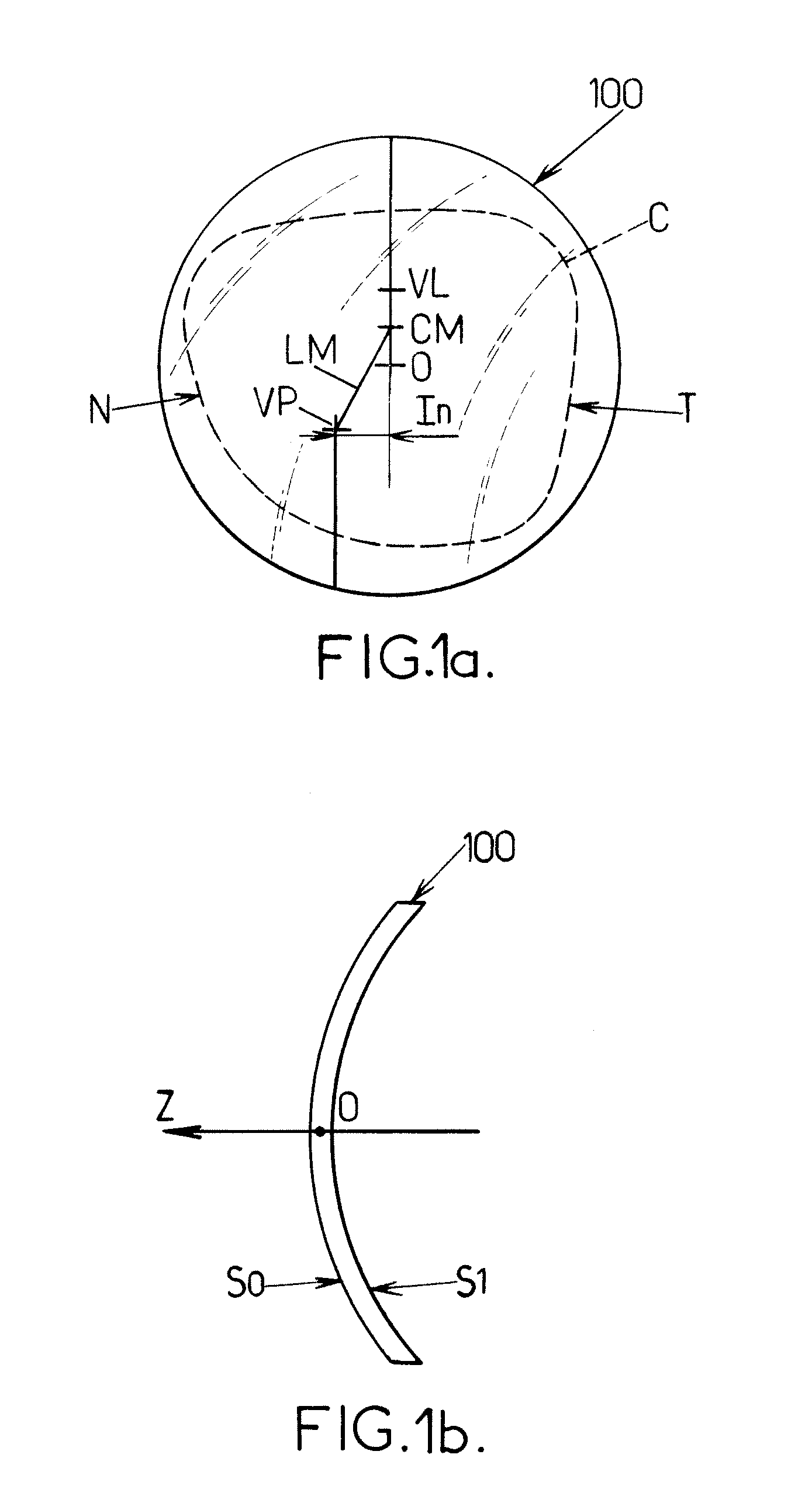
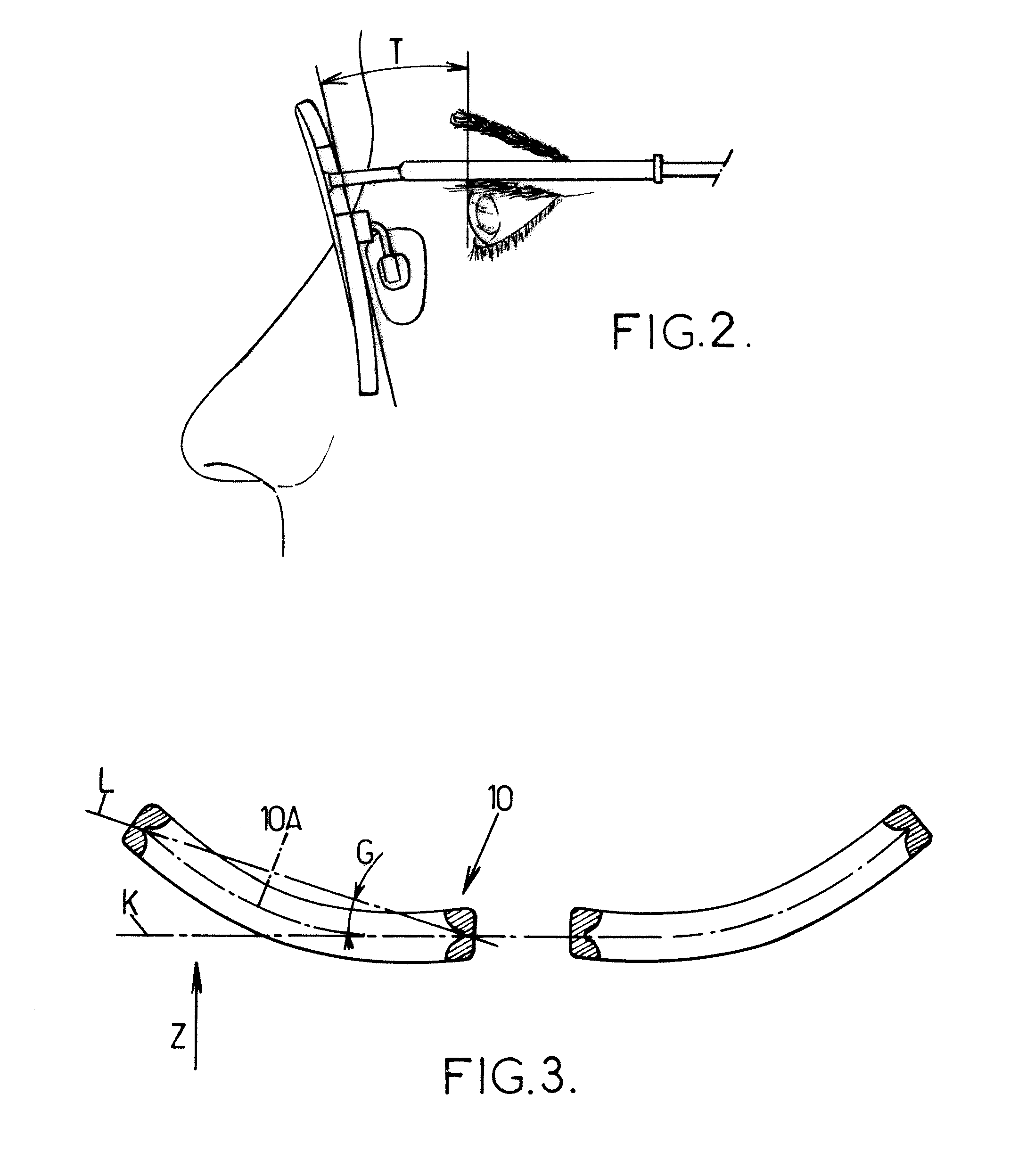
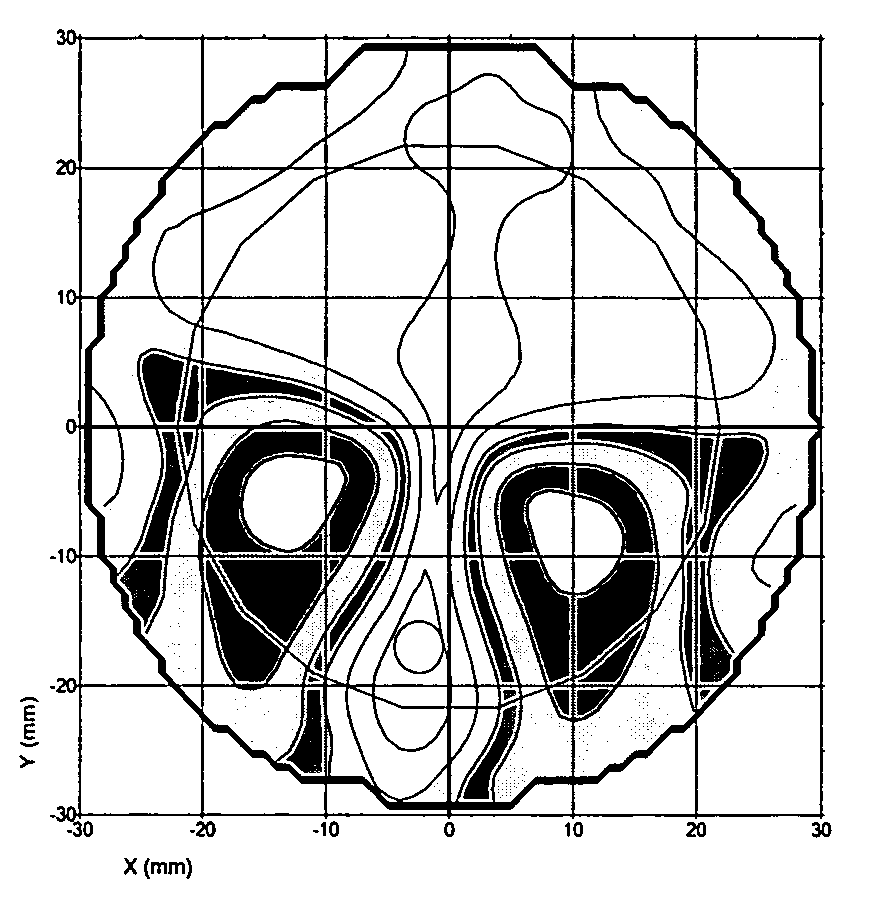
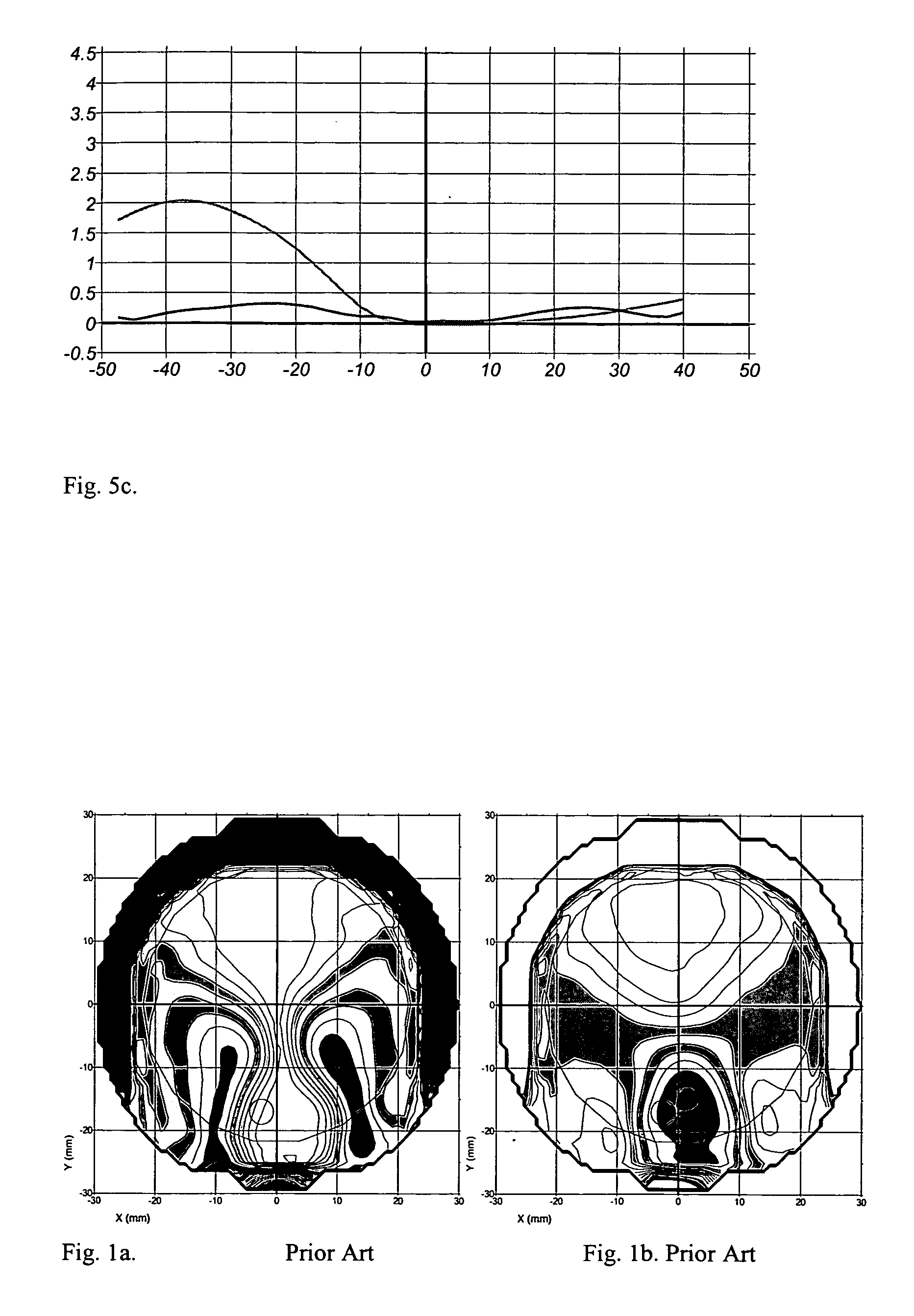
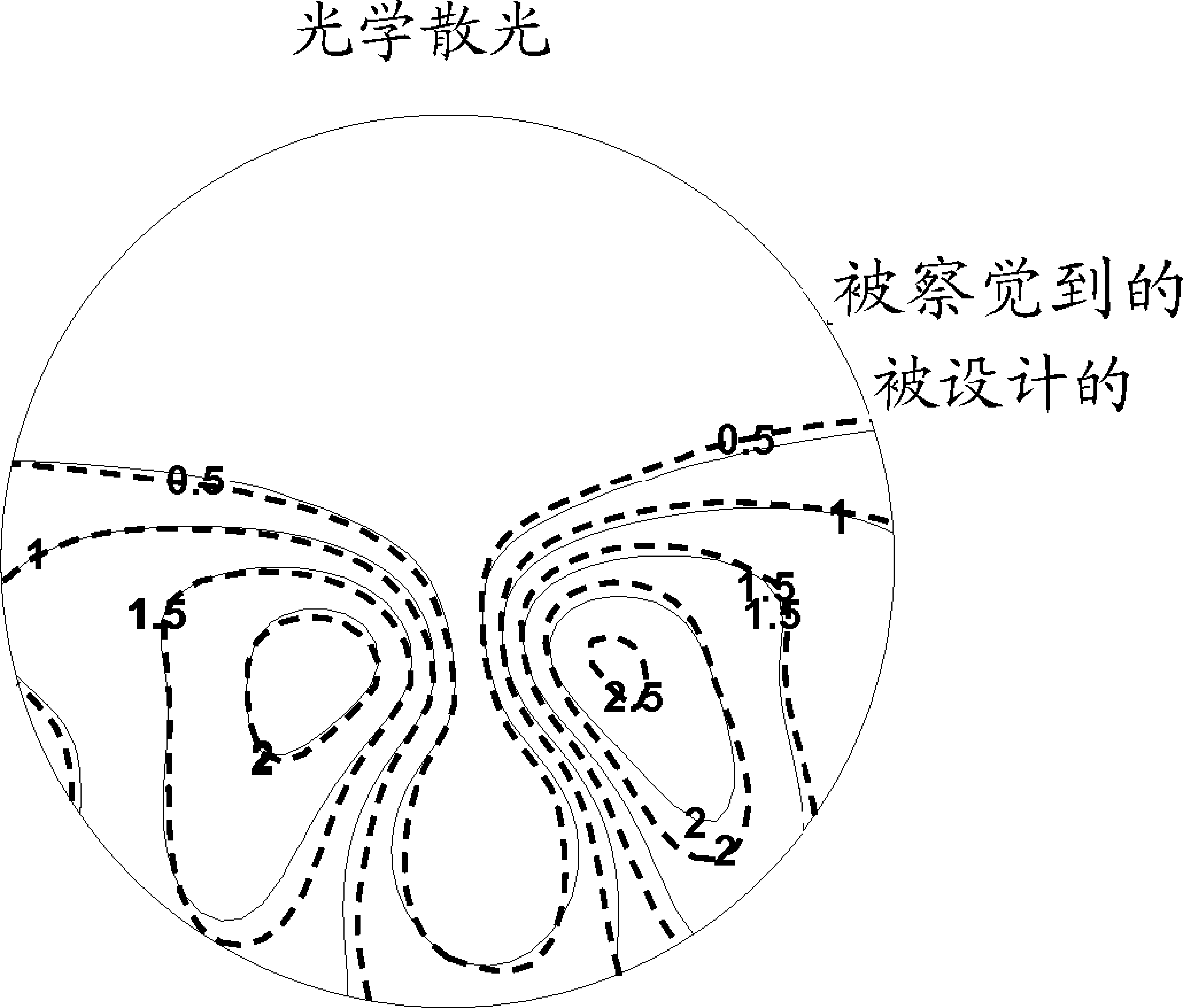
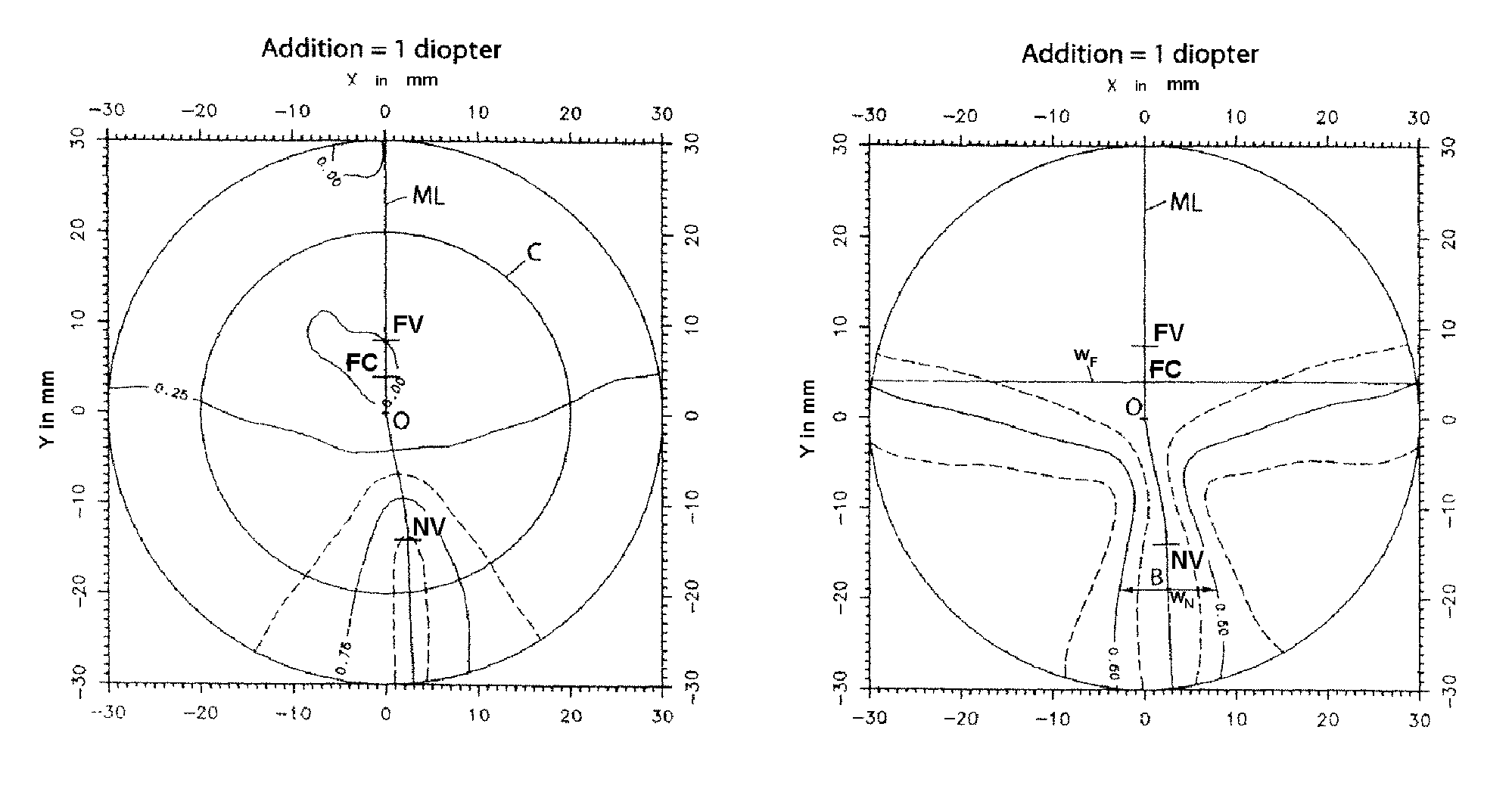
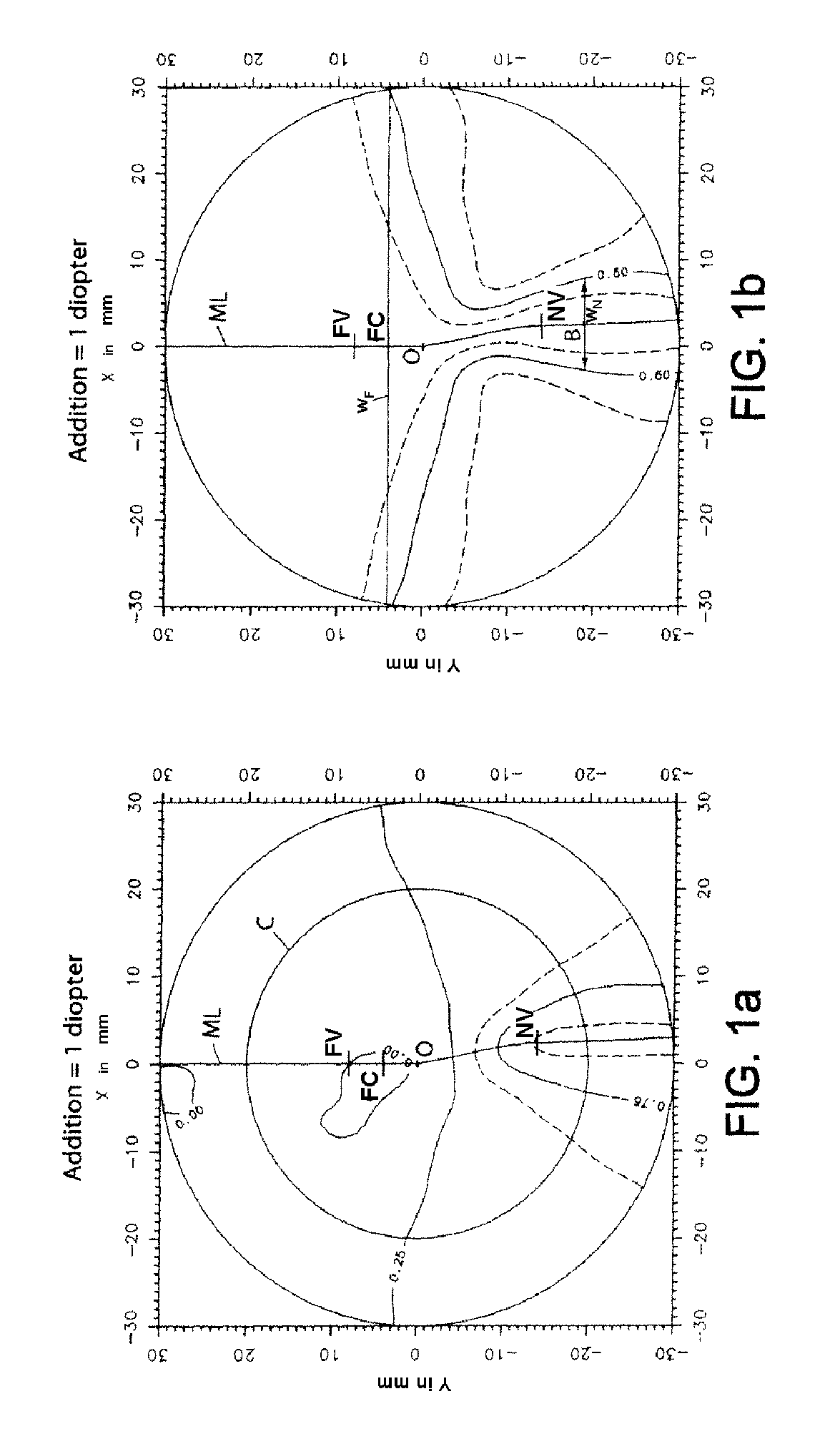
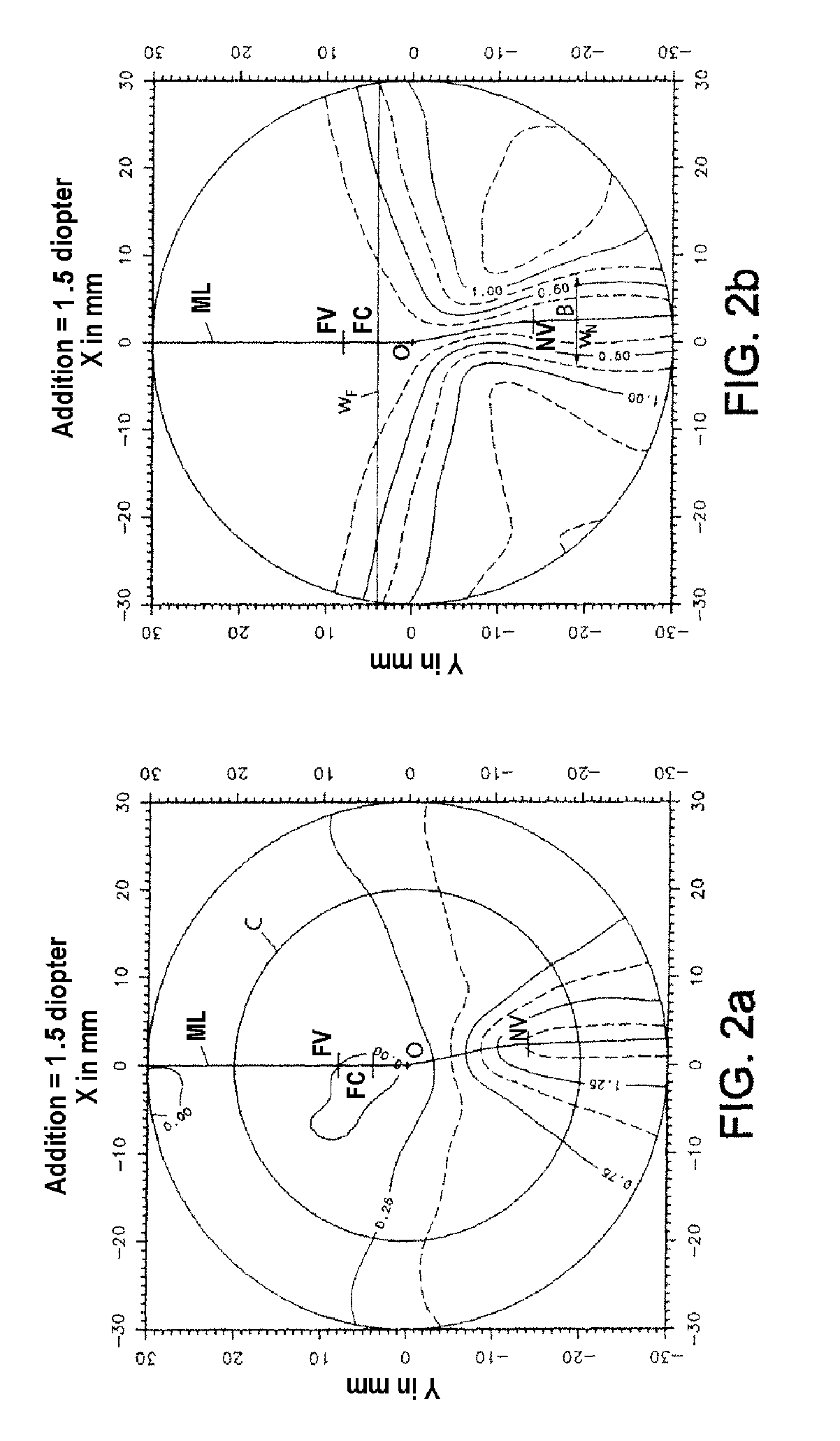
Patents
Literature
73 results about "Progressive addition lenses" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
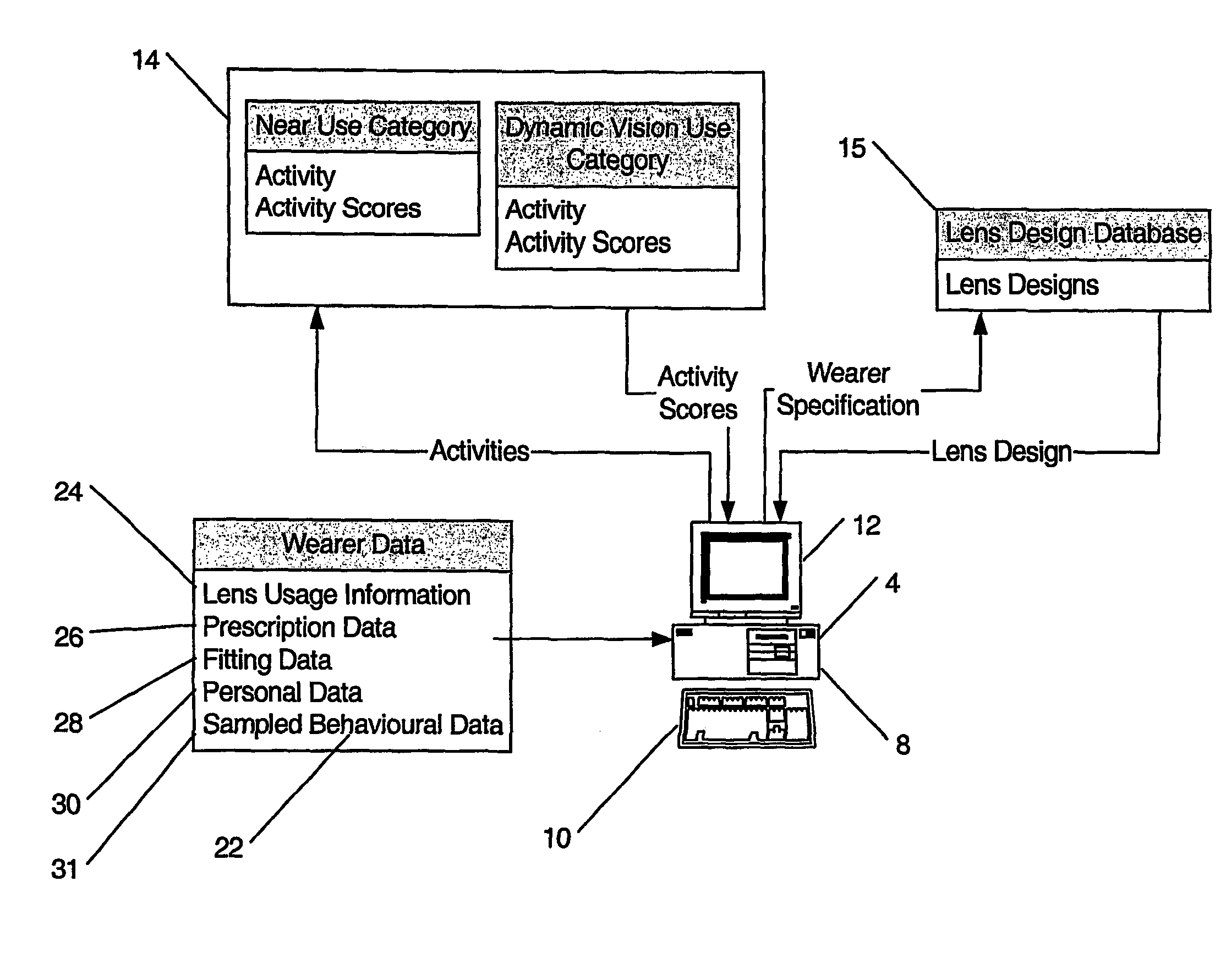
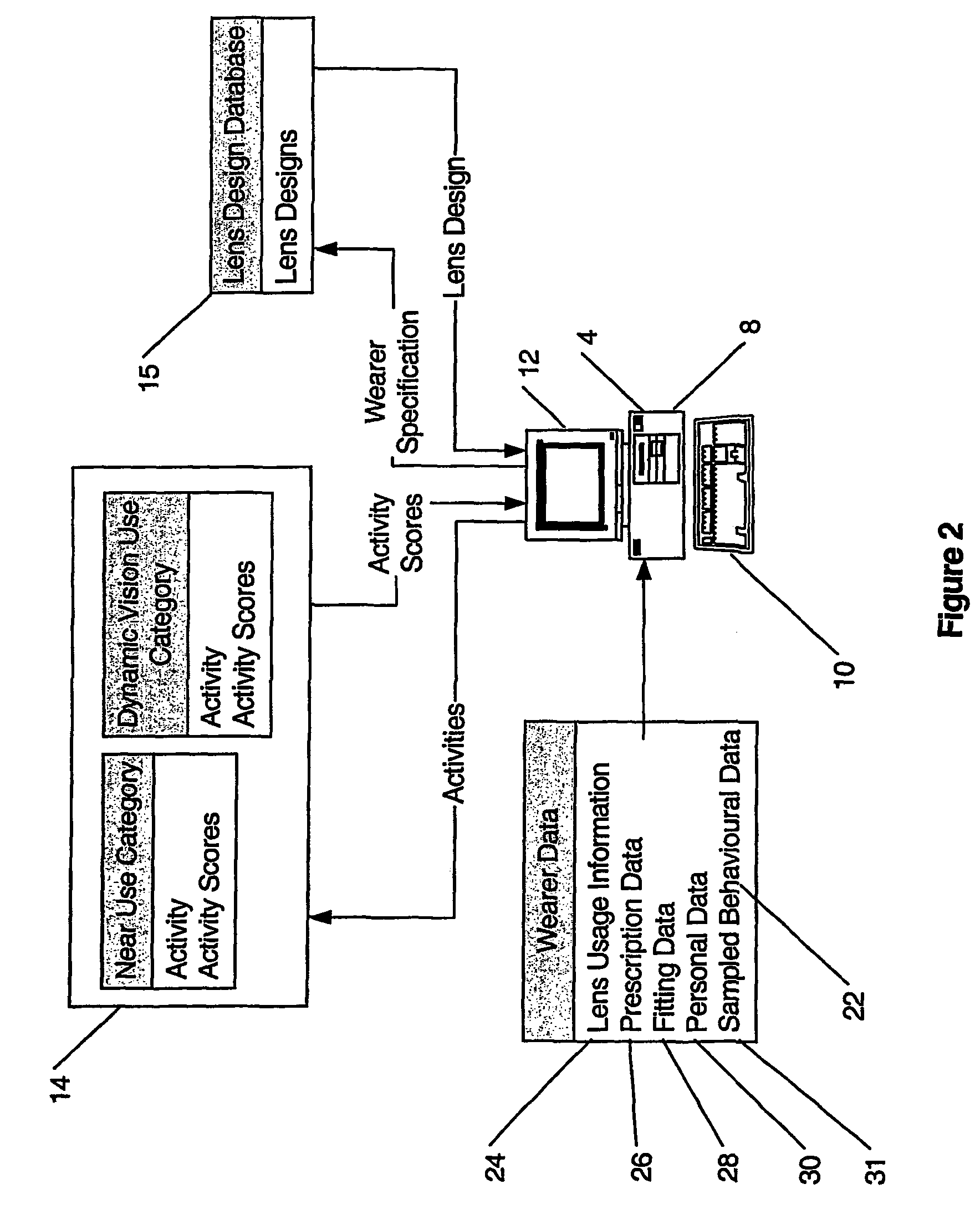
Inventor
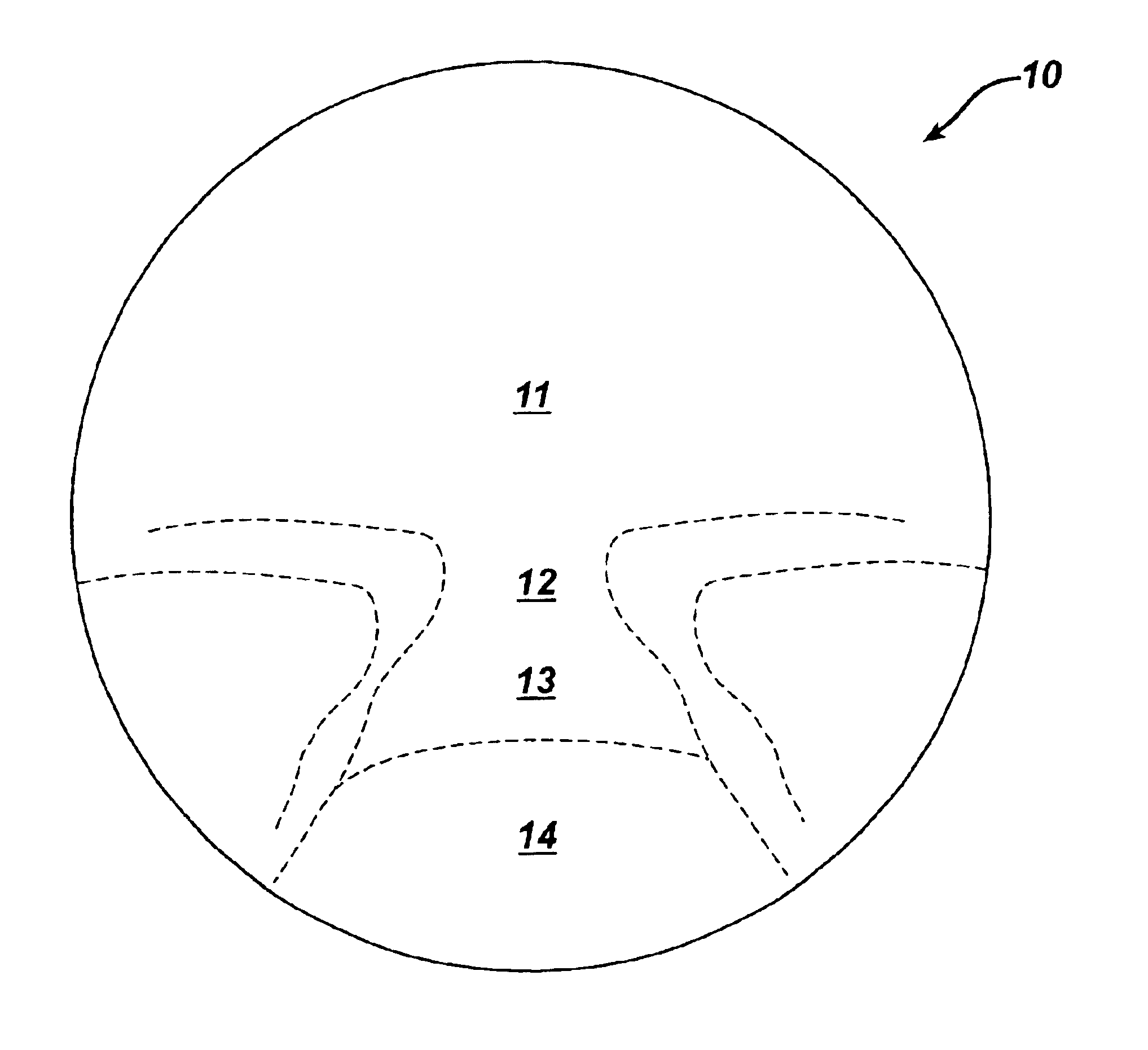
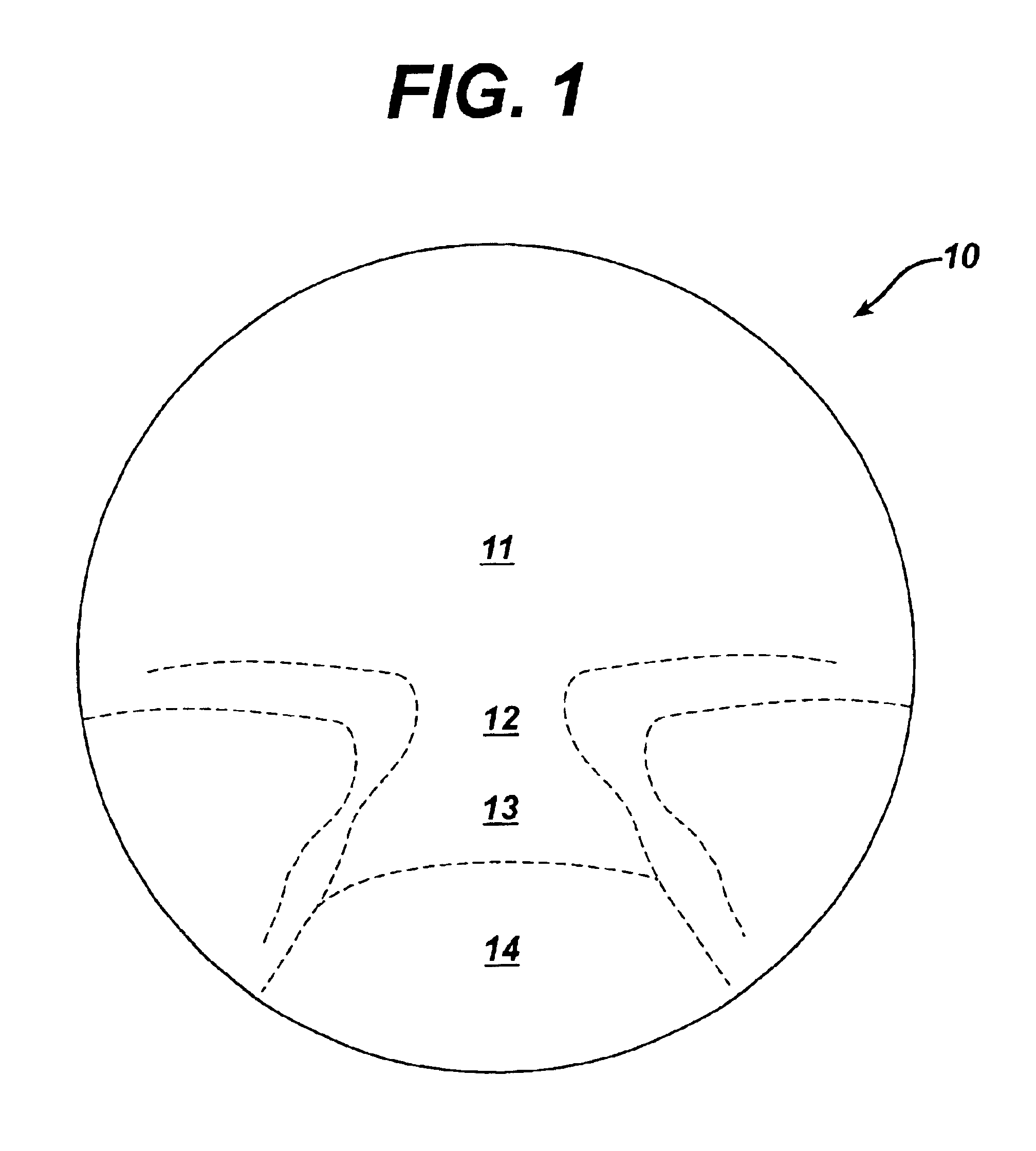
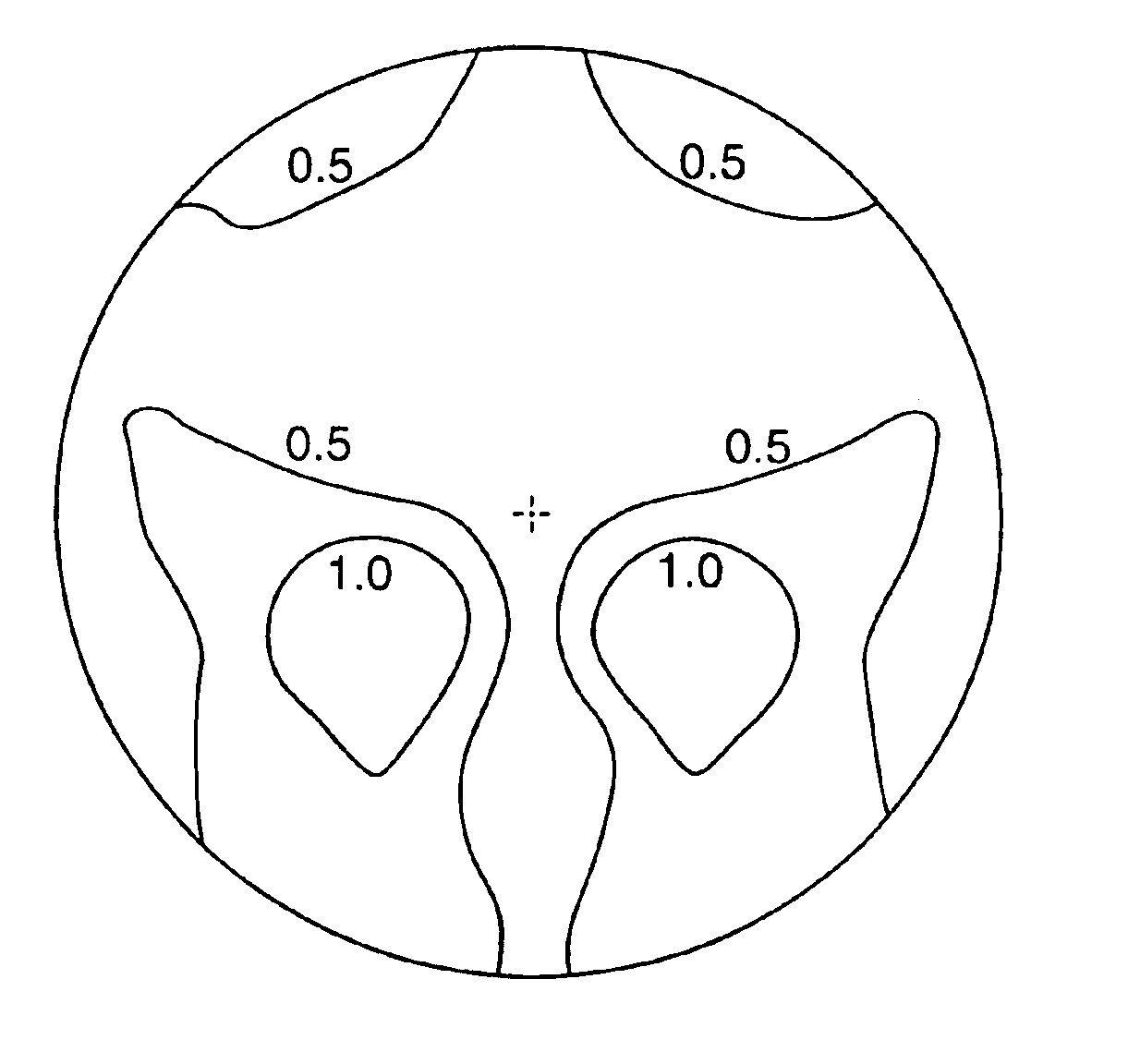
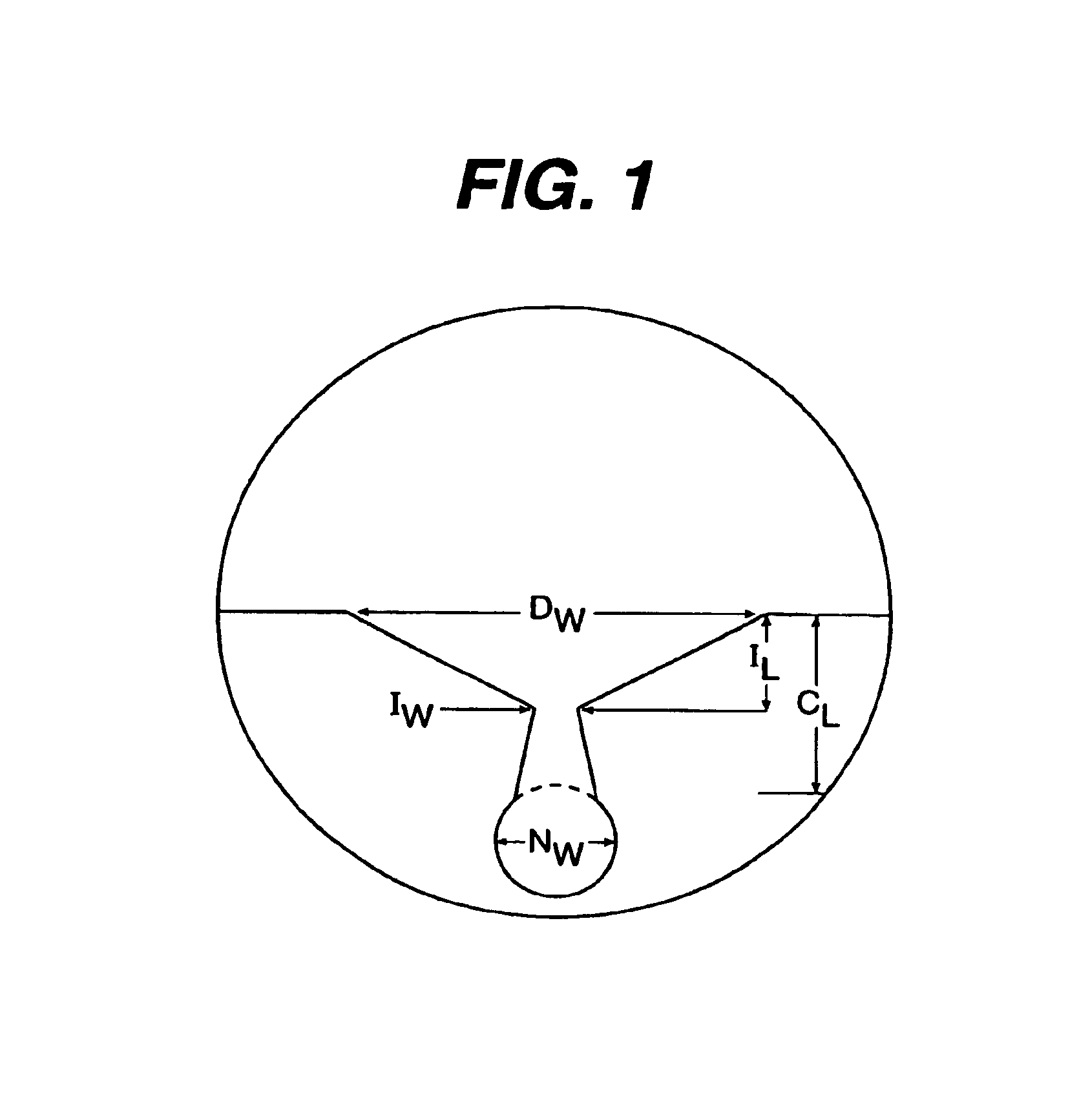
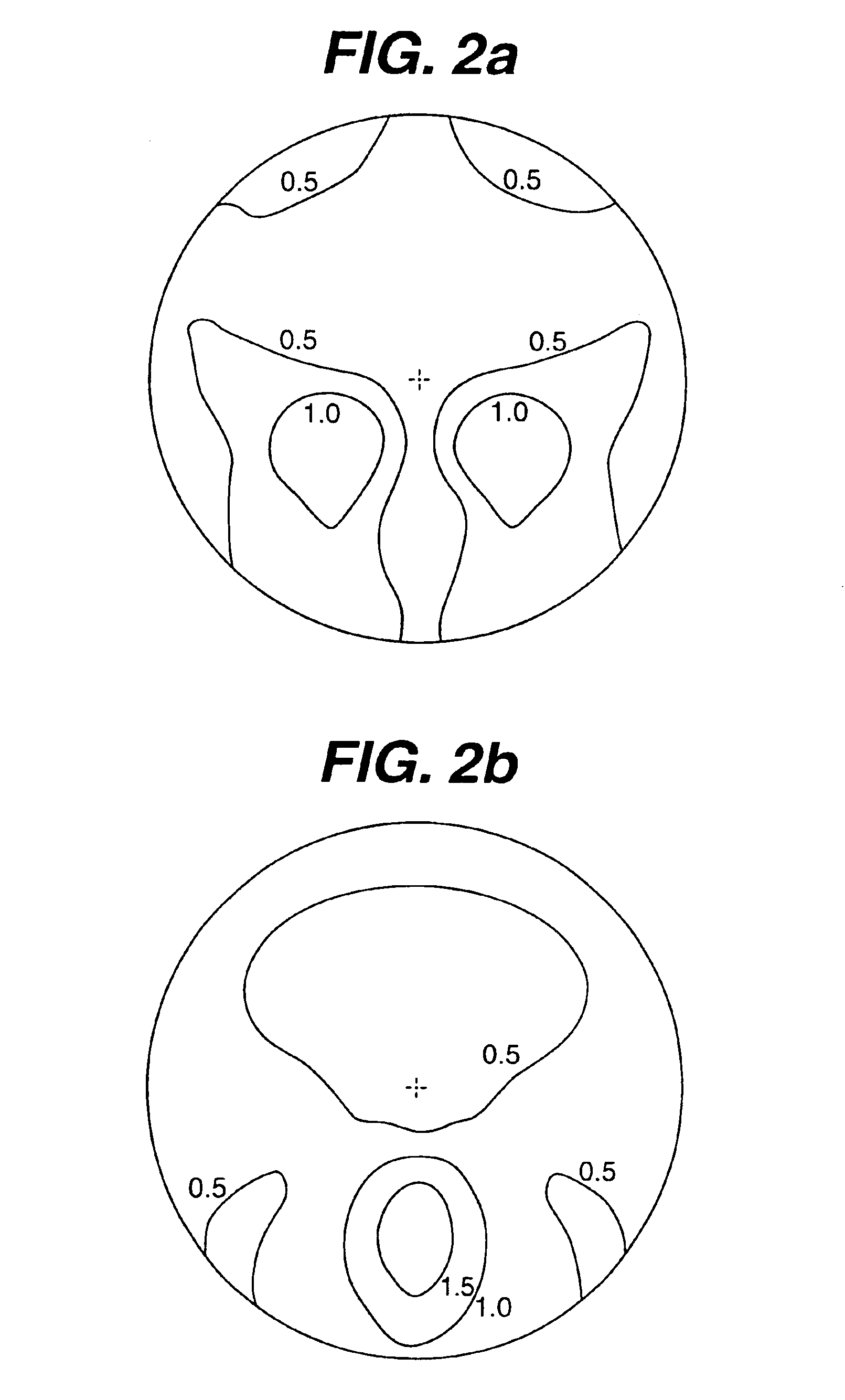
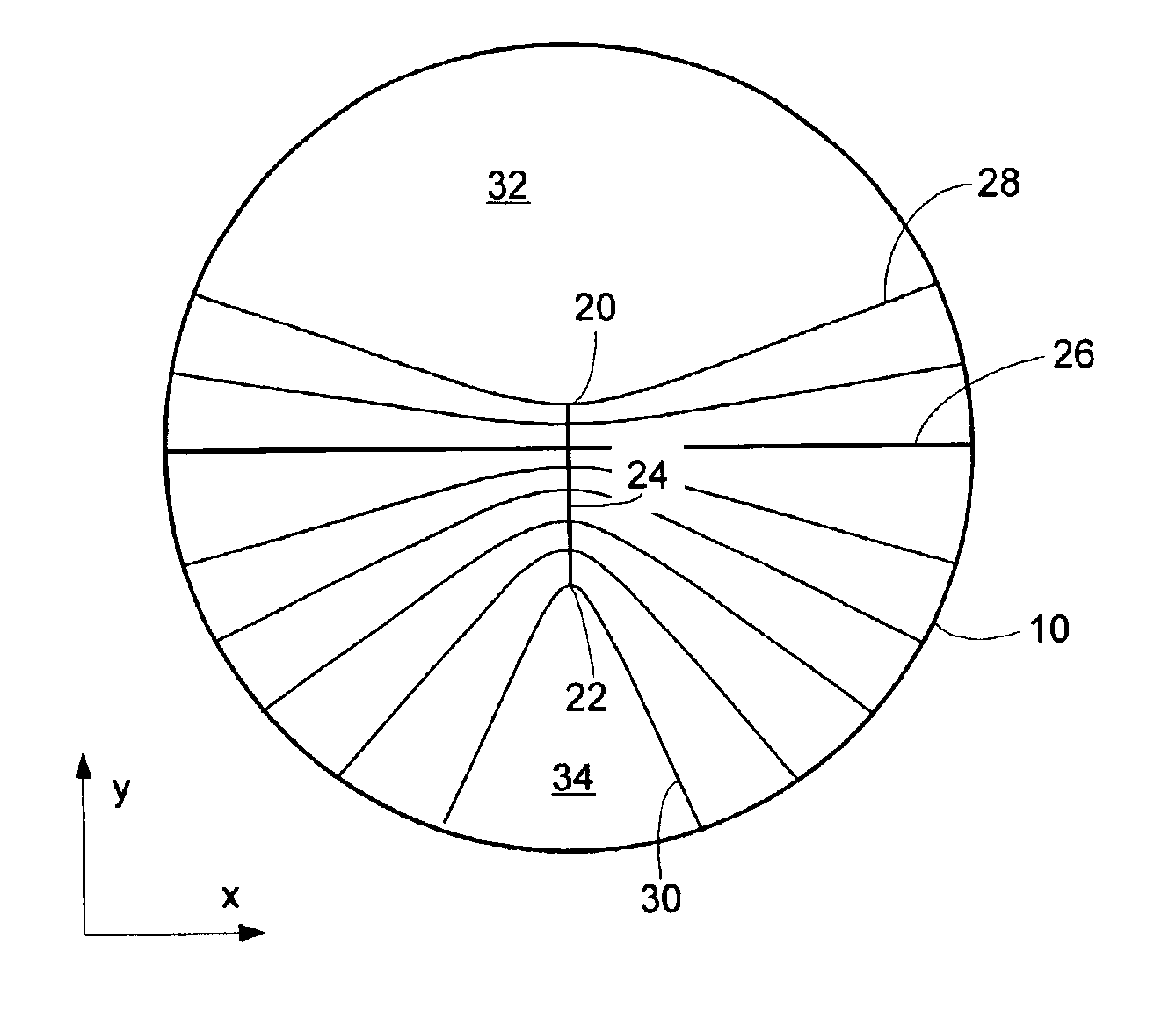
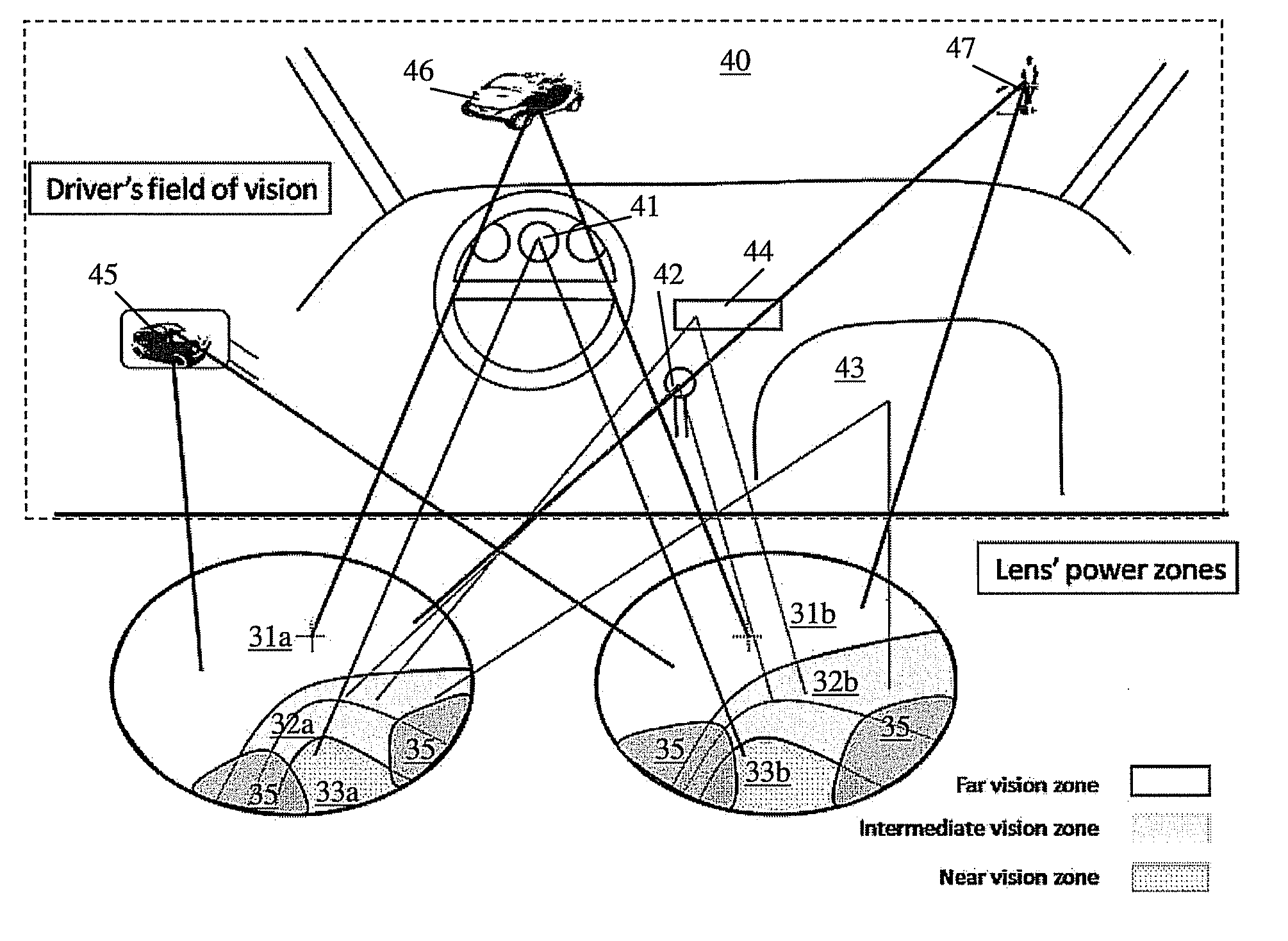
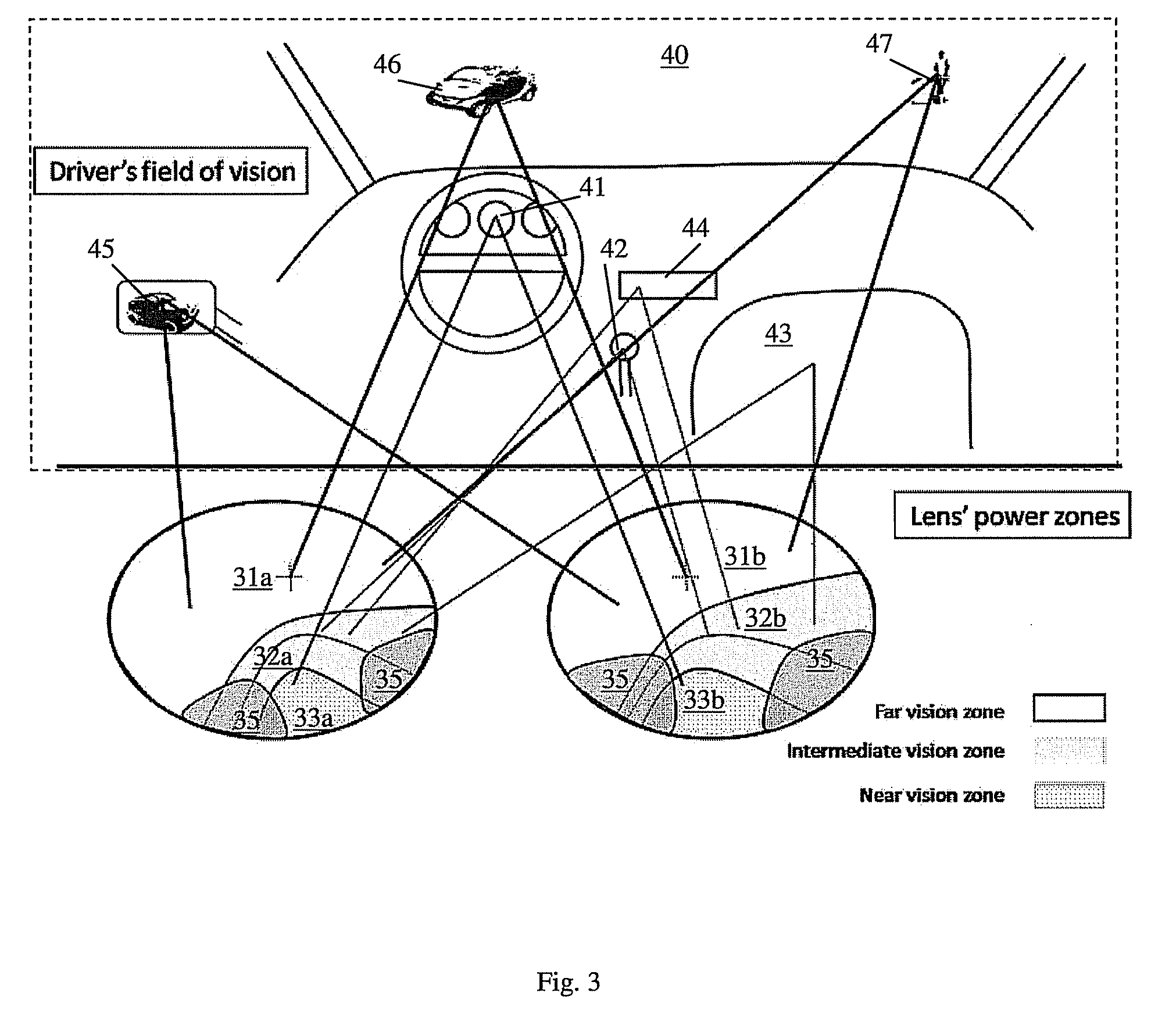
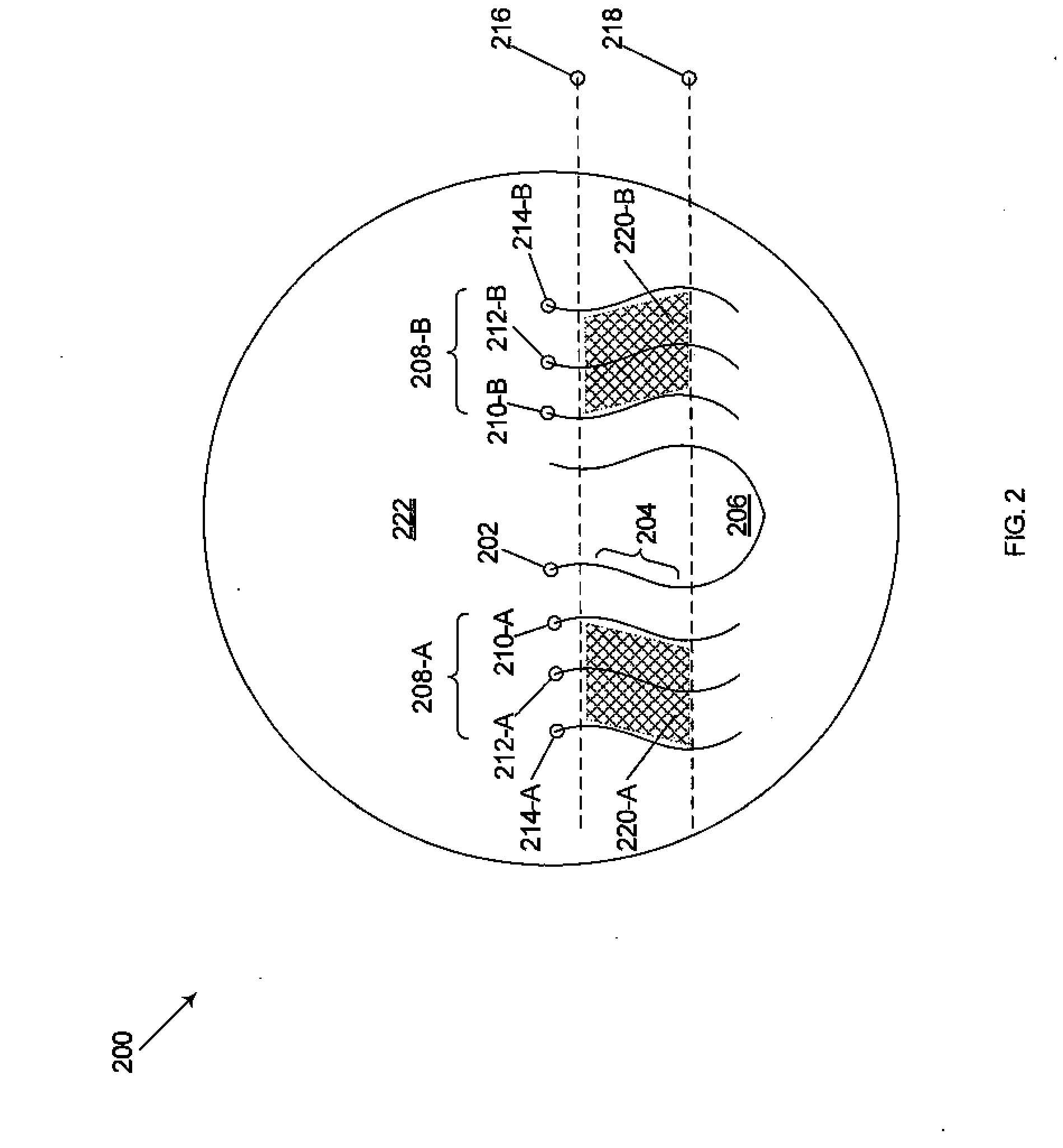
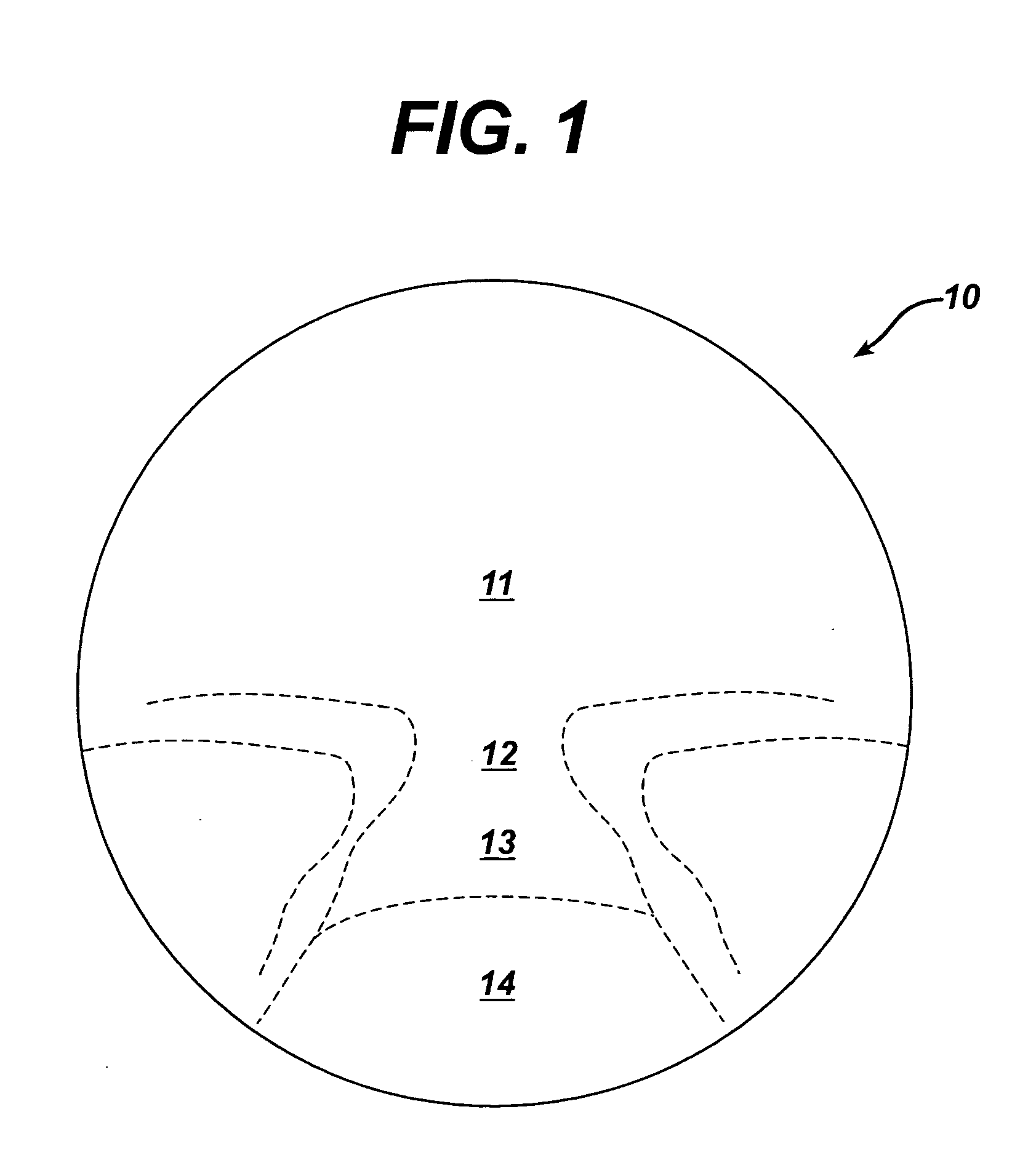
Progressive addition lenses with an additional zone
The invention provides multifocal lenses containing at least four zones of refractive power. The zones are positioned such that the wearer is able to use the inferior-most portion of the lens to clearly view objects at distances more than about 45 cm from the eye.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
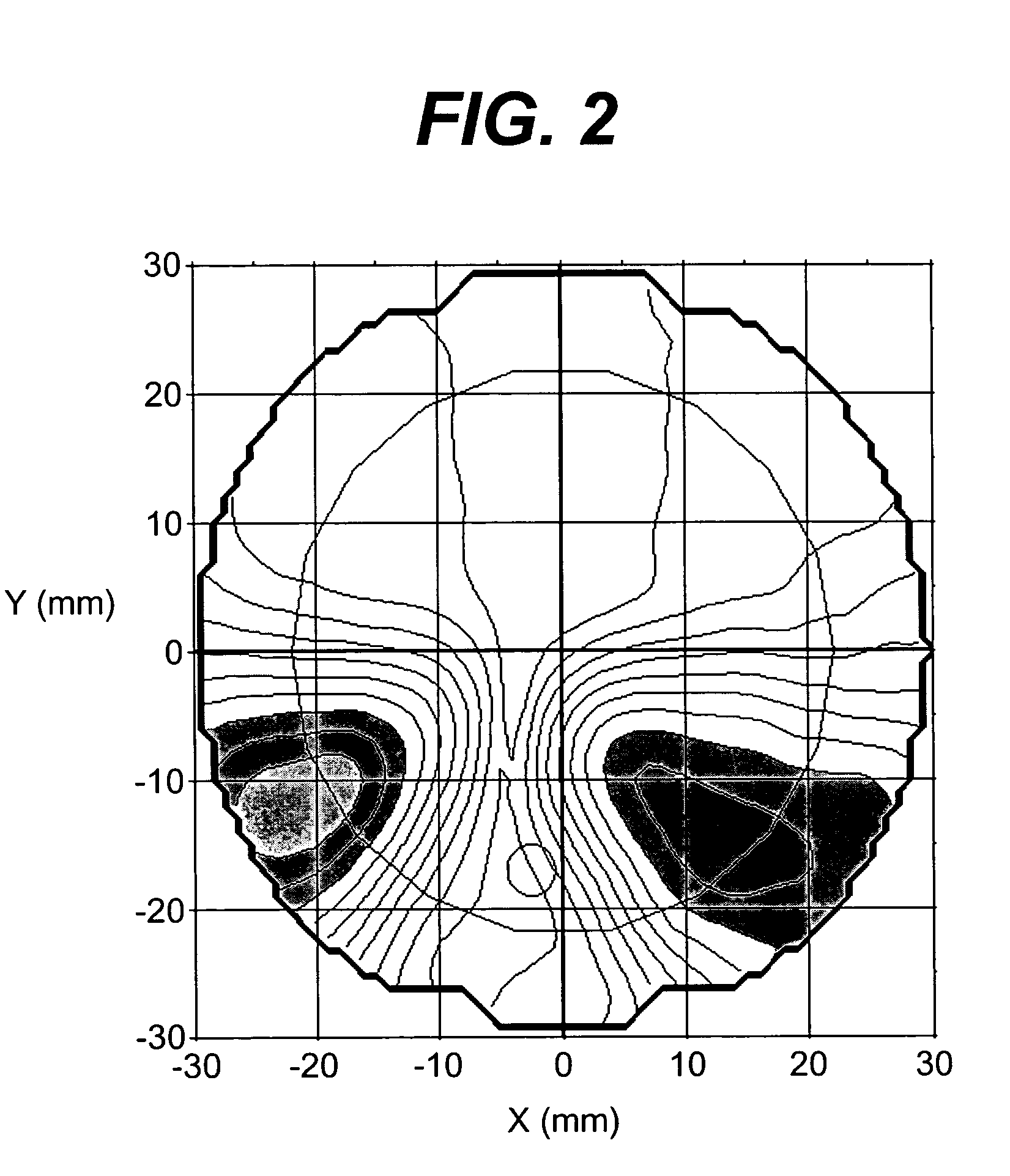
Progressive addition lenses
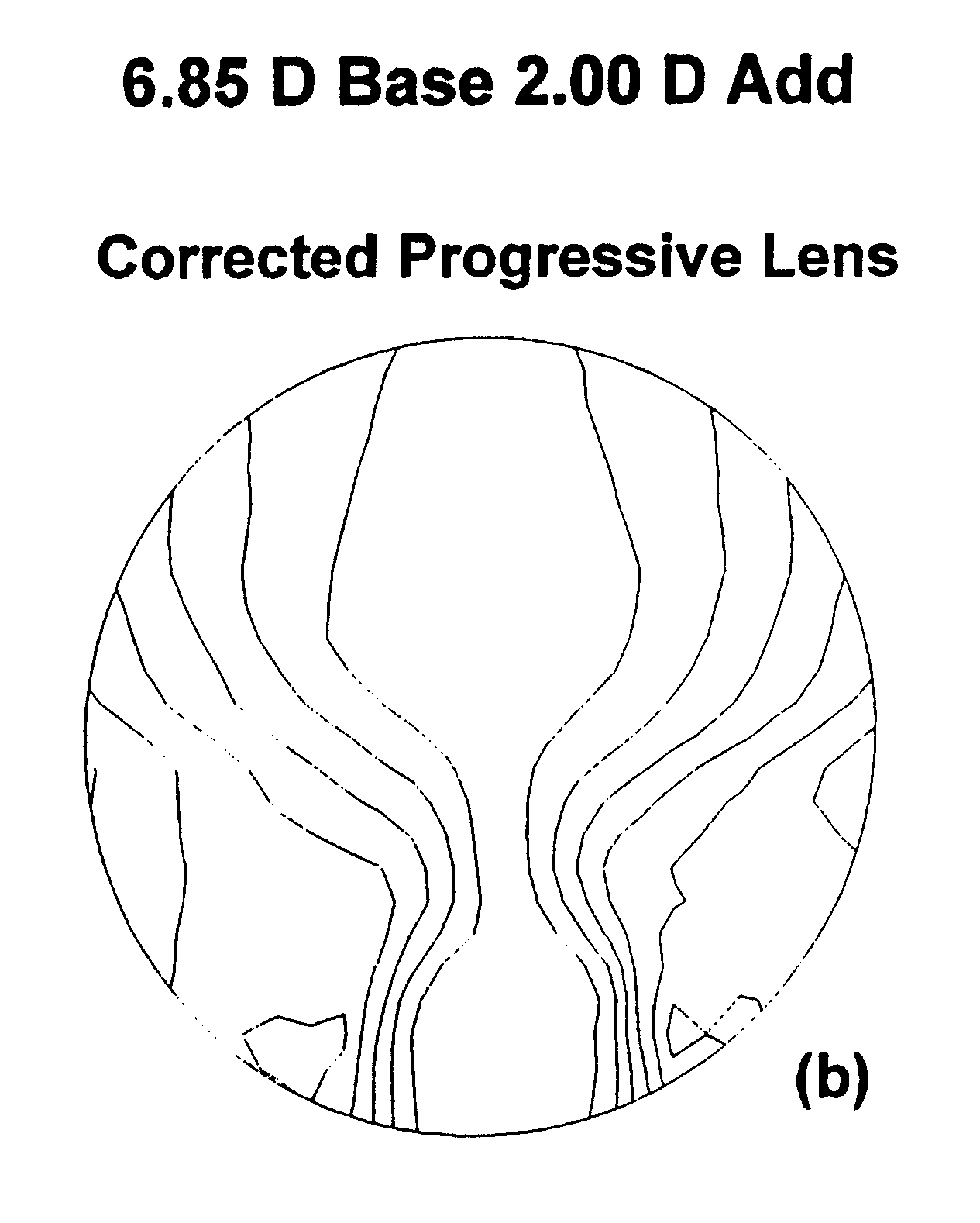
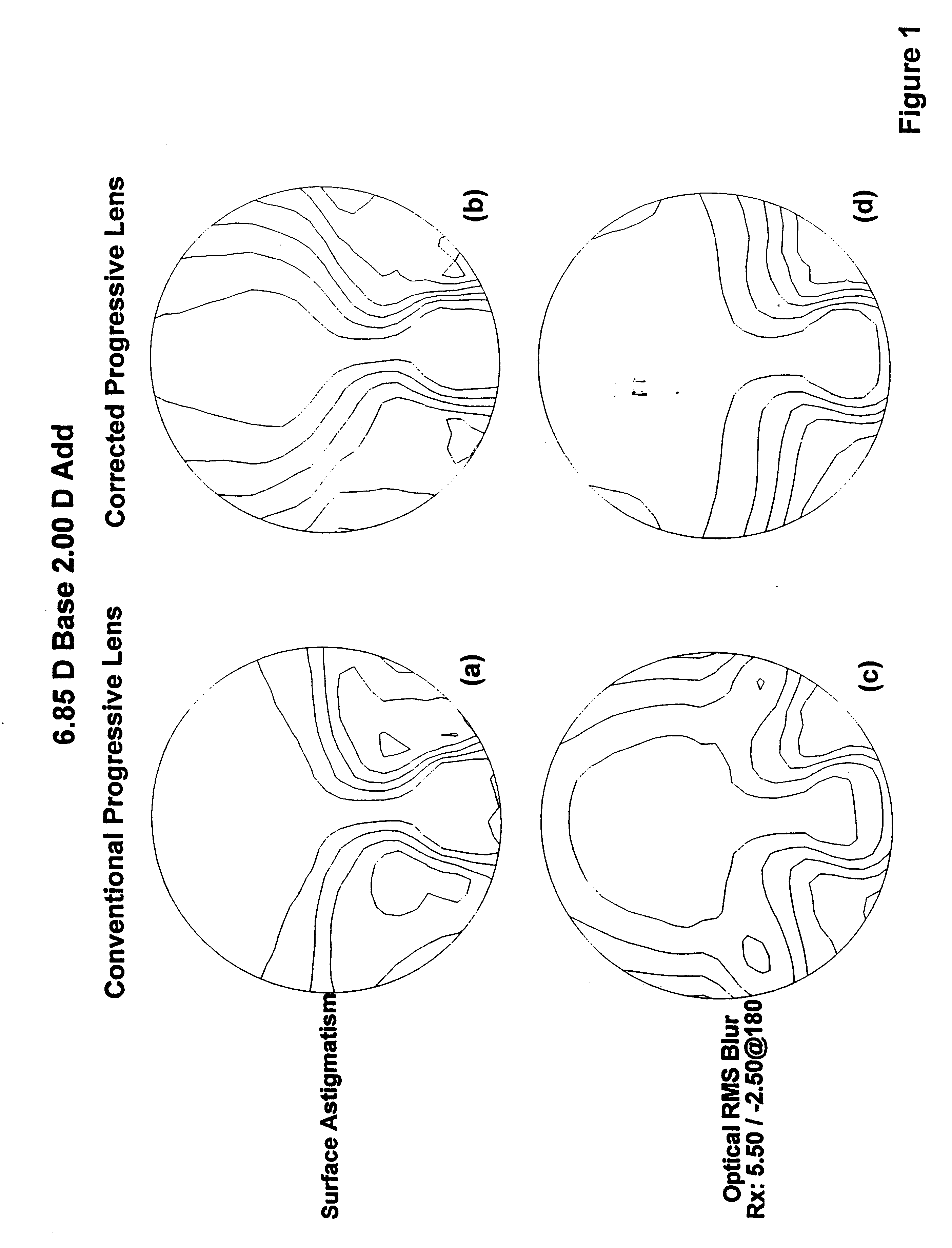
The present provides progressive addition lens designs and lenses in which unwanted lens astigmatism is reduced as compared to conventional progressive addition lenses. The lenses of the invention containing at least one surface that is a composite of a progressive surface design and a regressive surface design.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Method for designing progressive addition lenses
InactiveUS6956682B2Total lens maximum astigmatism can be reducedElectromagnetic transmissionOptical partsOphthalmologyProgressive addition lenses
The invention provides a method for designing progressive surfaces and lenses produced using image blur to construct a merit function. The shape of a lens surface, or surfaces, is arbitrarily defined and optimized to minimize the image blur based merit function.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Prescribing and/or dispensing ophthalmic lenses
ActiveUS20050122472A1Reduce sagittal addition powerReduce edge thicknessSpectales/gogglesEye surgeryMedical prescriptionProgressive addition lenses
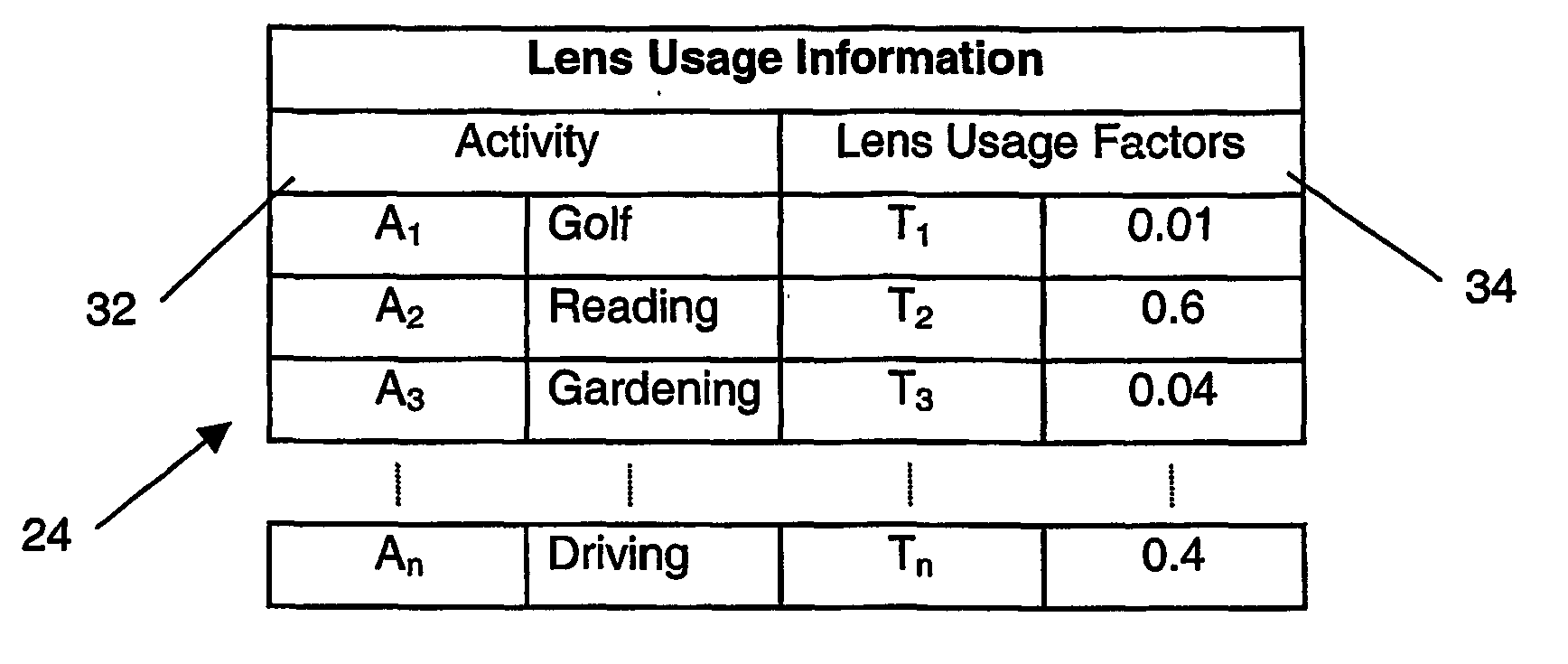
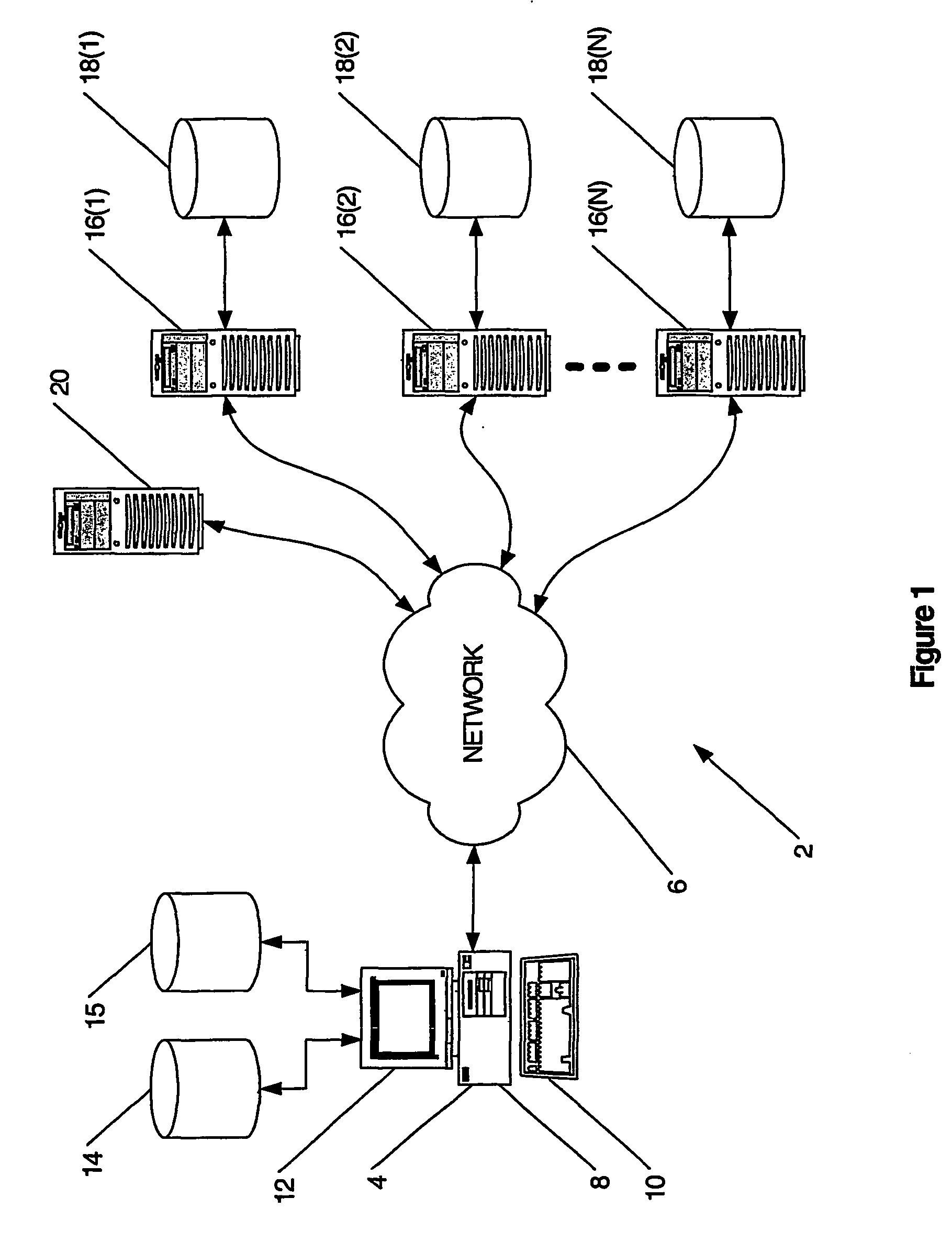
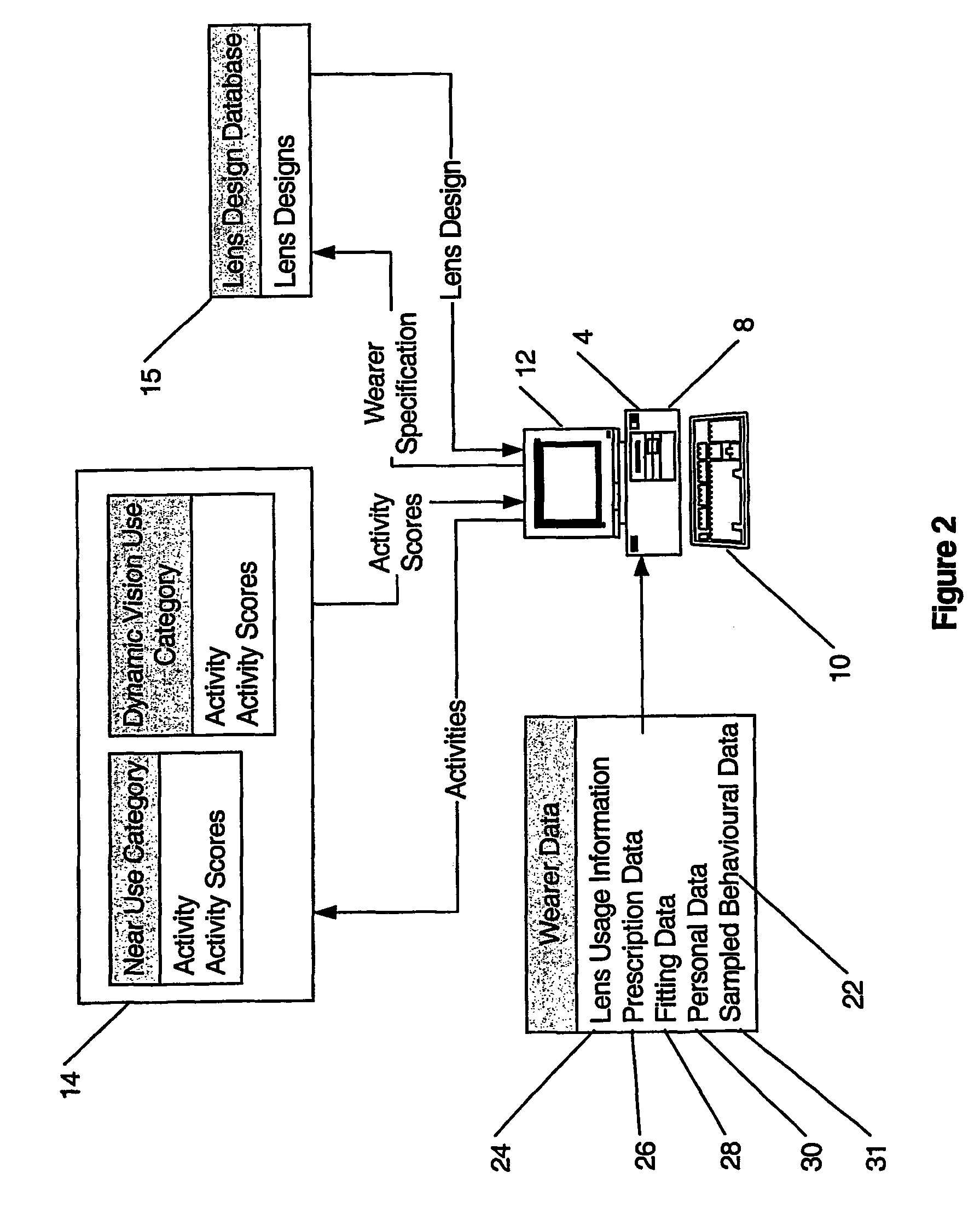
The present invention involves the prescribing and / or dispensing ophthalmic lenses, such as progressive addition lenses, for a wearer. In one form of the invention lens usage information is obtained from a wearer and entered into a programmed computer. The programmed computer processes the lens usage information to provide a separate weighted lifestyle score for each of one or more respective lifestyle score categories, such that each weighted lifestyle score is a function of a predetermined relationship between the respective lifestyle score category and at least ophthalmic lens design feature. The programmed computer then selects or designs an ophthalmic lens design using one or more of the weighted lifestyle scores such that the selected or designed ophthalmic lens has at least one lens design feature which has been customised using one or more of the weighted lifestyle scores.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION AUSTRALIA HO
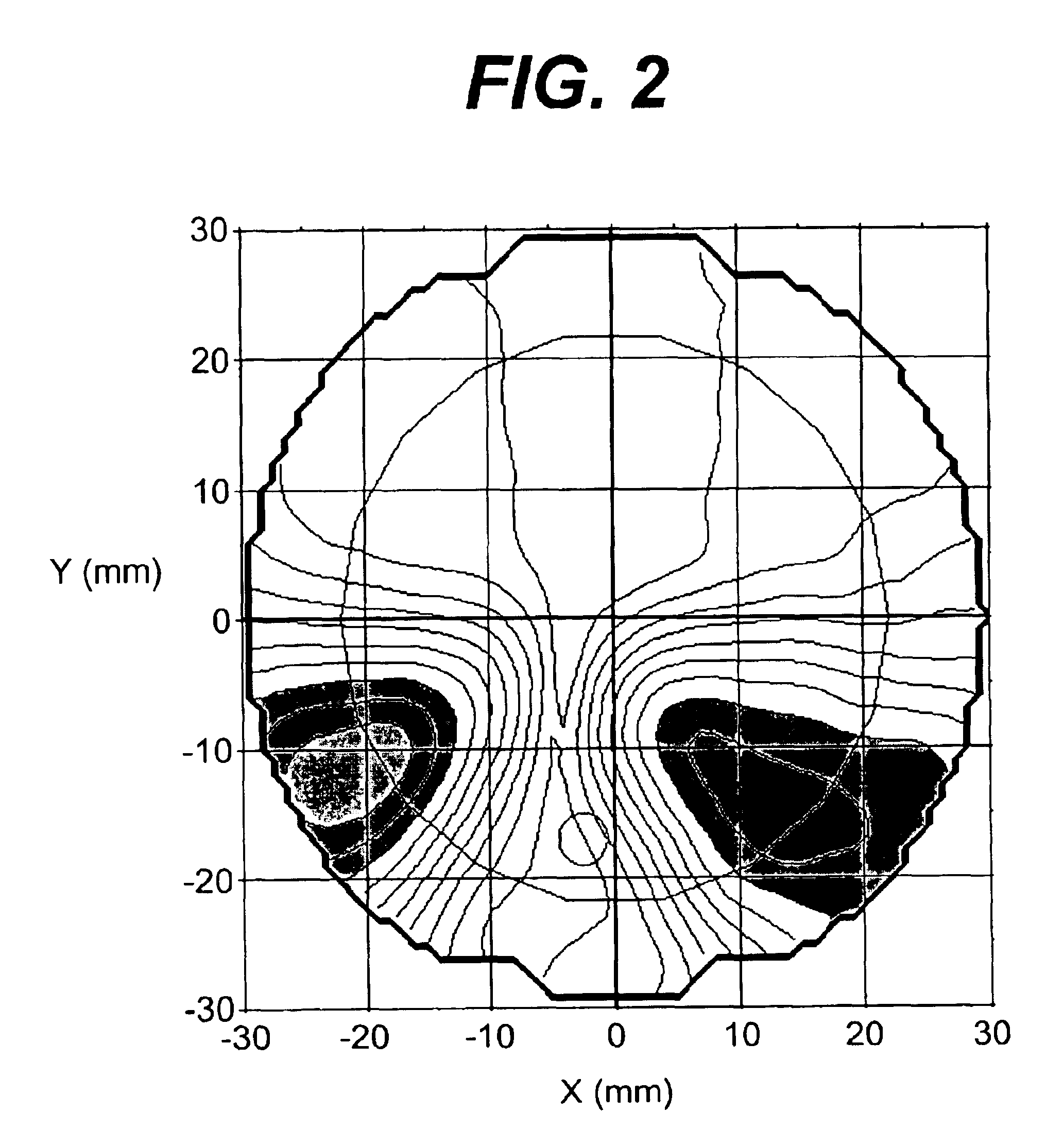
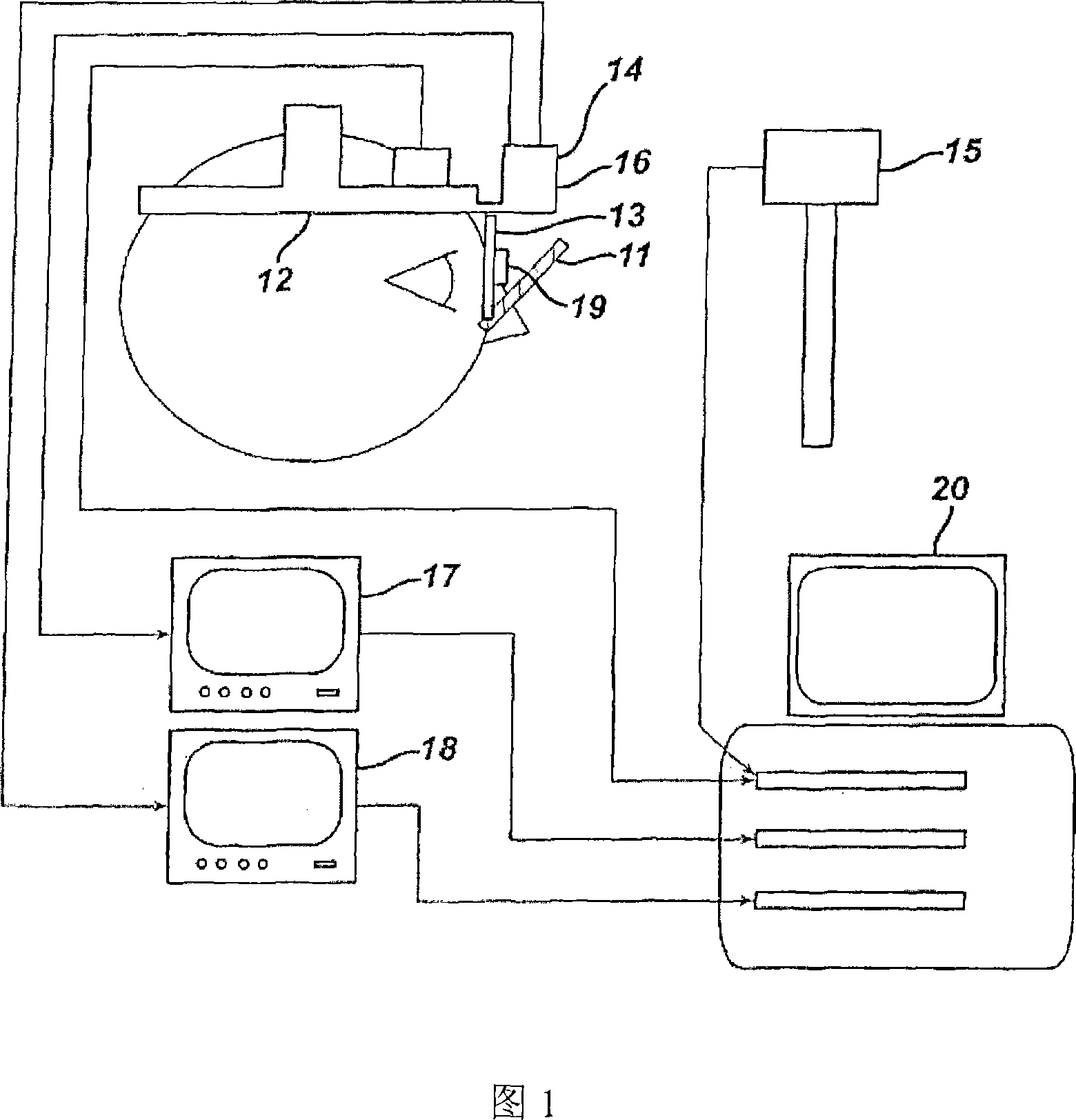
Image quality mapper for progressive eyeglasses
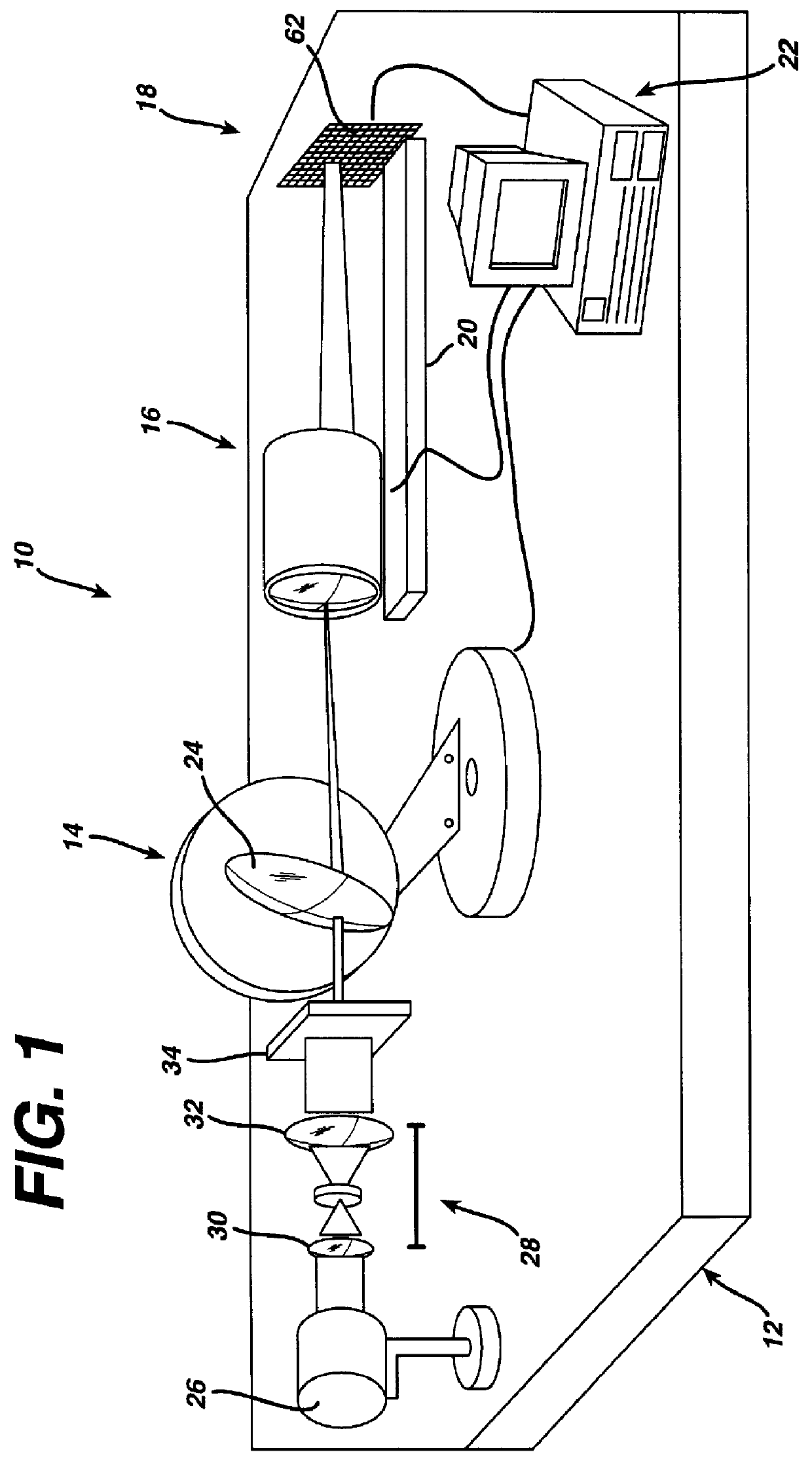
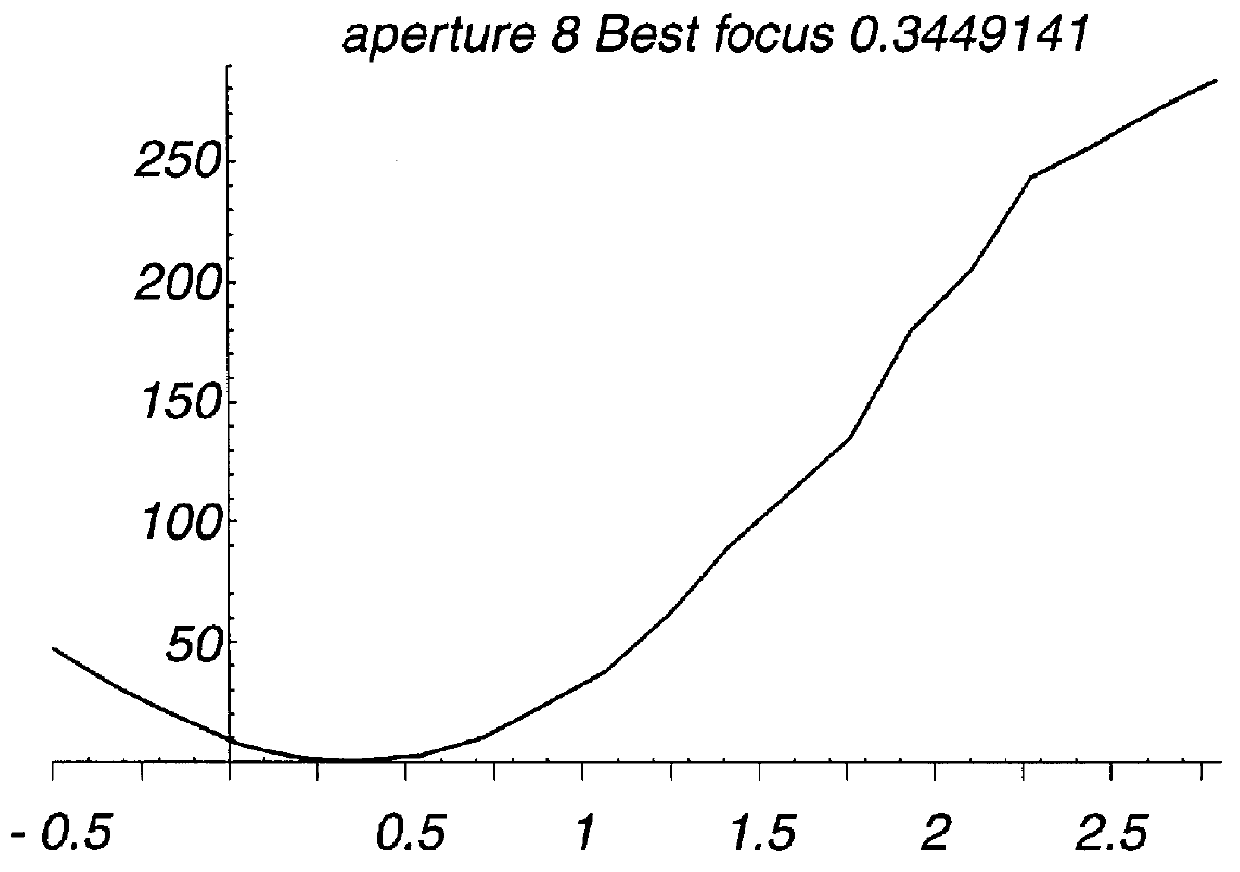
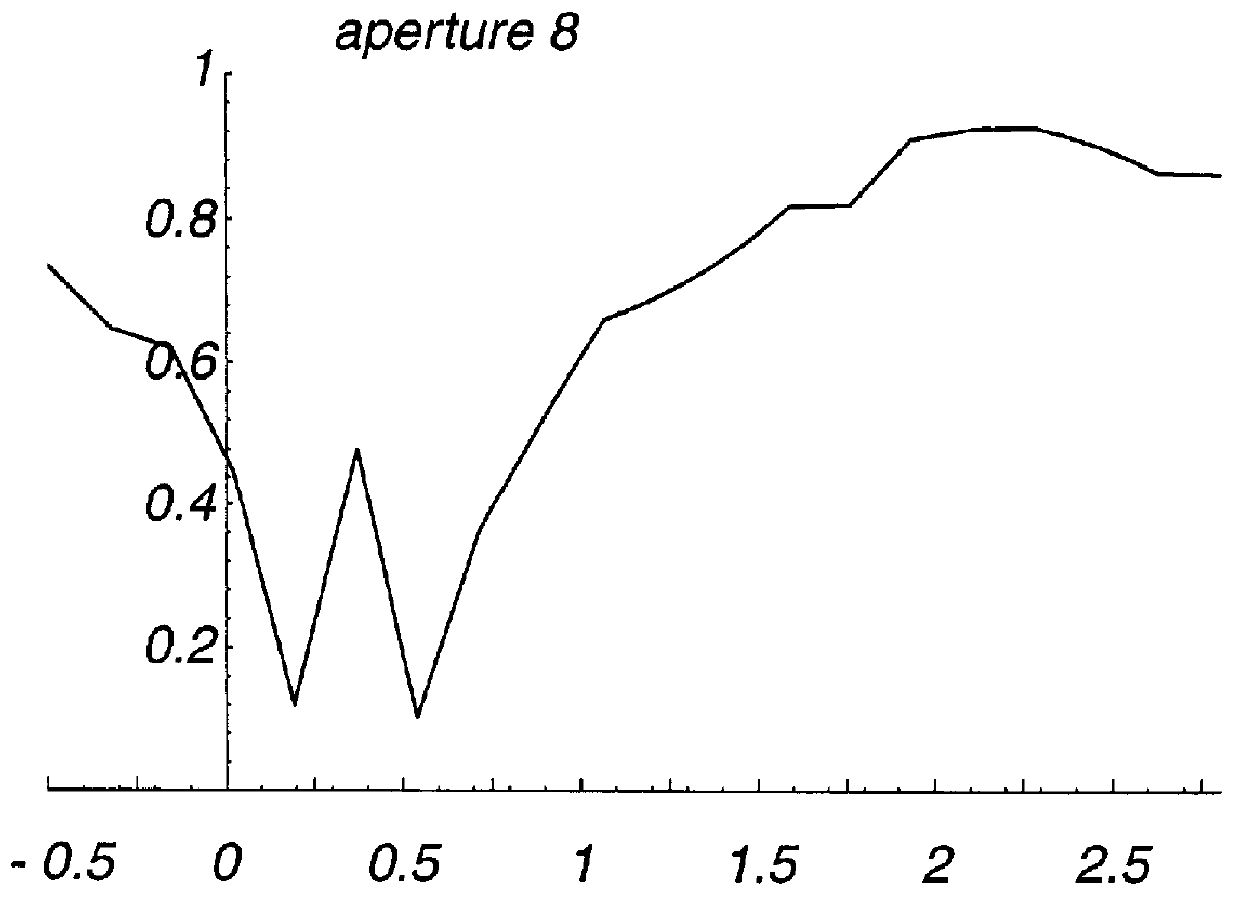
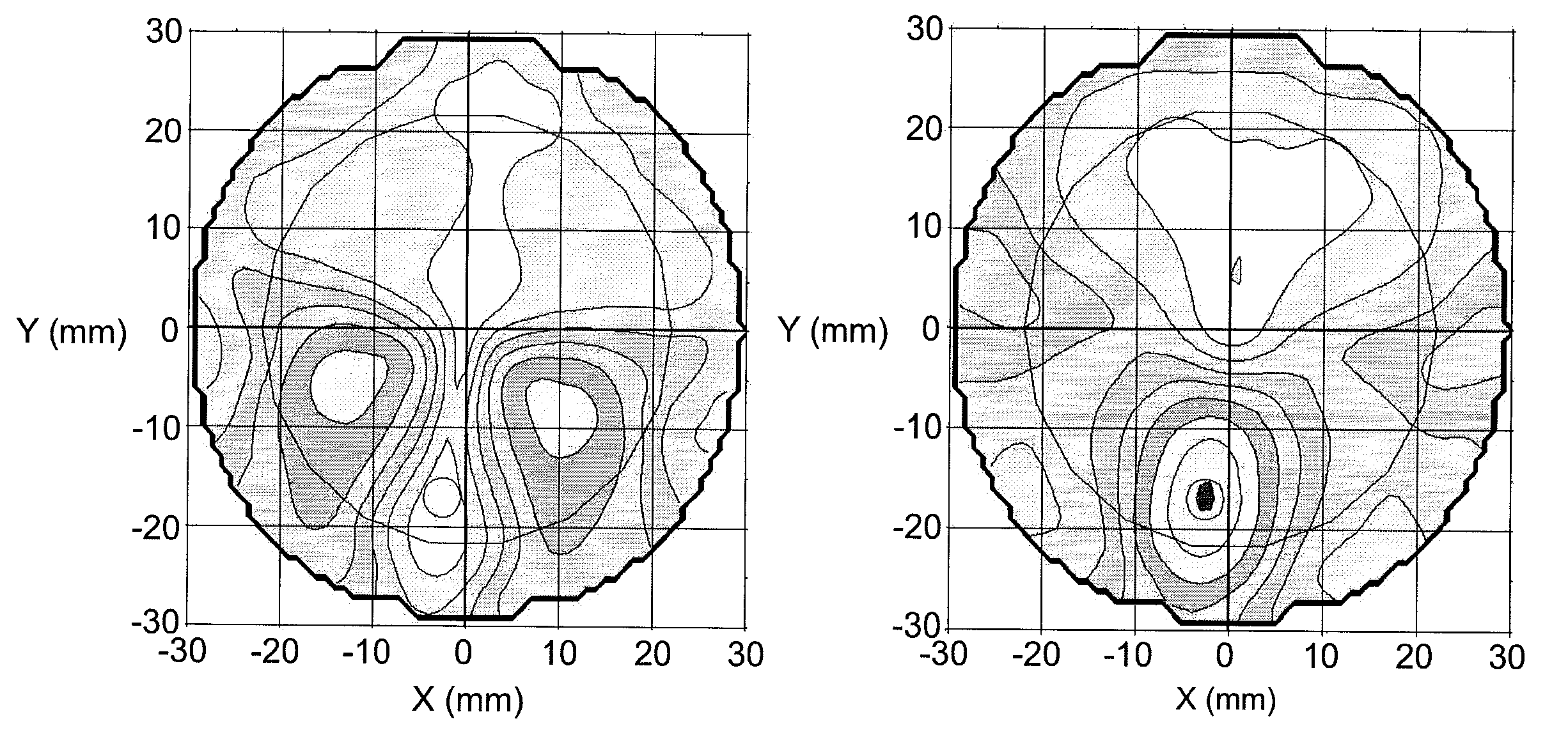
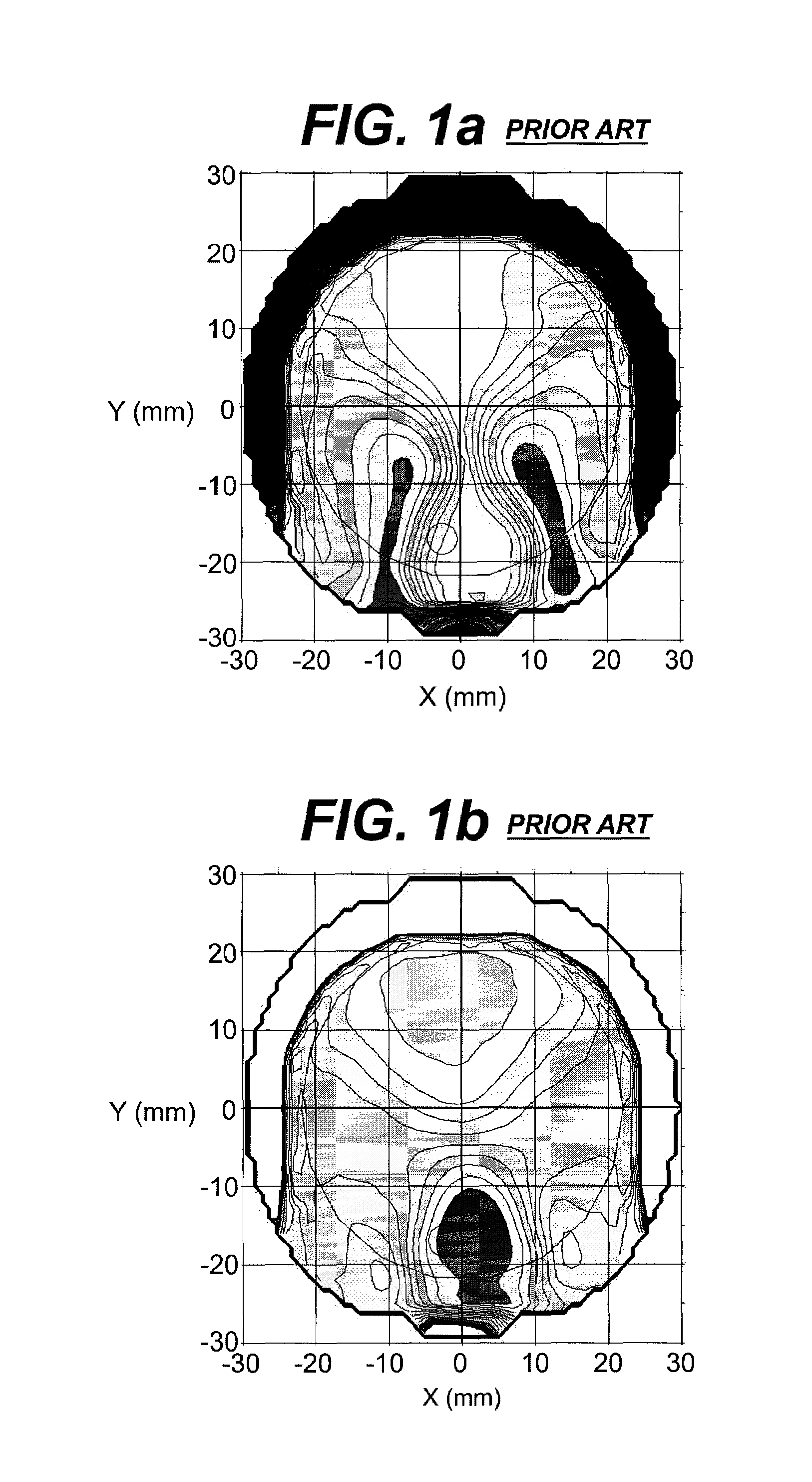
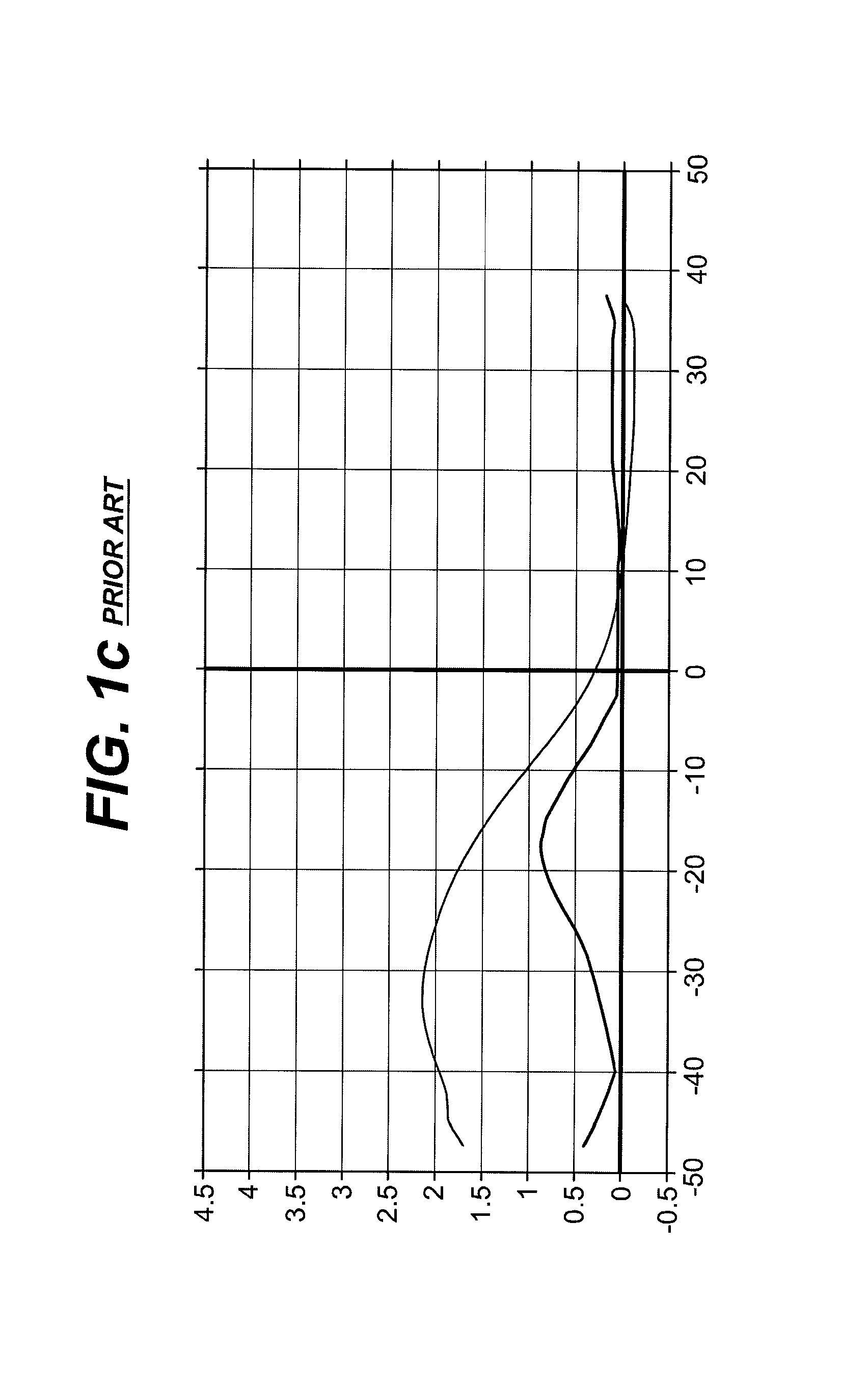
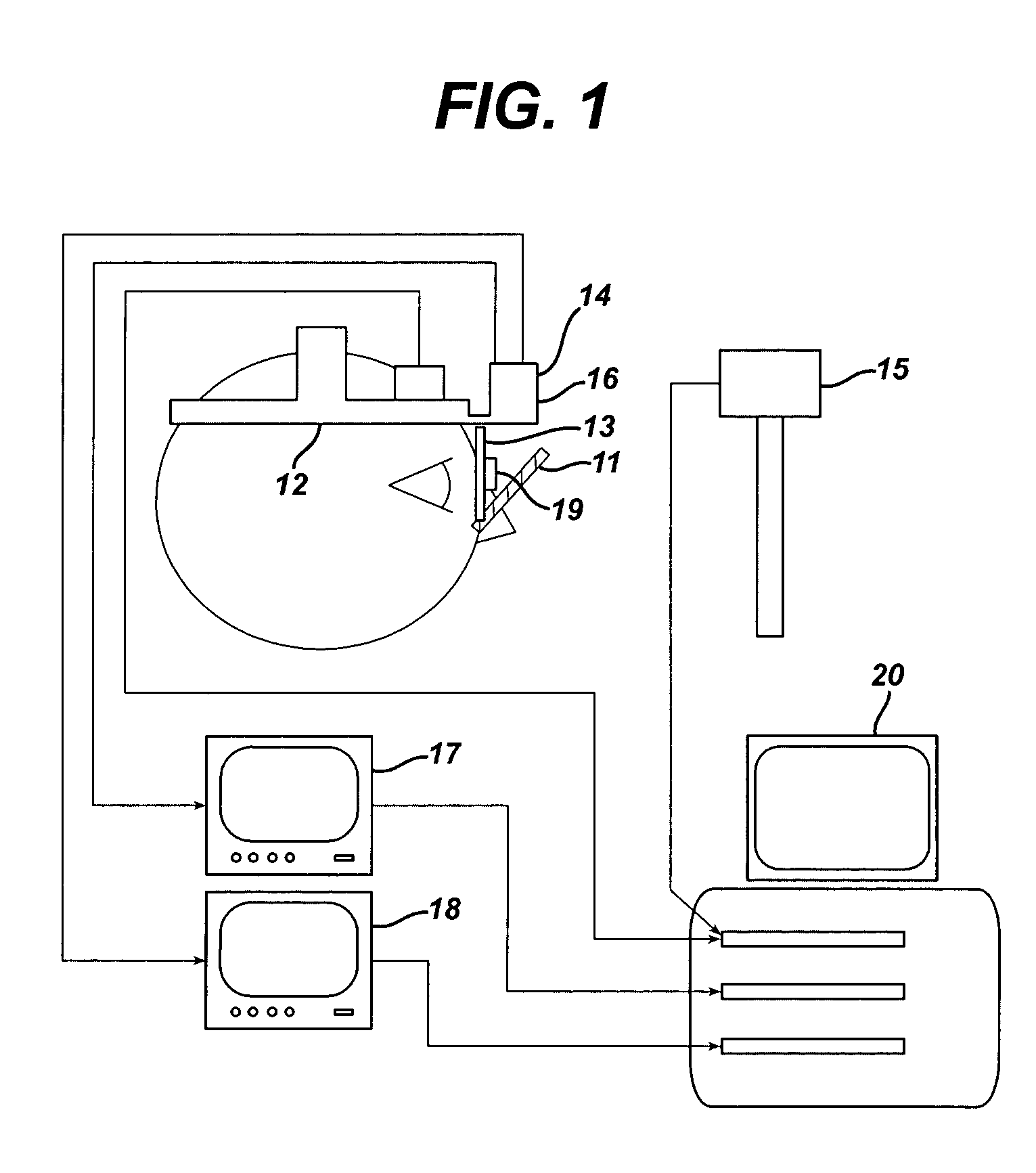
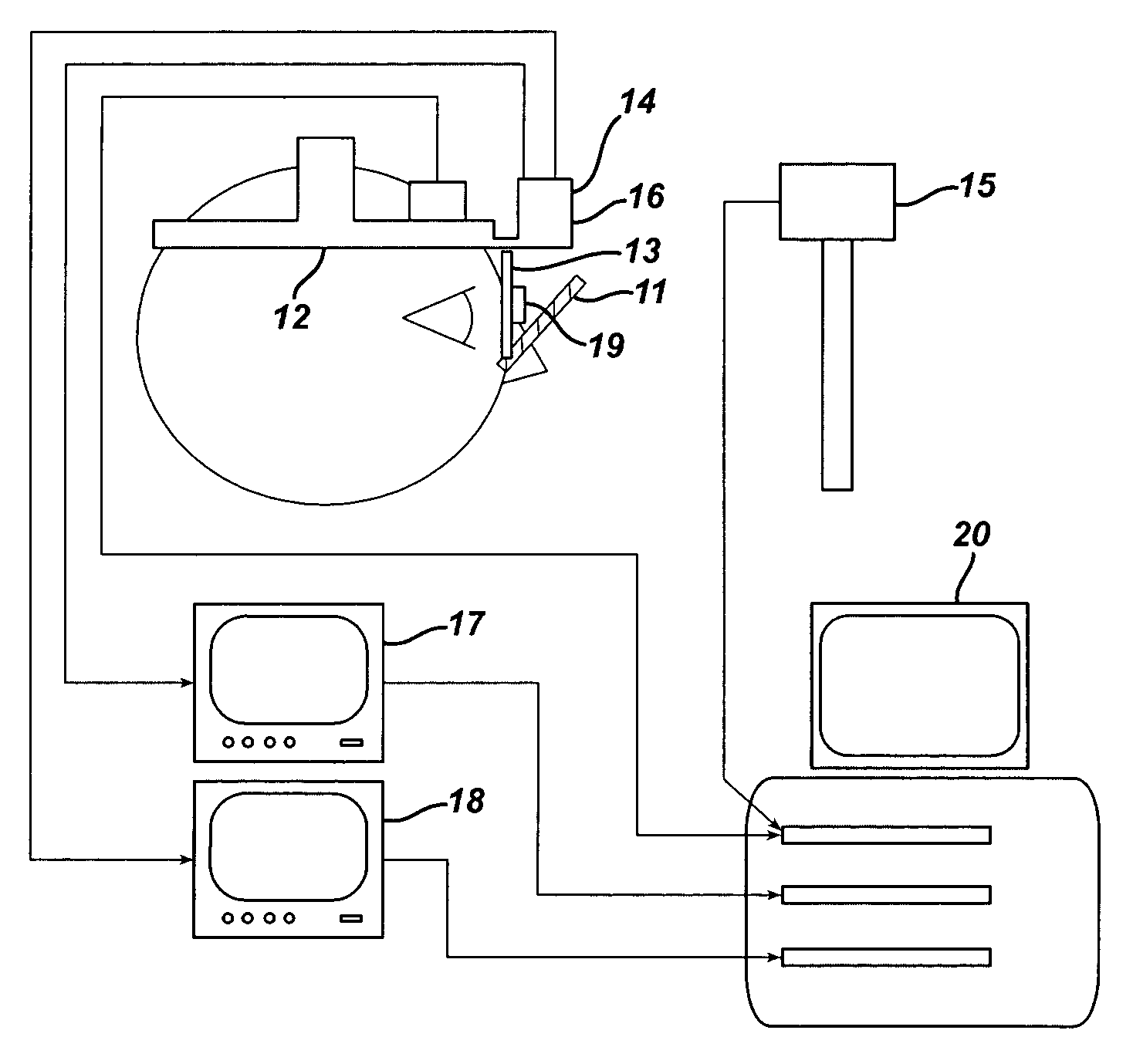
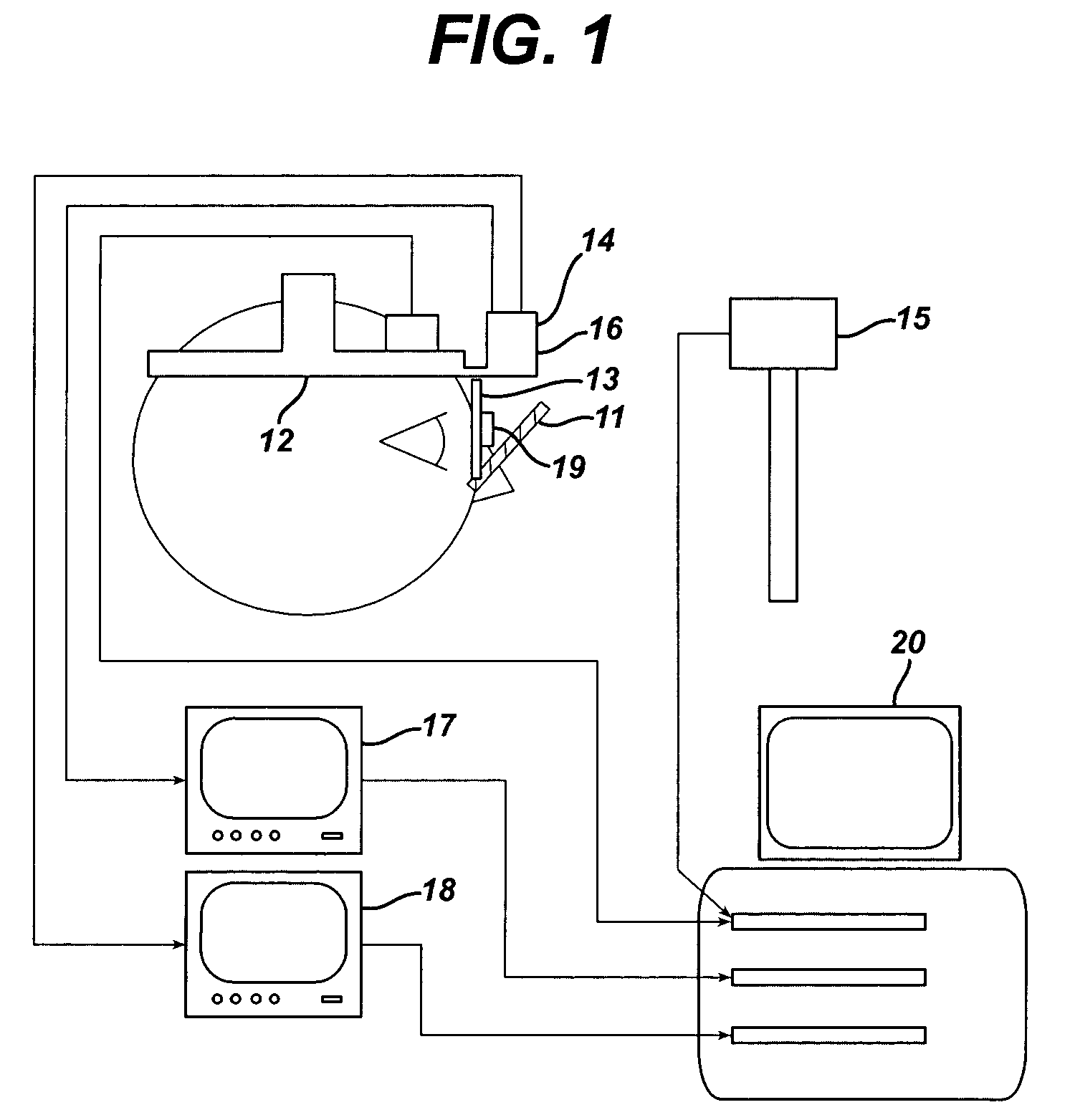
An instrument and method for optical testing of an eyeglass lens, including progressive addition lenses, to obtain image quality measurements includes an illumination system for presenting a beam of light to a test lens, a test lens positioning system for rotating the test lens so that different areas on the lens are illuminated, a zoom lens for focusing the beam at a constant effective focal length, a detection system for recording and measuring image quality of the test lens, and an alignment boom for conveying the zoom lens and the detection system such that the optical axis remains aligned with the beam existing the test lens. The instrument is fully automated and capable of obtaining measurements of the power, astigmatism, prism and modulation transfer function at various locations on the surface of the lens.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
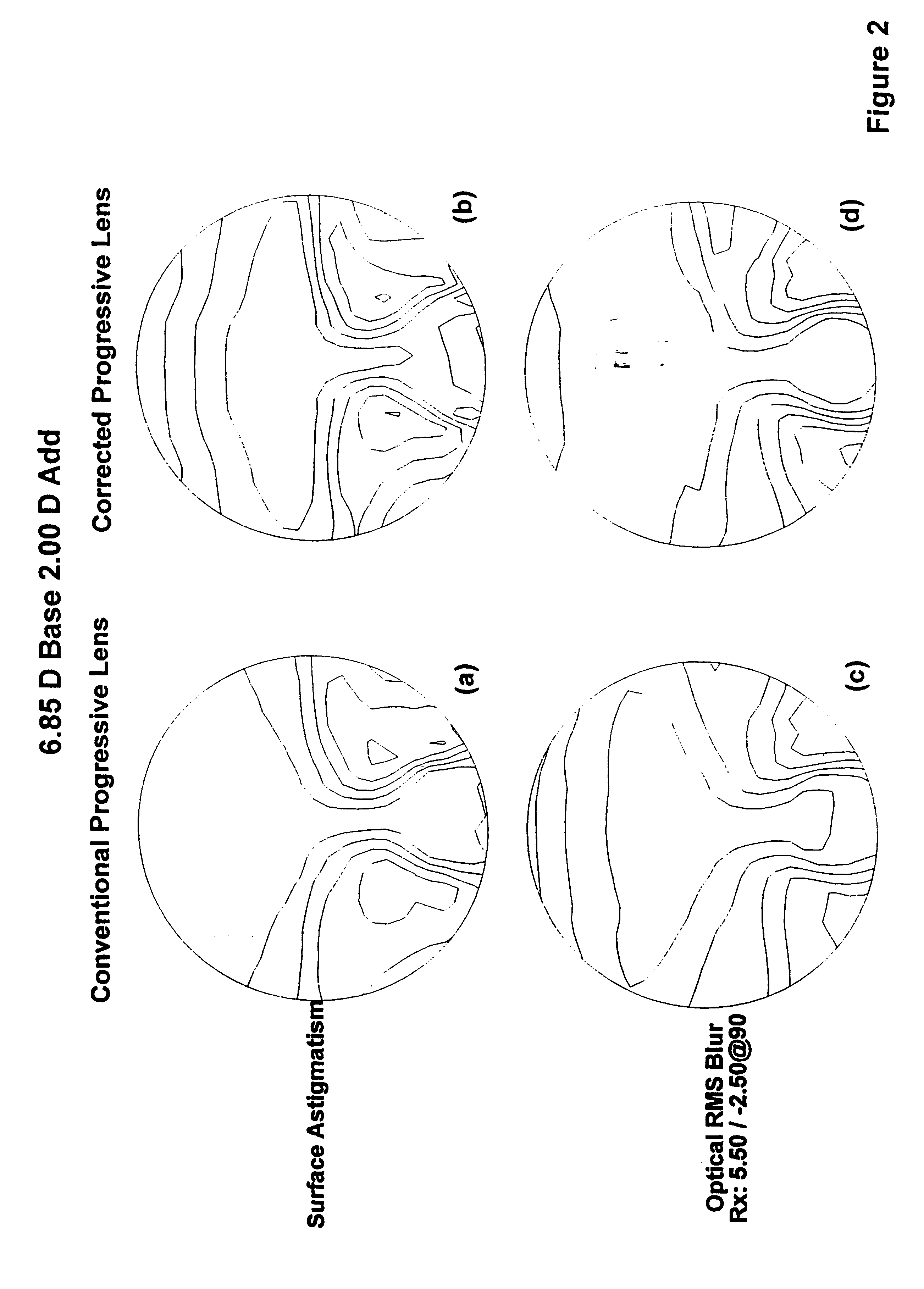
Short corridor progressive addition lenses with reduced unwanted astigmatism
The invention provides lenses produced by the adding of two or more surfaces, in which lenses both the length of the corridor is shortened and the maximum unwanted astigmatism is reduced.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Method for designing spectacle lenses taking into account an individual's head and eye movement
ActiveUS20050088616A1Eye diagnosticsOptical partsOphthalmology departmentProgressive addition lenses
A method for designing ophthalmic lenses, including progressive addition lenses, and lenses produced by the method are provided. The method permits the direct correlation of an individual's subjective assessment of the lens' performance and the objective measure of lens performance relative to the individual. The method permits generation of lens designs based on the head and eye movement of the individual and the designing of customized lenses.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Method for designing spectacle lenses taking into account an individual's head and eye movement
A method for designing ophthalmic lenses, including progressive addition lenses, and lenses produced by the method are provided. The method permits the direct correlation of an individual's subjective assessment of the lens' performance and the objective measure of lens performance relative to the individual. The method permits generation of lens designs based on the head and eye movement of the individual and the designing of customized lenses.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
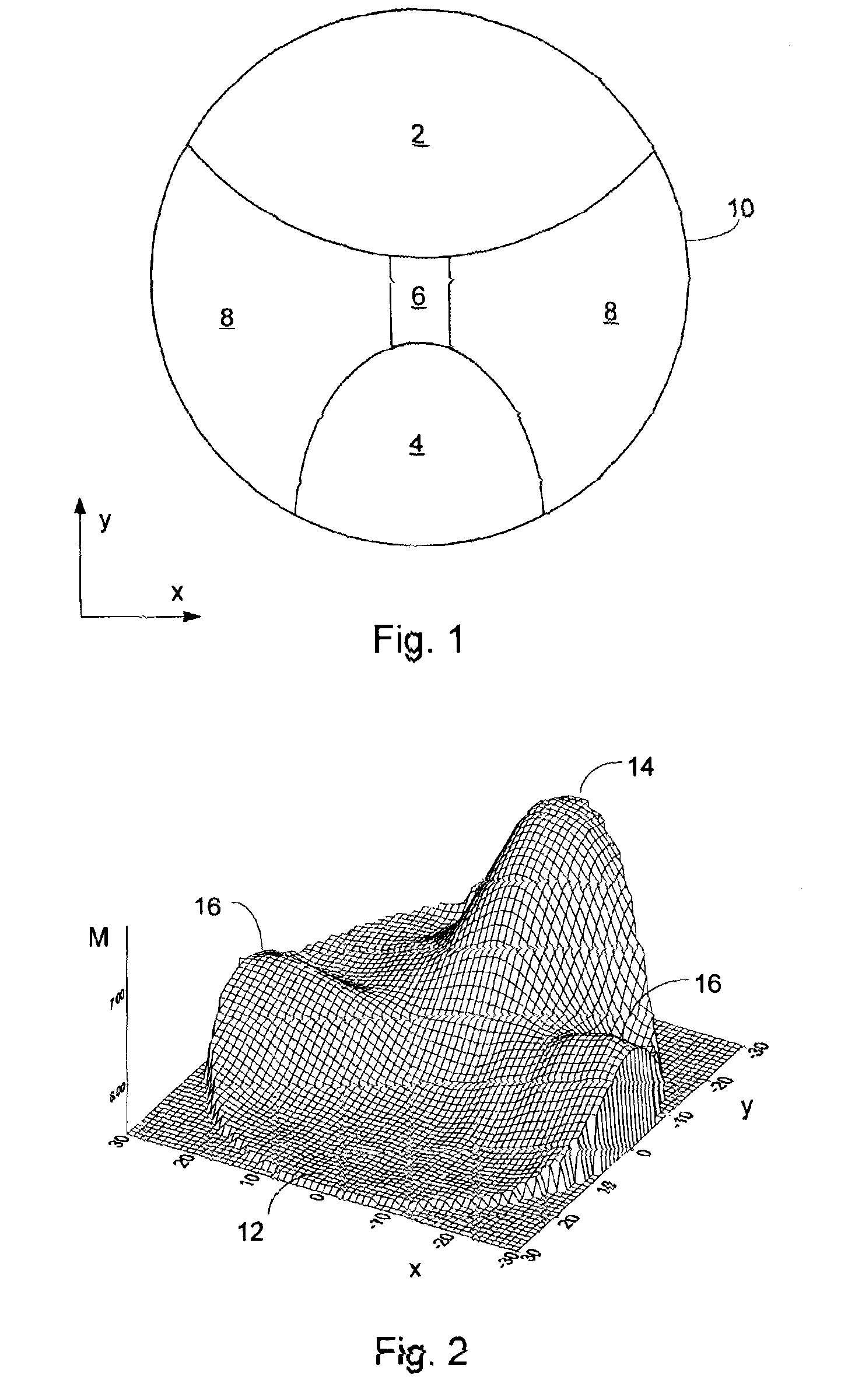
Progressive lens
InactiveUS6260967B1Good optical performanceReduce astigmatismSpectales/gogglesOptical partsMultifocal lensesLens plate
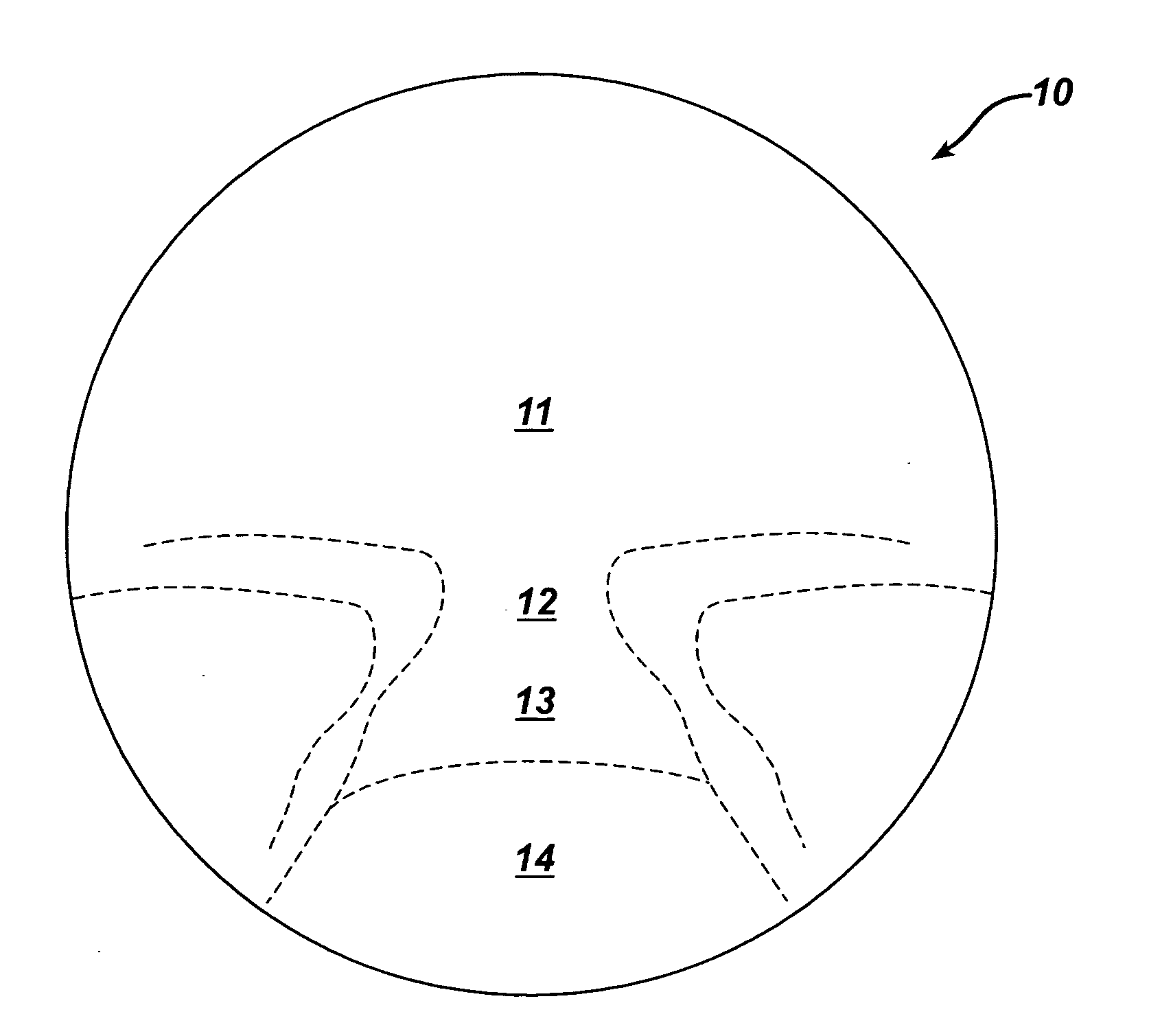
A progressive ophthalmic lens element having a front surface that includes an upper viewing zone having a surface power suitable for distance vision, a lower viewing zone having a surface power suitable for near vision, and a corridor of relatively low astigmatism connecting the upper and lower viewing zones, the corridor being a part of an intermediate viewing zone having a surface power varying from that of the upper viewing zone to that of the lower viewing zone. The progressive ophthalmic lens element also has a back surface. The invention is then characterized by the front surface including at least one correction to improve optical performance of the lens element by at least partially compensating for a cylinder correction applied to, or to be applied to, the backsurface.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION AUSTRALIA HO
Progressive addition power lens
A system and method for designing a progressive lens. Mean power is specified at points distributed over the entire surface of the lens and lens height is specified around the edge of the lens. Lens height is determined at the points consistent with the specified mean power and the lens edge height in part by solving a partial differential equation of the elliptic type subject to the lens edge height as a boundary condition. A successive over-relaxation technique may be employed to converge on the solution to the partial differential equation, and an over-relaxation factor may be determined to most efficiently relax the equation.
Owner:CROSSBOWS OPTICAL
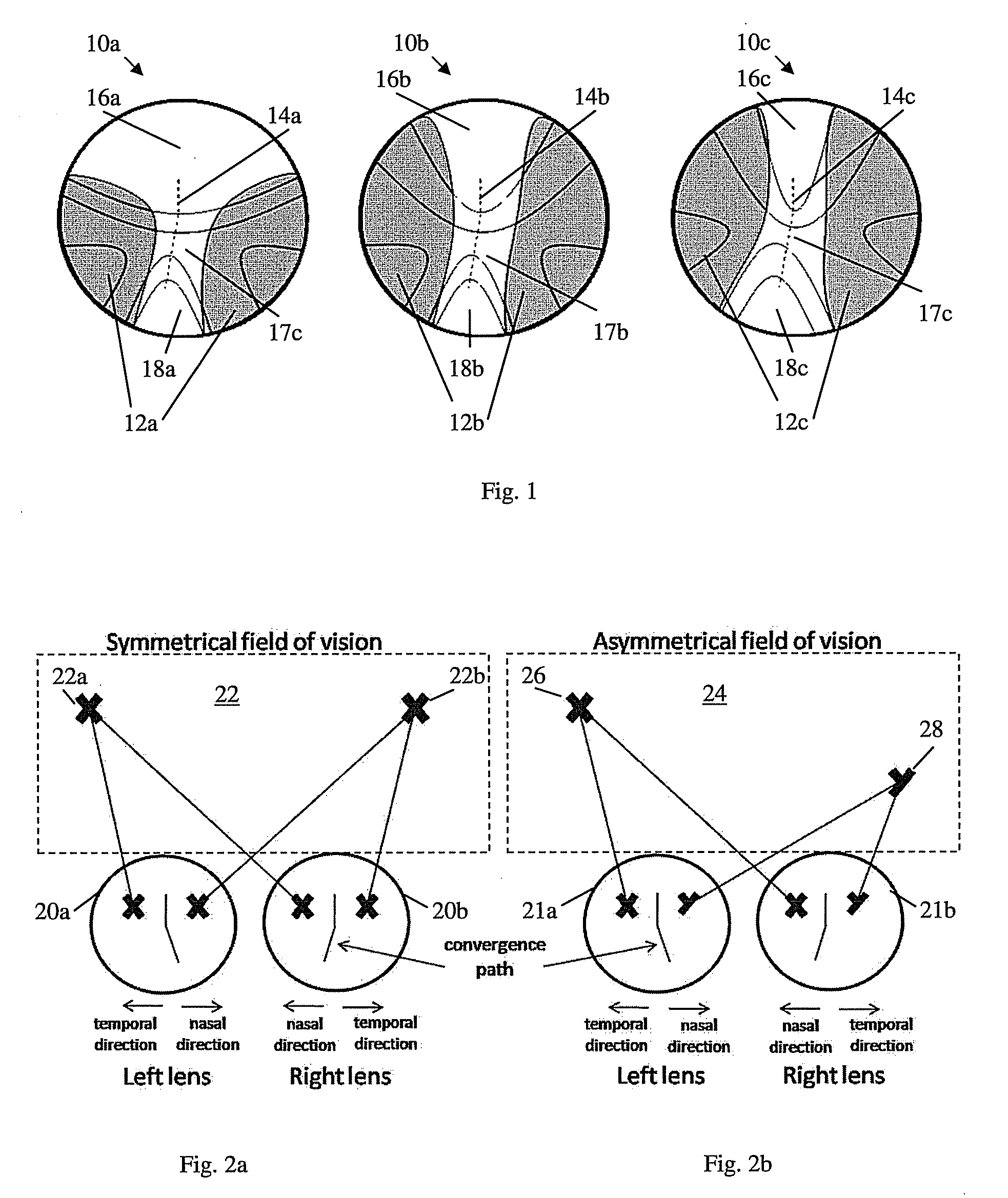
Assymetrical progressive lens
Owner:SHAMIR OPTICAL IND LTD
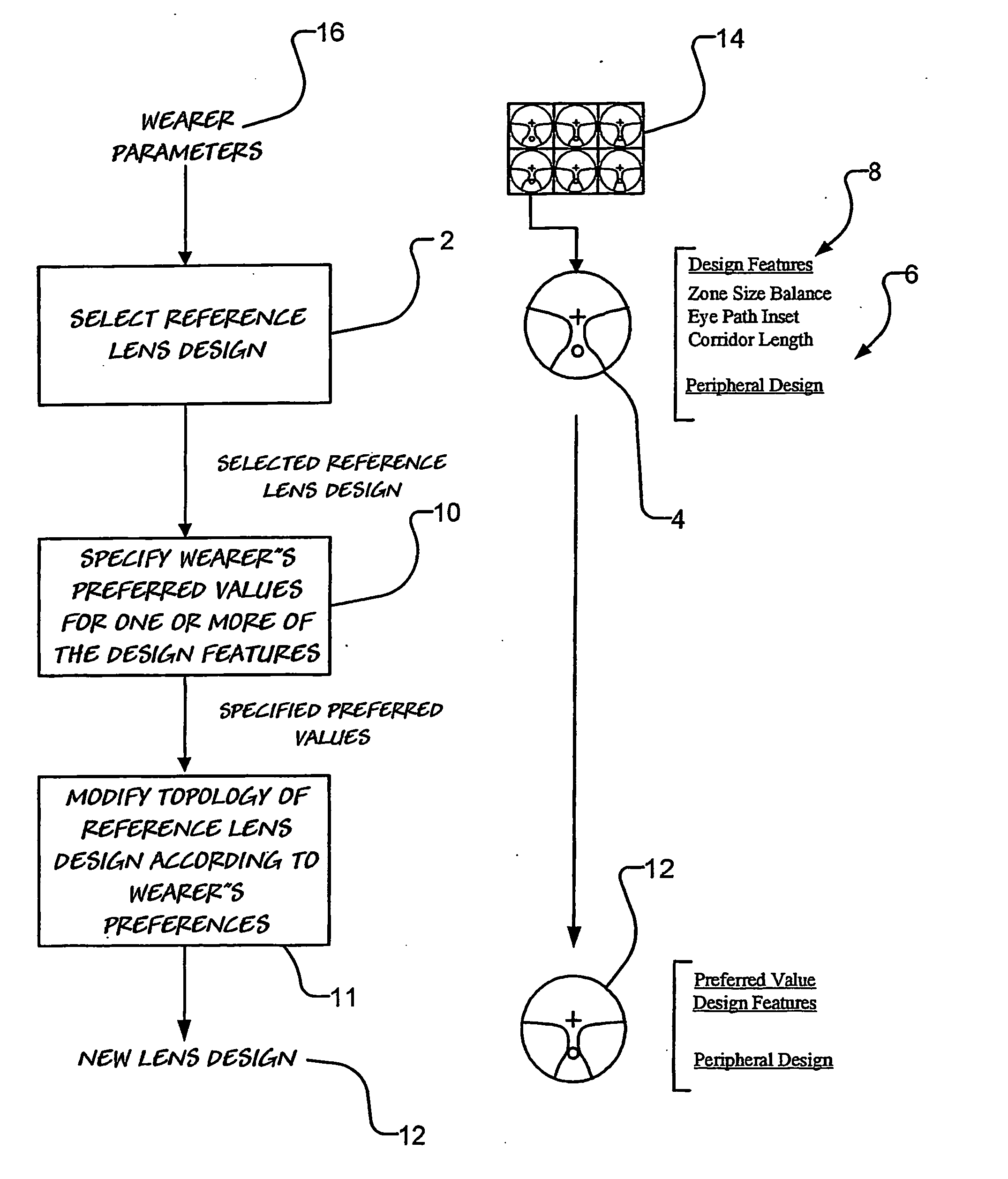
Method of designing progressive lenses
ActiveUS20050270482A1Stay connectedEasy assessment processEye diagnosticsSpecial data processing applicationsMultifocal lensesEngineering
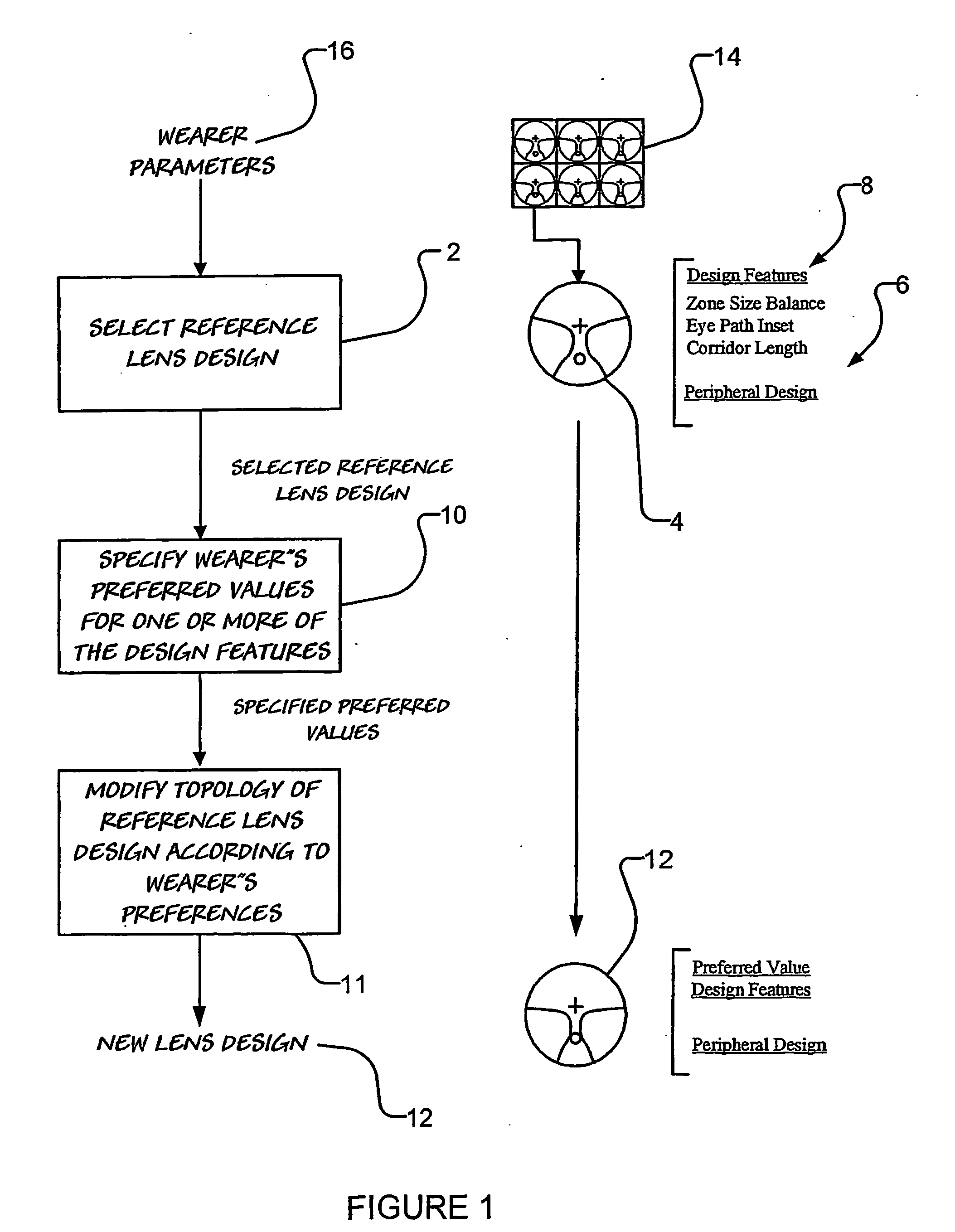
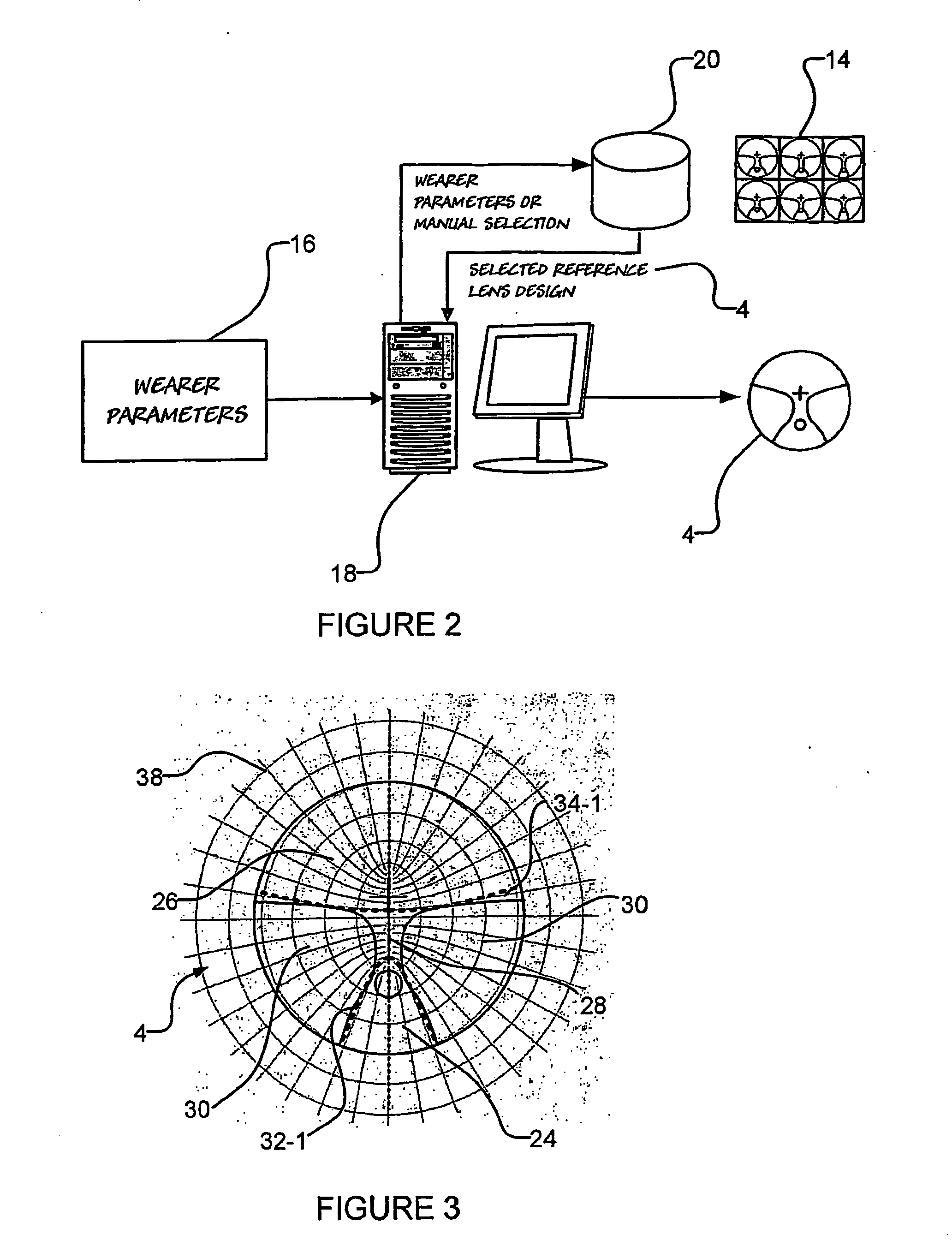
A method and system for designing a progressive lens is disclosed. The method includes modifying a reference progressive lens design having a peripheral design which is suitable for a wearer and design features with known values. The modification of the reference progressive lens design provides a new progressive lens design in which at least one of the design features have been customised according to the wearer's preference. The new progressive lens design has substantially the same peripheral design as the reference progressive lens design.
Owner:SOLA INT HLDG
Progressive addition lenses with adjusted image magnification
ActiveUS7275822B2Magnification provided by the lens can increaseHigh magnificationEye diagnosticsOptical partsOphthalmologyRetinal function
The invention provides a method for increasing the magnification of a lens without changing the dioptric power. The method of the invention uses a measurement or an estimate of an individual's retinal function in designing the lens to provide the magnification needed by the individual without increasing the dioptric power of the individual's lens.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
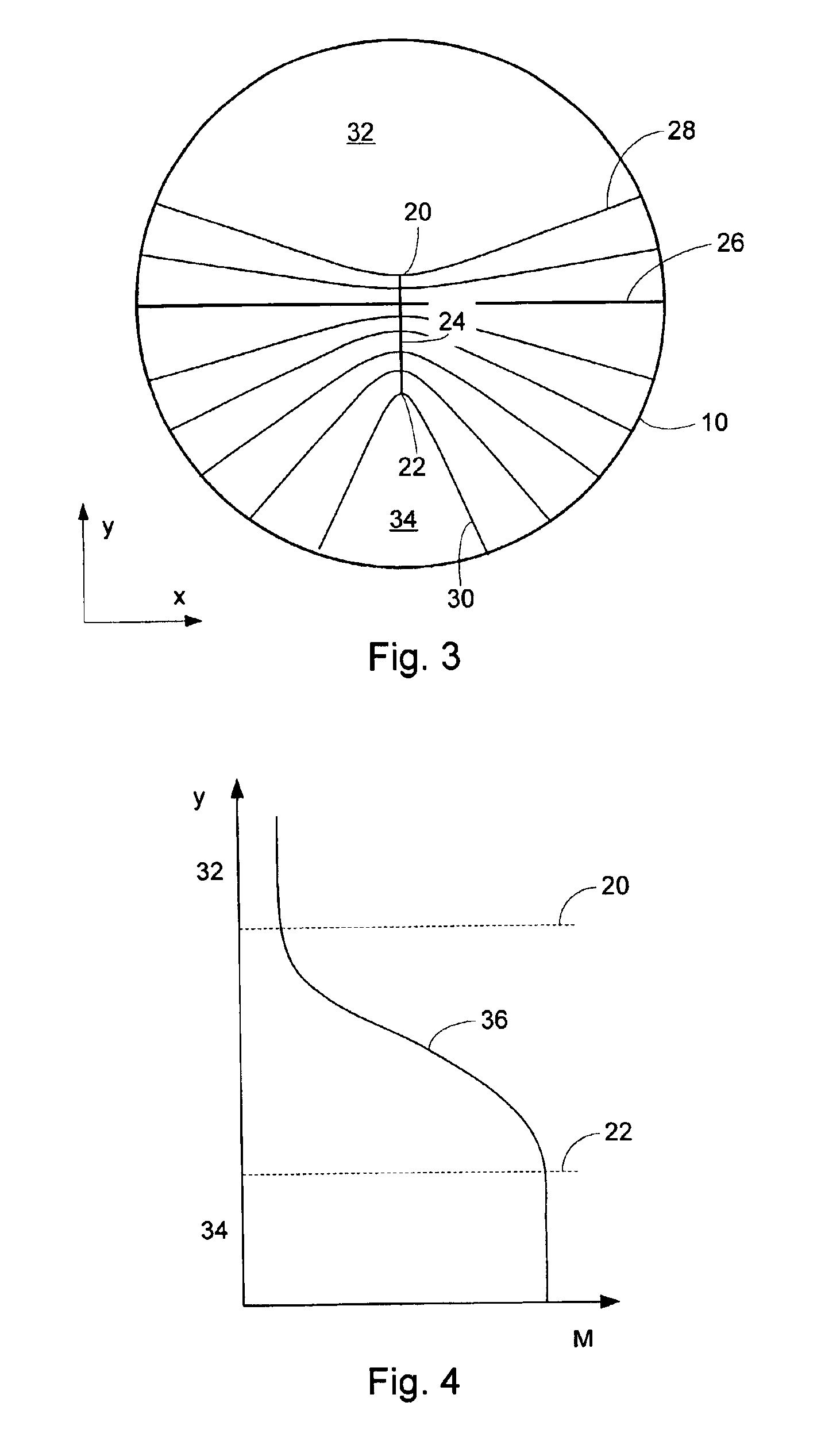
Step zone progressive lens
The present invention provides a progressive lens comprising at least one area with gradually increasing optical power, the area having a first region where the gradient of the optical power decreases towards a second region with reduced gradient of optical power, and a third region following the second region where the gradient of the optical power increases. The present invention further provides a method for producing progressive lens, the method comprising computing location on the lens on which a second region with reduced gradient of optical power should be produced and a required optical power in the second region; producing based on the computations an area on the lens with gradually increasing optical power, the area having a first region where the gradient of the optical power decreases towards the second region, and a third region following the second region where the gradient of the optical power increases.
Owner:SHAMIR OPTICAL IND LTD
Multi-focal ophthalmic lens with base in prism
Owner:LEGACY OPTICS
Method for Determining the Inset of a Progressive Addition Lens
ActiveUS20110184830A1Improve accuracyComputation using non-denominational number representationEye diagnosticsPrismProgressive addition lenses
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Short corridor progressive addition lenses with reduced unwanted astigmatism
The invention provides lenses produced by the adding of two or more surfaces, in which lenses both the length of the corridor is shortened and the maximum unwanted astigmatism is reduced.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Progressive addition power lens
A system and method for designing a progressive lens. Mean power is specified at points distributed over the entire surface of the lens and lens height is specified around the edge of the lens. Lens height is determined at the points consistent with the specified mean power and the lens edge height in part by solving a partial differential equation of the elliptic type subject to the lens edge height as a boundary condition. A successive over-relaxation technique may be employed to converge on the solution to the partial differential equation, and an over-relaxation factor may be determined to most efficiently relax the equation.
Owner:CROSSBOWS OPTICAL
Selecting and/or designing ophthalmic lenses
ActiveUS7980692B2Increase powerReduce aberrationSpectales/gogglesEye surgeryMedical prescriptionEye lens
The present invention involves the prescribing and / or dispensing ophthalmic lenses, such as progressive addition lenses, for a wearer. In one form of the invention lens usage information is obtained from a wearer and entered into a programmed computer. The programmed computer processes the lens usage information to provide a separate weighted lifestyle score for each of one or more respective lifestyle score categories, such that each weighted lifestyle score is a function of a predetermined relationship between the respective lifestyle score category and at least ophthalmic lens design feature. The programmed computer then selects or designs an ophthalmic lens design using one or more of the weighted lifestyle scores such that the selected or designed ophthalmic lens has at least one lens design feature which has been customised using one or more of the weighted lifestyle scores.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION AUSTRALIA HO
Method for designing spectacle lenses taking into account an individual's head and eye movement
A method for designing ophthalmic lenses, including progressive addition lenses, and lenses produced by the method are provided. The method permits the direct correlation of an individual's subjective assessment of the len's performance and the objective measure of lens performance relative to the individual. The method permits generation of lens designs based on the head and eye movement of the individual and the designing of customized lenses.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
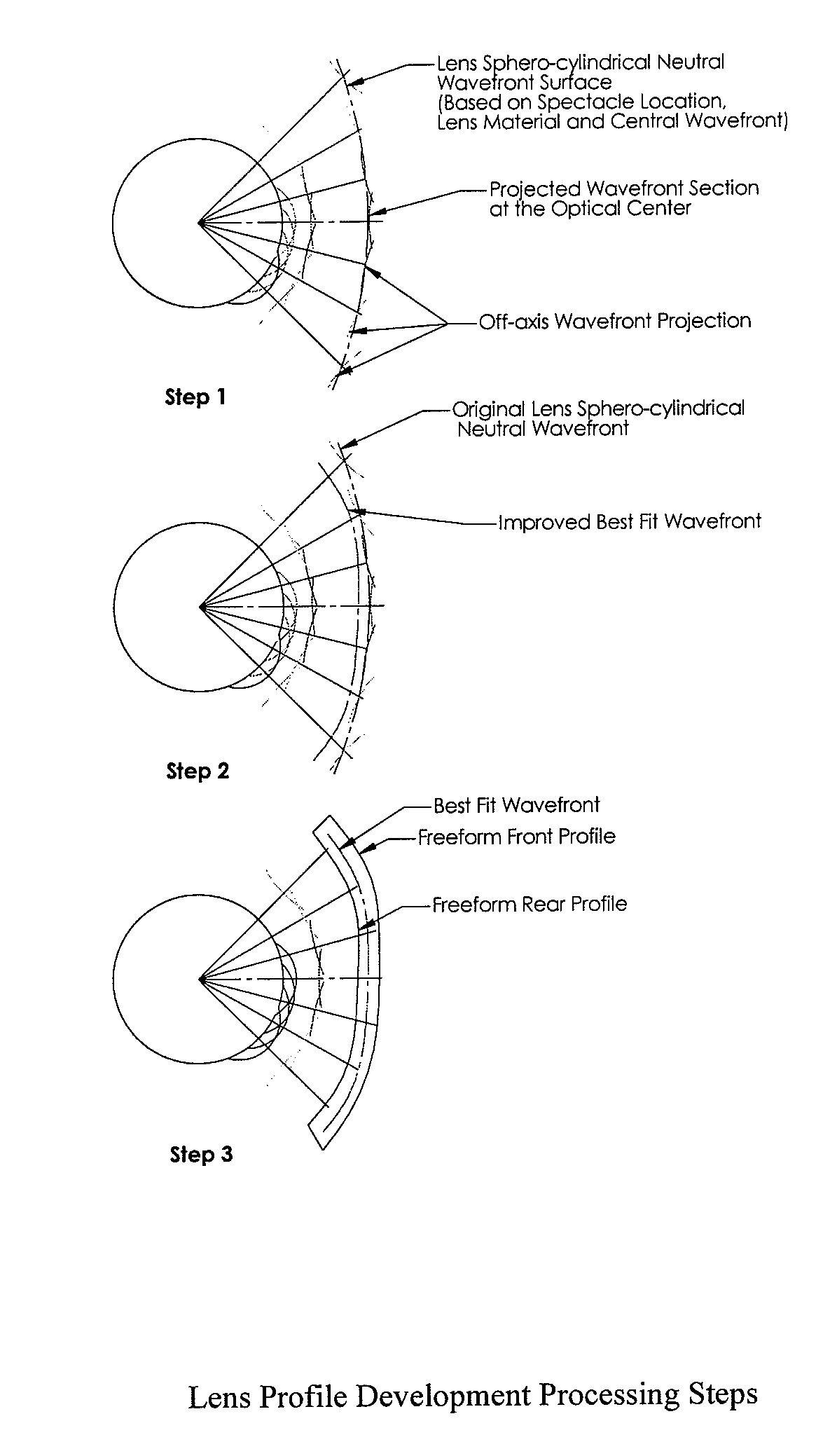
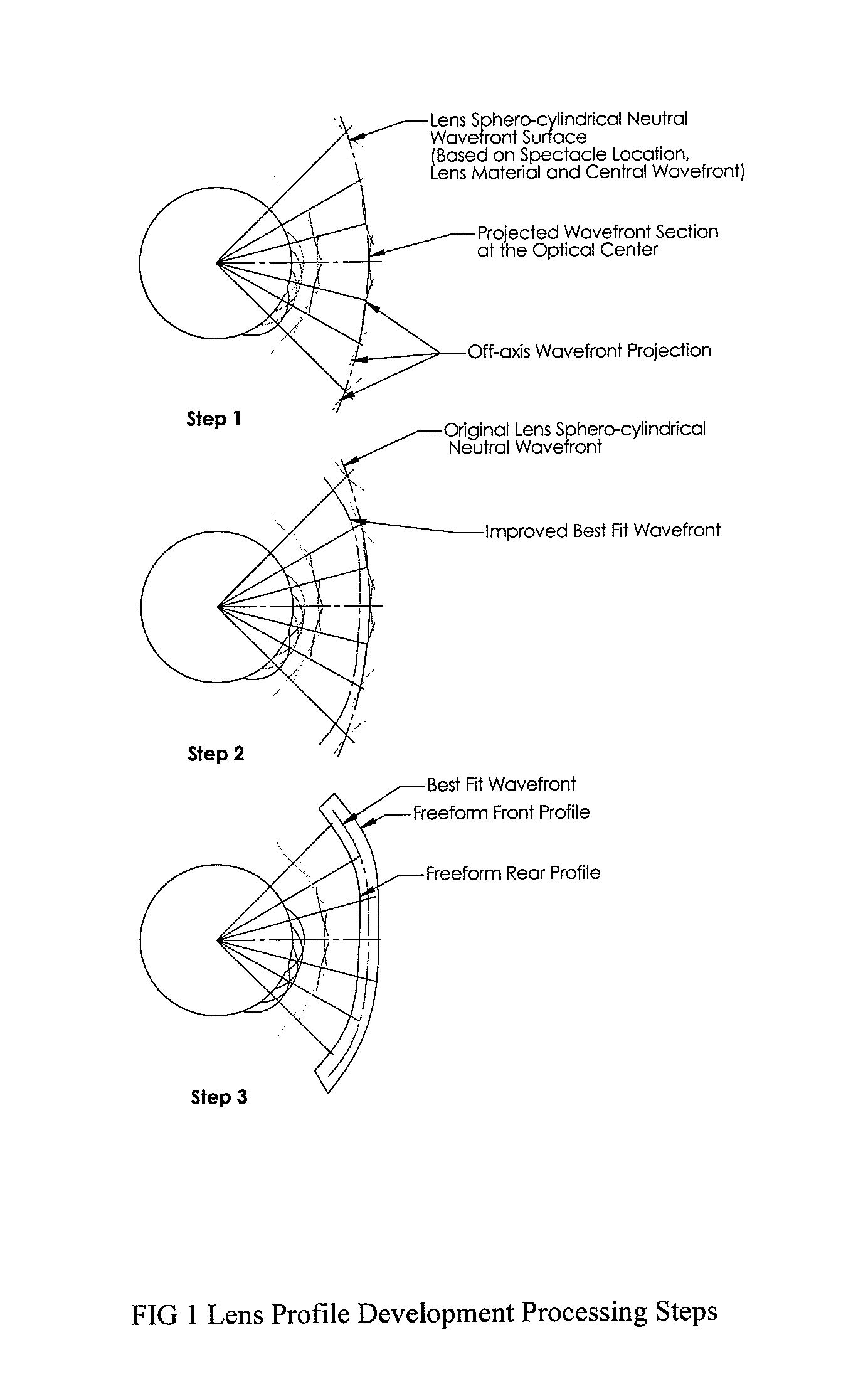
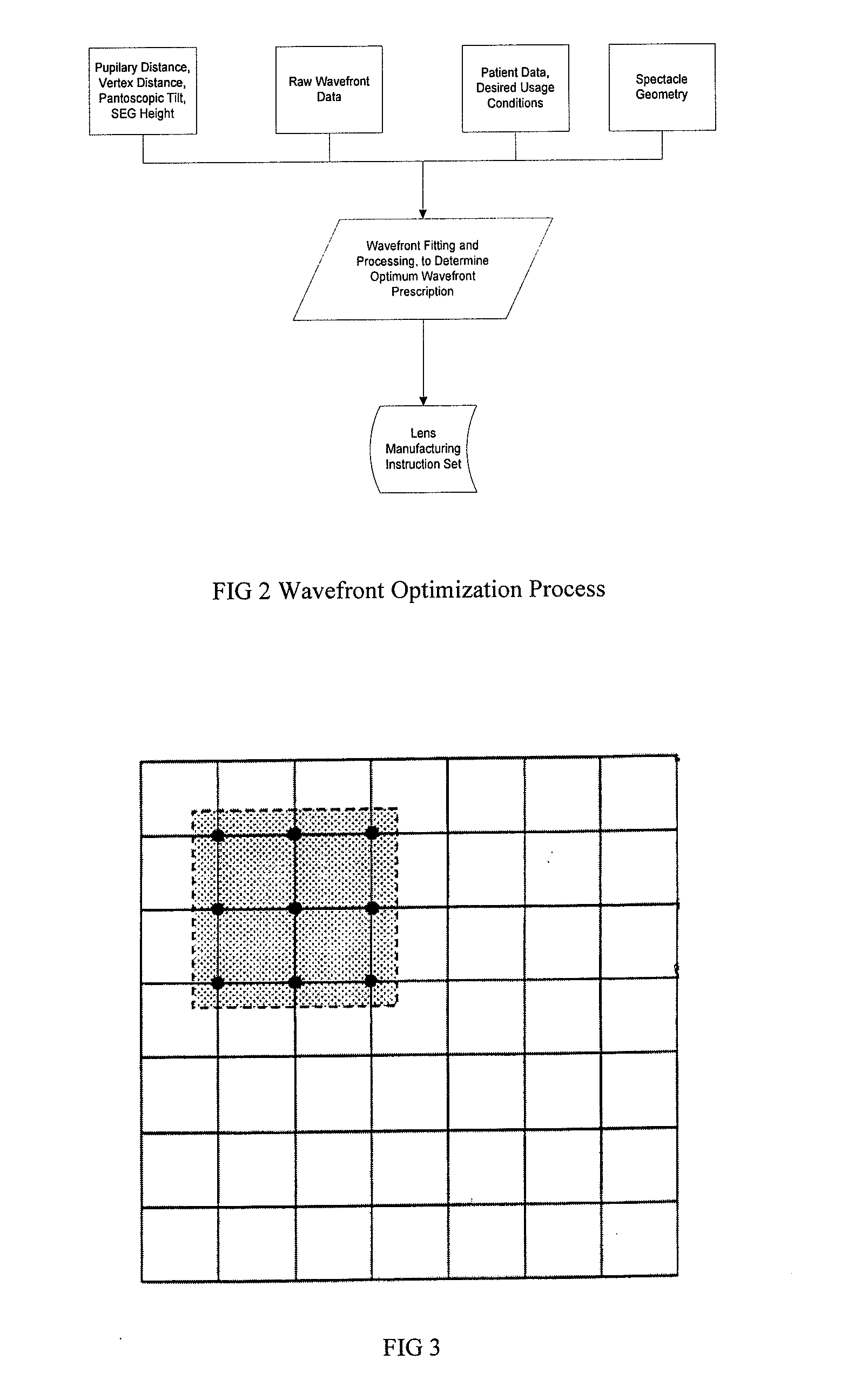
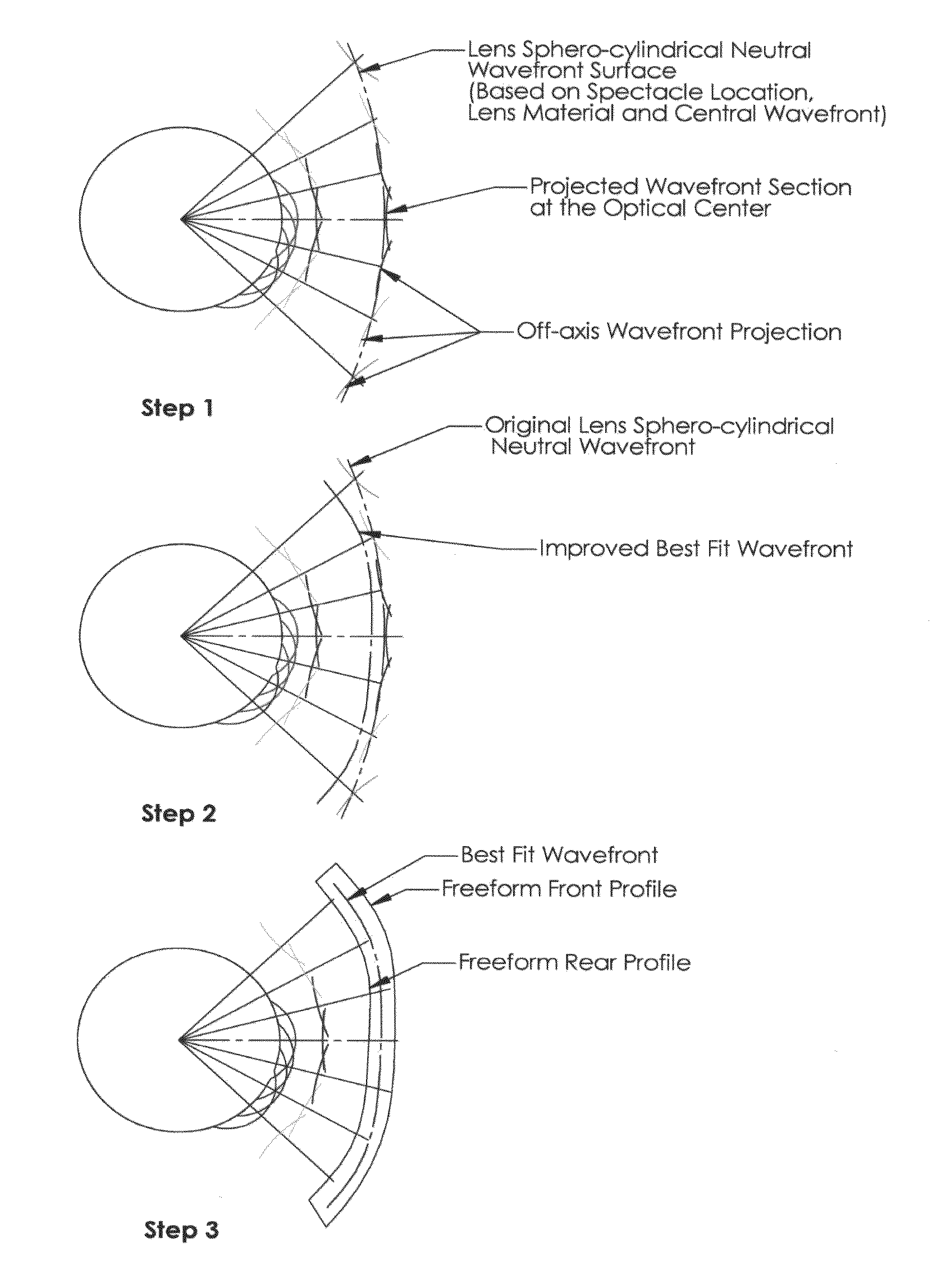
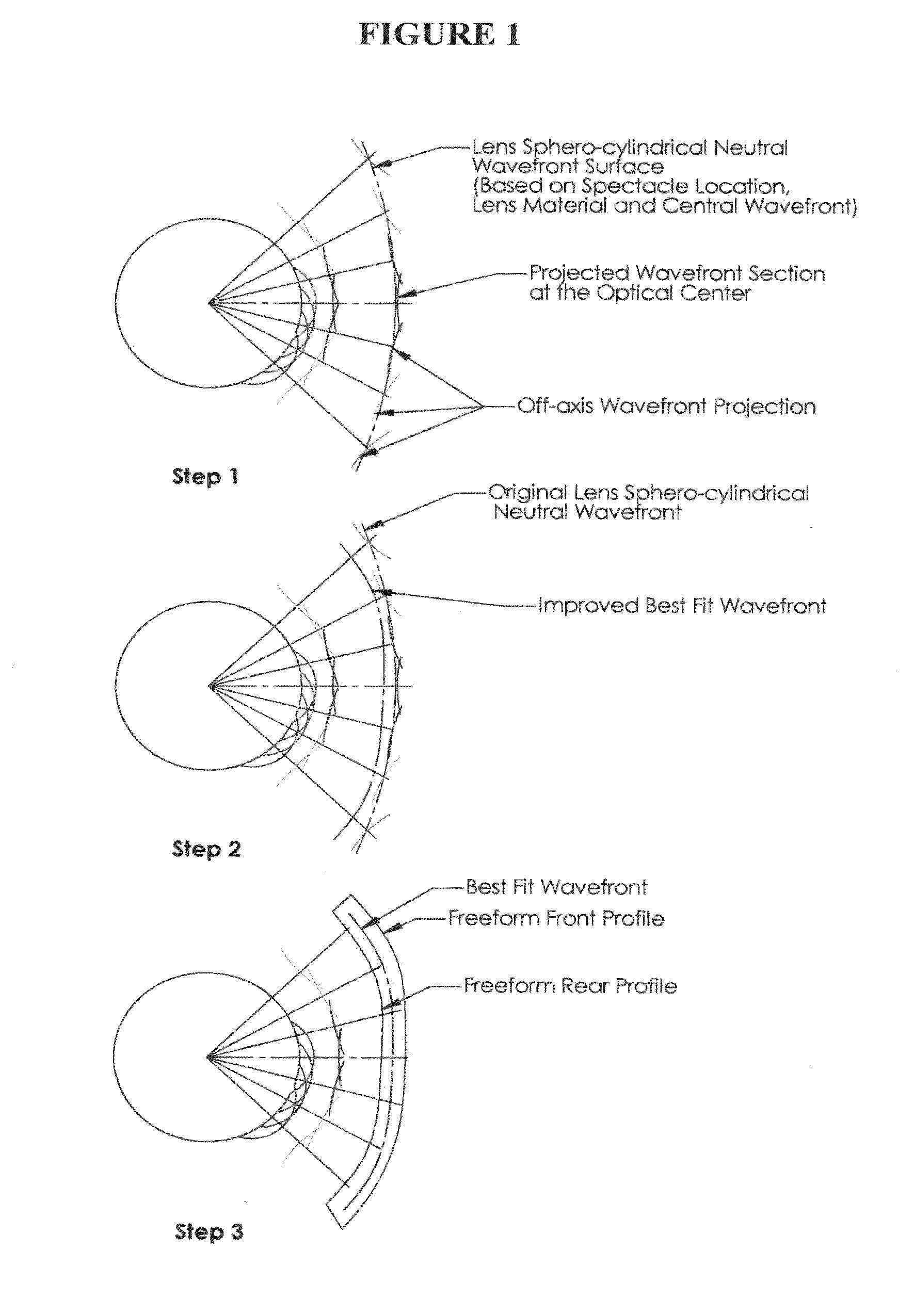
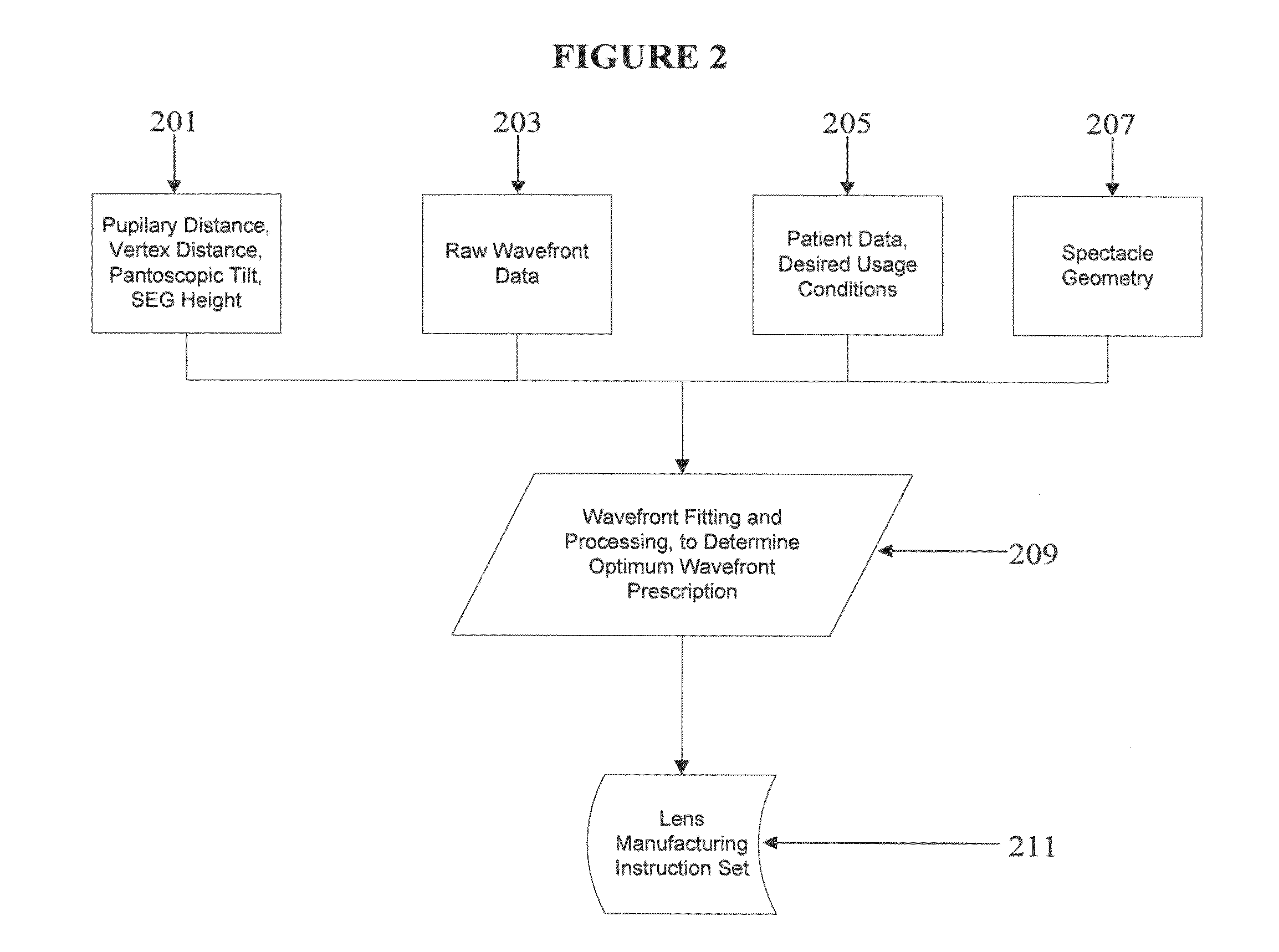
Method of designing progressive addition lenses
Embodiments of the invention pertain to a method for producing a spectacle lens with optimal correction across the entire lens taking into account the patient's complete measured wavefront. Specific embodiments can also take into account one or more additional factors such as vertex distance, segmental fitting height, pantoscopic tilt, and use conditions. The lens wavefront can be achieved by optimizing a corrected wavefront, where the corrected wavefront is the combined effect of the patient's measured wavefront and the lens wavefront. The optimization of the corrected wavefront can involve representing the measured wavefront and the lens wavefront on a grid. In an embodiment, the grid can lie in a plane. During the optimization, a subset of the grid can be used for the representation of the measured wavefront at a point on the grid so as to take into account the portions of the measured wavefront that contribute to the corrected wavefront at that point on the grid.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Adhesive optical film to convert an eyeglass lens to a progressive lens
ActiveUS9995948B2Reasonable low cost solutionLow costSpectales/gogglesAuxillary optical partsUses eyeglassesMultifocal lenses
Apparatus and methods are described, including a corrective optical film for converting a corrective single-focal lens to a multi-focal lens and / or a progressive lens. A thickness and / or a curvature of the corrective optical film is different in different regions of the corrective optical film, such that the corrective optical film is configured, upon being adhered to the single-focal lens, to change a focal length of the single-focal lens differently in different regions of the single-focal lens. Other applications are also described.
Owner:ADDON OPTICS LTD
Wavefront optimized progressive lens
A method for designing a progressive lens, the method includes obtaining a wavefront measurement of an eye, the wavefront measurement including information about second order aberrations of the eye and about higher order aberrations of the eye; determining an initial design for the progressive lens based on the wavefront measurement, the initial design including, for one or more points on the lens, information about second order aberrations of the progressive lens and higher order aberrations of the progressive lens, the initial design providing a target correction for the eye in the absence of the higher order aberrations of the eye; determining information about how changes in one or more higher order aberrations of the eye affect a second order correction for the aberrations of the eye based on information derived from the wavefront measurement; modifying the initial design of the progressive lens to provide a final progressive lens design, wherein the modification accounts for an expected variation of the correction from the target correction due to one or more higher order aberrations of the initial progressive lens design and the information about how changes in one or more higher order aberrations of the eye affect the second order correction for the aberrations of the eye; and outputting the final lens design.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION INC +1
Progressive ophthalmic lens
ActiveUS8186829B2Improve comfortEasy to viewOptical partsMultifocal lensesProgressive addition lenses
The invention provides a progressive ophthalmic lens suitable to be worn by a person engaged in a sporting activity. For this purpose the lens has a far vision region which is enlarged, and a peripheral field of vision which is separated and whose mean sphere gradients are gentle. When a progressive lens of this kind is allocated to a wearer, the lens can have an addition value that is approximately equal to a prescribed value, or an addition value that is less than the prescribed value.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
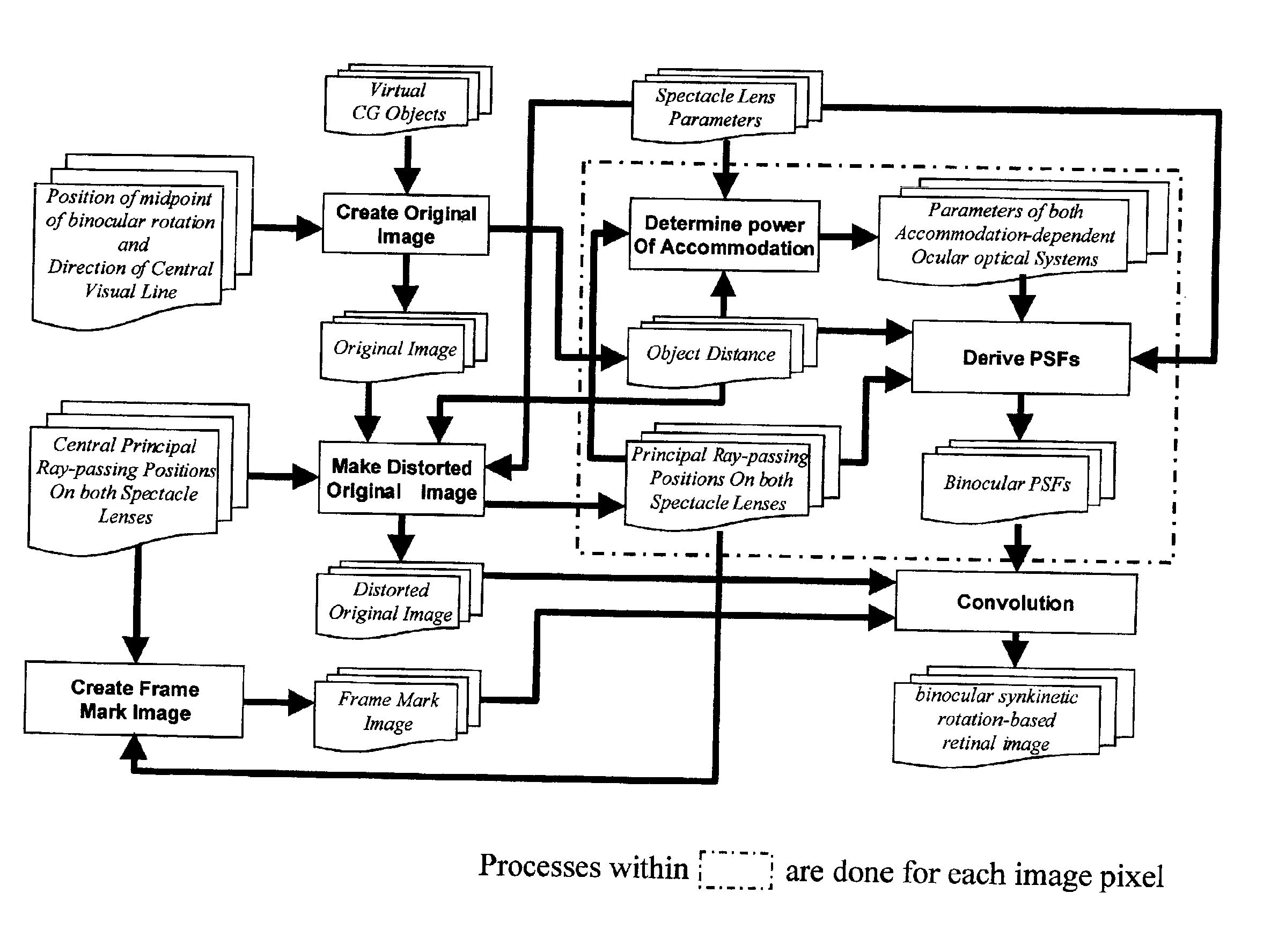
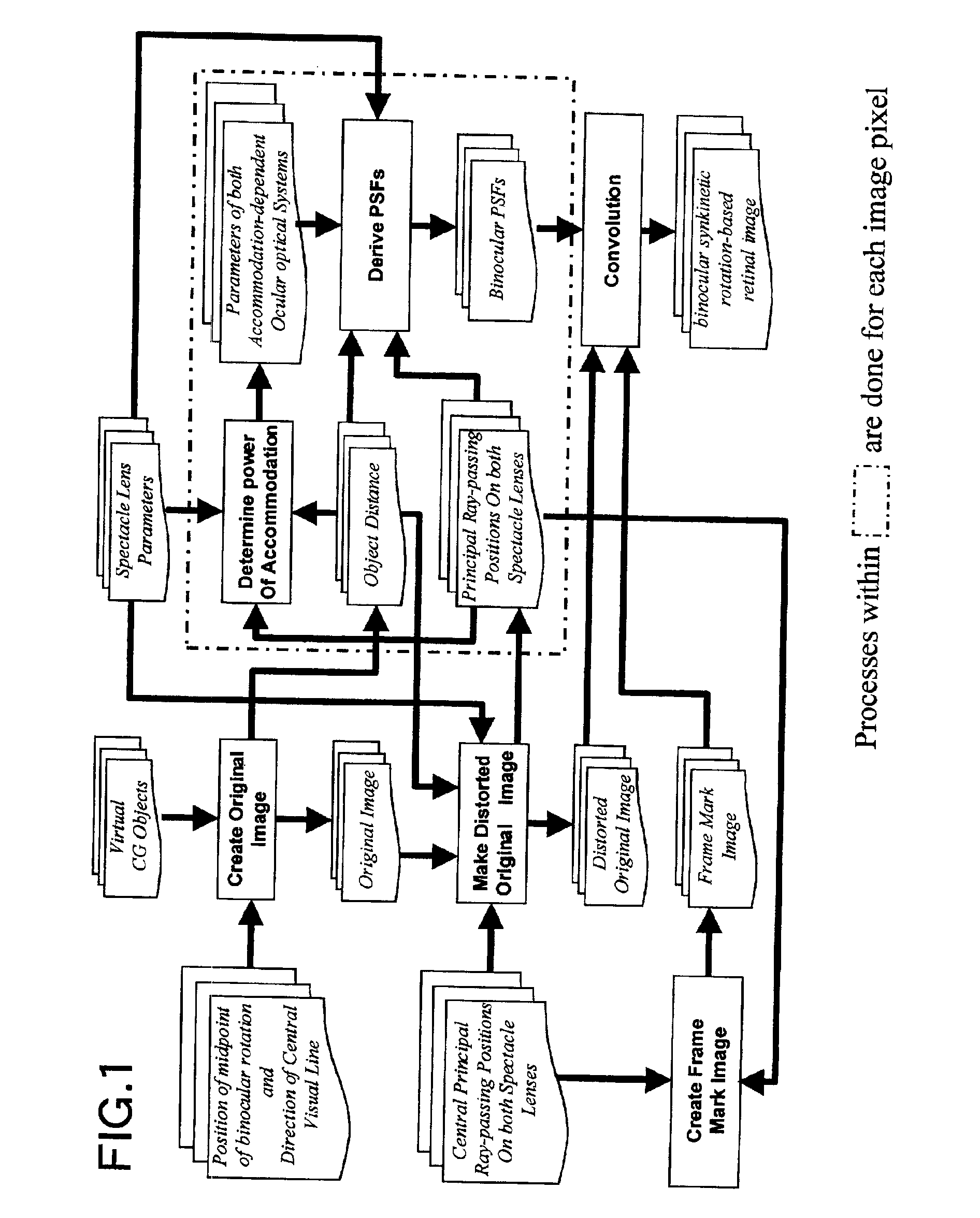
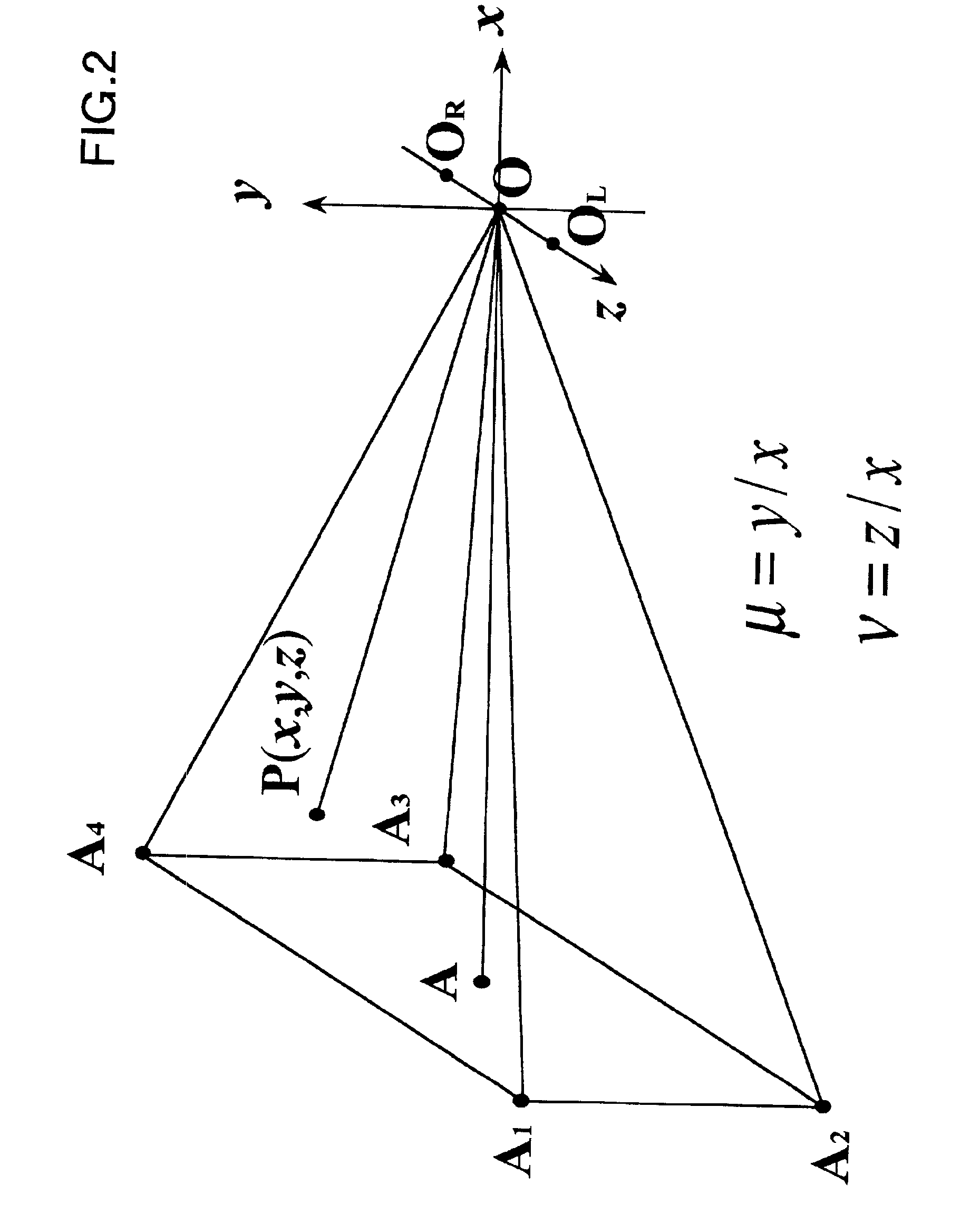
Method for simulating an ocular optical system and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS7039563B2Computation using non-contact making devicesComputation using non-denominational number representationEyepieceObject point
A method and apparatus for simulating an ocular optical system that enables simulating visual perception having fluctuation, distortion and blur in the use of spectacle lenses such as progressive addition lenses. A binocular synkinetic rotation-based retinal image is created, defined as an image obtained by rotating both eyeballs toward each object point in a visual field, then, uniting images projected on the foveae of right and left eyes and to produce a united image. An original image is created wherein the midpoint of binocular rotation is placed at a specific position, and objects within a specific pyramidal visual field are observed. A distorted original image is obtained by observing the visual field through spectacle lenses using the ray tracing method. Point Spread Functions (PSF's) are derived, wherein right and left monocular PSF's are obtained and a united binocular PSF is derived from both monocular PSF's. Visual perception through spectacle lenses is simulated by convoluting of the distorted original image and the united binocular PSFs with respect to each pixel of the original image.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Methods of designing progressive addition lenses
Embodiments of the invention pertain to a method for producing a spectacle lens with optimal correction across the entire lens that take the patient's complete measured wavefront into account. Specific embodiments also consider one or more additional factors such as vertex distance, intermediate power, add power, segmental fitting height, pantoscopic tilt, and use conditions. The lens wavefront can be achieved by optimizing a corrected wavefront, where the corrected wavefront is the effect of the patient's measured wavefront and / or the lens wavefront. The optimization of the corrected wavefront can involve representing the measured wavefront and / or the lens wavefront on a grid. In an exemplary embodiment, the grid can lie in a plane. During the optimization, a subset of the grid can be used for the representation of the measured wavefront at a point on the grid so that the portions of the measured wavefront that contribute to the corrected wavefront at that point on the grid are taken into account. The progressive addition lens can be utilized for distance, intermediate and reading use wherein the power progression is non-linear in any number or all of the near, intermediate, and far zones.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Progressive addition lens design
Aspects of the present invention provide progressive addition lenses (PALs) and techniques for designing PALs that result in improved visual performance for the wearer. PALs of the present invention can have vision zones with widths that are more in line with the actual or functional sizes used by wearers. PALs of the present invention can also introduce controlled amounts of unwanted astigmatism into one or more vision zones. By allowing vision zones to include manageable levels of astigmatism, the resulting PAL can avoid the harsh build-up of astigmatism typically found in conventional PALs at the periphery of the channel and viewing zones. Further, PALs of the present invention can be designed using a merit function to achieve an optimized iterative design that accounts for astigmatism vector orientation and not simply astigmatism magnitude as is the case with conventional PAL design.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
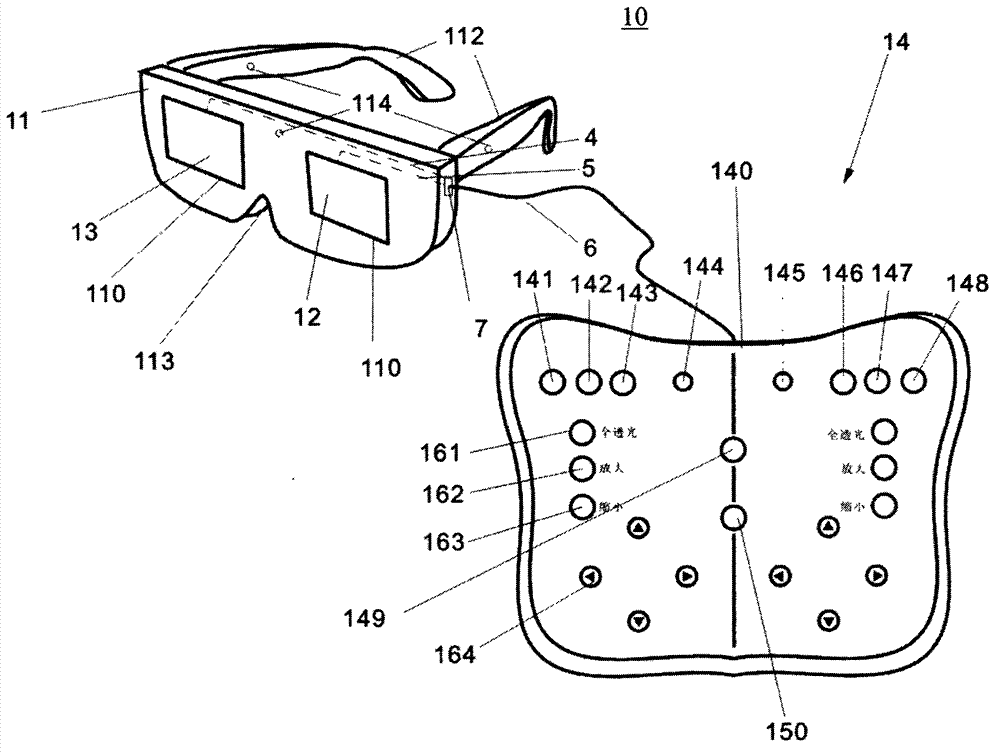
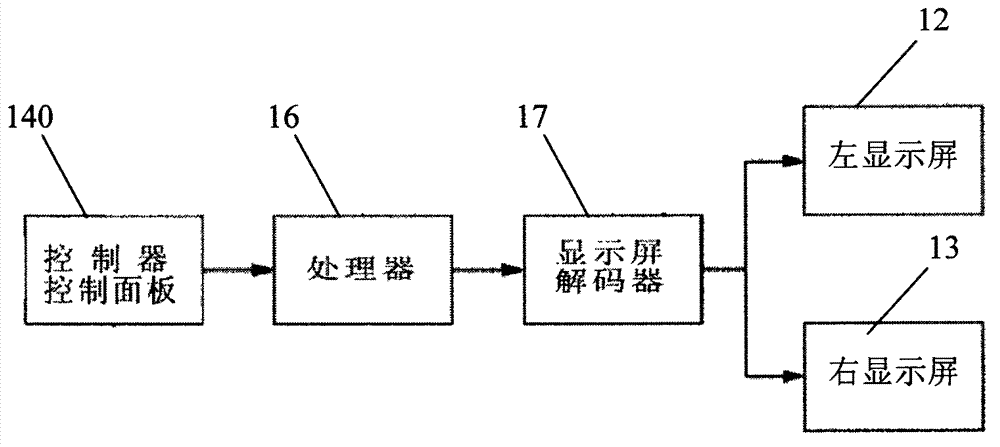
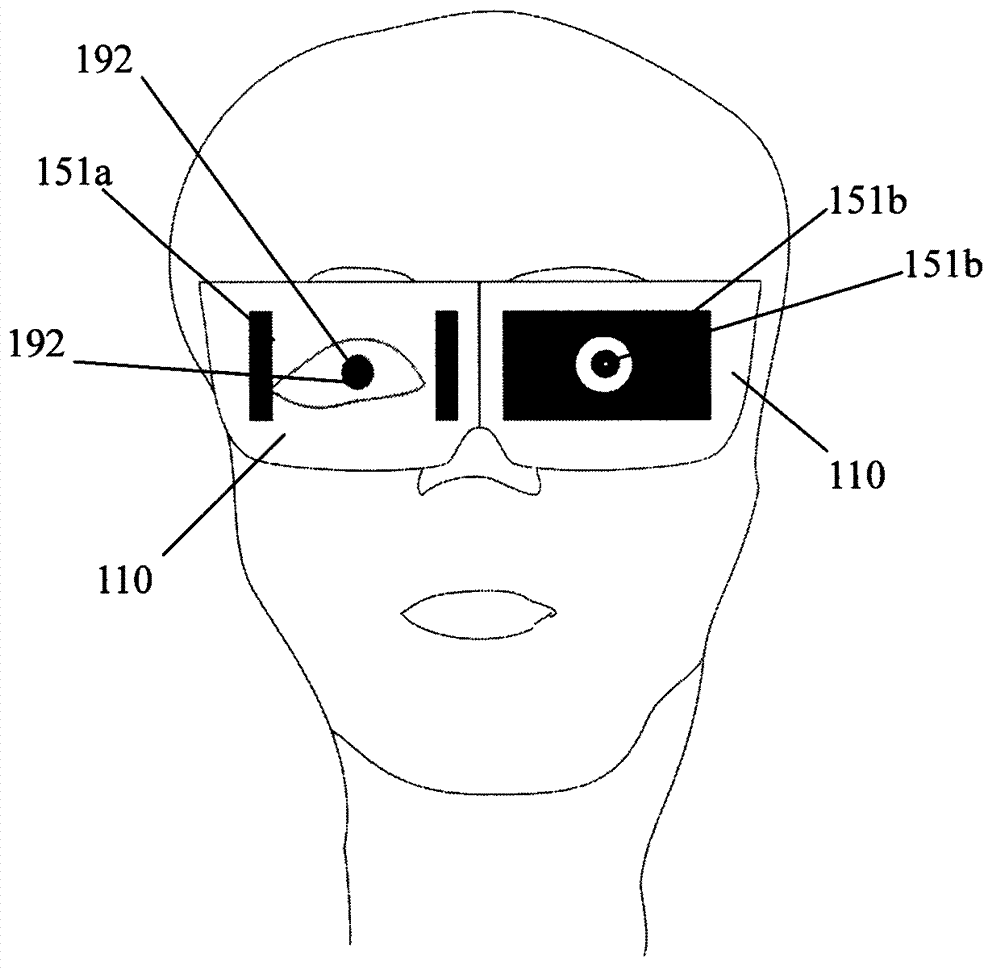
Centrometer
ActiveCN102961119AAccurate measurementGuaranteed accuracyEye diagnosticsPupillary distanceDisplay device
The invention relates to a centrometer, which comprises a bracket for wearing, a control unit and a display device, wherein the display device is arranged on the bracket; and the control unit is electrically connected with the display device, and is used for controlling the display device to display the shape and position of a pattern for visual detection and to measure visual data. According to the centrometer, a visual detection image is displayed by using a display screen, and the shape and position of the visual detection image are controlled by using the control unit, so that an interpupillary distance can be measured accurately, and the centrometer is very safe for human eyes. Moreover, the centrometer can also be used for rapidly and accurately measuring the interpupillary distance when double eyes watch along a plurality of directions, the interpupillary distance and the like when a single eye watches along a plurality of directions, and the relative position relation of the left eye or right eye vision center of binocular vision or mono-vision. The centrometer can be further used for measuring the interpupillary distance and the position relation thereof conveniently during fitting of double-light or multi-light progressive addition lenses; and moreover, the centrometer is used for measuring the stress situation of ciliary muscle on the aspects of ophthalmology medicine and research and assisting in correcting strabismus.
Owner:SHENZHEN HENGXING SHIGUANG TECH
Device and process for progressive addition lens design
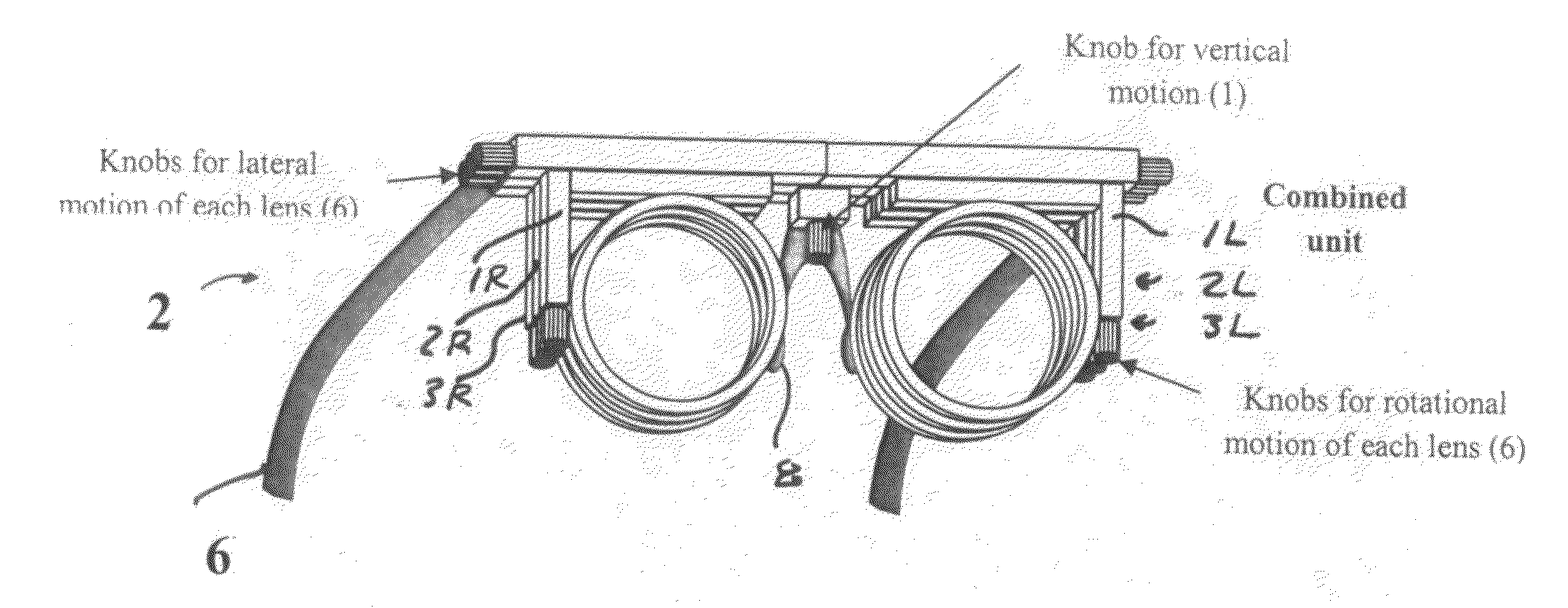
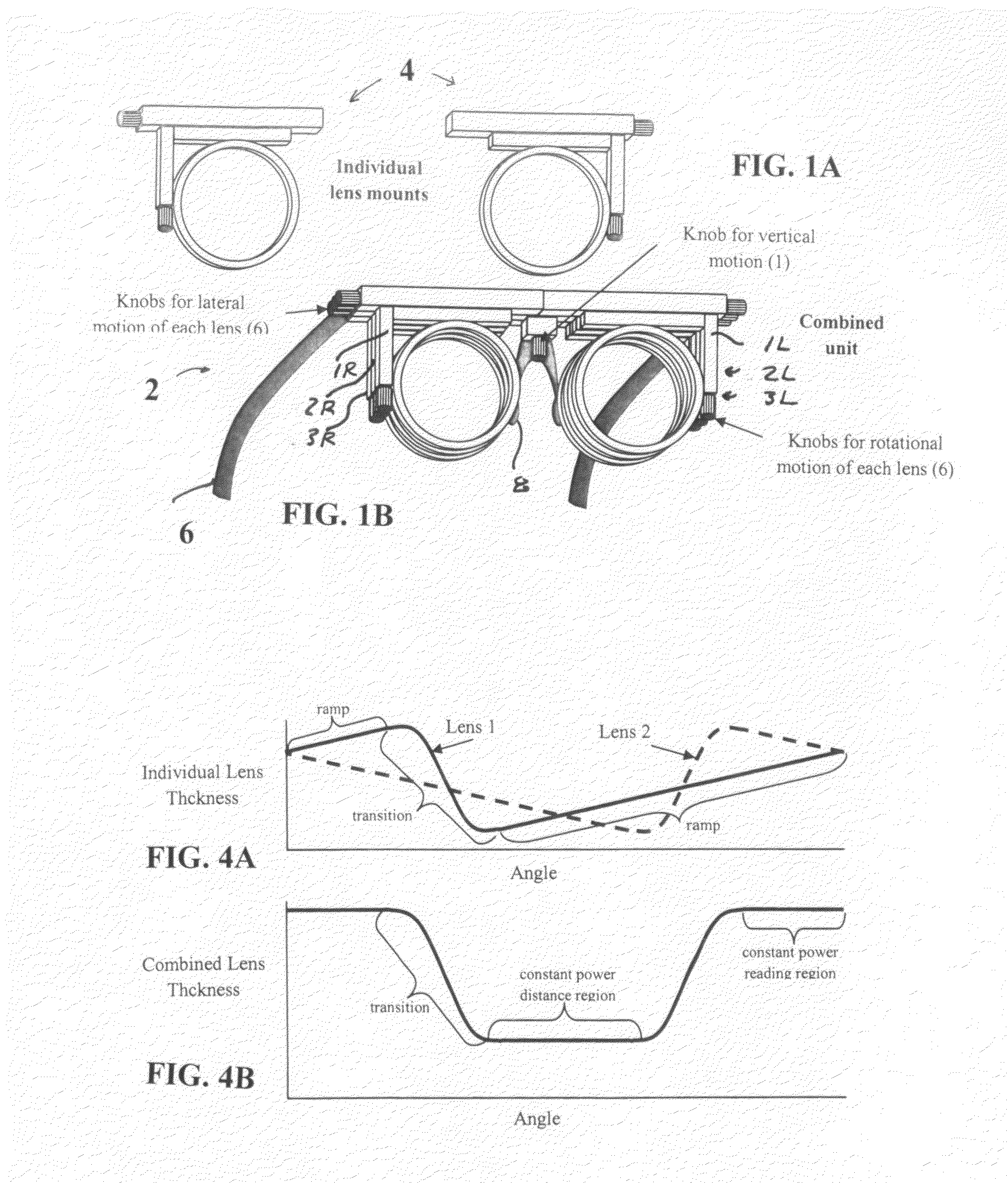
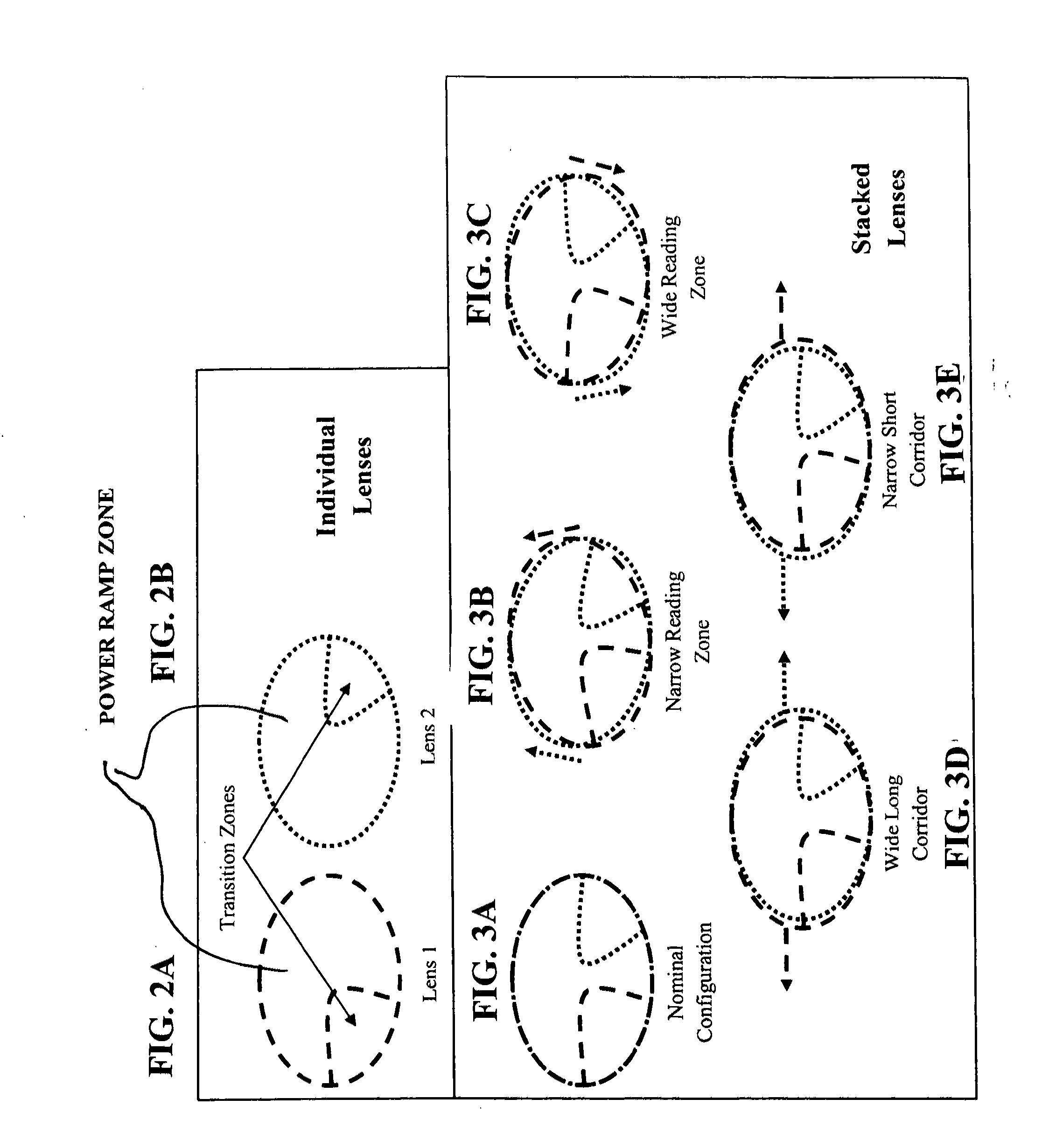
A progressive addition lens design device for designing progressive addition lenses to permit a patient to experience a variety of distance vision fields and reading vision fields. The device includes a frame adapted to hold in place in front of each of a patient's eyes three lens mounts, each lens mounts being adapted for adjustment in rotation and side-to-side translation. A third lens displaying the patient's base prescription mounted in one of the lens. A first and second lens is mounted in the other two lens mounts. The first and second lenses, each have a transition zone and a power ramp zone and they have complementary surfaces so that when stacked together they create a standard progressive addition lens with a distance vision field, a reading vision field and transition region. When the first and second lenses are moved relative to each other the locations of the distance vision field, the reading vision field and the transition region are adjusted allowing the patient to experience a variety of distance vision fields, reading vision fields, and transition regions
Owner:SPIVEY BRETT +1
Progressive addition lenses with an additional zone
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com