High surface quality GaN wafer and method of fabricating same
a technology of gan wafers and wafers, applied in the field of alxgayinzn, can solve the problems of poor device performance, significant thermal stress, internal stress, etc., and achieve the effect of superior surface quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
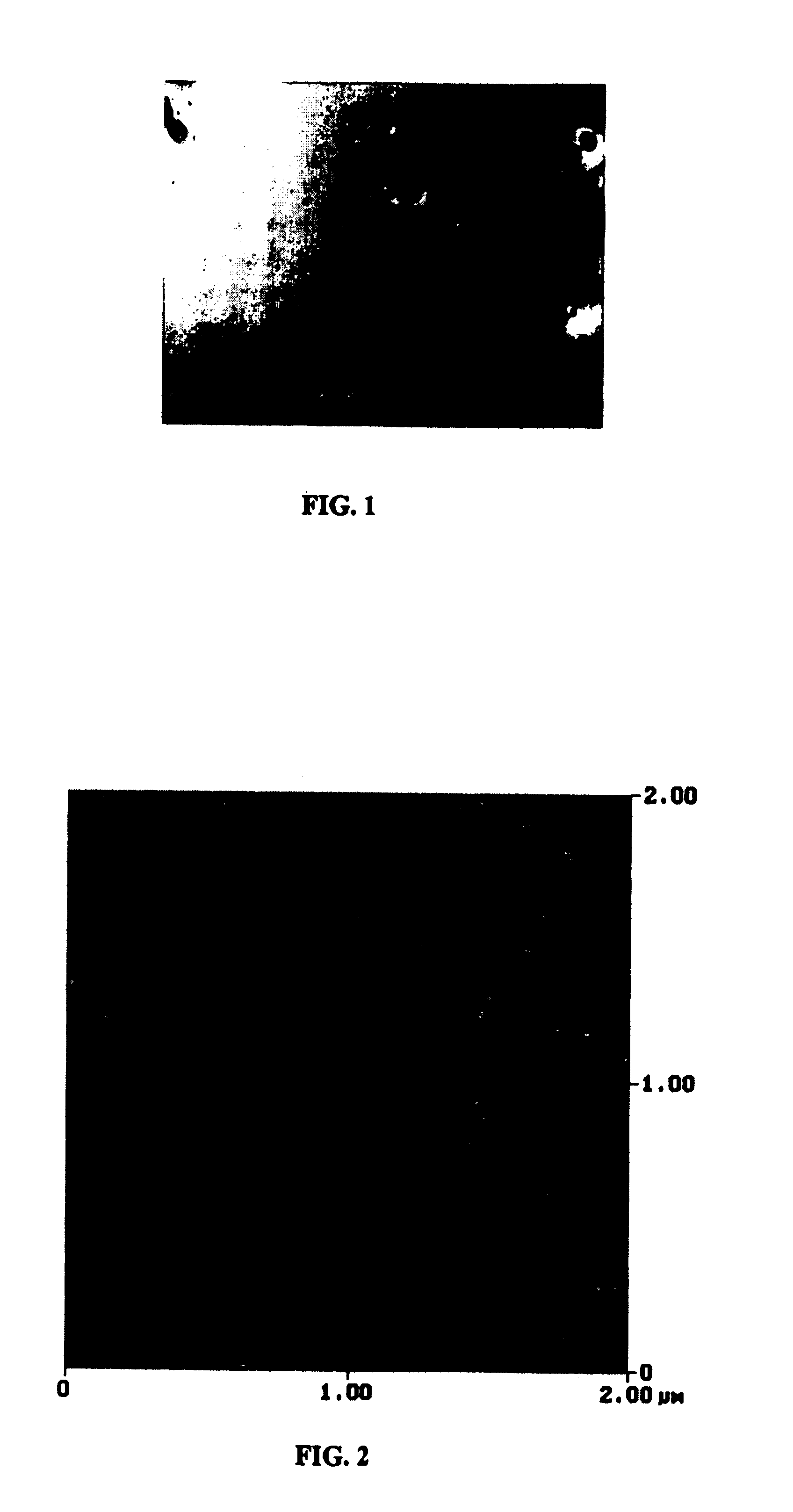
[0136] A GaN film several hundred microns thick was grown on a sapphire substrate by an HVPE process and then separated from the sapphire substrate. The resultantly formed freestanding GaN wafer blank exhibited a textured Ga-surface with a RMS roughness of about 4 nm in a 2×2 μm area.
[0137] The GaN wafer blank was then polished at the Ga-side with an acidic silica slurry without undergoing a lapping process.
[0138] After polishing, it was observed that the surface morphology of such GaN wafer was greatly improved, with the textured surface being entirely removed. The RMS roughness was reduced to below 0.3 nm in a 2×2 μm2 area.
example 2
[0139] Thick GaN films with thickness in the range from 200-500 microns were grown on 2″ sapphire substrates by an HVPE process. The GaN films then were separated from the sapphire substrate, to yield freestanding GaN wafer blanks.
[0140] Flats for the GaN films were marked as 30° off the sapphire substrate's flat. The GaN wafer blanks then were sized into wafer shapes with diameter of 30, 35, and 40 mm using a particle beam jet. To prevent wafer breakage during wafer sizing, it was preferable to mount the GaN wafer on a glass plate of at least 1 mm thickness, using wax.
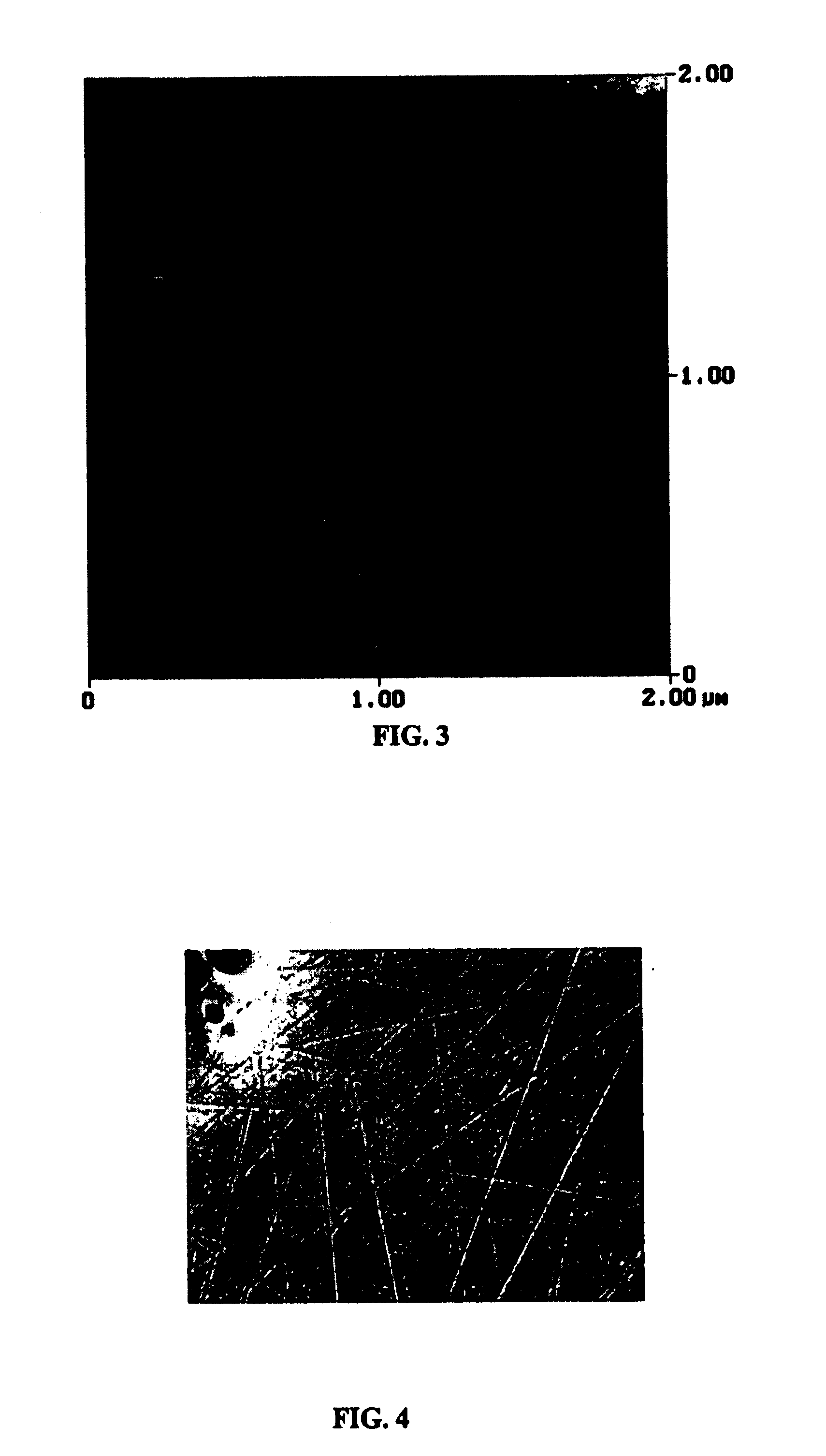
[0141] Nine GaN wafers were mounted on a lap fixture with wax with the N-side facing the lap fixture. A steel block was placed on top of each wafer while the wax cooled. The GaN wafers were first lapped on the Ga-side with diamond slurry of 9 μm in diameter on a cast iron lapping plate. Before lapping, a large thickness variation existed between the wafers and within each wafer. After lapping, uniformity of wafer th...
example 3
[0144] Three GaN wafer blanks were mounted on a lap fixture with wax with the Ga-side facing the lap fixture. A steel block was placed on top of each wafer while the wax cooled. The GaN wafers were first lapped on the N-side with diamond slurry of 9 μm in diameter on a Lapmaster 15 lapping machine with cast iron lapping plate until a uniform mat finish was achieved.
[0145] After the N-side was lapped, the GaN wafers were removed from the lap fixture by heating on a hot plate. The wafers were cleaned and mounted on a lap fixture with wax with the N-side facing the lap fixture. A steel block was placed on top of each wafer while the wax cooled. The GaN wafers were lapped on the Ga-side with diamond slurry of 9 μm in diameter on a cast iron lapping plate until a desirable wafer thickness was obtained. Subsequently, the GaN wafers were lapped with diamond slurry of 6 μm in diameter on a copper lapping plate until surface features from the previous lapping step were removed.
[0146] After...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| RMS surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com