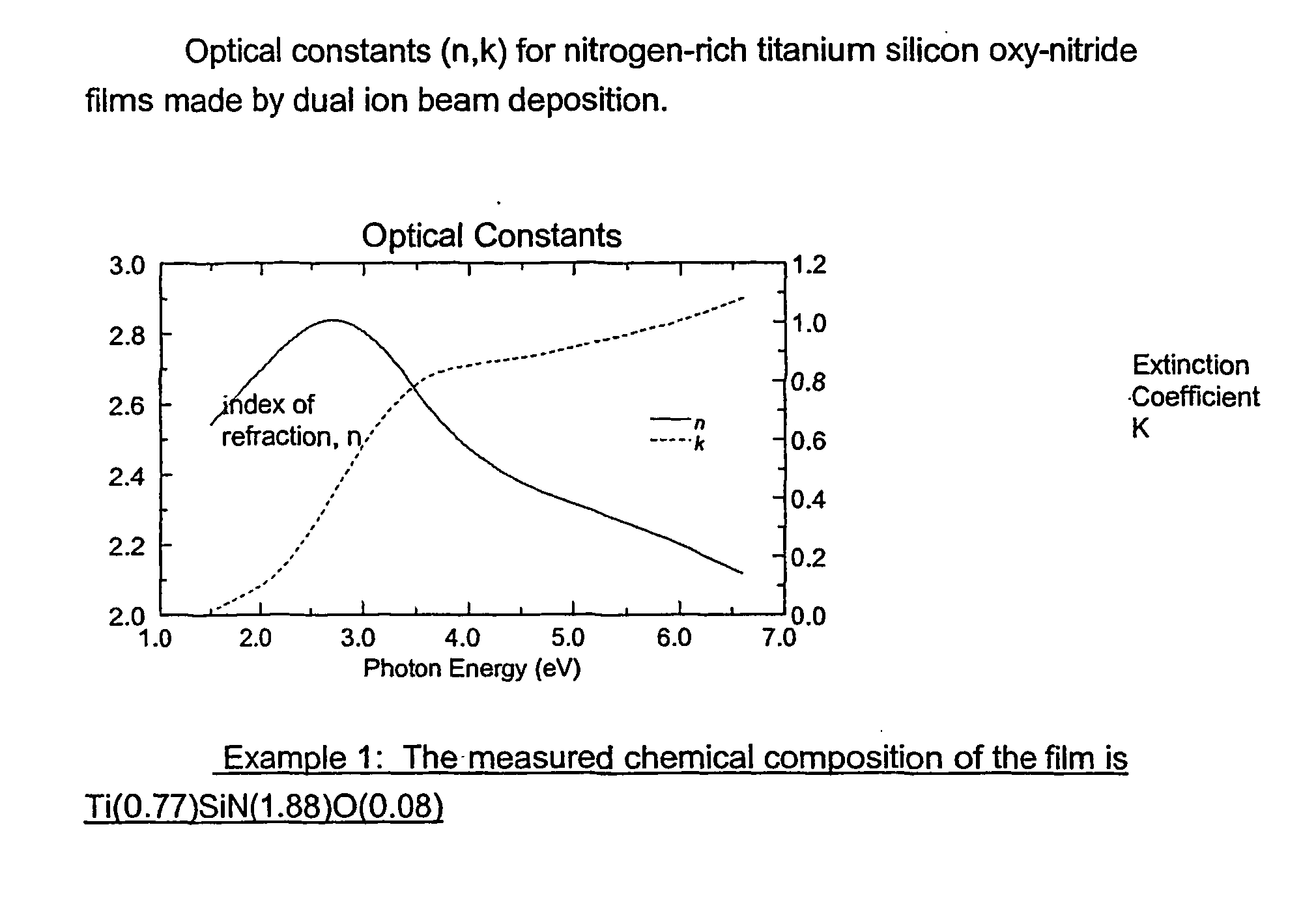
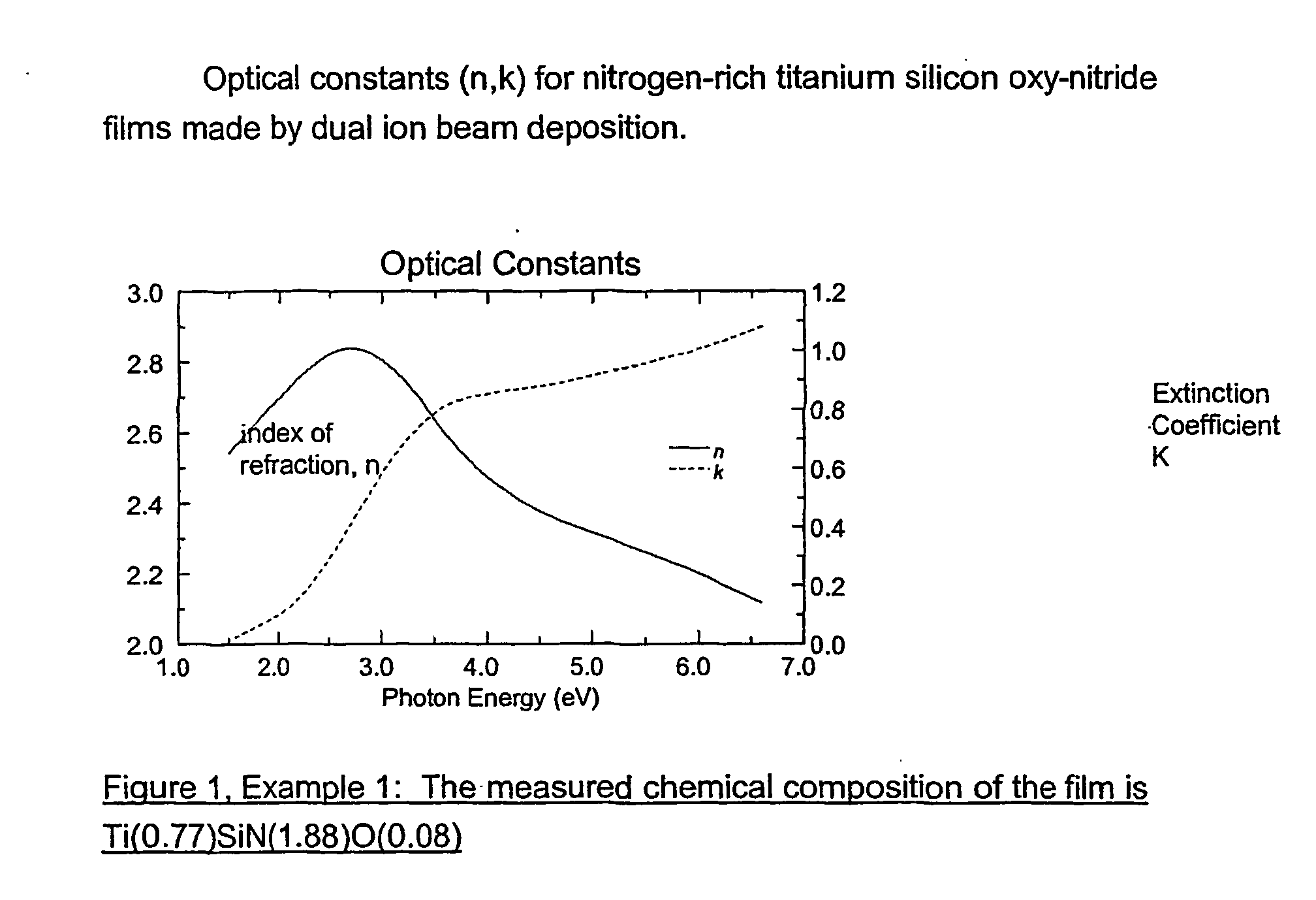
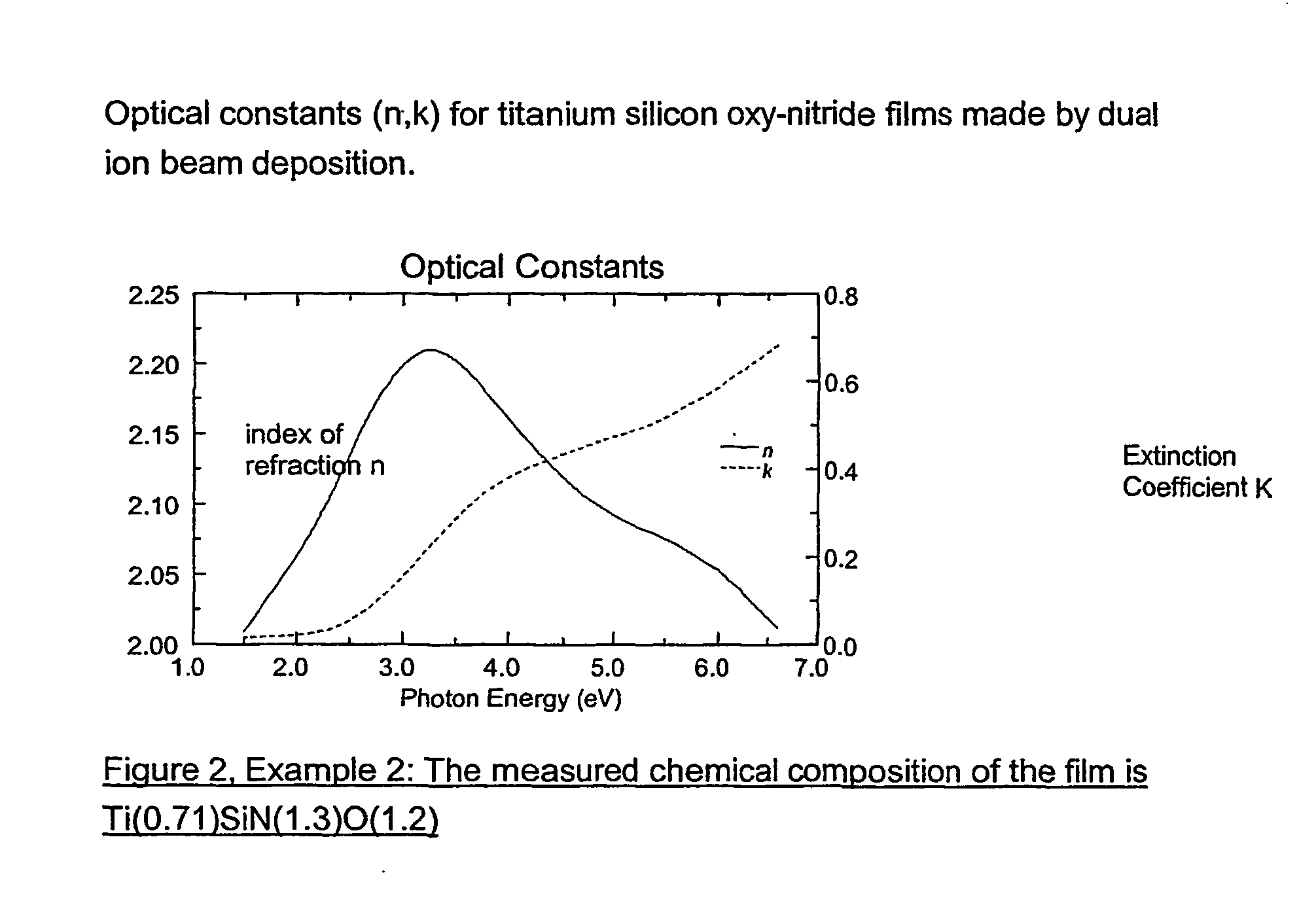
Patents
Literature
163 results about "Ion beam deposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
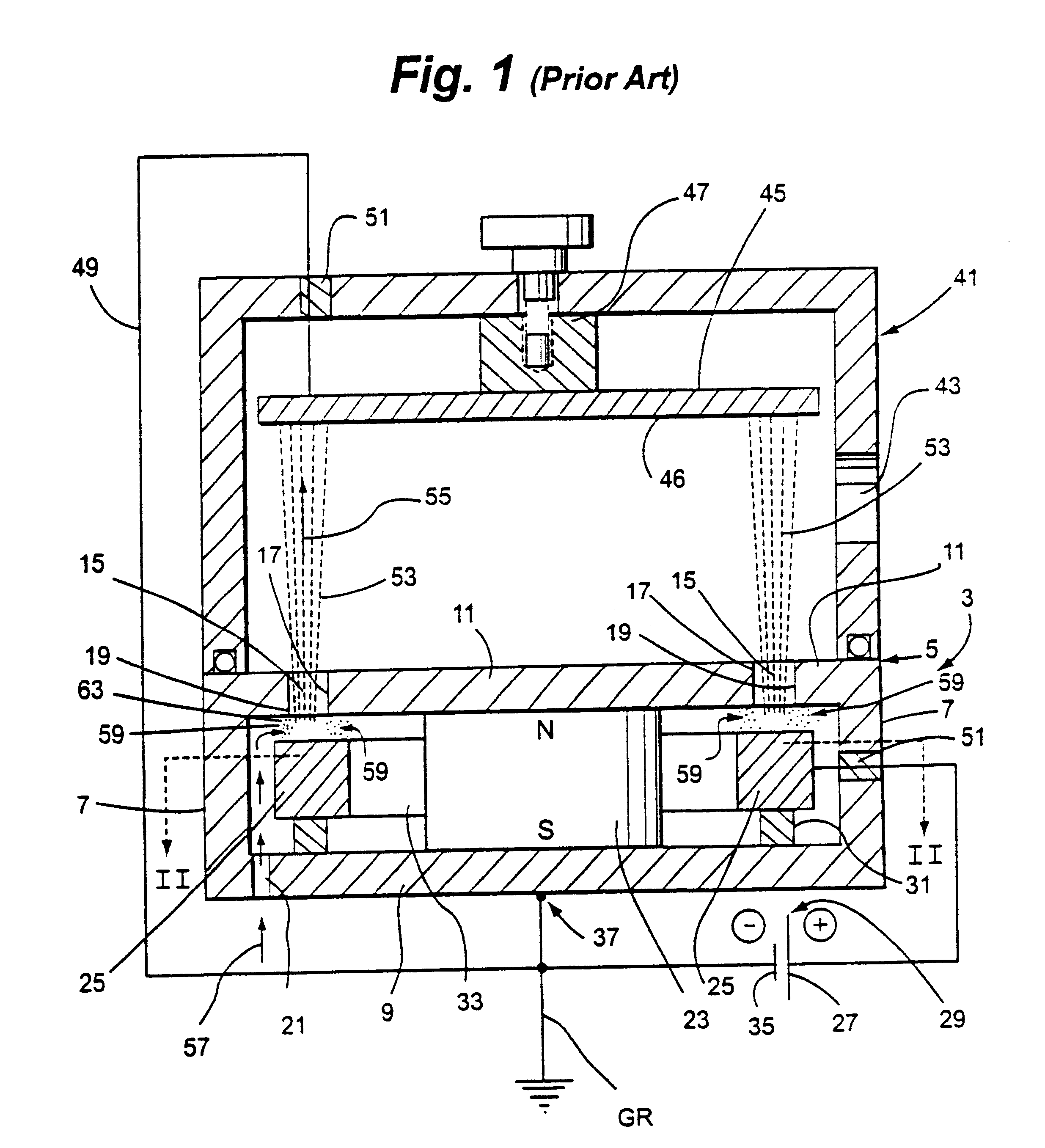
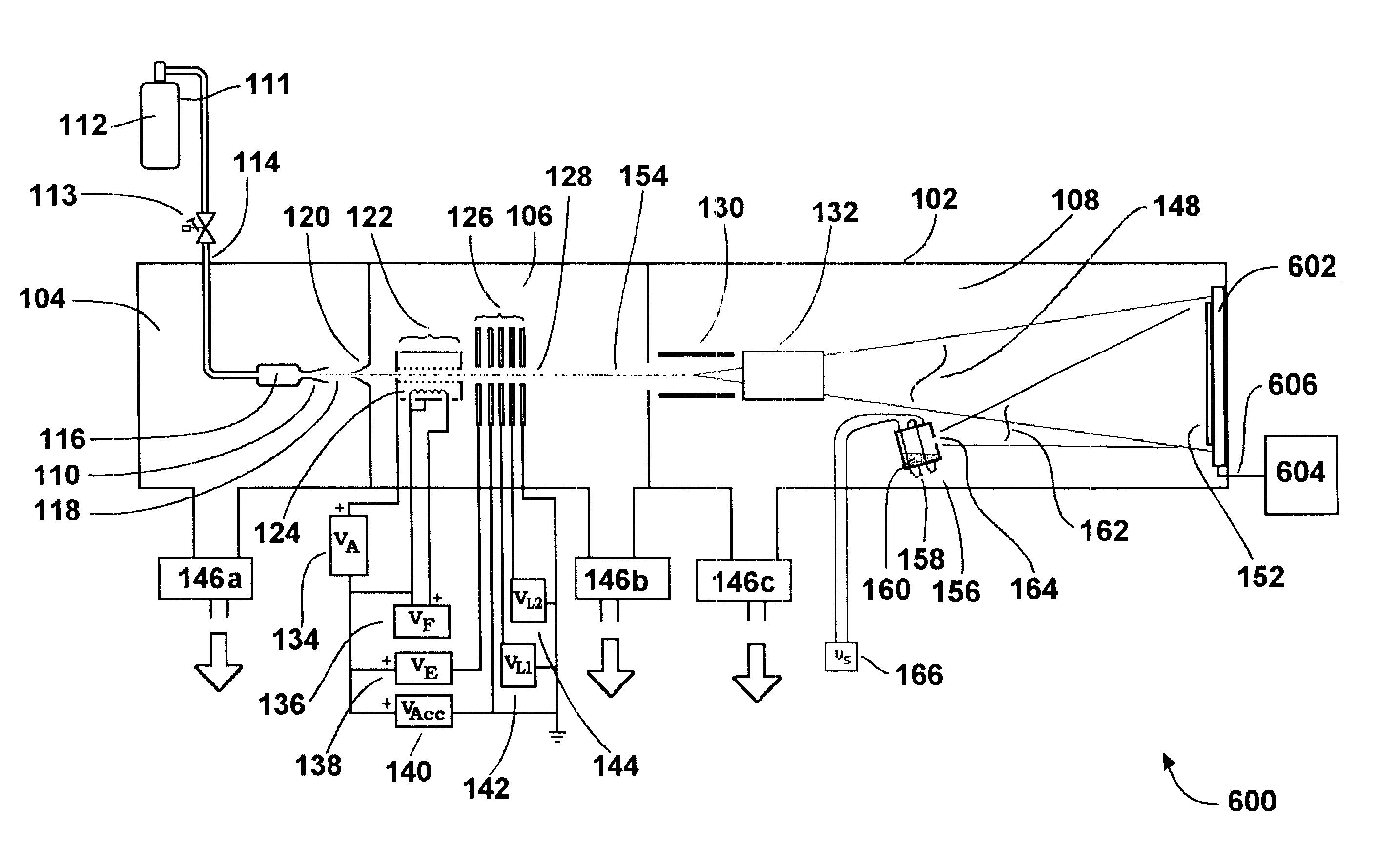
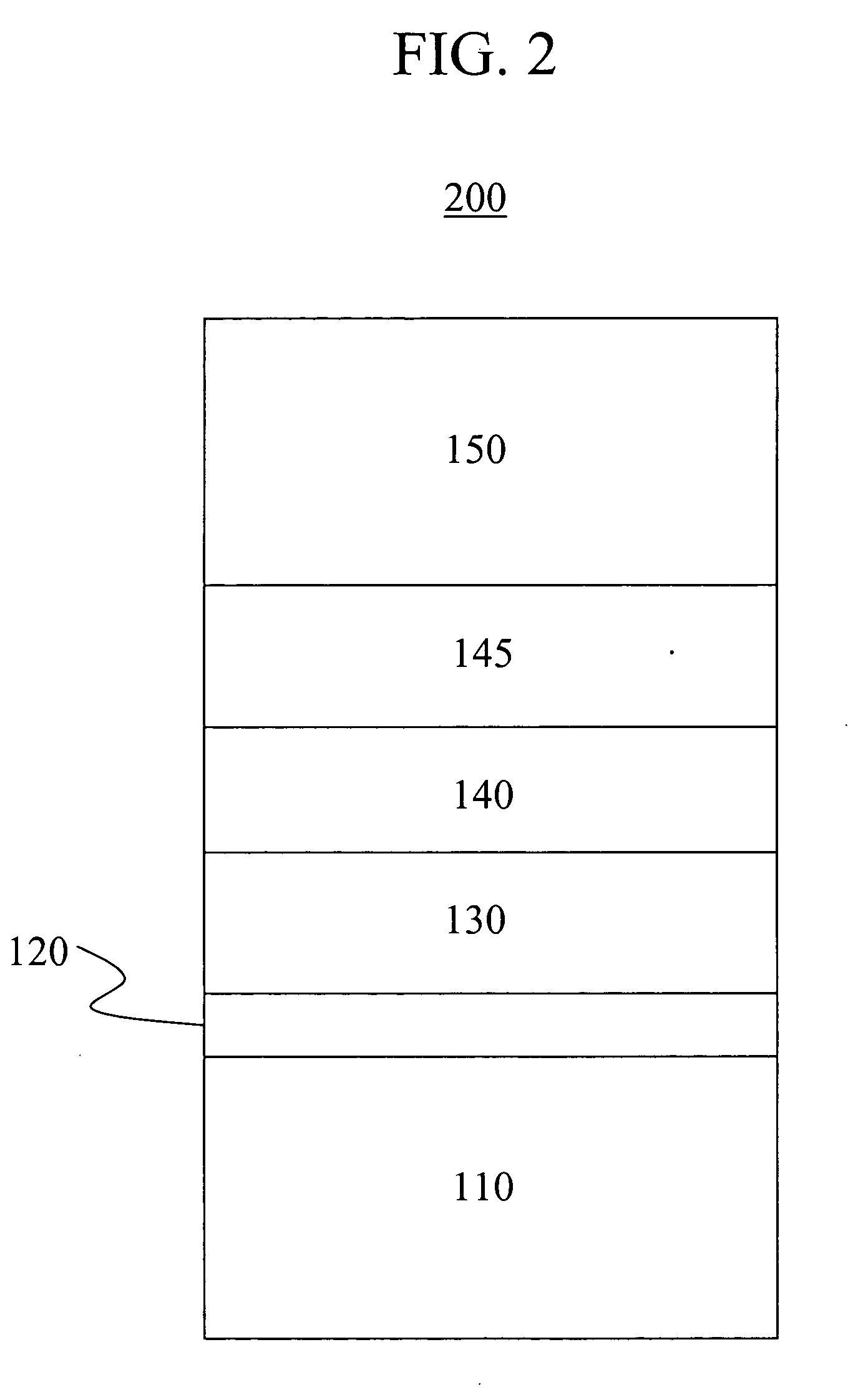
Ion beam deposition (IBD) is a process of applying materials to a target through the application of an ion beam. An ion beam deposition apparatus typically consists of an ion source, ion optics and the deposition target. Optionally a mass analyzer can be incorporated.
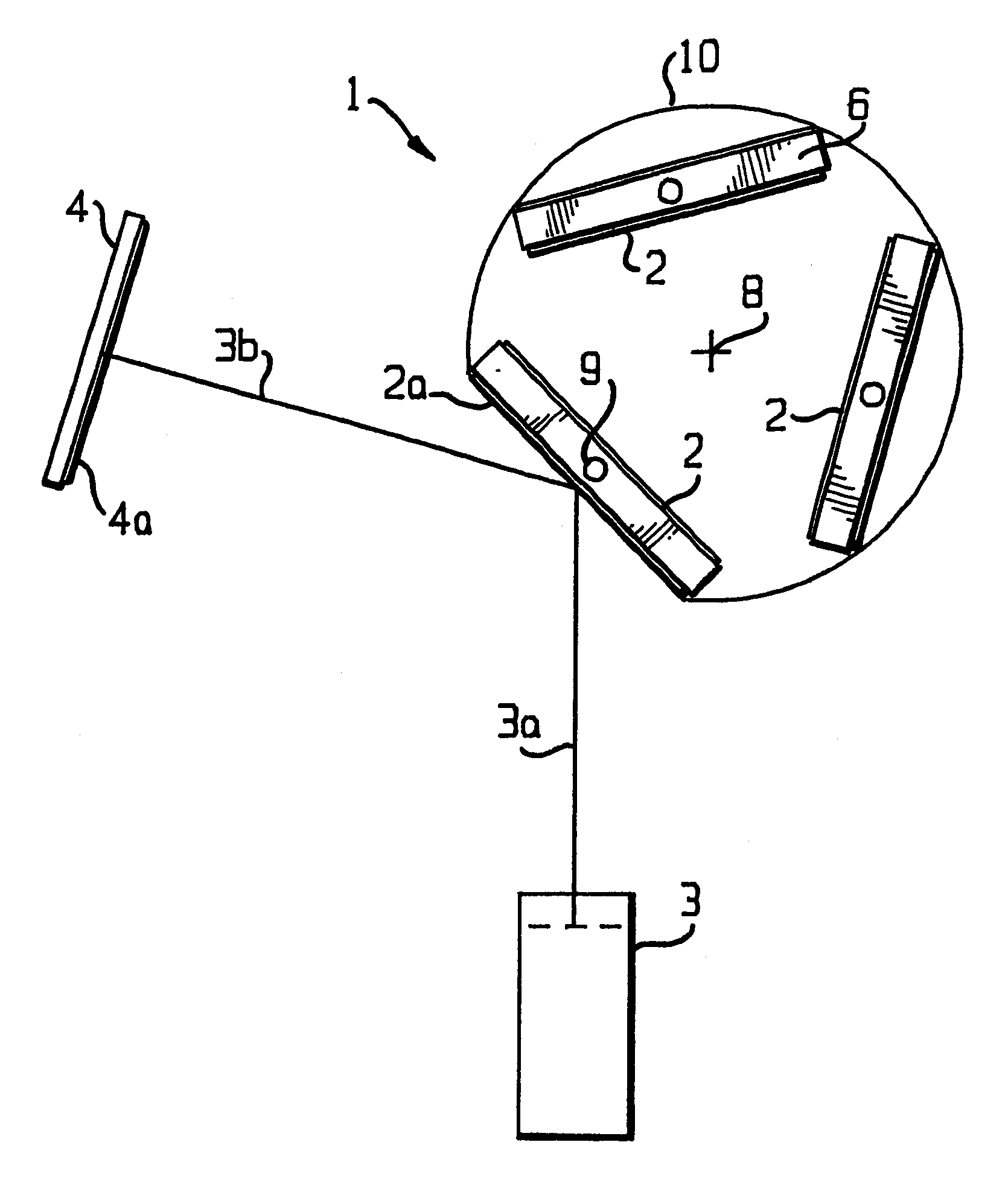
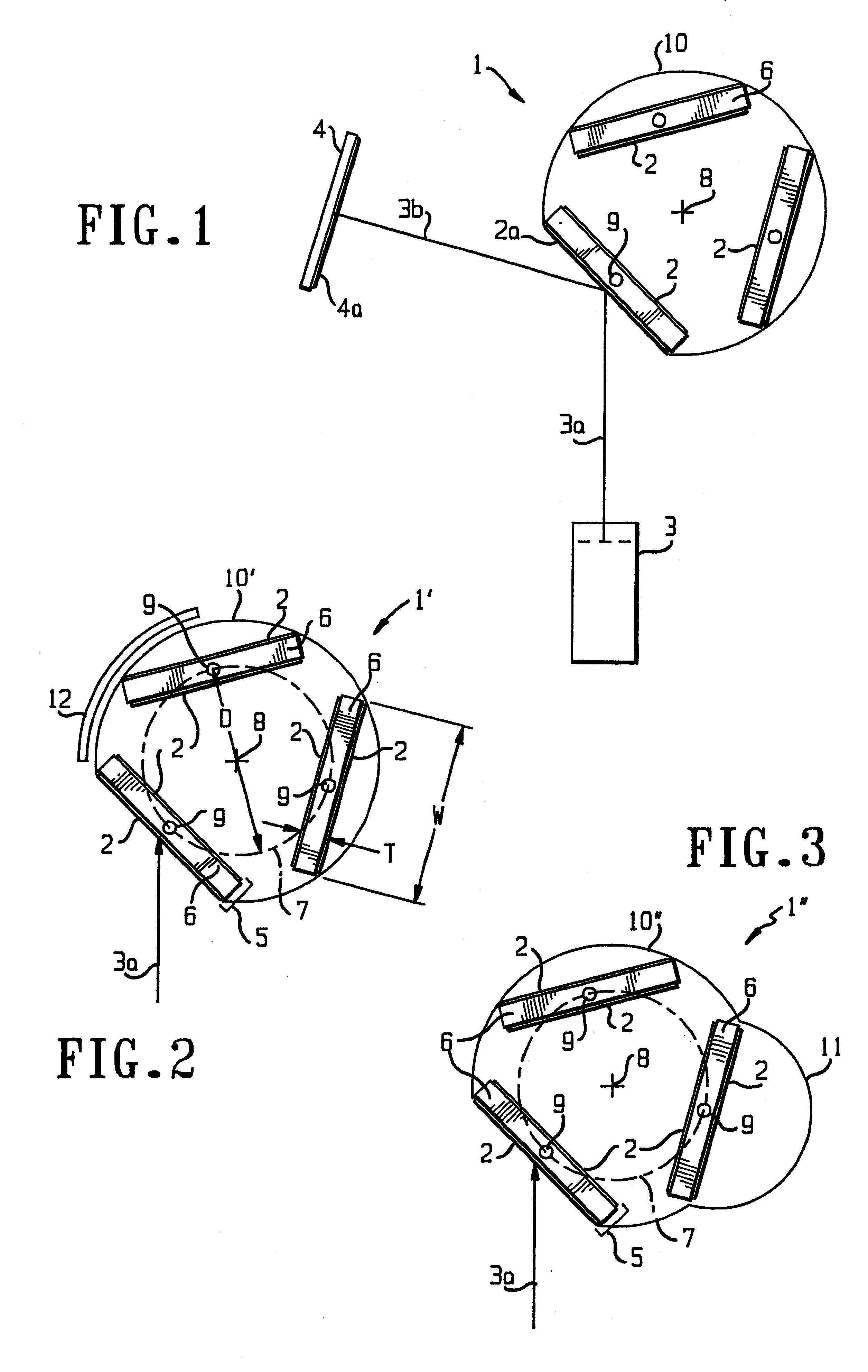
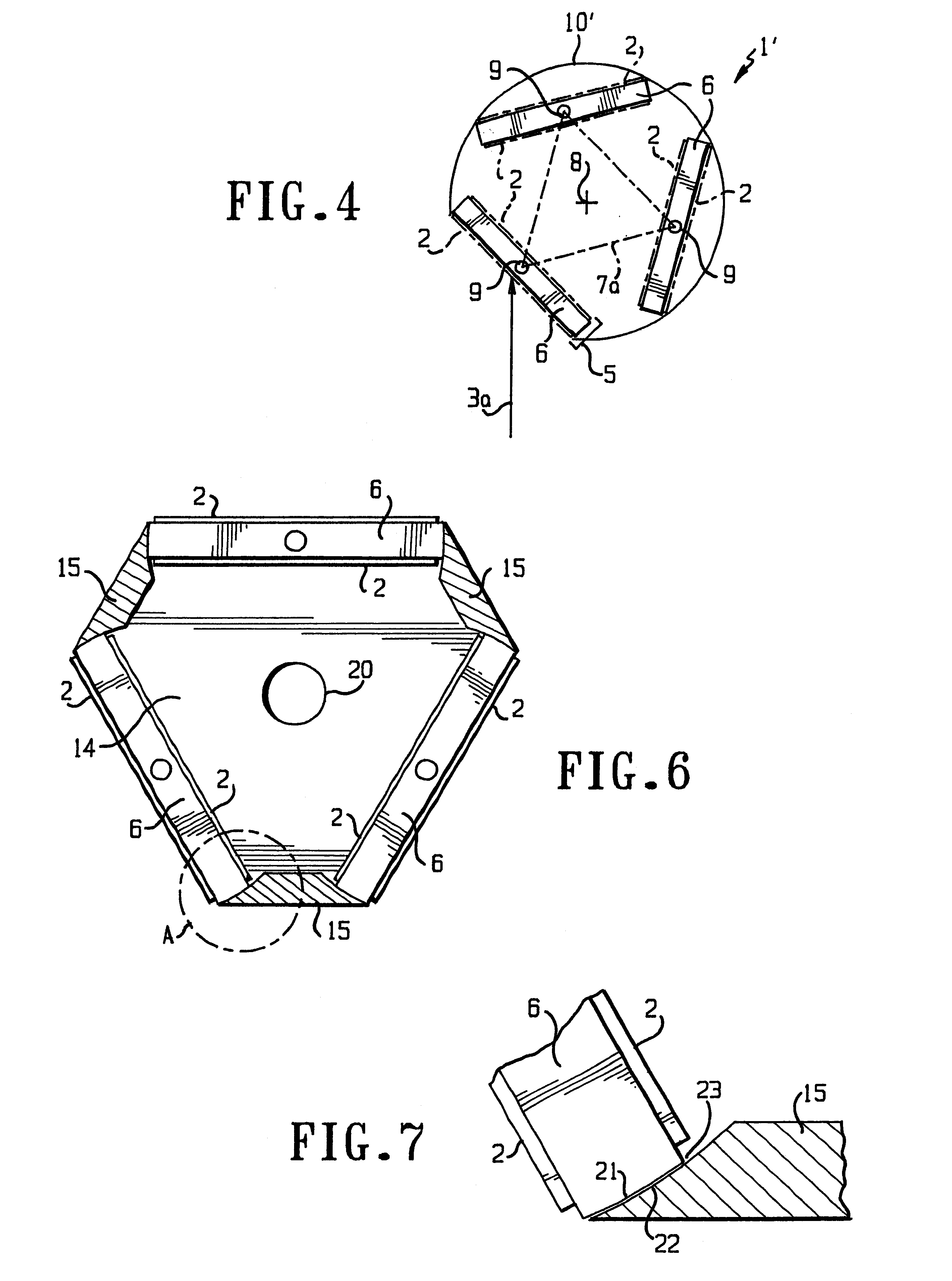
Target assembly for ion beam sputter deposition with multiple paddles each having targets on both sides
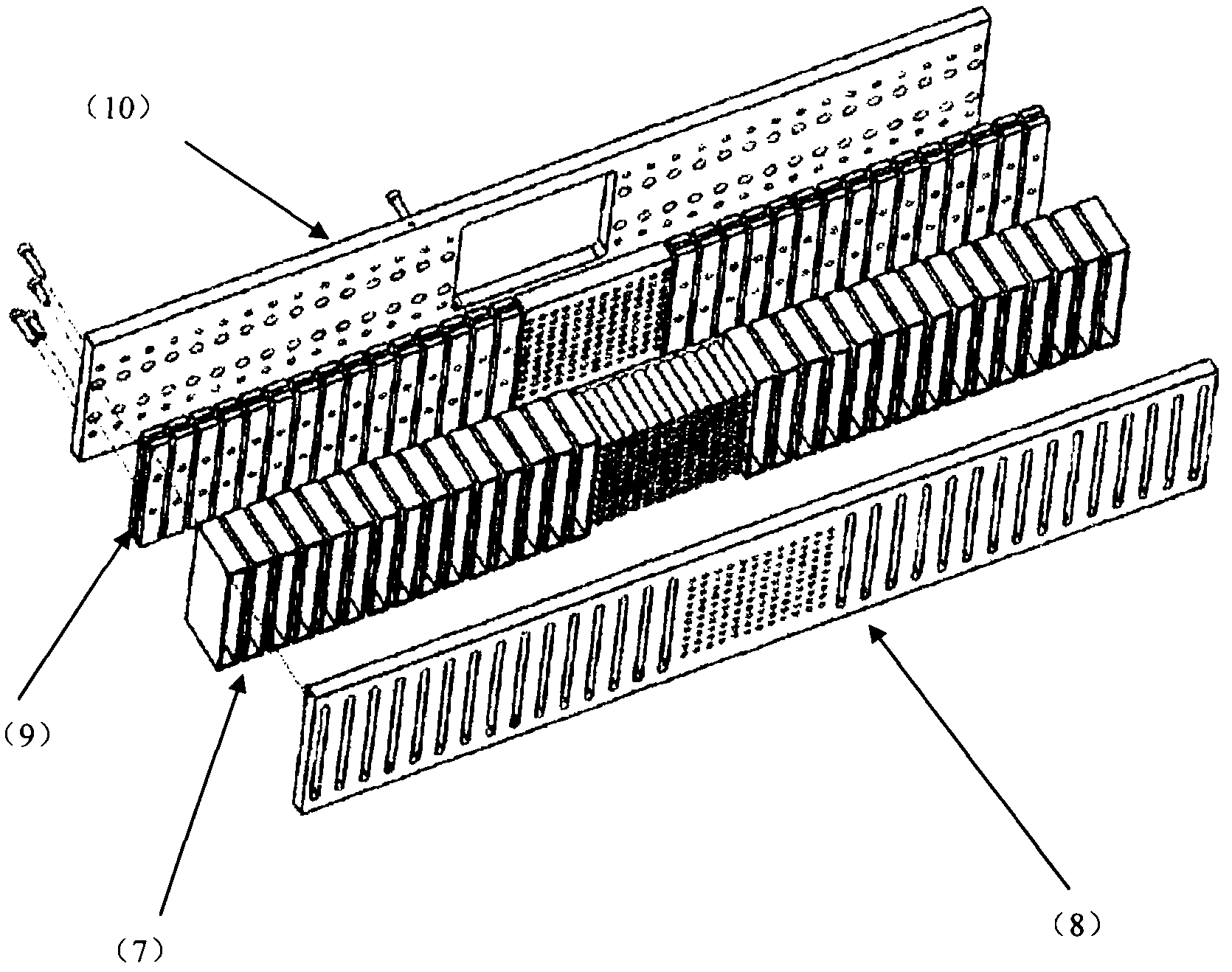
InactiveUS6224718B1Small space volumeSimple designCellsElectric discharge tubesAtomic physicsIon beam deposition
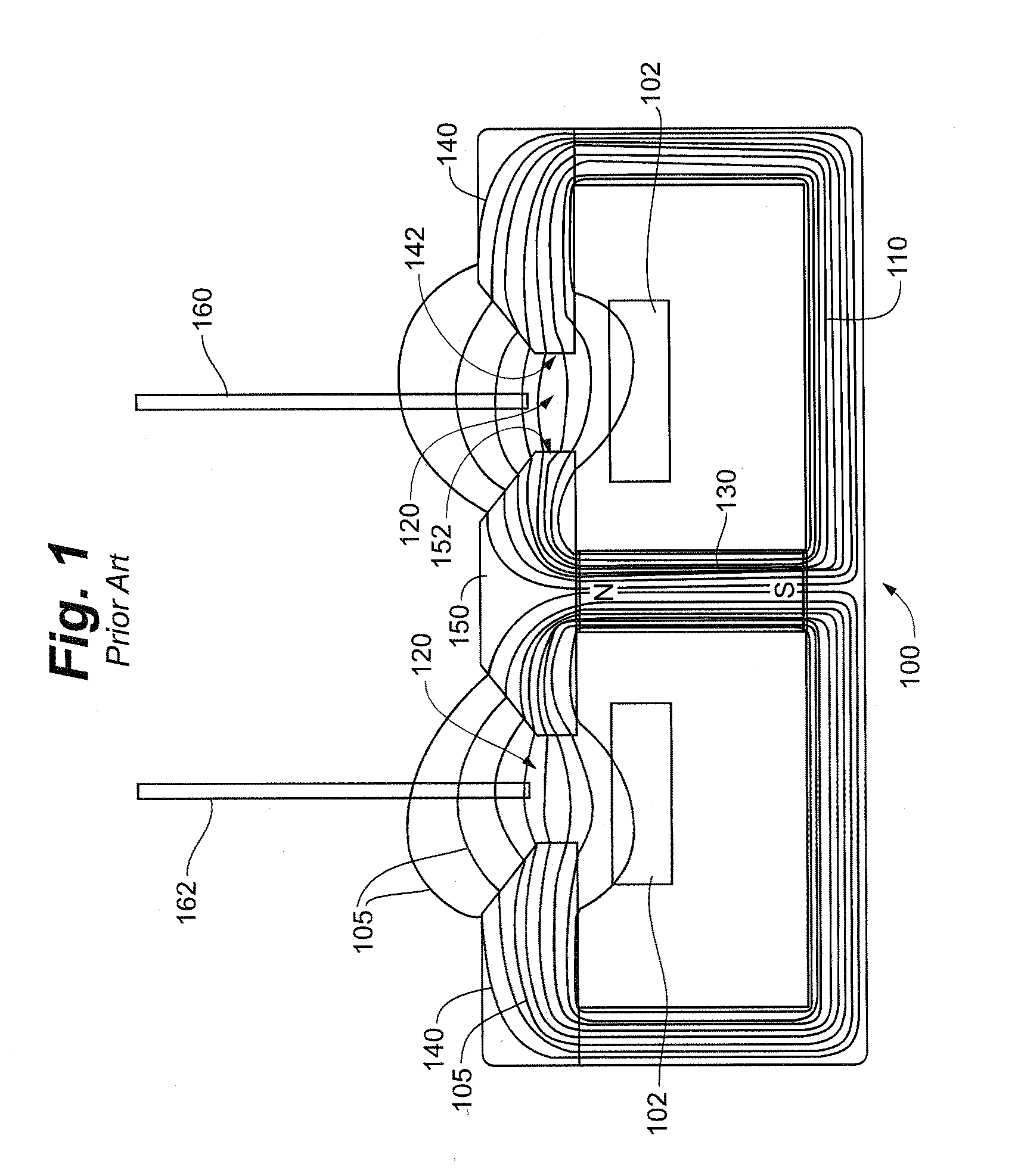
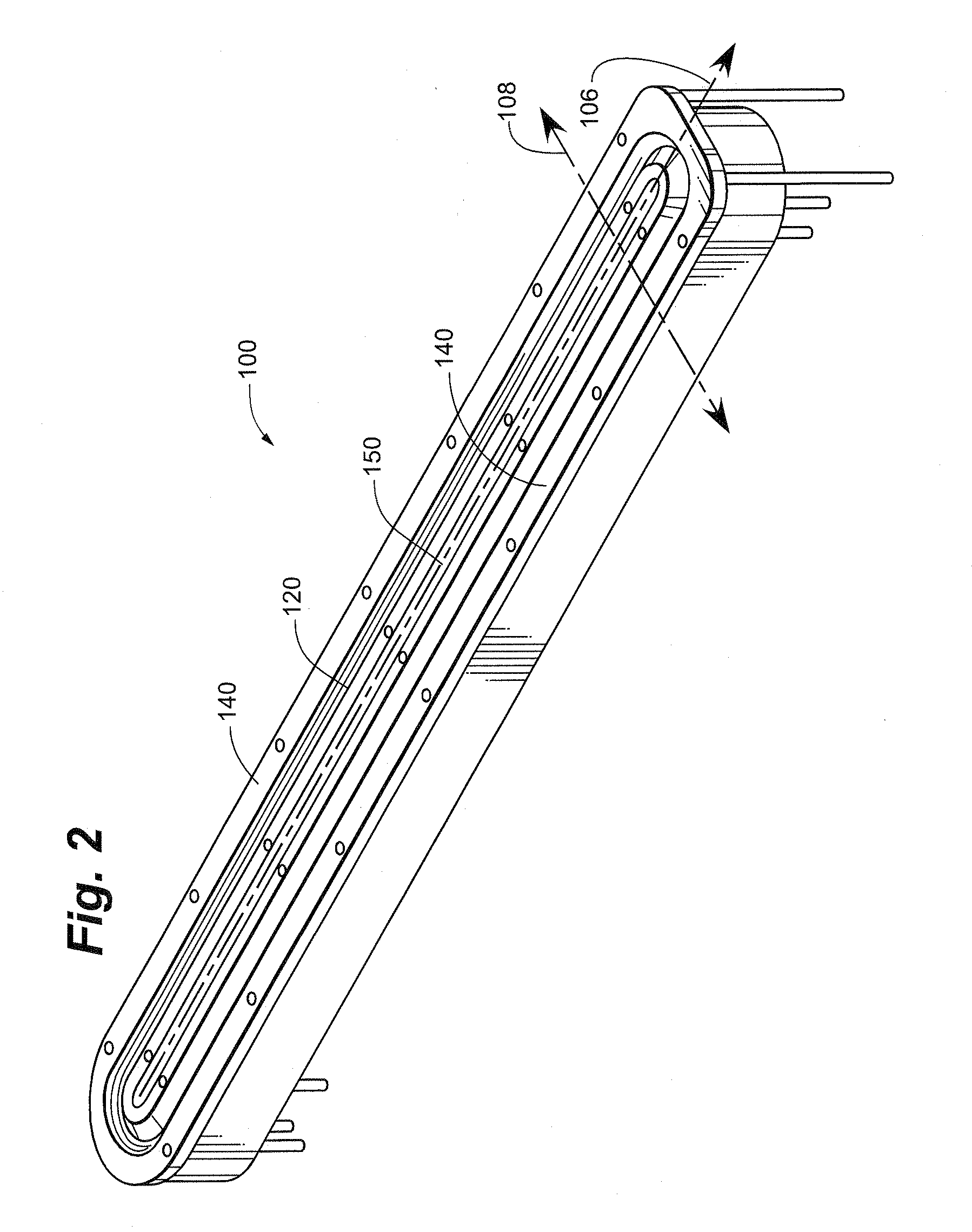
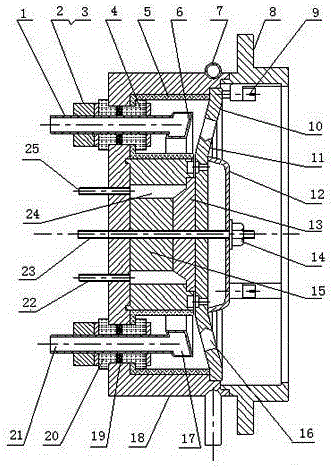
An ion beam sputtering target assembly has six sputter targets arranged in pairs on three paddles and disposed upon the circumference of a circular holder. The circular holder can be rotated about its axis in such a way as to bring any one of the target pairs to be exposed to the sputtering ion beam to deposit a film on substrate. The paddle is rotated to bring a desired target in the pair into position for sputtering. An alternative embodiment is provided with an enlarged region which allows one of the target paddles to be rotated about its axis while that target paddle is in an inactive, non-sputtering rotary position.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Cold cathode ion beam deposition apparatus with segregated gas flow
InactiveUSRE38358E1Reduce the possibilityVacuum evaporation coatingElectric arc lampsCold cathodeProduct gas
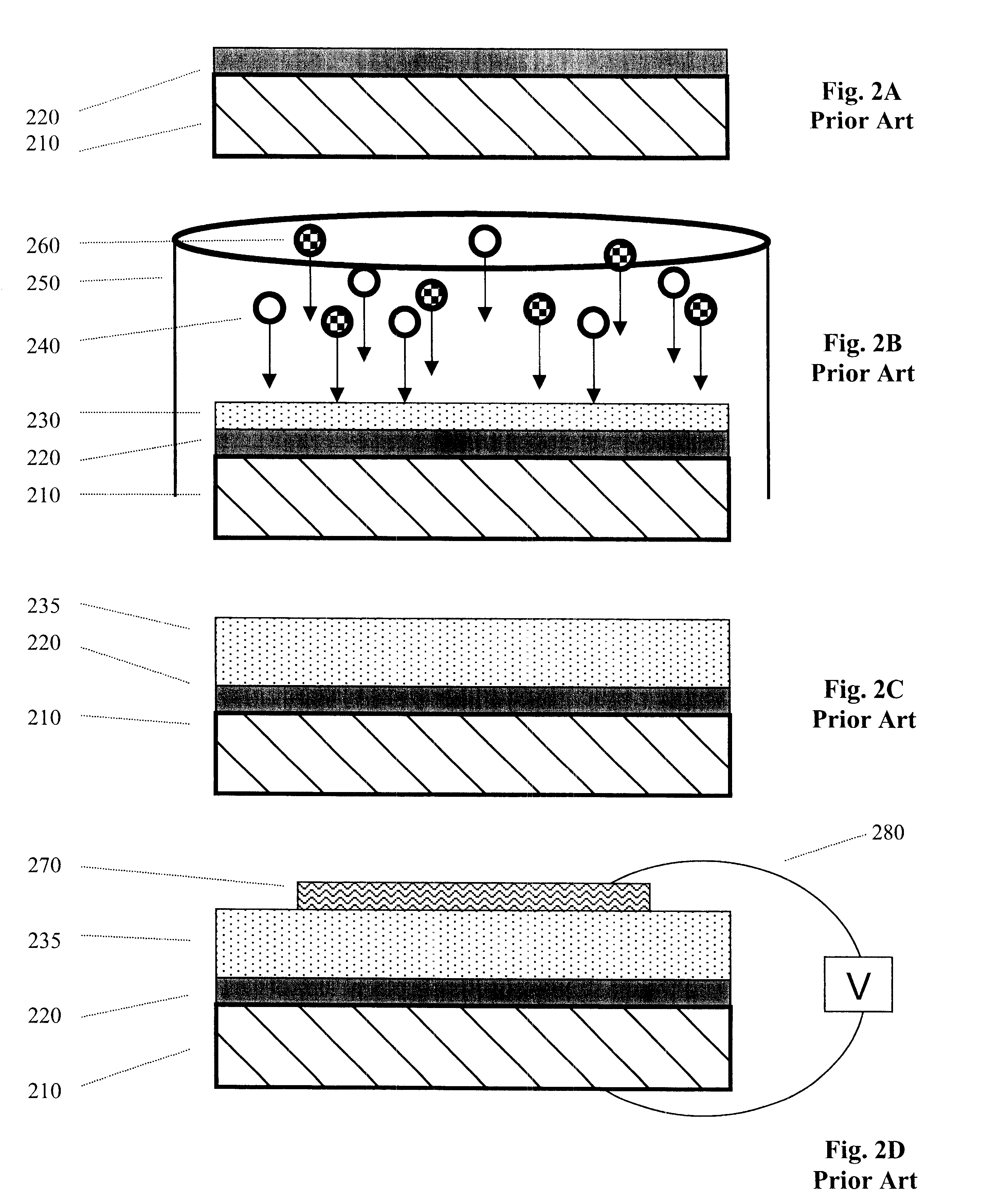
A cold cathode closed drift ion source is provided with segregated gas flow. A first gas may be caused to flow through or along a path around a peripheral portion of an anode so as to pass through the electric gap between the anode and cathode. A second gas (different from the first gas) may be caused to flow toward the ion emitting slit, without much of the second gas having to pass through the electric gap(s). If it is desired to utilize a gas which produces insulative material (e.g., an organosilicon gas), this gas may be used as the second gas. Accordingly, insulative material buildup in the electric gap between the anode and cathode may be reduced, and changes in beam chemistry can be achieved without unduly altering ion beam characteristics.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Method for preparing multi-metal element doped diamond film
InactiveCN101787512AImprove performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCathodic arc depositionIon bombardment
The invention discloses a method for preparing a multi-metal element doped diamond film, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: removing a pollution layer on matrix surface by using the ultrasonic cleaning technology, carrying out ion beam bombardment cleaning on the matrix surface by using inert gas ion beam produced by an ion source, carrying out metal ion bombardment cleaning on the matrix surface by using metal ions produced by a cathodic arc source under a condition of high workpiece negative bias, preparing a gradient transition layer by using a cathodic arc deposition or ion beam assisted magnetron sputtering (IBAMS), and synthesizing a multi-metal element doped DLC film on the transition layer by using ion beam deposition and mosaic composite target magnetron sputtering, wherein the ion beam deposition is realized by introducing carbon gas in the ion source; and the mosaic composite target doped multiple metal are used, and the main body material of the mosaic composite target can be any one of Ti, Cr, W, Zr, Nb and Ta, and the mosaic block material is one or more of other metals except the above main body materials.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Interface control for film deposition by gas-cluster ion-beam processing
InactiveUS6498107B1Improve practicalitySimple interfaceTransistorElectric discharge tubesIon beam depositionReactive deposition
Methods are disclosed for gas-cluster ion-beam deposition of thin films on silicon wafers rendered free of native oxides by termination of the surface bonds and subsequent reactive deposition. Hydrogen termination of the surface of silicon renders it inert to reoxidation from oxygen-containing environmental gasses, even those found as residue in vacuum systems, such as those used to deposit films. Nitrogen termination improves the interface with overlying metal-oxide thin films. The film is formed in intimate contact with the silicon crystal surface forming a nearly ideal interface.
Owner:JDSU OPTICAL
Sputter coating apparatus including ion beam source(s), and corresponding method
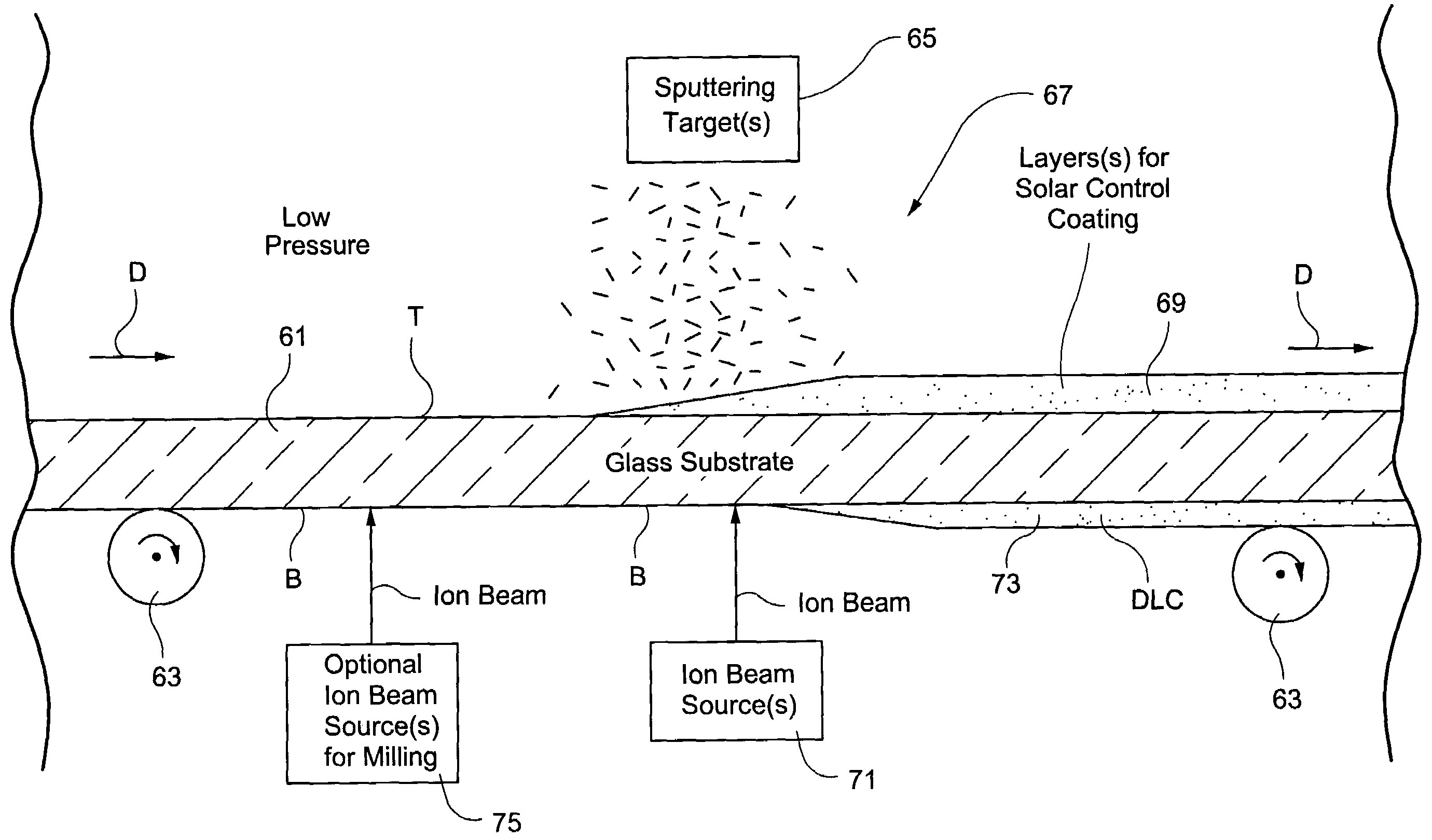
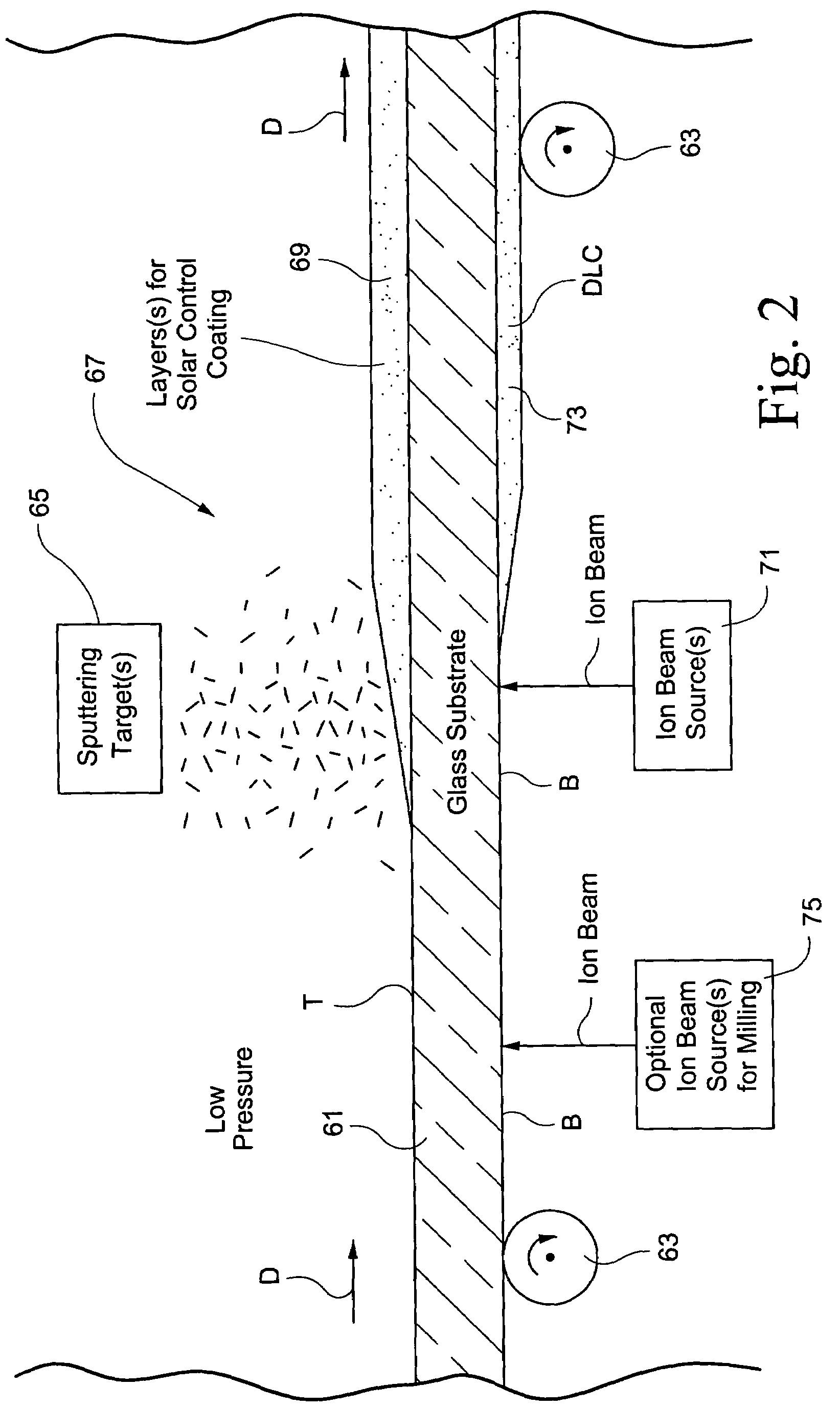
A coating apparatus deposits a first coating (single or multi-layered) onto a first side of a substrate (e.g., glass substrate) passing through the apparatus, and a second coating (single or multi-layered) onto the other or second side of the substrate. In certain example embodiments, the first coating may be deposited via sputtering while the second coating is deposited via ion beam deposition. In such a manner, it is possible to coat both sides of the substrate in a single apparatus in an efficient manner. In other embodiments, the coating apparatus may sputter a coating onto a first side of the substrate and ion beam mill at least one surface of the substrate as the substrate passes through the coating apparatus. In other embodiments of this invention, a dual mode chamber may be provided that is adapted to receive a removable ion beam module on one side of a substrate and a removable sputtering module on the other side of the substrate. The different removable modules may or may not be used simultaneously in different embodiments of this invention.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Dynamic mask for producing uniform or graded-thickness thin films
A method for producing single layer or multilayer films with high thickness uniformity or thickness gradients. The method utilizes a moving mask which blocks some of the flux from a sputter target or evaporation source before it deposits on a substrate. The velocity and position of the mask is computer controlled to precisely tailor the film thickness distribution. The method is applicable to any type of vapor deposition system, but is particularly useful for ion beam sputter deposition and evaporation deposition; and enables a high degree of uniformity for ion beam deposition, even for near-normal incidence of deposition species, which may be critical for producing low-defect multilayer coatings, such as required for masks for extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUVL). The mask can have a variety of shapes, from a simple solid paddle shape to a larger mask with a shaped hole through which the flux passes. The motion of the mask can be linear or rotational, and the mask can be moved to make single or multiple passes in front of the substrate per layer, and can pass completely or partially across the substrate.
Owner:EUV
Hydroxylapatite coating magnesium alloy medical inner implantation material and method of preparing the same
The invention relates to a hydroxyapatite coating magnesium alloy medical implantation material and a preparation method thereof. The hydroxyapatite coating magnesium alloy medical implantation material is characterized in that: the surface of a magnesium alloy substrate is attached with a hydroxyapatite coating layer. The preparation method of the hydroxyapatite coating magnesium alloy medical implant material can adopt the bionic solution growing method, the ion beam deposition method, the coating and sintering process, the plasma spray method, the discharge plasma sintering method or the electrophoresis deposition method. The magnesium alloy material with the hydroxyapatite coating structure which is provided by the invention can effectively slow down the degradation rate of the magnesium alloy; at the same time, the coating layer can not only have great tissue compatibility, but can also be conductive to connective tissue attachment and the growth of the bone tissues, improve the bone healing rate and shorten the healing time.
Owner:BEIJING ALLGENS MEDICAL SCI & TECH +1
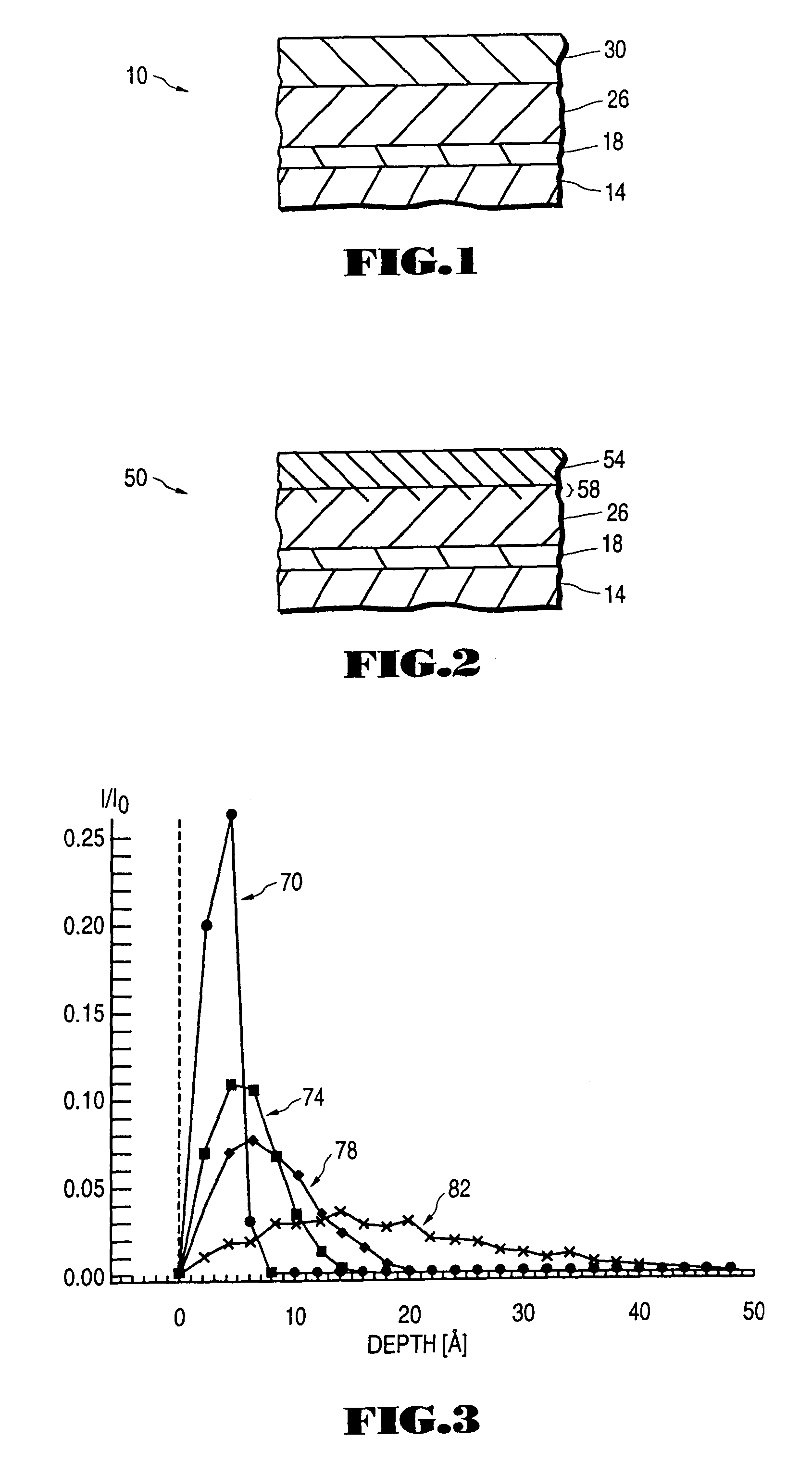
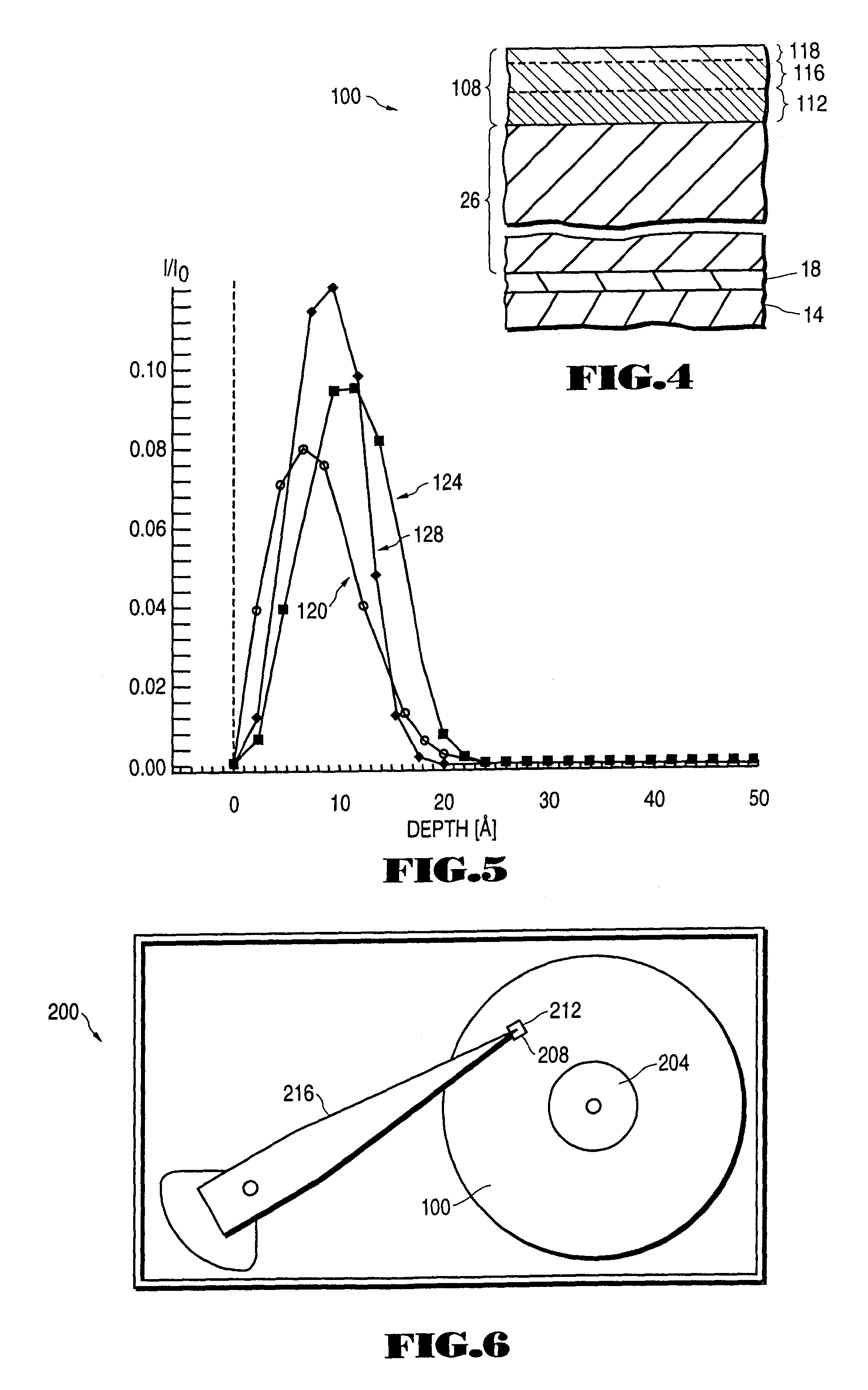
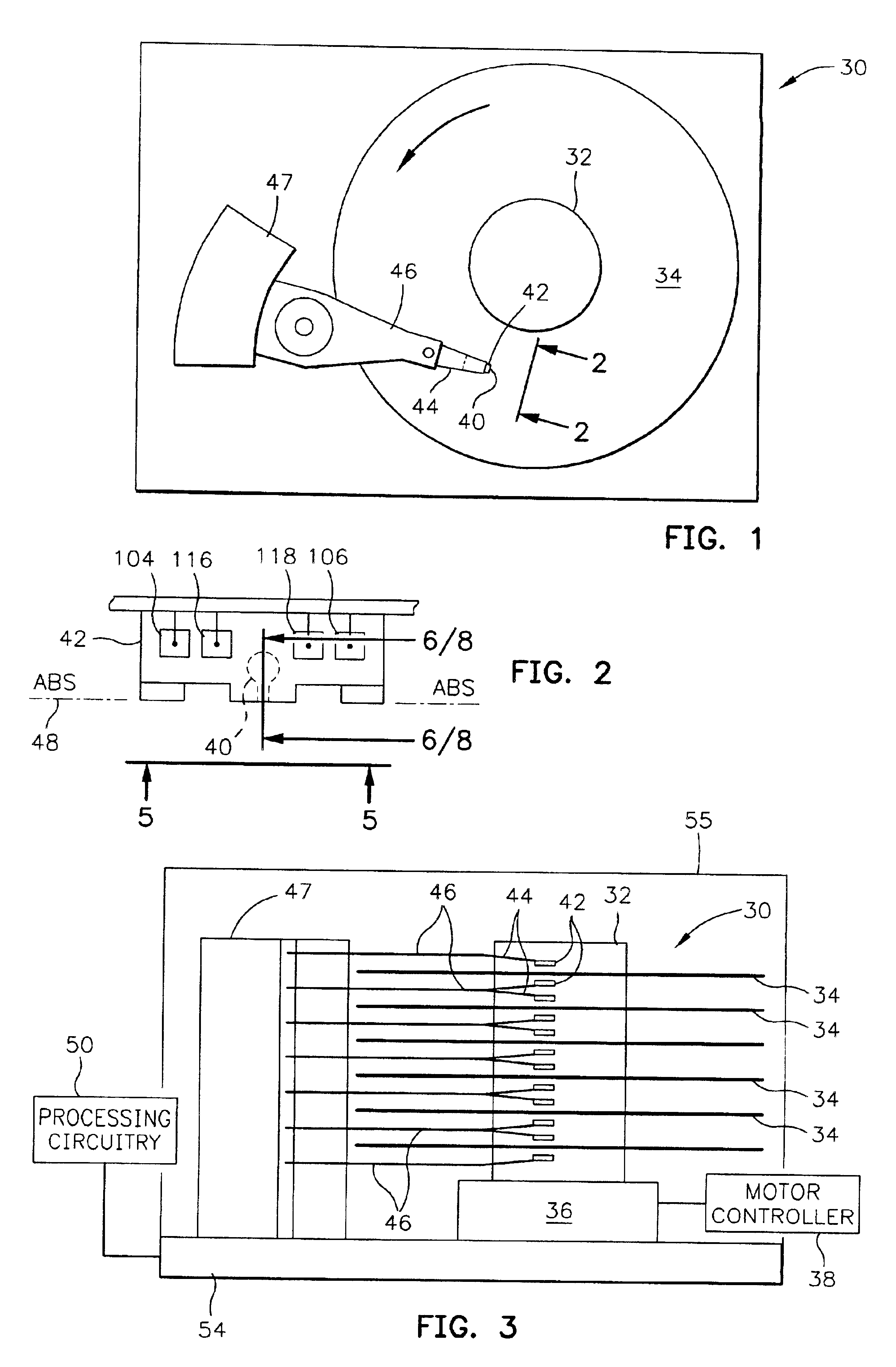
Energy gradient ion beam deposition of carbon overcoats on rigid disk media for magnetic recordings
InactiveUS7018729B2Good mechanical and corrosion protectionWithout degrading magnetic property of magneticVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringEnergy gradient
The fabrication of the overcoat layer starts with a low energy ion beam to avoid magnetic layer implantation problems, followed by higher deposition energies where the higher energy atoms are implanted into the previously formed lower energy overcoat layer, rather than the magnetic layer. The energy gradient ion beam deposition process therefore results in a thin overcoat layer that is denser than a comparable layer formed by low energy magnetron sputtering, and which overcoat layer provides good mechanical and corrosion protection to the magnetic layer, without degrading the magnetic properties of the magnetic layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Ion beam process for deposition of highly abrasion-resistant coatings
InactiveUSRE37294E1High hardnessReduce coefficient of frictionLayered productsVacuum evaporation coatingEye lensVacuum chamber
An ion beam deposition method is provided for manufacturing a coated substrate with improved abrasion resistance, and improved lifetime. According to the method, the substrate is first chemically cleaned to remove contaminants. In the second step, the substrate is inserted into a vacuum chamber, and the air in said chamber is evacuated. In the third step, the substrate surface is bombarded with energetic ions to assist in the removal of residual hydrocarbons and surface oxides, and to activate the surface. <DEL-S DATE="20010724" ID="DEL-S-00001">Alter<DEL-E ID="DEL-S-00001"> <INS-S DATE="20010724" ID="INS-S-00001">After <INS-E ID="INS-S-00001">the substrate surface has been sputter-etched, a protective, abrasion-resistant coating is deposited by ion beam deposition. The ion beam-deposited coating may contain one or more layers. Once the chosen thickness of the coating has been achieved, the deposition process on the substrates is terminated, the vacuum chamber pressure is increased to atmospheric pressure, and the coated substrate products having improved abrasion-resistance are removed from the vacuum chamber. The coated products of this invention have utility as plastic sunglass lenses, ophthalmic lenses, bar codes scanner windows, and industrial wear parts that must be protected from scratches and abrasion.
Owner:MORGAN ADVANCED CERAMICS
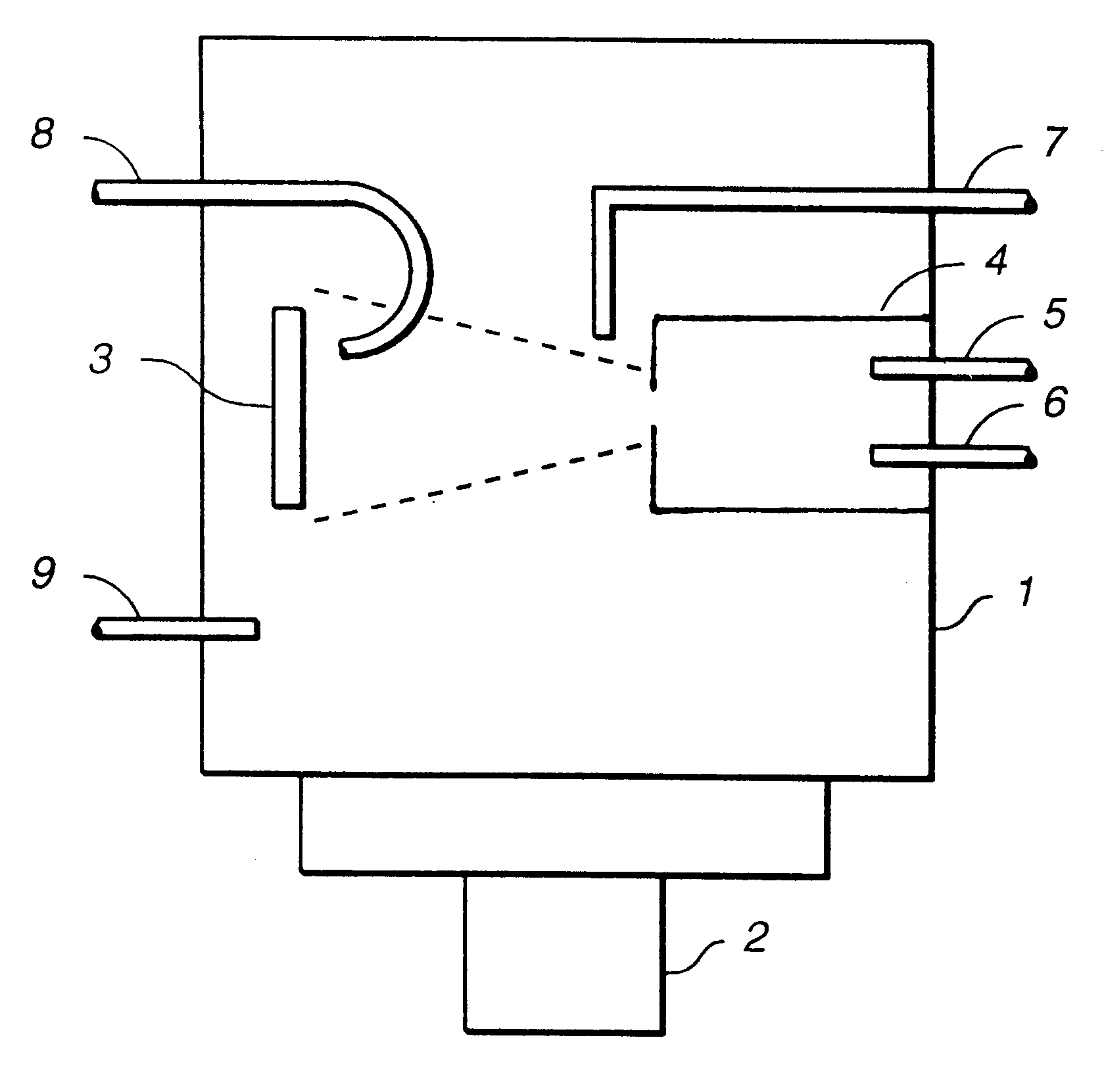
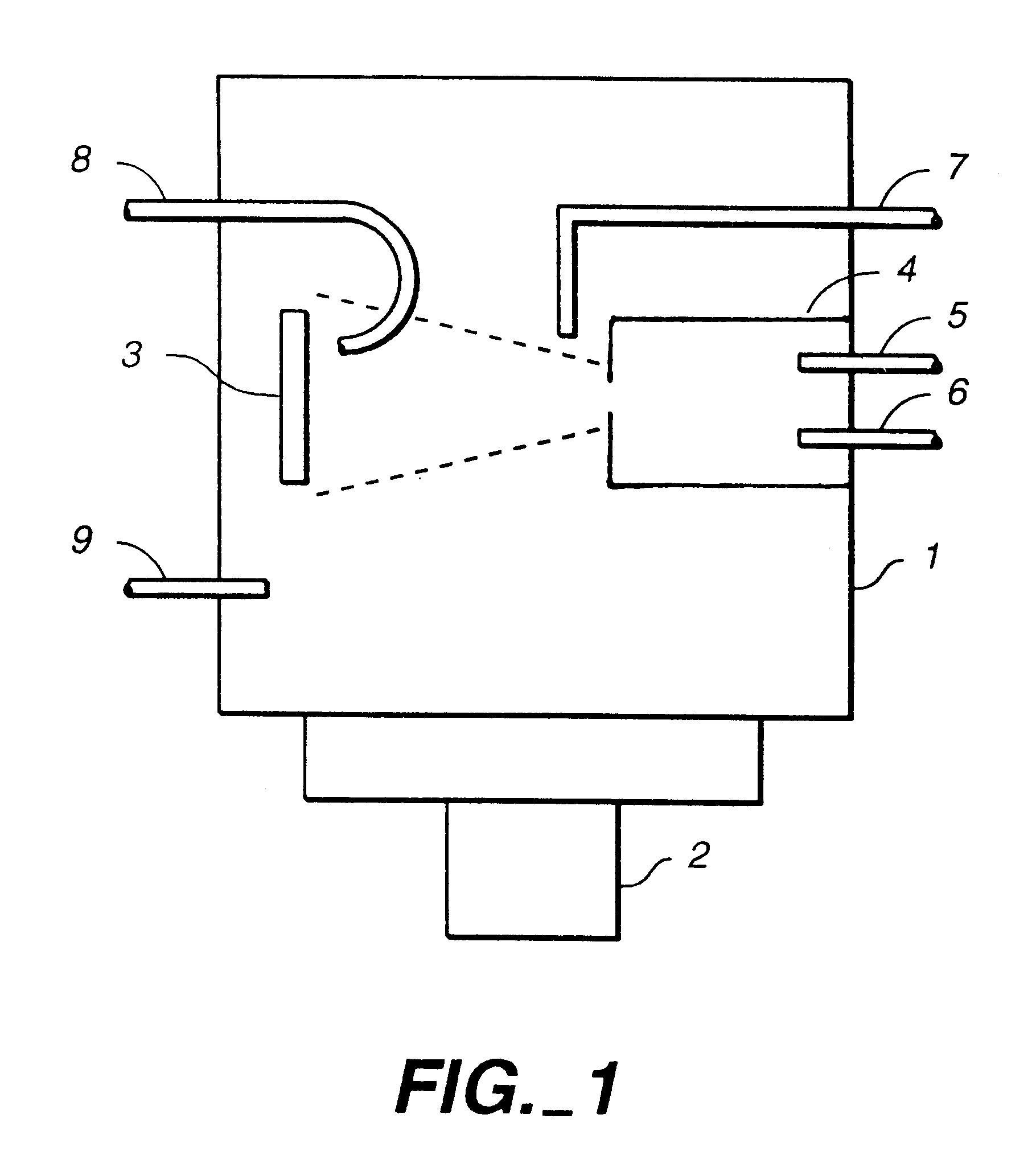
Methods and apparatuses for directing an ion beam source
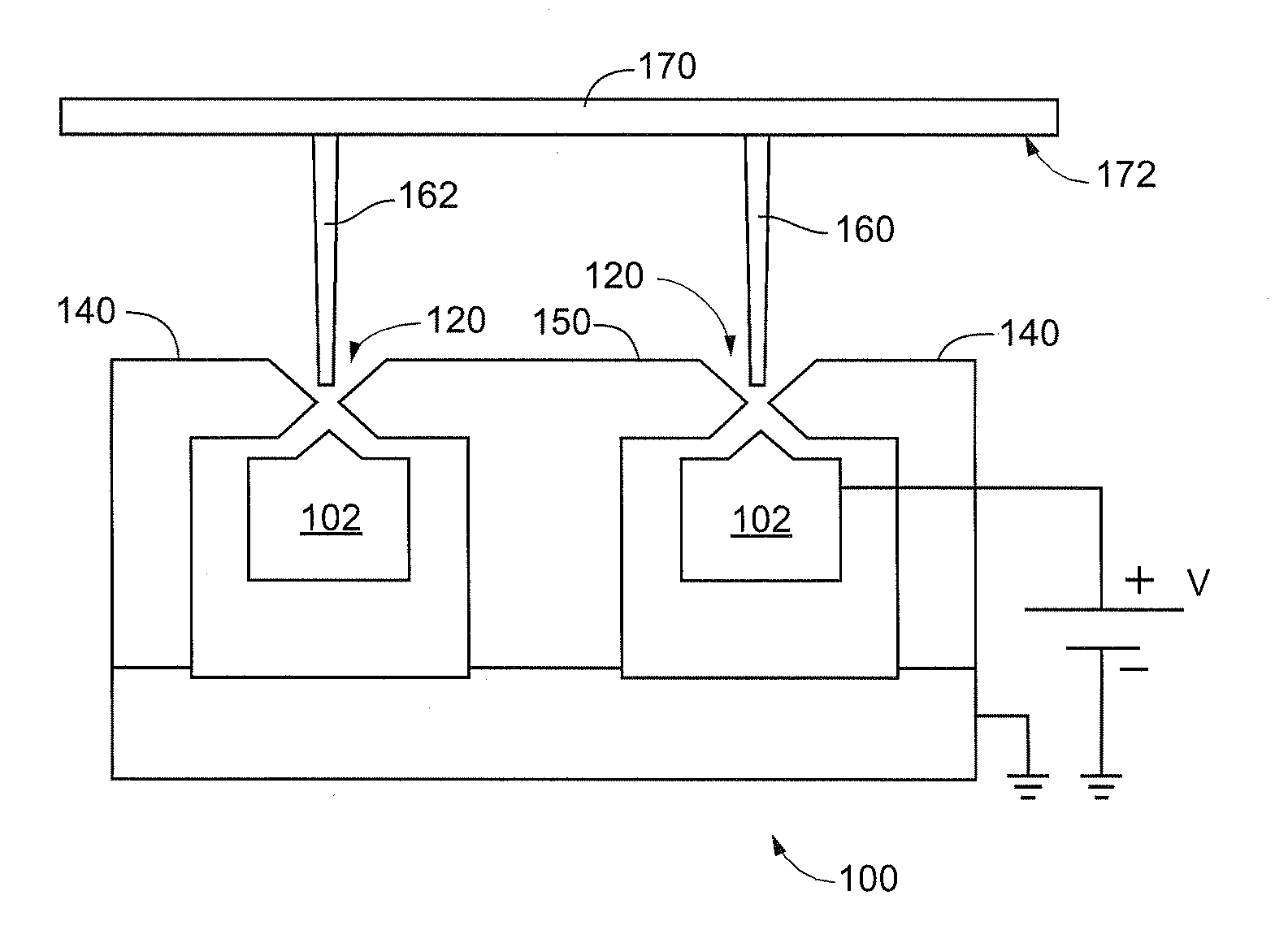
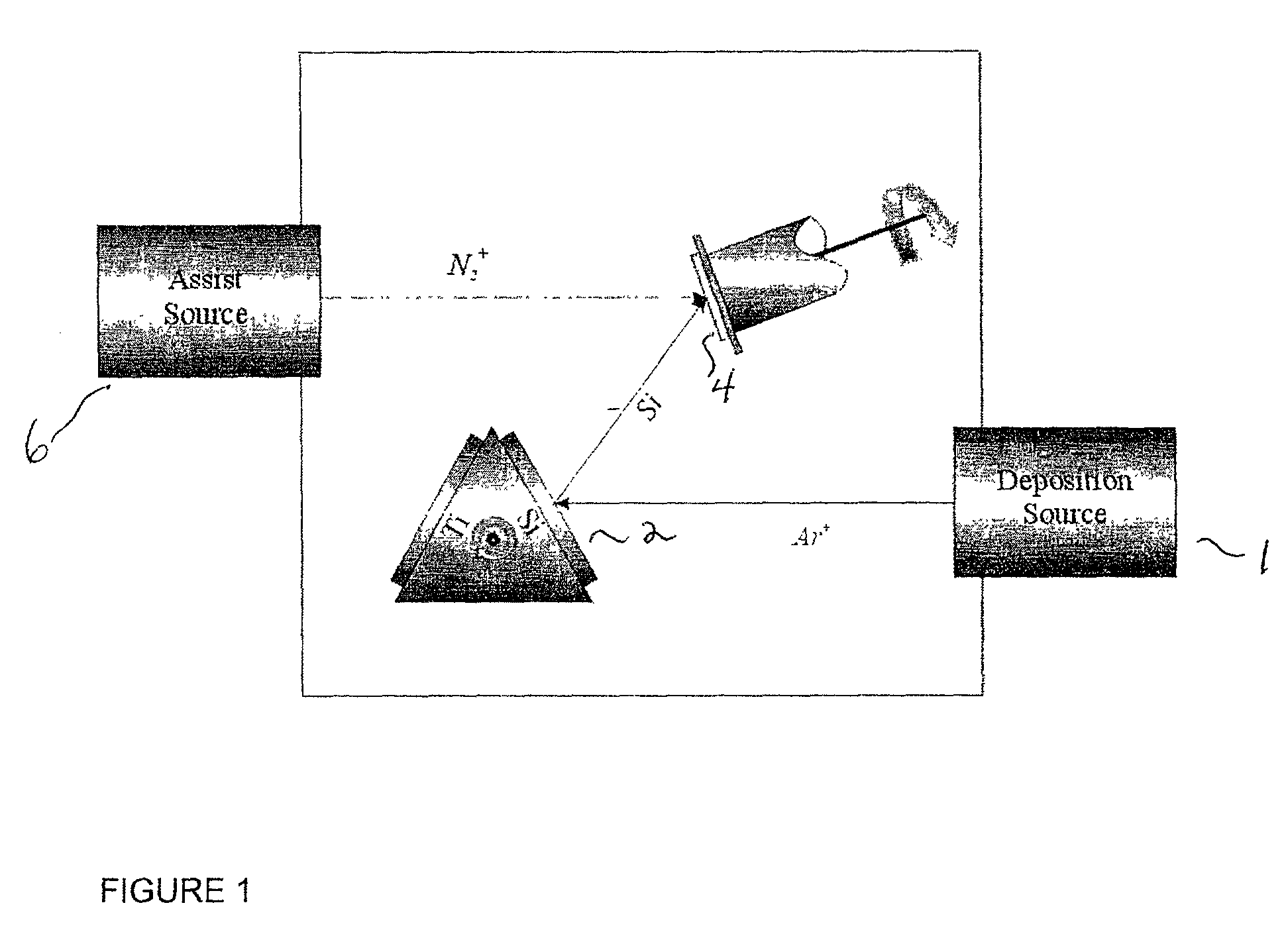
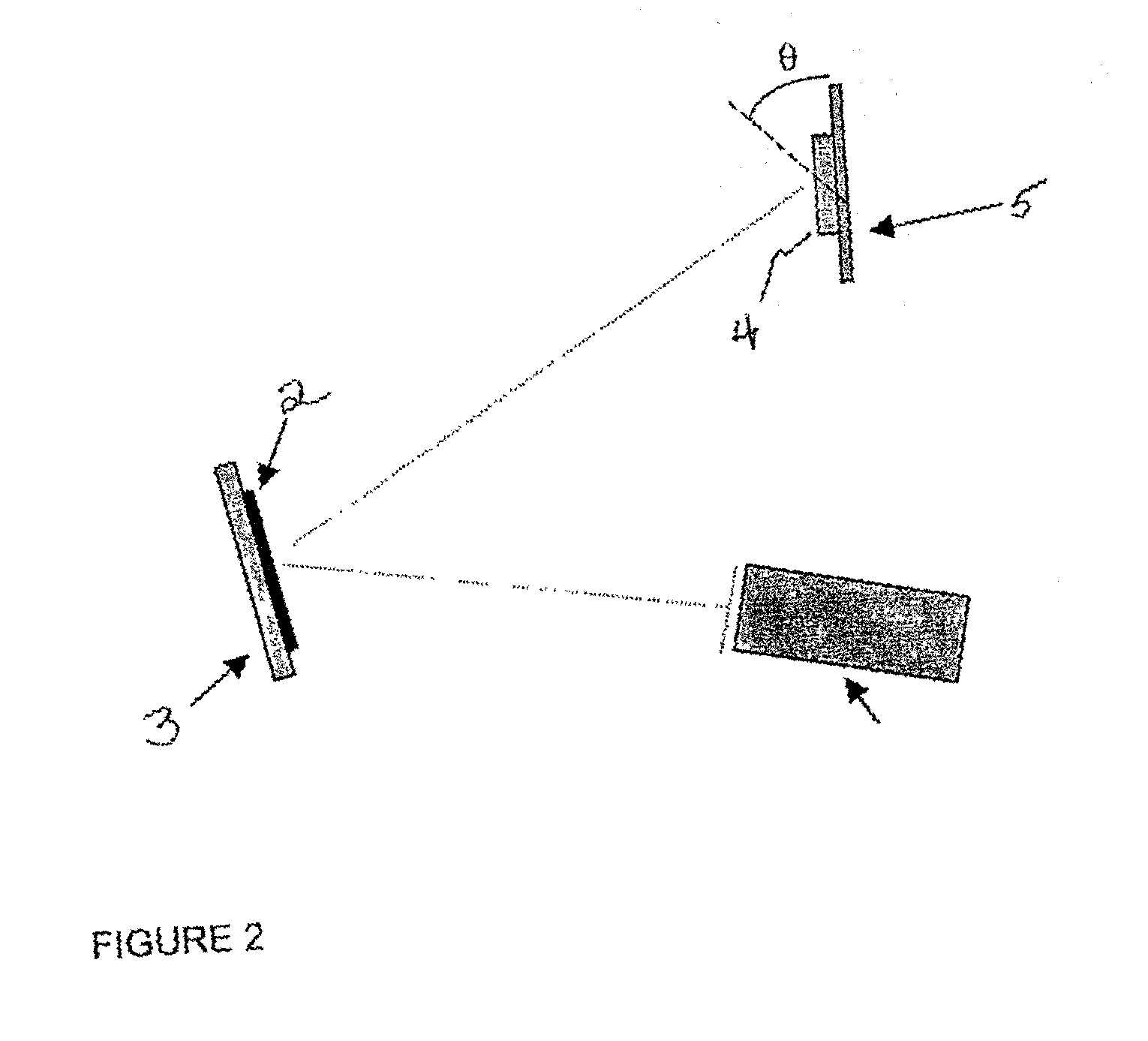
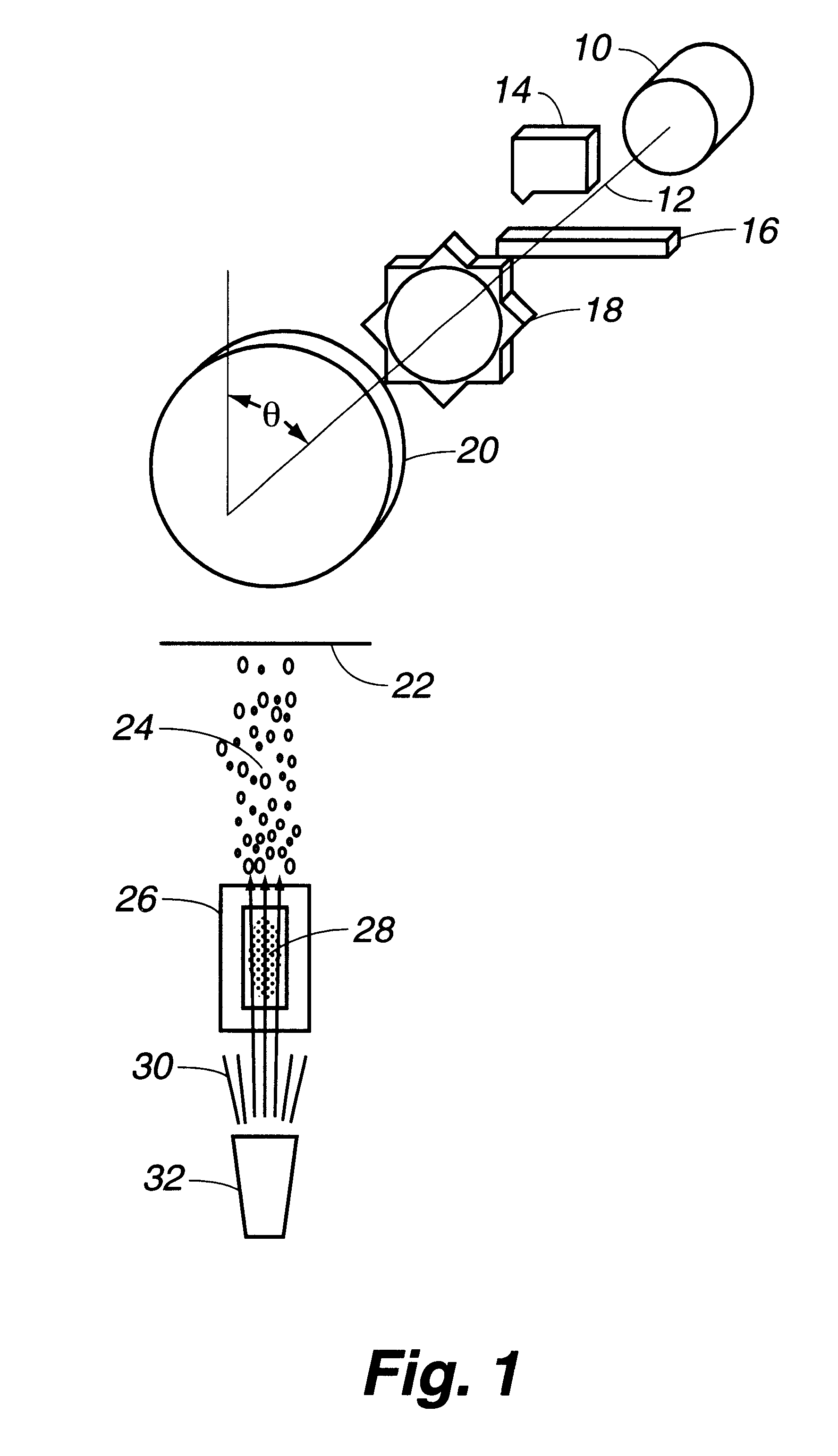
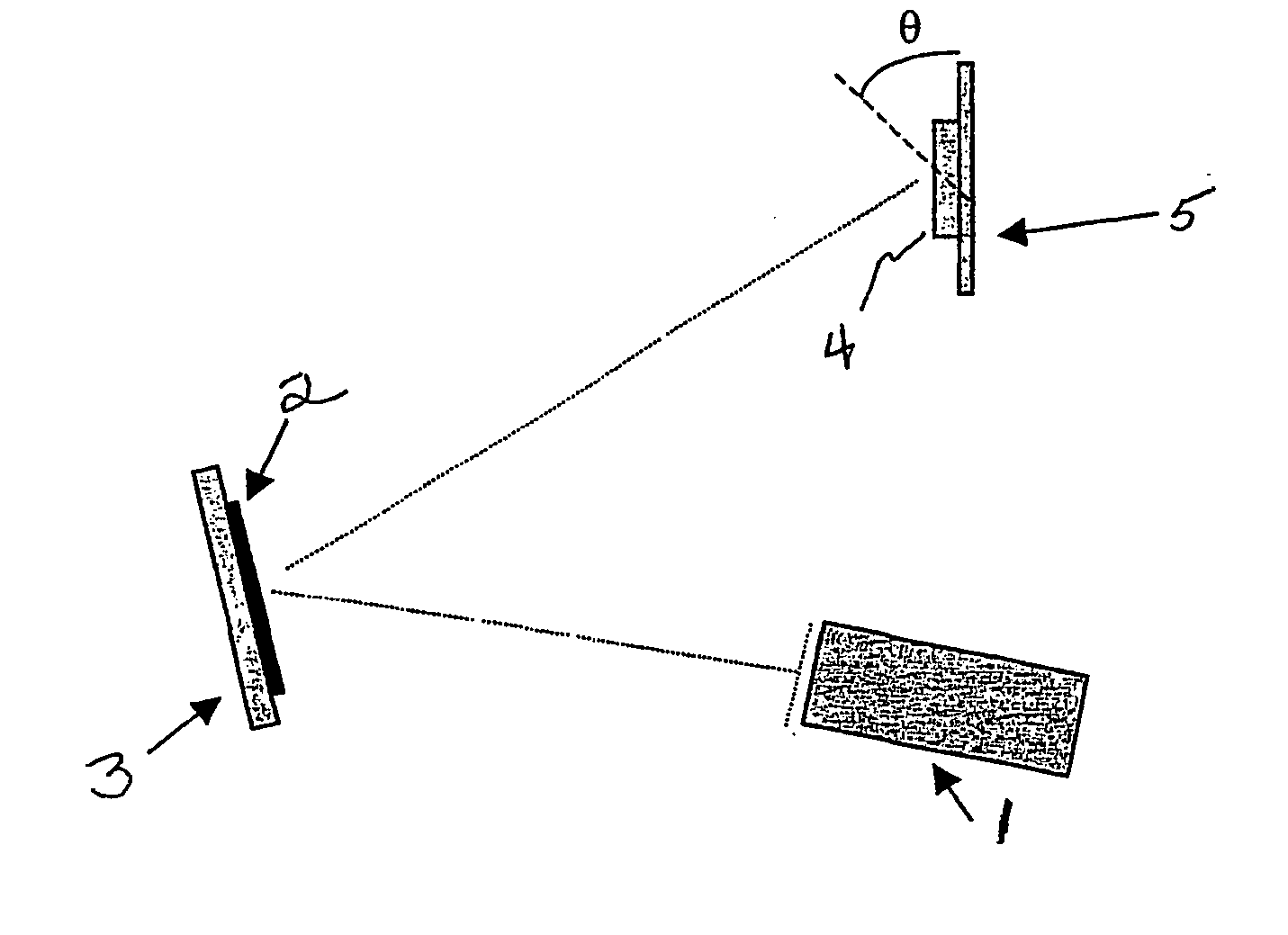
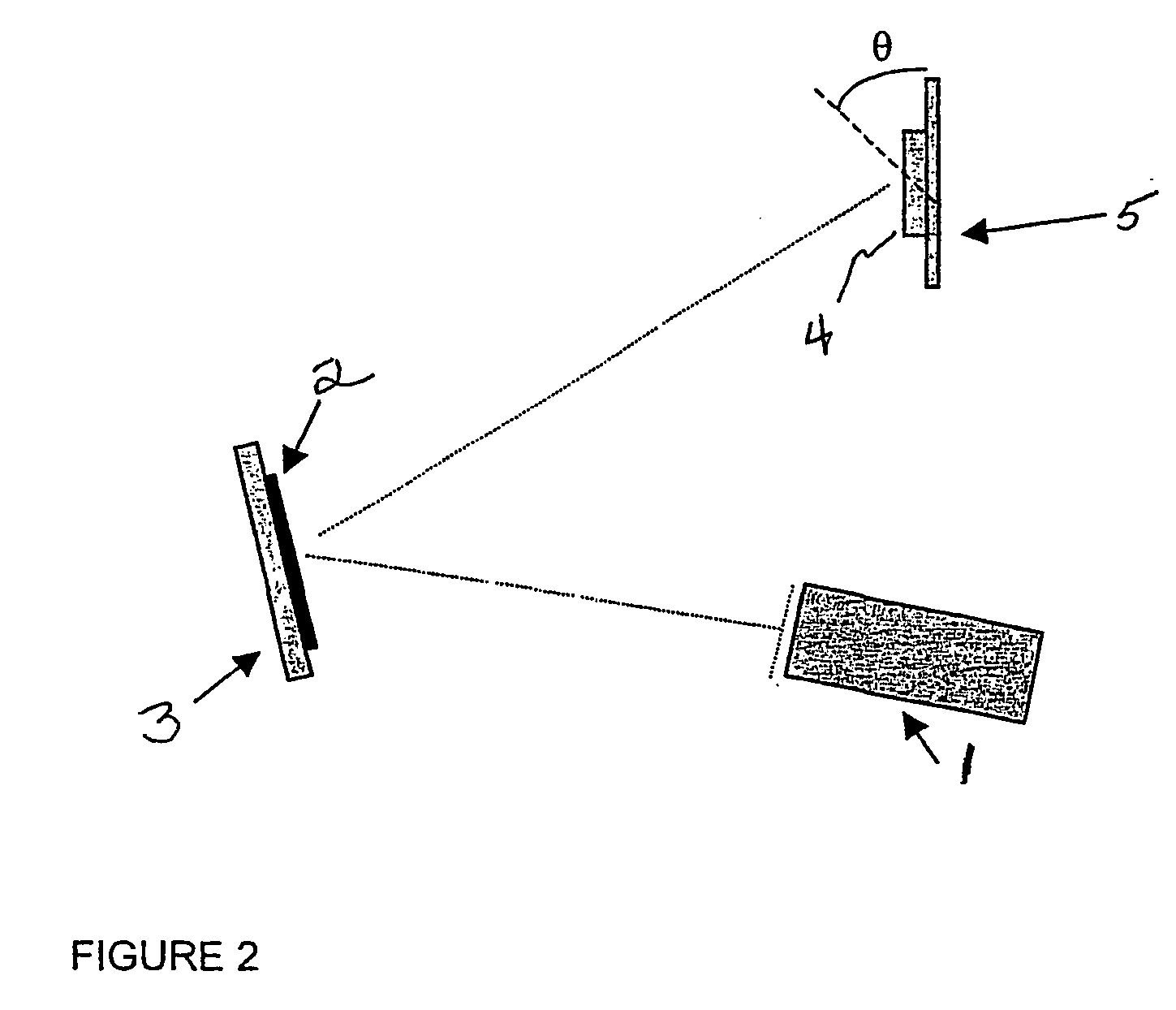
A method and apparatus for directing an ion beam toward a surface of a substrate is disclosed. Certain embodiments of the invention relate generally to ion beam sources adapted to direct ion beams toward a surface of a substrate at an oblique angle of incidence relative to the surface. Certain embodiments of the invention are adapted to direct two ion beam portions toward a substrate surface, the ion beam portions having substantially equal throw distances. Preferred embodiments of the invention may be useful in etching applications, where the angle of incidence and throw distance of two ion beam portions are well suited for etching the surface of a substrate.
Owner:CARDINAL CG +1
Ion-beam deposition process for manufacturing multi-layered attenuated phase shift photomask blanks
InactiveUS20020197509A1Electric discharge heatingVacuum evaporation coatingPhase shiftedTransmittance
A single ion-beam deposition, or a dual ion-beam deposition process for fabricating attenuating phase shift photomask blanks capable of producing a phase shift of 180° and having an optical transmissivity of at least 0.001 at selected lithographic wavelengths <400 nm, comprising at least one layer of an optically transmitting and / or one layer of optically absorbing elemental or a compound material in a periodic or an aperiodic arrangement.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
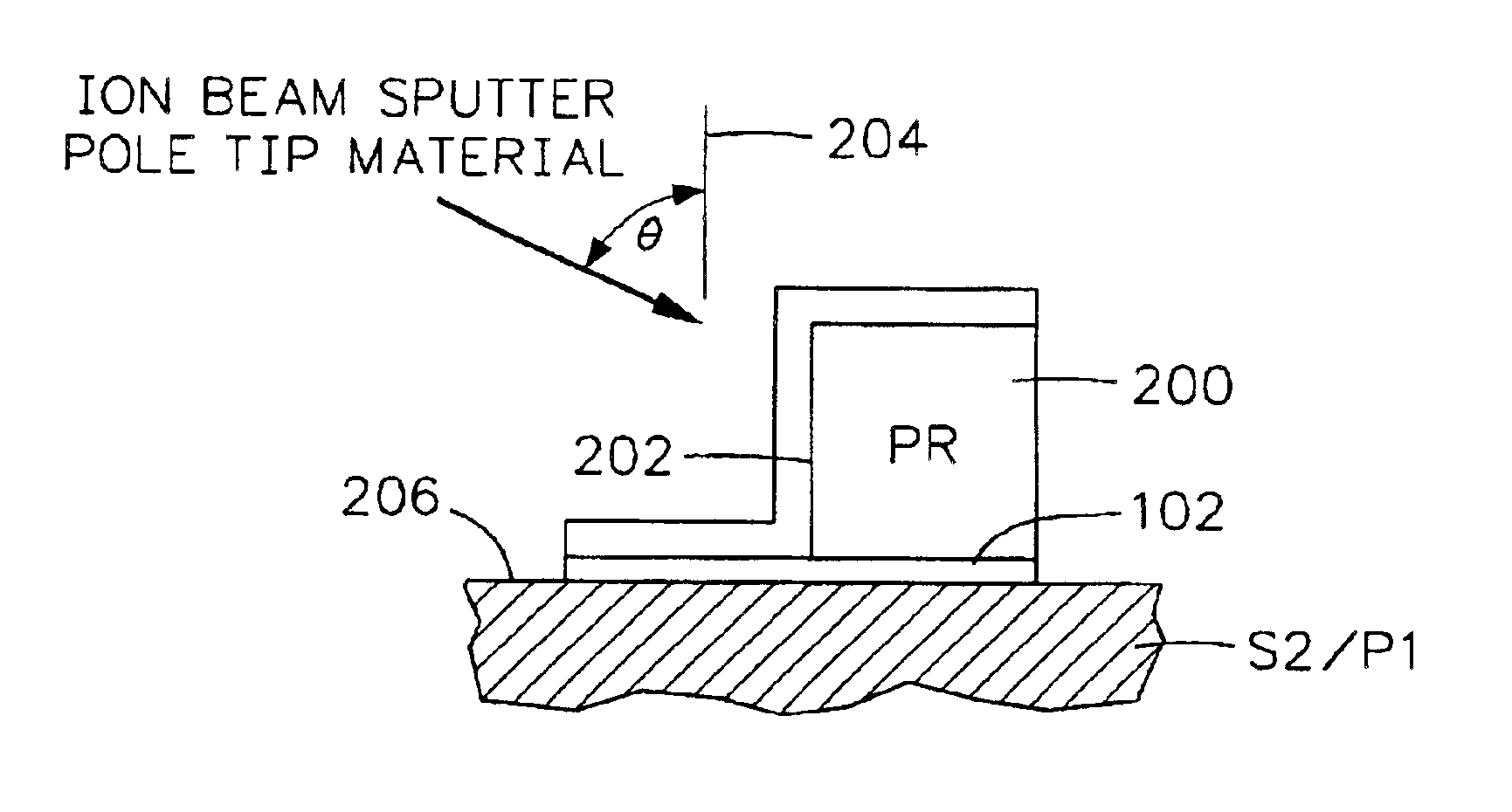
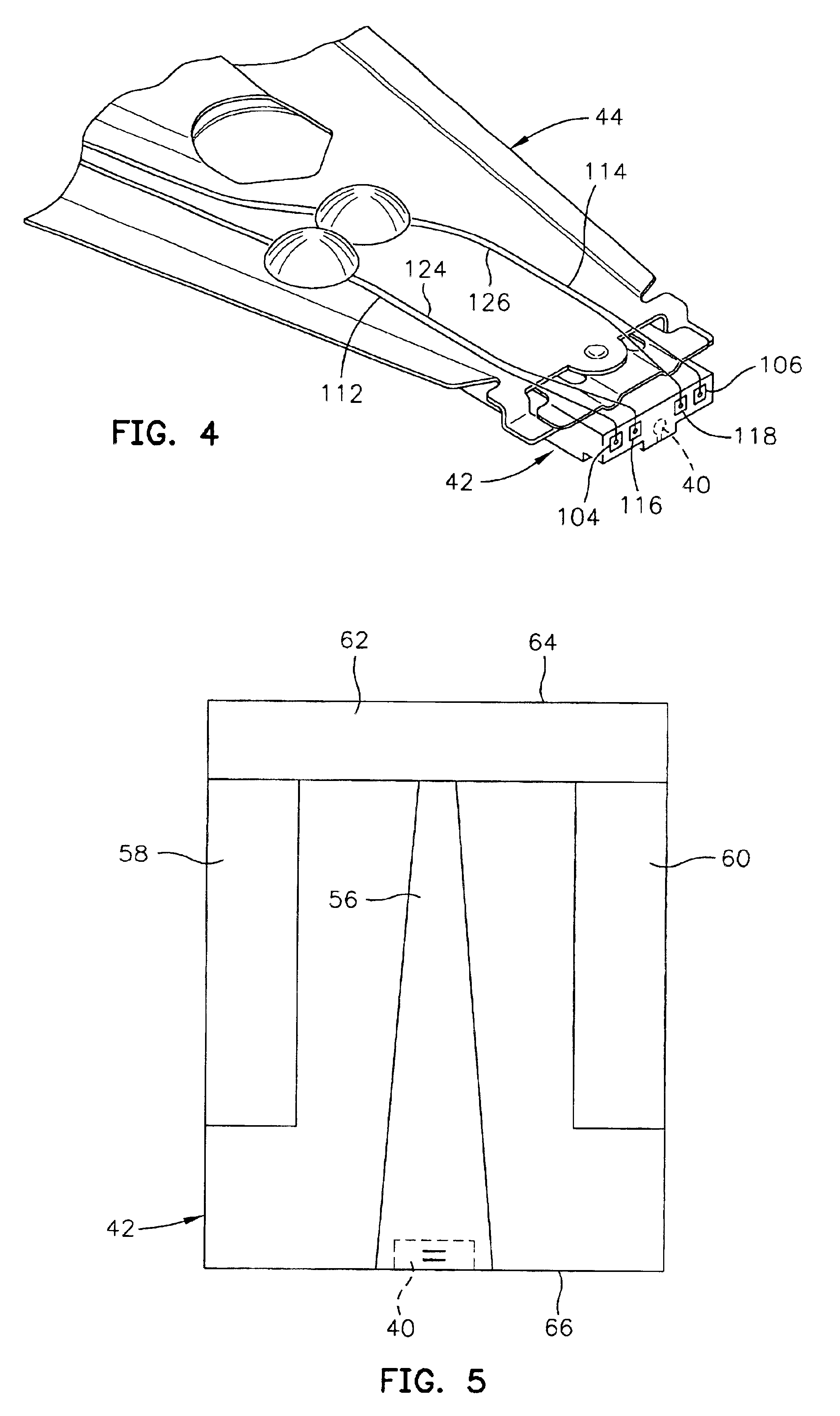
Method of making a narrow pole tip by ion beam deposition
InactiveUS6862798B2Manufacture head surfaceElectrical transducersIon beam depositionElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method of making a magnetic head assembly wherein the magnetic head assembly has a write head with a pole tip includes the steps of forming a shaping layer on an underlying layer wherein the shaping layer has a side surface and a top surface, ion beam sputter depositing a ferromagnetic material layer on the underlying layer and on the side and top surfaces of the shaping layer and removing first and second portions of the ferromagnetic material layer from the underlying layer and the top surface of the shaping layer, respectively, leaving a remaining portion of the ferromagnetic material layer on the side surface of the shaping layer which is the aforementioned pole tip.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Ion-beam deposition process for manufacture of binary photomask blanks
An ion-beam film deposition process is described for fabricating binary photomask blanks for selected lithographic wavelengths <400 nm, the said film essentially consisting of the MO<subscript>x< / highlight>C<subscript>y< / highlight>N<subscript>z < / highlight>compound where M is selected from chromium, molybdenum, tungsten, or tantalum or combination thereof in a single layer or a multiple layer configuration.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for preparing transverse phase transition memory by using single-walled carbon nanotube as electrode
ActiveCN101521177AReduce contact areaEasy to operateNanostructure manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReactive-ion etchingElectron-beam lithography
The invention provides a method for preparing a transverse phase transition memory by using a single-walled carbon nanotube as an electrode. The method comprises the following steps: first, cleaning a semi-conductor substrate to remove stains on the surface of the substrate; depositing a medium layer on the substrate surface by a chemical vapor deposition method; preparing a transverse single walled carbon nanotube array on the medium layer by the chemical vapor deposition method; depositing a plurality of mask targets for photoetching and contact electrodes contacted with each carbon nanotube; etching the carbon nanotube by electron beam lithography and reactive ion etching to form an electrode couple array; depositing a phase transition material on the etched carbon nanotube between electrode couples by a magnetron sputtering method and electronic photetching technology; depositing an adiathermal protecting region on a structure with the deposited phase transition material by an ion beam deposition method and electron beam lithography; and preparing each test electrode, thereby forming the transverse phase transition memory with low power consumption.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
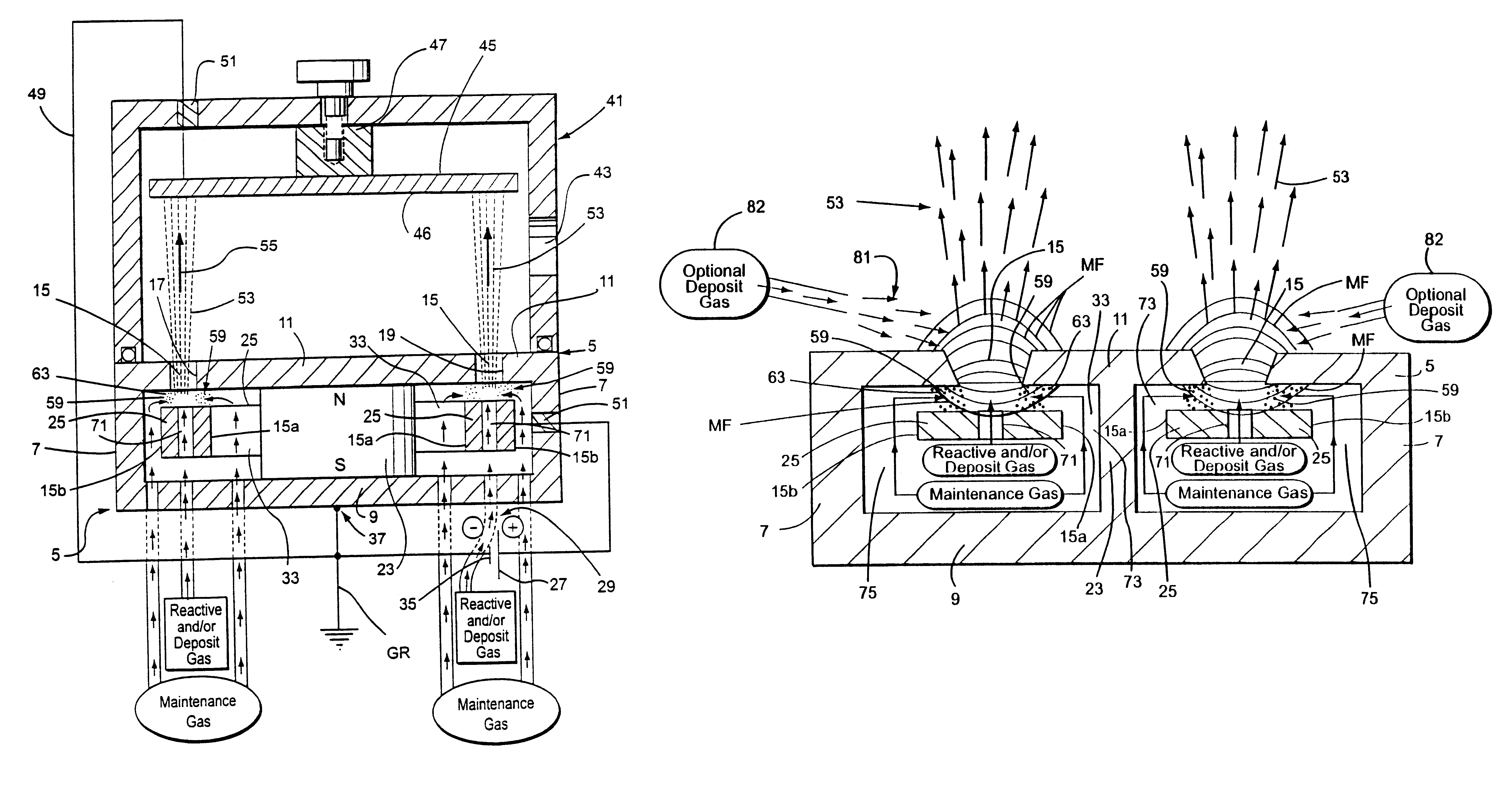
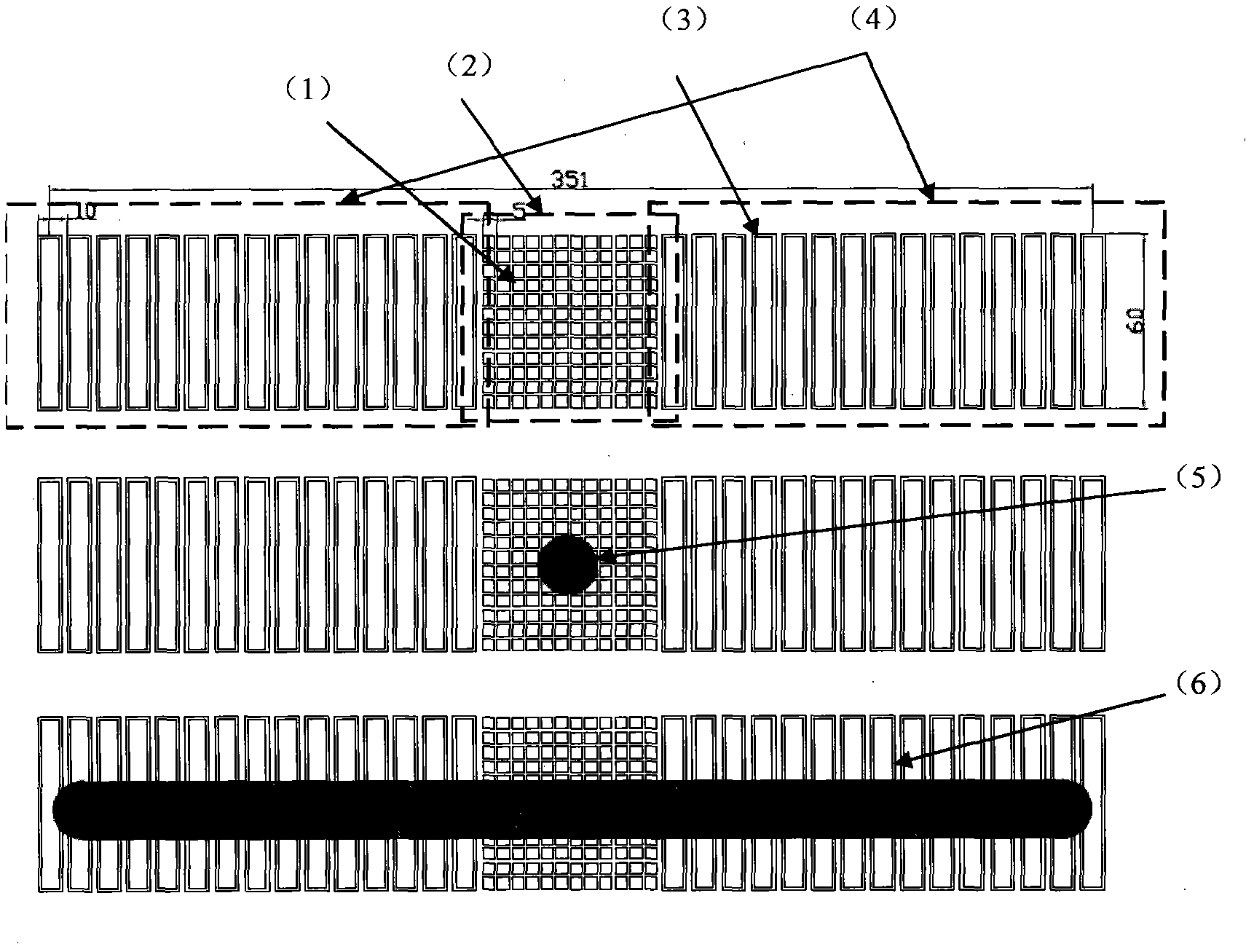
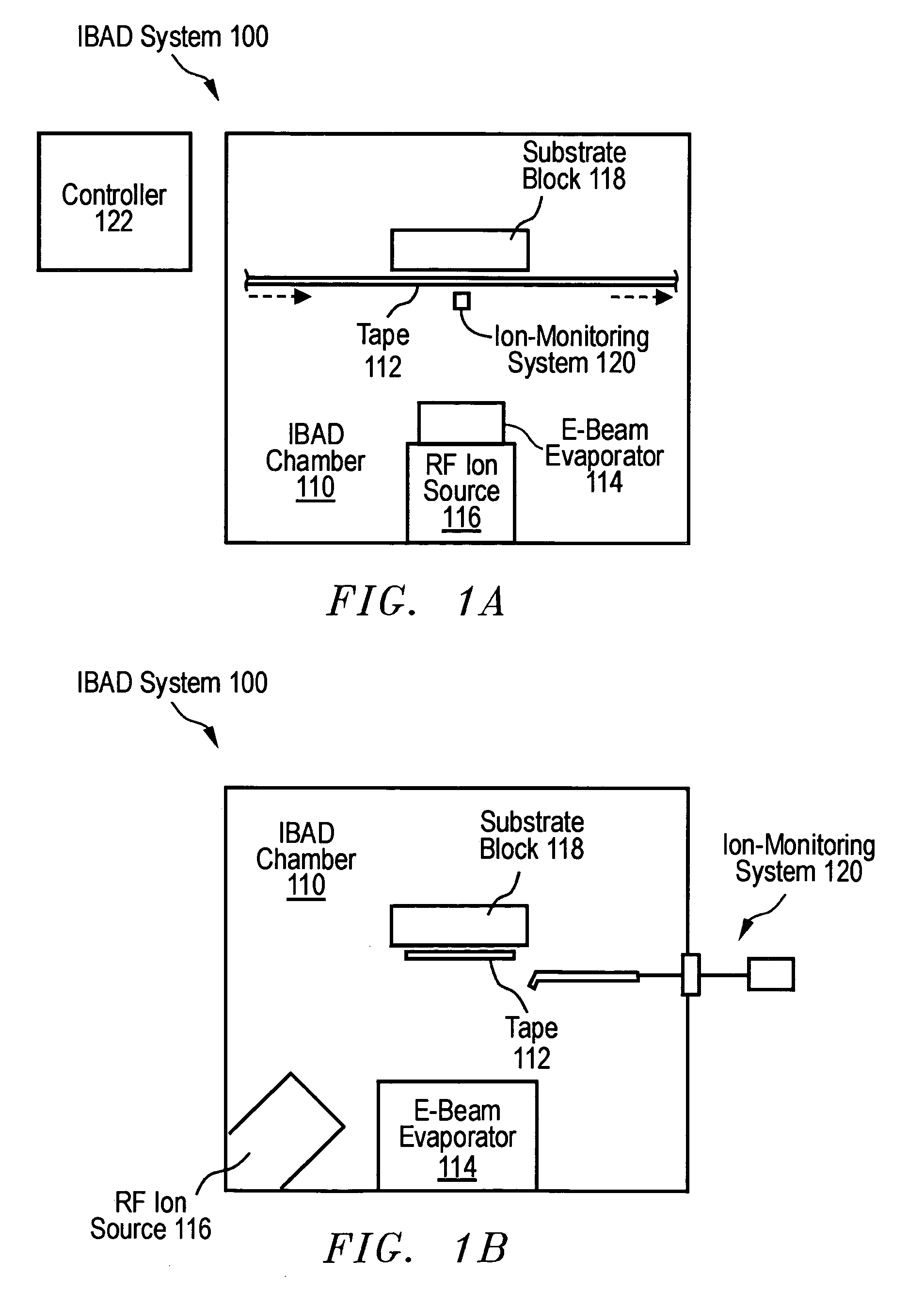
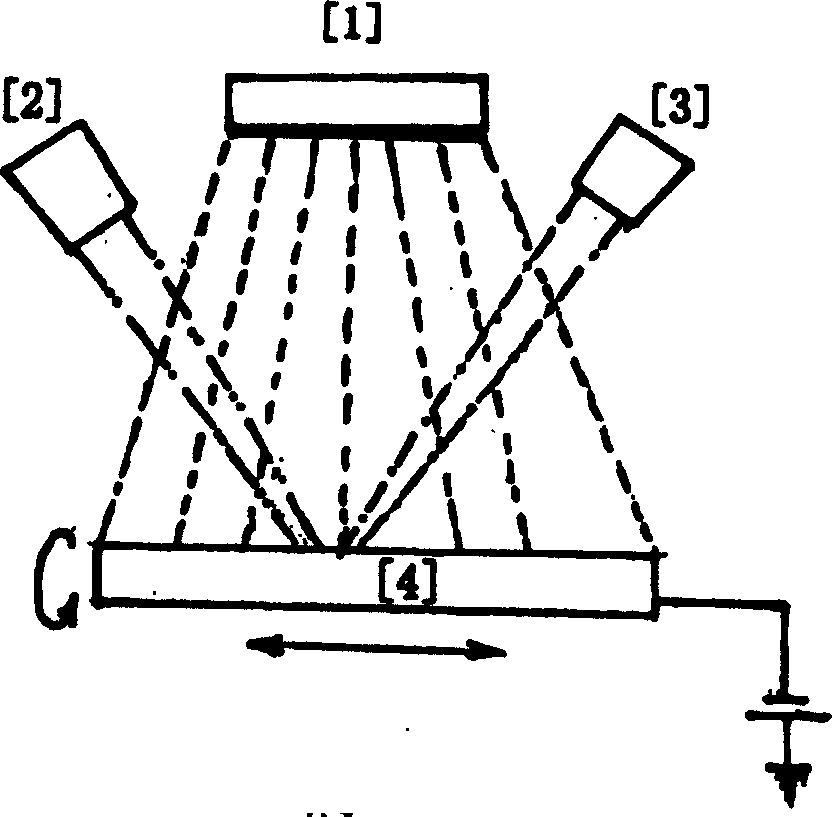
Device for detecting ion beam section density distribution and uniform ion beam distribution in real time
ActiveCN102867722AImprove qualityAdjust control parameters in real timeElectric discharge tubesX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentState variationDensity distribution
The invention discloses an array composite Faraday cup capable of detecting beam spot section density distribution of ion beam current under a focusing condition and uniform beam distribution under a scanning condition. The array composite Faraday cup comprises a two-dimensional Faraday cup array (2) and two one-dimensional Faraday cup arrays (4), wherein the two-dimensional Faraday cup array (2) is positioned at the center, and the one-dimensional Faraday cup arrays (4) are positioned on two sides respectively. The array composite Faraday cup is characterized in that the two-dimensional Faraday cup array (2) at the center is used for detecting beam spot section density distribution of ion beams under the focusing condition (5), and the one-dimensional Faraday cup arrays (4) on the two sides are used for detecting uniform beam distribution of the ion beams under the scanning condition (6). By the aid of the array composite Faraday cup, distribution and state change of the ion beams can be detected in real time, and detection instantaneity and accuracy can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING SHUOKE ZHONGKEXIN ELECTRONICS EQUIP CO LTD
Ion sources and methods of operating an electromagnet of an ion source
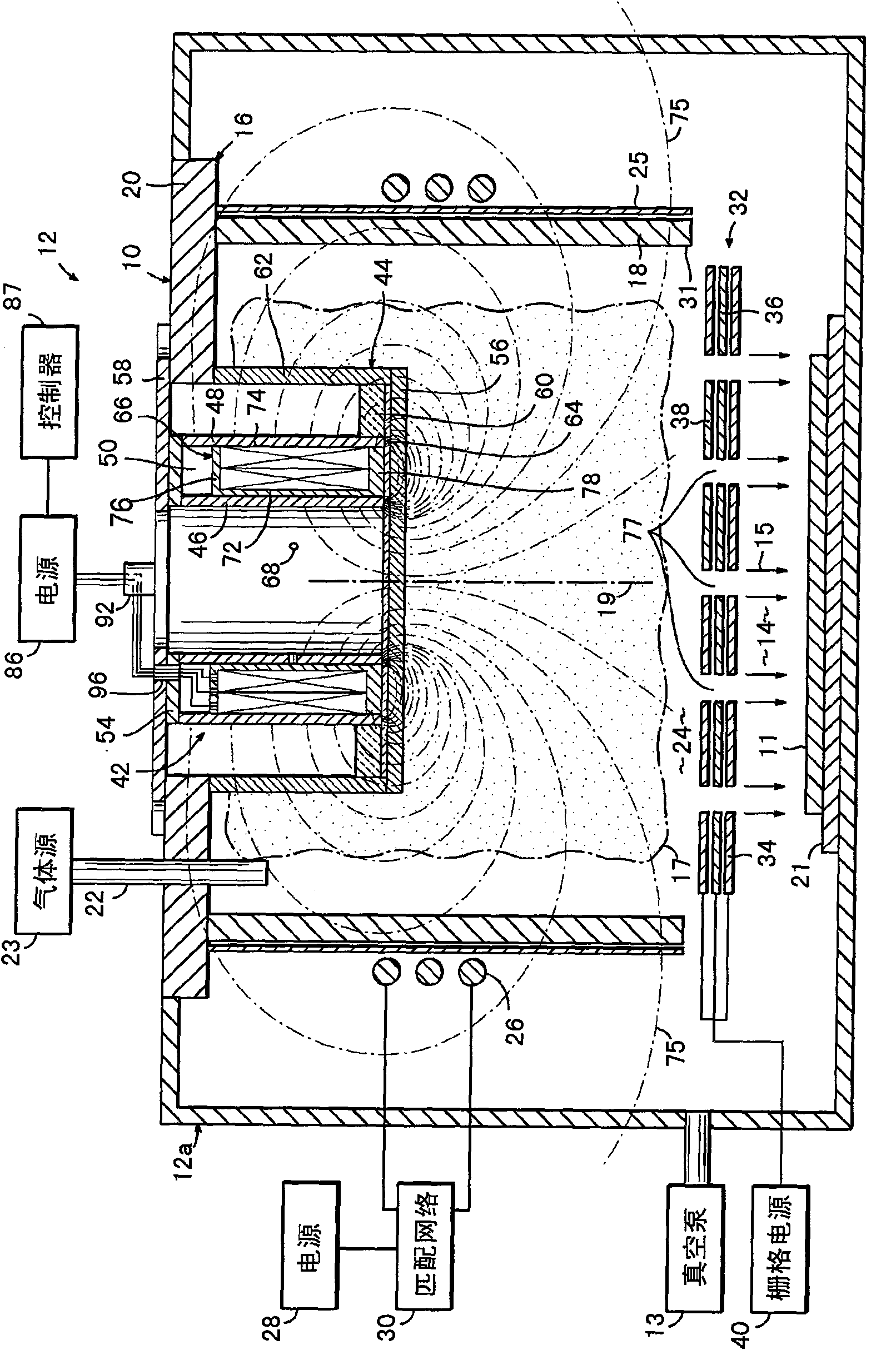
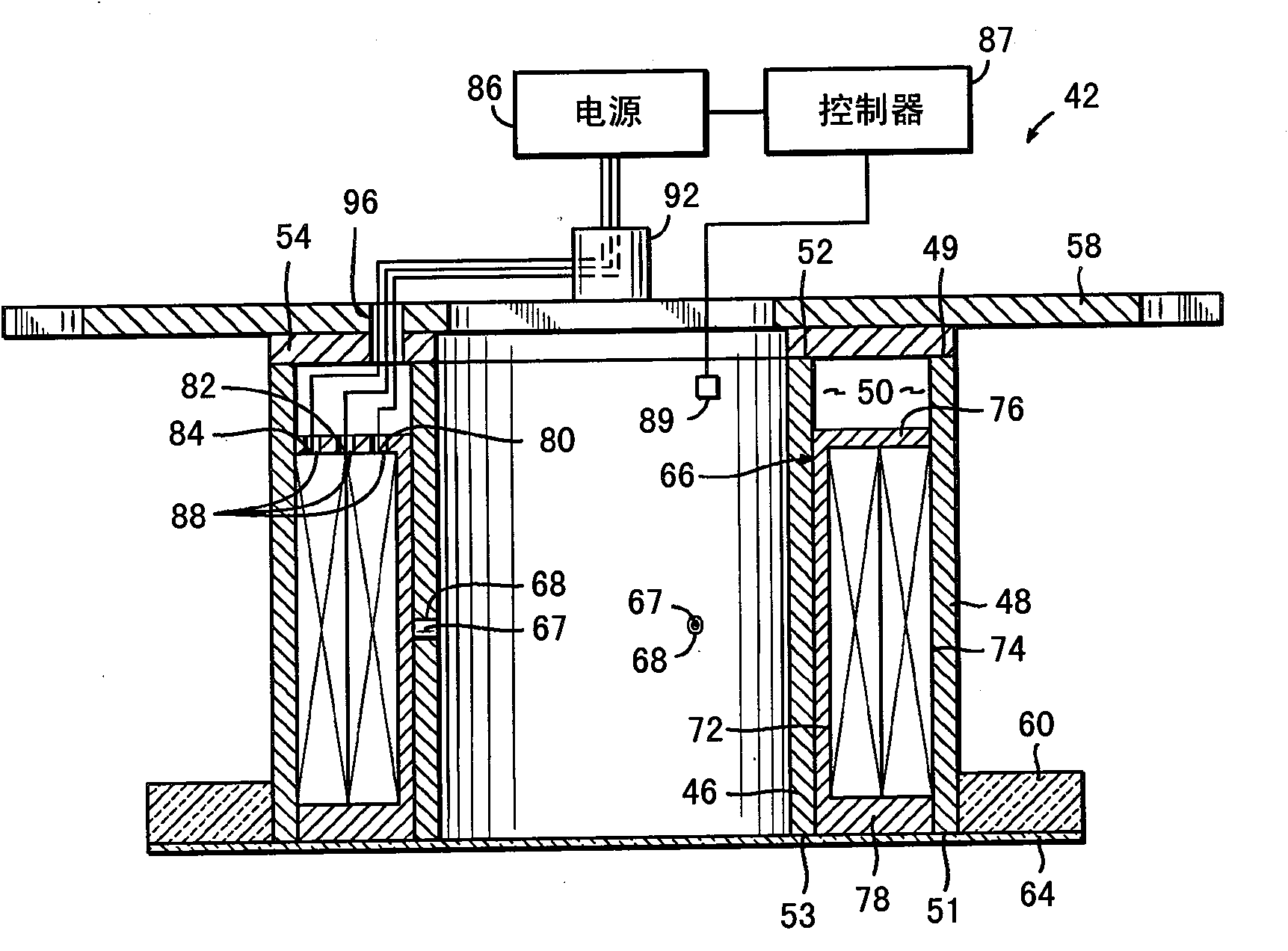
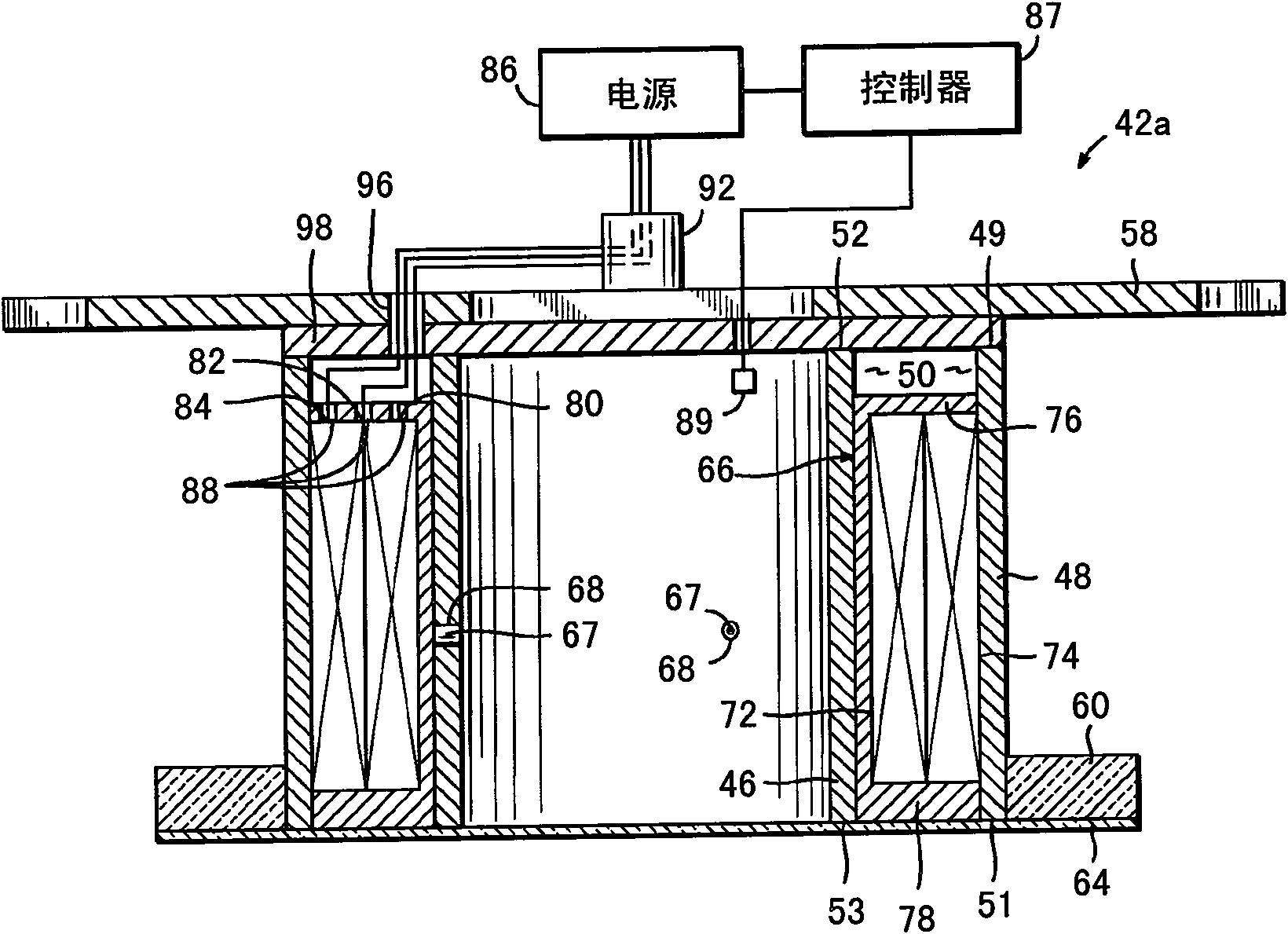
ActiveCN101681781AVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingVolumetric Mass DensityPlasma density distribution
Ion sources and methods of operating an electromagnet of an ion source for generating an ion beam with a controllable ion current density distribution. The ion source (10) includes a discharge chamber (16) and an electromagnet (42; 42a-d) adapted to generate a magnetic field (75) for changing a plasma density distribution inside the discharge chamber (16). The methods may include generating plasma (17) in the discharge space (24), generating and shaping a magnetic field (75) in the discharge space (24) by applying a current to an electromagnet (42; 42a-d) that is effective to define the plasma density distribution, extracting an ion beam (15) from the plasma (17), measuring a distribution profile for the ion beam density, and comparing the actual distribution profile with a desired distribution profile for the ion beam density. Based upon the comparison, the current applied to the electromagnet (42; 42a-d) may be adjusted to modify magnetic field (75) the magnetic field in the discharge space and, thereby, alter the plasma density distribution.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
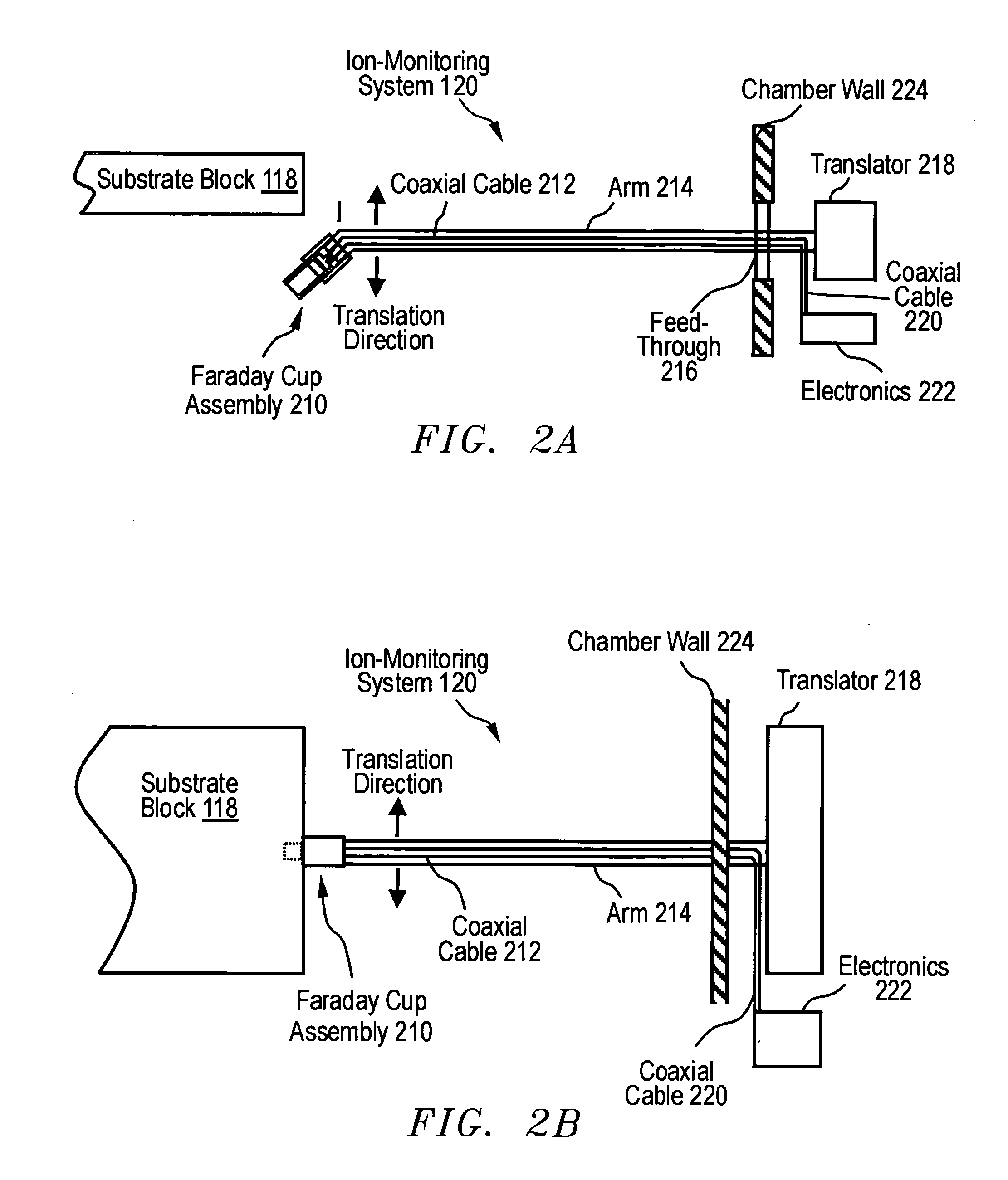
Method of measuring ion beam position
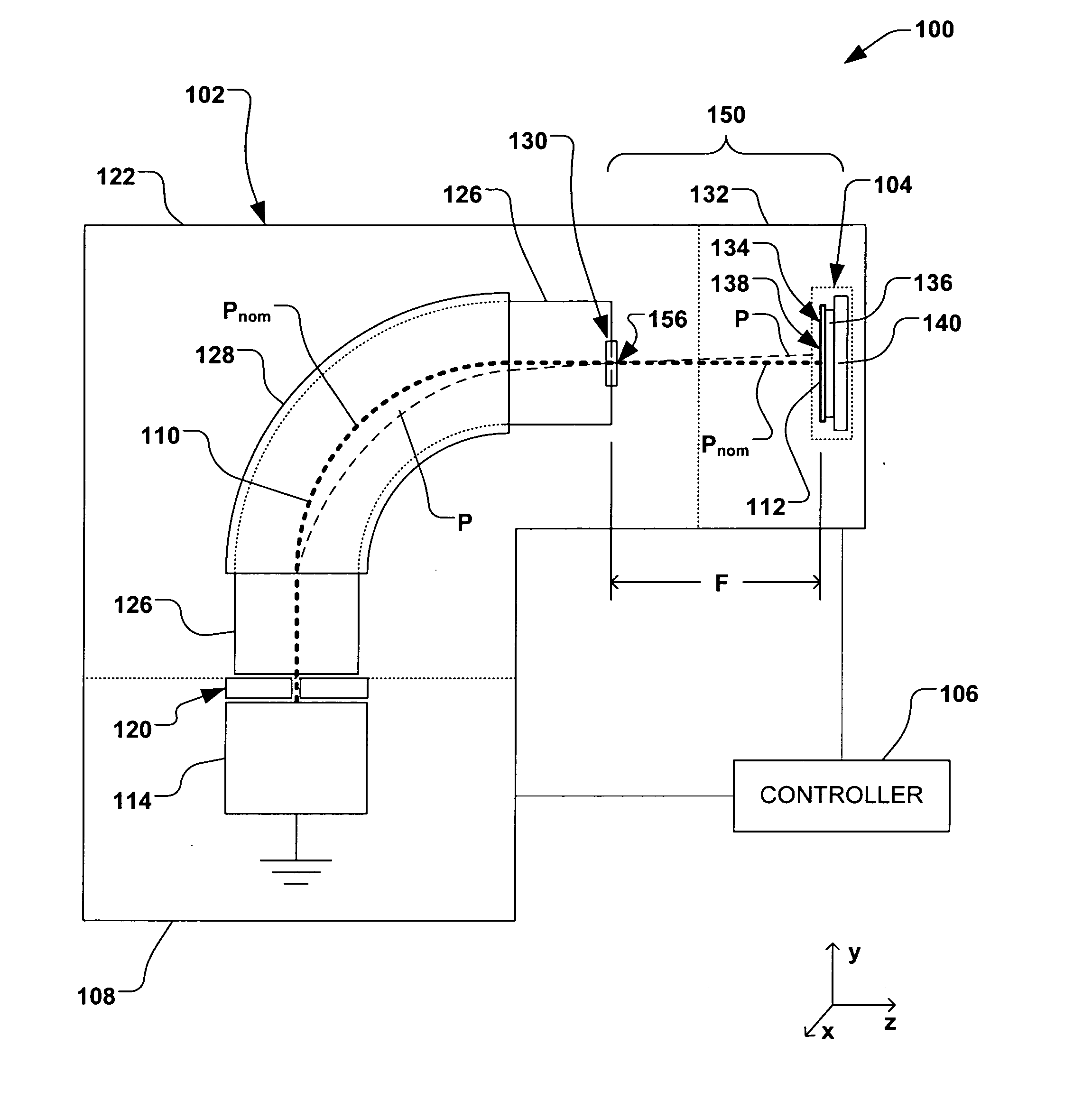
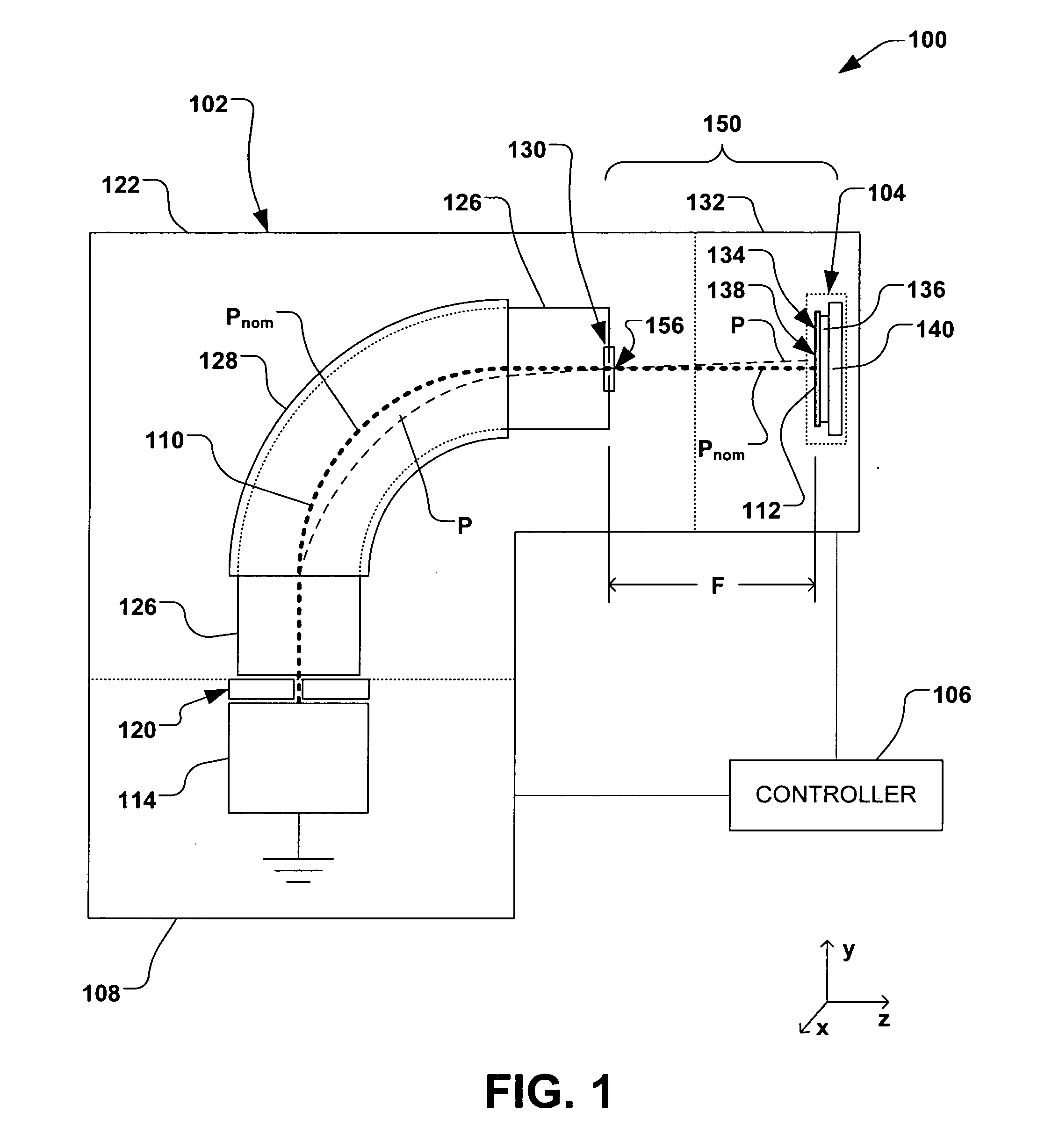
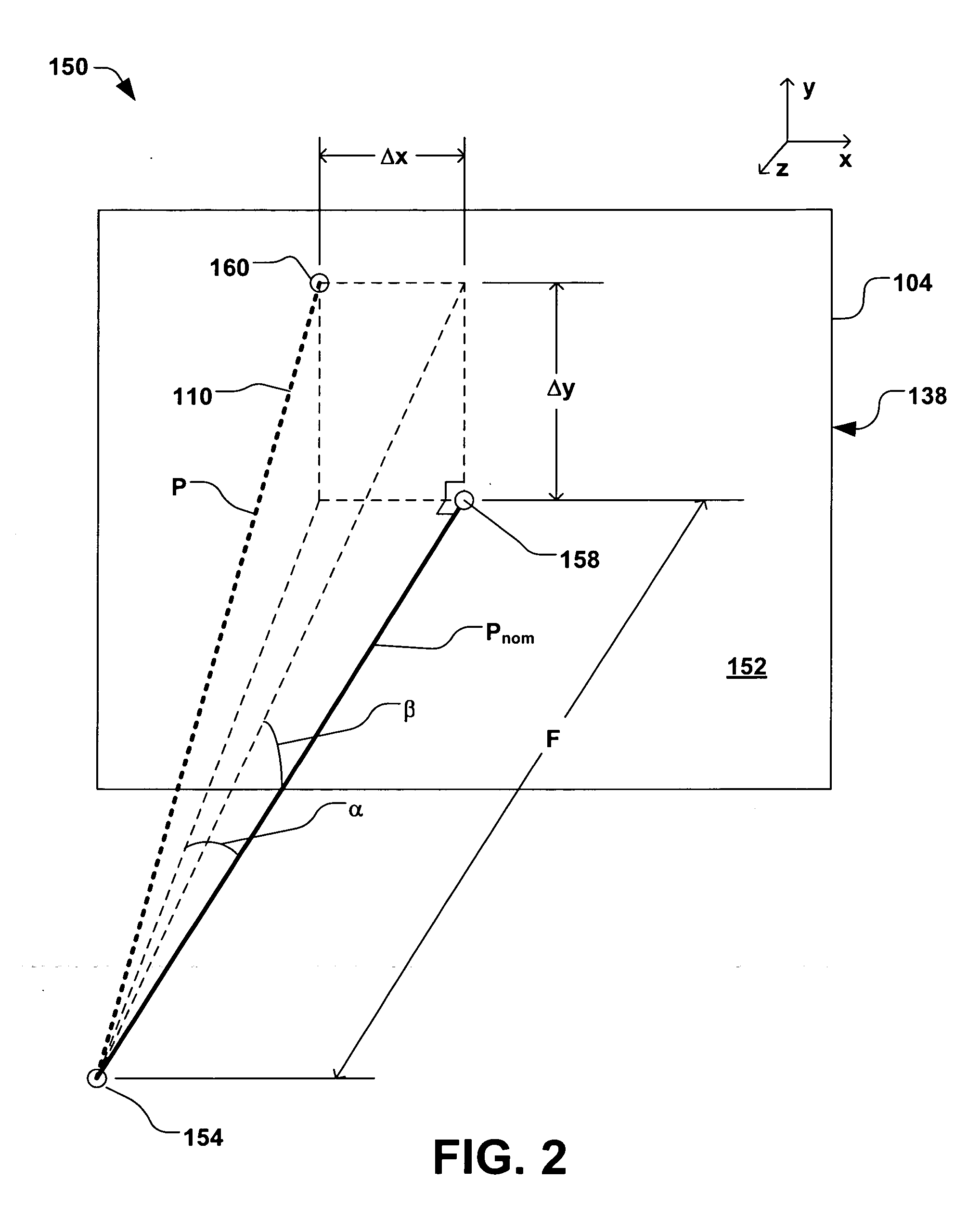
ActiveUS20060219955A1Overcome limitationsOptical radiation measurementGas discharge lampsAngle of incidenceMeasurement device
A system, apparatus, and method for determining position and two angles of incidence of an ion beam to a surface of a workpiece is provided. A measurement apparatus having an elongate first and second sensor is coupled to a translation mechanism, wherein the first sensor extends in a first direction perpendicular to the translation, and wherein the second sensor extends at an oblique angle to the first sensor. The first and second elongate sensors sense one or more characteristics of the ion beam as the first and second sensors pass through the ion beam at a respective first time and a second time, and a controller is operable to determine a position and first and second angle of incidence of the ion beam, based, at least in part, on the one or more characteristics of the ion beam sensed by the first sensor and second sensor at the first and second times.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
Process and apparatus for making oriented crystal layers
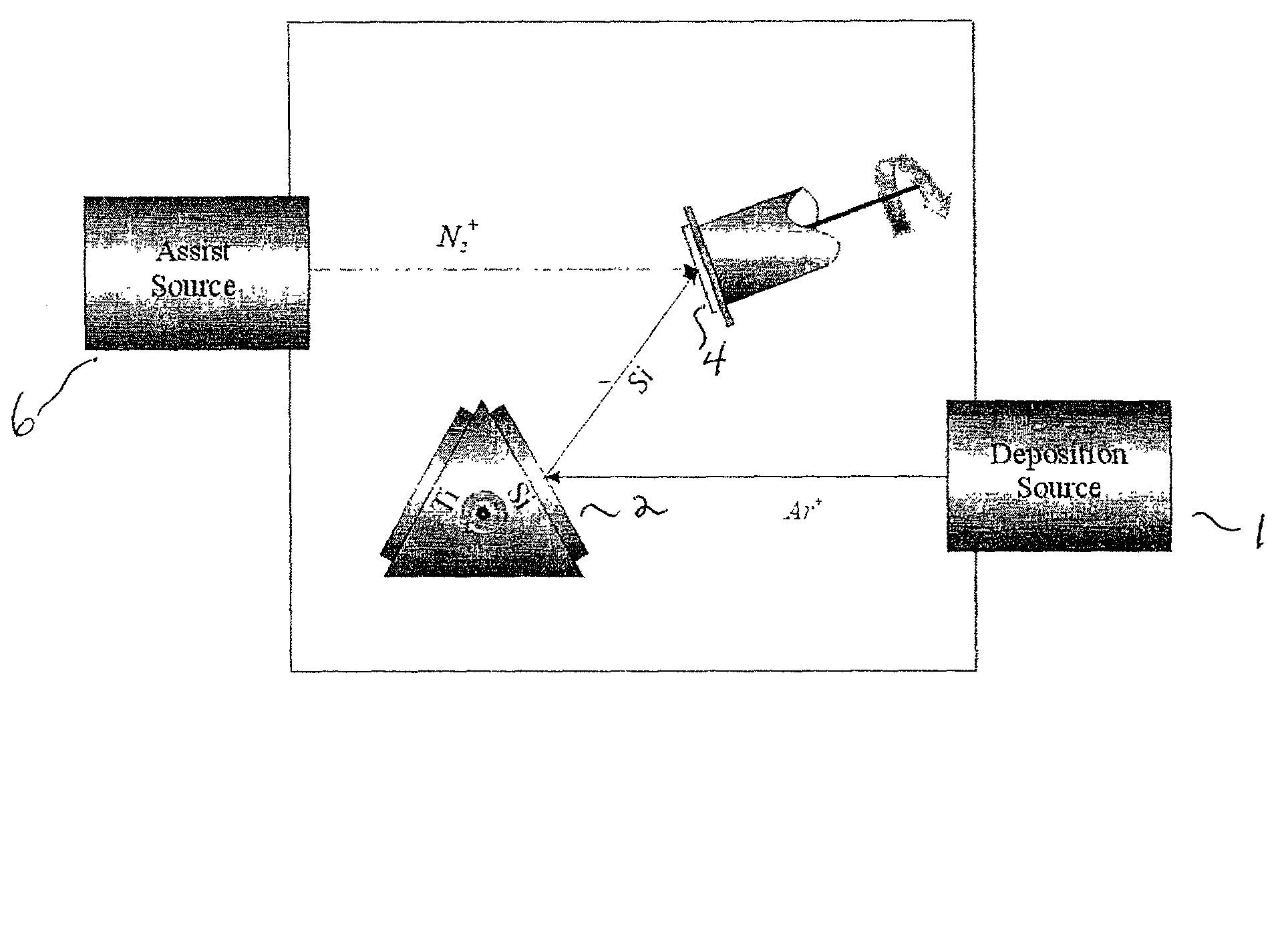
Thin films of single crystal-like materials are made by using flow-through ion beam deposition during specific substrate rotation around an axis in a clocking action. The substrate is quickly rotated to a selected deposition position, paused in the deposition position for ionized material to be deposited, then quickly rotated to the next selected deposition position. The clocking motion can be achieved by use of a lobed cam on the spindle with which the substrate is rotated or by stopping and starting a stepper motor at long and short intervals. Other symmetries can be programmed into the process, allowing virtually any oriented inorganic crystal to be grown on the substrate surface.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Method for manufacturing a tunnel junction magnetic sensor using ion beam deposition
InactiveUS20080152834A1Avoids target poisoningQuality improvementNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsOxygen ionsIon deposition
A method for forming a MgO barrier layer in a tunnel junction magnetoresistive sensor (TMR). The MgO barrier layer is deposited by an ion beam deposition process that results in a MgO barrier layer having exceptional, uniform properties and a well controlled oxygen content. The ion beam deposition of the barrier layer includes placing a wafer into an ion deposition chamber and placing Mg target into the chamber. An ion beam from an ion beam gun is directed at the target thereby dislodging Mg atoms from the target for deposition onto the wafer. Oxygen is introduced into the chamber by one or both of pumping molecular oxygen (O2) into the chamber and / or introducing oxygen ions into the chamber from a second ion beam gun. The use of ion beam deposition avoids oxygen poisoning of the Mg target, such as would occur using a more conventional plasma vapor deposition technique.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Focused ion beam apparatus and focused ion beam irradiation method
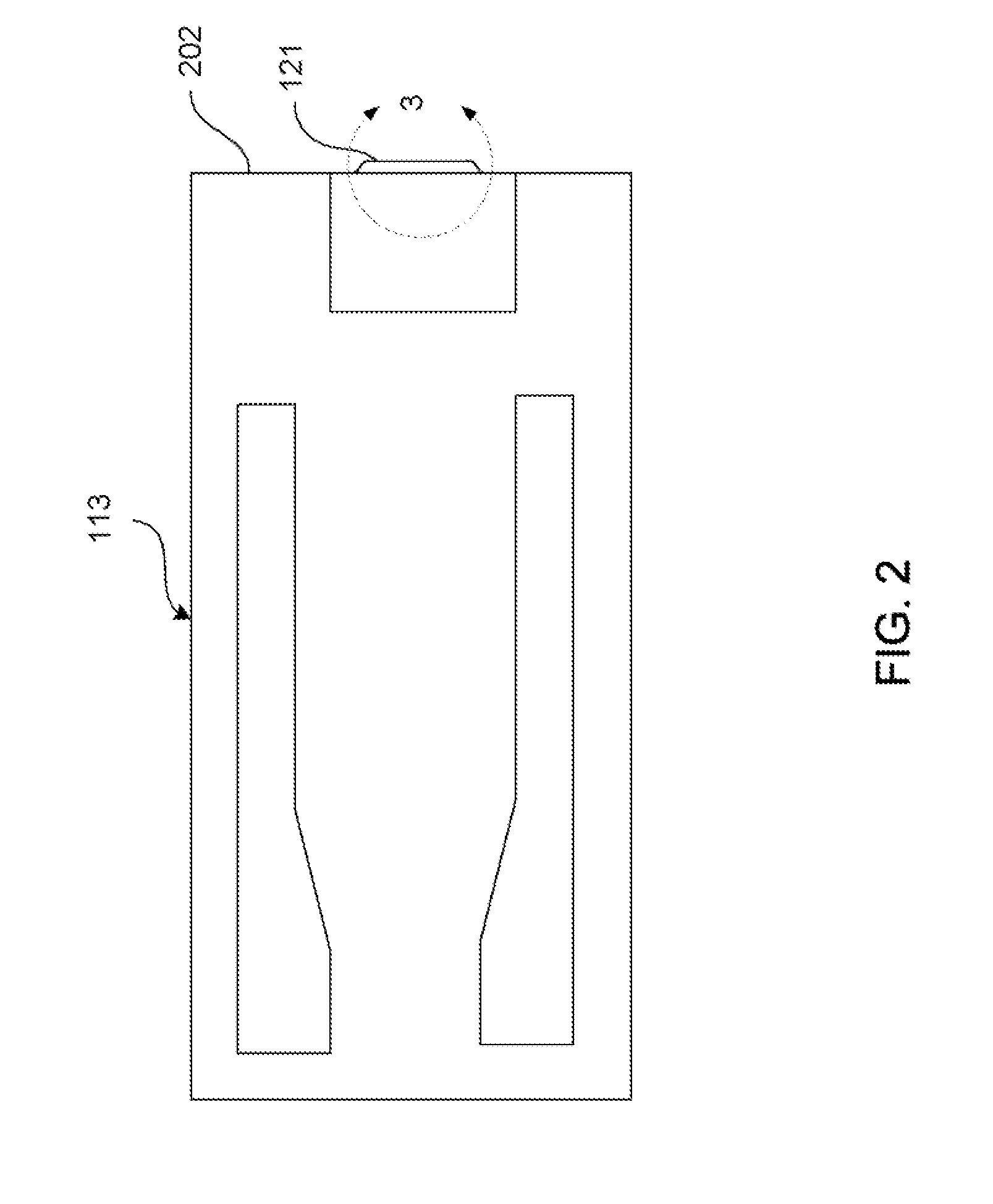
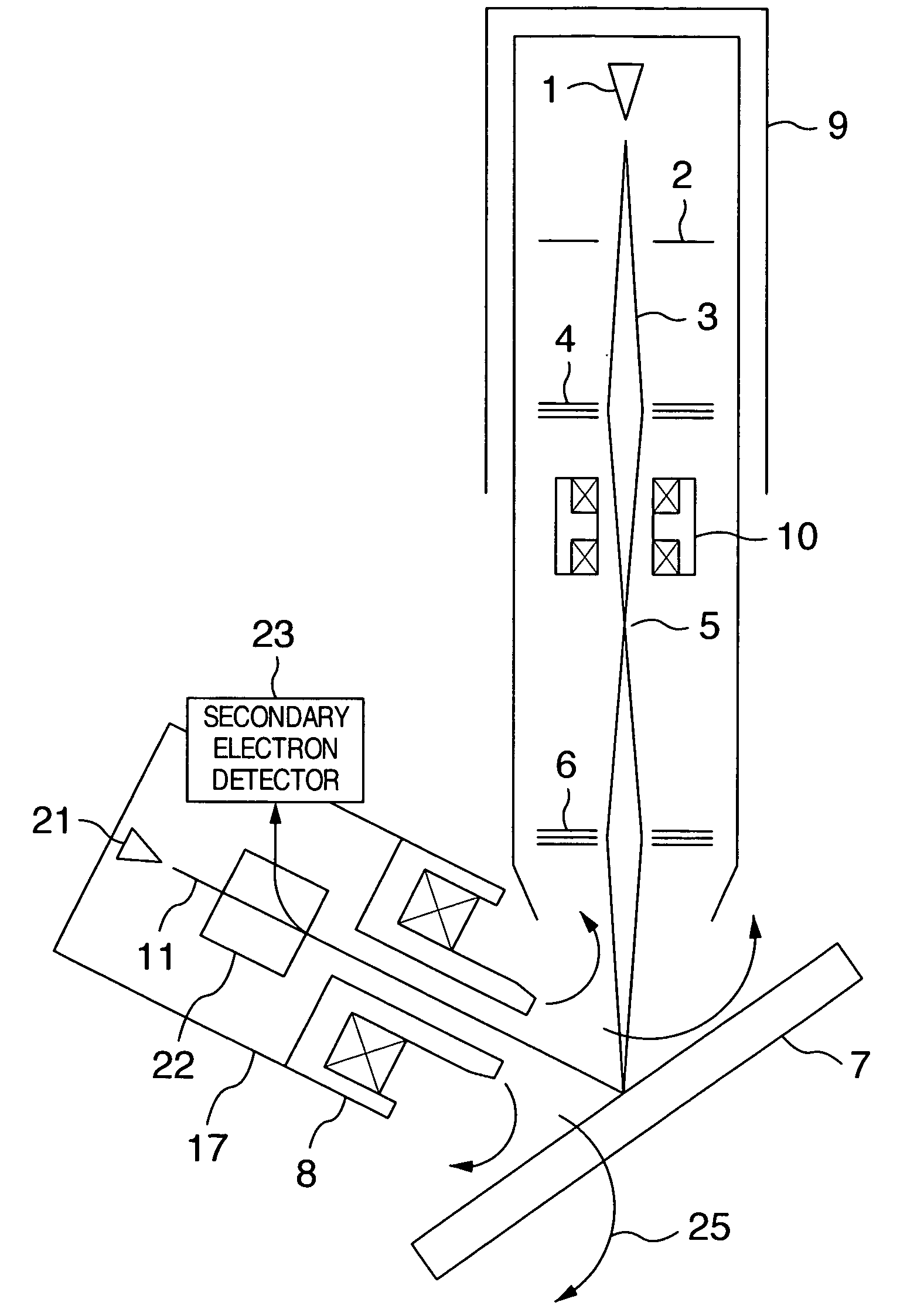
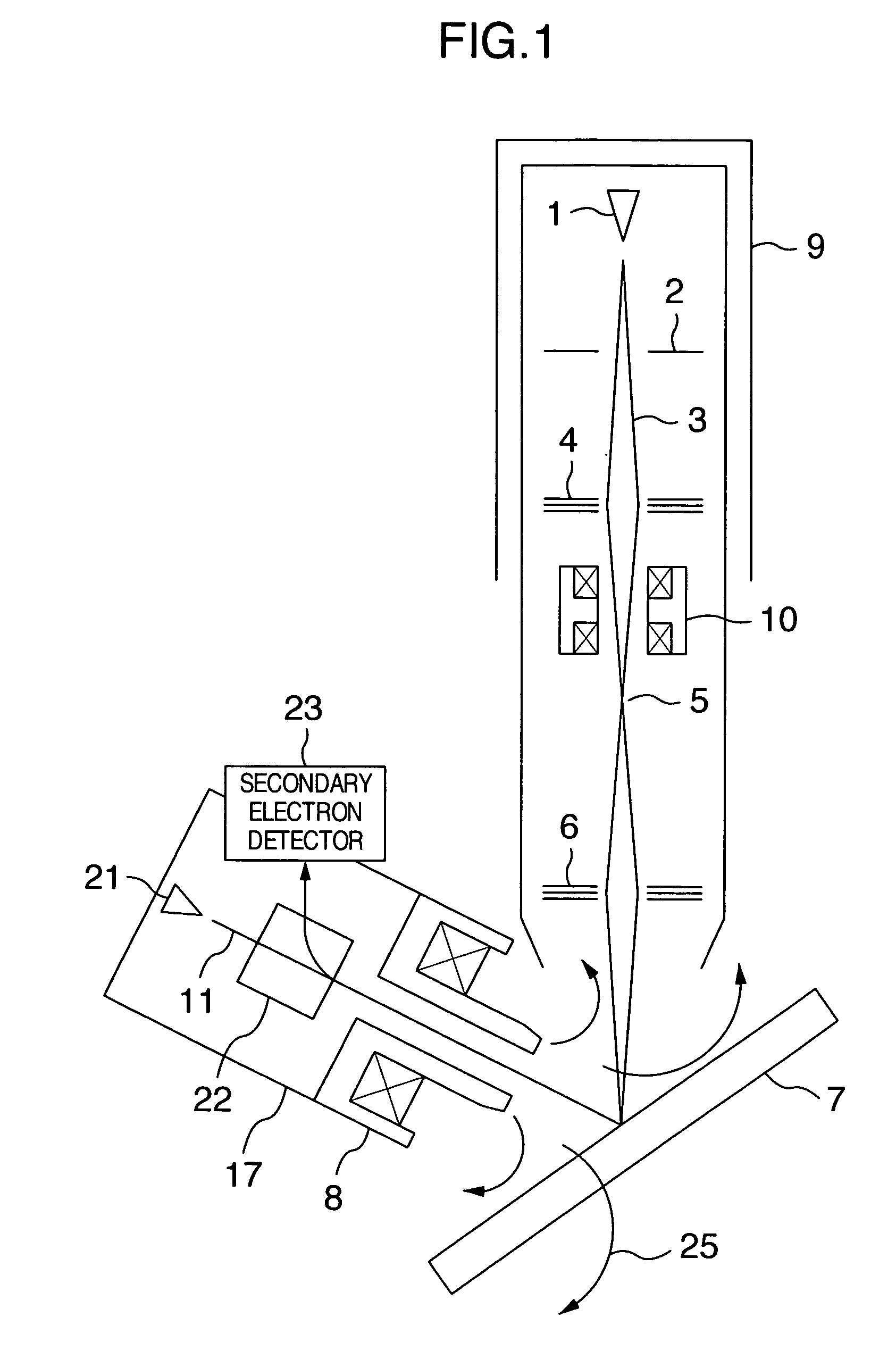
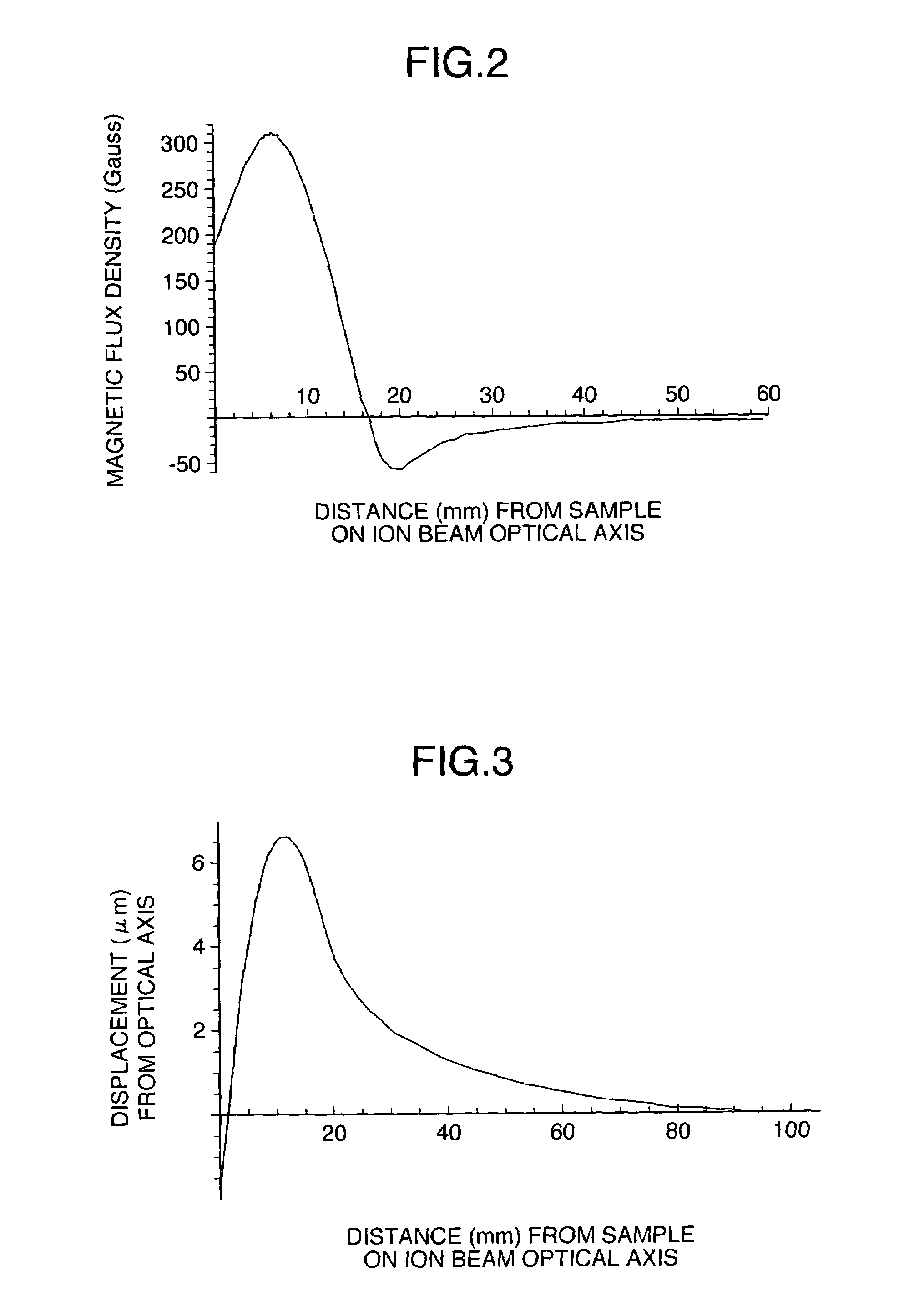
ActiveUS7411192B2High resolutionStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationOptical axisIsotope
A focused ion beam apparatus and a focused ion beam irradiation method are disclosed. Even in the case where a magnetic field exists on the optical axis of an ion beam and the particular magnetic field undergoes a change, the ion beam is focused without separating the isotopes on the sample at the same ion beam spot position as if the magnetic field is not existent. A canceling magnetic field is generated on the optical axis of the ion beam from a canceling magnetic field generator thereby to offset the deflection of the ion beam due to the external magnetic field.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
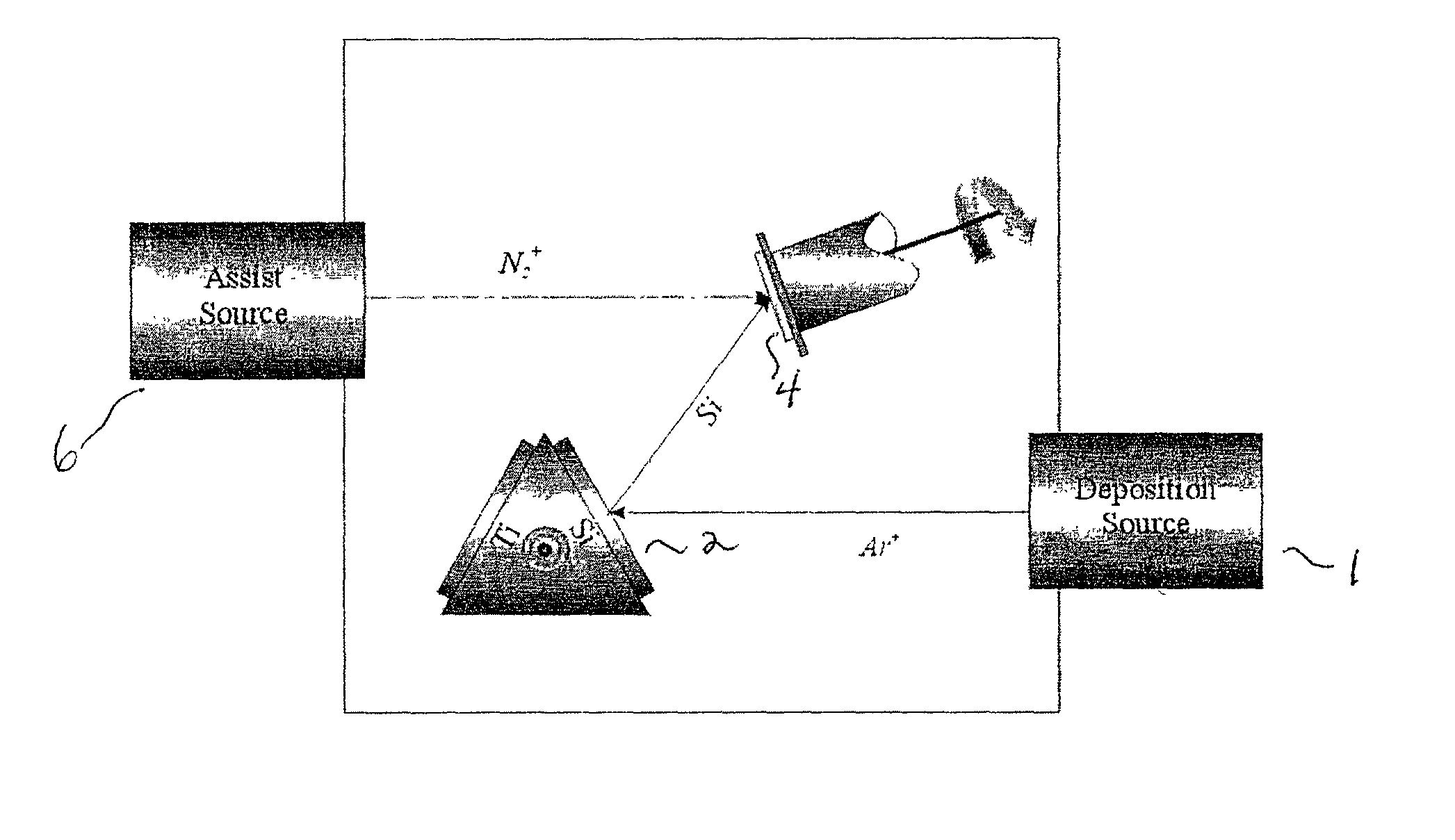
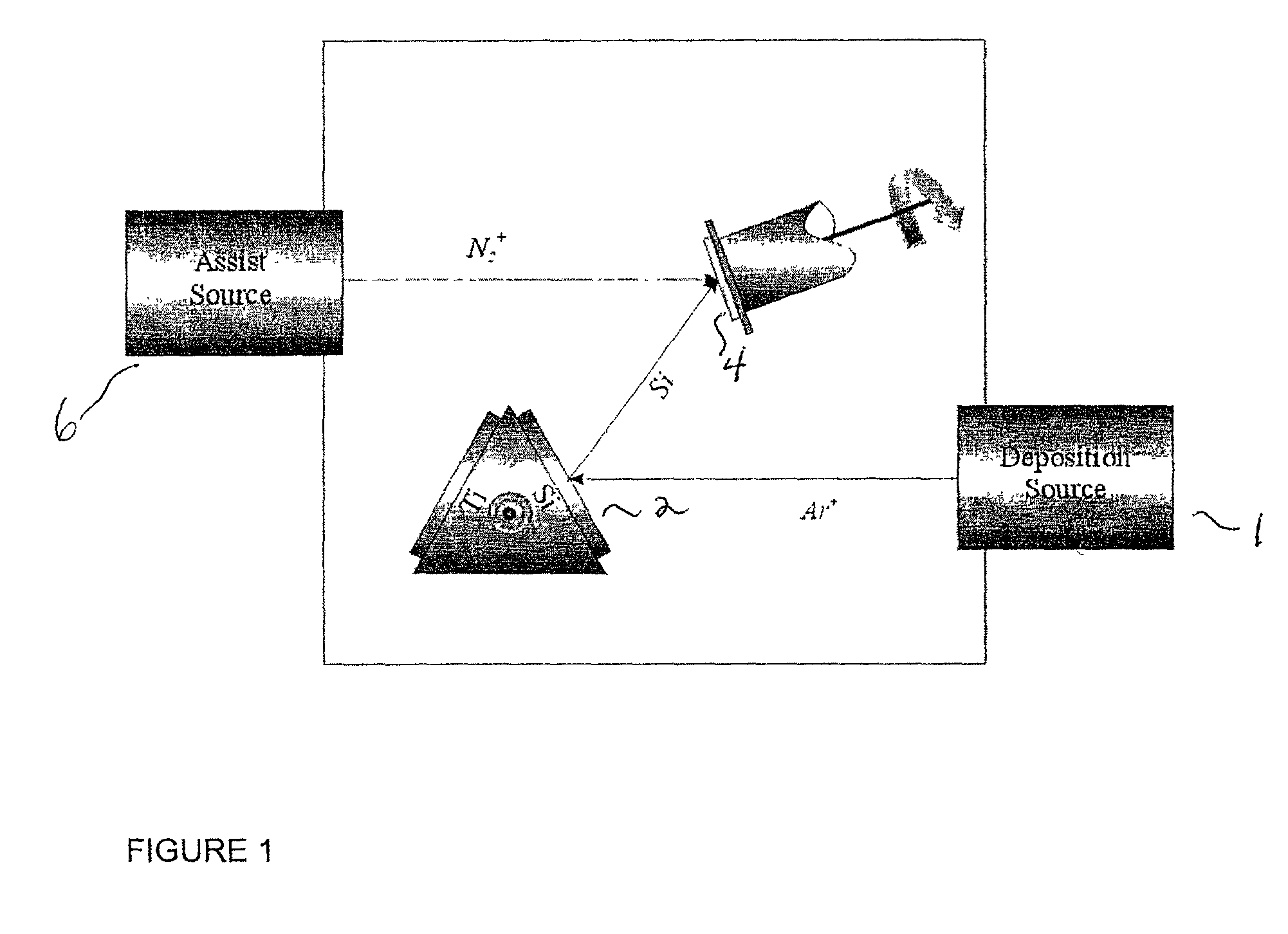
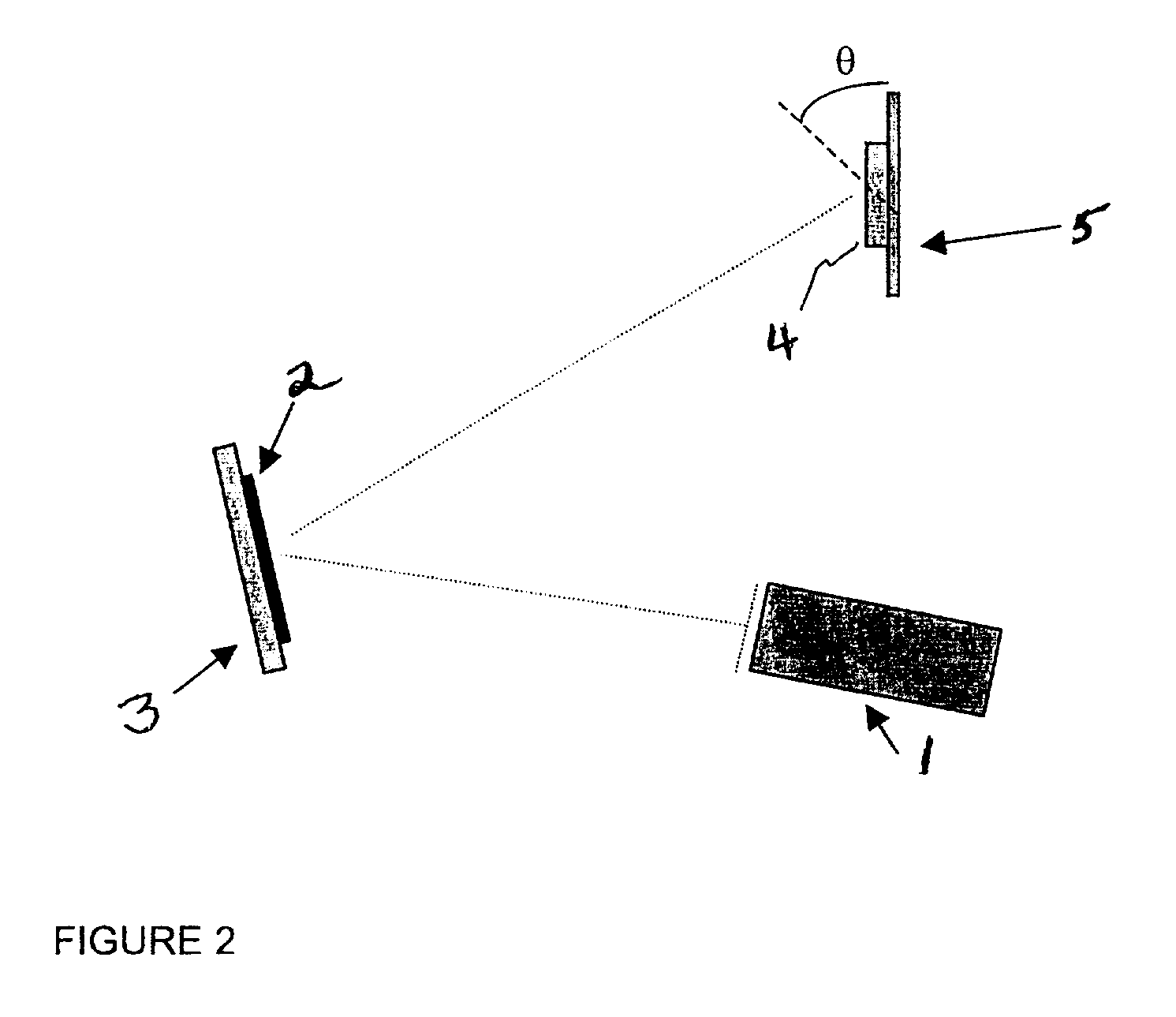
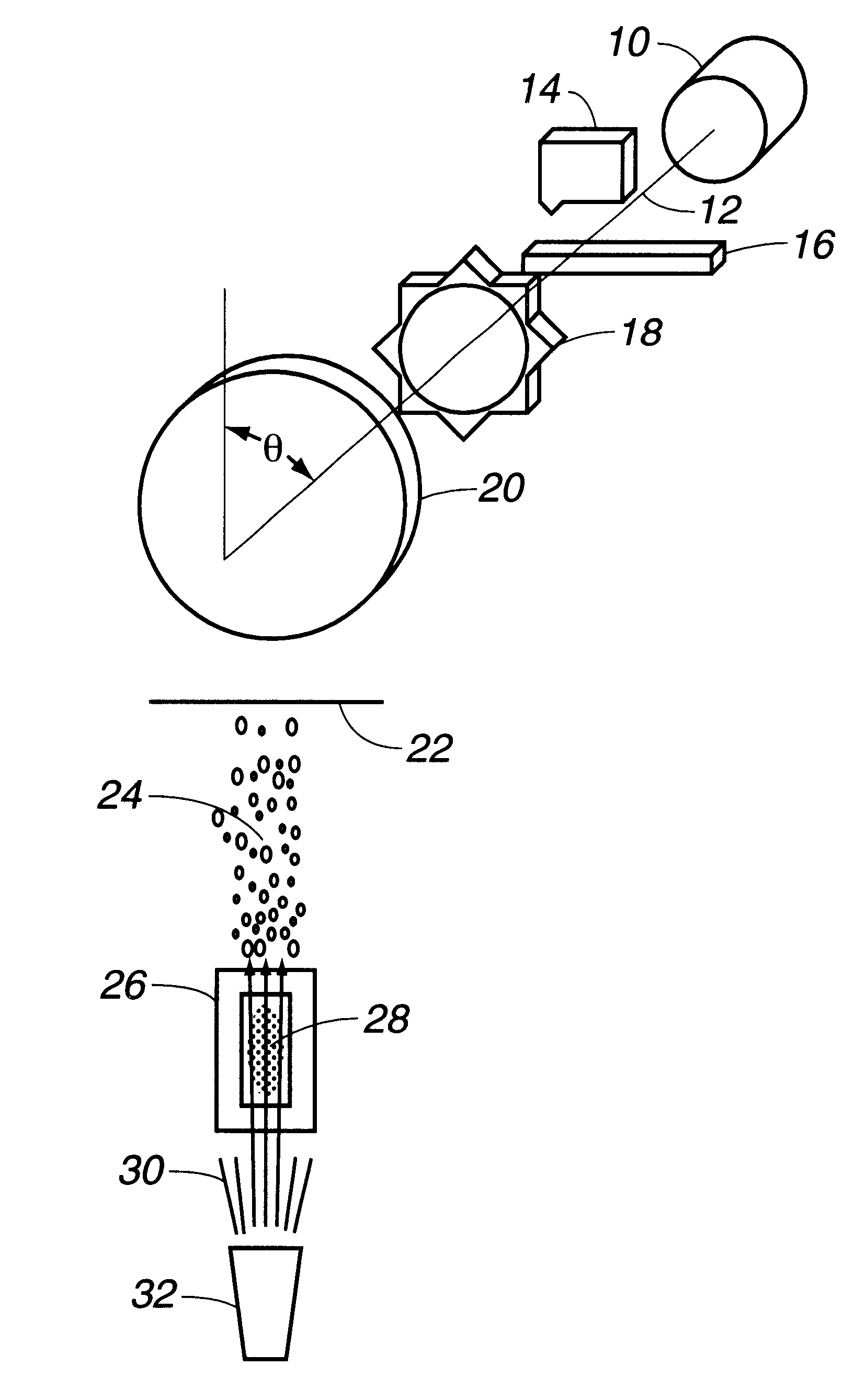
Direct ion beam deposition method and system
InactiveUS20060225998A1Avoid overall overheatingFacilitating ion emission of the deposit materialCellsElectric discharge tubesIonizationElectron
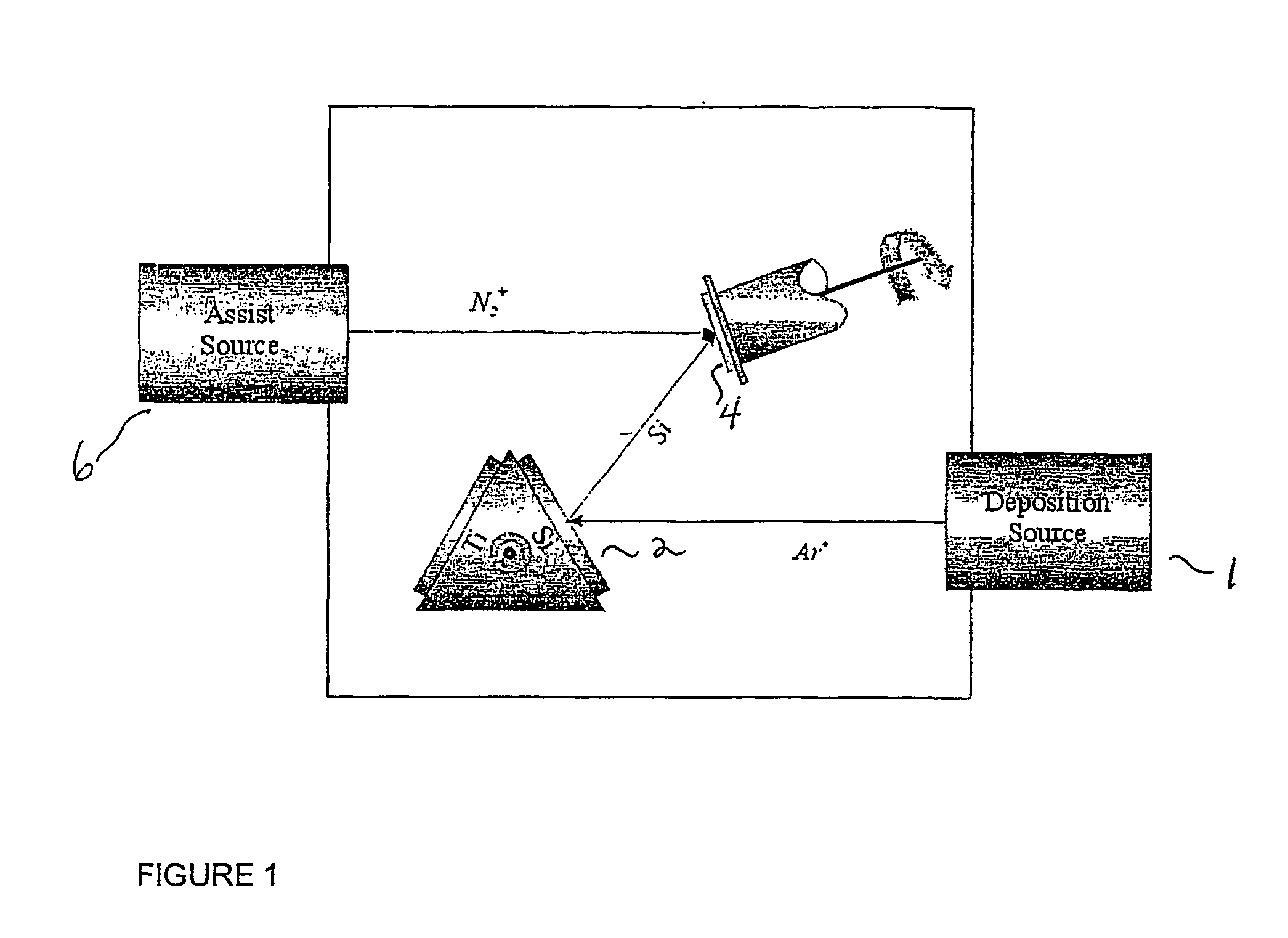
Disclosed herein is a direct ion beam deposition method through ion beam sputtering. The method comprises the steps of: a) providing a workpiece on which a certain material is to be deposited with a certain desired thickness; b) providing a deposit material having a certain area from which the deposit material is discharged into a certain working gas atmosphere; c) transforming the working gas atmosphere into a plasma atmosphere by bombarding electrons widely to the working gas atmosphere; d) emitting a surface material by means of a sputter from the deposit material exposed in the plasma atmosphere; e) exposing the emitted deposit material to an ionization environment; f) and providing energy to the deposit material by applying an electric potential to the step e) to thereby be radiated on a corresponding face of the workpiece. A direct ion beam deposition system is also disclosed.
Owner:SONG SEOK KYUN
Superconductor fabrication processes
InactiveUS20050249869A1Current/voltage measurementVacuum evaporation coatingVolumetric Mass DensityIon beam-assisted deposition
A method of forming a superconductive device is provided, including providing a substrate having a dimension ratio of not less than about 102, depositing a buffer film to overlie the substrate by ion beam assisted deposition utilizing and ion beam, monitoring spatial ion beam density of the ion beam over a target area, and depositing a superconductor layer to overlie the buffer film. Monitoring may be carried out by utilizing an ion detector having an acceptance angle of not less than 10°.
Owner:SUPERPOWER INC
Aligned crystalline semiconducting film on a glass substrate and method of making
A semiconducting structure having a glass substrate. In one embodiment, the glass substrate has a softening temperature of at least about 750° C. The structure includes a nucleation layer formed on a surface of the substrate, a template layer deposited on the nucleation layer by one of ion assisted beam deposition and reactive ion beam deposition, at least on biaxially oriented buffer layer epitaxially deposited on the template layer, and a biaxially oriented semiconducting layer epitaxially deposited on the buffer layer. A method of making the semiconducting structure is also described.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Method for preparing metal sulfide diamond-like carbon composite film
InactiveCN101787521AVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCathodic arc depositionComposite film
The invention relates to a method for preparing a metal sulfide DLC composite film. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly using the ultrasonic washing technology to remove the surface contamination layer of a basal body; using the inert gas ion beam generated by an ion source to carry out the ion beam bombardment washing on the surface of the basal body; using the metal ion generated by a cathodic arc source to carry out the metal ion bombardment washing on the surface of the basal body under the high workpiece negative bias condition; using the cathodic arc deposition or ion beam assisted magnetron sputtering technology to prepare a gradient transition layer; using the ion beam deposition on an intermediate layer and magnetron sputtering technology to synthesize a doped DLC film doped with at least one metal element of W, Mo and Fe; and finally obtaining the high-sulfur metal sulfide / DLC composite film by using the ion vulcanization, wherein the ion beam deposition is realized by introducing carbonaceous gas to the ion source, and sulfureous gas is used as the sulfur source.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
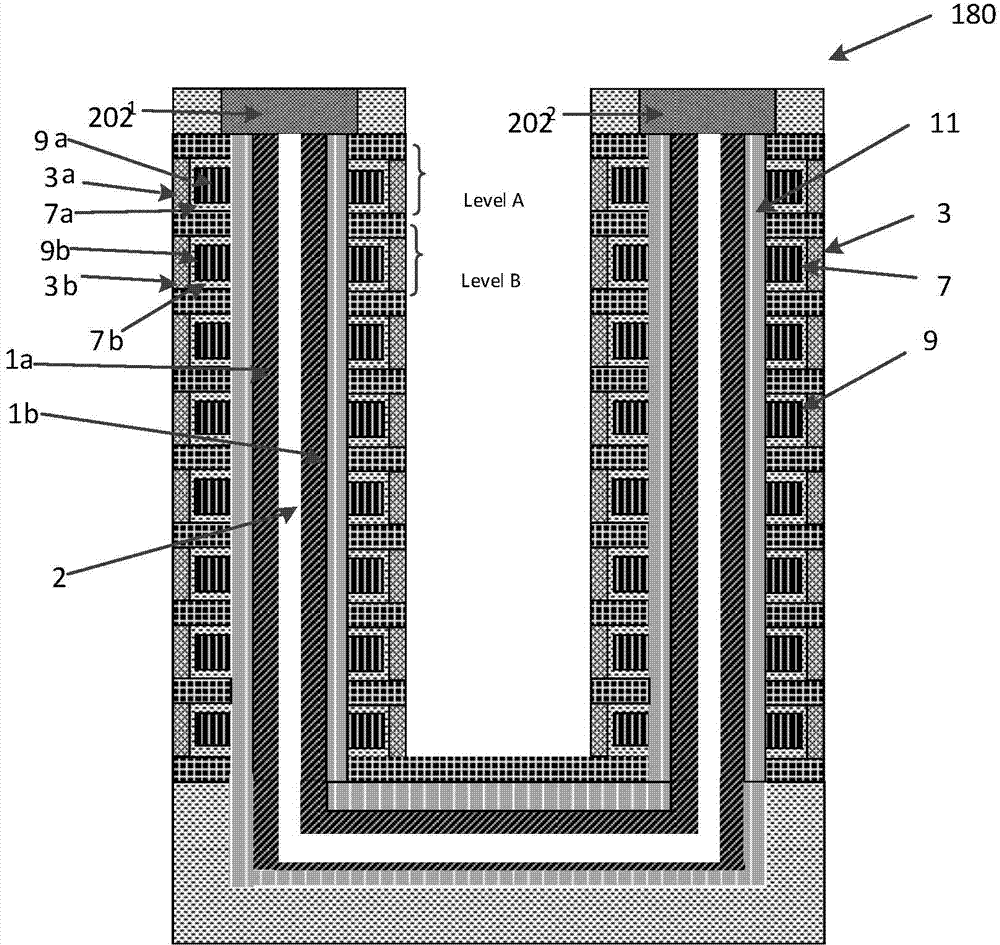
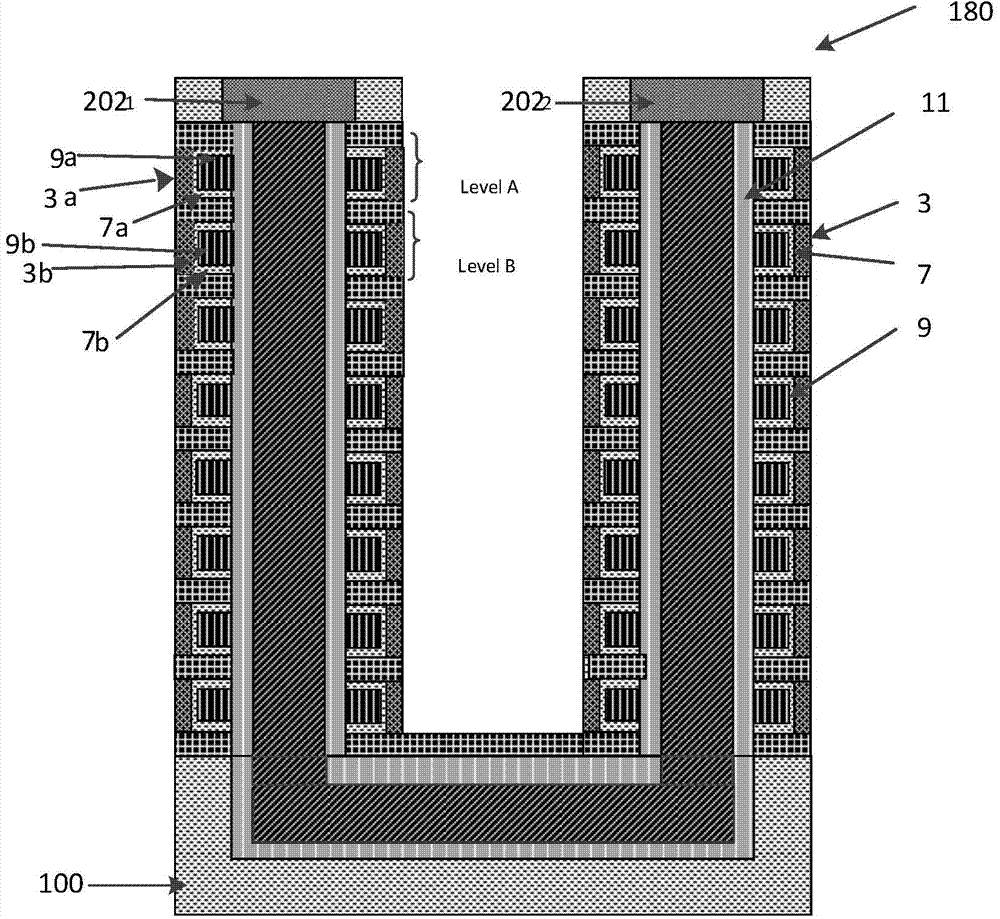
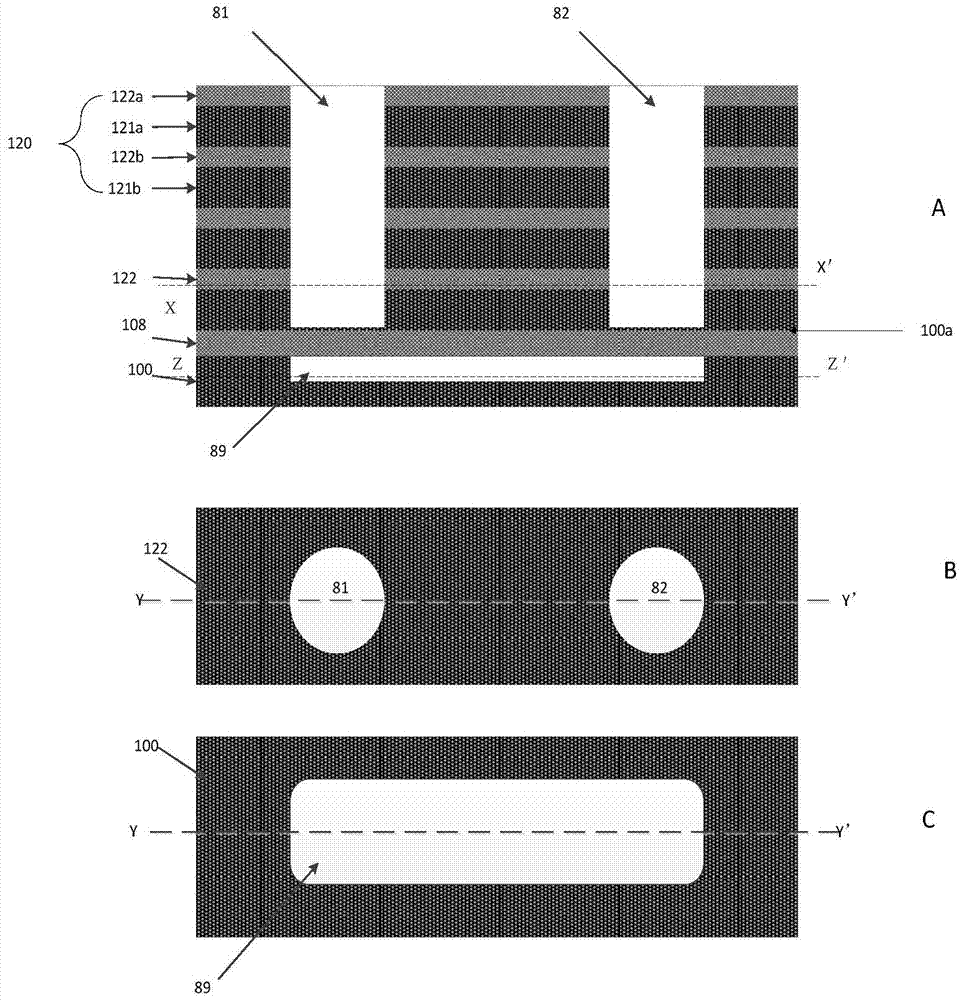
Three-dimensional semiconductor memory device based on deep hole filling and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104269405ASedimentation effectImprove storage densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerElectrode Contact
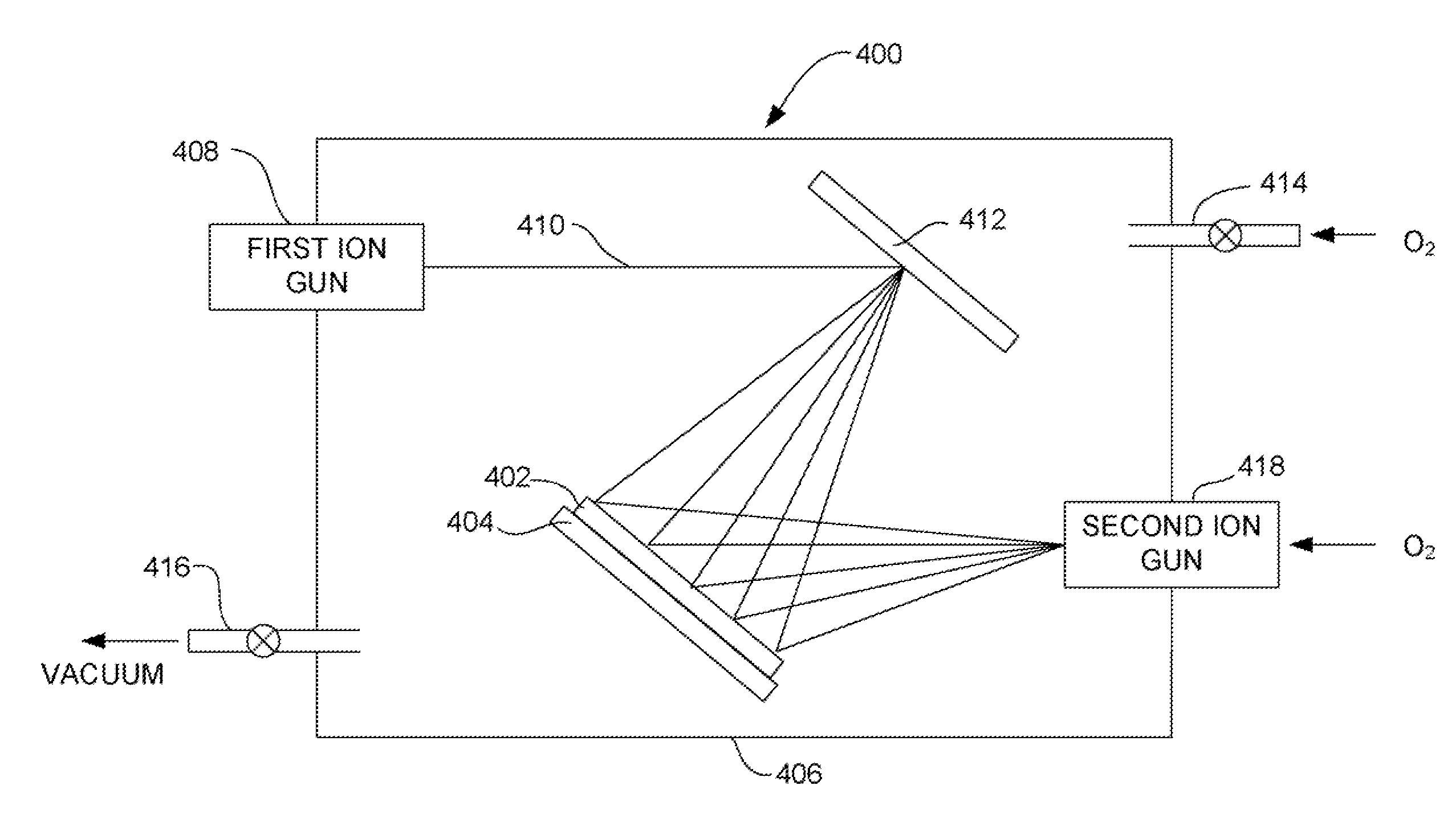
The invention discloses a three-dimensional semiconductor memory device based on deep hole filling and a preparation method of the three-dimensional semiconductor memory device. The preparation method is suitable for preparing a U-shaped channel of the three-dimensional semiconductor memory device. The double-ion-beam deposition technology is adopted, a target material is bombarded with one beam of ions, molecules of the target material overflow and are deposited in a deep hole along a trail, the surface of the deep hole is bombarded with the other beam of ions, the deposited material can not cover the top of the deep hole, and therefore it is guaranteed that the U-shaped channel of the three-dimensional semiconductor memory device is completely formed. Electrodes of the three-dimensional semiconductor memory device with the U-shaped channel are led out from the upper side of the device, so that the electrode contact area is reduced; meanwhile, an NAND string of the U-shaped three-dimensional semiconductor memory device can comprise a stacking structure formed by alternately stacking at least one layer of semiconductors and an insulation layer, the number of devices in the unit area is increased, and therefore the memory density of the three-dimensional semiconductor memory device with the U-shaped channel can be greatly increased.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ion-beam deposition process for manufacturing attenuated phase shift photomask blanks
An ion-beam deposition process for fabricating attenuating phase shift photomask blanks, capable of producing a phase shift of 180°, and which can provide tunable optical transmission at selected lithographic wavelengths<400 nm, comprising at least one layer of material of general formulae MzSiOxNy or MzAlOxNy, is described.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method of preparing high temperature wear resistant coating
InactiveCN1459514ATightly boundQuality assuranceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingWear resistantRefractory
A technology for preparing antiwear refractory coated layer features that the atom beam deposition is used to prepare coated layer, the electronic (or laser) beam treatment is used to control the microstructure of coated layer, and the iron beam technique is used to improve the adhesion between coated layer and substrate, and different coated layers.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for preferentially growing metallic single-walled carbon nanotube by using non-metallic silicon oxide as catalyst
ActiveCN103303904ANo diffusionNo metal contaminationMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon nanotubesNano siliconCarbon nanotube
The invention relates to the field of direct controllable preparation of metallic single-walled carbon nanotubes, and particularly discloses a method for preferentially growing a metallic single-walled carbon nanotube by using non-metallic silicon oxide as a catalyst. A silicon oxide film is deposited on a silicon substrate with nano silicon oxide thermal oxidization layer by an Ar ion beam deposition method, nucleation and precipitation of nano particles are realized by control on pretreatment conditions, and regulation on particle size and distribution is also realized, finally, the metallic single-walled carbon nanotube with the diameter about 1.2nm is obtained under proper growth conditions, and the content of the metallic single-walled carbon nanotube is more than 80% of the amount of the single-walled carbon nanotubes. In the method provided by the invention, starting from controlling the catalyst on which the single-walled carbon nanotube depends in the nucleation phase, based on the property of high melting point of the non-metallic catalyst, the direct growth of the single-walled carbon nanotube with narrower diameter distribution is realized, the bottleneck of metallic single-walled carbon nanotube control preparation in the present stage is broken, and new knowledge is provided for the nucleation mechanism of the single-walled carbon nanotube with special structure.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ion-beam deposition process for manufacturing multi-layered attenuated phase shift photomask blanks
A single ion-beam deposition, or a dual ion-beam deposition process for fabricating attenuating phase shift photomask blanks capable of producing a phase shift of 180° and having an optical transmissivity of at least 0.001 at selected lithographic wavelengths <400 nm, comprising at least one layer of an optically transmitting and / or one layer of optically absorbing elemental or a compound material in a periodic or an aperiodic arrangement.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Focused anode layer ion source device
InactiveCN106653557AScientific and reasonable structure designExtended service lifeElectron/ion optical arrangementsIon sources/gunsCooling effectHigh intensity
The invention discloses a focused anode layer ion source device, which comprises a shell, wherein an anode ring and a cathode ring are oppositely arranged in the shell at an interval; an intake pipe is also fixedly arranged on the shell; the surfaces of the anode ring and the cathode ring are circular conical surfaces; the cathode ring comprises an outer cathode ring and an inner cathode ring; the outer cathode ring and the inner cathode ring are arranged in the same circular conical surface; and the conical surface of the anode ring is parallel to that of the cathode ring. The focused anode layer ion source device is scientific and reasonable in structure design; the anode ring and the cathode ring are set to be parallel circular conical surfaces, generated ion beams are focused towards the axis direction and the ion beams of which the sections are solid circles are formed within a distance range far away from the focusing point; the ion beam density is concentrated and the section uniformity is good; through a design of multiple groups of water-cooling systems, the cooling effect on a magnetic path and the inner cathode ring is ensured; the service life of the inner cathode ring can be prolonged; and the continuous high-intensity working time of the ion source is prolonged and the reliability of the ion source is strengthened.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com