Ion sources and methods of operating an electromagnet of an ion source
An ion source, electromagnet technology, applied in the field of ion beam
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
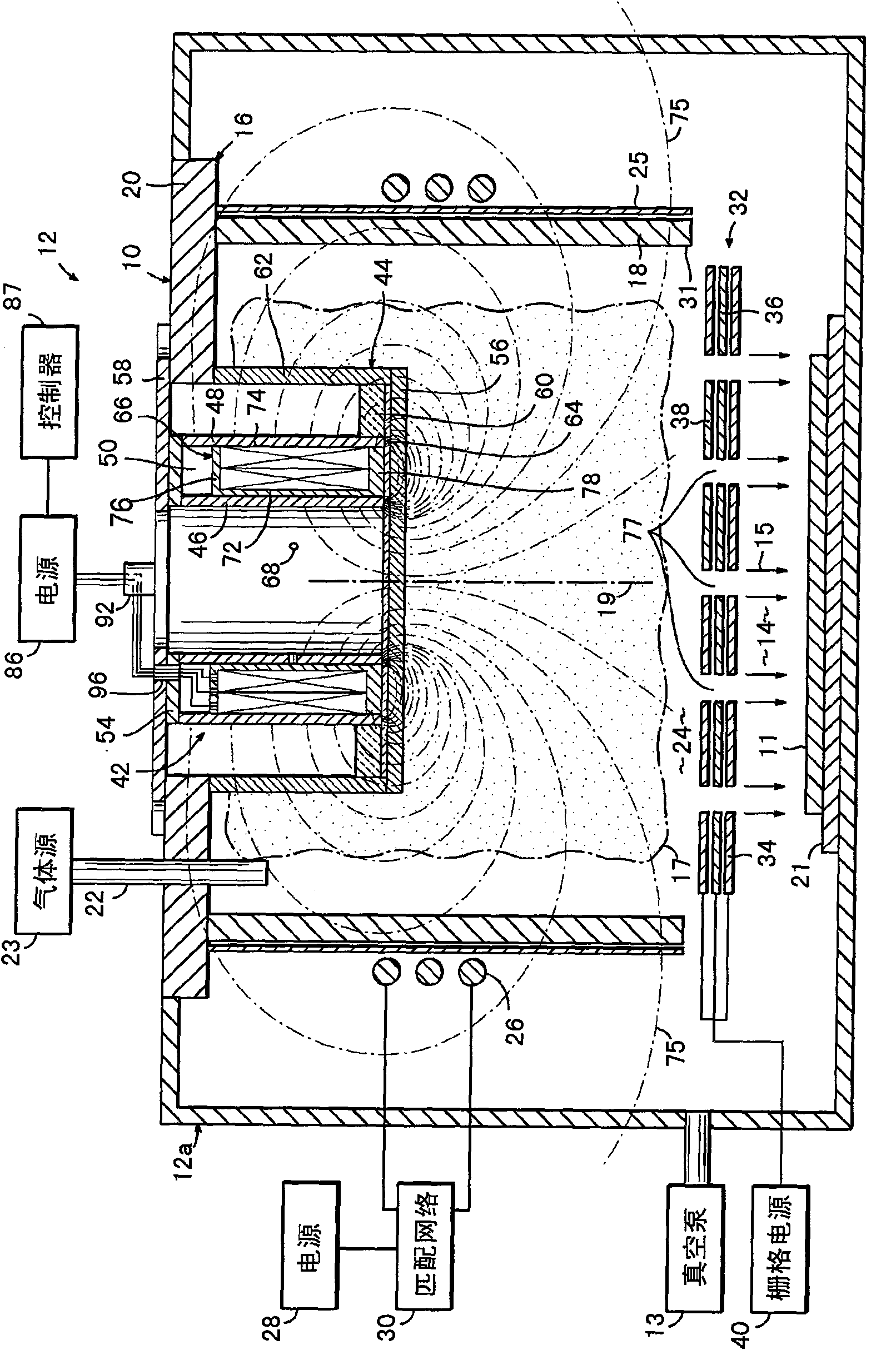
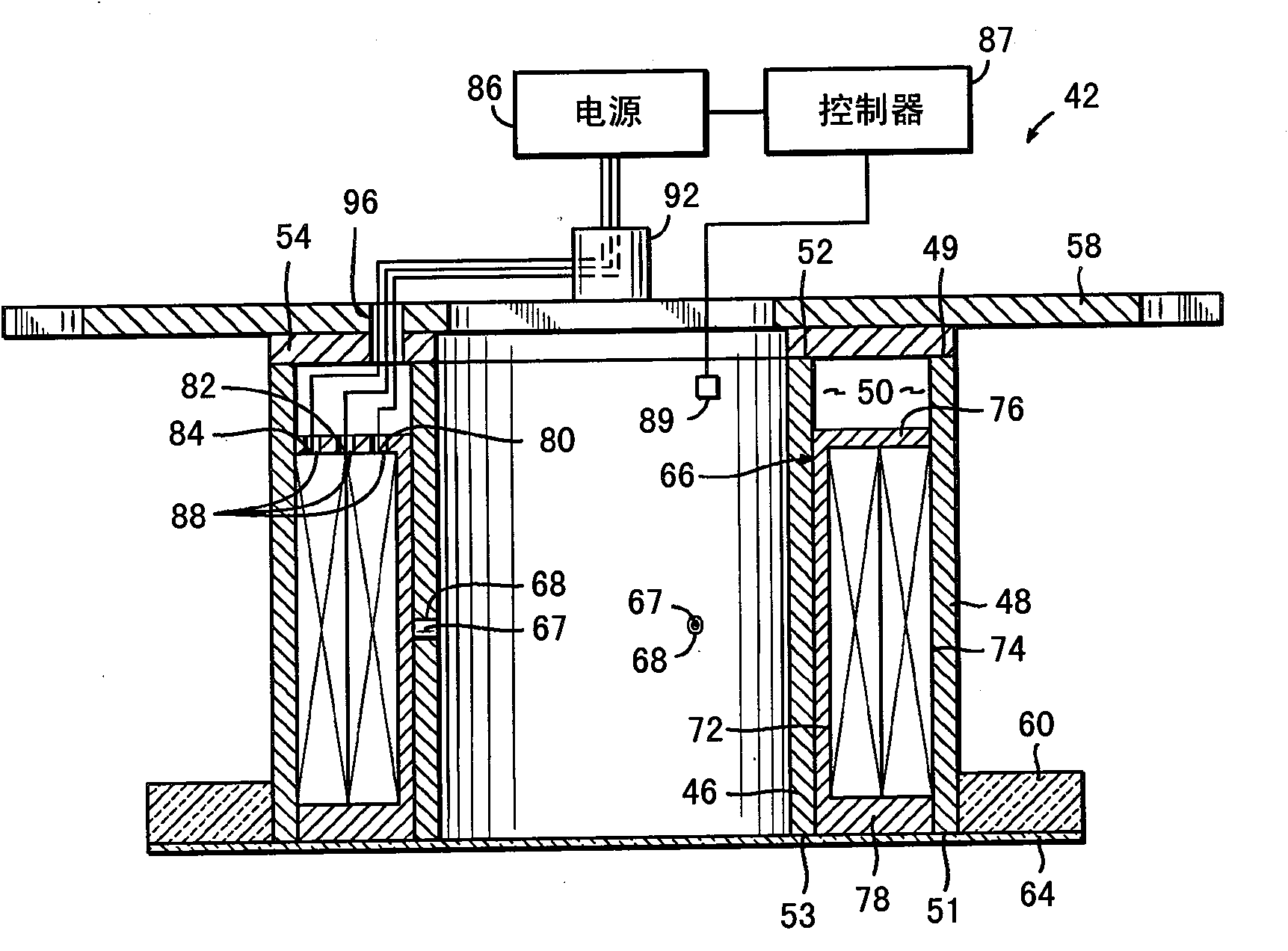
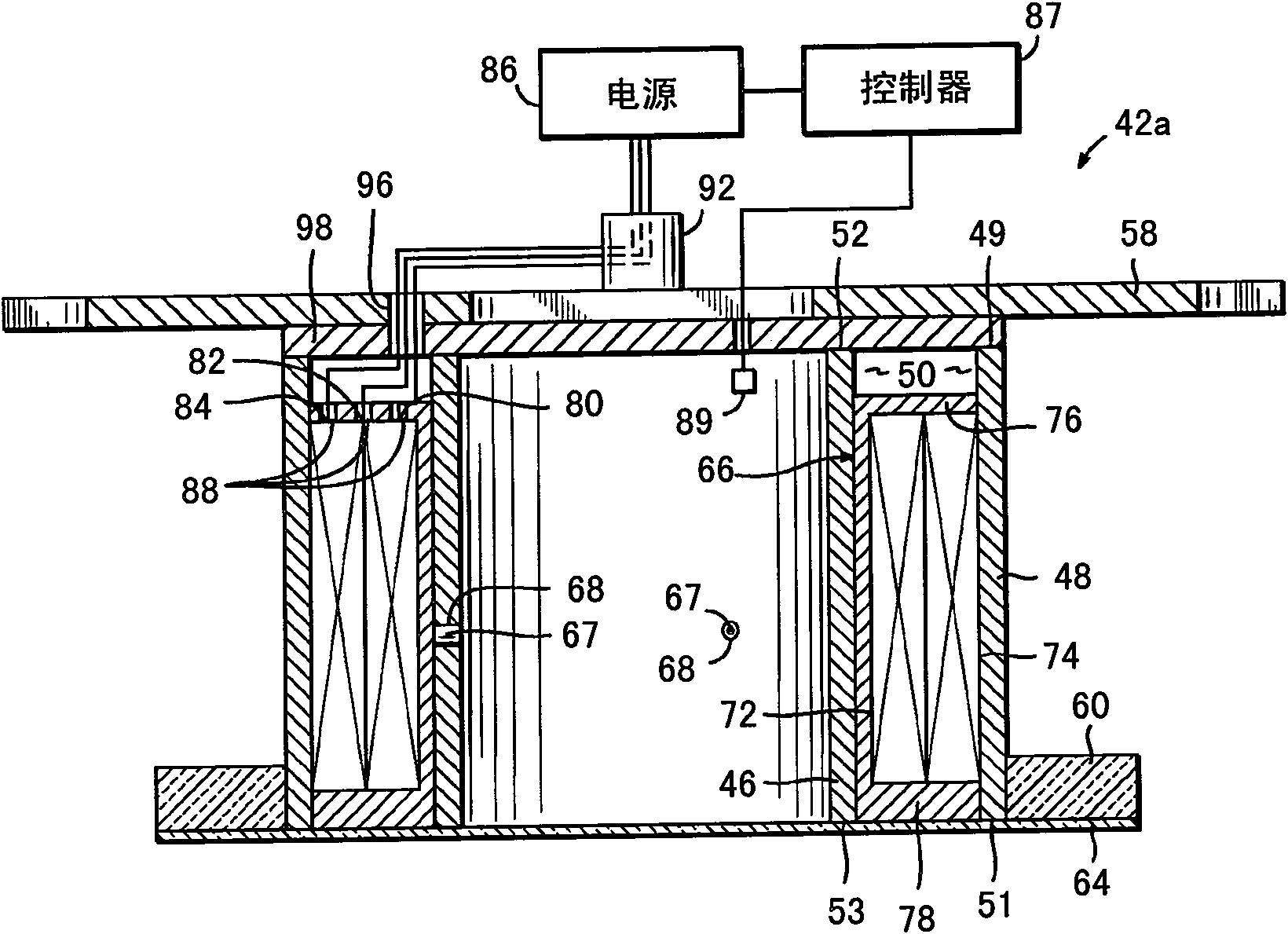
[0088] Ion source with electromagnet assembly, otherwise substantially the same as electromagnet 42b ( Image 6 ) is the same, but with each of the inner and outer coils comprising a single coil of 970 turns, in order to measure the current supplied to the radially outermost coil of the electromagnet 42b, between the radially innermost coil of the electromagnet and the power supply The room is equipped with an ammeter. The coils of the radially outermost electromagnets are disconnected from the power source so that only the innermost coils of the electromagnet 42b are energized. An electrical probe is inserted into the beam and placed in the plane of the substrate perpendicular to the direction of incidence of the beam. The voltage of the electrical probes, which are charged under the substrate processing conditions, is measured. This voltage is considered to be a measurement of neutralizing the broad ion beam.
[0089] A 1200V, 650mA positively charged ion beam was extract...
example 2
[0096] As evidence that the electromagnets were operated under controlled conditions without reducing the directivity of the ion beam, the "local divergence angle" of the angular distribution of the ions was evaluated for optimal electromagnet current settings for different locations in the beam and compared to the same Equivalent results obtained without electromagnets at process parameters are compared. The "local divergence angle" is determined by etching the substrate under the shield aperture and measuring the size of the etched spot, essentially as in J.R.Kahn, et al. in J.Vac.Sci.Technol.A14(4), Jul / Aug 1996, p. 2106-2112 pages (reference figure 1 ), in addition to using a silicon oxide-coated silicon wafer as a substrate, and using a nanospectrophotometer (Nanometrics Nanospec) with high-resolution etch depth and lateral position measurements TM 8000) to determine the etch depth profile. The entire disclosure of this publication is incorporated herein by reference. ...
example 3
[0101] A series of ion etch profiles, normalized for display, were generated using the ion source and operating parameters of Example 1 (except for the current applied to the electromagnet), and as Figure 9 shown. With no current applied to the coils of the electromagnet (and thus no field strength), the plasma density distribution and plasma ion flux distribution are characterized by a convex profile, which is reflected in the ion etch profile 200 . at relatively low field strengths B L , the convexity of the plasma density distribution and the plasma ion flux distribution increases with increasing field strength, as shown by the ion etch profile 210 . at relatively high field strengths B H , the plasma density distribution and the plasma ion flux distribution change shape to become more concave as the field strength increases. Finally, the plasma density distribution and plasma ion flux distribution become concave, as shown by the ion etch profile 220 .
[0102] at rela...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com