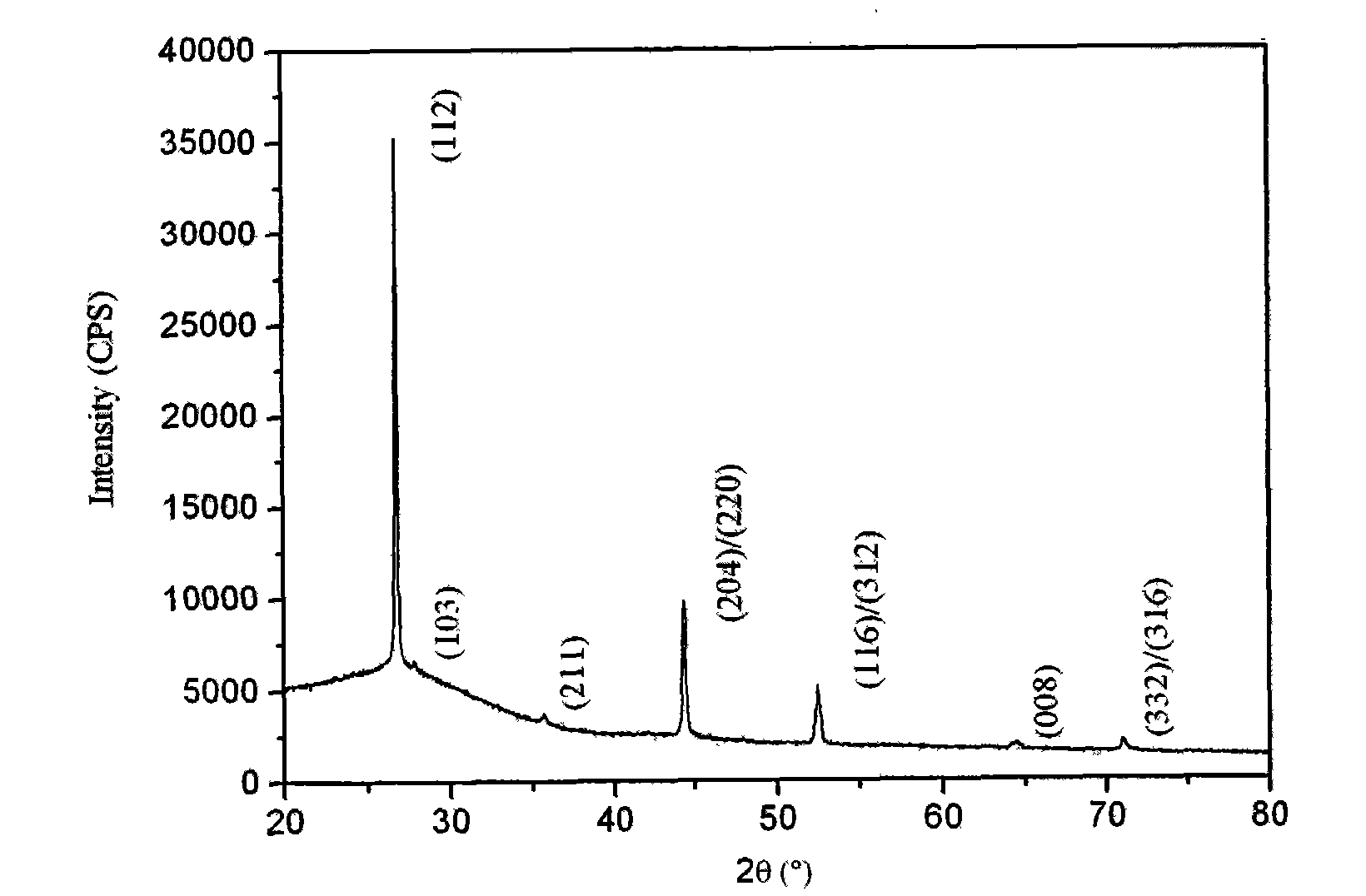
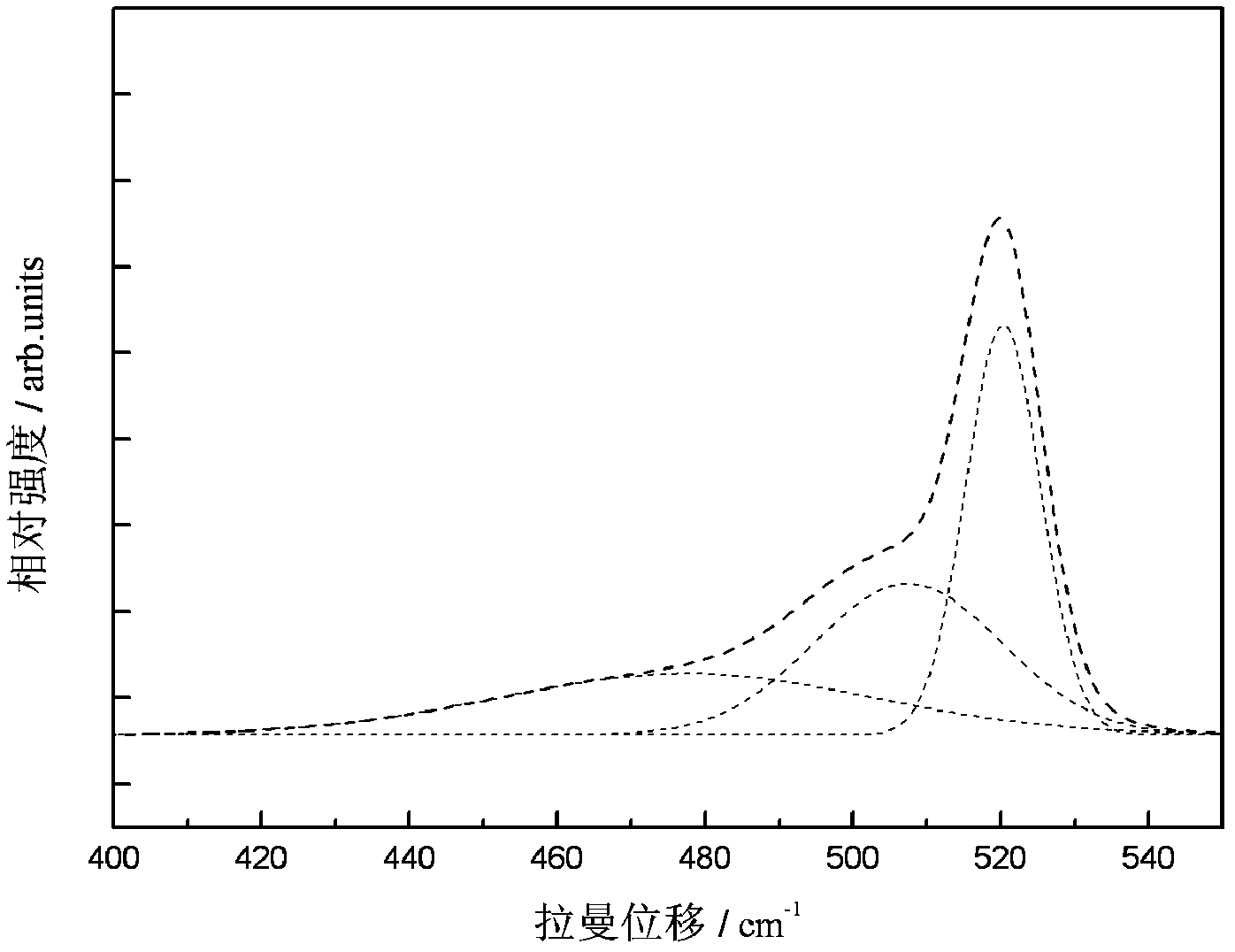
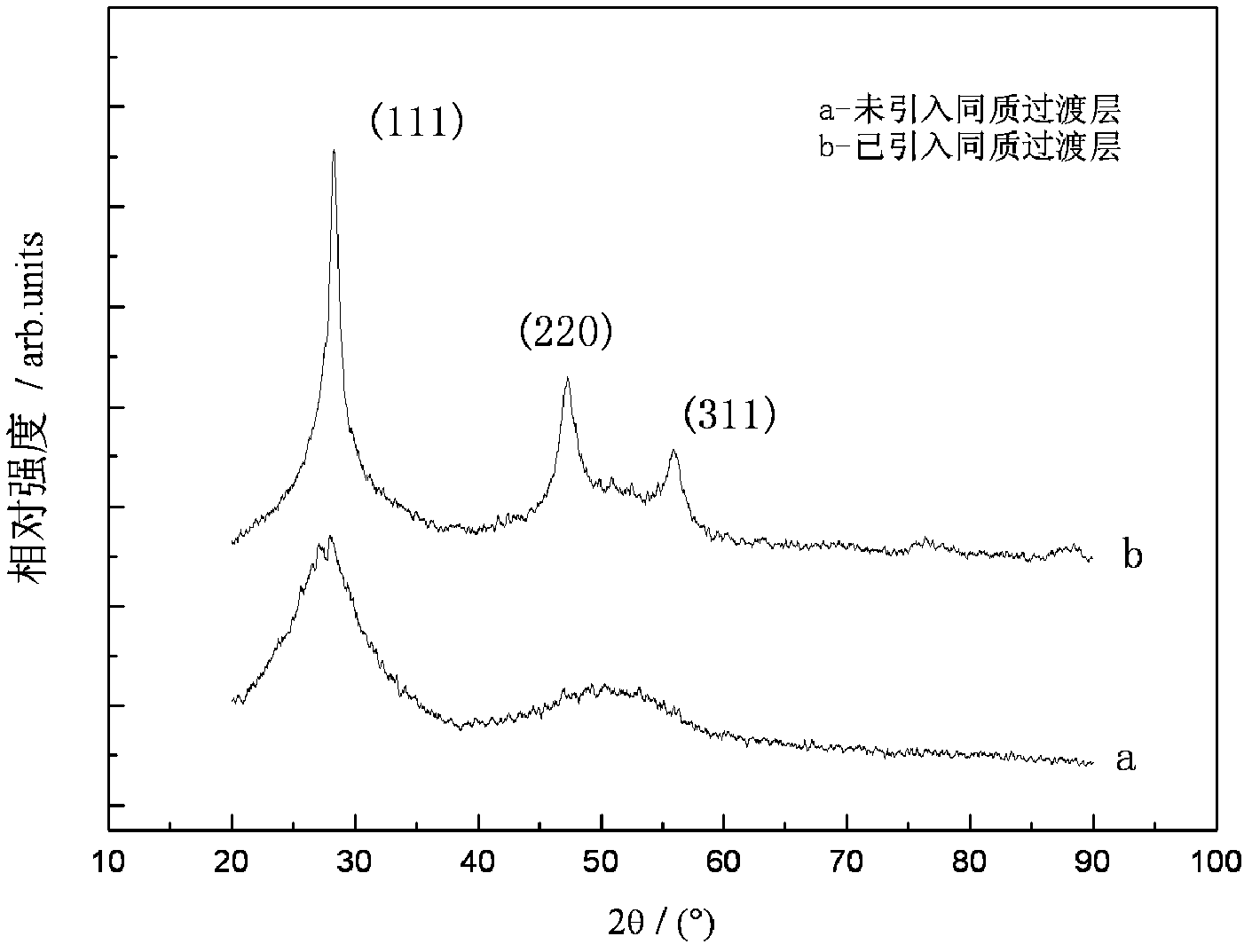
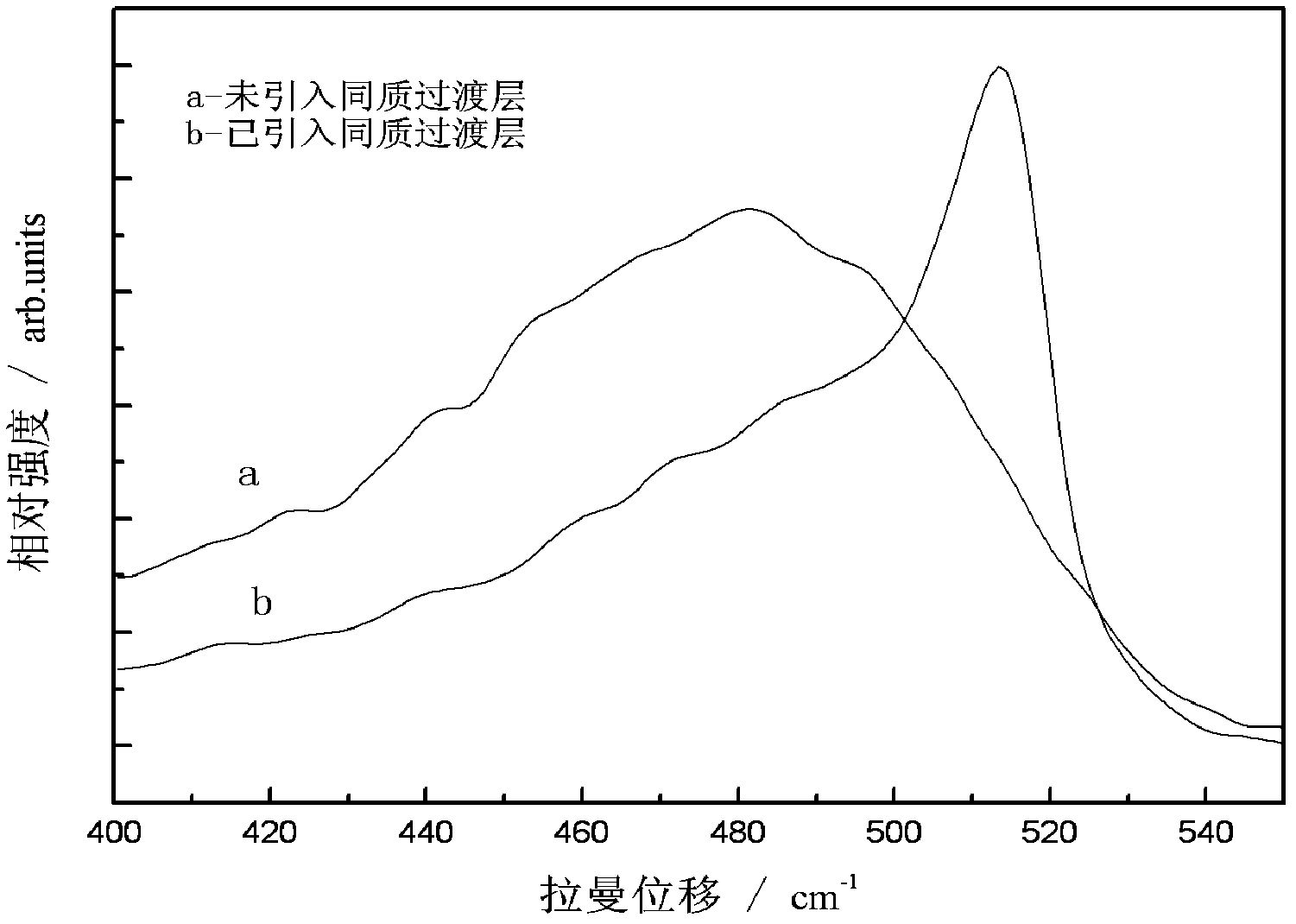
Patents
Literature
76 results about "Ion beam sputtering deposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
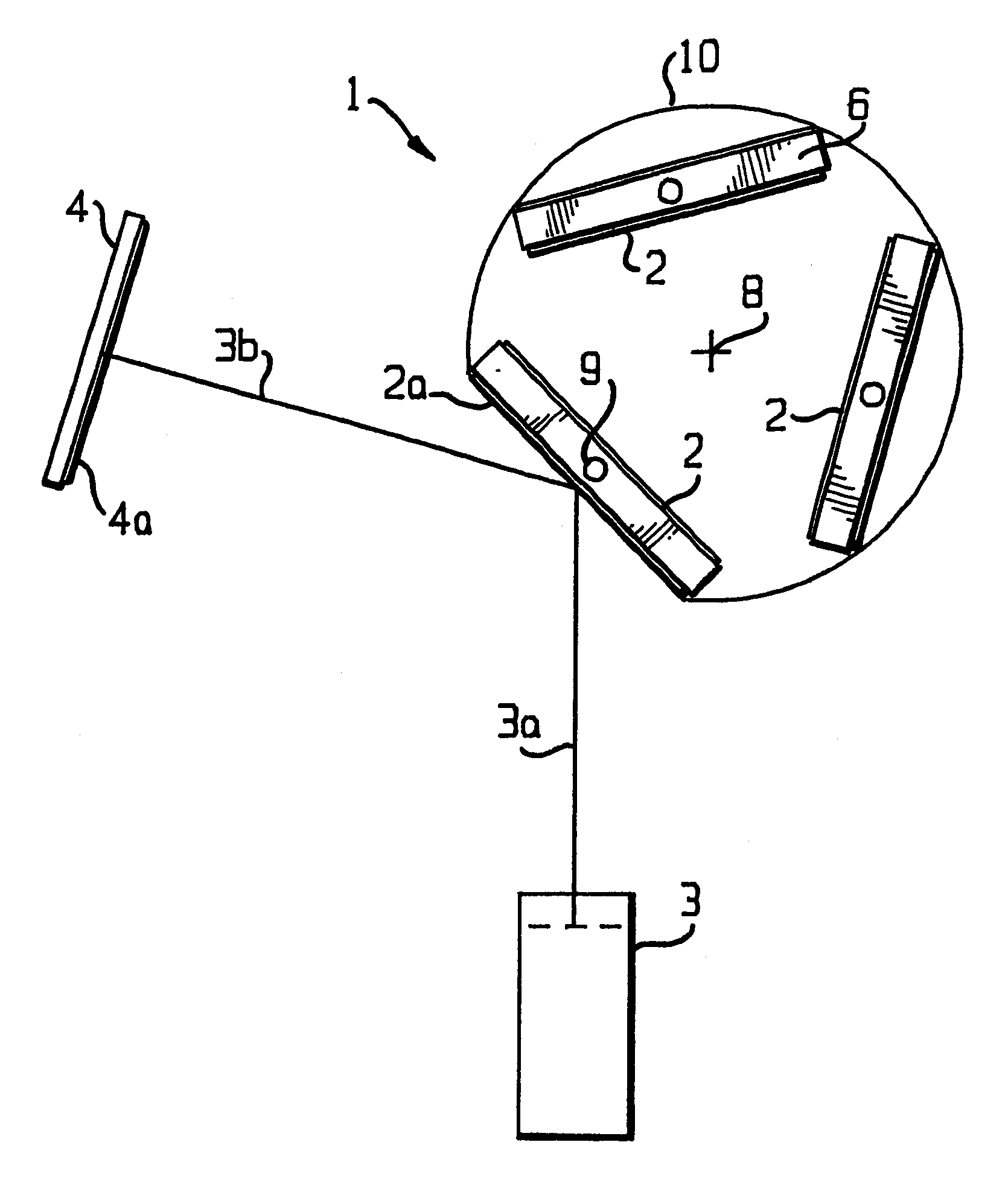
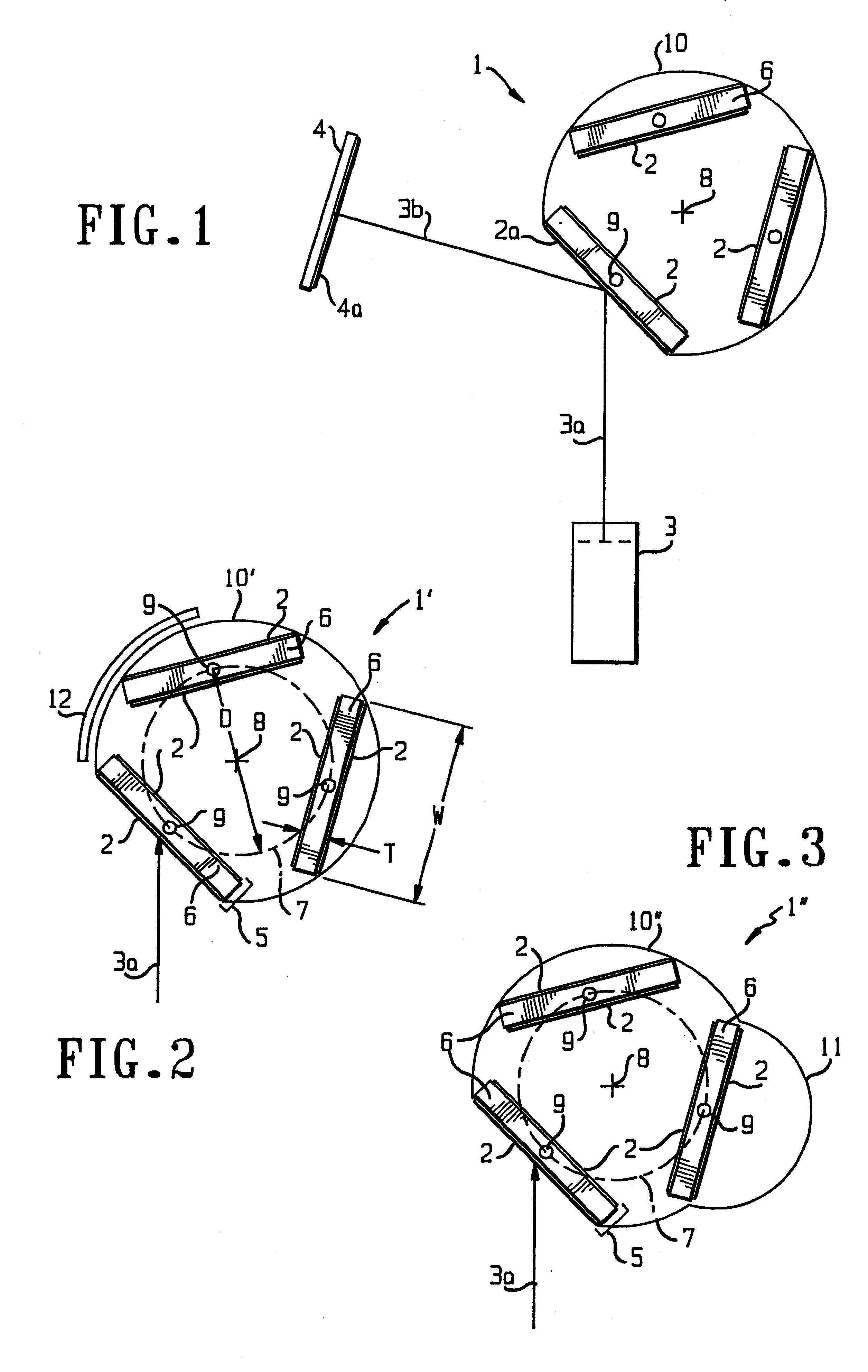
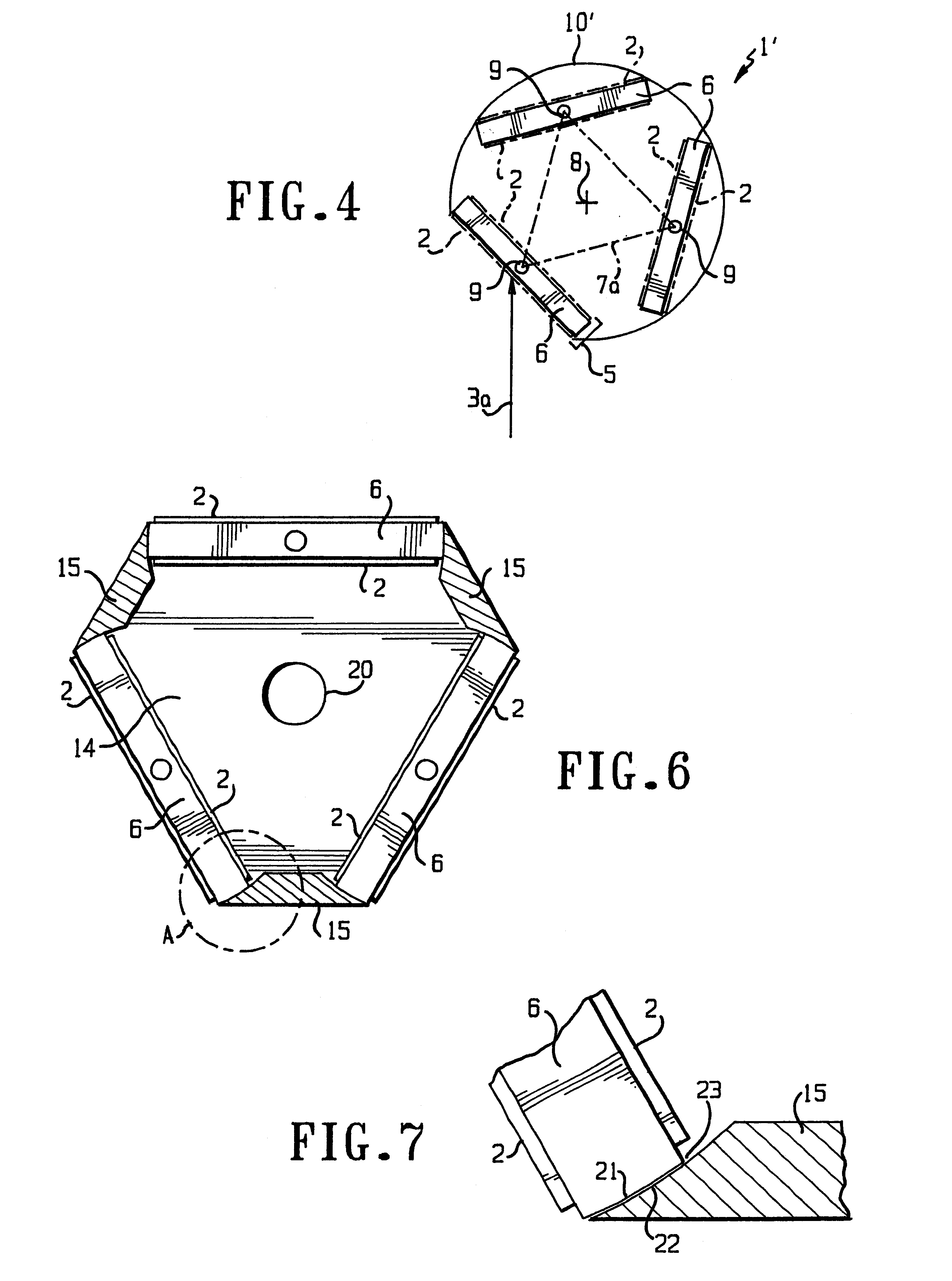
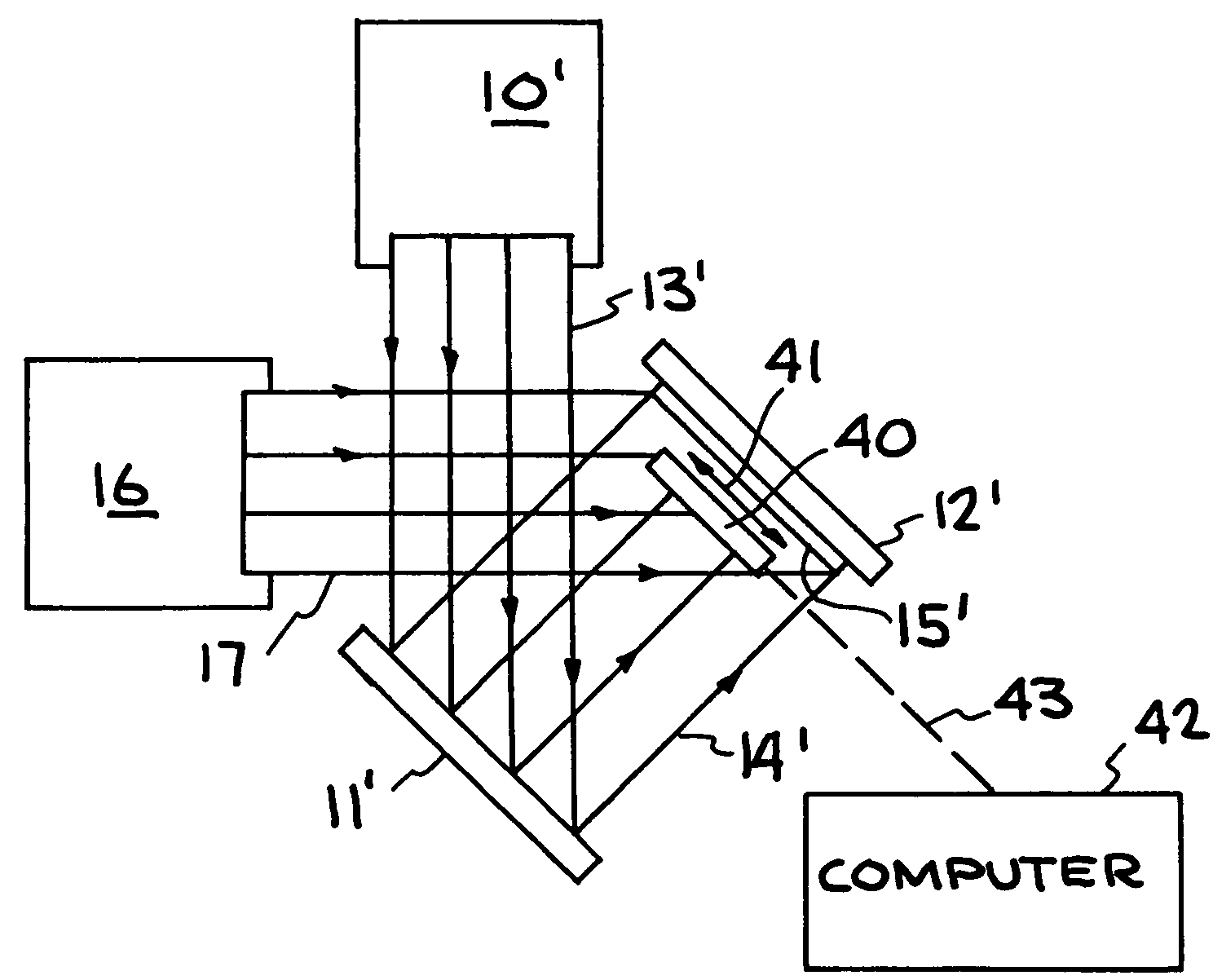
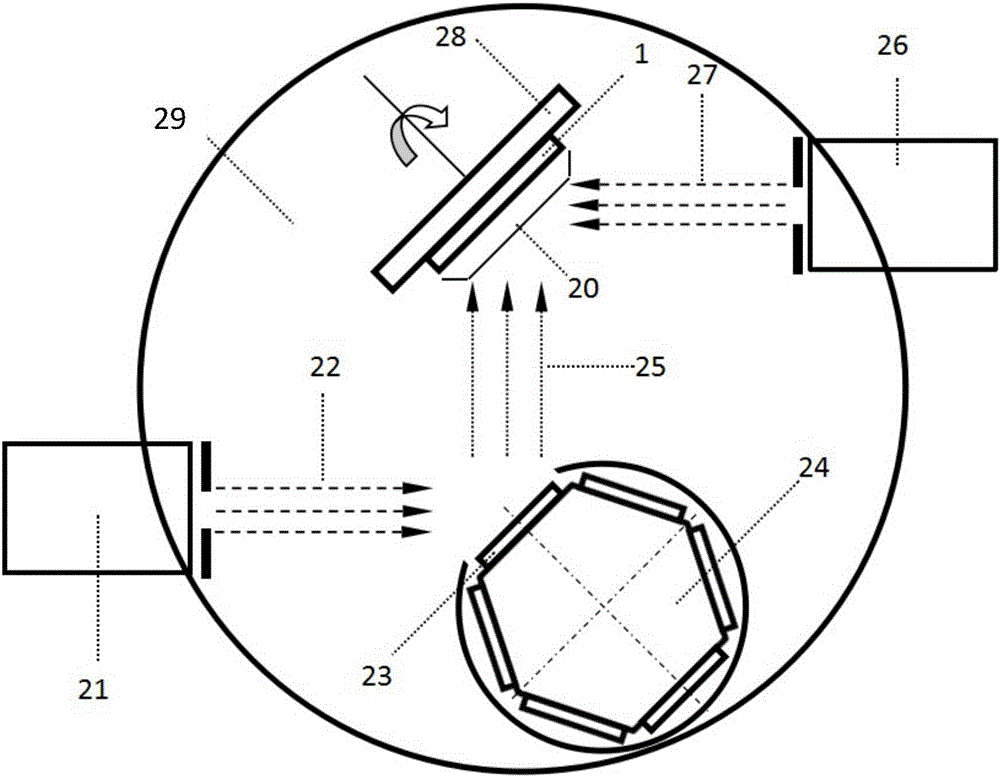
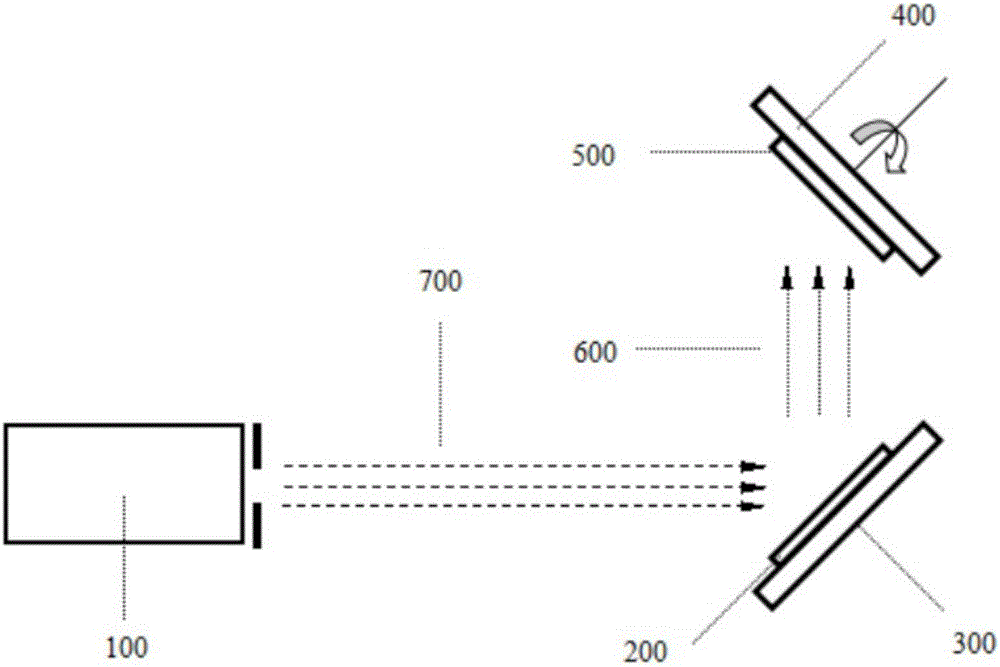
Target assembly for ion beam sputter deposition with multiple paddles each having targets on both sides
InactiveUS6224718B1Small space volumeSimple designCellsElectric discharge tubesAtomic physicsIon beam deposition
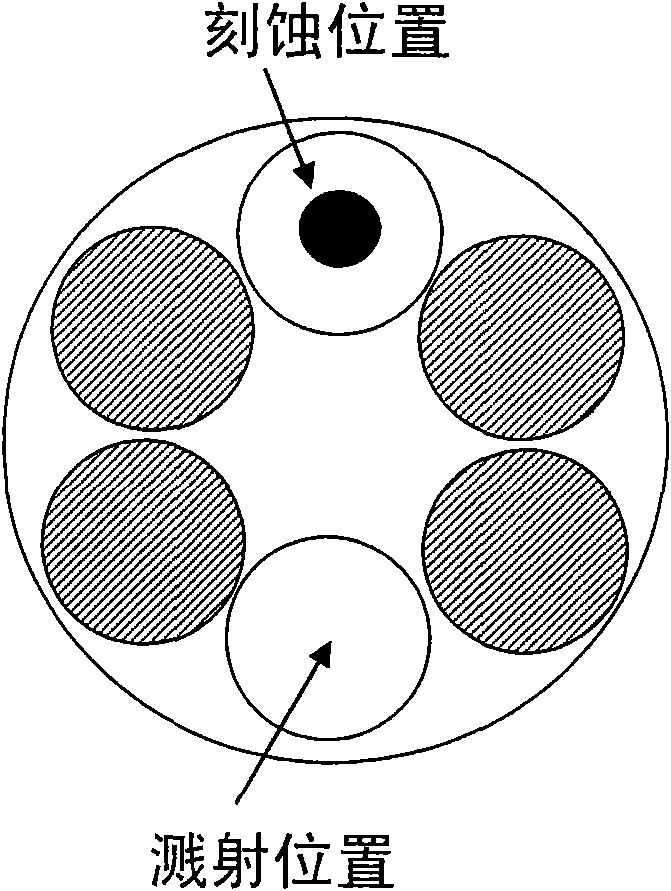
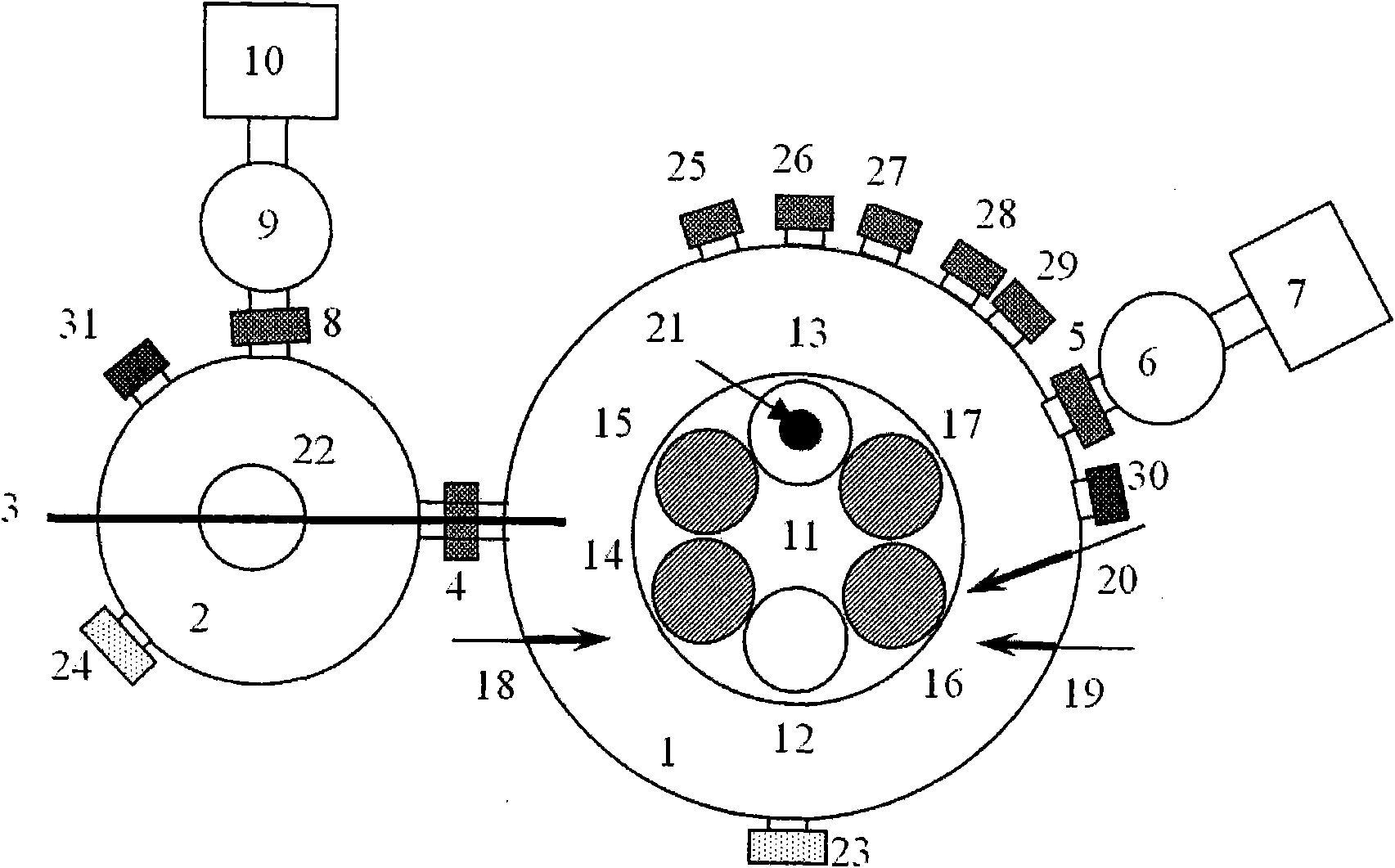
An ion beam sputtering target assembly has six sputter targets arranged in pairs on three paddles and disposed upon the circumference of a circular holder. The circular holder can be rotated about its axis in such a way as to bring any one of the target pairs to be exposed to the sputtering ion beam to deposit a film on substrate. The paddle is rotated to bring a desired target in the pair into position for sputtering. An alternative embodiment is provided with an enlarged region which allows one of the target paddles to be rotated about its axis while that target paddle is in an inactive, non-sputtering rotary position.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Dynamic mask for producing uniform or graded-thickness thin films
A method for producing single layer or multilayer films with high thickness uniformity or thickness gradients. The method utilizes a moving mask which blocks some of the flux from a sputter target or evaporation source before it deposits on a substrate. The velocity and position of the mask is computer controlled to precisely tailor the film thickness distribution. The method is applicable to any type of vapor deposition system, but is particularly useful for ion beam sputter deposition and evaporation deposition; and enables a high degree of uniformity for ion beam deposition, even for near-normal incidence of deposition species, which may be critical for producing low-defect multilayer coatings, such as required for masks for extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUVL). The mask can have a variety of shapes, from a simple solid paddle shape to a larger mask with a shaped hole through which the flux passes. The motion of the mask can be linear or rotational, and the mask can be moved to make single or multiple passes in front of the substrate per layer, and can pass completely or partially across the substrate.
Owner:EUV
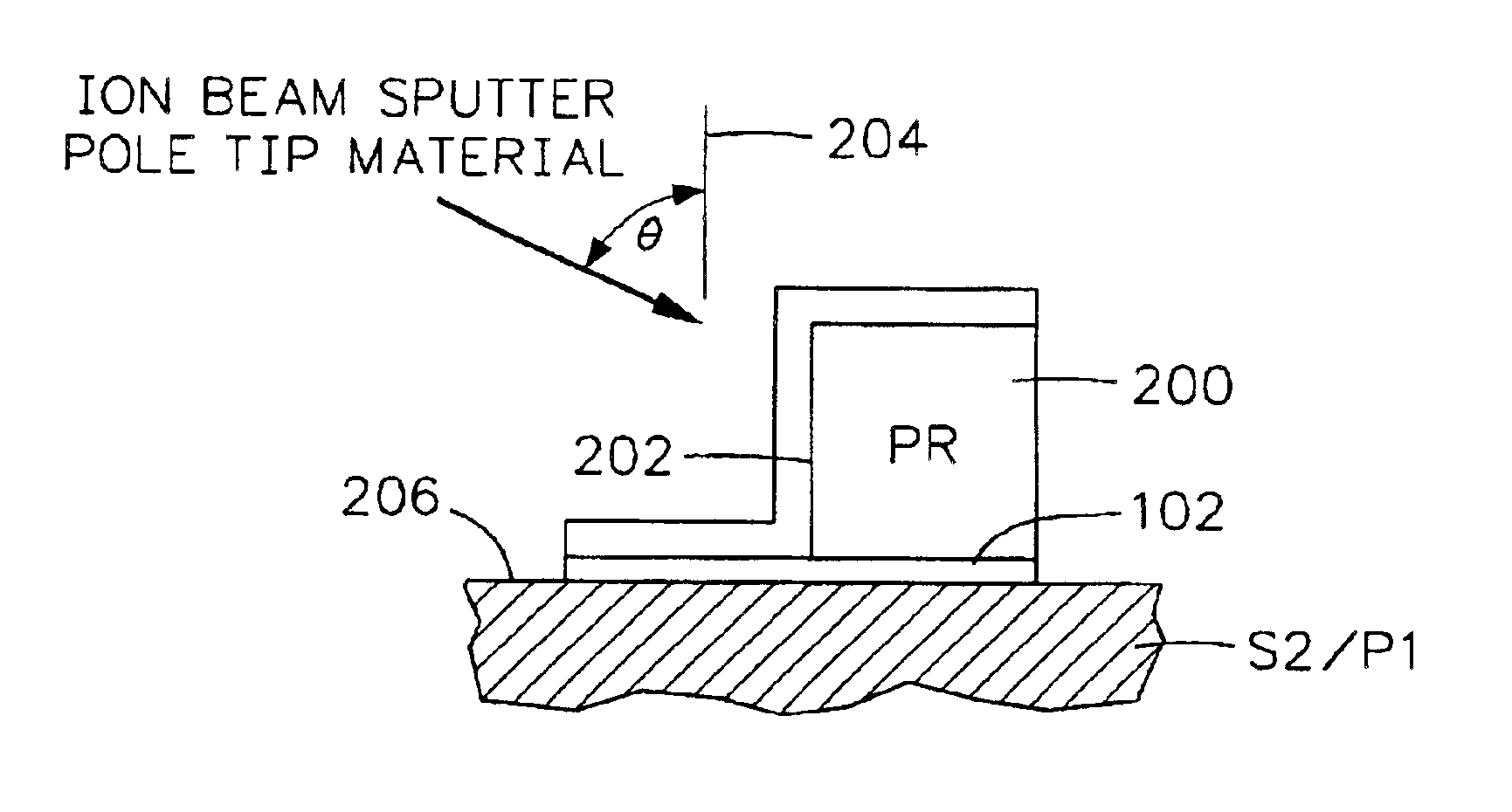
Method of making a narrow pole tip by ion beam deposition
InactiveUS6862798B2Manufacture head surfaceElectrical transducersIon beam depositionElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method of making a magnetic head assembly wherein the magnetic head assembly has a write head with a pole tip includes the steps of forming a shaping layer on an underlying layer wherein the shaping layer has a side surface and a top surface, ion beam sputter depositing a ferromagnetic material layer on the underlying layer and on the side and top surfaces of the shaping layer and removing first and second portions of the ferromagnetic material layer from the underlying layer and the top surface of the shaping layer, respectively, leaving a remaining portion of the ferromagnetic material layer on the side surface of the shaping layer which is the aforementioned pole tip.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Multi-ion-beam sputter-deposition technology for doping with diamond-like carbon (DLC) coating
InactiveCN101787518AImprove performanceRealize complementary advantagesVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDlc coatingGrown film
The invention relates to a multi-ion-beam sputter-deposition technology for doping a diamond-like carbon (DLC) coating. The technology is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly, washing to removing a polluted layer on the surface of a workpiece by utilizing ultrasonic waves, and carrying out ion beam bombardment washing on the surface of the workpiece by utilizing an argon-ion beam generated by an ion source to obtain an atomic scale clean surface; then preparing a gradient transition layer by utilizing an auxiliary ion beam sputter-deposition method; and finally, synthesizing a multi-element doped DLC coating on the gradient transition layer by utilizing multi-ion-beam sputtering and low-energy ion beam auxiliary deposition. In the process of synthesizing the multi-element doped DLC coating by utilizing the multi-ion-beam sputtering and the low-energy ion beam auxiliary deposition, carbon particles and metallic particles which are generated by bombarding a graphite target and a metallic target are deposited by using a sputtering ion source, and gas ions generated by an auxiliary deposition ion source continuously bombard the surface of a grown film layer to regulate and control the microstructure of the film layer and realize multi-element doping.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Method for preparing bismuth, antimony and telluride base thermoelectric film
ActiveCN103060750AHigh ion energyImprove qualityThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentVacuum evaporation coatingRepeatabilityHot Temperature
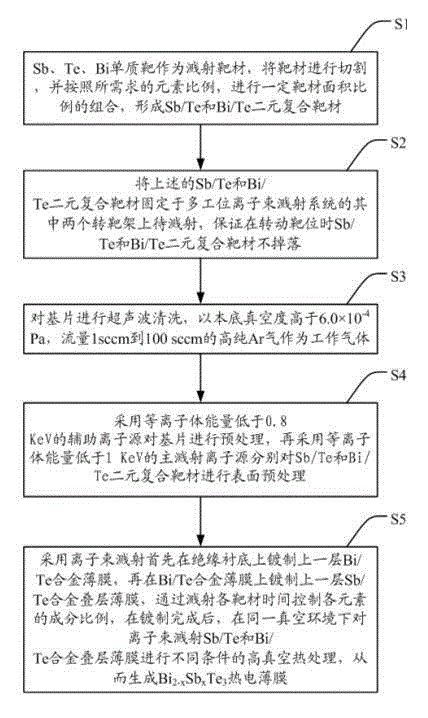
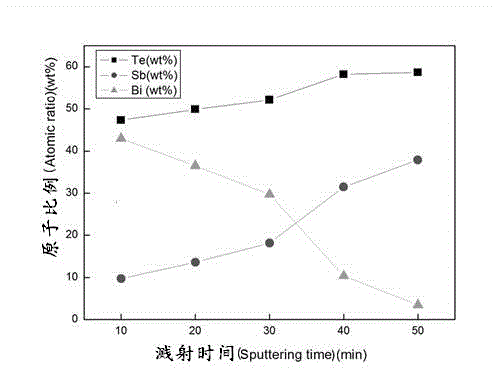
The invention discloses a method for preparing a bismuth, antimony and telluride base thermoelectric film and particularly relates to a Bi[2-x]SbxTe3 base thermoelectric film. In the Bi[2-x]SbxTe3, x is not less than 0.1 and not more than 2.0. According to the method, the ion-beam sputtering depositing method is adopted, two binary complex targets which are Sb / Te and Bi / Te are used as sputtering target materials, the area proportions of the two target materials and the ion-beam sputtering parameters are controlled, and the high-temperature in situ heat treatment is carried out in the same vacuum environment to prepare the Bi[2-x]SbxTe3 thermoelectric film. The method has the advantages of simple process, good repeatability and high utilization rate of raw materials. Due to the adoption of the method, the high-precision controllable doping of elements of the Bi[2-x]SbxTe3 thermoelectric film can be realized, the structure of the Bi[2-x]SbxTe3 thermoelectric film can be optimized effectively, and the thermoelectric properties can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
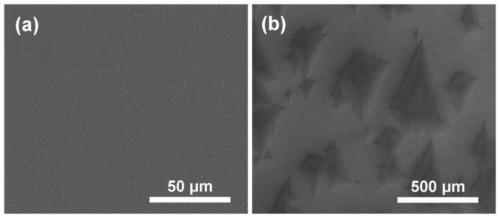
Silicon nano cone array coated with gold film as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105197882AHigh SERS activityElectromagnetic field enhancementMaterial nanotechnologyIndividual molecule manipulationSulfur hexafluoridePolystyrene
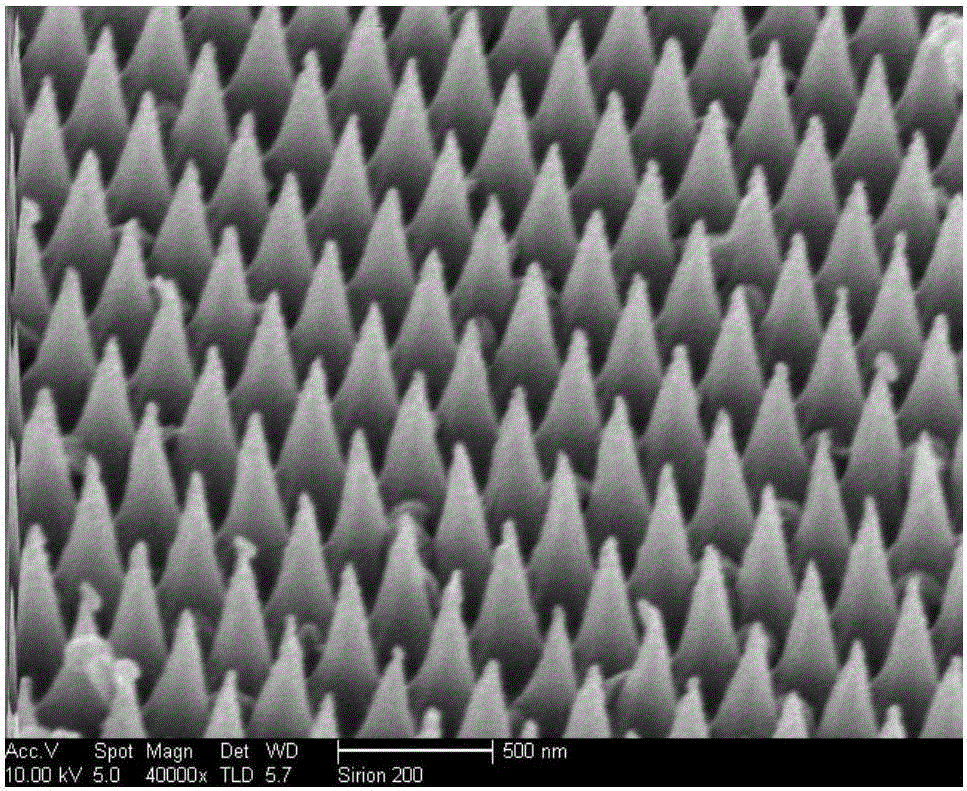
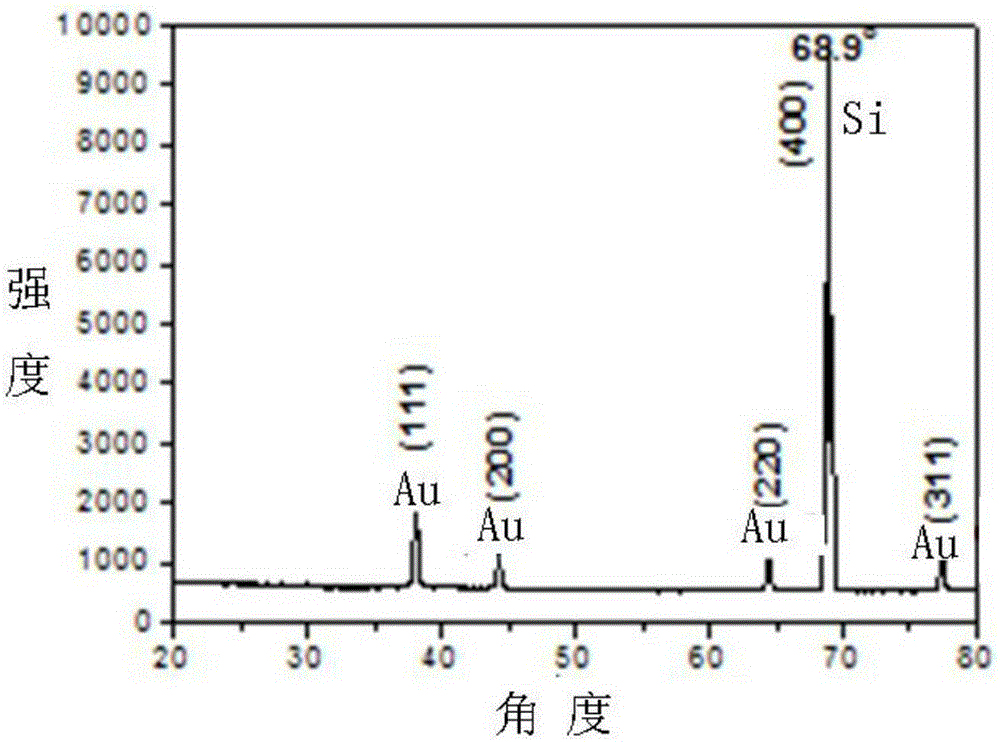
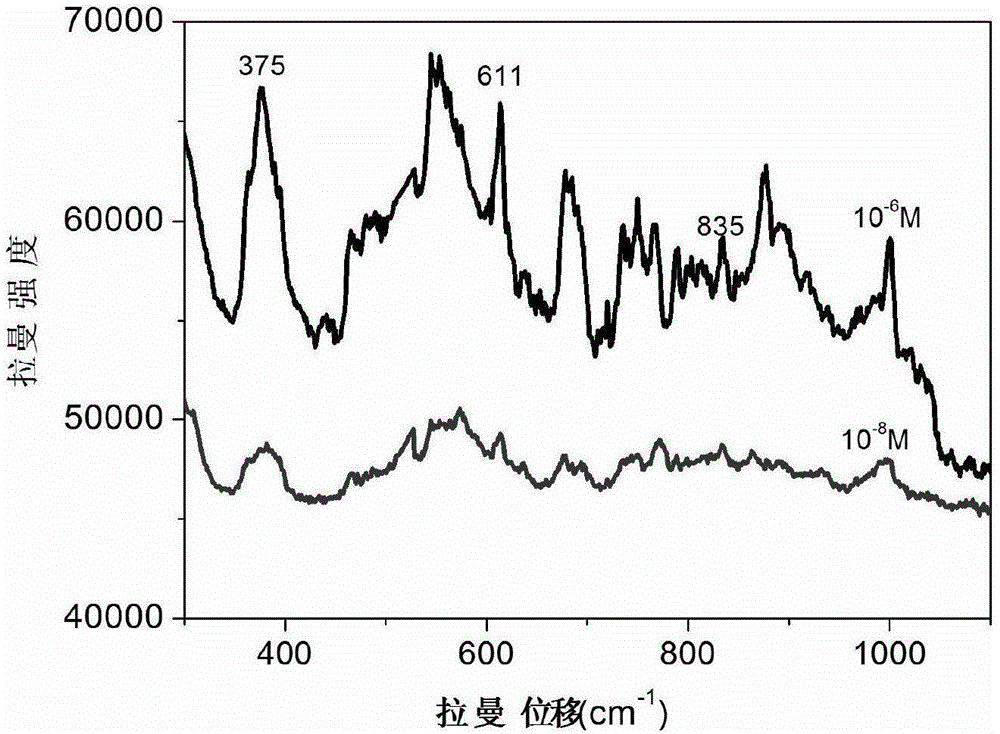
The invention discloses a silicon nano cone array coated with a gold film as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The array is a silicon nano cone sequence array with a surface coated with a gold film, wherein the conical bottom diameter of silicon nano cones forming the silicon nano cone sequence array is 180nm to 220nm, the cone height is 450nm to 550nm, the cone period is 250nm to 350nm, and the thickness of the gold film is 15nm to 25nm. The preparation method comprises the following steps: first synthesizing polystyrene colloidal spheres on a silicon substrate to form a single-layer colloidal crystal template by virtue of a gas-liquid interface self-assembling technology, placing the silicon substrate with the single-layer colloidal crystal template in a sulfur hexafluoride atmosphere, etching the silicon substrate by virtue of plasma to obtain the silicon substrate with silicon nano cone sequence array, and depositing the gold film on the silicon substrate with the silicon nano cone sequence array by utilizing an ion beam sputtering technology or thermal evaporation deposition technology to obtain a target product. The silicon nano cone array can be used as an active substrate of surface enhanced raman scattering to measure the content of clenbuterol hydrochloride attached thereon.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
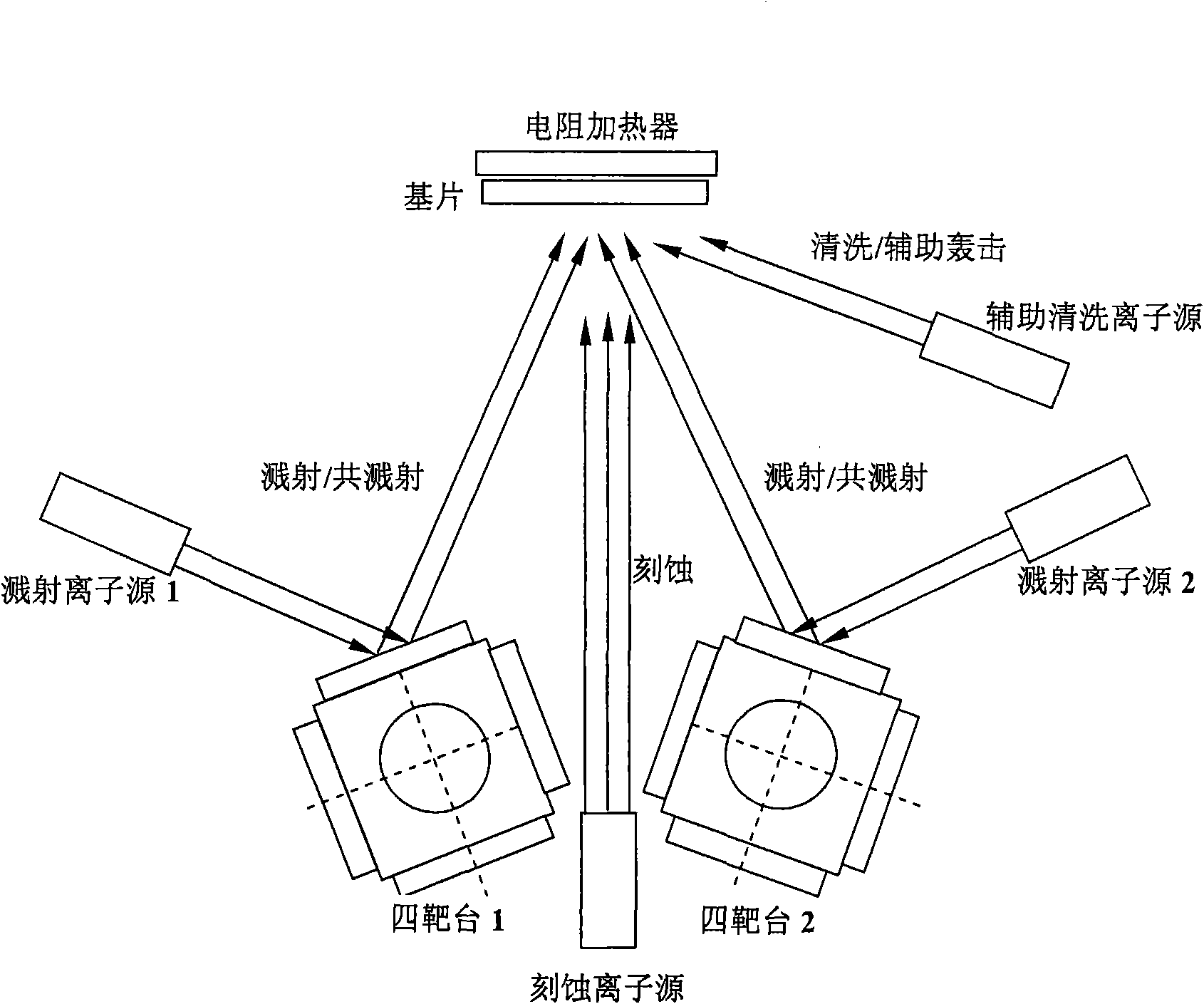
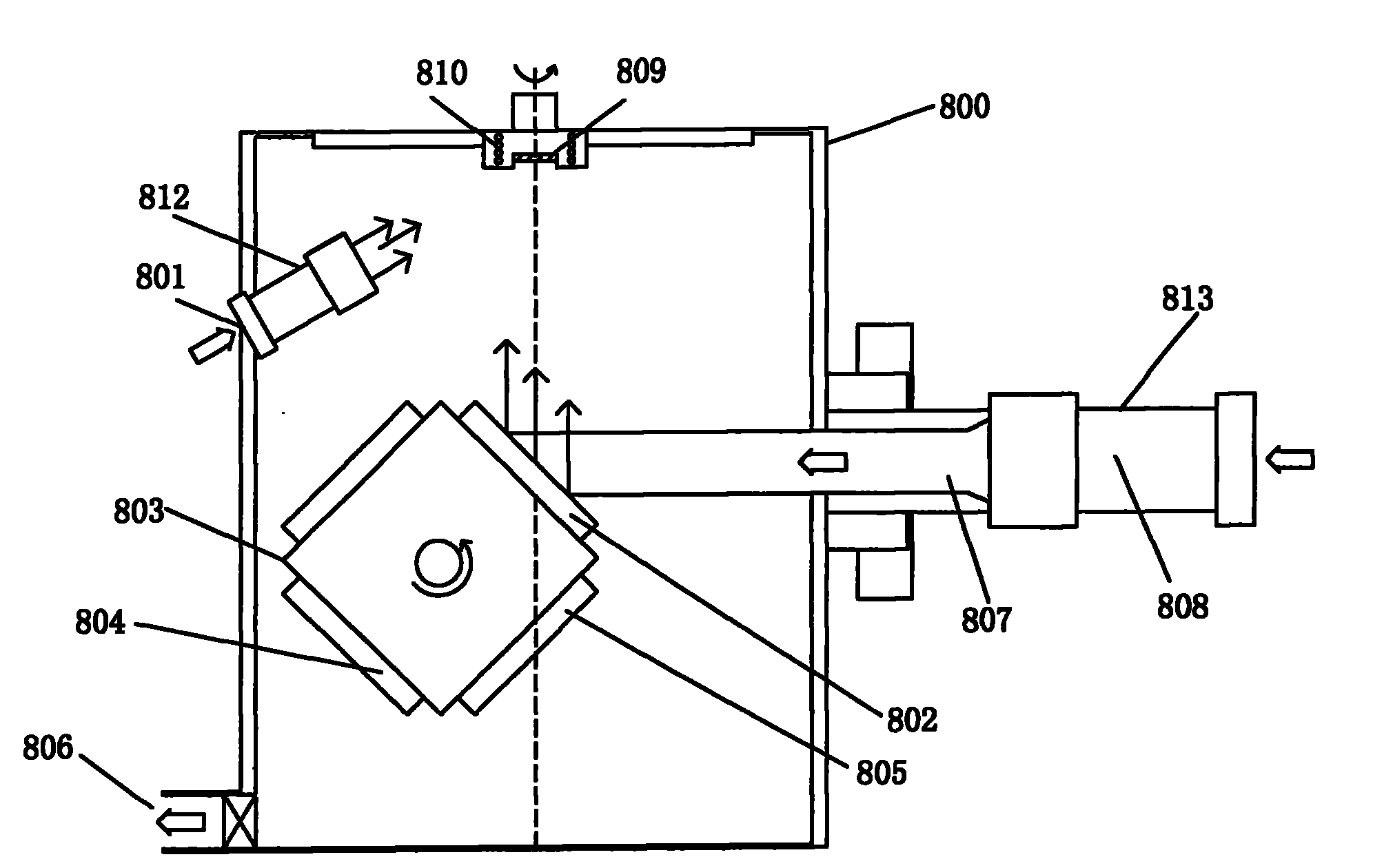
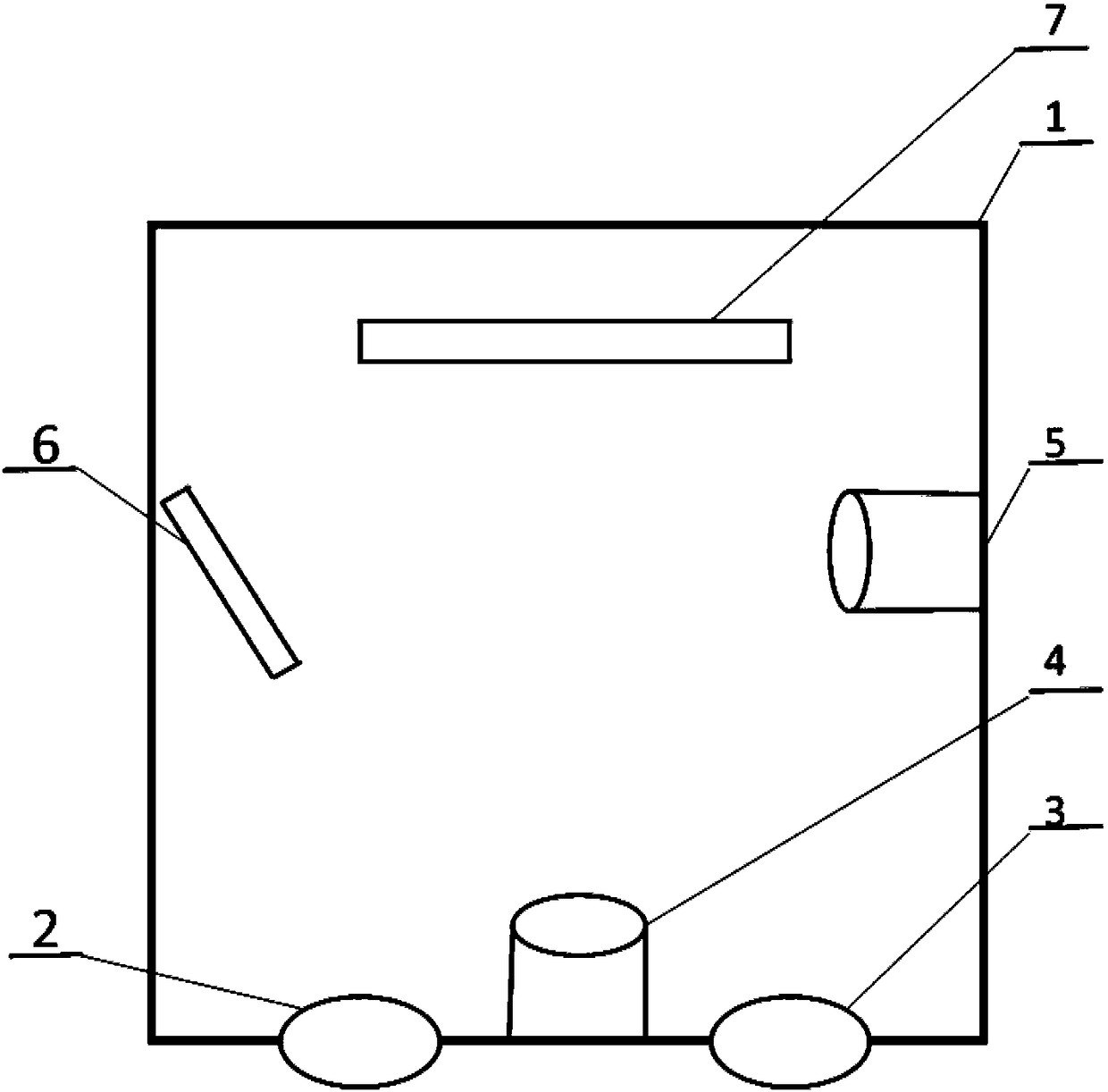
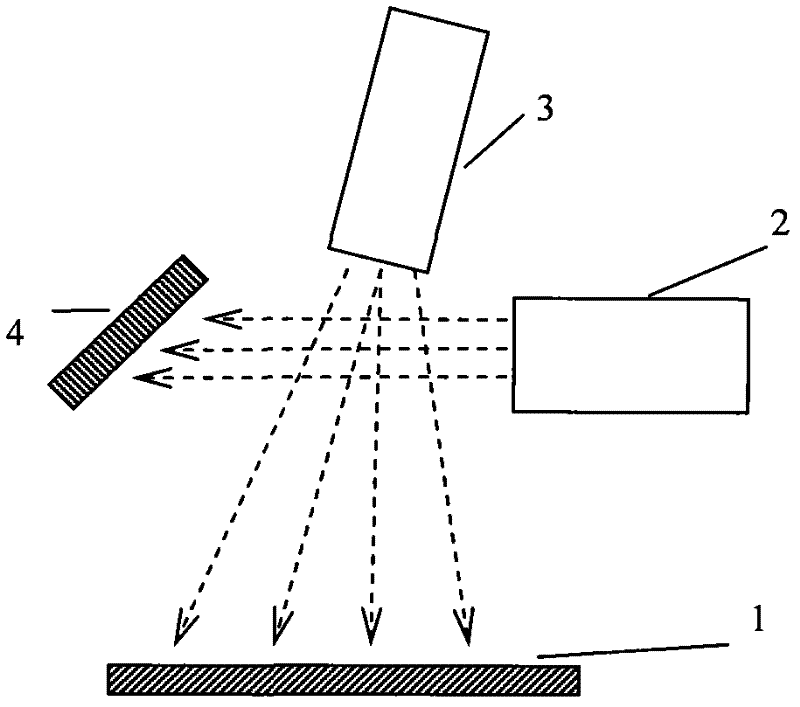
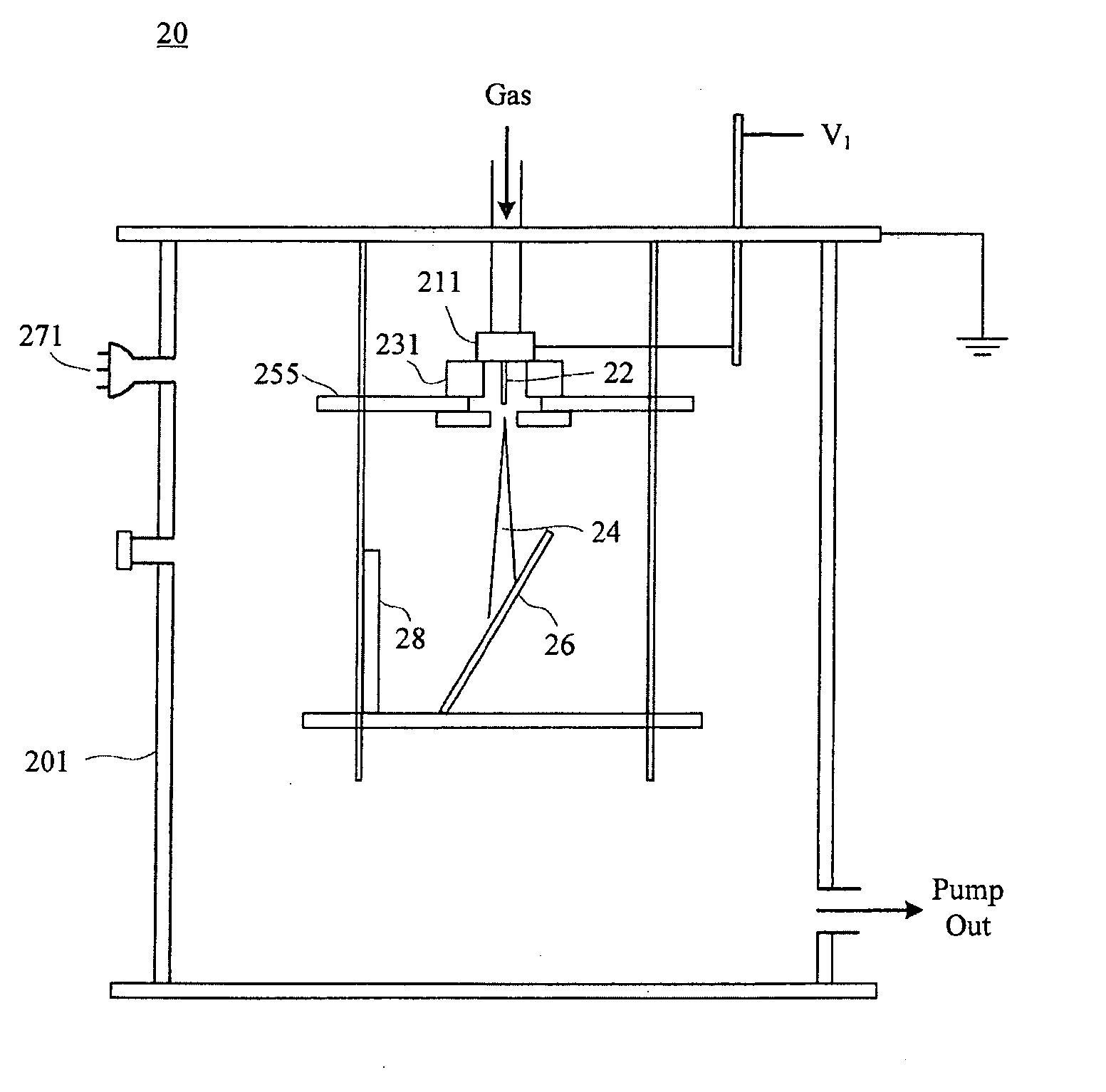
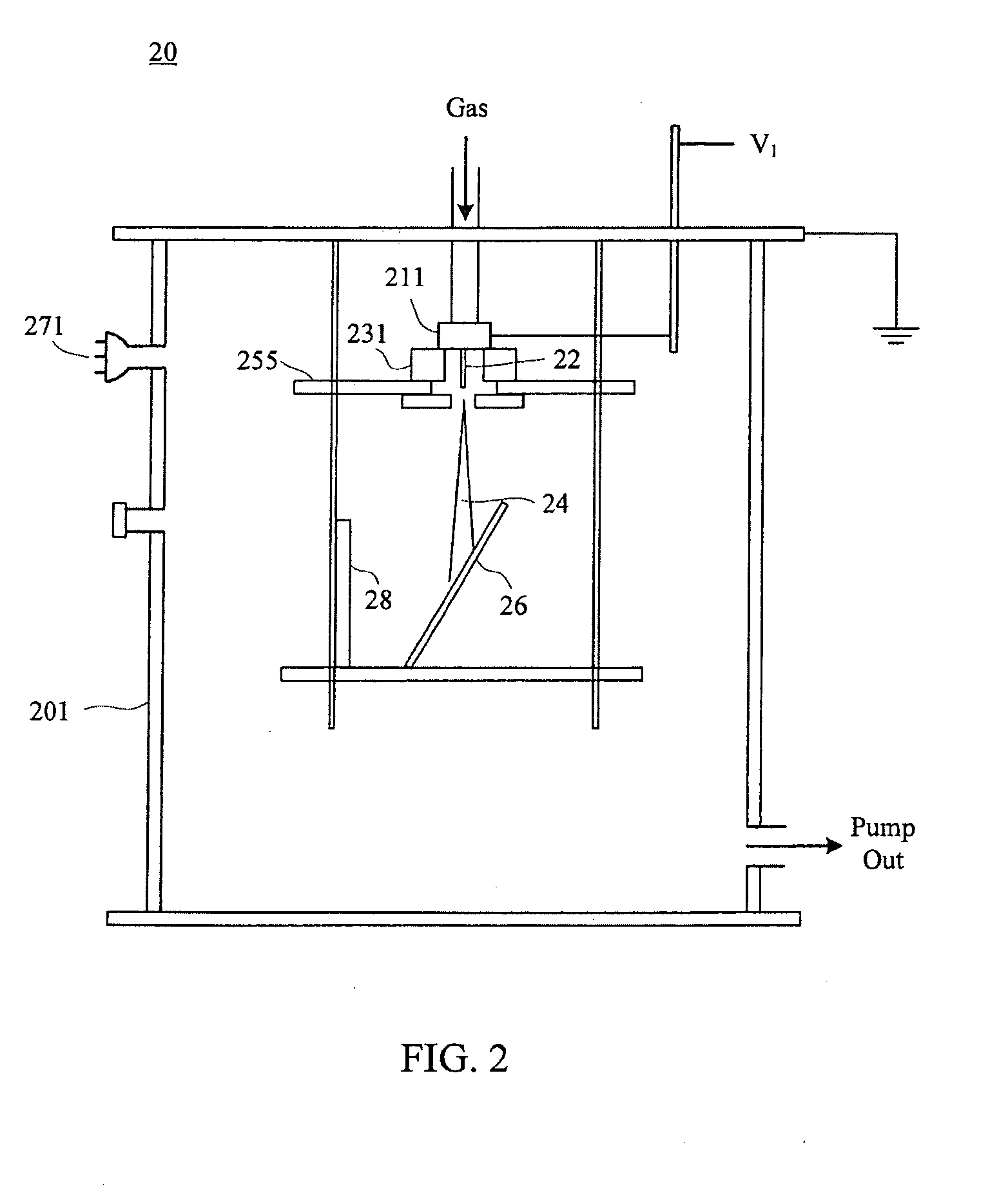
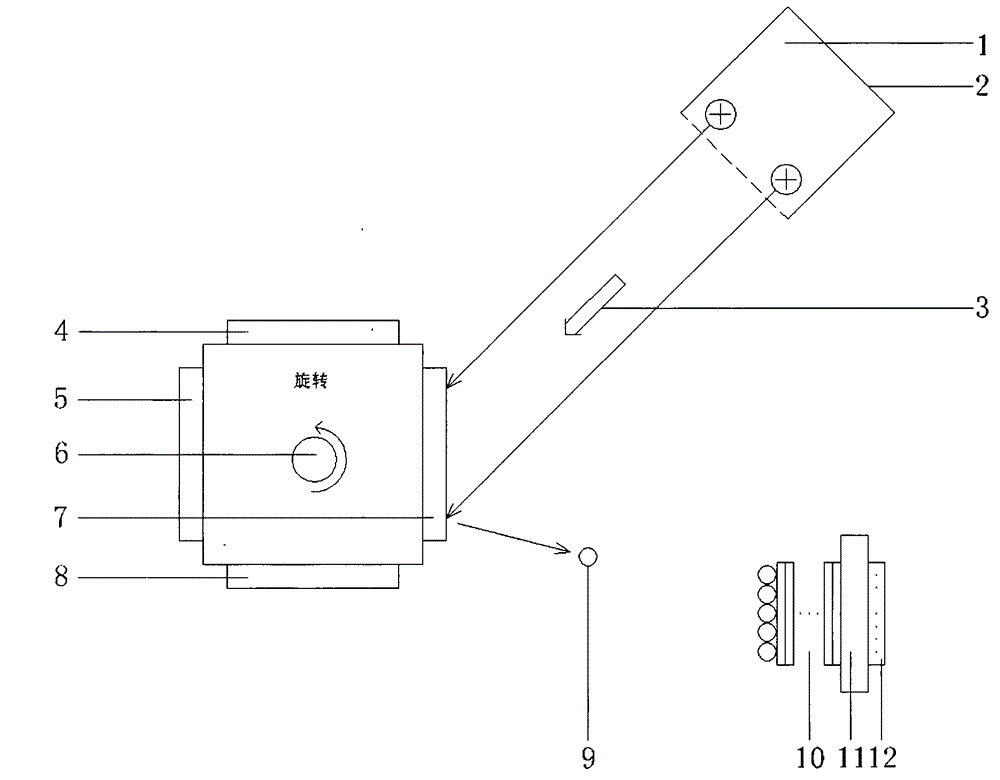
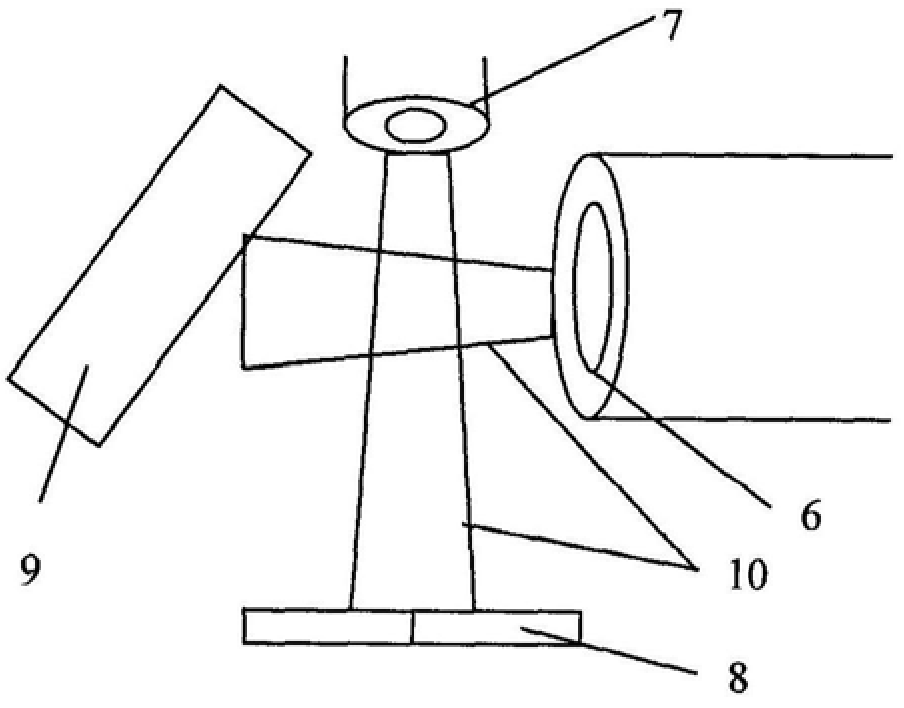
Multifunctional ion beam sputtering deposition and etching equipment
InactiveCN101880863AEasy to manufactureSimple structureVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingTarget surfaceIon beam
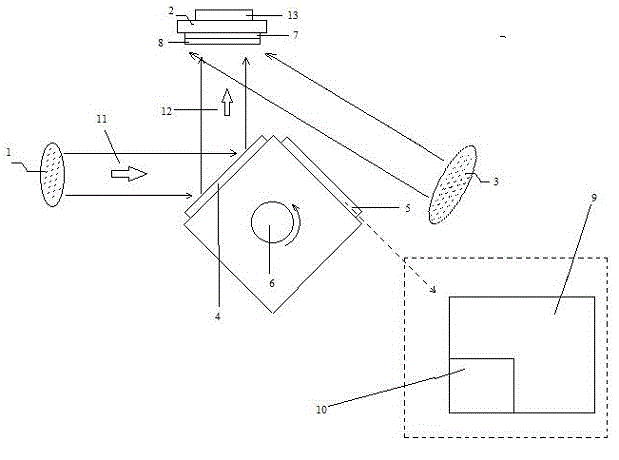
The invention discloses multifunctional ion beam sputtering deposition and etching equipment which comprises a vacuum chamber, a sputtering deposition and etching workbench, an etching ion source, two sputtering target platforms, two sputtering ion sources and an assistant cleaning ion source, wherein the sputtering deposition and etching workbench is arranged in the top middle position of the vacuum chamber, and the lower surface thereof is parallel to the horizontal plane; the etching ion source is arranged in the bottom middle position of the vacuum chamber and opposite to the sputtering deposition and etching workbench; the two sputtering target platforms are arranged at the lower part of the vacuum chamber and symmetrical bilaterally to the direction of an ion beam emitted by the etching ion source; the two sputtering ion sources are arranged in the middle of the vacuum chamber and symmetrical bilaterally to the direction of the ion beam emitted by the etching ion source; the emitted ion beam and a target surface loaded on the sputtering target platforms form an angle of 45 DEG; the assistant cleaning ion source is arranged in the middle of the vacuum chamber; and the emitted ion beam and the lower surface of the sputtering deposition and etching workbench form an angle of 30 DEG. The equipment has various functions and can be used for sputtering deposition, etching, polishing thinning and heat treatment of media and metal materials.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Controllable preparation method of electrochromic WO3 film
ActiveCN104178731ALow integrated transmittance in colored stateLarge optical modulation amplitudeVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDisplay deviceElectrochromism
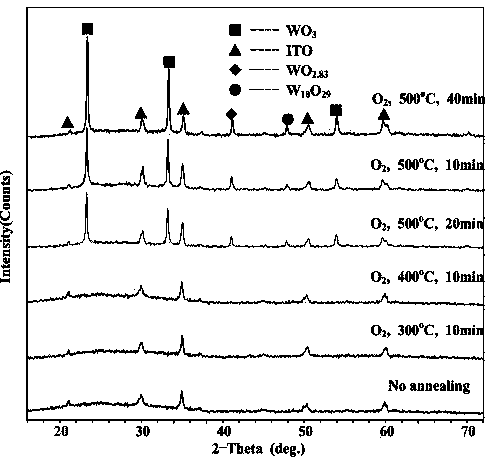
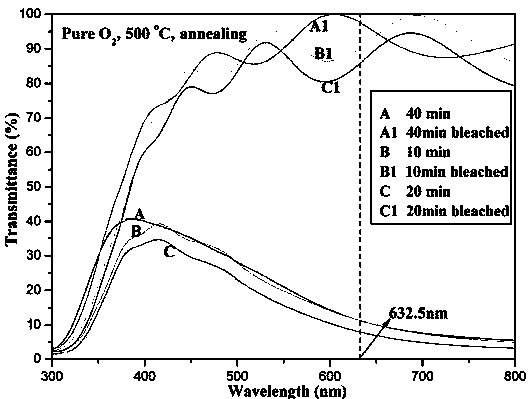
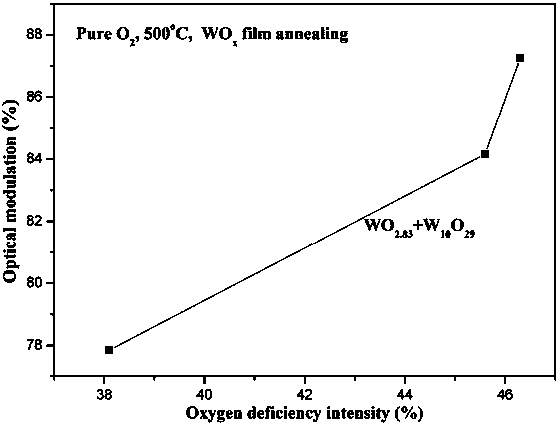
The invention relates to a preparation method of a WO3 film. An ion-beam sputtering deposition technique and a subsequent annealing treatment technique are combined to prepare the electrochromic WO3 film with favorable optical properties, and the strength of the anaerobic phase in the WO3 film is controlled to regulate the optical modulation properties. By using ITO (indium tin oxide) conducting glass as the substrate, the ion-beam sputtering deposition technique is utilized to prepare the WOx film; and by using 99.999% pure O2 as an annealing atmosphere, the WOx film is subjected to annealing treatment at different temperatures for different time periods to prepare the WO3 film containing anaerobic phase. When the WO3 film is subjected to Li<+> electrochemical coloring / discoloring reaction, after the discoloring voltage is applied, the prepared electrochromic WO3 film has the advantages of low coloring-stage integral transmittivity, adjustable anaerobic phase strength, large optical modulation amplitude and favorable controllability. The WO3 film is simple in preparation technique and is hopeful to be applied to the fields of smart windows, electronic information display devices, no-glare reflectors and the like.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Novel self-assembly method of ordered Ge/Si quantum dot array by nano-pore replication and sputtering deposition
InactiveCN103117210AAvoid damageEasy to removeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoholeSolar cell
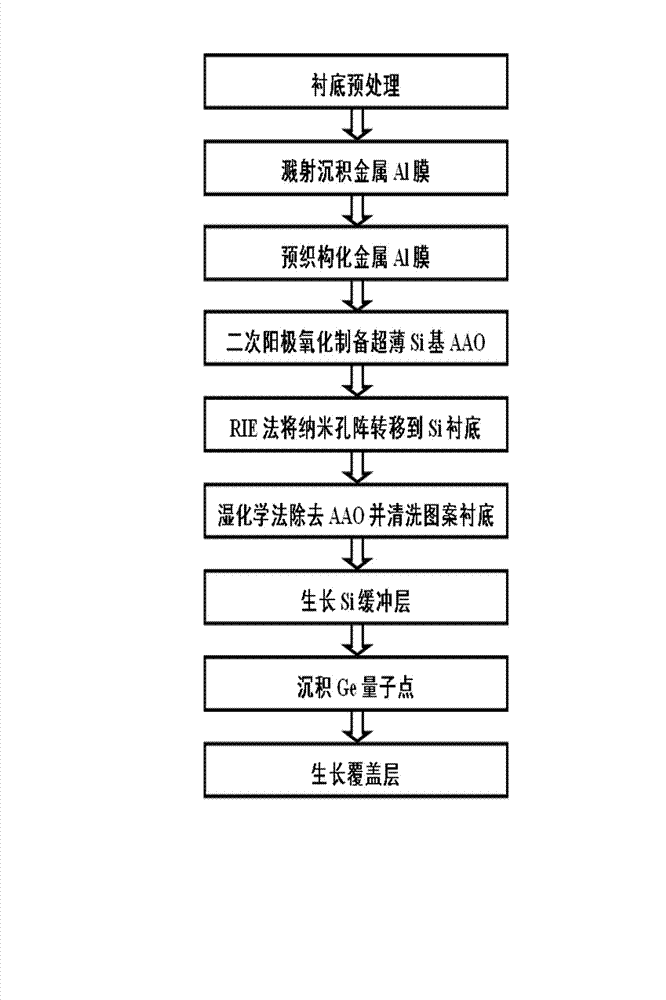
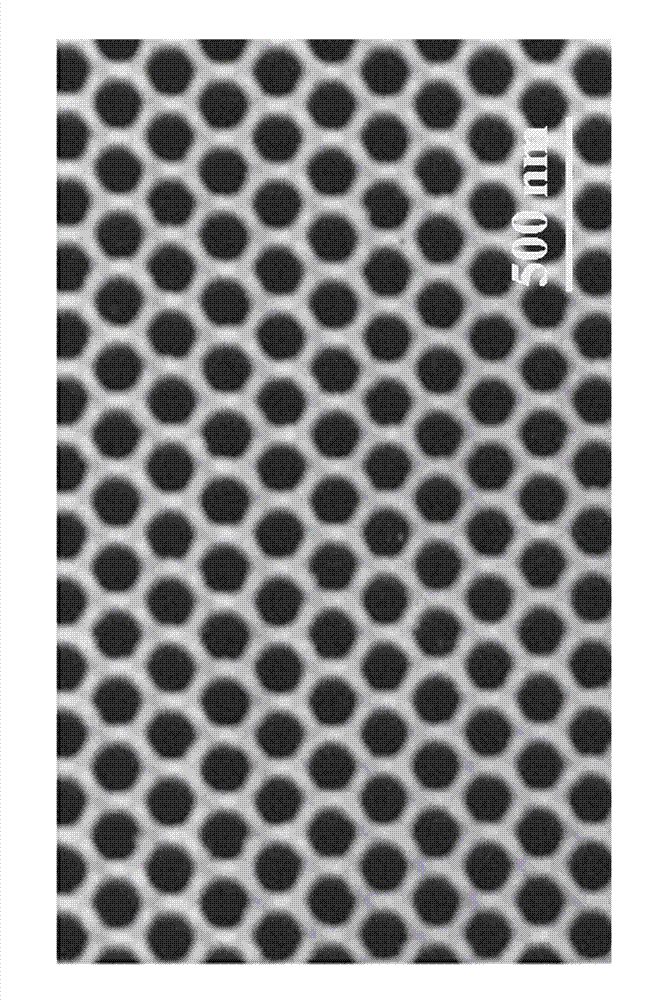
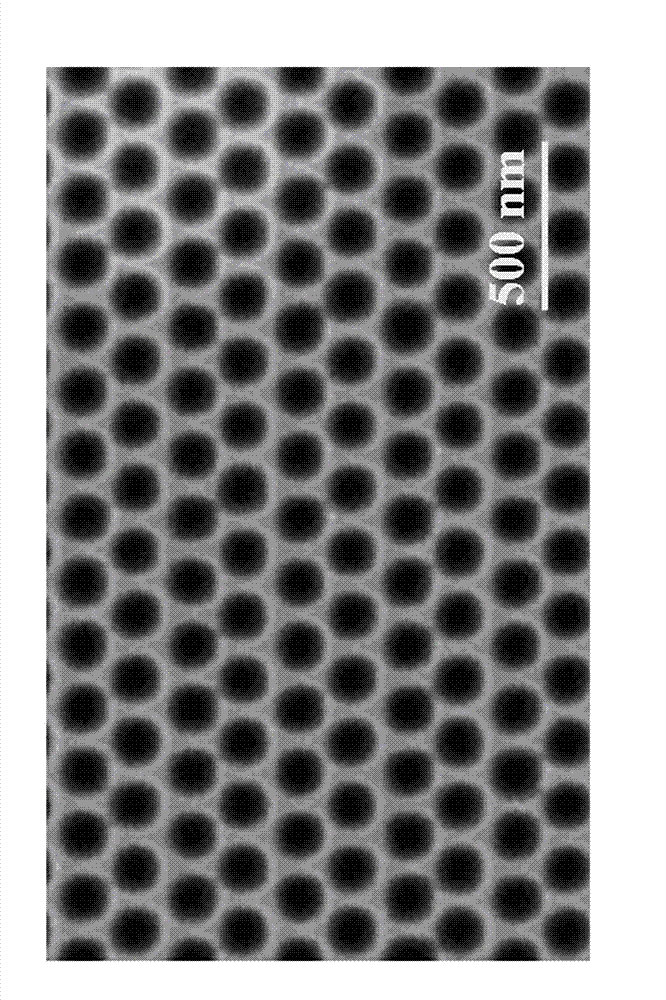
The invention provides a method of self-assembly growth of a large-area, even and ordered Ge quantum dot array on a Si substrate by sputtering deposition. The method includes preparation of ultrathin Si-based AAO (anodic aluminum oxide), preparation of a pattern substrate by nano-pore replication, and self-assembly growth of the even, ordered Ge quantum dot array on the surface of the pattern substrate by ion beam sputtering. Quantum dot growth process matching with the pattern substrate is obtained by controlling ion beam sputtering deposition temperature, ion beam flux voltage, and buffer layer thickness, so that Ge quantum dot nano-pores evenly and orderly grow at nucleation center. Even-size Ge quantum dots obtained are in hexagonal symmetrical distribution on the surface of the Si substrate, and the diameter of the quantum dots is adjustable. The method effectively overcomes the defects that distribution of the self-assembled Ge / Si quantum dots is random and disorder in position, the size is uneven, controllability is low, and preparation cost is high. The large-area, even, ordered and small-sized Ge quantum dot array is prepared at low cost. The method is applicable to manufacture of devices such as silicon-base quantum-dot light emitters, quantum-dot photoelectric detectors and efficient quantum-dot solar cells.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
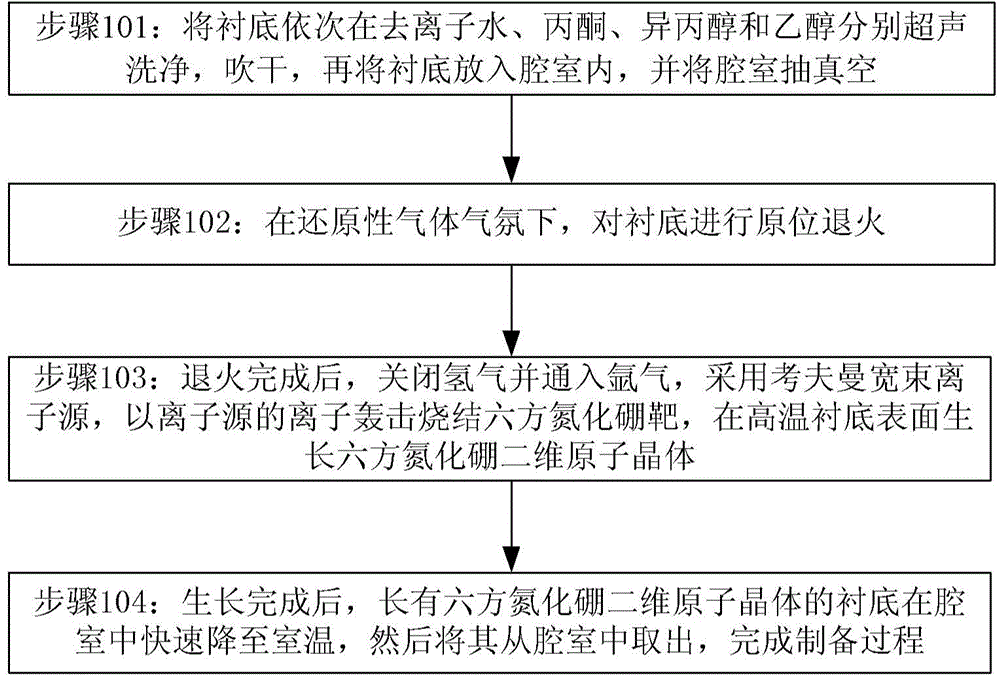
Method for preparing hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) two-dimensional atomic crystal
InactiveCN104313684AAchieve preparationLow costPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsHexagonal boron nitrideCopper foil
The invention provides a method for preparing a hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) two-dimensional atomic crystal, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: introducing reducing gas into a reaction chamber, and carrying out in-situ annealing on a copper foil substrate to remove the surface oxide layer; and bombarding an h-BN target with an argon ion beam by an Ion Beam Sputtering Deposition (IBSD) process to deposit the h-BN two-dimensional atomic crystal on the copper foil substrate surface at high temperature. By regulating the growth conditions, the h-BN monocrystal domain with the dimension of 5 mu m or so can be obtained, and a high-quality h-BN continuous film can also be obtained by prolonging the growth time. The method solves the problems of excessive precursor pyrolysis byproducts, low controllability and the like in the CVD (chemical vapor deposition) process for preparing the h-BN two-dimensional atomic crystal, and provides a new way for preparing the large-area high-quality h-BN two-dimensional atomic crystal.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
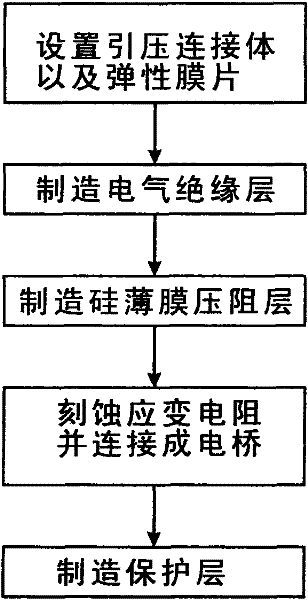
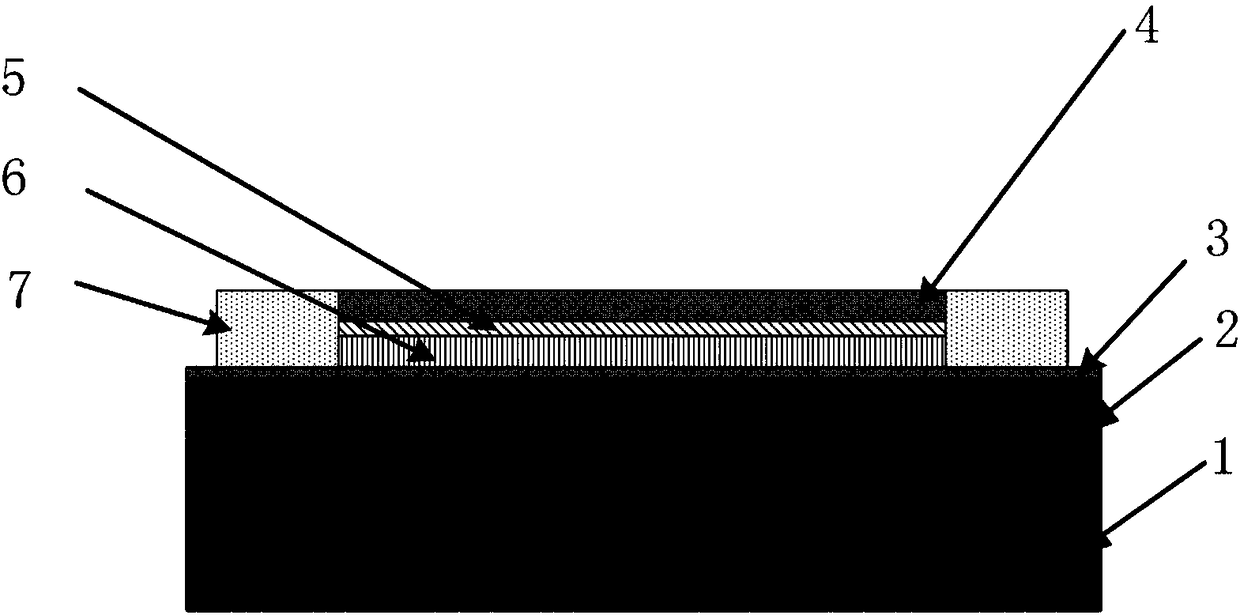
Pressure strain device manufactured by sputtering silicon film with ion beams and method thereof
InactiveCN102175363AImprove compactnessImprove stabilityFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationVacuum evaporation coatingPhysical shapeNanoscopic scale
The invention relates to a pressure strain device manufactured by sputtering a silicon film with ion beams and a method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: firstly arranging a lead pressure connector and a metal elastic film integrated with the lead pressure connector; forming a first electric isolating layer on the metal elastic film by using a printing sintering method or sputtering method; forming a silicon film piezoresistive layer on the electric isolating layer by using an ion beam sputtering deposition method; etching a strain gage physical shape structure on the silicon film piezoresistive layer by using a superfine etching technology; and coating a medium sizing material on the piezoresistive layer to form a protection layer. According to the method, the pressure strain device is manufactured by sputtering the silicon film with ion beams and the silicon material is deposited layer by layer in nanometer scale, the formed film has excellent compactness and stability and the manufactured pressure strain device has high sensitivity, long service life and excellent stability. The process for manufacturing the electric isolating layer by adopting the printing sintering method is convenient, has high yield and is suitable for mass production.
Owner:东莞市百赛仪器有限公司
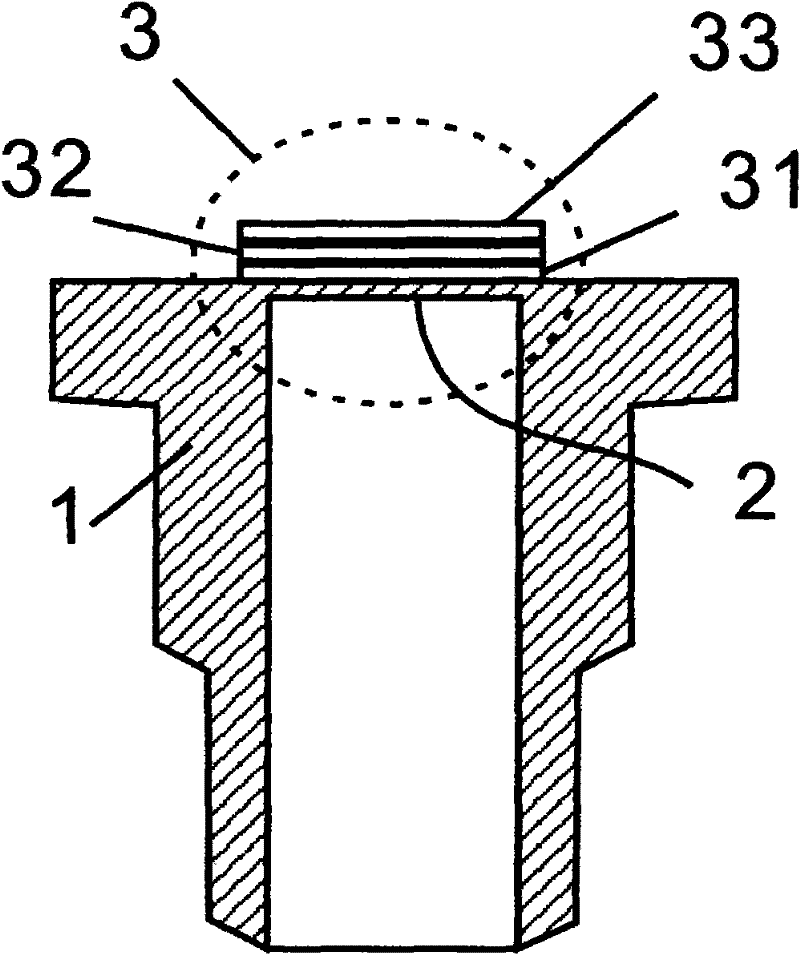
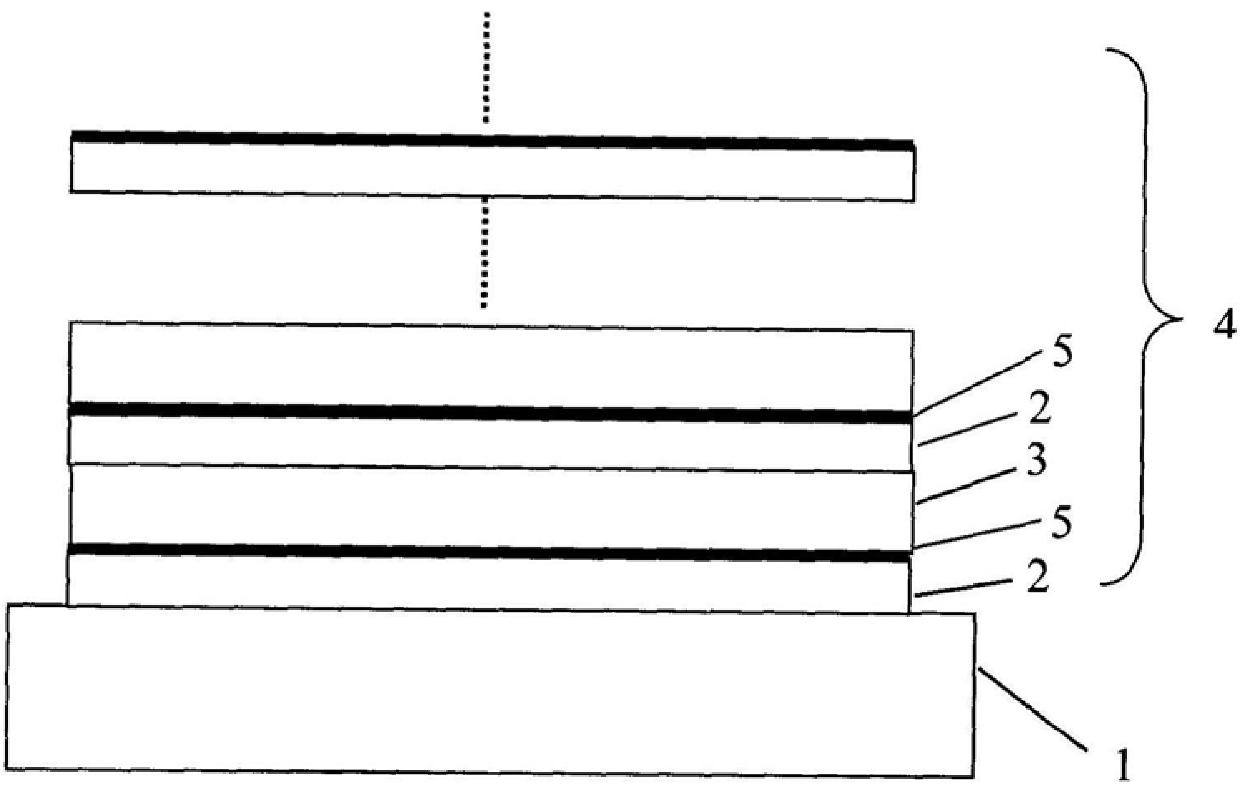
High-temperature thin film strain meter of composite protection layer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108088610AImprove protectionImprove high temperature stabilityDecorative surface effectsFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationRadio frequency magnetron sputteringOxidation resistant
The invention relates to a high-temperature thin film strain meter of a composite protection layer and a preparation method thereof. The strain meter comprises a high-temperature alloy component substrate, an alloy transition layer, an aluminum oxide insulating layer, an aluminum oxide protection layer, an aluminum intermediate layer, a PdCr strain layer and a Pt electrode. the strain meter takesa high-temperature alloy component as a substrate, a transition layer alloy is firstly subjected to magnetron sputtering on the substrate and is subjected to high-temperature oxidation to generate a thin-layer aluminum oxide film, the aluminum oxide insulating film is deposited by double ion beam sputtering, and a PdCr strain layer is subjected to radio frequency magnetron sputtering on the insulating film, and the ion beams sputter AL intermediate layer and an AL2O3 protective layer. The strain meter is suitable for the real-time measurement of the strain of a component in the high-temperature working process, a universal MEMS patterning process is adopted, and the PDCR is sputtered to serve as a strain layer, the ion beams sputter to prepare Al and Al2O3 to obtain a composite protectionlayer by heat treatment, so that the oxidation of the PdCr thin film is prevented, and the oxidation resistance and the stability of the strain meter are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Infrared broadband antireflection microstructure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108710164AAddress the needs of large aspect ratiosImprove transmittanceCoatingsRefractive indexEvaporation
The invention provides an infrared broadband antireflection microstructure comprising a substrate, a nanostructure array layer and a low-refractive-index layer which are arranged from the bottom to the top in turn. The nanostructure array layer is provided with nanostructures which are perpendicular to the main axis of the surface of the substrate, and the cross section of the nanostructures has atriangular, conical, parabolic or Gaussian isogradient structure. A layer of low-refractive-index material is added to the nanostructure array, and the low-refractive-index layer is realized by the ion beam sputtering deposition technology or the electron beam evaporation ion beam auxiliary deposition technology so as to avoid water absorption. The thickness of the low-refractive-index layer is adjusted so that the broadband antireflection effect of the nanostructure array layer can be enhanced, high transmittance of broadband range can be realized and the transmitting curve is flatter.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High temperature synchronous compensation film strain gauge and its preparation method
ActiveCN106403804AGuaranteed Optimal RatioImprove insulation performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringRadio frequency magnetron sputtering
The invention provides a high temperature synchronous compensation film strain gauge and its preparation method. The strain gauge employs a high temperature alloy component as its substrate. And based on the substrate, the method is performed through the following steps: magnetically sputtering on the substrate a transitional alloy layer and oxidizing it at a high temperature for a thin oxidized aluminum film; sputtering the double ion beam to deposit an oxidized aluminum insulation film; radio frequency magnetically sputtering on the insulation film to deposit a suspension compensation layer column, a PdCr strain layer, and a suspension compensation PdCr strain layer; and sputtering Cr before high temperature oxidation to form a Cr2O3 protection layer. The invention is suitable for real time measurement in the working process of the component. Through the universal MEMS graphical technology, the sputtering PdCr as a strain layer and the preparation of a suspension PdCr strain layer to realize temperature compensation, the influence of temperature change on the strain measurement of the component can be compensated; therefore, the measurement efficiency of the strain gauge is increased, more particularly so at high temperatures. After the high temperature passivation of the magnetically sputtered Cr protection layer, the structure becomes more compact; better bonding effect can be achieved; and protection becomes available to the functional structure.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
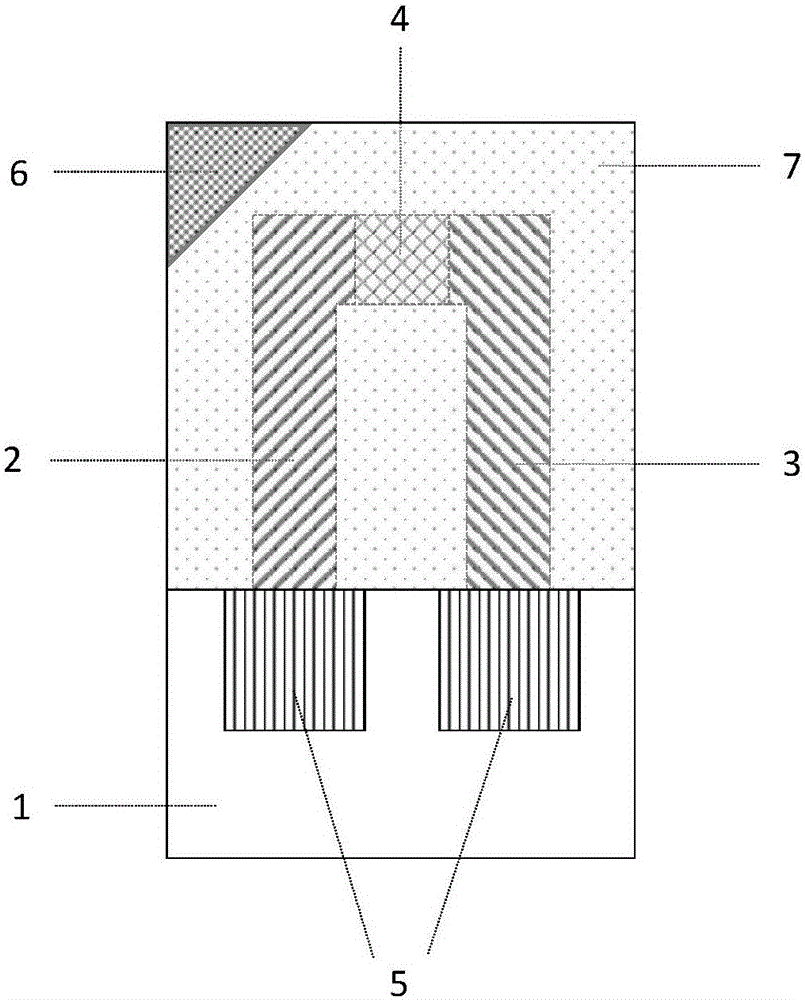
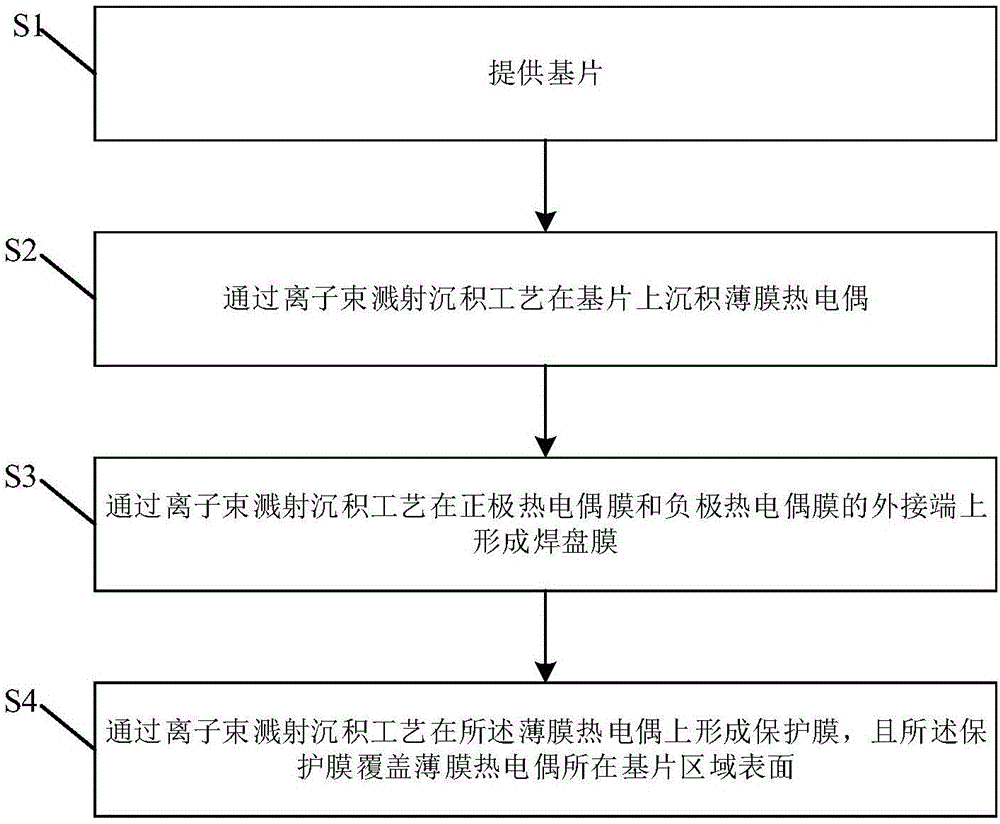
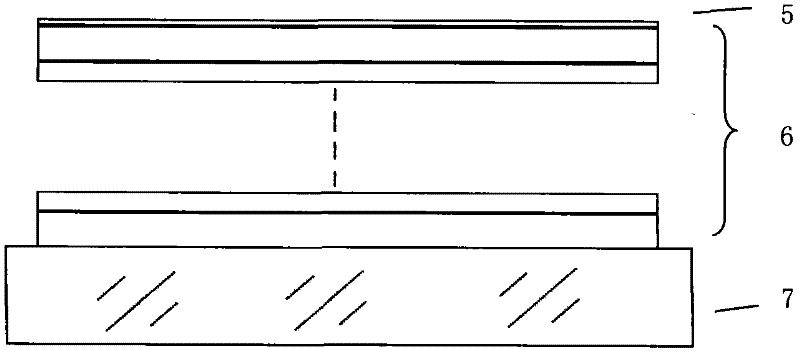
Thin film temperature sensor and manufacturing method
ActiveCN106197718AHigh measurement accuracyReduce thicknessThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsVacuum evaporation coatingThin film thermocouplesTemperature response
The invention relates to a thin film temperature sensor and a manufacturing method. The thin film temperature sensor at least comprises a substrate, a thin film thermocouple, bonding pad films and a protective film, wherein the thin film thermocouple is formed on the substrate through the ion beam sputtering deposition technology; the thin film thermocouple comprises a positive pole thermocouple film and a negative pole thermocouple film, and the inner end of the positive pole thermocouple film and the inner end of the negative pole thermocouple film are in butt joint to form a thermocouple connection point; the bonding pad films are formed at the outer end of the positive pole thermocouple film and the outer end of the negative pole thermocouple film through the ion beam sputtering deposition technology and are used for being connected with an external lead; the protective film covers the thin film thermocouple through the ion beam sputtering deposition technology and covers the surface of the area, where the thin film thermocouple is located, of the substrate. The thin film temperature sensor is manufactured through the ion beam sputtering deposition technology, multiple layers of the manufactured thin films are high in density and high in adhesive force, the plated thin film thermocouple is small in thickness and quick in temperature response, and after being packaged, the thermocouple is small in size and high in measurement precision.
Owner:北京埃德万斯离子束技术研究所股份有限公司
Method for preparing thin film solar cell adsorbing layer CuInSe2 film
InactiveCN101777604ATypical chalcopyrite structureLow resistivityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCopperPellicle membrane
The invention discloses a method for preparing a thin film solar cell adsorbing layer CuInSe2 film, comprising the following steps of: sputtering Cu, In and Se targets successively to prepare a ternary laminate or a ternary period laminate film by accurately regulating the iron beam sputtering parameter, and the like by adopting an iron beam sputtering sedimentation method, and annealing at high temperature to prepare the CuInSe2 film under the same high-vacuum environment. The method for preparing thin film solar cell adsorbing layer CuInSe2 film has optimized process and simple operation and improves the use ratio of materials; the prepared CuInSe2 film has typical copper phrite structure; the Cu / In / Se atomic ratio approaches the ideal stoichiometric ratio 1:1:2 of CIS; Cu is slightly richer than In; the optical band gap is 1.05eV; the absorption coefficient of light is as high as 105cm<-1>; and the resistivity of the thin film is less than 0.01omega cm. The invention satisfies the performance requirement of high-efficiency photovoltaic device.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Method for preparing microcrystalline silicon film by two-step method of ion beam and magnetron sputtering and device for coating composite film by ion beam and magnetron sputtering
ActiveCN102605335AReduce manufacturing costIncrease crystallization rateVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingComposite filmIon beam-assisted deposition
The invention belongs to the technical field of microcrystalline silicon films for solar batteries, particularly relates to a method for preparing the microcrystalline silicon film by a two-step method of ion beam and magnetron sputtering and a device for coating a composite film by the ion beam and the magnetron sputtering. The method comprises the following steps: (1) ion beam coating: sputtering a silicon target on a substrate by ion beam sputtering (IBS) deposition or ion beam assisted deposition (IBAD), pre-depositing a silicon homogeneous transition layer, wherein the silicon homogeneous transition layer is 50-200nm in thickness; and (2) magnetron sputtering coating: depositing a silicon film on the silicon homogeneous transition layer by the magnetron sputtering. The method for preparing the microcrystalline silicon film can fully improve the crystalline ratio of the microcrystalline silicon film, at the same time can effectively reduce the internal stress between the film and the substrate and increase the bonding strength between the film and the substrate; and the method is realized through the device for coating the composite film by the ion beam and the magnetron sputtering and finished in a same vacuum room, so as to save equipment cost.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
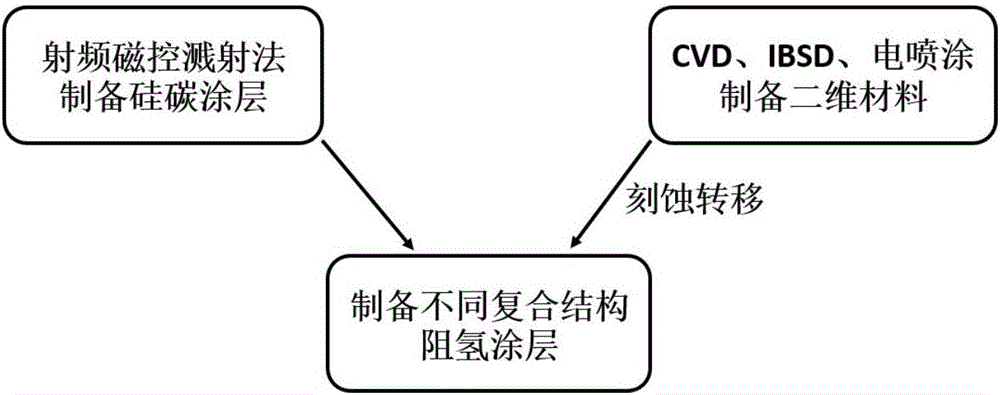
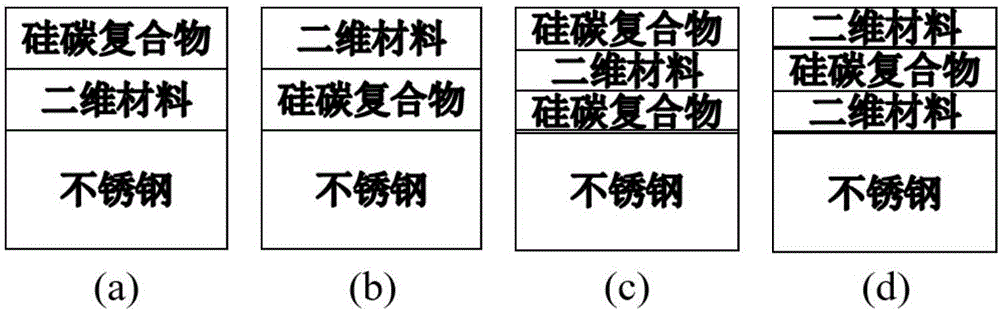
Two-dimensional material adjusting and controlling silicon-carbon composite structure hydrogen resisting coating and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN106283052AExcellent hydrogen resistanceSuperimposed coating processCarbon compositesHydrogen
The invention discloses a two-dimensional material adjusting and controlling silicon-carbon composite structure hydrogen resisting coating. The two-dimensional material adjusting and controlling silicon-carbon composite structure hydrogen resisting coating is characterized in that a coating structure comprises a silicon-carbon compound and a two-dimensional material; a two-dimensional material coating is formed by stacking graphene of a two-dimensional structure or hexagonal boron nitride of a two-dimensional structure or molybdenum disulfide of a molybdenum disulfide layer by layer, the layer number ranges from 1 to 10, and the thickness of the two-dimensional material coating ranges from 0.34 nm to 28 nm; and the silicon-carbon compound is formed by sputtering a silicon carbide target material, and the thickness of the silicon-carbon compound ranges from 0.5 micron to 2 microns. A preparing method of the two-dimensional material adjusting and controlling silicon-carbon composite structure hydrogen resisting coating includes the step that the two-dimensional material is prepared by adopting a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) technology and an ion beam sputtering deposition (IBSD) technology and with the combination of an etching transferring technology. A composite coating technology is adopted and has a hydrogen resisting effect superior to that of a single coating; introduction of the two-dimensional material is brought forwards for the first time on the basis of an original silicon-carbon compound hydrogen resisting coating; and by the adoption of an existing technological method, composite structures of different forms are designed and prepared, and the layer number is taken into consideration.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
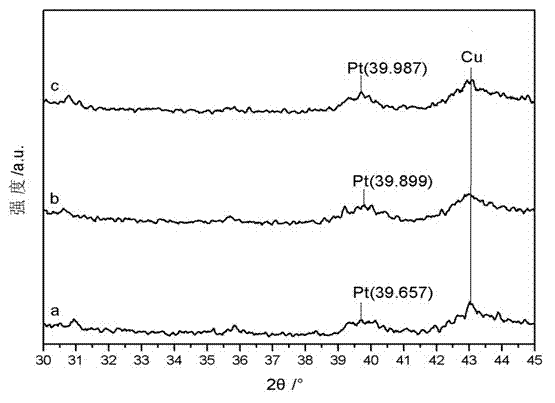
Carbon-carrying core-shell type platinoid-platinum catalyst for indirect electrolytic hydrogen production and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102517604AImprove bindingReduce usageElectrolytic organic productionElectrodesPtru catalystMetallurgy
The invention provides a carbon-carrying core-shell type platinoid-platinum catalyst for indirect electrolytic hydrogen production and a preparation method of the catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: using graphite fiber as a carbon carrier, carrying out ultrasonic cleaning with analytically pure acetone, carrying out ion beam cleaning under a vacuum environment, and carrying out conventional multi-target ion-beam sputtering deposition to obtain carbon-carrying nanocrystalline film catalyst; and soaking in H2SO4 solution, carrying out ultrasonic cleaning with deionized water, and carrying out constant temperature dry-out treatment in a vacuum environment to obtain the carbon-carrying core-shell type platinoid-platinum catalyst for indirect electrolytic hydrogen production, wherein the Pt content and the Cu content on the carbon carrier of the obtained catalyst are 0.190-0.200mg / cm2 and 0.030-0.080mg / cm2 respectively; and the mass ratio of unit area carbon carrier and reactive metal Pt carried on the carbon carrier is (1,000-1,842):1, and the mass ratio of Pt and Cu carried on unit area carbon carrier is (2.5-6.3):1. According to the invention, the binding of the catalyst particles with the carbon carrier is enhanced, and the catalyst is more stable, so as to improve catalysis efficiency and reduce the usage of noble metals.
Owner:昆明理工大学设计研究院有限公司
Comprehensive depositing and coating device and comprehensive coating method
ActiveCN108342699AImprove performanceAvoid multiple drawsVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCrucibleEvaporation
The invention relates to a comprehensive depositing and coating device and a comprehensive coating method integrating electron beam evaporation, ion beam assistance and ion beam sputtering. The devicecomprises a comprehensive depositing system formed by a left electronic gun crucible, a right electronic gun crucible, an ion source auxiliary source, an ion source main source, a sputtering target material and a fixture plate. According to the comprehensive depositing and coating device and the comprehensive coating method provided by the invention, the advantages of an electron beam evaporationand deposition technology, an ion beam assistance deposition technology and an ion beam sputtering deposition technology are combined, so that the quality of a coating can be improved, the coating efficiency can be improved, and the coating cost is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Reflecting mirror with low loss and high reliability
The invention relates to a reflecting mirror with high reliability for a laser gyro prepared through ion beam sputtering. The reflecting mirror is prepared by the following steps of: alternately plating a regularTiO2 / SiO2 film high reflective coating with 1 / 4 working wavelength on a nano-grade quartz base by adopting a double-ion-beam sputtering and depositing process, plating a layer of extremely thin air interface layer material HfO2 at the outermost layer, and carrying out postprocessing under the condition of 340 DEG C / 6h on a reflecting mirror film in the air after the plating is finished. The reflecting mirror provided by the invention has extremely low loss and dispersion, a high laser damage resistant threshold, heat stability within 340 DEG C and favorable plasma discharging environment resisting capacity and can keep stable optical property of over 15000Sec in an environment with the plasma energy of 200w. The reflecting mirror prepared by using the technology provided by the invention has stable working property in a gyro resonator, has high environment reliability and can meet the application requirement of a high-precision laser gyro.
Owner:FLIGHT AUTOMATIC CONTROL RES INST
Capillaritron ion beam sputtering system and thin film production method
InactiveUS20090236217A1Reduce the impactReduce surface roughnessCellsElectric discharge tubesZinc atomRoot mean square
A capillaritron ion beam sputtering system and a thin film production method are disclosed. By utilizing reactive capillaritron ion beam sputtering deposition, argon and oxygen are passed through a capillaritron ion source simultaneously. Argon is being ionized and accelerated by a voltage to bombard a zinc target and create zinc atoms, while oxygen atoms are created at the same time. Zinc atom and oxygen atom are combined to form ZnO to deposit on a substrate. The stoichiometric properties, deposition rate, transmission properties, surface roughness and film density of the as-deposited film can be altered by adjusting capillaritron ion beam energy and oxygen partial pressure. Using preferred processing parameters, the root-mean-square surface roughness of the as-deposited film can be smaller than 1.5 nm, while the transmission coefficient at visible range can be greater than 80%.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Zinc antimonide-based thermoelectric film and preparation method thereof
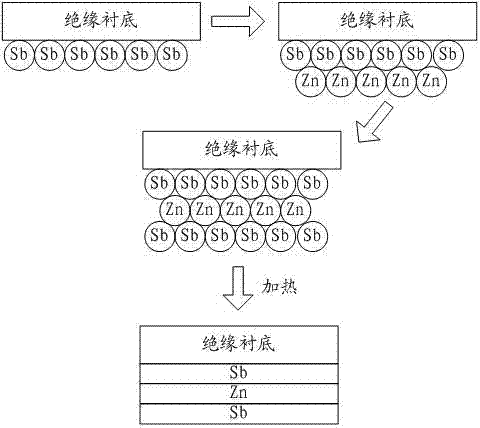
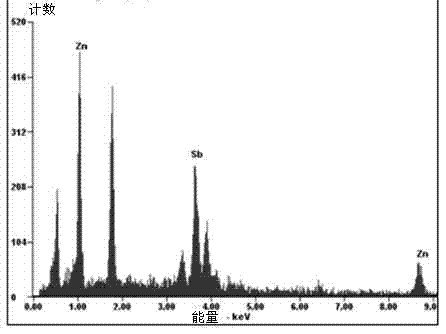
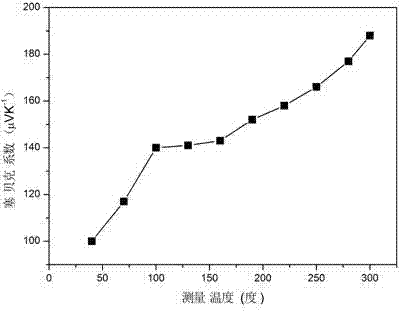
ActiveCN103572243AIncrease contentGood adhesionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingZinc antimonideRepeatability
The invention discloses a zinc antimonide-based thermoelectric film and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of plating a Sb film layer on an insulating substrate by an ion beam sputtering deposition method, plating a Zn film layer on the Sb film layer, plating a Sb film layer on the Zn film layer obtained by the previous step, and then carrying out high-temperature in-situ heat treatment in an inert gas atmosphere to obtain the zinc antimonide-based thermoelectric film. The preparation method has simple processes, good repeatability and a high raw material utilization rate, prevents a loss of Zn in high-temperature annealing, realizes high-precision control and controllable doping on elements of the zinc antimonide-based thermoelectric film, effectively optimizes a film structure and improves film thermoelectric properties.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
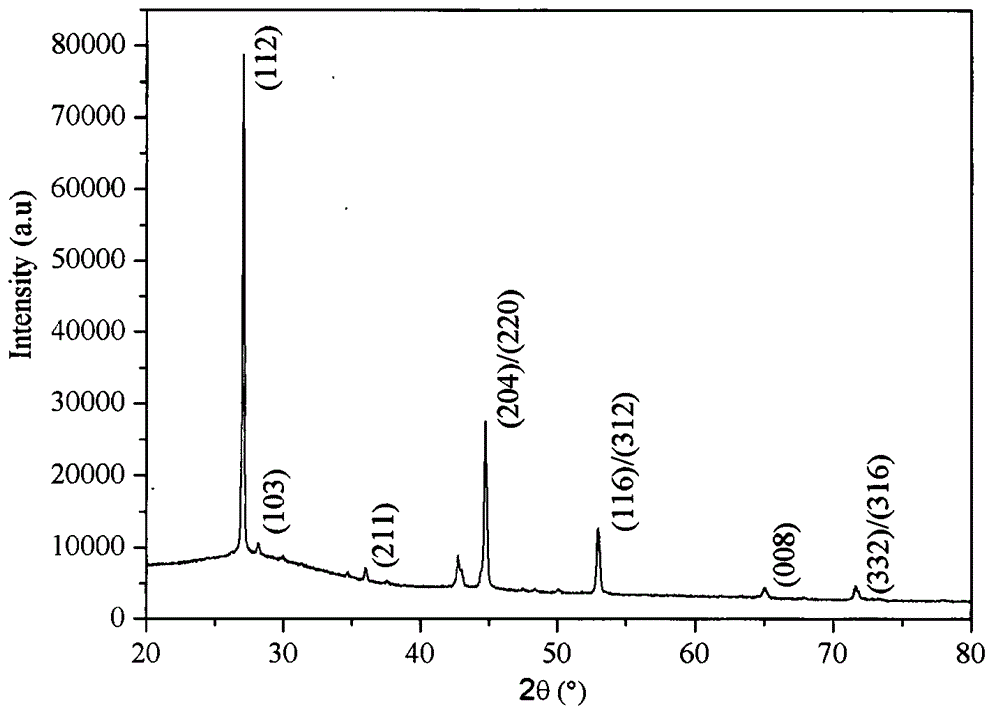
Method for preparing large-area single-oriented hexagonal boron nitride two-dimensional atomic crystal
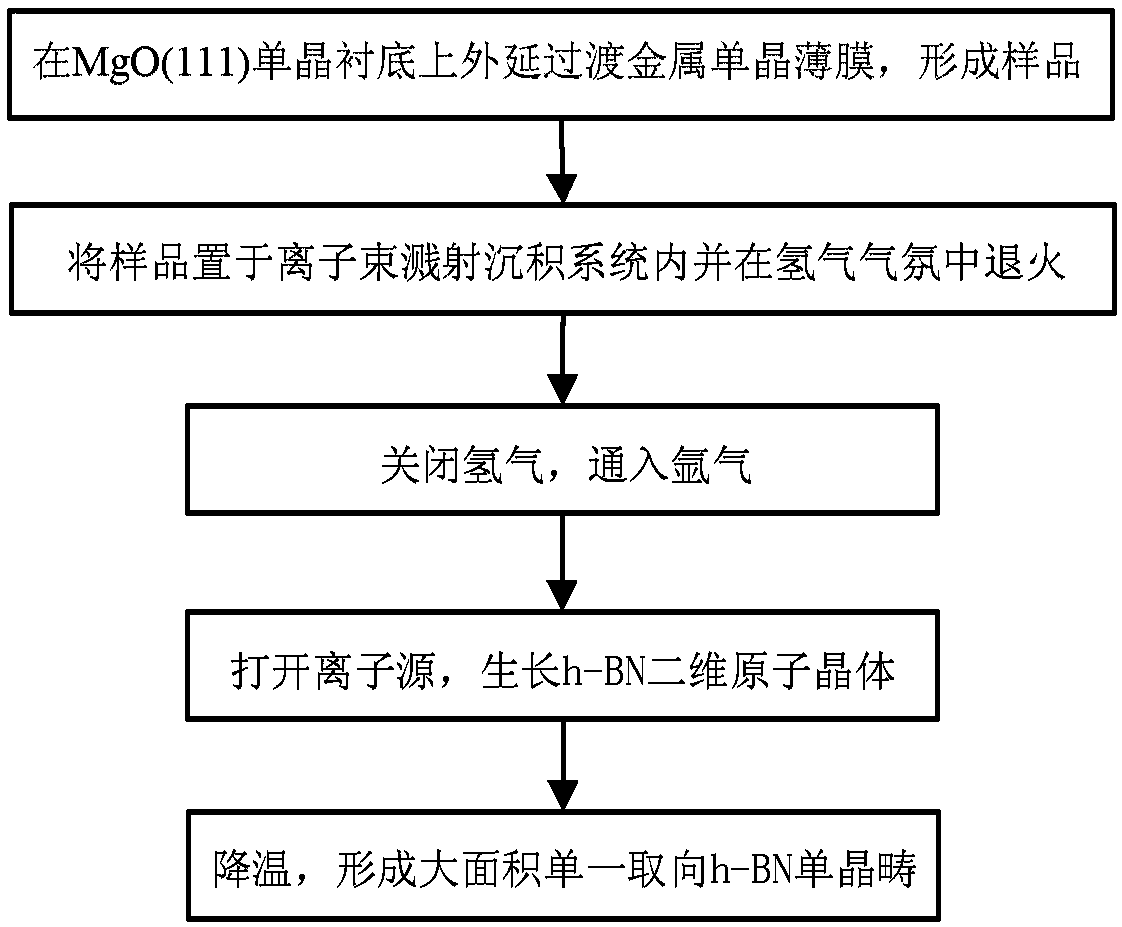
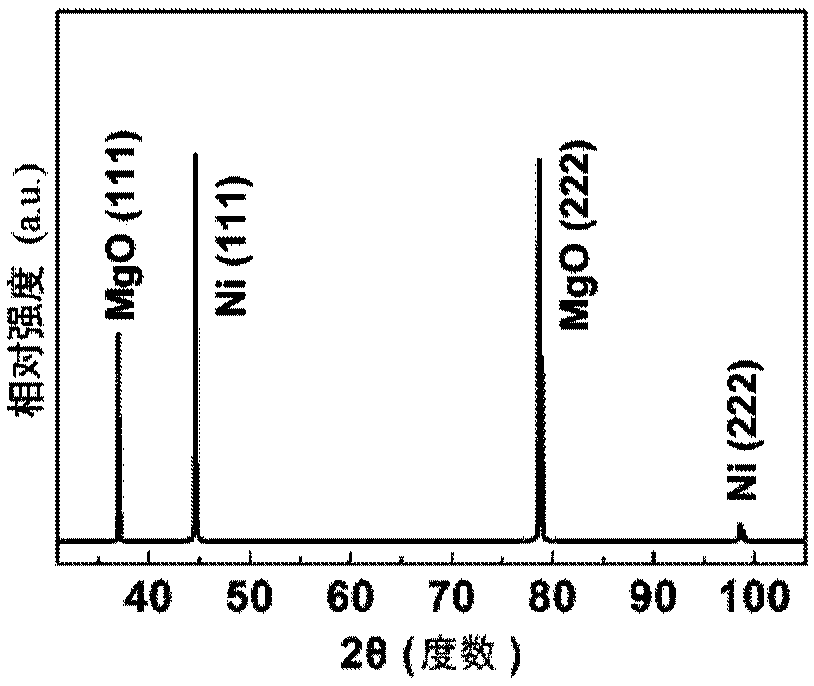
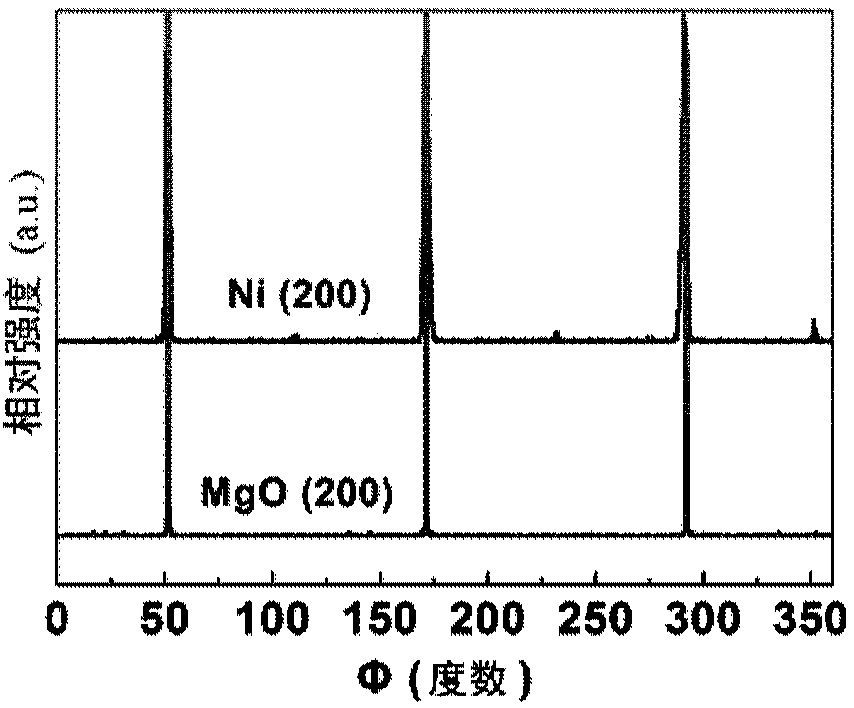
ActiveCN108193276ASmall sizeQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthVacuum evaporation coatingHexagonal boron nitrideHydrogen atmosphere
The invention discloses a method for preparing a large-area single-oriented hexagonal boron nitride two-dimensional atomic crystal. The method comprises the following steps: epitaxially depositing a predetermined thickness of a transition metal single crystal film on a MgO (111) single crystal substrate to form a sample; placing the sample in a chamber of an ion beam sputter deposition system, vacuumizing, heating in a hydrogen atmosphere and annealing in situ; turning off the hydrogen to restore the chamber in the ion beam sputter deposition system to a vacuum environment, and introducing Argon gas to the chamber; bombarding a high-purity boron nitride target placed in the chamber of the ion beam sputtering deposition system with an ion source, so that the sputtered boron and nitrogen atoms are deposited on the surface of the sample to grow and form a hexagonal boron nitride two-dimensional atomic crystal; cooling the hexagonal boron nitride two-dimensional atomic crystal to finally obtain single-oriented hexagonal boron nitride single crystal domains. The method provided by the invention can be used to prepare single-oriented h-BN crystal domains, and has the advantages of simplepreparation process, good controllability, low cost, and non-toxic and harmless by-products, and contributes to achieve the preparation of large-size high-quality h-BN films.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for manufacturing Cu (In, Ga) Se2 thin film of thin-film solar cell absorption layer
ActiveCN102751387AIncrease profitGood adhesionFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingAlloyGa element
The invention discloses a novel method for manufacturing Cu (In, Ga) Se2 thin film of a thin-film solar cell absorption layer. The method includes steps of employing a method of ion beam sputtering deposition, taking high-purity Cu, In, Se and an alloy of CuxGa1-x as sputtering target materials, successively sputtering elements or alloy target materials to manufacture a precursor thin-film lamination or periodic lamination thin film by accurately controlling ion beam sputtering parameters, and manufacturing the Cu (In, Ga) Se2 thin film by means of high-temperature in-situ heat treatment in the same vacuum environment. The method for manufacturing Cu (In, Ga) Se2 thin film of the thin-film solar cell absorption layer is optimized in doping process, simple in operation and capable of improving a utilization ratio of raw materials, realizing doping of the Ga element on the basis of the Cu (In, Ga) Se2 thin films and effectively controlling radial distribution of the Ga element. The structure and performance of the Cu (In, Ga) Se2 thin film manufactured by the method can meet performance requirements of high-efficient photovoltaic devices, and a new way is explored for development and utilization of the solar cell.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
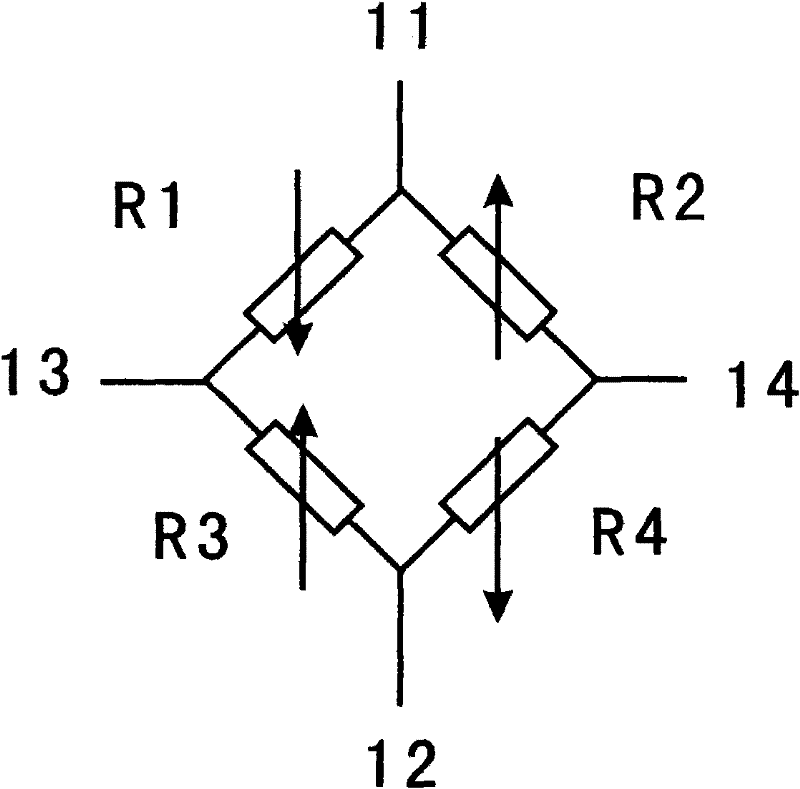
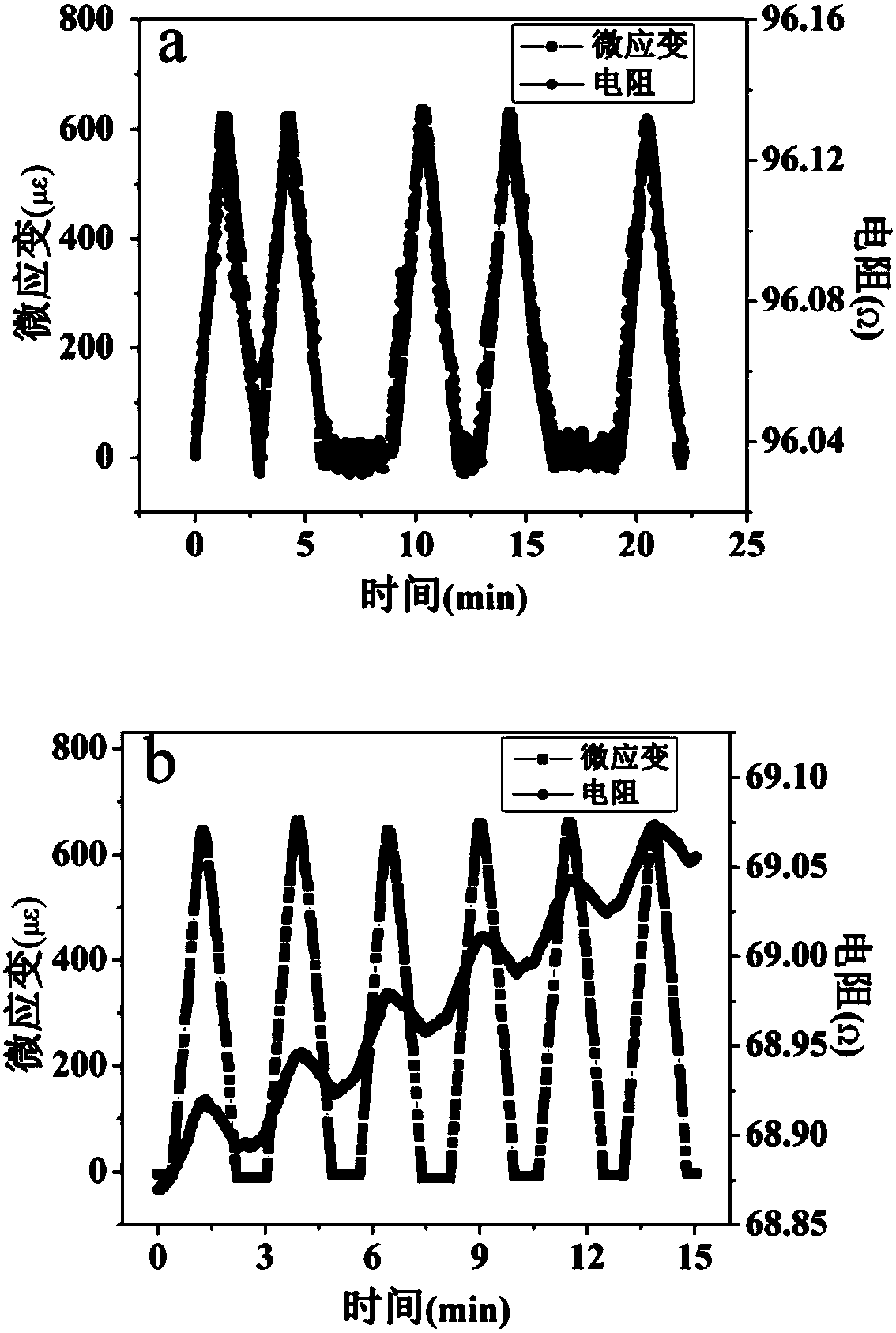
Strain thin film for thin film pressure sensor, preparation method of strain thin film, thin film pressure sensor core
ActiveCN105547535AHigh melting pointSmall temperature coefficient of resistanceForce measurementThin film sensorFilm resistance
The invention discloses a strain thin film for a thin film pressure sensor, a preparation method of a strain thin film, a thin film pressure sensor core. The strain thin film is a tantalum nitride thin film. The preparation method includes the following steps that: (1) an ion beam sputtering deposition method is adopted to bombard tantalum nitride targets, a tantalum nitride thin film preparation layer can be deposited on an elastic substrate required by a thin film sensor; and (2) annealing treatment is carried out, and the strain thin film for the thin film pressure sensor can be obtained. The thin film pressure sensor core comprises a buffer layer, an insulating layer and a tantalum nitride thin film resistance layer which are sequentially arranged on the elastic substrate. The strain thin film for the thin film pressure sensor and the strain thin film prepared by the preparation method of the invention have the advantages of high strain factor, low resistance temperature coefficient and excellent electrical conductivity. The thin film pressure sensor core has the advantages of high sensitivity and high reliability in a harsh environment.
Owner:48TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
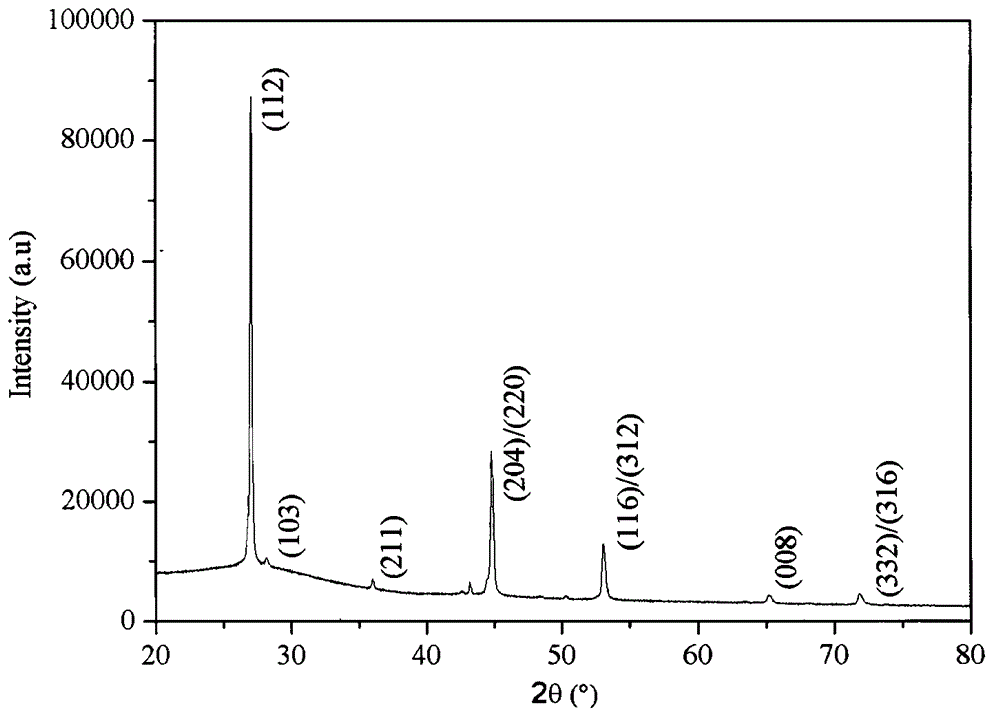
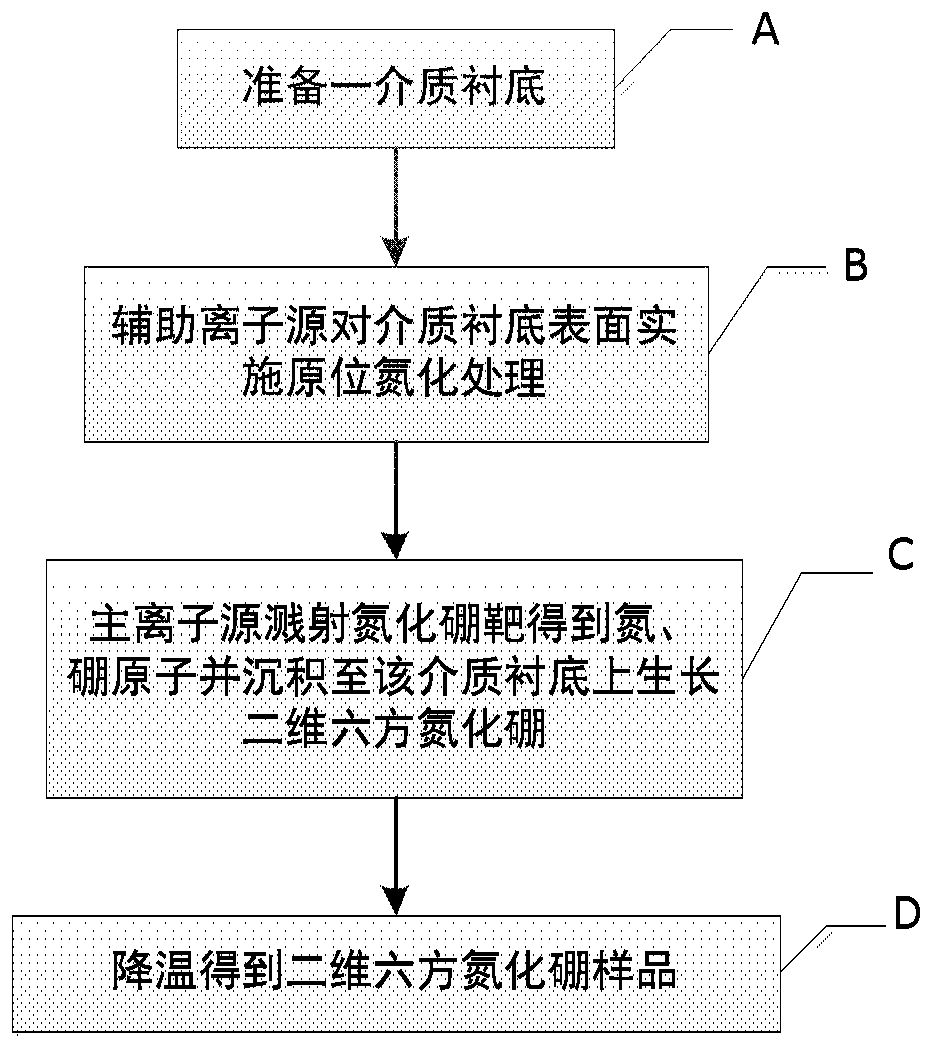
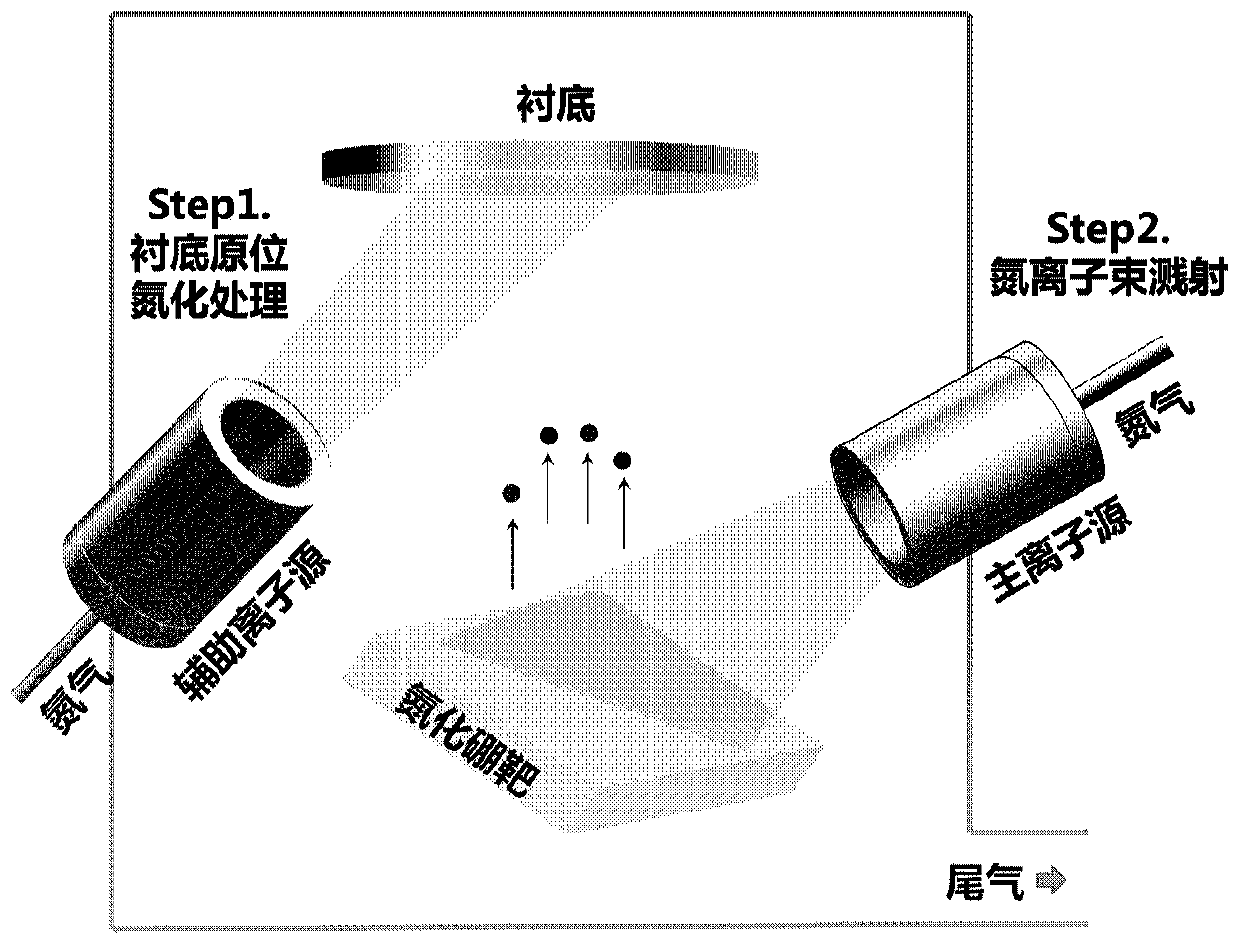
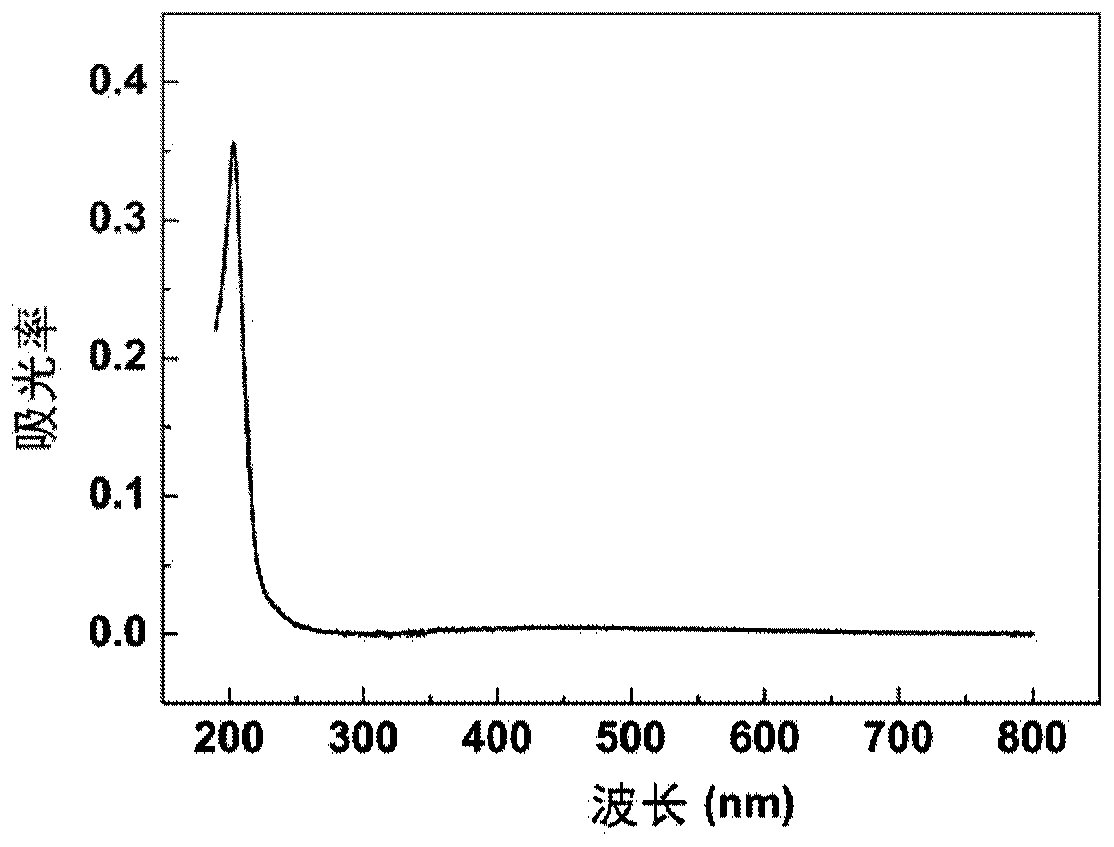
Method for directly growing two-dimensional hexagonal boron nitride on dielectric substrate
ActiveCN110629184AAvoid breakingAvoid pollutionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHexagonal boron nitrideDielectric substrate
The invention discloses a method for directly growing two-dimensional hexagonal boron nitride on a dielectric substrate. The method comprises the following steps that the dielectric substrate is prepared, the dielectric substrate is preset in an ion beam sputter deposition chamber, the deposition chamber comprises a boron nitride target, an auxiliary ion source and a main ion source, and the deposition chamber is pre-pumped to a back bottom vacuum degree; the auxiliary ion source performs in-situ nitridation treatment on the surface of the dielectric substrate, the main ion source sputtering the boron nitride target to obtain nitrogen and boron atoms and depositing the nitrogen and the boron atoms onto the dielectric substrate to grow the two-dimensional hexagonal boron nitride; and the sample of the two-dimensional hexagonal boron nitride is obtained by cooling. According to the method for directly growing the two-dimensional hexagonal boron nitride on the dielectric substrate, the crystal quality of hexagonal boron nitride on the dielectric substrate can be improved, the controllability is good, the surface of the prepared thin film is flat, the uniformity is good, and the methodhas very important significance for the application of hexagonal boron nitride optoelectronics.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-element alloy thin-film resistor, preparation method and multi-element target material
InactiveCN106282944AReduce manufacturing costIncrease resistanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingManganesePhotoresist
The invention relates to a multi-element alloy thin-film resistor, a preparation method and a multi-element target material. The preparation method includes the following steps of preparing the multi-element target material containing nickel, chromium, manganese and silicon, fixing the target material to a target table, fixing a base material with prepared photoresist to a rotary working table, conducting vacuumizing to make the vacuum degree not larger than 5*10<-4> Pa, inflating an ion source with argon with working pressure intensity of 2.0*10<-2> Pa, conducting glow discharge to generate plasmas, conducting leading-out, bundling, accelerating and neutralizing to form an argon ion bundle to attack the multi-element target material on the target table, depositing sputtered particles on the surface of the base material to form a multi-element alloy thin film, and removing residual photoresist to obtain the multi-element alloy thin-film resistor. By means of the multi-element target material containing nickel, chromium, manganese and silicon, the resistance value of the thin-film resistor prepared through an ion bundle sputter deposition process can reach 200-700 kilohm; meanwhile, the resistance temperature coefficient is reduced to 5 ppm, and the production cost of the thin-film resistor is reduced.
Owner:北京埃德万斯离子束技术研究所股份有限公司
A coating method for thin film of laser gyroscope reflector
InactiveCN106507849BQuality improvementReduce lossMirrorsVacuum evaporation coatingScattering lossRefractive index
The invention relates to a method for coating a thin film of a laser gyro reflector, in particular to a method for coating a high-reflection film system on an ultra-smooth substrate that does not reach the Angstrom level. When the coating method of laser gyroscope mirror film of the present invention is by adopting ion beam sputtering deposition technology to prepare multilayer oxide optical film, every high refractive index layer (such as odd numbers such as 1, 3, 5 in the high reflection film system) is plated The layer is a high refractive index layer), pause for a period of time, and then use the oxygen-argon mixed ion beam to treat the coating surface, and then pause for a period of time, then proceed to the next layer of plating, and cycle in turn until all the layers are plated. The coating method of the thin film of the laser gyroscope reflector of the invention helps to reduce the absorption loss and volume scattering loss of the film layer, thereby preparing a high-quality and low-loss reflector on the ultra-smooth substrate that does not reach the Angstrom level. At the same time, it has the characteristics of simple operation, low cost and good economy, and has high practical application value.
Owner:FLIGHT AUTOMATIC CONTROL RES INST
Method for obtaining single-crystal boron nitride film by ion beam sputtering deposition
InactiveCN111139526AEasy to controlEasy and controllable preparationPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsGrown filmSingle crystal
The invention relates to the field of researches on two-dimensional layered materials, in particular to a method for obtaining a single-crystal boron nitride film through ion beam sputtering deposition. The method comprises the following steps: ultrasonically cleaning a single crystal substrate by using acetone, ethanol and deionized water in sequence; immersing the cleaned single crystal substrate into a hydrofluoric acid solution for treatment; placing a high-purity Ni target on a target position of a direct-current magnetron sputtering instrument, and epitaxially growing a Ni (111) orientedfilm on the single crystal substrate; fixing a nickel / single crystal substrate on a sample support, putting the sample support into a growth chamber of ion beam sputtering deposition equipment, and carrying out film growth through hydrogen and argon treatment; and cooling the grown film to obtain the large-size single-crystal boron nitride film.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com