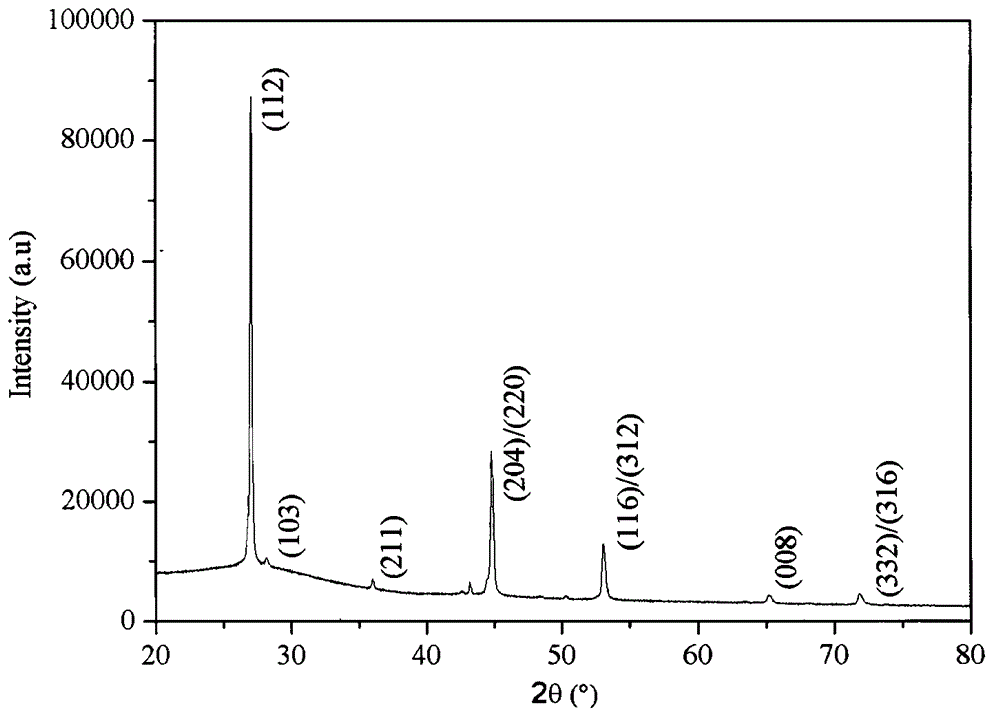
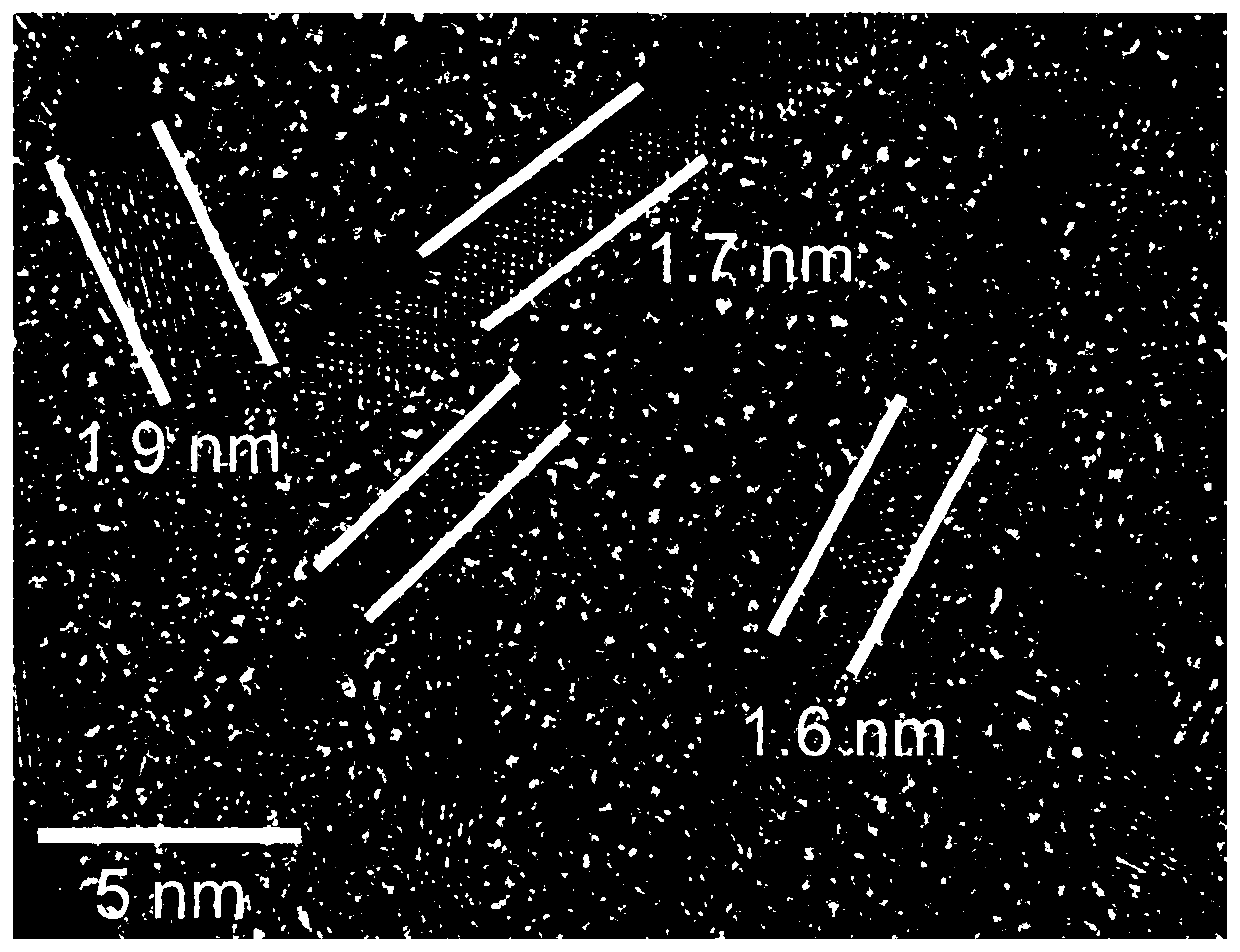
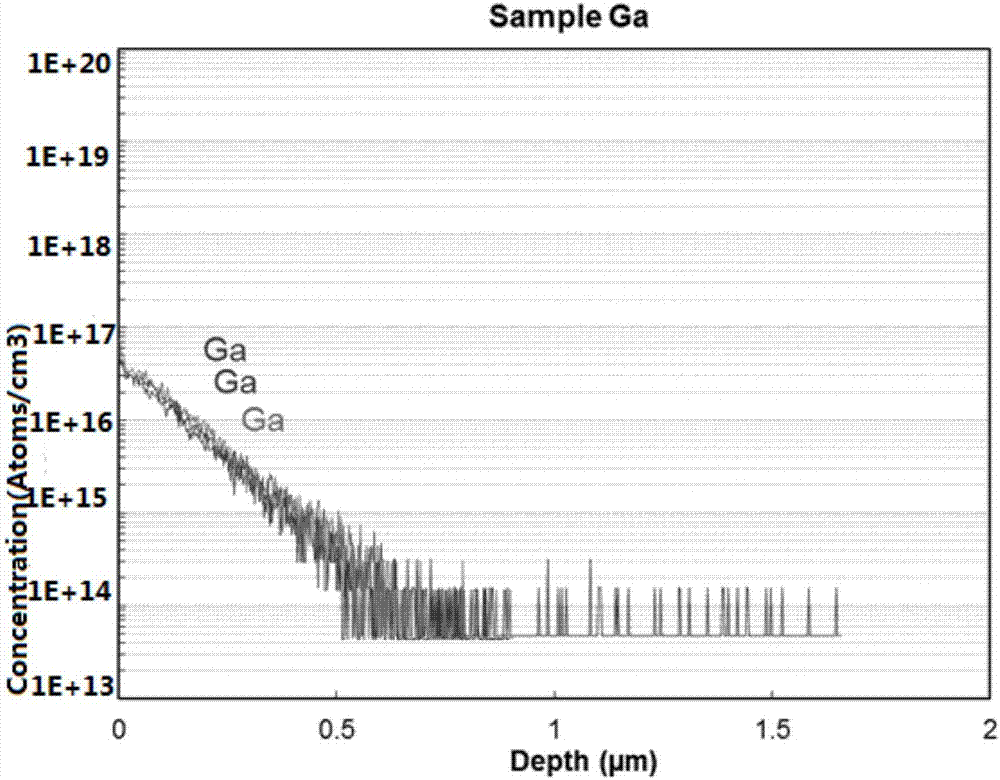
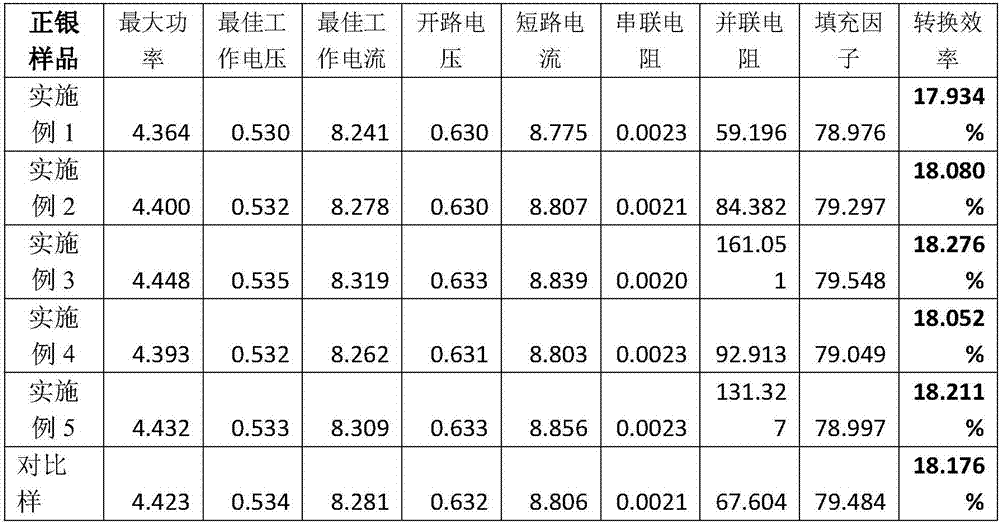
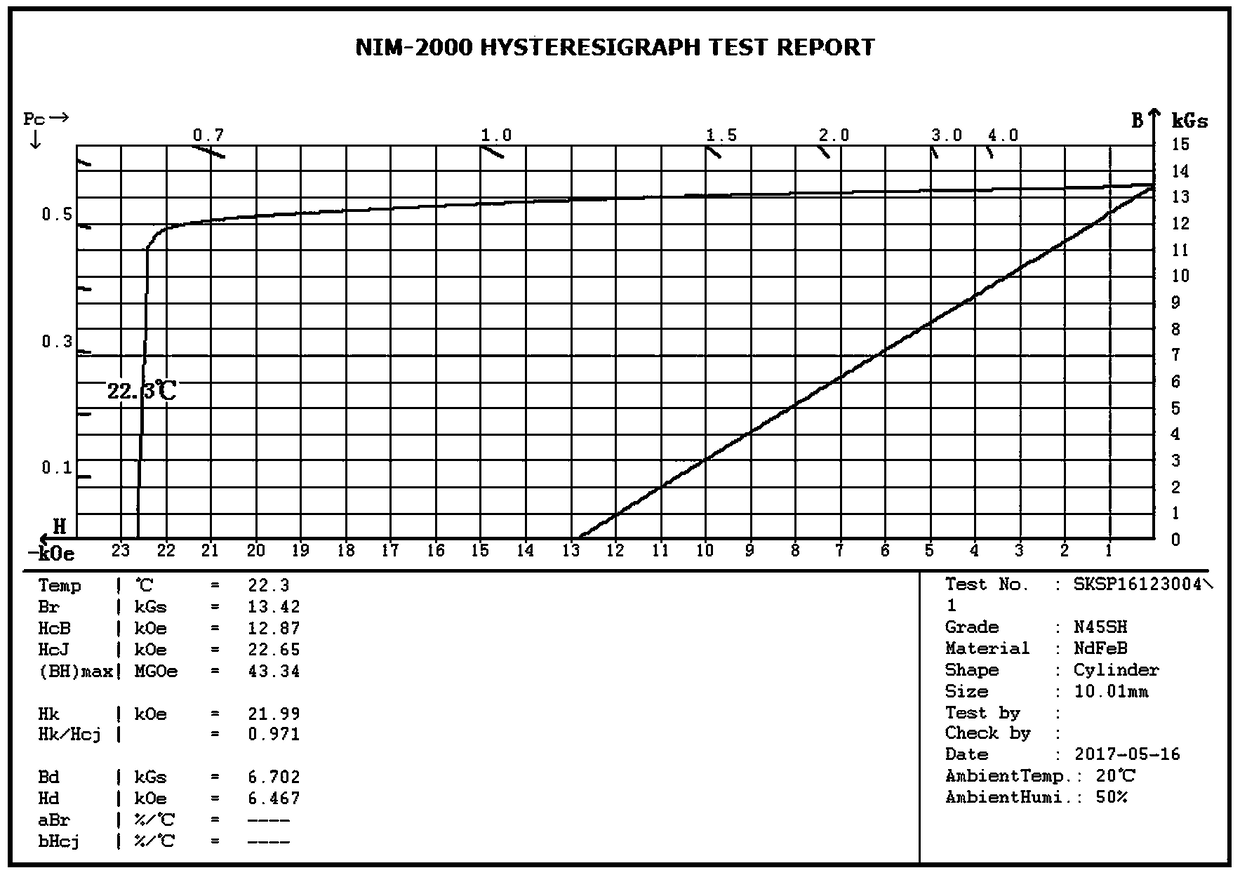
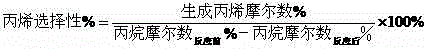Patents
Literature
59 results about "Ga element" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
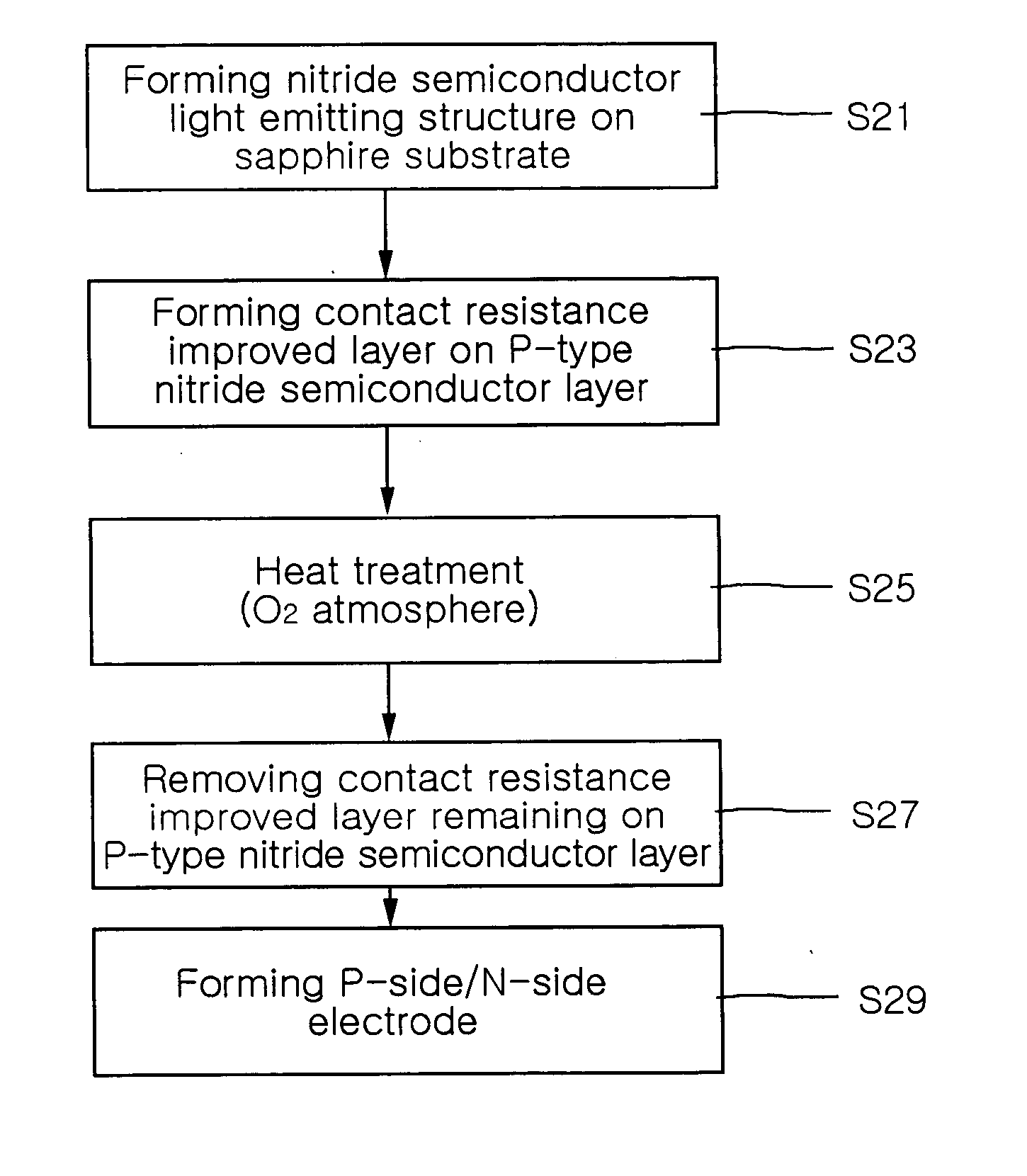
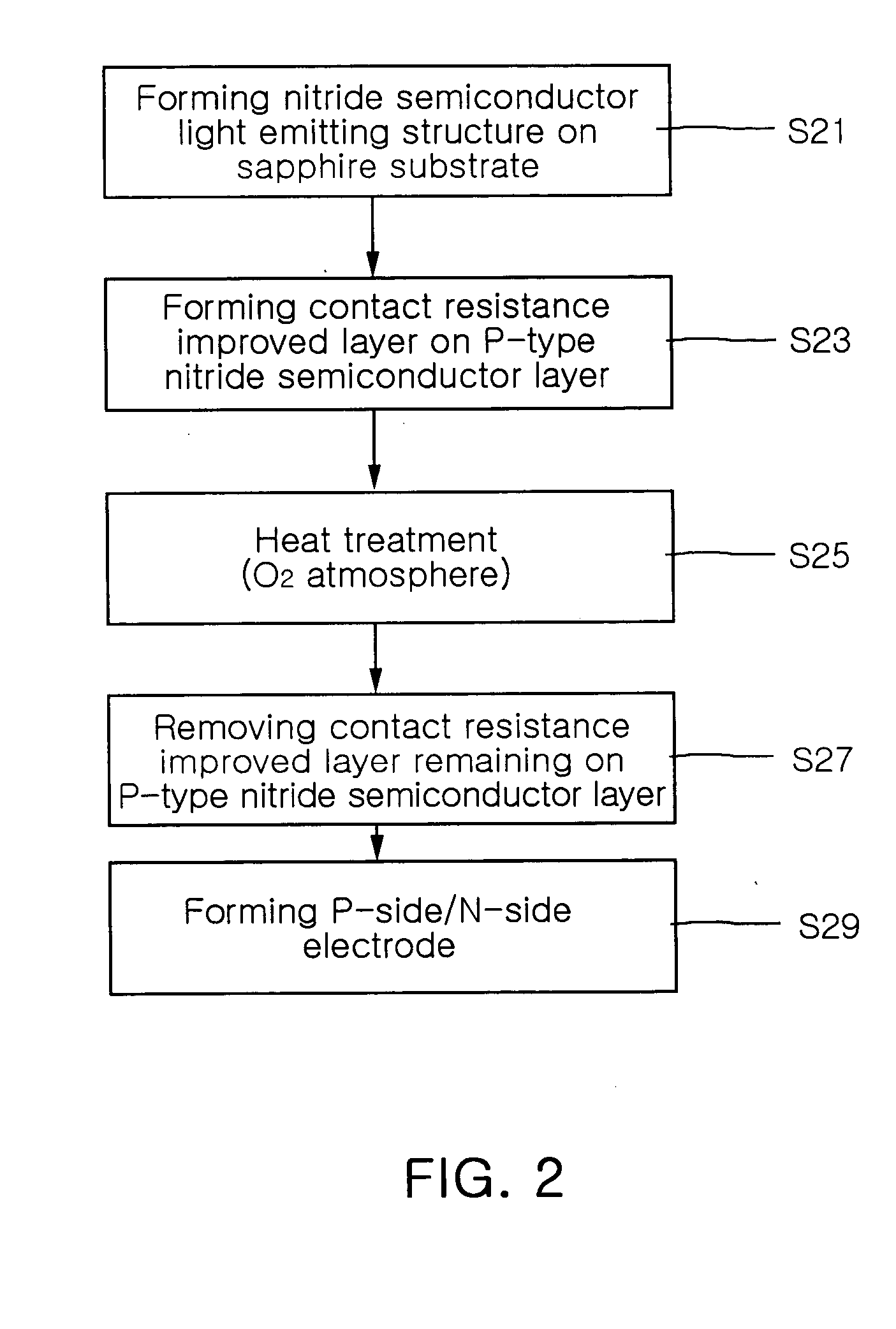
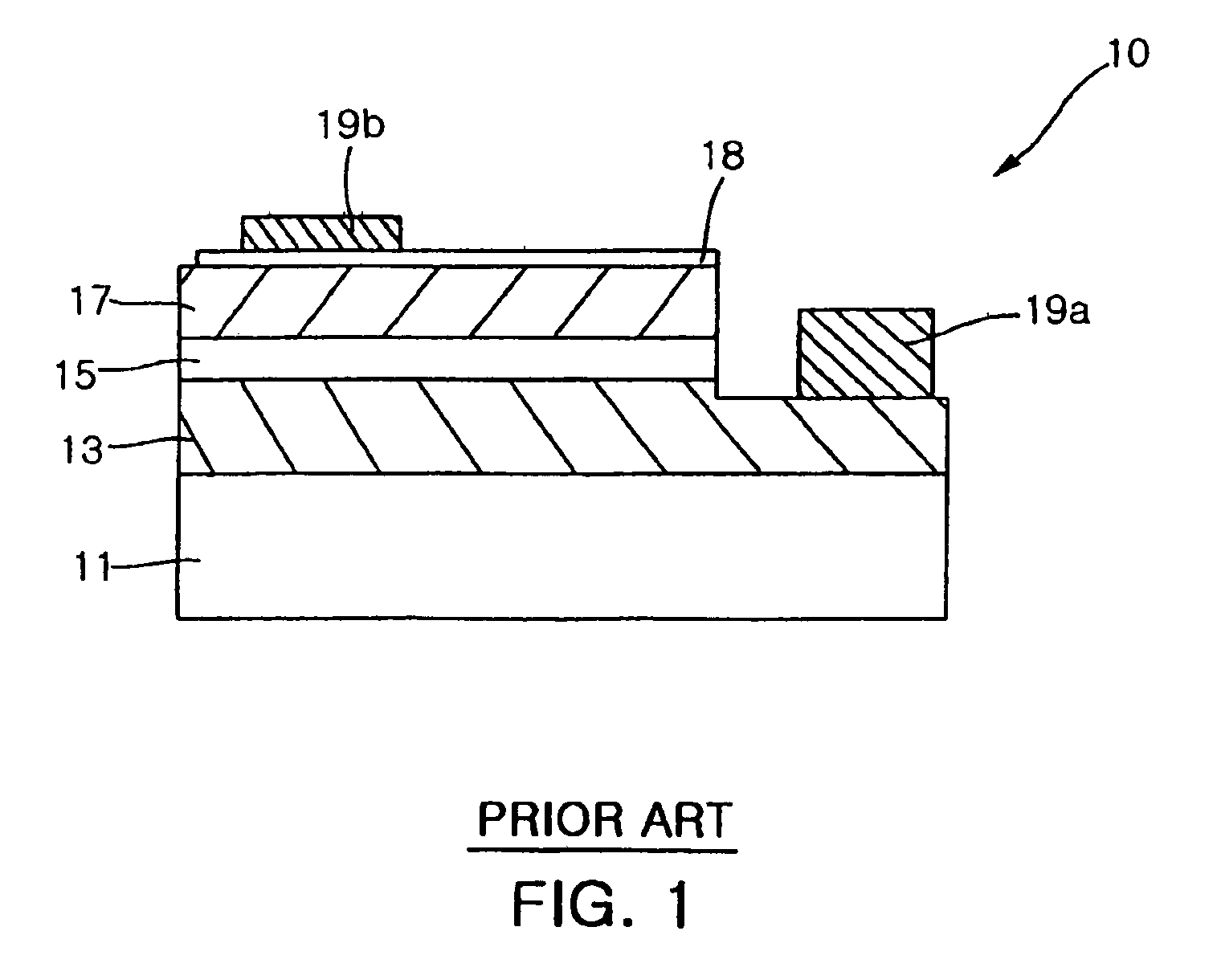
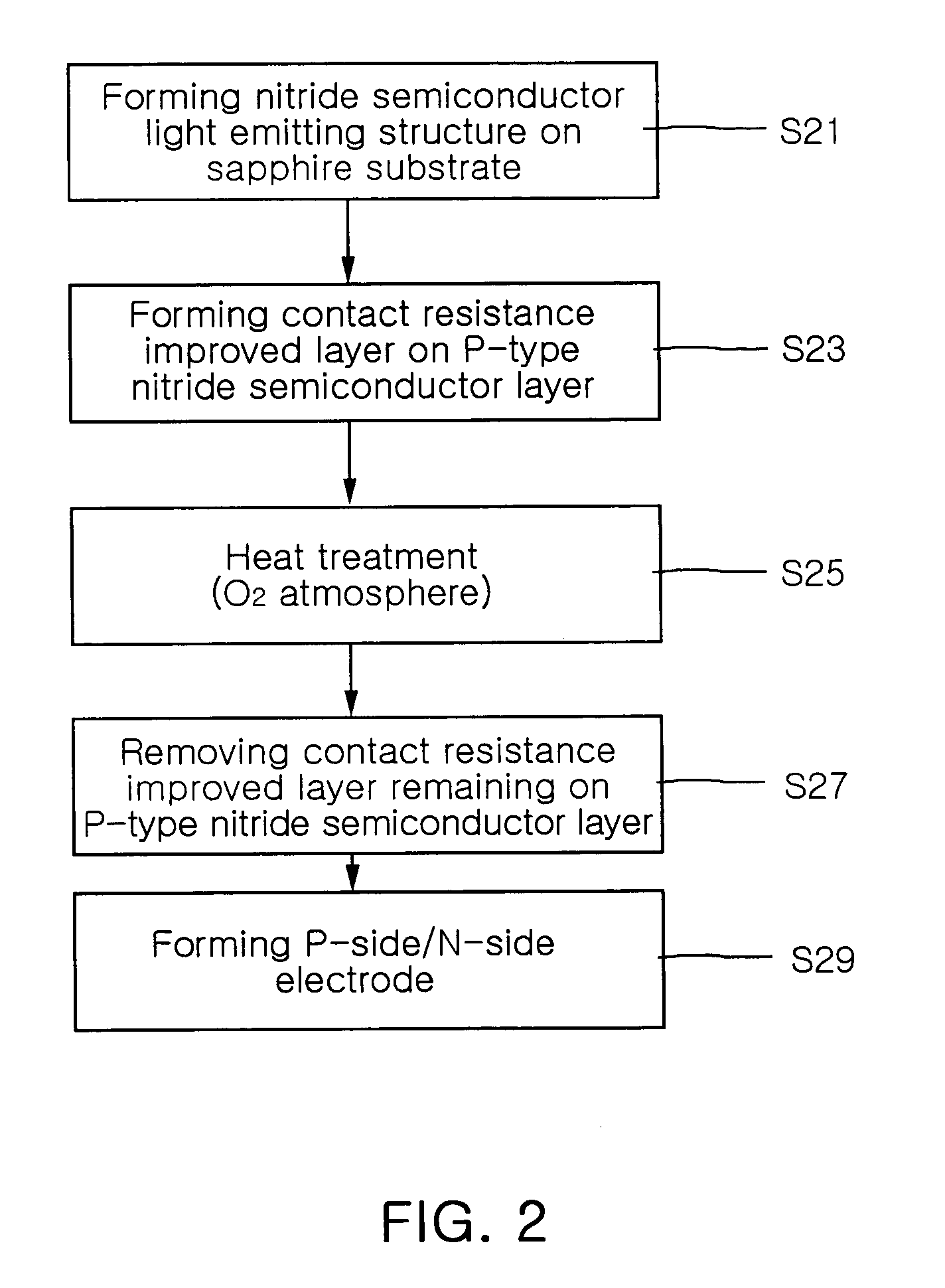
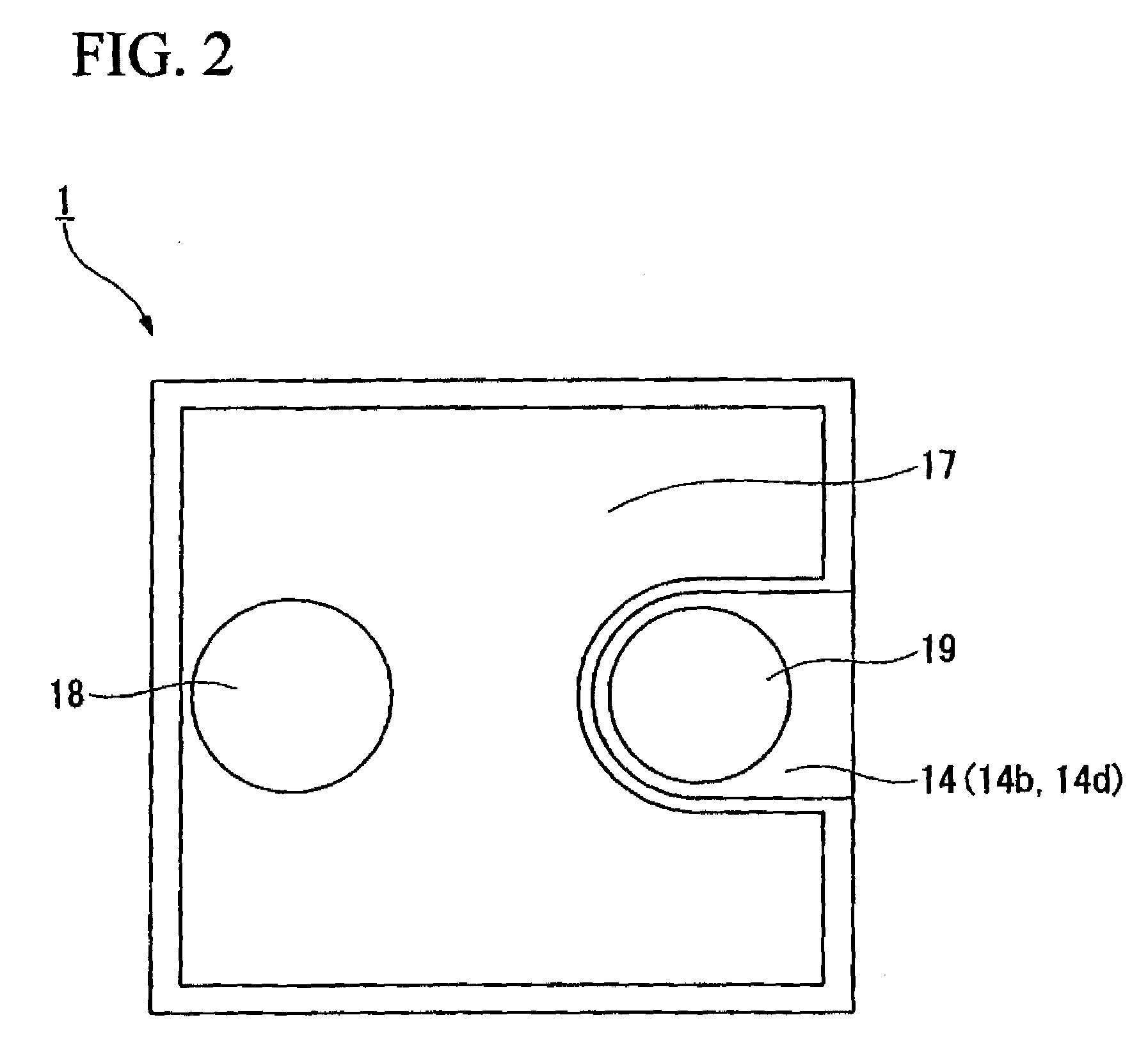
Method of manufacturing gallium nitride based semiconductor light emitting device
InactiveUS20050142820A1Increase brightnessReduce contact resistanceFrom solid stateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGa elementGallium nitride
A method of manufacturing a gallium nitride (GaN)-based semiconductor light emitting device includes forming a contact resistance improved layer on a p-type GaN-based semiconductor layer with at least one metal selected from the group of Au, Mg, Mn, Mo, Pd, Pt, Sn, Ti and Zn, heat-treating the p-type GaN-based semiconductor layer so that elements in the contact resistance improved layer diffuse into the p-type GaN-based semiconductor layer and that Ga elements in the p-type GaN-based semiconductor layer dissolve into the contact resistance improved layer, and removing the contact resistance improved layer remaining on the p-type GaN-based semiconductor layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for manufacturing group iii nitride semiconductor, method for manufacturing group iii nitride semiconductor light-emitting device, group iii nitride semiconductor light-emitting device, and lamp
ActiveUS20100301379A1Efficiently formedDislocation increasePolycrystalline material growthVacuum evaporation coatingGa elementLight emitting device
A method for manufacturing a Group III nitride semiconductor of the present invention includes a sputtering step of forming a single-crystalline Group III nitride semiconductor on a substrate by a reactive sputtering method in a chamber in which a substrate and a Ga element-containing target are disposed, wherein said sputtering step includes respective substeps of: a first sputtering step of performing a film formation of the Group III nitride semiconductor while setting the temperature of the substrate to a temperature T1; and a second sputtering step of continuing the film formation of the Group III nitride semiconductor while lowering the temperature of the substrate to a temperature T2 which is lower than the temperature T1.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Glass sealing material as well as preparation and use methods thereof
The invention relates to a glass sealing material as well as preparation and use methods thereof. The glass sealing material comprises the following raw material components at a molar ratio: 0-10 of B2O3, 0-5 of Al2O3, 25-60 of SiO2, 10-25 of CaO, 10-25 of SrO and 5-25 of Ca2O3. According to the invention, a Ga element is added in the glass sealing material so as to form a non-proliferation layer, thus effectively reducing the proliferation of Cr ions in a Cr-containing stainless steel alloy connection pole toward the sealing glass and significantly improving the high temperature chemical stability of sealing microcrystal glass; preparation raw materials are simple and available, and process is stable; and a reverse glass network structure in which SiO2 is used as a main body is obtained,cost is low, and process is simple and practicable, thereby achieving the conditions of practicality and industrialization.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method of manufacturing gallium nitride based semiconductor light emitting device
InactiveUS6946372B2Increase brightnessReduce contact resistanceFrom solid stateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGa elementGallium nitride
A method of manufacturing a gallium nitride (GaN)-based semiconductor light emitting device includes forming a contact resistance improved layer on a p-type GaN-based semiconductor layer with at least one metal selected from the group of Au, Mg, Mn, Mo, Pd, Pt, Sn, Ti and Zn, heat-treating the p-type GaN-based semiconductor layer so that elements in the contact resistance improved layer diffuse into the p-type GaN-based semiconductor layer and that Ga elements in the p-type GaN-based semiconductor layer dissolve into the contact resistance improved layer, and removing the contact resistance improved layer remaining on the p-type GaN-based semiconductor layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
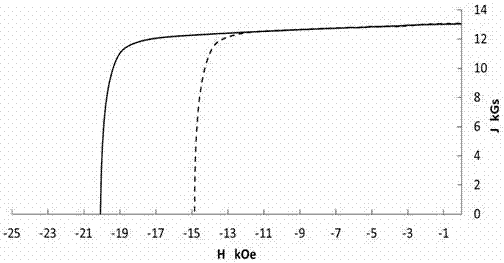
Giant magnetostrictive large volume Fe81Ga19 alloy material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a giant magnetostrictive large volume Fe81Ga19 alloy material and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of the alloy material and the atom percent of the alloy material is Fe81at.% and Ga19 at.%; the preparation method comprises the steps of Fe element and Ga element arc melting, solidification remelting superheat cycle process and high undercooling activation unidirectional solidification. The invention adopts high undercooling activation process so that Fe-Ga alloy blocks can be obtained while the alloy has the giant magnetostrictive property. The magnetostrictive strain of the Fe-Ga alloy blocks is above 500*10 generally and the maximum magnetostrictive strain can reach 830*10.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
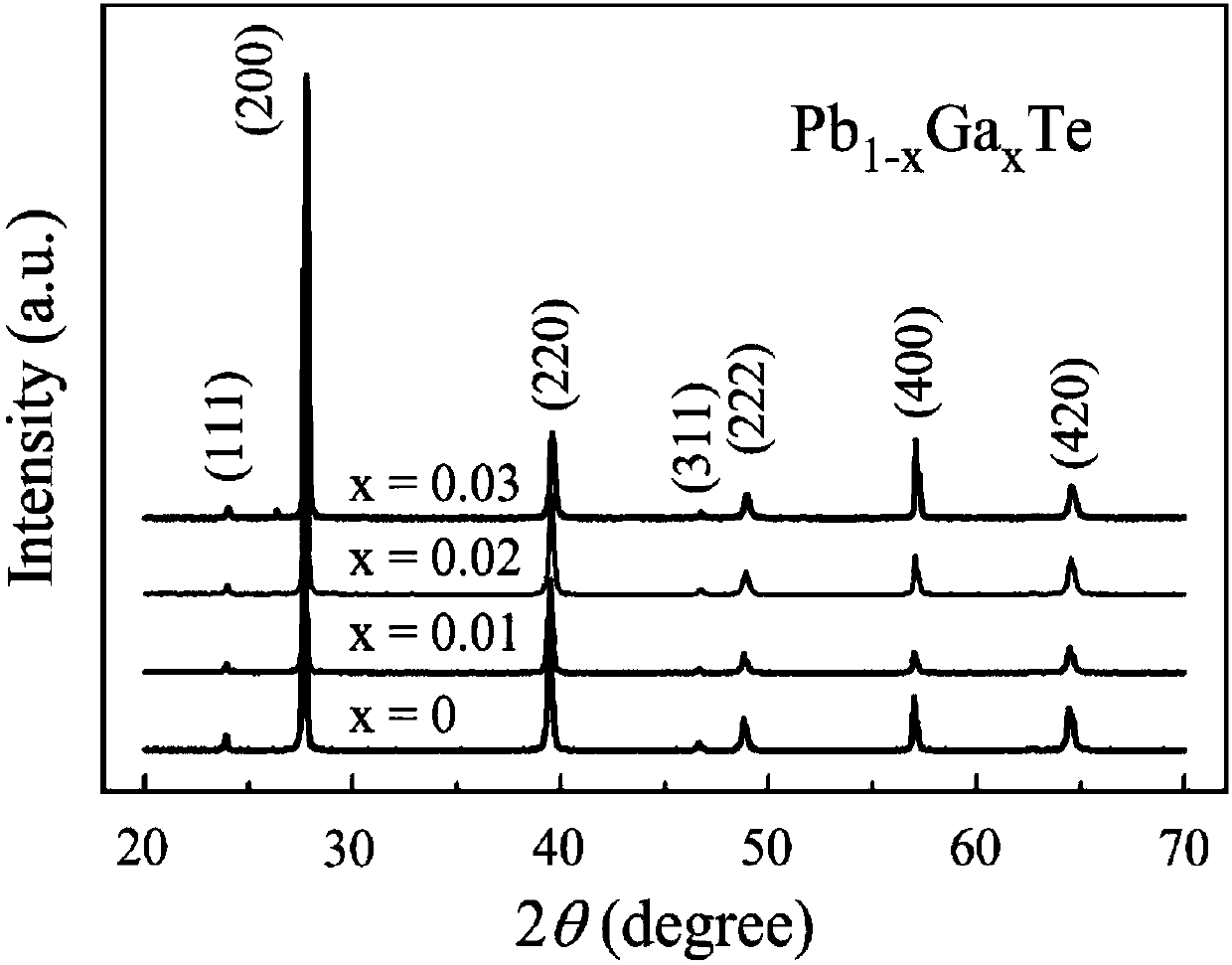
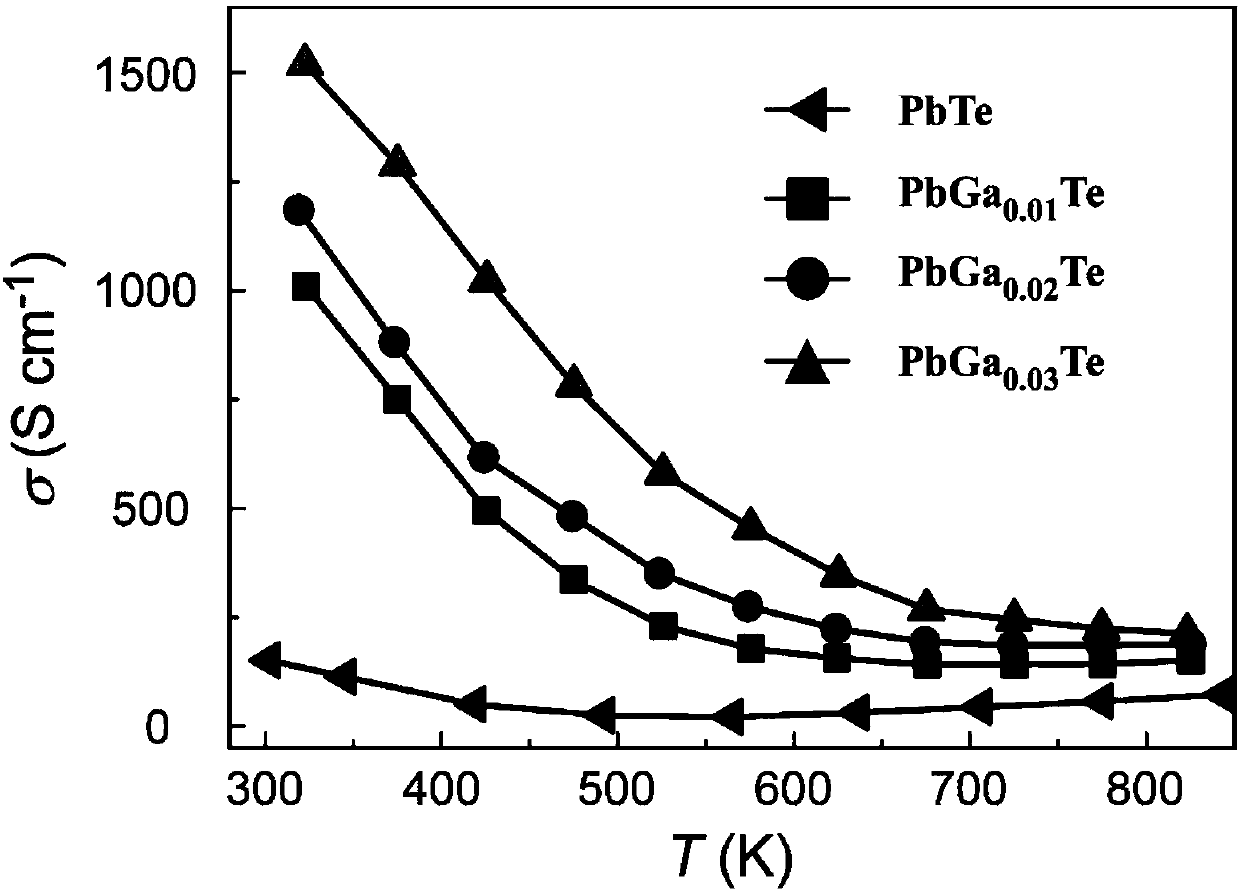
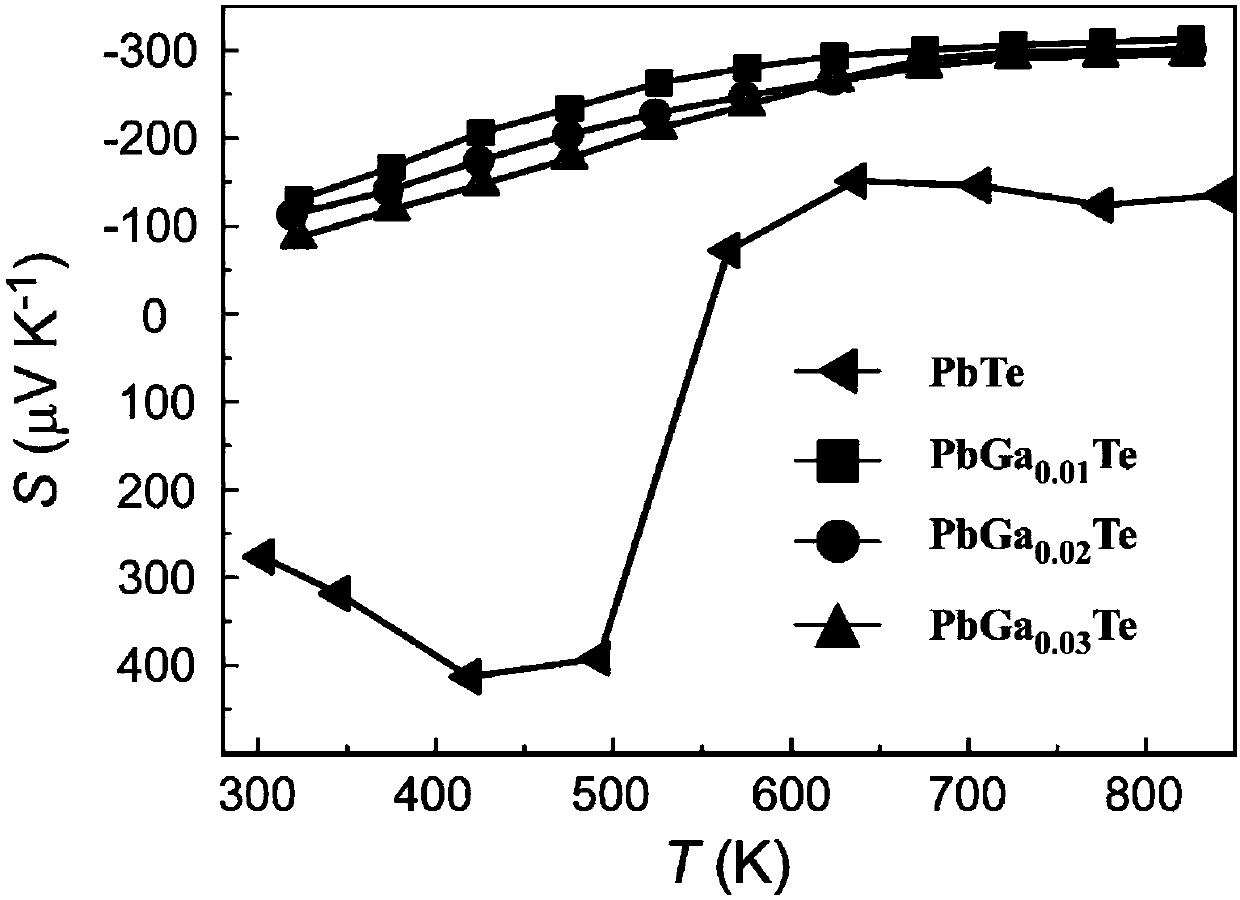
Method for effectively enhancing PbTe thermoelectric performance based on Ga element doping
ActiveCN107565011AImprove thermoelectric performanceHigh crystallinityThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsPhase formationGa element
The invention belongs to the field of material, and relates to a method for effectively enhancing PbTe thermoelectric performance based on Ga element doping. Pb powder, Te powder and Ga blocks are weighed and taken according to the element proportion of 1:x:1-x, wherein the value of x is taken as 0.01-0.05; and the mixture is ground, mixed and compacted into a piece and then put in a quartz tube to perform vacuum pumping and tube sealing, and sintering and discharge plasma sintering are performed in turn so that the Ga-doped PbTe compound thermoelectric material can be obtained. According to the method for enhancing the PbTe thermoelectric figure of merit based on Ga element doping, the method can be used for preparation of the PbTe doped sample and enhancement of the performance so that the process operation is easy and the repeatability is high. According to the method, the phase formation degree, the compactness and the microstructure of the PbTe compound can be controlled by adjusting the temperature increasing and decreasing rate, the phase formation temperature, the thermal preservation time and other process parameters so that the controllability is high; and the prepared Gadoped PbTe compound has the characteristics of high degree of crystallization, less impurity, high compactness, low thermal conductivity and high thermoelectric performance.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
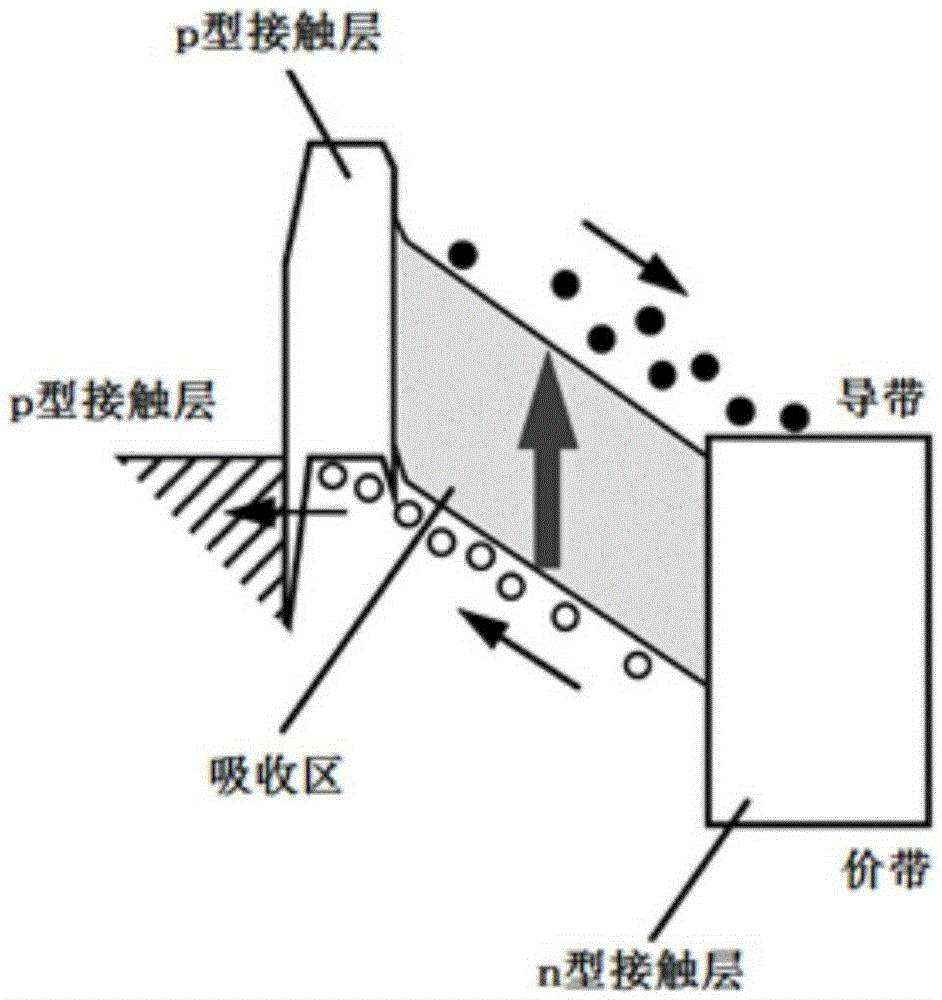
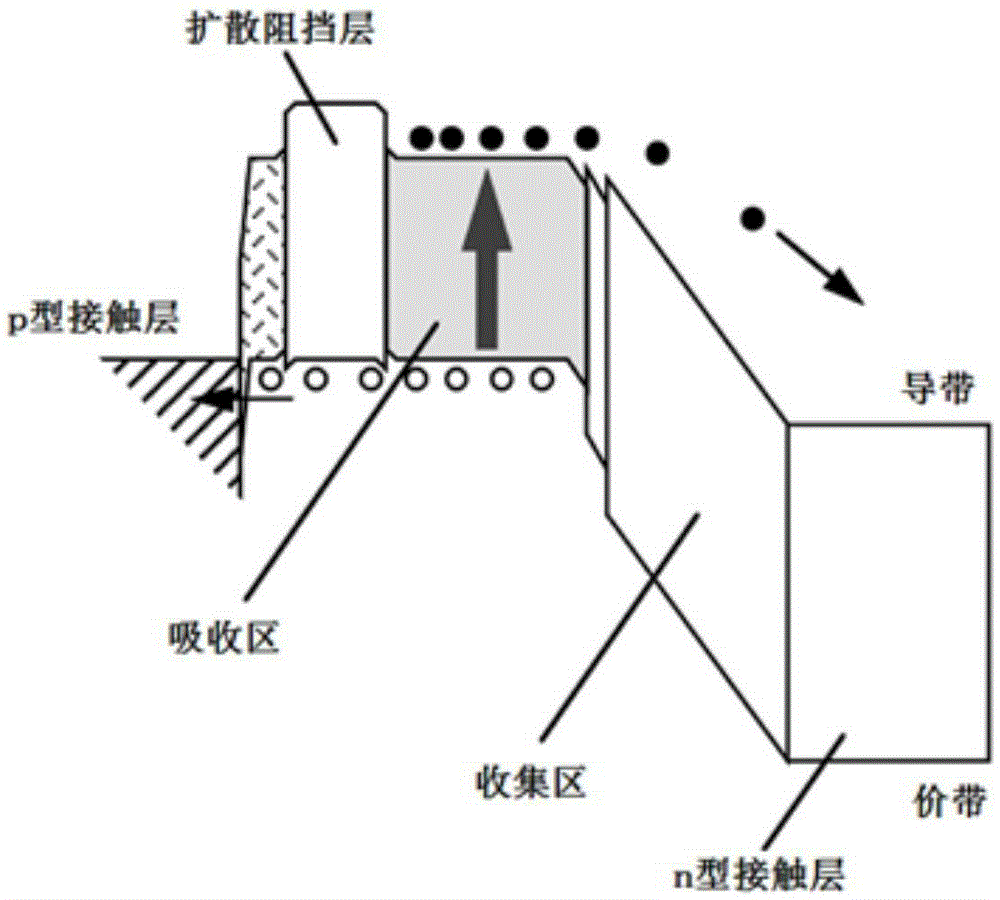
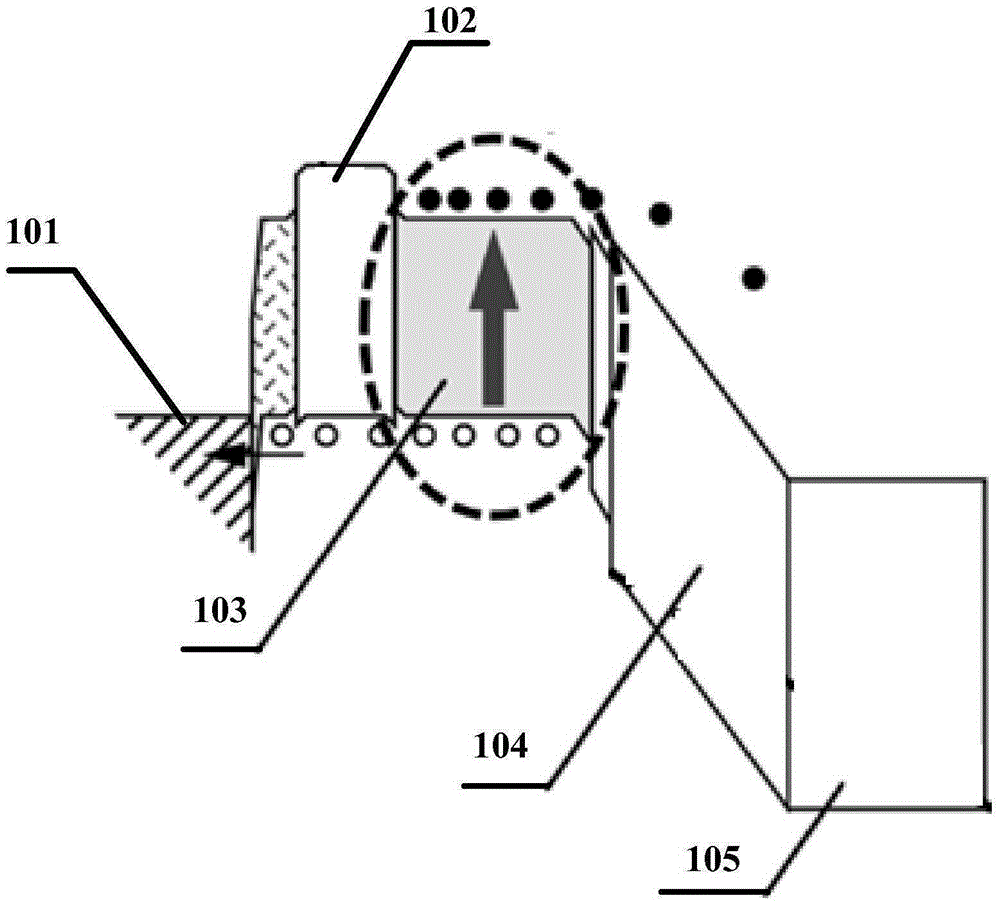
Absorption region structure for unitraveling carrier photodiode
InactiveCN105390556AAccelerated driftReduced transit timeSemiconductor devicesAs elementElectrical field strength
The invention provides an absorption region structure for a unitraveling carrier photodiode. The absorption region structure employs an In1-xGaxAsyP1-y material for growth, wherein the x and y express material components of a Ga element and a As element, the x is larger than 0 and is less than 1 and the y is larger than 0 and is less than or equal to 1; and the component parameters x and y change in a linear gradient mode or in a step type gradient mode, so that the gradient change of the forbidden band width in the absorption region is realized. Moreover, with selection of the component parameters x and y, the lattice constant of the In1-xGaxAsyP1-y material matches InP and the forbidden band width is not larger than that of photon energy of laser with the wavelength of 1.5 microns. According to the invention, with utilization of a built-in electric field introduced by a gradient energy band structure, the electric field intensity in the absorption region can be enhanced obviously; and the drift of electrons can be accelerated effectively based on the enhanced electric field and the transition time at the absorption region can be shortened. Therefore, the electron transition time in the absorption region of the unitraveling carrier photodiode can be reduced effectively. And utilization of the absorption region structure has the great significance in improving the bandwidth of the device and realizing the ultra-high-speed wireless communication system based on the device.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
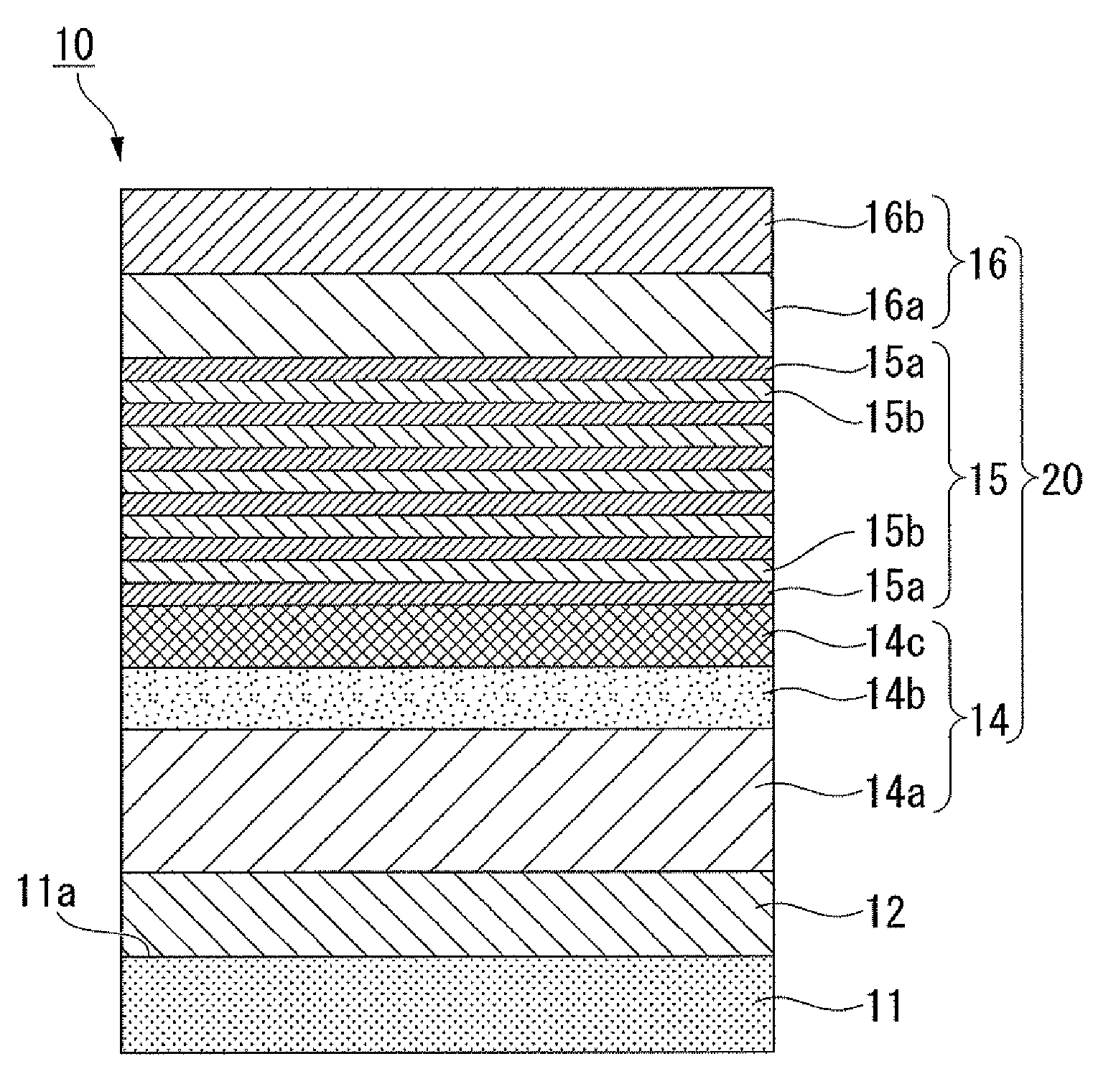
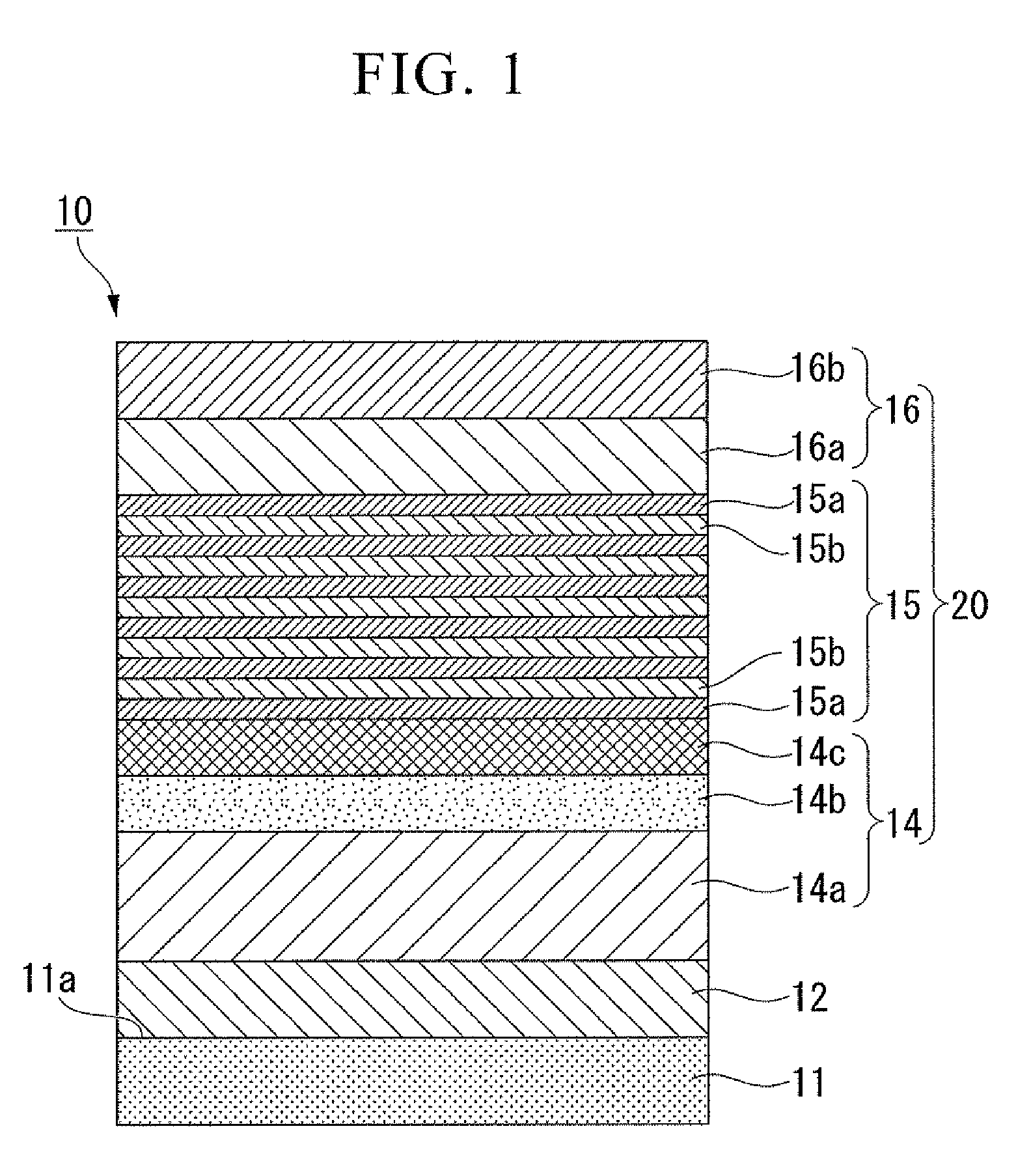
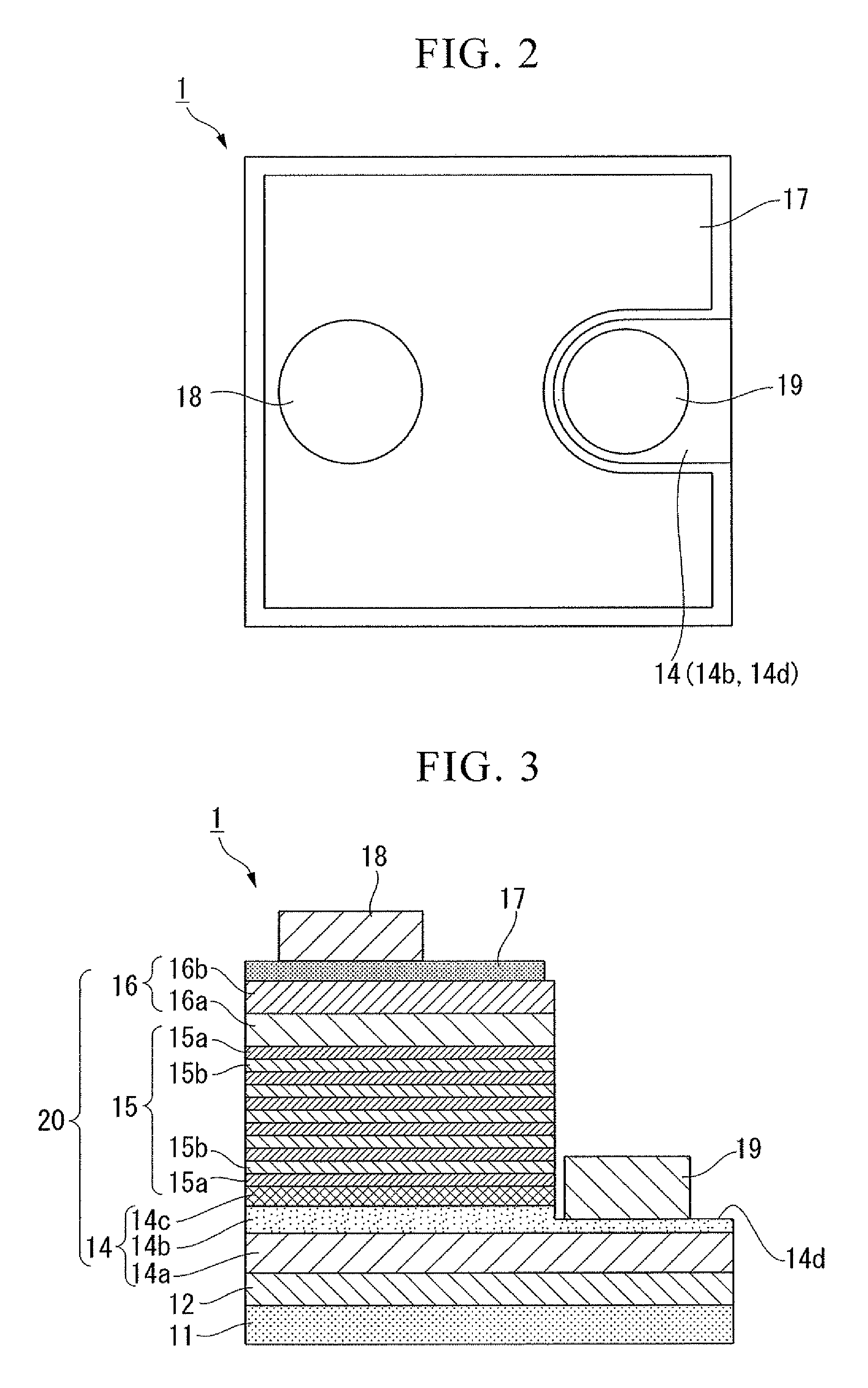
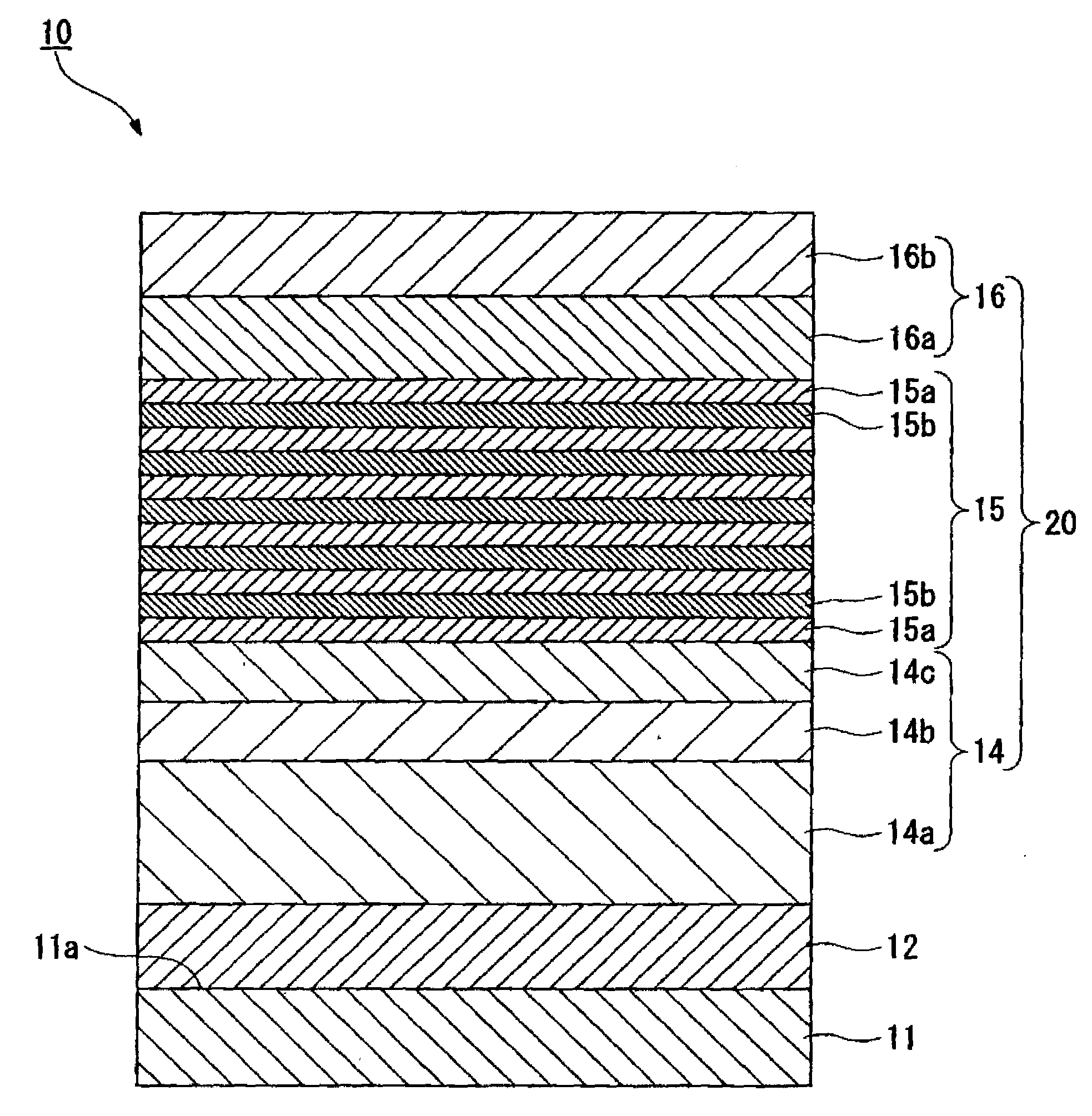
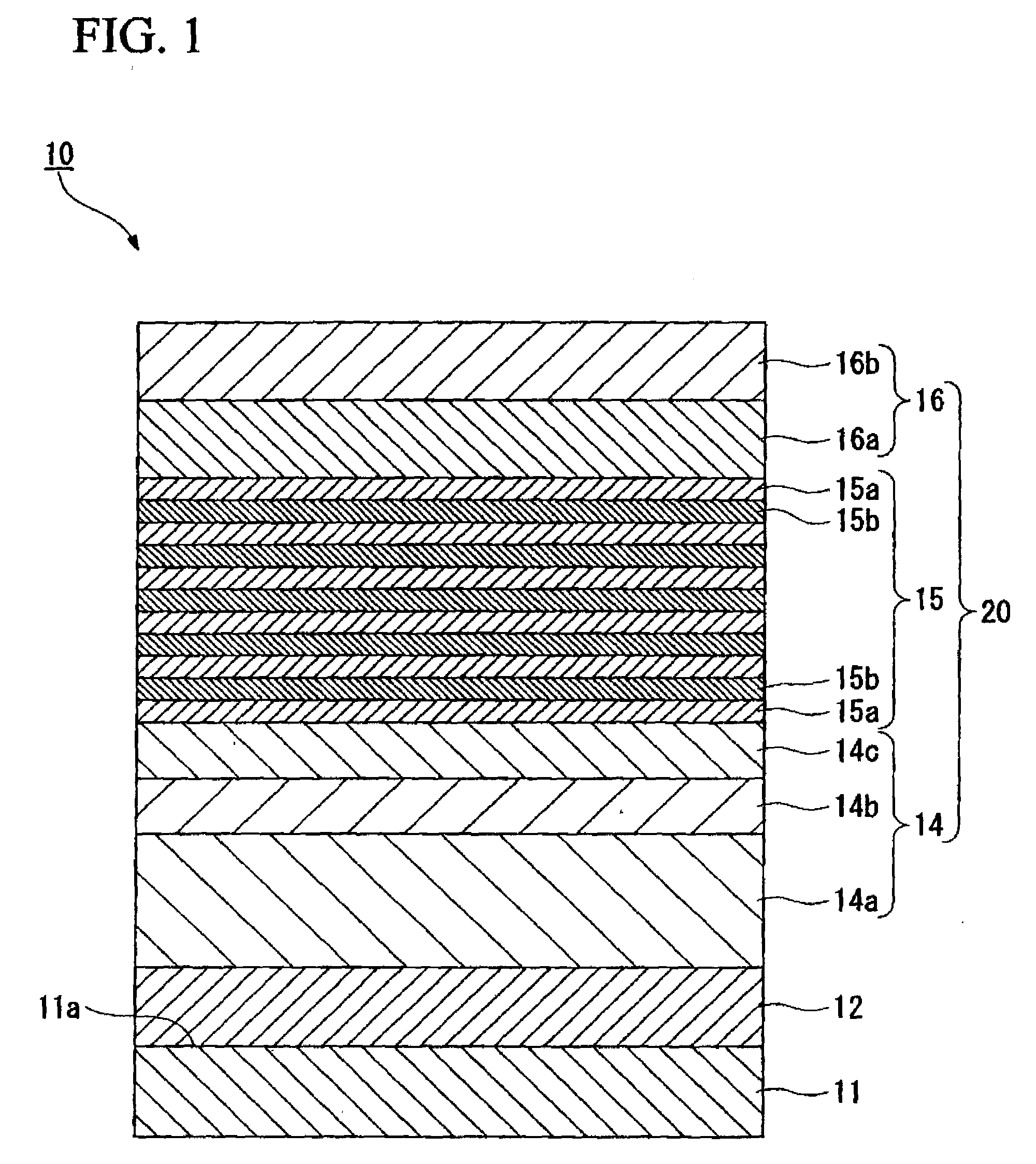
Process for producing iii group nitride compound semiconductor light emitting device, iii group nitride compound semiconductor light emitting device and lamp
ActiveUS20080116478A1Improve balanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGa elementLight emitting device
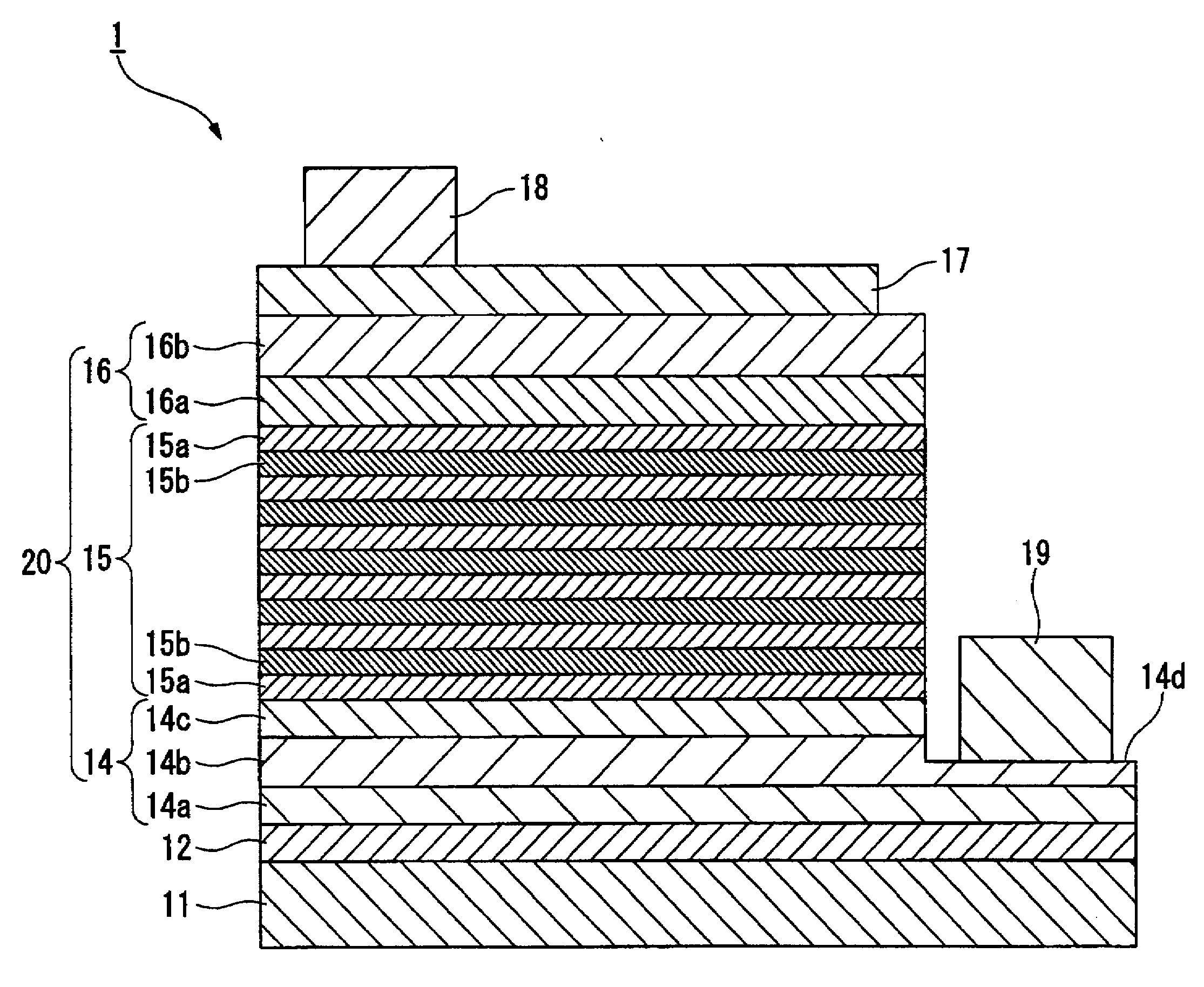
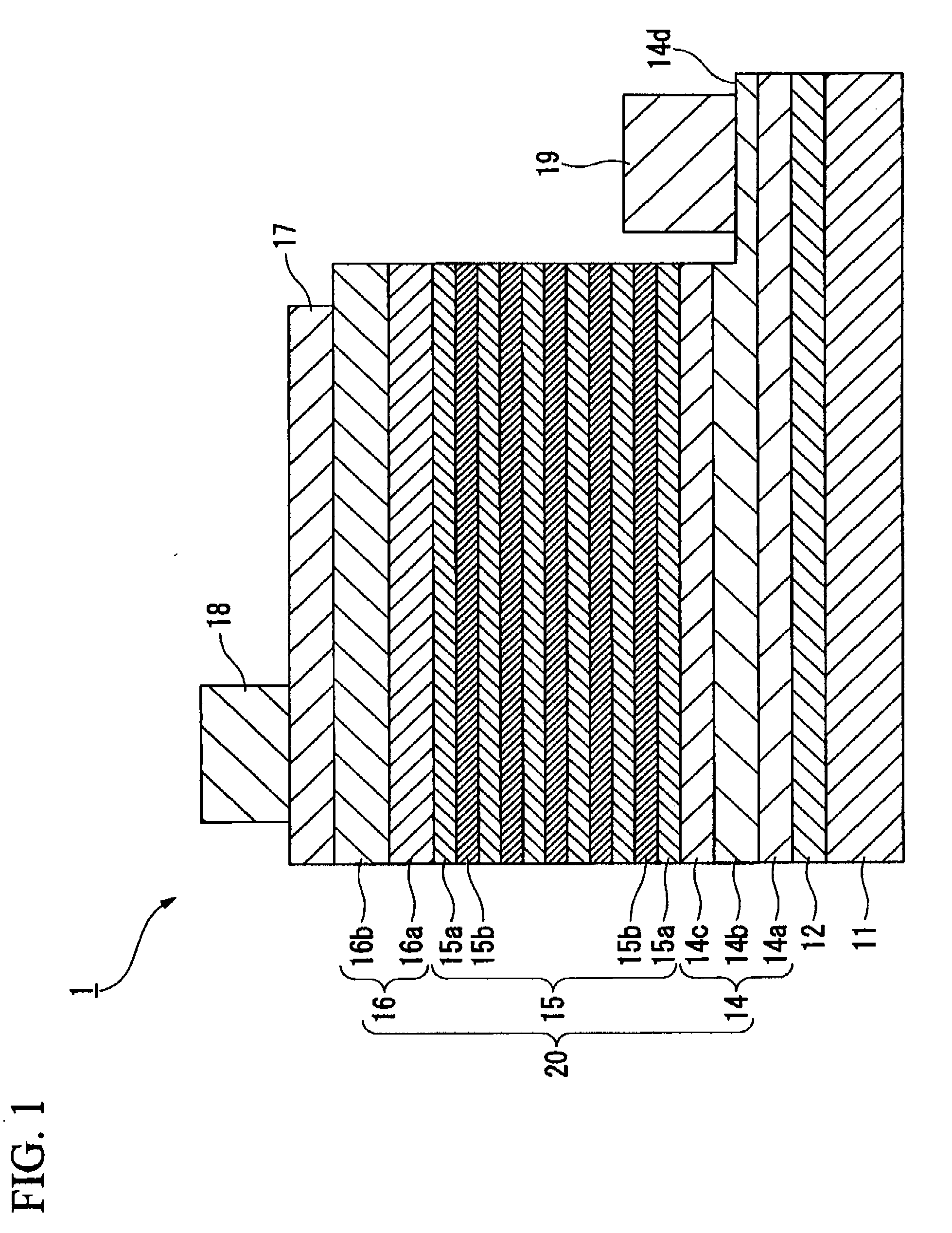
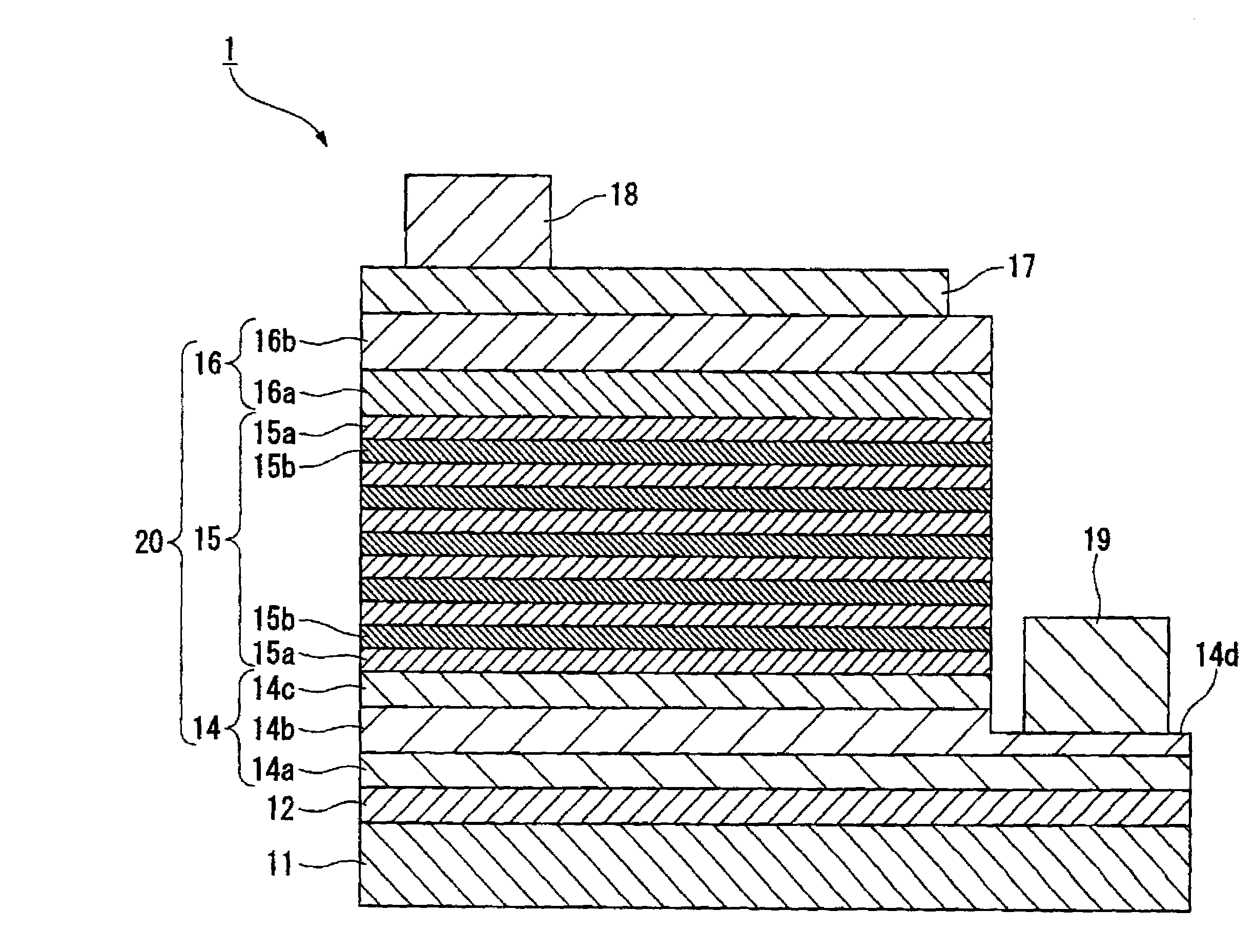
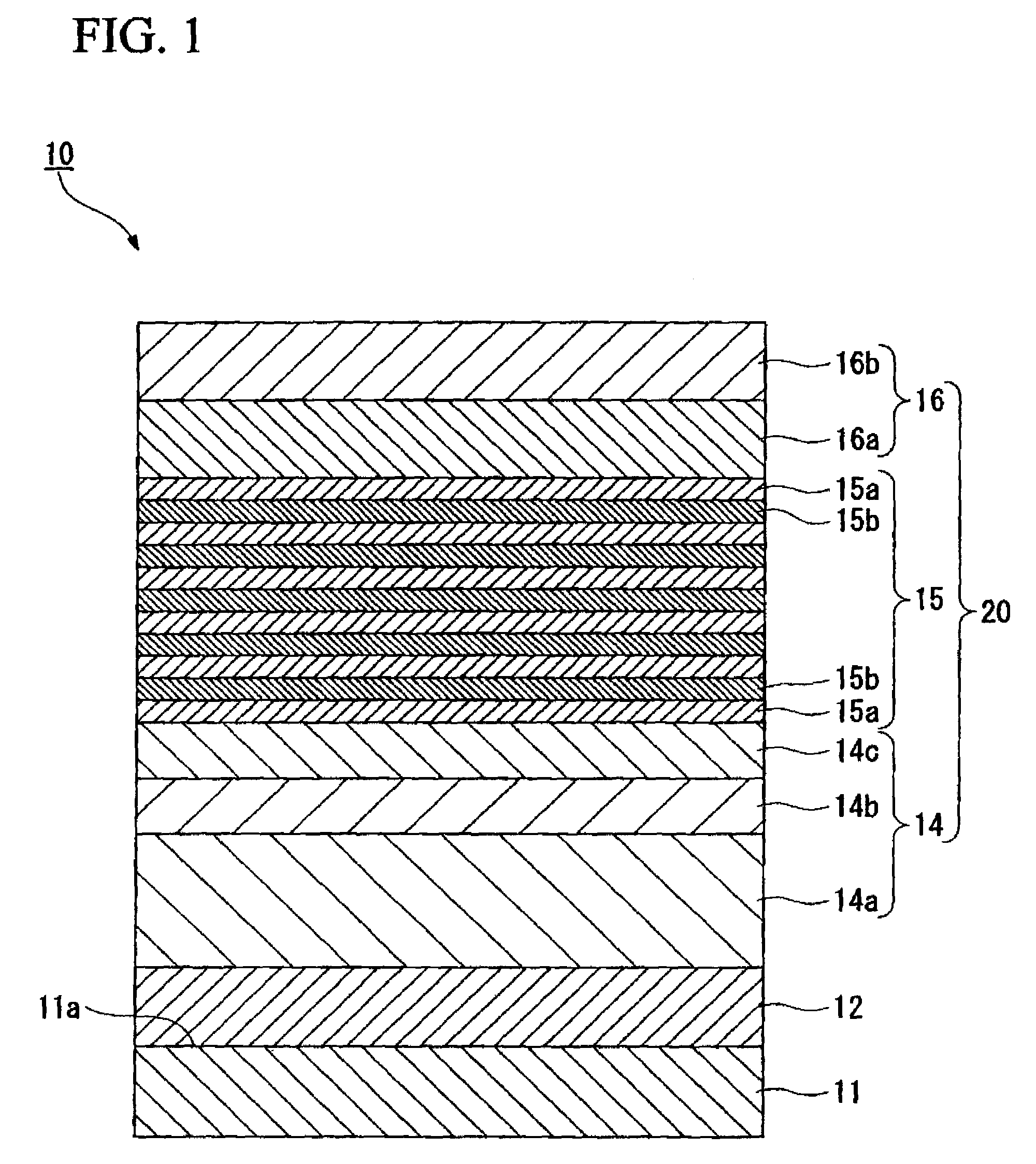
A process for producing a group III nitride compound semiconductor light emitting device, the group III nitride compound semiconductor light emitting device and a lamp, having excellent producability and excellent light emitting characteristics are provided. Such a process for producing a group III nitride semiconductor light emitting device is a process for producing a group III nitride semiconductor light emitting device having a semiconductor layer 20 constituted by laminating an n-type semiconductor layer, a light-emitting layer 15 and a p-type semiconductor layer 16. Each of these consists of a group III nitride semiconductor, including a step of forming at least a part of the semiconductor layer 20 by a sputtering method, in which upon forming the p-type semiconductor layer 14 by a sputtering method, a Ga target containing Ga element, and a dopant target consisting of a mixture of an element having a small crystal composition of elements contained in the p-type semiconductor layer 14 and a dopant element is used as a sputtering target, and power is applied simultaneously to both the Ga target and the dopant target.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
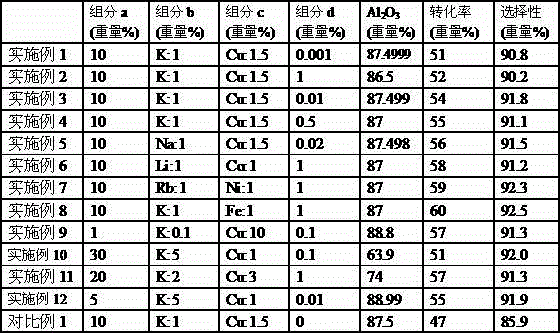
Catalyst for dehydrogenating light alkane and application of catalyst
The invention relates to a catalyst for dehydrogenating light alkane and application of the catalyst in order to mainly solve the problem of relatively-low activity of a dehydrogenating catalyst prepared in the prior art. The problem is better solved through the technical scheme that the catalyst for dehydrogenating light alkane comprises the following components in parts by weight: 1-30 parts of a Cr element or an oxide of the Cr element (a), 0.1-5 parts of Li, Na, K and Rb elements or oxides of the Li, Na, K and Rb elements (b), 0.1-10 parts of Cu, Co, Ni and Fe elements or oxides of the Cu, Co, Ni and Fe elements (c), 0.001-1 part of a Ga element or an oxide of the Ga element (d), and 54-99 parts of Al2O3 (e). The catalyst can be used for industrial production of light olefin prepared by dehydrogenating light alkane.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
R-T-B type sintered permanent magnet
InactiveCN107369512AImprove coercive forceReduce manufacturing costPermanent magnetsInorganic material magnetismRare earthSintered magnets
The invention discloses an R-T-B type sintered permanent magnet. The sintered permanent magnet is characterized in that contents of impurity elements are controlled in the preparation process to enable that C is less than or equal to 800ppm, O is less than or equal to 800ppm and N is less than or equal to 200ppm in the sintered magnet; the microstructure of the magnet comprises an R2T14B main phase, a crystal boundary phase and a triangular region 1, wherein the crystal boundary phase refers to a separation part between two main phase crystal particles; the crystal boundary phase comprises a first crystal boundary phase in the direction of easy orientation axis of the magnet and a second crystal boundary phase perpendicular to the direction of easy orientation axis of the magnet; the crystal structures of the two types of crystal boundaries are both face-centered cubic structures; the triangular region 1 is a rare earth-rich phase with high content of Al+Ga elements, and the rare earth-rich phase is an amorphous phase, wherein the component atomic percentages satisfy the relation as follows: Pr+Nd is greater than or equal to 65% and less than or equal to 88%; Al+Ga is greater than or equal to 10% and less than or equal to 25%; O is less than or equal to 10%; and other elements Fe+Cu+Co is less than or equal to 2%. By virtue of the magnet structure, coercivity can be greatly improved.
Owner:YANTAI DONGXING MAGNETIC MATERIALS INC
Molecular beam epitaxial (MBE) growth method of Bi element regulated and controlled GaAs-based nanowire crystal structure
InactiveCN103320866AGrowth Made EasyAchieve controlled growthPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsNanowireCrystal structure
The invention discloses a molecular beam epitaxial (MBE) growth method of a Bi element regulated and controlled GaAs-based nanowire crystal structure. A Bi element is introduced as an activating agent during the growing process of nanowires in an MBE growth chamber, the ionicity of GaAs is reduced, and the formation of a nanowire zinc blende structure is promoted. The method is characterized in that the Bi evaporator source temperature is regulated during the process of nanowire growth according to the beam equivalent partial pressure of a Ga element so as to control the beam equivalent partial pressure of the Bi element and to ensure that the ratio of the beam equivalent partial pressure of the Bi element to that of the Ga element is x, and the value of x can influence the regulating and controlling ability of the Bi element to the nanowire crystal structure and influence the feature and the phase structure purity of the nanowires. The method has the benefits that the growth of the GaAs-bases nanowires with the zinc blende crystal structure can be easily realized without changing the growth process conditions of MBE, and thus the method is beneficial to the controlled growth of the GaAs-based nanowires with the wurtzite and zinc blende structure and the formation of a homogeneous heterophase heterogeneous structure of the nanowires, and provides an excellent material for preparing nanoscale photoelectronic devices.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polishing method, polishing apparatus and GaN wafer
ActiveUS20120001193A1Keep for a long timeImprove accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLapping machinesNeutral phHigh surface
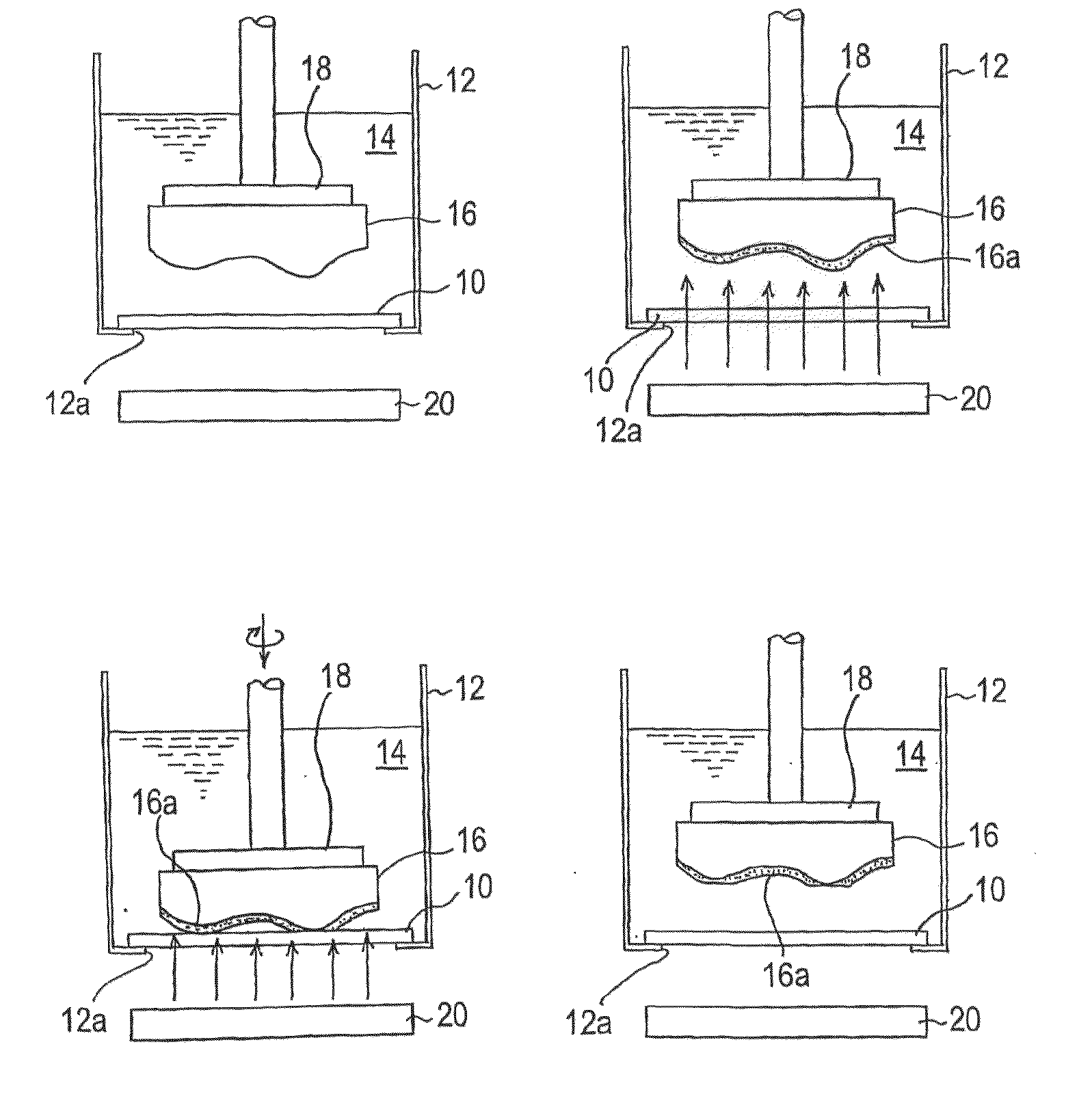
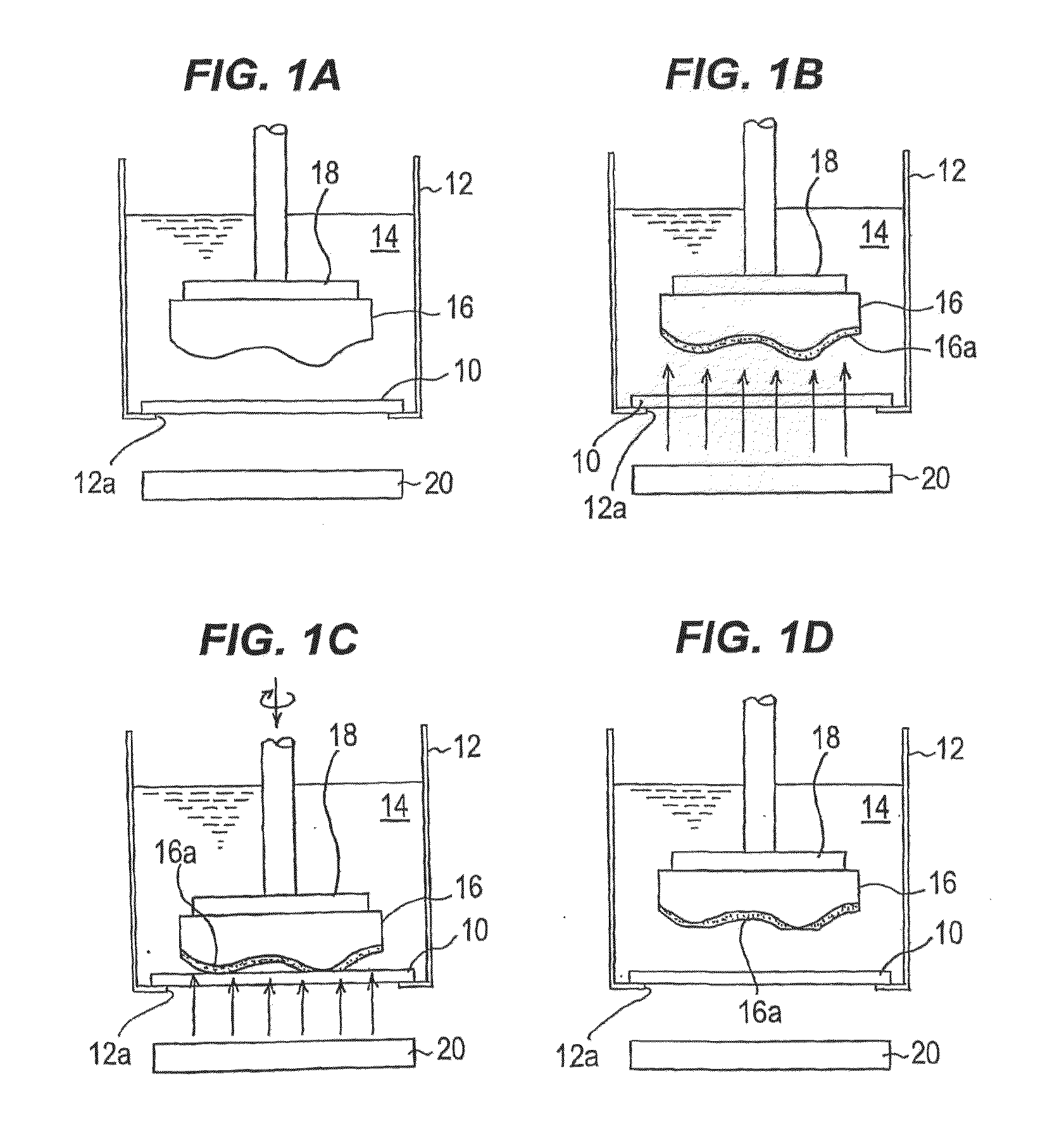
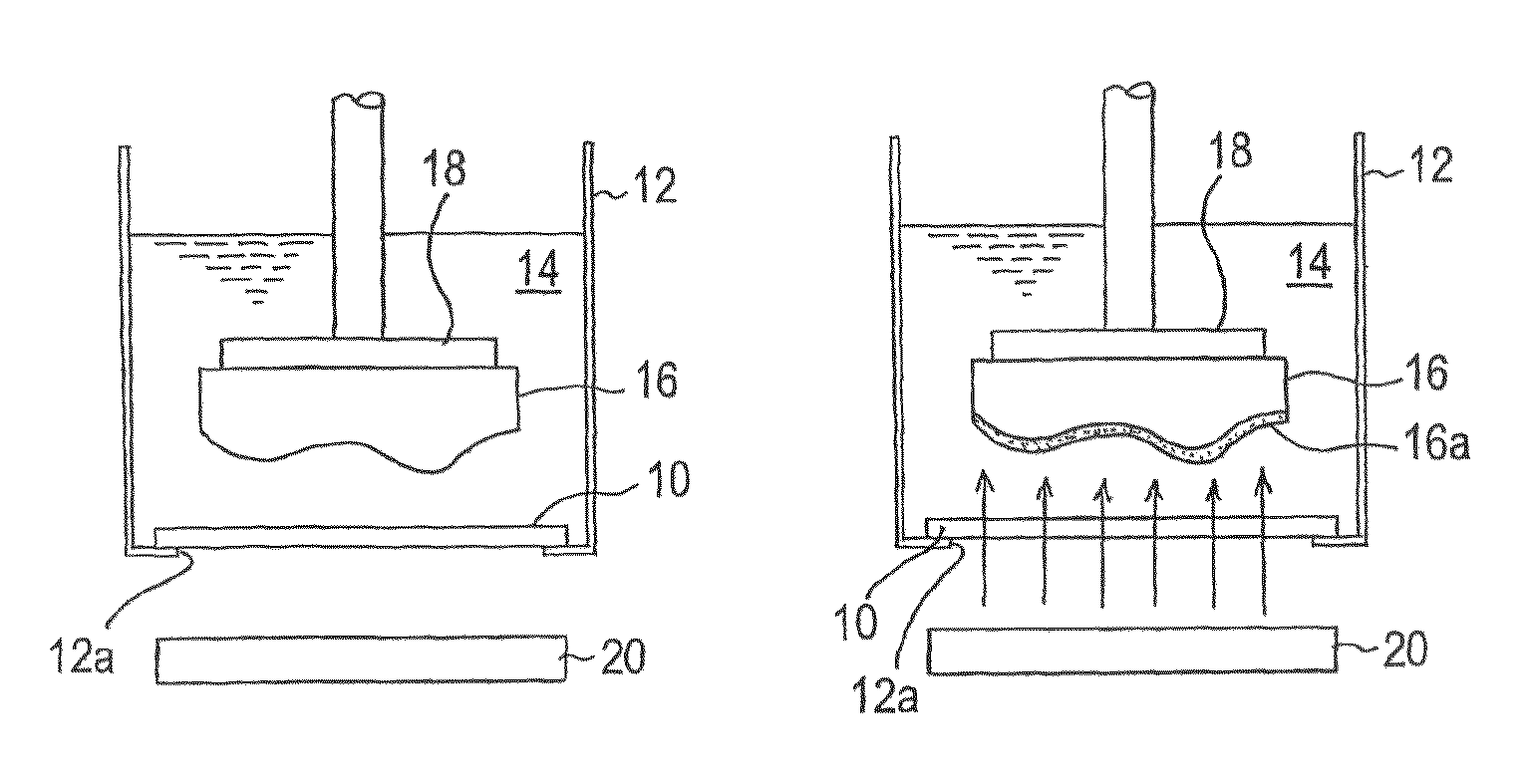
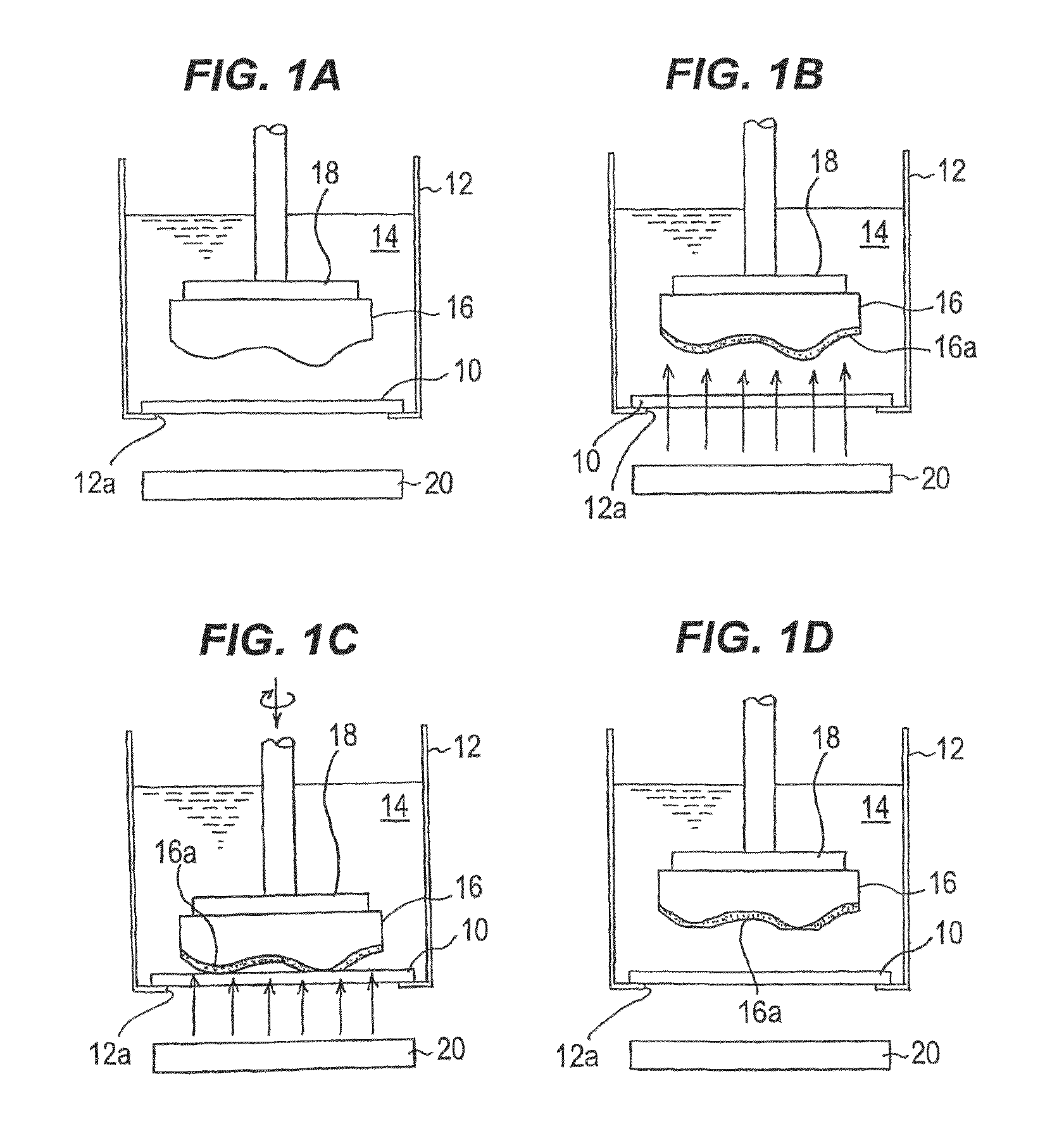
A polishing method can process and flatten, in a practical processing time and with high surface accuracy, a surface of a substrate of a Ga element-containing compound semiconductor. The polishing method includes: bringing a Ga element-containing compound semiconductor substrate (16) into contact with a polishing tool (10) in the presence of a processing solution (14) comprising a neutral pH buffer solution containing Ga ions; irradiating a surface of the substrate with light or applying a bias potential to the substrate, or applying a bias potential to the substrate while irradiating the surface of the substrate with light, thereby forming Ga oxide (16a) on the surface of the substrate; and simultaneously moving the substrate and the polishing tool relative to each other to polish and remove the Ga oxide formed on the surface of the substrate.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV +1
High-strength and high-corrosion-resistance biomedical Mg-Ga alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention aims to provide a high-strength and high-corrosion-resistance biomedical Mg-Ga alloy and a preparation method thereof. The alloy comprises the following chemical components of, by weight, 4.5%-10.0% of Ga and the balance Mg element and other inevitable impurities. By adding a proper amount of the Ga element is added into a pure magnesium matrix, alloy grains can be refined, and the mechanical strength and the corrosion resistance of the alloy are improved. In addition, a Zn element can be added, the Mg-Zn-Ga phase can be separated from the alloy by adjusting a heat treatment system, so that the alloy is further strengthened. The alloy is excellent in biocompatibility, has the biological functions of promoting bones and the like, and is a multifunctional biomedical degradablemagnesium alloy material with excellent comprehensive performance, and has an important application value in the medical fields such as orthopedic implants.
Owner:烟台浩忆生物科技有限公司
Apparatus for manufacturing group iii nitride compound semiconductor light-emitting device, method of manufacturing group iii nitride compound semiconductor light-emitting device, group iii nitride compound semiconductor light-emitting device, and lamp
InactiveUS20080121924A1Easy to optimizeReduce device sizeCellsPolycrystalline material growthPower applicationDopant
A Group III nitride compound semiconductor light-emitting device manufacturing apparatus with a simple structure, which it is capable of easily optimizing the density of a dopant element in the crystals of a Group III nitride compound semiconductor and forming layers with high efficiency using a sputtering method. The manufacturing apparatus includes: a chamber; a Ga target containing a Ga element and a dopant target containing a dopant element, the Ga target and the dopant target being placed within the chamber; and a power application unit that applies power to the Ga target and the dopant target simultaneously or alternately.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Ga-doped ZnO nano ink and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106118216ASynthesis conditions are simpleDoping Concentration ControlInksZno nanoparticlesGa element
The invention provides Ga-doped ZnO nano ink and a preparation method thereof. A Ga element can be codoped in ZnO nano ink through soluble salt, and a mole ratio between the Ga element and a Zn element is (1 to 12) to 100. The preparation method of the Ga-doped ZnO nano ink comprises the following steps: adding soluble Ga salt and soluble Zn salt in a solvent, and uniformly mixing, thus obtaining a precursor solution; mixing and stirring the obtained precursor solution with an alkali solution, thus obtaining a mixed solution; adding acetone in the mixed solution, and then centrifuging, thus obtaining sediment; finally dispersing the sediment in a dispersion solvent, thus obtaining nanoparticle ink. According to the preparation method provided by the invention, the synthetic conditions are simple and easy, a protective atmosphere is not needed, an additional organic ligand is not needed to be added, and regulation and control on Ga doping concentration can be realized; low-temperature solution film forming can be realized by doped ZnO nanoparticles obtained in the invention, and a high-quality charge transfer layer thin film can be obtained without an aftertreatment means.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
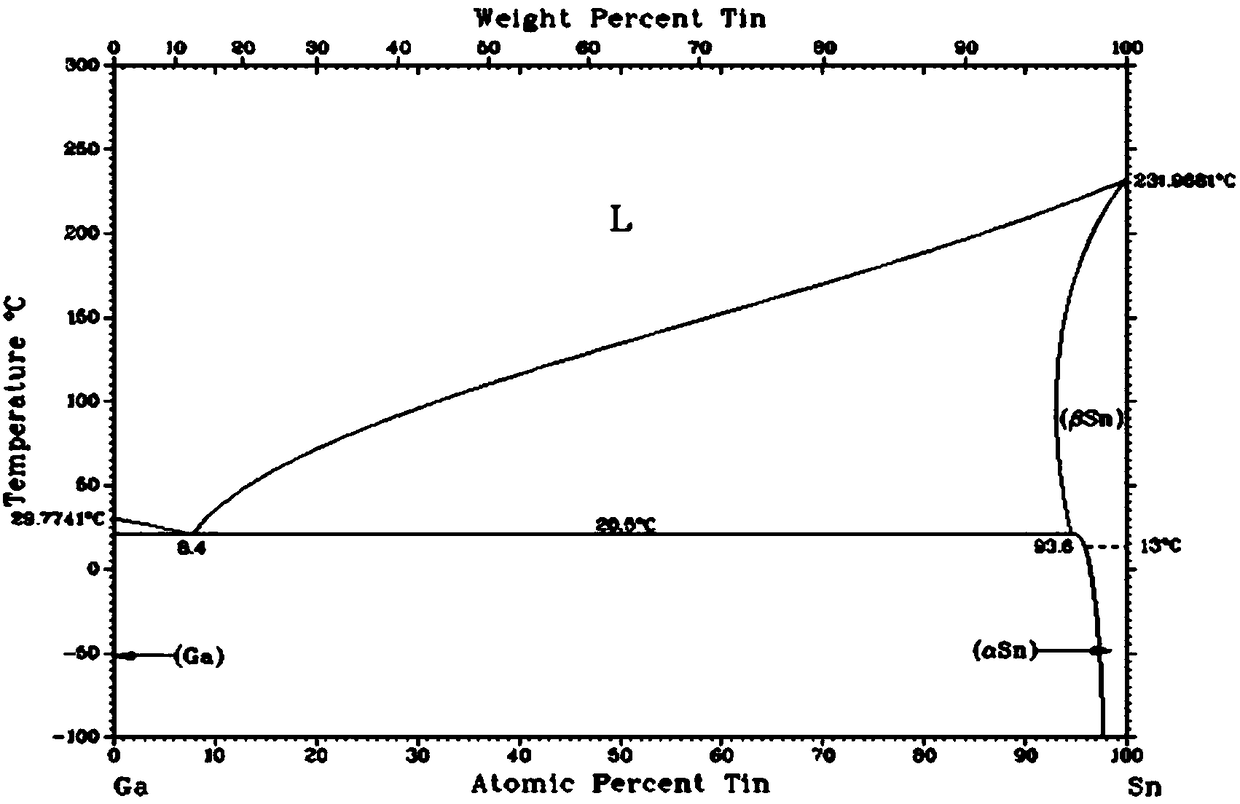
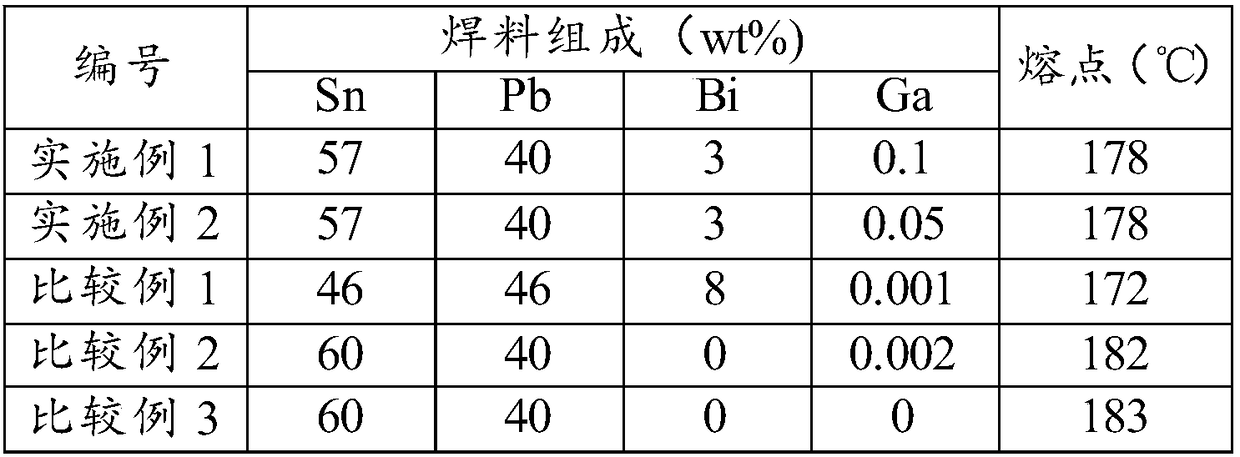
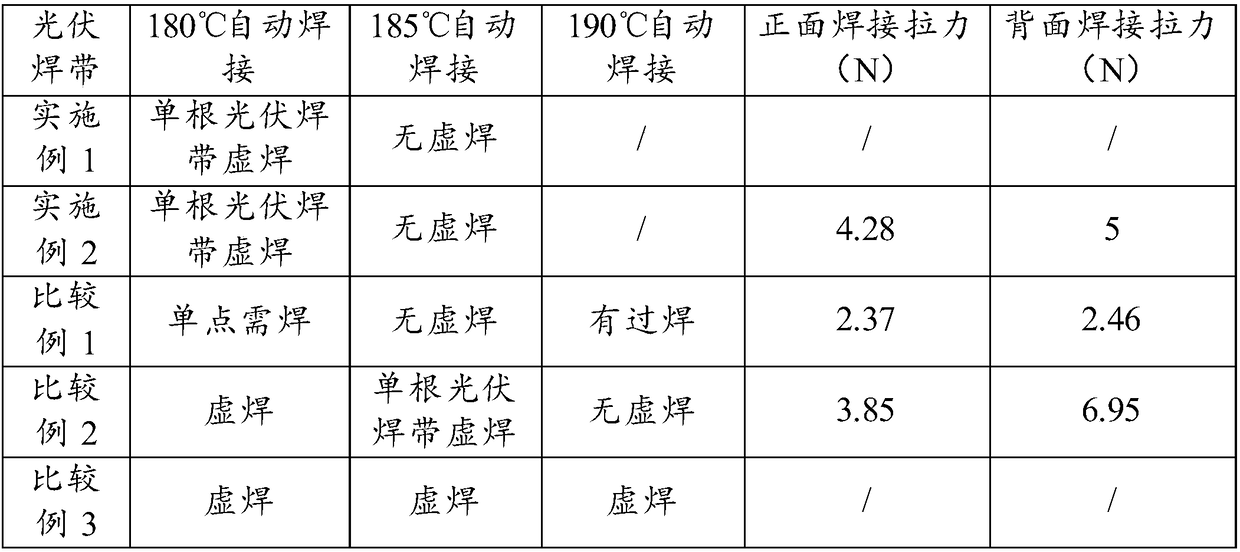
Photovoltaic solder strip, preparation method therefor, and photovoltaic assembly
ActiveCN108365042AIdeal repair rateImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationGa elementSoldering
The invention provides a photovoltaic solder strip, and the solder strip comprises a conductive base strip and a tin soldering layer wrapping the conductive base strip. The tin soldering layer contains 55-65wt% of Sn, 35-45wt% of Pb, 1-5wt% of Bi, and 0.0005-0.5wt% of Ga. According to the invention, the soldering flux is formed by the four materials of Sn-Pb-Bi-Ga at a specific proportion. In particular, the melting point of the soldering flux is 145-170 DEG C after the Bi and Ga elements are added. The method can maintain the better soldering tension while achieving the low-temperature welding, and guarantees the ideal repair rate of the assembly. In addition, the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the photovoltaic assembly of the photovoltaic solder strip provided by the invention iseffectively improved.
Owner:JINKO SOLAR CO LTD +1
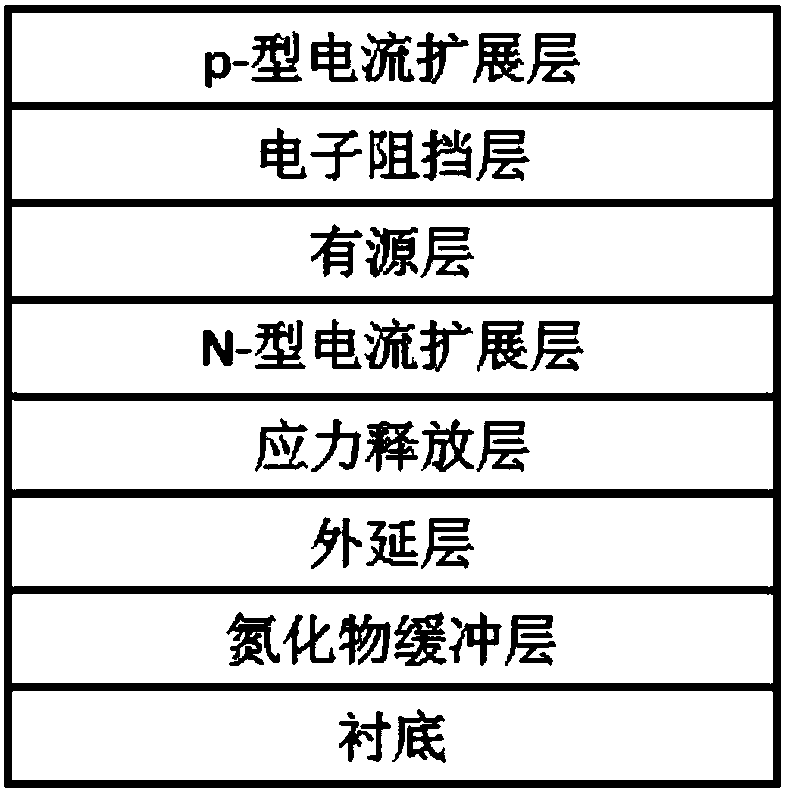
AlGaN-based ultraviolet LED device and preparation method and application thereof
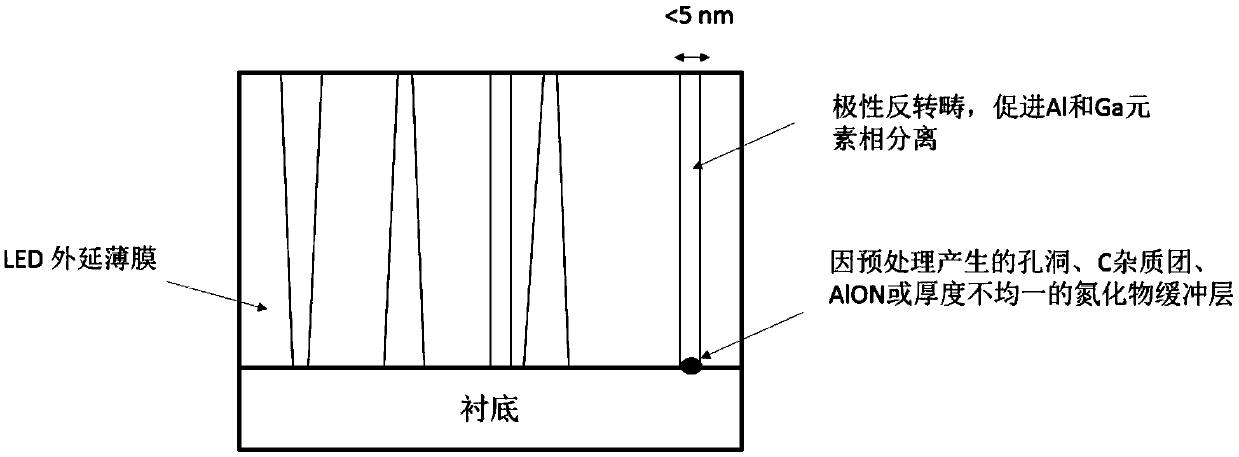
ActiveCN110459652AReduce non-radiative recombination effectsImprove luminous efficiencySemiconductor devicesUltravioletGa element
The invention discloses an AlGaN-based ultraviolet LED device and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that a nitride buffer layer grows on a substrate; the nitride buffer layer is pretreated, wherein the pretreatment includes plasma treatment, high temperature thermal annealing treatment, metal organic source precursor pretreatment and the like;an epitaxial layer, a stress relief layer, an n-type current spreading layer, a multilayer quantum well active layer, an electron blocking layer and a p-type current spreading layer are sequentiallyformed on the nitride buffer layer. According to the invention, the AlGaN-based ultraviolet LED device can realize Al and Ga phase separation of an active region and a quantum threshold effect similarto In enrichment in InGaN, leading to Ga element enrichment; and the device is favorable for radiation recombination of carriers, which improves the radiation composite efficiency and improves the luminous efficiency of the ultraviolet LED device.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
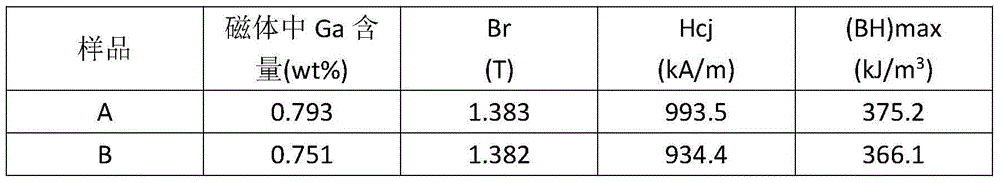
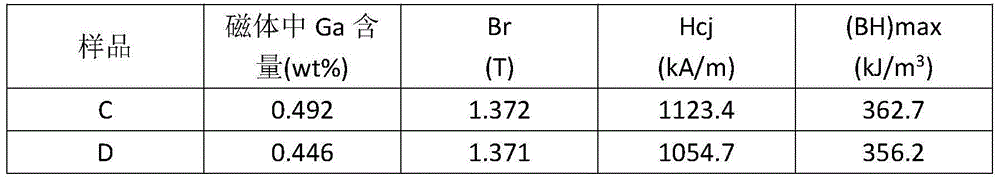
Method for alloying Ga element through neodymium-iron-boron permanent magnet material
InactiveCN104593660AHigh melting pointEliminate the step of drilling and sealing GaMagnetic materialsRare earthGa element
The invention relates to a method for alloying a Ga element through a neodymium-iron-boron permanent magnet material, and belongs to the field of rear earth permanent magnet materials. The method can be used for smelting an alloy by utilizing a Fe-Ga alloy as a raw material with other neodymium-iron-boron raw materials together. The method comprises the following steps: smelting the Fe-Ga alloy and other neodymium-iron-boron raw materials together, then carrying out powder preparation, oriented pressing, sintering and tempering heat treatment to obtain a product. Because the melting point of metal Ga is about 30 DEG C, the metal Ga easily forms a liquid state at normal temperature, and if the metal Ga is taken as the raw material, the metal Ga generally needs to be enclosed into a Fe or Nd block through punching when a neodymium-iron-boron alloy ingredient is smelted. According to the method, the melting point of the Fe-Ga alloy is far higher than normal temperature, the Ga element is added in the form of the Fe-Ga alloy, so that the step of enclosing the metal Ga into the Fe-or Nd block through the punching can be completely omitted, the volatilization of the Ga element in a smelting process can be greatly reduced, the utilization rate of Ga is enhanced, and further higher magnet property is obtained. The method disclosed by the invention can effectively utilize the waste product obtained in the production of the magnetostrictive material Fe-Ga alloy and is easy to operate and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
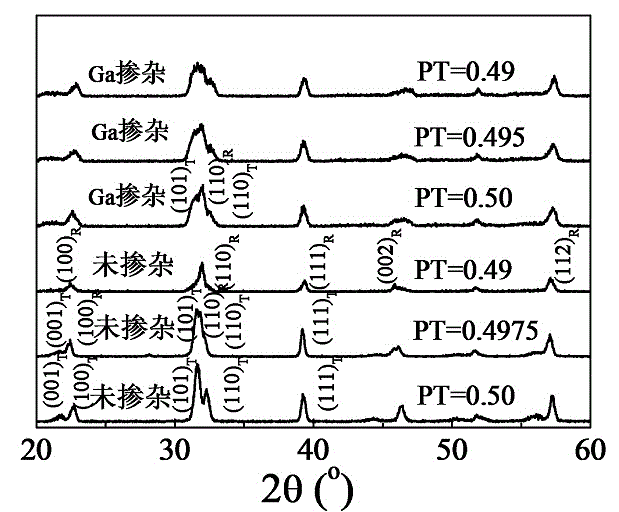
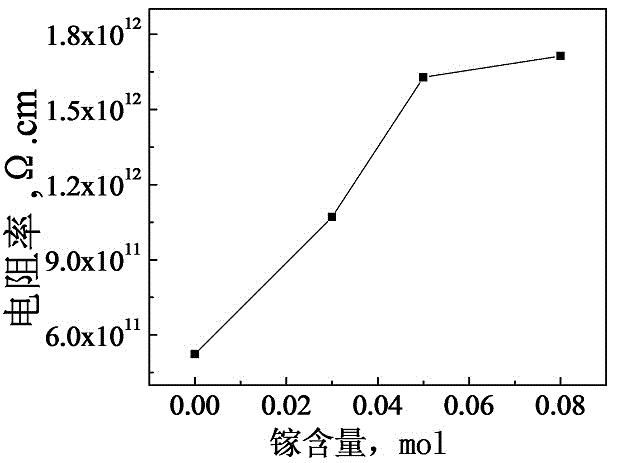
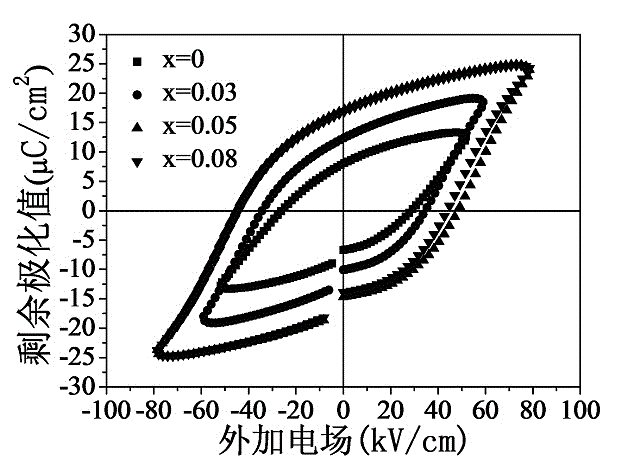
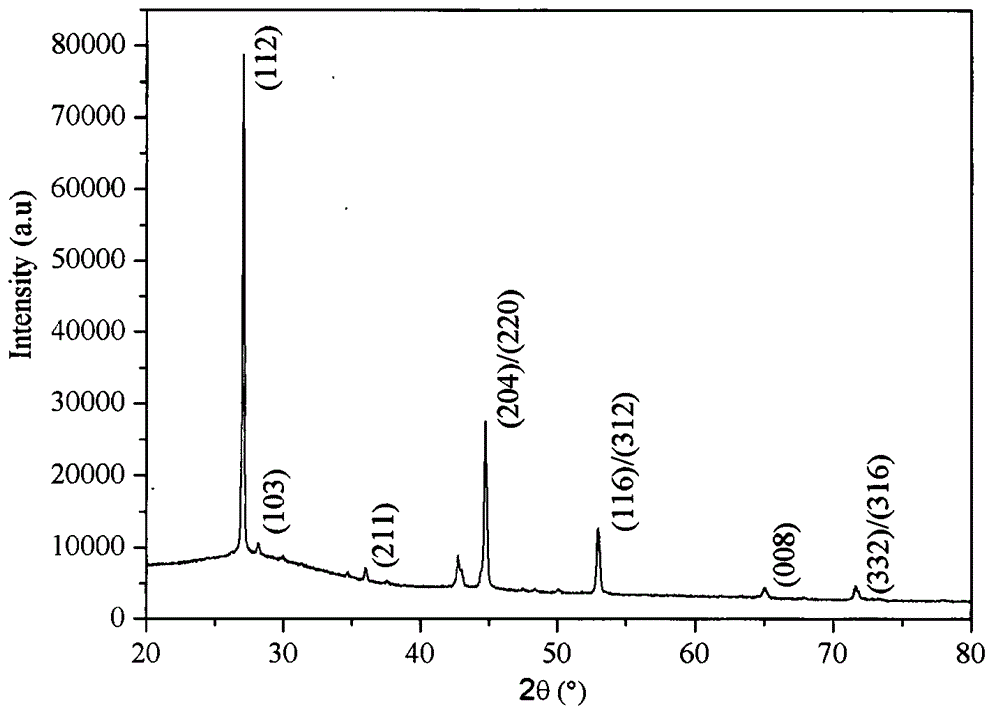
Ga-modified (Bi0.8Gd0.2) FeO3-PbTiO3 piezoelectric ceramic and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103951407AImprove insulation performanceImprove piezoelectric performanceGa elementPiezoelectric constant
The invention discloses a Ga-modified (Bi0.8Gd0.2) FeO3-PbTiO3 (BGF-PT) piezoelectric ceramic. The piezoelectric ceramic has a chemical formula represented by (Bi0.8Gd0.2) (Fe1-xGax) O3-PbTiO3, wherein x is less than 0.1, namely Ga element is introduced into the BGF-PT system to form a BGGF-PT piezoelectric ceramic solid solution system. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the BGGF-PT piezoelectric ceramic. The preparation method comprises the steps of burdening the raw materials according to the chemical formula, carrying out ball milling, mixing, carrying out a calcining synthesis at a temperature range of 750 DEG C, carrying out ball milling and calcining synthesis repeatedly for many times to obtain fine and uniform BGF-PT powder, tabletting and sintering to obtain the ceramic product. According to the piezoelectric ceramic disclosed by the invention, the BGGF-PT piezoelectric ceramic, with the advantages of low lead content, large morphotropic phase boundary range, good insulativity, superior piezoelectric constant and high performance, is prepared by modifying the BGF-PT system piezoelectric ceramic material by adopting the Ga element.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for manufacturing Cu (In, Ga) Se2 thin film of thin-film solar cell absorption layer
ActiveCN102751387AIncrease profitGood adhesionFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingAlloyGa element
The invention discloses a novel method for manufacturing Cu (In, Ga) Se2 thin film of a thin-film solar cell absorption layer. The method includes steps of employing a method of ion beam sputtering deposition, taking high-purity Cu, In, Se and an alloy of CuxGa1-x as sputtering target materials, successively sputtering elements or alloy target materials to manufacture a precursor thin-film lamination or periodic lamination thin film by accurately controlling ion beam sputtering parameters, and manufacturing the Cu (In, Ga) Se2 thin film by means of high-temperature in-situ heat treatment in the same vacuum environment. The method for manufacturing Cu (In, Ga) Se2 thin film of the thin-film solar cell absorption layer is optimized in doping process, simple in operation and capable of improving a utilization ratio of raw materials, realizing doping of the Ga element on the basis of the Cu (In, Ga) Se2 thin films and effectively controlling radial distribution of the Ga element. The structure and performance of the Cu (In, Ga) Se2 thin film manufactured by the method can meet performance requirements of high-efficient photovoltaic devices, and a new way is explored for development and utilization of the solar cell.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Metal material for proton exchange membrane fuel cell cathode catalyst and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a metal material for a proton exchange membrane fuel cell cathode catalyst. An alloy formed by platinum and gallium has a one-dimensional nanowire structure having the length of40-80nm and the diameter of 1-2nm, is provide. The invention also provides a preparation method of the metal material. Firstly Pt nanowires are obtained by reduction of the divalent metal platinum under the organic liquid condition, and a trivalent metal gallium compound and a reducing agent are added into the Pt nanowires and the alloy of Pt and Ga with the one-dimensional nanowire structure isobtained through reduction reaction. The structure of the Pt-Ga alloy material is the one-dimensional nanowire structure, the mass activity of the catalyst supported by carbon is more than nine timesof that of the Platinum-carbon nano-catalyst, the area activity of the catalyst is more than seven times than that of the Platinum-carbon nano-catalyst and the mass activity performance loss of the catalyst is only 15.7% when it is recycled 30000 times in oxygen atmosphere. Besides, the preparation method can realize high content doping of Ga element to Pt nanowires and the content is controllable, the use of the Pt element can be effectively reduced according to the requirements and the battery cost can be reduced; meanwhile, the reaction condition is mild and operation is simple.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Low-temperature matrix impregnation material of rock cutting tool and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a low-temperature matrix impregnation material of a rock cutting tool and a preparation method thereof. The matrix impregnation material is composed of the following componentsincluding, by mass, 65%-97% of copper alloy, 0.9%-2.8% of Sn powder and 0.3%-1% of Ga. The Sn and Ga elements in the matrix impregnation material provided by the invention have the three main effectsthat firstly, the sintering temperature of the rock cutting tool is lowered, diamond is better protected, and sharp declining of the comprehensive performance of the diamond is slowed down; secondly,a multi-element alloy formed by adding the two metal elements in a matrix enables the holding capacity for the diamond to be enhanced; and thirdly, the bending strength, the hardness and abrasion resistance of the matrix material are further improved.
Owner:TANGSHAN JINSHI SUPER ABRASIVE
Low-light-induced-degradation solar cell front side silver paste and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107346671AReduce light-induced attenuationImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialPhotovoltaic energy generationSilver pasteBismuth compound
The invention discloses low-light-induced-degradation solar cell front side silver paste and a preparation method thereof. According to the technical scheme, the low-light-degradation solar cell front side silver paste is composed of, by mass percentage, 80-93% of silver powder, 5-15% of organic carrier and 0.5-6% of glass powder, wherein the purity of the silver powder is 99.9-99.999%, the average particle size is 0.5-10 microns, the preferred average particle size is 0.5-3 microns, and the glass powder is TPBC glass powder. The preparation method of the low-light-degradation solar cell front side silver paste includes the following steps: (1) preparing organic carrier; (2) preparing glass powder; (3) mixing silver paste; and (4) dispersing silver paste. The advantage is that the invention relates to a novel tellurate glass powder system, the glass powder is a Te-Pb-Bi-Ga glass system, and the TPBC glass system uses a tellurium-plumbum-bismuth compound combination. A certain amount of Ga element is intentionally added to the glass component in order to reduce the light induced degradation of silicon wafers. Experiments show that the rate of light induced degradation is reduced while the photoelectric conversion efficiency of silicon-based cells is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI TRANSCOM ELECTRONICS TECH
Preparation method for sintered neodymium iron boron permanent magnet free of heavy rare earths
InactiveCN108417375AImprove performanceShort sintering timeInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementGa element
The invention discloses a preparation method for a sintered neodymium iron boron permanent magnet free of heavy rare earths. By virtue of the preparation method, the content of a B element is reduced,the volume fraction of a neodymium iron boron main phase is reduced, the volume fraction of a grain boundary phase is improved, and the content of a Ga element is increased. After the normal temperature is quickly heated to 300-350 DEG C, heat preservation is not performed, and instead, slow heating is performed to 1,050-1,070 DEG C, then short-term densifying is carried out, and then the temperature is cooled to 1,000-1,040 DEG C, and low-temperature sintering is carried out. By adopting the sintering process, the stage type heating and heat preservation and degassing processes in the conventional sintering process are avoided, the permanent magnet sintering time is shortened, the production efficiency is improved, and electric energy is saved; and meanwhile, by virtue of the sintering process, continuous degassing is facilitated, formation of tiny pores in the permanent magnet can be prevented, the magnet density is increased, and the sintered neodymium iron boron permanent magnet free of any heavy rare earths can be produced stably without adding the rare earth elements of Dy, Tb, Ho and the like and without lowering the permanent magnet residual magnetism.
Owner:NINGBO SONGKE MAGNETIC MATERIAL
Method for growing nitride light-emitting diode (LED) epitaxial wafer with reversed V-shaped coarsening surface
InactiveCN102969425AIncrease brightnessShort extended free pathSemiconductor devicesGa elementGallium nitride
A method for growing a nitride light-emitting diode (LED) epitaxial wafer with a reversed V-shaped coarsening surface belongs to the photoelectric technology field of semiconductors. Firstly a high dislocation density gallium nitride (GaN) epitaxial film is achieved on a sapphire substrate, and the method for growing a nitride LED with the reversed V-shaped coarsening surface is achieved through density. Dislocation can be released on a multi-quantum wells (MQWs) surface to form a V-shaped pit, low-temperature high-pressure growth is used for growing pGaN, an expansion free-path of the Ga element at low temperature and high pressure is short, three-dimensional growth serves as a main mode, and the V-shaped pit is not easy to fill in a growing process. Therefore, the V-shaped pit is equivalently released in the growing process, further a pGaN coarsening surface with the reversed V-shaped surface is formed, accordingly the nitride LED with the reversed V-shaped coarsening surface is obtained, and light intensity is 100% promoted.
Owner:YANGZHOU ZHONGKE SEMICON LIGHTING
Polishing method, polishing apparatus and GaN wafer
ActiveUS9233449B2Keep for a long timeImprove accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLapping machinesNeutral phHigh surface
A polishing method can process and flatten, in a practical processing time and with high surface accuracy, a surface of a substrate of a Ga element-containing compound semiconductor. The polishing method includes: bringing a Ga element-containing compound semiconductor substrate (16) into contact with a polishing tool (10) in the presence of a processing solution (14) comprising a neutral pH buffer solution containing Ga ions; irradiating a surface of the substrate with light or applying a bias potential to the substrate, or applying a bias potential to the substrate while irradiating the surface of the substrate with light, thereby forming Ga oxide (16a) on the surface of the substrate; and simultaneously moving the substrate and the polishing tool relative to each other to polish and remove the Ga oxide formed on the surface of the substrate.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV +1
Low-silver lead-free solder alloy
InactiveCN102107339AMeet the assembly requirementsLow costWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaProduction lineChemical composition
The invention discloses a low-silver lead-free solder alloy. The alloy comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.01 to 1.0 percent of Ag, 0.1 to 3.0 percent of Cu, 0.001 to 0.1 percent of Ni, 0.001 to 0.1 percent of P and the balance of Sn, wherein the Ni content is further optimized to be 0.005 to 0.08 weight percent, and the P content is further optimized to be 0.005 to 0.08 percent; and a Ga element can be further added. Compared with the ordinary lead-free Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu alloy, the solder alloy has the characteristics that: the cost of raw materials is reduced due to low used silver content; and since the elements such as Ni, P and the like are added and the content of the elements are optimized, the dissolution of a copper element of a bonding pad of a component in the wave soldering process in a tin furnace can be effectively reduced, the frequency of replacing solder in the tin furnace is lower, the service life of the solder is prolonged, and the using cost is saved for a production line.
Owner:YIK SHING TAT INDUSTRIALCO LTD +1
Process for producing group III nitride compound semiconductor light emitting device, group III nitride compound semiconductor light emitting device and lamp
ActiveUS7585690B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGa elementLight emitting device
A process for producing a group III nitride compound semiconductor light emitting device, the group III nitride compound semiconductor light emitting device and a lamp, having excellent producability and excellent light emitting characteristics are provided. Such a process for producing a group III nitride semiconductor light emitting device is a process for producing a group III nitride semiconductor light emitting device having a semiconductor layer 20 constituted by laminating an n-type semiconductor layer, a light-emitting layer 15 and a p-type semiconductor layer 16. Each of these consists of a group III nitride semiconductor, including a step of forming at least a part of the semiconductor layer 20 by a sputtering method, in which upon forming the p-type semiconductor layer 14 by a sputtering method, a Ga target containing Ga element, and a dopant target consisting of a mixture of an element having a small crystal composition of elements contained in the p-type semiconductor layer 14 and a dopant element is used as a sputtering target, and power is applied simultaneously to both the Ga target and the dopant target.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Optical device
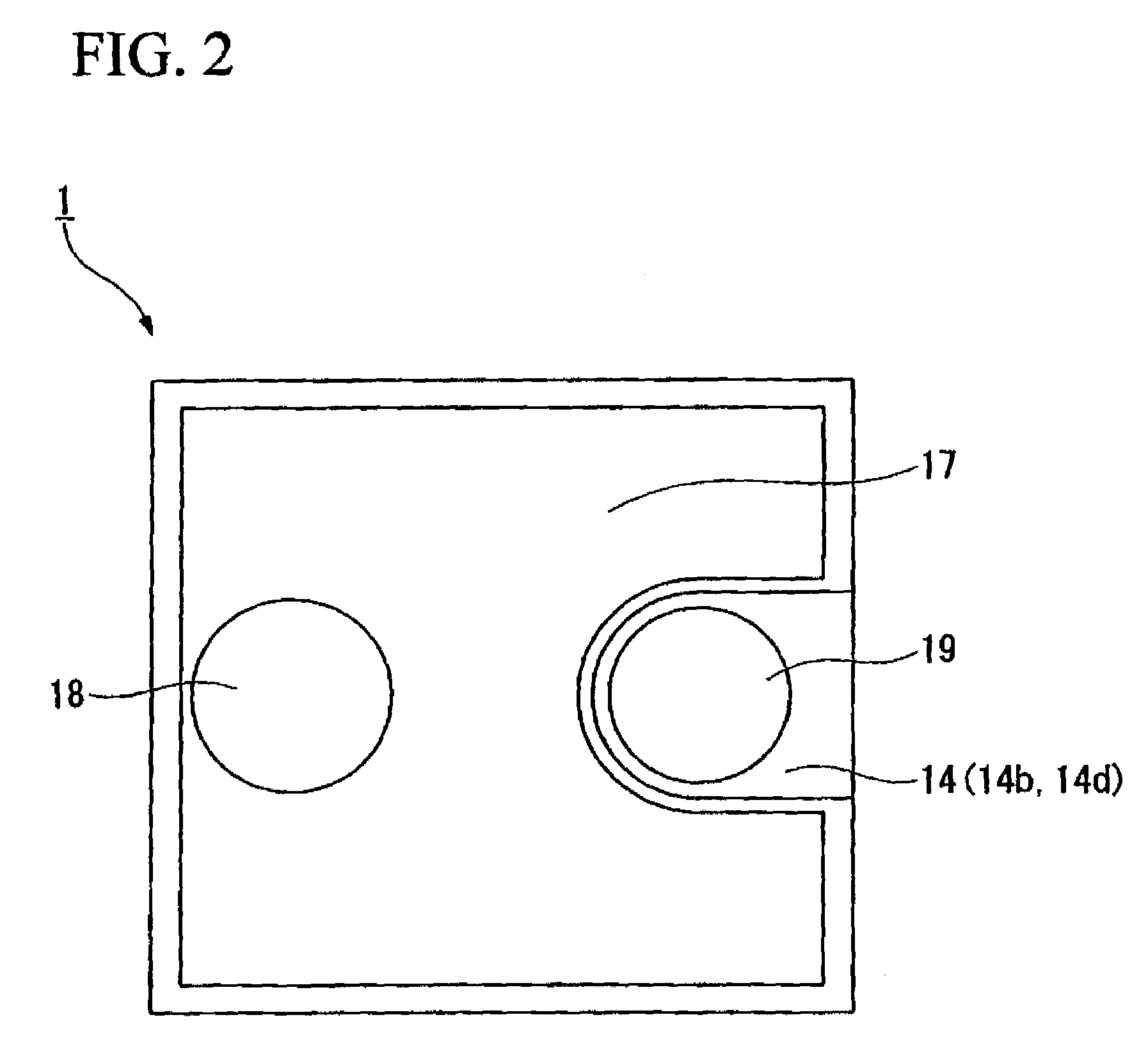
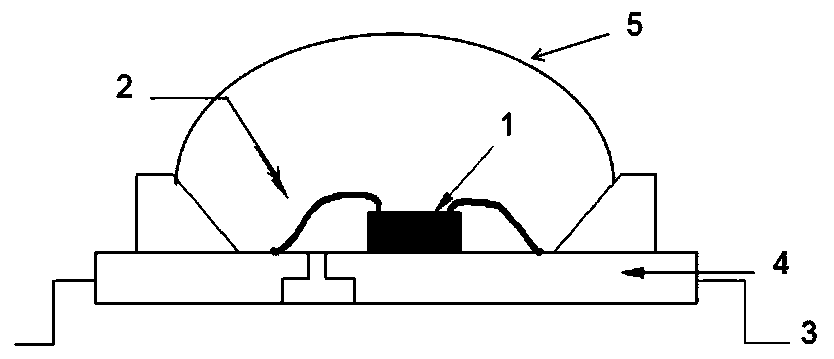
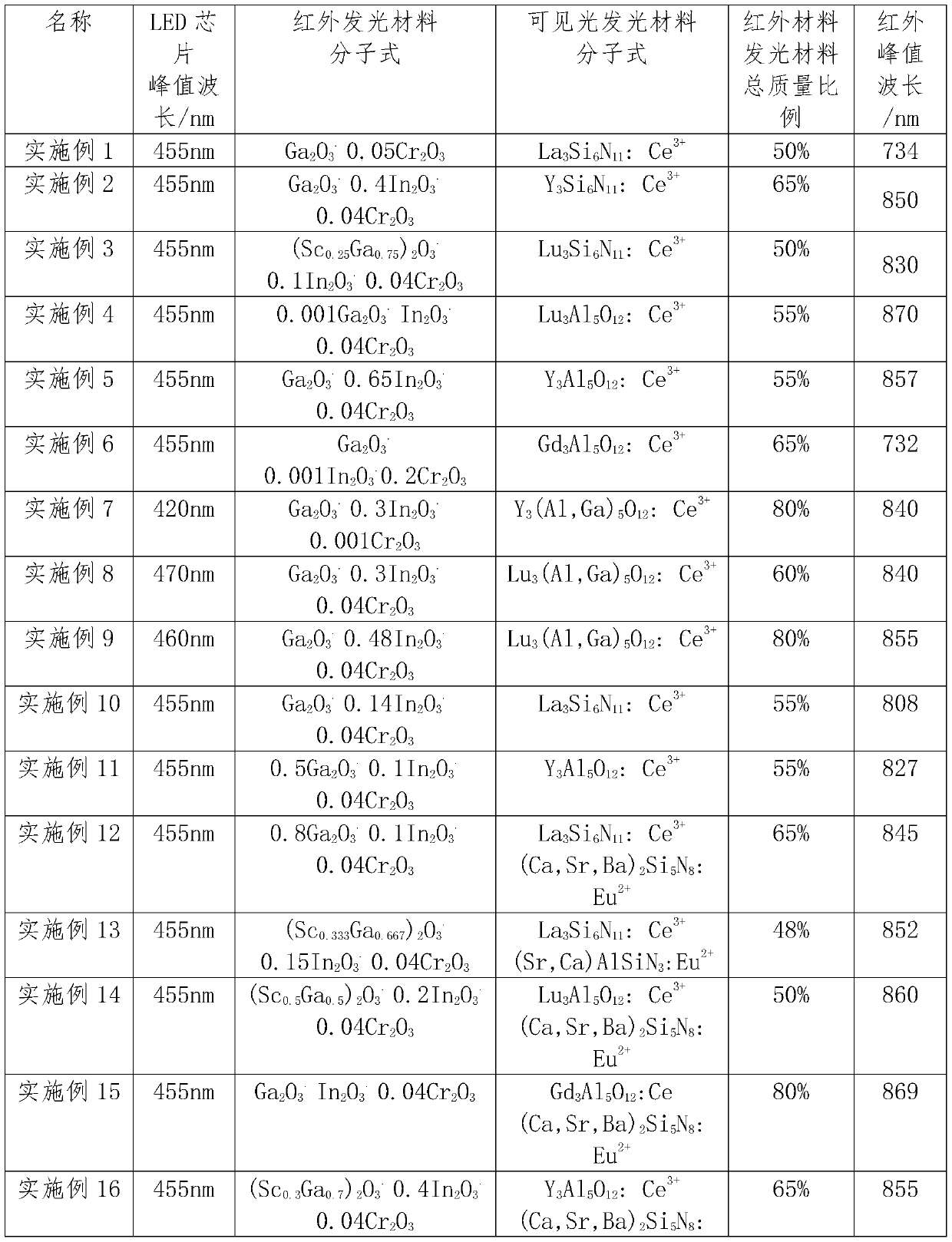
ActiveCN110444651ASimple packaging processReduce packaging costsSemiconductor devicesCrystal structureGa element
The invention relates to an optical device. The optical device comprises an LED chip, a Ce<3+> simulated visible light-emitting material and a near-infrared light-emitting material xA<2>O<3>.yIn<2>O<3>.bR<2>O<3> compound, wherein an A element in the near-infrared light-emitting material is Sc and / or Ga element, an R element is one or two of elements of Cr, Yb, Nd or Er, Cr is doubtlessly contained, x is more than or equal to 0.001 but less than or equal to 1, y is more than or equal to 0 but less than or equal to 1, b is more than or equal to 0.001 but less than or equal to 0.2, and b / (x+y) ismore than or equal to 0.001 but less than or equal to 0.2. The near-infrared light-emitting material has a crystal structure same as Beta-Ga2O3. In the optical device, an implementation mode of an LED chip combined with the near-infrared light-emitting material and the visible light-emitting material is utilized, near infrared light emitting and visible light emitting are simultaneously achievedby the same LED chip, the package process is greatly simplified, the package cost is reduced, the optical device has the characteristics of high light-emitting efficiency, excellent reliability, highinterference resistance and the like, and white-light compensation can be achieved. The optical device provided by the embodiment of the invention has great application prospect in the field of security and protection.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
A preparation method of room temperature high magnetic energy product corrosion resistant sintered NdFeB
ActiveCN103456451BHigh energy productLow melting pointInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementHigh energy
The invention discloses a preparation method of room temperature high magnetic energy product corrosion resistant sintered NdFeB. On the basis of preparing Nd(Pr)-Fe-B alloy powders without heavy rare earth elements such as Dy, using the powder coating process based on magnetron sputtering, Co, Al and Cu, Ga, Nb and other alloying elements At the same time, it is sputtered onto the surface of the airflow mill powder, and the Co and Al elements that increase the electrochemical corrosion potential, the Cu and Nb elements that inhibit the grain growth, and the Ga elements that reduce the melting point of the grain boundary and improve the grain boundary are introduced into the grain boundary. Lowering the temperature of the subsequent heat treatment process inhibits the excessive growth of grains and at the same time makes the alloying elements diffuse moderately near the grain boundaries during the sintering process. The invention obtains high magnetic energy product and excellent corrosion resistance through the control of grain boundary phase ratio and potential, and realizes the preparation of high magnetic energy product corrosion-resistant sintered NdFeB at room temperature.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com