Patents
Literature
375 results about "Elastic substrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
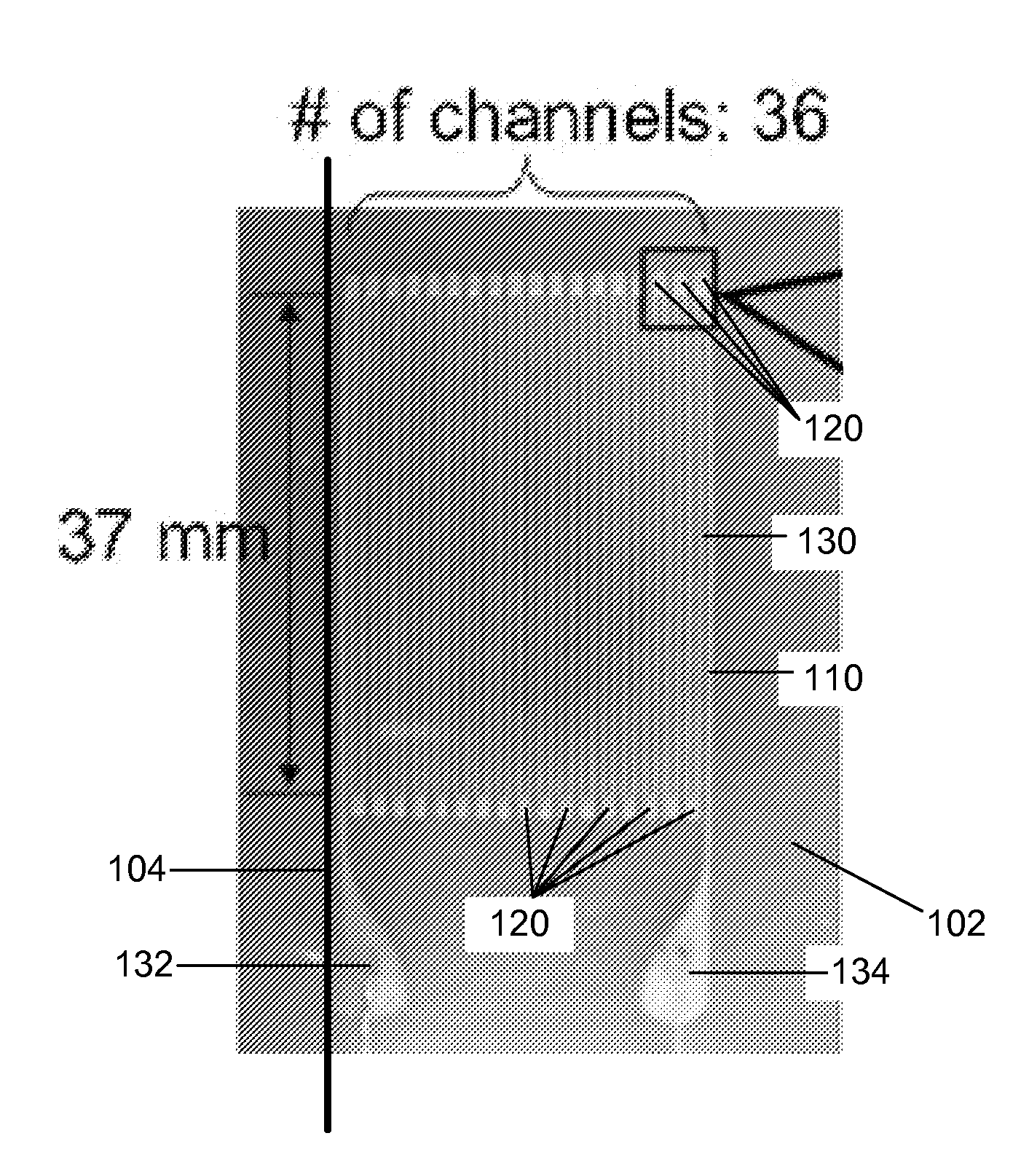
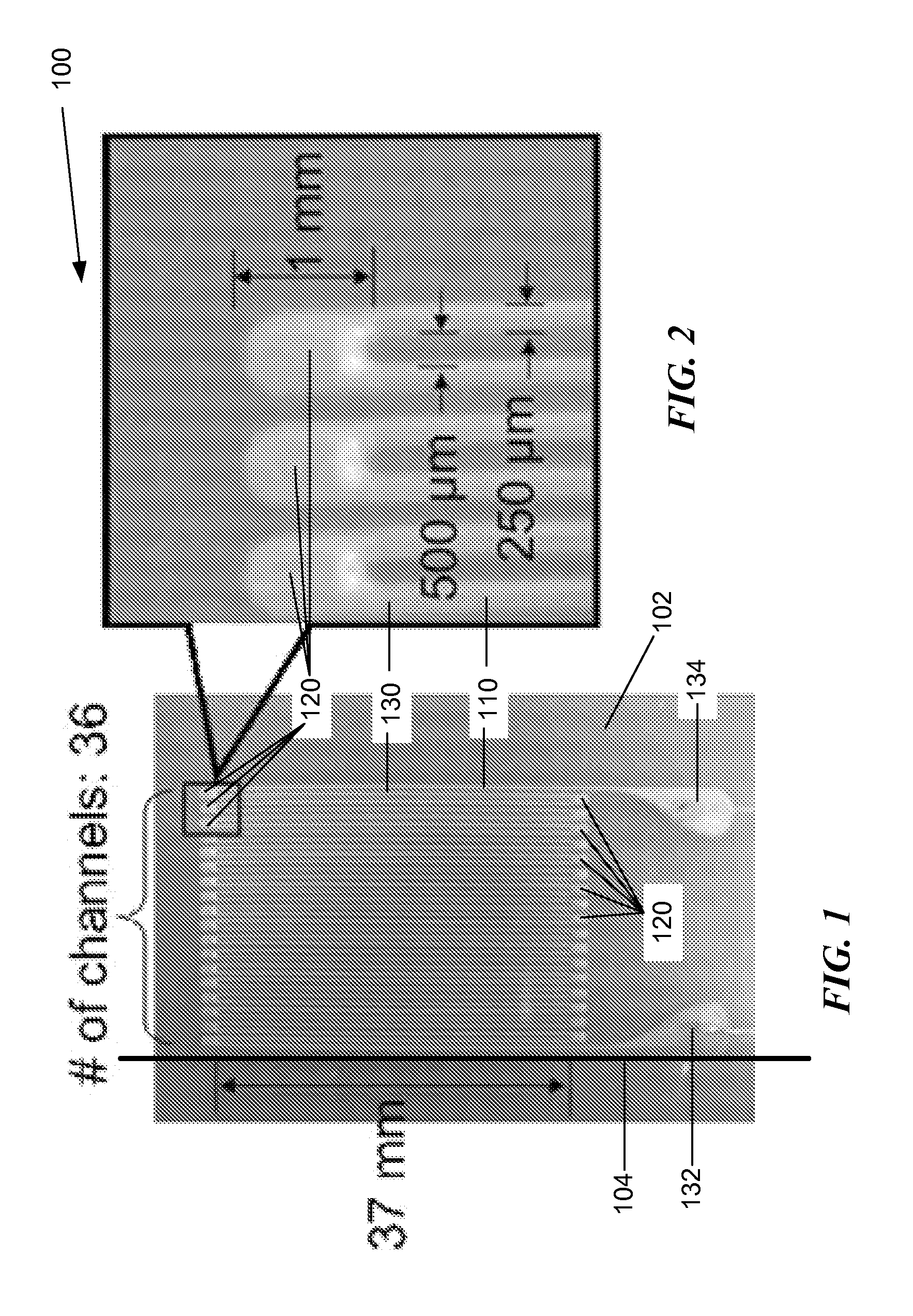
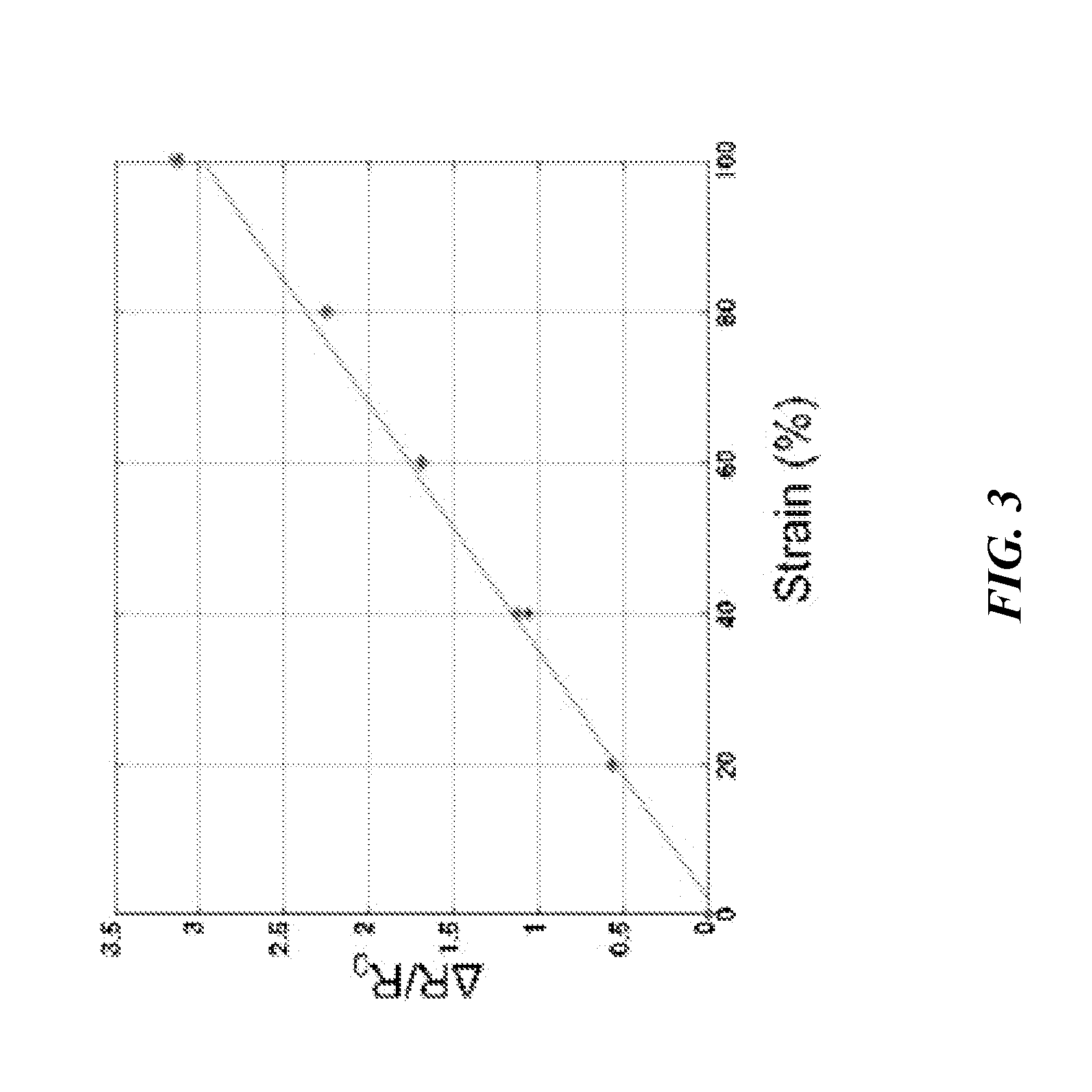
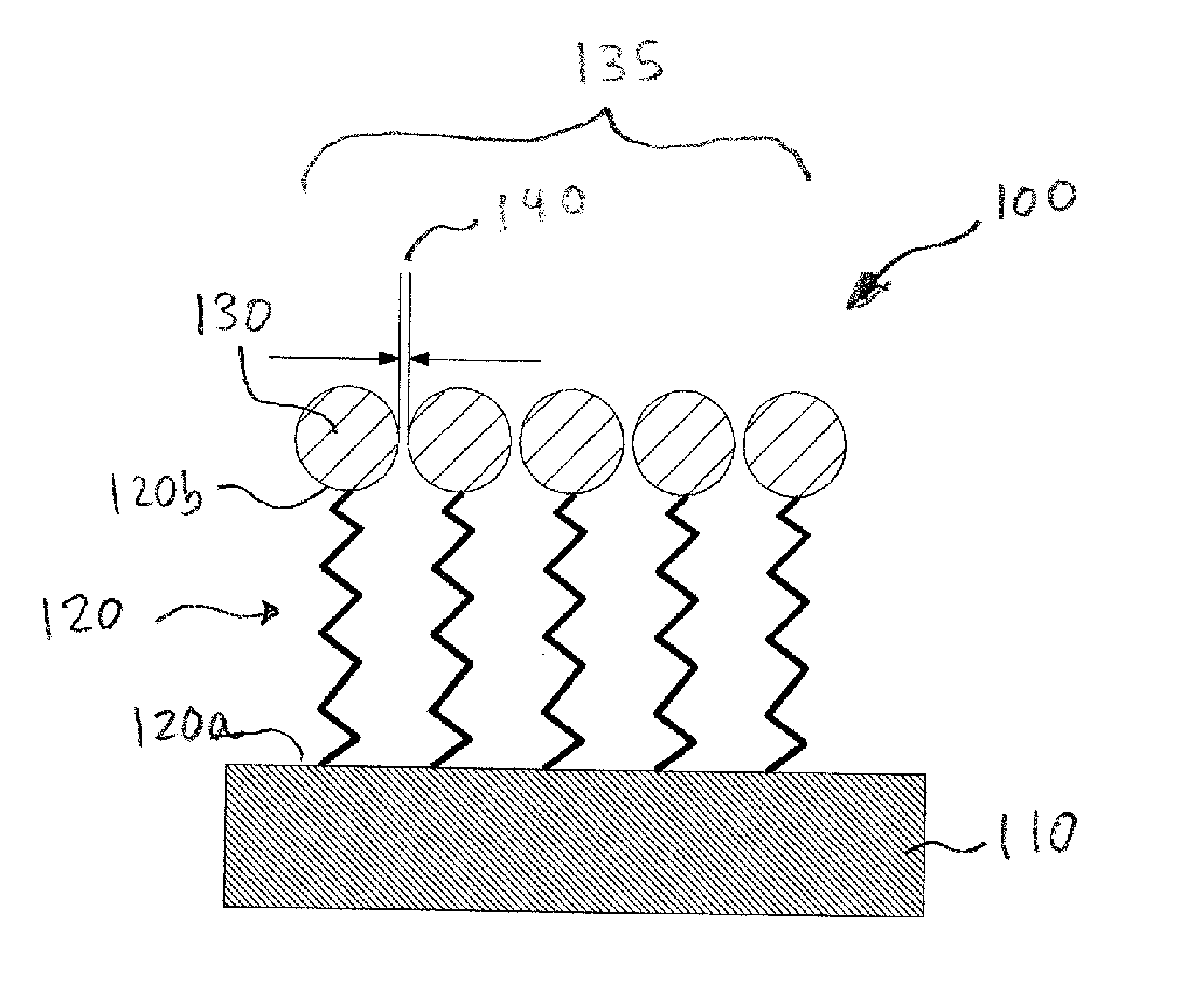
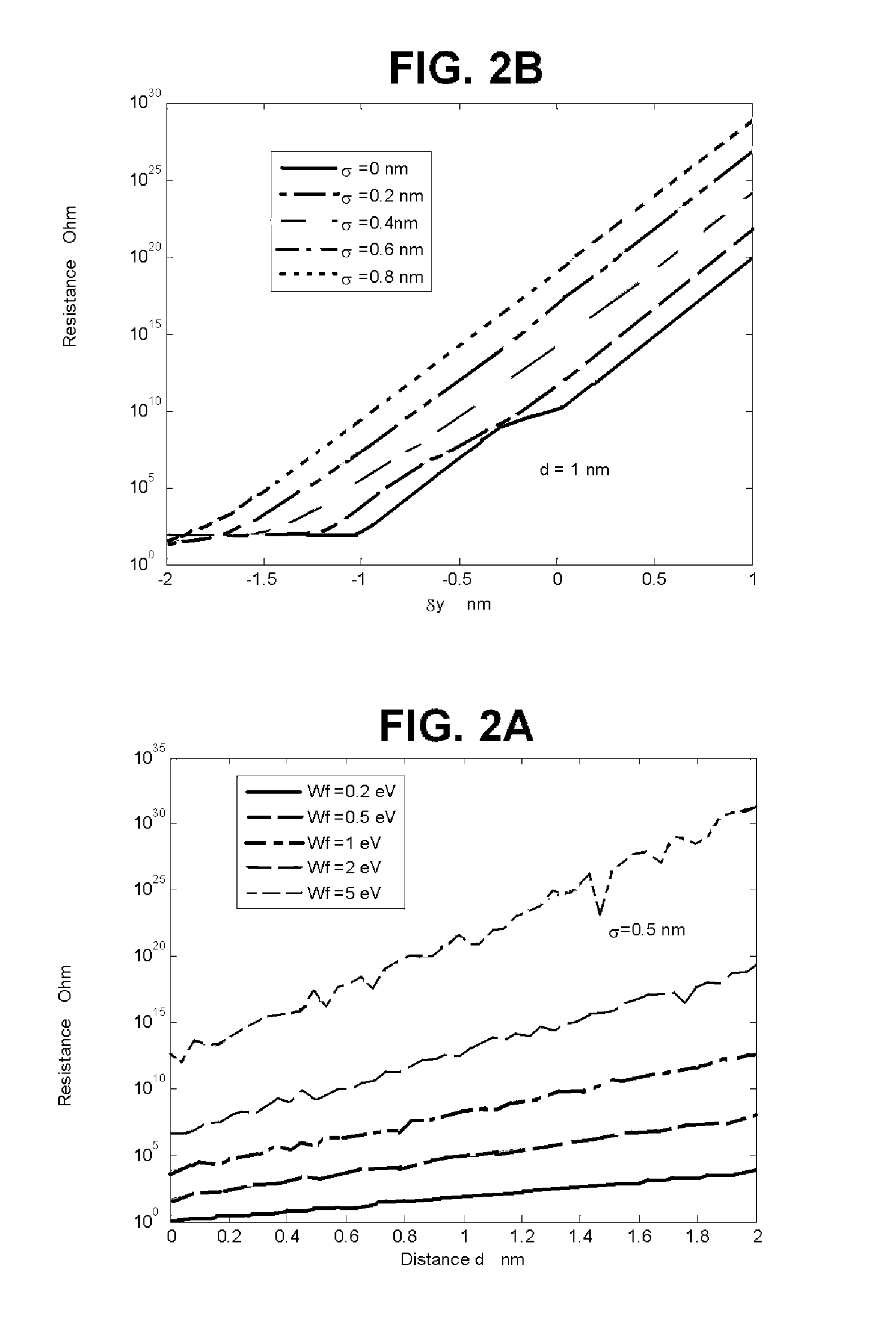
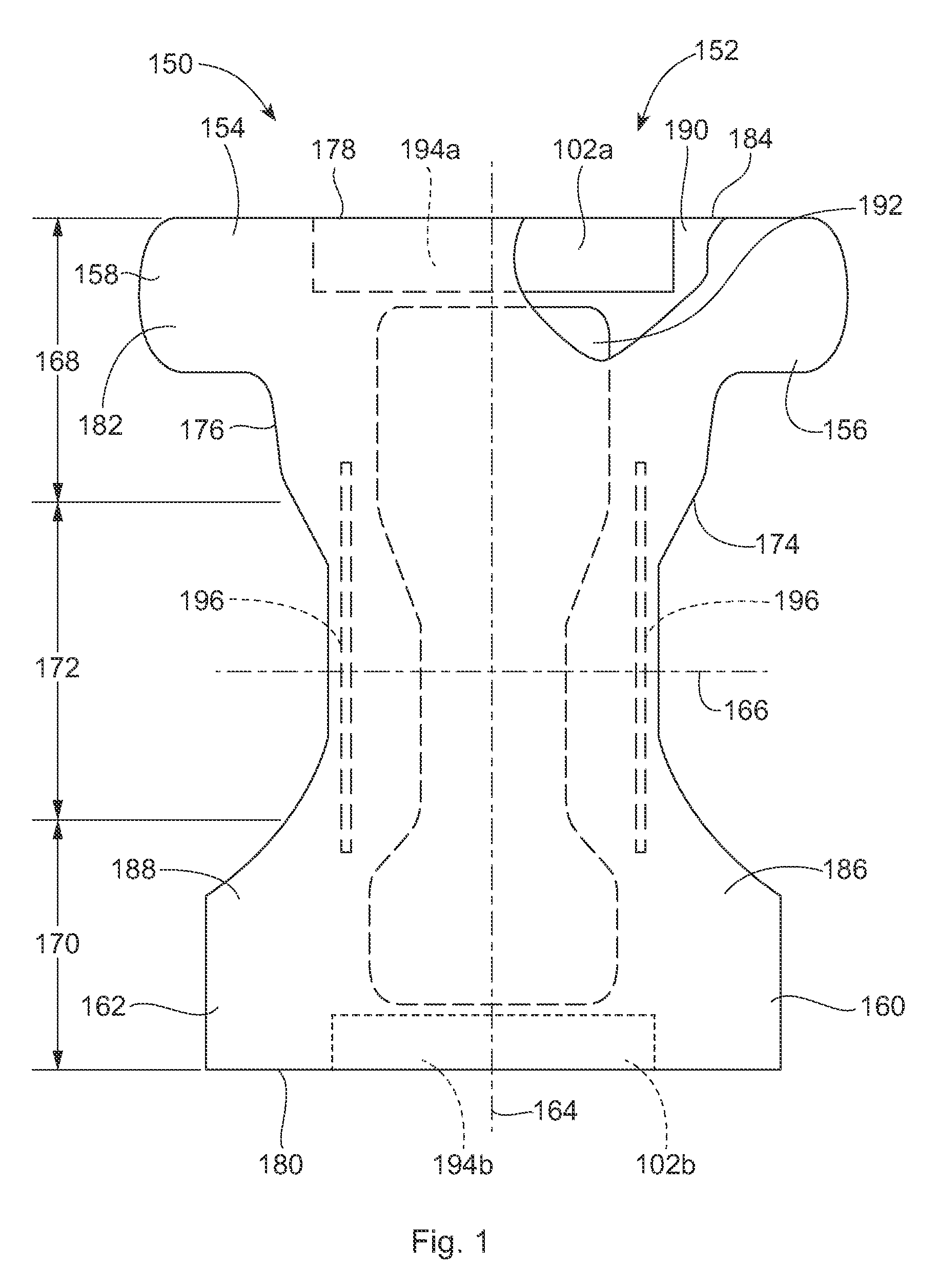
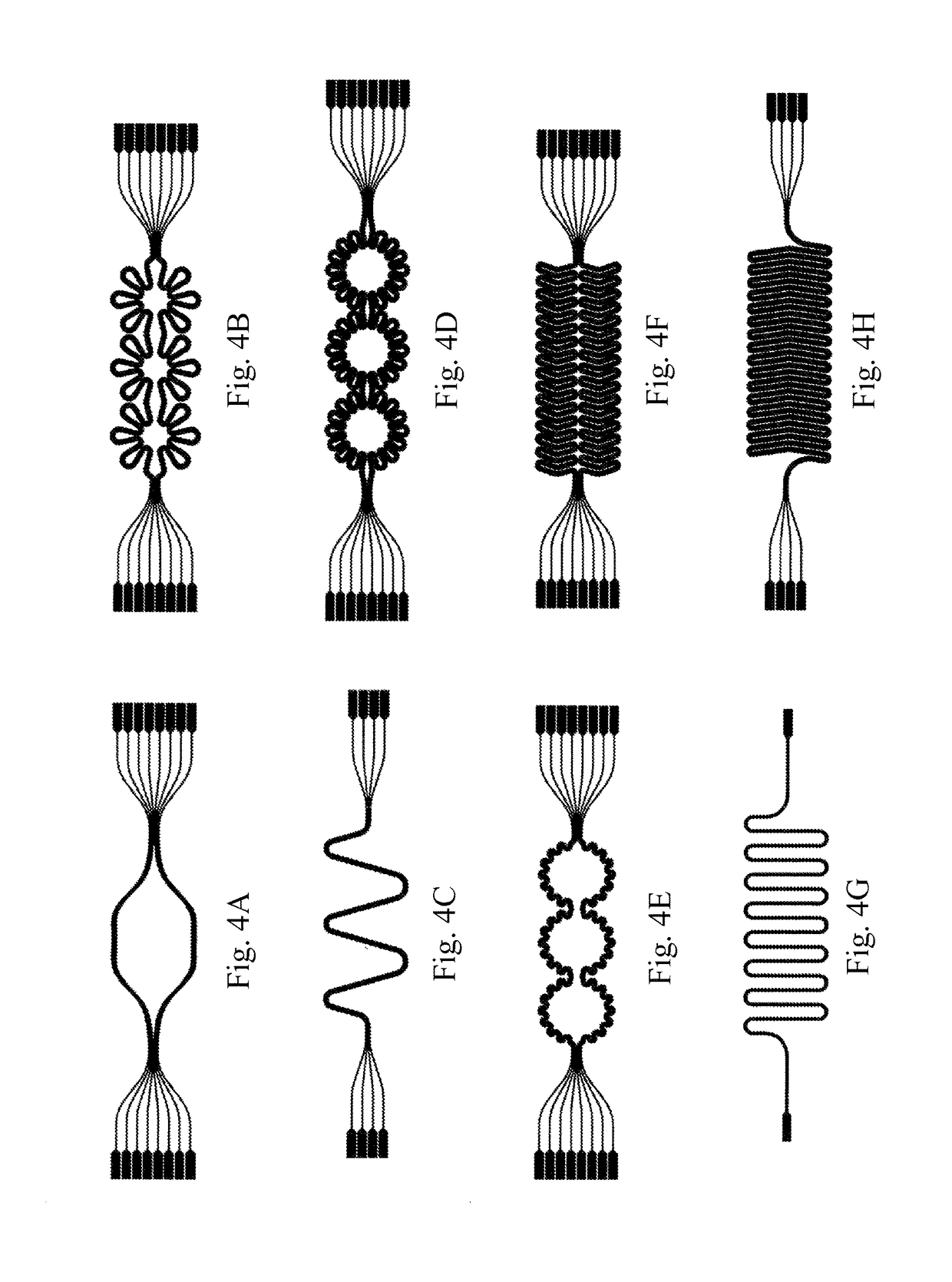
Artificial skin and elastic strain sensor
ActiveUS20140238153A1Sufficient cross-sectional areaHigh sensitivitySkin implantsSolesElectrical resistance and conductanceElastic substrate
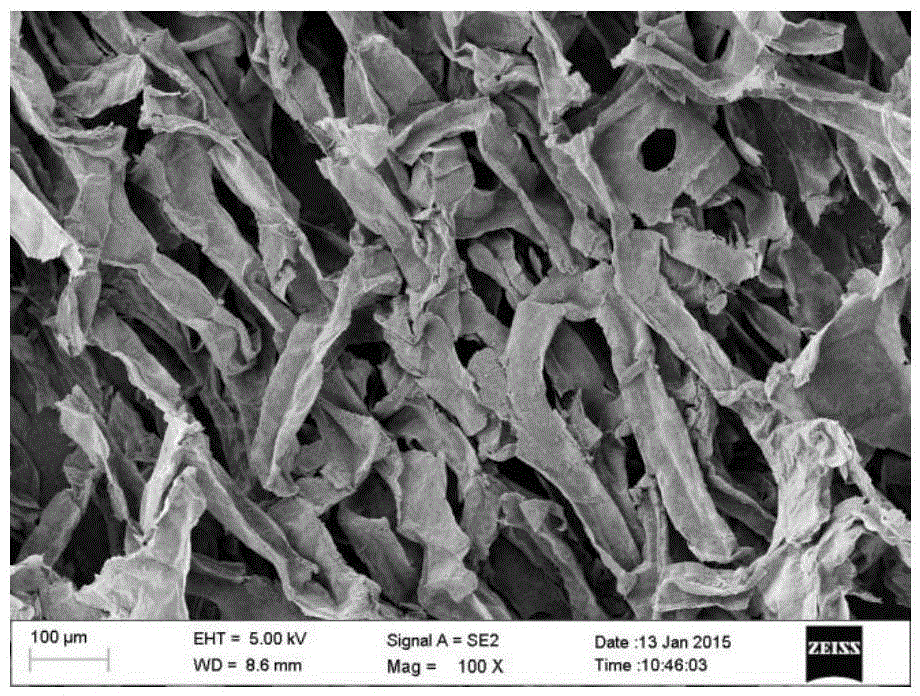
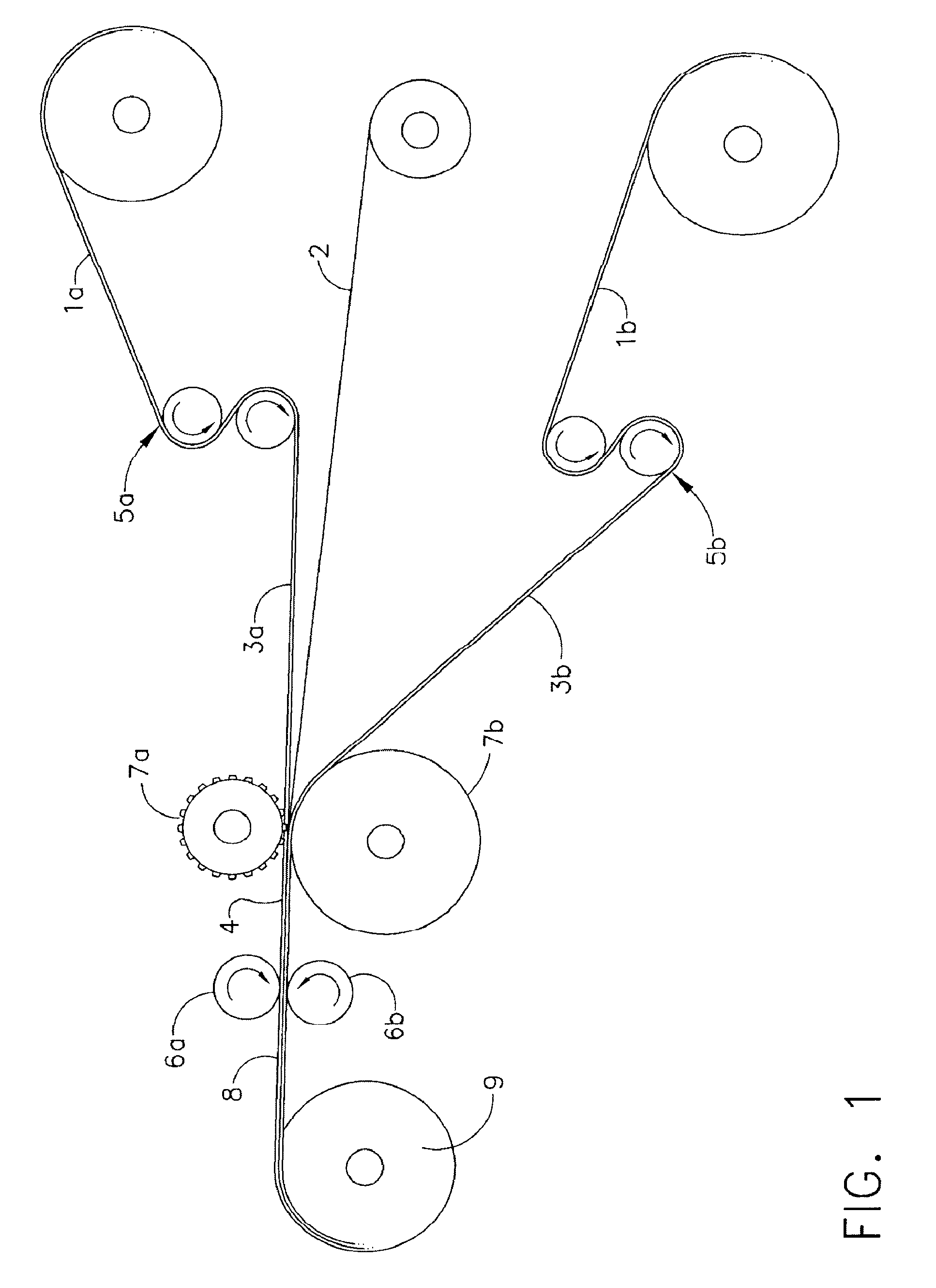
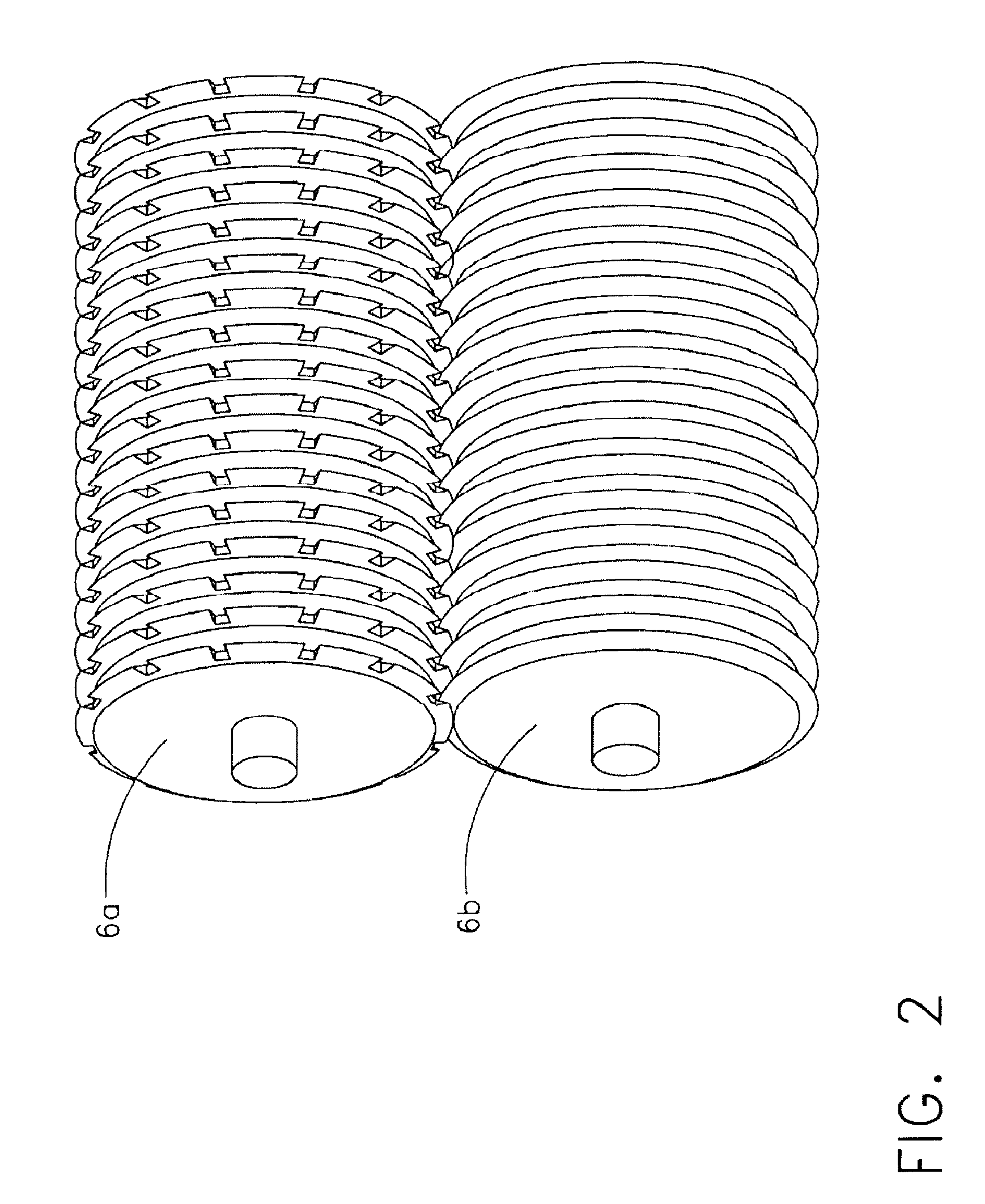
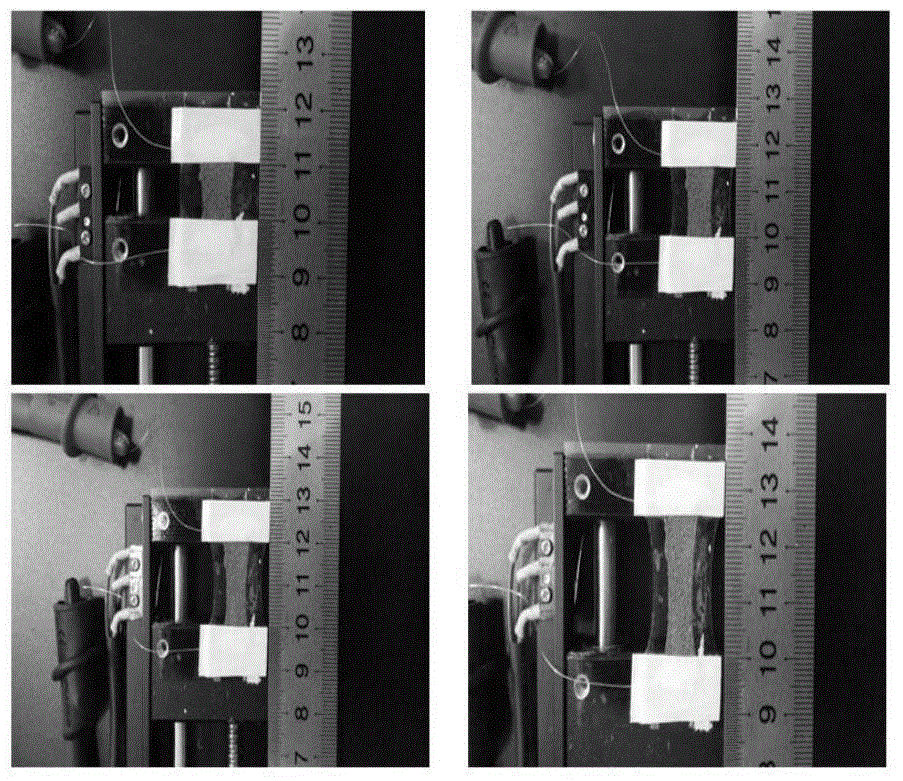
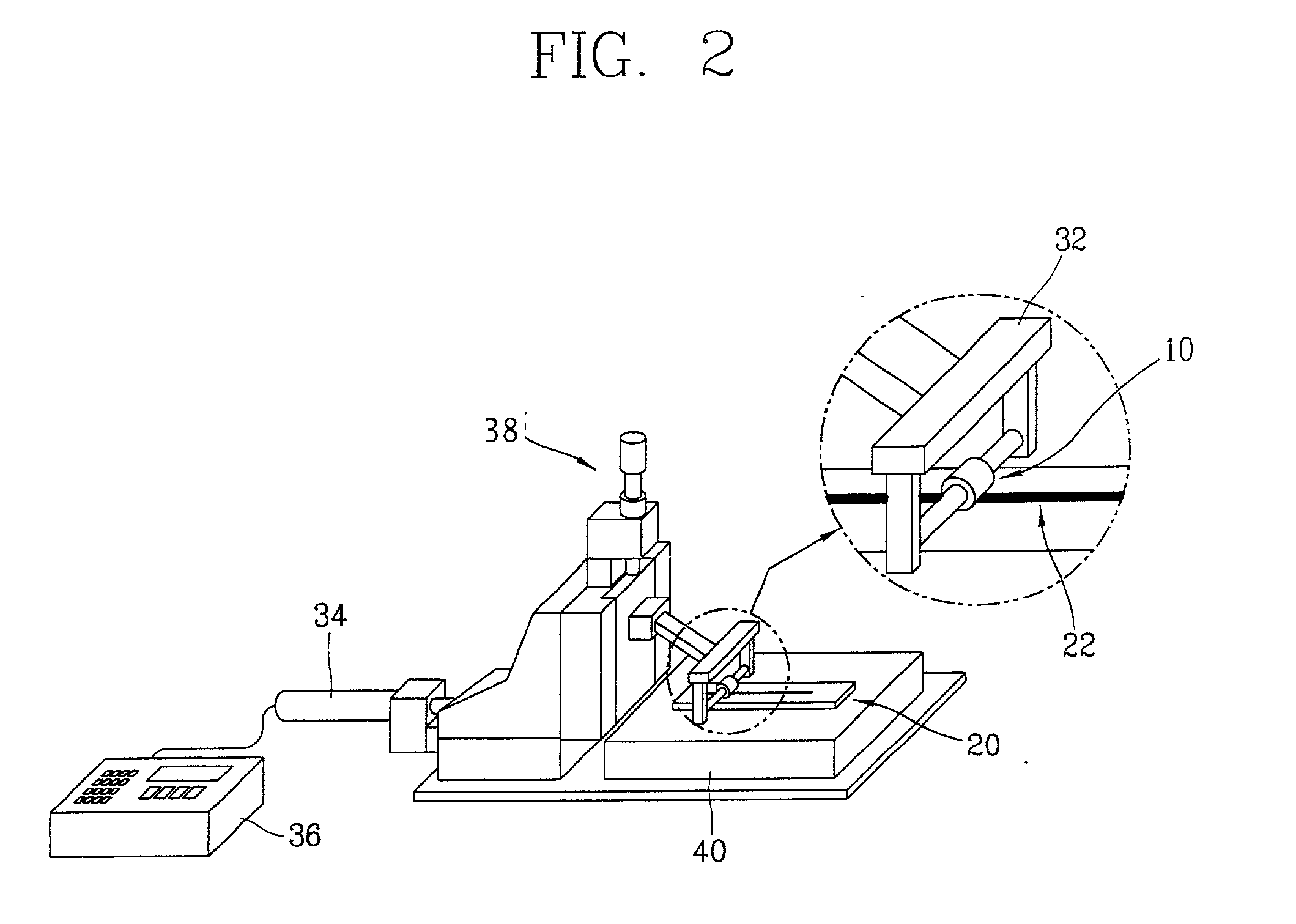
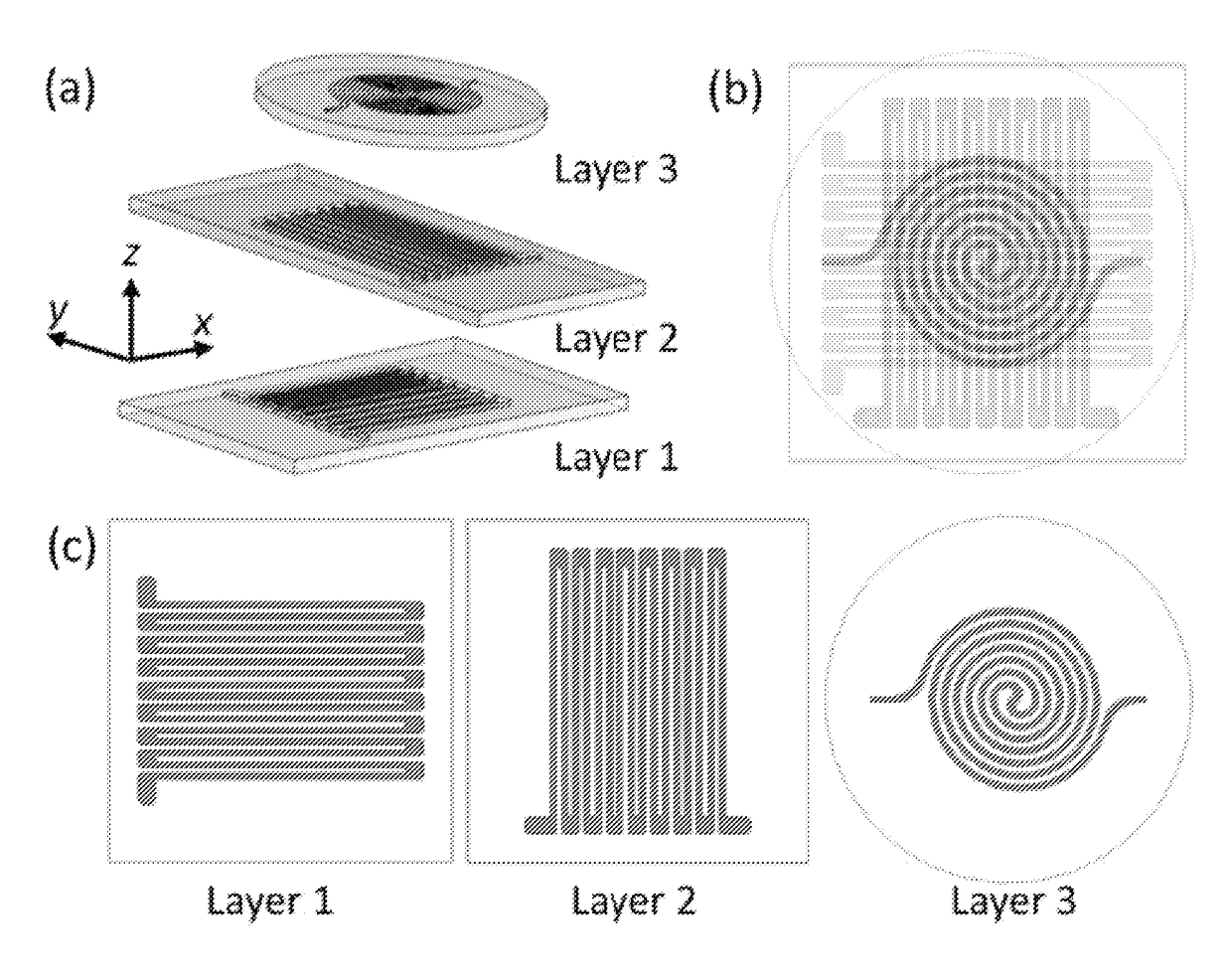
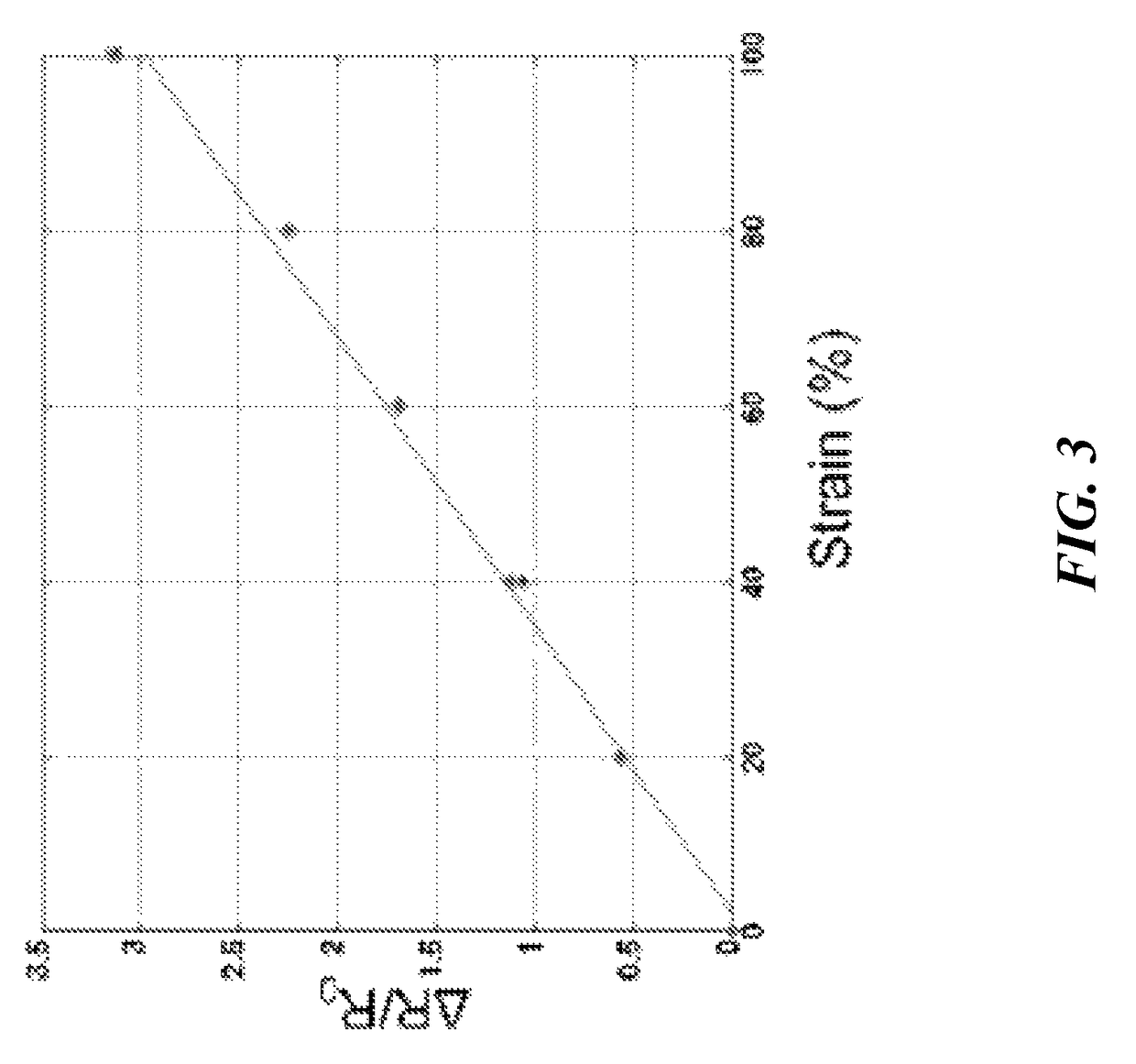
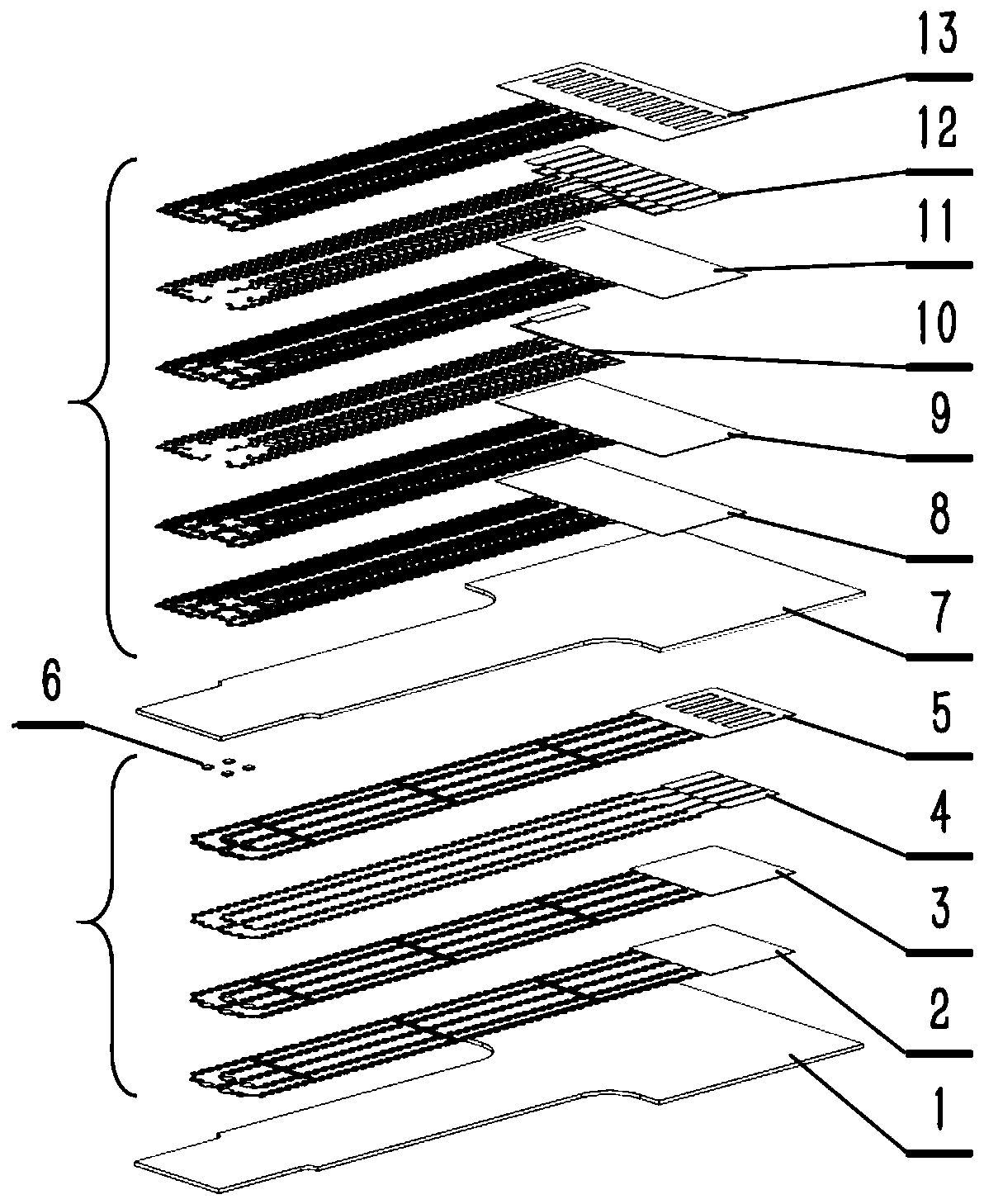
An elastic strain sensor can be incorporated into an artificial skin that can sense flexing by the underlying support structure of the skin to detect and track motion of the support structure. The unidirectional elastic strain sensor can be formed by filling two or more channels in an elastic substrate material with a conductive liquid. At the ends of the channels, a loop port connects the channels to form a serpentine channel. The channels extend along the direction of strain and the loop portions have sufficiently large cross-sectional area in the direction transverse to the direction of strain that the sensor is unidirectional. The resistance is measured at the ends of the serpentine channel and can be used to determine the strain on the sensor. Additional channels can be added to increase the sensitivity of the sensor. The sensors can be stacked on top of each other to increase the sensitivity of the sensor. In other embodiments, two sensors oriented in different directions can be stacked on top of each other and bonded together to form a bidirectional sensor. A third sensor formed by in the shape of a spiral or concentric rings can be stacked on top and used to sense contact or pressure, forming a three dimensional sensor. The three dimensional sensor can be incorporated into an artificial skin to provide advanced sensing.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Elastic laminate and method of making
An elastic laminate for use as a tear resistant diaper side panel. The elastic laminate comprises an elastic substrate bonded to at least one layer of a tensioned spunbond nonwoven web comprising thermoplastic filaments comprising at least about 10% by weight polyethylene. The laminate is then incrementally stretched in the transverse direction to provide a service stretch greater than 100% and a strength ratio greater than 0.35. In one embodiment, the elastic substrate is bonded between the tensioned nonwoven webs by point bonding or hot melt adhesives. Also disclosed is a method for making an elastic laminate comprising the steps of providing at least one layer of a tensioned spunbond nonwoven web comprising thermoplastic filaments comprising at least about 10% by weight polyethylene, providing an elastic substrate, bonding the elastic substrate and the at least one layer of nonwoven web to provide an elastic laminate, and incrementally stretching the laminate in the transverse direction to provide a service stretch greater than 100% and a strength ratio greater than 0.35.
Owner:ADVANTAGE CREATION ENTERPRISE
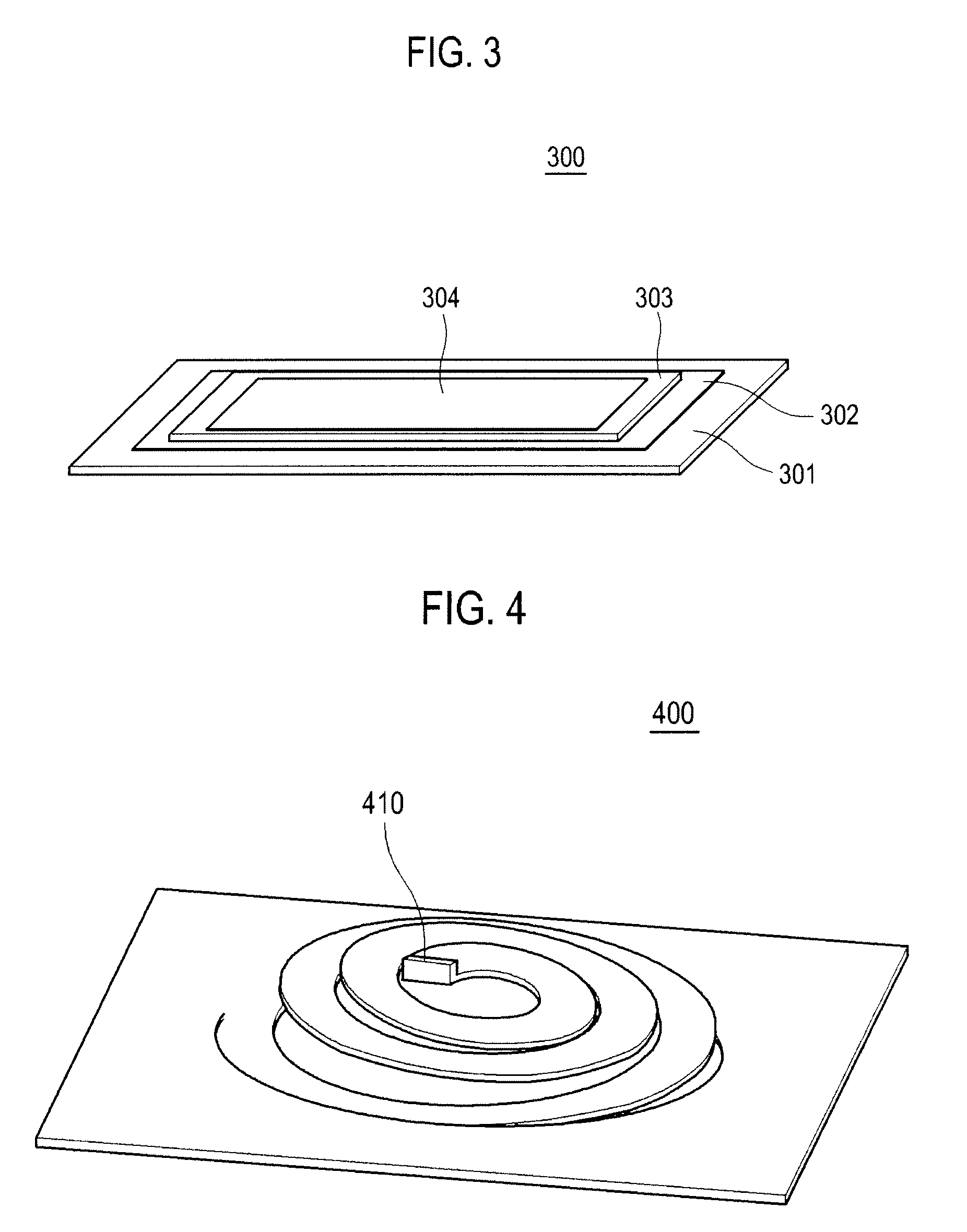
High Efficiency Piezoelectric Energy Harvester Having Spiral Structure
InactiveUS20100084947A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksElastomerEnergy harvester
The present invention relates to a piezoelectric energy harvester having a high energy transformation efficiency and a low natural frequency. The piezoelectric energy harvester includes an elastic substrate having a spiral spring structure, a first electrode formed on the elastomeric substrate, a piezoelectric film formed on the first electrode and a second electrode formed on the piezoelectric film.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Nanoscale Sensor
InactiveUS20070127164A1Improve reliabilityEasy to measureMaterial nanotechnologyAcceleration measurement using interia forcesOptical propertyElastic substrate
A plurality of densely packed nano-particles are arrayed on a elastic substrate via an intervening spacer by a combination of self-assembly methods or imprinting. The coated substrate is useful as a sensor device as the substrate is sufficiently non-rigid such that the deformation increases the separation between nano-particles resulting in a measurable change in the physical properties of the array. When the array comprises of closely packed conductive nano-particles deformation of the substrate disturbs the electrical continuity between the particles resulting in a significant increase in resistivity. The various optical properties of the device may exhibit measurable changes depending on the size and composition of the nano-particles, as well as the means for attaching them to the substrate.
Owner:PHYSICAL LOGIC
Apparatus and Method for Making a Layered Elastic Substrate
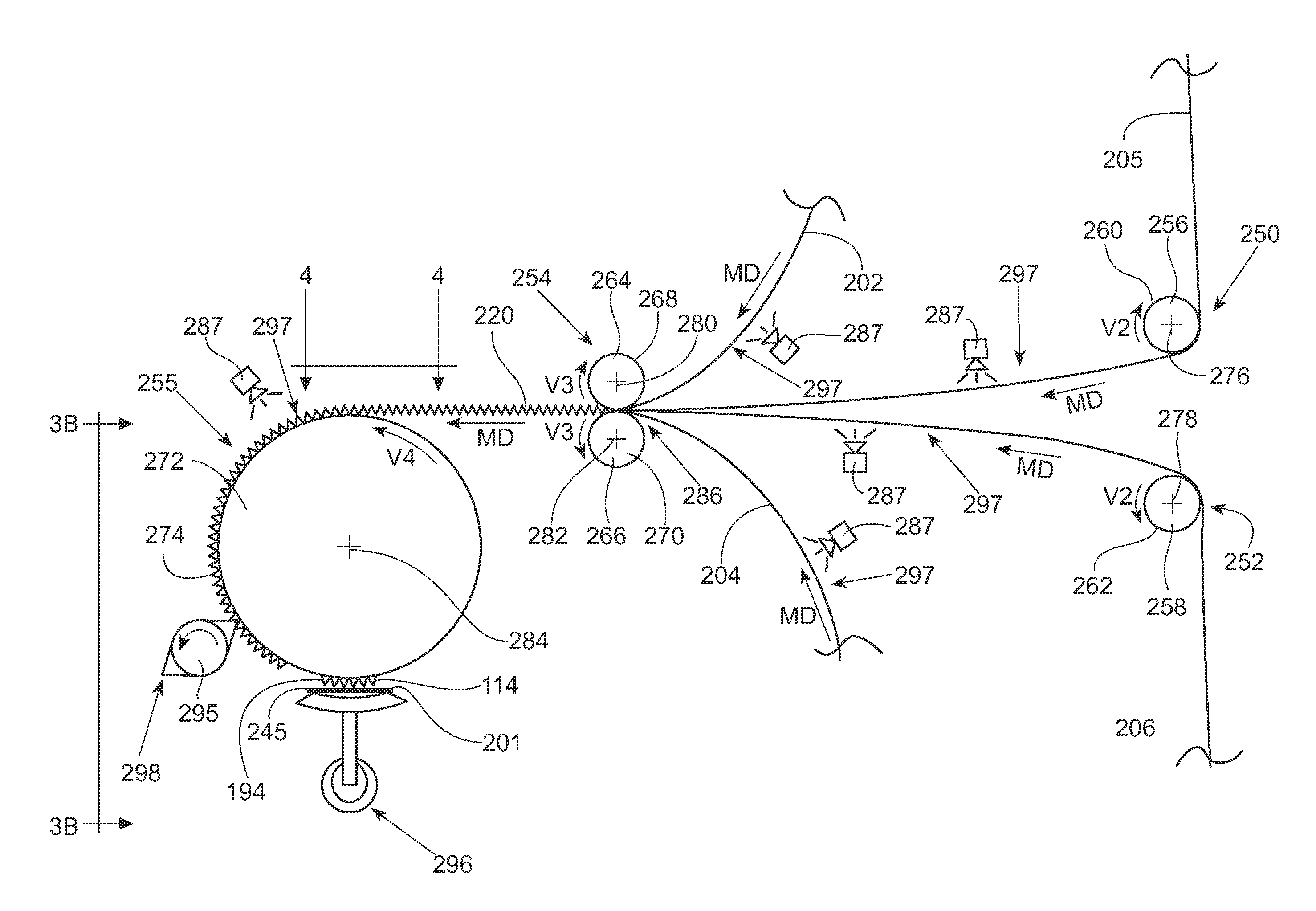
A first elastic material is advanced in a machine direction in a stretched state to a first metering device at a speed, V1. A second elastic material is advanced in the machine direction in a stretched state to a second metering device at a speed, V2. First and second substrate layers are advanced in a machine direction to a third metering at a speed, V3, along with the first and second elastic materials. The first and second elastic materials are bonded to the first and second substrate layers at the third metering device to form a layered elastic substrate. The layered elastic substrate is advanced to a fourth metering device at a speed, V4. V1 is less than V2, V3 is greater than V1 and V2, V4 is less than V3, and V4 is greater than V1 and V2.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
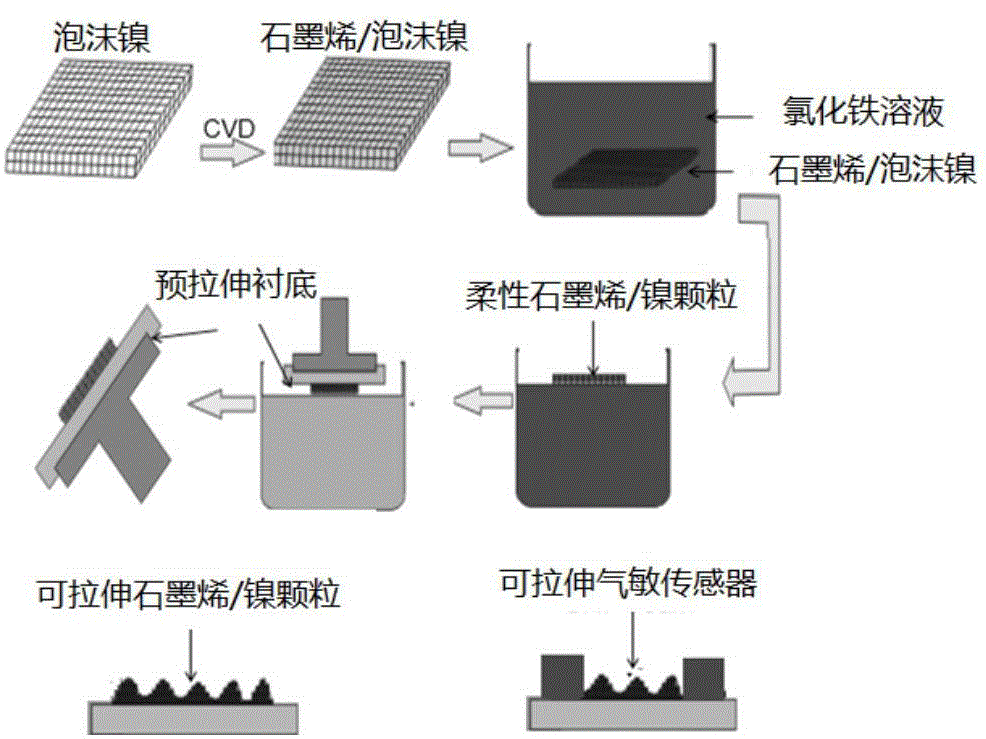
Preparation method of spongy graphene-based stretchable gas sensor
InactiveCN104807861APrecise control of growth temperatureDefect peak lowMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial resistanceElastic substrateGas phase
The invention relates to a preparation method of a spongy graphene-based stretchable gas sensor. Firstly, a spongy graphene material is prepared on nickel foam with a chemical vapor deposition method, the prepared graphene / nickel foam is immersed in an etching solution and slowly reacts, accordingly, most of nickel metal is replaced chemically, the nickel metal is turned into small nickel particles, a spongy graphene / nickel particle mixing structure is fished out of the etching solution with a seal type fishing method and then is cleaned and dried, a prestretching elastic substrate is slowly recovered to the original length or area, electrodes are prepared at two ends of the graphene / nickel particle mixing structure, and the stretchable gas sensor is obtained. The gas sensor has high conductivity and good gas sensitive characteristic, is low in cost and controllable and can realize large-area growth.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Fresnel zone plate based on elastic materials
A dynamically variable, amplitude grating based diffractive optic including: a substantially transmissive, elastic substrate; a substantially opaque, elastic material formed in a predetermined pattern on the first surface of the elastic substrate; and a substrate mount coupled to the elastic substrate to hold it under tension. The predetermined pattern of the substantially opaque, elastic material substrate forms an amplitude grating on the elastic substrate. The substrate mount includes a variable tensioner to stretch the elastic substrate and the substantially opaque, elastic material, thereby allowing at least one optical property of the amplitude grating to be dynamically varied. Alternatively, the elastic substrate may include at least one substantially transparent portion and at least one substantially opaque portion, the substantially opaque portion(s) arranged in a predetermined pattern to form the amplitude grating within the elastic substrate rather than on its surface.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Bistable piezoelectric cantilever beam vibrator device
InactiveCN102064745ABroaden the resonance frequency bandEnhanced Vibration ResponsePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityElastic substrate
The invention discloses a bistable piezoelectric cantilever beam vibrator device, which consists of a pedestal, piezoelectric ceramic, an elastic substrate, an electrode, a mass block and a pair of permanent magnets, wherein the piezoelectric ceramic is adhered to the elastic substrate; the electrode is plated on the piezoelectric ceramic; the mass block and a first permanent magnet are fixed at the free end of the elastic substrate; a second permanent magnet is arranged at a position, corresponding to the first permanent magnet, on the pedestal; and the first and second permanent magnets arearranged in a way that the same polarities are opposite. In the device provided by the invention, a piezoelectric cantilever beam vibrator can form a nonlinear bistable system by utilizing a nonlinear repulsive force between the permanent magnets, and can produce stochastic resonance phenomena under certain conditions to remarkably improve piezoelectric vibration generation efficiency in a broadband low-frequency vibration environment; and the device is particularly suitable for highly-efficiently capturing broadband, low-frequency and low-amplitude vibration energy.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method and apparatus for attaching elastic components to absorbent articles
A first substrate advances in the first direction and a second substrate advances in the second direction. The first substrate advances onto an outer circumferential surface of a drum in a stretched state. The first substrate may be cut into discrete lengths of elastic substrate. The drum may be configured with vacuum to hold the discrete length of elastic substrate in a stretched state. The second substrate may advance in the second direction by a conveyor. The conveyor includes a roller having a curved outer surface that deforms the second substrate so as to define a curve in the first direction. A tamper apparatus intermittently displaces a deformed portion of the second substrate into contact with a discrete length of elastic substrate on the outer circumferential surface of the drum. The discrete length of elastic substrate bonds with the second substrate and is removed from the drum.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Handling and delivering fluid through a microchannel in an elastic substrate by progressively squeezing the microchannel along its length
Minute or infinitesimal amounts of fluid can be accurately delivered through microchannels formed in an elastic polymeric substrate. External (mechanical) force is applied on the substrate to progressively squeeze the microchannel along its length to push or pull the fluid through the microchannel. Fluids can be delivered at a constant rate and amount regardless of the kind of the fluid since fluid delivery is not affected by the physical properties of the fluid. The delivery rate of the fluid is determined in the ranges between femtoliters / sec and milliliters / sec by the size of the microchannel and the area of the substrate being pressed by the applied external (mechanical) force. Such techniques of fluid delivery can be applied to various fields including lab-on-a-chip technology, monitoring of chemical and biological processing, portable analyzing instruments, fine chemistry, clinical diagnosis and development of new medicines.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC +1
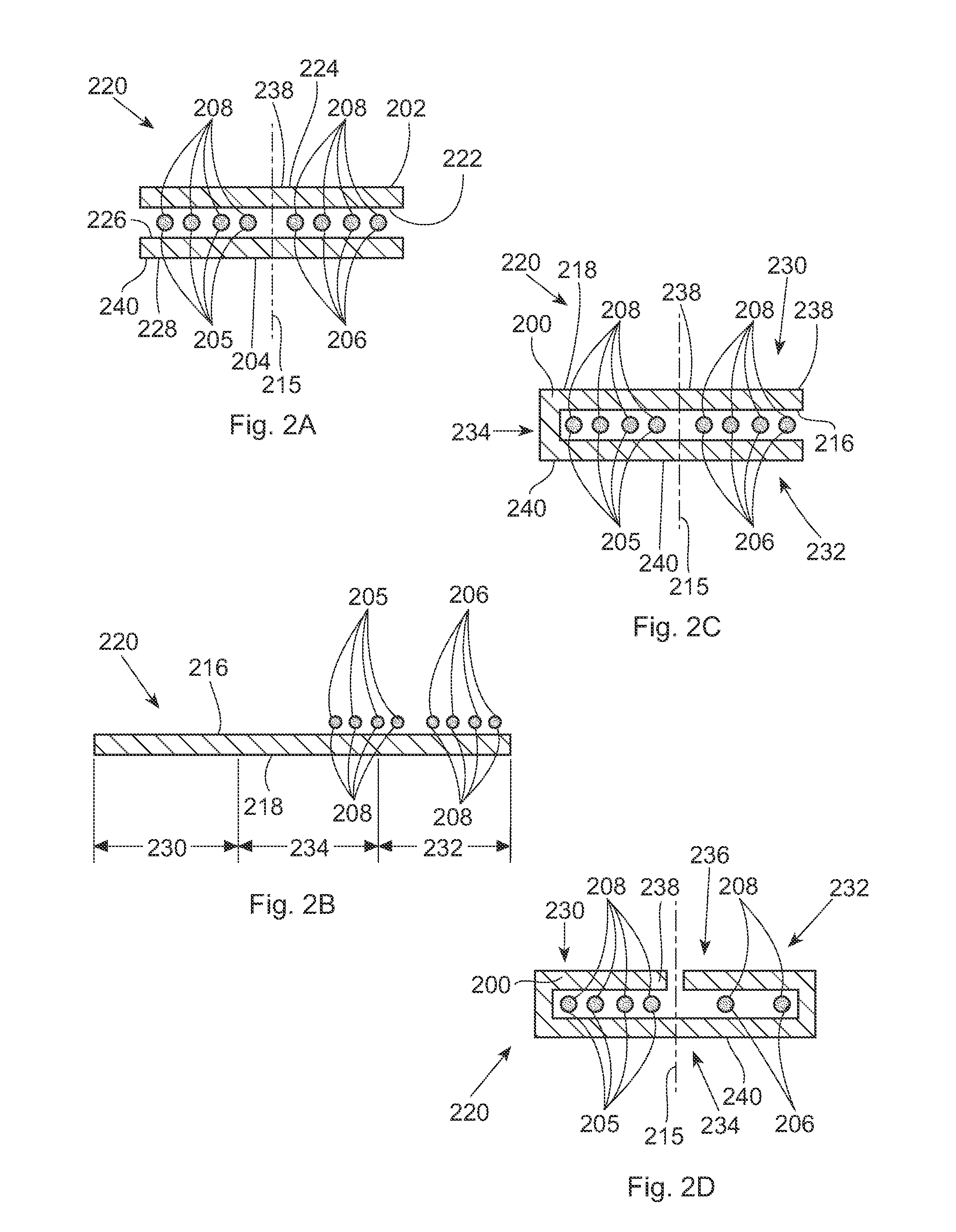
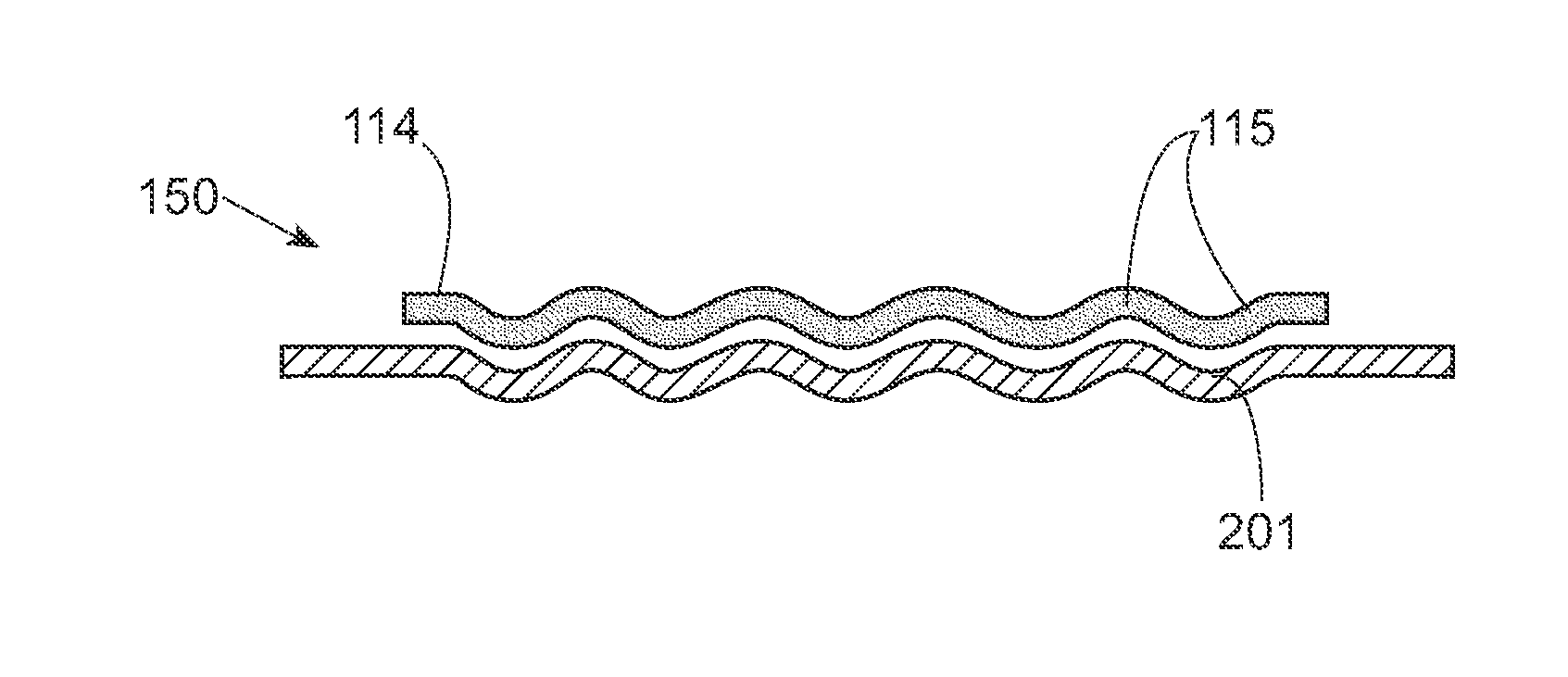
Stretchable conductor design and methods of making
ActiveUS9554465B1Circuit bendability/stretchabilityPrinted circuit manufactureElectrical conductorElastic substrate
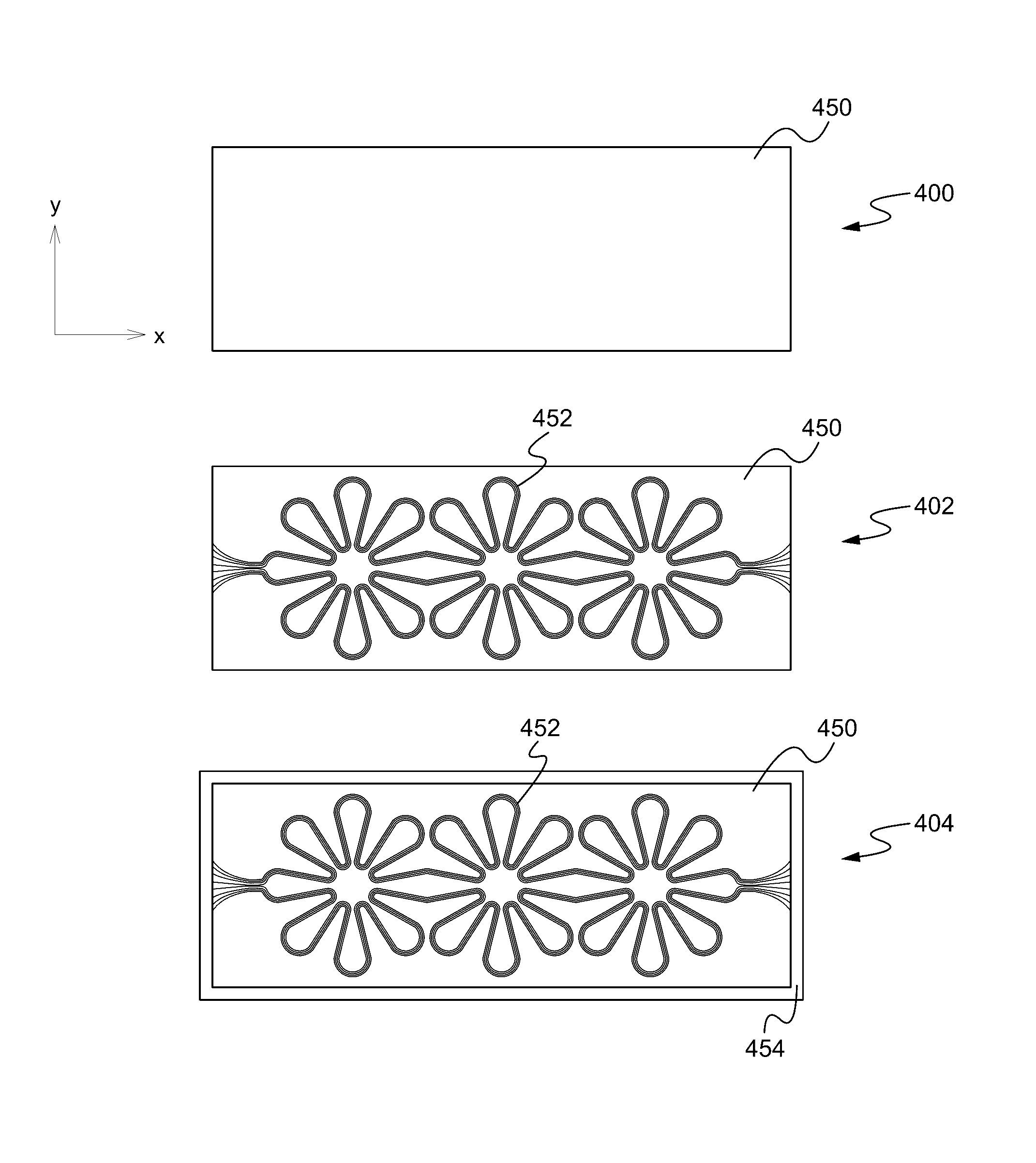
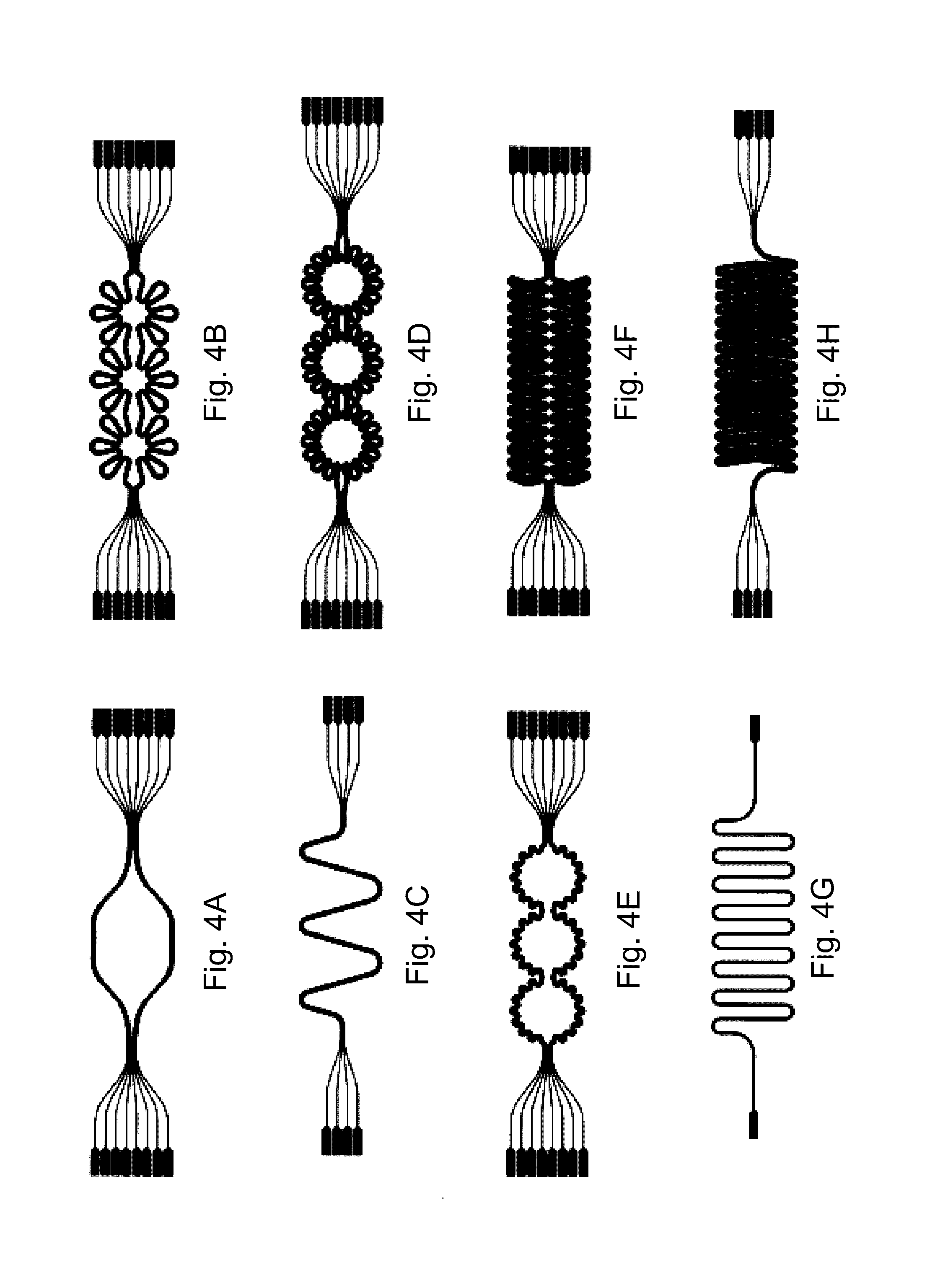
A stretchable interconnect includes a plurality of electrically conductive traces formed as a complex pattern on an elastic substrate. The form of the electrically conductive traces is such that when the elastic substrate is in a relaxed, or non-stretched, state each of the electrically conductive traces forms a tortuous path, such as a waveform, along the elastic substrate. The tortuous path of the electrically conductive traces provides slack such that as the elastic substrate is stretched the slack is taken up. Once released, the elastic substrate moves from the stretched position to the relaxed, non-stretched position, and slack is reintroduced into the electrically conductive traces in the form of the original tortuous path.
Owner:FLEXTRONICS AP LLC
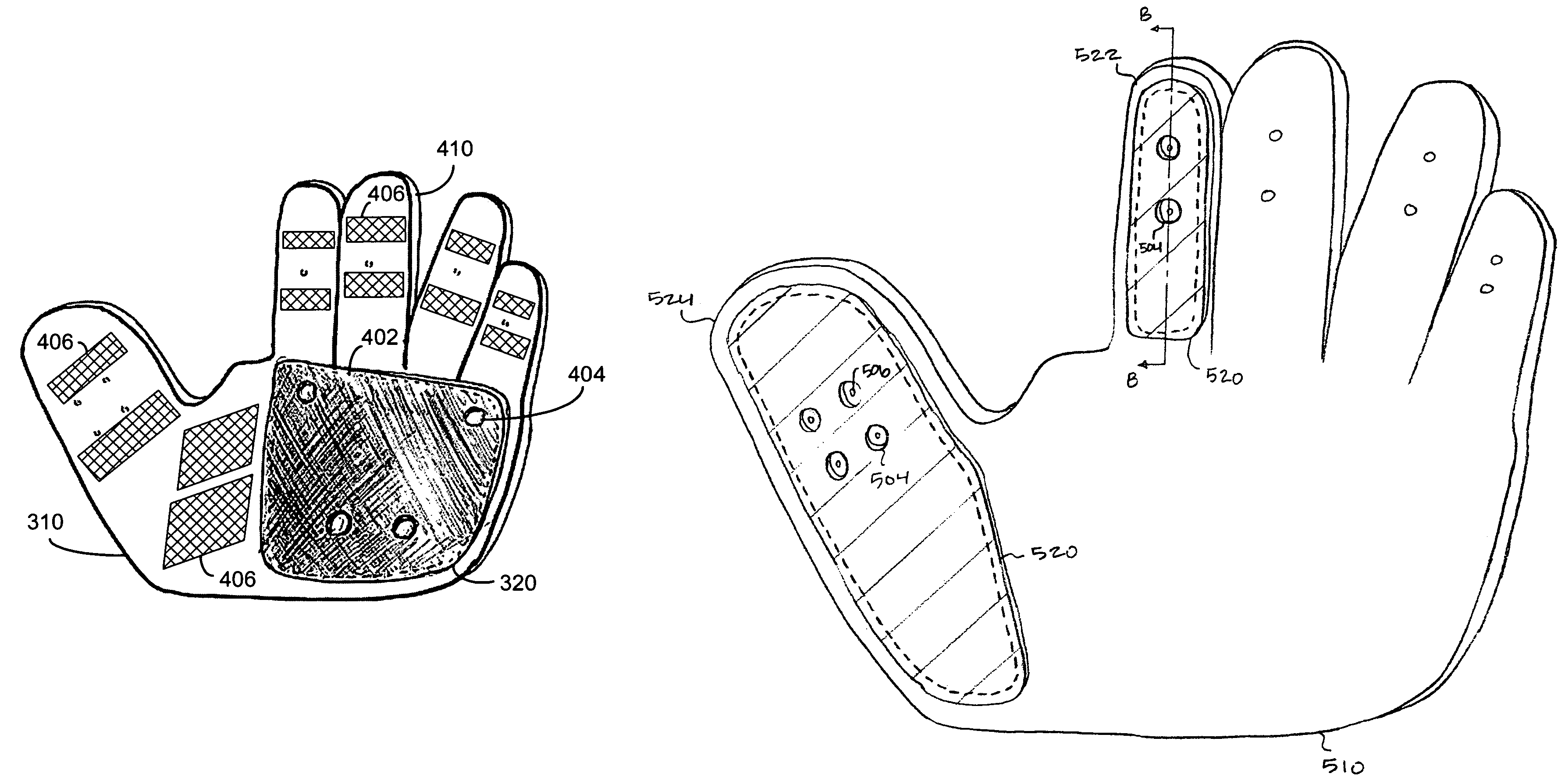
Protective glove with independent pads
ActiveUS7370373B2Flexible gloveEliminate resistanceGlovesSport apparatusElastic substrateBiomedical engineering
A protective glove having an elastic substrate, a first pad segment attached to the elastic substrate, and a second pad segment attached to the elastic substrate independently from the first pad segment. The elastic substrate can be disposed over an area intended to substantially cover a forearm, a wrist, a back of a hand, a finger, and / or a thumb of a user wearing the glove. The elastic substrate can be stretchable in different directions and to different degrees in the areas around each pad segment, thereby enabling independent movement of the individually attached pad segments to accommodate any number of contours and flex points. Other embodiments provide methods for manufacturing a protective glove having independent pads.
Owner:WM T BURNETT IP
Stretchable linear supercapacitor and lithium ion battery preparation method
ActiveCN104392845AEvenly dispersedReduce weightMicroscopic fiber electrodesHybrid capacitor electrodesFiberElastic substrate
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of the micro energy storage device, particularly relates to a stretchable linear supercapacitor and a lithium ion battery preparation method. A spring-like oriented carbon nanotube fiber is prepared and is twisted to form a spiral unit, wherein the spiral unit can be stretched by over 300%; and then the processed fiber is used as the electrode to construct a stretchable supercapacitor. Moreover, the fiber can be combined with lithium manganate and lithium titanate nano particles to form composite fibers respectively used as the positive electrode and the negative electrode; and thus a stretchable lithium ion battery can be constructed. According to the invention, compared with other micro devices, the stretchable linear supercapacitor and stretchable linear lithium ion battery have novel structures. The stretching function can be realized without the need of an elastic substrate, thereby reducing the weight and size of the device and improving the specific capacity and the energy density of the device and thus providing the important innovation for the micro device field. Meanwhile, the supercapacitor and the battery having high flexibility are easy to manufacture and integrate and have good application prospects.
Owner:YANTAI TAYHO ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Friction nanometer generator with elastic structure
The invention provides a friction nanometer generator with an elastic structure. The friction nanometer generator comprises an elastic bases, a plurality of generating units and a mass block, wherein the elastic base is an s-shaped and bent multi-layer folding structure; two layers of adjacent bases are mutually connected to form a V-shaped or U-shaped sunken structure; a generating unit comprises a first friction unit and a second friction unit in face to face, and the first friction unit and the second friction unit are respectively arranged on two layers of adjacent bases; the mass block vibrations up and down under the vibration energy effect; the first friction unit and the second friction unit are mutually contacted and separated under the effect of the elastic base; and an electric signal is generated between the electrode of the first friction unit and the electrode of the second friction unit. The parallel connection of multiple generator units are realized on a support structure of the elastic substrate, and the optimal output frequency range of the generator is adjusted by adjusting the mass block, and the environment vibration energy can be converted into electric energy in the low frequency range of 3-30 hz.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NANOENERGY & NANOSYST
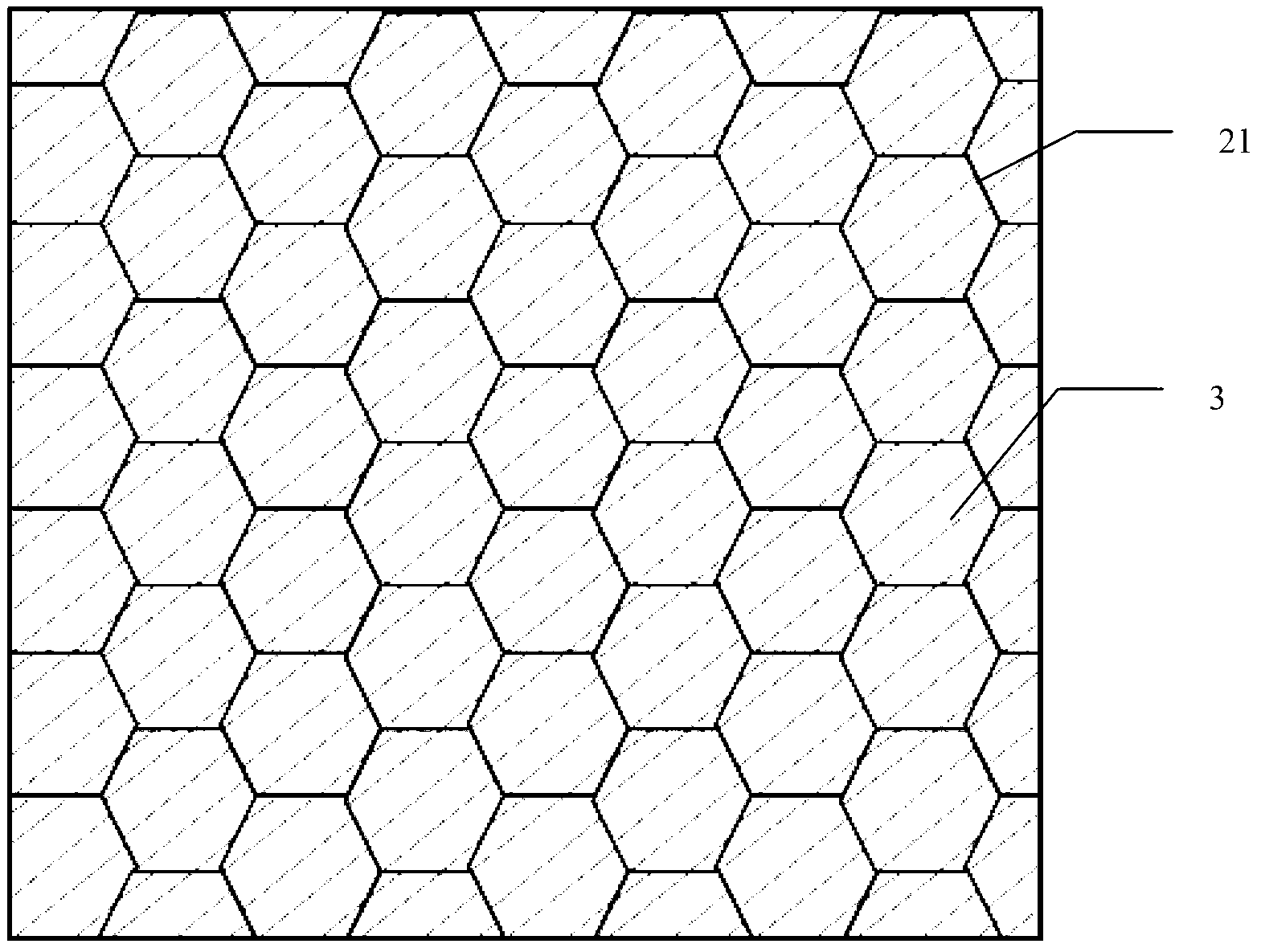
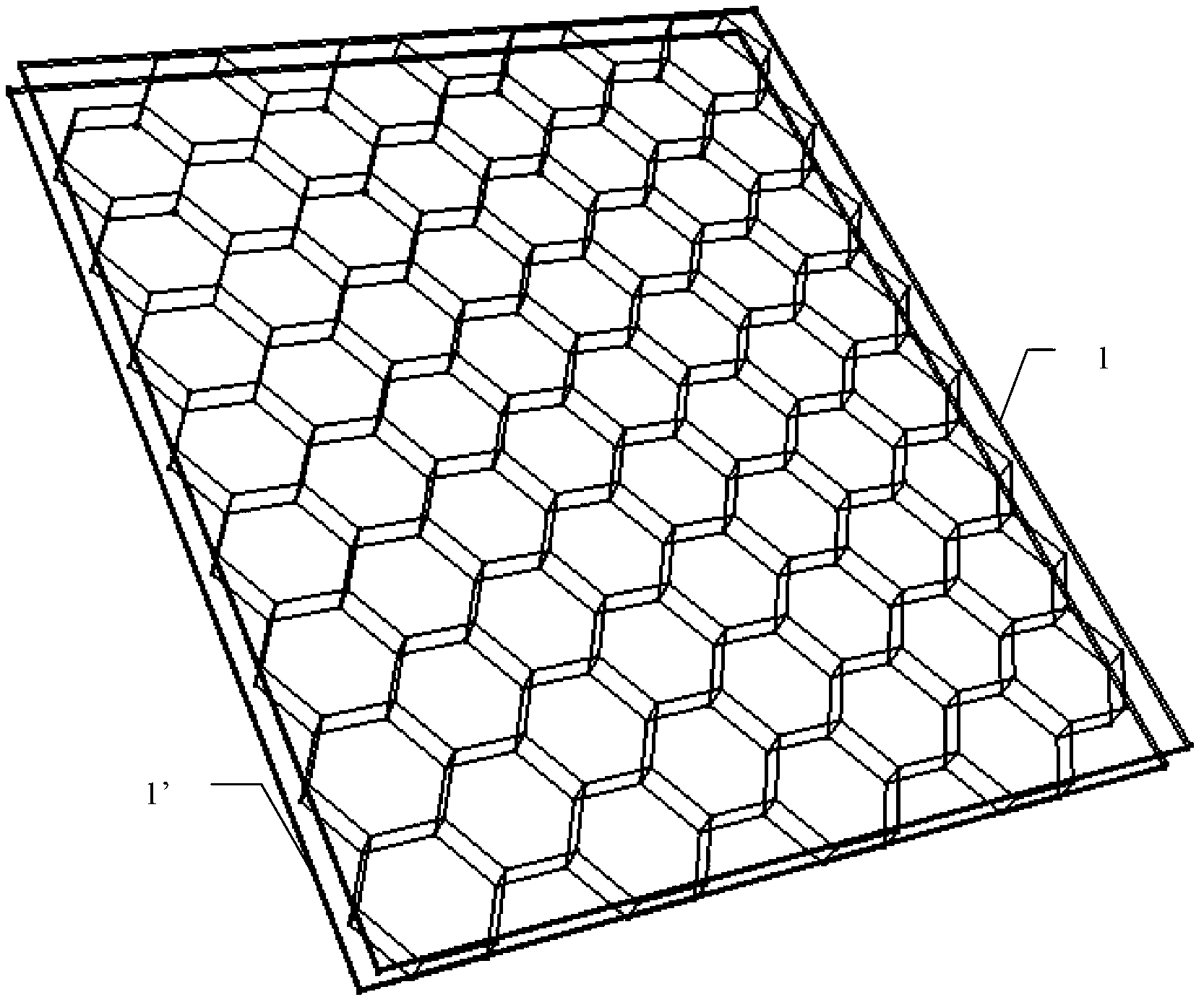
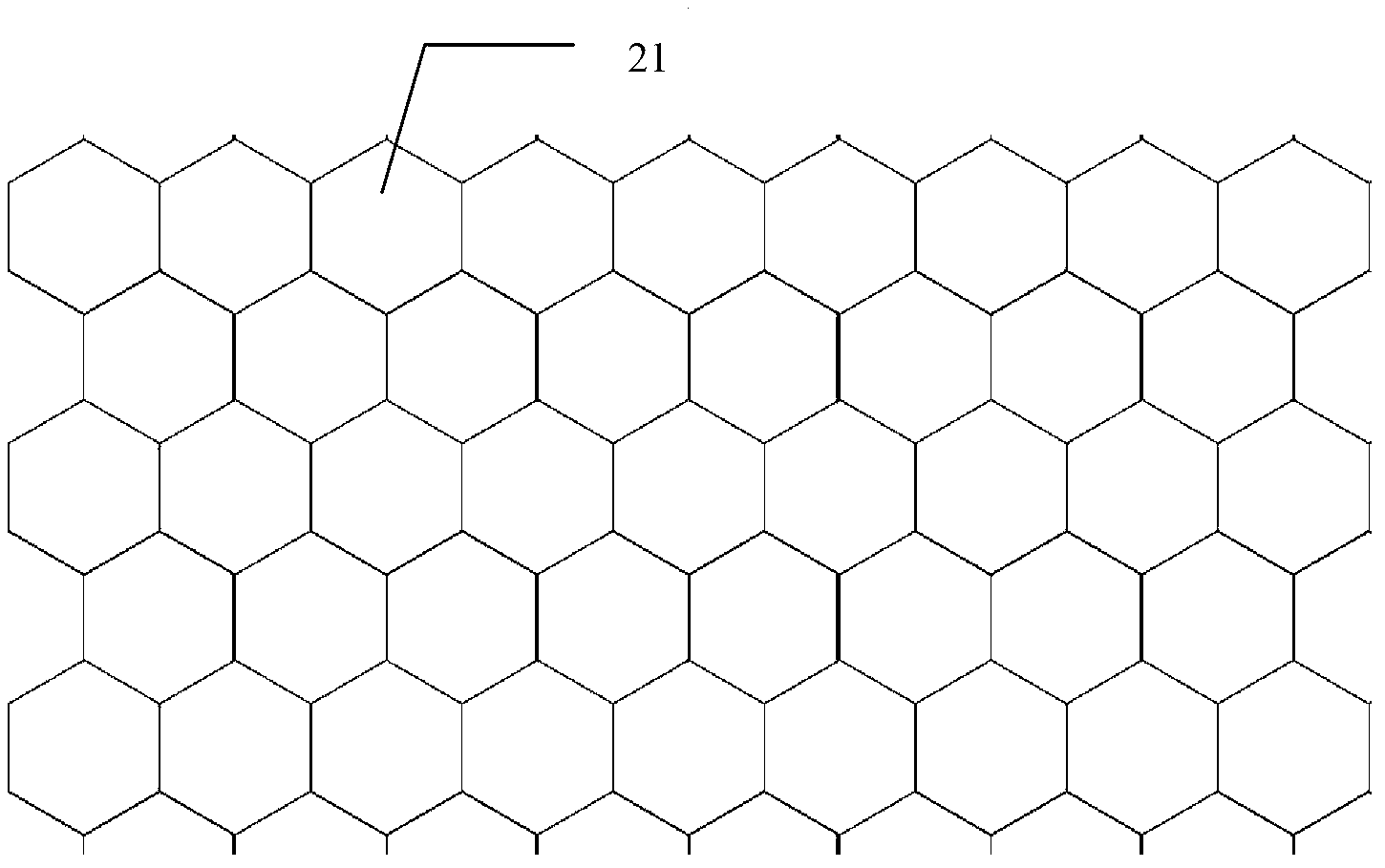
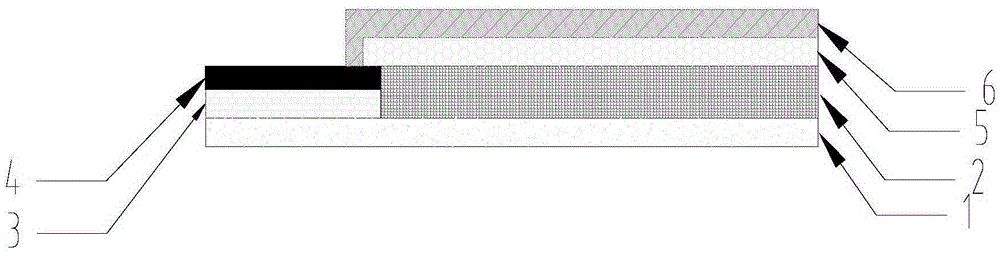
Deformation skin for aircraft
InactiveCN102700704AImproved ability to transfer loadsAchieve optimizationFuselage bulkheadsPolyurethane elastomerMorphing
The invention discloses a deformation skin for an aircraft. The deformation skin for the aircraft is formed by connecting N continuous cellular units (21), wherein the N is a natural number. The deformation skin for the aircraft is characterized in that: elastic substrates (3) are filled in the cellular units (21). According to the deformation skin for the aircraft, the capability of the deformation skin of transferring load is improved as high as possible on the premise of ensuring the deformation capability by a method for compounding different performance materials, the problem of contradiction between higher elastic deformation and transfer of airload under the action of lower driving force is solved, the local flow fields are actively controlled further by mean of an electrostrictive effect of polyurethane elastomers, and the deformation skin has the capability of deforming in different scales. According to the deformation skin, the properties of intelligent morphing aircrafts are comprehensively optimized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Graphene pressure sensor, manufacturing method thereof and purpose thereof
ActiveCN105300574AHigh sensitivityImprove stabilityForce measurement using piezo-resistive materialsElastic substratePressure sense
The invention provides a graphene pressure sensor and a manufacturing method thereof. The graphene pressure sensor is characterized in that the graphene pressure sensor is at least composed of an elastic substrate layer, a graphene pressure sensing layer and a packaging layer, wherein the elastic substrate layer comprises a sensing area, an overlapping area and an electrode area; the graphene pressure sensing layer is attached to the sensing area, and the graphene pressure sensing layer is in direct contact with the electrode area so as to form the overlapping area; the packaging layer covers the graphene pressure sensing layer and the overlapping layer between the graphene pressure sensing layer and the electrode area. The graphene pressure sensor is high in sensitivity, good in stability and long in expected service lifetime, in addition, the manufacturing cost is low, the process is simple, and the process is controllable.
Owner:2D CARBON CHANGZHOU TECH INC
Method of making stretchable interconnect using magnet wires
InactiveUS9674949B1Freedom of movementCircuit bendability/stretchabilityDielectric materialsElastic substrateEngineering
A stretchable wire assembly includes a metal wire coupled between two elastic substrates. The two elastic substrates are selectively coupled together, and the metal wire is attached to one or both elastic substrates at select locations. The form of the metal wire is such that when the elastic substrates are in a relaxed, or non-stretched, state the metal wire forms a tortuous path, such as a waveform, along the coupled elastic substrates. The tortuous path of the metal wire provides slack such that as the elastic substrates are stretched the slack is taken up. Once released, the elastic substrates move from the stretched position to the relaxed, non-stretched position, and slack is reintroduced into the metal wire in the form of the original tortuous path.
Owner:FLEXTRONICS AP LLC
Stretching organic electroluminescence device with periodically regular crease structure
ActiveCN105405983AImprove flexibilityFlat surfaceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingElastic substrate
The invention discloses a stretching organic electroluminescence device with a periodically regular crease structure, belongs to the technical field of photoelectrons, and particularly relates to the stretching organic electroluminescence device with a periodically regular crease, which is high in efficiency, high in stability and high in tensile strength. The stretching organic electroluminescence device is prepared by the following steps: processing a long-period grating structure on the surface of an elastic substrate by a femtosecond laser ablation process; obtaining an organic electroluminescence device by combining a vacuum evaporation technology and a demolding technology; and finally combining the elastic substrate with the long-period grating structure and the organic electroluminescence device. The stretching organic electroluminescence device has very high stretching stability; the photoelectric property of the device only slightly fluctuates along with the change of the tensile strength; and more importantly, the properties of the device only lightly attenuate in multiple repeated tensile tests, so that the stretching organic electroluminescence device has very high practical value.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
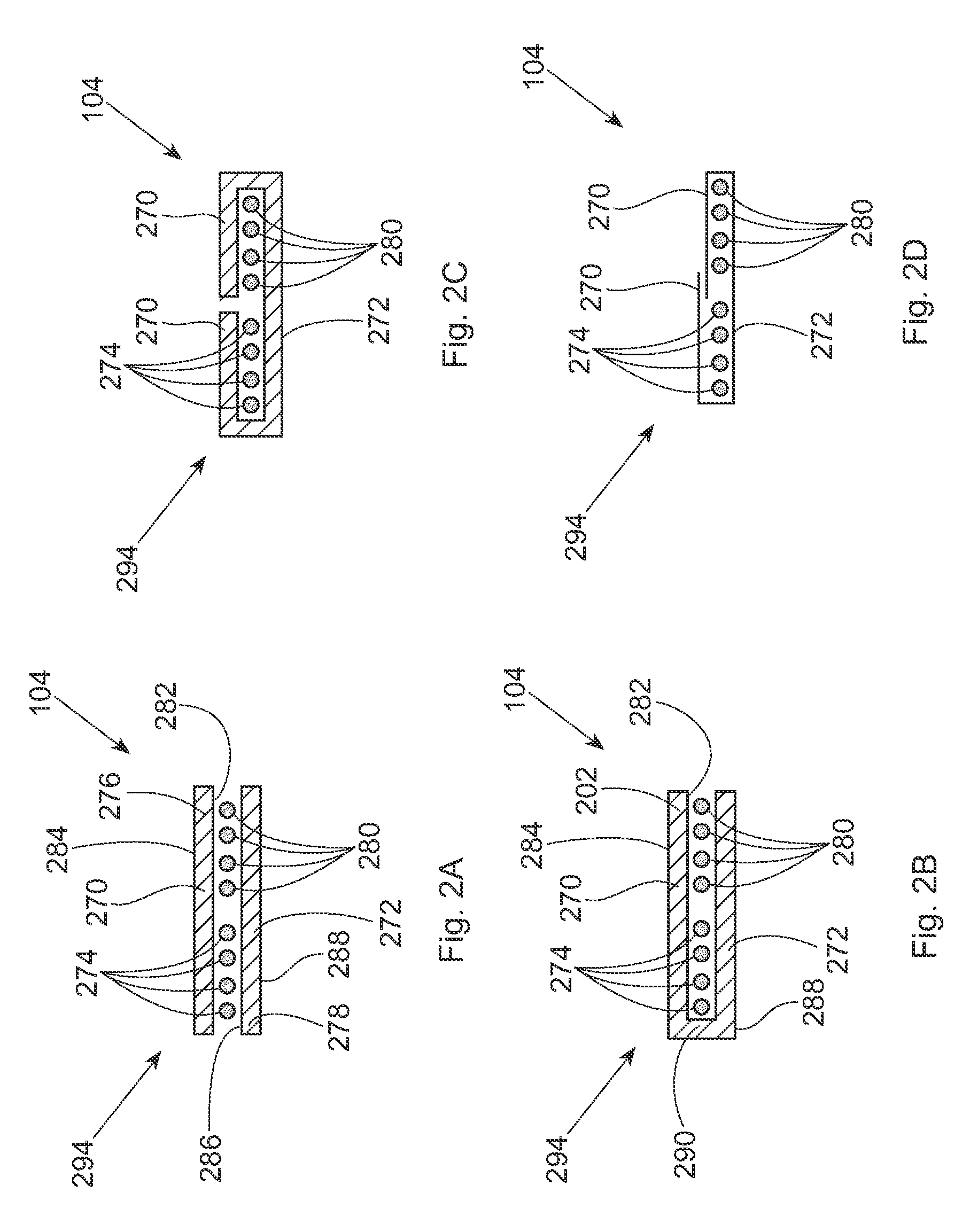
Artificial skin and elastic strain sensor
ActiveUS9841331B2High sensitivityImprove the immunityInput/output for user-computer interactionSolesElectrical resistance and conductanceElastic substrate
An elastic strain sensor can be incorporated into an artificial skin that can sense flexing by the underlying support structure of the skin to detect and track motion of the support structure. The uni-directional elastic strain sensor can be formed by filling two or more channels in an elastic substrate material with a conductive liquid. At the ends of the channels, a loop port connects the channels to form a serpentine channel. The channels extend along the direction of strain and the loop portions have sufficiently large cross-sectional area in the direction transverse to the direction of strain that the sensor is unidirectional. The resistance is measured at the ends of the serpentine channel and can be used to determine the strain on the sensor. Additional channels can be added to increase the sensitivity of the sensor. The sensors can be stacked on top of each other to increase the sensitivity of the sensor. In other embodiments, two sensors oriented in different directions can be stacked on top of each other and bonded together to form a bidirectional sensor. A third sensor formed by in the shape of a spiral or concentric rings can be stacked on top and used to sense contact or pressure, forming a three dimensional sensor. The three dimensional sensor can be incorporated into an artificial skin to provide advanced sensing.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Photoelectric integrated stretchable flexible neural electrode and preparation method
ActiveCN110367977AGuaranteed reliabilityLong-term implantationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElastic substrateEngineering
The invention provides a photoelectric integrated stretchable flexible neural electrode and a preparation method. The flexible neural electrode comprises a first elastic substrate, a photostimulationelectrode, a second elastic substrate and a recording electrode, and the photostimulation electrode and the recording electrode are both in snakelike curved wire arrangement structures. The lower surface of the photostimulation electrode is provided with a first silicon dioxide layer, and the photostimulation electrode is bonded to the surface of the first elastic substrate by strong chemical bonds generated in condensation reaction of the first silicon dioxide layer and the first elastic substrate. The upper surface of the photostimulation electrode is provided with the second elastic substrate, the lower surface of the recording electrode is provided with a second silicon dioxide layer, and the recording electrode is bonded to the surface of the second elastic substrate through strong chemical bonds generated in condensation reaction of the second silicon dioxide layer and the second elastic substrate, so that the recording electrode and the photostimulation electrode are integratedstructurally. The flexible neutral electrode is available for long-term implantation, high in flexibility and capable of bearing deformation influences of brain tissue expansion and shrinkage and thelike.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Stretchable coaxial fibrous friction electricity generating and sensing device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106787931AImprove output performanceImprove flexibilityMaterial nanotechnologyFriction generatorsMicro nanoElectricity
The invention belongs to the technical field of friction electricity generating and in particular relates to a stretchable coaxial fibrous friction electricity generating and sensing device and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: utilizing macromolecular materials of different dielectric constants as a friction electricity generating layer and an oriented carbon nanotube film as a charge inducing and collecting electrode; firstly swathing the oriented carbon nanotube film on a fibrous macromolecular elastic substrate to be taken as an inner-layer electrode, then sequentially constructing two macromolecular friction generating layers with micro-nano structures on the contact surfaces on the surface of the carbon nanotube film, then swathing a carbon nanotube film layer to be taken as an outer-layer electrode, and finally encapsulating, so that the stretchable coaxial fibrous friction electricity generating device is obtained. The device is simple in preparation process, has good flexibility and respectively can produce an electric signal under the actions of stretching, bending, compressing and twisting, so that mechanical energy in different directions and different forms in an external environment can be collected and converted into electric energy; and the device can be taken as a power supply for supplying power to wearable electronic equipment and also can be taken as a sensing device for detecting motion and physiological signals of a human body.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Preparation method and application of flexible stretchable sensing array based on bidirectional pre-stretching elastic substrate and aligned carbon nanotubes
ActiveCN107747957AEasy to prepareRealize large area preparationConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyEpoxyElastic substrate
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a flexible stretchable sensing array based on a bidirectional pre-stretching elastic substrate and aligned carbon nanotubes. The preparation method comprises the steps of tiling a column of carbon nanotube films on the bidirectional pre-stretching elastic substrate; then spraying a dielectric layer mixed solution, vertically tiling another column of carbon nanotube films, wherein the perpendicularly crossing portion of the nanotubes forms a capacitor, and the acquired capacitor is of a CNTs / dielectric layer / CNTs structure; spraying the mixed solution again to serve as a protection layer; releasing the elastic substrate to the initial state so as to form a complex folded structure; and finally fixing a sensing unit by using anepoxy resin adhesive to obtain a capacitive flexible stretchable sensing array.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV +1
Integrated turning force measuring tool system with embedded film sensors
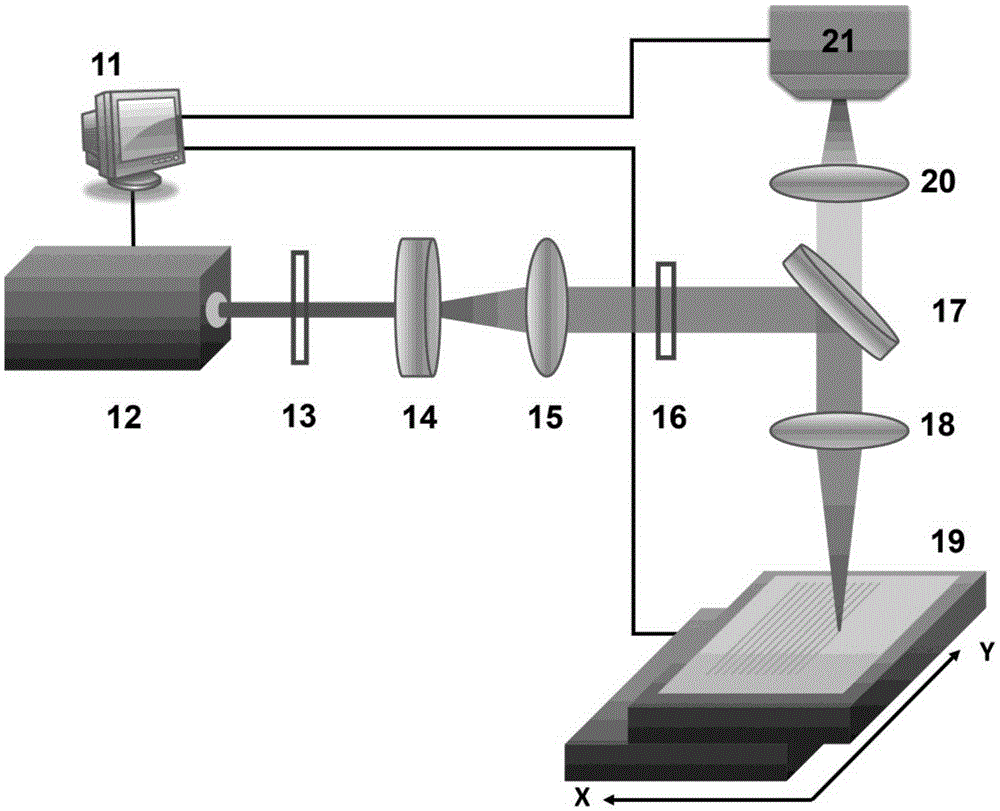
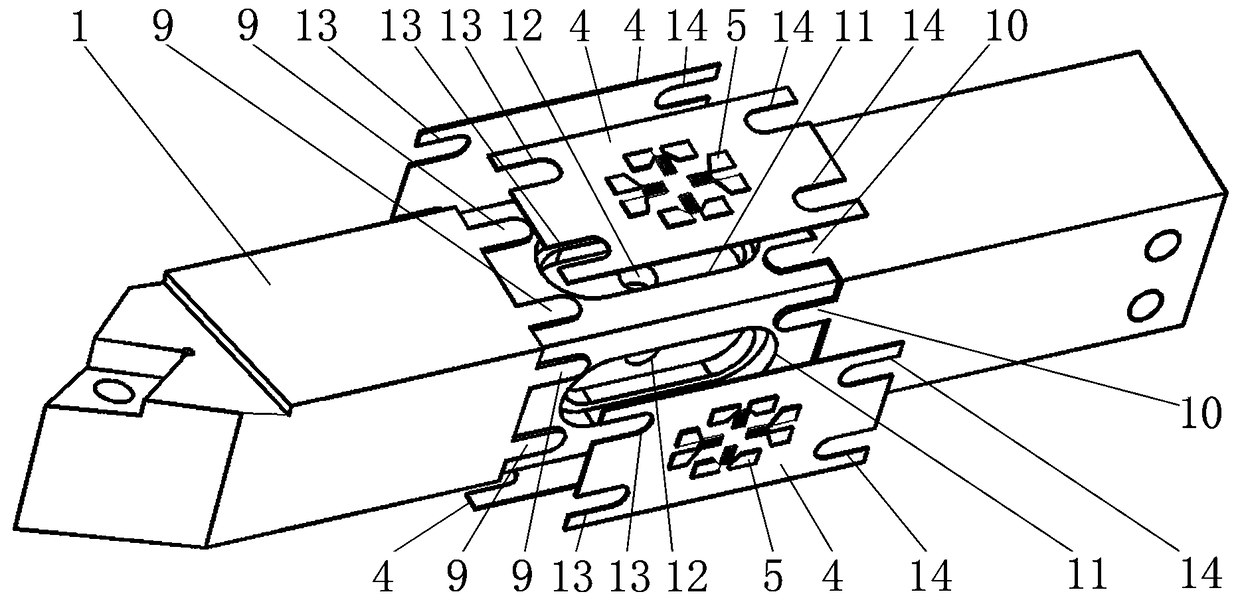
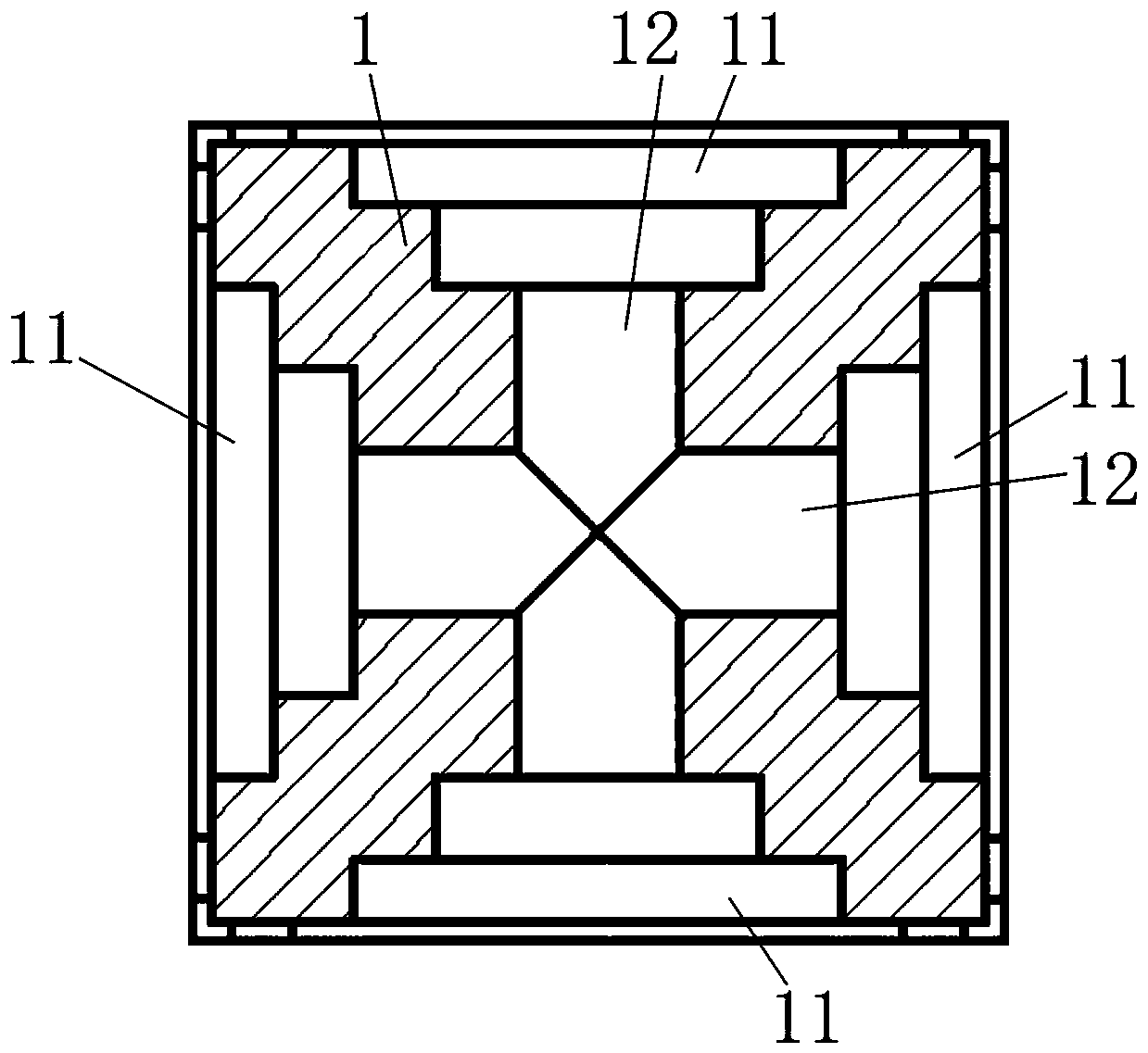
InactiveCN109175419AHigh measurement accuracyNo mutual interferenceAuxillary equipmentMeasurement/indication equipmentsThin film sensorElastic substrate
The invention relates to a turning force measuring technology in turning machining, in particular to an integrated turning force measuring tool system with embedded film sensors. The problems that anexisting turning force measuring technology is low in measuring precision and limited in application range are solved. The integrated turning force measuring tool system with the embedded film sensorscomprises a turning tool bar, a turning tool blade, a first sunk screw, square elastic substrates, the film sensors, a Wheatstone electrical bridge module, second sunk screws, a signal processing unit and a PC; the middles of the four side faces of the turning tool bar are each provided with a square positioning groove; a runway-shaped groove is formed in the center of the groove bottom of each square positioning groove; the four square elastic substrates are embedded into the four square positioning grooves respectively; and the four film sensors are arranged at the centers of the outer sidefaces of the four square elastic substrates in a magneto-sputtering deposition mode. The integrated turning force measuring tool system with the embedded film sensors is suitable for turning machining in various occasions (such as a laboratory and a production field).
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
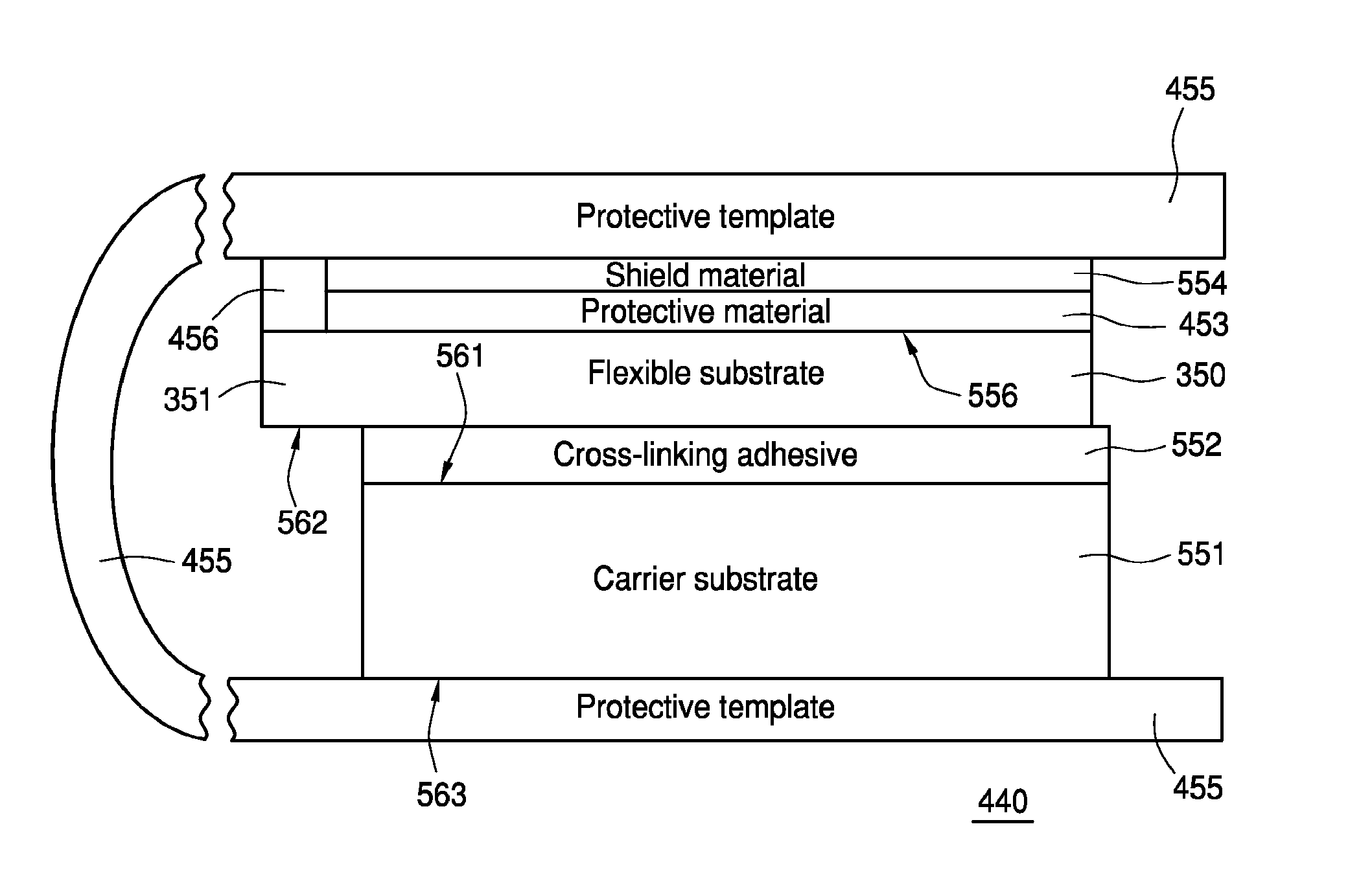
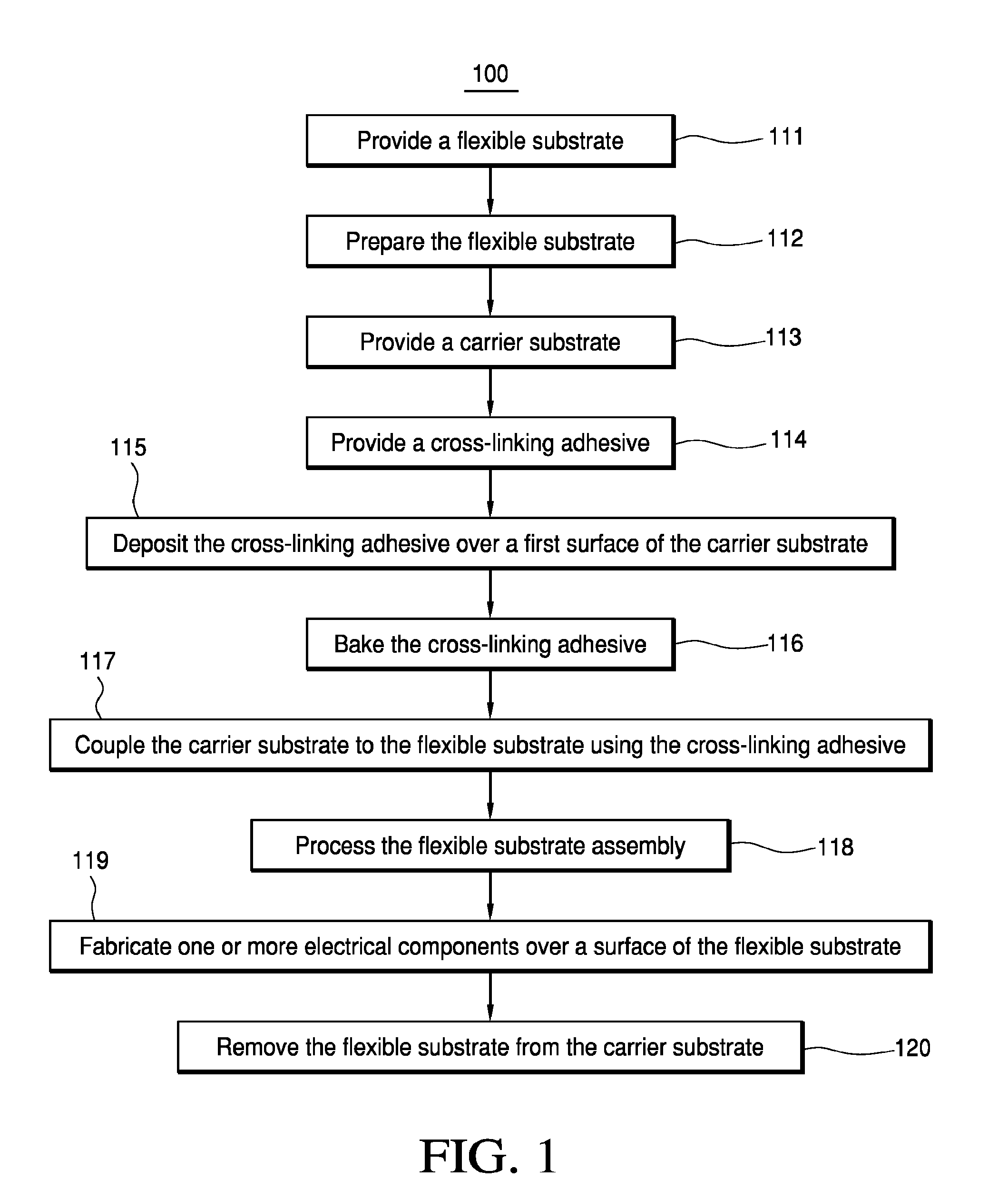
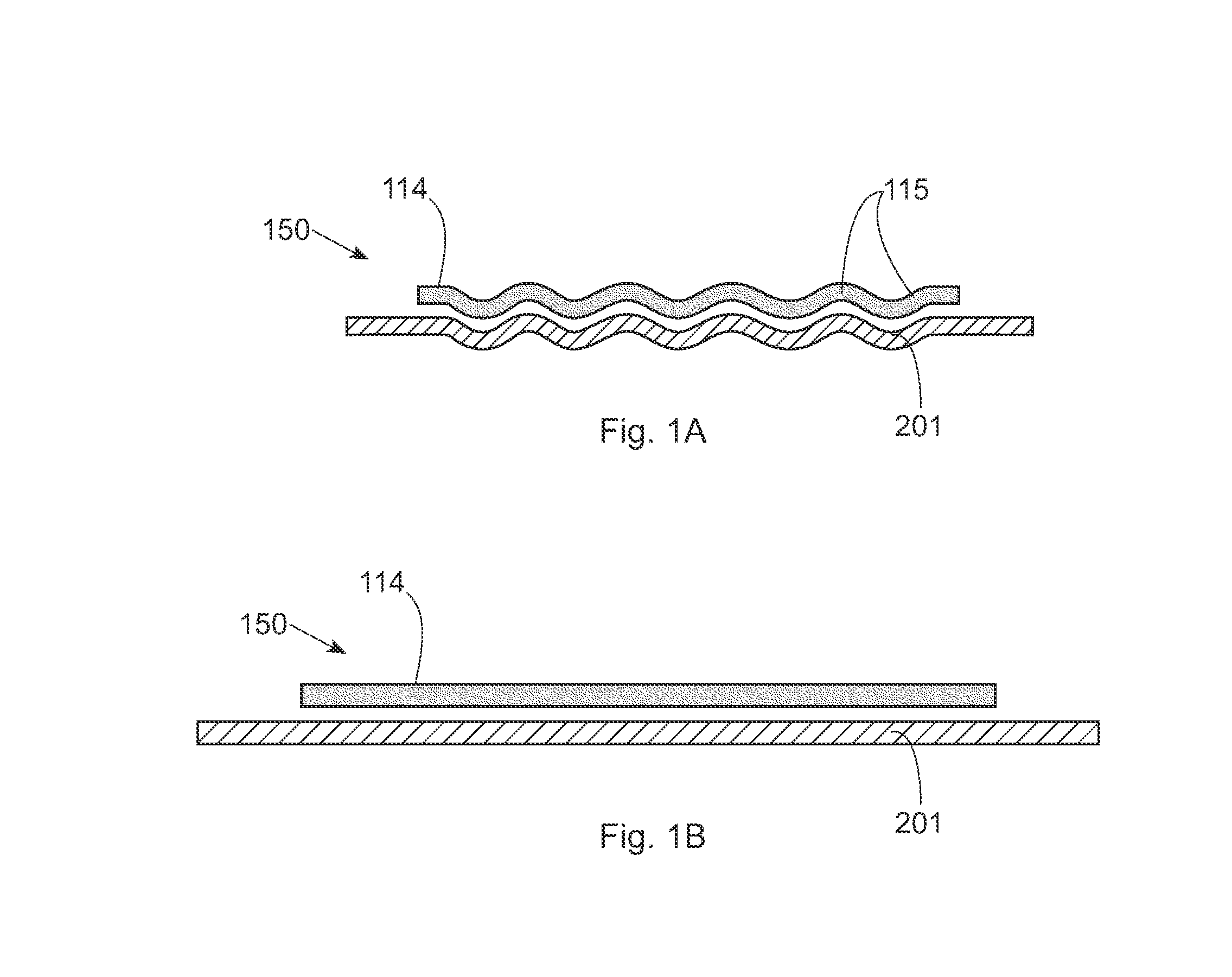
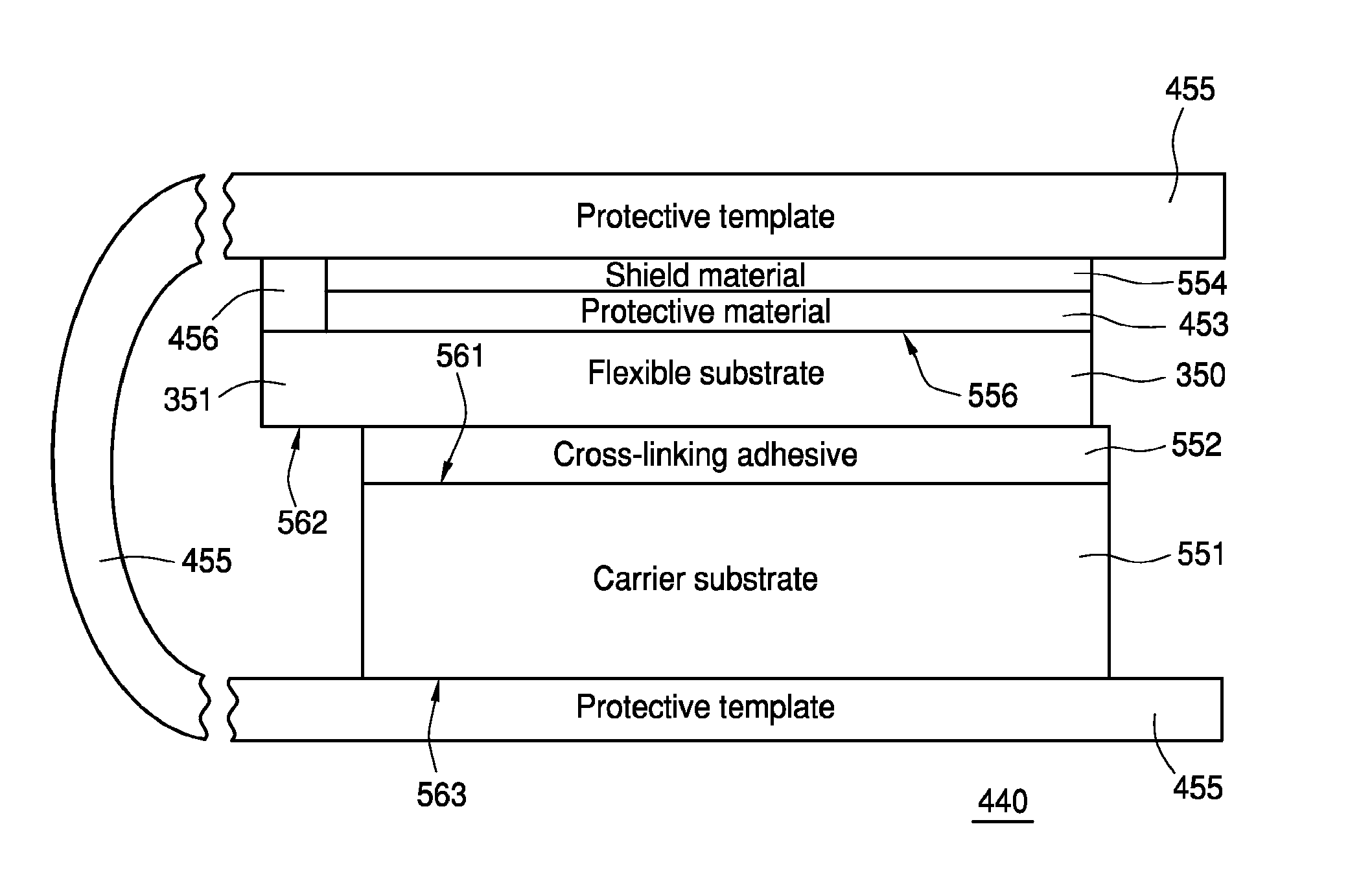
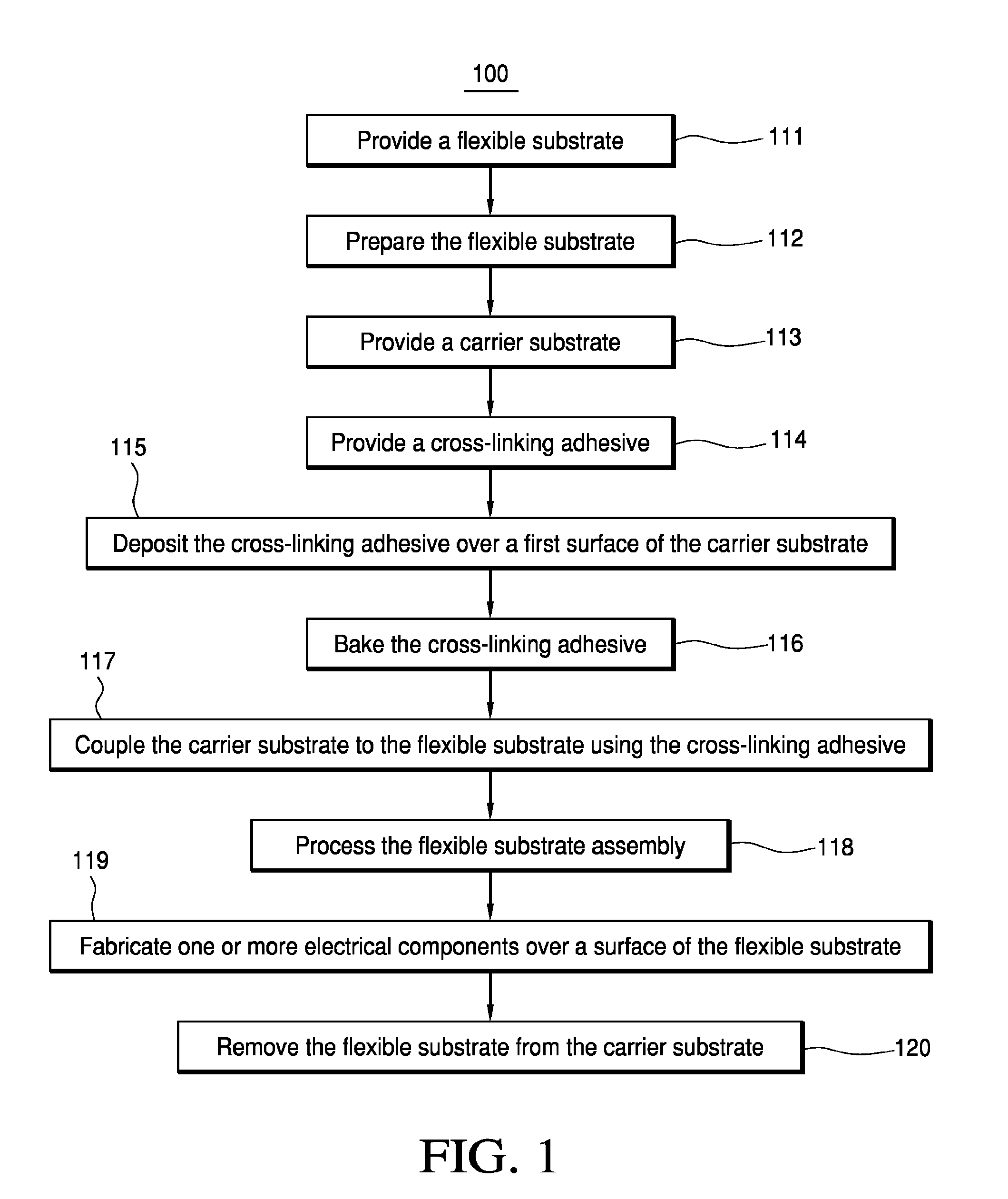
Method of preparing a flexible substrate assembly and flexible substrate assembly therefrom
Some embodiments teach a method of preparing a flexible substrate assembly. The method can include: (a) providing a carrier substrate; (b) providing a cross-linking adhesive; (c) providing a plastic substrate; and (d) coupling the carrier substrate to the plastic substrate using the cross-linking adhesive. Other embodiments are disclosed in this application.
Owner:ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS A BODY OF THE STATE OF ARIZONA ACTING FOR & ON BEHALF OF ARIZONA STATE UNIV SCOTTSDALE AZ
Preparation method of photocuring type superhydrophobic composite film
ActiveCN107226920ARapid preparation with superhydrophobic propertiesHas superhydrophobic propertiesCoatingsCross-linkComposite film
The invention discloses a preparation method of a photocuring type superhydrophobic composite film. The composite film comprises an elastic substrate and a surface superhydrophobic layer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing the elastic substrate: uniformly mixing a photoinitiator with a prepolymer, and carrying out ultraviolet irradiation on an obtained mixture to obtain a precured elastic substrate; secondly, preparing turbid liquid: uniformly dispersing a polymer with low surface energy, the photoinitiator, a cross-linking agent and micro and / or nano hydrophobic particles in a solvent to obtain the turbid liquid; thirdly, preparing the superhydrophobic composite film: coating the elastic substrate with the turbid liquid, and then carrying out ultraviolet irradiation curing treatment to obtain the composite film with superhydrophobicity. According to the superhydrophobic composite film prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the elastic substrate and the superhydrophobic layer are integrated by chemical crosslinking; the uperhydrophobic composite film has the advantages of simple preparation process, good friction resistance and tensile resistance, stable superhydrophobic effect and the like; the coating is not easy to fall off.
Owner:CHENGDU SCI & TECH DEV CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
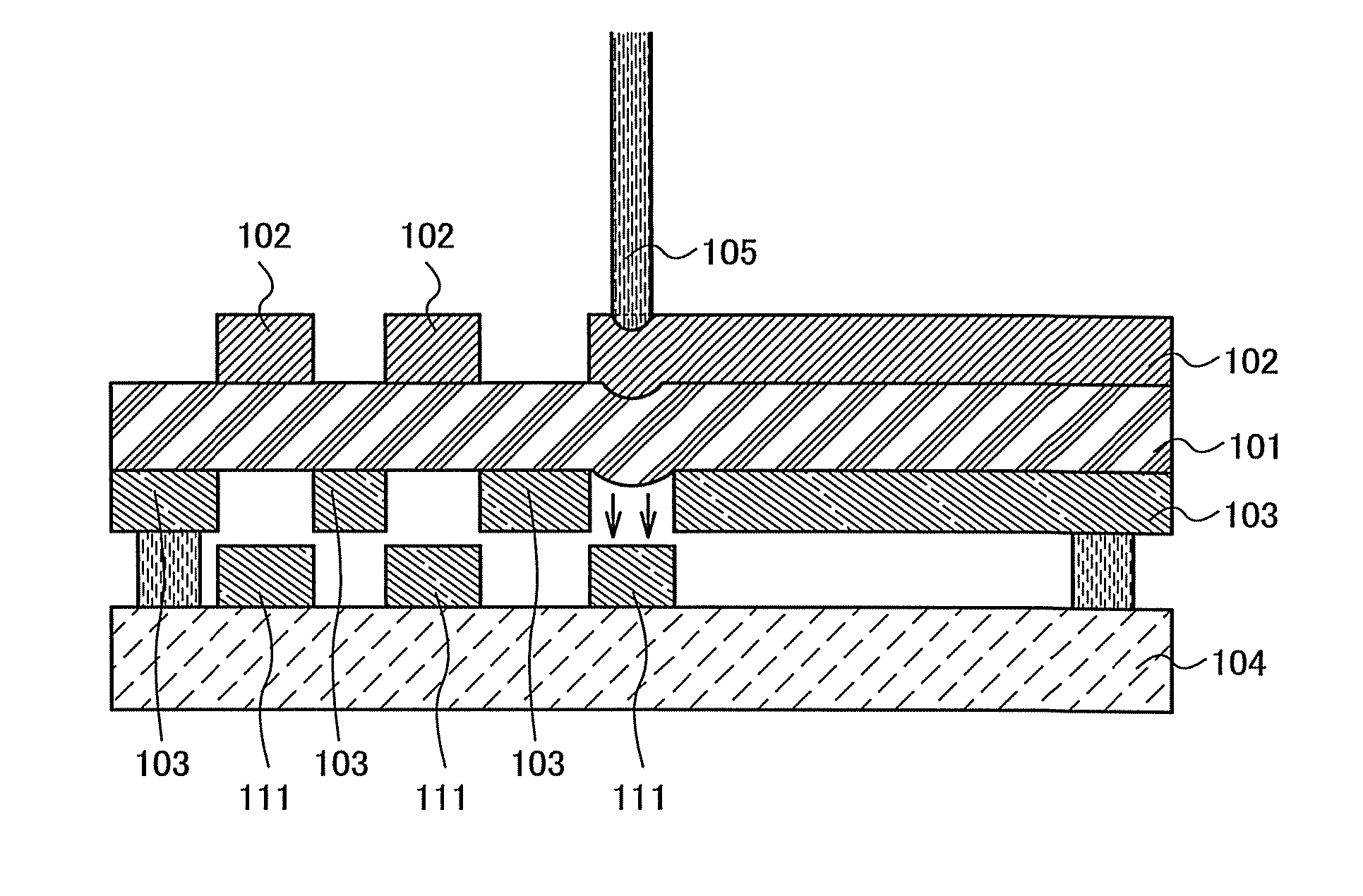
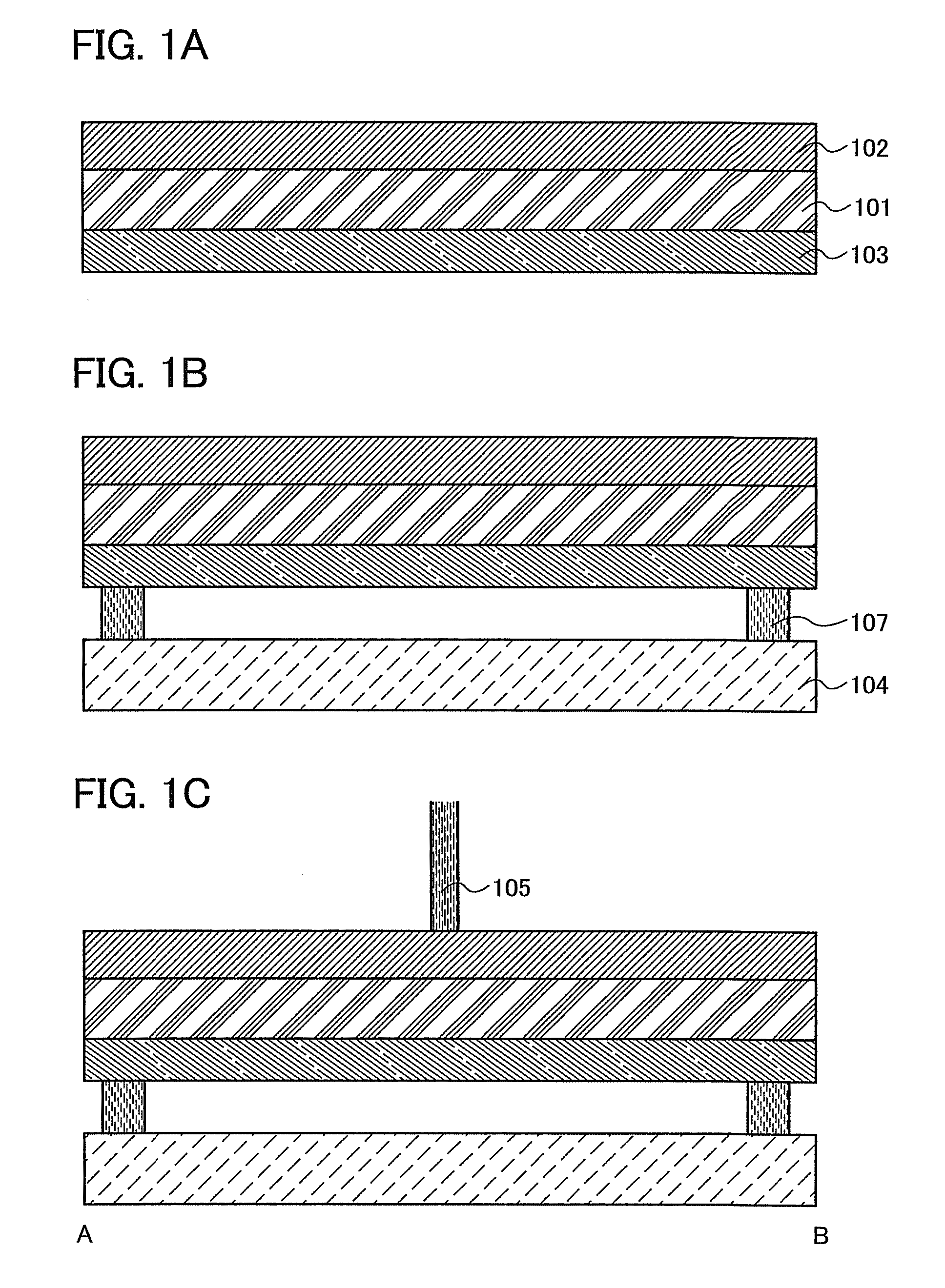
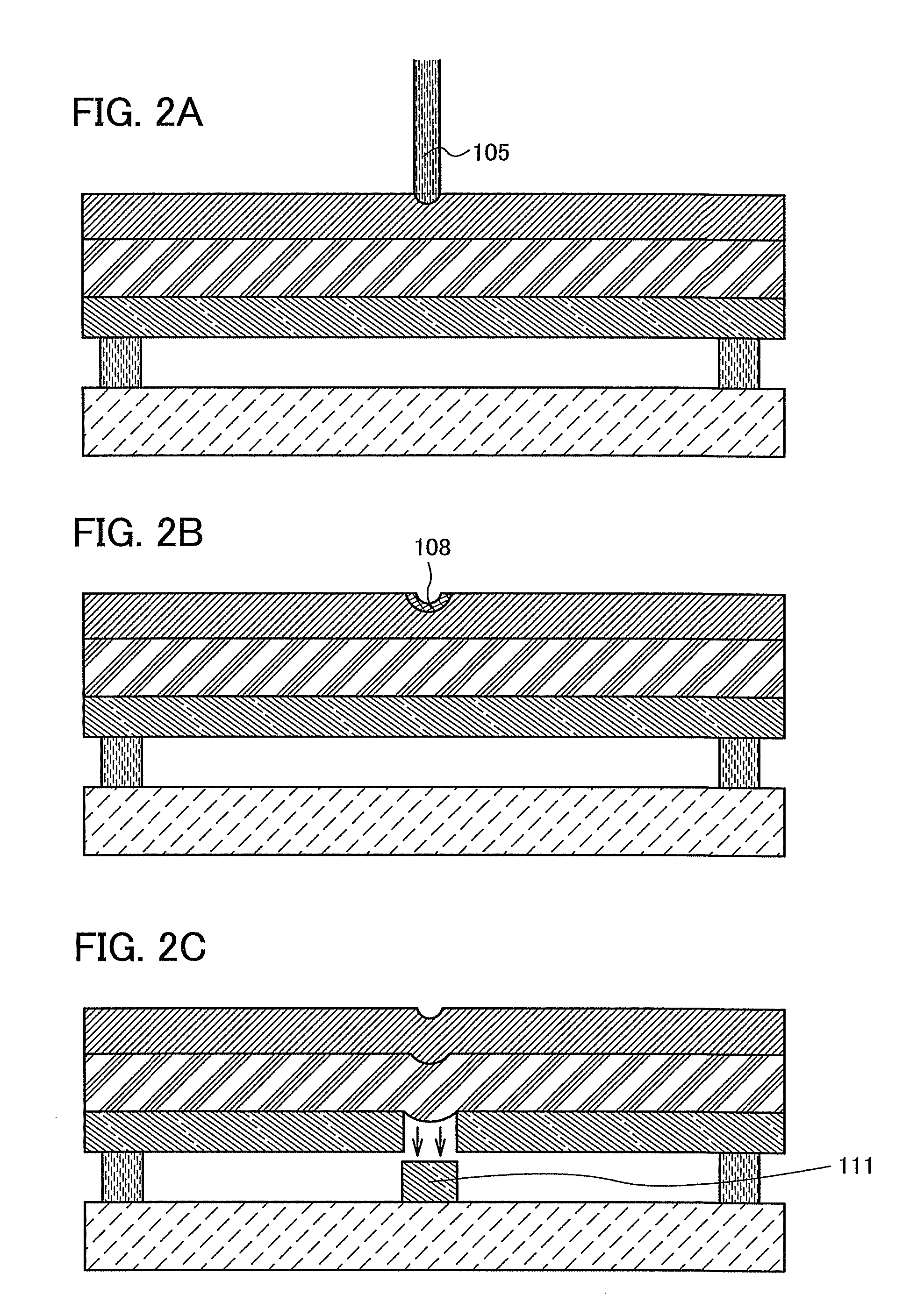
Film formation method and method for manufacturing light-emitting element
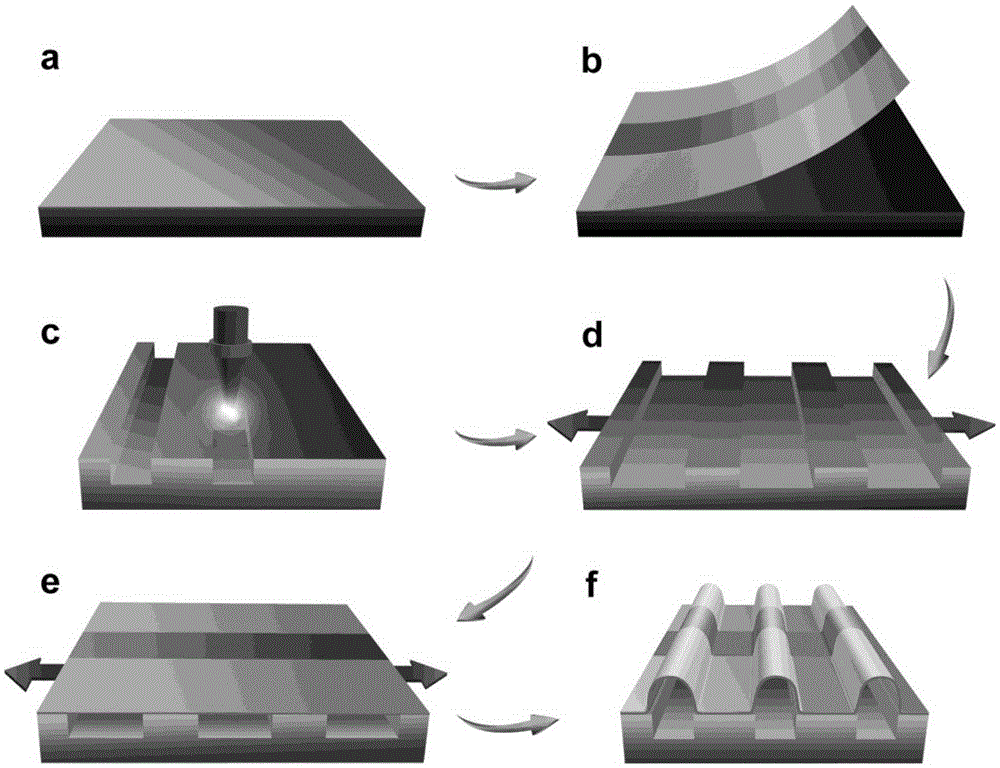
InactiveUS8383193B2Improve directivityUniform thicknessDiffusion transfer processesSolid-state devicesElastic substrateOptoelectronics
There is a problem in a method for forming an EL layer by heating with light and transferring an organic material in that the organic material is not uniformly transferred. The present invention relates to a film formation method including the steps of forming a metal film over a first surface of an elastic substrate; forming an organic material layer onto a second surface of the elastic substrate which is opposite to the first surface; placing the second surface of the elastic substrate and a substrate on which a film is to be formed, with a space between the second surface of the elastic substrate and the substrate on which a film is to be formed; heating locally and rapidly the metal film from a first surface side of the elastic substrate to deform the elastic substrate by expansion of the metal film; and transferring the organic material layer from the elastic substrate onto the substrate on which a film is to be formed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
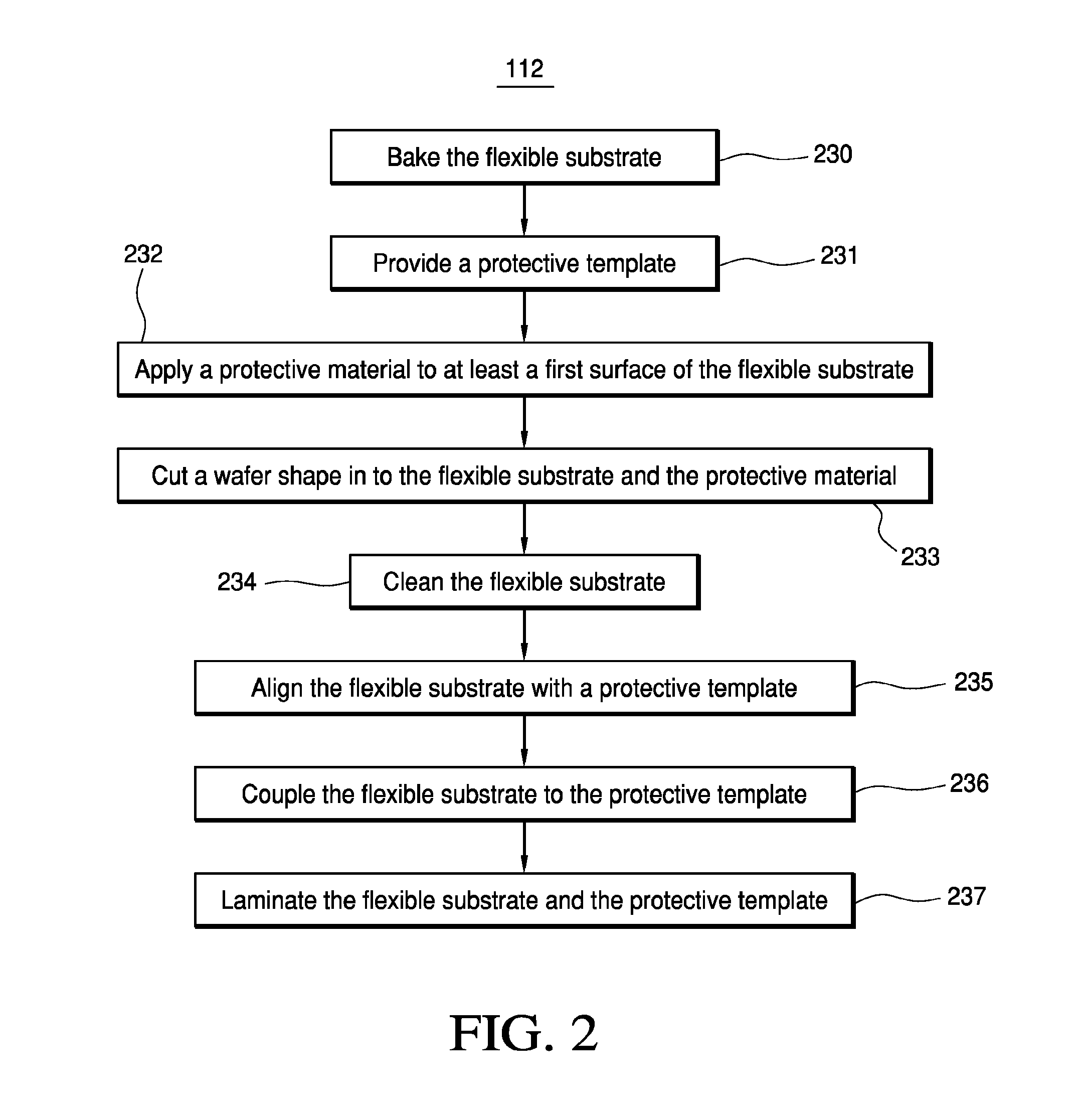
Apparatus and Method for Making a Layered Elastic Substrate
A method for making a layered elastic substrate includes advancing a first substrate layer and a second substrate layer in a machine direction. An elastic material is advanced in the machine direction in a stretched state. The elastic material may be bonded to the first substrate layer and the second substrate layer in a stretched state to form a layered elastic substrate. The layered elastic substrate may advance through a first metering device at speed, V1, and through a second metering device at speed, V2, subsequent to advancing through the first metering device, wherein V1 is greater than V2. As a result, the elastic material, and thus the layered elastic substrate, may be stretched to a first elongation at the first metering device and relaxed to a second elongation at the second device. The layered elastic substrate is cut and bonded to a continuous length of web material.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method of preparing a flexible substrate assembly and flexible substrate assembly therefrom
Some embodiments teach a method of preparing a flexible substrate assembly. The method can include: (a) providing a carrier substrate; (b) providing a cross-linking adhesive; (c) providing a plastic substrate; and (d) coupling the carrier substrate to the plastic substrate using the cross-linking adhesive. Other embodiments are disclosed in this application.
Owner:ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS A BODY OF THE STATE OF ARIZONA ACTING FOR & ON BEHALF OF ARIZONA STATE UNIV SCOTTSDALE AZ
Hopkinson press rod system with true triaxial dynamic loading and testing functions and method
ActiveCN108548942AControl amplitudeControl pulse widthTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesAccelerometerElastic substrate
The invention relates to a Hopkinson press rod system with true triaxial dynamic loading and testing functions and a method. By using a true triaxial Hopkinson rod device, and imposing a controllablesingle-shaft impact overload on a fixed substrate (basis) of a triaxial high g value accelerometer, by use of the Poisson effect of an elastic substrate, synchronous overload is generated in other twovertical (auxiliary axes Y and Z) directions which are perpendicular to the loading (main axis X) direction. Based on a triaxial direction elastic rod, the accelerator triaxial g value response is acquired, so it is achieved that dynamic calibration is simultaneously performed on the triaxial high g value accelerometer in three orthogonal directions. The beneficial effects are that the Hopkinsonpress rod system is not only an excitation signal generator, but also a signal acquirer. Thus, a complex decoupling structure can be avoided; simultaneous loading in three directions can be achieved;single-axis or bi-axis dynamic characteristic calibration can be performed; and the system is widely applicable, simple in operation, high in repeatability and high in measurement precision.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Strain sensor, forming method thereof, strain sensor array and forming method thereof
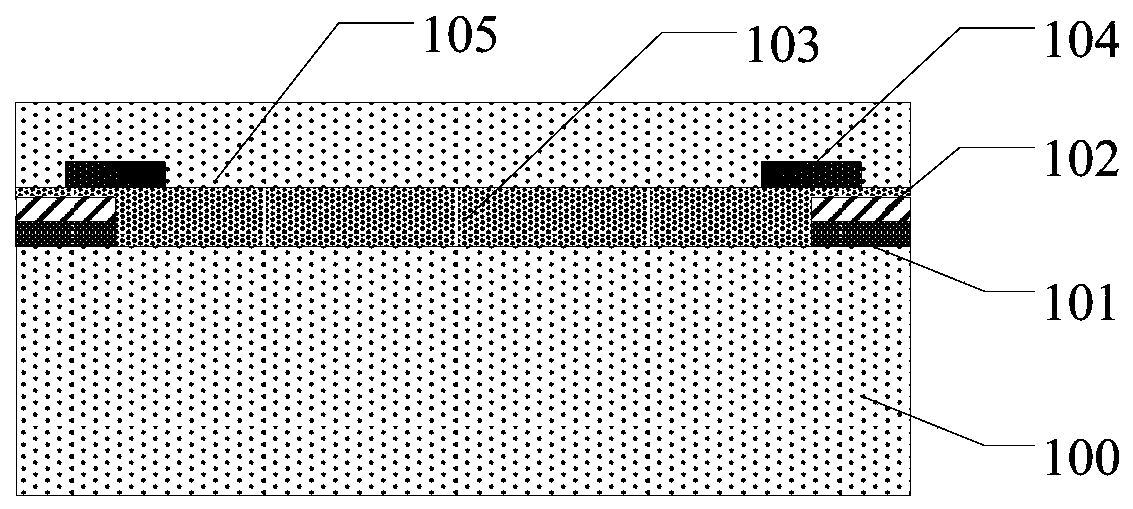
ActiveCN109839232ADoes not affect the readout resultImprove stabilityForce measurementElastic substrateEngineering
The invention provides a strain sensor, a forming method thereof, a strain sensor array and a forming method thereof. The strain sensor comprises an elastic substrate, a sensitive film located on thesurface of partial elastic substrate, and electrodes which are located on the surface of the elastic substrate and are connected with both ends of the sensitive film. A plasticized layer is formed between each electrode and the elastic substrate. The performance of the strain sensor is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com