Method for repairing fused quartz optical damage component
An optical damage and repair method technology, applied in the field of optical materials and optical components, can solve the problems of increasing the overall roughness of optical components, large residual stress in the component repair area, reducing the laser damage threshold of components, etc., to eliminate residual stress and repeatability. High and low operating costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
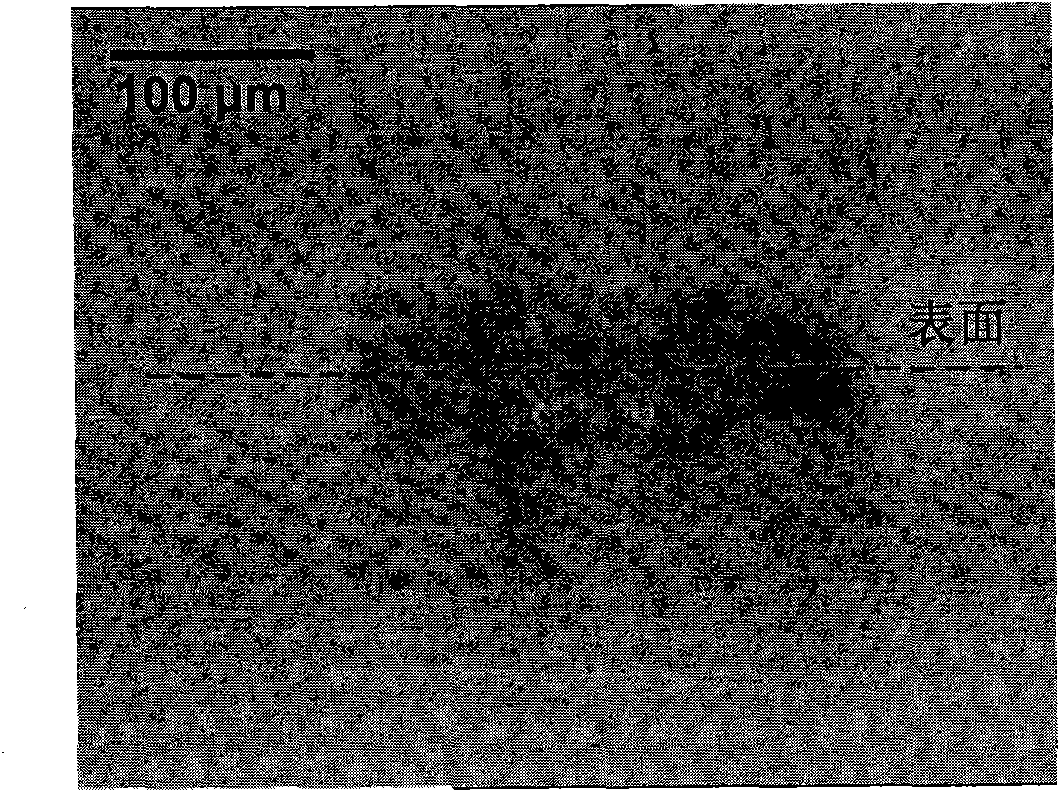
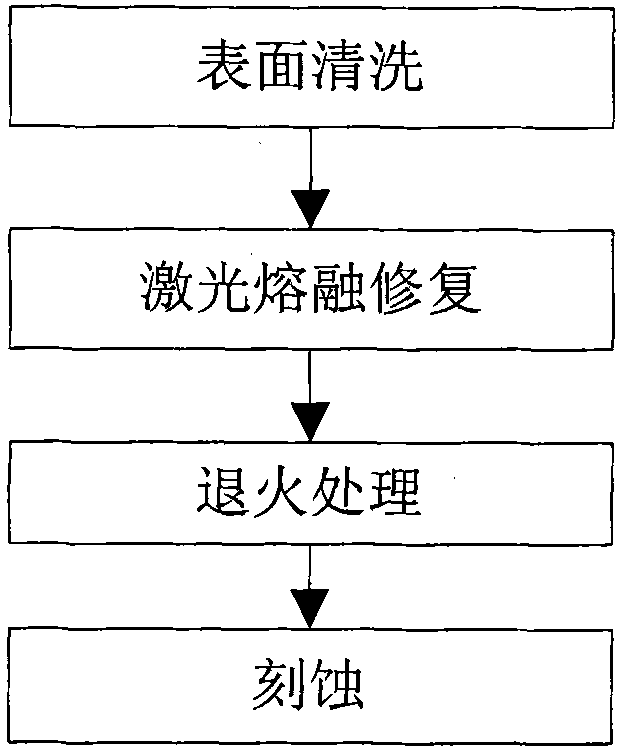
[0026] Optically polished fused silica elements with a size of 40×60 mm and a thickness of 4 mm were etched with 1% hydrofluoric acid solution for 10 minutes, cleaned with deionized water and dehydrated with absolute ethanol before use; three times the wavelength of 355 nm A series of damage points with a size of about 300 microns were produced on the prepared fused silica element with a frequency Nd:YAG ultraviolet laser (wherein, figure 2 , 3 Shown is an optical photo of a damage point); the optical element is cleaned by raster scanning with an ultraviolet laser below the damage growth threshold, and the overlapping rate of the laser spot is more than 50% during the scanning process; an infrared carbon dioxide laser with a wavelength of 10.6 microns is used Carry out laser melting repair on the damaged point on the component. The carbon dioxide laser spot used is Gaussian distribution, the spot diameter is 4 mm, the laser frequency is 15000 Hz, and the repair power is gradu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com