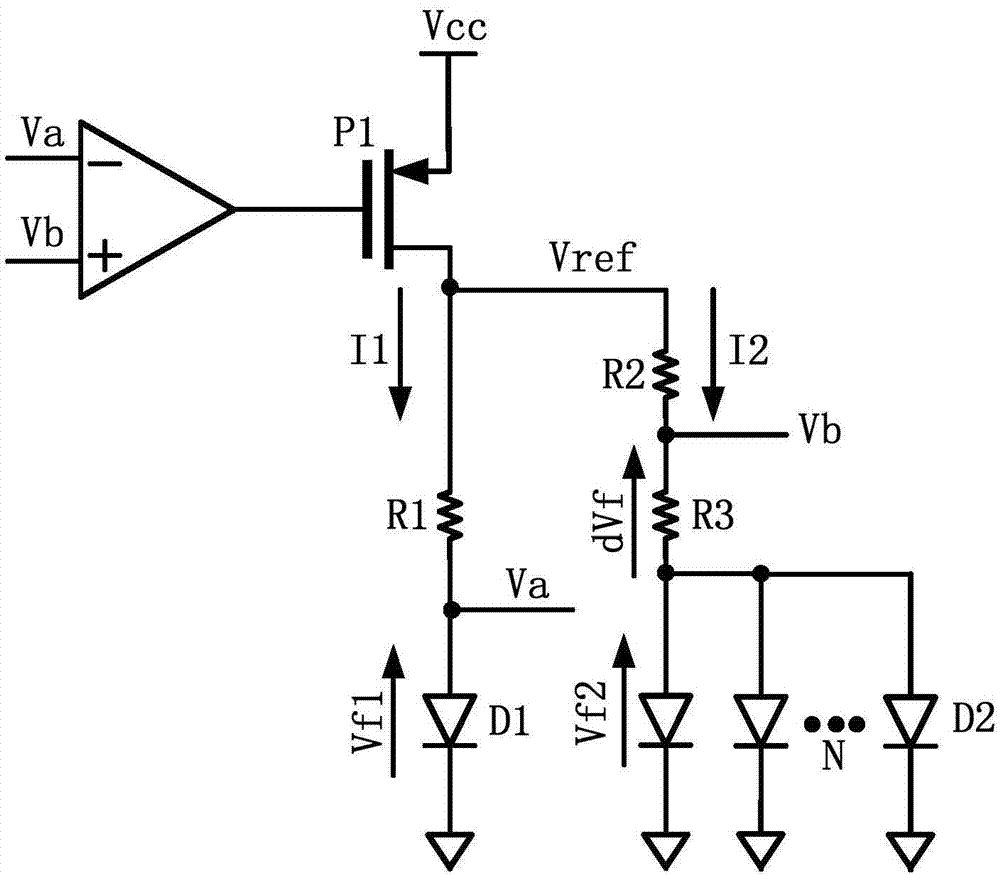
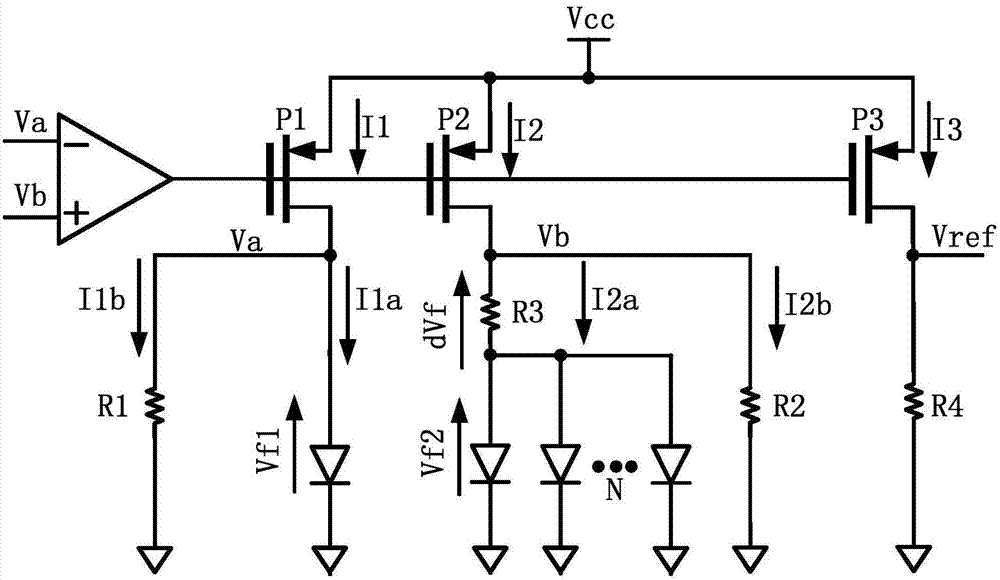
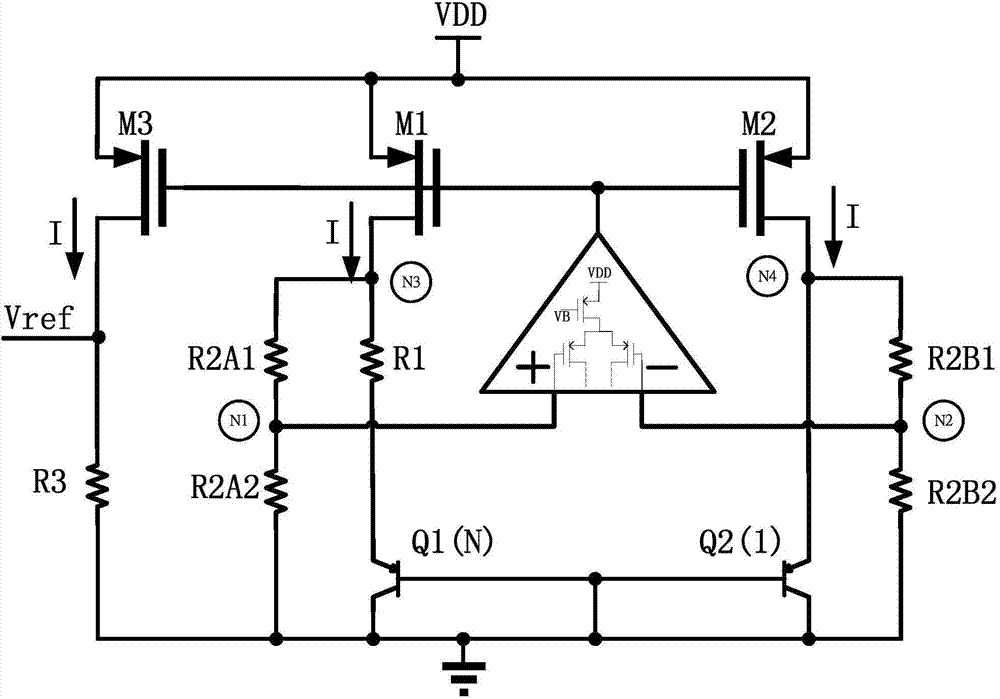
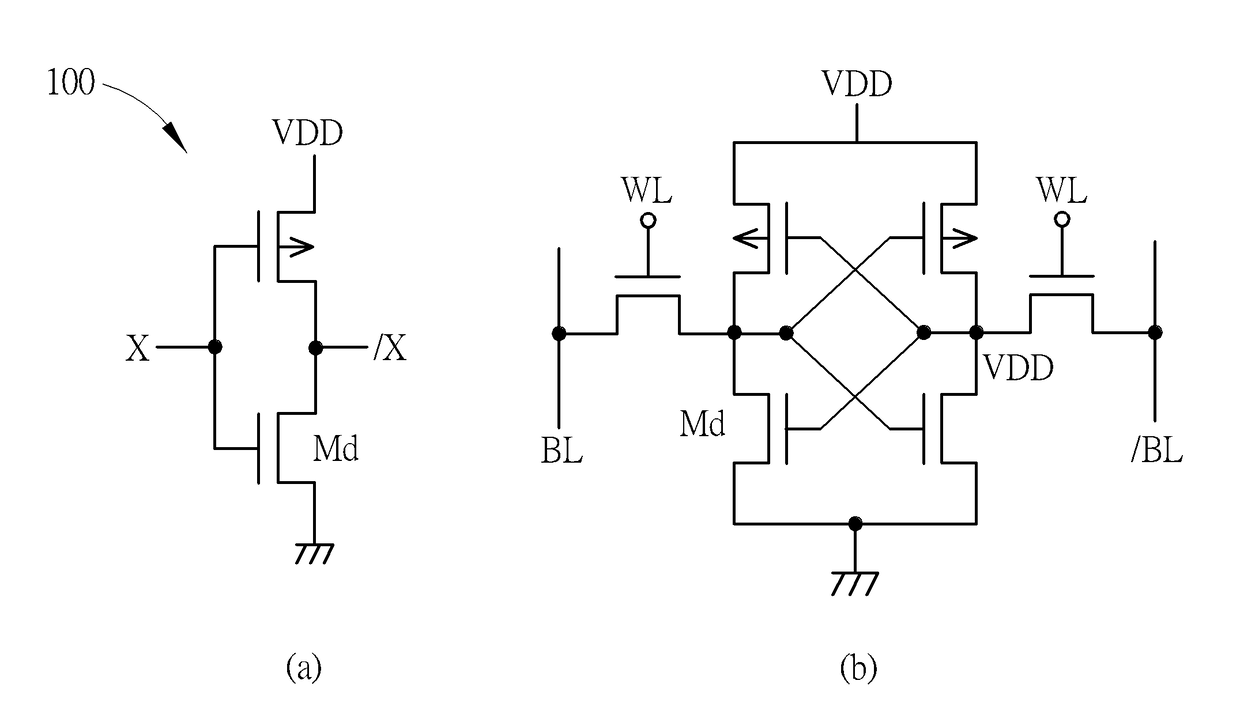
Patents
Literature
102 results about "Low voltage cmos" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
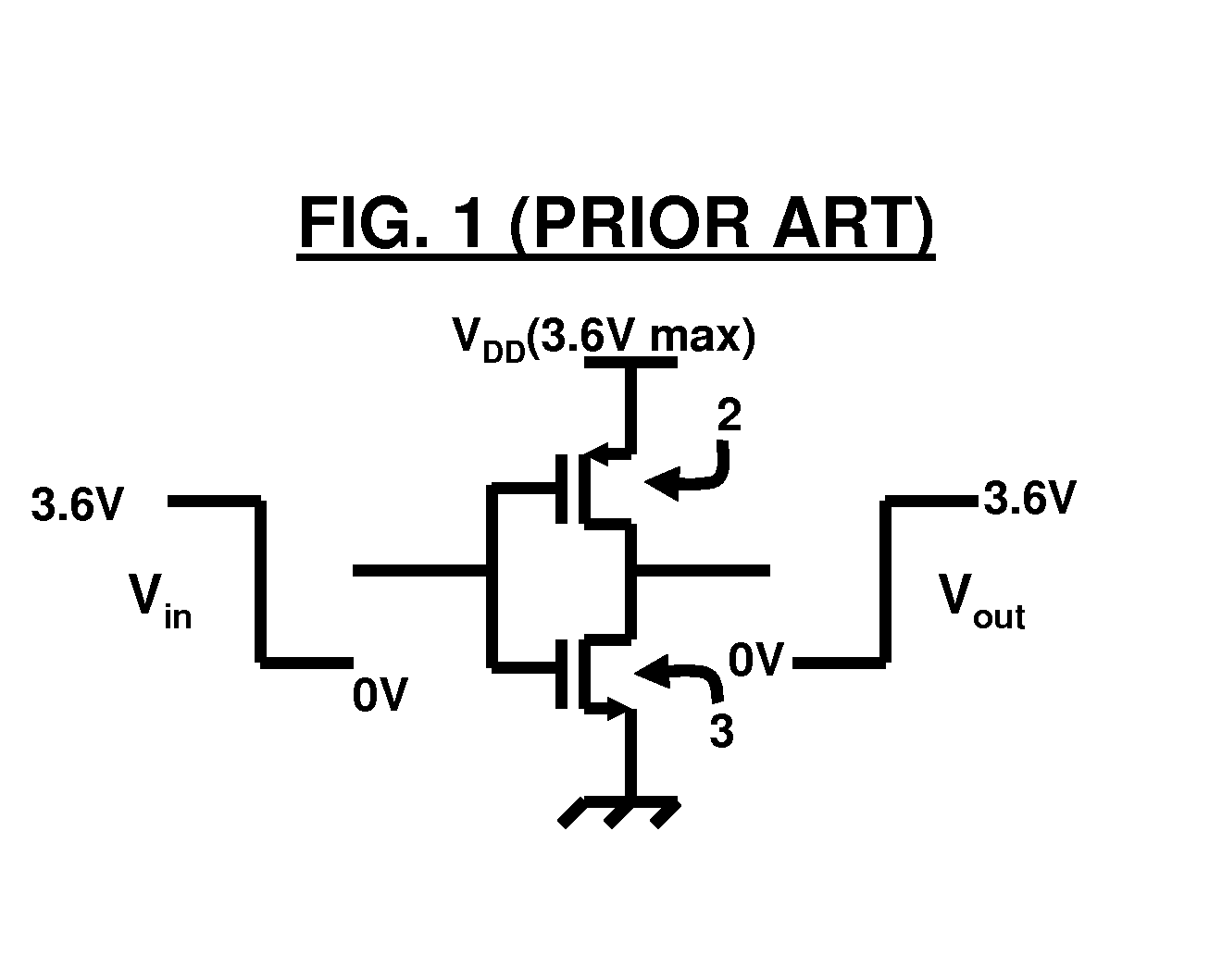
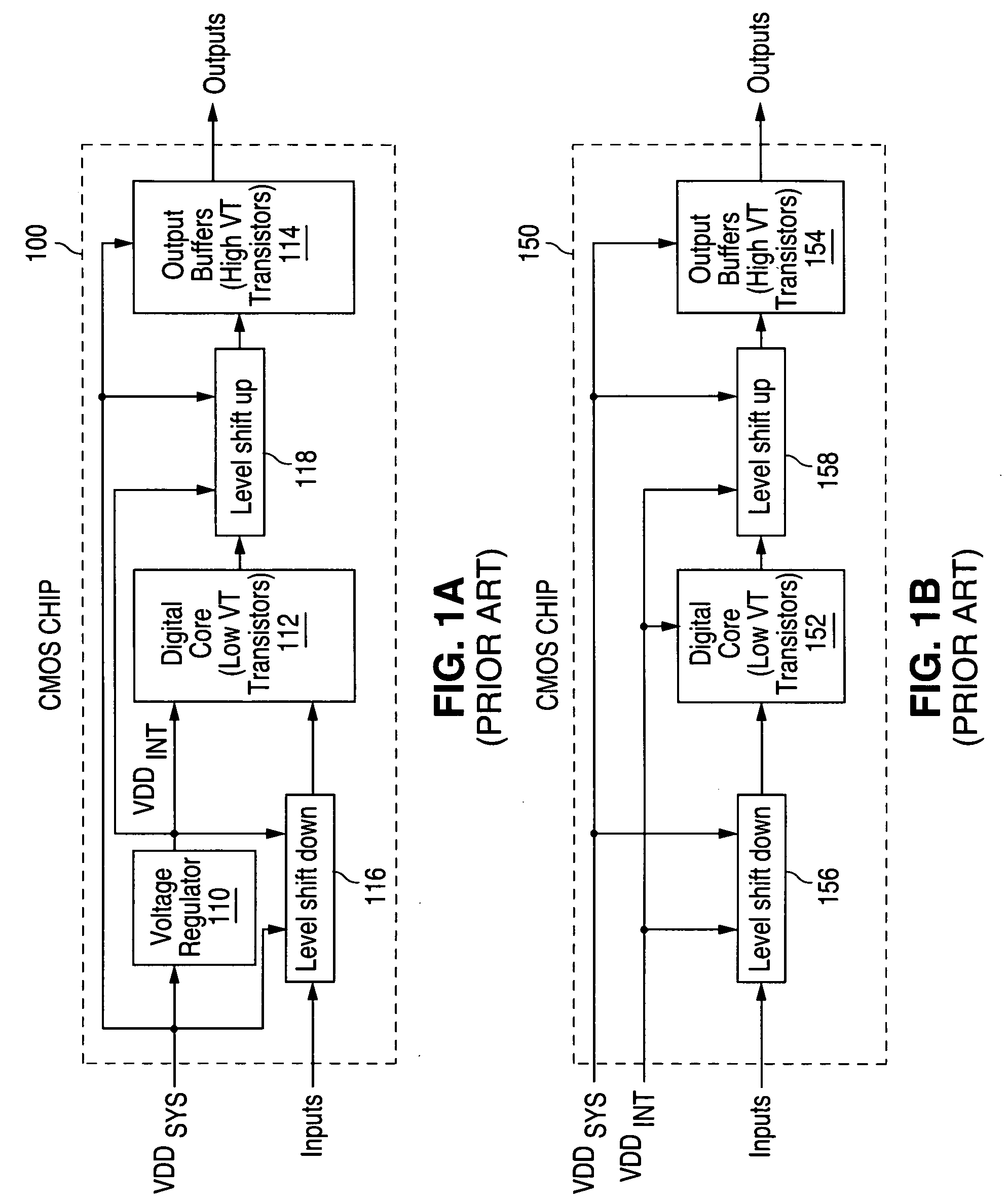
Low-Voltage CMOS (LVC) IDT’s low-voltage CMOS (LVC) logic family is comprised of high-performance bus interface components intended for low-voltage applications. These devices are fully compatible with industry-standard components with similar designations and are specified for both 3.3 V and 2.5 V operation.
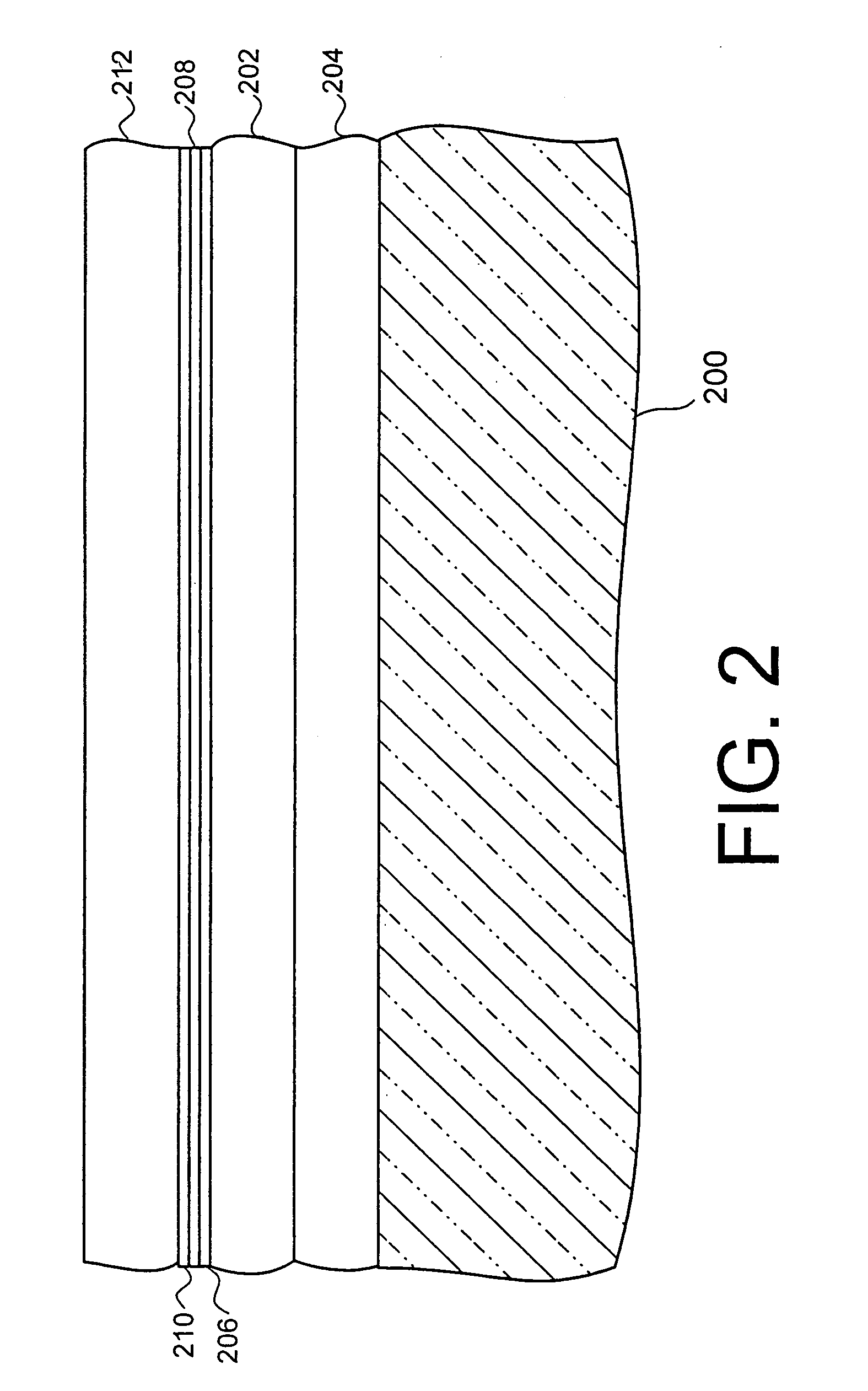
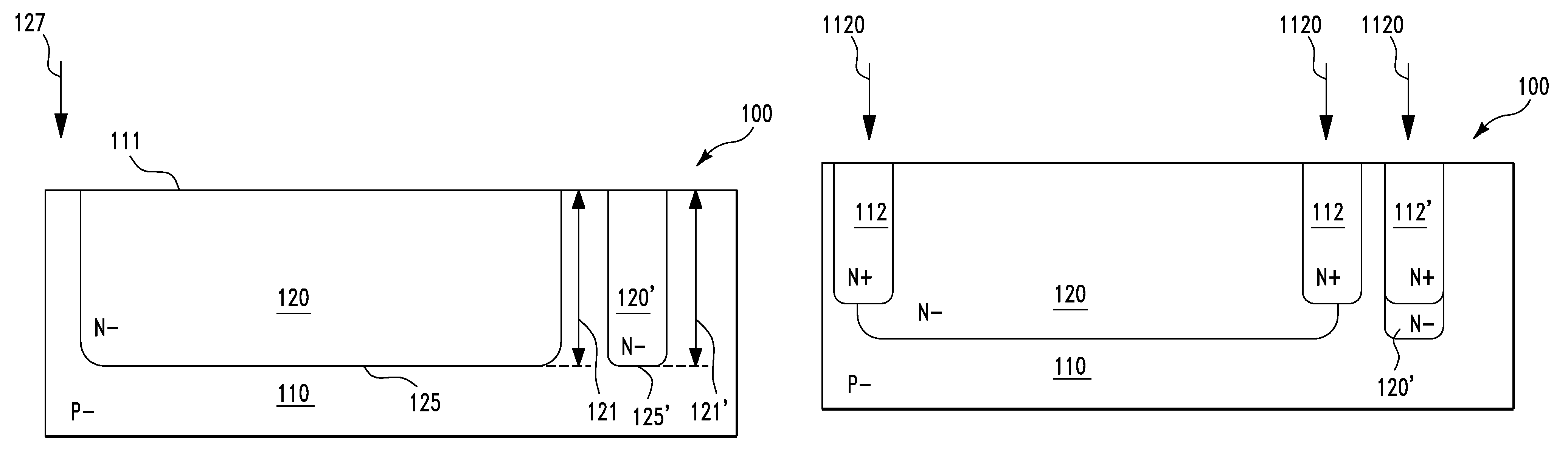
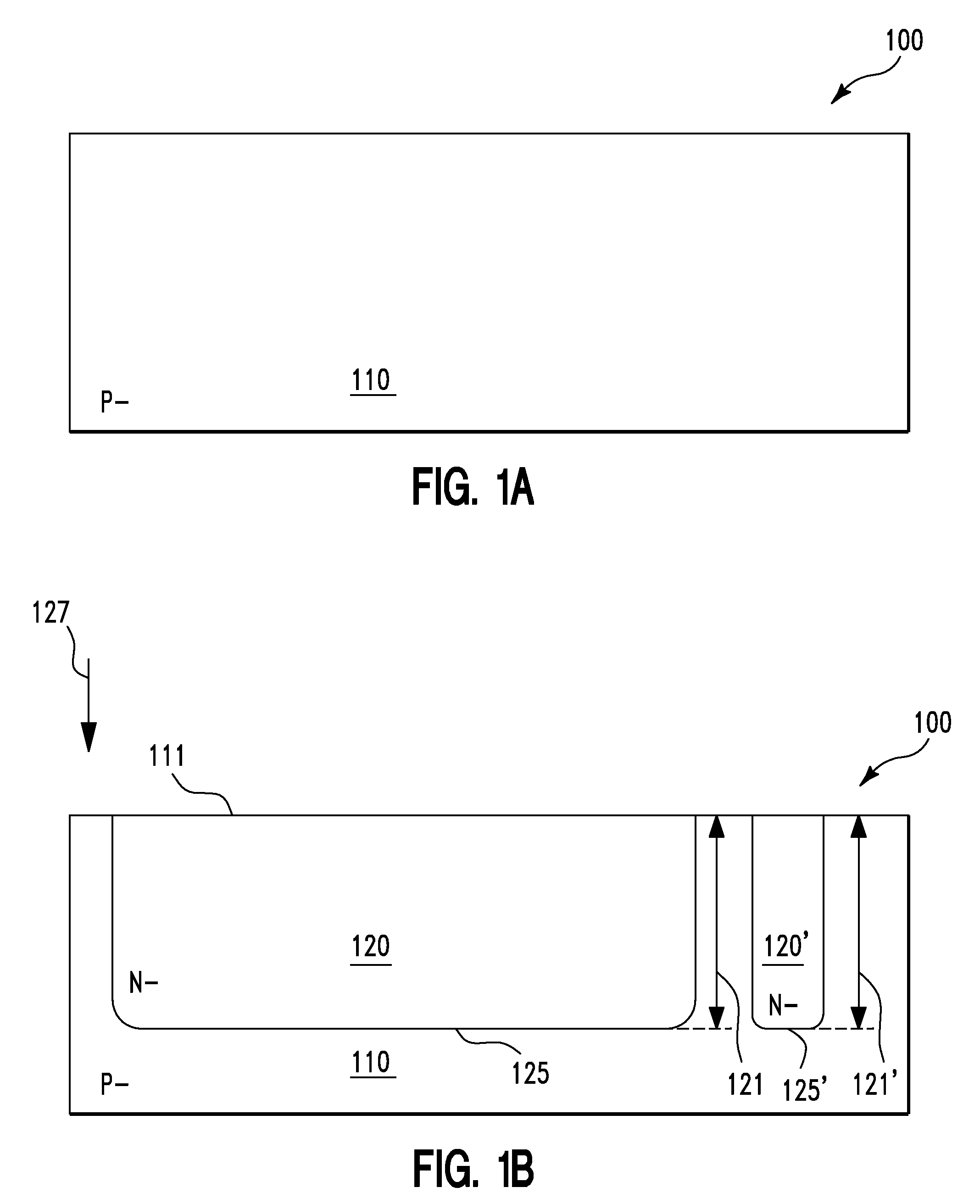
Double gated transistor and method of fabrication
InactiveUS7288445B2High densityImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon symmetricLow voltage cmos
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
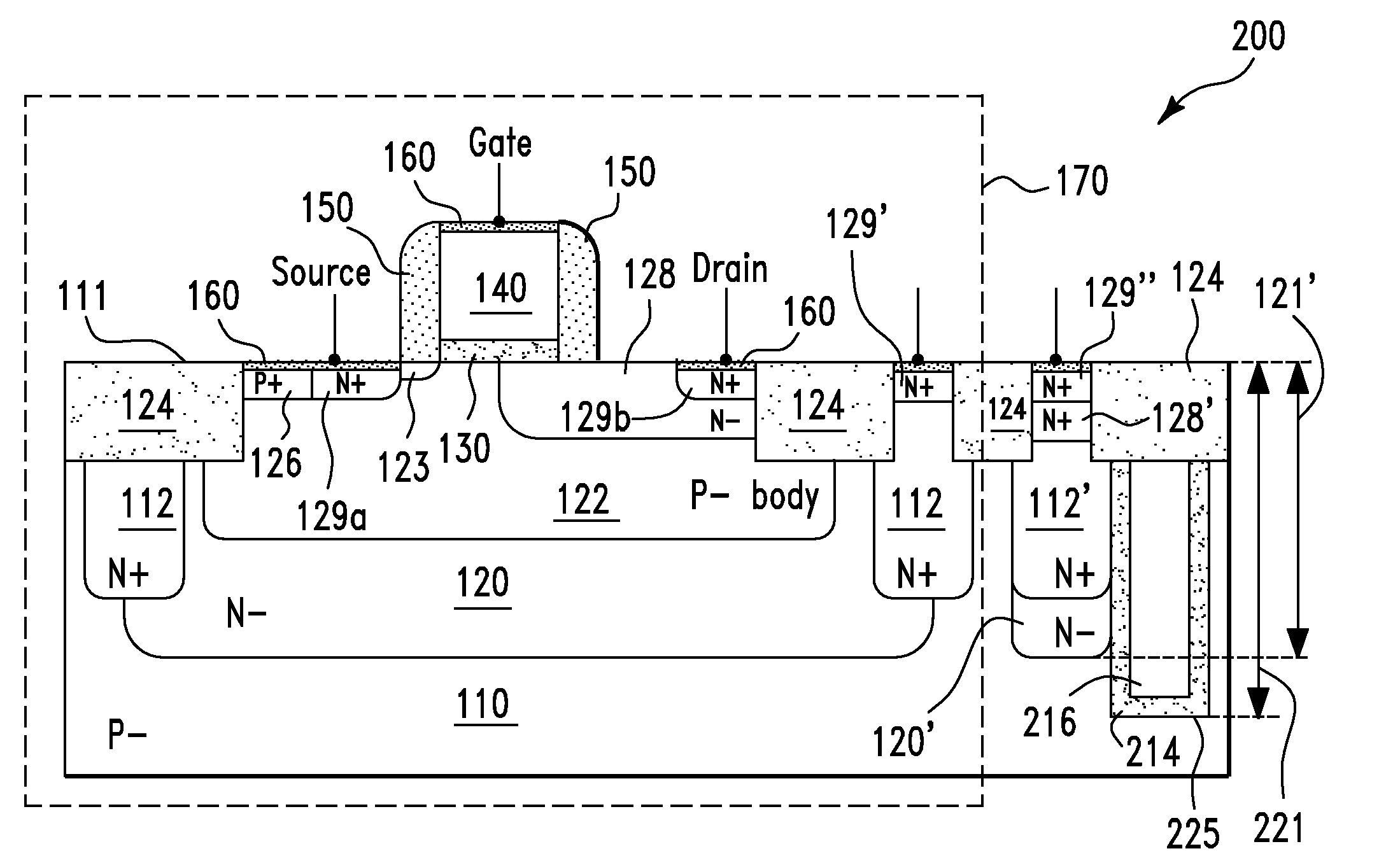
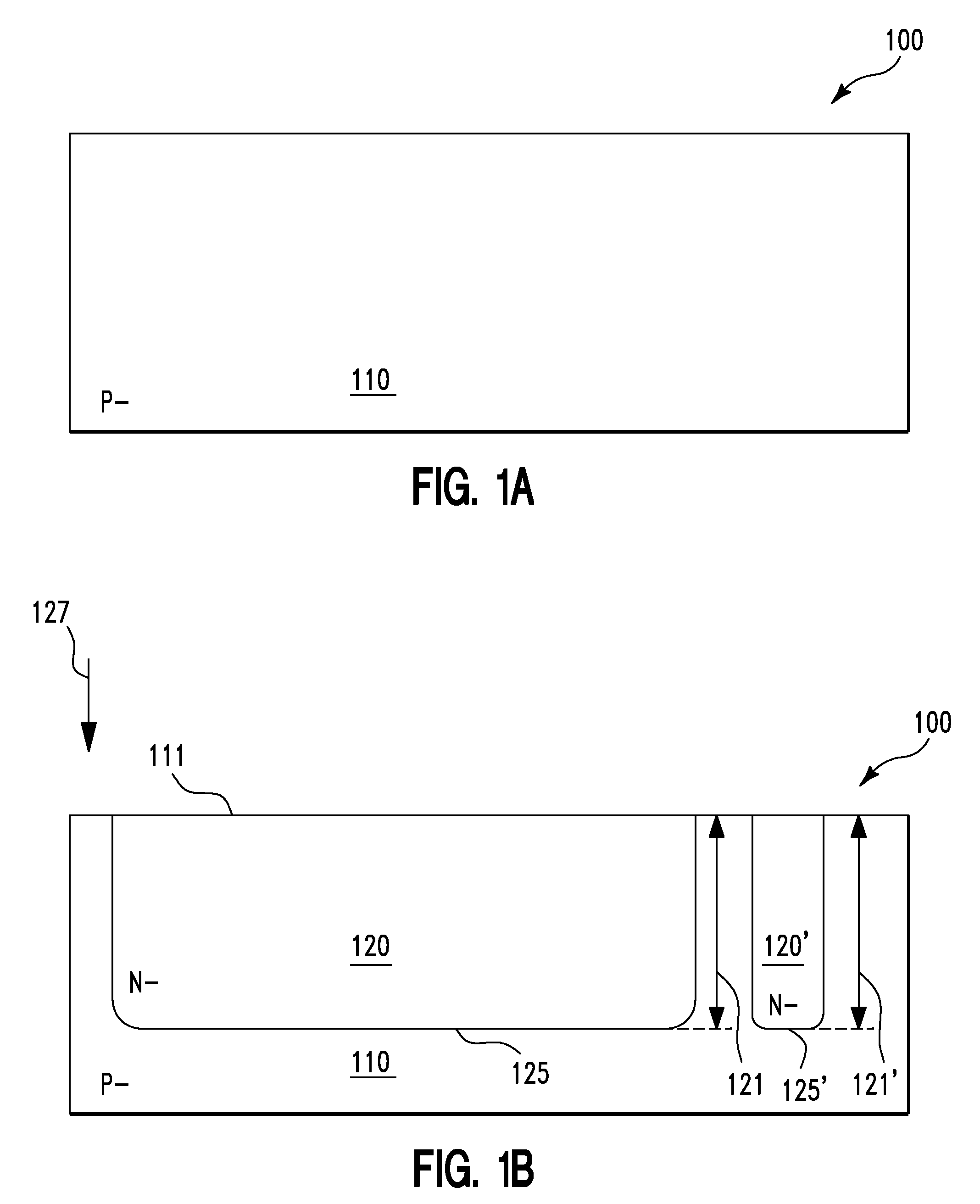
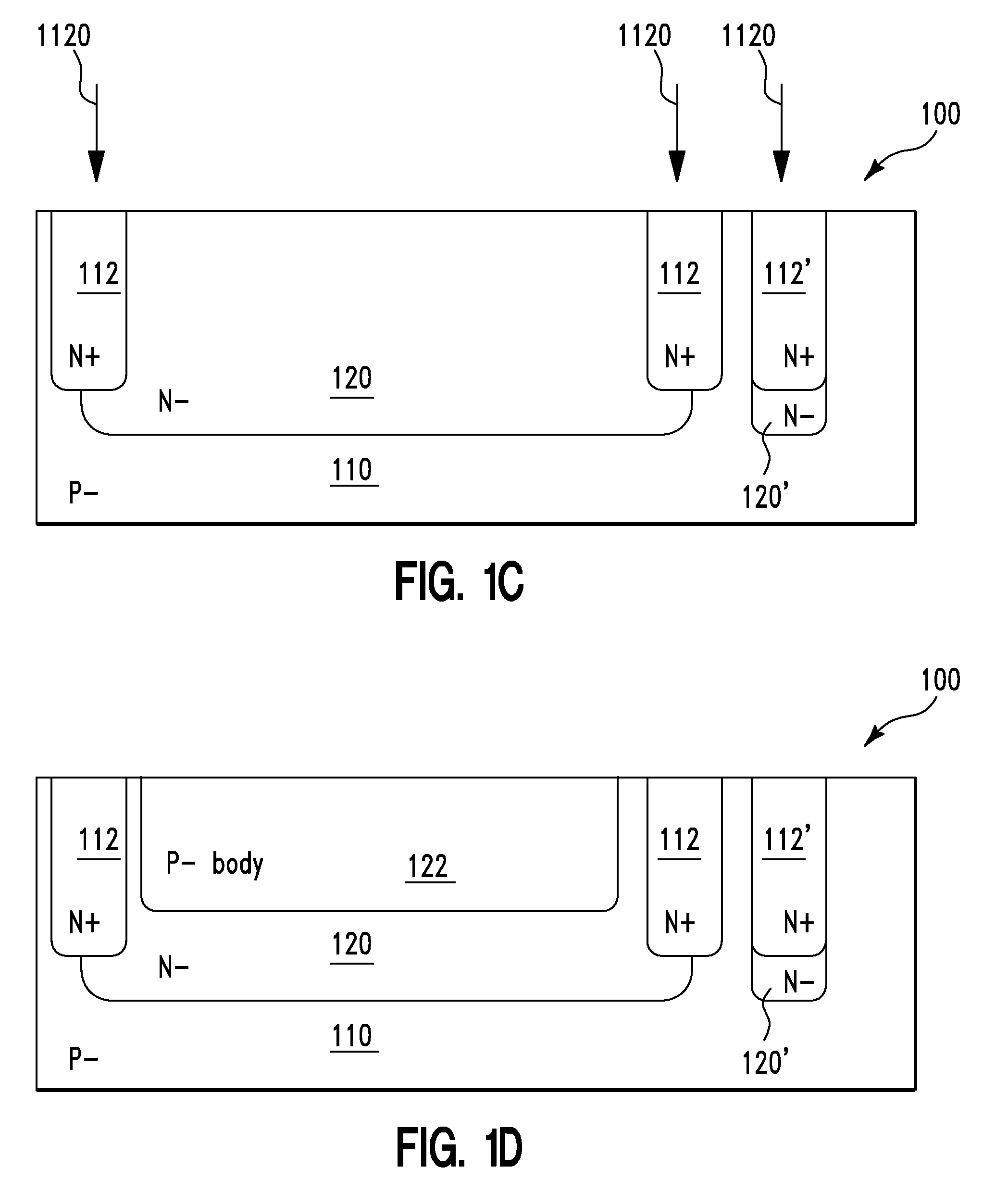
Guard ring structures for high voltage CMOS/low voltage CMOS technology using ldmos (lateral double-diffused metal oxide semiconductor) device fabrication
A semiconductor structure and a method for forming the same. The method includes providing a semiconductor structure. The semiconductor structure includes a semiconductor substrate. The method further includes simultaneously forming a first doped transistor region of a first transistor and a first doped guard-ring region of a guard ring on the semiconductor substrate. The first doped transistor region and the first doped guard-ring region comprise dopants of a first doping polarity. The method further includes simultaneously forming a second doped transistor region of the first transistor and a second doped guard-ring region of the guard ring on the semiconductor substrate. The second doped transistor region and the second doped guard-ring region comprise dopants of the first doping polarity. The second doped guard-ring region is in direct physical contact with the first doped guard-ring region. The guard ring forms a closed loop around the first and second doped transistor regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
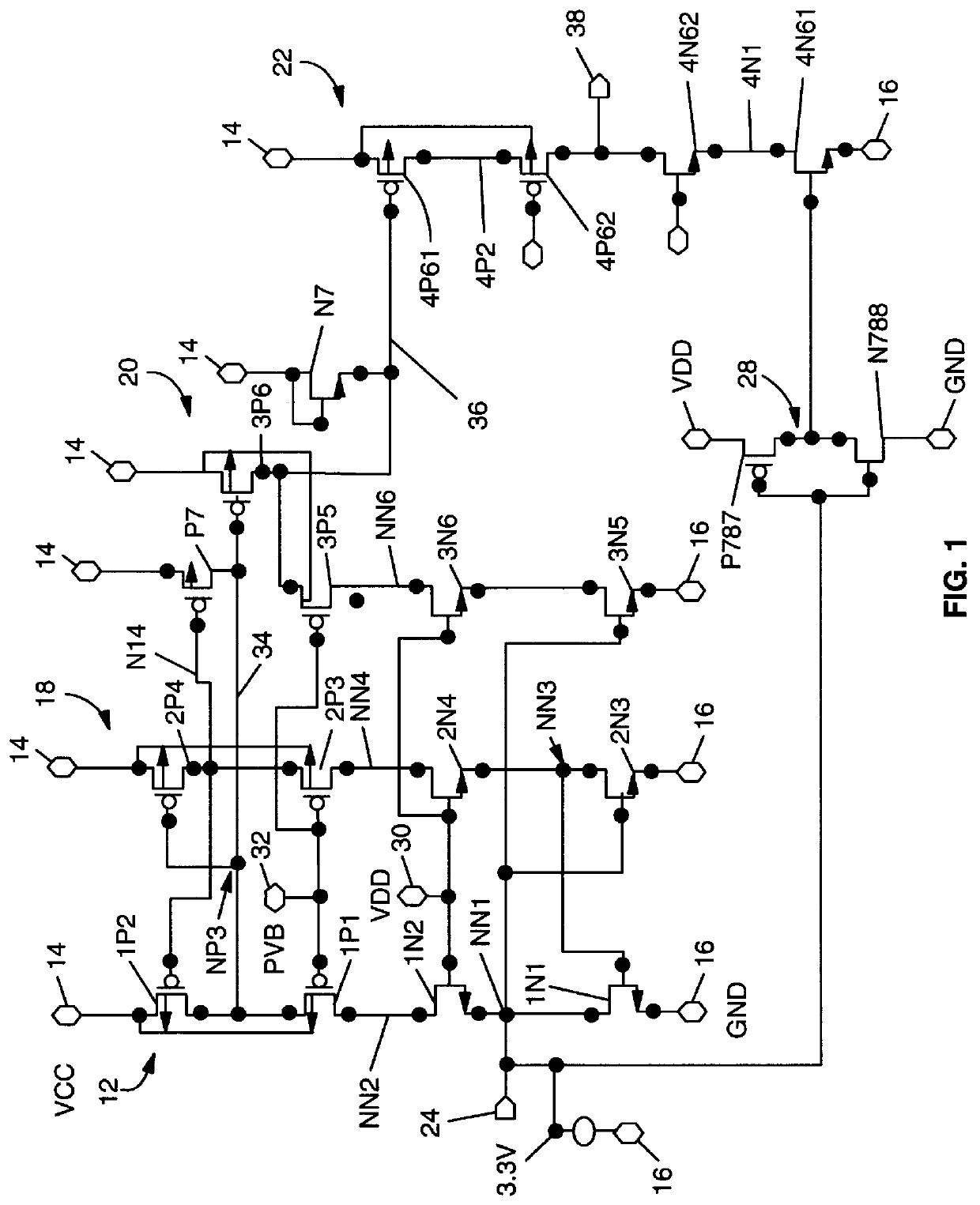
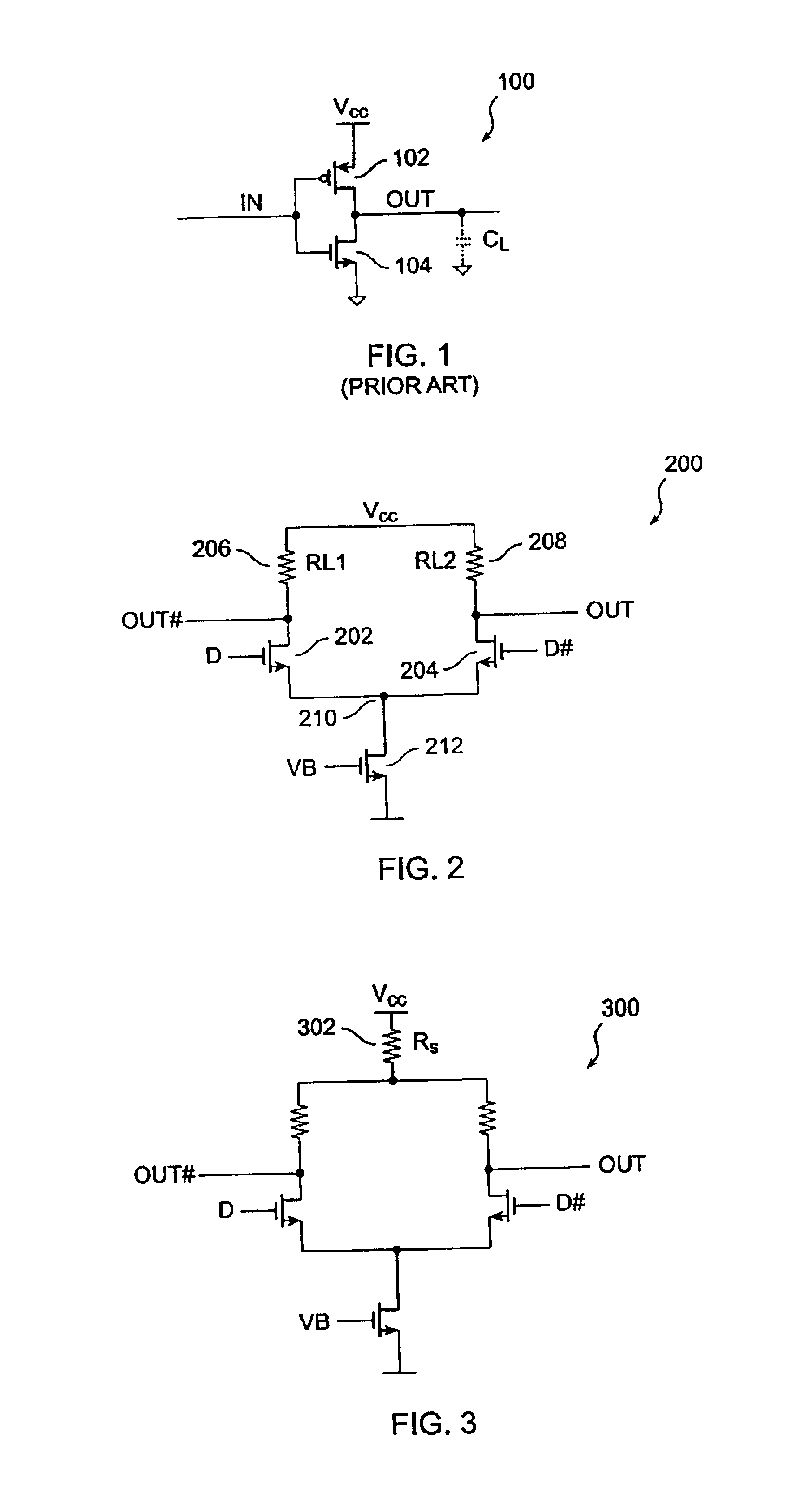
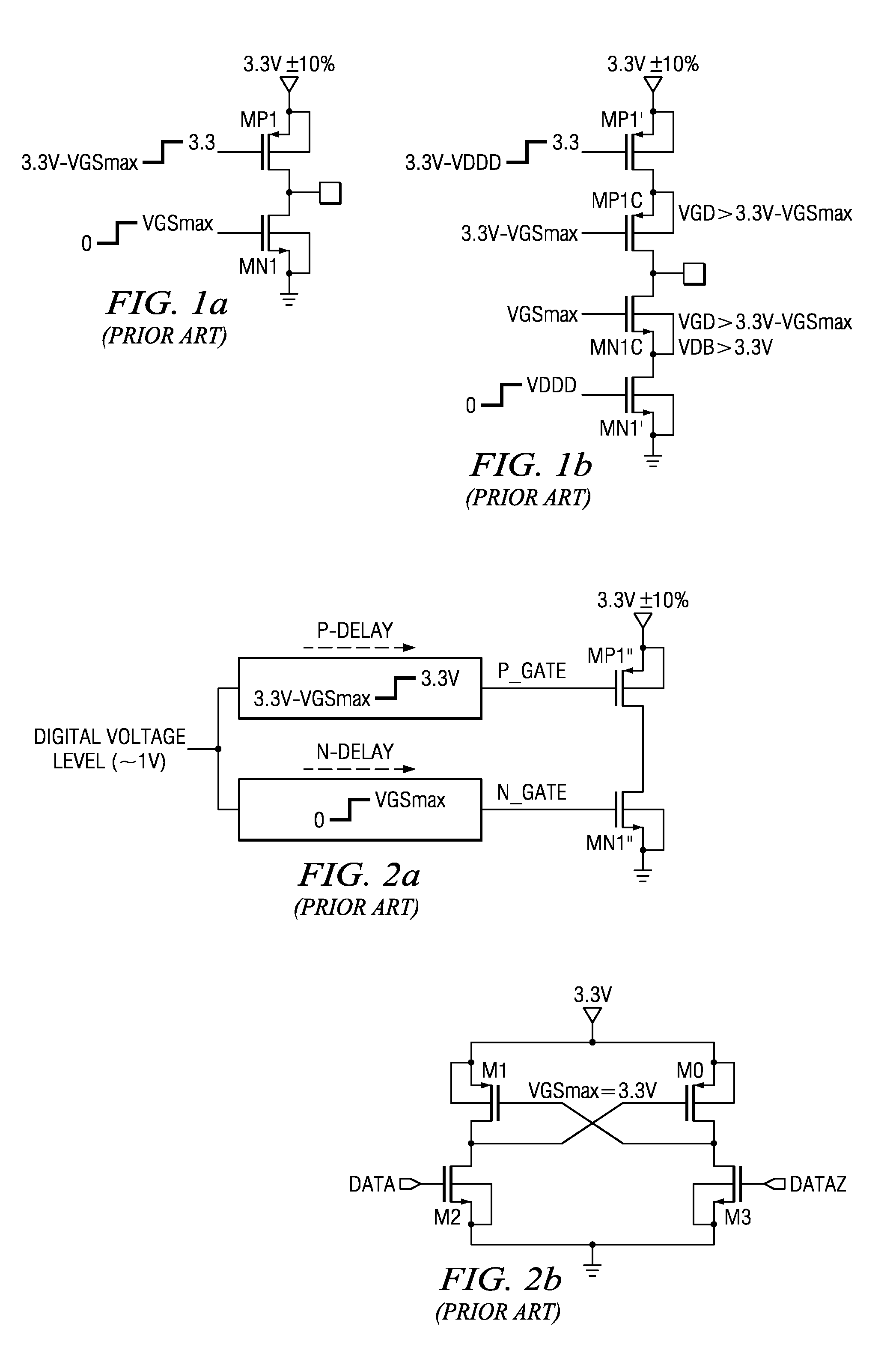
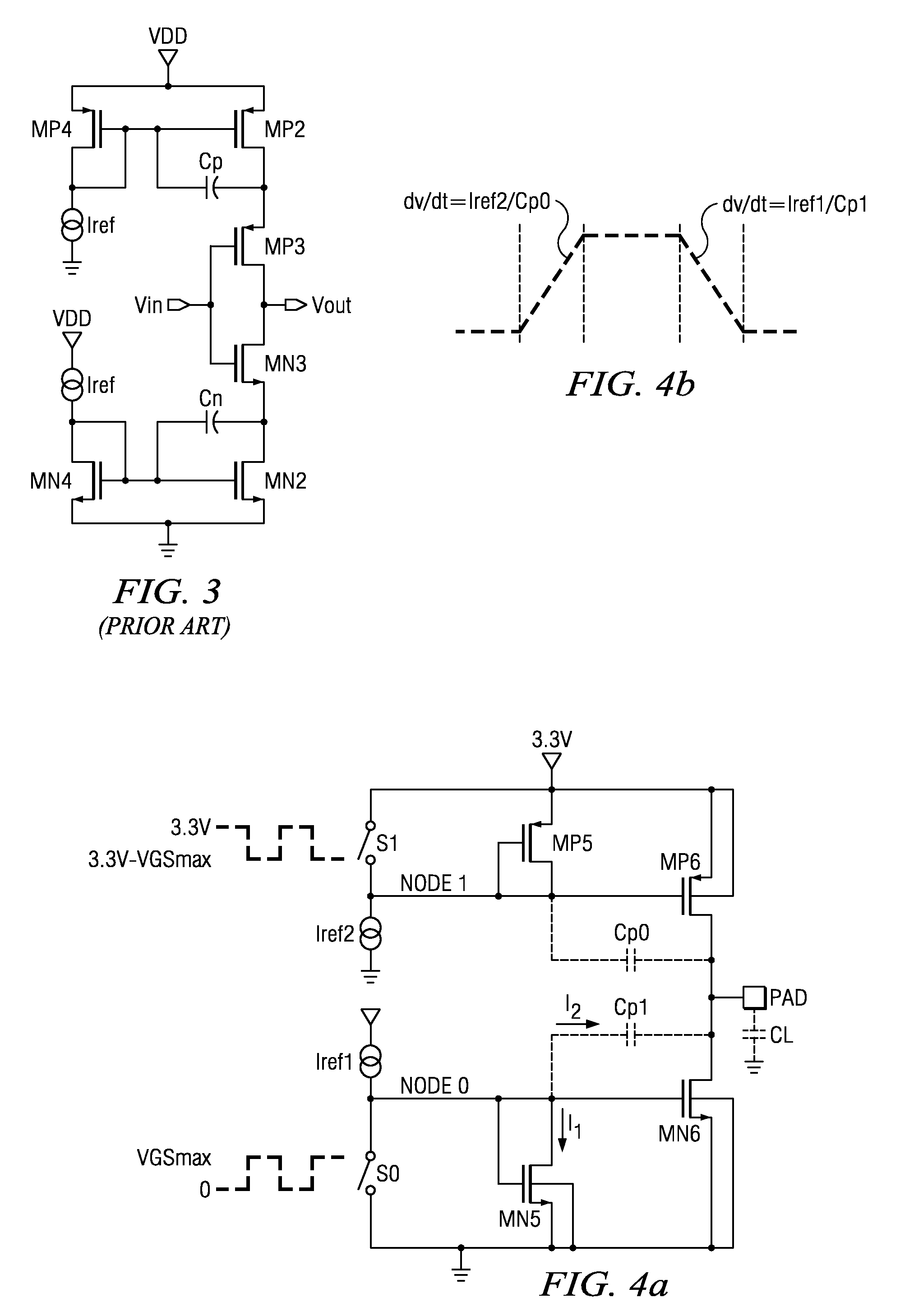
Low voltage CMOS circuit for on/off chip drive at high voltage
InactiveUS6031394AAvoid failureReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionCMOSCascode
A low voltage CMOS circuit and method provide output current ability meeting multimode requirements of high voltage off-chip drivers while protecting the CMOS devices from various breakdown mechanisms. The circuit and method utilize intermediate voltages between two power rails and voltage division techniques to limit the voltages to acceptable limits for drain-to-source, gate-to-drain, and gate-to-source of CMOS devices in any chosen technology. The circuit comprises first and second CMOS cascode chains connected between a high voltage power rail, e.g 5 volt and a reference potential power rail, e.g. ground. Each CMOS cascode chain comprises first and second p-type MOS devices in series with first and second n-type MOS devices. An input circuit is coupled to a node at the midpoint of the first CMOS cascode chain. A bias voltage, typically 3.3 volts is connected to the NMOS devices in the first and CMOS cascode chains. A second bias voltage is coupled to the PMOS devices in the first and second CMOS cascode chains. An output is provided from the second CMOS cascode chain to a third CMOS cascode chain for purposes of providing sufficient pullup capability to drive an output circuit comprising a fourth CMOS cascode chain between the high and reference potentials without exceeding the breakdown mechanisms for any MOS device in the CMOS cascode chains.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
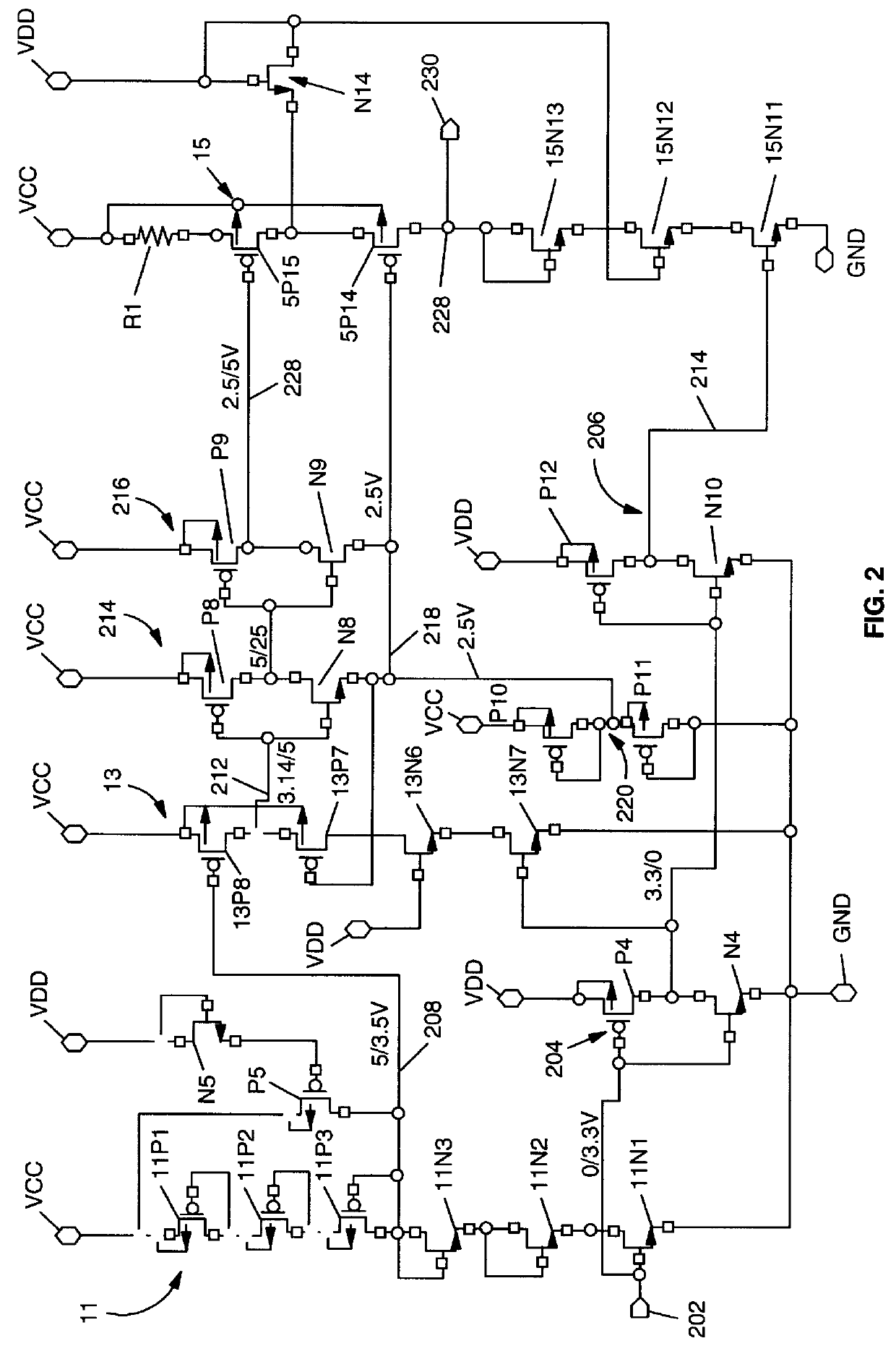
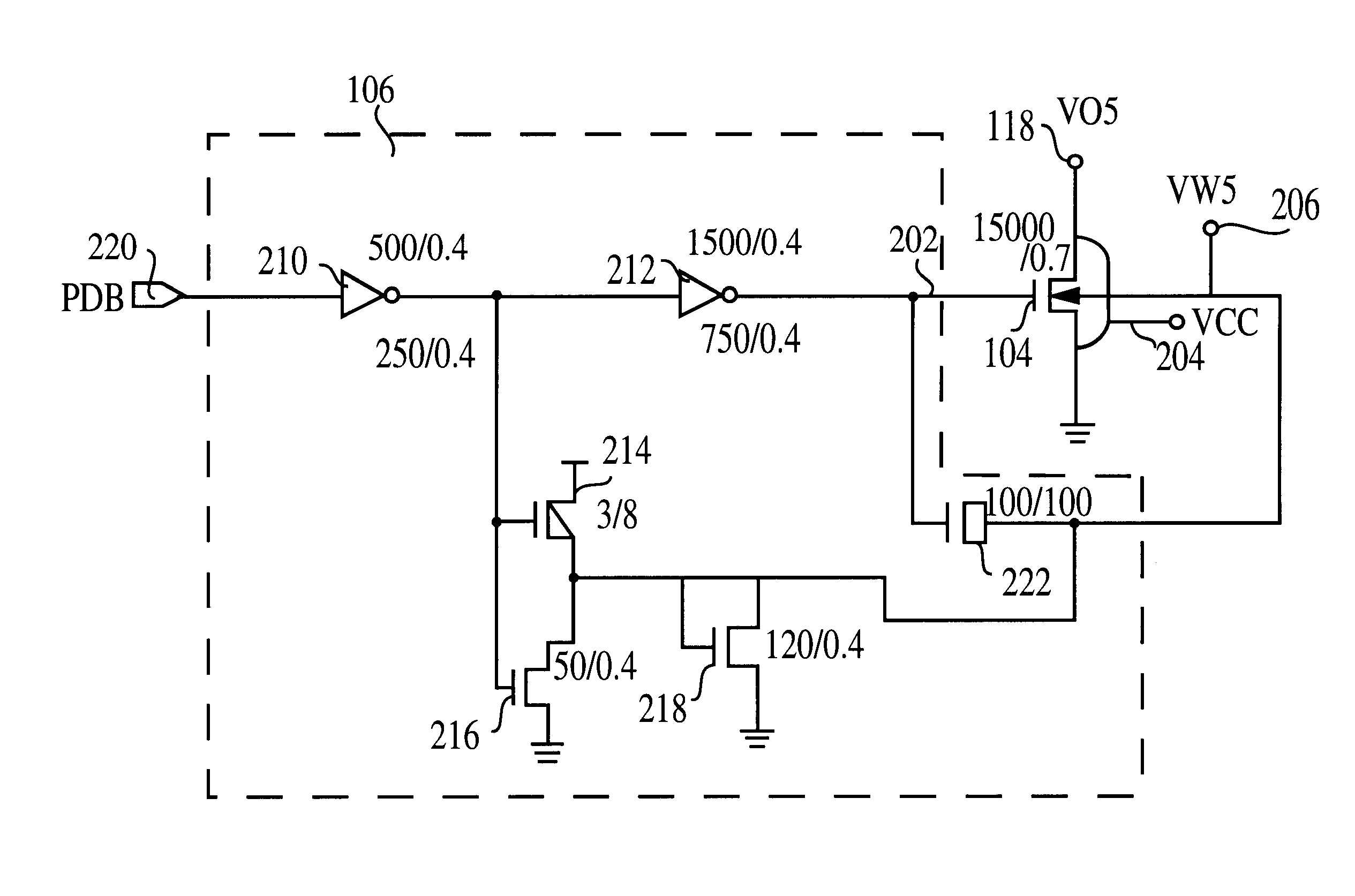
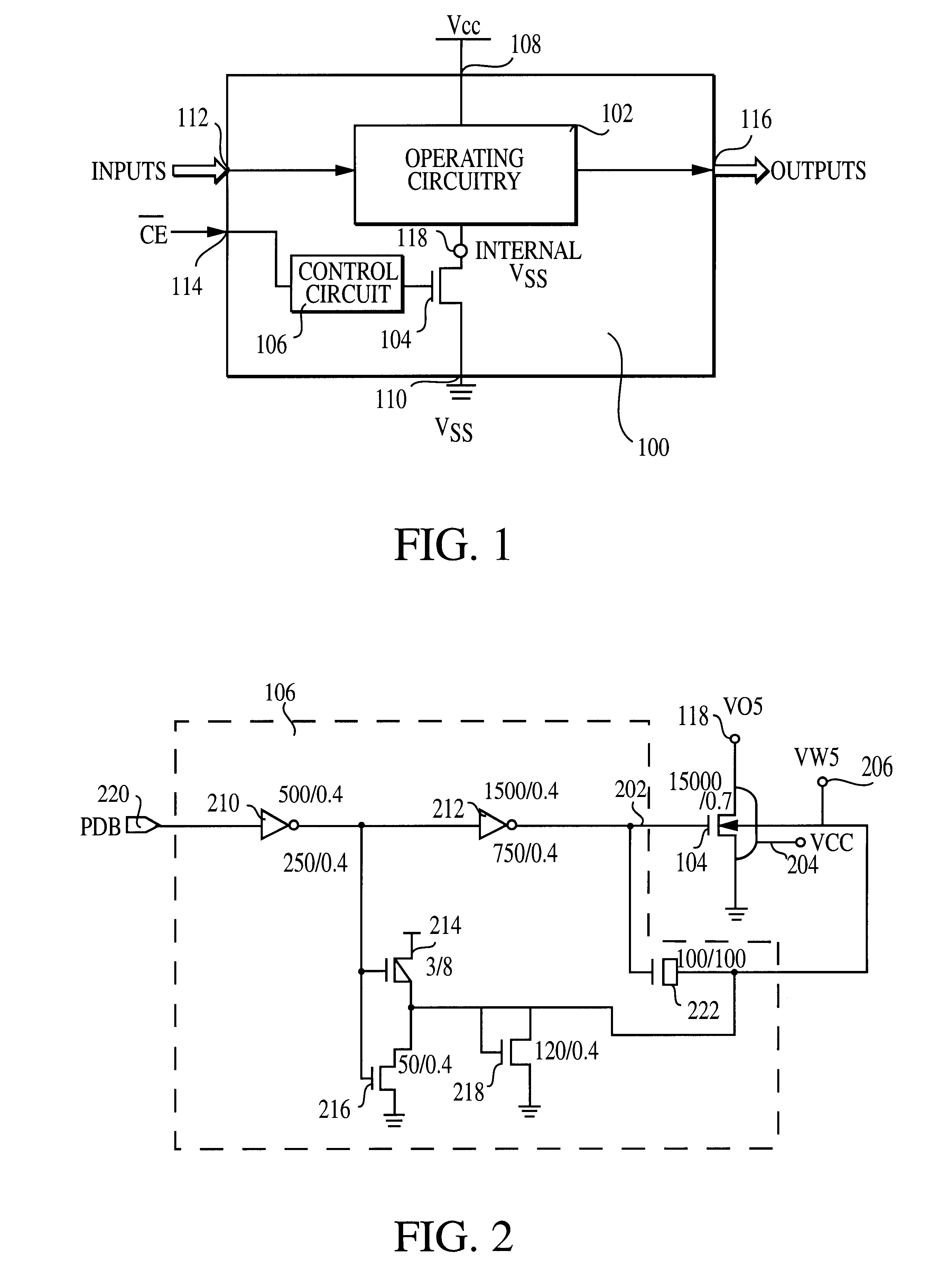
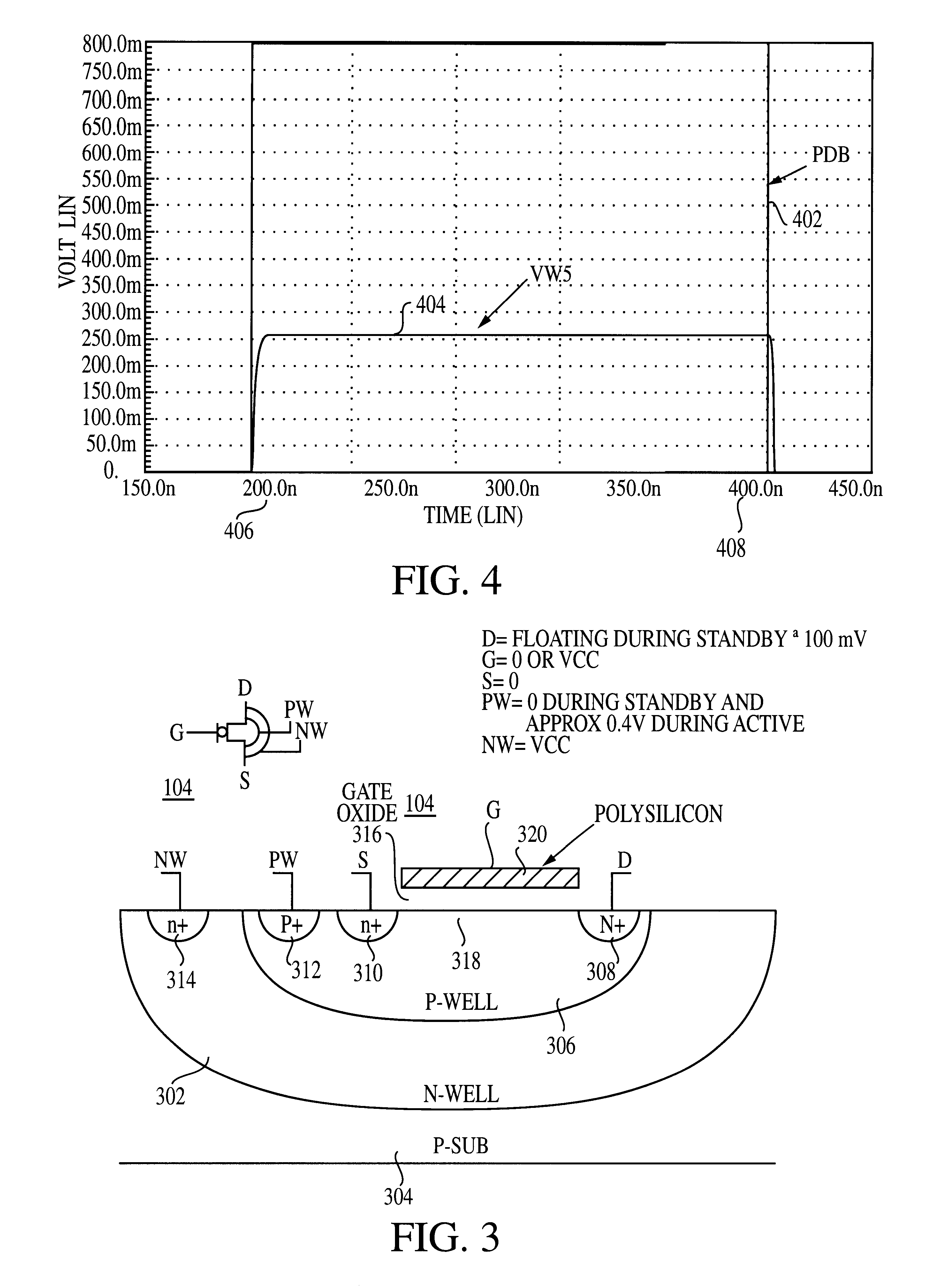
Use of biased high threshold voltage transistor to eliminate standby current in low voltage integrated circuits
InactiveUS6225852B1Turn fasterLower threshold voltagePower reduction by control/clock signalElectric pulse generator detailsStandby currentLow voltage cmos
An integrated circuit (100) includes a first input (108) to receive a first operating voltage Vcc and a second input (110) to receive a second operating voltage Vss. Operating circuitry (102) of the integrated circuit is coupled to the first input to power the operating circuitry. A transistor (104) is coupled between the second input and the operating circuitry to selectively provide the second operating voltage to the operating circuitry of the integrated circuit. The well containing the transistor is biased to provide a reverse body effect and reduce the threshold voltage of the transistor to allow operation at very low Vcc.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
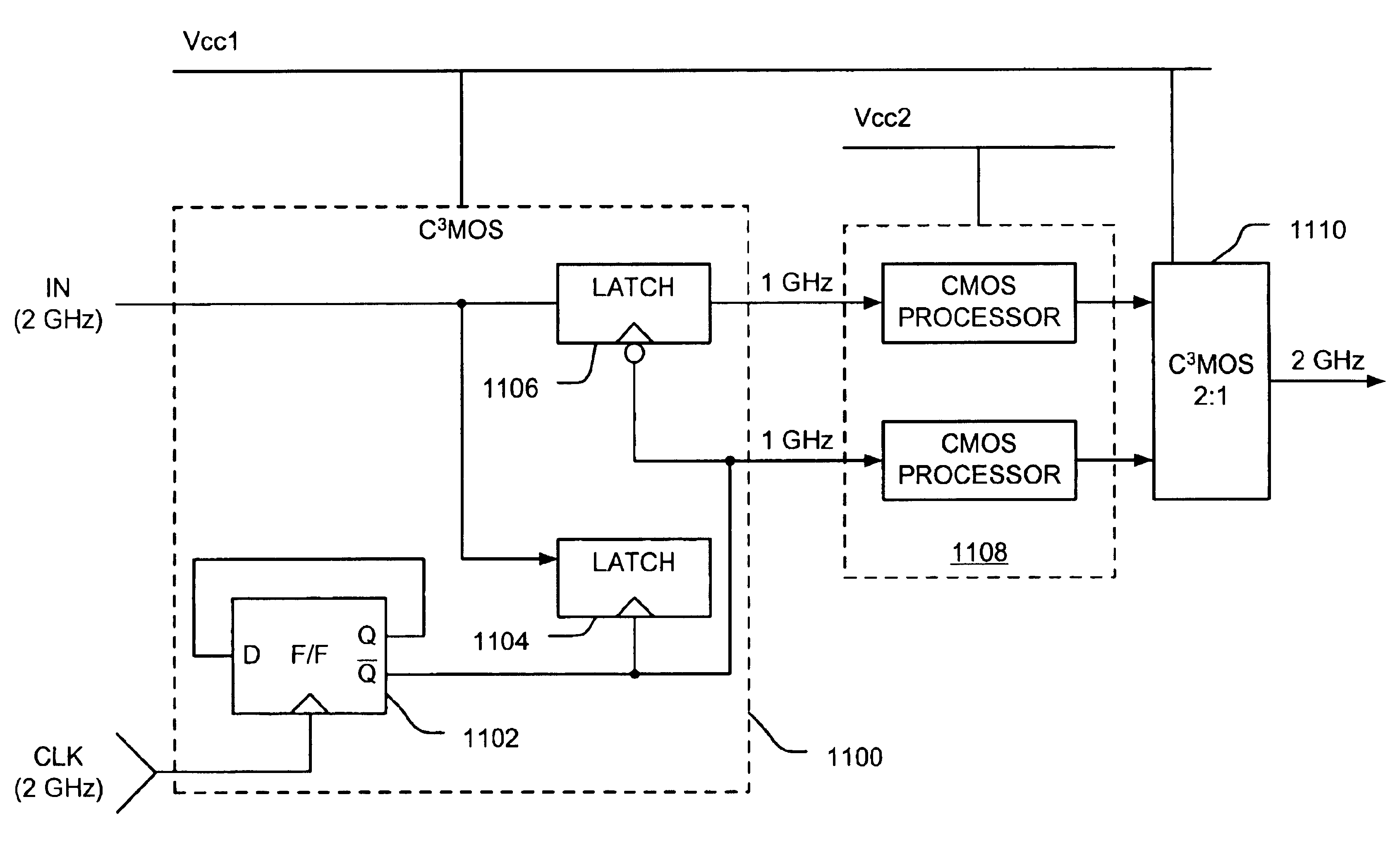
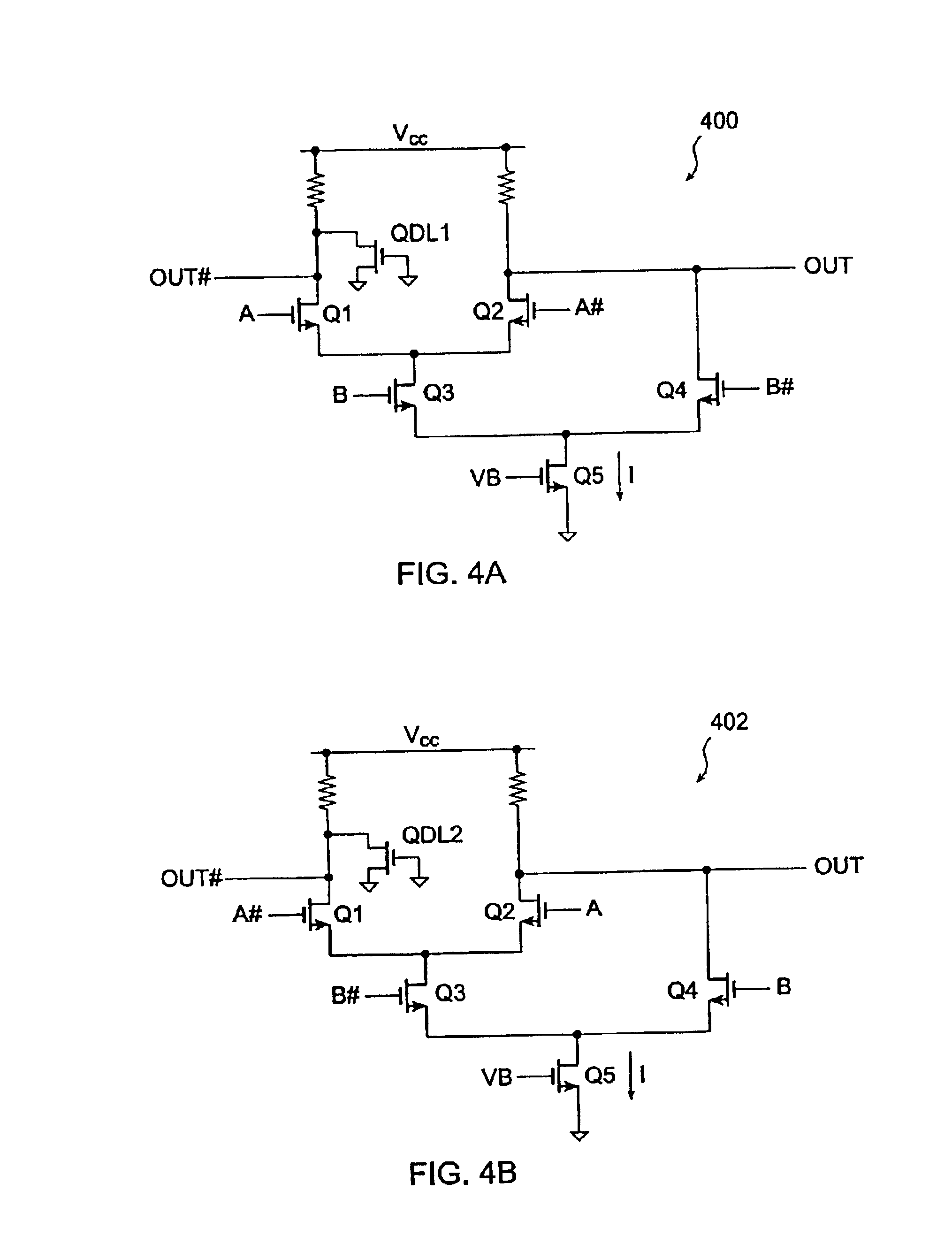
Current-controlled CMOS circuit using higher voltage supply in low voltage CMOS process
InactiveUS6911855B2Speed maximizationDissipates static currentElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorTransceiverEngineering
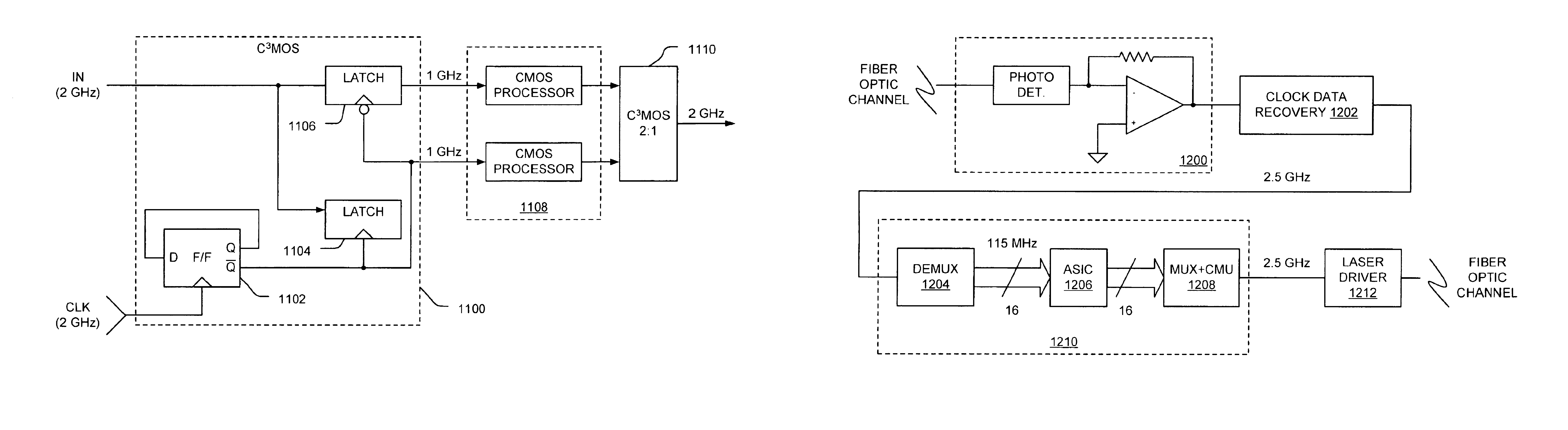
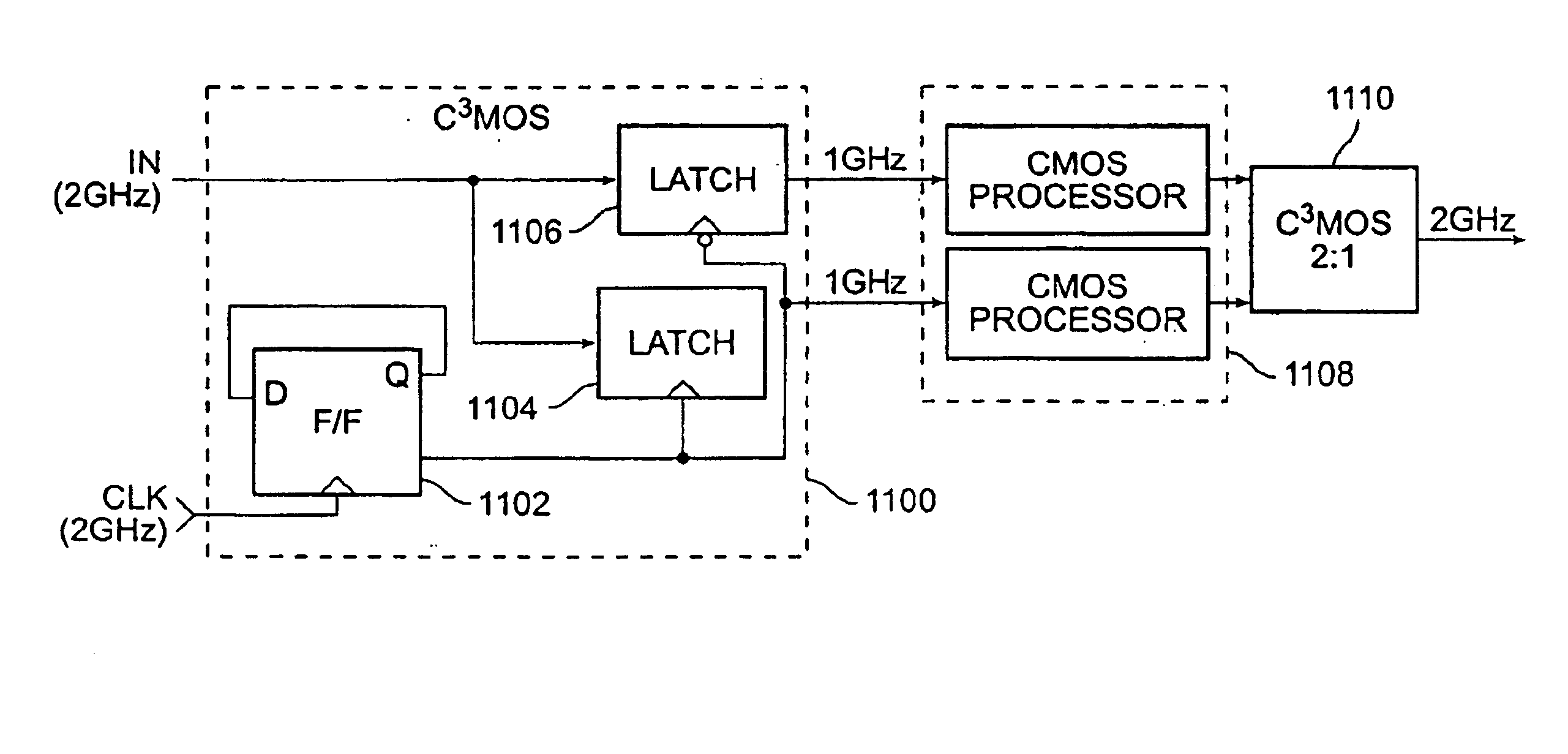
Various circuit techniques for implementing ultra high speed circuits use current-controlled CMOS (C3MOS) logic fabricated in conventional CMOS process technology. An entire family of logic elements including inverter / buffers, level shifters, NAND, NOR, XOR gates, latches, flip-flops and the like are implemented using C3MOS techniques. Optimum balance between power consumption and speed for each circuit application is achieve by combining high speed C3MOS logic with low power conventional CMOS logic. The combined C3MOS / CMOS logic allows greater integration of circuits such as high speed transceivers used in fiber optic communication systems. The C3MOS structure enables the use of a power supply voltage that may be larger than the voltage required by the CMOS fabrication process, further enhancing the performance of the circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
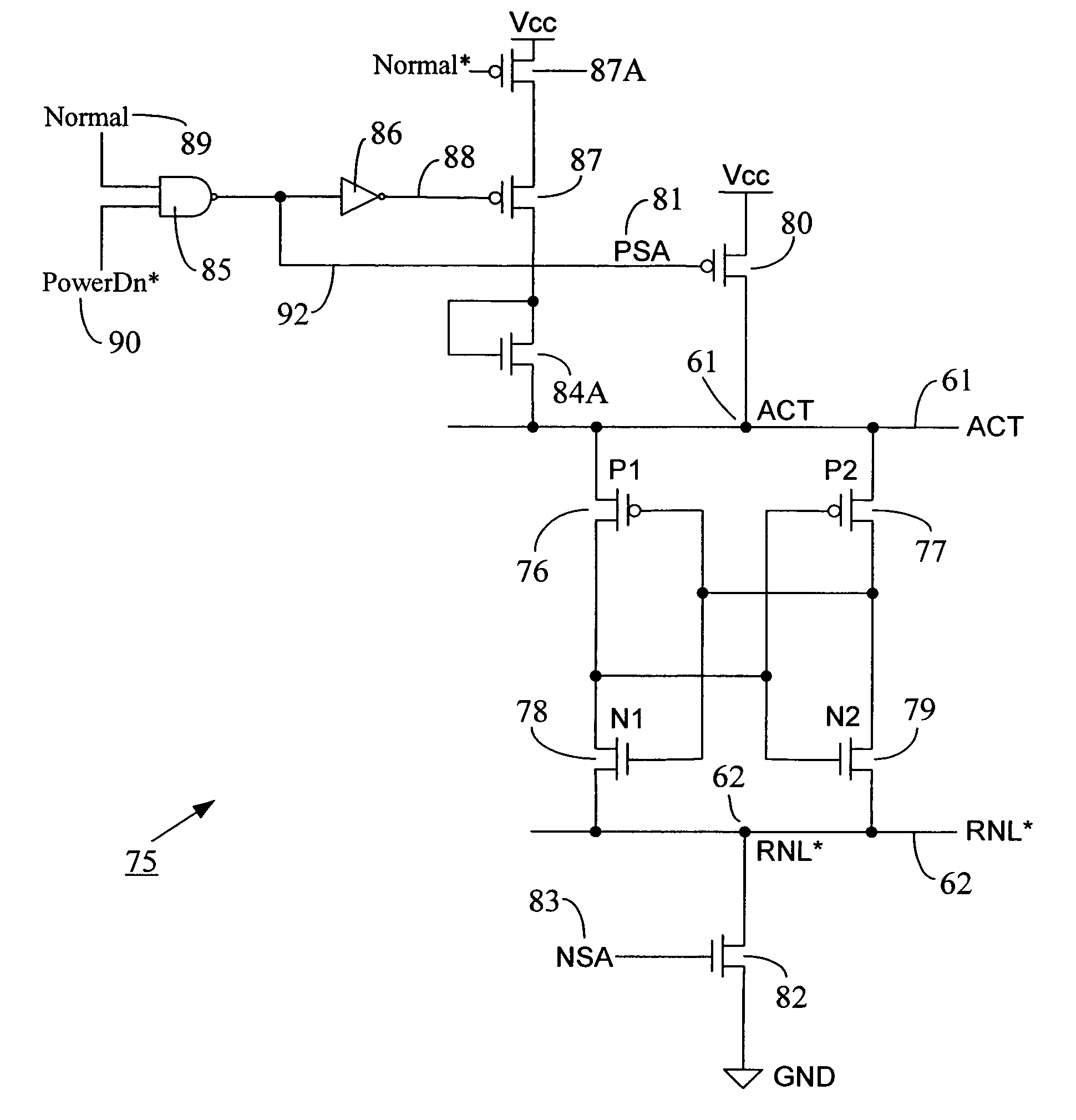
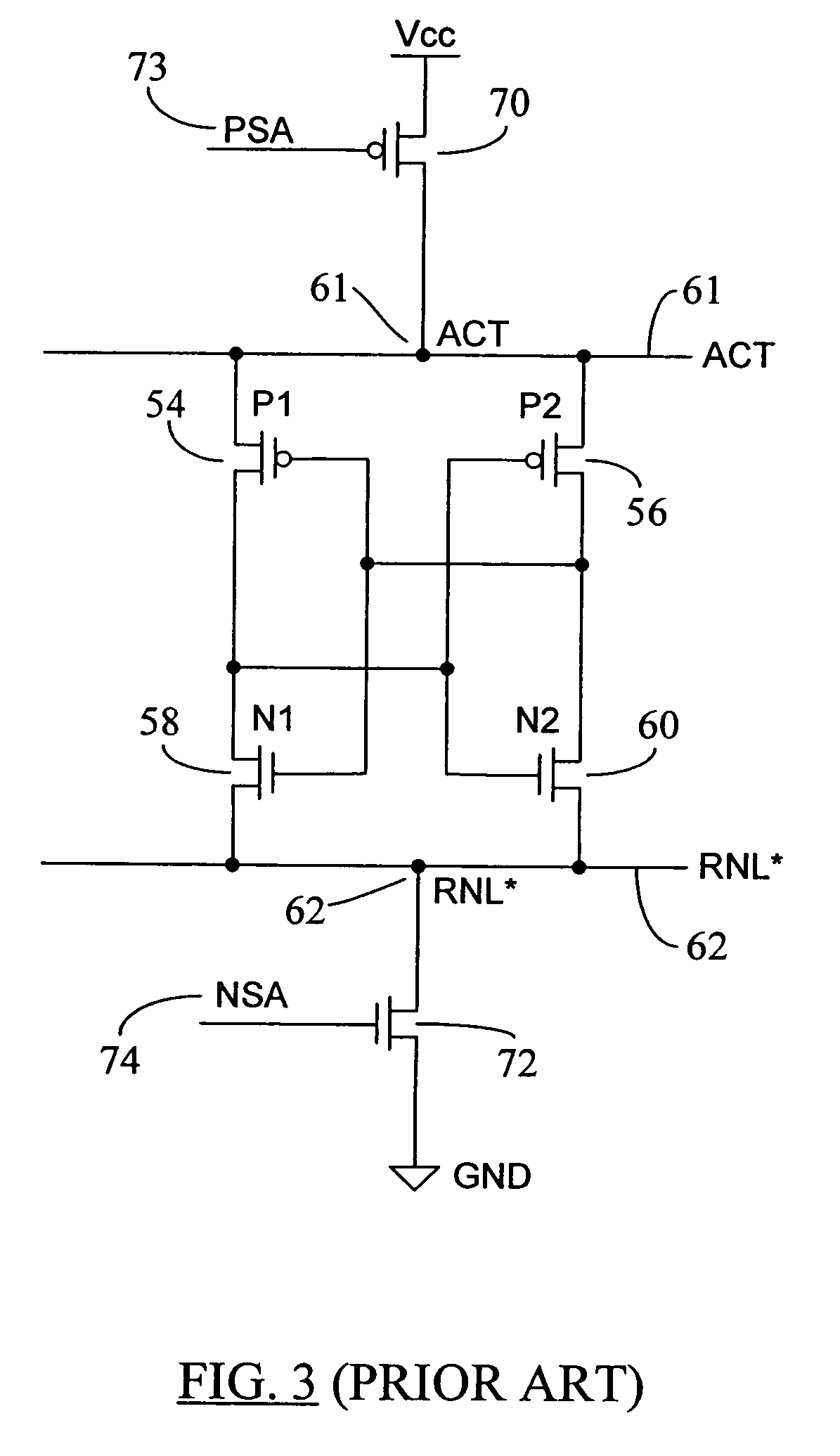
Low voltage sensing scheme having reduced active power down standby current
ActiveUS7372746B2Reduces active power down standby leakage currentReduce voltageDigital storageControl lineEngineering
A low voltage sensing scheme reduces active power down standby leakage current in a memory device. During memory's active power down state, the leak current may increase because of the use of P and Nsense amplifiers having low threshold voltages (Vth) for low Vcc sensing of data signals. A clamping device or diode is used between a Psense amplifier control line (e.g. ACT) and Vcc and / or between an Nsense amplifier control line (e.g. RNL*) and Vss (ground potential). The clamping diode is not enabled during normal memory operations, but is turned on during active power down mode to reduce leakage current through ACT and / or RNL* nodes. The clamping device connected to the ACT node may reduce the voltage on the ACT line during power down mode, whereas the clamping device connected to the RNL* node may increase the voltage on the RNL* line during power down mode to reduce sense amplifier leakage current through these nodes.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
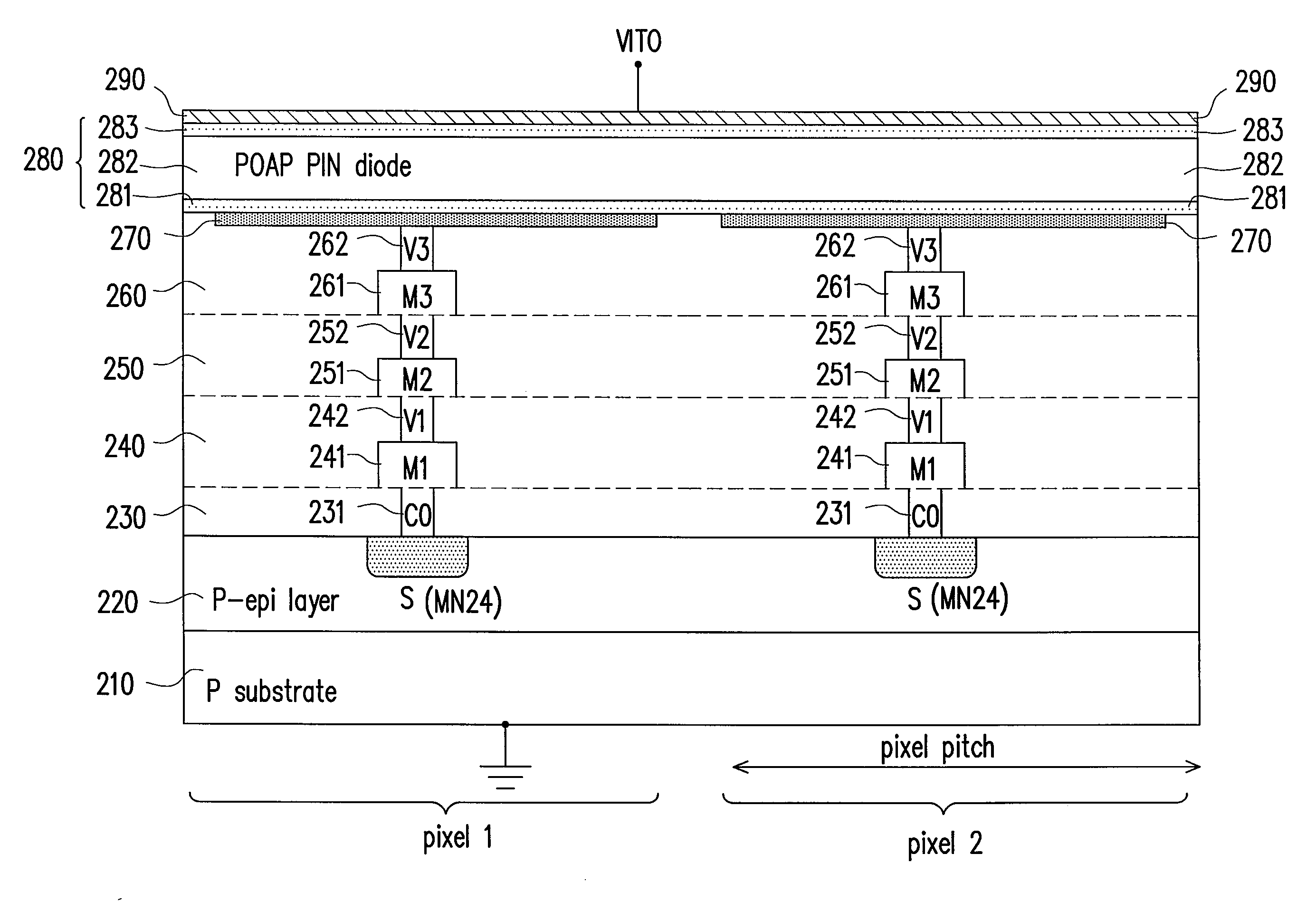
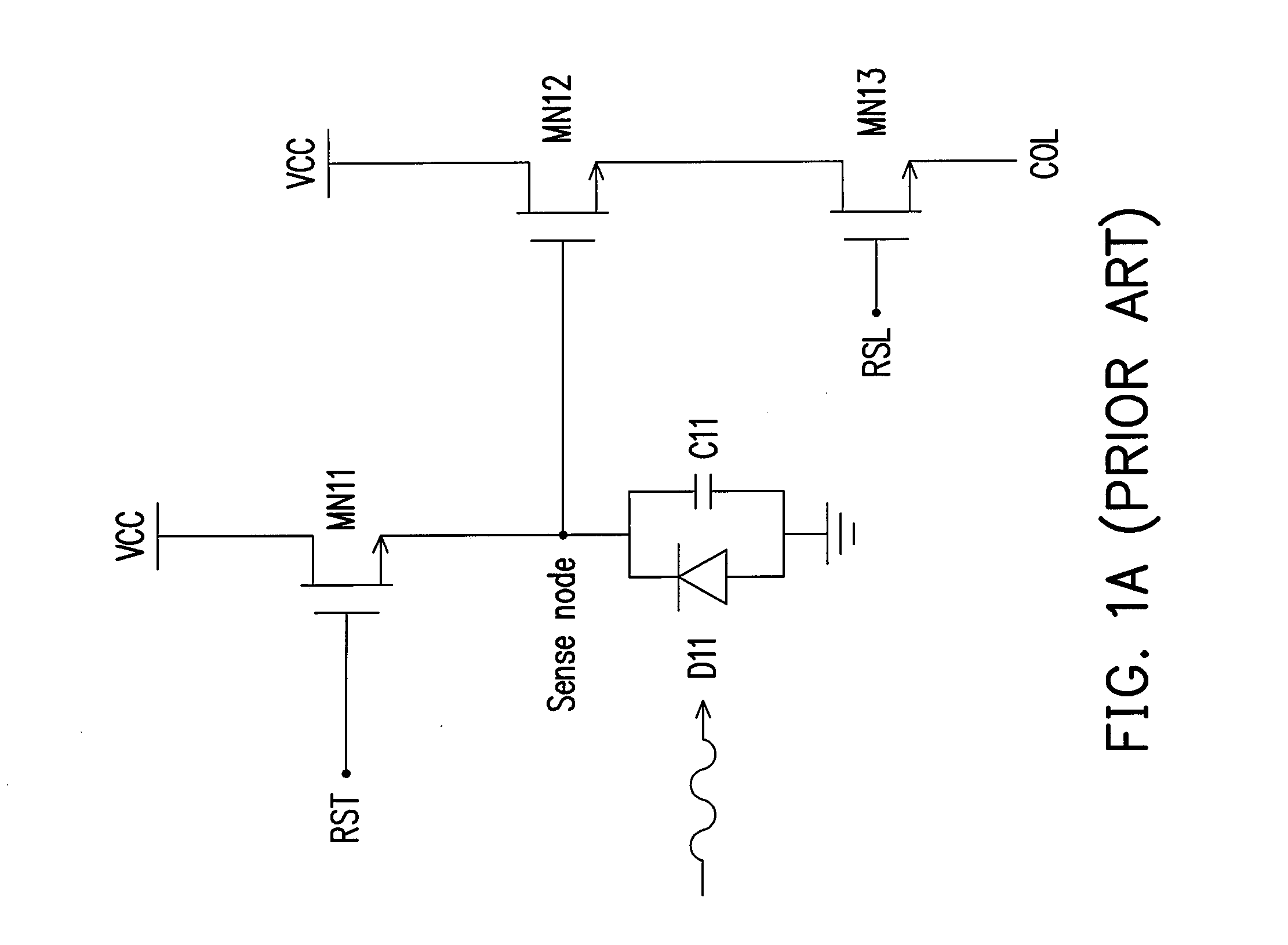
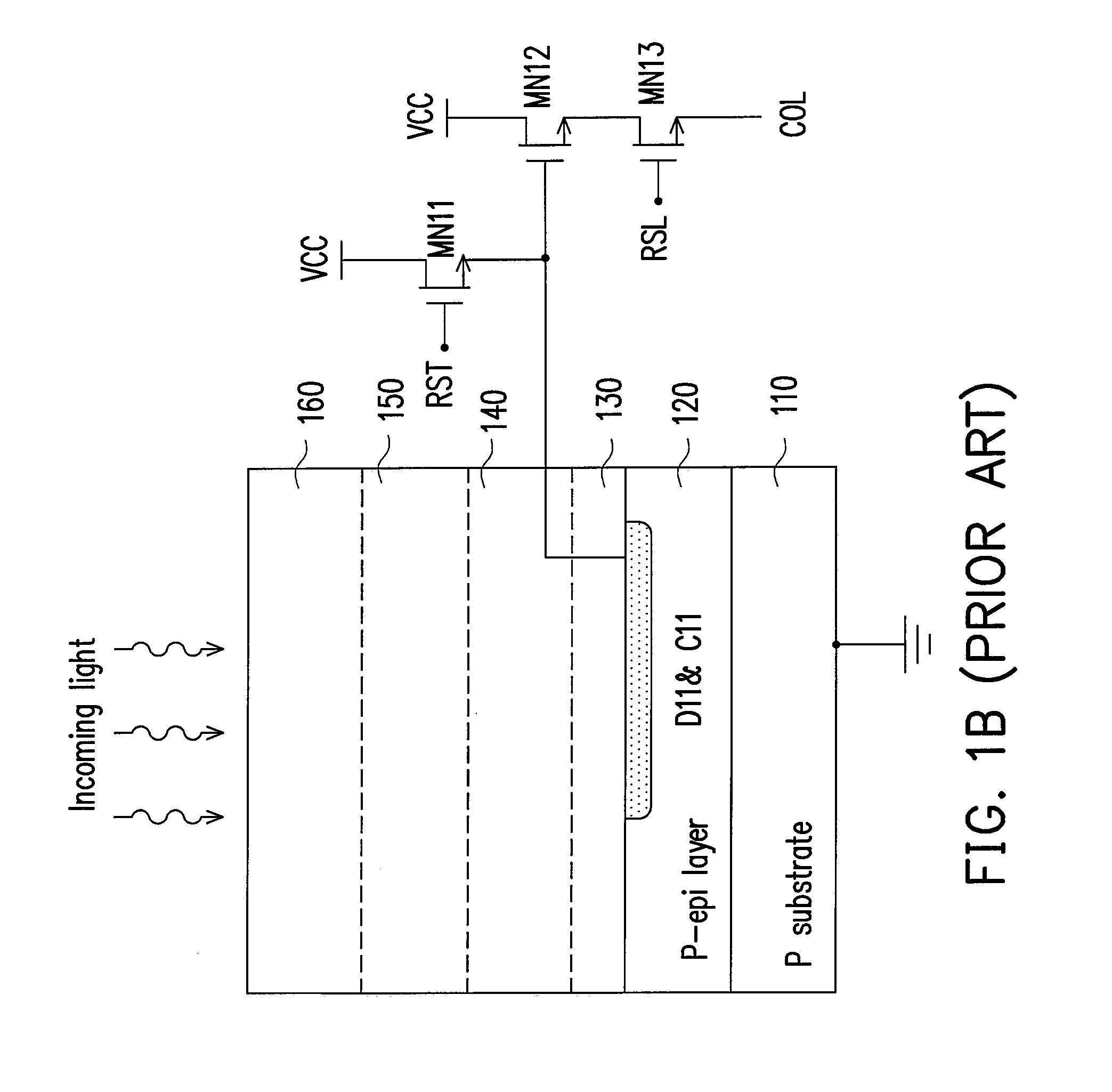
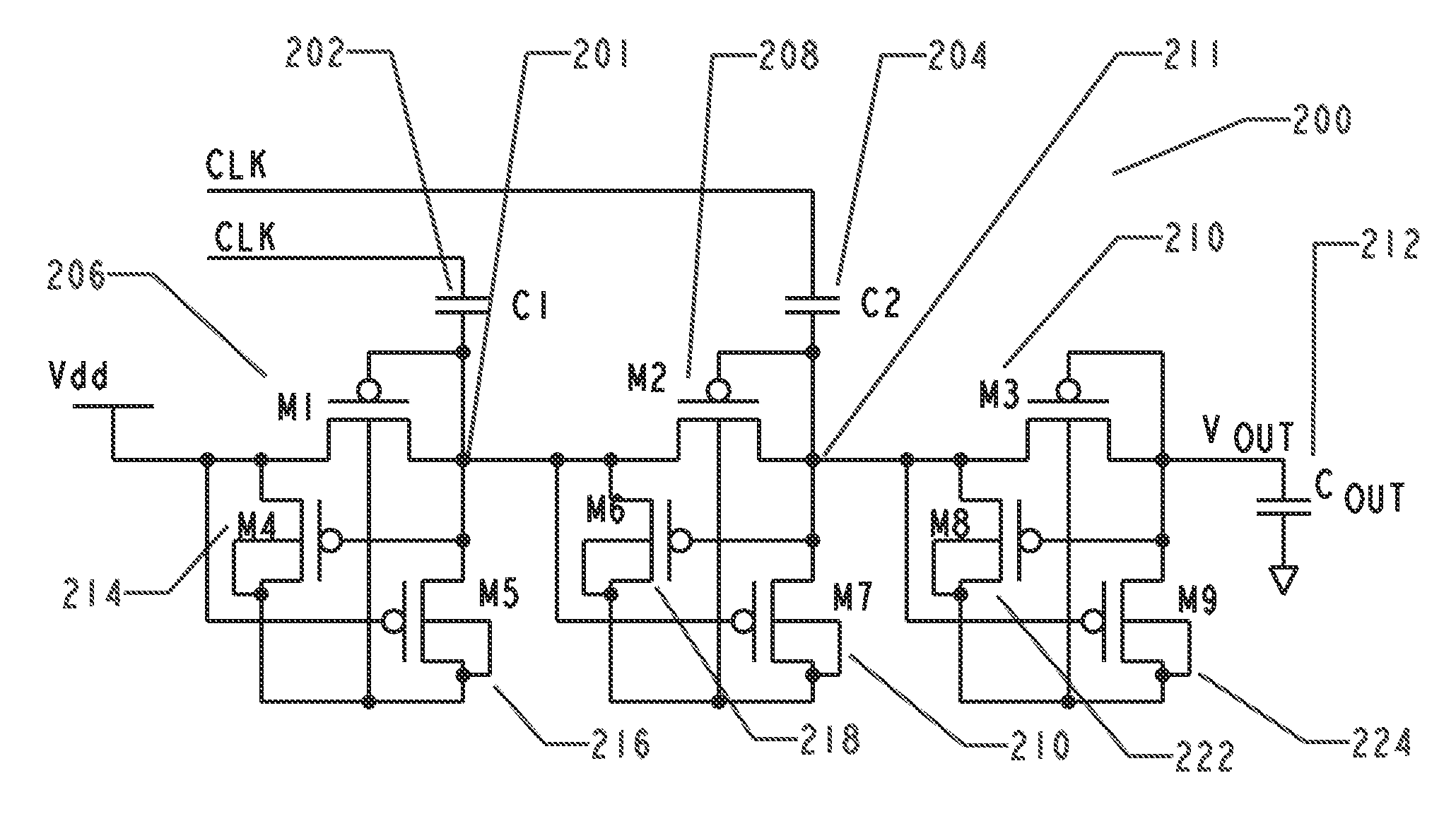
Image sensor structure
InactiveUS20090039397A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSLow voltage cmos
An avalanche photodiode is deposited and integrated directly on top of CMOS readout circuitry. The anode of the avalanche photodiode may be independently biased at high voltage so that the avalanche photodiode may be operated in an avalanche multiplication mode. The avalanche photodiode has a multi-layered structure which is not pixilated; and photo-carrier generation and carrier multiplication may take place in the same layer or in different layers. A constant-gate-bias transistor isolates the high-voltage avalanche photodiode from the low-voltage the CMOS readout circuitry.
Owner:MICROMEDIA TECH CORP
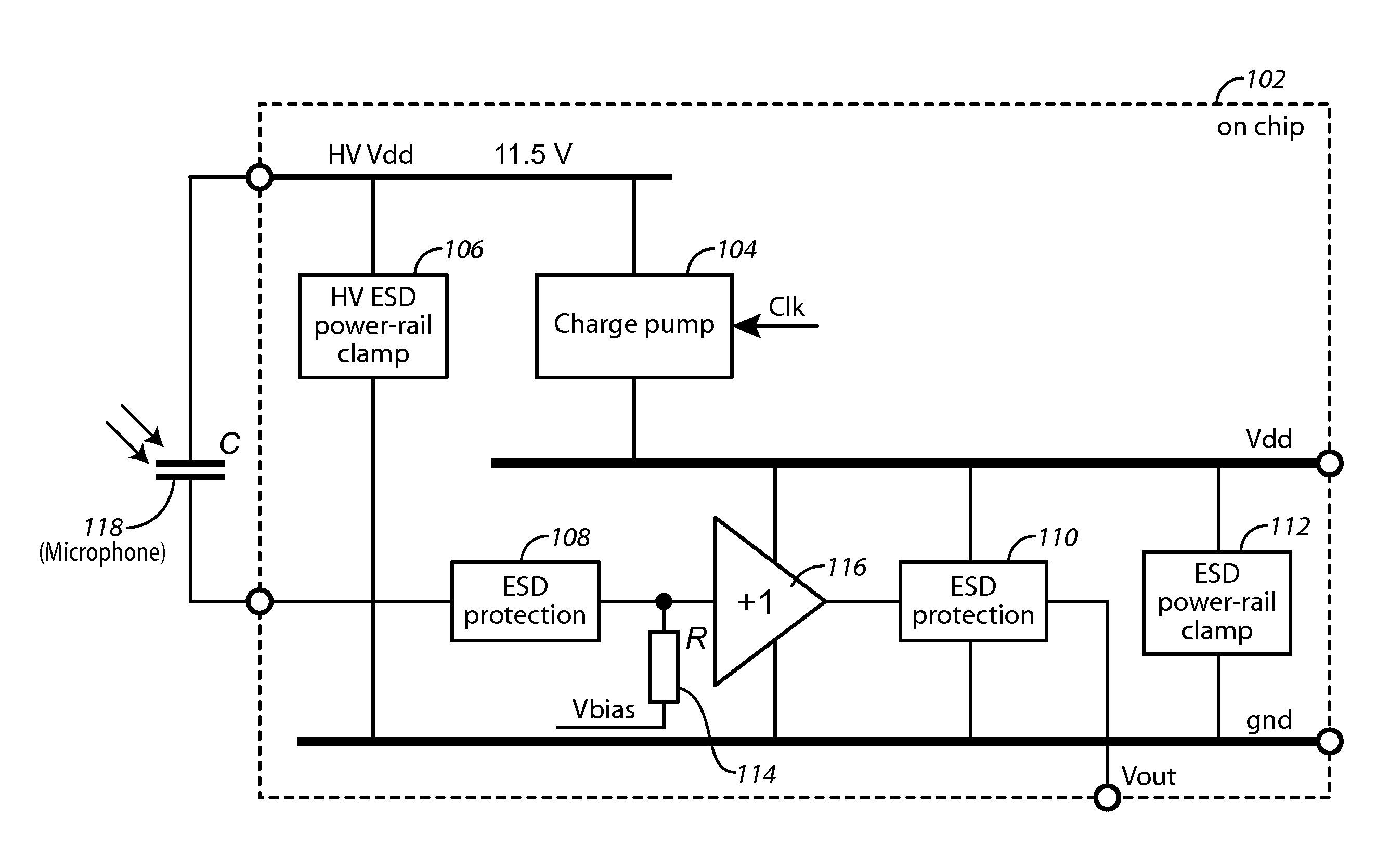
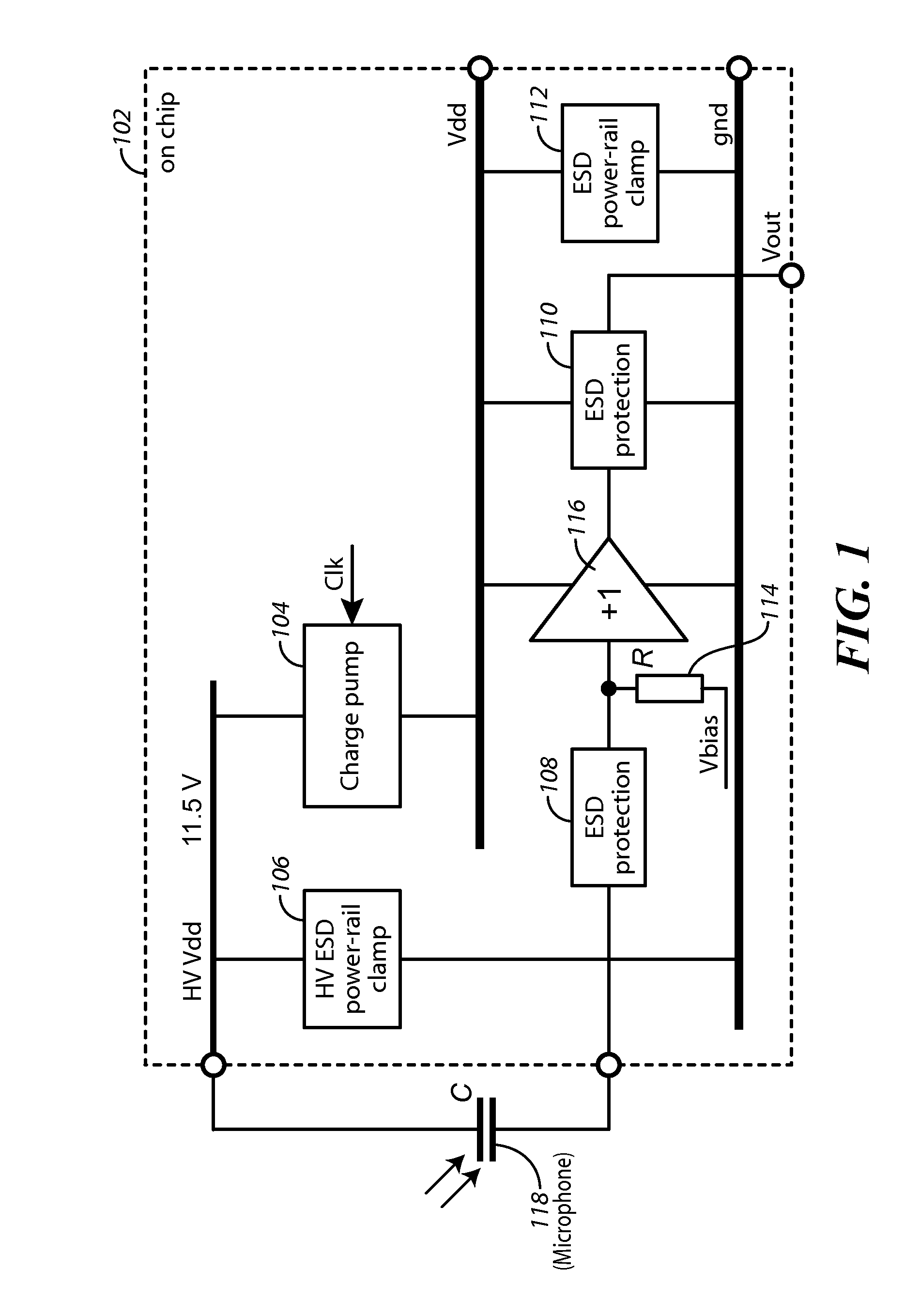
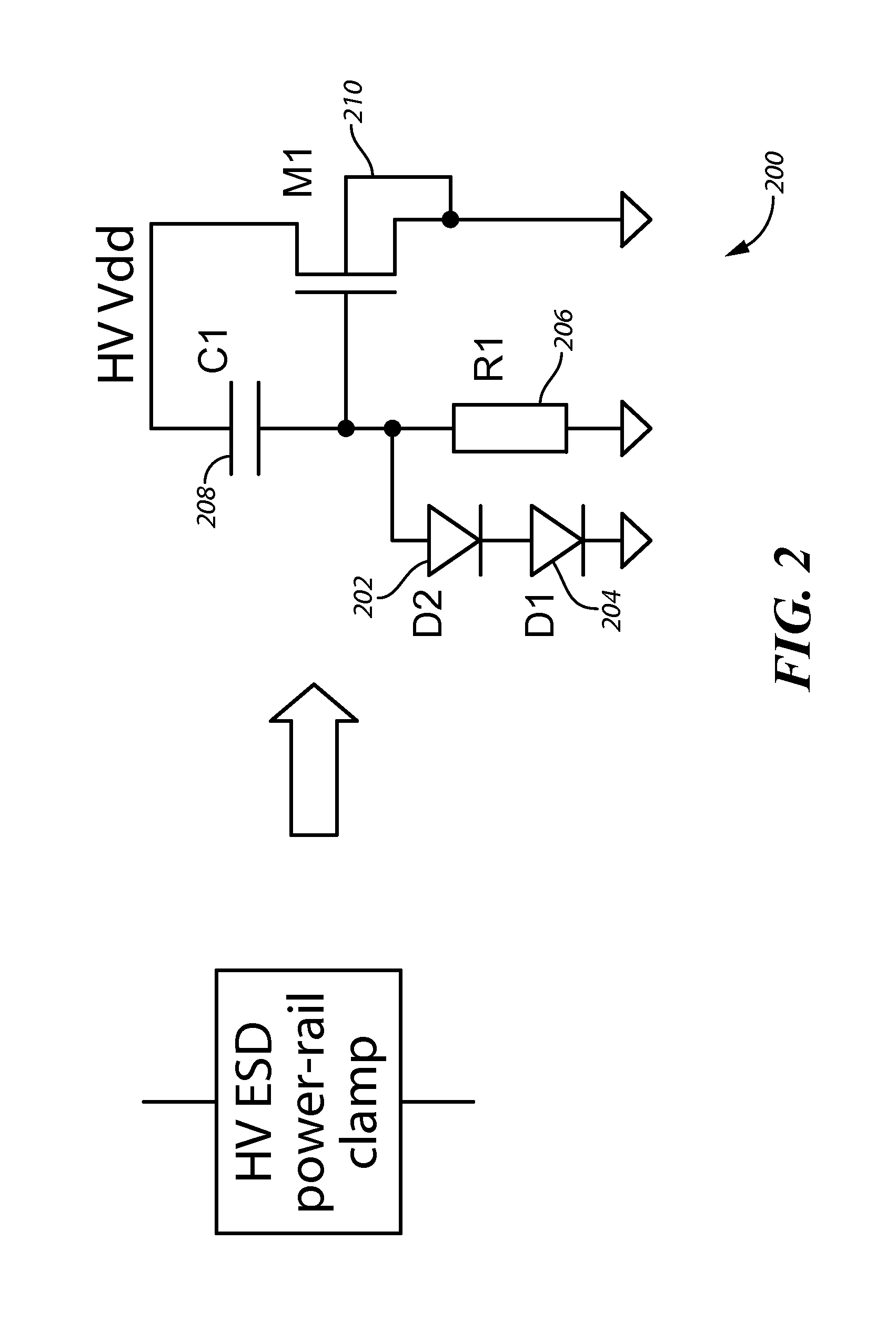
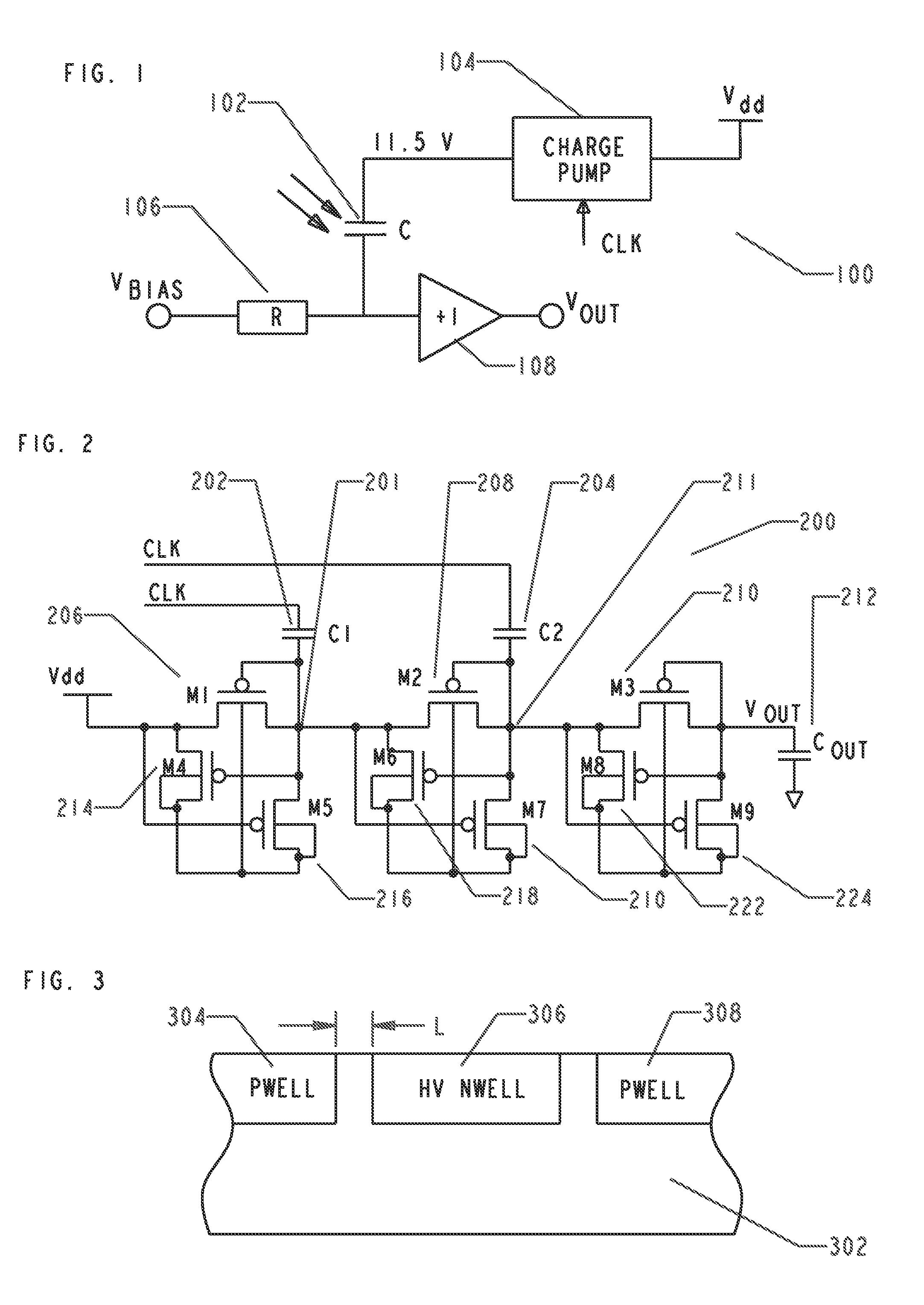
Apparatus and Method For High Voltage I/O Electro-Static Discharge Protection
An electronics chip includes a charge pump and at least one high voltage (HV) electro-static discharge (ESD) module. The charge pump is configured to provide a predetermined voltage across a microphone. The devices described herein are implemented in a standard low voltage CMOS process and has a circuit topology that provides an inherent ESD protection level (when it is powered down), which is higher than the operational (predetermined) DC level. At least one high voltage (HV) electro-static discharge (ESD) module is coupled to the output of the charge pump. The HV ESD module is configured to provide ESD protection for the charge pump and a microelectromechanical system (MEMS) microphone that is coupled to the chip. The at least one HV ESD module includes a plurality of PMOS or NMOS transistors having at least one high voltage NWELL / DNWELL region formed within selected ones of the PMOS or NMOS transistors. The at least one high voltage NWELL / DNWELL region has a breakdown voltage sufficient to allow a low voltage process to be used to construct the chip and still allow the HV ESD module to provide ESD protection for the chip.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
Current-controlled CMOS circuit using higher voltage supply in low voltage CMOS process
InactiveUS6982583B2Speed maximizationIncrease circuit speedExclusive-OR circuitsMultiple input and output pulse circuitsTransceiverHigh voltage
Various circuit techniques for implementing ultra high speed circuits use current-controlled CMOS (C3MOS) logic fabricated in conventional CMOS process technology. An entire family of logic elements including inverter / buffers, level shifters, NAND, NOR, XOR gates, latches, flip-flops and the like are implemented using C3MOS techniques. Optimum balance between power consumption and speed for each circuit application is achieve by combining high speed C3MOS logic with low power conventional CMOS logic. The combined C3MOS / CMOS logic allows greater integration of circuits such as high speed transceivers used in fiber optic communication systems. The C3MOS structure enables the use of a power supply voltage that may be larger than the voltage required by the CMOS fabrication process, further enhancing the performance of the circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Current-controlled CMOS circuit using higher voltage supply in low voltage CMOS process
InactiveUS6897697B2Speed maximizationDissipates static currentExclusive-OR circuitsElectronic switchingTransceiverEngineering
Various circuit techniques for implementing ultra high speed circuits use current-controlled CMOS (C3MOS) logic fabricated in conventional CMOS process technology. An entire family of logic elements including inverter / buffers, level shifters, NAND, NOR, XOR gates, latches, flip-flops and the like are implemented using C3MOS techniques. Optimum balance between power consumption and speed for each circuit application is achieve by combining high speed C3MOS logic with low power conventional CMOS logic. The combined C3MOS / CMOS logic allows greater integration of circuits such as high speed transceivers used in fiber optic communication systems. The C3MOS structure enables the use of a power supply voltage that may be larger than the voltage required by the CMOS fabrication process, further enhancing the performance of the circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
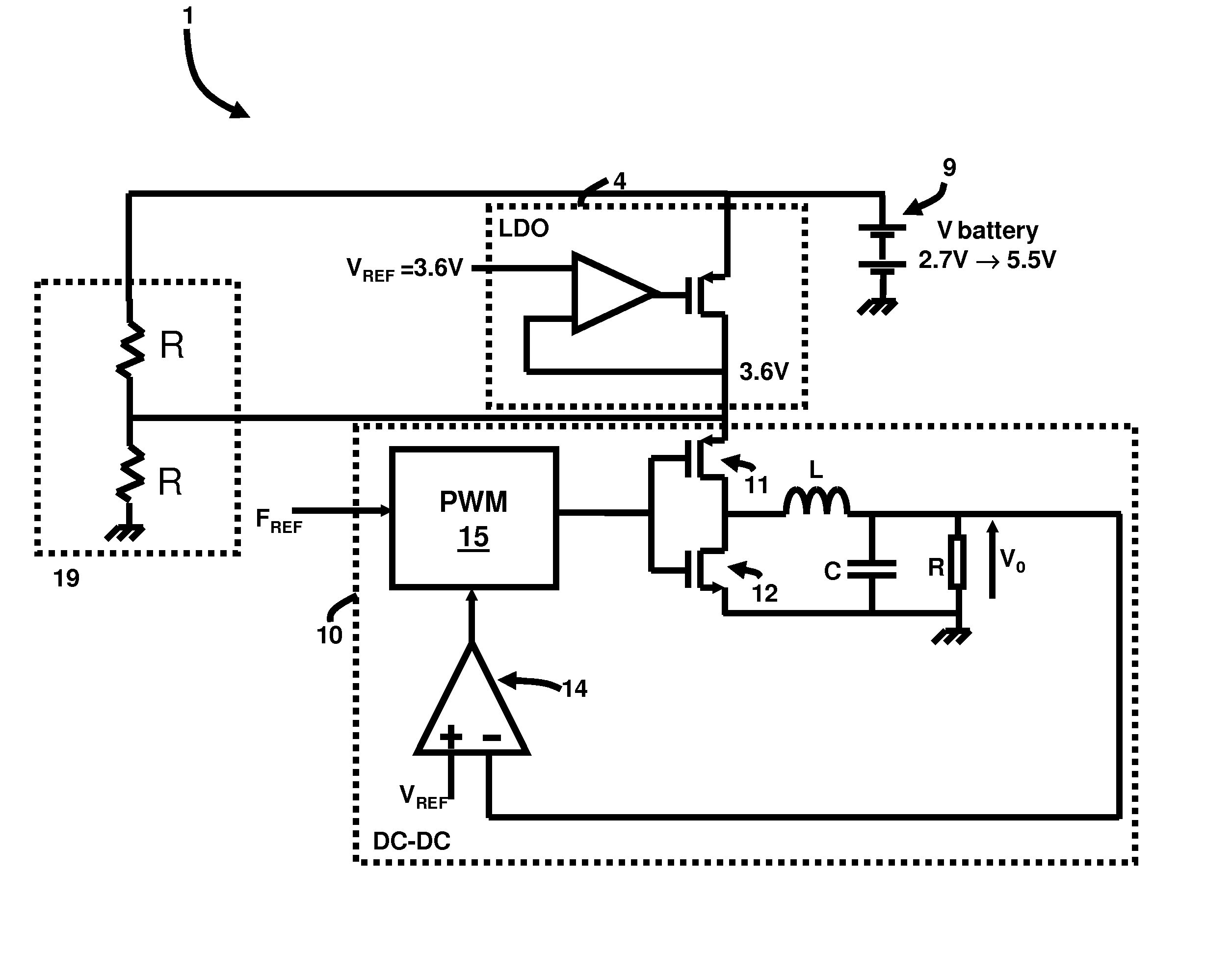
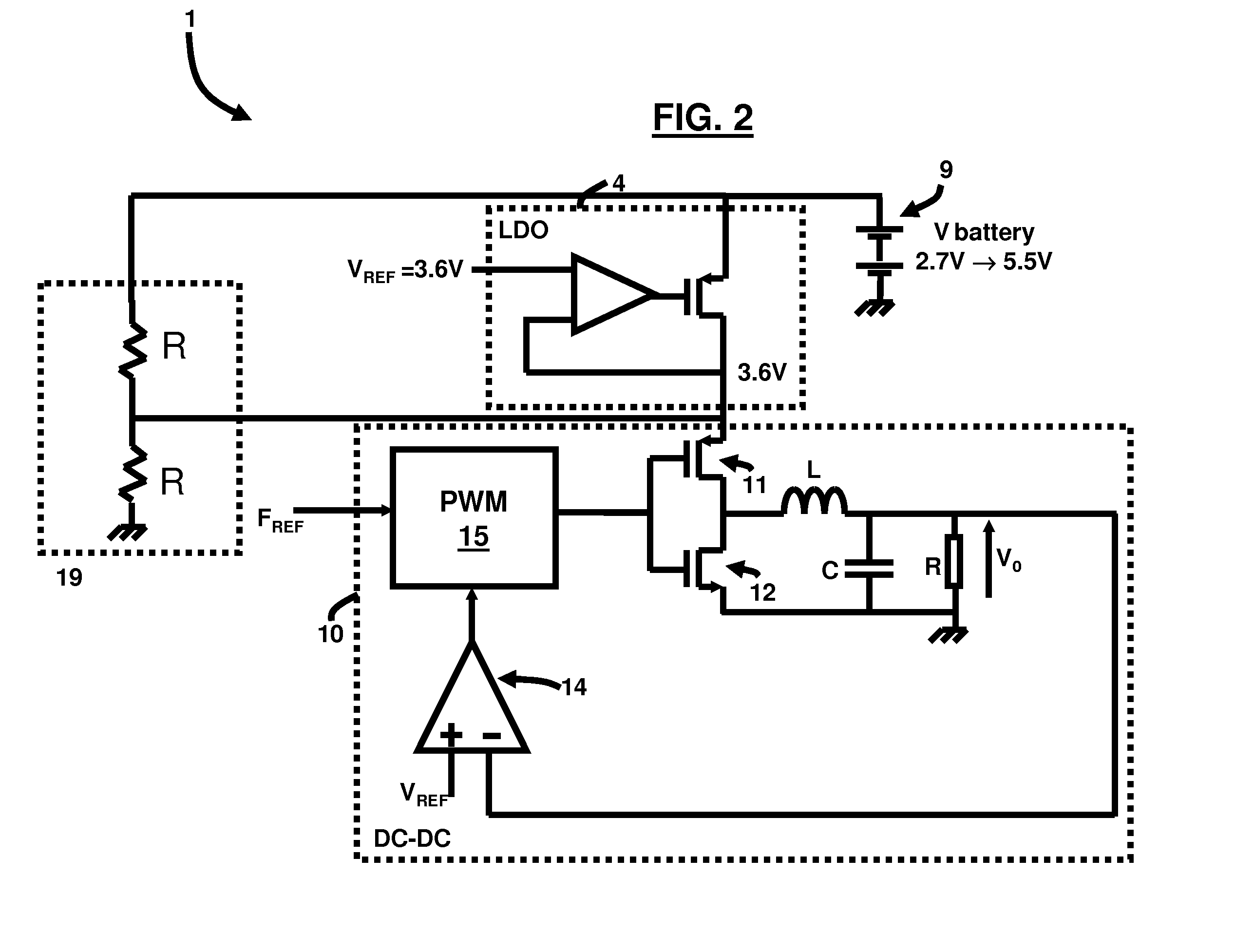
Integrated CMOS dc-dc converter implementation in low-voltage CMOS technology using ldo regulator
InactiveUS20090021228A1Improve efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionCMOSLow voltage cmos
An electrical circuit and method of power management of a cellular telephone includes a battery adapted to produce a battery voltage; a LDO regulator operatively connected to the battery and adapted to provide a constant supply voltage from the battery voltage; and a DC-DC converter operatively connected to the LDO regulator, wherein the DC-DC converter is adapted to step down the constant supply voltage to a lower voltage level, wherein the LDO regulator and the DC-DC converter are embedded on a single integrated circuit chip. The constant supply voltage equals 3.6V at an output of the LDO, and the constant supply voltage is applied to an input of the DC-DC converter. Moreover, the battery voltage equals at most 5.5V.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
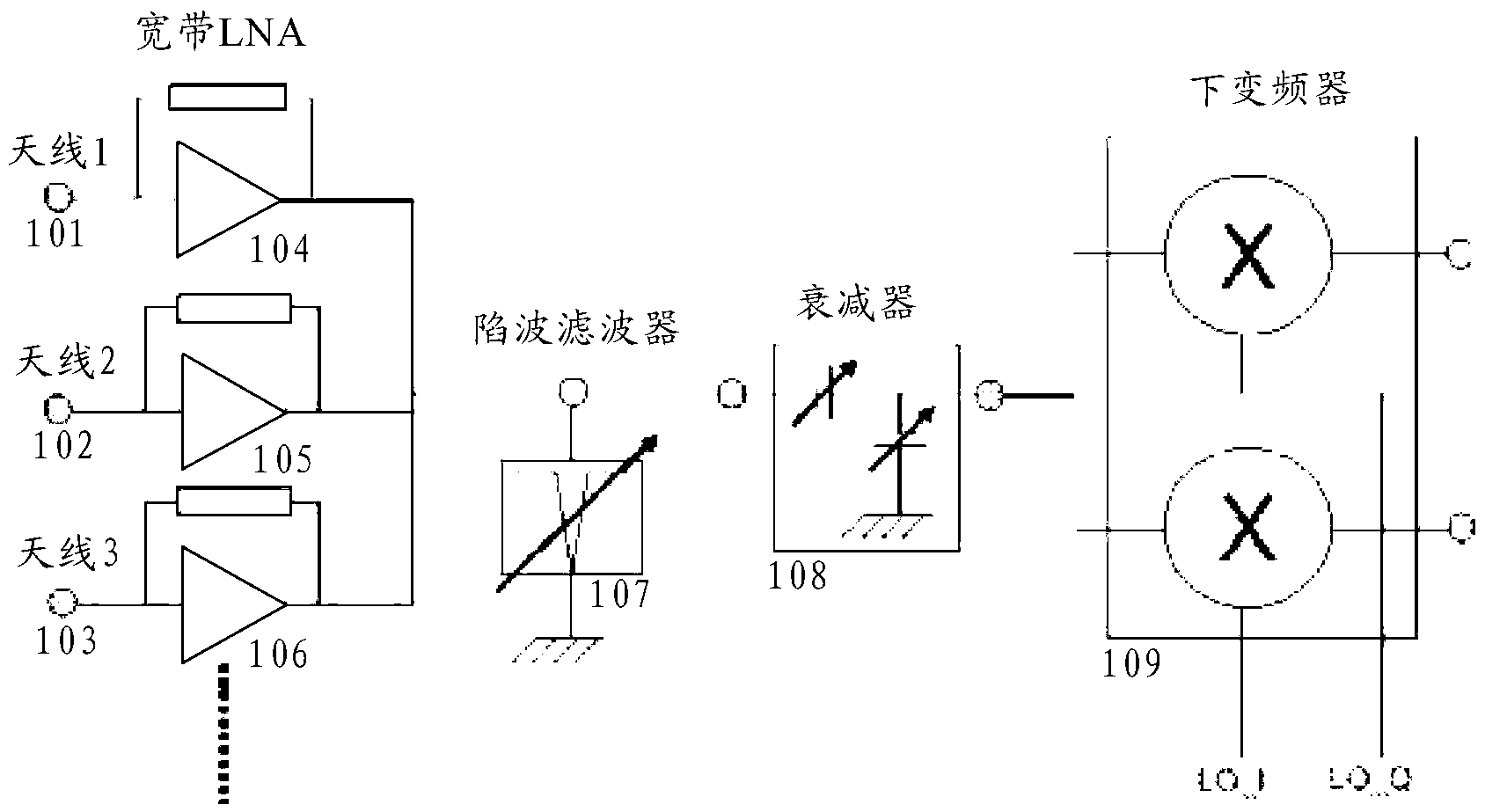
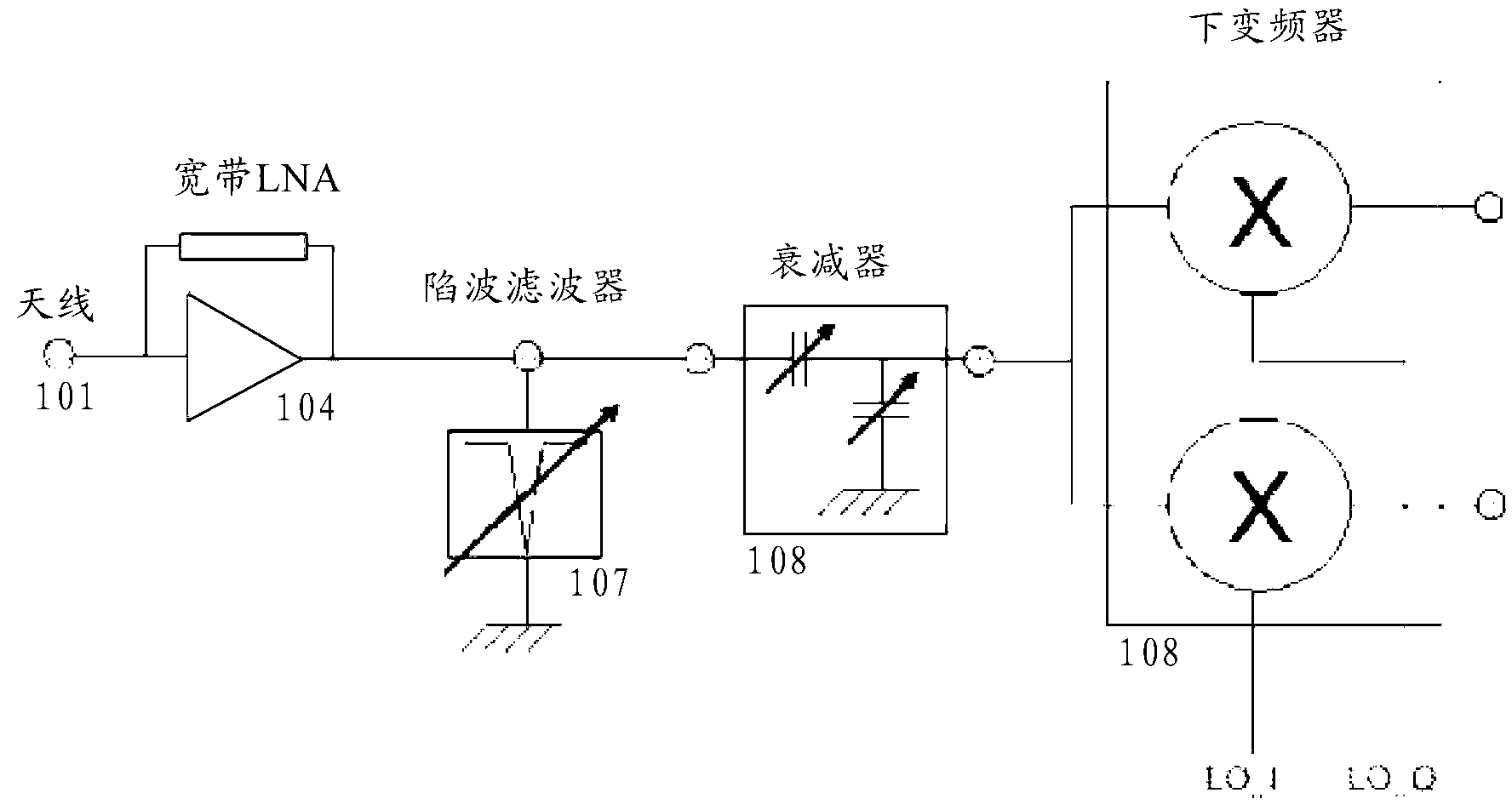
Rejection of RF interferers and noise in a wireless communications transceiver
An adaptable, reconfigurable, multi-band SAW-less radio receiver and / or transmitter is described that can operate within the limitations of 40nm and similar low voltage CMOS technology nodes, comprising: 1) A current output node from a single LNA or a number of LNAs. In the latter case, the current output node sums all of the separate LNA outputs. 2) A shunt style of steerable frequency notch filter for attenuating interferers added to the LNA current output node. 3) An adaptable negative conductance circuit that allows the amount of interference rejection provided by the notch filter to be varied with the bias current setting and RF device size setting. 4) An adaptable negative conductance circuit that allows parasitic resistance such as that encountered in a 40nm or similar low voltage CMOS technology node to be compensated for. The level of compensation can be a function of the setting of bias current and RF device width. 5) An overdrive monitor circuit that provides a signal which indicates the distribution of the available supply voltage between devices in the negative conductance circuit. This signal in turn can be applied to a local analog loop which adjusts the bias current and RF device width within the negative conductance circuit to maximize the linearity of the notch filter for a specific level of notch filter rejection. Alternatively, this control loop can be closed through the digital baseband. 6) A shunt style of steerable frequency notch filter placed prior to the PPA (pre-power amplifier) or PPAs in a cellular transmitter for rejecting transmitter noise occurring in the corresponding receiver band and / or spurious frequency components. 7) A steerable frequency notch filter placed prior to the LO (local oscillator) input to a frequency upconverter (transmitter application) or frequency downconverter (receiver application) to attenuate out of band noise and / or spurious frequency components.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
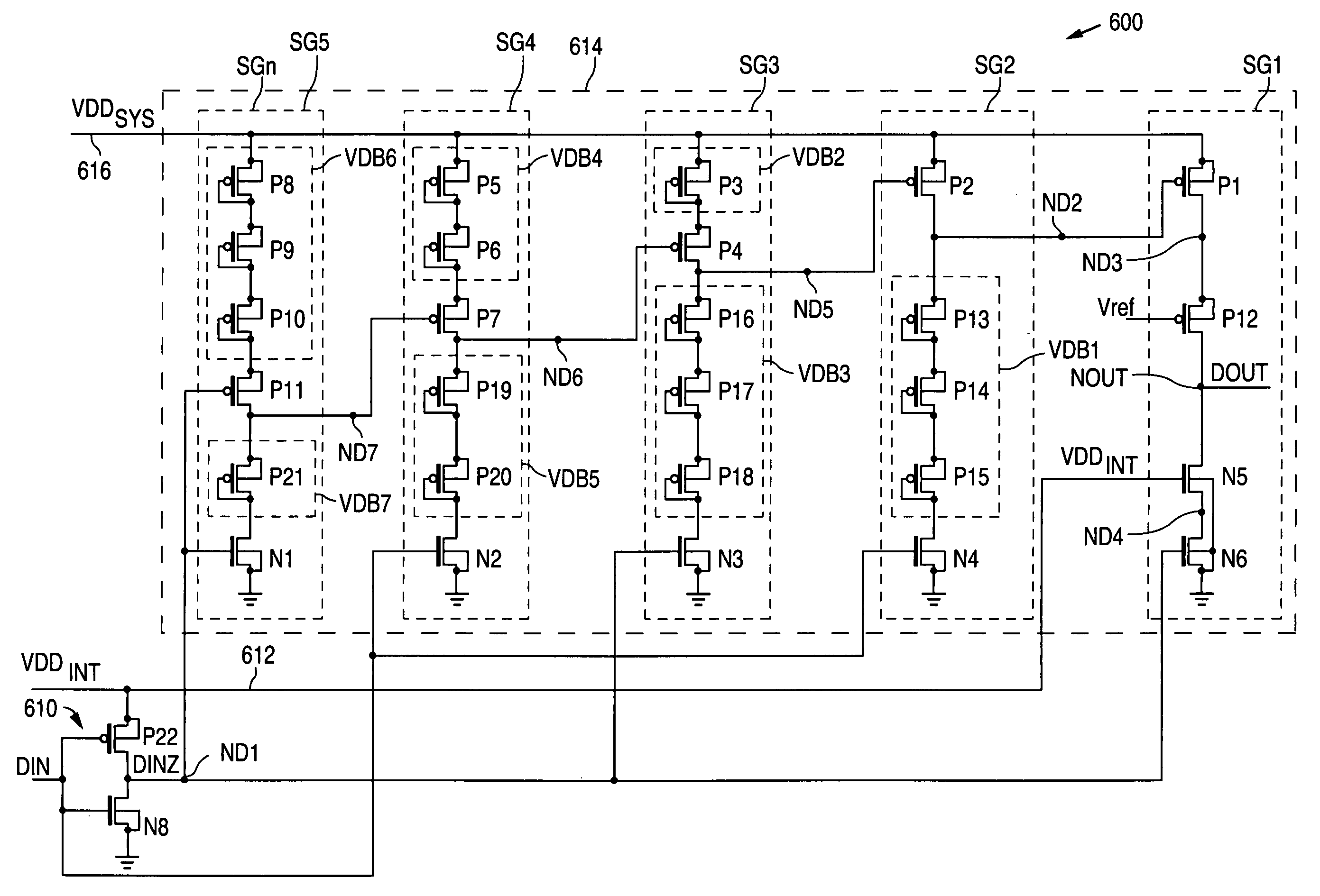
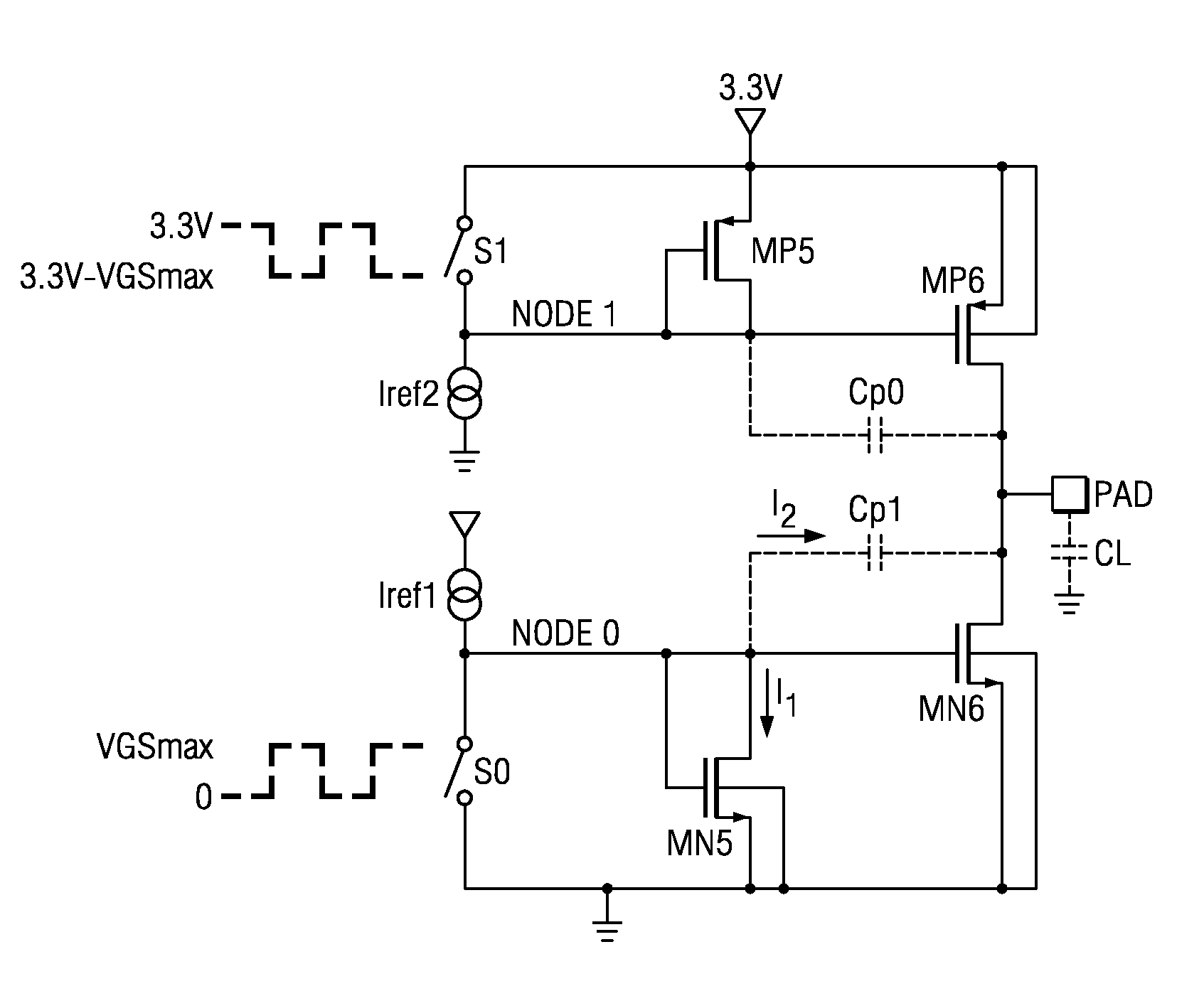
Level shifting input buffer circuit
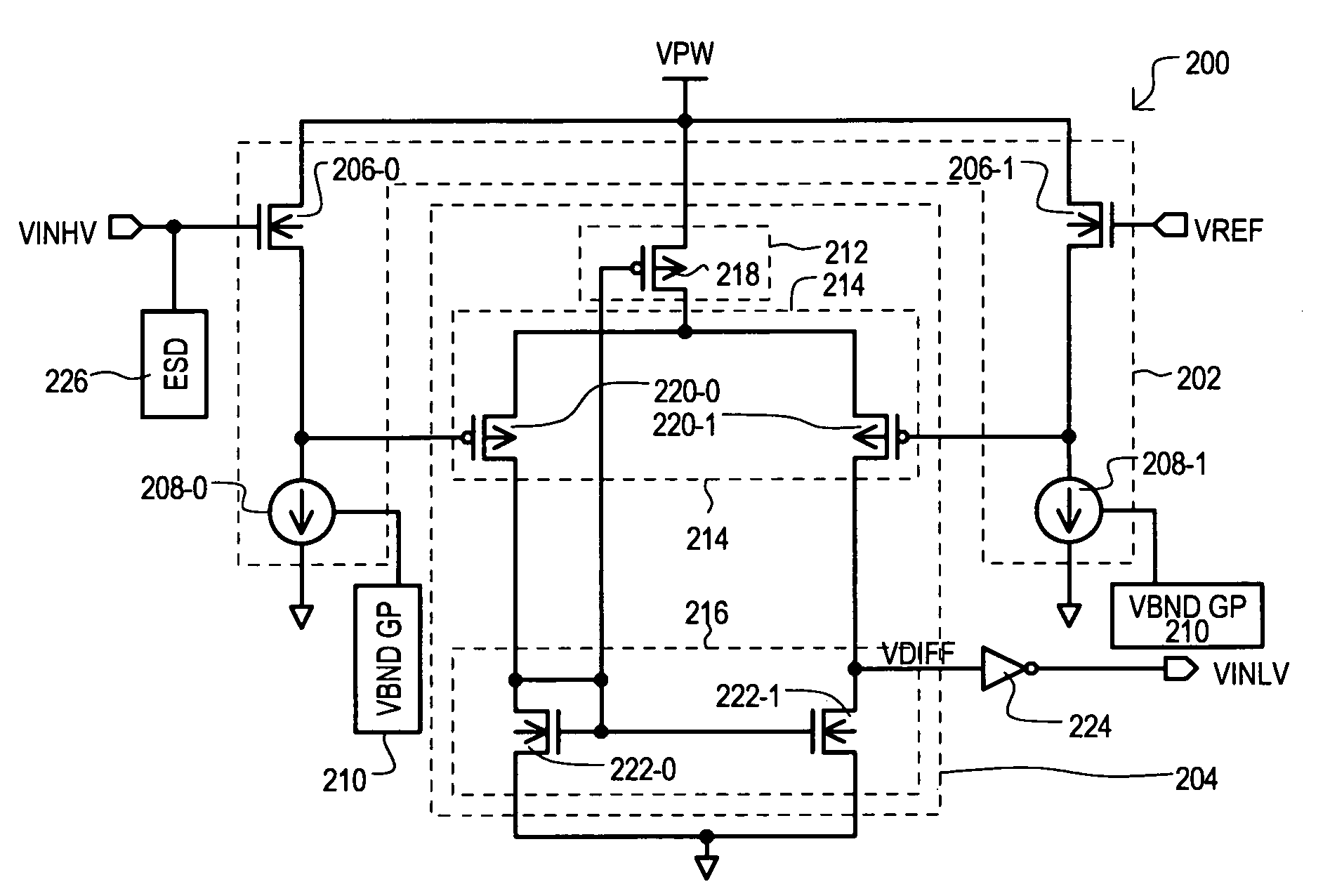
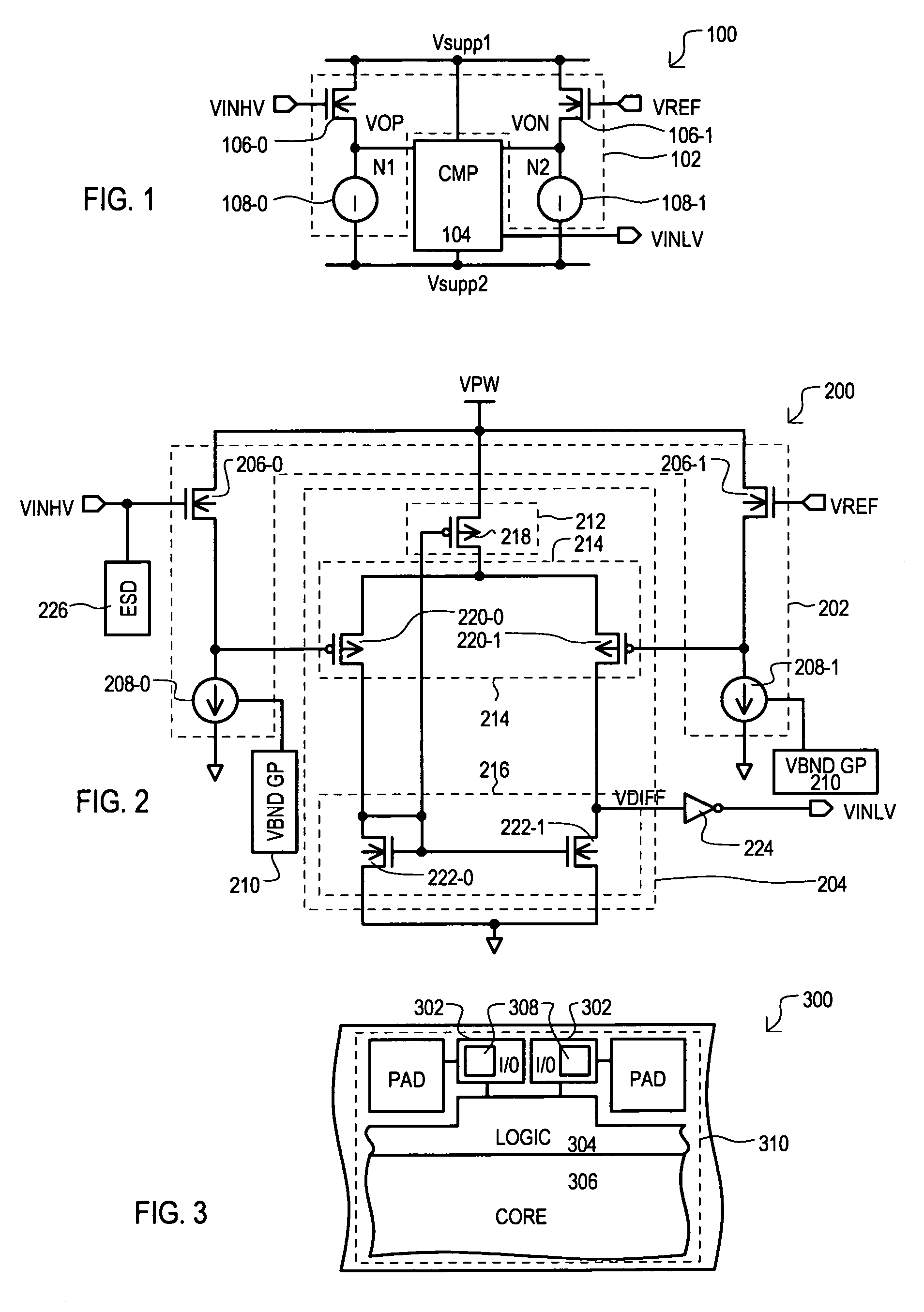
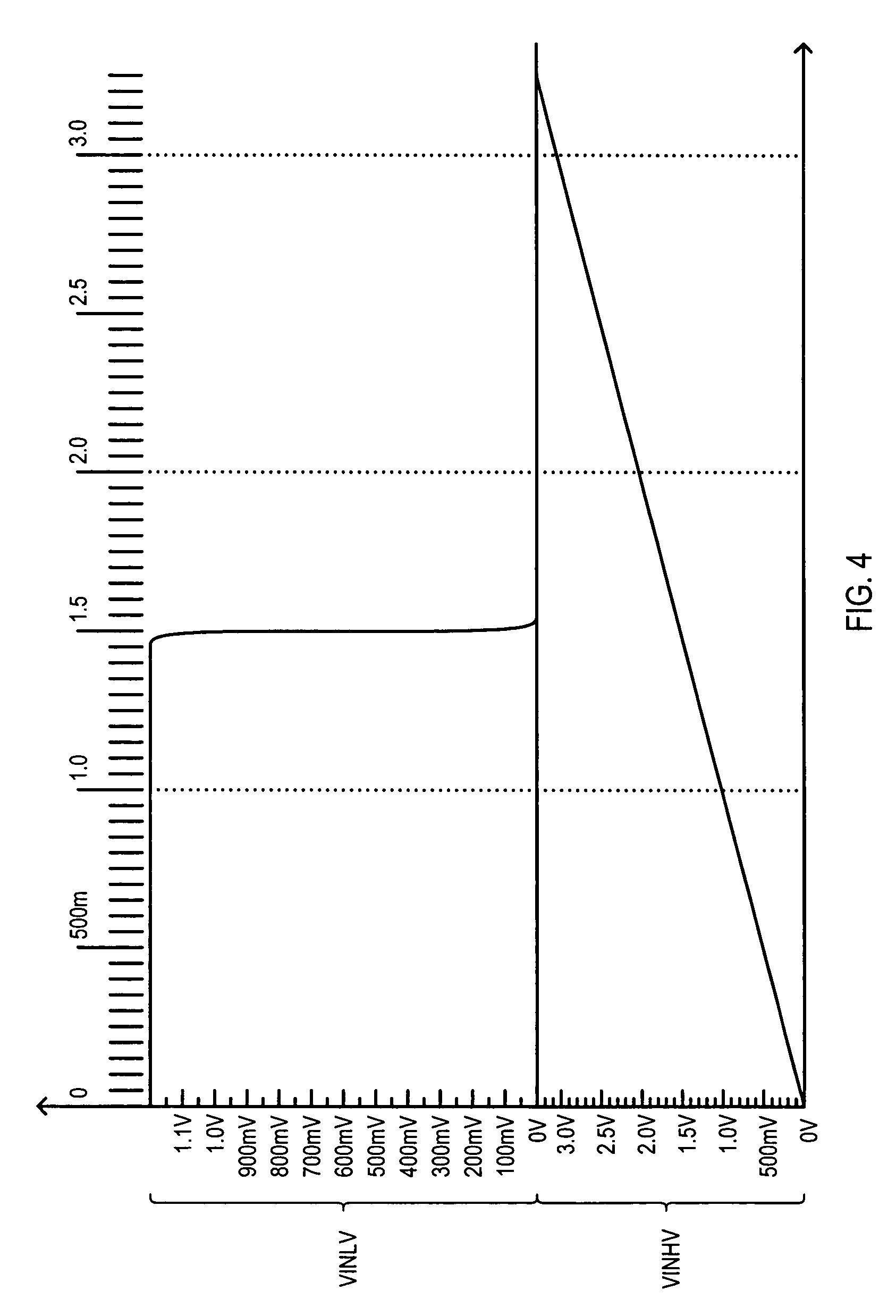
ActiveUS7276953B1More compact circuitReduce distortionPulse automatic controlLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsLevel shiftingDuty cycle distortion
An input circuit (200) operating at a predetermined power supply voltage (VPW) can level shift a high voltage input signal (VINHV) from a higher voltage value to the lower power supply voltage (VPW) level. An input circuit (200) can include input transistors (206-0 and 206-1) having a source-follower configuration. A first input transistor (206-0) receives a high voltage input signal (VINHV) and a second input transistor (206-1) receives a reference voltage (VREF), which can both reach levels greater than power supply voltage (VPW). A compare circuit (204) can reduce duty cycle distortion to generate a lower voltage input signal (VINLV). Input circuit (200) can provide level shifting from LVTTL levels to low voltage CMOS levels without the need for multiple power supply voltages.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
High-voltage microfluidic droplets actuation by low-voltage fabrication technologies
InactiveUS20140054174A1Improve breakdown voltageReduce leakage currentCellsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesMicrofluidicsEngineering
A bi-state-switch low-voltage fabrication technique is able to be used to construct microfluidic systems leveraging well-established low-voltage semiconductor fabrication technologies to achieve high-voltage droplet actuation applications with lower costs, smaller device sizes, and also less time. Also, the electrode cells are able to be made using the well-established low-voltage CMOS fabrication technologies, which can be used to make large-scale integrated microelectronics and microfluidics.
Owner:WANG GARY CHORNG JYH
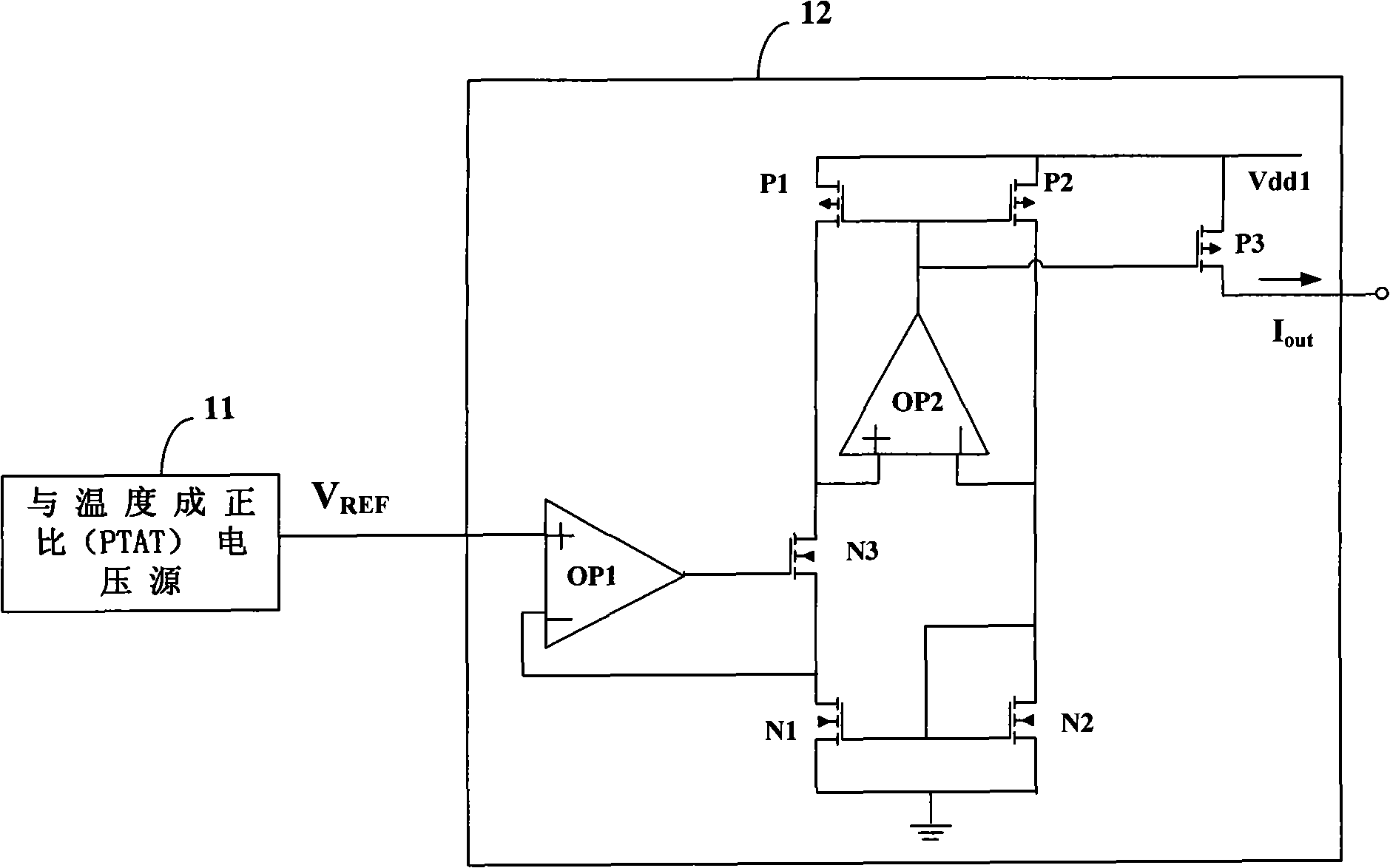
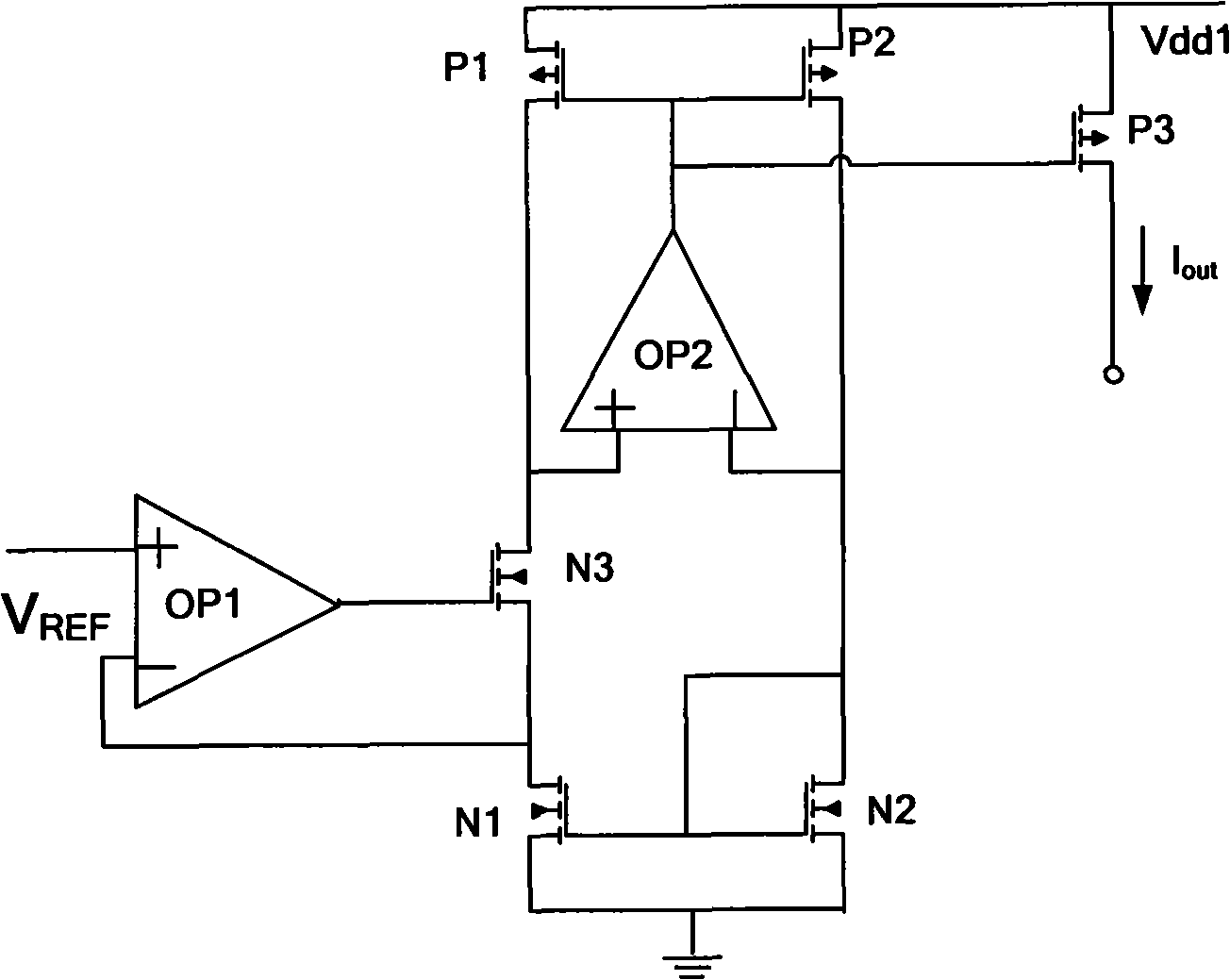
Low voltage CMOS current source
ActiveCN101561689AImprove featuresGood temperature characteristicsElectric variable regulationProcess deviationsCMOS
The invention discloses a low voltage CMOS current source, and belongs to the field of analog integrated circuit. The low voltage CMOS current source comprises a PTAT voltage source, a current converting circuit and a mirror image circuit which are connected with the PTAT voltage source, wherein, the PTAT voltage source is used for generating a reference voltage V[REF] with a positive temperature coefficient; and the current converting circuit and the mirror image circuit are used for converting the reference voltage V[REF] into a reference current, and outputting the reference current by a current mirror relation. The low voltage CMOS current source has good power supply property and temperature property, and process deviation of the CMOS current source has little influence on an output current value of the CMOS current source.
Owner:陕西光电子先导院科技有限公司
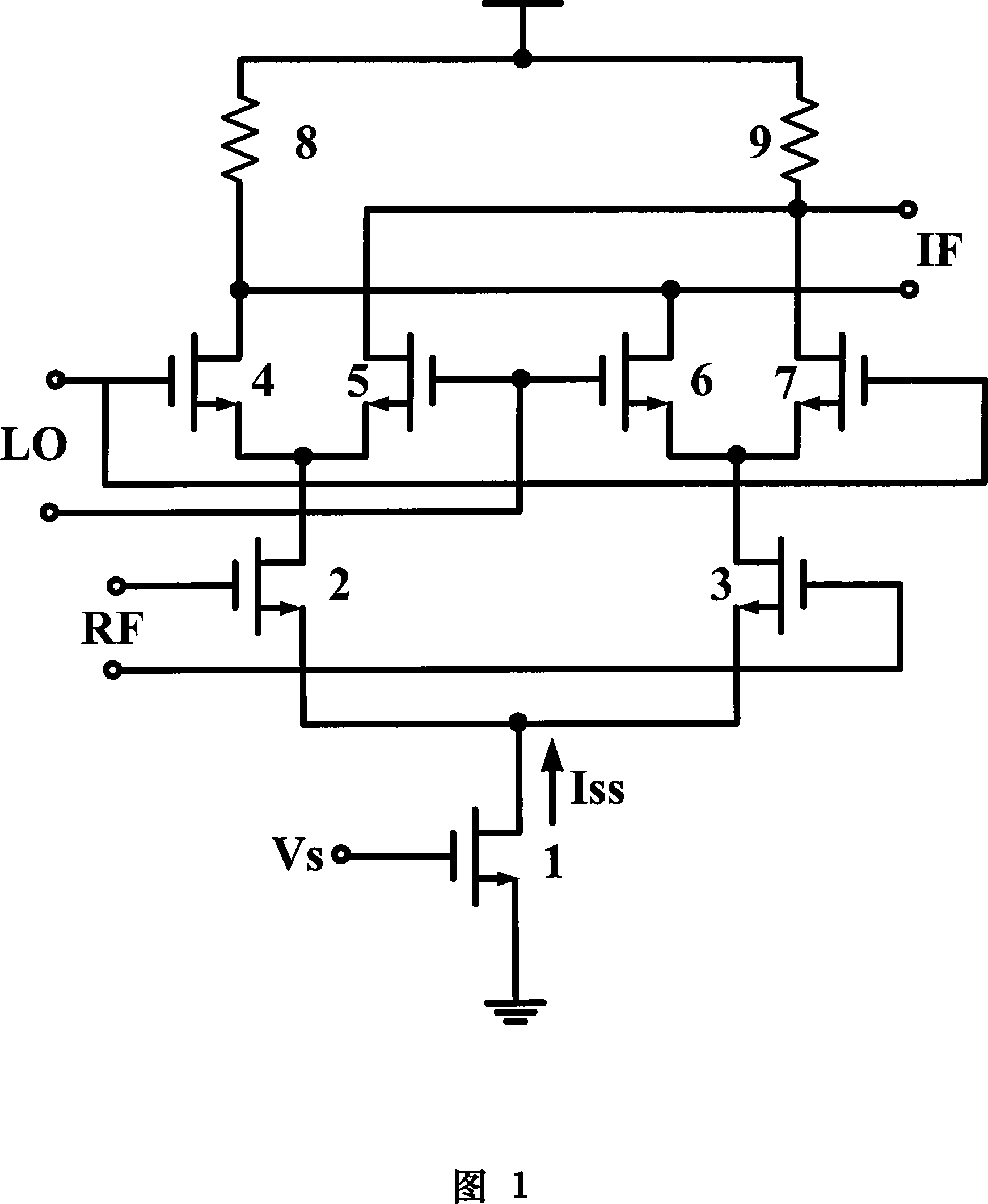
A low-voltage frequency mixer
InactiveCN101188402ALower requirementReduce power consumptionModulation transference balanced arrangementsBeacon systems using radio wavesLow noiseEngineering
The invention provides a low-voltage CMOS folding co-source co-grid mixer. The mixer includes the following parts: a pair of transconductance poles composed of NMOS tubes, tow pairs of switch poles composed of NMOS tubes, a pair of load poles composed of NMOS, and a current source. In the structure of the mixer circuit, the transconductance poles are connected with the switch poles in a co-source co-grid method. The invention solves the problems of the high power supply high voltage caused by the overlapping of the transconductance poles and the switch poles of the traditional Gilbert mixer, and the compromise design between the high transconductance and the high linearity of the transconductance poles and the low noise of the switch poles. The invention can be used in the application of the deep submicron RF CMOS circuit, in particular in the design developing of the satellite navigation double-system compatible receiver radio frequency integrated circuit. The invention has bright application prospect in both the military and the civilian fields.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Slew-rate controlled pad driver in digital CMOS process using parasitic device cap
ActiveUS20080246512A1Logic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsDriver circuitParasitic capacitance
A slew-rate controlled driver circuit in an integrated circuit fabricated in a low voltage CMOS process, having an input node and an output node. A PMOS pull-up transistor is provided, having a source connected to one side of a power supply, having a gate, and having a drain connected to the output node. The PMOS transistor also has a parasitic capacitance between its gate and drain, having a value that may vary from one integrated circuit to the next from process variations and in response to varying circuit conditions. A current source generates a current having a level corresponding to the value of the parasitic capacitance, and to provide that current to the gate of the PMOS transistor. A level shifter receives an input signal having a voltage varying in a first range provides as output signal to the gate of the PMOS transistor shifted to a level suitable for the PMOS transistor. An NMOS pull-down transistor is also provided, connected to the other side of the power supply, with a similar and corresponding current source and level shifter as has the PMOS transistor.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
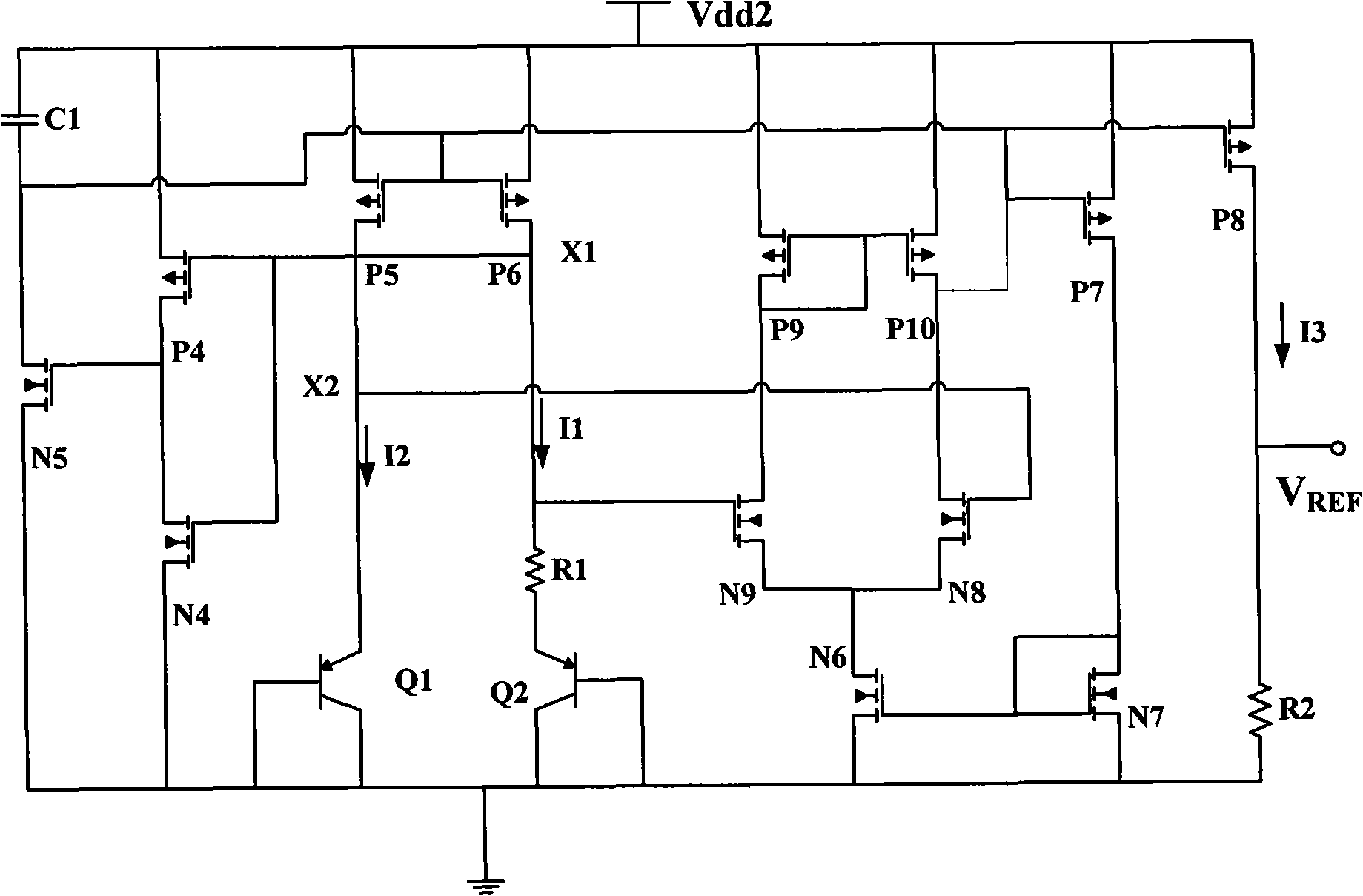
High-performance high-reliability reference voltage source of low-voltage complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS)
ActiveCN104503530AIncrease temperature coefficientImproved noise suppressionElectric variable regulationEngineeringVoltage source
The invention discloses a high-performance high-reliability reference voltage source of a low-voltage complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS). The high-performance high-reliability reference voltage source comprises a starting circuit, an automatic biasing voltage generating circuit, a main bias current generating circuit and a reference voltage generating circuit, wherein direct current input ends of the starting circuit, the automatic biasing voltage generating circuit, the main bias current generating circuit and the reference voltage generating circuit are connected with a direct current power source VDD, the starting circuit and the automatic biasing voltage generating circuit are connected with the main bias current generating circuit, the automatic biasing voltage generating circuit generates stable bias voltage by means of feedback with the main bias current generating circuit and transmits the stable bias voltage to the main bias current generating circuit, the main bias current generating circuit is connected with the reference voltage generating circuit, and reference voltage Vref with low power consumption and low temperature coefficient is output by the reference voltage generating circuit. According to the high-performance high-reliability reference voltage source of the low-voltage CMOS, the CMOS reference voltage source is easy to implement in the CMOS process, the compatibility is good, and high performance and high reliability can be achieved under low voltage.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
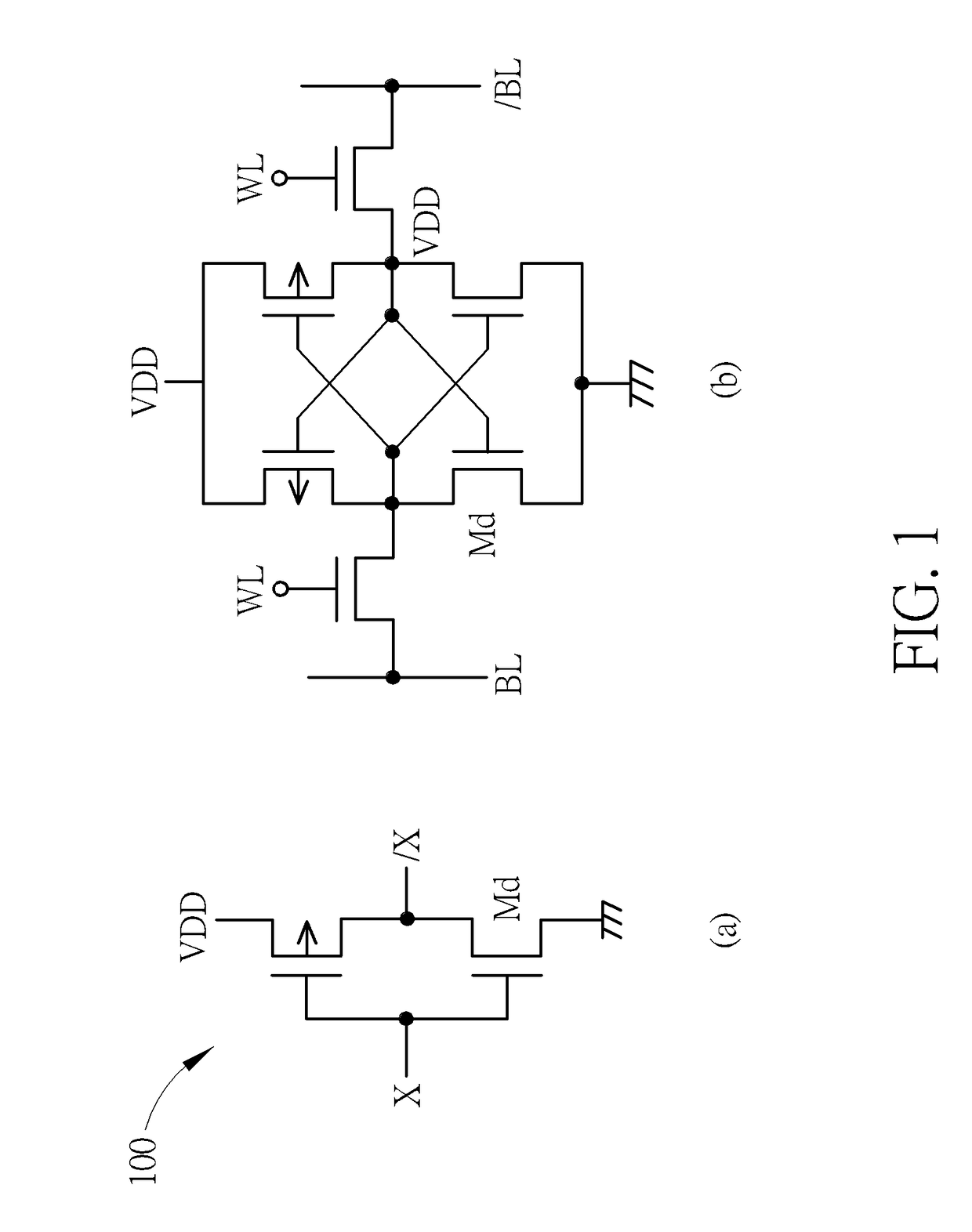
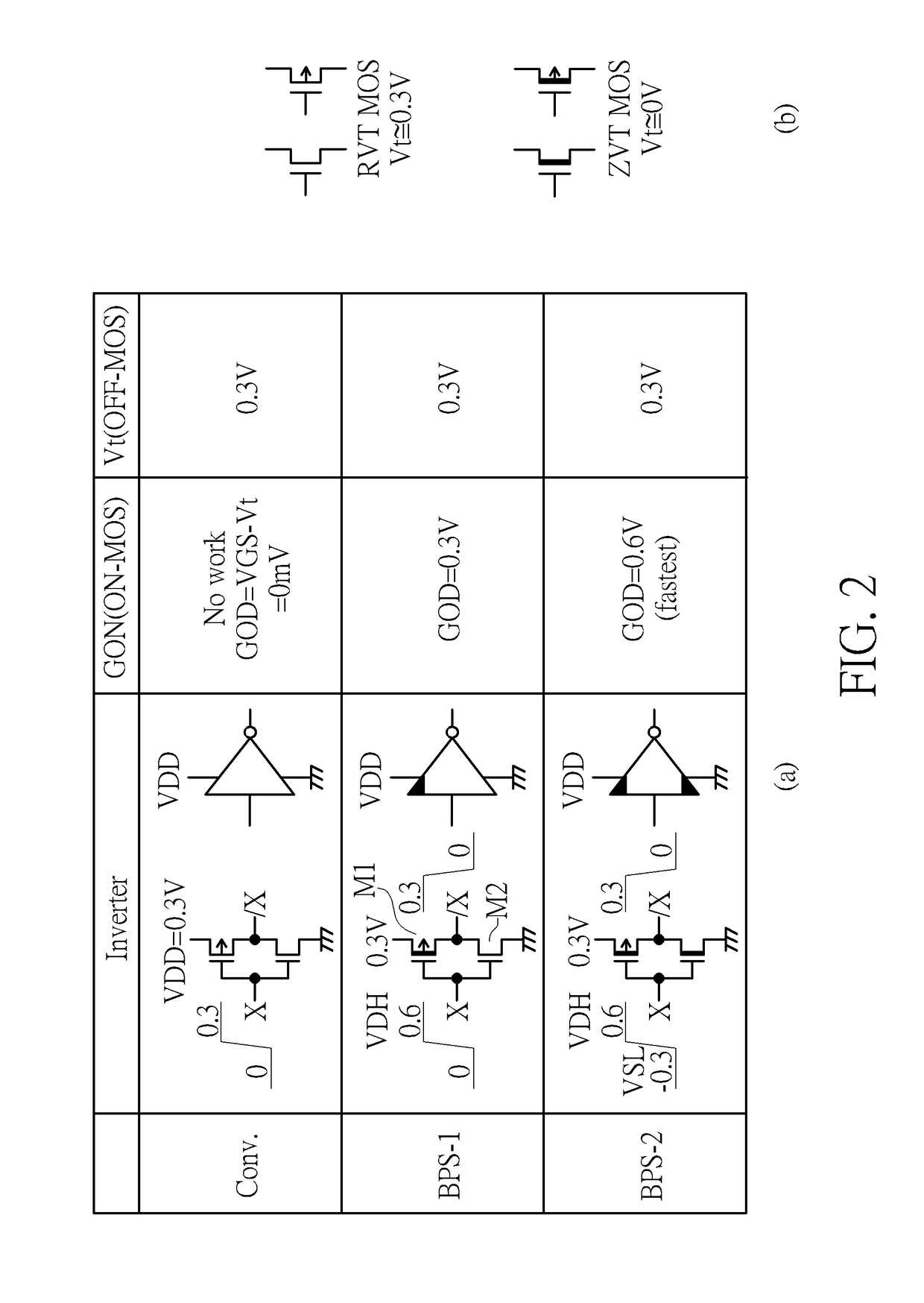
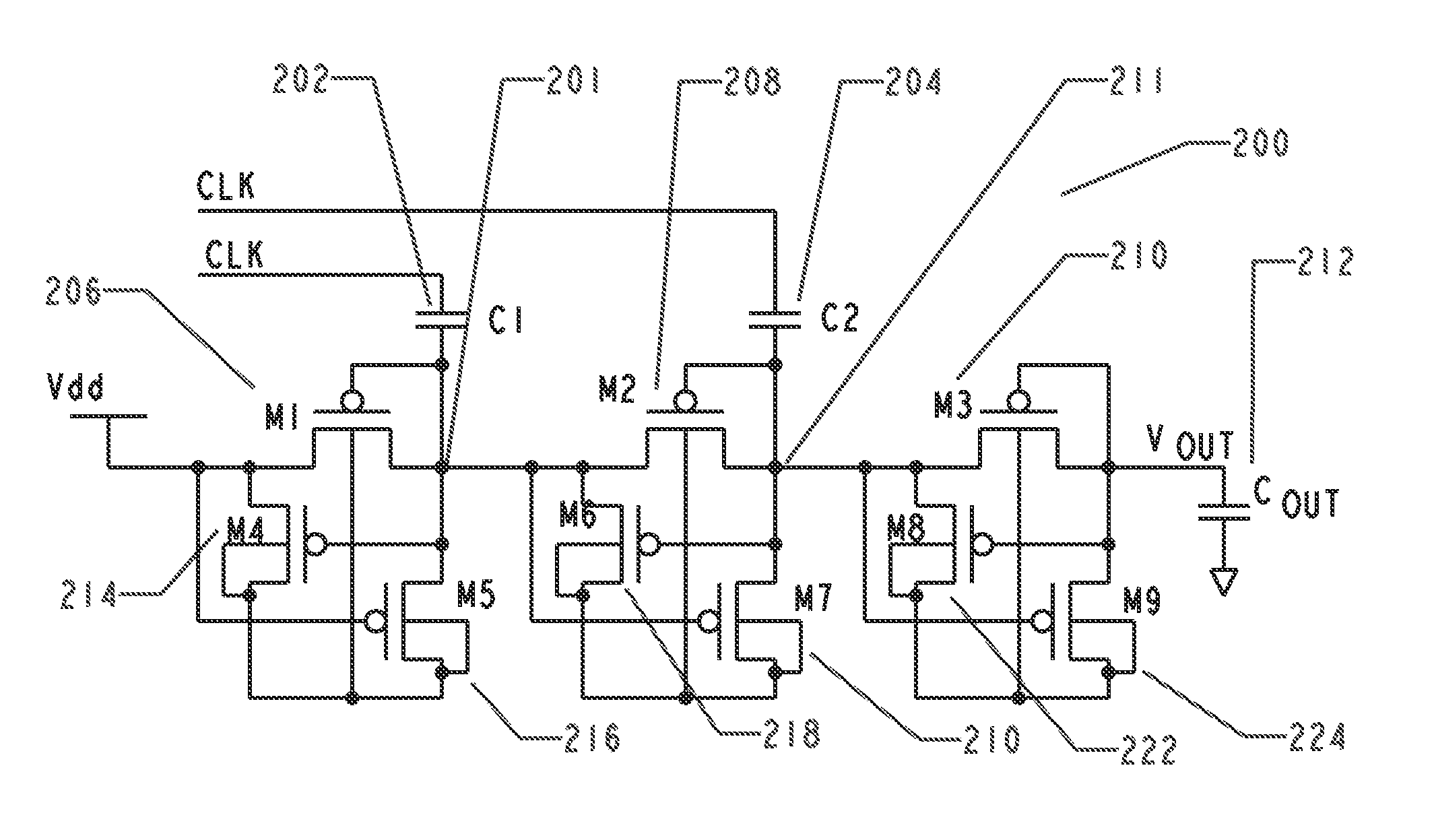
Ultra-low-voltage CMOS circuit and the same for memory
A memory includes a plurality of memory cells and a plurality of peripheral circuits. Each memory cell has a first inverter and a second inverter, the first inverter is supplied by a first power supply rail and a second power supply rail, and the second inverter is supplied by a third power supply rail and a fourth power supply rail. A first voltage difference is applied across the first power supply rail and the second power supply rail, a second voltage difference is applied across the third power supply rail and the fourth power supply rail, and the first voltage difference is less than the second voltage difference. The plurality of peripheral circuits use at least one of boosted power supplies corresponding to the second voltage difference and gate-source differentially-driven circuits.
Owner:ETRON TECH INC
Guard ring structures for high voltage CMOS/low voltage CMOS technology using LDMOS (lateral double-diffused metal oxide semiconductor) device fabrication
A semiconductor structure and a method for forming the same. The method includes providing a semiconductor structure. The semiconductor structure includes a semiconductor substrate. The method further includes simultaneously forming a first doped transistor region of a first transistor and a first doped guard-ring region of a guard ring on the semiconductor substrate. The first doped transistor region and the first doped guard-ring region comprise dopants of a first doping polarity. The method further includes simultaneously forming a second doped transistor region of the first transistor and a second doped guard-ring region of the guard ring on the semiconductor substrate. The second doped transistor region and the second doped guard-ring region comprise dopants of the first doping polarity. The second doped guard-ring region is in direct physical contact with the first doped guard-ring region. The guard ring forms a closed loop around the first and second doped transistor regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
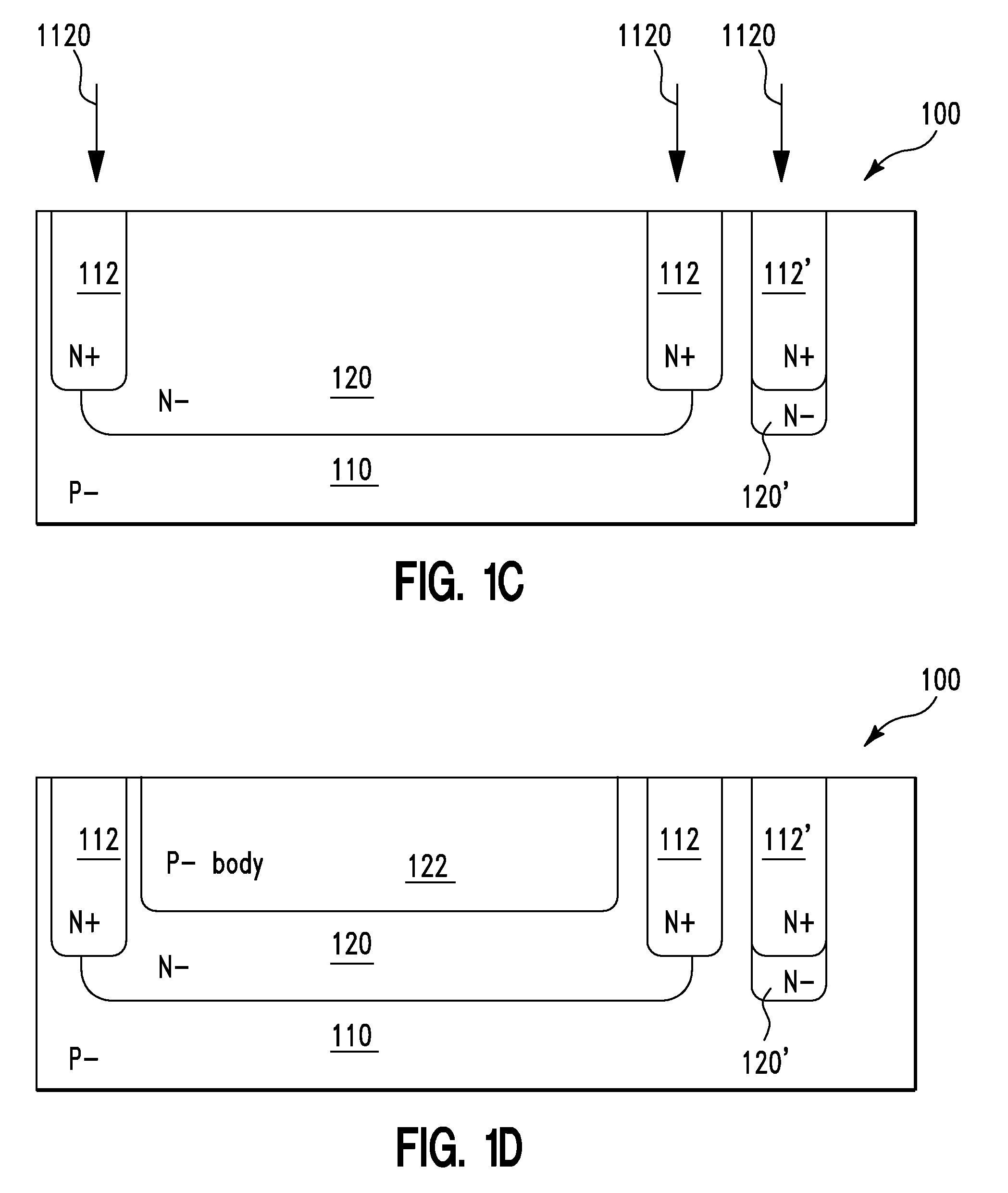
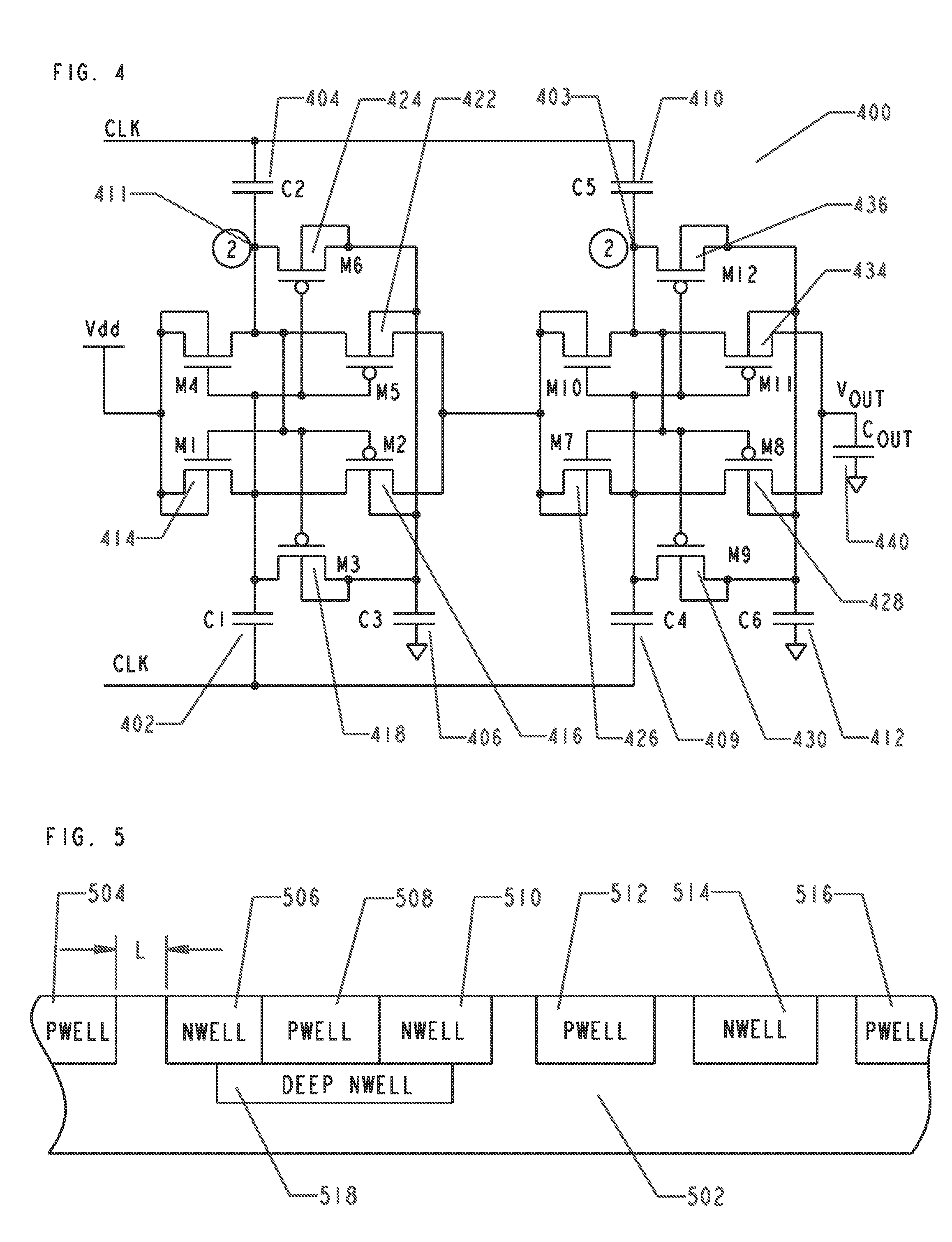
High voltage CMOS output buffer constructed from low voltage CMOS transistors
ActiveUS20090261865A1Pulse automatic controlReliability increase in field effect transistorsLow voltage cmosCMOS
A high voltage CMOS output buffer is constructed from low voltage CMOS transistors. The output buffer employs a series of unique CMOS inverter stages, each of which contains a switched PMOS transistor, one or more voltage drop blocks, and a switched NMOS transistor. The voltage drop blocks are composed of stacked PMOS transistors that are diode-connected—i.e., the PMOS gate terminal is connected to the PMOS drain terminal, and the PMOS body (N-well) terminal is connected to the PMOS source terminal. The diode-connected PMOS transistors reduce the voltage across the transistor gate oxide to a safe value, for all internal PMOS / NMOS transistors inside the CMOS output buffer.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Method for manufacturing high-voltage lateral dual-diffusion N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) based on standard complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor transistor (CMOS) process
ActiveCN102184871ASimple processIdeal high drive currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLOCOSP type silicon
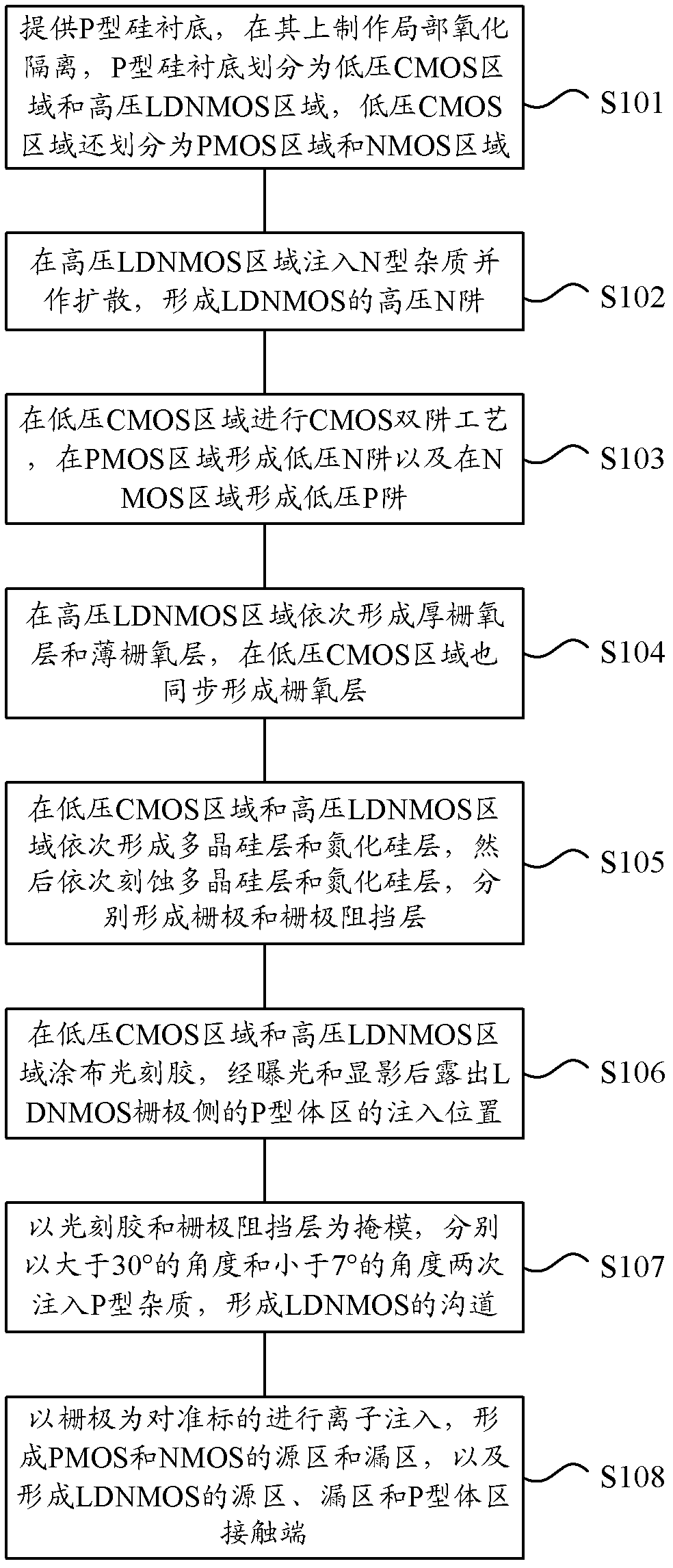
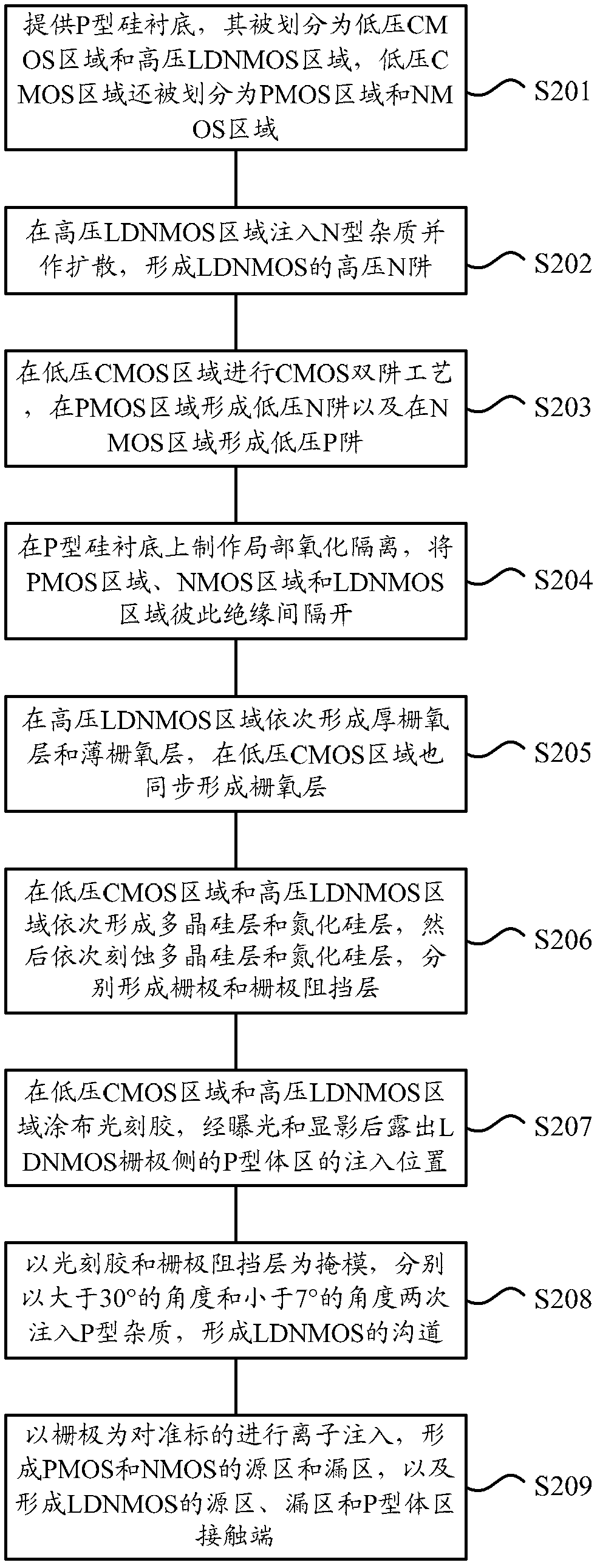
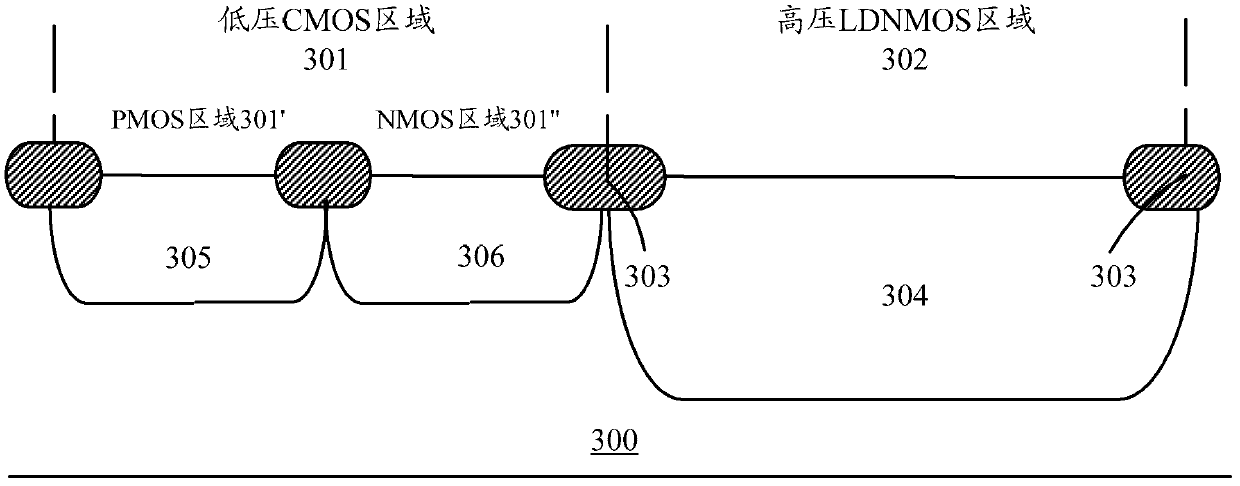
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a high-voltage lateral dual-diffusion N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) based on a standard complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor transistor (CMOS) process. The method comprises the following steps of: providing a P type silicon substrate, manufacturing local oxidation of silicon (LOCOS) on the P type silicon substrate, and dividing theLOCOS into a low-voltage CMOS area and a high-voltage lateral diffused N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (LDNMOS) area; injecting phosphor into the LDNMOS area and diffusing the phosphor to form a high-voltage N well; performing a two-well process in the CMOS area to form a low-voltage N well and a low-voltage P well; sequentially forming a thick gate oxide layer and a thin gate oxide layer in the LDNMOS area; sequentially forming a polysilicon layer and a silicon nitride layer and sequentially etching the polysilicon layer and the silicon nitride layer to form a grid electrode and a buffering layer respectively; coating a photoresist, and exposing the injection position of a P type area of the LDNMOS area after exposing and development; injecting P type ions for two times at the anglesof more than 30 degrees and less than 7 degrees respectively to form channels of an LDNMOS, wherein the photoresist and the buffering layer serve as masks; and forming source areas and drain areas ofa P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) and an NMOS, and contact ends of a source area, a drain area and a P type area of the LDNMOS by taking the grid electrode as an alignment mark. Because a large-angle injection process is used for forming the channels after the grid electrode is formed, a long-time high-temperature heating process is not required and the process is compatible.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON MFG CO LTD
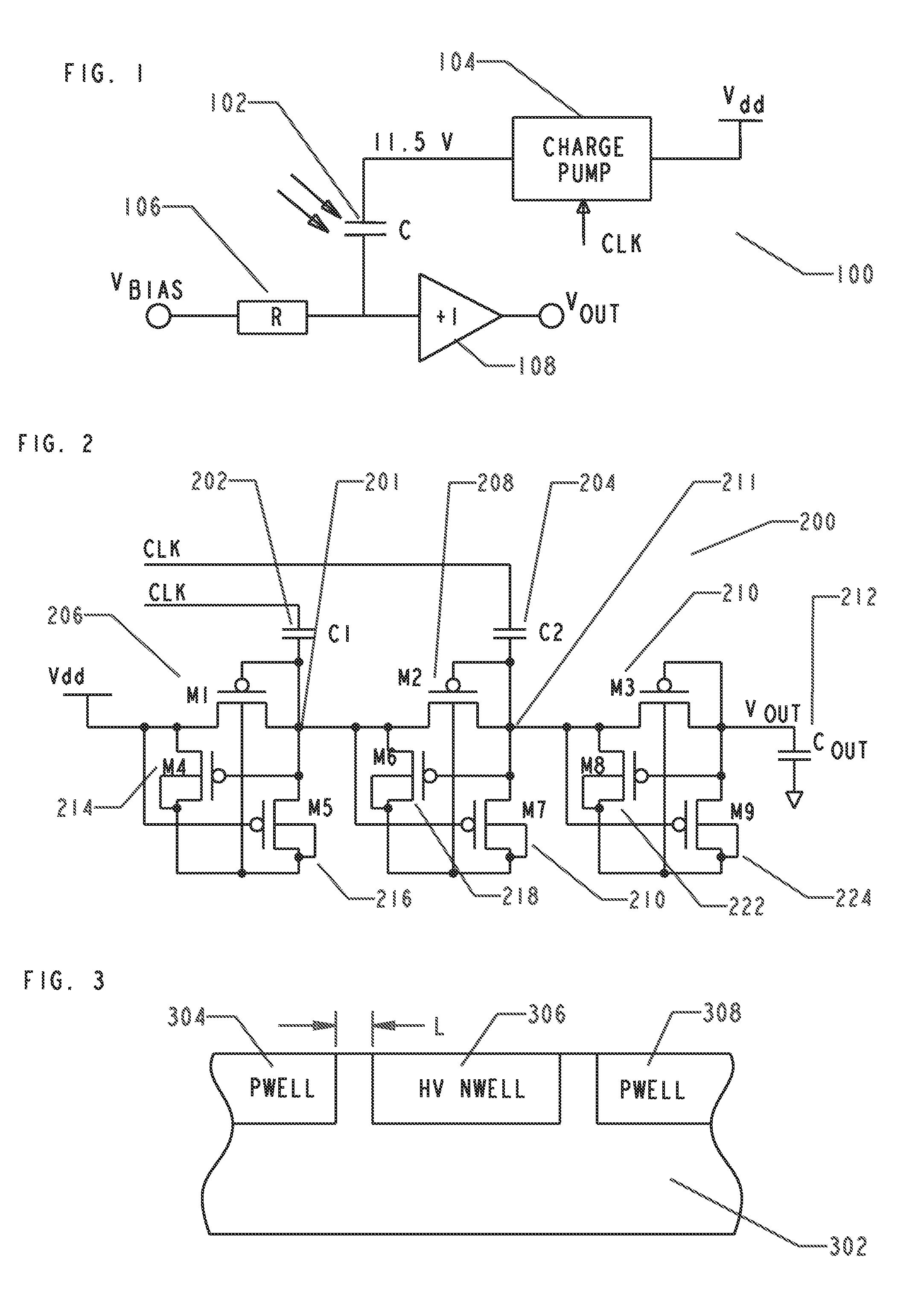
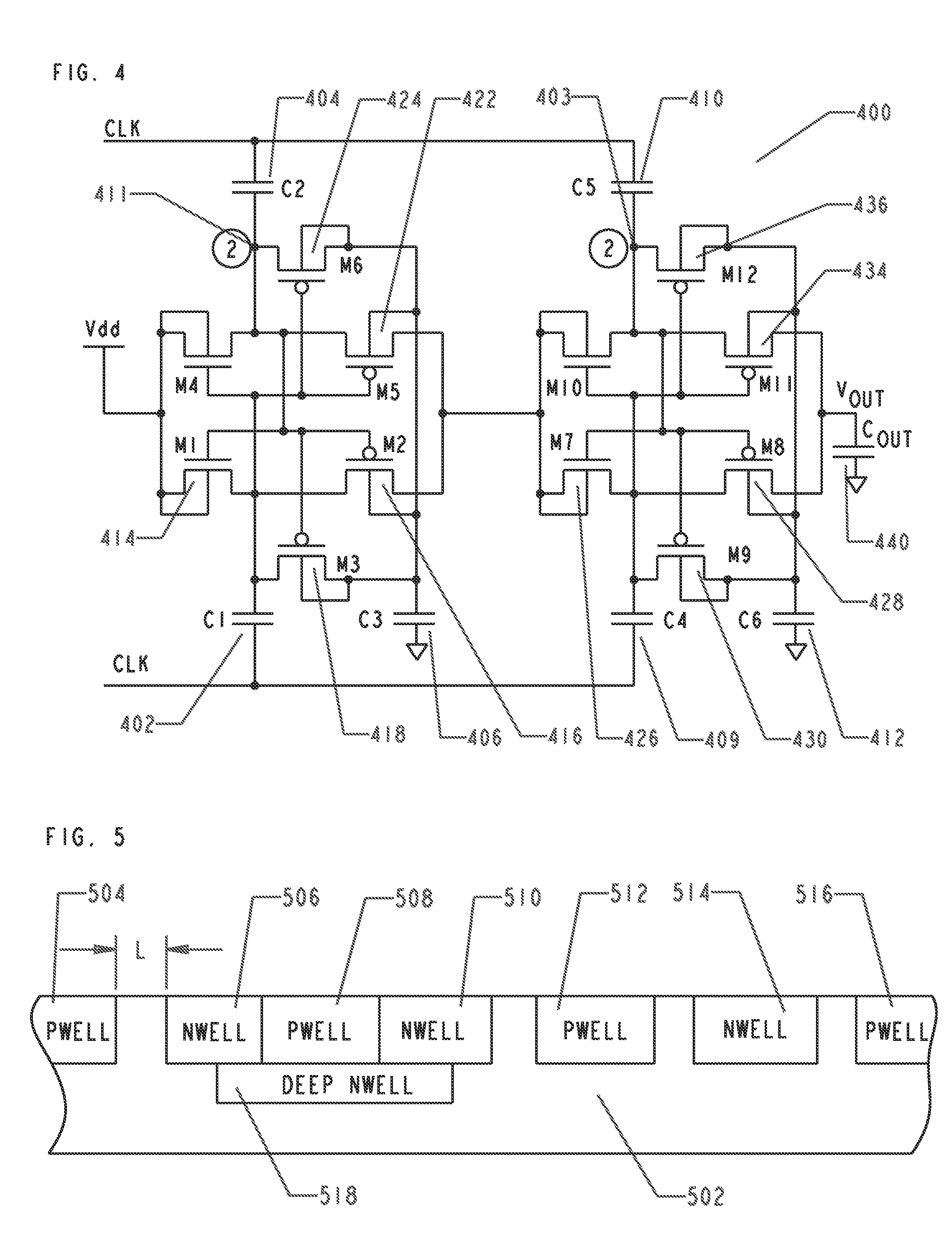
High voltage multiplier for a microphone and method of manufacture
InactiveUS9059630B2Apparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectrostatic transducer microphonesSound energyCondenser microphone
A microphone circuit includes a condenser microphone and a charge pump. The condenser microphone is configured to receive sound energy and responsively convert the sound energy into a microphone output voltage. The charge pump is implemented in a low voltage CMOS process. It is coupled to the microphone and is configured to supply a bias voltage to the microphone allowing the microphone to operate. By using a proper circuit topology, whose maximum output voltage is limited by the breakdown voltage between the NWELL and the substrate, and by blocking the formation of the PWELL around the NWELL at a predetermined distance so that the NWELL is surrounded by a very lightly doped substrate from all sides, the maximum output voltage of the charge pump is increased significantly.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
Slew-rate controlled pad driver in digital CMOS process using parasitic device cap
A slew-rate controlled driver circuit in an integrated circuit fabricated in a low voltage CMOS process, having an input node and an output node. A PMOS pull-up transistor is provided, having a source connected to one side of a power supply, having a gate, and having a drain connected to the output node. The PMOS transistor also has a parasitic capacitance between its gate and drain, having a value that may vary from one integrated circuit to the next from process variations and in response to varying circuit conditions. A current source generates a current having a level corresponding to the value of the parasitic capacitance, and to provide that current to the gate of the PMOS transistor. A level shifter receives an input signal having a voltage varying in a first range provides as output signal to the gate of the PMOS transistor shifted to a level suitable for the PMOS transistor. An NMOS pull-down transistor is also provided, connected to the other side of the power supply, with a similar and corresponding current source and level shifter as has the PMOS transistor.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
High Voltage Multiplier For A Microphone And Method Of Manufacture
A microphone circuit includes a condenser microphone and a charge pump. The condenser microphone is configured to receive sound energy and responsively convert the sound energy into a microphone output voltage. The charge pump is implemented in a low voltage CMOS process. It is coupled to the microphone and is configured to supply a bias voltage to the microphone allowing the microphone to operate. By using a proper circuit topology, whose maximum output voltage is limited by the breakdown voltage between the NWELL and the substrate, and by blocking the formation of the PWELL around the NWELL at a predetermined distance so that the NWELL is surrounded by a very lightly doped substrate from all sides, the maximum output voltage of the charge pump is increased significantly.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
Drive bootstrap circuit for switching tube of switching power supply converter
The invention discloses a drive bootstrap circuit for a switching tube of a switching power supply converter, belonging to the filed of semiconductor technology, and comprising a bootstrap capacitor, a low-voltage CMOS inverter, three high-voltage CMOS inverters, an MOS tube voltage switching mechanism and a switch breakover mechanism. The device further improves the grid control voltage of a power tube so as to reduce the breakover resistance of a power switching tube from the aspect of circuit structure.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Double gated vertical transistor with different first and second gate materials
InactiveUS6960806B2High densityImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesNon symmetricEngineering
Accordingly, the present invention provides a double gated transistor and a method for forming the same that results in improved device performance and density. The preferred embodiment of the present invention uses provides a double gated transistor with asymmetric gate doping, where one of the double gates is doped degenerately n-type and the other degenerately p-type. By doping on of the gates n-type, and the other p-type, the threshold voltage of the resulting device is improved. In particular, by asymmetrically doping the two gates, the resulting transistor can, with adequate doping of the body, have a threshold voltage in a range that enables low-voltage CMOS operation. For example, a transistor can be created that has a threshold voltage between 0V and 0.5V for nFETs and between 0 and −0.5V for pFETs.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
High-voltage microfluidic droplets actuation by low-voltage fabrication technologies
A bi-state-switch low-voltage fabrication technique is able to be used to construct microfluidic systems leveraging well-established low-voltage semiconductor fabrication technologies to achieve high-voltage droplet actuation applications with lower costs, smaller device sizes, and also less time. Also, the electrode cells are able to be made using the well-established low-voltage CMOS fabrication technologies, which can be used to make large-scale integrated microelectronics and microfluidics.
Owner:WANG GARY CHORNG JYH
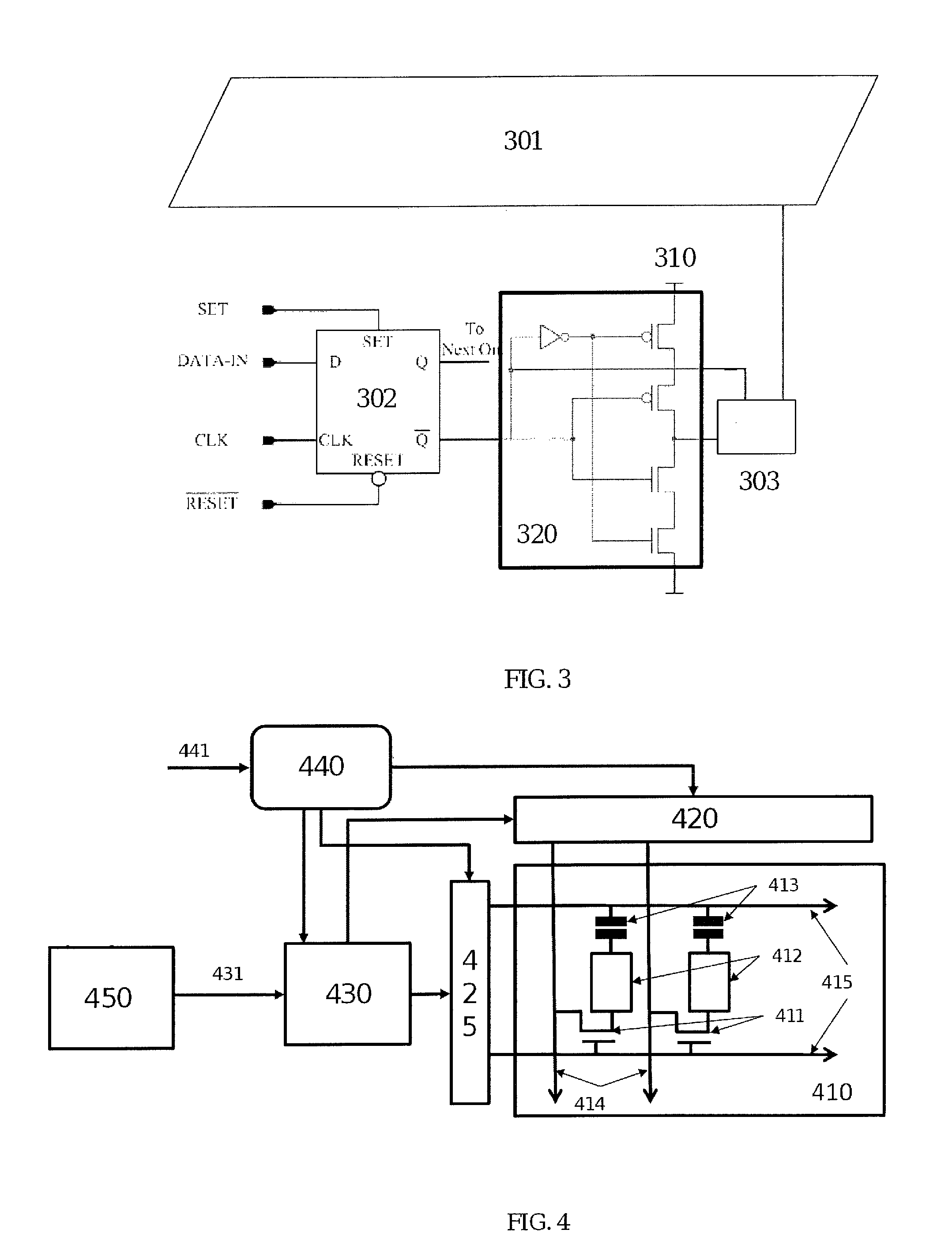
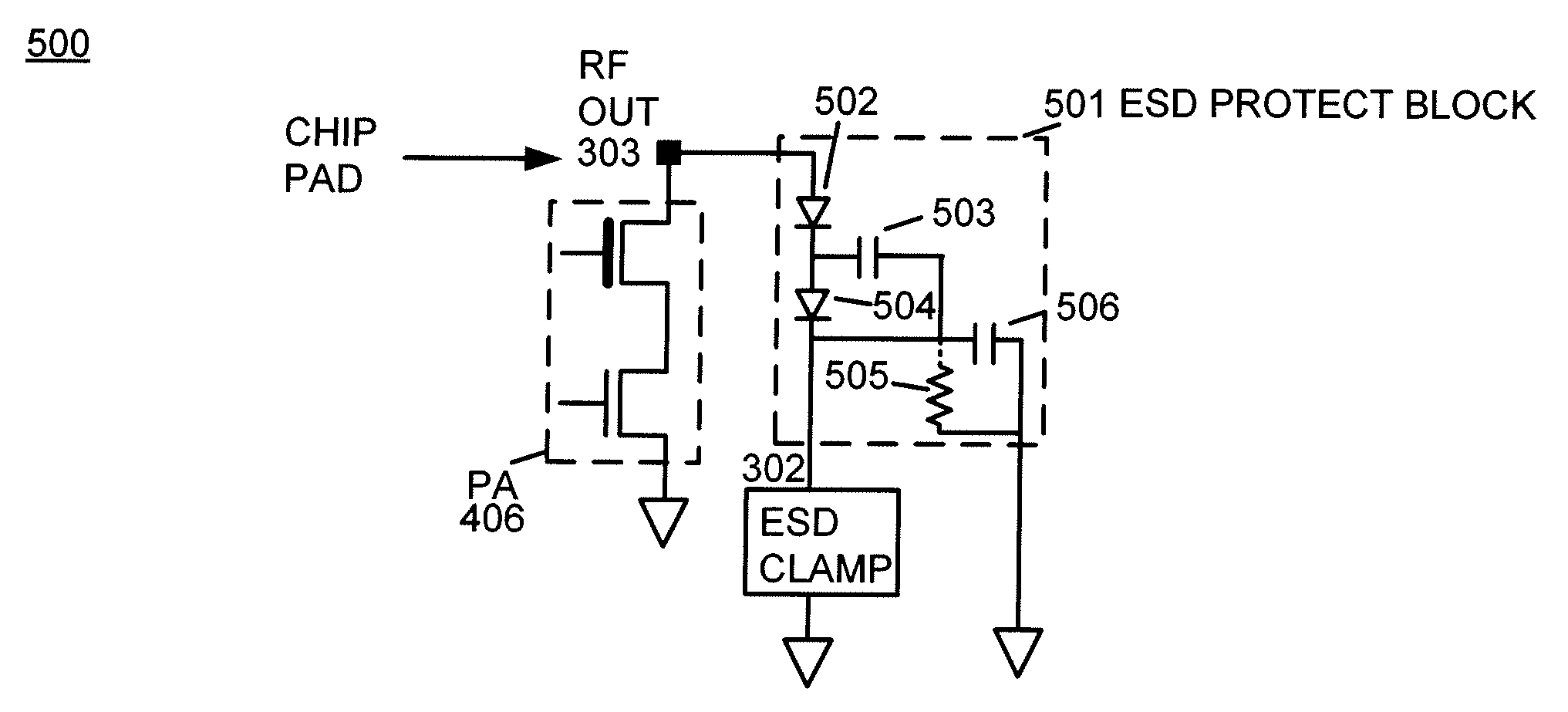
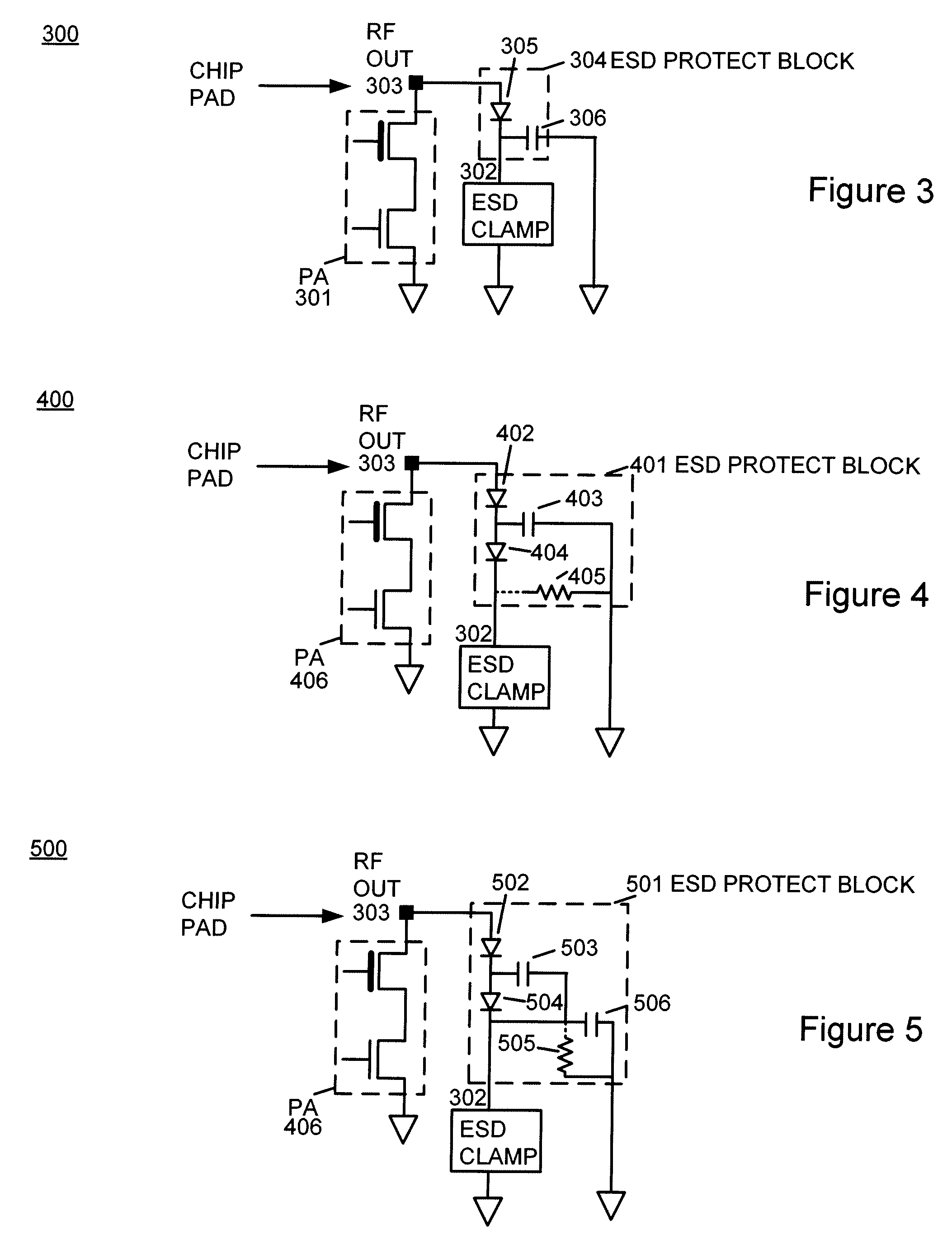
Apparatus and method for electrostatic discharge protection of a transmit integrated circuit
ActiveUS7787227B1Minimal distortion of outputInhibition of activationSolid-state devicesAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesTransmitted powerEngineering
An apparatus and method for providing electrostatic discharge protection of a transmit integrated circuit including an ESD protect block coupled to an integrated circuit pad in a package without bond wires, and an ESD clamp circuit coupled between the ESD protect block and ground. During transmission, one or more capacitors within the ESD protect block may charge up to various levels near the peak transmit voltage, which reverse biases one or more diodes in the ESD protect block, thereby buffering the transmit circuit from the capacitive load of the ESD clamp circuit. The ESD protect block may prevent the ESD clamp circuit from activating due to the high peak voltages output from the transmit circuit. An embodiment of the ESD protect block may apply particularly to transmit power amplifier circuits in which the output signal peaks at twice the supply voltage. In one embodiment applicable for lower voltage CMOS processes, the ESD protect block includes a diode and a capacitor. In another embodiment applicable for higher voltage CMOS processes, the ESD protect block includes two diodes, one or two capacitors, and an optional resistor.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
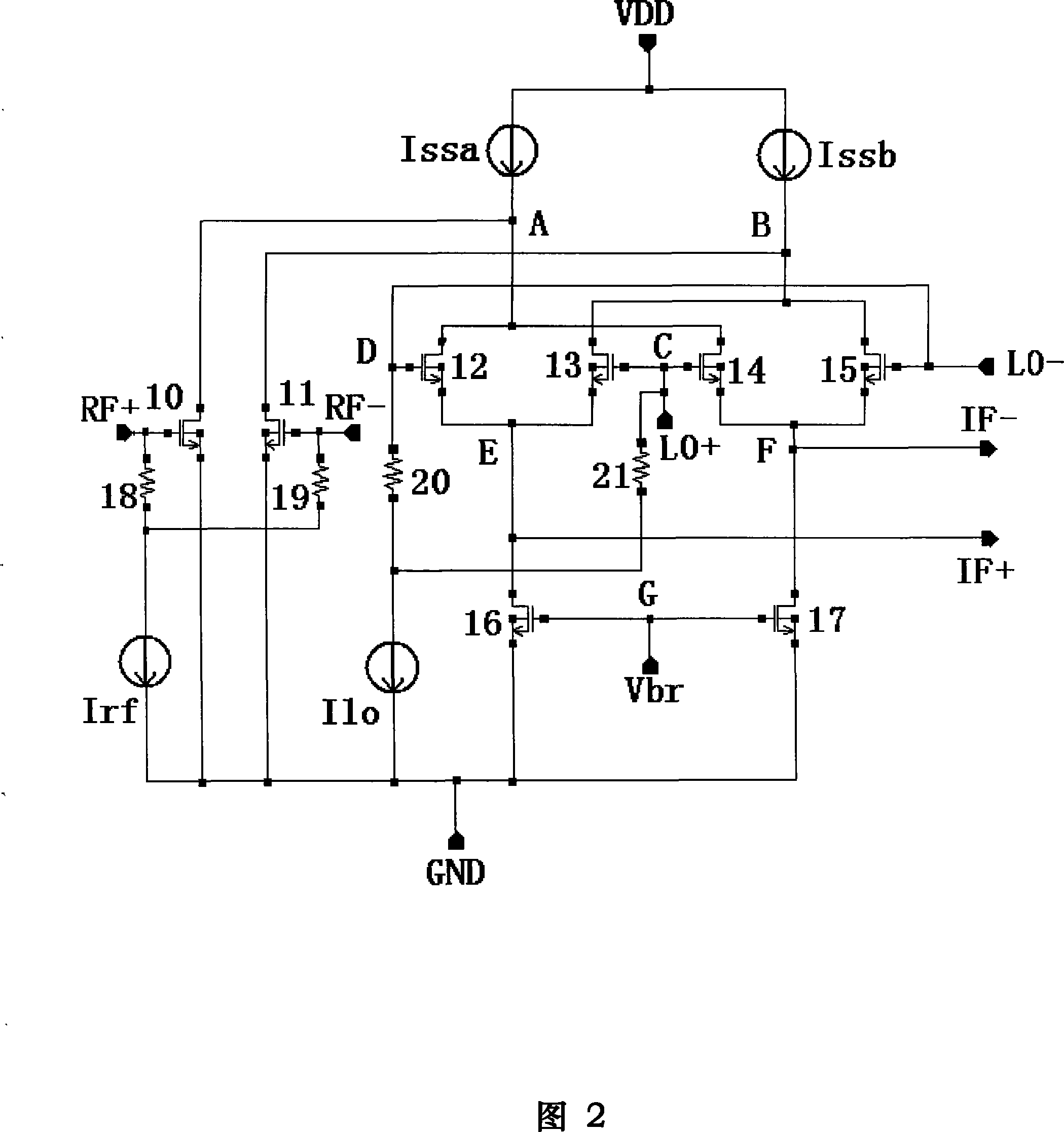
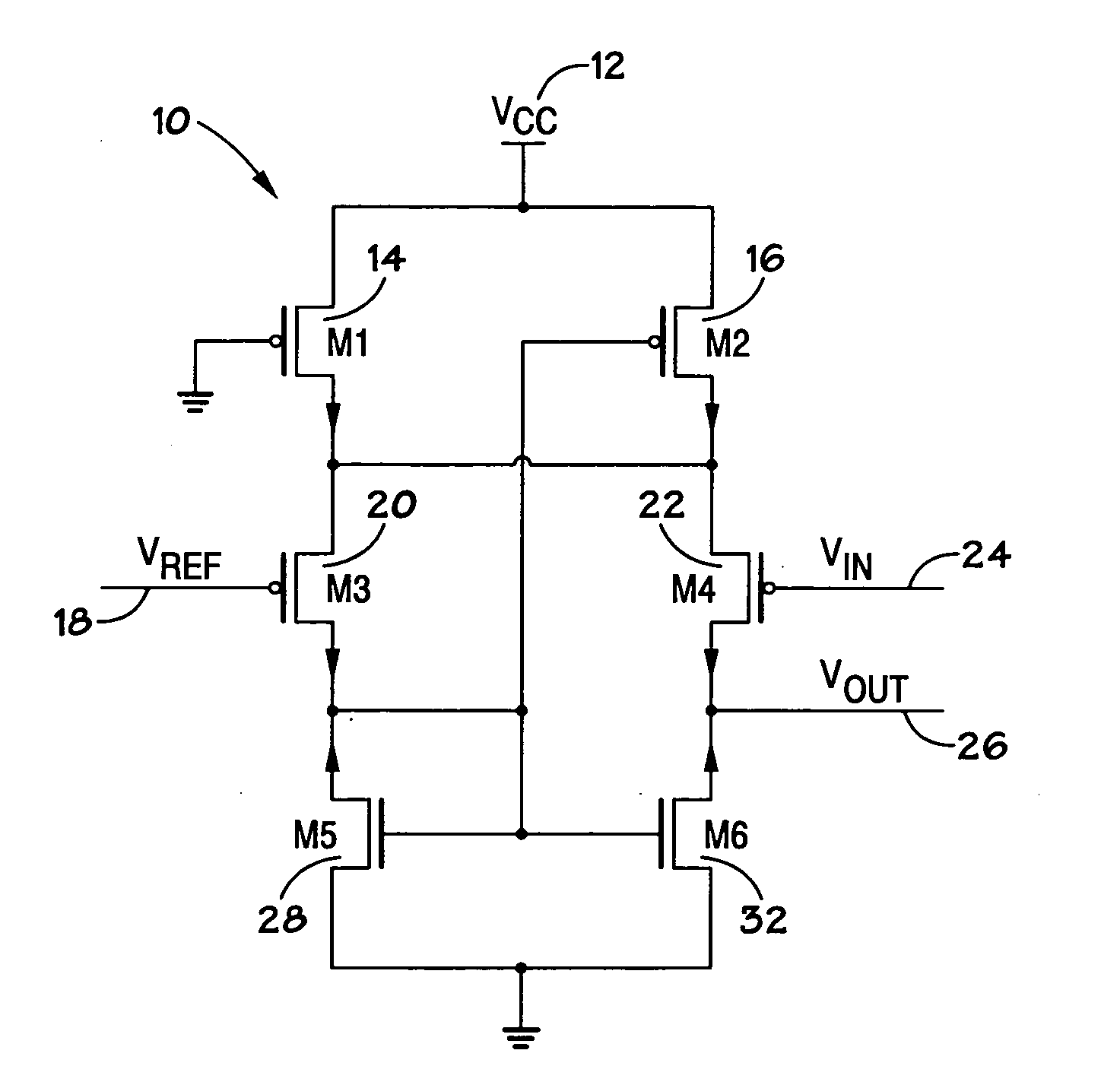
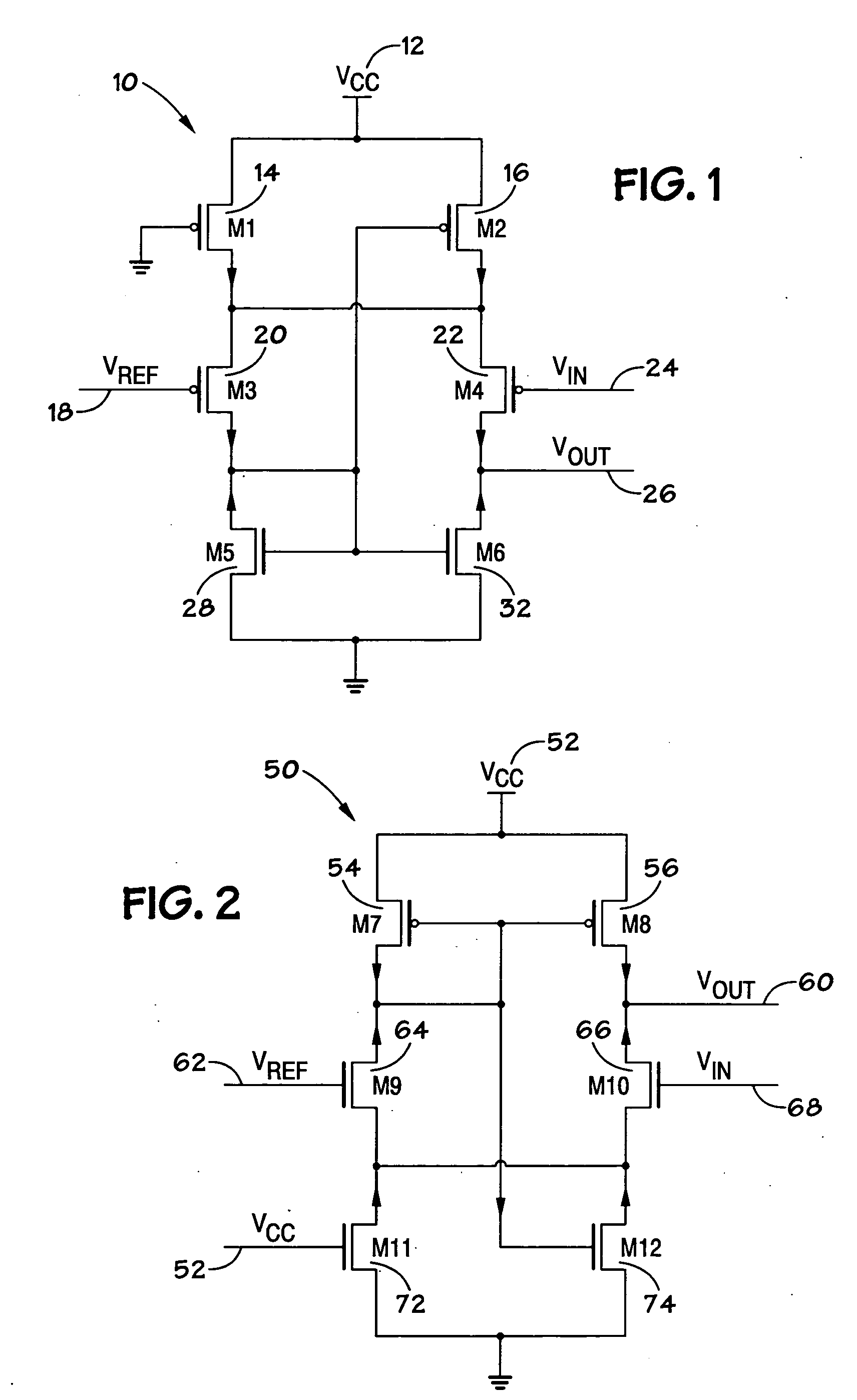
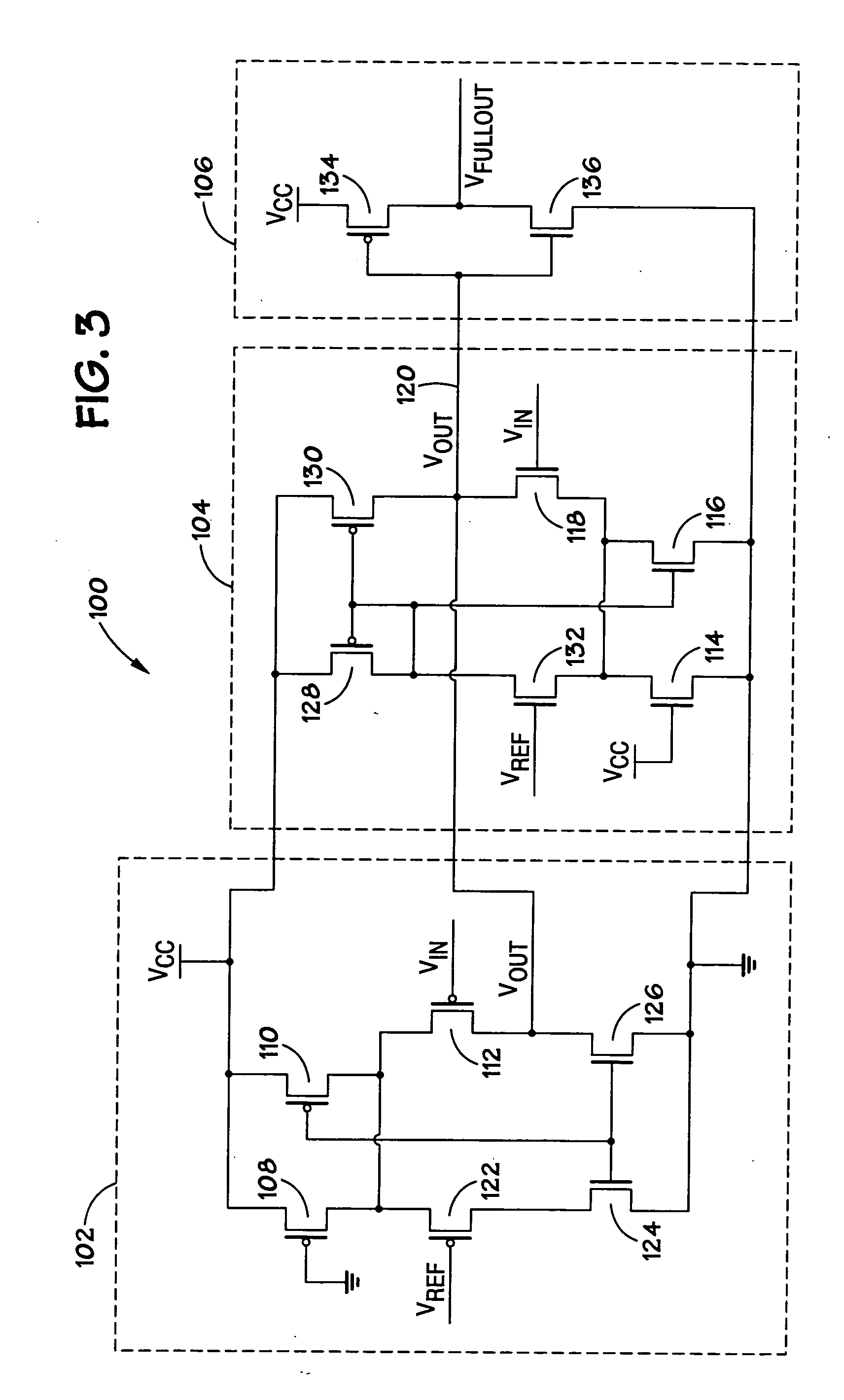
Low voltage CMOS differential amplifier
ActiveUS20060139097A1Reduce power supply voltageDifferential amplifiersPulse manipulationEngineeringLow voltage cmos
A low voltage CMOS differential amplifier is provided. More specifically, there is provided a device comprising a differential pair coupled to a first tail current transistor and to a component wherein the first tail current transistor is configured to provide a tail current to the differential pair and the component is configured to provide a tail current to the differential pair when the first tail current transistor is operating in a triode region or in a cut-off region.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com