Patents
Literature
395 results about "Carbon dioxide laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The carbon dioxide laser (CO₂ laser) was one of the earliest gas lasers to be developed. It was invented by Kumar Patel of Bell Labs in 1964, and is still one of the most useful. Carbon dioxide lasers are the highest-power continuous wave lasers that are currently available. They are also quite efficient: the ratio of output power to pump power can be as large as 20%. The CO₂ laser produces a beam of infrared light with the principal wavelength bands centering on 9.4 and 10.6 micrometers (μm).
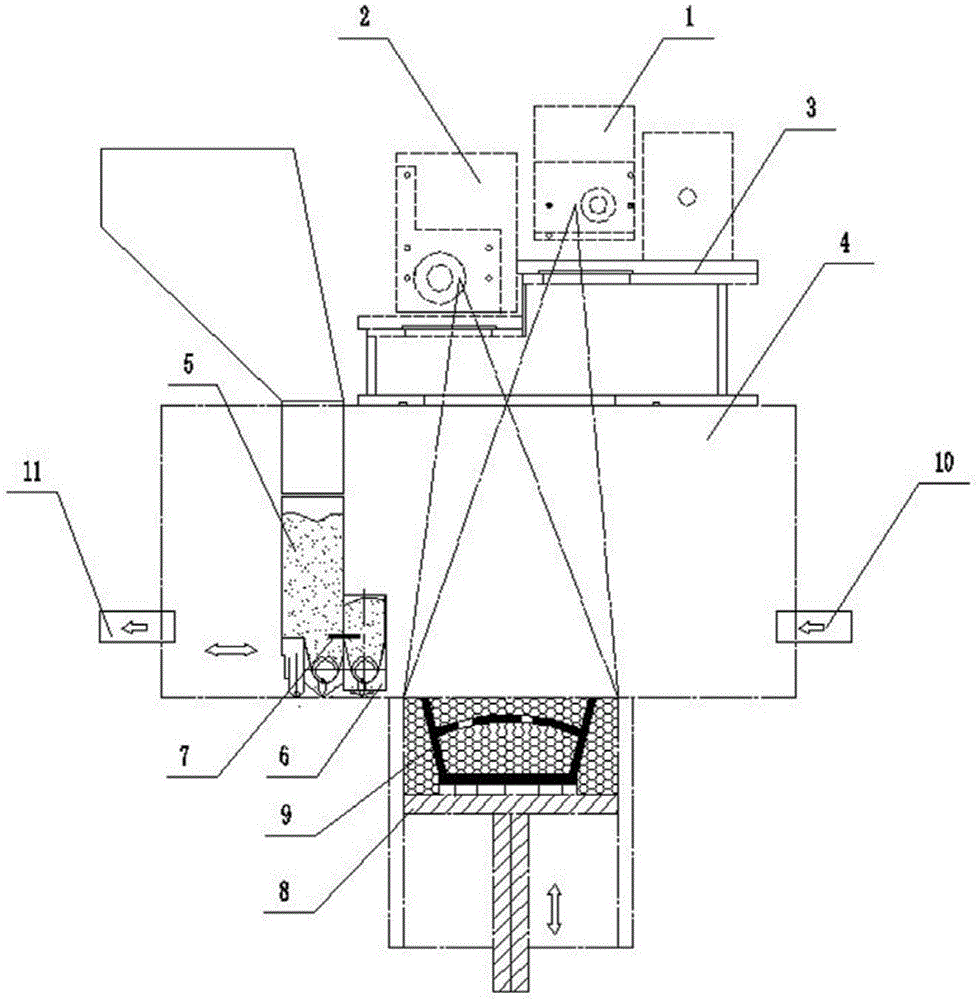
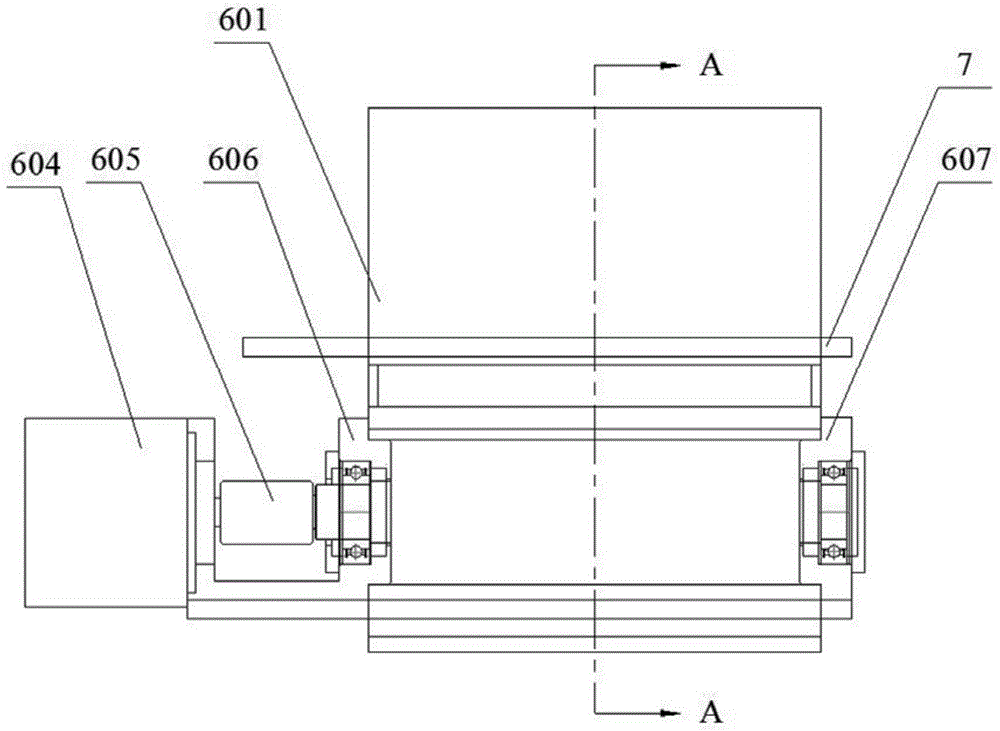
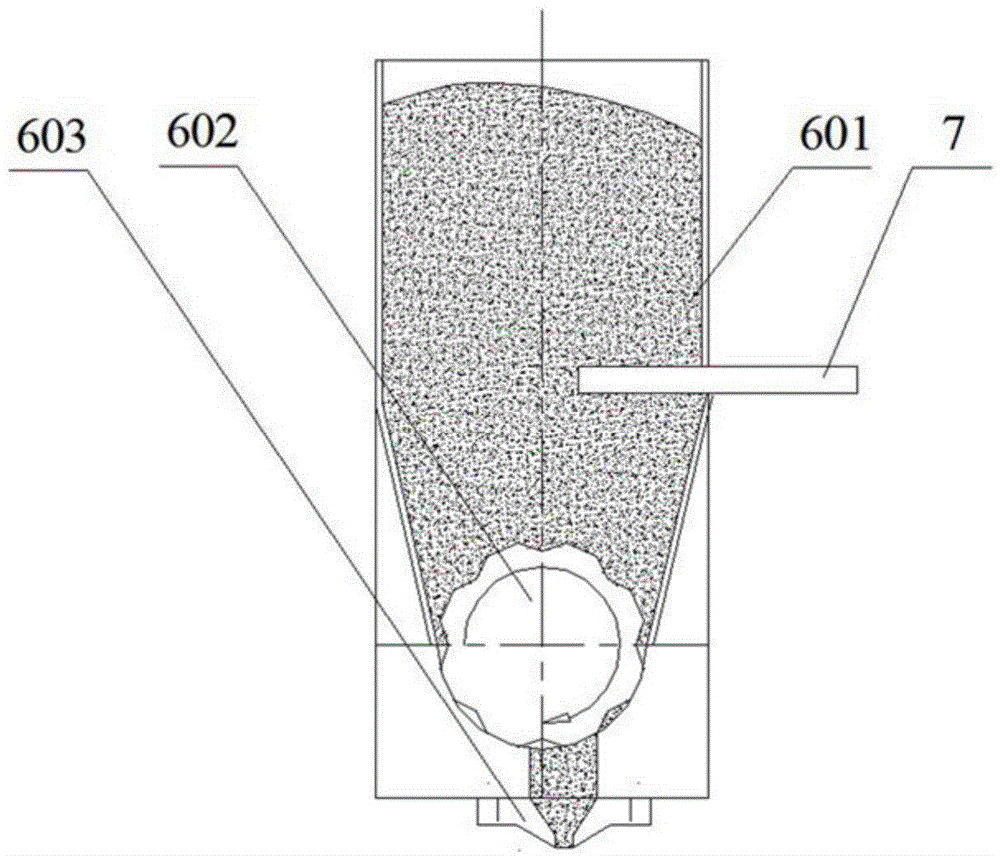
Apparatus and method for improving chamfer quality of disk edge surfaces with laser treatment
A carbon dioxide laser is used as a non-mechanical means for smoothing and polishing the as-cut chamfer surface at the edge of the disk. Applying laser radiation to the glass surface causes transient melting and resolidification. Due to surface tension effects, the glass resolidifies to produce a surface that is significantly smoother than it was before irradiation. If scratches or abrasive marks are present on the glass surface prior to irradiation, the irradiation process "polishes out" these defects as long as they are not too deep. At a wavelength near 10 mum, the penetration depth of the radiation into the glass is approximately 1 mum. Therefore, scratches and defects of this order of magnitude are eliminated. The quality of the resulting modified chamfer surface is far superior to the original mechanically ground and polished surface.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Glass-plate cutting machine
InactiveUS7642483B2Improve cut qualityQuality improvementFine working devicesGlass reforming apparatusLight beamEngineering
A glass plate cutting machine using a laser beam is provided to solve problems, such as uneven glass section and slanting cutting. By using the glass plate cutting machine of the current invention, the glass plate is irradiated with a first carbon dioxide laser beam of 0.05-2 joule / mm2 on a long oval shaped area of 20-200 mm2 according to an expected cutting line thereof, and immediately cooled with water, to generate a scribe line, which is then further irradiated with a second carbon dioxide laser beam of 0.1-0.5 joule / mm′ on the area of 20-200 mm2 thus obtaining a superior glass section.
Owner:RORZE SYST
Method of drilling a hole through Co2 laser directly
InactiveCN1761378AHigh precisionGuaranteed alignmentConductive material chemical/electrolytical removalLaser beam welding apparatusEtchingCopper foil
Drilling method of carbon dioxide laser includes steps: preparing locating point on layer next to the outer layer; before pressfitting added layer, browning oxidizing surface of target bonding pad; after pressfitting added layer, milling location hole / polishing edge, washing surface under high pressure; browning front surface of copper, thinning and coursing the surface before drilling hole by layer; first time to drill hole by laser; positioning film perforation by using plate location hole in original etching method for making window of copper, burning through copper foil and resin above the locating point on layer next to the outer layer so as to expose the locating point; second time to drill hole by laser; using the exposed locating point as position fixing to make micro hole inplate; washing surface under high pressure to remove browning layer after drill hole. The invention saves dry film and etching liquid, and raises process precision.
Owner:WUS PRINTED CIRCUIT (KUNSHAN) CO LTD
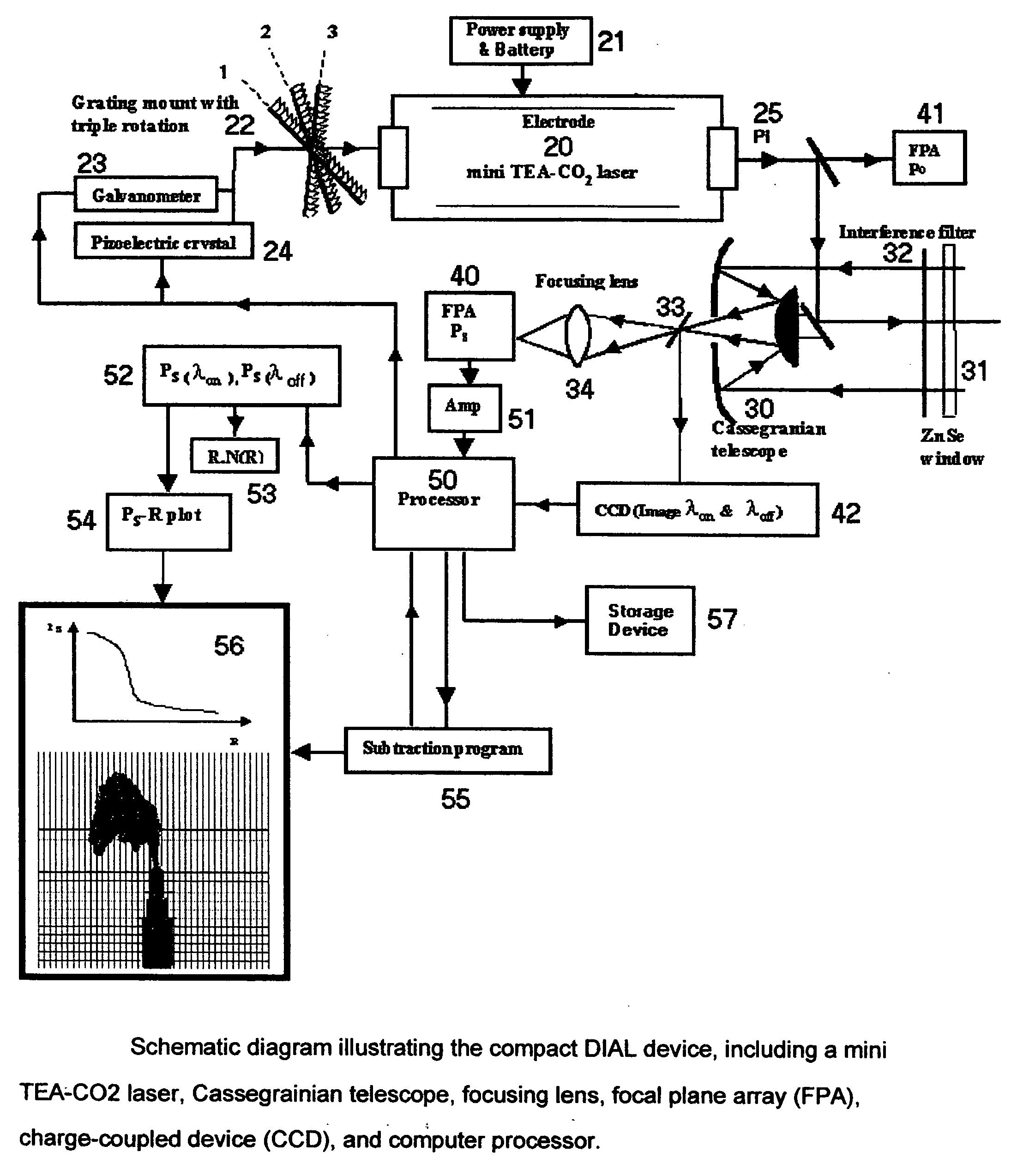
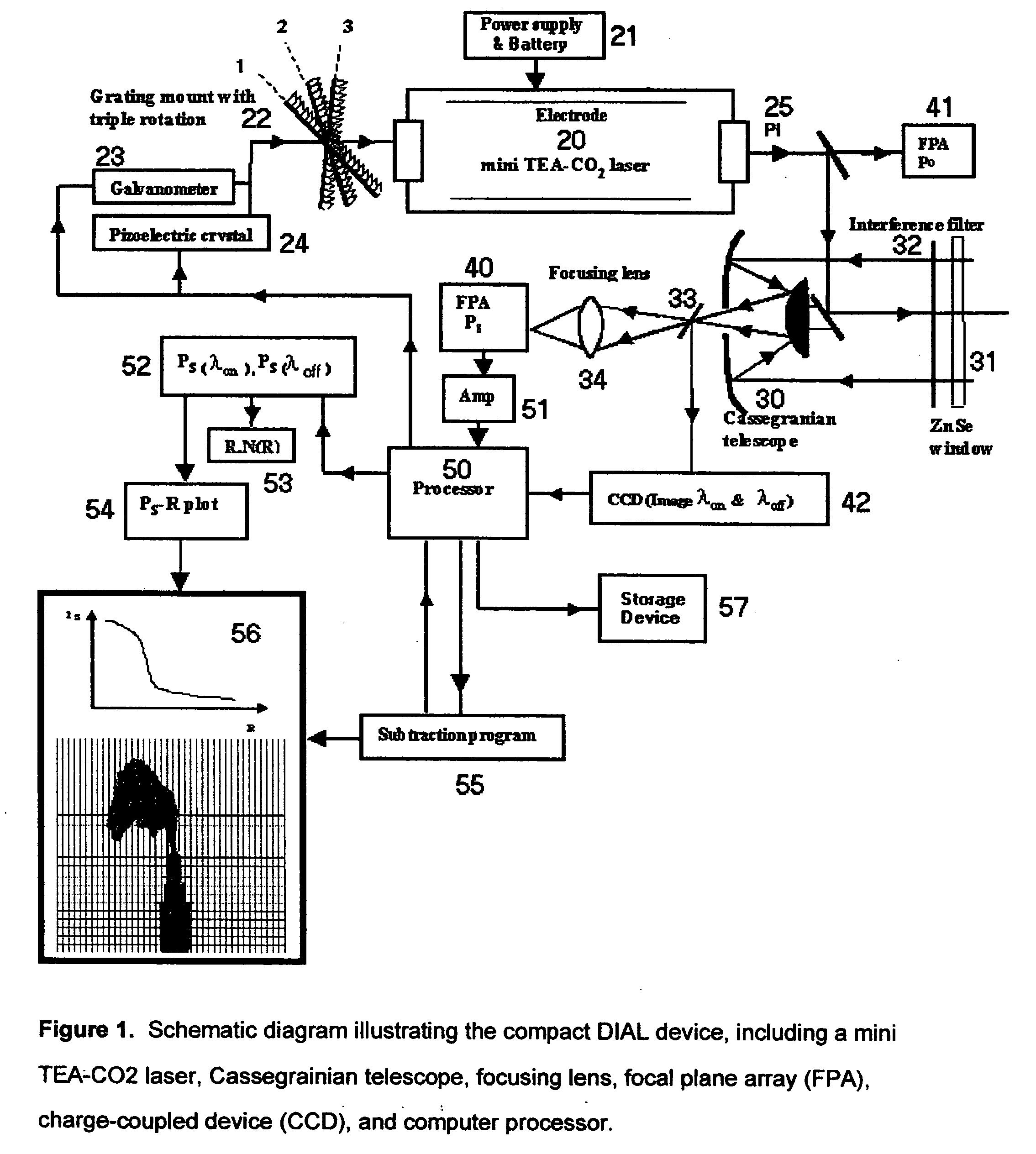
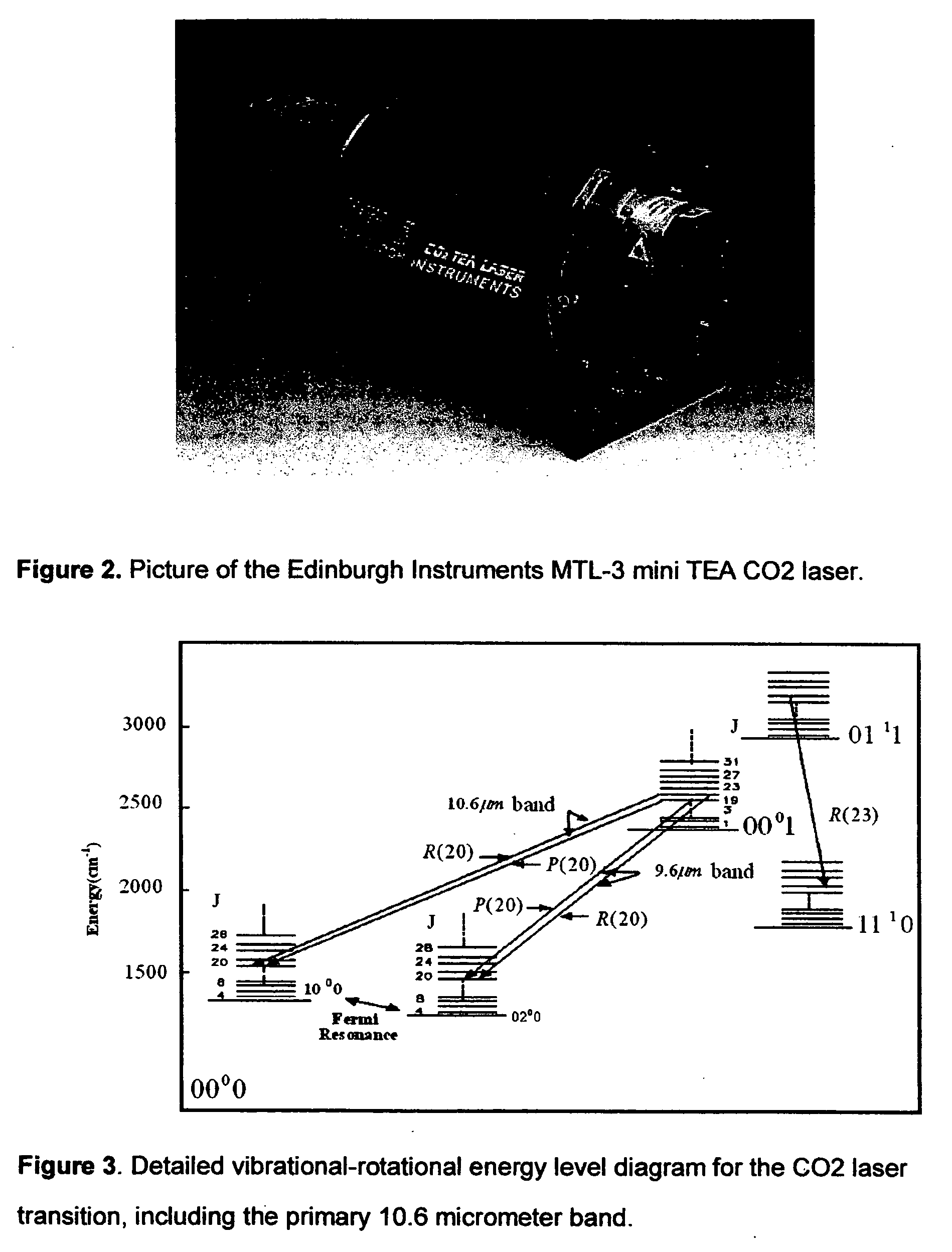
Machine for detecting sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) leaks using a carbon dioxide laser and the differential absorption lidar ( DIAL) technique and process for making same
InactiveUS20070018104A1Minimal manipulationQuantify distanceRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsSulfur hexafluorideRechargeable battery pack
A machine for detecting sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) leaks using the mid-infrared differential absorption lidar (DIAL) technique with a commercically available, air-cooled, compact, pulsed transversely-excited-atmospheric (TEA) carbon dioxide (CO.sub.2) laser, a Cassegranian optical telescope for focusing both the laser emission and returning reflected signal, a user-operated focusing mechanism, a two-dimensional, thermoelectrically-cooled focal plane array (FPA) sensitive in the mid-infrared wavelength range (10.2-10.6 micrometers), a charge-coupled device (CCD) for 2-D imaging, a computer-based control system to rapidly switch the laser wavelength between 10.2470 micrometers, 10.7415 micrometers, and 10.5518 micrometers to utilize the Differential Absorption Lidar (DIAL) chemical detection technique, a rechargeable battery pack and power supply, and an image and data storage device using a solid-state memory stick.
Owner:PARVIN PARVIZ +1
Optical fiber F-P (Fabry-Perot) cavity pressure sensor with temperature self compensation
InactiveCN103644987AForce measurement by measuring optical property variationGratingSelf compensation
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical fiber sensing, and relates to an optical fiber F-P (Fabry-Perot) cavity pressure sensor with temperature self compensation. The F-P cavity pressure sensor with temperature self compensation adopts an optical fiber with an optical grating as a transmission optical fiber and adopts an optical F-P cavity as a pressure sensitive element, wherein the F-P cavity sensitive element is a non-intrinsic optical fiber F-P cavity, and the optical fiber gating and the optical F-P cavity are connected in a mode of glue bonding or carbon dioxide laser welding. According to the mode of pressure sensing, the sensor is divided into side pressure type optical fiber F-P cavity pressure sensors with temperature self compensation and end pressure type optical fiber F-P cavity pressure sensors with temperature self compensation.
Owner:BEIJING CHANGCHENG INST OF METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT AVIATION IND CORP OF CHINA
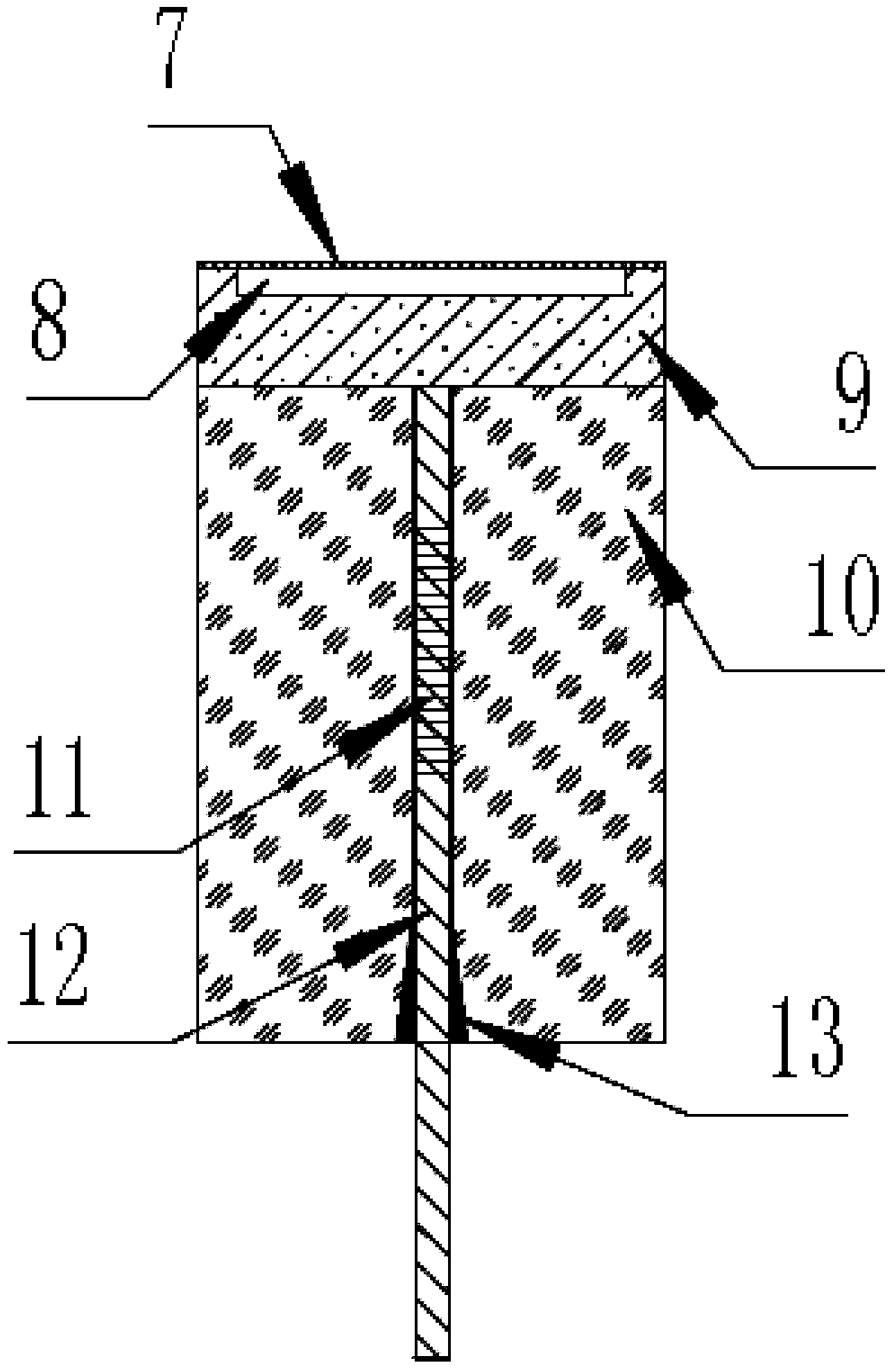
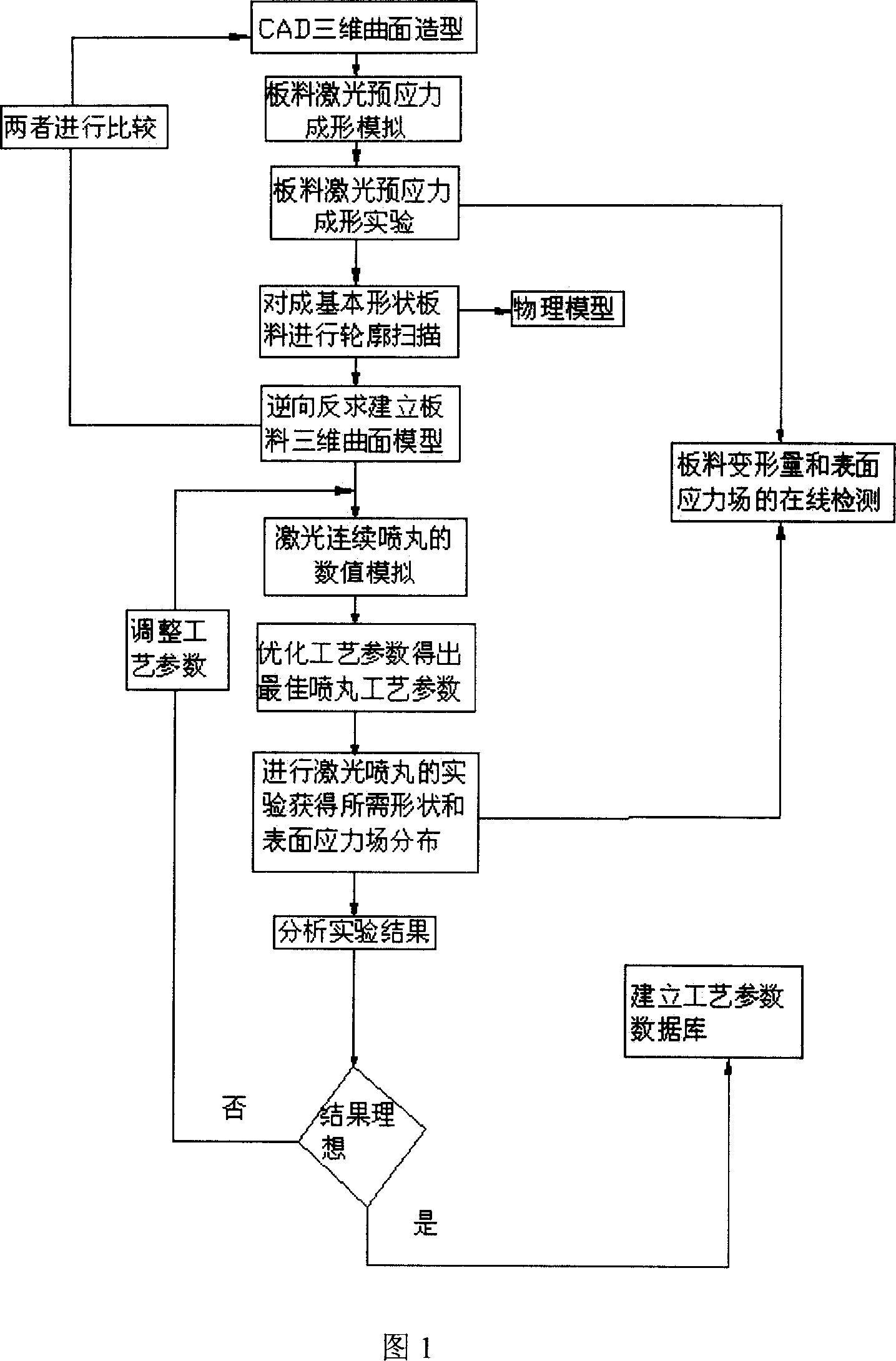
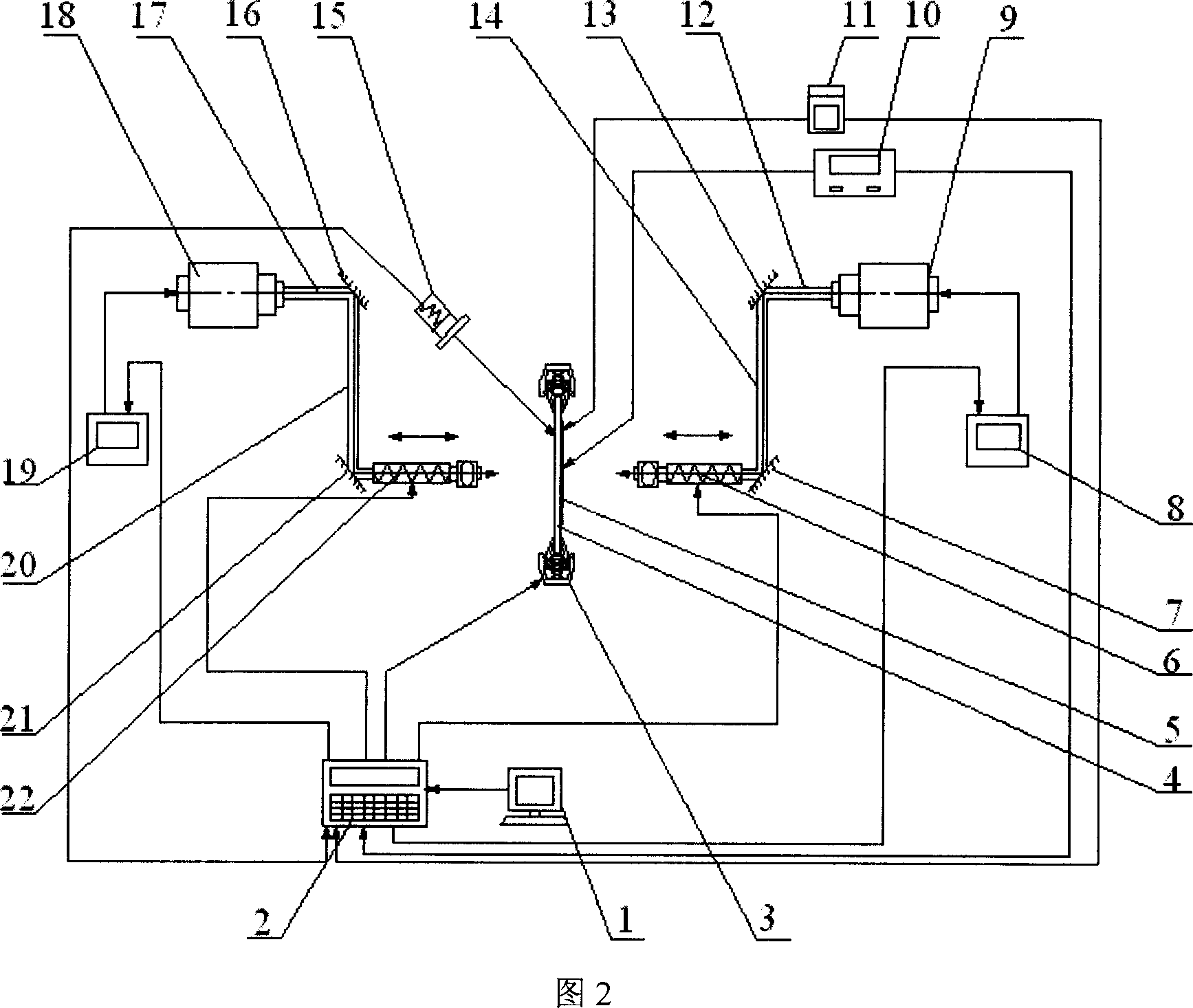
Method and apparatus of forming cut deal laser prestress composite shot blasting
InactiveCN101011777AImprove surface qualityImprove fatigue resistanceNumerical controlLaser beam welding apparatusSurface stressLaser light
A cut deal laser inherent stress composite peen forming features in the clipper using robot, using carbon dioxide to realize the basic formation, profile measuring feedback system controlling the deformation quantity, left stress meter measuring the surface stress of the board, optical scanning the pre formation, realizing board through model analog software, getting optimized process parameter instructing laser consecutive peen formation, using neodymium glass laser providing short pulse strong laser light, laser impact wave as the force source of precise forming, using the profile feedback device and on line measuring board surface stress left stress to control the deformation quantity to realize precision forming with complex shapes.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Minisize plasma pen for removing speckle of skin
InactiveCN101259036ANo painReduce manufacturing costSurgical instrument detailsRadiation therapyFrequency changerTransformer
The invention relates to a micro plasma pen for removing freckles on skin, and comprises a plasma skin cleaning head, a handle shell, a micro transducer arranged in the shell, a power output controller and a power module. The pen is characterized in that: a high and variable frequency plasma power occurrence circuit made of an integrated circuit chip or a semiconductor microprocessor MCU is installed in the shell; and in a loop, a circuit connection is formed by a medium and high frequency output magnetic core transformer or a ceramic piezoelectric type medium and high frequency transformer. Since the mini plasma pen for removing the freckles on the skin has a small size, a long service life and extremely low cost, the pen has the advantages of no pain when put into use, a self-sterilizing function, capability of being used as a tool for personal beautifying like nail clippers and small blades, a large social demand of nearly for anyone, and capability of replacing a carbon dioxide laser epidermal freckle removing machine in a hospital on a plurality of occasions.
Owner:徐小羚
Copper-clad board suitable for making hole with carbon dioxide laser, method of making hole in said copper-clad board and printed wiring board comprising said copper-clad board
InactiveUS6736988B1Not easy to peel offPromote absorptionInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementLight absorption dielectricsSurface layerHigh absorption
A copper-clad board suitable for making a hole with a carbon dioxide gas laser, which copper-clad board is obtained by disposing a double-side-treated copper foil provided with a metallic-treatment layer having a high absorption rate of a carbon dioxide gas laser energy on at least one surface, at least on an outer layer of a thermosetting resin composition layer such that the metallic-treatment layer is formed on a shiny surface of the copper foil which shiny surface is to be a surface layer, and laminate-forming the double-side-treated copper foil and the thermosetting resin composition layer under heat and pressure, to make an alloy of the metallic-treatment layer and the copper by the above heating, a method of making hole in the above copper-clad board and a printed wiring board comprising the above copper-clad board.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Dual selective laser sintering and nonmetal and metal melting 3D (three-dimensional) printing system
ActiveCN104923786ACompact structureImprove forming efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencySelective laser sinteringReciprocating motion
The invention discloses a dual selective laser sintering and nonmetal and metal melting 3D (three-dimensional) printing system which comprises two laser scanning devices, a main powder spreading device and a control device. The 3D printing system is characterized by further comprising an auxiliary powder spreading device integrally connected with the main powder spreading device through a connecting support and positioned in front of the main powder spreading device, the auxiliary powder spreading device and the main powder spreading device horizontally and bidirectionally reciprocate, metal powder and nonmetal powder are placed in the main powder spreading device and the auxiliary powder spreading device respectively, the main powder spreading device spreads a layer of metal powder when moving every time, the auxiliary powder spreading device controlled by the control device quantitatively spreads the nonmetal powder downwards at fixed points, and the spread nonmetal powder can be covered by later spread metal powder. The 3D printing system has the advantages that part forming efficiency can be effectively improved by dual-laser composite scanning, the metal powder is preheated while the nonmetal powder is sintered by carbon dioxide laser, and the defects such as warping and cracking of metal parts can be effectively avoided.
Owner:GUANGZHOU OGGI3D ELECTROMECHANICAL
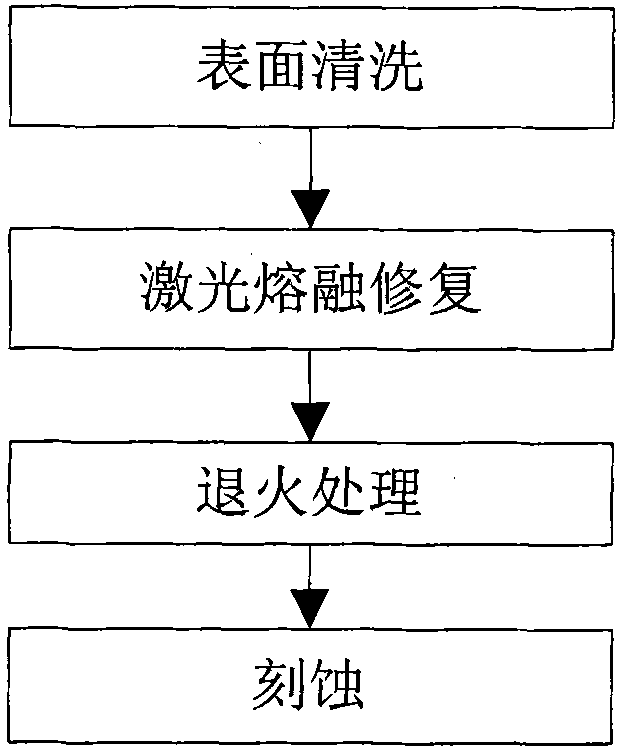
Method for repairing fused quartz optical damage component
The invention discloses a method for repairing a fused quartz optical damage component, which belongs to the technical field of the optical material and the optical component, in particular to a method for repairing and processing laser damage of a fused quartz optical component. The method comprises the following steps: firstly adopting infrared carbon dioxide laser to carry out laser fusion repair on the damage part of the fused quartz optical damage component; and then carrying out annealing treatment on the fused quartz optical damage component subjected to laser fusion repair. The method can carry out complete repair on the fused quartz optical damage component and eliminate residual stress caused by the laser fusion repairing process. The fused quartz optical component repaired by the method can revert to the state of the ideal fused quartz optical component. And the method also can inhibit the increase of the damage points of the fused quartz optical component. The method can prolong the service life of the fused quartz optical component, greatly reduces operation cost and has the characteristics of strong process controllability, high repetitiveness and stable performance.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
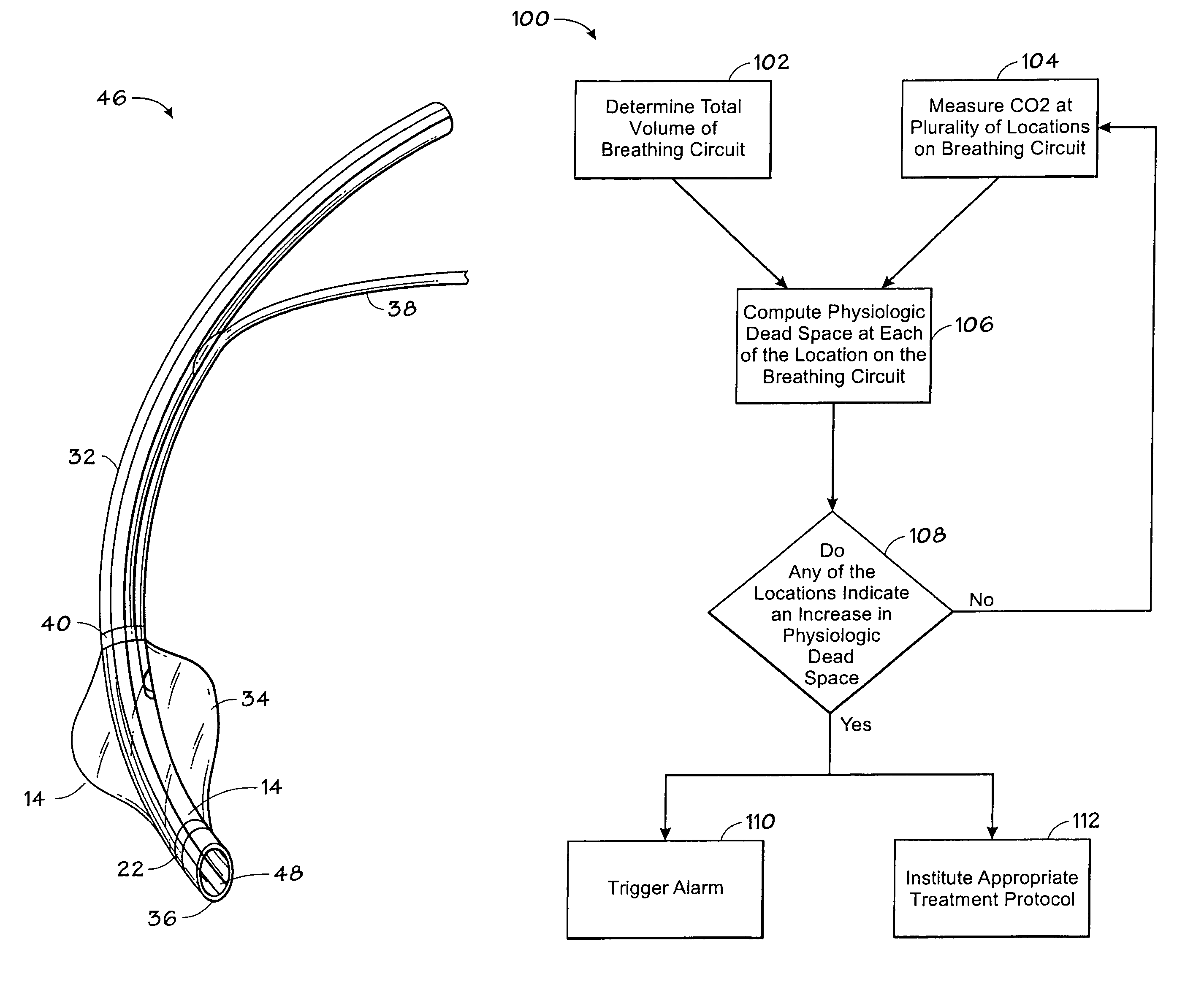
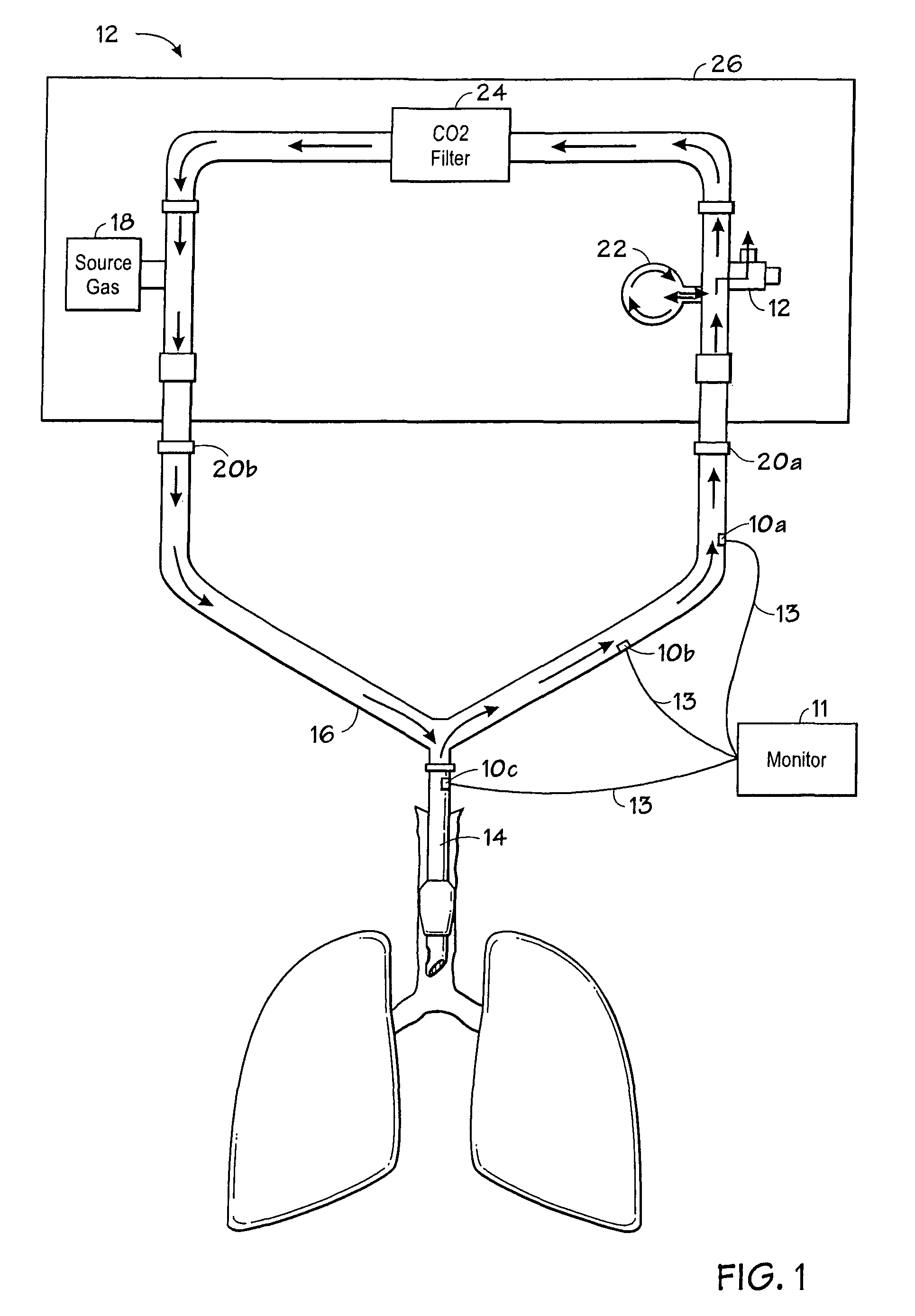
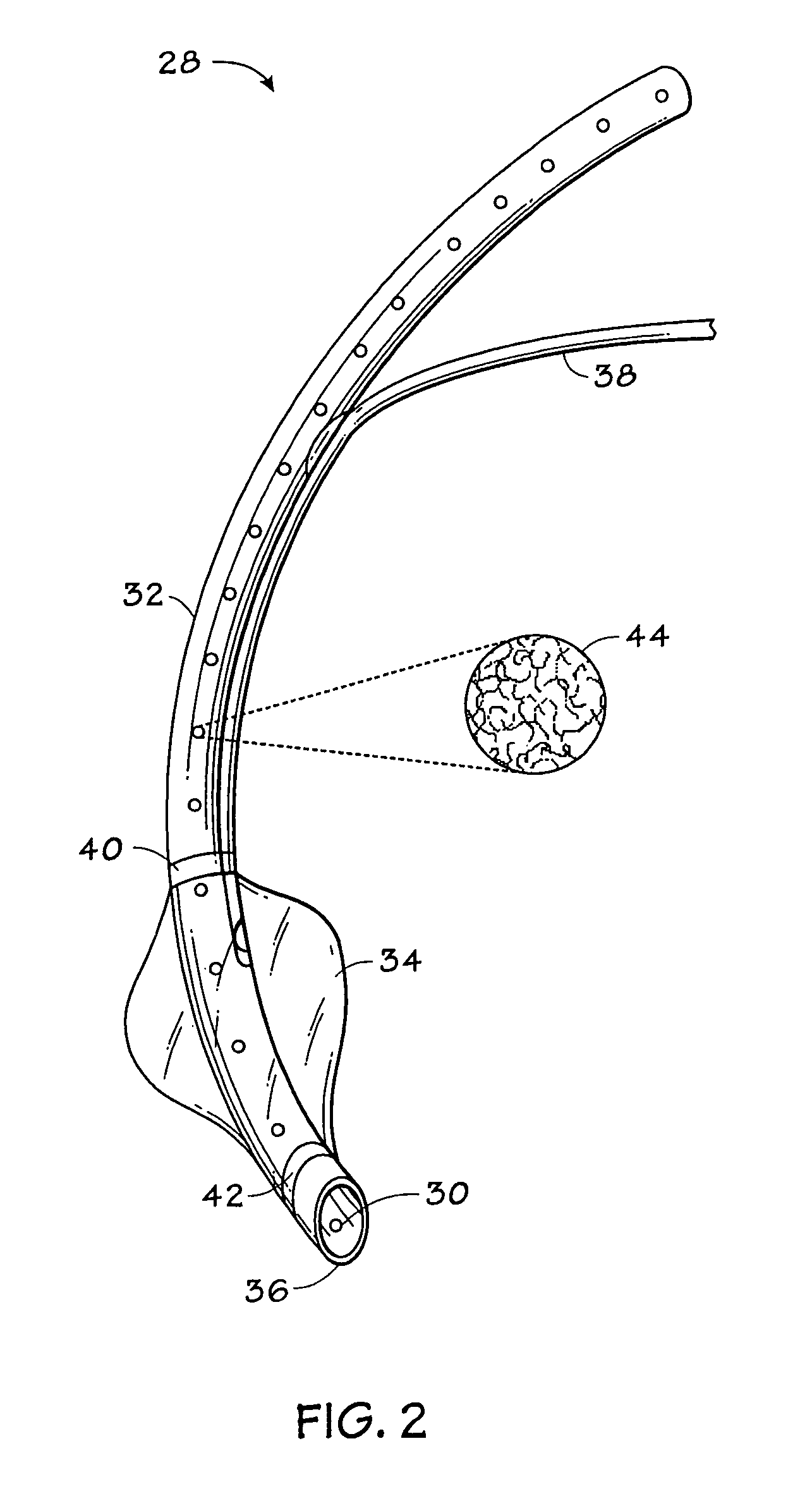
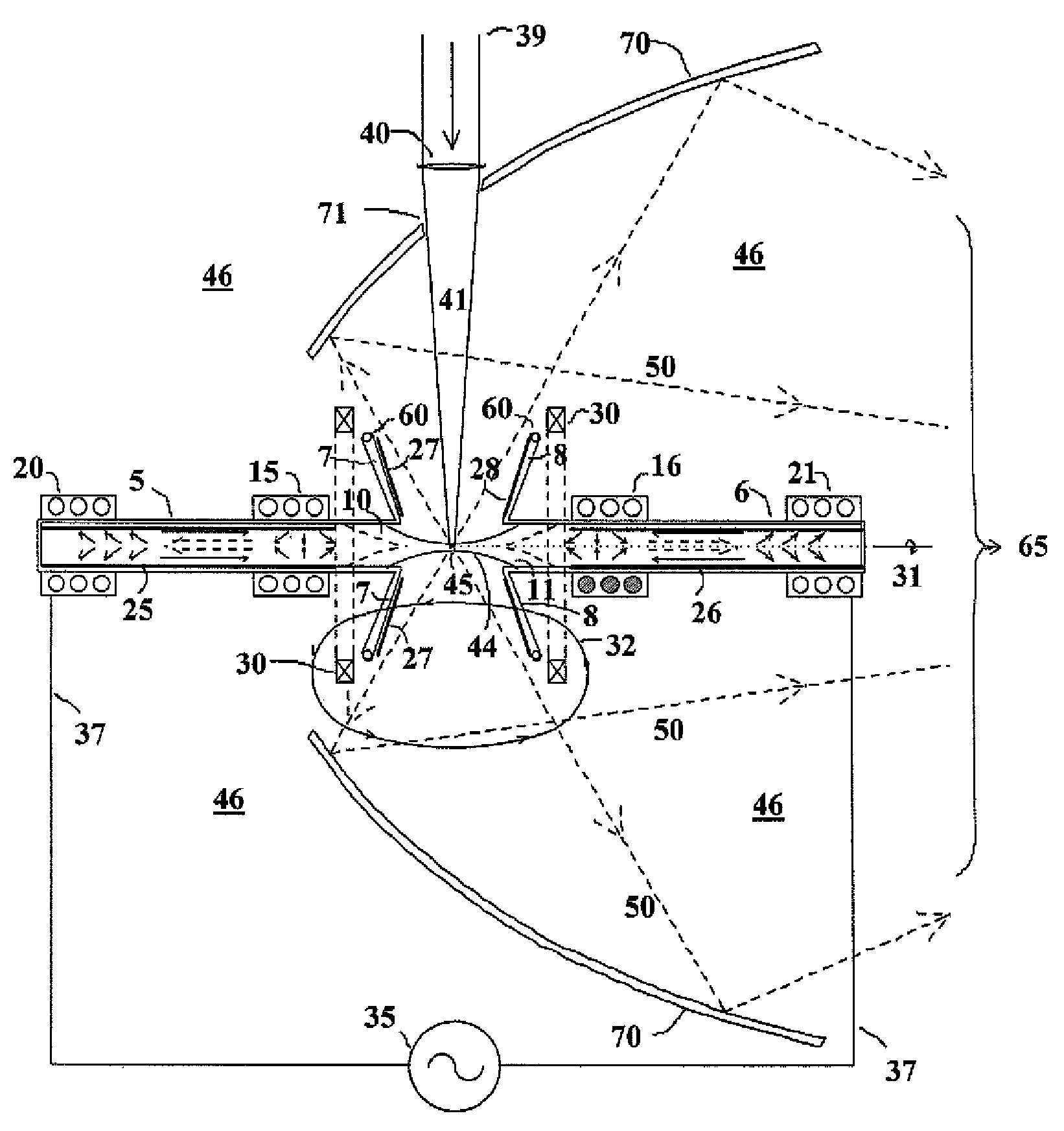
Carbon dioxide-sensing airway products and technique for using the same
InactiveUS7992561B2Tracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesVentilator settingsBiomedical engineering
An airway device is provided that may track the flow of respiratory gases through the device with sensing elements at a plurality of locations along the gas flow path of the device. Such a device may be useful for assessing a variety of clinical states, for adjusting patient ventilator settings, or for determining whether or not an airway device has been properly inserted into a patient airway.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Laser Heated Discharge Plasma EUV Source With Plasma Assisted Lithium Reflux
InactiveUS20090224182A1Ultraviolet radiation is enhancedAvoid dischargeRadiation pyrometryX-ray tube with very high currentRefluxLength wave
A self-magnetically confined lithium plasma that has an applied axial magnetic field is irradiated at sub-critical density by a perpendicularly oriented carbon dioxide laser to generate extreme ultraviolet photons at the wavelength of 13.5 nm with high efficiency, high power and small source size. Lithium reflux is facilitated by ionization, electric field induced drift toward, and capture on surfaces intersected perpendicularly by the applied axial magnetic field.
Owner:PUREX
Laser heated discharge plasma EUV source
InactiveUS20090212241A1Keep energy smallHigh energyRadiation pyrometryPhotometryLength waveExtreme ultraviolet
A self-magnetically confined lithium plasma which also may have an applied axial magnetic field is irradiated at sub-critical density by a carbon dioxide laser to generate extreme ultraviolet photons at the wavelength of 13.5 nm with high efficiency, high power and small source size.
Owner:PUREX
Photocatalytic sealed CO2 laser tube
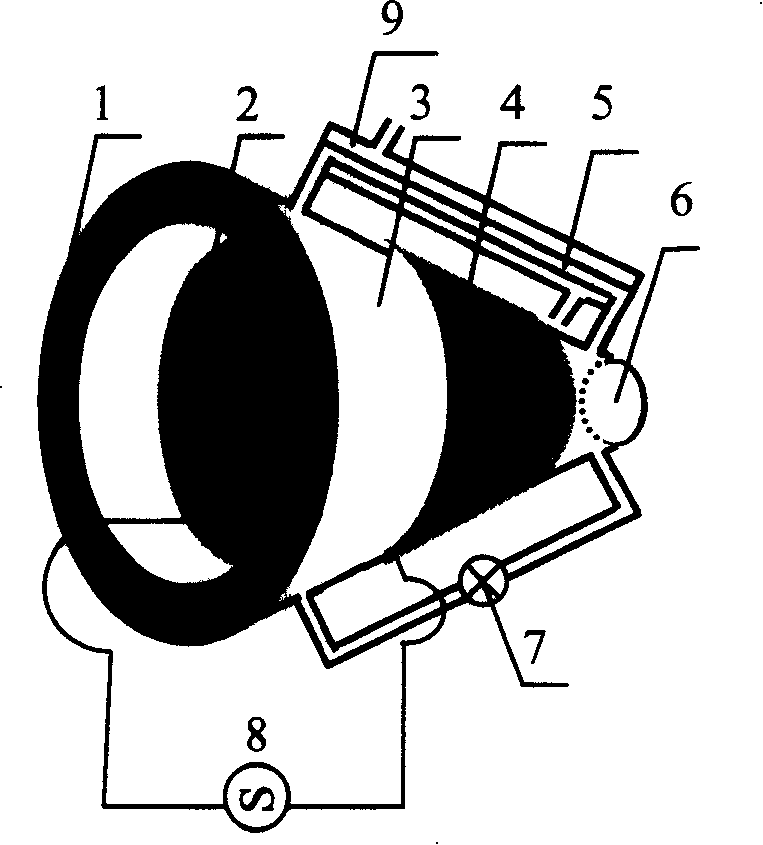
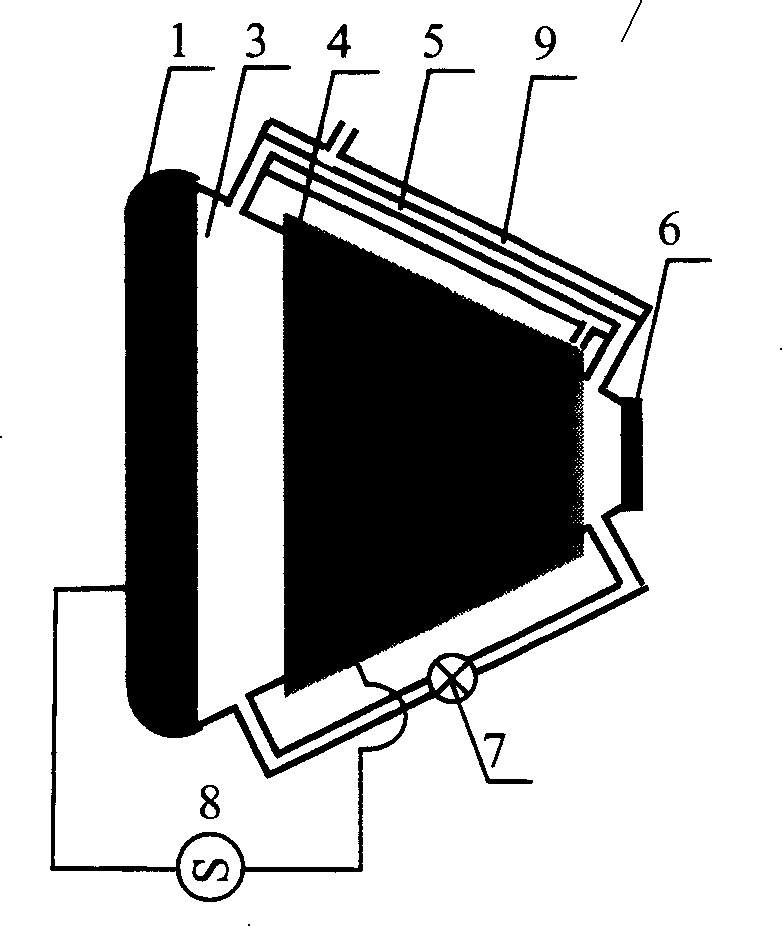
InactiveCN101060226ARestore concentrationOvercoming activation energyGas laser constructional detailsEpoxyEngineering
The related sealing-type CO2 laser tube comprises: a metal-plated full reflection mirror 1, a muffler 2 set in tube 4 to connect sheath 3 and tube 5, a gas storage sheath 3, a water cooling tube 4 set on top of a discharge tube 5 together in sheath 3, an output mirror 6 together with mirror 1 bonded on ends of laser tube ends by epoxy resin, the TiO2 photo catalyst 8 coated on inner wall of tube 5 and electrodes 7 / 9, and two electrodes 7 / 9 coaxial arranged on ends of tube 5. This invention is simple and convenient, prolongs product life time, reduces cost, and has well social and economic benefits.
Owner:王向阳
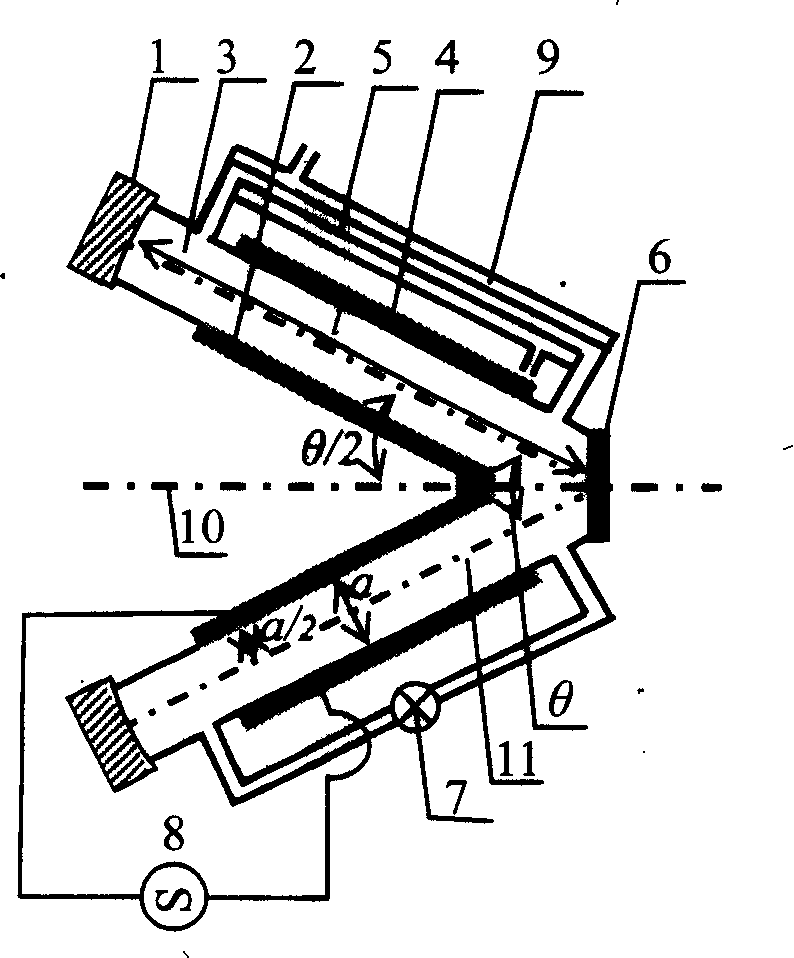
Phase-locked axisymmetric folding combined carbon dioxide laser
The invention relates to a construction method and a device of a large-power phase-locked carbon dioxide laser, in particular to a construction method and a device of obtaining large-power phase-locked carbon dioxide output by the folding combined axisymmetric structural arrangement and the discharge excitation of a plurality of discharge tubes. A quartz discharge tube or a glass discharge tube is arranged on a system shaft, and holophotes are respectively stuck to one end of each quartz or glass discharge tube while the same intersecting point formed by central lines on the inner reflecting surface of a laser output mirror is far away from a folding point; the output mirror is the only output mirror, adopts parallel plane mirrors or a planoconvex lens and is provided with a convergence system at the back, and a convergent cell large-power laser beam is obtained behind the convergence system; laser oscillation in the discharge tubes arranged in pairs is controlled by reflecting a first surface of a first mirror of the convergence system behind the output mirror or with the convex surface of the planoconvex lens, therefore, convergence beams obtained have favorable coherence.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for drilling holes on printed circuit board
InactiveCN101722367AFast processingAchieve the purpose of drillingLaser beam welding apparatusOptoelectronicsCopper foil
The invention relates to a method for drilling holes on a printed circuit board, comprising the following steps: providing the printed circuit board which comprises a substrate covered by a copper foil which has the thickness of 12-18 Mum on at least one side surface; washing the surface of the copper foil with acid and alkaline, neutralizing the acid and alkaline and cleaning the acid and alkaline; chemically etching the copper foil with etching solution which contains organic matter, sulfuric acid (H2SO4), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and copper ion to form a plurality of micro holes on the surface of the copper foil, wherein the organic matter can be uniformly dispersed and adsorbed on the surface of the copper foil, and the H2SO4 and H2O2 can etch the position where no organic matter is adsorbed; irradiating the position where holes to be drilled on the printed circuit board with the carbon dioxide laser and breaking down the copper foil and the substrate to finish drilling holes on the printed circuit board.
Owner:COMPEQ MFG
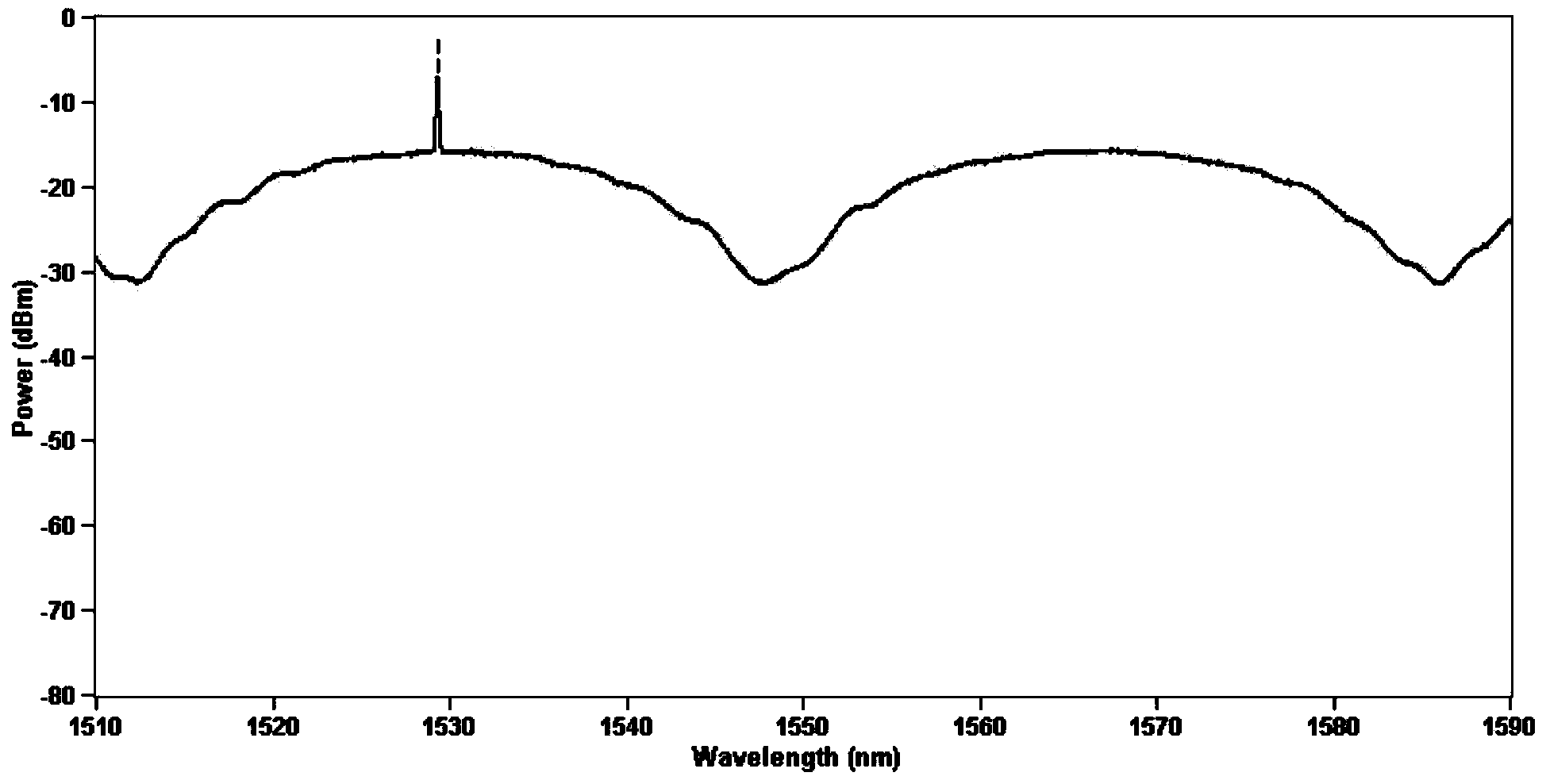
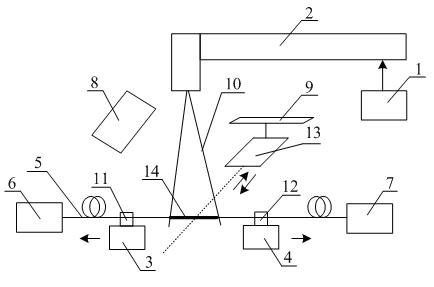
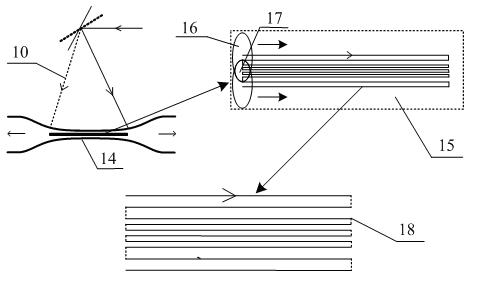
Optical fibre fused tapering method using high-frequency pulse carbon dioxide laser as heat source
ActiveCN102147499AReduce energy consumptionPrecise controlCoupling light guidesBeam splittingOptical communication
The invention relates to an optical fibre fused tapering method using high-frequency pulse carbon dioxide laser as a heat source. The method precisely adjusts laser beams based on the good heat absorption performance of a silica optical fibre close to the carbon dioxide laser wavelength and the characteristics that the high-frequency carbon dioxide laser can generate a continuous high temperature, so that a fused tapered optical fibre is drawn while the laser beams heat up the optical fibre continuously along a certain optical fibre length. The method is mainly characterized by: designing a reasonable laser beam scanning track graph, and ensuring that the laser beams scan the optical fibre all the time during the whole drawing procedure and that a heat area stable enough can be generated on the optical fibre; and simultaneously adjusting the parameters of the carbon dioxide laser beams and the step length of a stepping motor, so as to ensure the heat and force balance of the optical fibre during the drawing procedure. The method does not pollute the optical fibre, and is not influenced by the indoor airflow, oxygen content and the like; and the heat source is similar to a point heat source, and the manufacture precision of the fused tapered optical fibre is greatly improved. The fused tapered optical fibre manufactured by the method can be widely used in the fields like beam splitting and connection of light, optical fibre sensing, optical filters, optical communications and the like; and the application potential is huge.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Photography system for welding process of compound heat reservoir in carbon dioxide laser-melting argon-arc welding
InactiveCN1963663APrecise adjustment of total intensityAvoid damageTelevision system detailsLaser detailsCamera lensUltraviolet
This invention relates to one carbon diode laser and metallic arc welding compound thermal source cameral system, which comprises semiconductor laser, floodlight tube, 3D optical adjust rack, multiple ultraviolet antireflection film, round bias vibration combination, intervene filter slices, cameral lens, transfer head and cameral machine, wherein, the former three parts form light source structure; later three parts form image forming structure; the cameral and transfer head form cameral structure; the light structure is at one side of cameral subject and the image forming structure and structure are connected through transfer head at other side of the subject.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and device for improving corrosion resistance of stainless steel weld seams
InactiveCN103320800AReduce corrosion susceptibilityPlay the role of the first layer of protectionMetallic material coating processesNumerical controlSS - Stainless steel
The invention discloses a method and a device for improving the corrosion resistance of stainless steel weld seams. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, preparing a kind of nanoscale metal corrosion inhibitor particles; then, injecting the nanoscale metal corrosion inhibitor particles into stainless steel weld seams by using a carbon dioxide laser so as to form an anti-corrosion layer; and finally, carrying out shock strengthening treatment on the surfaces of the stainless steel weld seams by using a nanosecond laser, so that a high-amplitude residual compressive stress layer with a certain depth is formed at a stainless steel weld seams area. The device for implementing the method comprises a computer control system, a powder feeder, an argon gas protection device, the carbon dioxide laser, an omni-directional reflector, a transmitting mirror, a powder feeding nozzle, a stainless steel welding part, a clamping device, a three-axis numerical control workbench, a flexible attaching film and the nanosecond laser. According to the invention, the corrosion sensitivity of the stainless steel weld seams in a corrosive environment can be greatly reduced, and the service life of the stainless steel weld seams can be prolonged, therefore, the method and device disclosed by the invention are applicable to the improvement of the corrosion resistance of various stainless steel weld seams, and also can be expanded to the improvement of the corrosion resistance of weld seams of aluminum alloys and titanium alloys and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Laser restoring process for surface of high carbon alloy roller
InactiveCN102677049ASmall amount of deformationNo crackMetallic material coating processesLaser beam welding apparatusHigh carbonLap joint
The invention relates to a laser restoring process for the surface of a high carbon alloy roller. The laser restoring process comprises the following steps: (A) processing the surface of the roller, and carrying out failure analysis on the roller; (B) optimizing process parameters according to failure analysis results of the roller, and carrying out laser cladding; adopting a preset powder-feeding mode to enable a fast-transverse-flow carbon dioxide laser serving as a light source to carry out continuous screwfeed lap joint scanning on the roller; and enabling adopted alloy powder to comprise, by weight, no more than 0.15% of C, 12.5%-14.5% of Cr, 1.3%-1.8% of B, 0.5%-1.5% of Si, 0.5%-1.5% of Mo, and the balance Fe; and (C) performing detection. The laser restoring process for the surface of the high carbon alloy roller carries out laser cladding on the surface of the roller to enable the dimensions of the roller to meet the using requirements, a roller base body and a cladding layer are combined tightly, the thickness and the hardness of the cladding layer are uniform, and abrasion resistance of the roller can be enhanced.
Owner:DANYANG HONGTU LASER TECH
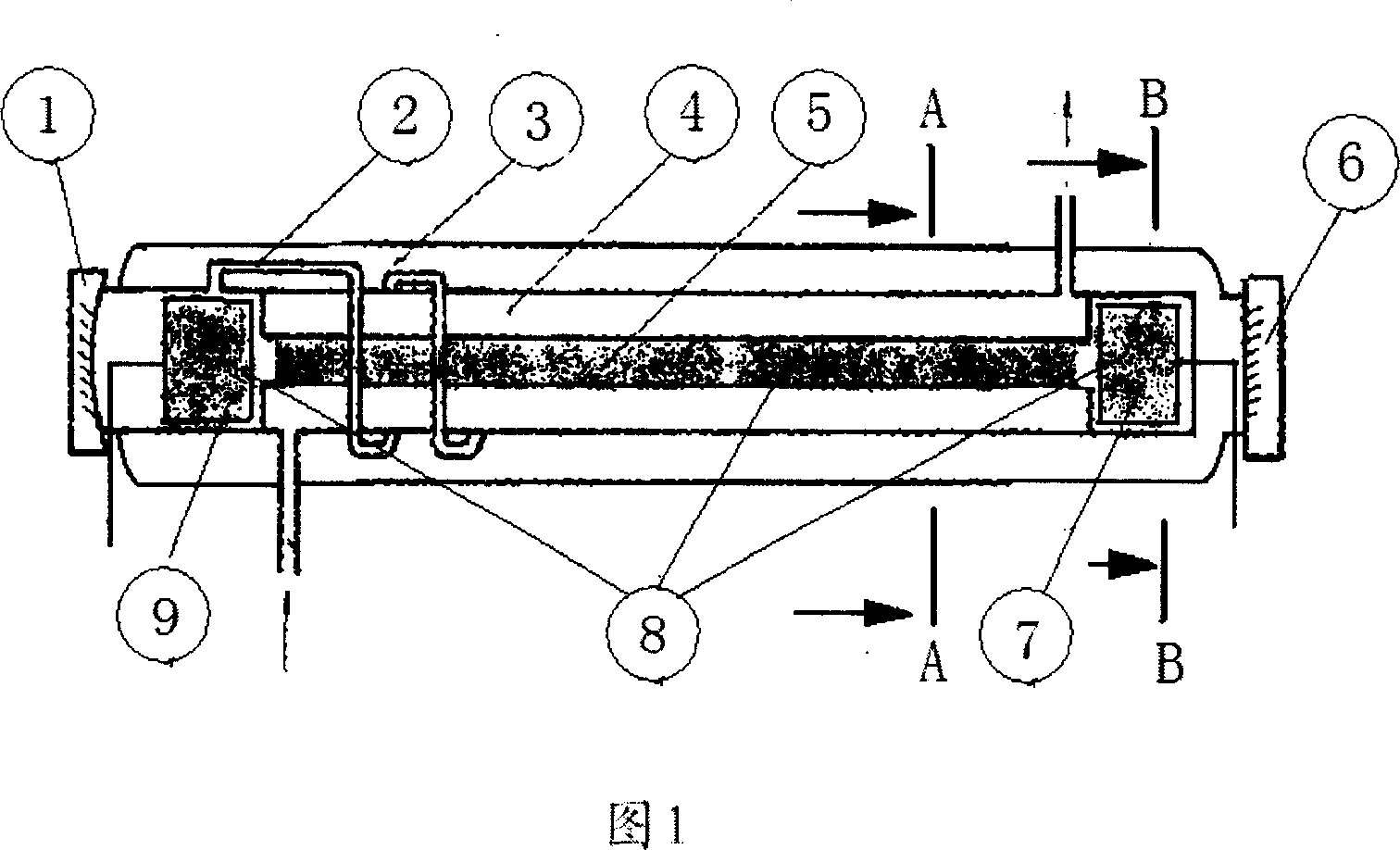
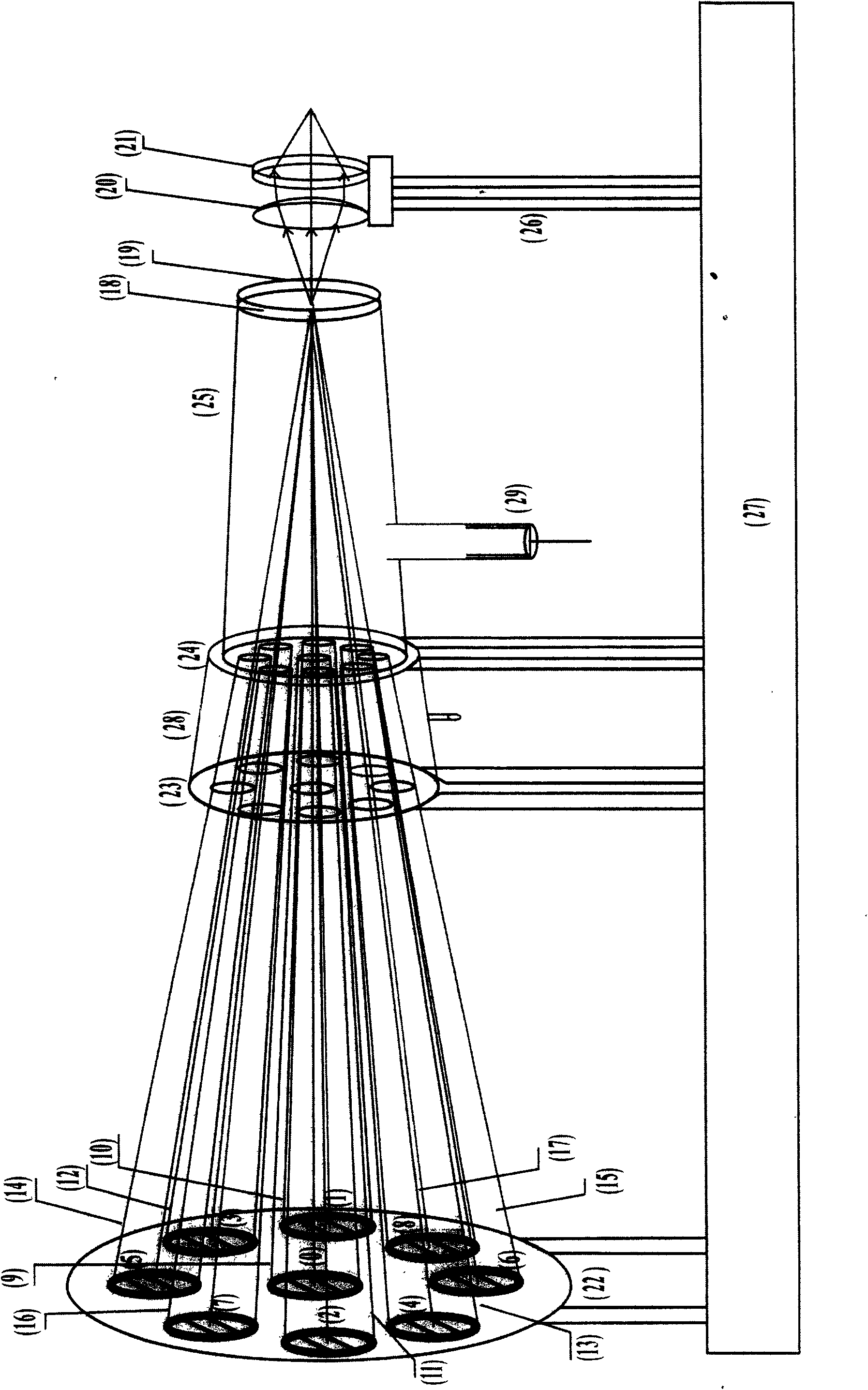
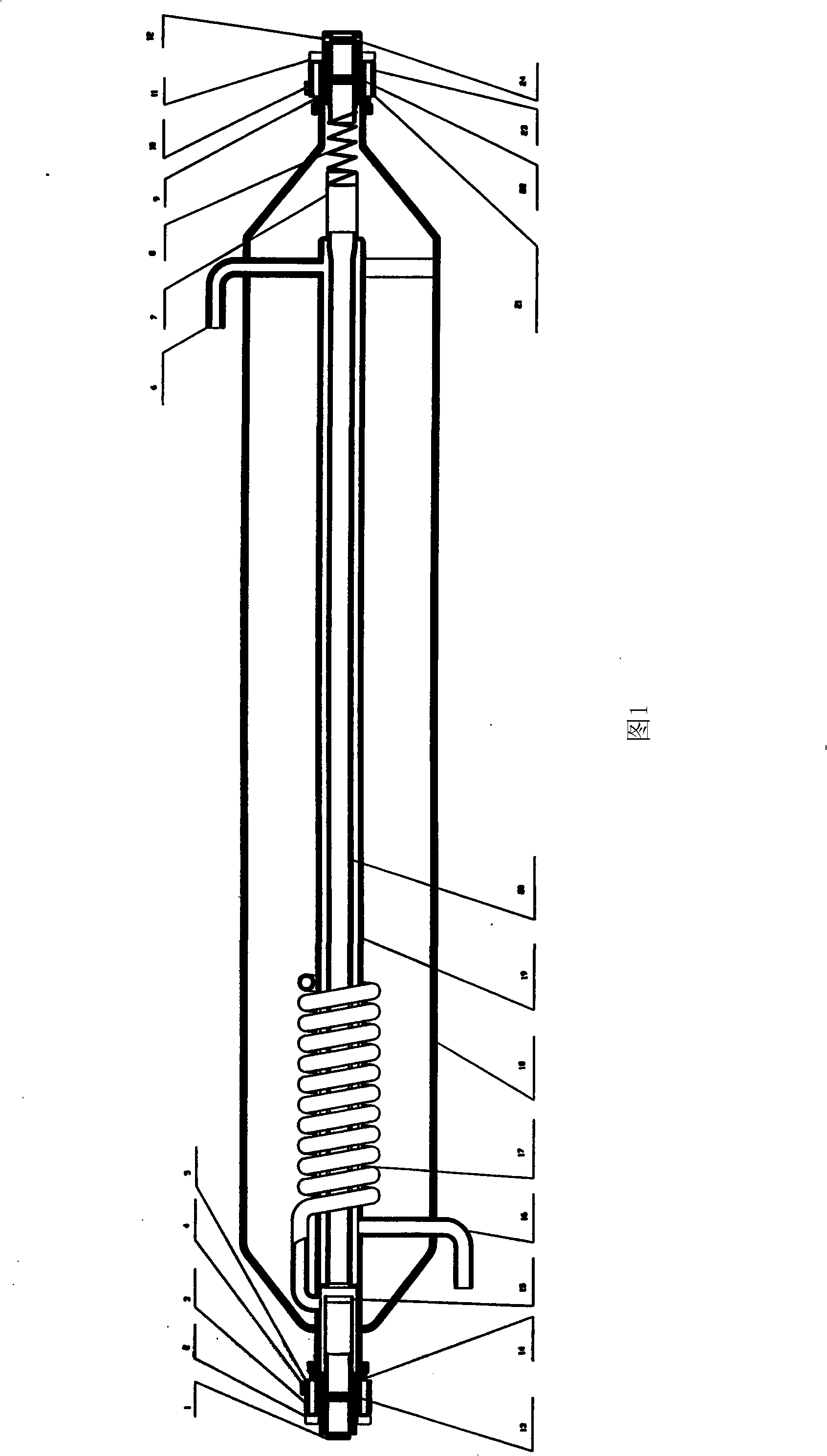
A CO2 laser with new structure
ActiveCN101262112AIncrease output powerHigh beam qualityGas laser constructional detailsOptoelectronicsLaser cutting
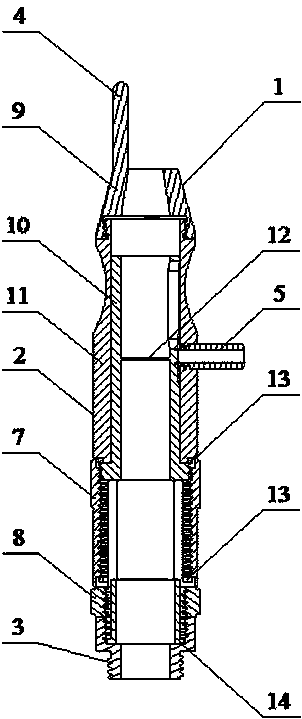
The invention relates to a carbon dioxide laser with new structure. Sealing and connecting metal structures at two sides can adjust the angle of a lens (1) and a lens (12); the major structure of the laser pipe shaft comprises a glass material discharge tube (20), a jacket pipe (19), an air-storing pipe (18), an air-returning pipe (17), a water inlet (16) and a water outlet (6); a resonant cavityis composed of a total reflective mirror (1) and an output mirror (23); an angle adjusting system for the total reflective mirror comprises a fixed flange (5), an adjustable flange (3), a soft metal gasket (13) and an adjusting screw (2); the metal structure of the angle adjusting system is sealed and connected with the glass structure of the laser pipe shaft by spacer flange chips (14)(9); a high pressure protective sleeve (24) plays a role in protecting the laser metal structure part with a high pressure; an output mirror protective sleeve (23) plays a role in protecting the output mirror (12) and releasing heat. The carbon dioxide laser is mainly applicable to the laser cutting and the carving machine tool with medium and small power and material processing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG RECI LASER TECH CO LTD
Method for fabricating three-dimensional optical echo wall mode micro-cavity by using femtosecond laser
InactiveCN102530852AIncrease varietyEasy to integrateMicrostructural devicesLaser beam welding apparatusSurface finishIrradiation
The invention discloses a method for fabricating a three-dimensional optical echo wall mode micro-cavity with high-quality factors by using femtosecond laser. The method comprises the following steps of femtosecond laser irradiation on a transparent material, chemical corrosion, carbon dioxide laser annealing and the like. According to the three-dimensional optical echo wall mode micro-cavity, fabricated according to the method disclosed by the invention, the size of a small support column, the size of a micro disc, and included angles of the small support column and the micro disc relative to a substrate are determined by a design. The profile of the micro-cavity is of a micro ring structure, the surface finish quality is extremely high, and the quality factors are very high.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
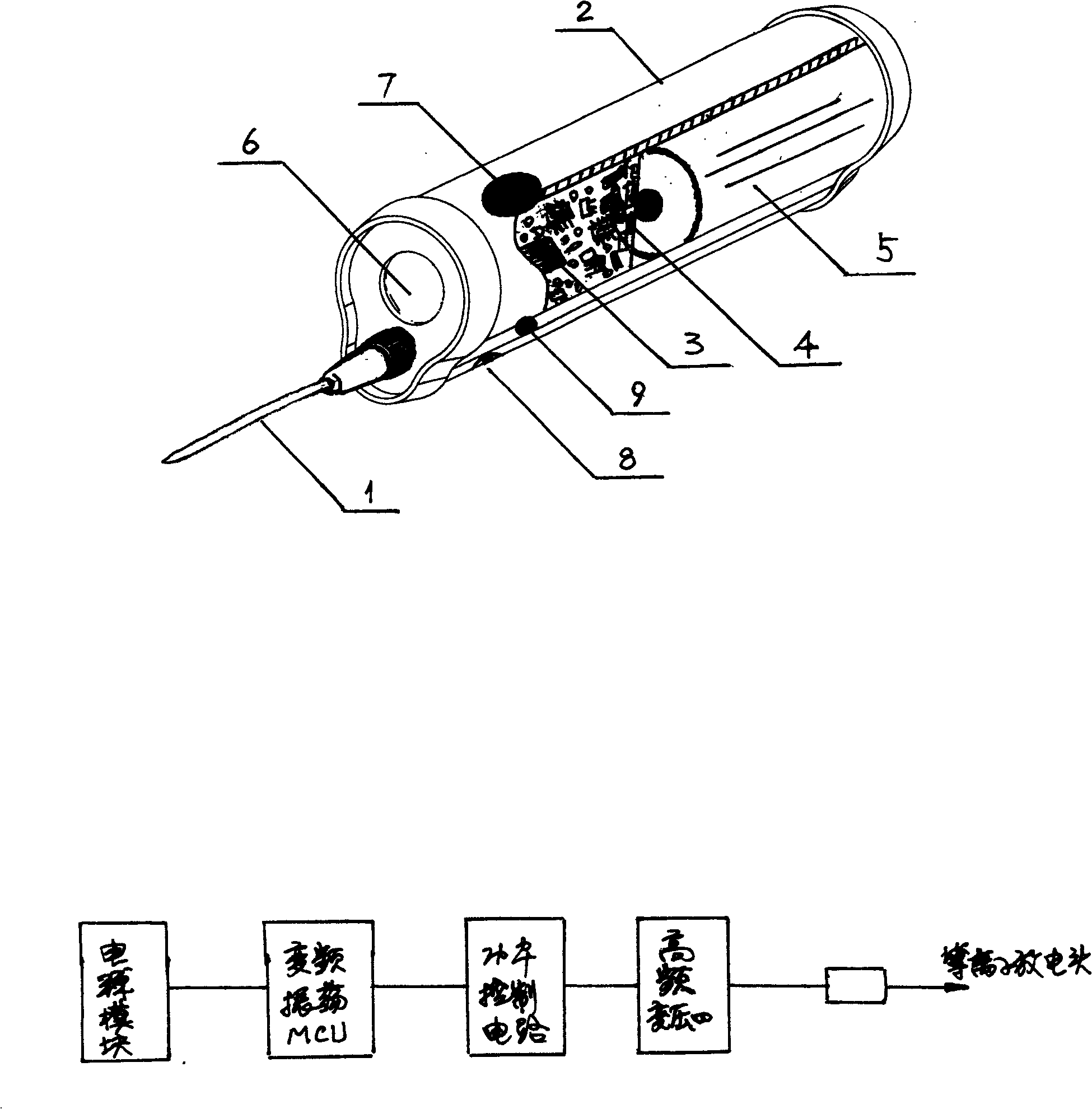
Adjuster for light spots output by carbon dioxide laser therapeutic machine terminal
The invention provides an adjuster for light spots output by a carbon dioxide laser therapeutic machine terminal. The light spot adjuster comprises a light spot adjustment main body with a hollow structure, wherein a laser beam input end is connected with a laser beam input end connection seat with a hollow structure; the laser beam input end connection seat is in threaded connection with a light guide arm of external laser input equipment and is used for introducing a laser beam; a laser output end is connected with a light spot positioning display cover for positioning and displaying the output light spots at a position to be treated; the light spot adjustment main body comprises a lens moving frame in which a focusing lens is fixed, a lens moving supporting frame, a lens moving frame supporting ring for supporting a moving space for the lens moving frame, a light spot adjustment handle, a smoke discharging device and a handle moving clearance adjustment ring. According to the adjuster disclosed by the invention, laser beam light spots with different light spot diameters can be obtained only by adjusting a distance between the focusing lens of the same specification and a treated tissue, and uniform and consistent laser beam light spots with different diameters can be scientifically, quickly and conveniently obtained.
Owner:武汉高科恒大光电股份有限公司
Laser-rotating wire stripping machine for wire insulation layer
ActiveCN103368106AQuality improvementReasonable designApparatus for removing/armouring cablesInsulation layerEngineering
The invention provides a laser-rotating wire stripping machine for a wire insulation layer. The laser-rotating wire stripping machine comprises a carbon dioxide laser, a first totally-reflecting mirror, a flexible clamping device, a wire positioning mechanism, a laser focus point adjusting mechanism, a light path rotating mechanism and a straight-line motion mechanism, wherein the first totally-reflecting mirror is arranged at the output end of the carbon dioxide laser; the flexible clamping device and the straight-line motion mechanism are fixedly arranged on a rack, and the light path rotating mechanism is fixedly arranged on the straight-line motion mechanism; and the laser focus point adjusting mechanism is fixedly arranged on the light path rotating mechanism. The light path rotating mechanism is used for reflecting laser beams reflected by the first totally-reflecting mirror to a wire, and enabling the laser beams to rotate around the axis of the wire, so that the laser rotates for 360 degrees around the wire for cutting. The straight-line motion mechanism is used for enabling the light path rotating mechanism fixedly positioned on the straight-line motion mechanism to do a straight-line motion, and the wire is axially cut by the laser. The laser-rotating wire stripping machine has the advantages of reasonable design and compact structure and can strip the insulation layers of wires with different diameters without scars and residues, and the processing quality of the wire is greatly increased.
Owner:WUHAN LINGYUN PHOTOELECTRONICS SYST
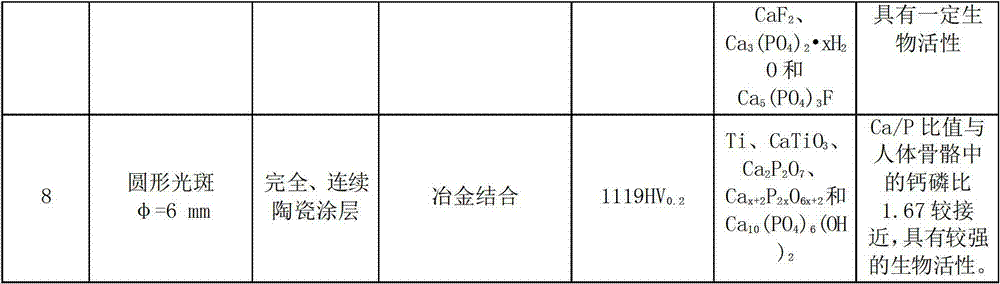
Method for preparing hydroxy apatite biological ceramic coating containing fluorine
InactiveCN102851664AReduce manufacturing costHigh bonding strengthMetallic material coating processesCeramic coatingTitanium alloy
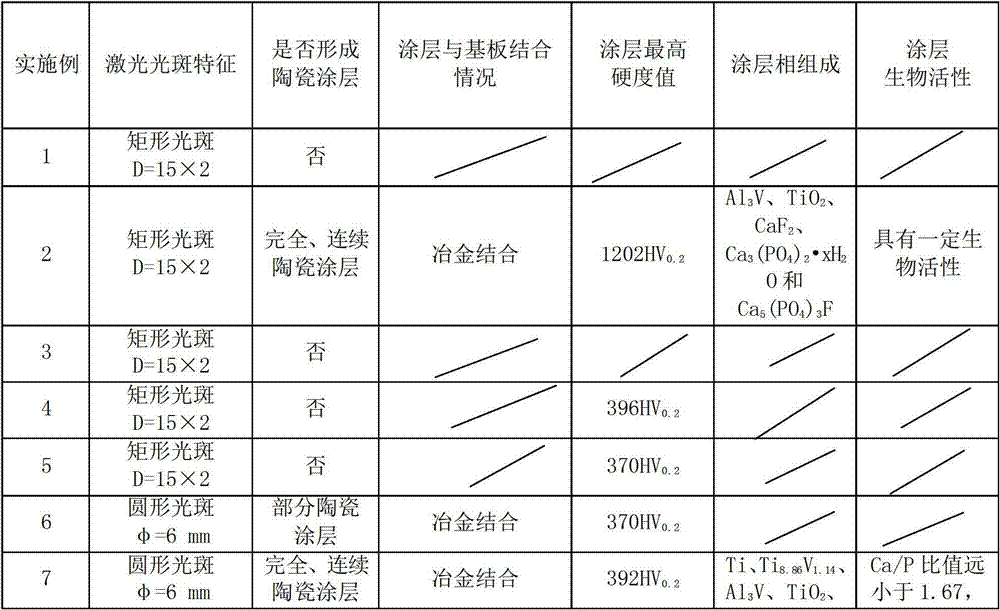
The invention discloses a method for preparing a hydroxy apatite biological ceramic coating containing fluorine. The method comprises the steps of evenly mixing 2.3% of calcium fluoride powder by weight and 97.7% of hydroxyapatite powder by weight, utilizing polyving akohol solution with concentration of 2% to serve as binder to allocate the mixed powder, presetting the allocated mixed powder on a titanium alloy base plate, and utilizing a carbon dioxide laser to perform broadband laser cladding on the titanium alloy base plate to generate the hydroxy apatite biological ceramic coating containing the fluorine, wherein the cladding process adopts two process parameters as follows: the laser output power P of the carbon dioxide laser ranges from 0.5kW to 1kW, the scanning speed V ranges from 150nm / min to 250nm / min, the rectangular spot dimension D is 15mm*2mm, and argon shield is adopted. By means of the method, good biological activity of the ceramic coating and high strength and good toughness of metal are combined together, and the hydroxy apatite coating containing the fluorine can protect the titanium alloy base plate from being corroded by the human physiological environment. Besides, the coating and the metal of the base plate are combined through the laser cladding preparation technique, so that the hydroxy apatite biological ceramic coating containing the fluorine meets mechanical performance requirements of implant materials.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Direct coding method for PCB
The invention relates to the field of PCB coding, and provides a direct coding method for a PCB. The direct coding method comprises the following steps: directly coding the PCB by using a carbon dioxide laser, wherein the size of the focus light spot of the carbon dioxide laser is equal to or smaller than 0.14 mm; aiming at two-dimensional codes or one-dimensional codes in different sizes requested on different PCBs, coding is realized by controlling the power of the carbon dioxide laser and selecting different coding modes. The high-precision, high-speed and programmable carbon dioxide laser is adopted to directly code the PCB, aiming at two-dimensional codes or one-dimensional codes in different requested sizes, the coding depth can be controlled by controlling the power of the carbon dioxide laser, and appropriate coding modes are selected, so that the PCB is not damaged in the coding process, automation can be achieved in the production process, and the labor and the materials can be saved; laser coding is not affected by assembling steps or environment, can be directly acted on the PCB, and the process lasting property is good, so that the effect that the code lasts for the whole life of the PCB is achieved.
Owner:苏州华工自动化技术有限公司
Pressure-sensitive adhesive film for laser beam cutting applications
InactiveUS20160107425A1Discoloration and burrs in the cutting edge may be preventedSuitable cutting propertyFilm/foil adhesivesAdhesive articlesEngineeringLength wave
The present invention provides pressure-sensitive adhesive films with a favourable visual appearance and surface printability without discoloration and burrs on the cutting edge after short-wavelength laser machining. At the same time, the PSA films of the present invention exhibit a favourable cuttability, allowing for high fiber laser as well as carbon dioxide laser cutting speeds. Since the use of the PSA films of the present invention as surface protecting films does not require extensive cleaning and polishing operations after the cutting process and the cutting process itself may be accelerated, the efficiency of laser machining methods may be improved.
Owner:NITTO BELGIUM NV
Multipath wire feed laser fused deposition modeling (LFDM) device and method
InactiveCN106926447AEfficient printingImprove molding efficiency3D object support structuresApplying layer meansEngineeringFused deposition modeling
The invention discloses a multipath wire feed laser fused deposition modeling (LFDM) device and method. The device comprises a wire feed nozzle composed of multiple wire conveying pipelines, a laser head and a carbon dioxide laser. The wire feed nozzle and the laser head are fixedly connected together through a connecting part to form a composite printing head. A steering engine is mounted on the connecting part so as to increase the freedom degree of the composite printing head. The laser head can transmit a rectangular laser beam, and the rectangular laser beam ejects out from the lateral direction of the laser head and irradiates and covers the ends of corresponding wires stretching out of the outer portion of the wire feed nozzle to carry out fusing on the ends. According to the device, on the basis of a traditional fused deposition technology, a laser fused deposition technology is developed, some problems existing in traditional equipment are solved, meanwhile, more functions are given to the novel device, and more possibilities and methods and thoughts for solving the problems are provided for the fused deposition modeling technology. Meanwhile, by means of linear multipath wire feed, an effective multi-conveying-pipeline arrangement manner is provided.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Ceramic shell, method for processing surface thereof, and electronic equipment
InactiveCN111031158AShallow depthTelephone set constructionsLaser beam welding apparatusLaser etchingErbium lasers
The invention provides a ceramic shell, a method for processing the surface thereof, and electronic equipment. The method comprises the steps: performing laser etching on the outer surface of the ceramic shell through a carbon dioxide laser to form a texture pattern, wherein the depth of the texture pattern is 0.005-0.09 mm. Therefore, not only can the three-dimensional texture be processed on thesurface of the ceramic shell, but also the ceramic surface (high gloss, bright surface) of the part which is not subjected to laser etching and the ceramic surface (relatively low gloss, matte surface) of the part which is subjected to laser etching form a surface appearance effect with alternate brightness and darkness or matte contrast, so the appearance effect of the surface of the ceramic shell is enriched; furthermore, due to the fact that the depth of the machined texture pattern is small, the ceramic shell with the small thickness can be prevented from being broken in the machining process, the surface machining yield of the ceramic shell can be improved, and it is effectively guaranteed that the obtained ceramic shell still has good mechanical strength such as falling resistance and impact resistance.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Hollow beam gas laser
InactiveCN101232147AExcitation process/apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionCarbon dioxideCarbon dioxide laser
The invention relates to a hollow beam gas laser, which belongs to the field of optics and optical engineering. The generation of a hollow laser beam can be divided into two kinds, wherein one is transforming a known beam, which is of technical difficulty in either the restrict requirement for the properties of the known beam or complex auxiliary optical component; and the other kind is directly generating and outputting the hollow beam from a laser, which is of a higher cost of the crystal for the solid device and the semiconductor laser for the pumping. The laser of the invention belongs to the first kind, and the invention relates to a method and device for outputting a hollow gas laser beam. The device has simple construction and stable output. The hollow carbon dioxide laser in watt level and the hollow helium neon laser in milliwatt level can be focused to a hollow beam at a very small dark field size, which can be used as optical tweezers, optical wrench, optical guide tube, etc. The laser is enabled to operate when clamped. Large-scale carbon dioxide laser can be applied in the aspect of material processing.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com