Patents
Literature
31results about How to "Avoid optical damage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
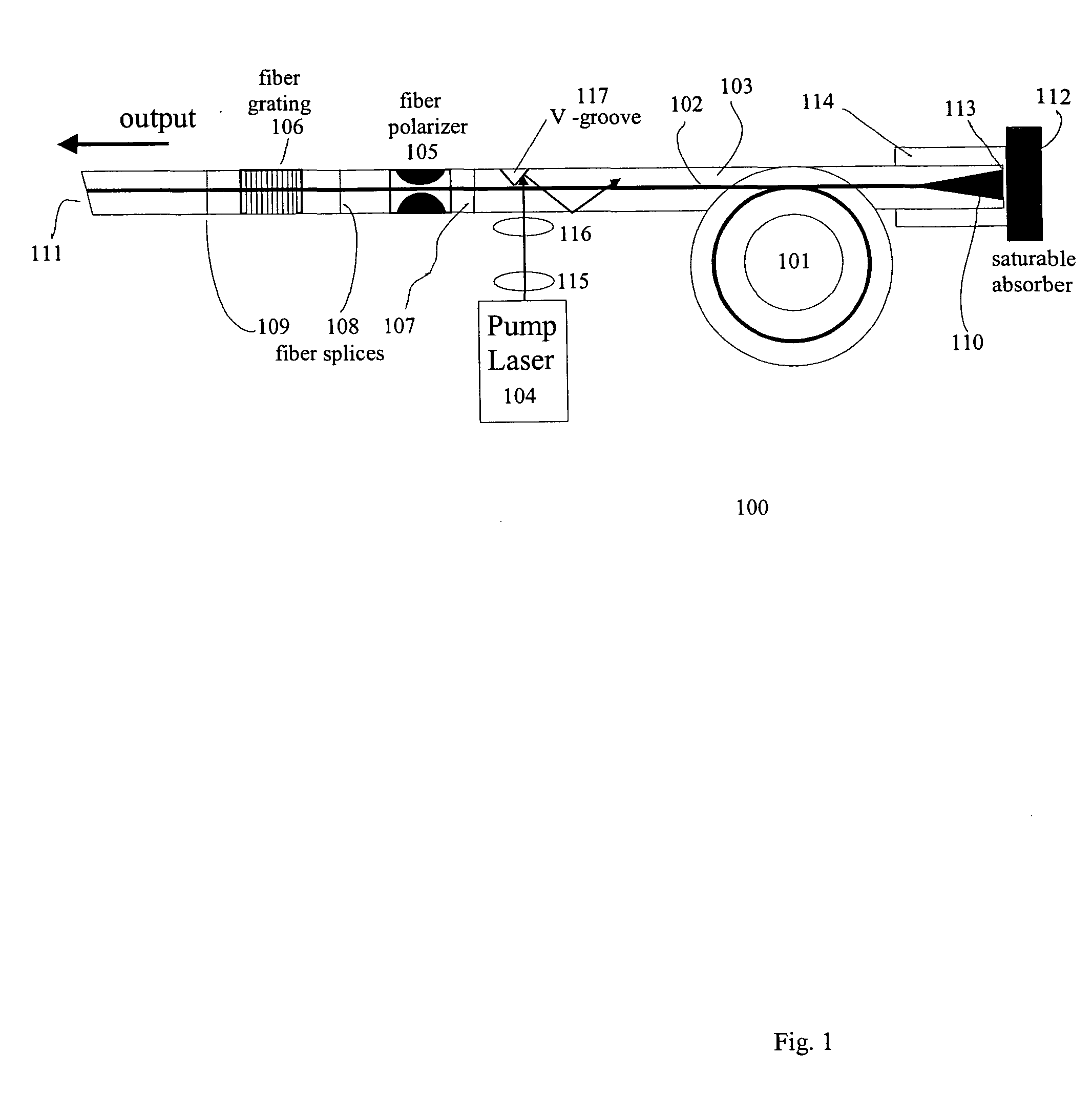
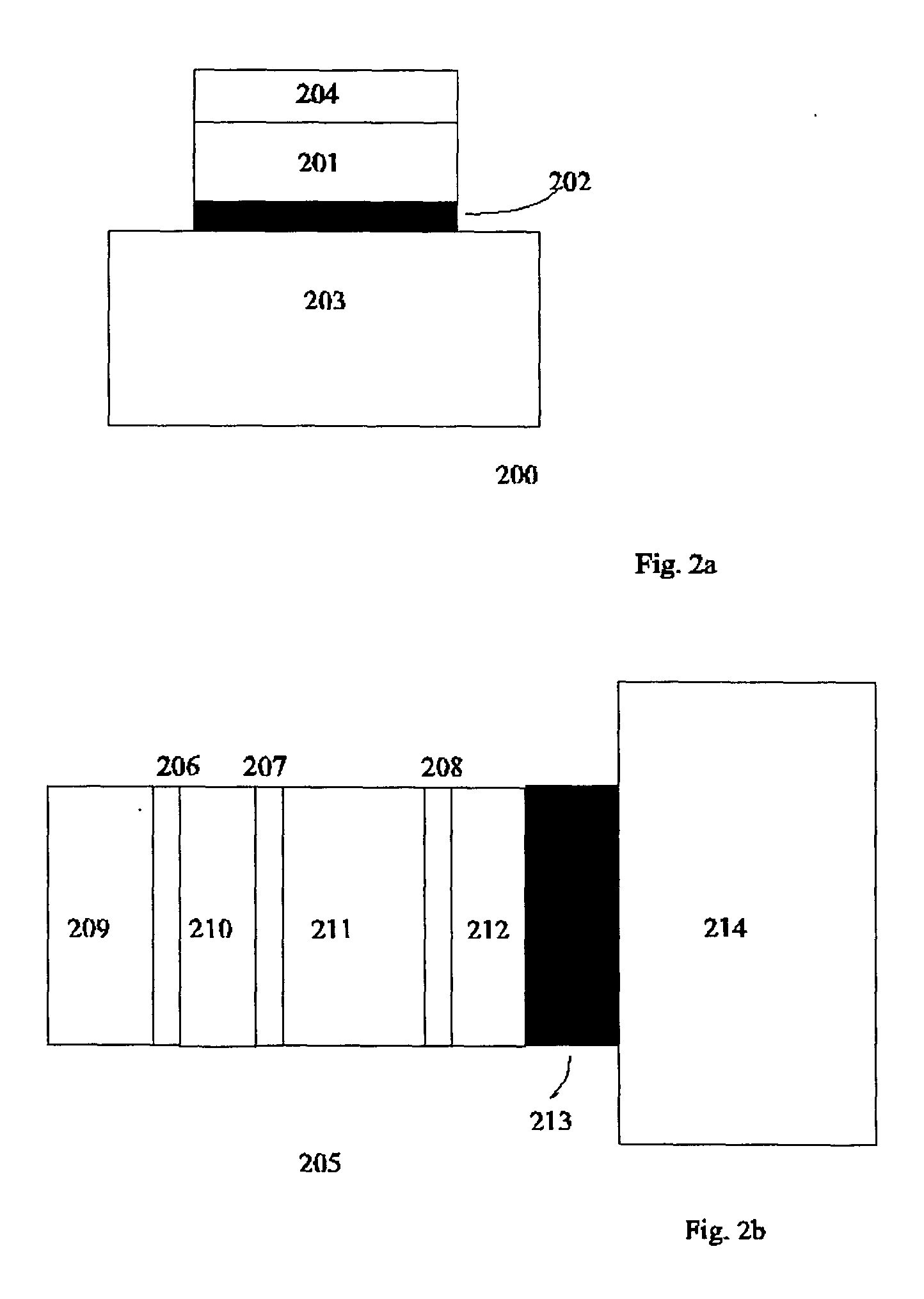
Polarization maintaining dispersion controlled fiber laser source of ultrashort pulses
InactiveUS7088756B2Easy to makeRelatively large bandwidthLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingFiber Bragg grating
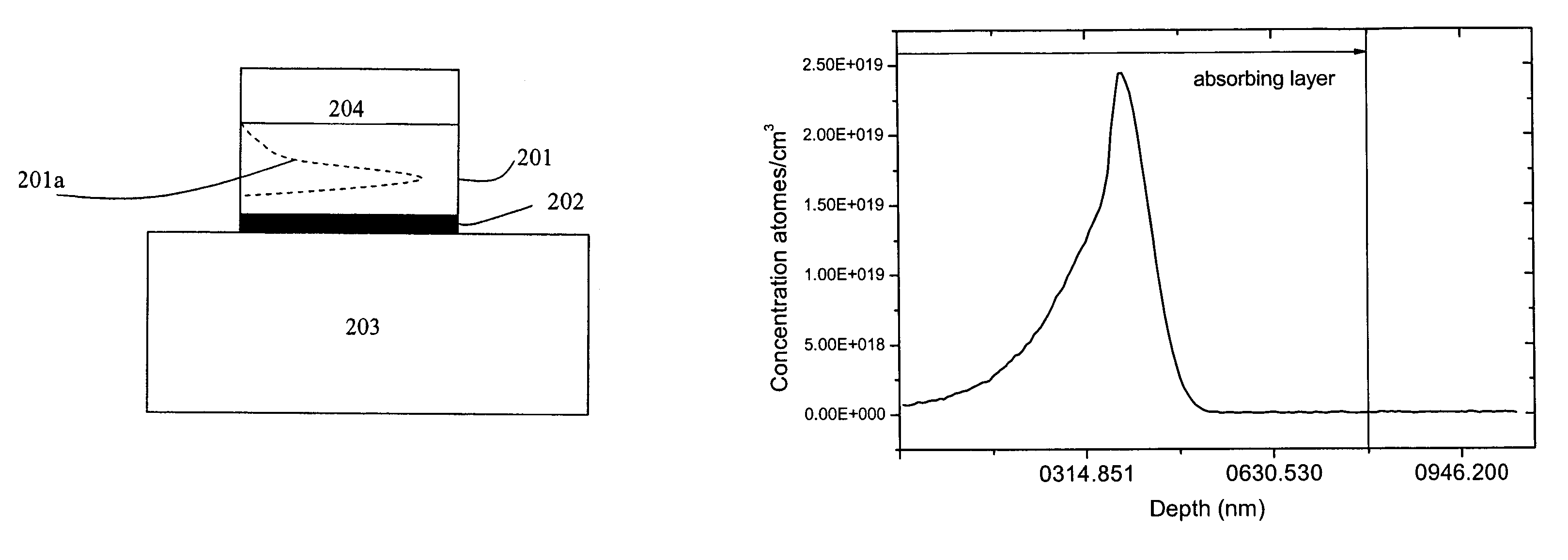
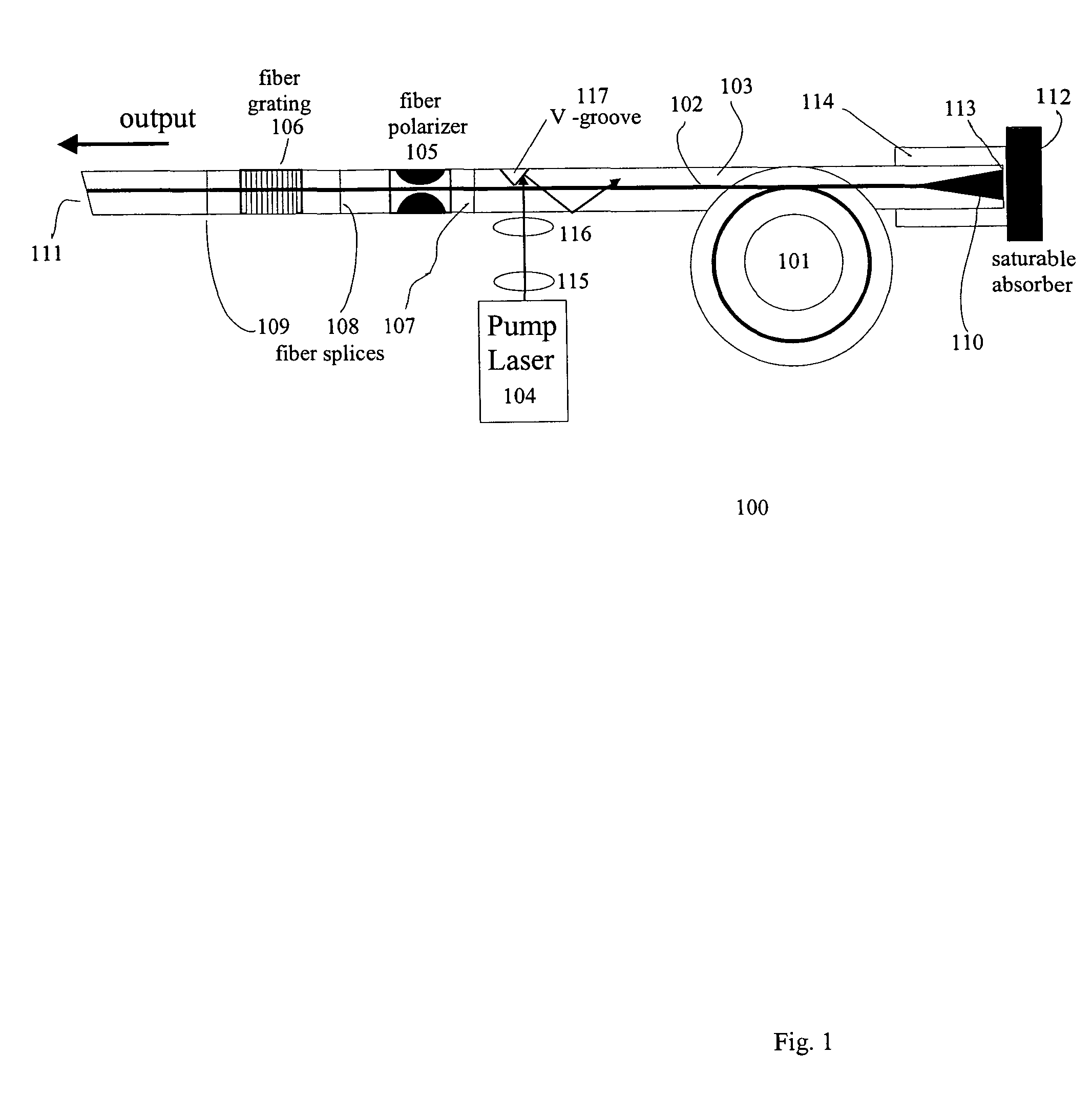
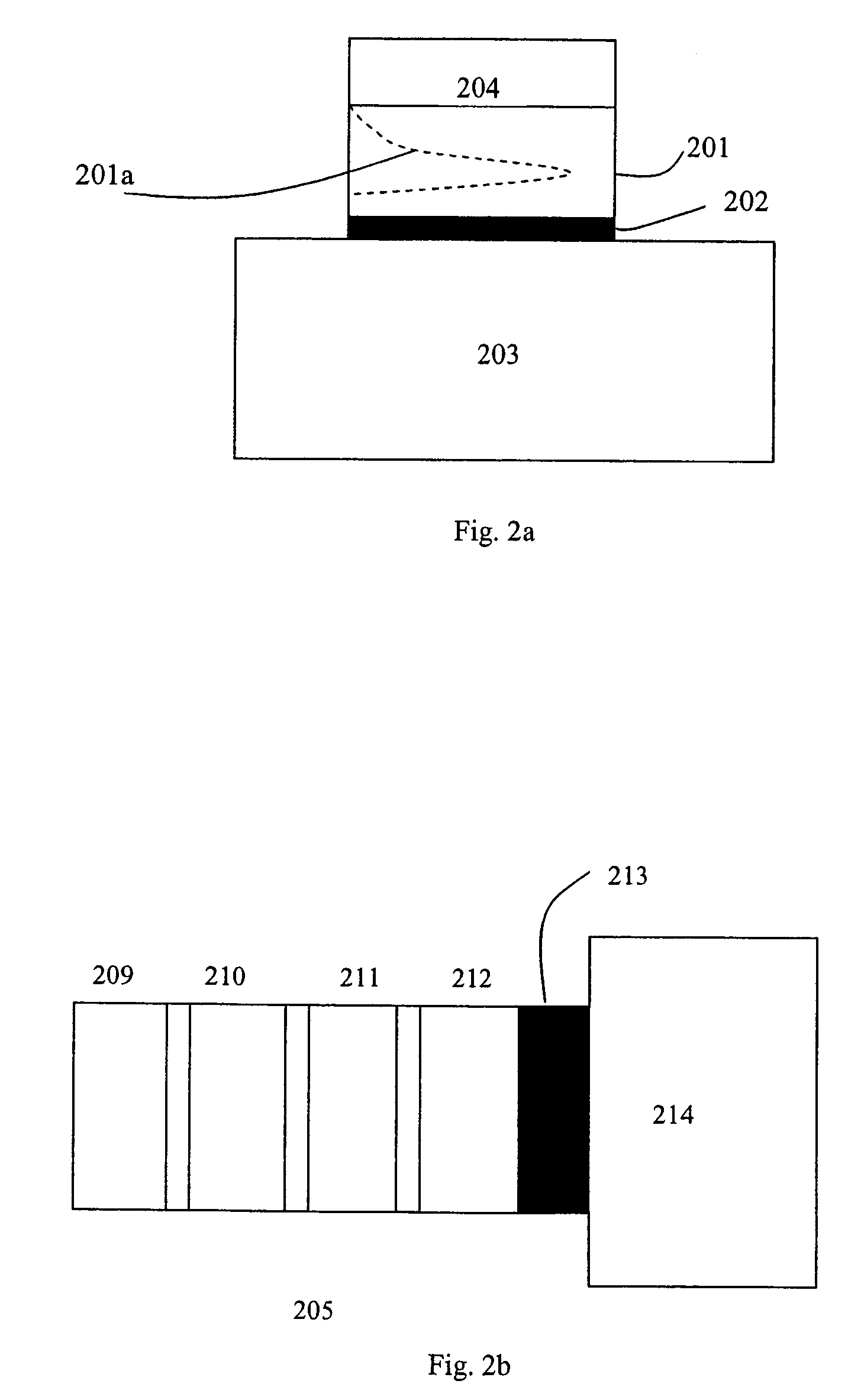
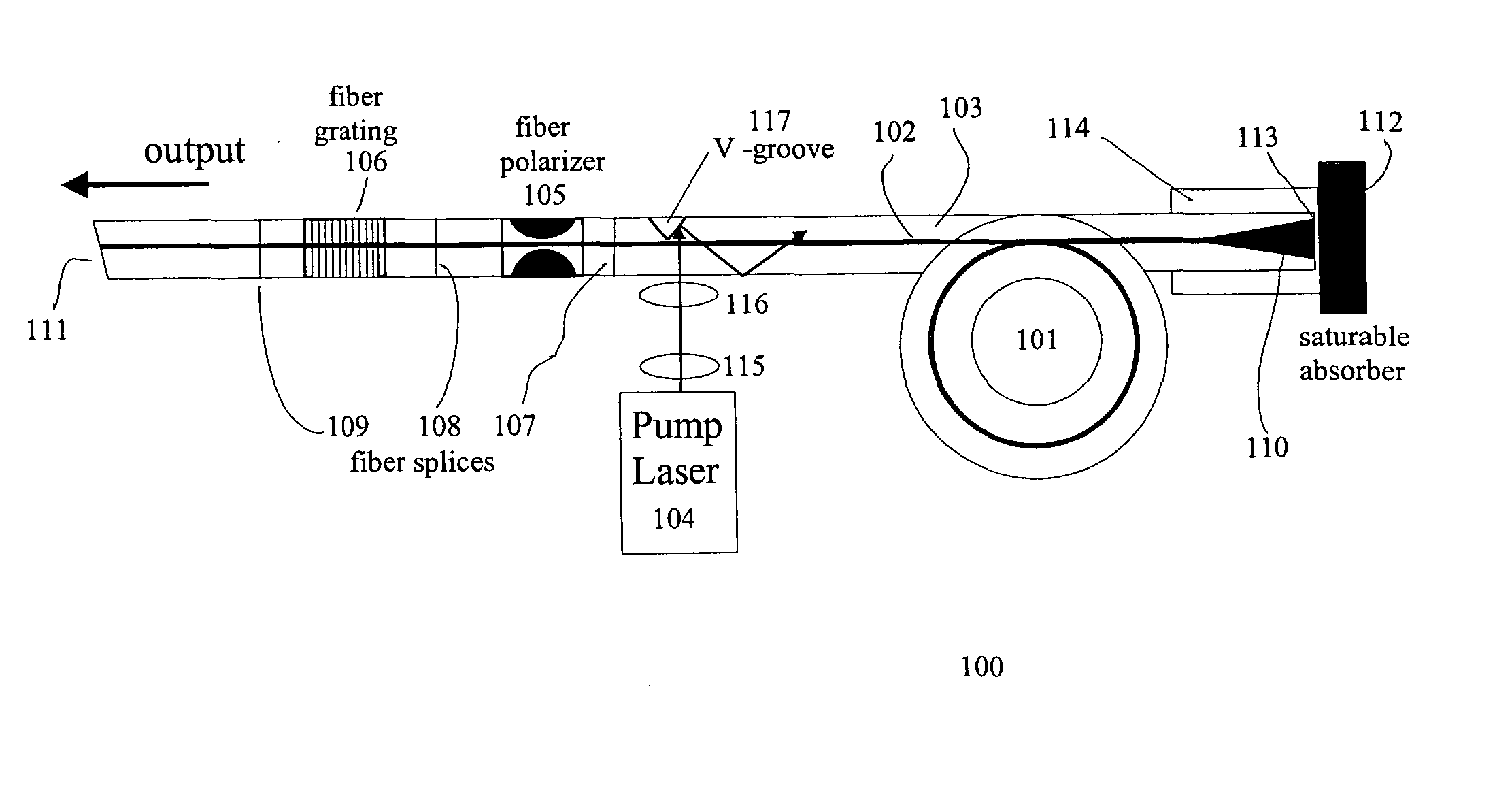
A modelocked linear fiber laser cavity with enhanced pulse-width control includes concatenated sections of both polarization-maintaining and non-polarization-maintaining fibers. Apodized fiber Bragg gratings and integrated fiber polarizers are included in the cavity to assist in linearly polarizing the output of the cavity. Very short pulses with a large optical bandwidth are obtained by matching the dispersion value of the fiber Bragg grating to the inverse of the dispersion of the intra-cavity fiber.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Polarization maintaining dispersion controlled fiber laser source of ultrashort pulses
InactiveUS20050018714A1Easy to makeRelatively large bandwidthLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionFiber chromatic dispersionGrating
A modelocked linear fiber laser cavity with enhanced pulse-width control includes concatenated sections of both polarization-maintaining and non-polarization-maintaining fibers. Apodized fiber Bragg gratings and integrated fiber polarizers are included in the cavity to assist in linearly polarizing the output of the cavity. Very short pulses with a large optical bandwidth are obtained by matching the dispersion value of the fiber Bragg grating to the inverse of the dispersion of the intra-cavity fiber.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
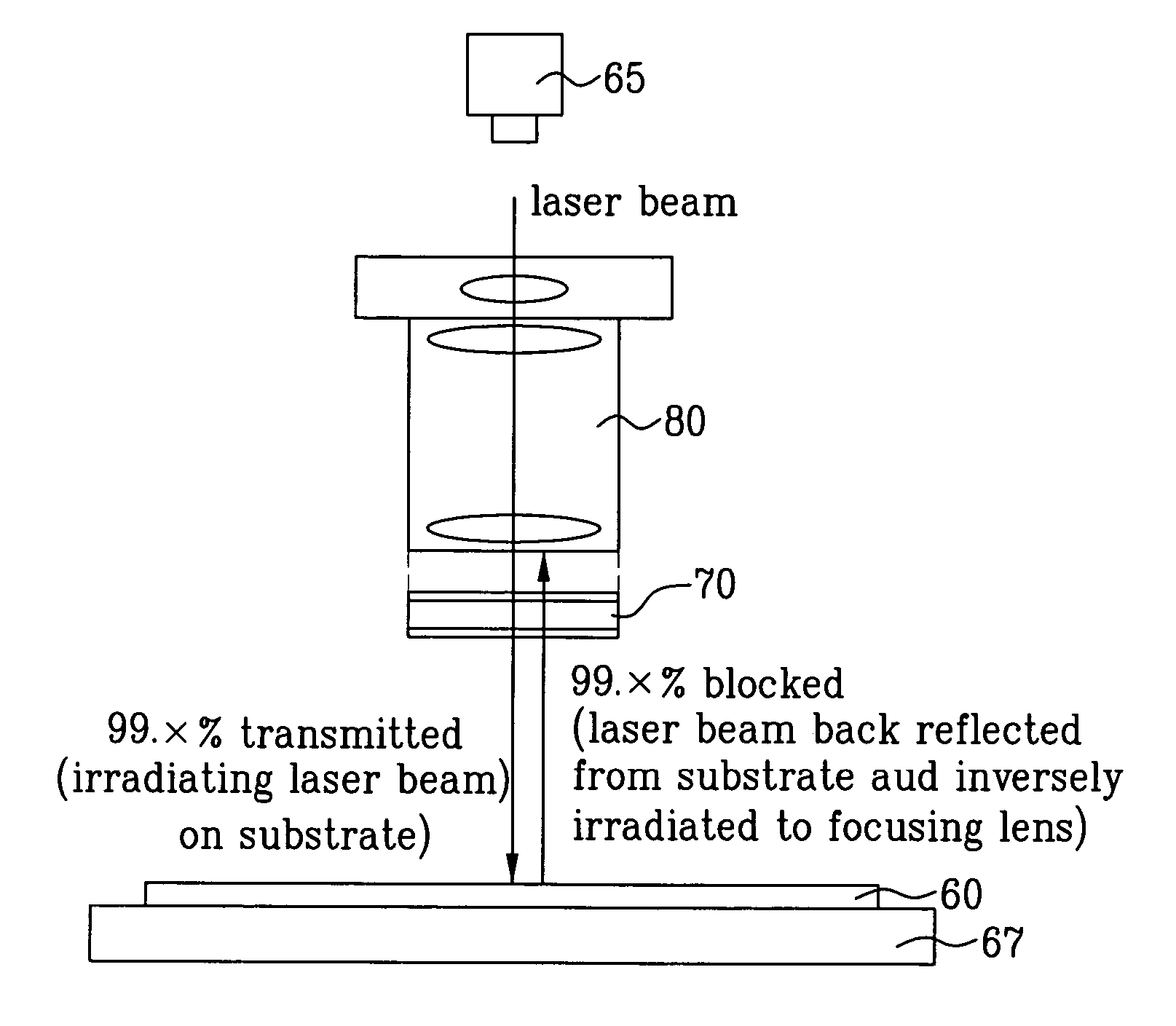
Sequential lateral solidification device
ActiveUS7326876B2Improving optical characteristicPrevent optical damageBy zone-melting liquidsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysicsLaser light
A sequential lateral solidification device, for enhancing optical characteristics of the device and for preventing damage caused by an ablation of a crystallization thin film, is disclosed. The device includes a laser light source generating a laser beam, a projection lens focusing the laser beam generated from the laser light source onto a substrate, a laser beam splitter between the projection lens and the substrate that passes the laser beam generated from the laser light source to irradiate the substrate and that blocks the laser beam reflected back from the substrate towards the projection lens, and a stage having the substrate mounted thereon.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Stable solid state raman laser and a method of operating same
InactiveUS6901084B2Avoid optical damageCavity stabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionResonant cavitySolid mass
The present invention relates to a stable solid-state Raman laser, the solid-state Raman laser including a resonator cavity defined by at least two reflectors, a laser material located in the resonator cavity and capable of generating a cavity laser beam which propagates within the resonator cavity, a solid Raman medium located in the resonator cavity for shifting the frequency of the cavity laser beam to produce a Raman laser beam which propagates within the resonator cavity; and an output coupler for coupling and outputting the Raman laser beam from the resonator cavity, wherein at least one parameter selected from the group consisting of the position of the laser material relative to the position of the Raman medium in the cavity, the length of the cavity and the curvature of at least one of the reflectors, is selected such that changes in the focal lengths of both the laser material and the Raman medium as a result of thermal effects in the laser material and the Raman medium during operation of the laser do not substantially cause instability in the power of the output Raman laser beam. A method of maintaining stable operation of a solid state Raman laser is also described.
Owner:MACQUARIE UNIV
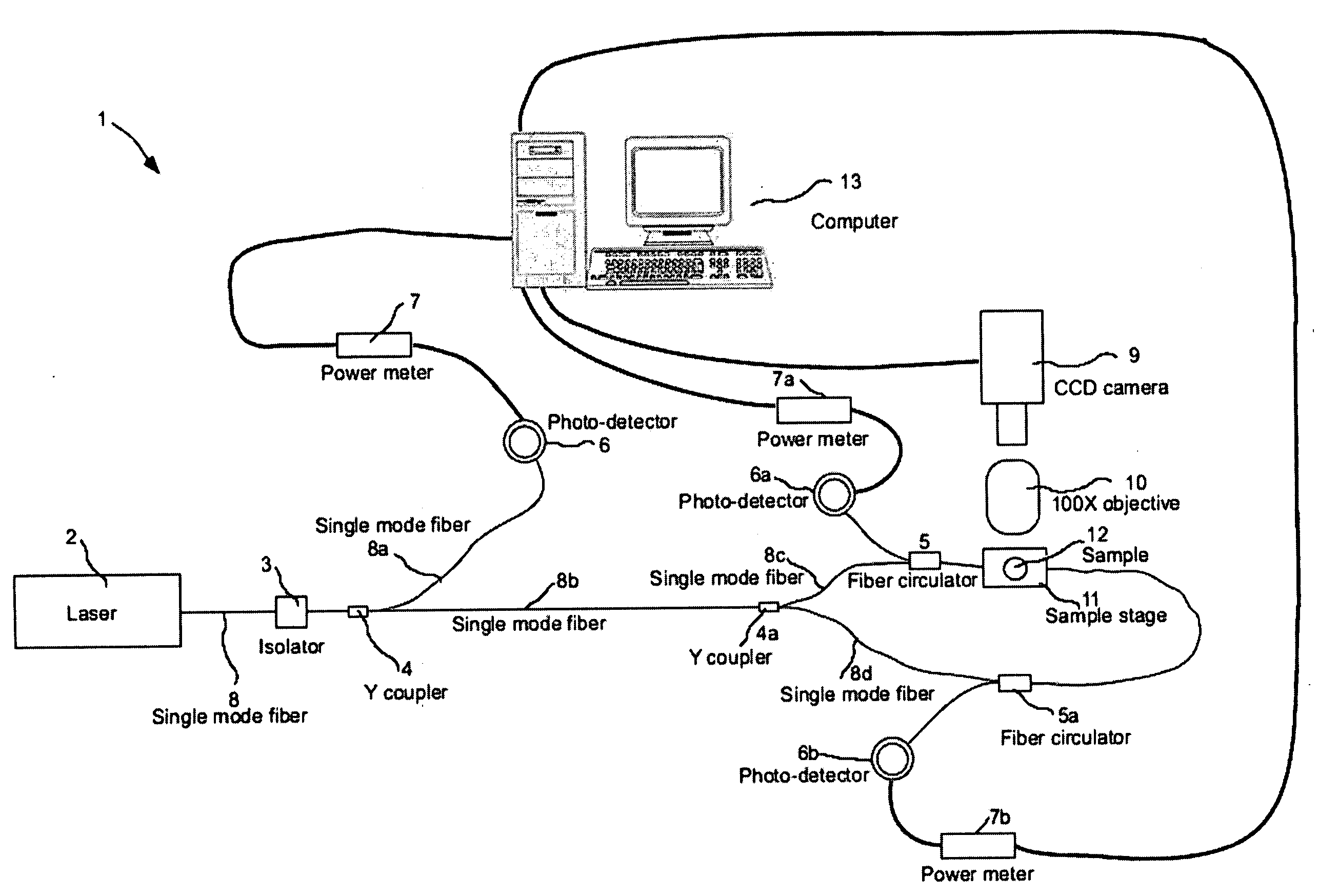
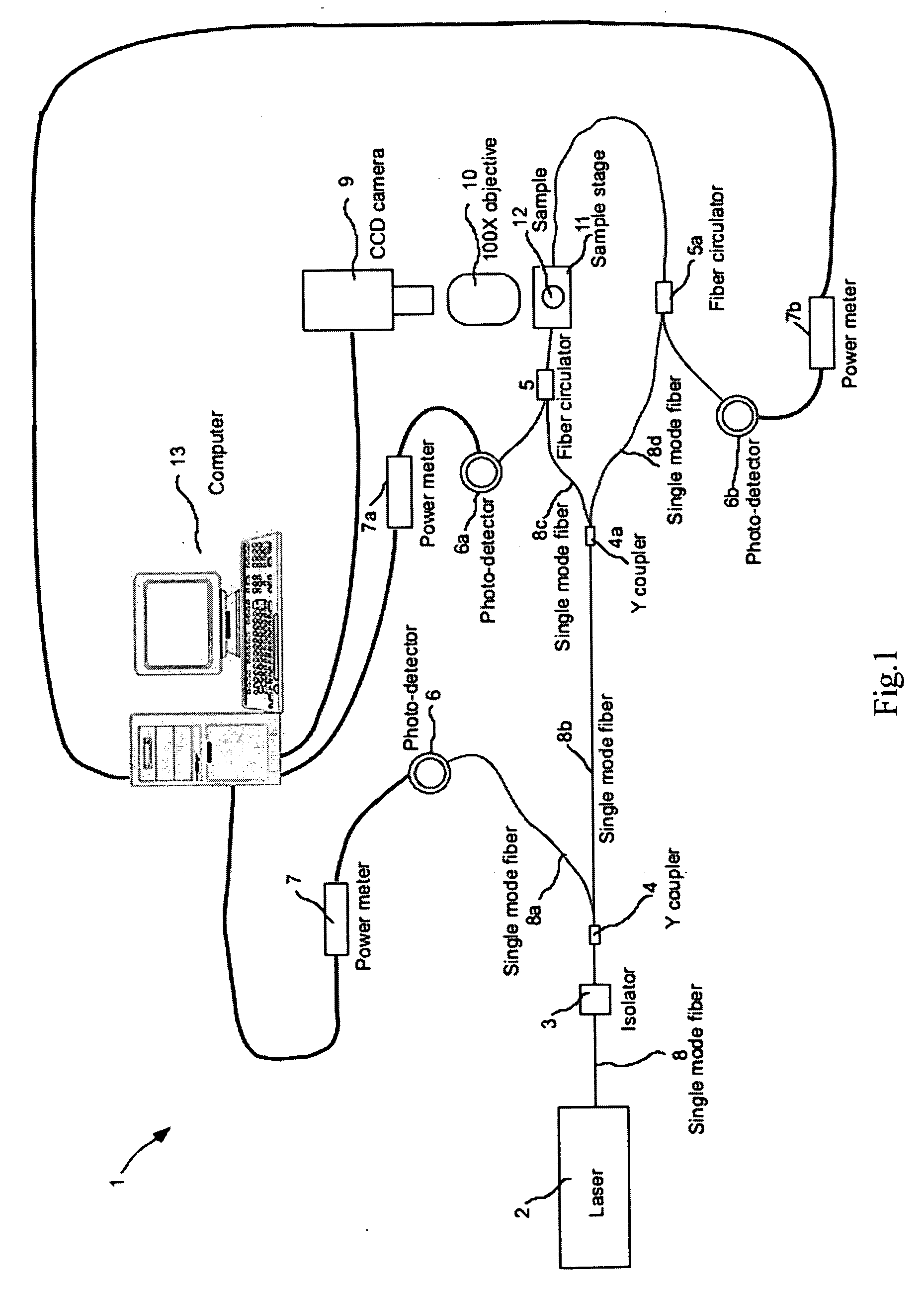
Device and method for simultaneous optical trapping, stretching, and real-time detection and measurement for morphological deformation of micro-particles
InactiveUS20070008528A1Reduce usageImprove detection efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansOptical powerSingle mode fiber coupling
The present invention provides a method and device for simultaneous optical trapping, stretching, and measurement of morphological deformation of a micro-particle in real-time. Using the setup of the present invention, the deformability of a living cell can be obtained in real-time by measuring the variation in coupling efficiency with optical power of light coupled from one single-mode fiber to the other through the lensing effect of the trapped-and-stretched micro-particle.
Owner:CHI HUNG LIN
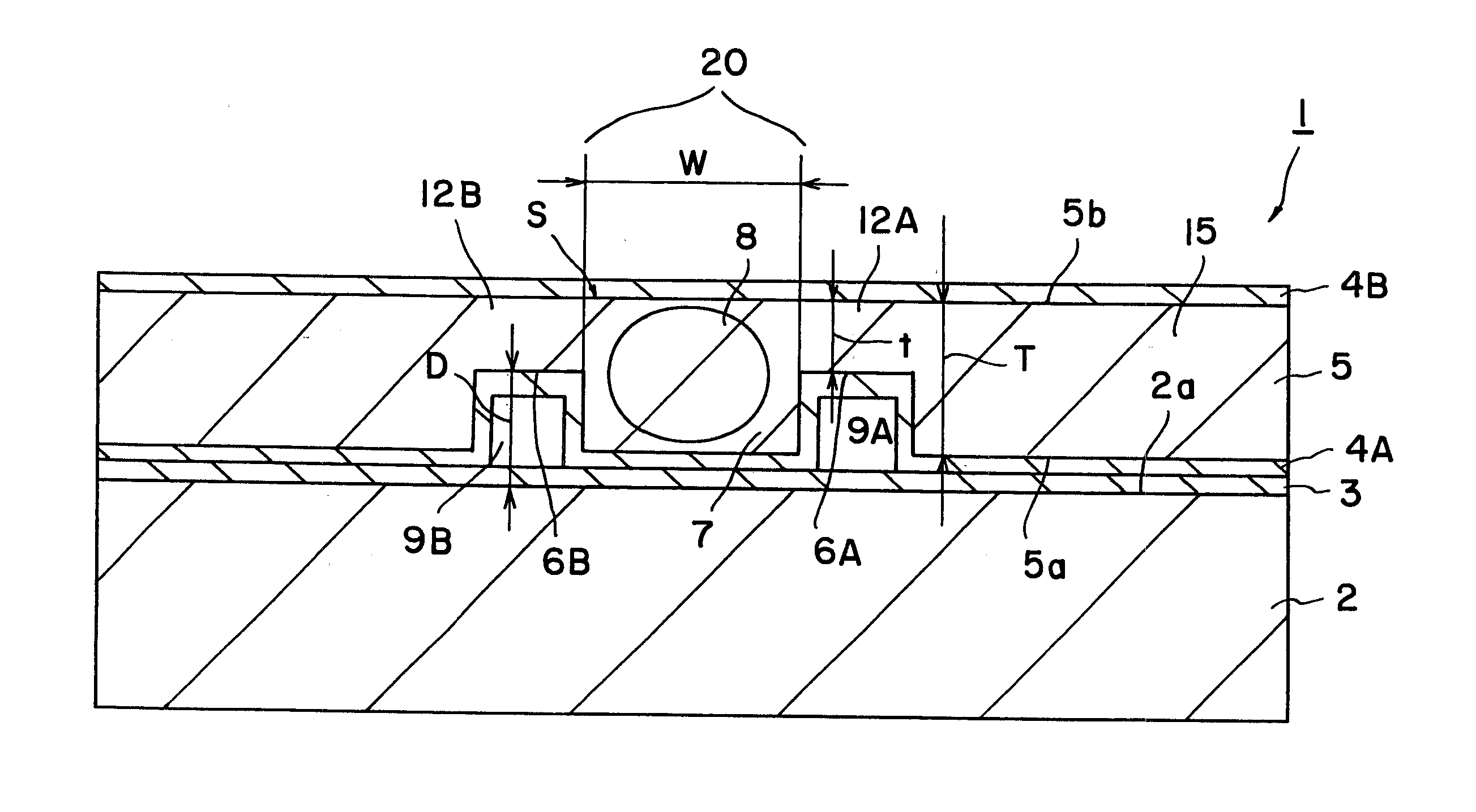
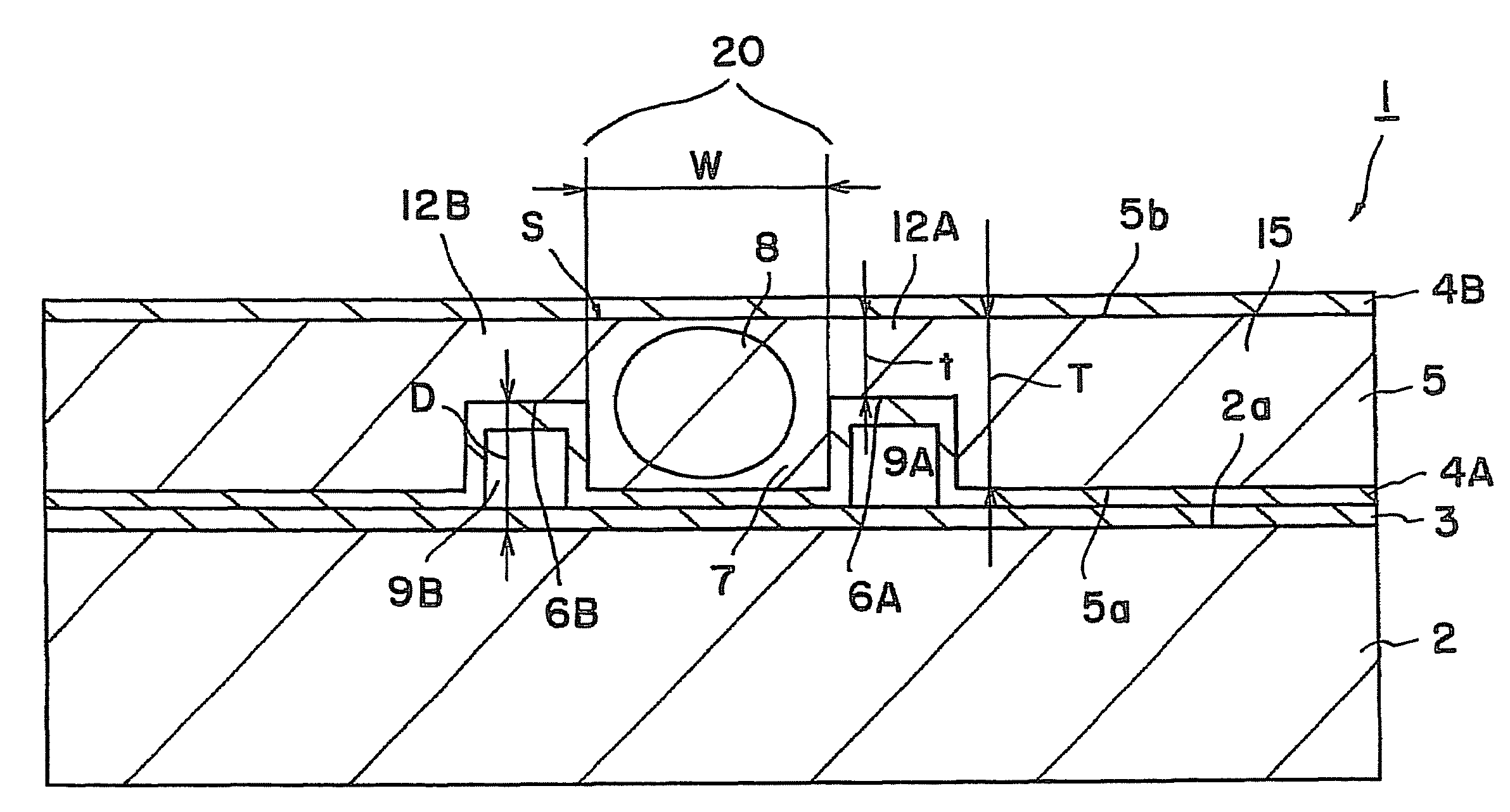
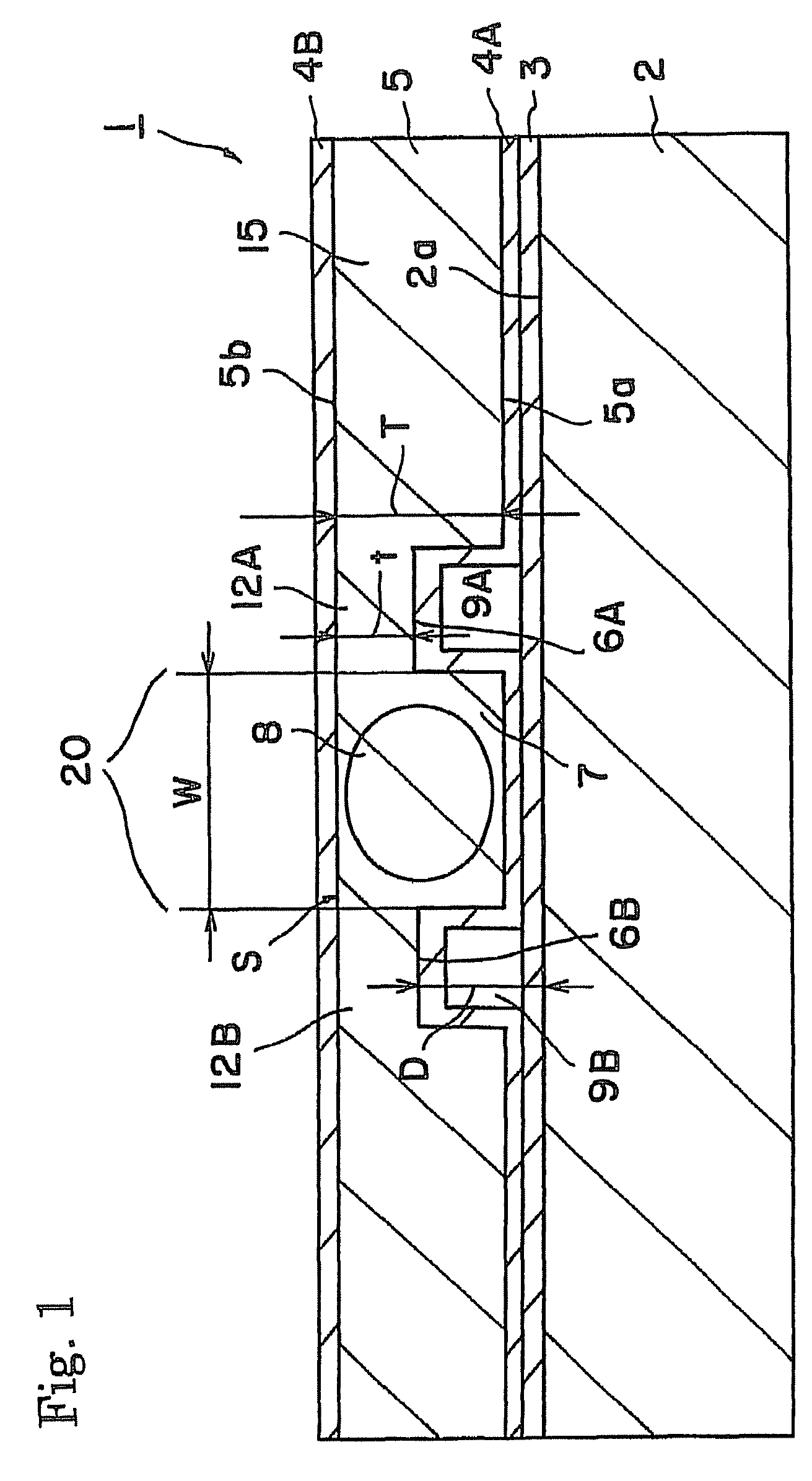
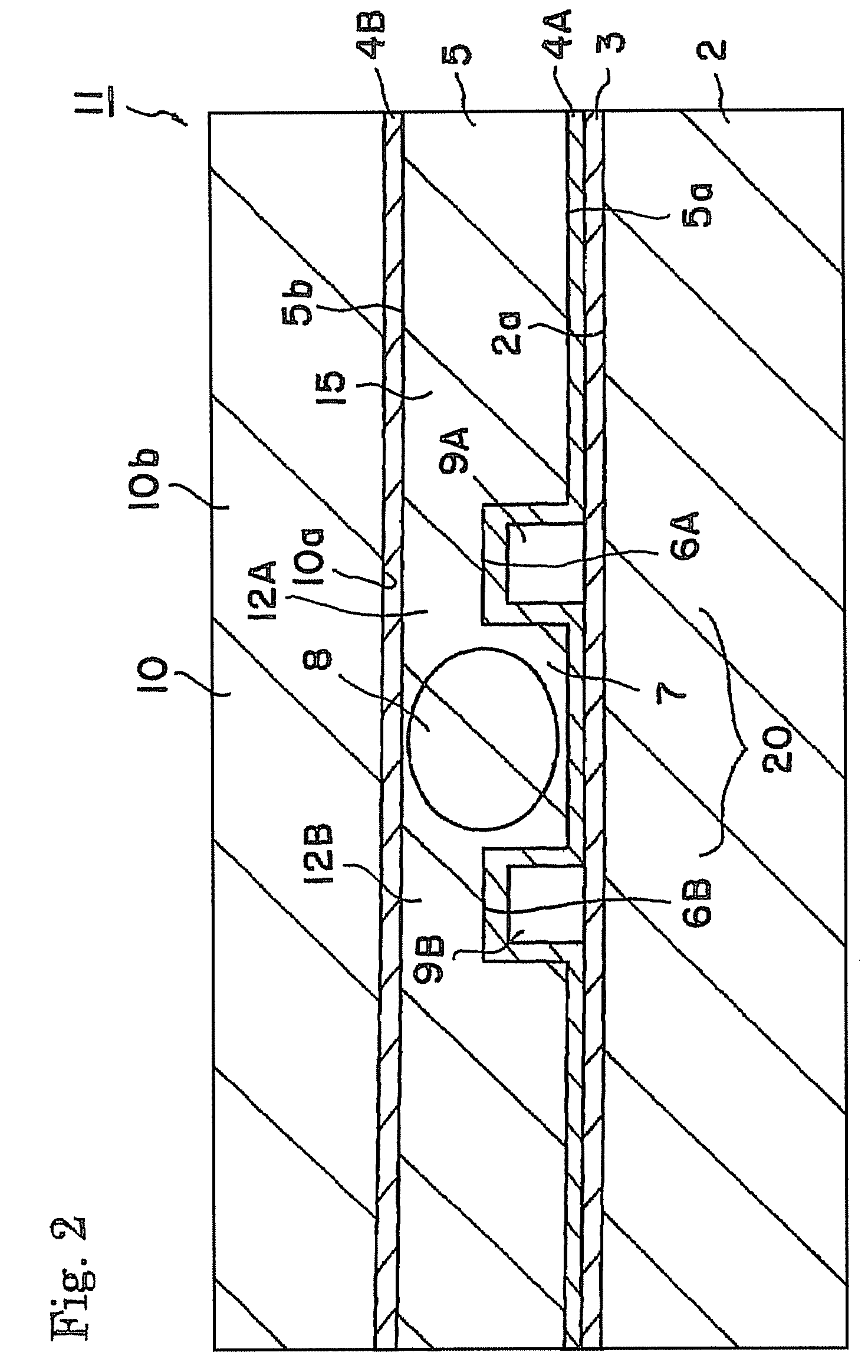
Wavelength converting devices
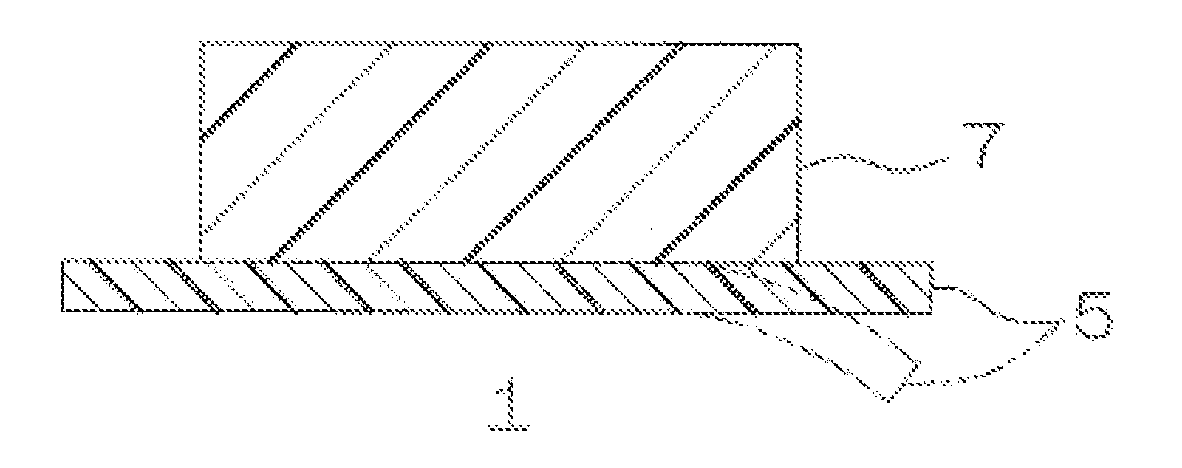
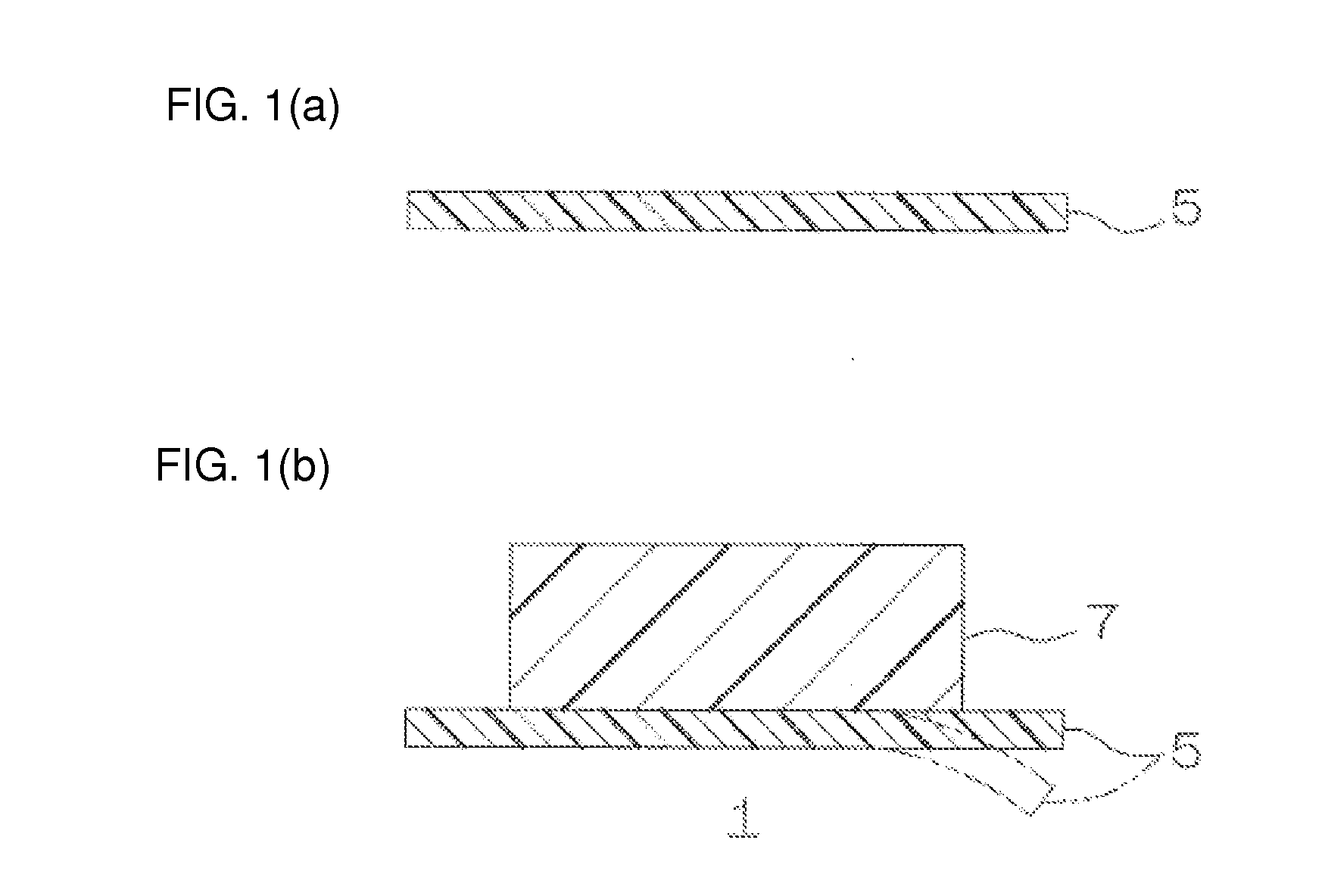
ActiveUS20070223081A1Increase output powerIncrease the cross-sectional areaLight demodulationOptical waveguide light guideLength waveWavelength conversion
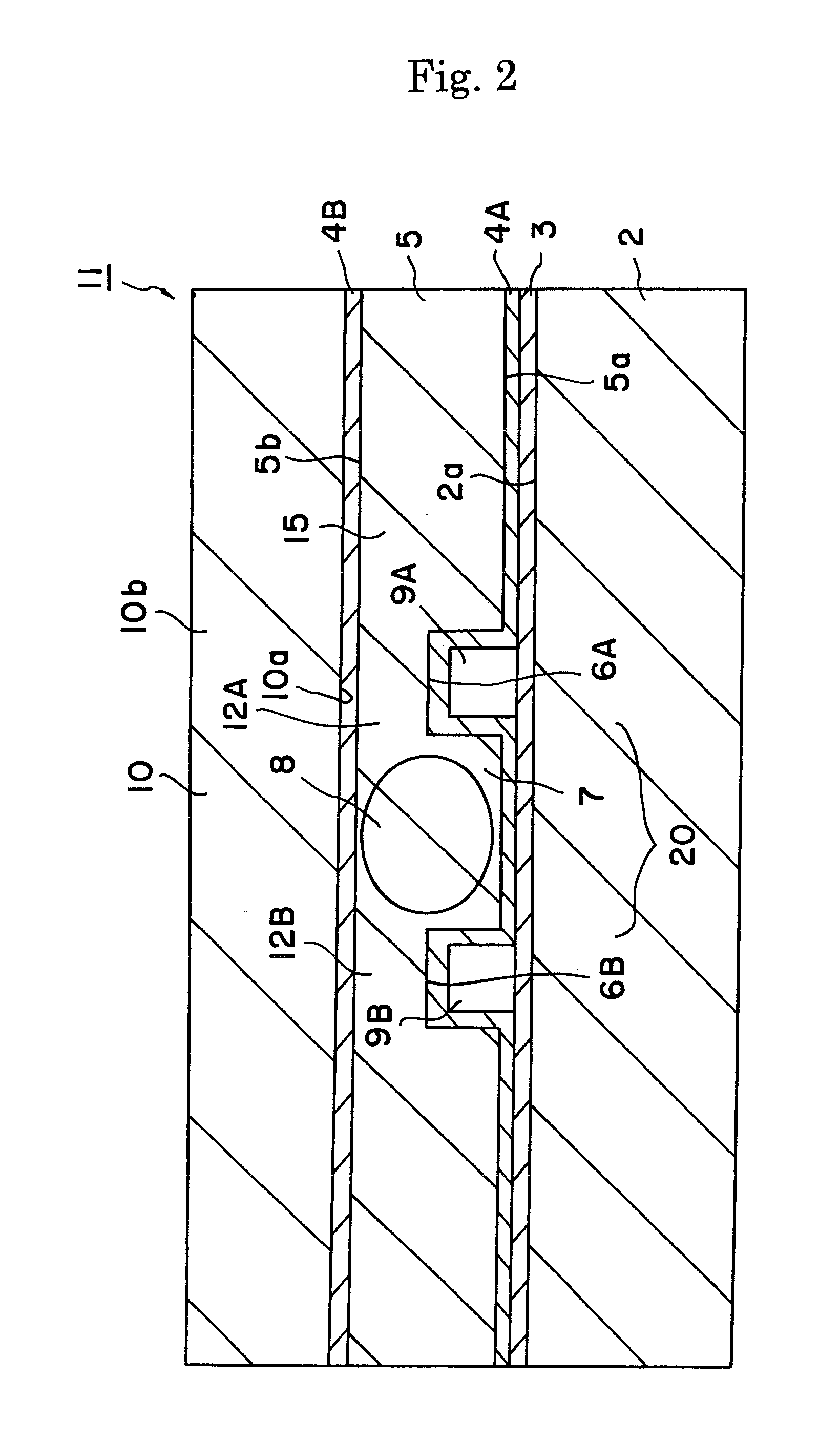
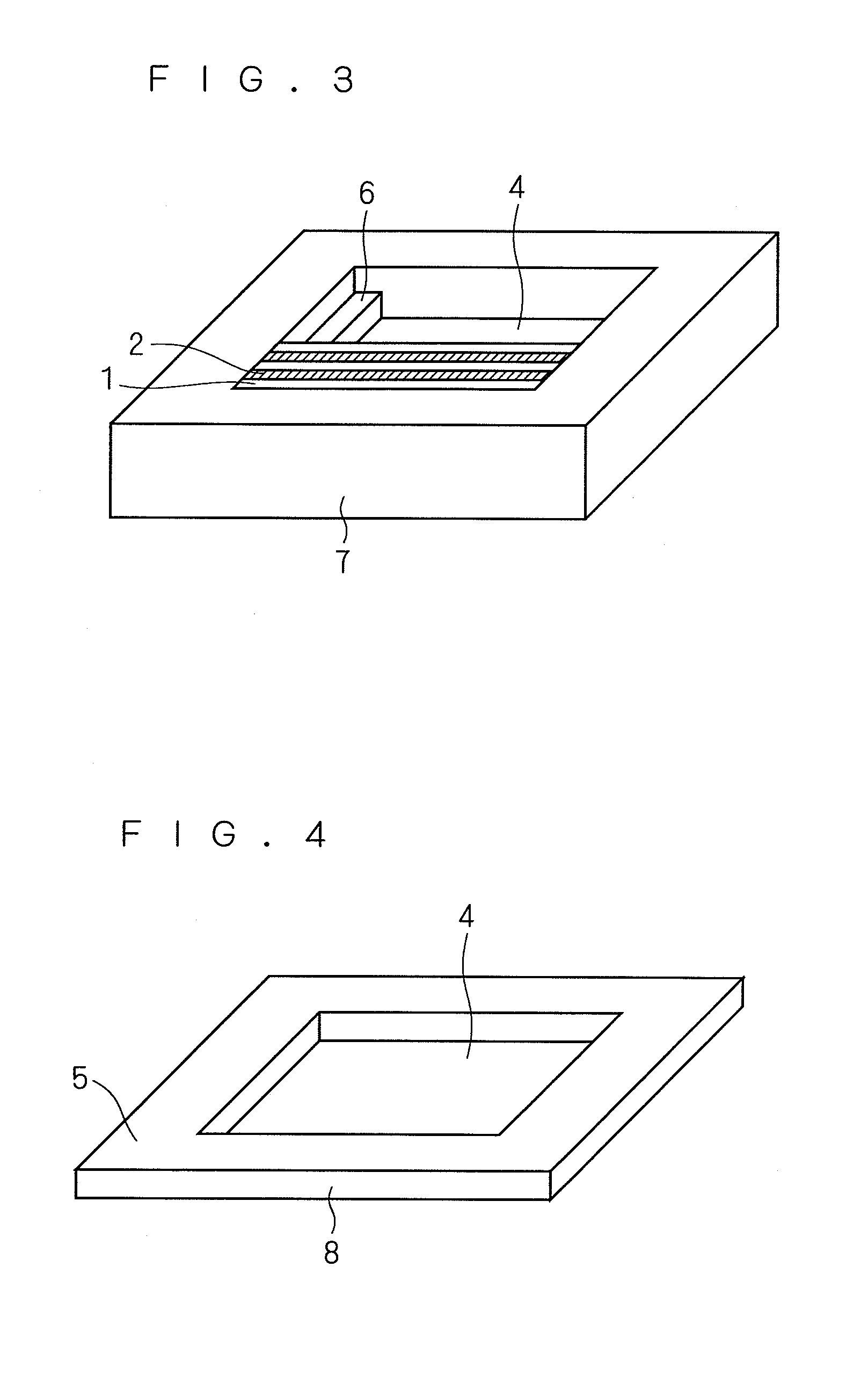
A wavelength converting device 1 has a substrate 5 made of an electro-optic material and converts a wavelength of a fundamental light to oscillate a converted light. A wavelength converting portion 7 is provided in the substrate 5 and has a cross sectional area of 0.0001 mm2 or larger and 0.01 mm2 or smaller. A pair of thinner portions 12A and 12B are provided in both sides of the wavelength converting portion, respectively, and thinner than the wavelength converting portion 7.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Optical communication system, method for supplying pump light, and distributed Raman amplifying apparatus
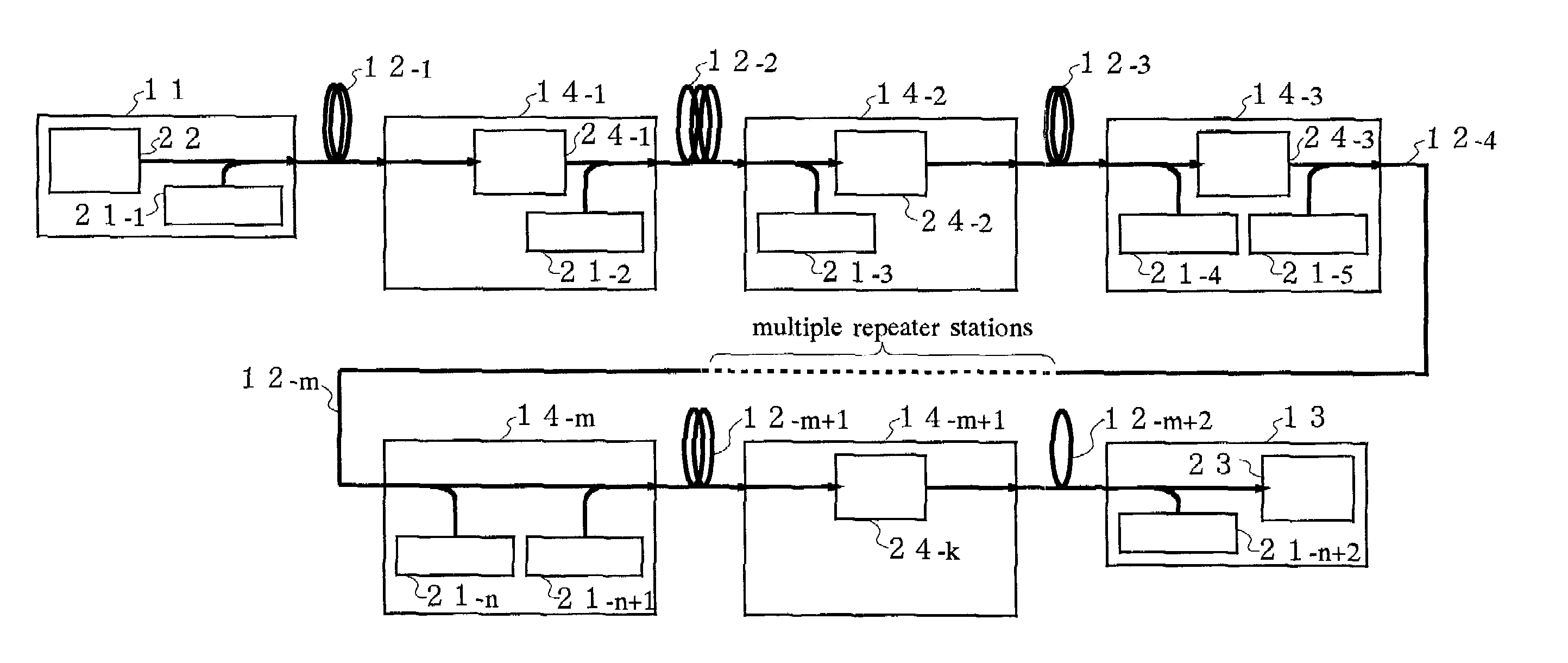
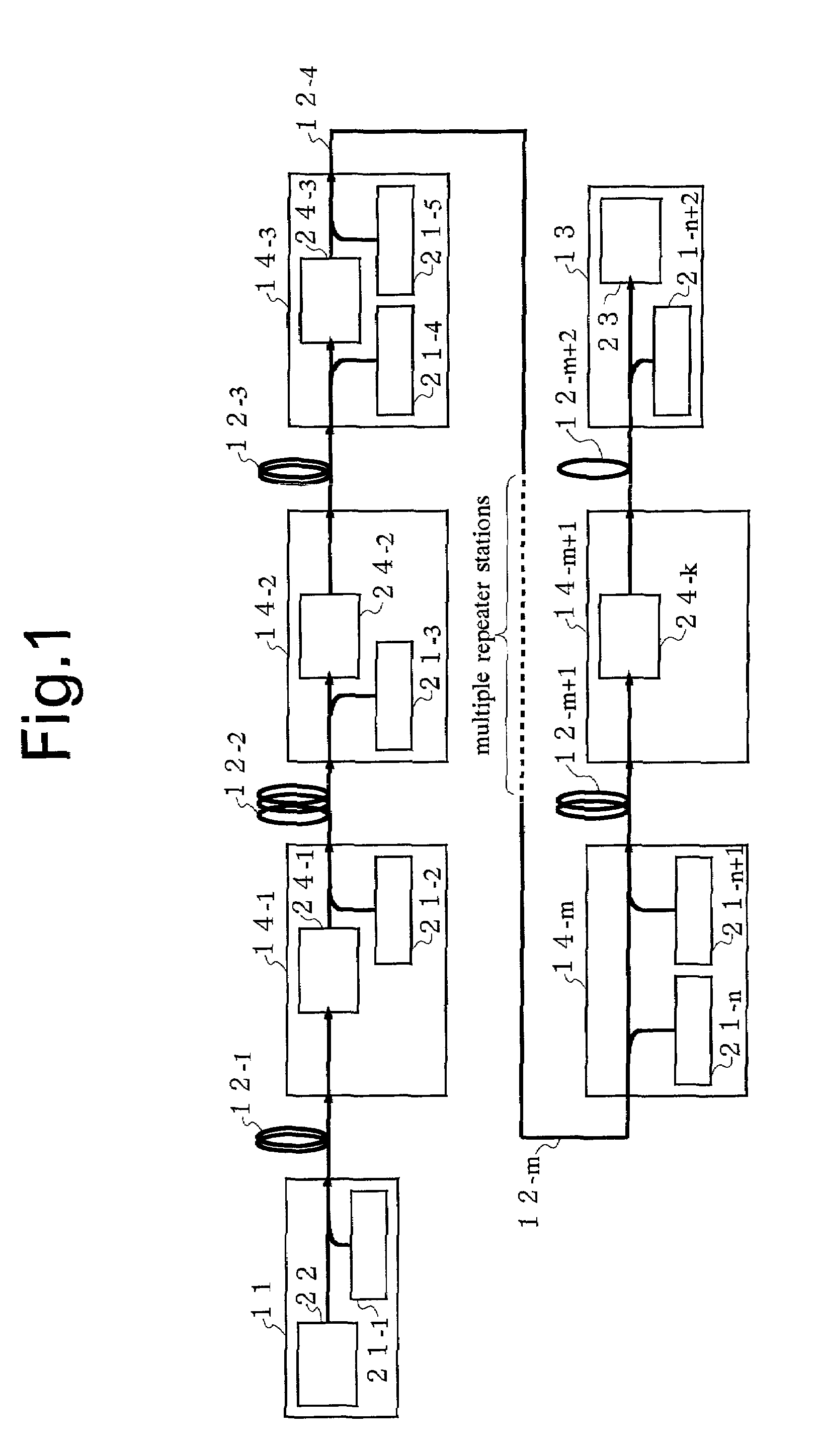
InactiveUS7233742B2Prevent optical damageGain flatWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionTransmission lineLight source
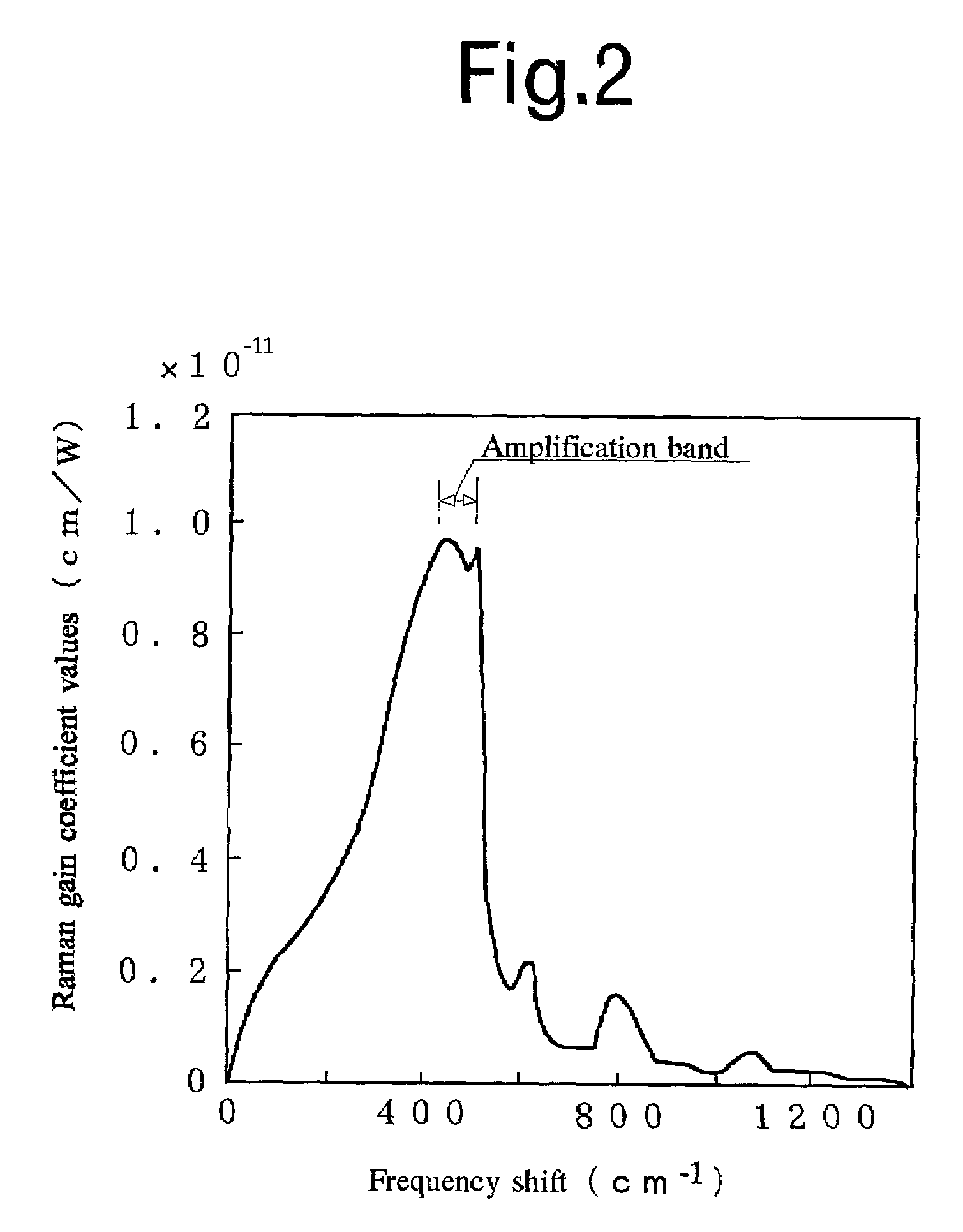
An optical communication system according to the invention comprises: a transmitting station 11; an optical transmission line 12 for transmitting an optical signal sent from the transmitting station 11; a receiving station 13 for receiving the optical signal outputted from the optical transmission line 12; a repeater station 14 provided at one point or more in the optical transmission line 12; and pump light sources 21 provided in at least two of the stations 11, 13, 14, for supplying pump light to the optical transmission line 12, wherein the pump light has two types or more of wavelength. It is possible to obtain a substantially flat gain as a function of wavelength in the whole optical communication system since the pump lights with different wavelengths are supplied from a plurality of points in the optical transmission line 12 and an optical signal is amplified with various Raman gain coefficients.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical device and coating applicator
InactiveUS20070263289A1High qualityHigh-quality imageLiquid surface applicatorsDiffusing elementsFresnel lensEngineering
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
Flexible flat optical cable
InactiveUS20120207438A1Avoid optical damageImprove reliabilityCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringOptical fiber
A flexible flat optical cable includes two flexible base sheets, one or more optical fiber core wires arranged between the base sheets and each comprising at least an optical fiber, and an adhesive layer provided between the base sheets to bond the base sheets. A non-adhesive region is formed on a surface of the base sheets or the adhesive layer adjacent, in a thickness direction of the base sheets, to at least a portion of the optical fiber core wires for allowing a portion of the optical fiber core wires to move in a direction intersecting with an axial direction of the optical fiber core wires.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Stack type optical disk changer
InactiveUS20050144627A1Maintain qualityAvoid separationRecord information storageRecord carrier contruction detailsEngineeringImage quality
The present invention discloses a stack type optical disk changer including a main frame, a cartridge slidably installed on the main frame, a plurality of disk trays slidably stacked in the cartridge, and a cartridge movement preventing means installed in the main frame, for selectively stopping movement of the cartridge. The stack type optical disk changer maintains quality of sound or image of an optical disk, and prevents damages of the optical disk, mis-operations and breakage, by preventing the optical disk from being separated from the tray.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Single and multi-stage high power optical isolators using a single polarizing element
An optical isolator for generally collimated laser radiation includes a single polarizing element, at least one Faraday optical element, at least one reciprocal polarization altering optical element disposed at the single polarizing element, at least one reflective optical element for reflecting radiation to provide an even number of passes through the at least one Faraday optical element, and a magnetic structure. The magnetic structure is capable of generating a magnetic field within the at least one Faraday optical element that is generally aligned with the even number of passes along a beam propagation axis. The optical isolator is configured to receive generally collimated laser radiation, which passes through the single polarizing element and the at least one reciprocal polarization altering optical element and which makes at least two passes through the at least one Faraday optical element, whereby generally collimated laser radiation is output from the optical isolator.
Owner:ELECTRO OPTICS TECH
Lighting device
InactiveUS20080266832A1Increase profitIncrease illuminationMeasurement apparatus componentsMachines/enginesDisplay designLight guide
A lighting device, for illuminating display designed parts on a display plate, includes at least one light source arranged at a rear side of the display plate, and a light guide body having a light guide portion for guiding the light toward its outer-circumferential portion to output the light toward the display designed parts through a front surface of the light guide portion. The outer-circumferential portion has an outer-circumferential side wall surface at is outer end. The light guide portion has at least one projecting portion projecting from the outer-circumferential side wall surface. The projecting portion is provided with a reflecting side surface formed along the outer-circumferential side wall surface so that the reflecting side surface can reflect the light traveling in the light guide portion to be outputted through the front surface of the light guide portion.
Owner:CALSONIC KANSEI CORP
Light beam generation
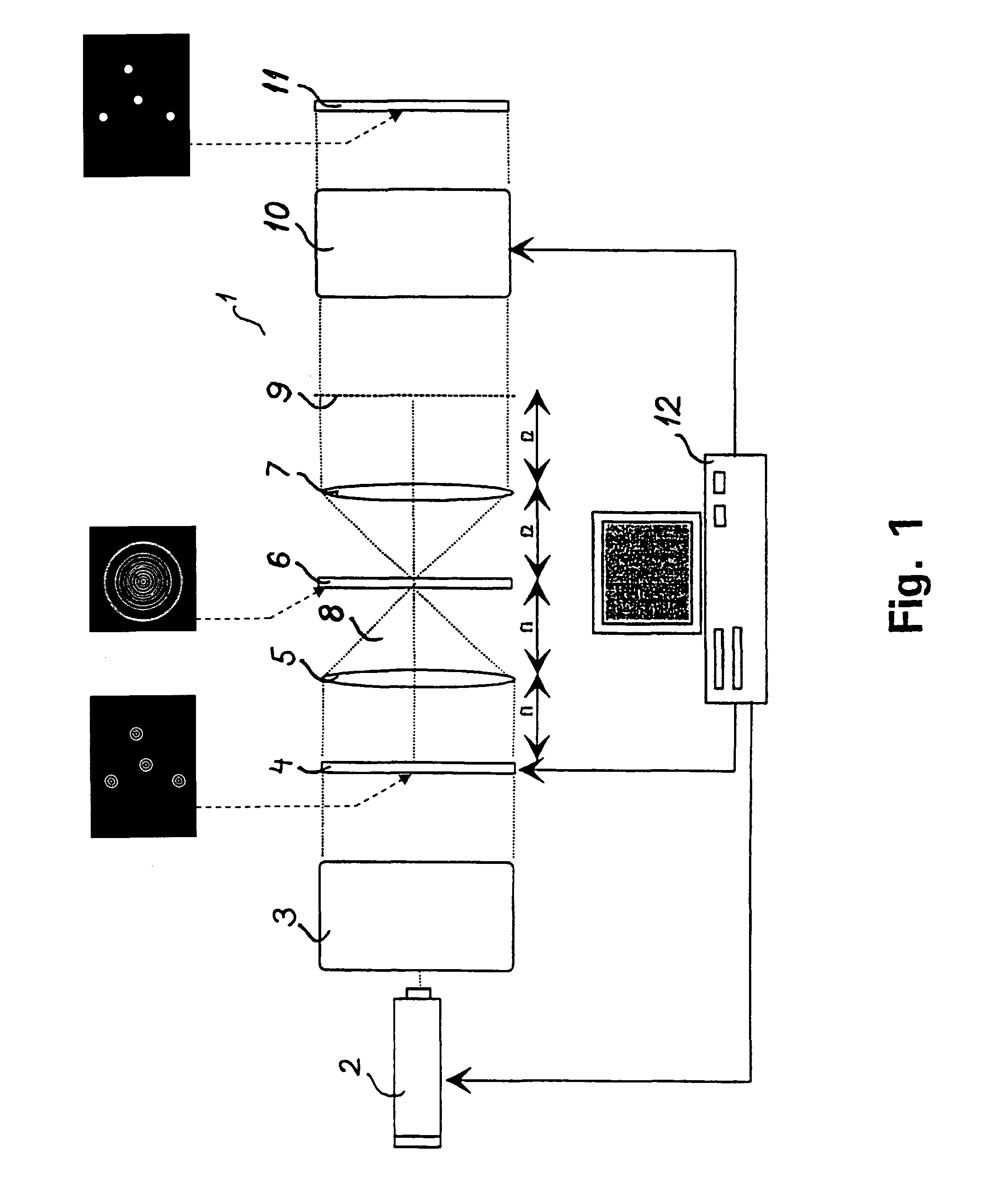
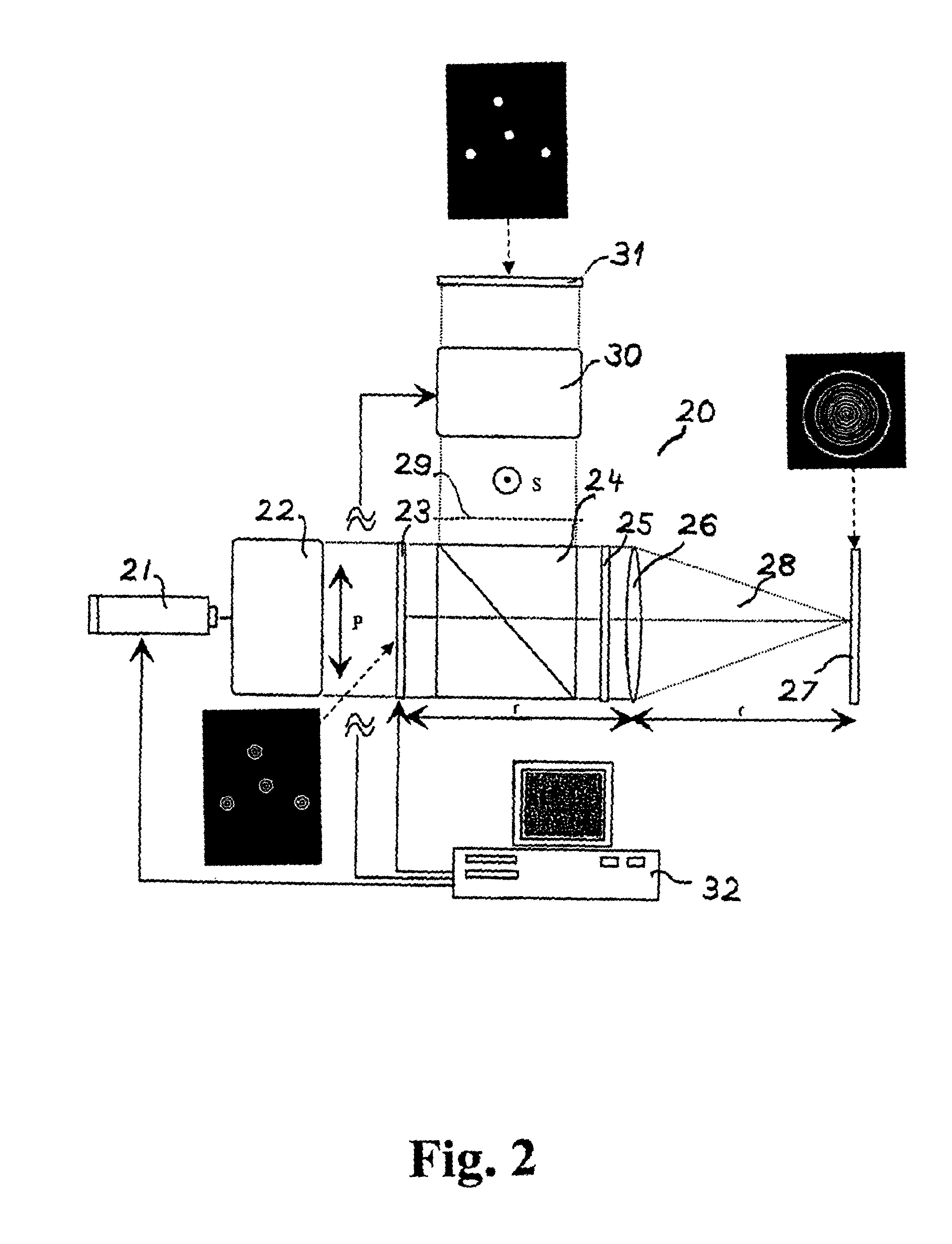
InactiveUS8125713B2Raise the intensity levelAvoid optical damageMicroscopesOptical computing devicesSpatial light modulatorPhase shifted
A method and system for synthesizing controllable light beams includes a spatially modulated light source that generates electromagnetic radiation with a set of replicas of a predetermined symbol, s, positioned at desired positions (xs, ys) in an object plane o(x, y) intersecting, preferably perpendicular to, the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic radiation, and having spatial amplitudes a(x-xs, y-ys), spatial phases φ(x-xs, y-ys), and spatial polarisation vectors p(x-xs, y-ys), a Fourier transforming lens for Fourier transforming the electromagnetic radiation, a first spatial light modulator for phase shifting the transformed electromagnetic radiation with the phase −Φ(u, v) of S*, S* the complex conjugate of the transformed symbol, a Fourier transforming lens for Inverse Fourier transforming the spatially modulated radiation, a set of light beams are formed propagating through the inverse Fourier plane (x′, y′) at desired positions (x′s, y′s), and a controller for controlling the position of a replica of the symbol, for movement of the light beam.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Encapsulating sheet and optical semiconductor element device
InactiveUS20130092973A1Good light transmissionBrightness loss can be suppressedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesMicroparticleSilicone
An encapsulating sheet is formed from an encapsulating resin composition which contains an encapsulating resin and silicone microparticles, and the mixing ratio of the silicone microparticles with respect to the encapsulating resin composition is 20 to 50 mass %.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Projection display apparatus and optical filter
InactiveUS20070058137A1Extended service lifeShortened lifetime of light source can be preventedProjectorsDisplay deviceLight beam
A projection display apparatus including a lighting system, a projection lens and a display device. The lighting system has a light source, a lens set, and an Yttrium Aluminum Garnet filter (YAG filter) is provided. The light source is suitable for providing a light beam. The lens set is disposed on the transmission path of the light beam. The YAG filter is disposed between the light source and the lens set and on the transmission path of the light beam as well. Additionally, the projection lens is disposed on the transmission path of the light beam. The display device is disposed between the lighting system and the projection lens and on the transmission path of the light beam as well. The projection apparatus having the YAG filter is benefited in dispelling the heat of the light source and optical devices, thereby extending lifetime of the light source and optical devices.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
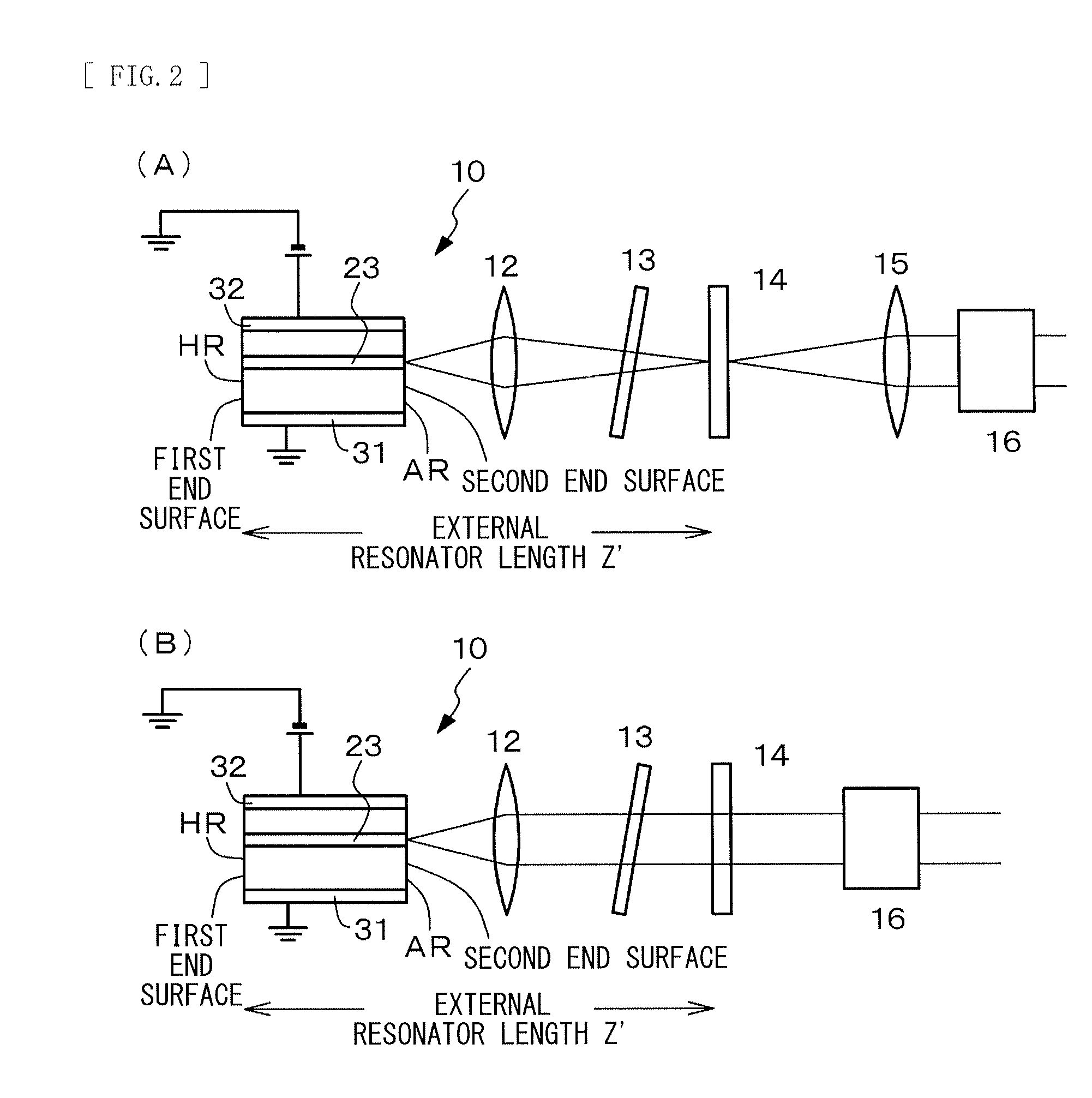
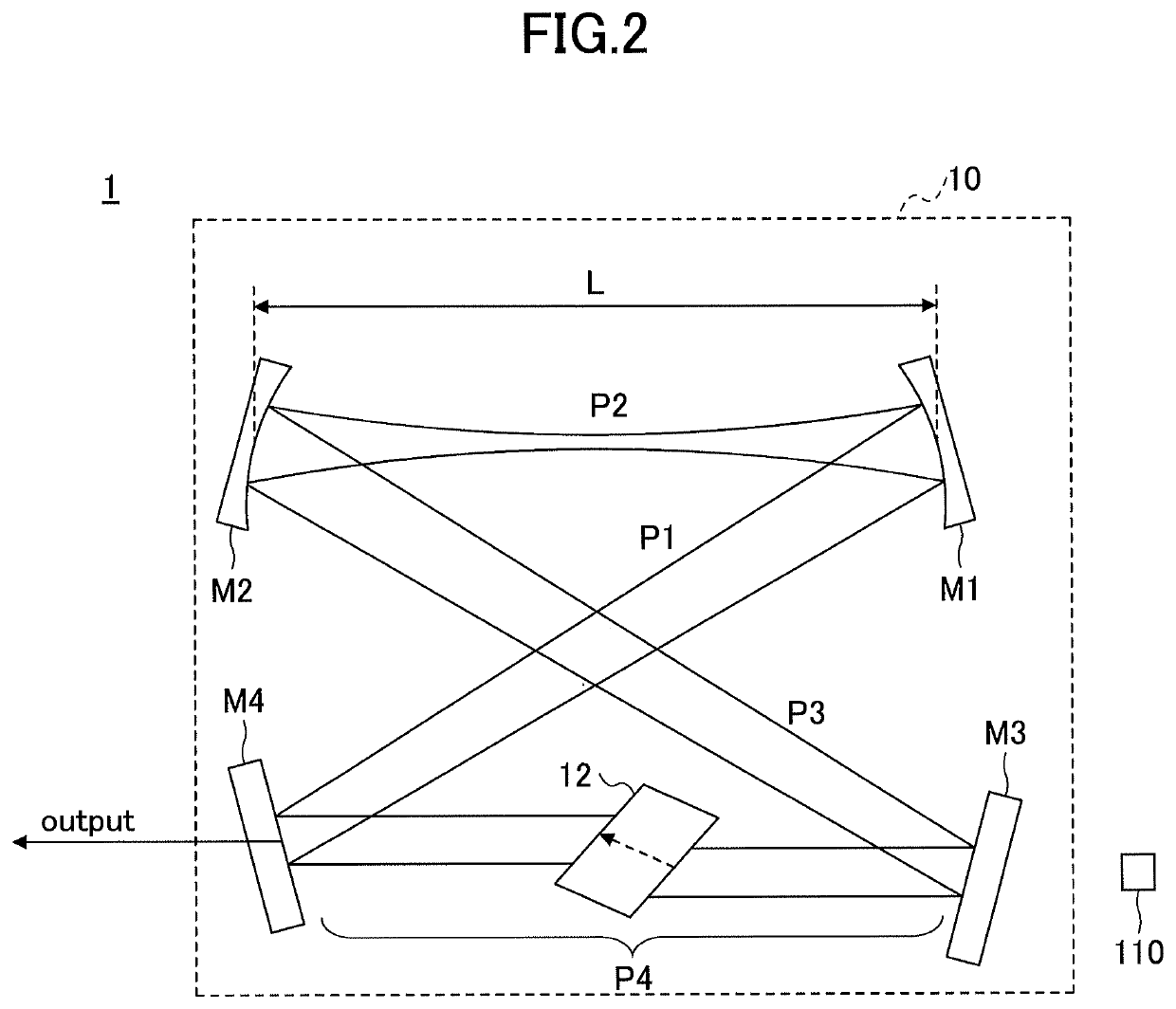
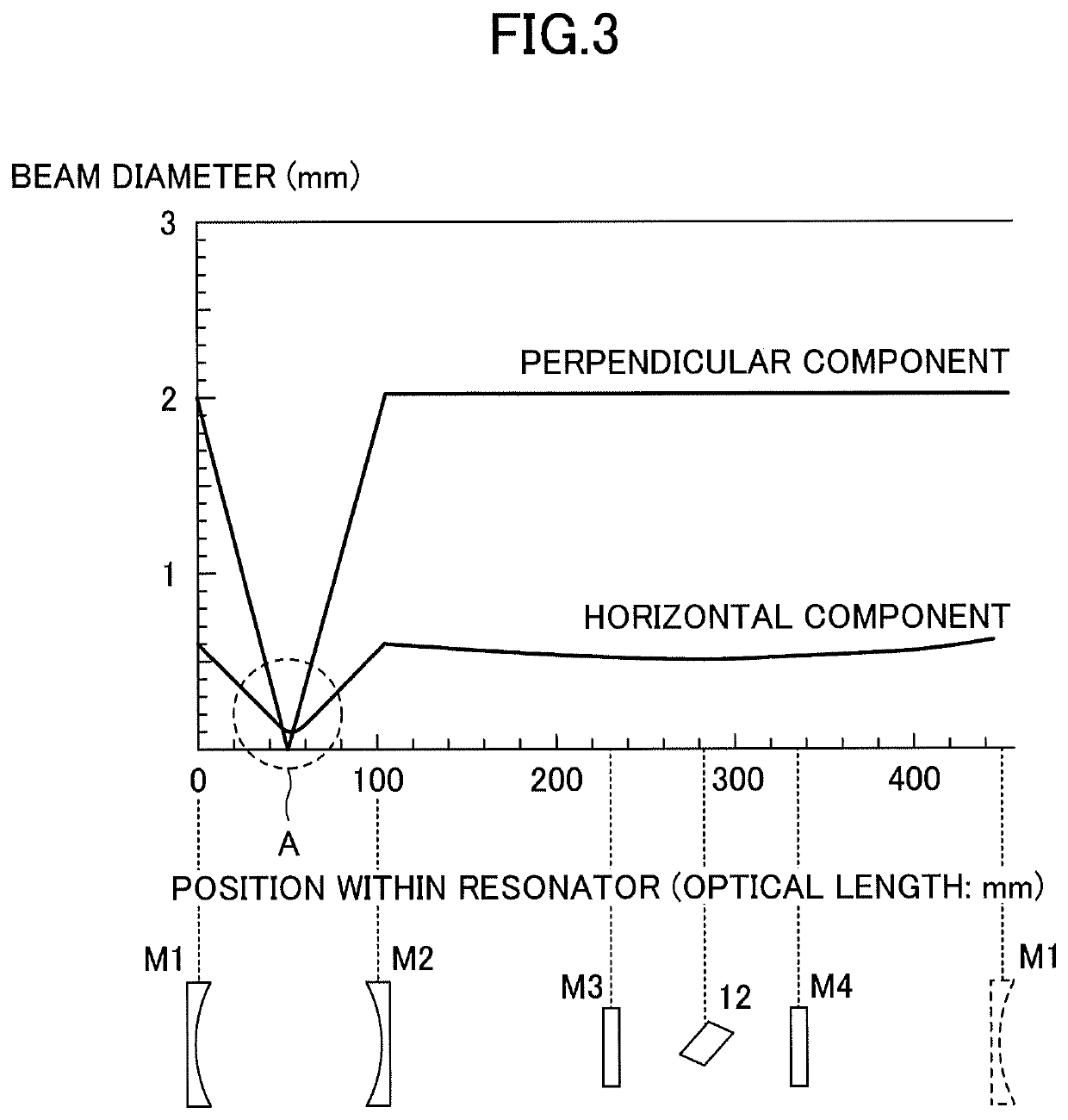
Laser resonator, and method of designing laser resonator
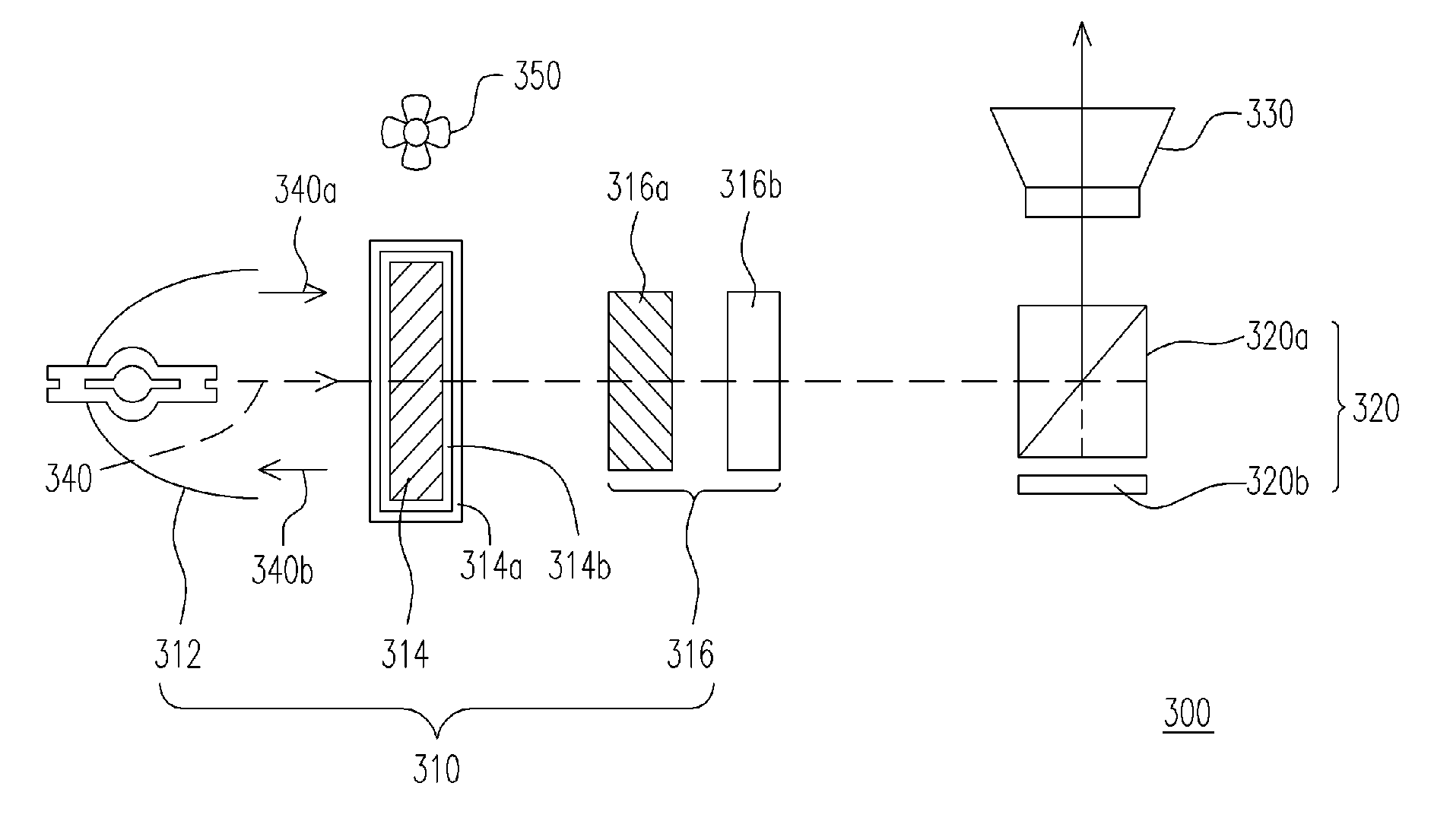
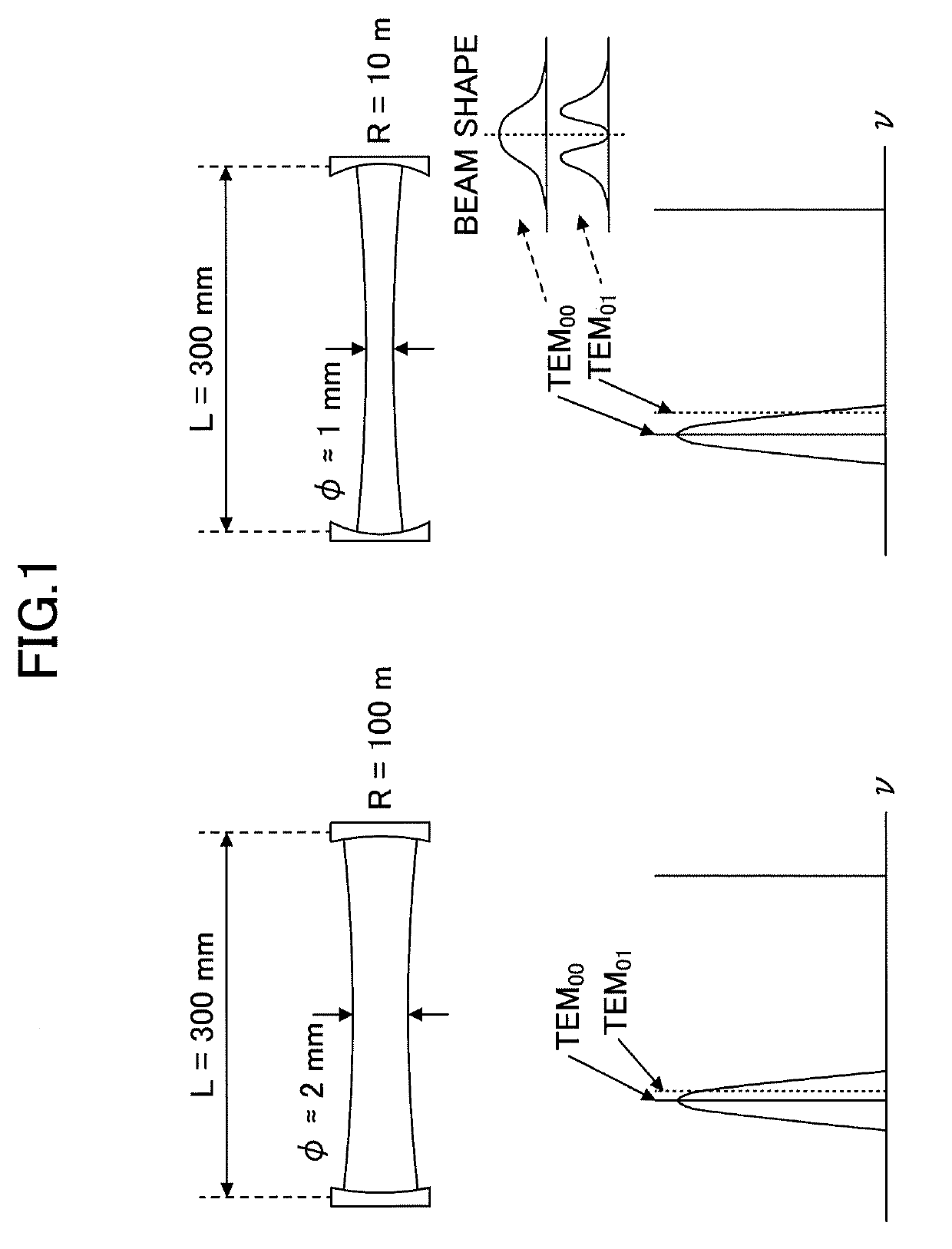
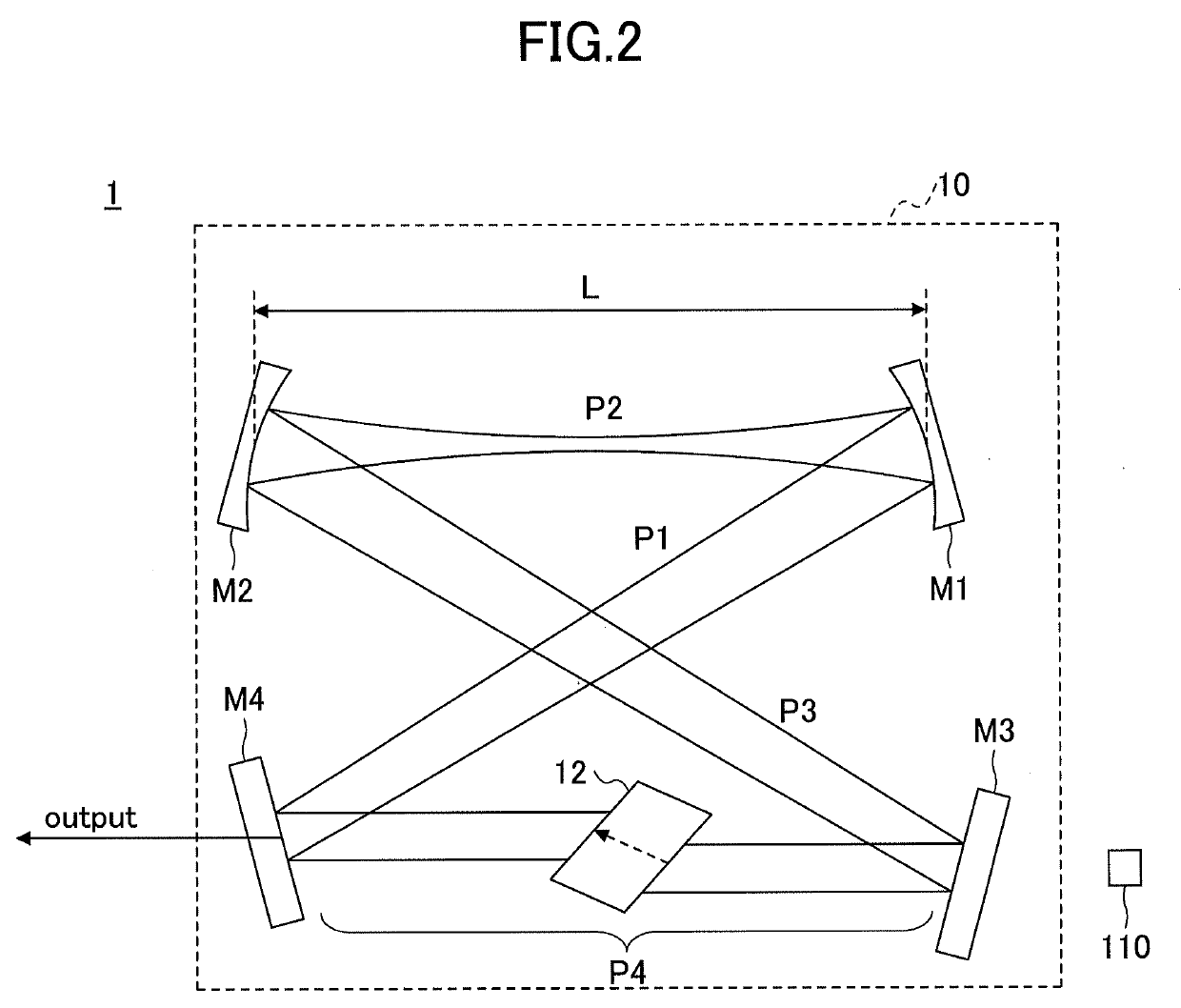
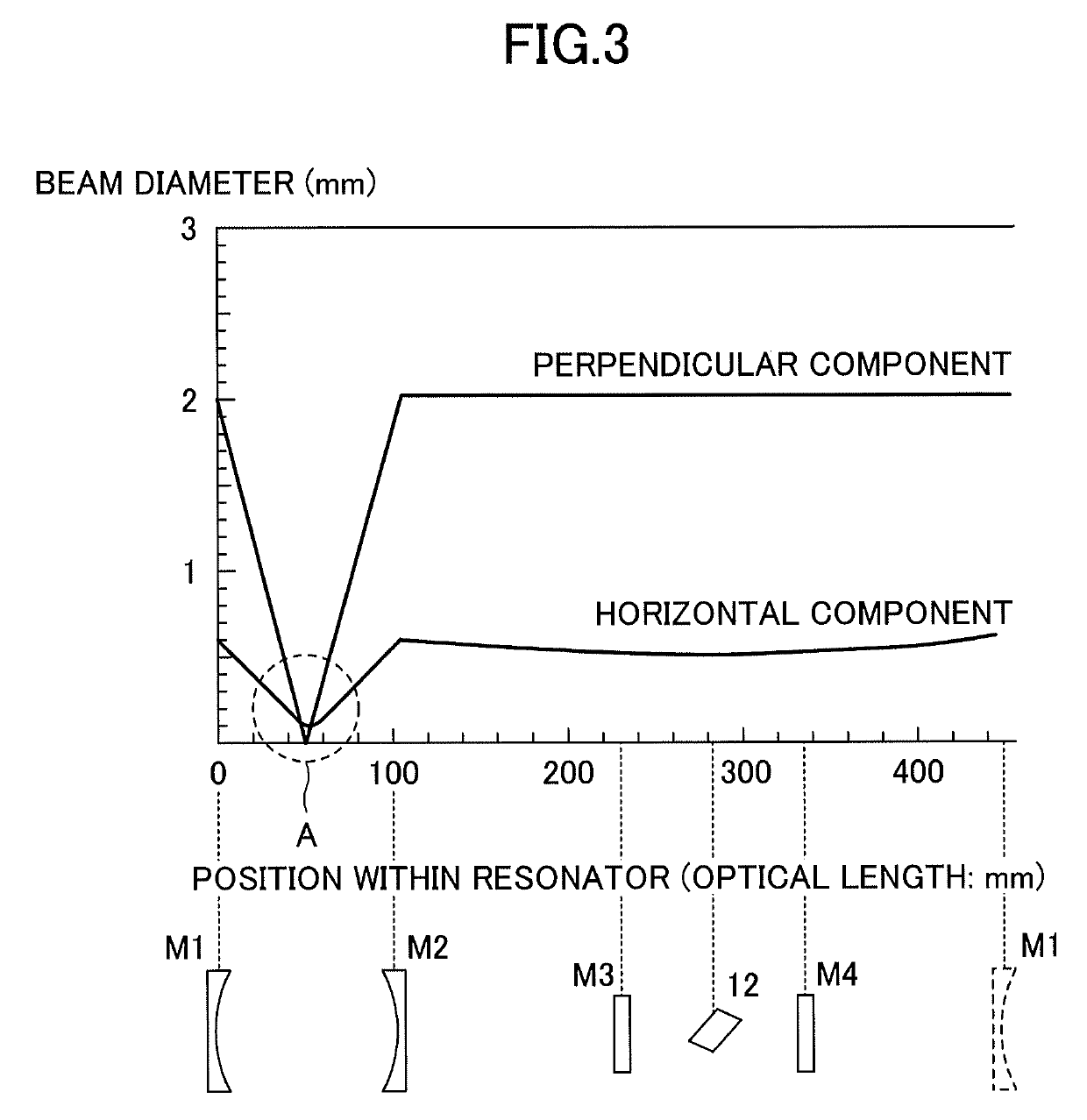
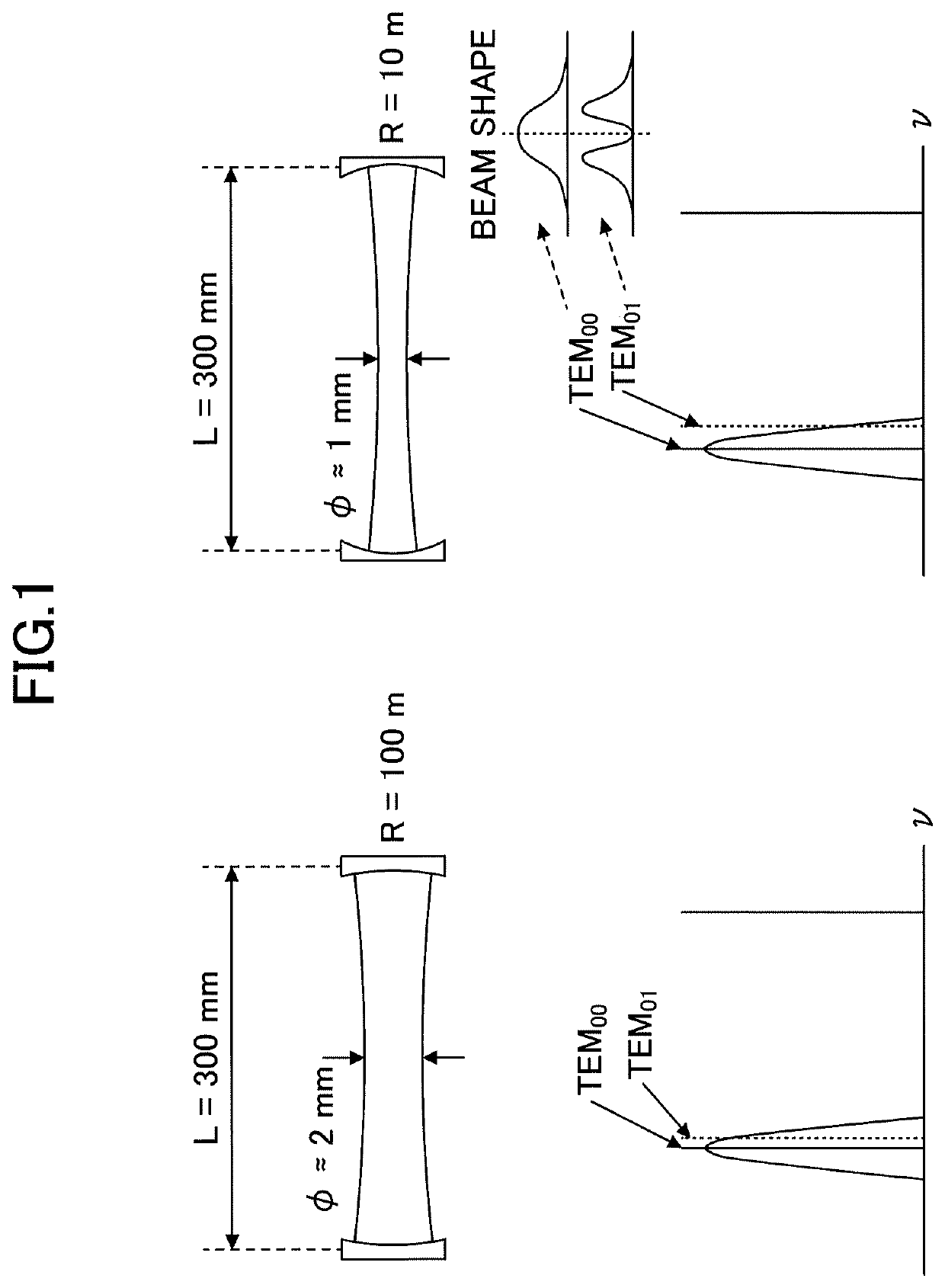
ActiveUS20190267769A1Avoid optical damageExcitation process/apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionBeam diameterLight beam
A laser resonator includes a pair of optical elements forming a first optical path having a focused beam waist, one or more mirrors forming a second optical path of approximately parallel light connected to the first optical path, and a laser medium arranged in the second optical path. Induced emission light generated from the laser medium reciprocates or circles in a path formed by the first optical path and the second optical path. A distance between the pair of optical elements is adjustable, and a beam diameter at the second optical path is adjusted by adjusting the distance between the pair of optical elements.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRO-COMMUNICATIONS
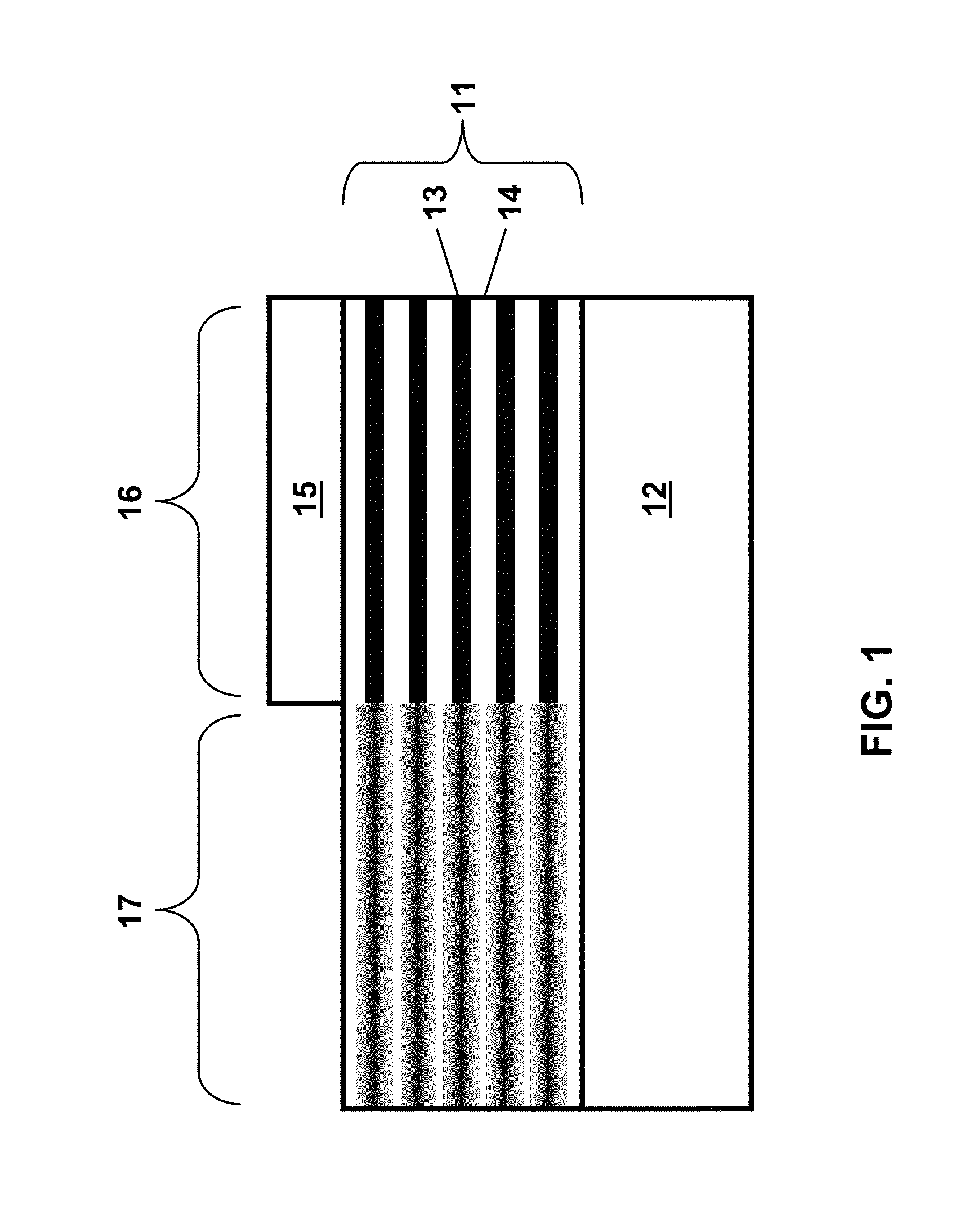
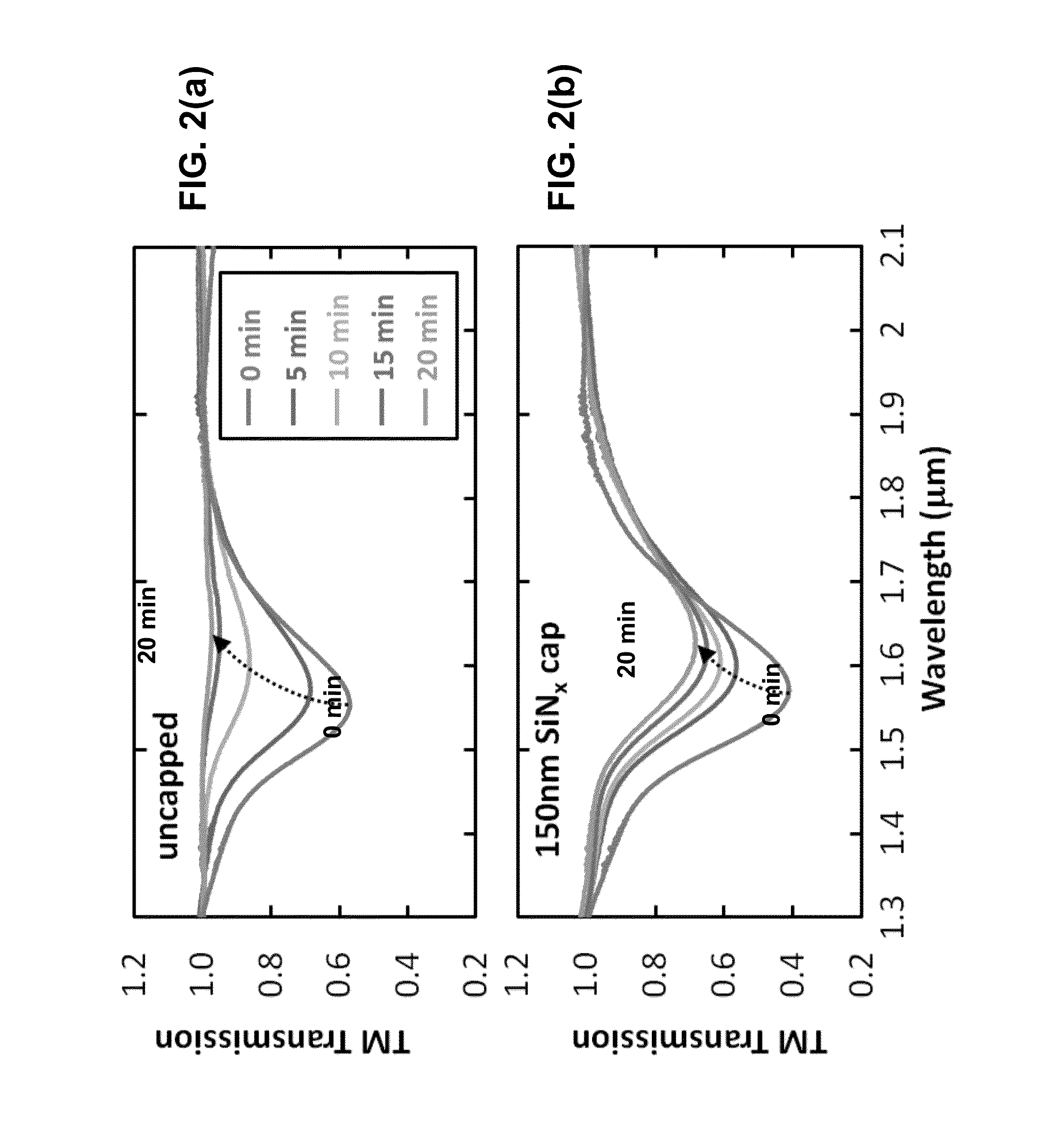
Selective layer disordering in III-nitrides with a capping layer
ActiveUS9368677B2Slowing down Si diffusionSuppress layerNanotechLaser detailsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
Selective layer disordering in a doped III-nitride superlattice can be achieved by depositing a dielectric capping layer on a portion of the surface of the superlattice and annealing the superlattice to induce disorder of the layer interfaces under the uncapped portion and suppress disorder of the interfaces under the capped portion. The method can be used to create devices, such as optical waveguides, light-emitting diodes, photodetectors, solar cells, modulators, laser, and amplifiers.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
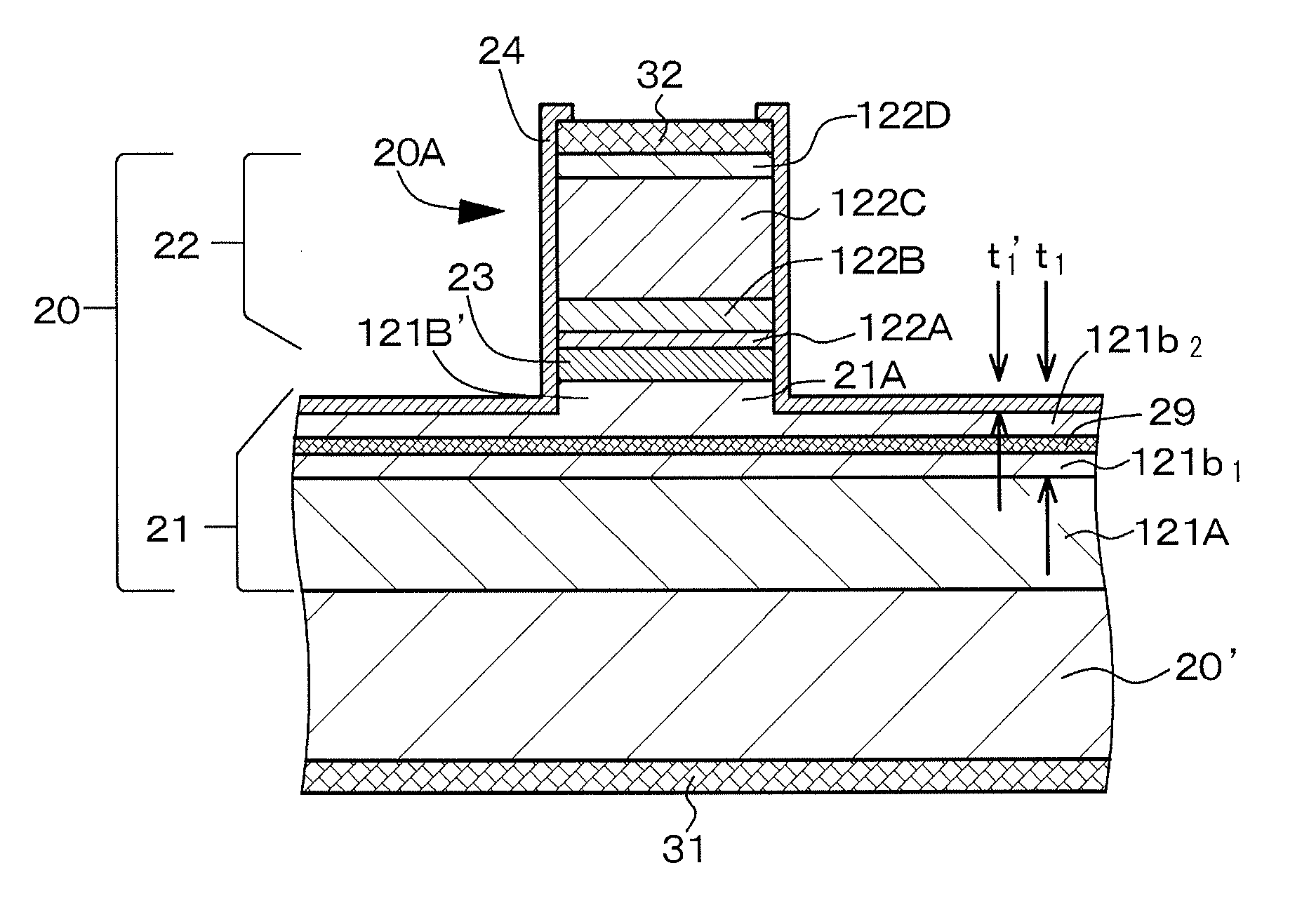
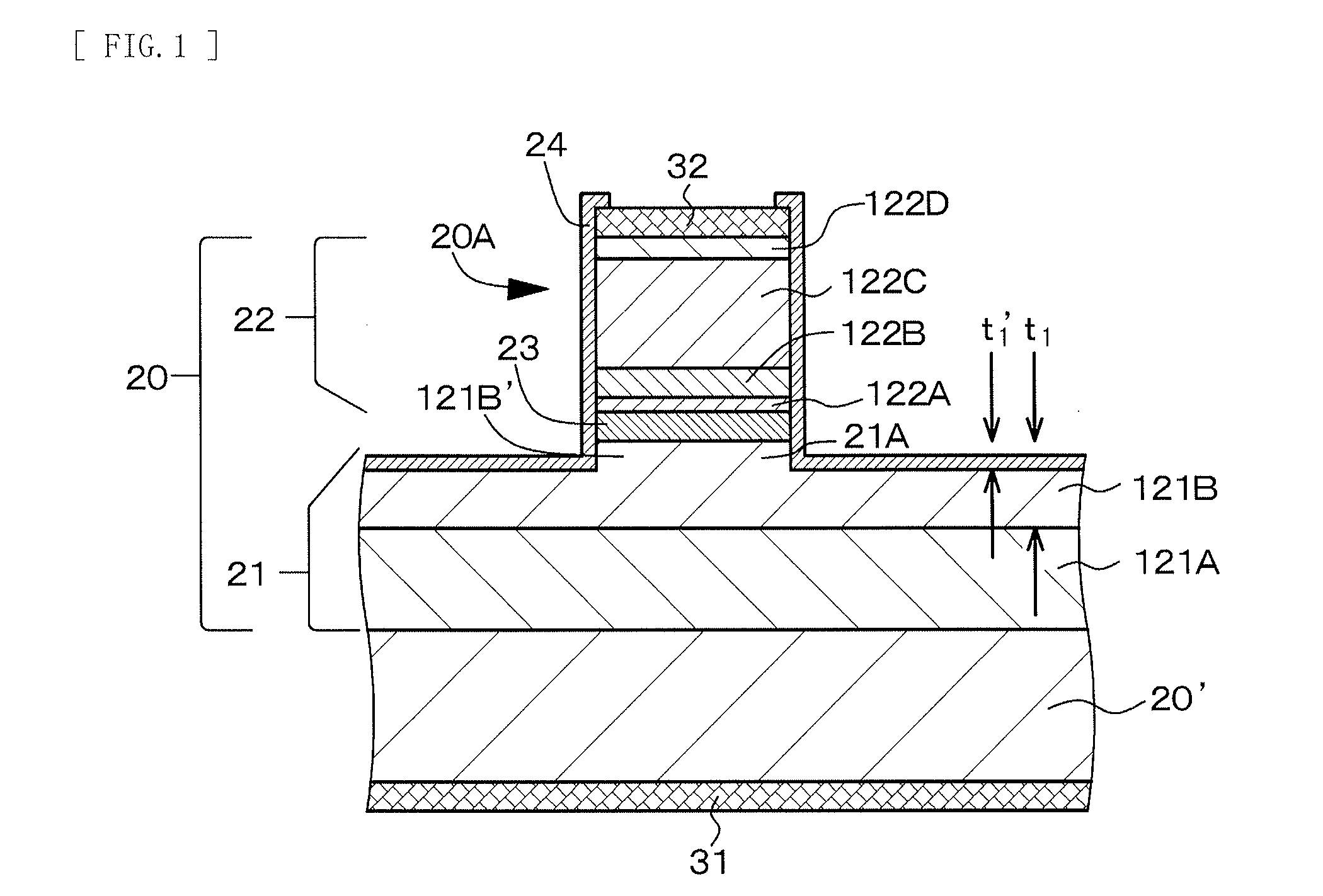
Light-emitting device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20150043603A1Quality improvementImprove reliabilityOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsLight beamActive layer
Provided is a high-output light-emitting device capable of emitting a light beam in a single mode. The light-emitting device includes a laminate structure body configured by laminating, in order, a first compound semiconductor layer, an active layer, and a second compound semiconductor layer on a base substrate, a second electrode, and a first electrode. The first compound semiconductor layer has a laminate structure including a first cladding layer and a first light guide layer in order from the base substrate, and the laminate structure body has a ridge stripe structure configured of the second compound semiconductor layer, the active layer, and a portion in a thickness direction of the first light guide layer. Provided that a thickness of the first light guide layer is t1, and a thickness of the portion configuring the ridge stripe structure of the first light guide layer is t1′, 6×10−7 m<t1 and 0(m)<t1′≦0.5·t1 are satisfied.
Owner:SONY CORP
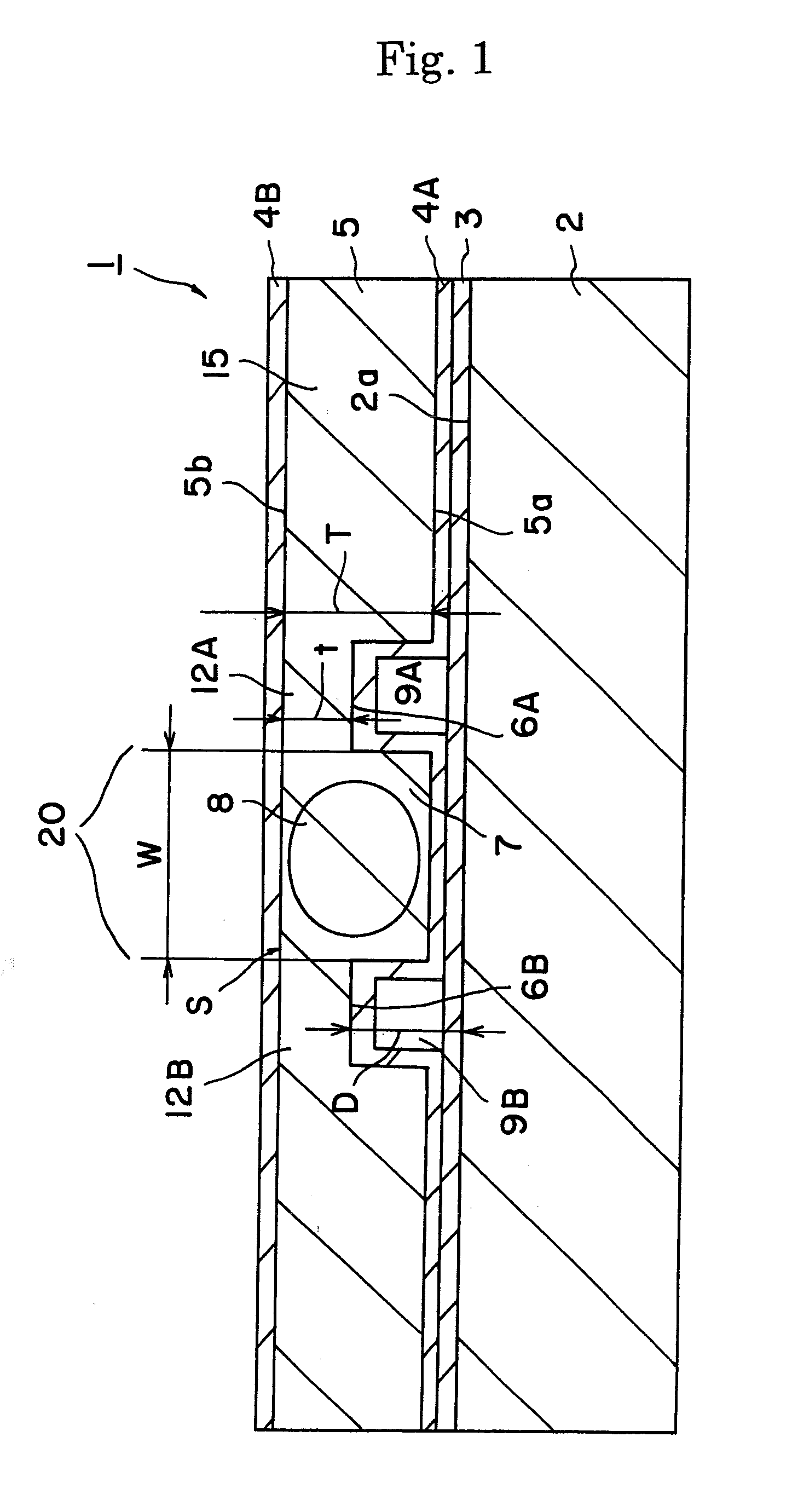
Wavelength converting devices
ActiveUS7738161B2Oscillation stabilityOpticalLight demodulationOptical waveguide light guideLength waveWavelength conversion
A wavelength converting device has a substrate made of an electro-optic material and converts a wavelength of a fundamental light to oscillate a converted light. A wavelength converting portion is provided in the substrate and has a cross sectional area of 0.0001 mm2 or larger and 0.01 mm2 or smaller. A pair of thinner portions are provided in both sides of the wavelength converting portion, respectively, and thinner than the wavelength converting portion.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Single and multi-stage high power optical isolators using a single polarizing element
An optical isolator for generally collimated laser radiation includes a single polarizing element, at least one Faraday optical element, at least one reciprocal polarization altering optical element disposed at the single polarizing element, at least one reflective optical element for reflecting radiation to provide an even number of passes through the at least one Faraday optical element, and a magnetic structure. The magnetic structure is capable of generating a magnetic field within the at least one Faraday optical element that is generally aligned with the even number of passes along a beam propagation axis. The optical isolator is configured to receive generally collimated laser radiation, which passes through the single polarizing element and the at least one reciprocal polarization altering optical element and which makes at least two passes through the at least one Faraday optical element, whereby generally collimated laser radiation is output from the optical isolator.
Owner:ELECTRO OPTICS TECH
Terahertz wave generation method and terahertz wave generation device
ActiveCN111033375AAvoid optical damageHigh repetition rateLaser detailsLight demodulationNonlinear optical crystalEngineering
Provided is a terahertz wave generation method used to generate a terahertz wave in a direction that satisfies non-collinear phase matching conditions by inputting pump light into a non-linear opticalcrystal capable of generating the terahertz wave based on an optical parametric effect, wherein the pump light input into the non-linear optical crystal has a pulse width of 10 ps or greater and lessthan or equal to 1 ns with a repetition frequency of 1 kHz or greater, so that the peak excitation power density thereof is greater than or equal to a given terahertz wave oscillation threshold and less than or equal to a given laser damage threshold, and the average excitation power density thereof is less than or equal to a given photorefractive effect generation threshold.
Owner:KK TOPCON +1
Method of manufacturing semiconductor laser using end-face-processing jig
InactiveUS7892866B2Avoid optical damagePrevent degradationLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCatastrophic optical damageNitride
The invention provides an end-face-processing jig that allows the formation of a reflectance control film on an end face of a semiconductor laser body while preventing possible degradation due to catastrophic optical damage (COD) of a semiconductor laser, and a method of manufacturing a semiconductor laser employing such an end-face-processing jig. A window part of the end-face-processing jig is made of at least one of an oxide and a nitride, and semiconductor laser bars are fixed by the end-face-processing jig so that their end faces are exposed through a window of the window part. In this condition, a reflectance control film is formed on the end faces of the semiconductor laser bars for the manufacture of a semiconductor laser. This prevents a metal from being taken in the reflectance control film, thus preventing the absorption of light caused by a metal taken in the reflectance control film. It is thus possible to form a reflectance control film on the end faces of semiconductor laser bars while preventing possible degradation due to COD of a semiconductor laser.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Picosecond seed source excitation device
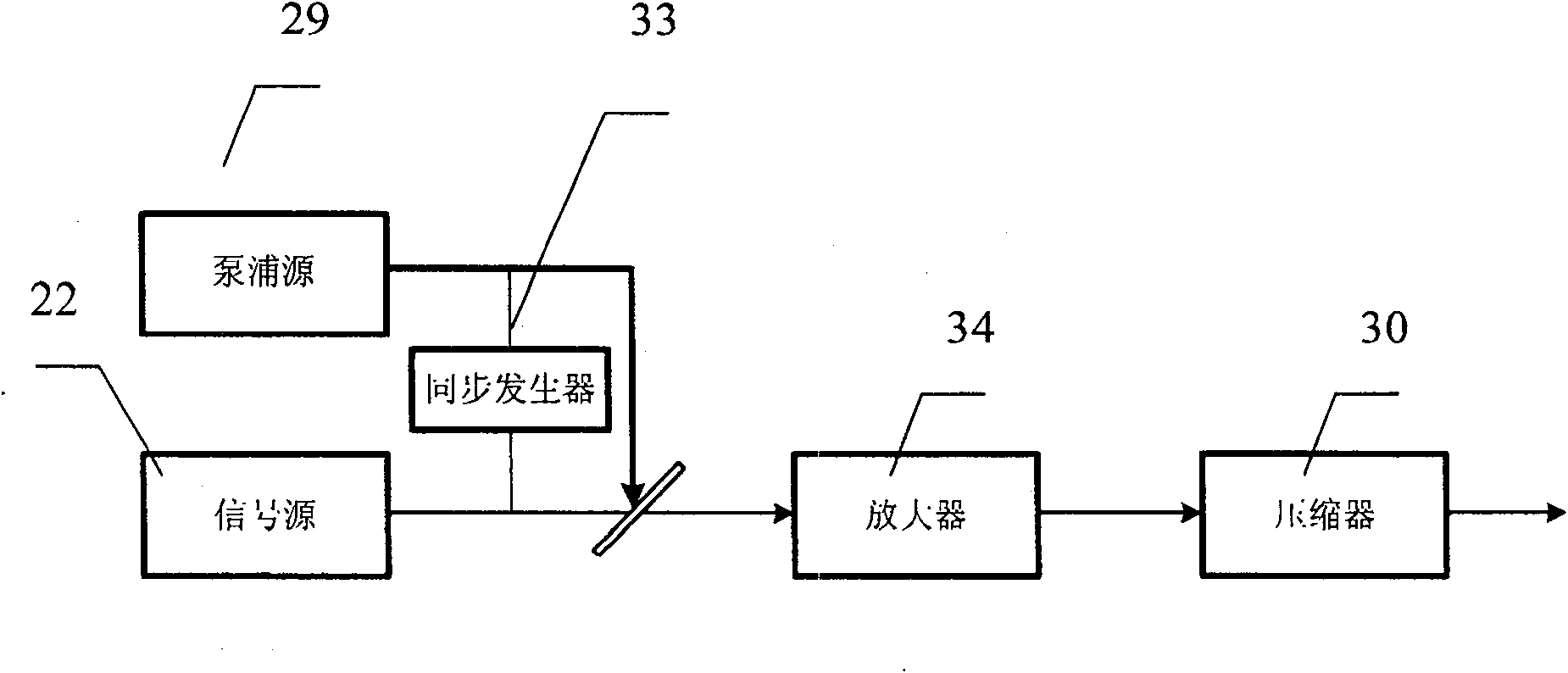
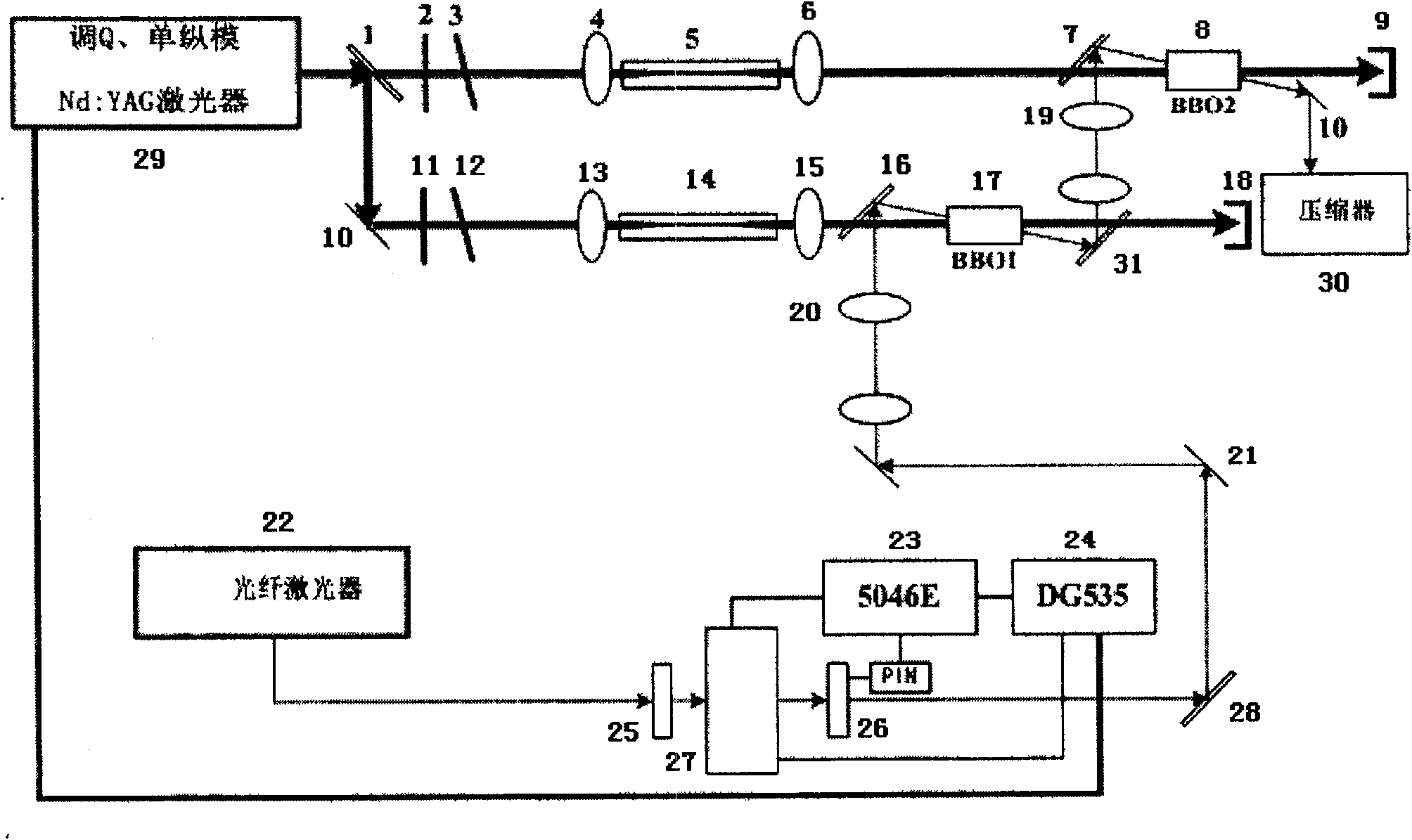
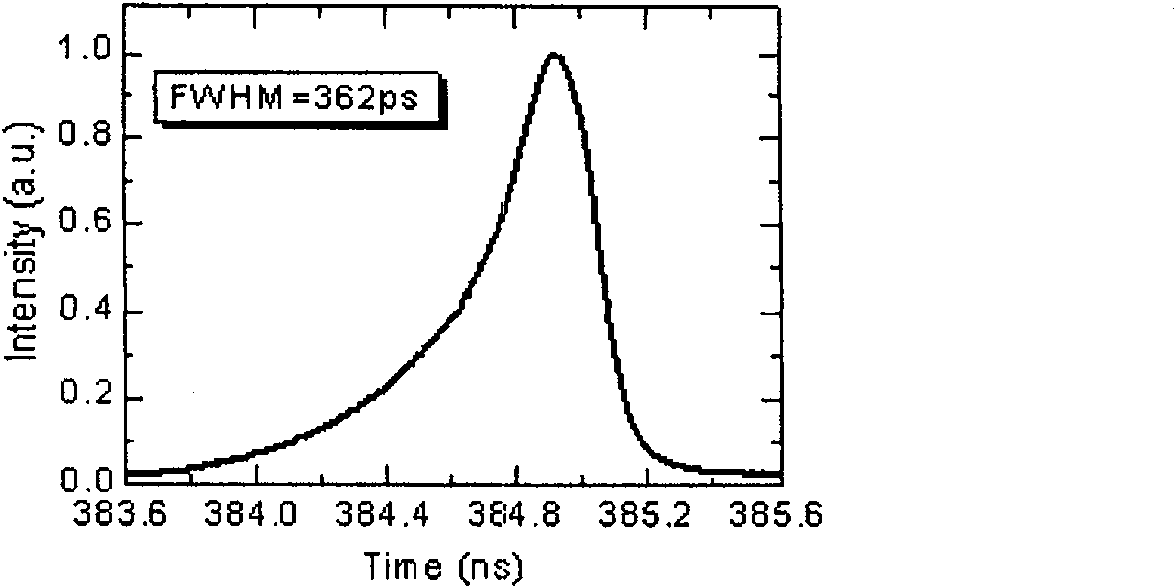
PendingCN113937607AAvoid influenceReduce lossActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionHigh energyDivergence angle
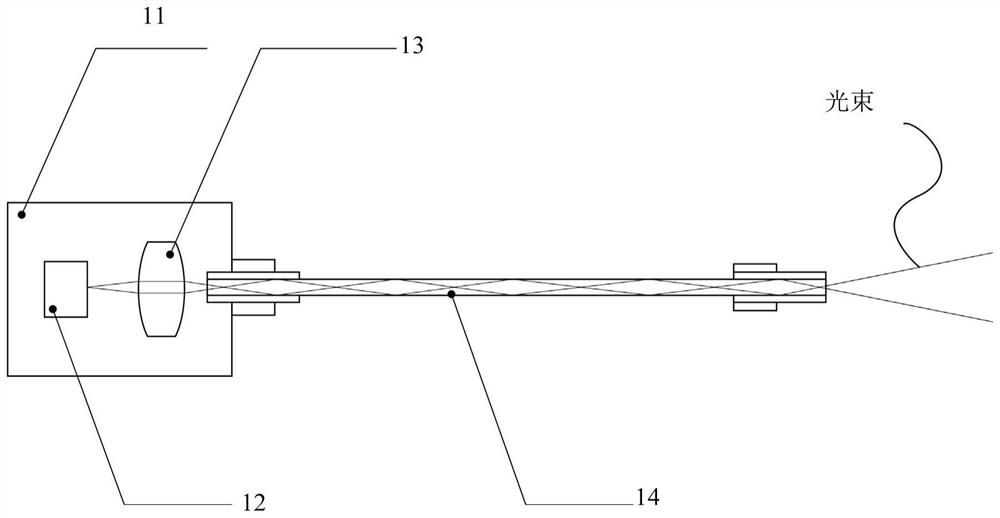
The invention provides a picosecond seed source excitation device, which is characterized in that a resonant cavity is formed by two end surfaces of an Nd:YAG&Cr<4+>:YAG bonding crystal, the Nd:YAG&Cr<4+>:YAG bonding crystal (4) is used as a passive Q-switching crystal, the Q value of the resonant cavity is adjusted by using the saturable absorption characteristic of the Nd:YAG&Cr<4+>:YAG bonding crystal (4) so as to achieve the Q-switching purpose, a collimating mirror (2) and a focusing mirror (3) perform beam shaping on incident pump light so as to make the pump light enter the Nd:YAG&Cr<4+>:YAG bonding crystal (4) at a specific angle and position to form a focus point in the crystal, then the divergence angle of the light beam is shaped and compressed through a concave beam expander lens (6) and a convex beam expander lens (8), and the light beam can pass through an isolator (7) in one direction, so that the influence of the return light on the crystal and the optical fiber and irreversible optical damage are avoided, and the characteristics of high energy, narrow pulse width, high light beam quality, high stability and the like are achieved so as to improve the energy conversion efficiency, reduce the device loss and prolong the service life.
Owner:KEY & CORE TECH INNOVATION INST OF THE GREATER BAY AREA +1
A gas mixture that prolongs the service life of CO2 lasers
The invention discloses a mixed gas for prolonging a service life of a carbon dioxide laser. The gas comprises nitrogen, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, oxygen, xenon and helium. A volume fraction inlcudes nitrogen 5-20%, carbon dioxide 5-20%, carbon monoxide 0-10%, oxygen 0-4%, xenon 3-10%, and the balance helium. The mixed gas can prevent decomposition of a CO2 gas, maintain stability of a CO2 component, and then ensure stability of laser output power of the carbon dioxide laser. The mixed gas can greatly improve the service life of the carbon dioxide laser and prolong the service life of more than 20%. In the invention, cost is low, the cost of the laser is greatly reduced, and optical damages of a mirror surface, which are caused by other surface treatment methods, are avoided.
Owner:LONGKOU KERUI LASER SCI & TECH LTD
Optical parameter amplification system based on full optical fiber laser
InactiveCN100561808CAvoid optical damageImprove stabilityExcitation process/apparatusActive medium shape and constructionAudio power amplifierSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Stack type optical disk changer
InactiveUS7454766B2Maintain qualityEfficiently preventing a cartridge and each tray from movingRecord information storageRecord carrier contruction detailsEngineeringImage quality
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
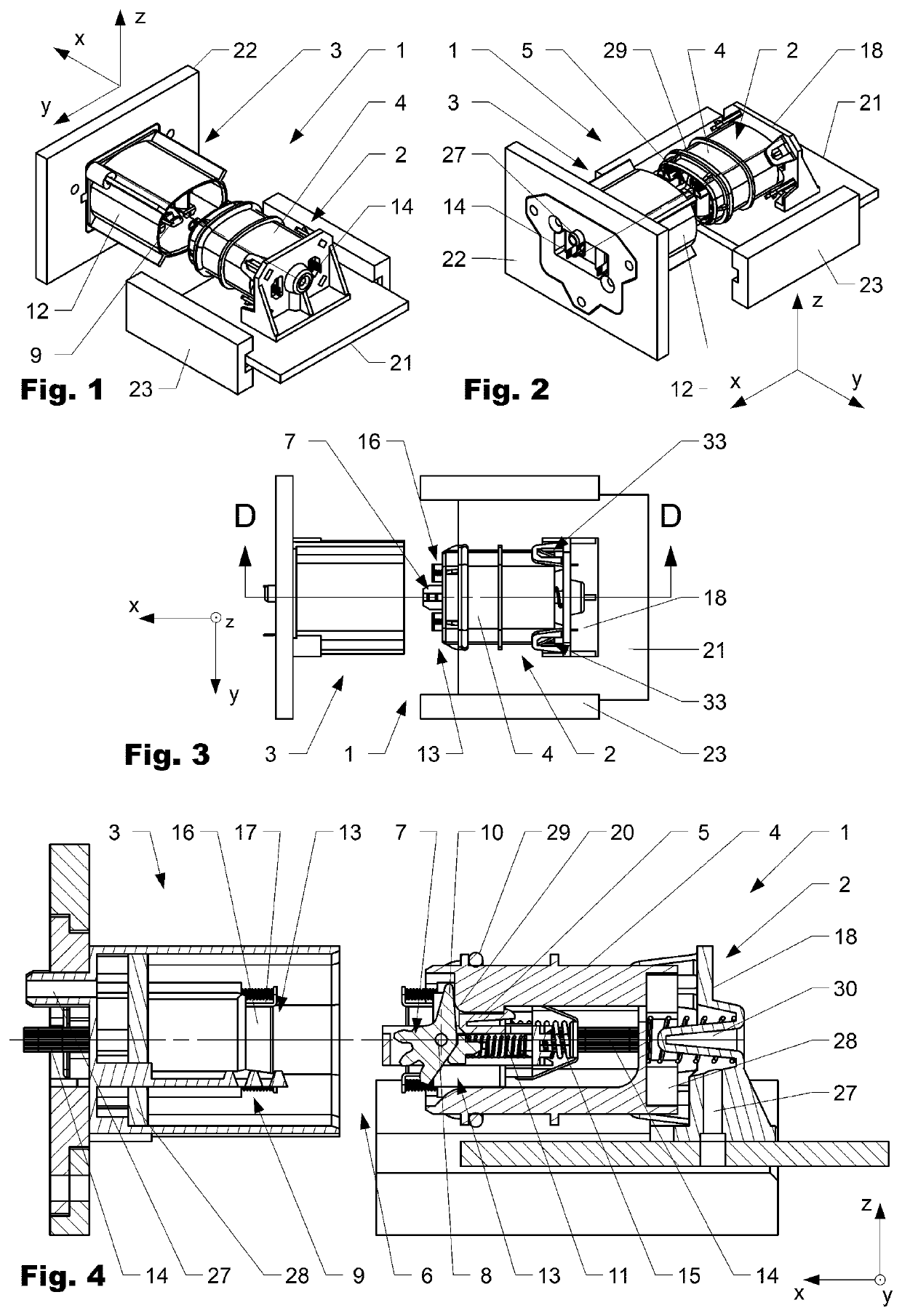
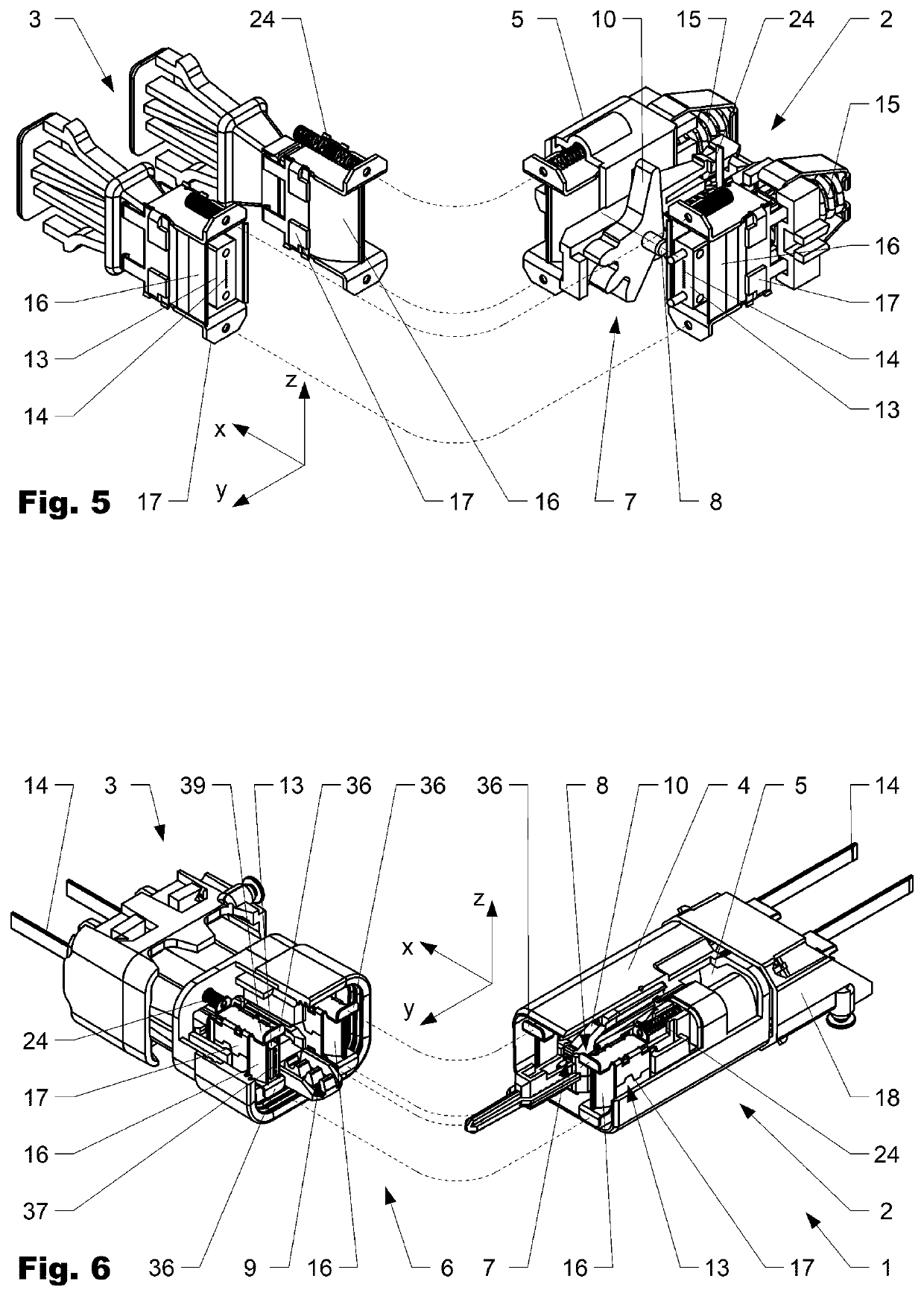
Optical connector assembly comprising a shutter
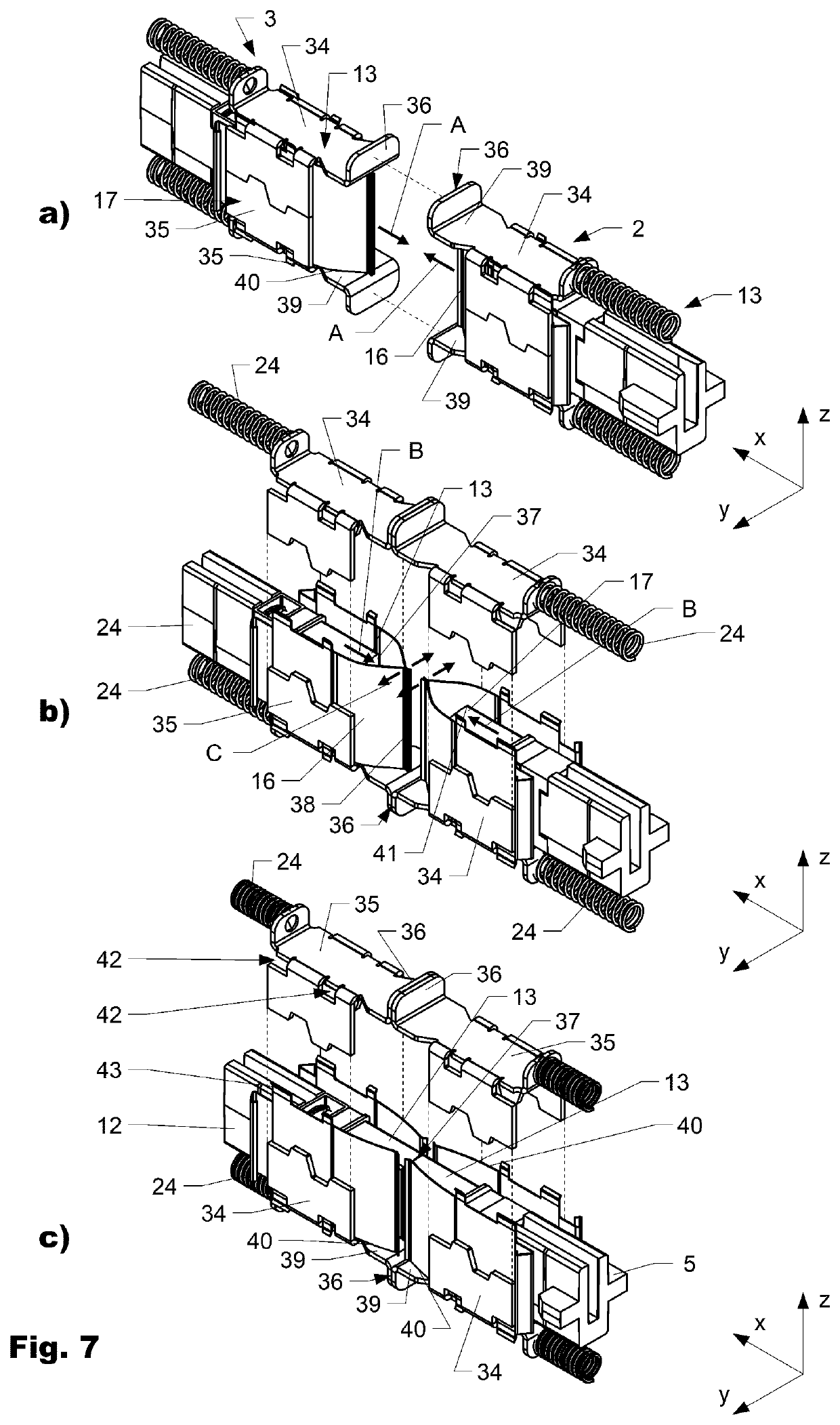
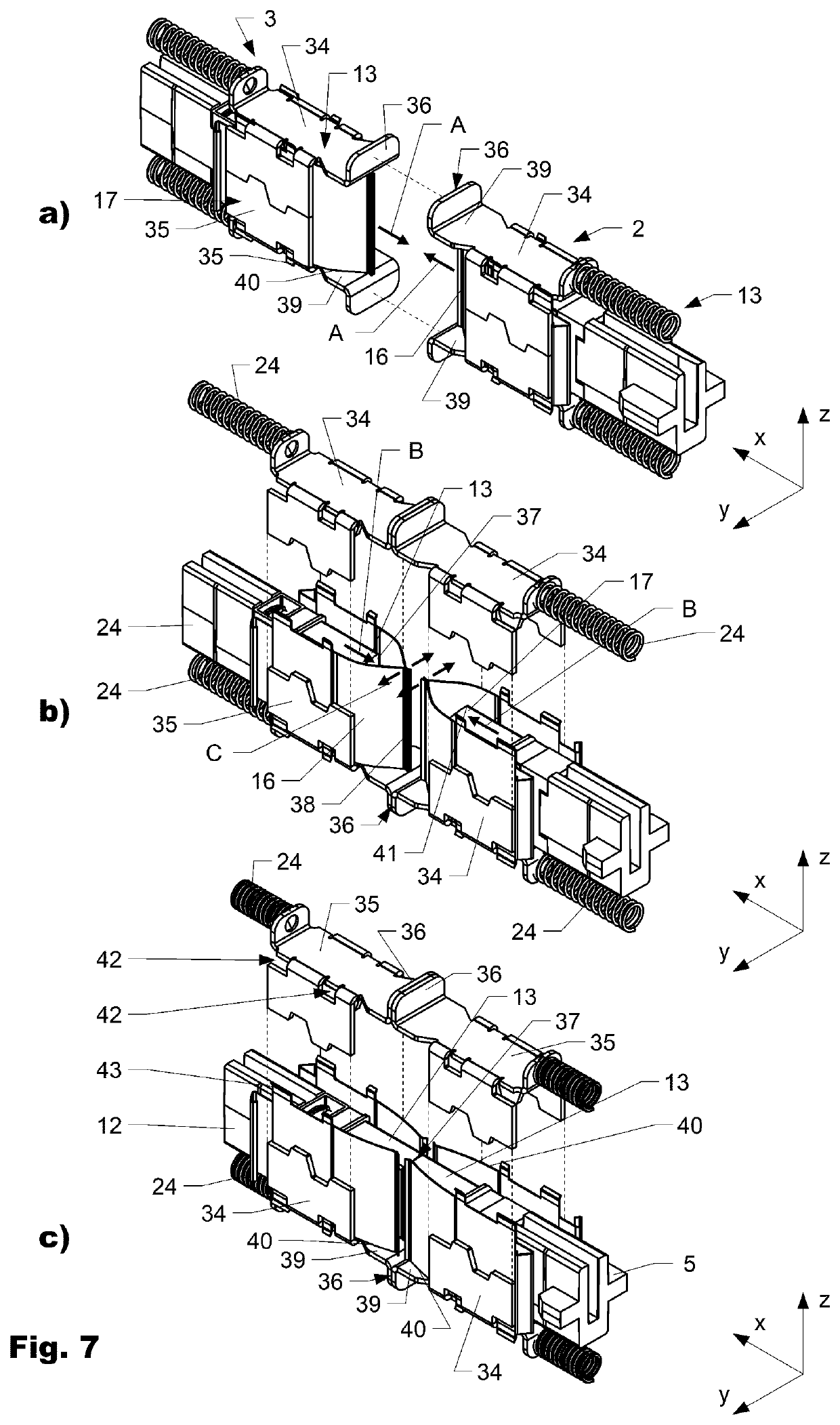
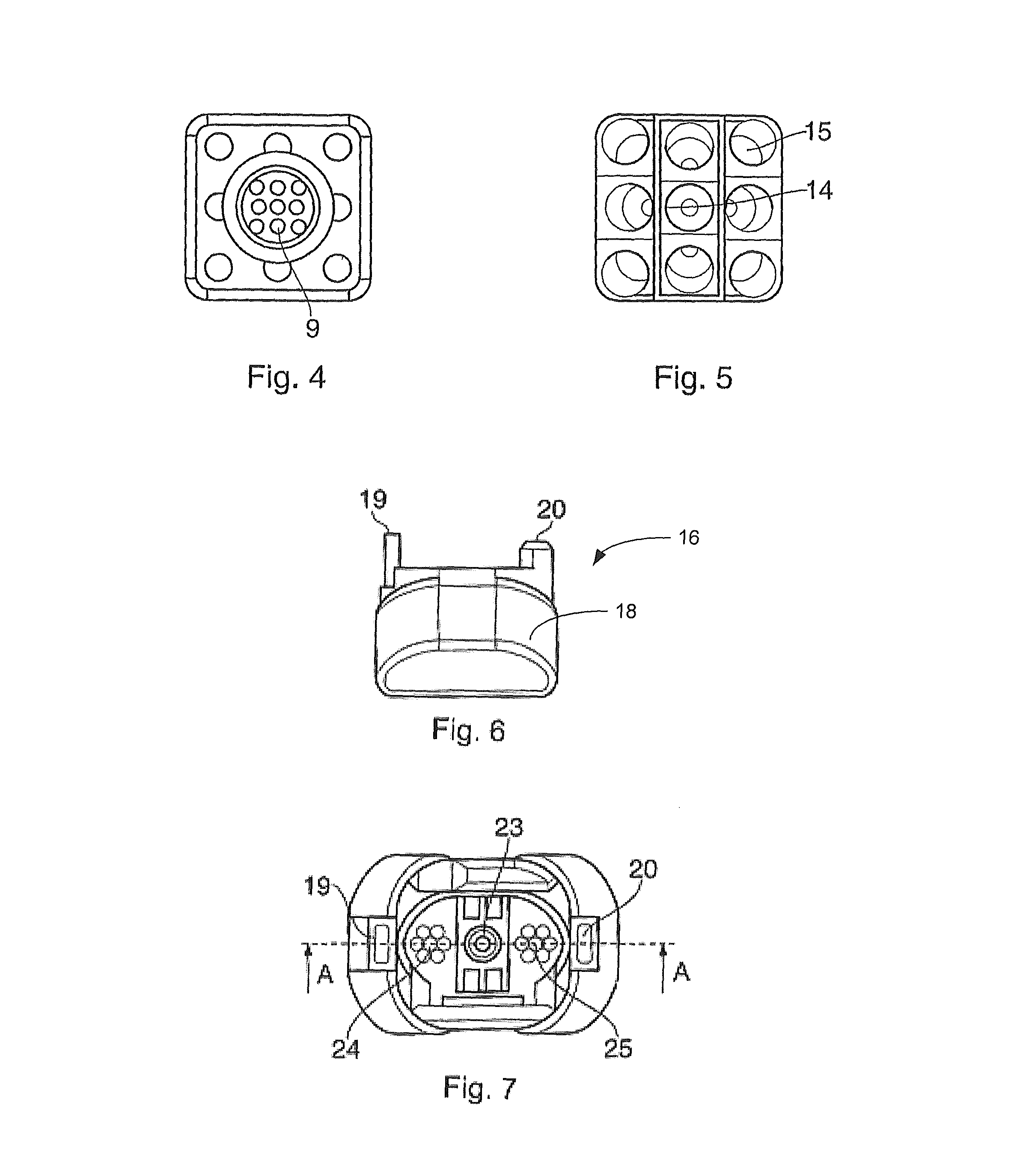
ActiveUS20200355874A1Prevent optical damageMinimize airflowCoupling light guidesWindow shutterFerrule
The invention is directed to a connector assembly (1) comprising a first connector part (2) which is interconnectable to a second connector part (3). The first connector part (2) comprises a ferrule (13) which is encompassed by a shutter frame (17) and a thereto attached shutter (16). The shutter (16) is arranged movable with respect to the ferrule (13) in a first direction (x) between a closed position, in which the shutter (16) encompasses a connection face (37) of the ferrule (13), and an open position, in which the connection face (37) is set free from the shutter (16). The shutter frame (17) and / or the shutter (16) comprises at least one locating surface (36) which during mating interacts with the second connector part (3) such that the shutter (16) is displaced relative to the ferrule (13) from the closed to the open position.
Owner:HUBERSUHNER AG
Optical connector assembly comprising a shutter
ActiveUS11194102B2Avoid optical damageMinimize airflowCoupling light guidesWindow shutterEngineering
The invention is directed to a connector assembly (1) comprising a first connector part (2) which is interconnectable to a second connector part (3). The first connector part (2) comprises a ferrule (13) which is encompassed by a shutter frame (17) and a thereto attached shutter (16). The shutter (16) is arranged movable with respect to the ferrule (13) in a first direction (x) between a closed position, in which the shutter (16) encompasses a connection face (37) of the ferrule (13), and an open position, in which the connection face (37) is set free from the shutter (16). The shutter frame (17) and / or the shutter (16) comprises at least one locating surface (36) which during mating interacts with the second connector part (3) such that the shutter (16) is displaced relative to the ferrule (13) from the closed to the open position.
Owner:HUBERSUHNER AG
Use of electromagnetic radiation in the treatment of sensory organs
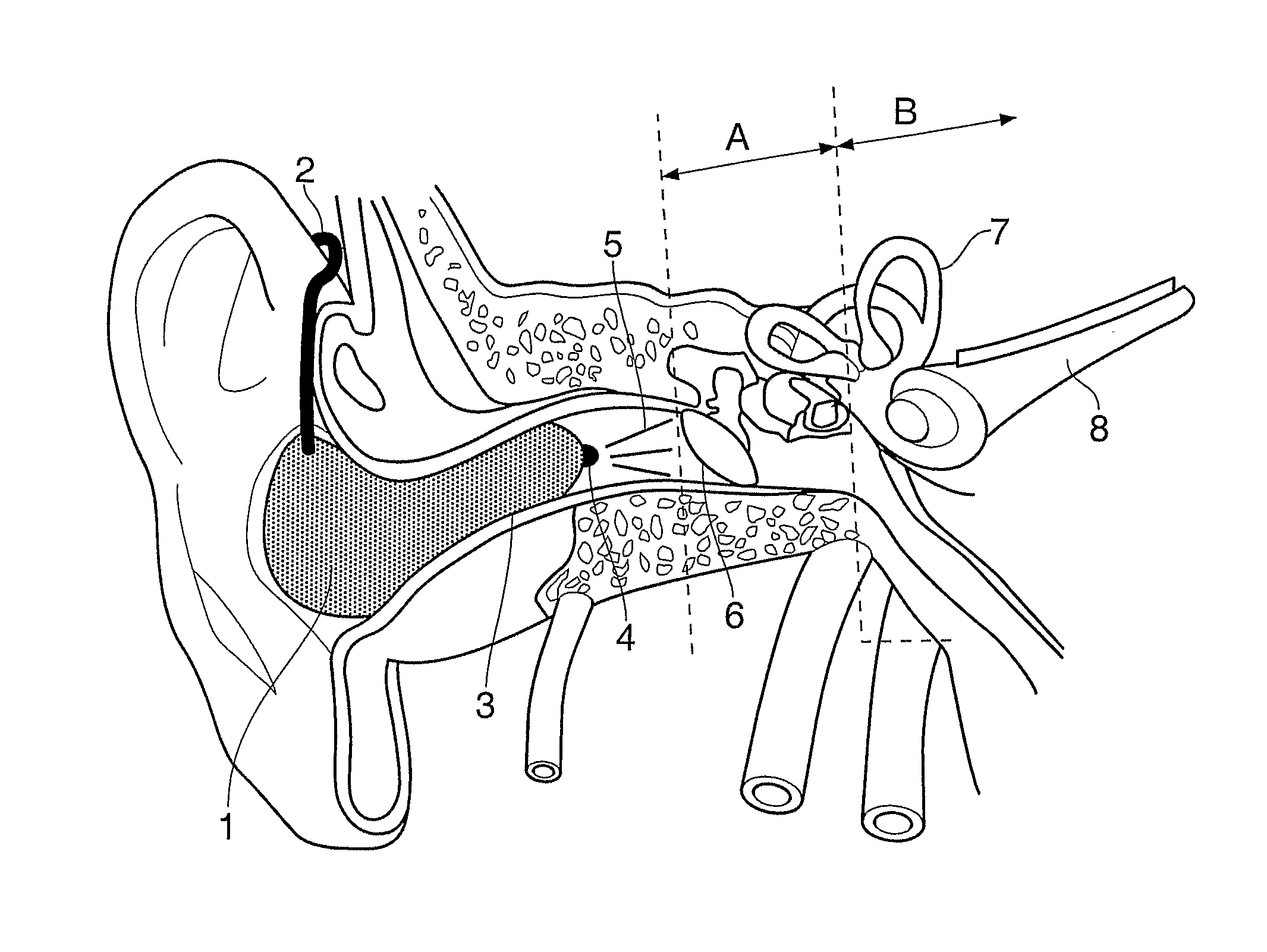
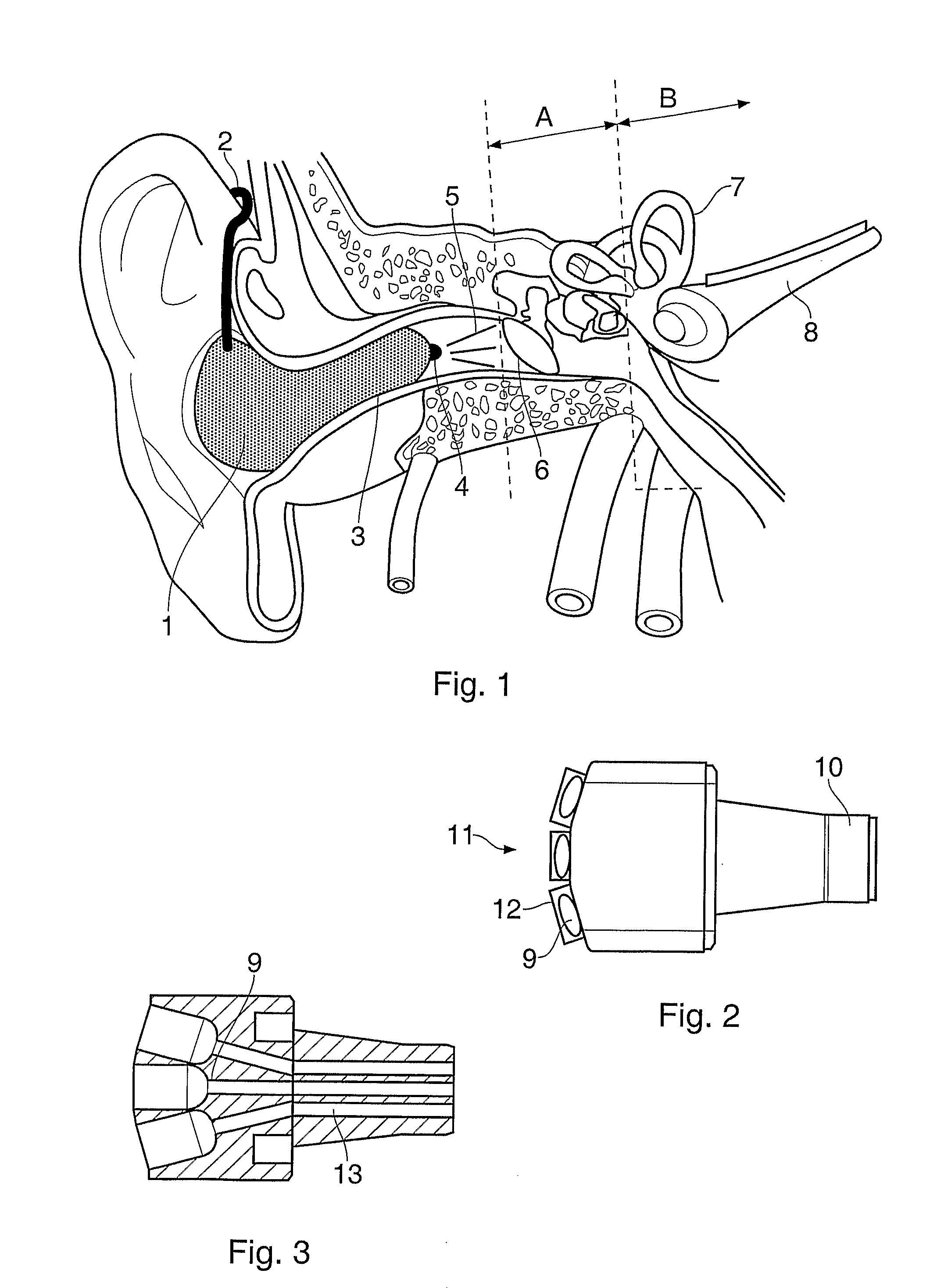
InactiveUS9108044B2Improve hearingEnhance cell viabilityLaser surgeryLight therapySensory organOptic nerve
A method of using and devices for delivering electromagnetic radiation of a selected wavelength for the treatment of conditions pertaining to cephalic sensory organs, in particular to treating conditions of the eye (ocular conditions) and conditions pertaining to the ear (otic conditions). The invention is in particular for the treatment of organelles associated with the acoustic and optic nerves and more particularly for the treatment of age related degeneration of such organelles. The invention also provides devices for treating ocular and otic conditions.
Owner:VIRULITE DISTRIBUTION
Laser resonator, and method of designing laser resonator
ActiveUS10763634B2Avoid optical damageExcitation process/apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionBeam diameterLight beam
A laser resonator includes a pair of optical elements forming a first optical path having a focused beam waist, one or more mirrors forming a second optical path of approximately parallel light connected to the first optical path, and a laser medium arranged in the second optical path. Induced emission light generated from the laser medium reciprocates or circles in a path formed by the first optical path and the second optical path. A distance between the pair of optical elements is adjustable, and a beam diameter at the second optical path is adjusted by adjusting the distance between the pair of optical elements.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRO-COMMUNICATIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com