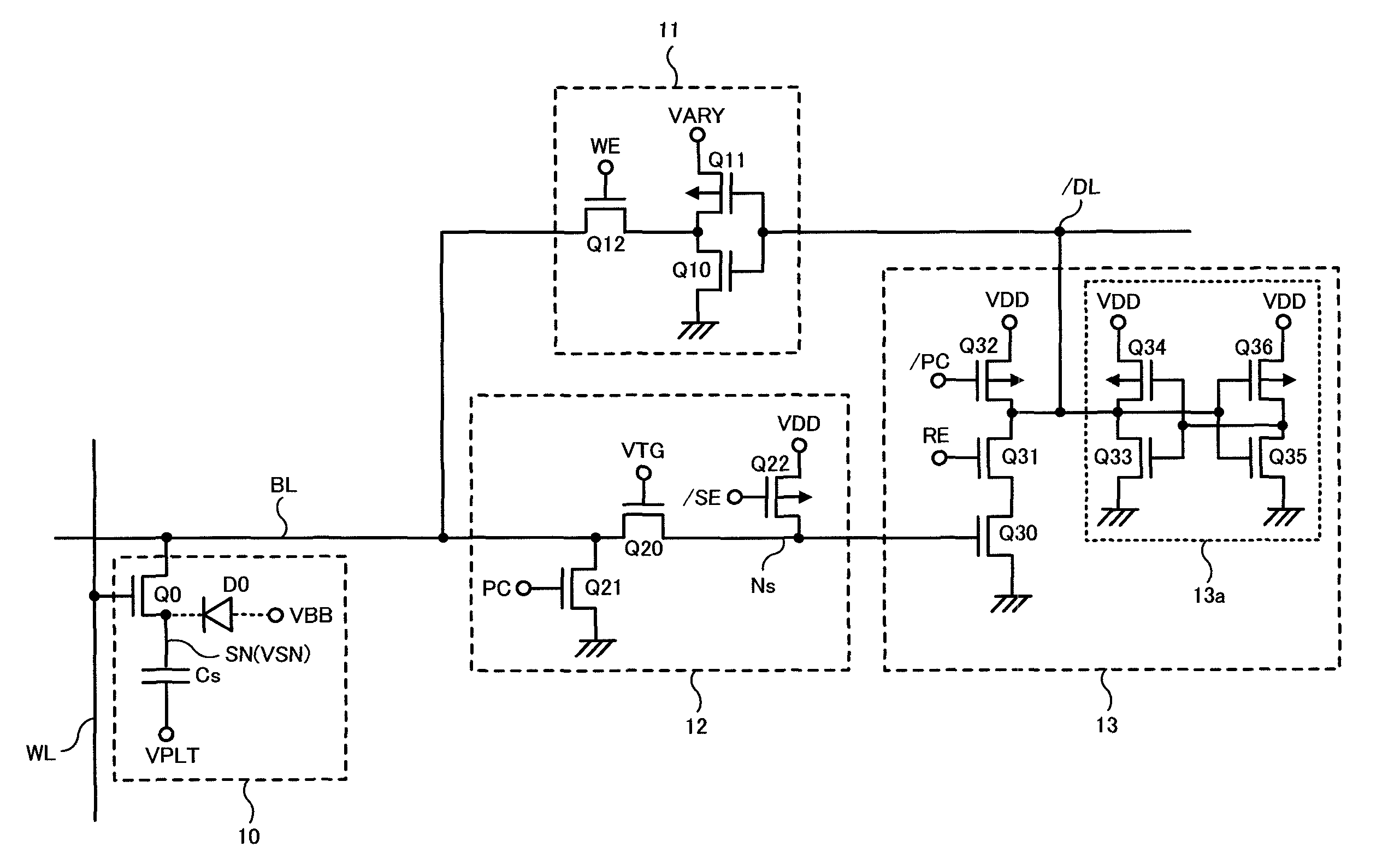
Semiconductor memory device and electronic apparatus mounting the same
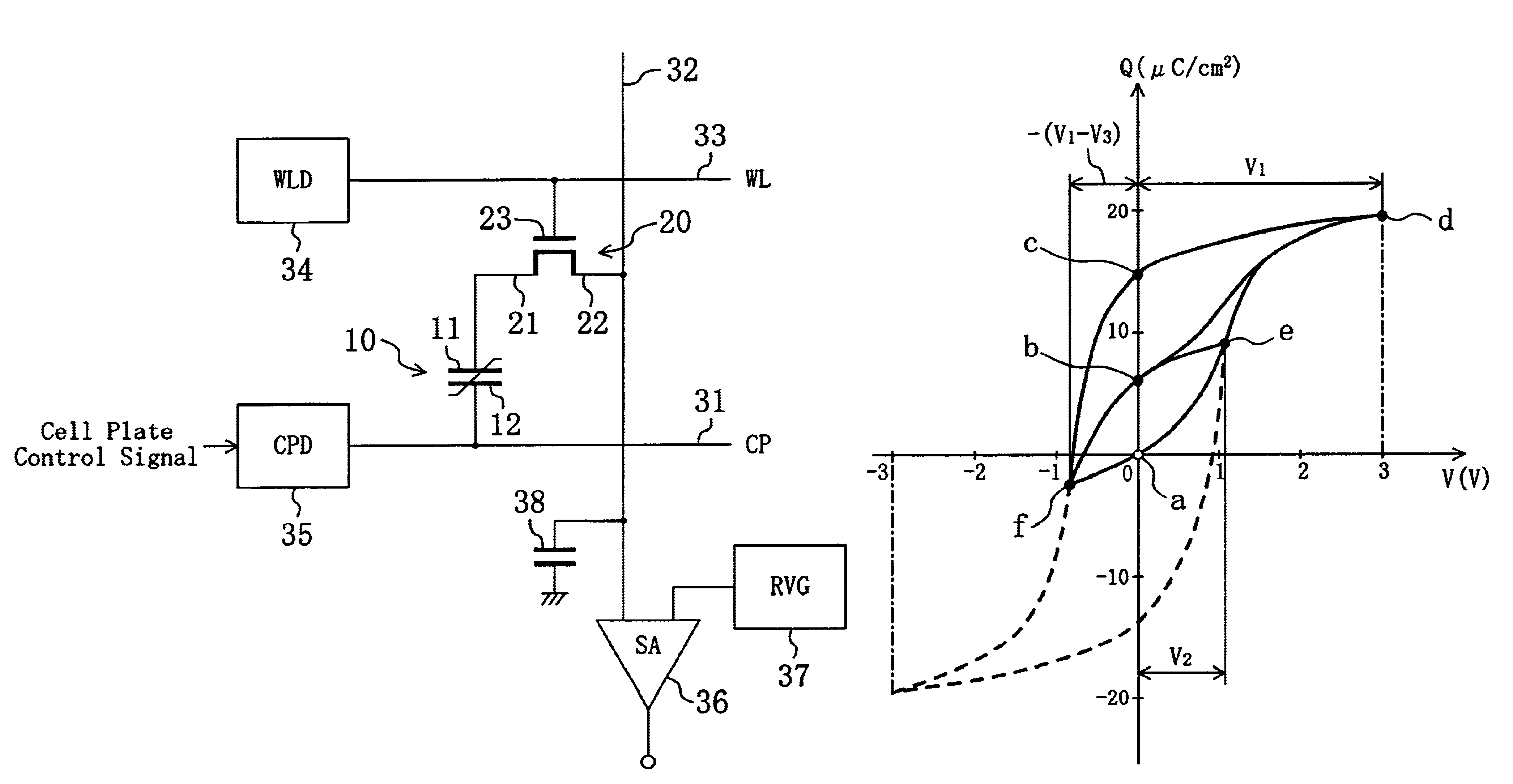
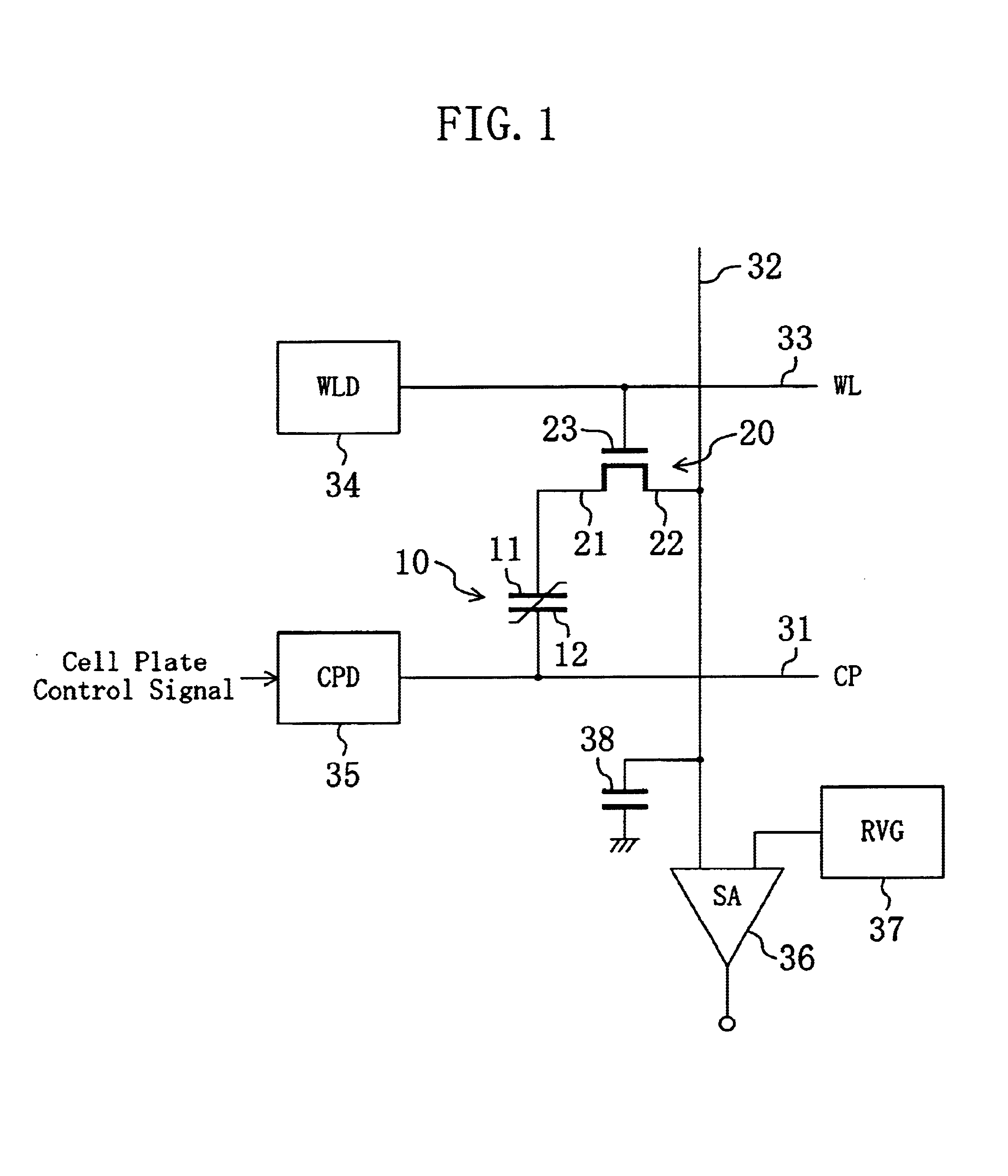
InactiveUS6950327B2Increase rewritable number of timeLong data retention lifetimeDigital storageVoltage pulseSemiconductor
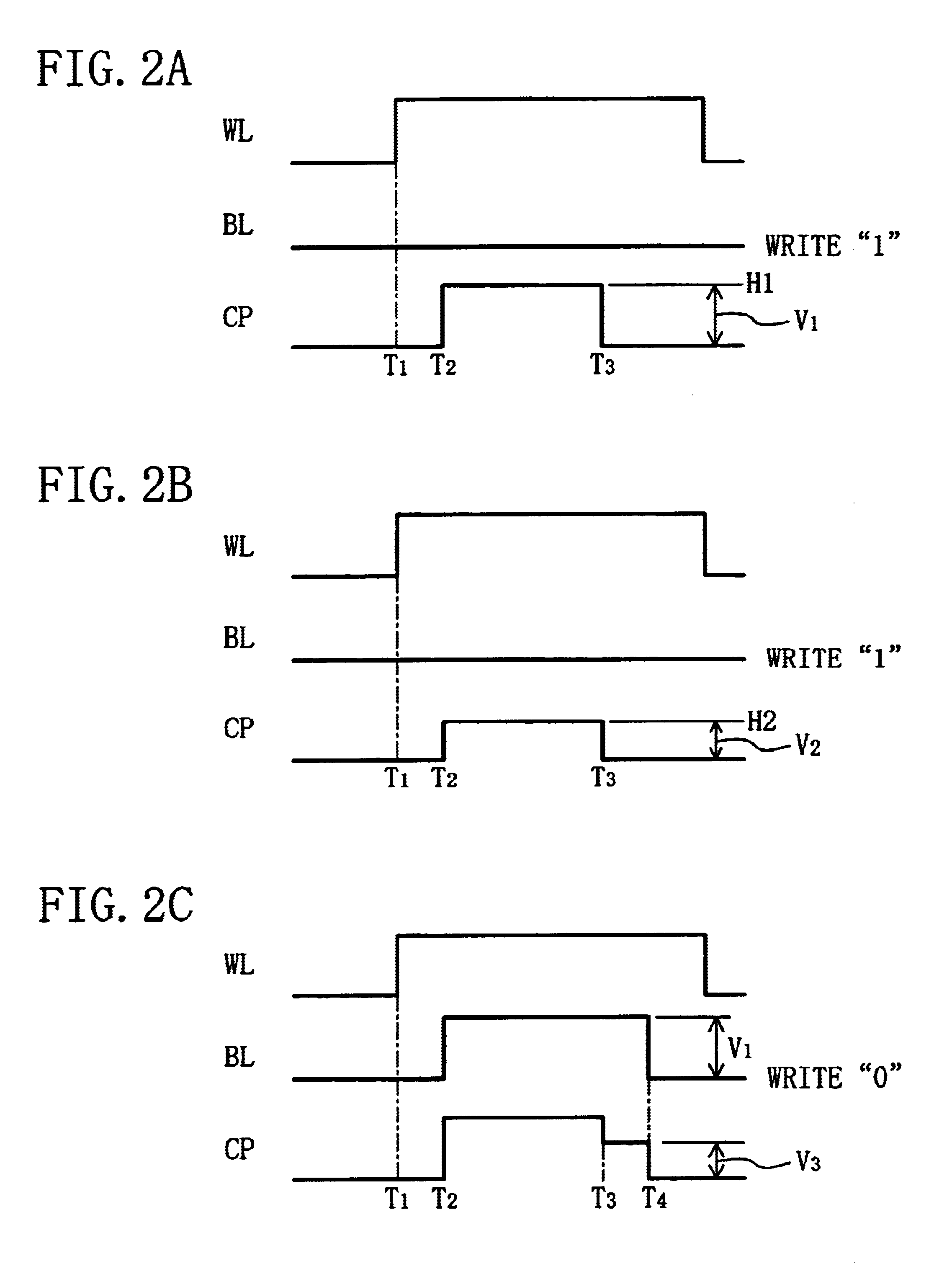
In a ferroelectric capacitor, two displacements (points b and c) of a remanent polarization correspond to data “1” and one displacement (point a) of the remanent polarization corresponds to data “0”. When the data “1” is written, either of two electric voltage pulses different in potential or in pulse width is applied to the ferroelectric capacitor to position the displacement of the remanent polarization in the ferroelectric capacitor at the point b or at the point c. When the data “0” is written, on the other hand, the displacement of the remanent polarization in the ferroelectric capacitor is positioned at the point a.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Semiconductor memory device having first and second floating gates of different polarity
InactiveUS9966476B2Total current dropImprove retentionTransistorSolid-state devicesValence bandElectrical polarity
A semiconductor memory device includes a first floating gate and a second floating gate of conductivity types with different polarities. Injection of electrons into the first floating gate via a tunnel insulating film is stored through a decrease in holes in a valence band of the second floating gate, and ejection of electrons from the first floating gate via the tunnel insulating film is stored through an increase in holes in the valence band of the second floating gate.
Owner:ABLIC INC
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS10263003B2High retention rateLower write voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorStorage cell
Provided is a semiconductor device which has a non-volatile memory including: a semiconductor substrate; a tunnel insulating film formed on a surface of the semiconductor device; a floating gate formed on the tunnel insulating film; a memory cell transistor drain region and a memory cell transistor source region formed from the surface to an inside of the semiconductor substrate in a vicinity of both ends of the floating gate; a first interface formed between the semiconductor substrate and the tunnel insulating film; and a second interface formed between the floating gate and the tunnel insulating film. The first interface and the second interface form an uneven structure having a curvature that changes at an identical period with respect to a place in sectional view.
Owner:ABLIC INC
mram storage array
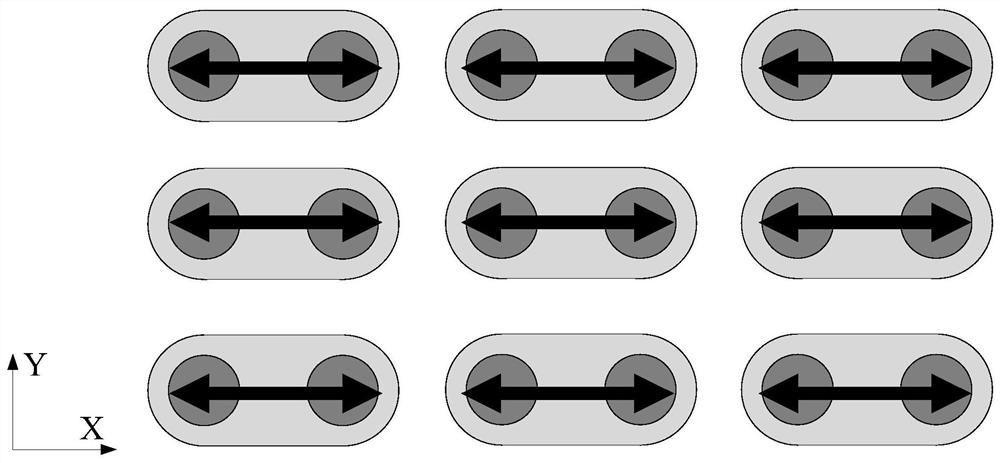
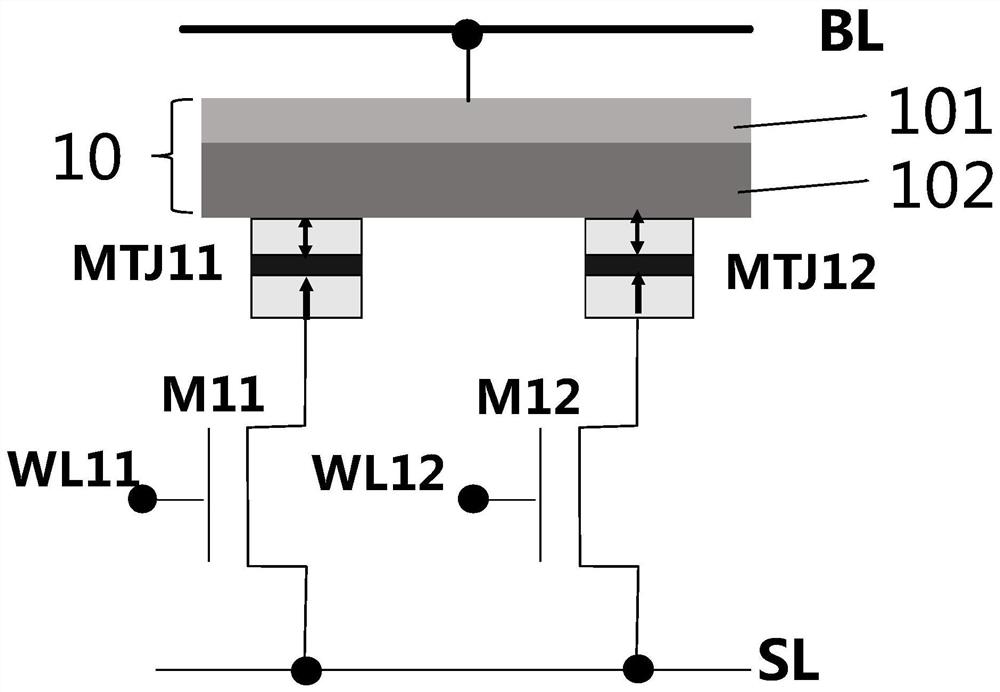
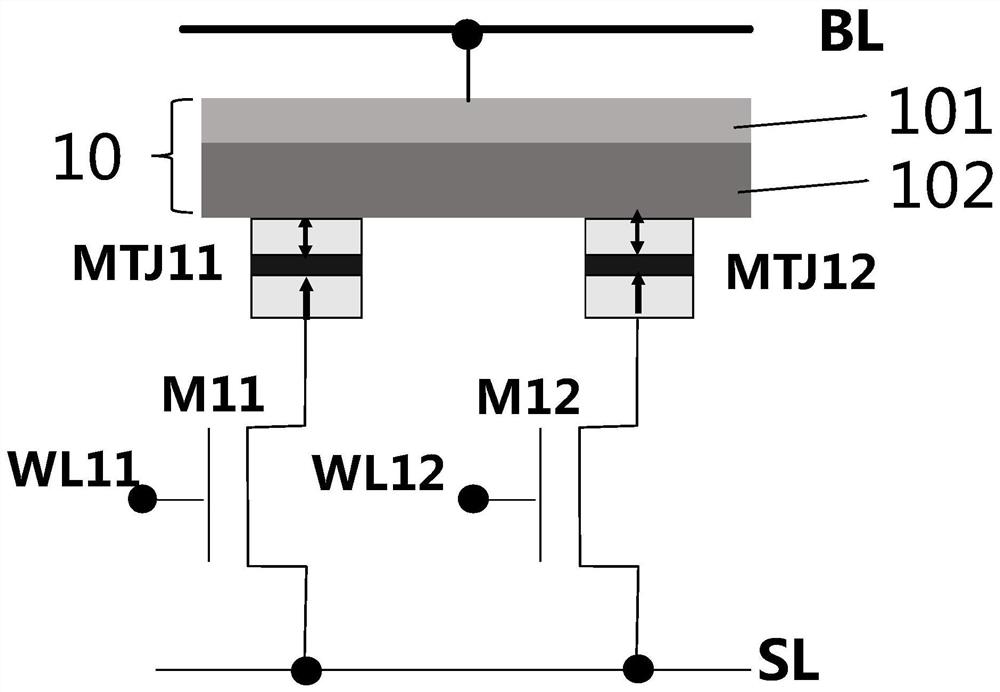
The present invention provides an MRAM memory array, comprising: a plurality of memory cells arranged in a rectangular array, the memory cells include MTJ cells, the magnetization direction of the MTJ cells is along the growth direction of the MTJ film, and two adjacent cells in the array The tops of the MTJ units in each of the storage units are provided with a common magnetic electrode, and all the magnetic electrodes in the array are arranged in the same direction, and the magnetic electrodes are used to provide one for the MTJ units in two adjacent storage units. The magnetic moment is used to assist the free layer of the MTJ unit to realize flipping; wherein, the cross-sectional shape of the MTJ unit in the storage unit is a circular shape, and the cross-sectional shape of the magnetic electrode shared by two adjacent storage units is A geometric shape with a major and minor axis. The invention can increase the density of the storage array.
Owner:CETHIK GRP +1
MRAM memory array
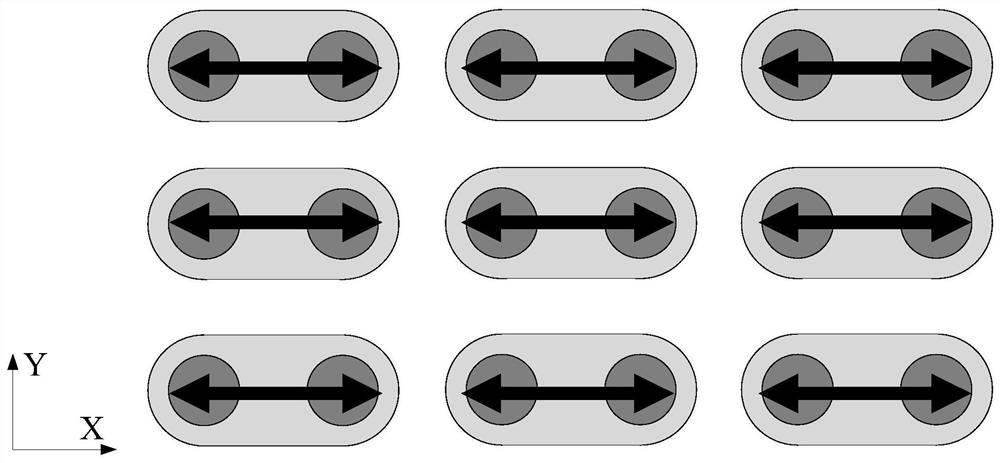
The invention provides an MRAM storage array. The array substrate comprises a plurality of storage units which are arranged in a rectangular array form, the storage unit comprises an MTJ unit. The magnetization direction of the MTJ unit is along the growth direction of the MTJ thin film; the tops of the MTJ units in every two adjacent storage units in the array are provided with a shared magneticelectrode, the arrangement directions of all the magnetic electrodes in the array are the same, and the magnetic electrodes are used for providing a magnetic moment for the MTJ units in every two adjacent storage units so as to assist the free layers of the MTJ units in realizing overturning; wherein the cross section of the MTJ unit in each storage unit is circular, and the cross section of the magnetic electrode shared by two adjacent storage units is in a geometrical shape with a long axis and a short axis. The density of the memory array can be improved.
Owner:CETHIK GRP +1
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20180277548A1High retention rateLower write voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorStorage cell
Provided is a semiconductor device which has a non-volatile memory including: a semiconductor substrate; a tunnel insulating film formed on a surface of the semiconductor device; a floating gate formed on the tunnel insulating film; a memory cell transistor drain region and a memory cell transistor source region formed from the surface to an inside of the semiconductor substrate in a vicinity of both ends of the floating gate; a first interface formed between the semiconductor substrate and the tunnel insulating film; and a second interface formed between the floating gate and the tunnel insulating film. The first interface and the second interface form an uneven structure having a curvature that changes at an identical period with respect to a place in sectional view.
Owner:ABLIC INC
Memory based on spin texture, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112928158AReduce power consumptionSmall sizeSemiconductor devicesHigh densityConductive materials
The invention relates to a memory based on spin texture. The memory comprises a substrate, a ferroelectric layer and a ferromagnetic layer; the ferroelectric layer is located on the substrate; the ferromagnetic layer is located on the ferroelectric layer; and the material of the substrate is a conductive material, the material of the ferroelectric layer is GeTe, SnTe or HfO2, and the material of the ferromagnetic layer is a material which conducts electrons and has spin polarization. The memory disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low power consumption, small size, high-density integration, simple structural design, high read-write speed and compatibility with a CMOS process. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the memory based on the spin texture.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Magnetization rotation element, magnetoresistive effect element, semiconductor element, magnetic recording array, and method for manufacturing magnetoresistive effect element
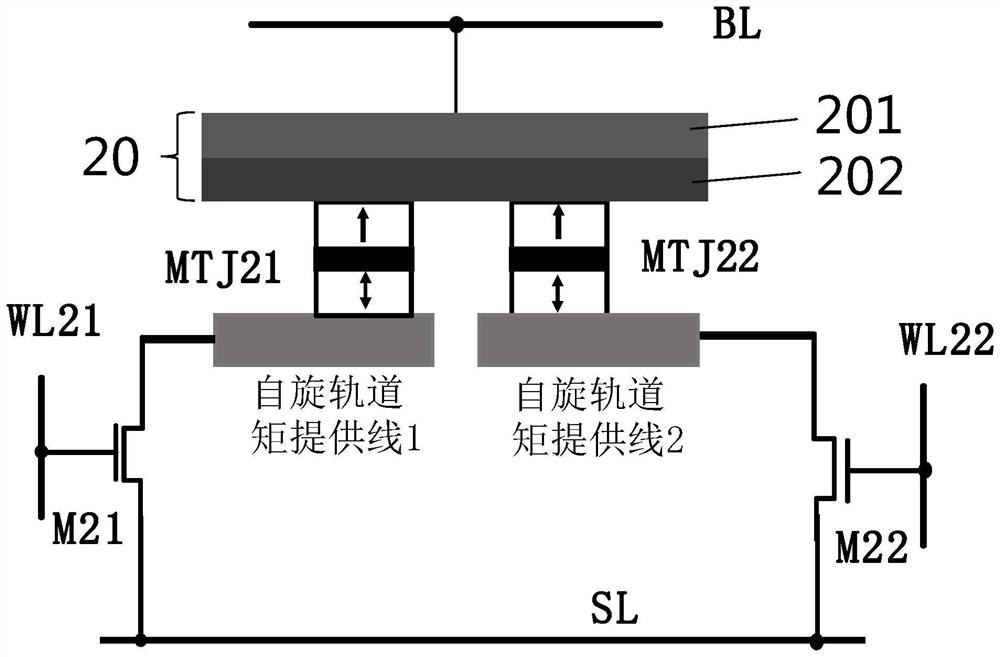
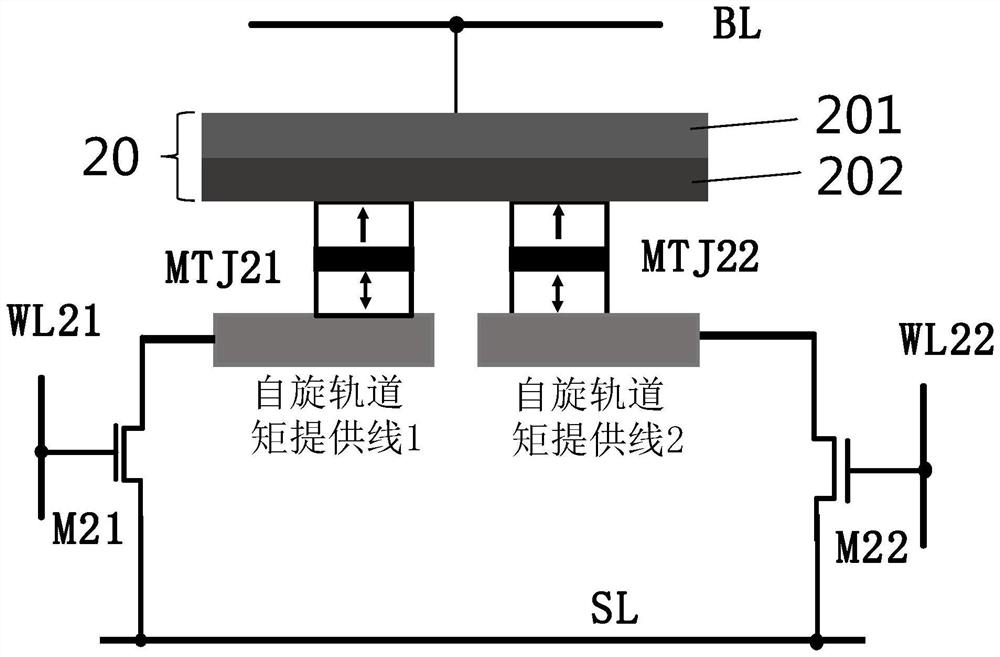
PendingCN112951984ALower write voltageMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMagnetic reluctanceCondensed matter physics
The invention provides a magnetized rotating element. The magnetized rotating element is provided with: spin-orbit torque wiring; and a first ferromagnetic layer which is located in a first direction with respect to the spin-orbit torque wiring and into which spin is injected from the spin-orbit torque wiring, the spin-orbit torque wiring having, in the first direction, a plurality of spin-generating layers and an insertion layer located between the plurality of spin-generating layers, the insertion layer has a lower electrical resistivity than the spin generation layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com