Patents
Literature
706 results about "Dc bias voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bias voltage is a low DC voltage, typically somewhere between 1.5 and 9.5V DC, used to power electronic circuitry located inside a condenser (or capacitor) type microphone’s capsule. It is usually a fixed amount of voltage, and it is important to provide the precise amount of voltage for a given capsule design.
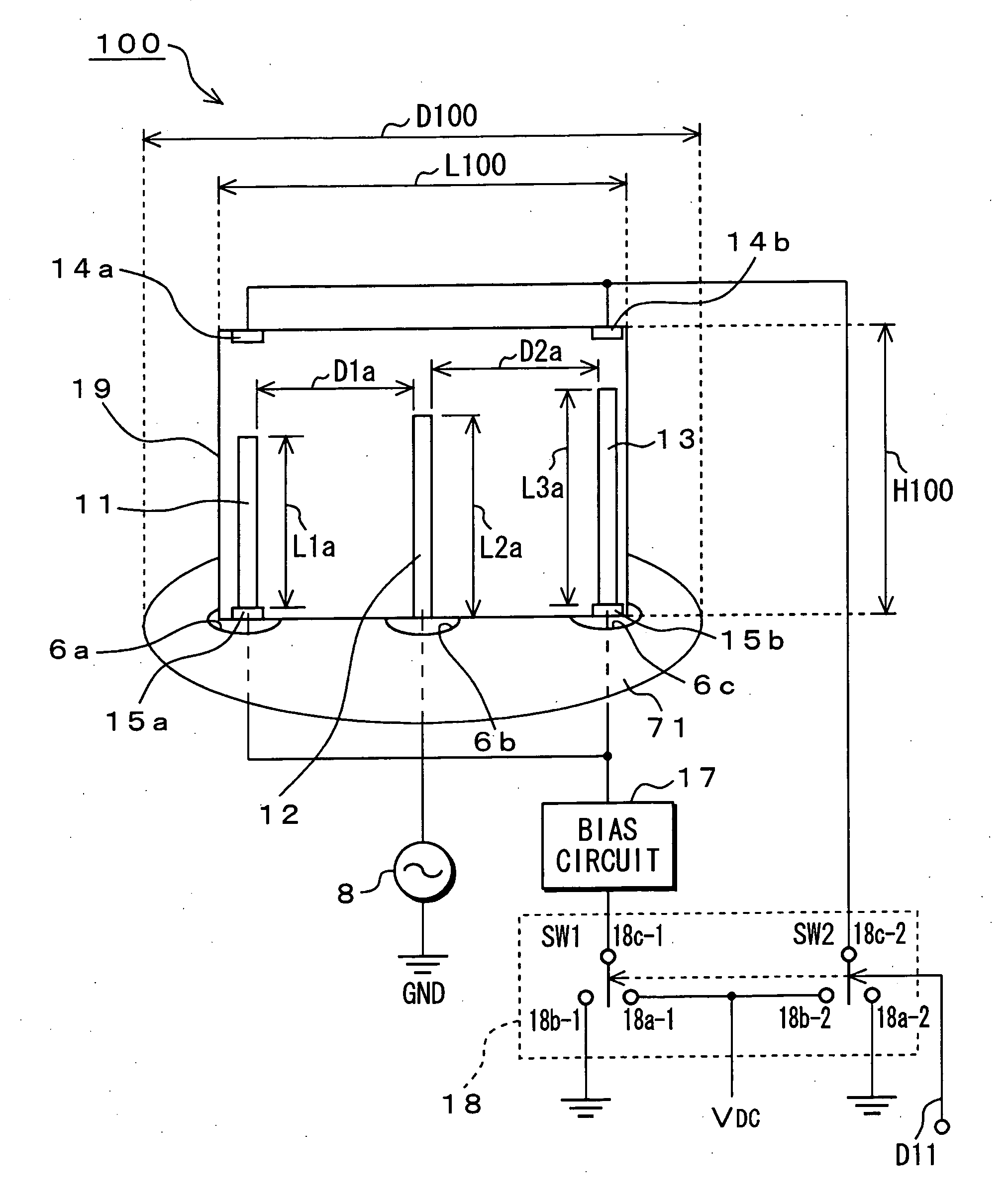
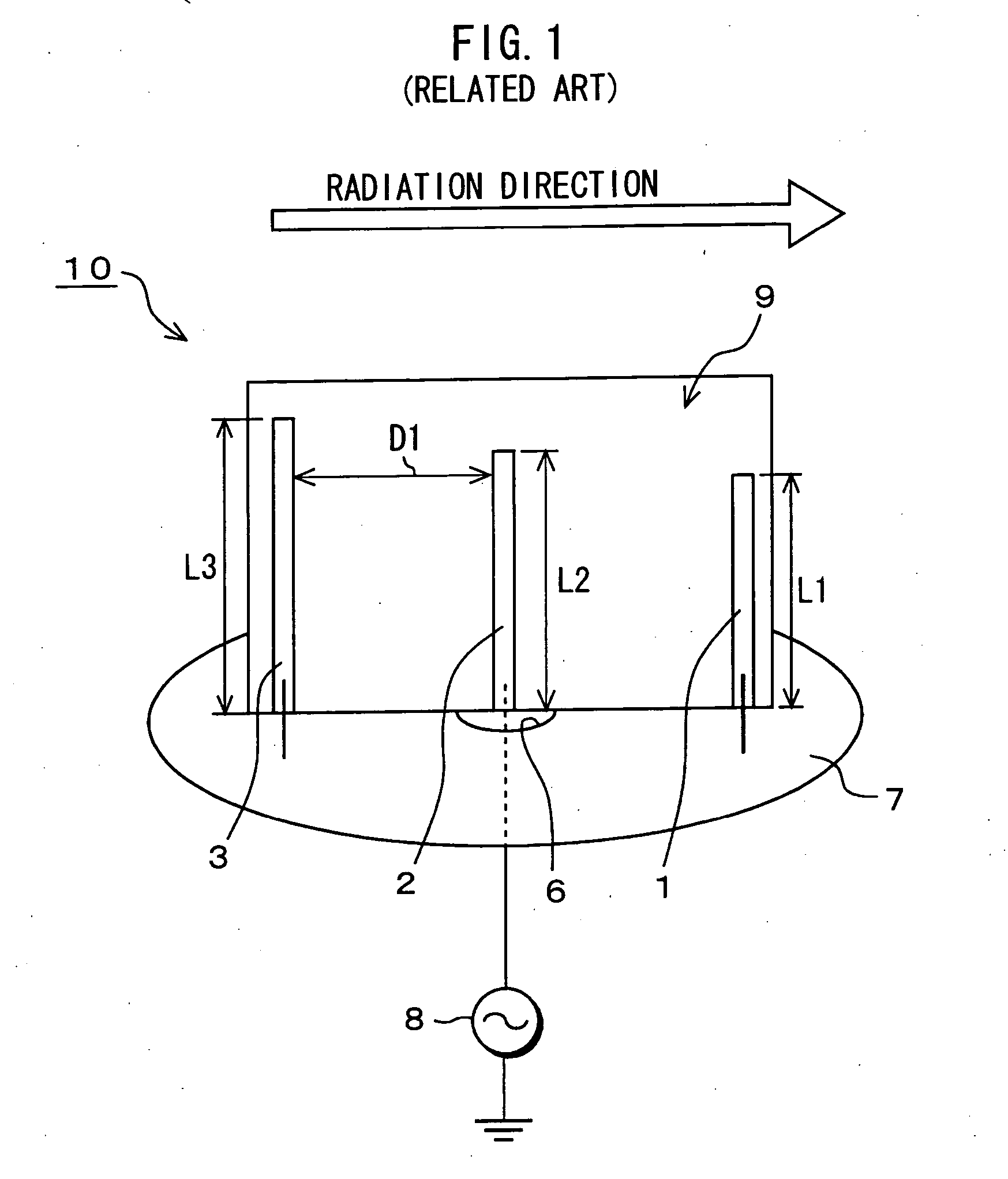
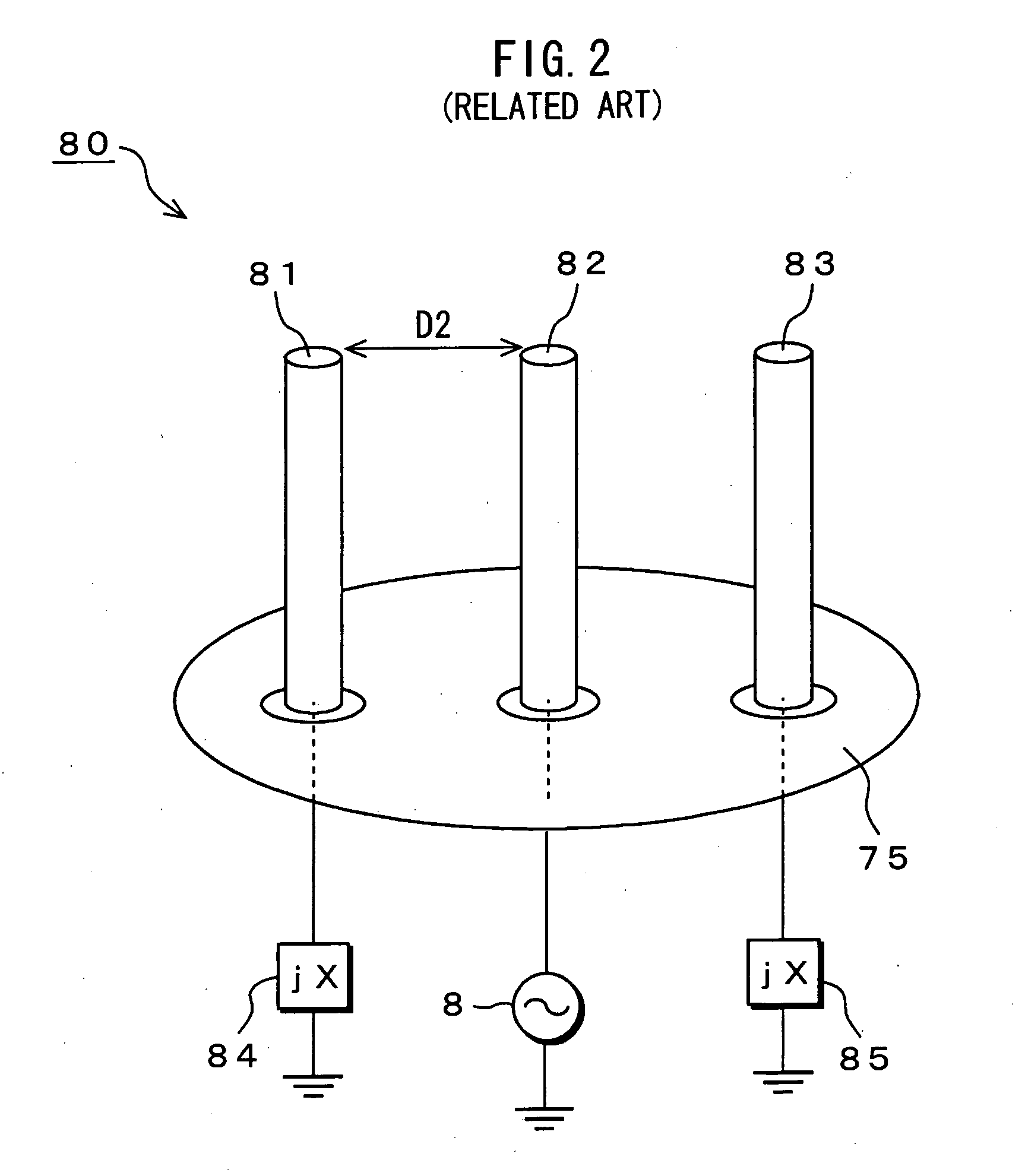
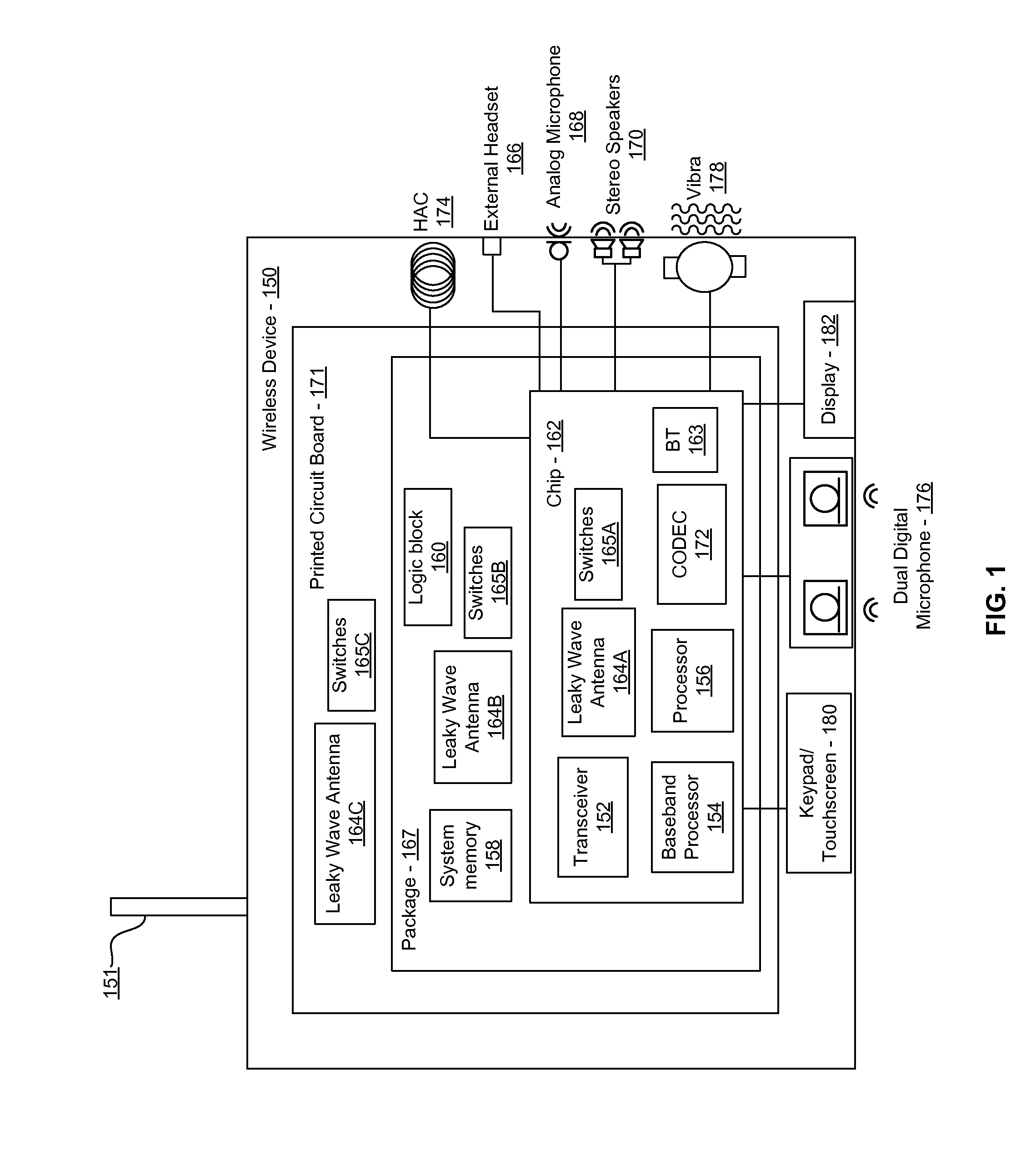
Antenna device, wireless communication apparatus using the same, and control method of controlling wireless communication apparatus
An antenna device has semi-conductive antenna bodies each having a predetermined length, which are positioned on a dielectric substrate, and control electrodes that are respectively connected with the semi-conductive antenna bodies. Direct-current biased voltage applied across each of the control electrodes is controlled to switch each of the antenna bodies between their insulation state and their conductive state.
Owner:SONY CORP
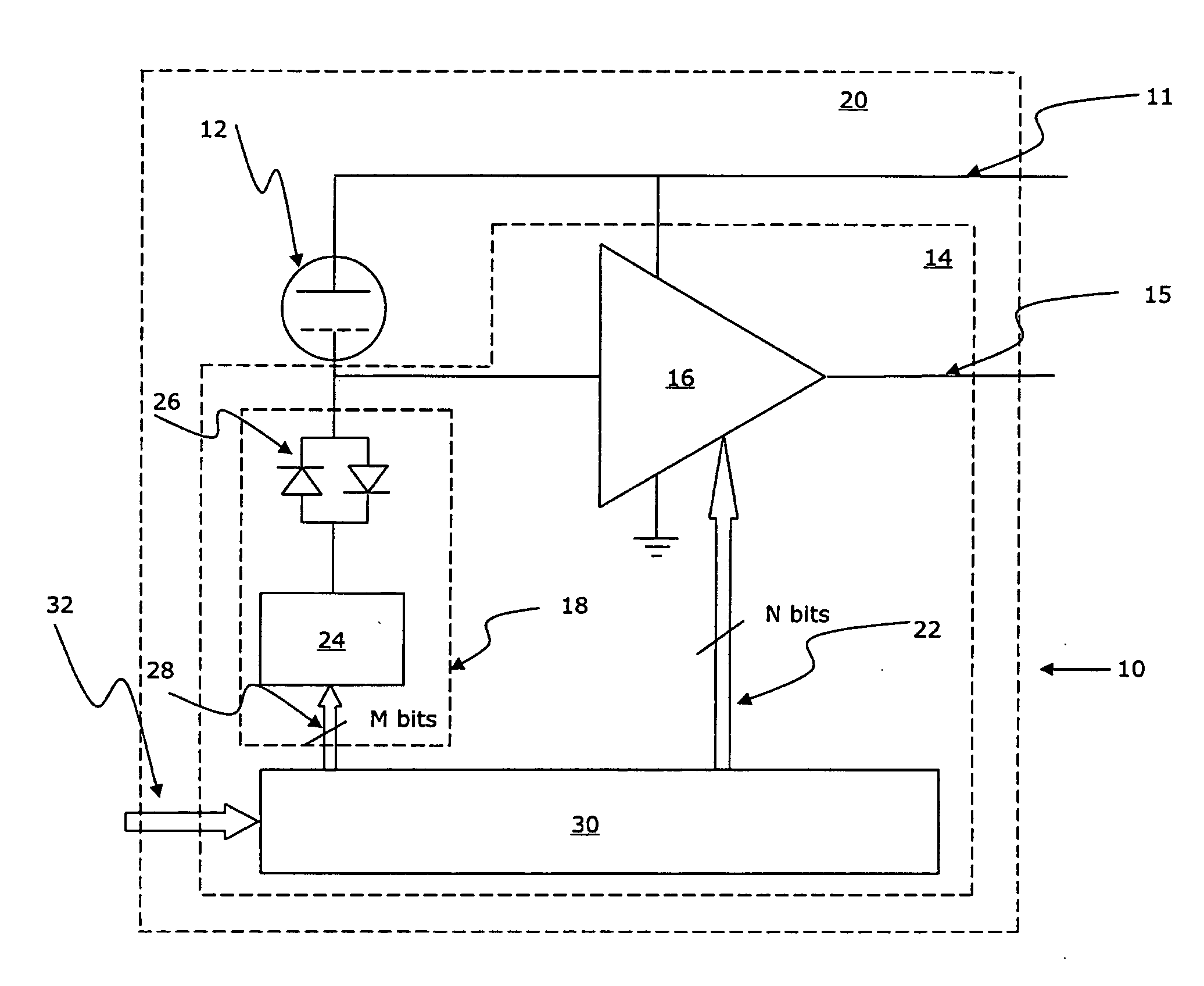
Calibrated microelectromechanical microphone
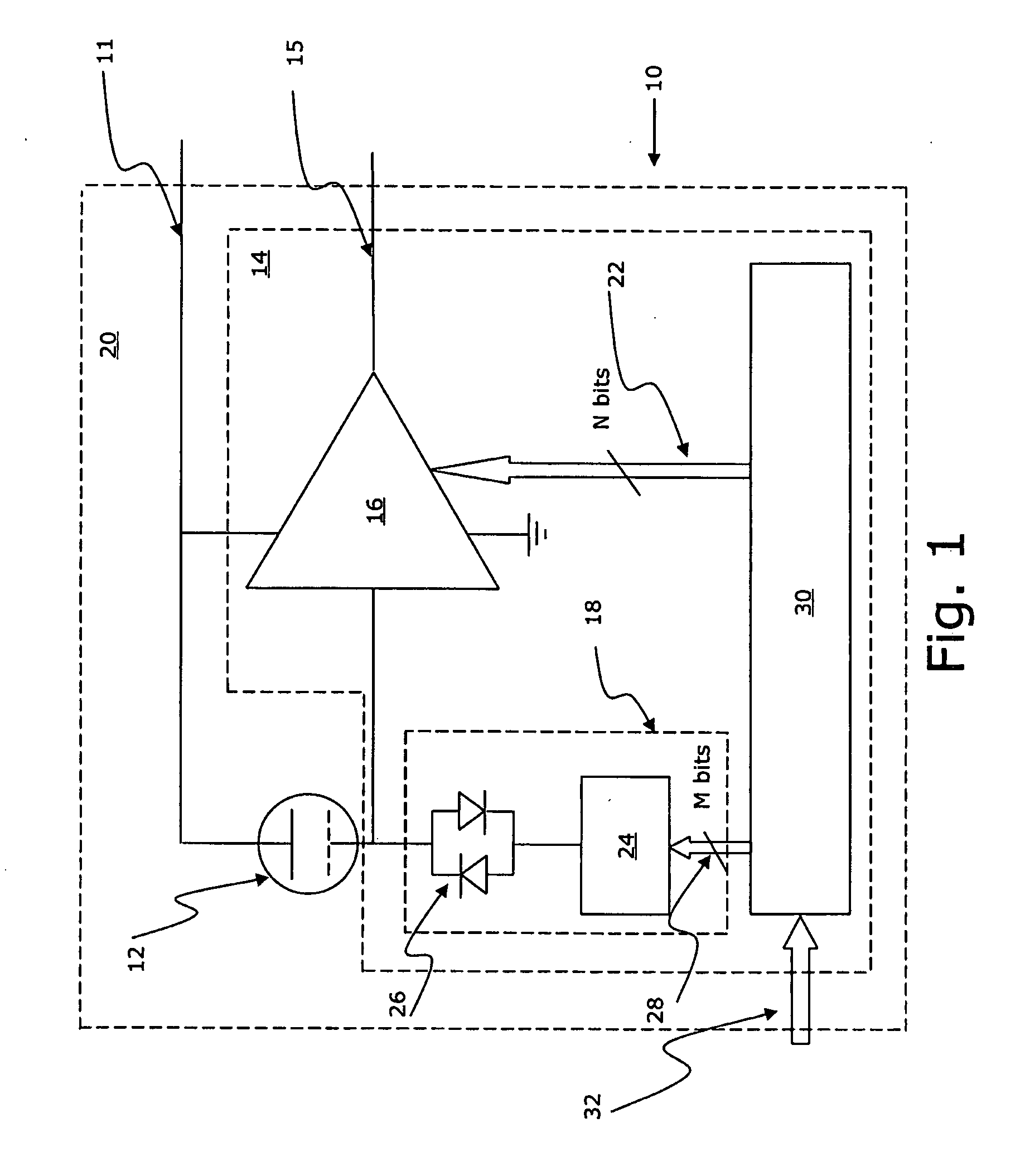
ActiveUS20080075306A1Improve production yieldMaximize sensitivitySemiconductor electrostatic transducersElectrostatic transducer microphonesVoltage generatorAudio power amplifier
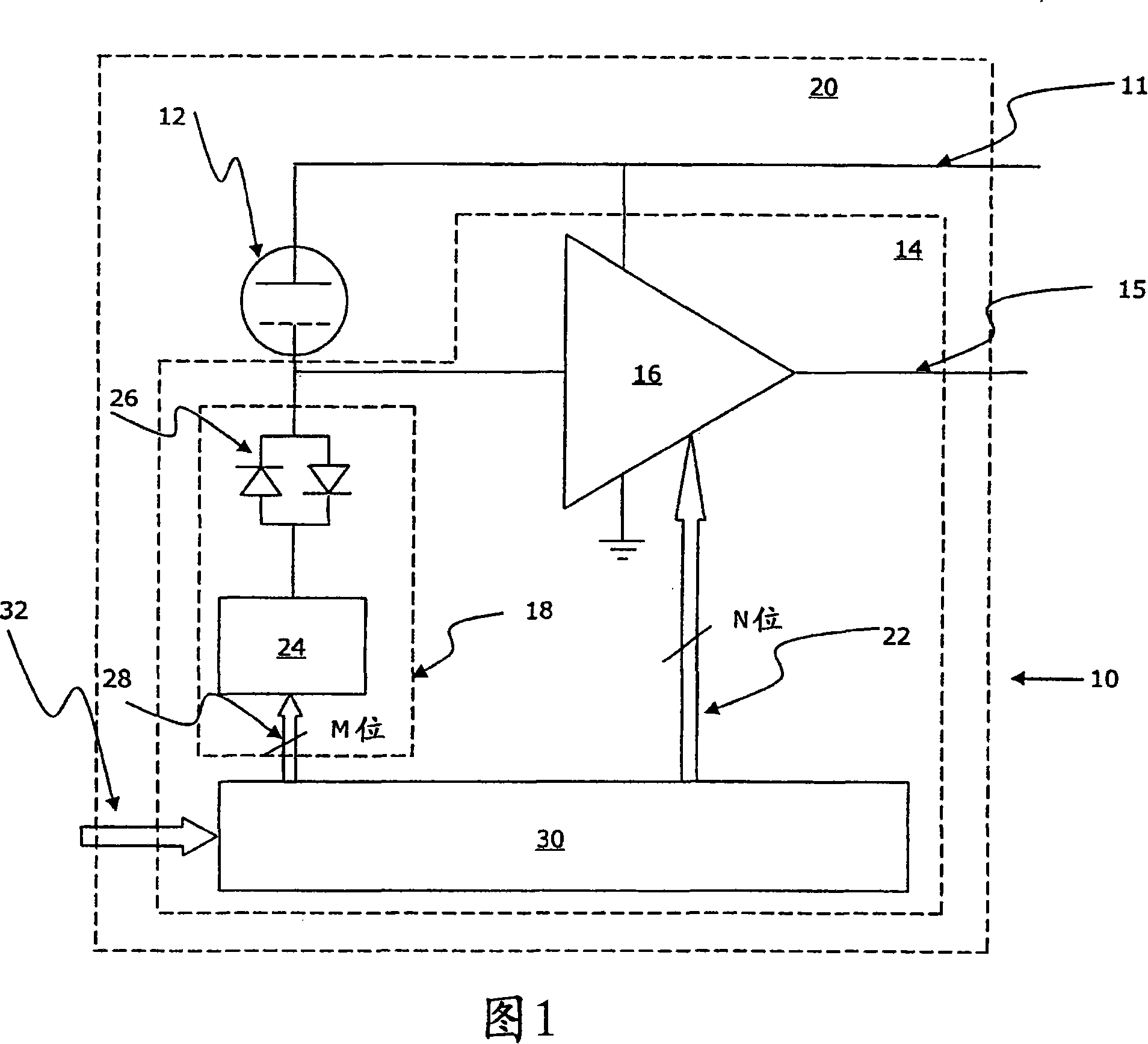
A MEMS microphone comprising a MEMS transducer having a back plate and a diaphragm as well as controllable bias voltage generator providing a DC bias voltage between the back plate and the diaphragm. The microphone also has an amplifier with a controllable gain, and a memory for storing information for determining a bias voltage to be provided by the bias voltage generator and the gain of the amplifier.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
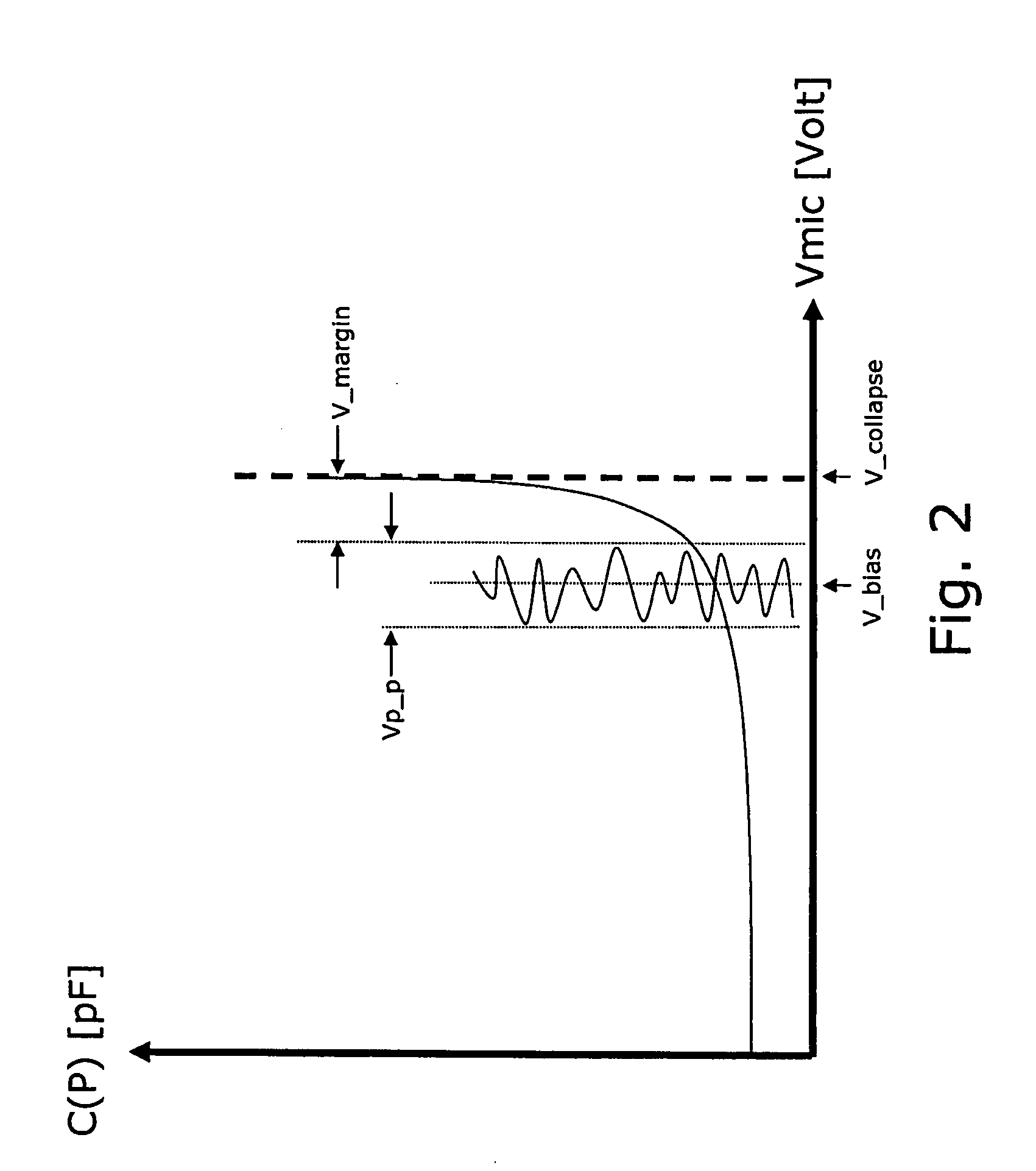
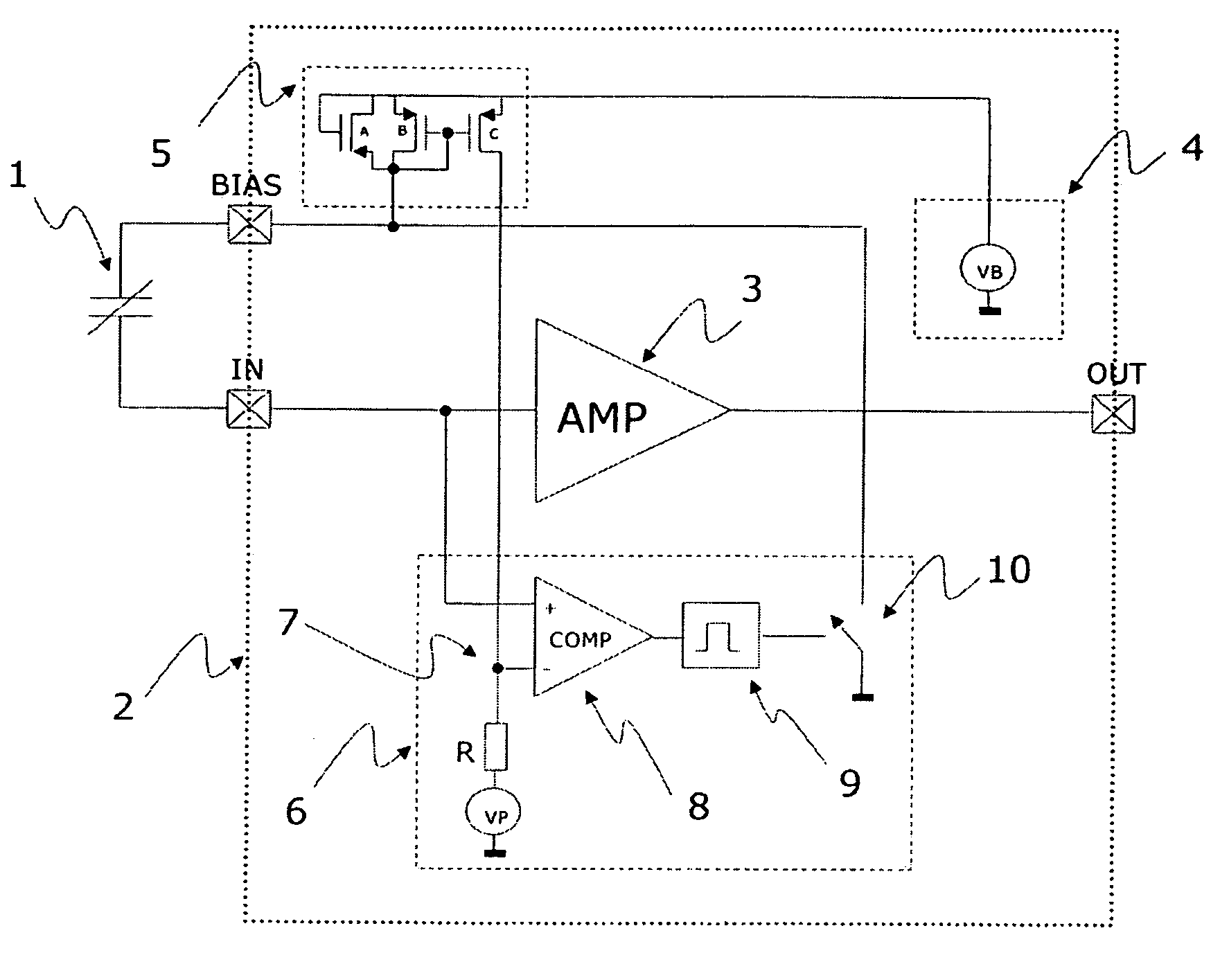
Detection and control of diaphragm collapse in condenser microphones
ActiveUS7548626B2Increase freedomMaximum flexibilityElectrostatic transducer microphonesTransducer protection circuitsTransducerEngineering
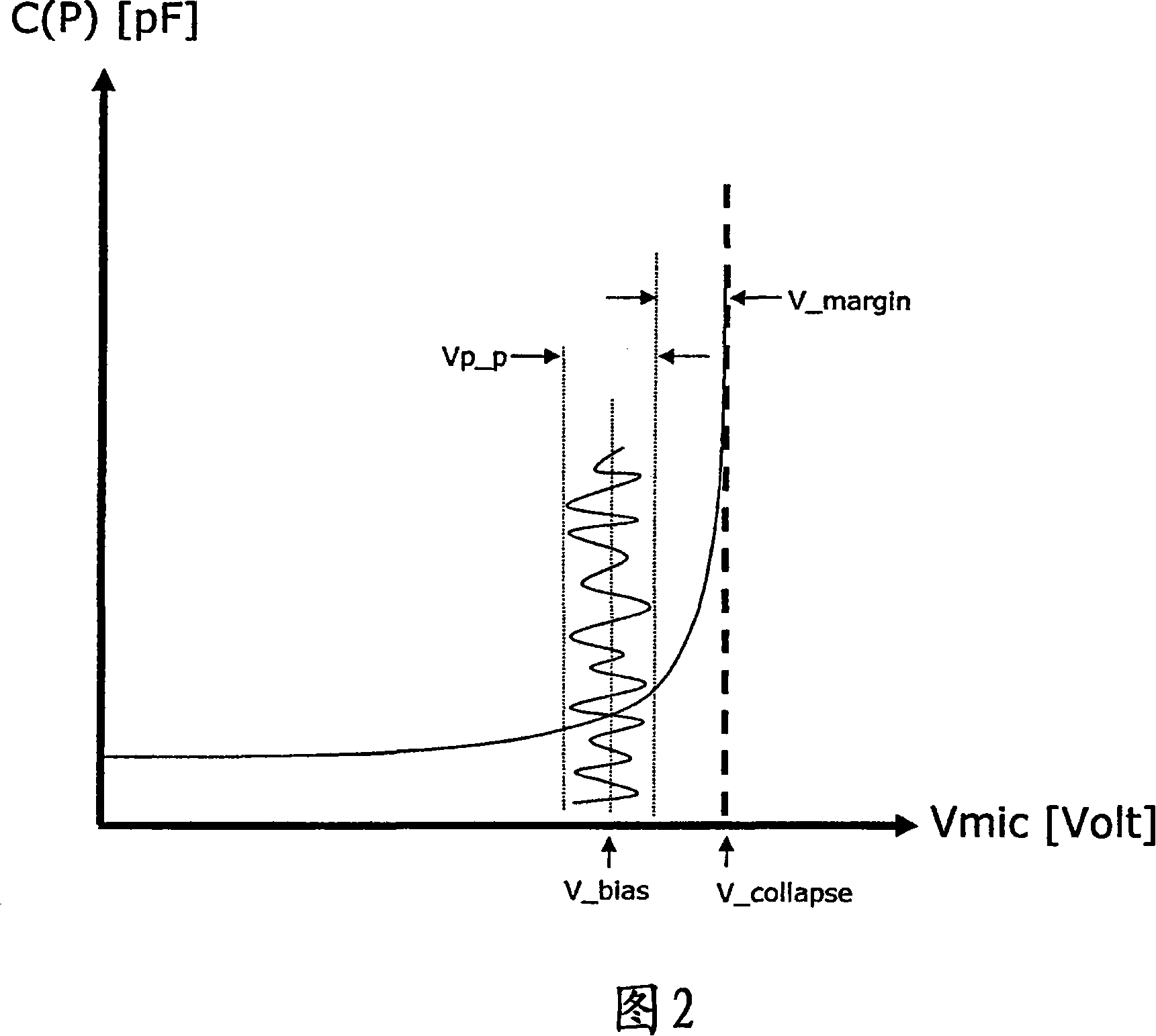
A condenser microphone is provided having a transducer element. A diaphragm has an electrically conductive portion. A back-plate has an electrically conductive portion. A DC bias voltage element is operatively coupled to the diaphragm and the back-plate. A collapse detection element is adapted to determine a physical parameter value related to a separation between the diaphragm and the back-plate. A collapse control element is adapted to control the DC bias voltage element based on the determined physical parameter value.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
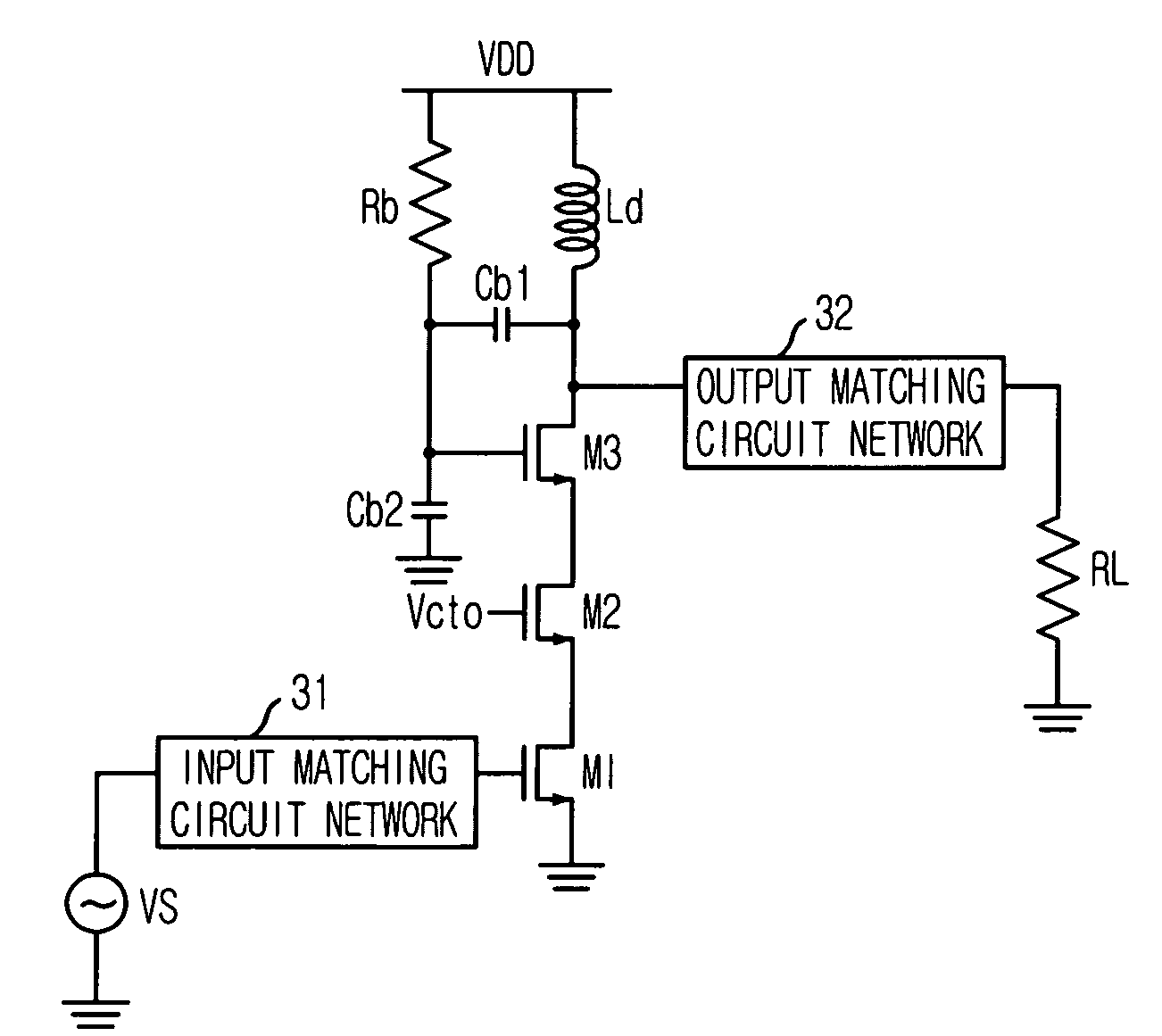
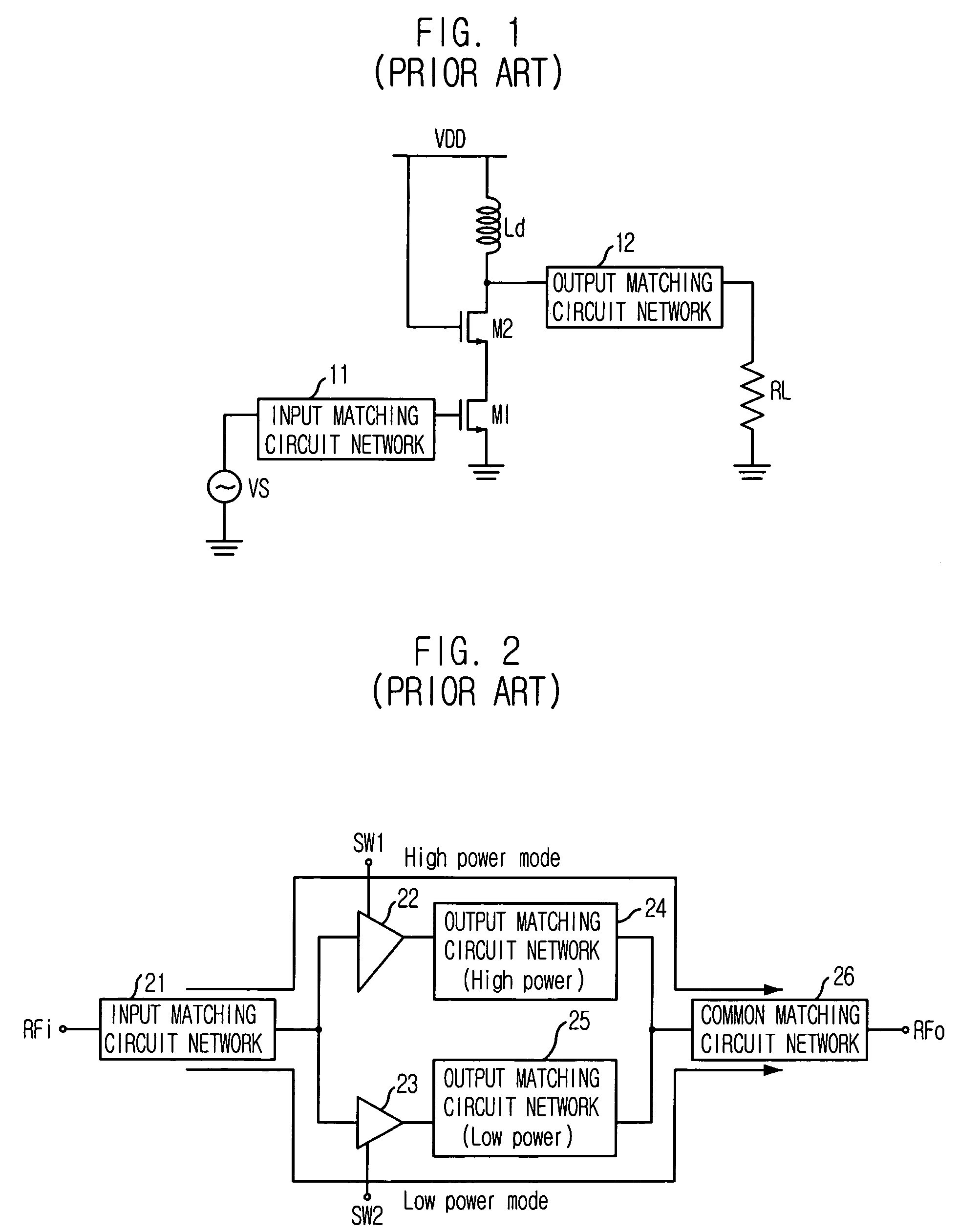
Triple cascode power amplifier of inner parallel configuration with dynamic gate bias technique
InactiveUS20060119435A1Easily embodiedIncrease output powerGated amplifiersAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierCascode
Provided is a power amplifier which fits to a deep-submicron technology in radio frequency wireless communication. The power amplifier includes a cascode including a first transistor which receives and amplifies an input signal, and a second transistor which is connected to the first transistor in series and operated by a DC bias voltage; a third transistor which is connected between the cascode and an output end, operated by a dynamic gate bias and outputting a signal; and a voltage divider which includes first and second capacitors that are connected between the output end, i.e. a drain of the third transistor, and a ground in series, and provides the dynamic bias to a gate of the third transistor.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
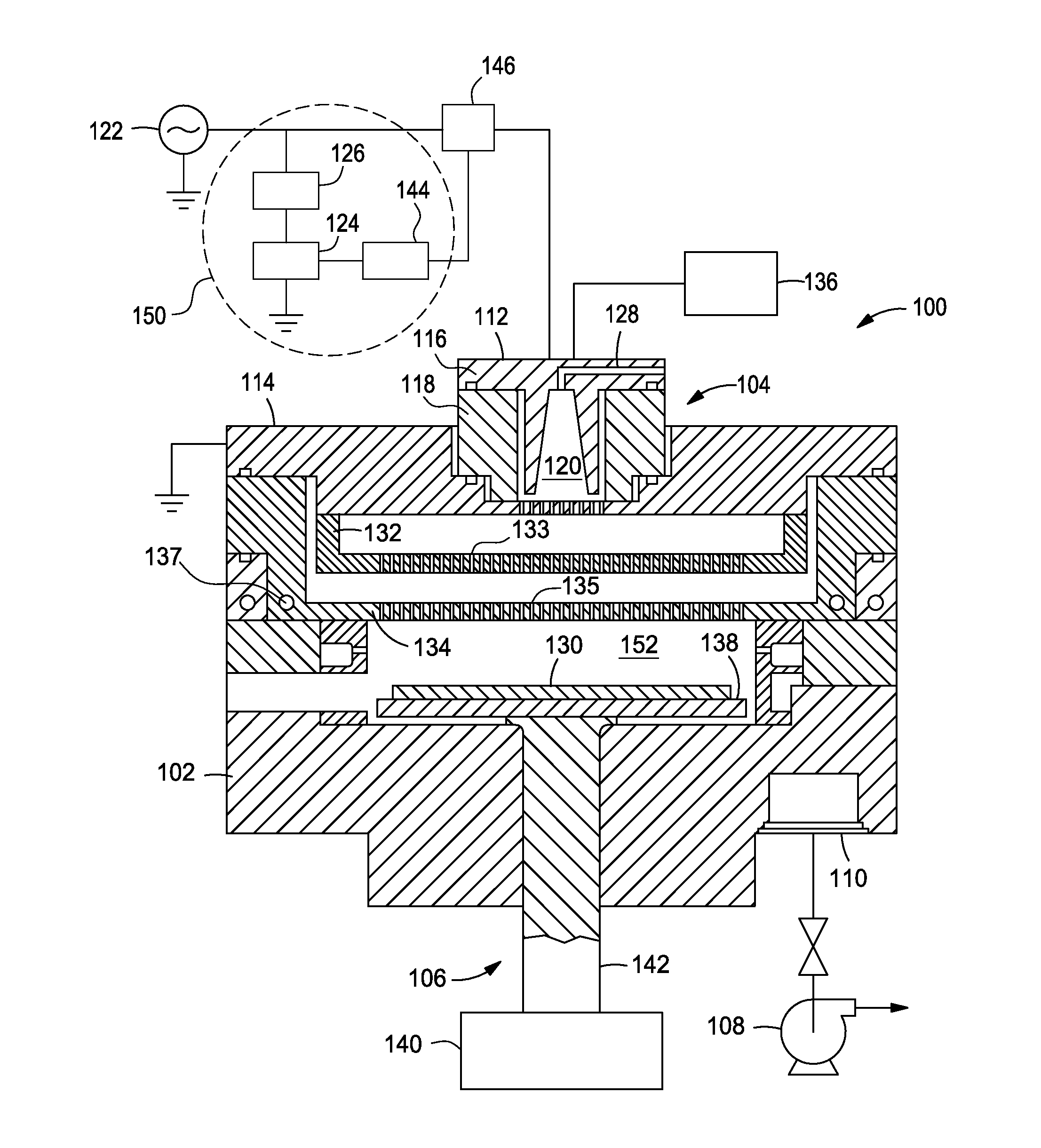
Particle generation suppresspr by DC bias modulation
Embodiments of the present disclosure generally relate to an apparatus and method for reducing particle generation in a processing chamber. In one embodiment, the methods generally includes generating a plasma between a powered top electrode and a grounded bottom electrode, wherein the top electrode is parallel to the bottom electrode, and applying a constant zero DC bias voltage to the powered top electrode during a film deposition process to minimize the electrical potential difference between the powered top electrode and the plasma and / or the electrical potential difference between the grounded bottom electrode and the plasma. Minimizing the electrical potential difference between the plasma and the electrodes reduces particle generation because the acceleration of the ions in the sheath region of the electrodes is reduced and the collision force of the ions with the protective coating layer on the electrodes is minimized. Therefore, particle generation on the substrate surface is reduced.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
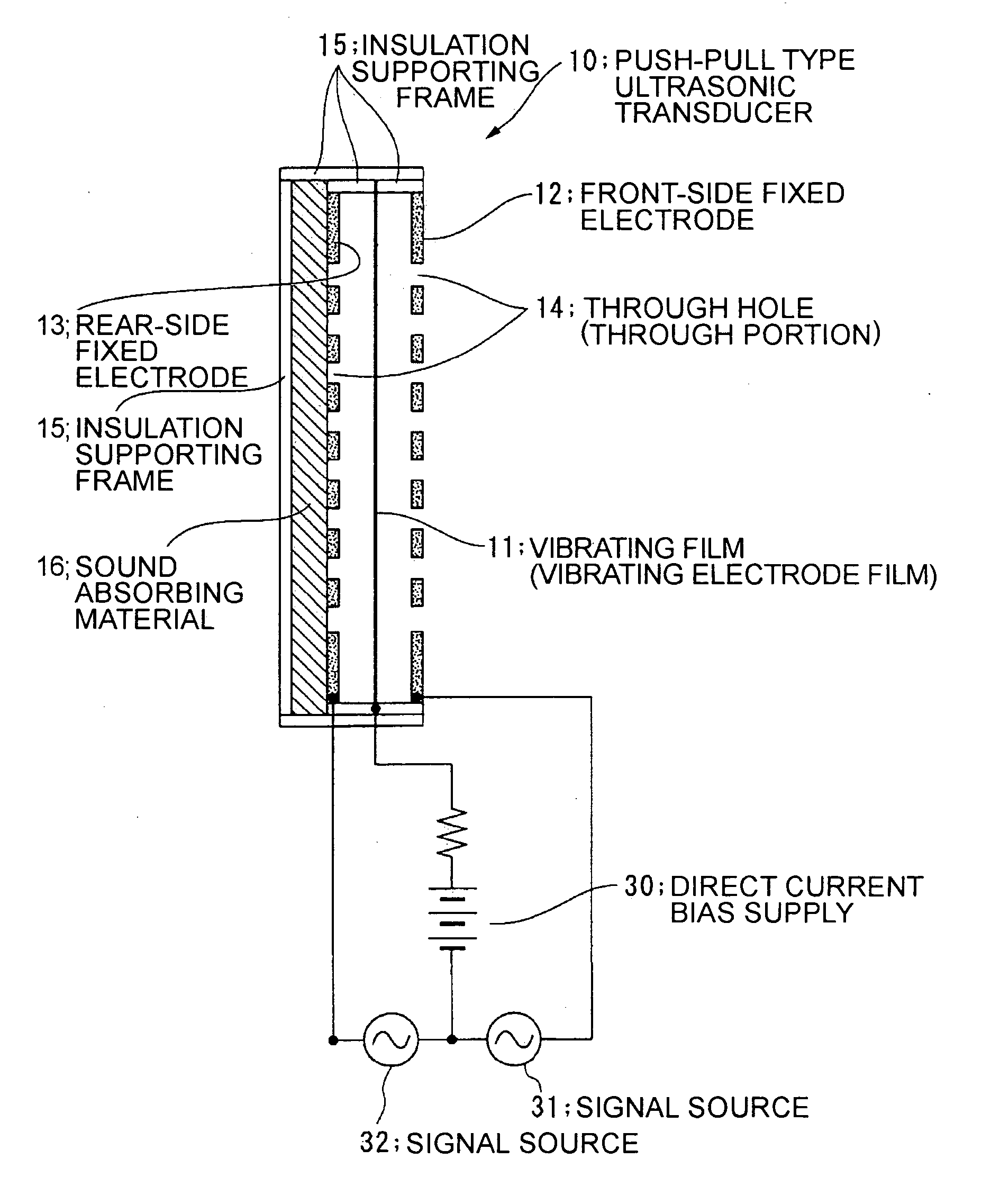
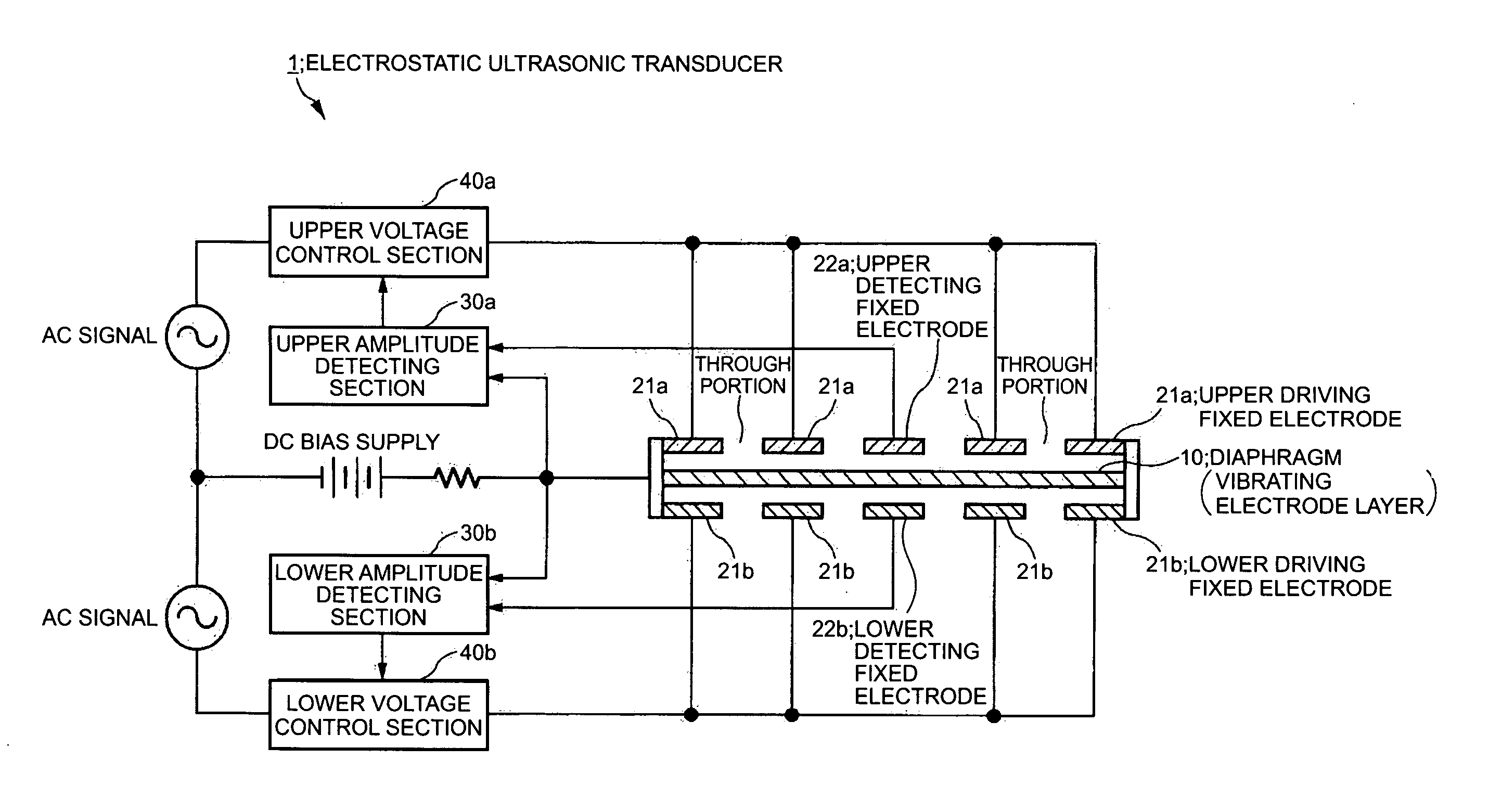
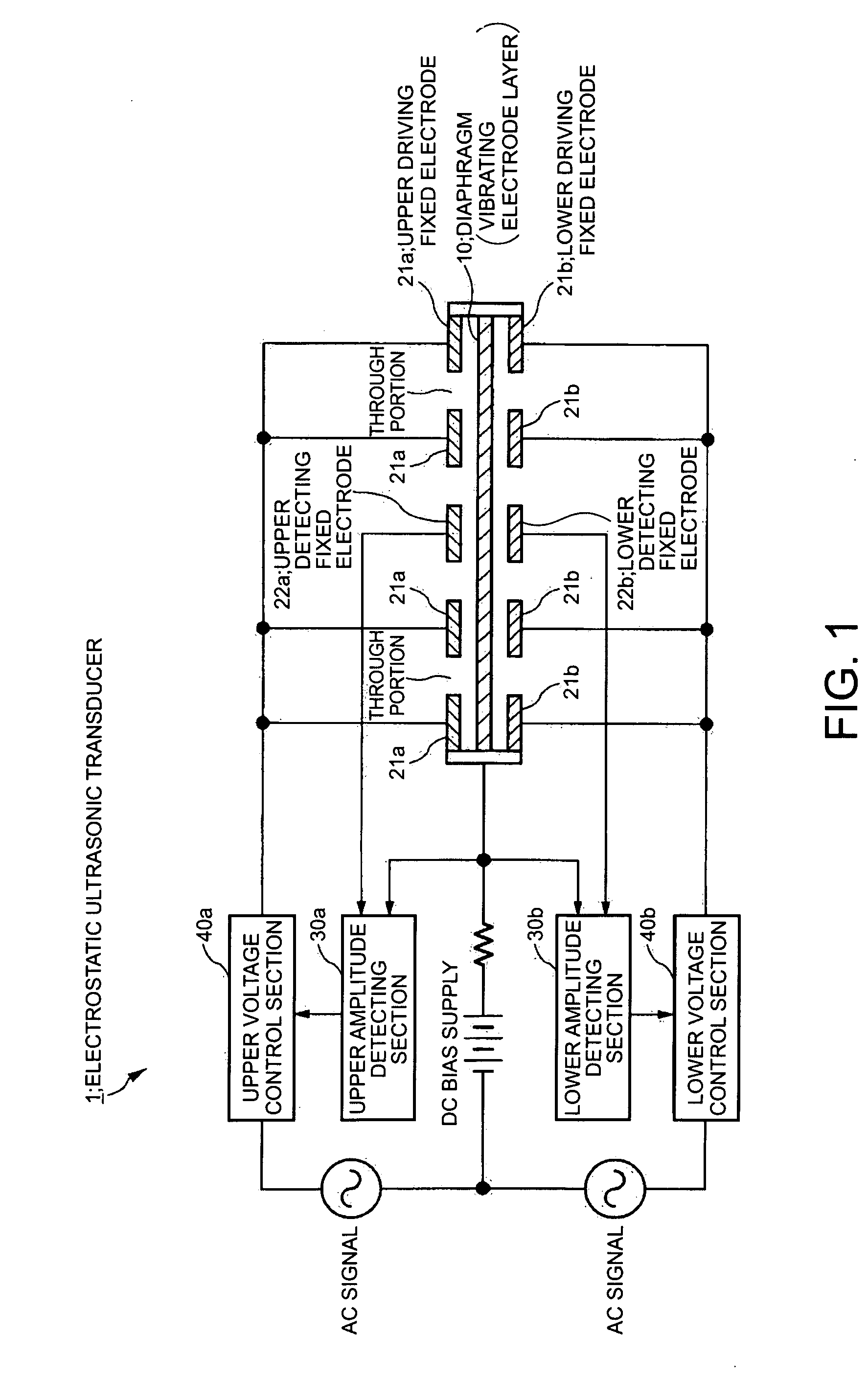
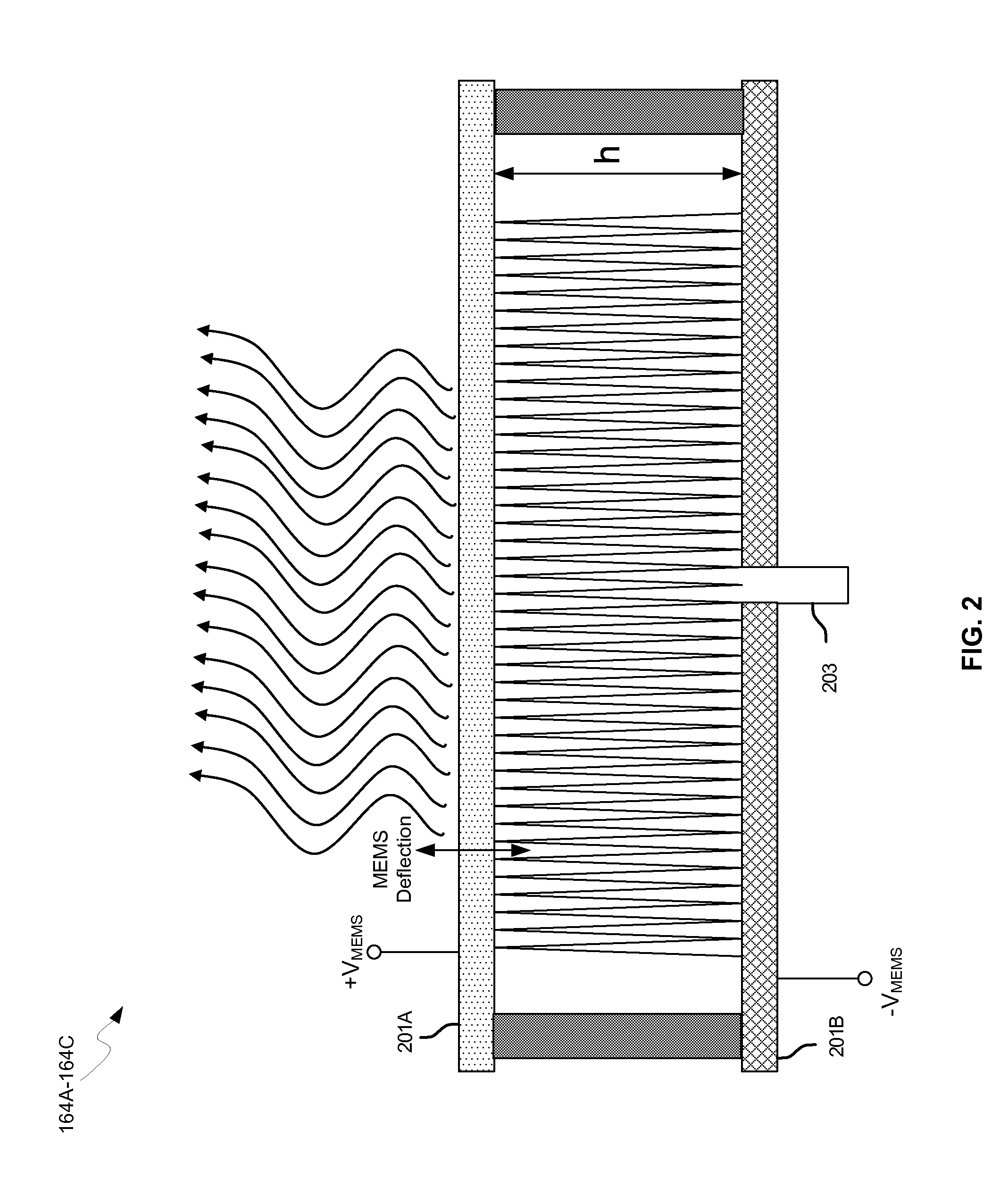
Electrostatic ultrasonic transducer and ultrasonic speaker
InactiveUS20060072770A1Small distortionImprove directionalityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersElectrostatic transducer loudspeakersUltrasonic sensorSonification
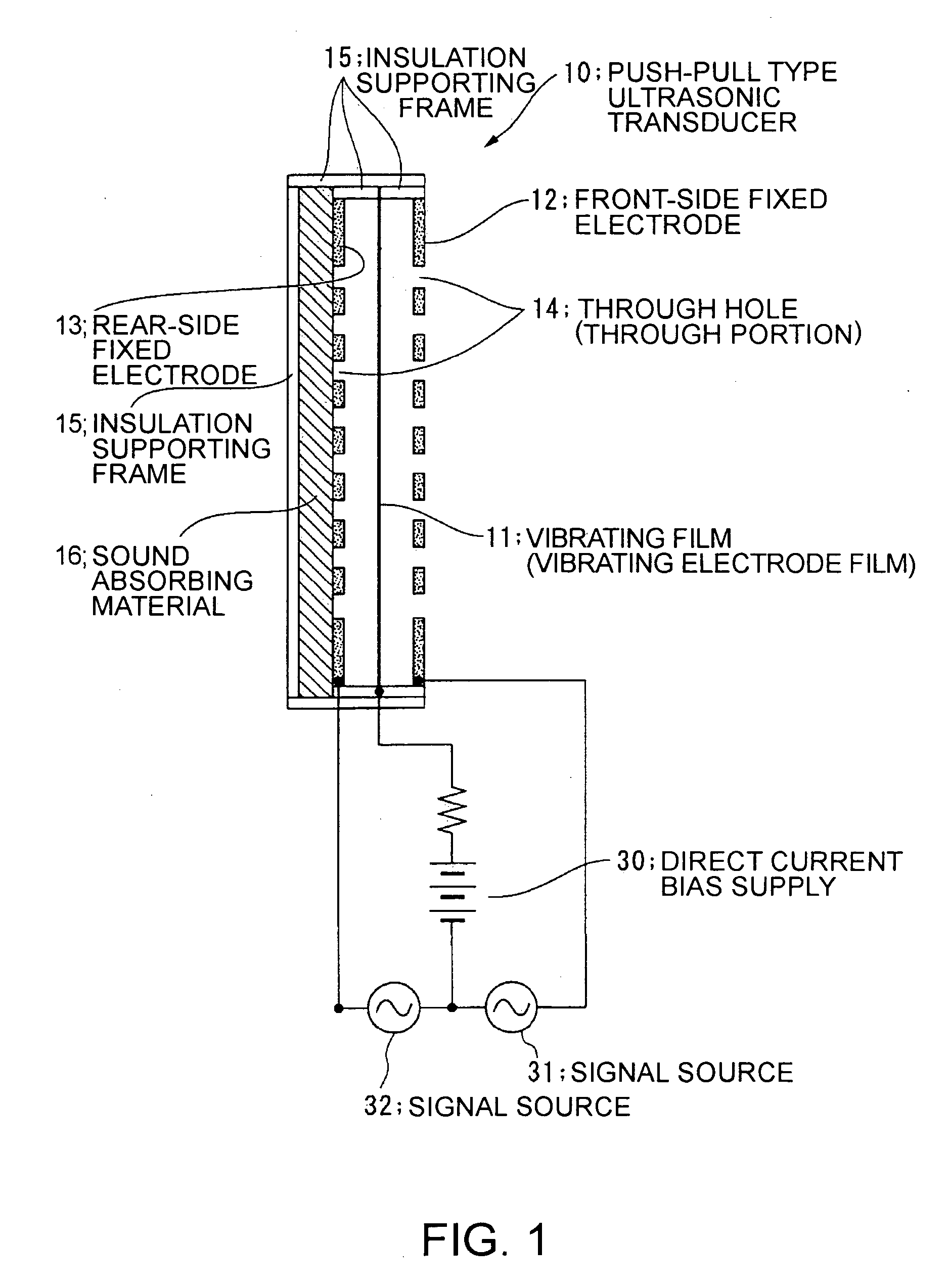
To provide an electrostatic ultrasonic transducer arranged so that sound wave is not radiated from the rear surface while utilizing advantages of a push-pull type electrostatic ultrasonic transducer. A push-pull type electrostatic ultrasonic transducer includes a vibrating film 11 having a conductive layer and a pair of fixed electrodes 12, 13 provided facing respective surfaces of the vibrating film, and applies a direct current bias voltage to the conductive layer of the vibrating film and applies an alternating current signal between the pair of fixed electrodes so as to allow the vibrating film to generate sound wave and outputting the sound wave generated from the vibrating film from two sound wave output surfaces via through holes provided in the respective pair of fixed electrodes. Plural through holes are provided in the front-side fixed electrode that sandwiches the vibrating film and through holes having the same shapes are provided in the rear-side fixed electrode in positions opposed to the respective through holes provided in the front-side fixed electrode, and a sound absorbing material 16 is provided facing the rear-side fixed electrode.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
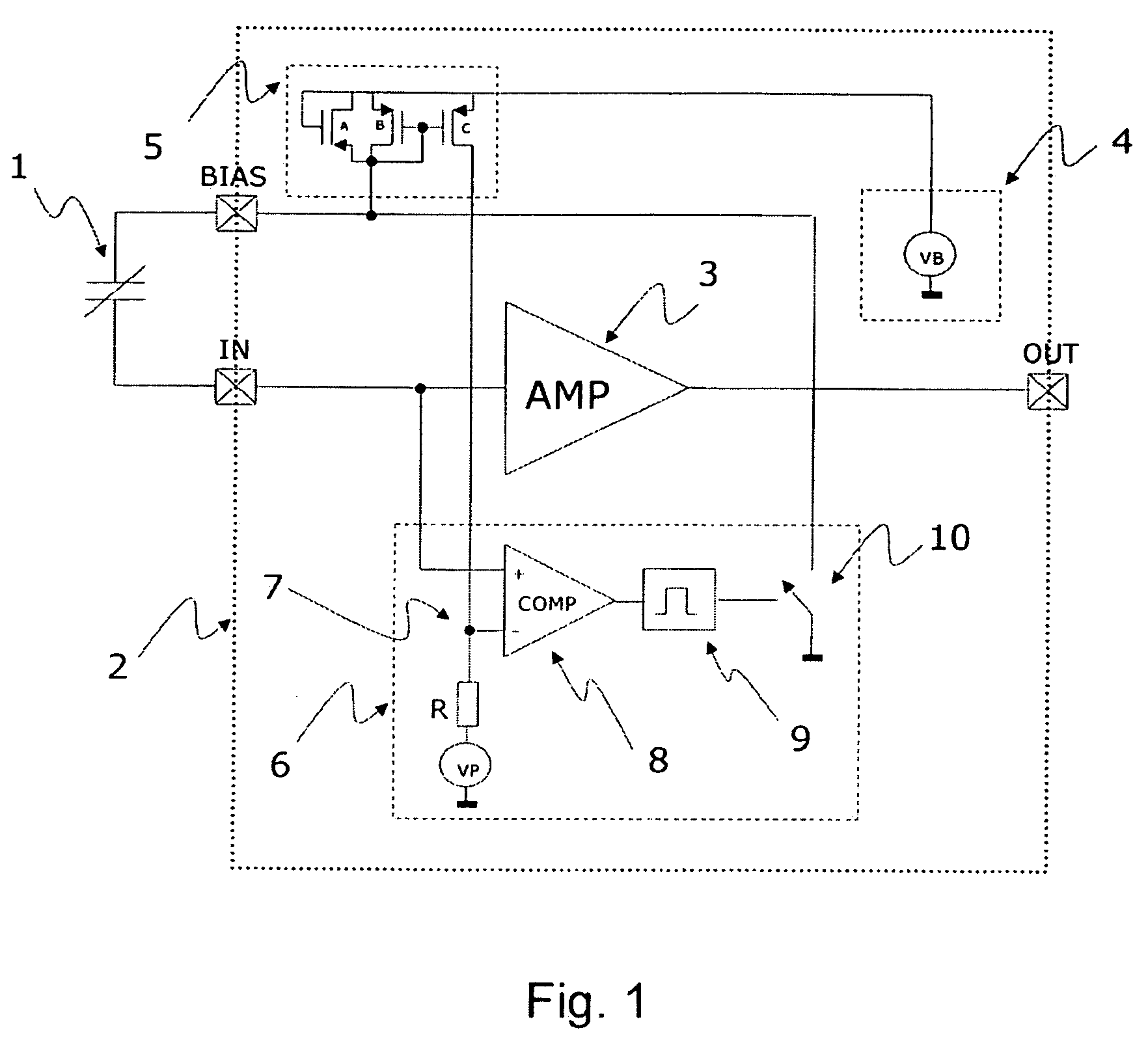
Detection and control of diaphragm collapse in condenser microphones
ActiveUS20060008097A1Increase freedomMaximum flexibilityElectrostatic transducer microphonesTransducer protection circuitsTransducerEngineering
A condenser microphone is provided having a transducer element. A diaphragm has an electrically conductive portion. A back-plate has an electrically conductive portion. A DC bias voltage element is operatively coupled to the diaphragm and the back-plate. A collapse detection element is adapted to determine a physical parameter value related to a separation between the diaphragm and the back-plate. A collapse control element is adapted to control the DC bias voltage element based on the determined physical parameter value.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Multi-cascode transistors
InactiveUS6888396B2Boards/switchyards circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceMOSFETCascode
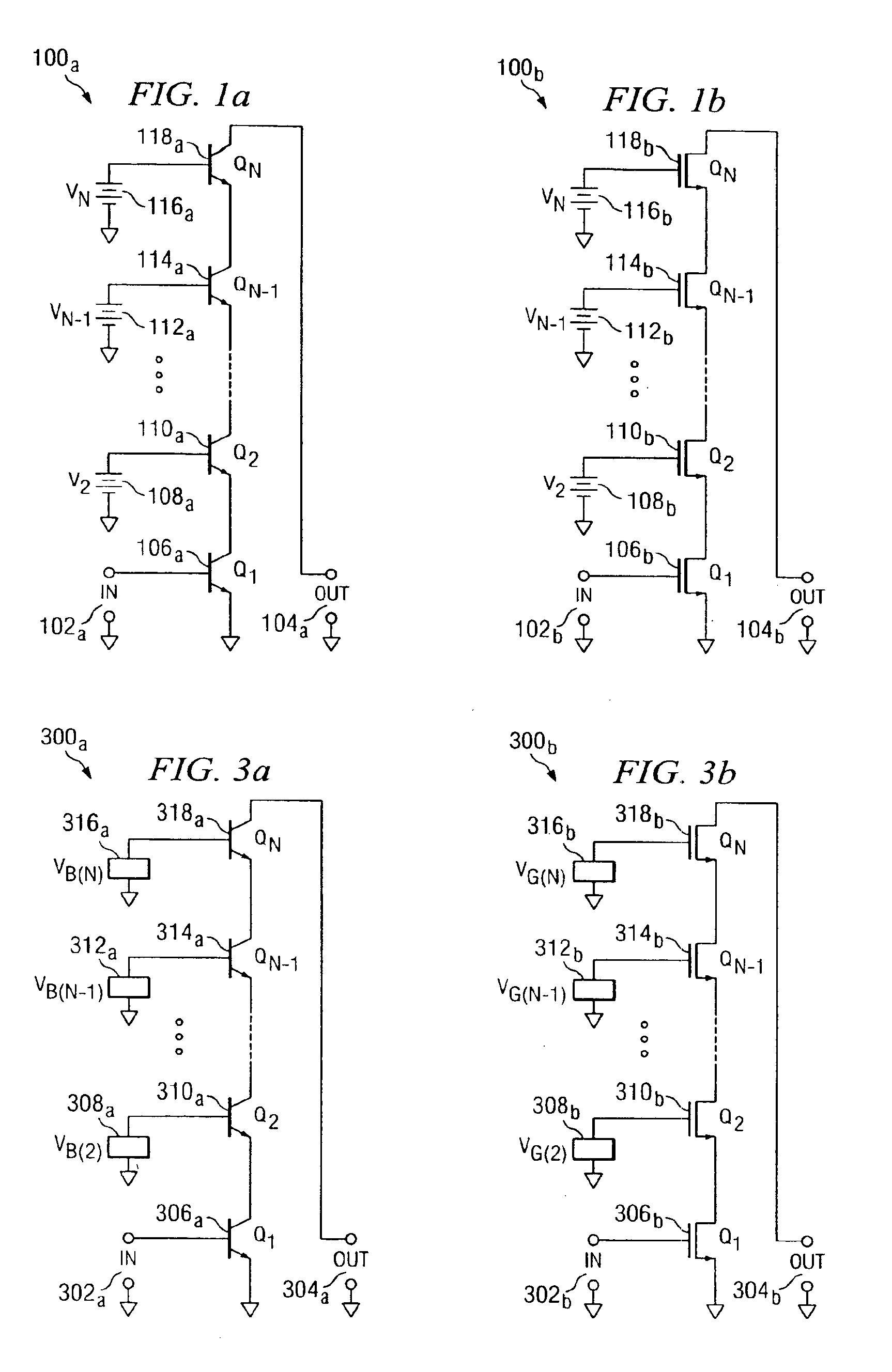
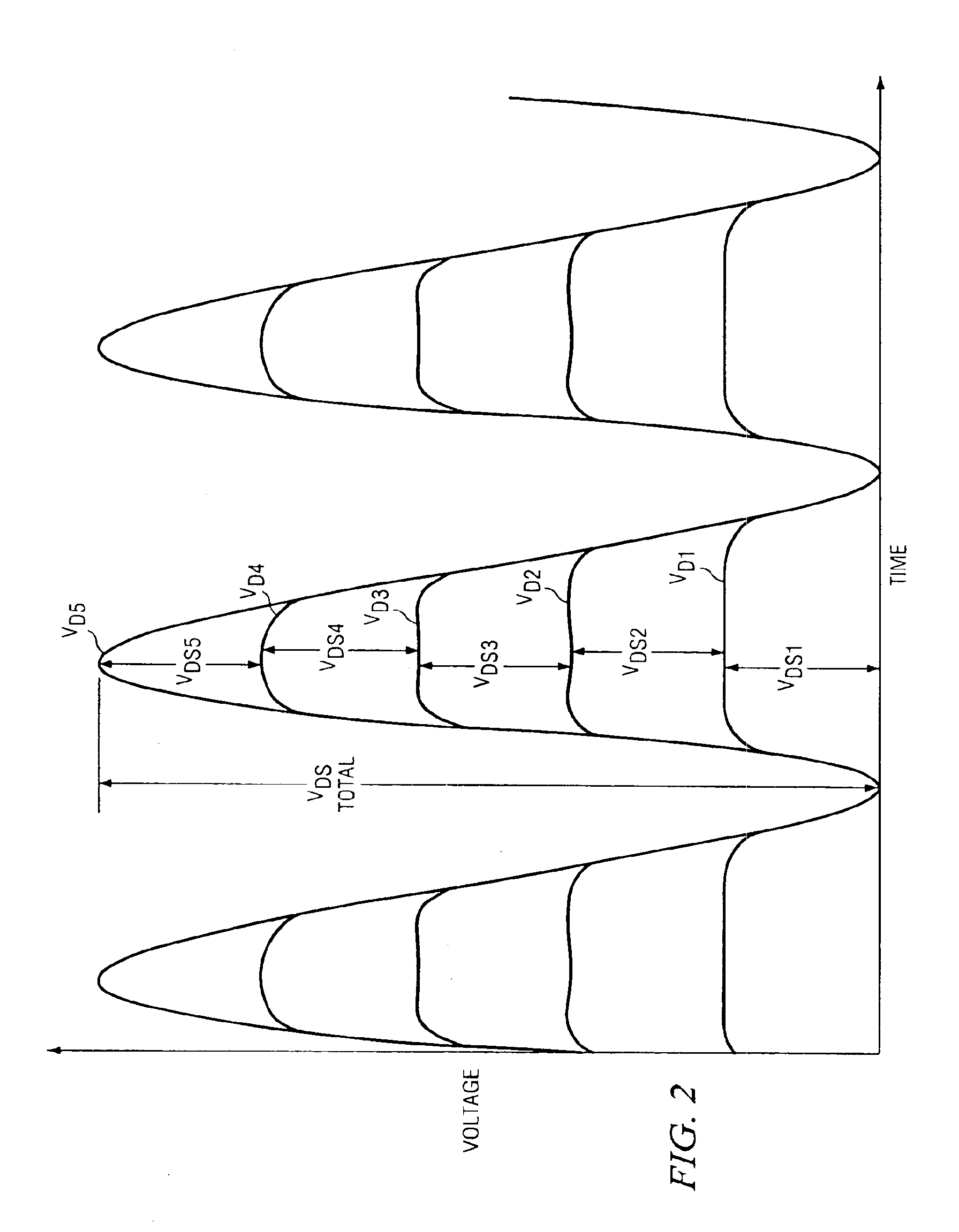
A cascode circuit with improved withstand voltage is provided. The cascode circuit includes three or more transistors, such as MOSFET transistors. Each transistor has a control terminal, such as a gate, and two conduction terminals, such as a drain and a source. The conduction terminals are coupled in series between two output terminals, such as where the drain of each transistor is coupled to the source of another transistor. A signal input is provided to the gate for the first transistor. Two or more control voltage sources, such as DC bias voltages, are provided to the gate of the remaining transistors. The DC bias voltages are selected so as to maintain the voltage across each transistor to a level below a breakdown voltage level.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
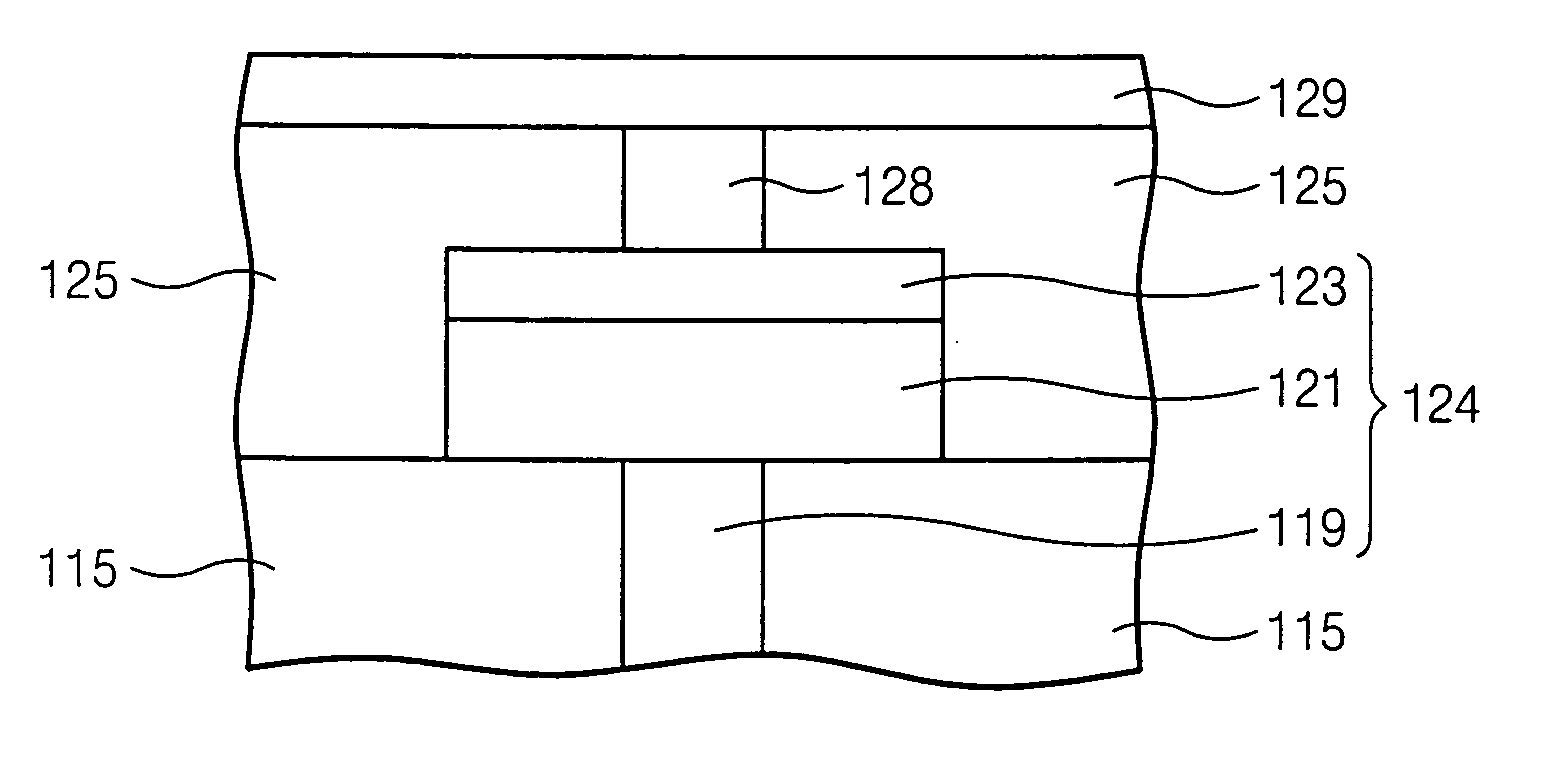
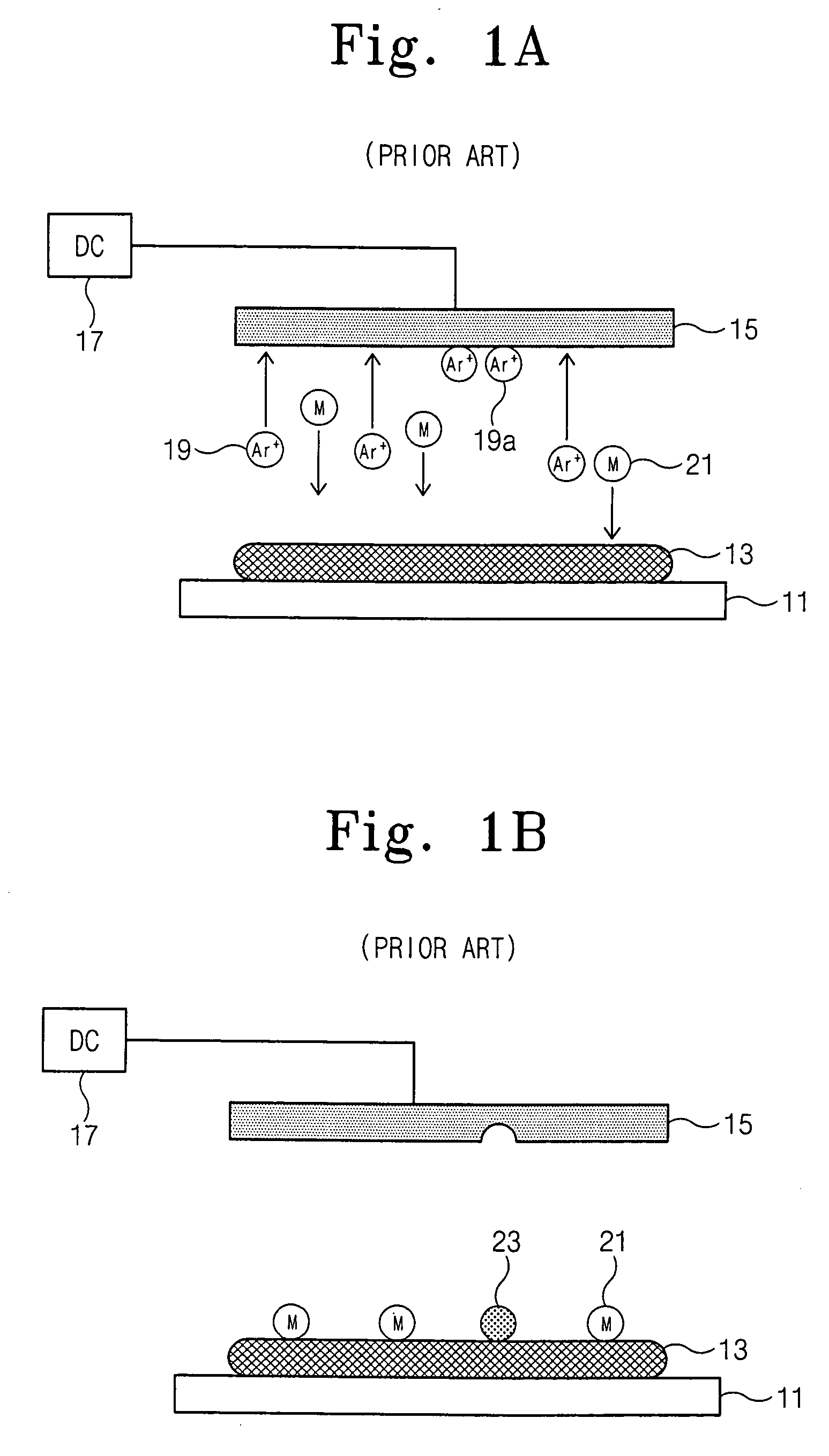
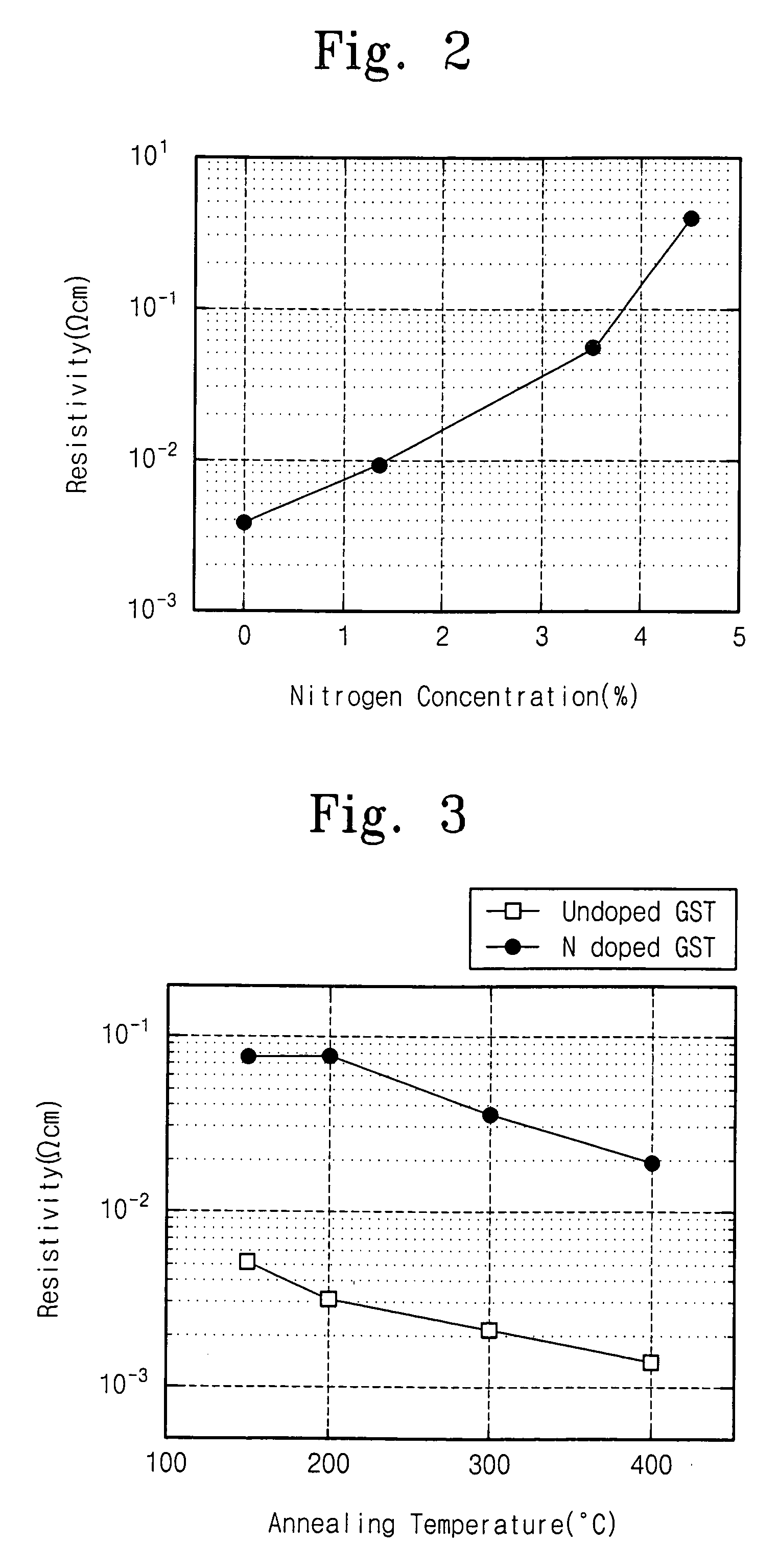
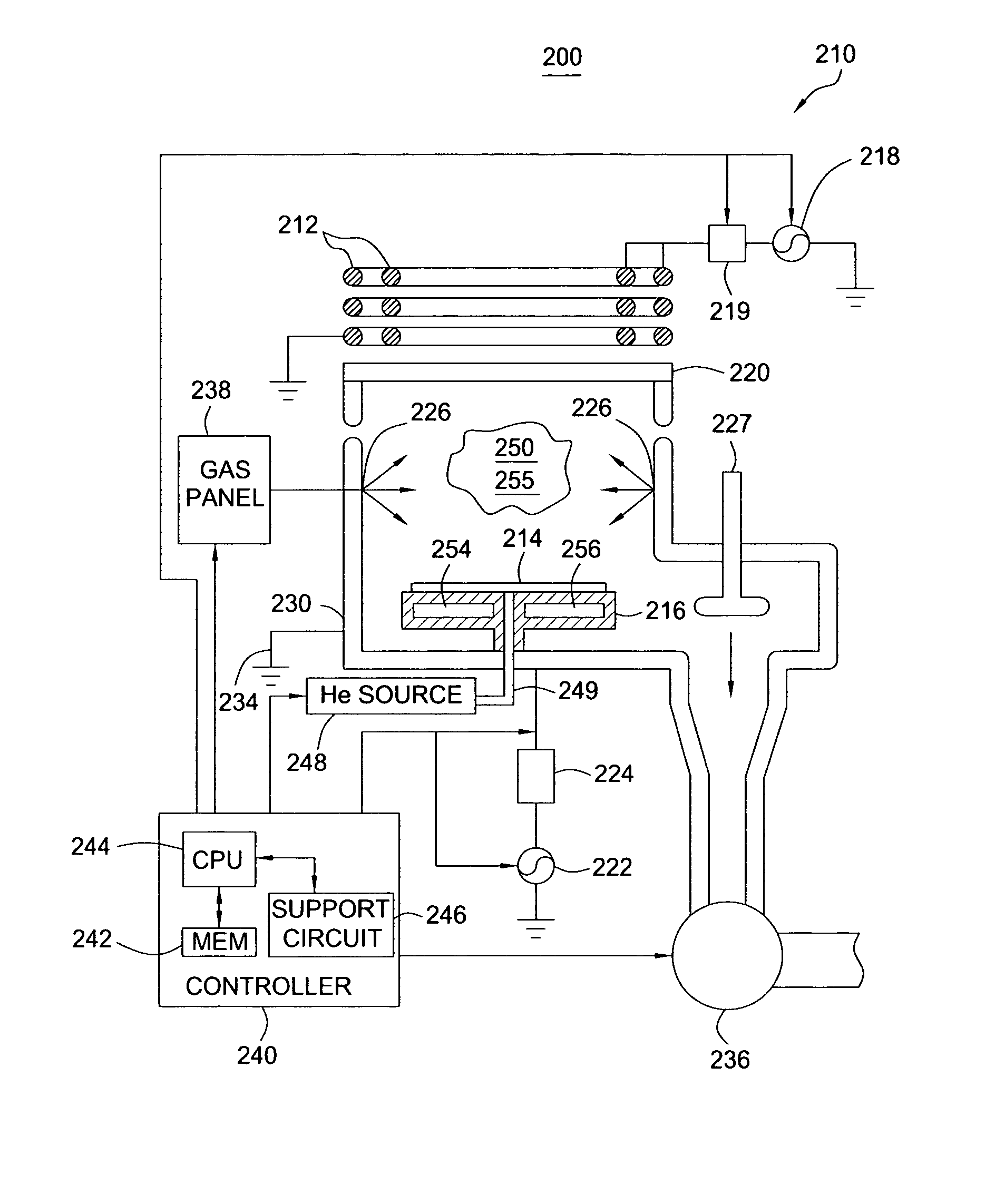
Methods for sputtering a target material by intermittently applying a voltage thereto and related apparatus, and methods of fabricating a phase-changeable memory device employing the same
InactiveUS20060027451A1Reduce the probability of depositionSmall crystal sizeCellsVacuum evaporation coatingSputteringPhase-change memory
A method of sputtering to deposit a target material onto a substrate includes supplying an ionized gas to the substrate and the target material. A first DC bias voltage having a polarity opposite that of the ionized gas is applied to the target material to attract ions theretoward. A second DC bias voltage having a polarity opposite that of the first DC bias voltage is intermittently applied to the target material to reduce ion accumulation thereon. Related apparatus and methods of fabricating phase-changeable memory devices are also discussed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
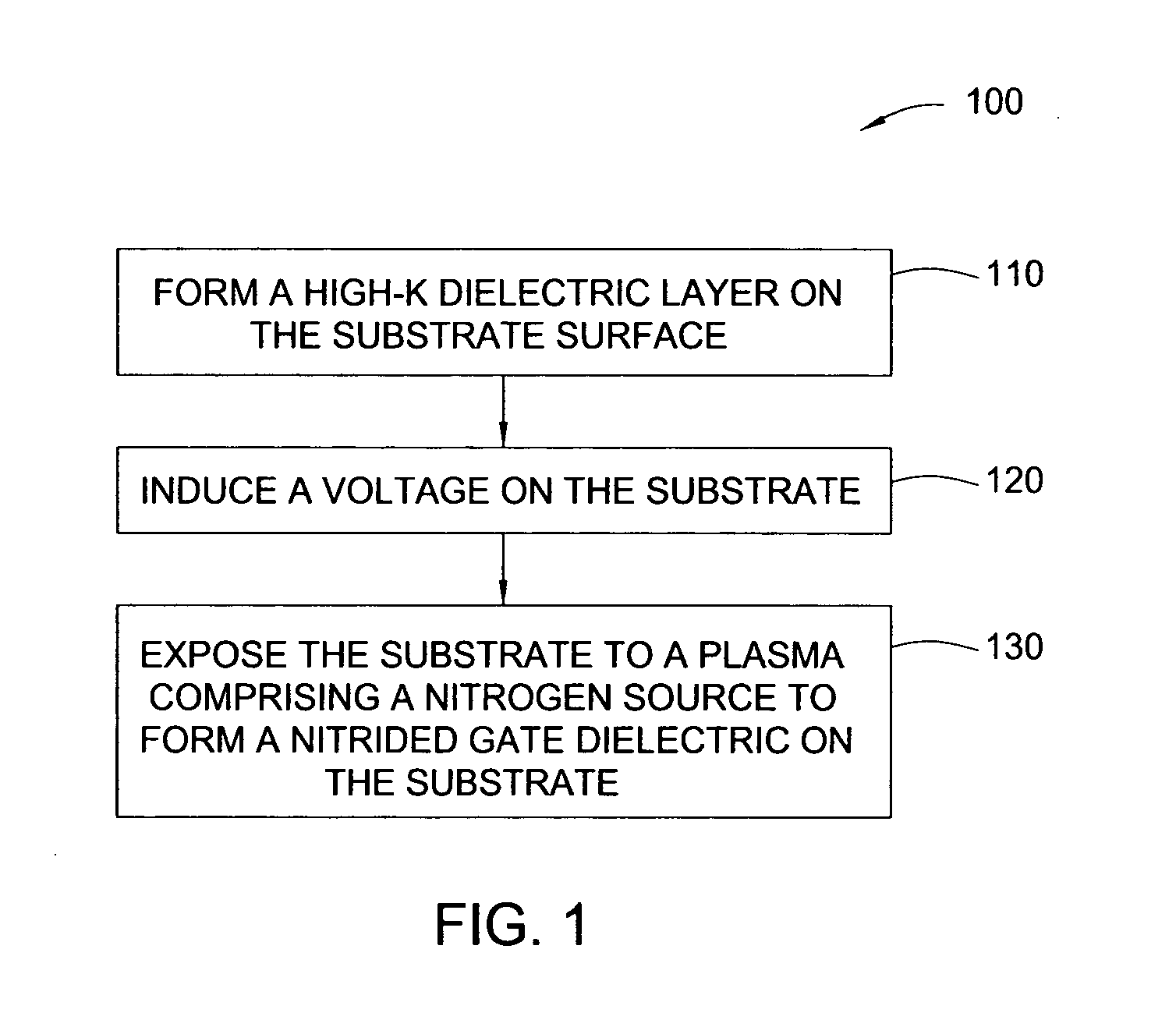
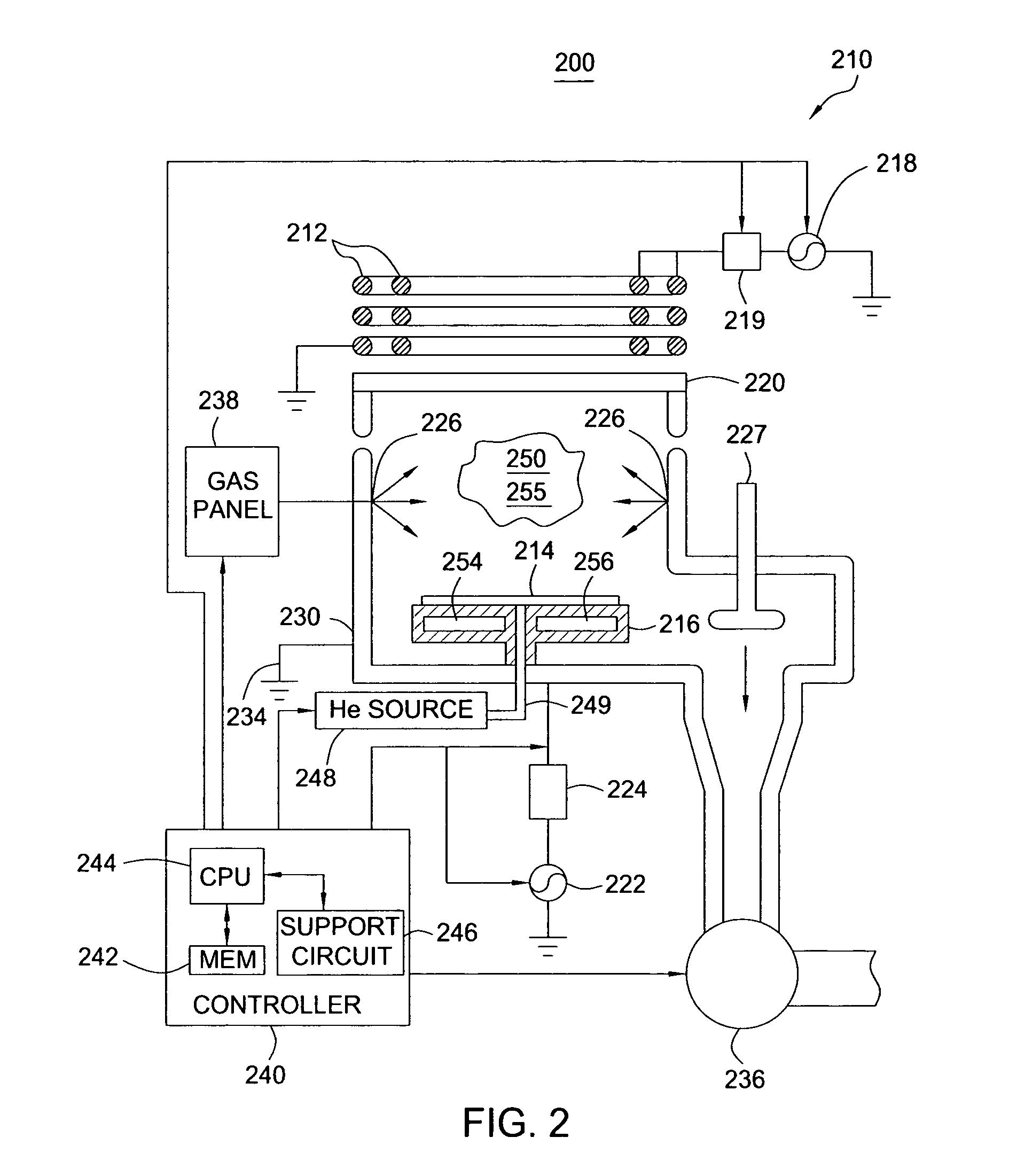
Nitrogen profile engineering in HI-K nitridation for device performance enhancement and reliability improvement
InactiveUS20070049043A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricPerformance enhancement
A method and apparatus for forming a nitrided gate dielectric. The method comprises incorporating nitrogen into a dielectric film using a plasma nitridation process to form a nitrided gate dielectric. The first step involves providing a substrate comprising a gate dielectric film. The second step involves inducing a voltage on the substrate. Finally, the substrate is exposed to a plasma comprising a nitrogen source while maintaining the voltage to form a nitrided gate dielectric on the substrate. In one embodiment, the voltage is induced on the substrate by applying a voltage to an electrostatic chuck supporting the substrate. In another embodiment, the voltage is induced on the substrate by applying a DC bias voltage to an electrode positioned adjacent the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Triple cascode power amplifier of inner parallel configuration with dynamic gate bias technique
InactiveUS7276976B2Increase output powerImprove efficiencyGated amplifiersAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierCascode
Provided is a power amplifier which fits to a deep-submicron technology in radio frequency wireless communication. The power amplifier includes a cascode including a first transistor which receives and amplifies an input signal, and a second transistor which is connected to the first transistor in series and operated by a DC bias voltage; a third transistor which is connected between the cascode and an output end, operated by a dynamic gate bias and outputting a signal; and a voltage divider which includes first and second capacitors that are connected between the output end, i.e. a drain of the third transistor, and a ground in series, and provides the dynamic bias to a gate of the third transistor.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
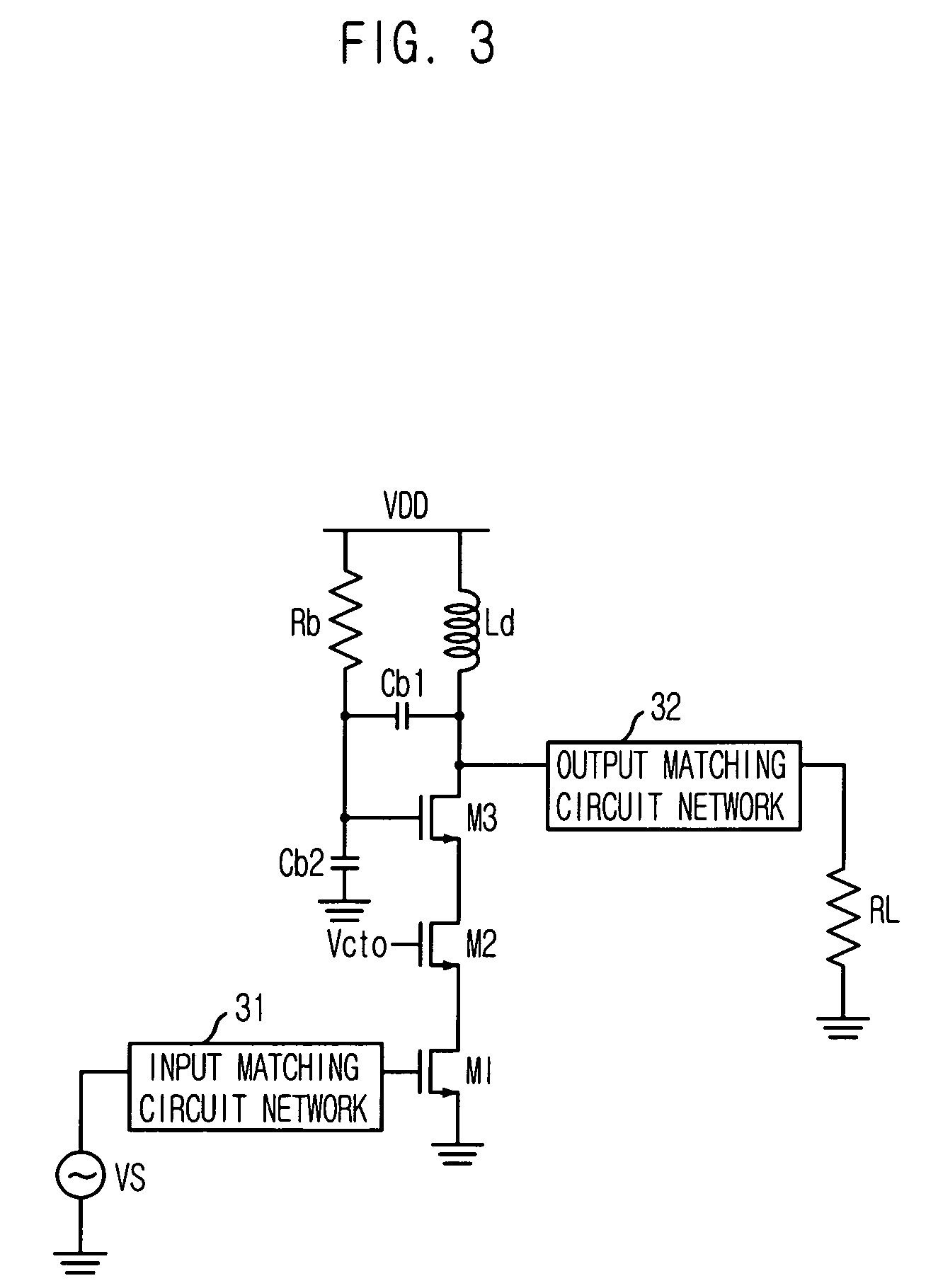
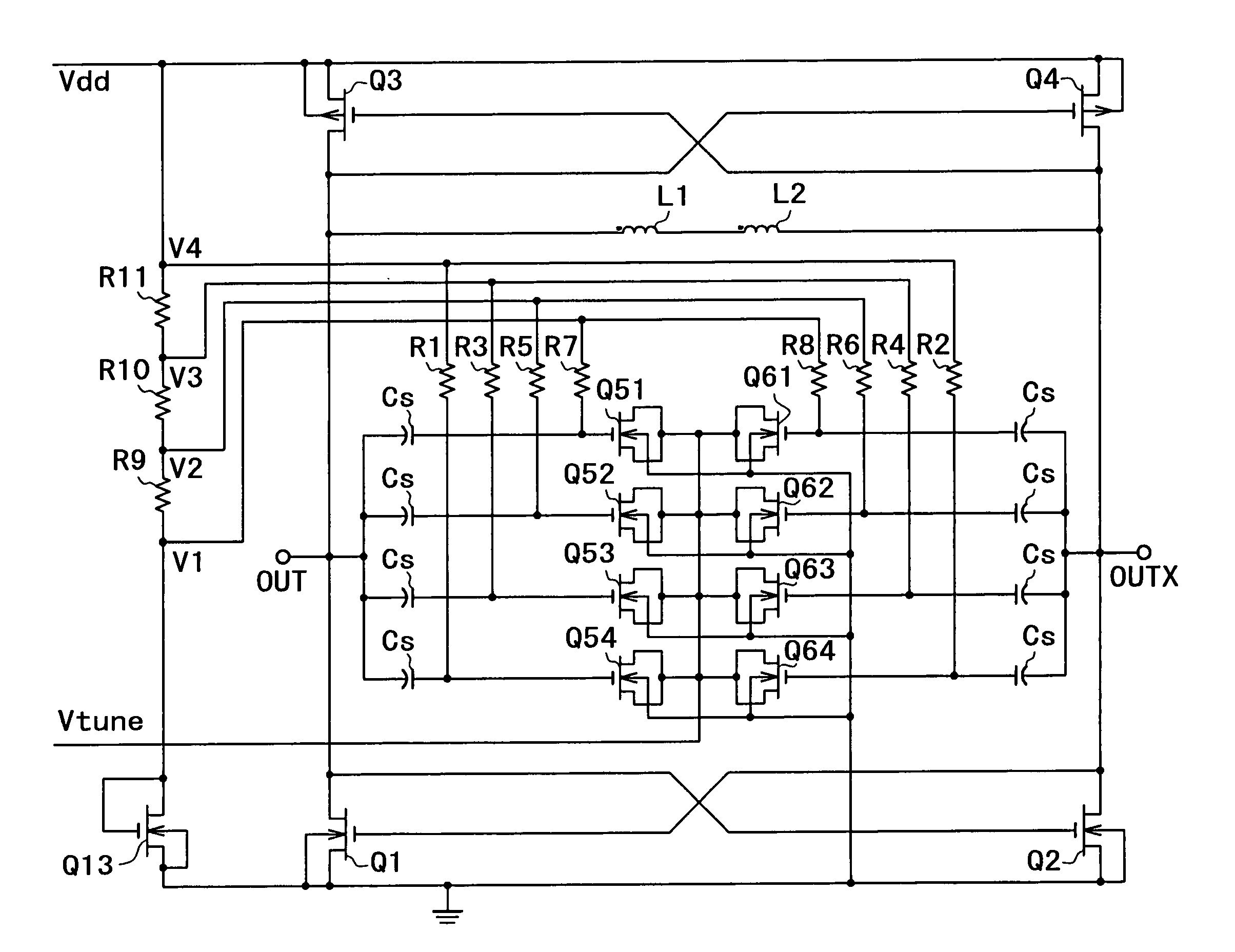
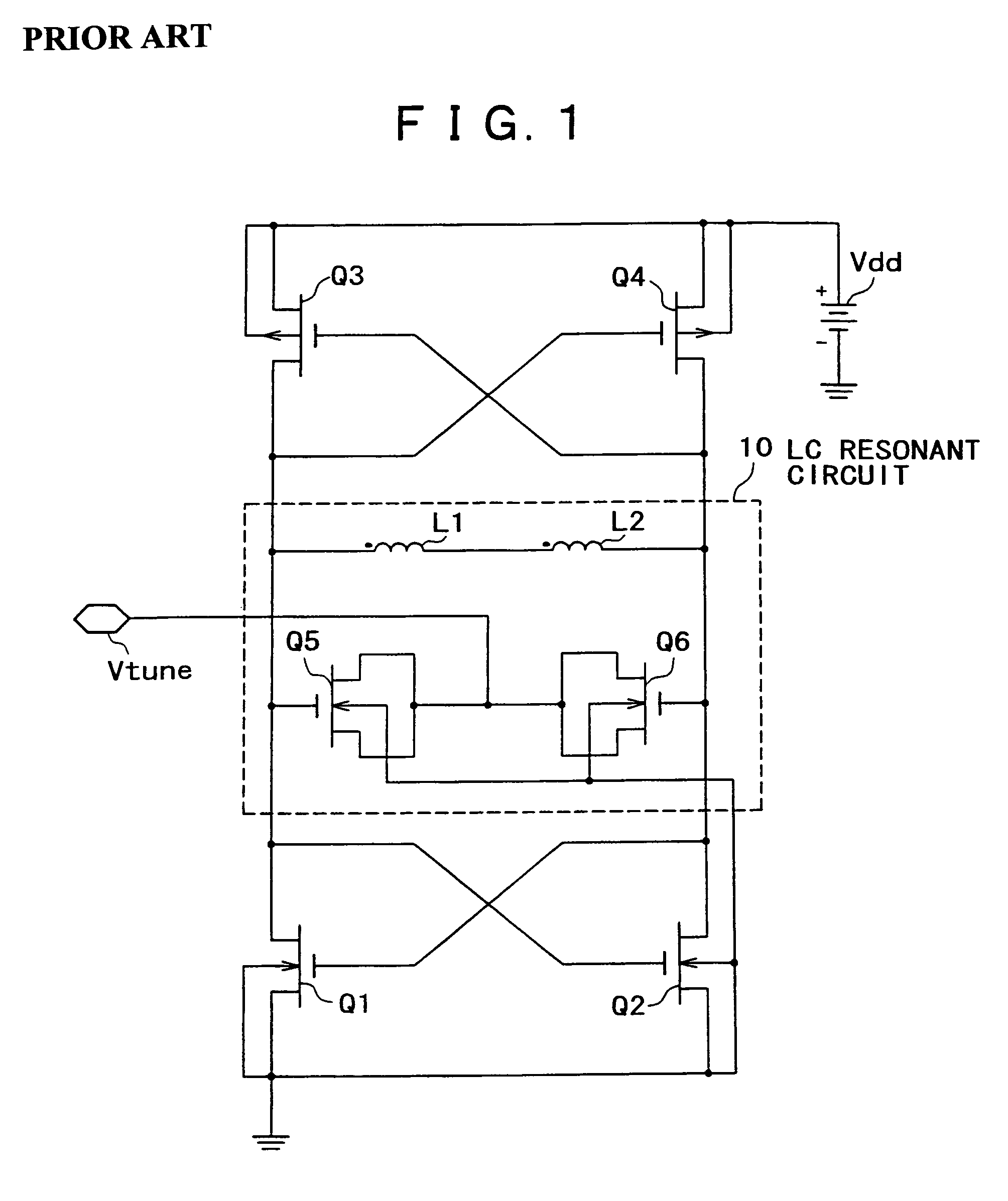
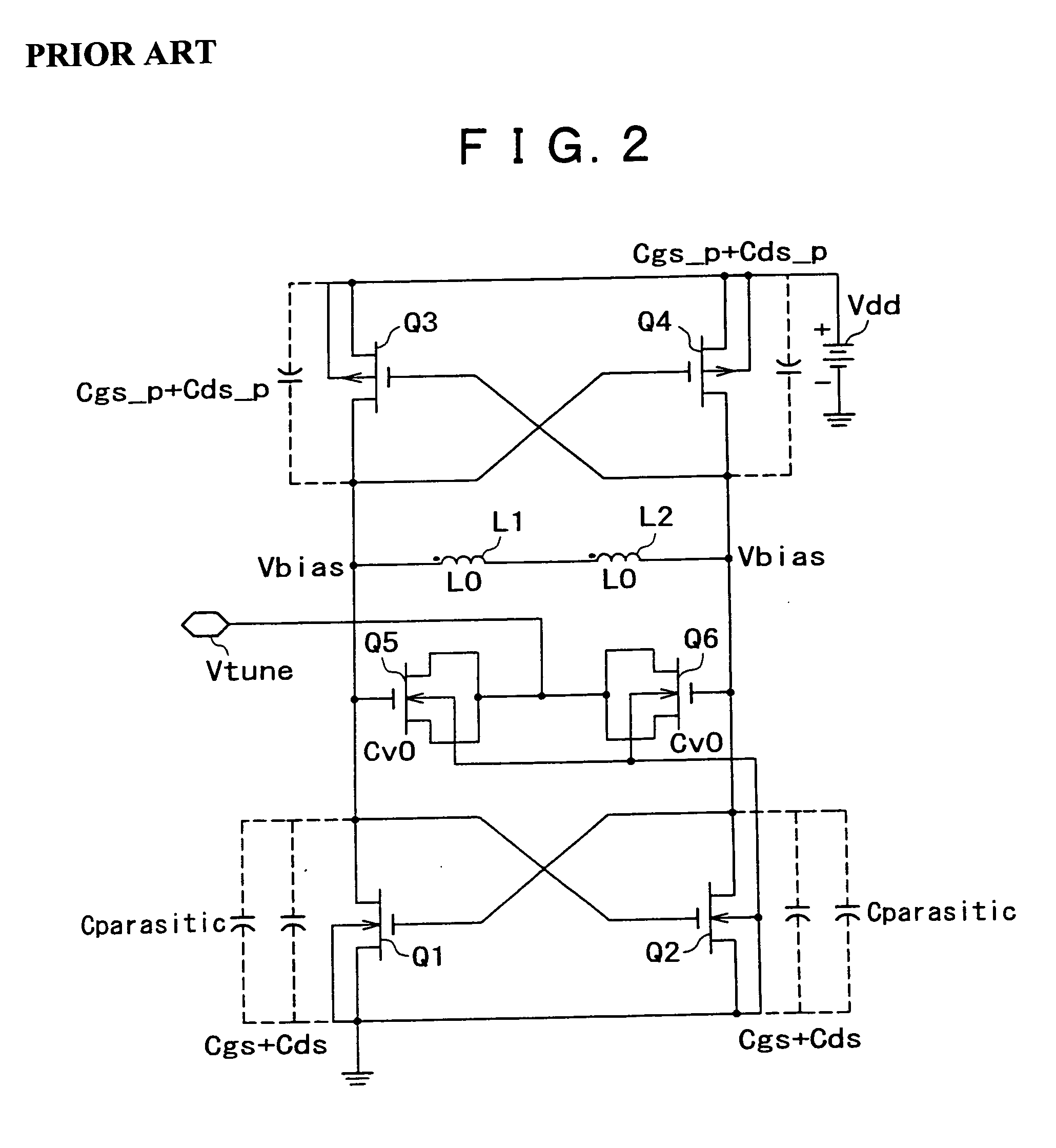
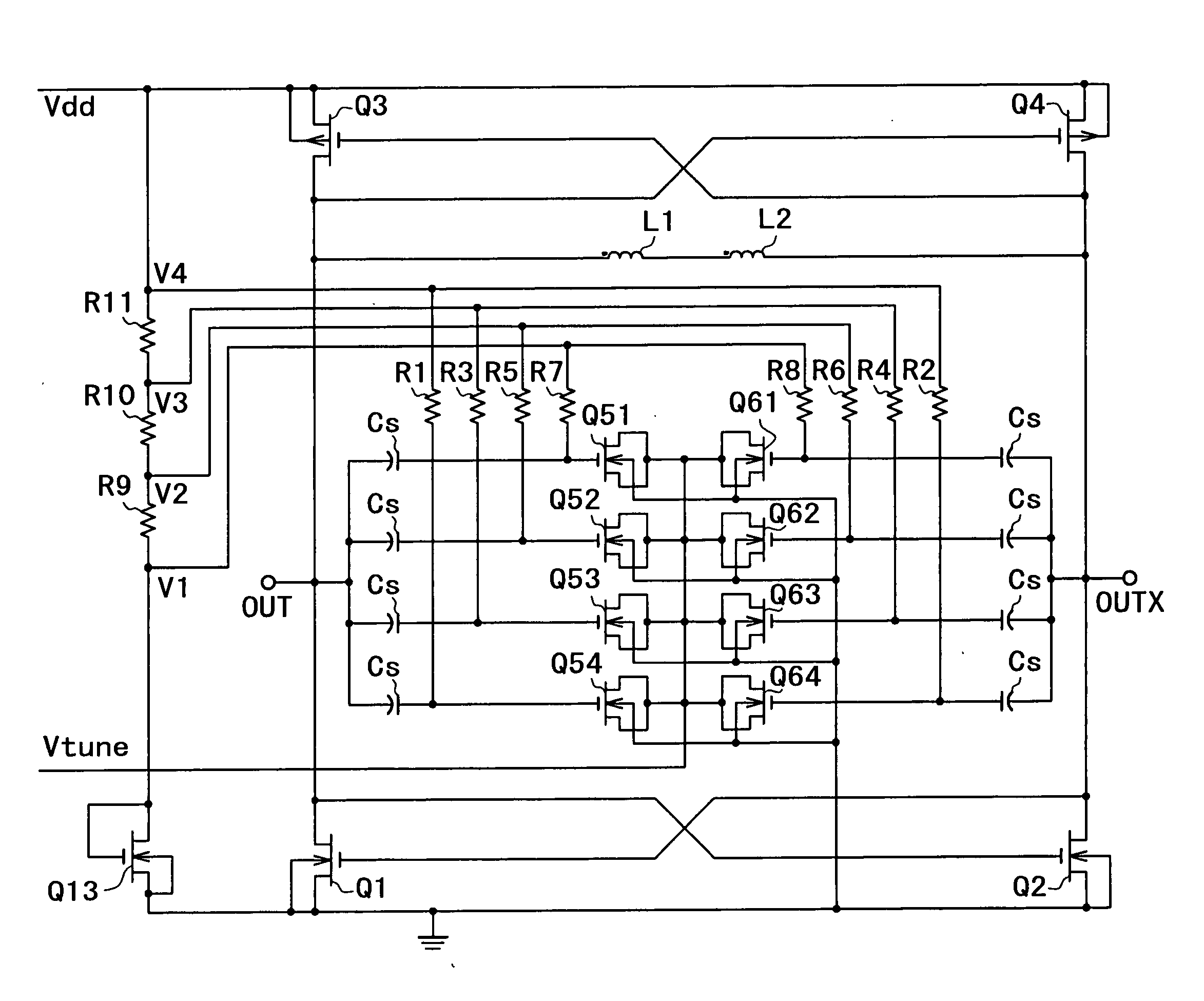
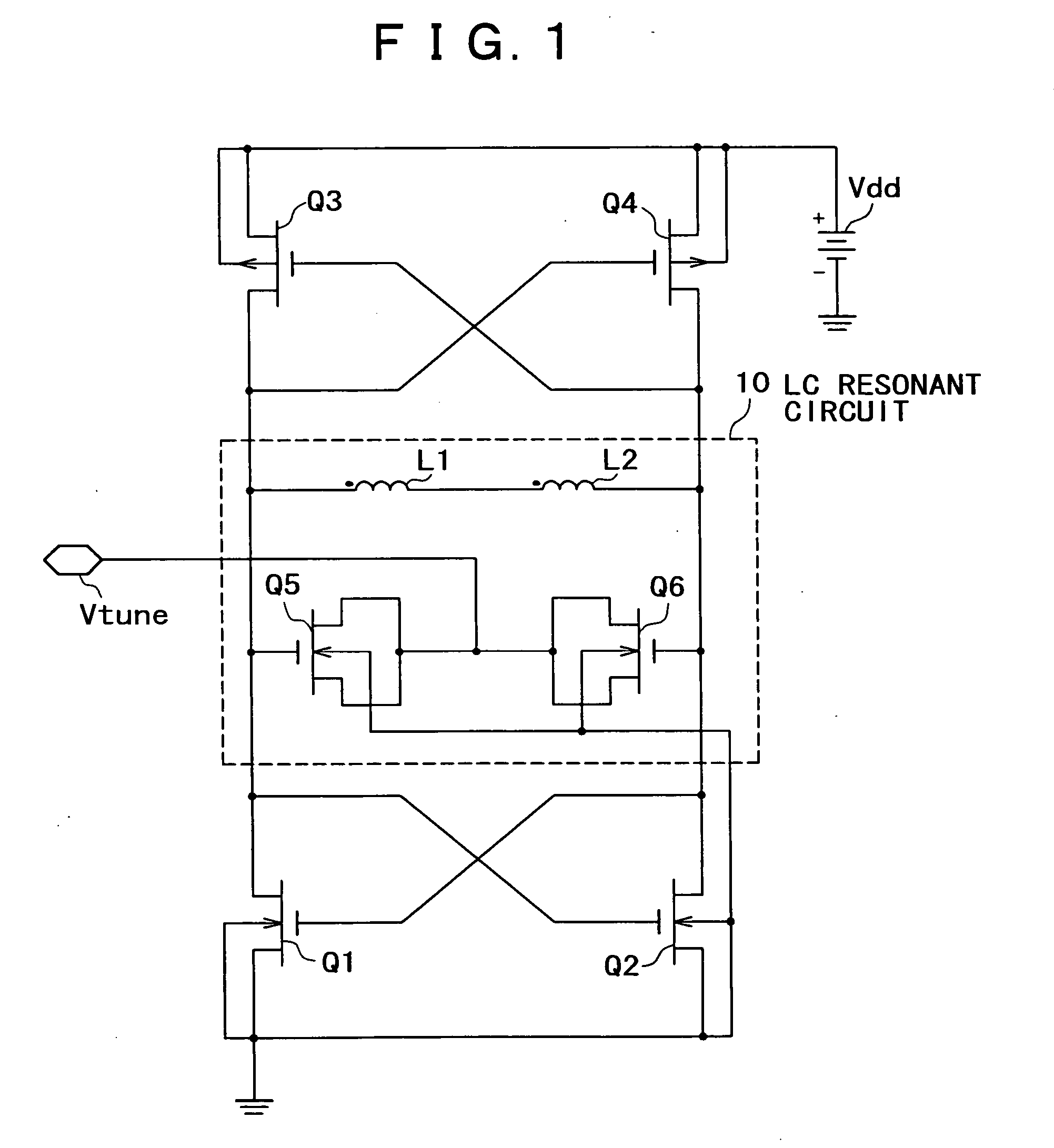
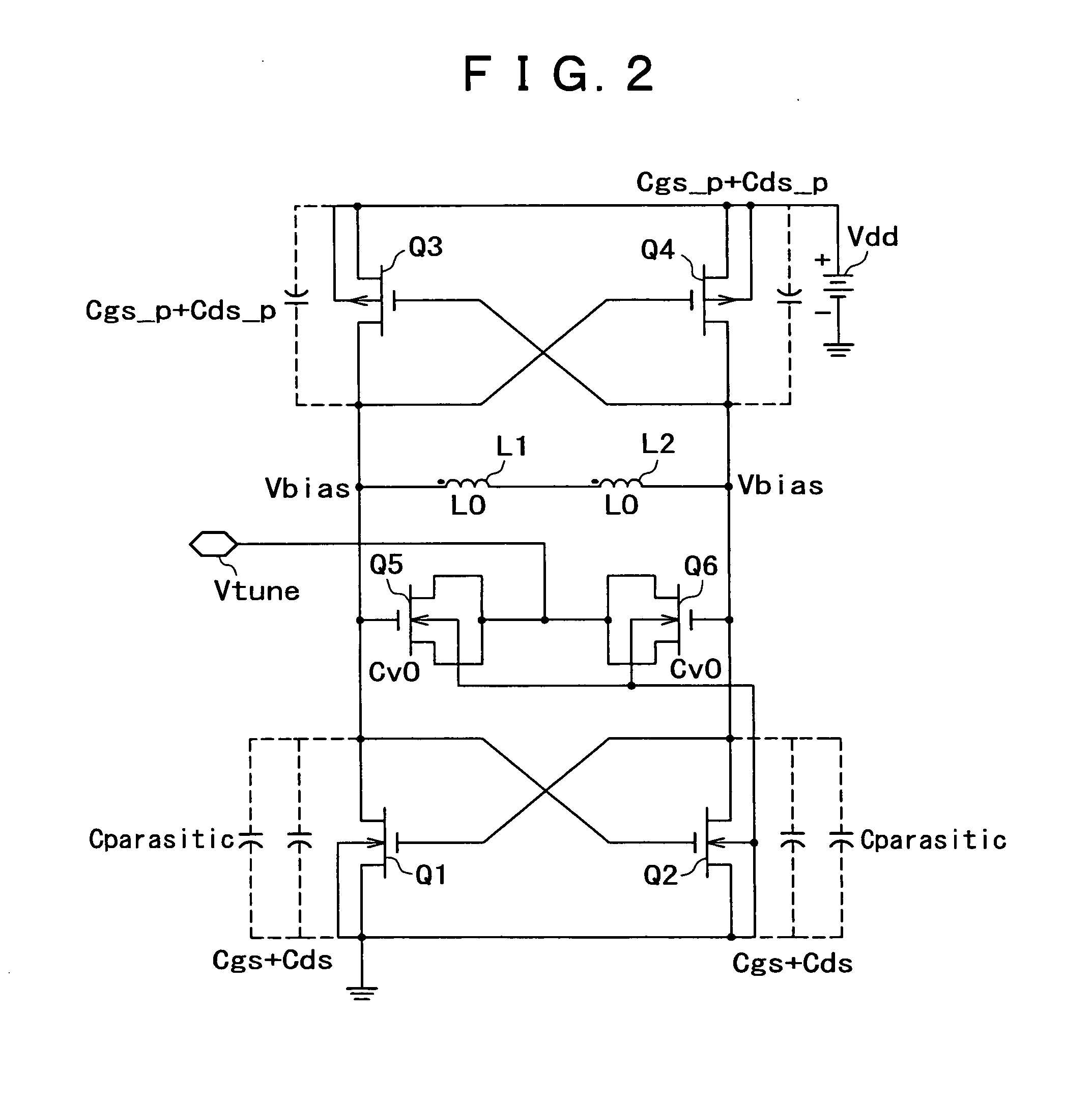
Resonant circuit and a voltage-controlled oscillator
InactiveUS7183870B2Improve phase noiseSimple compositionAngle modulation by variable impedenceAngle modulation detailsCapacitanceVoltage generator
A voltage-controlled oscillator comprising a resonant circuit and MOS transistors which constitute a negative resistance circuit of a differential structure. The resonant circuit consists of an inductance element and a MOS variable capacitance element connected in parallel therewith. The MOS variable capacitance element is divided into plural pairs connected in parallel with each other. A voltage division circuit generates staircase different-step DC bias voltages to be applied respectively to the gates of the plural divided MOS transistors. The divided MOS variable capacitance elements have a common terminal to which a common control voltage is applied. The resonant circuit is capable of reducing a load on the control voltage generator and improving the characteristics of the voltage-controlled oscillator.
Owner:SONY MOBILE COMM INC
Dual-element microstrip patch antenna for mitigating radio frequency interference
InactiveUS6930639B2High sensitivityLess sensitivitySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaHorizon
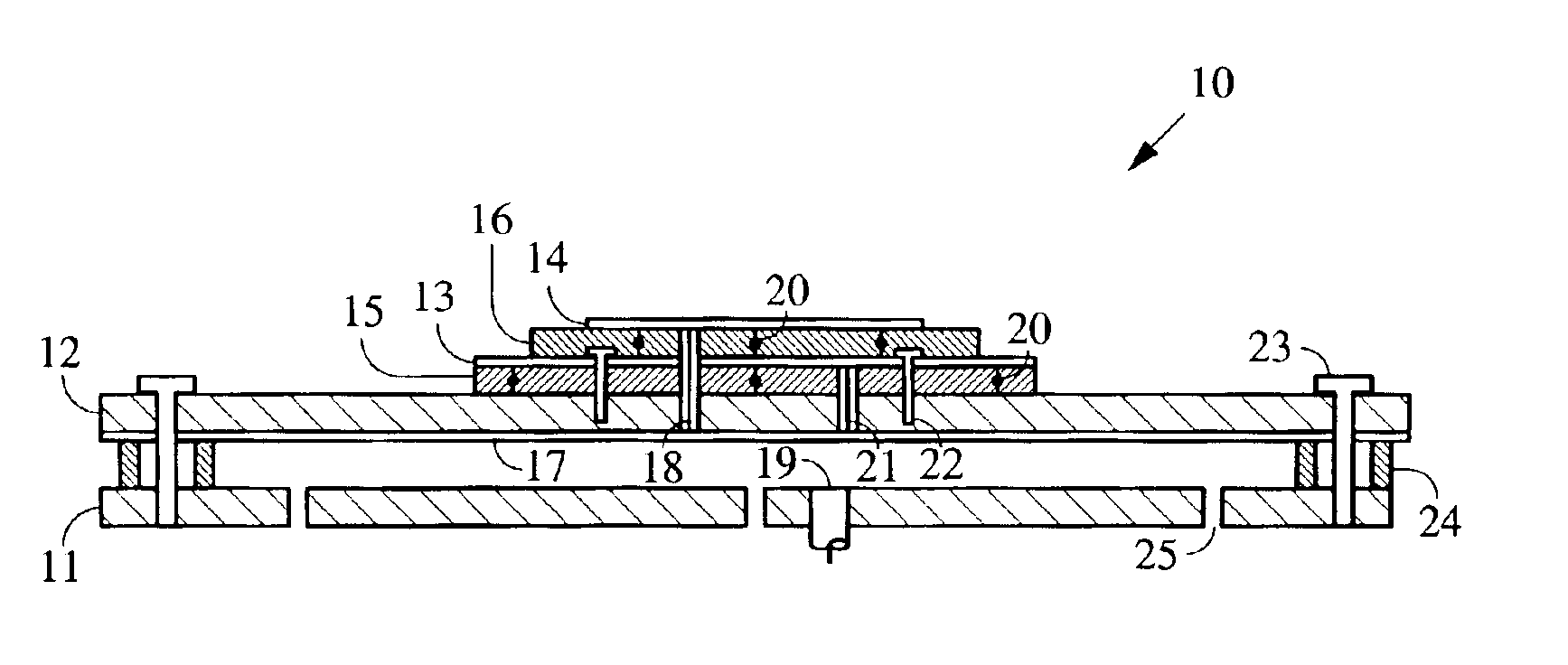
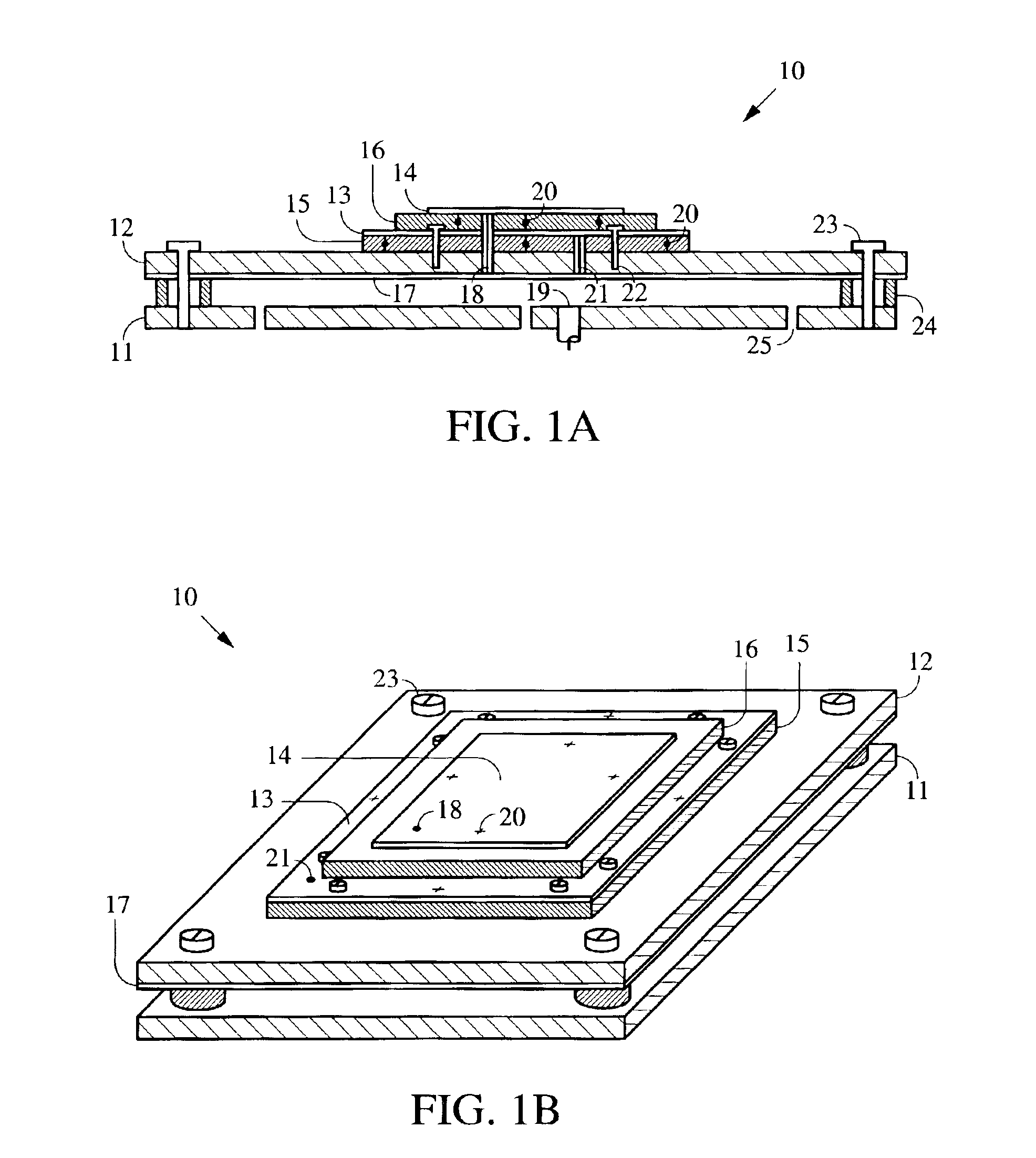
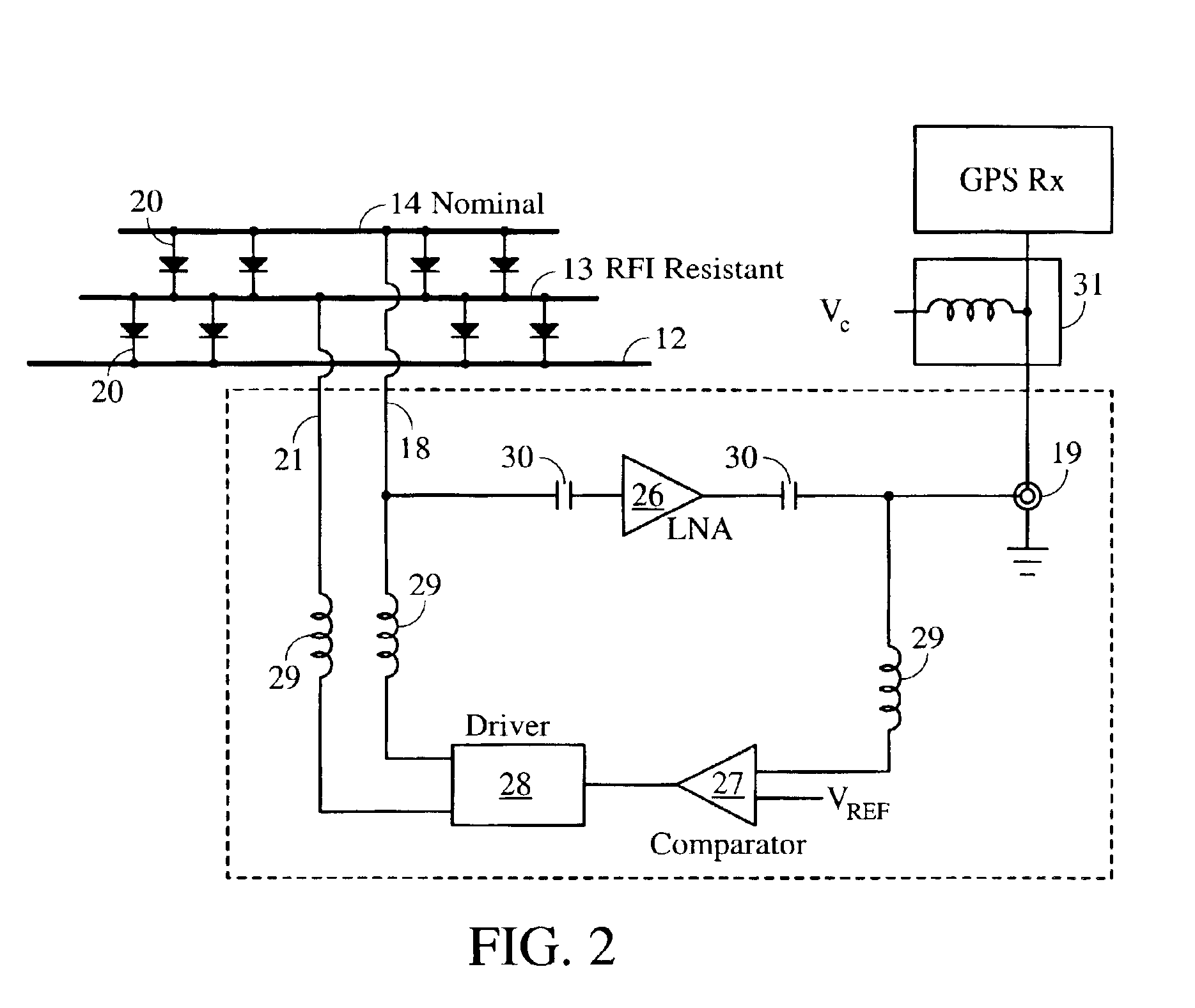
Method and apparatus for reducing radio frequency interference (RFI) using a dual-element patch antenna [10]. The antenna possesses two antenna elements [13, 14] having distinct radiation patterns. Either element may be independently selected using a DC bias voltage. Diodes [20] connected to the elements serve to disable one element when the other is selected. In one selected mode, a nominal radiation pattern provides a broad, hemispherical shaped sensitivity that is designed for acquiring and tracking all navigation satellites above the horizon. This nominal radiation pattern, however, is susceptible to interference that is present near or below the horizon. The second selectable radiation pattern of the dual-element antenna has comparatively higher gain toward zenith, and lower gain at and below the horizon to mitigate interference. This combination of features is packaged in a single antenna unit that can be a direct replacement for existing antennas. The dual-element antenna unit has a low vertical profile and is suitable for mounting on high-speed moving vehicles.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Resonant circuit and a voltage-controlled oscillator
InactiveUS20050030116A1Improve phase noiseSimple compositionAngle modulation by variable impedenceOscillations generatorsCapacitanceVoltage generator
A voltage-controlled oscillator comprising a resonant circuit and MOS transistors which constitute a negative resistance circuit of a differential structure. The resonant circuit consists of an inductance element and a MOS variable capacitance element connected in parallel therewith. The MOS variable capacitance element is divided into plural pairs connected in parallel with each other. A voltage division circuit generates staircase different-step DC bias voltages to be applied respectively to the gates of the plural divided MOS transistors. The divided MOS variable capacitance elements have a common terminal to which a common control voltage is applied. The resonant circuit is capable of reducing a load on the control voltage generator and improving the characteristics of the voltage-controlled oscillator.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM JAPAN INC
Tunable dual-band antenna using lc resonator
InactiveUS20100053007A1Easily incorporated into cell phoneEasily other wireless deviceSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsCapacitanceLc resonator
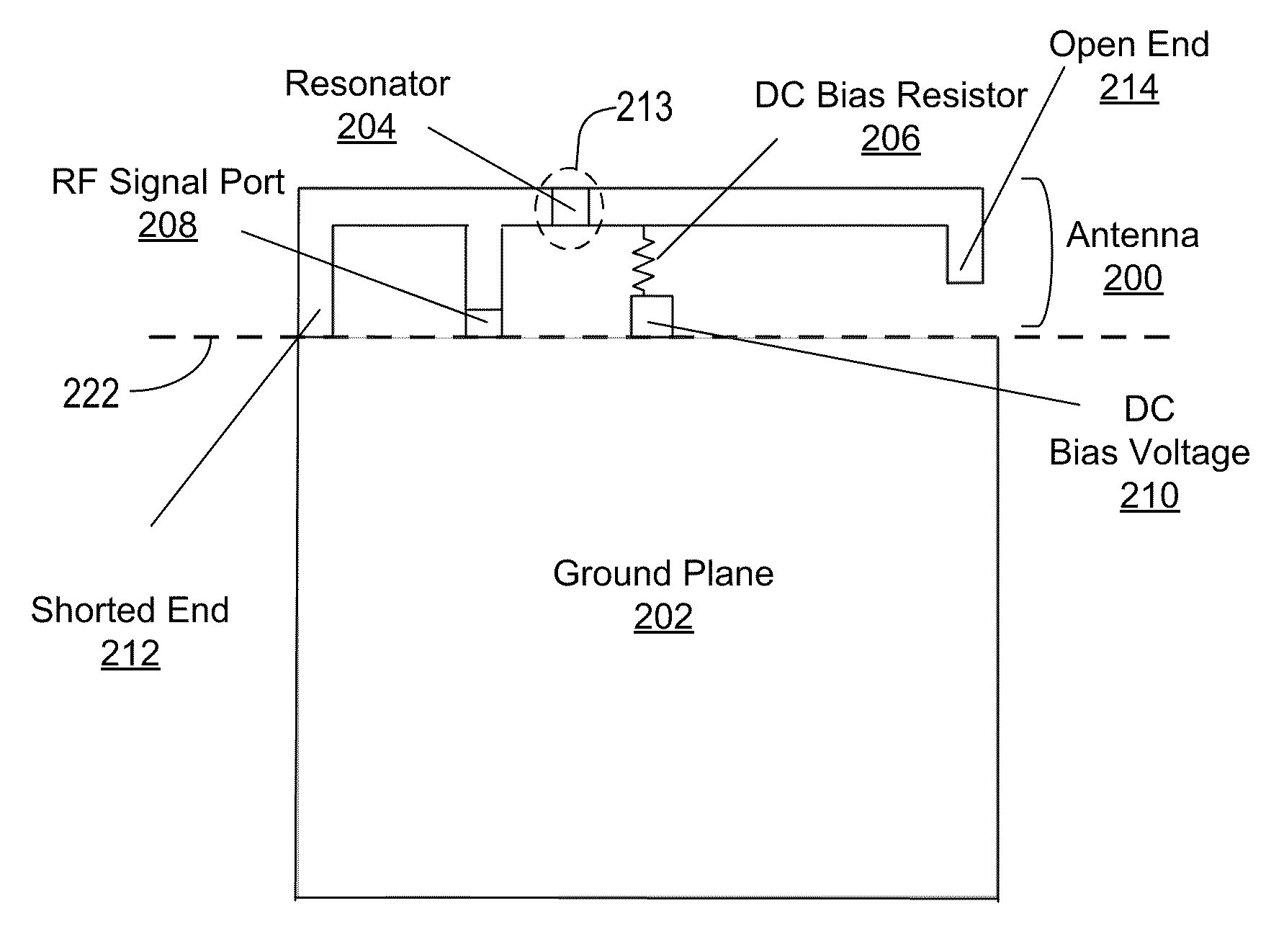
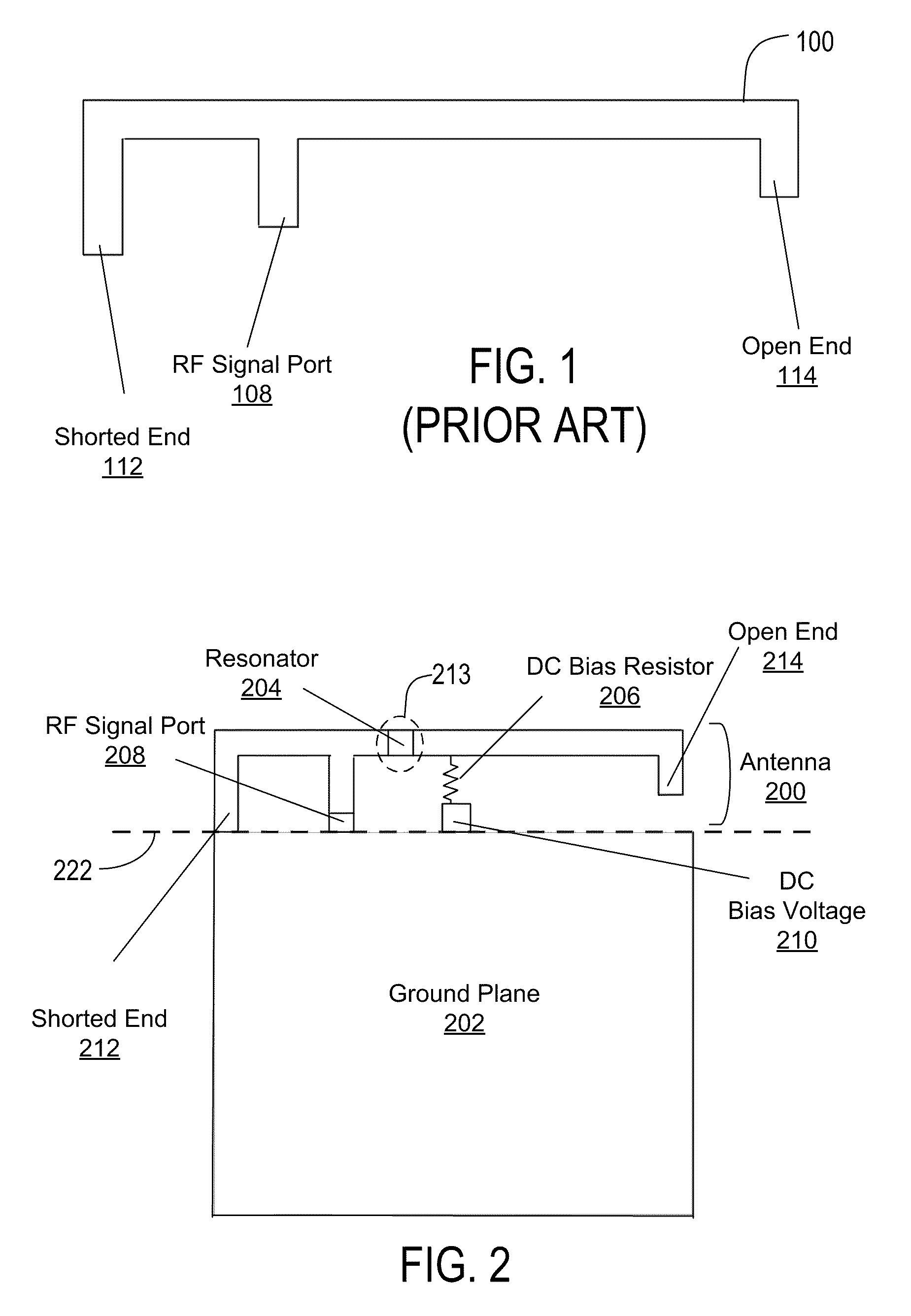
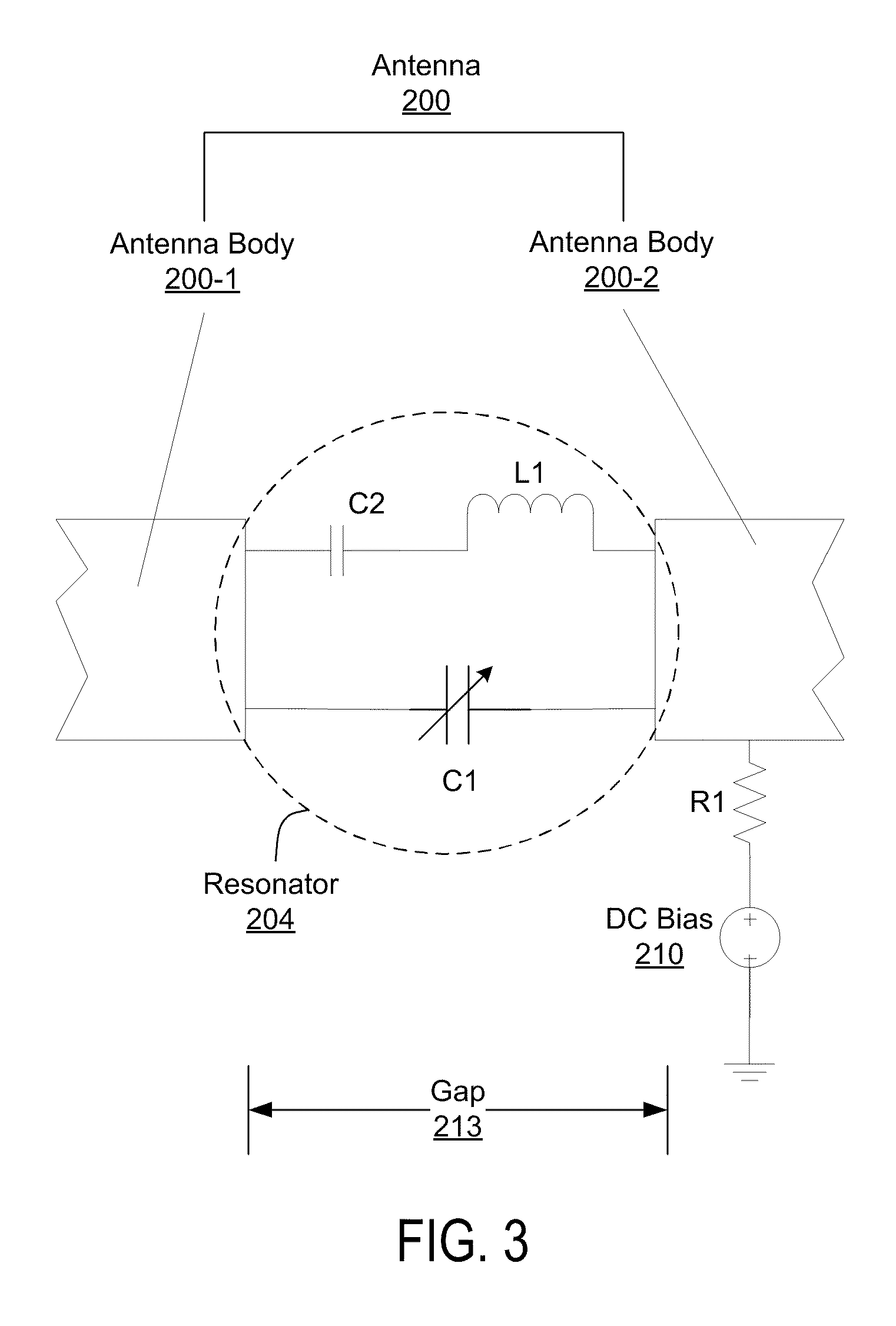
An Inverted-F antenna (IFA) includes a tunable parallel LC resonator physically inserted between two antenna bodies of the IFA structure. The LC resonator is comprised of a tunable capacitor C1 connected in parallel with a combination of a DC blocking capacitor C2 and an inductor L1 connected in series to each other. A DC bias voltage is applied to the tunable capacitor C1 through a DC bias resistor R1, in order to adjust the capacitance of the tunable capacitor C1. The IFA exhibits dual band characteristics, and its resonant frequencies and bandwidths may be turned by adjusting the capacitance of the tunable capacitor C1. The tunable capacitor C1 may be a BST capacitor.
Owner:AGILE RF
Shift register unit circuit, shift register, array substrate and liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20120293401A1Output shiftReduce the impactStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerLiquid-crystal display
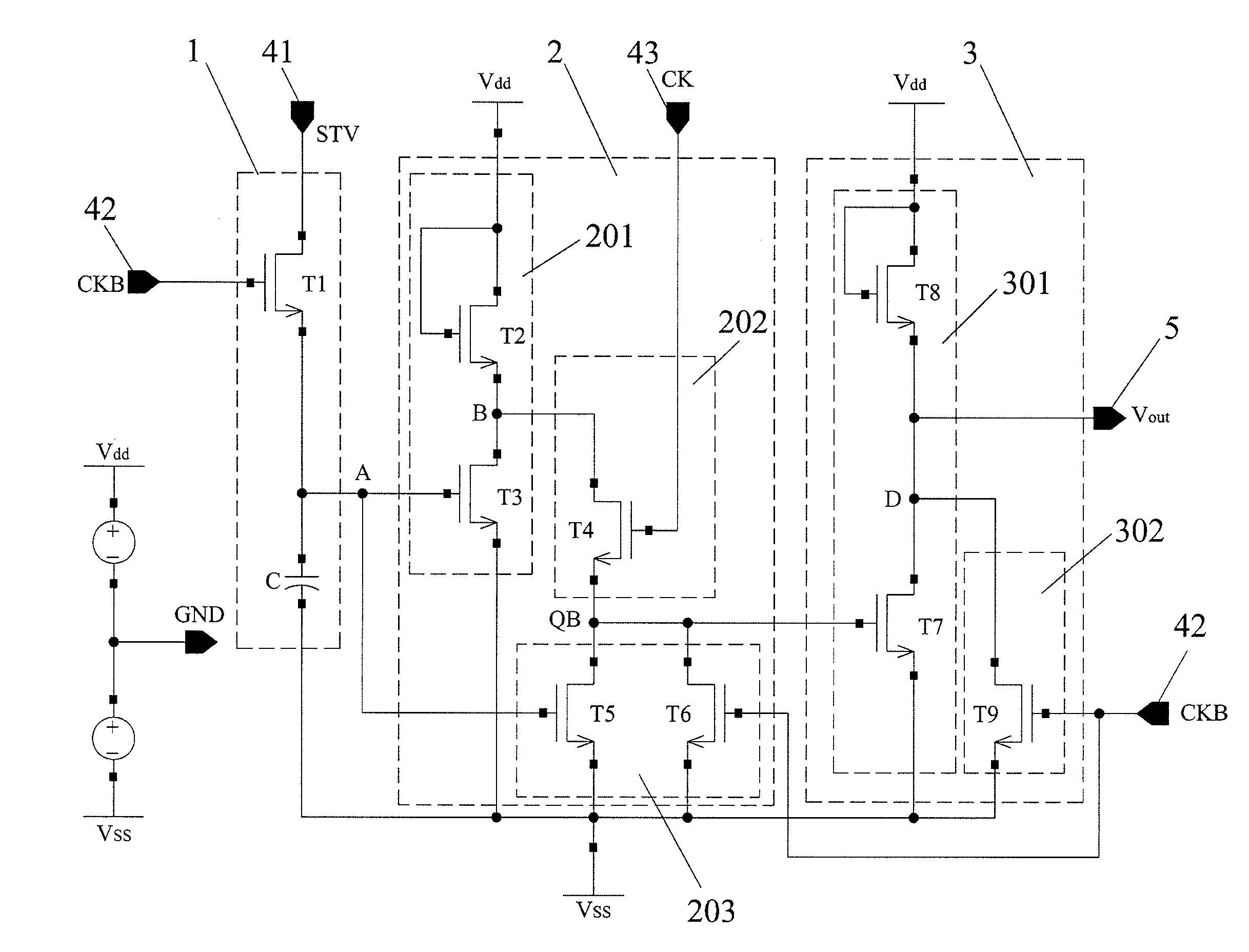
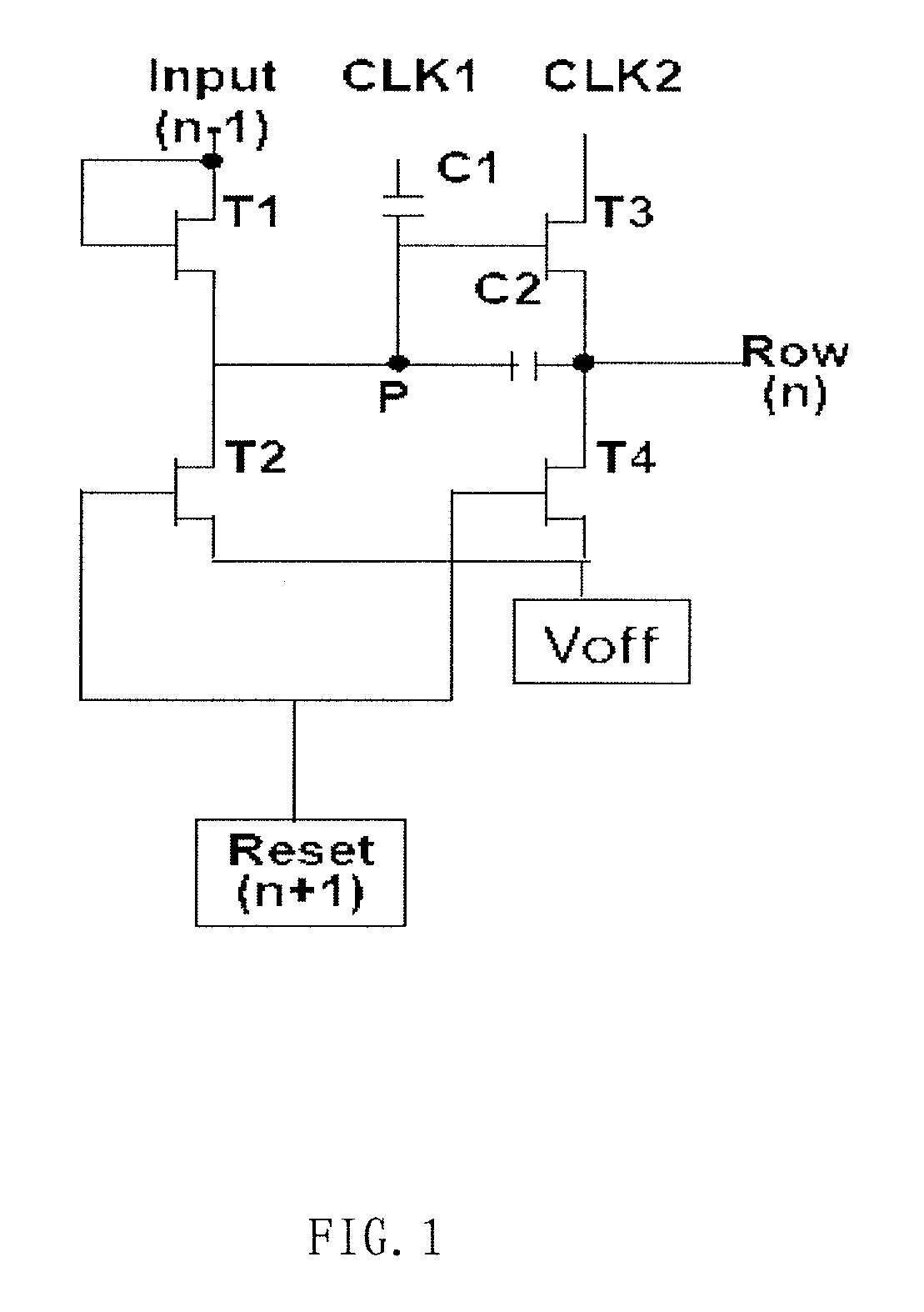
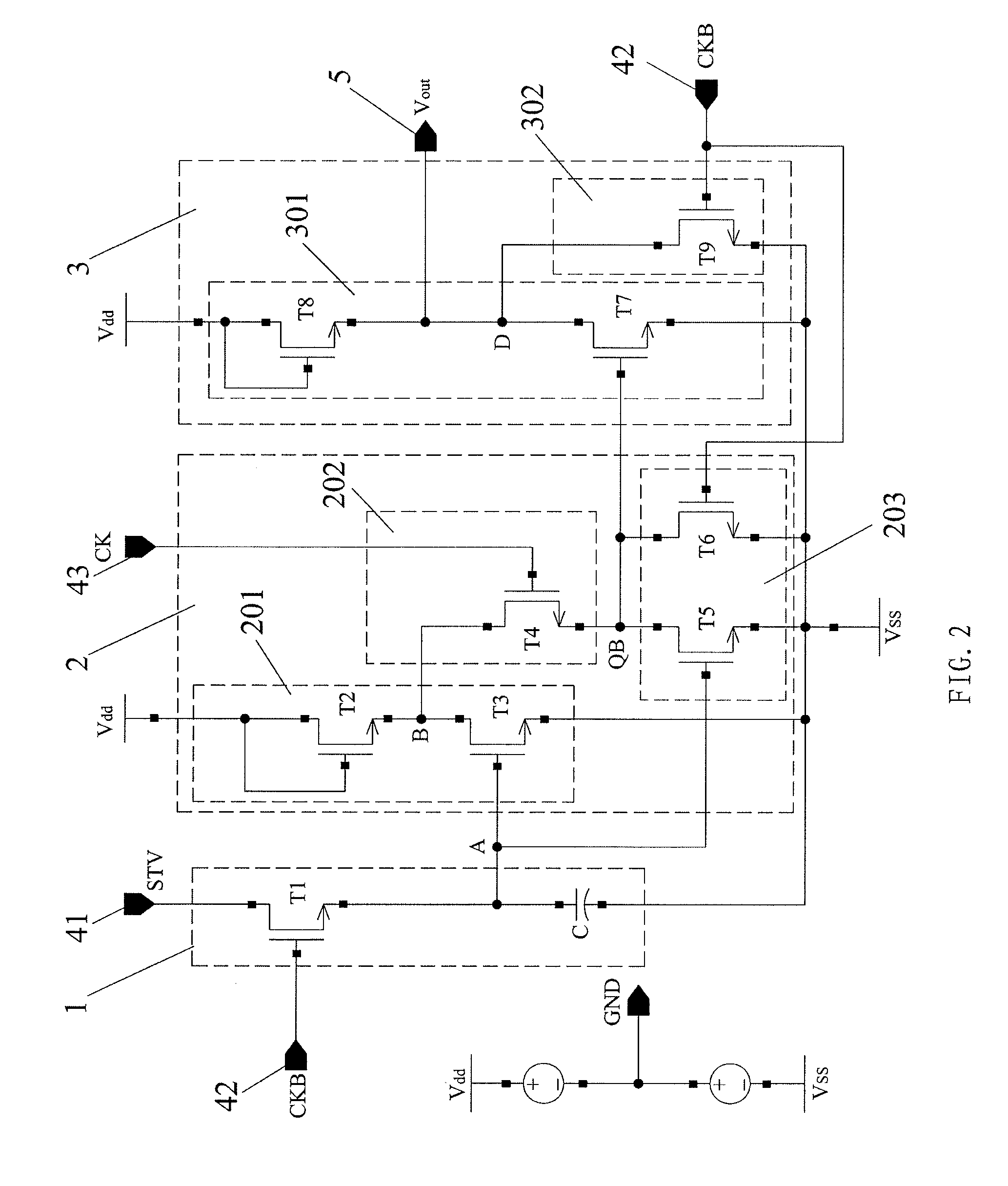
Embodiments of the disclosed technical solution provides a shift register unit circuit which operates based on two clock signals and comprises input terminals, a pre-charging circuit, a first level pulling-down circuit, a second level pulling-down circuit and a scan signal output terminal. Embodiments of the disclosed technical solution also provides a shift register having at least two shift register unit circuits connected in cascade, and further provides a liquid crystal display array substrate and a liquid crystal display. Embodiments of the disclosed technical solution settles problems that a threshold voltage of the pulling-down TFT would drift under a direct current bias voltage and a output is unstable due to a clock hopping, increases a reliability of the circuit and reduces power consumption.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
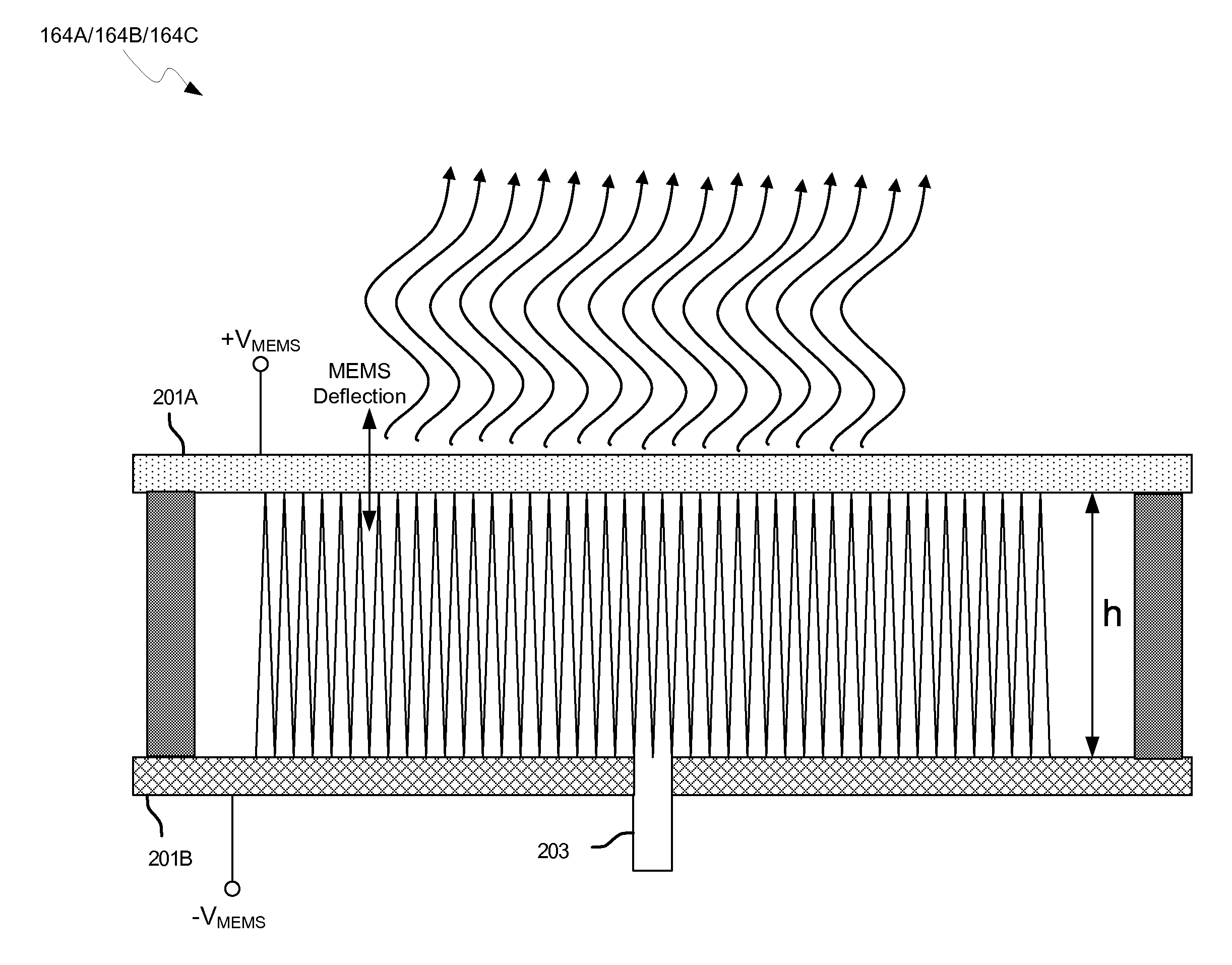
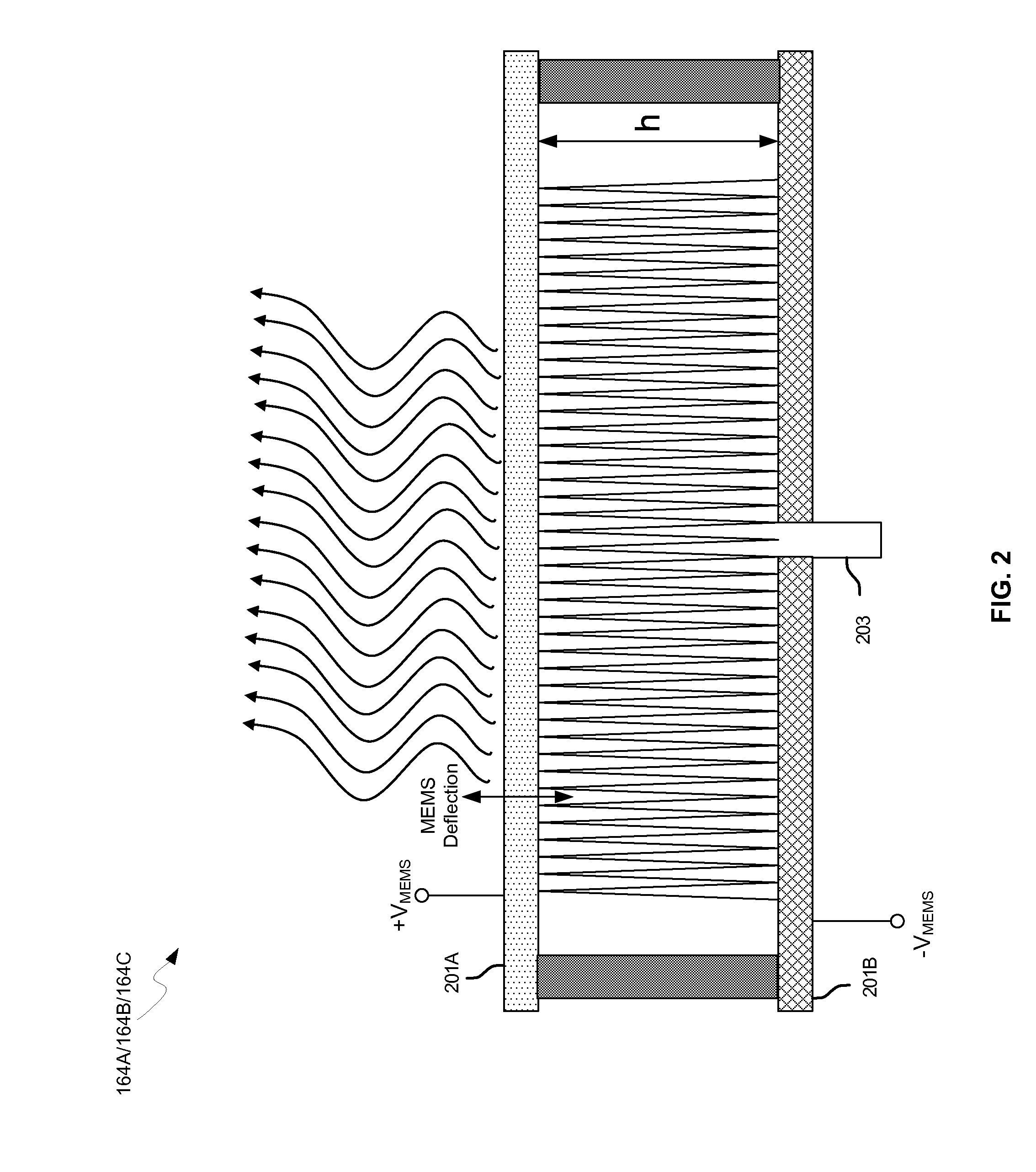
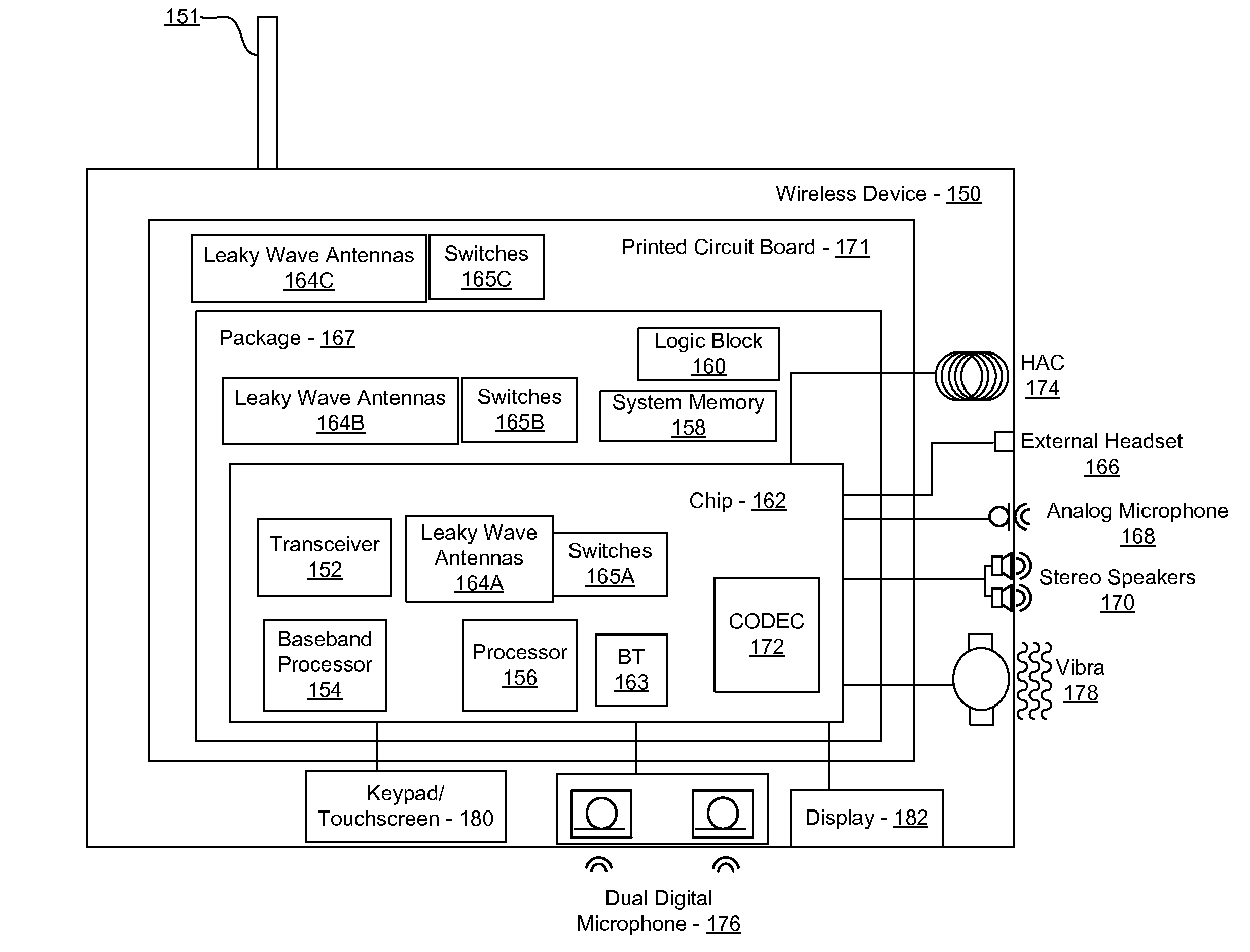
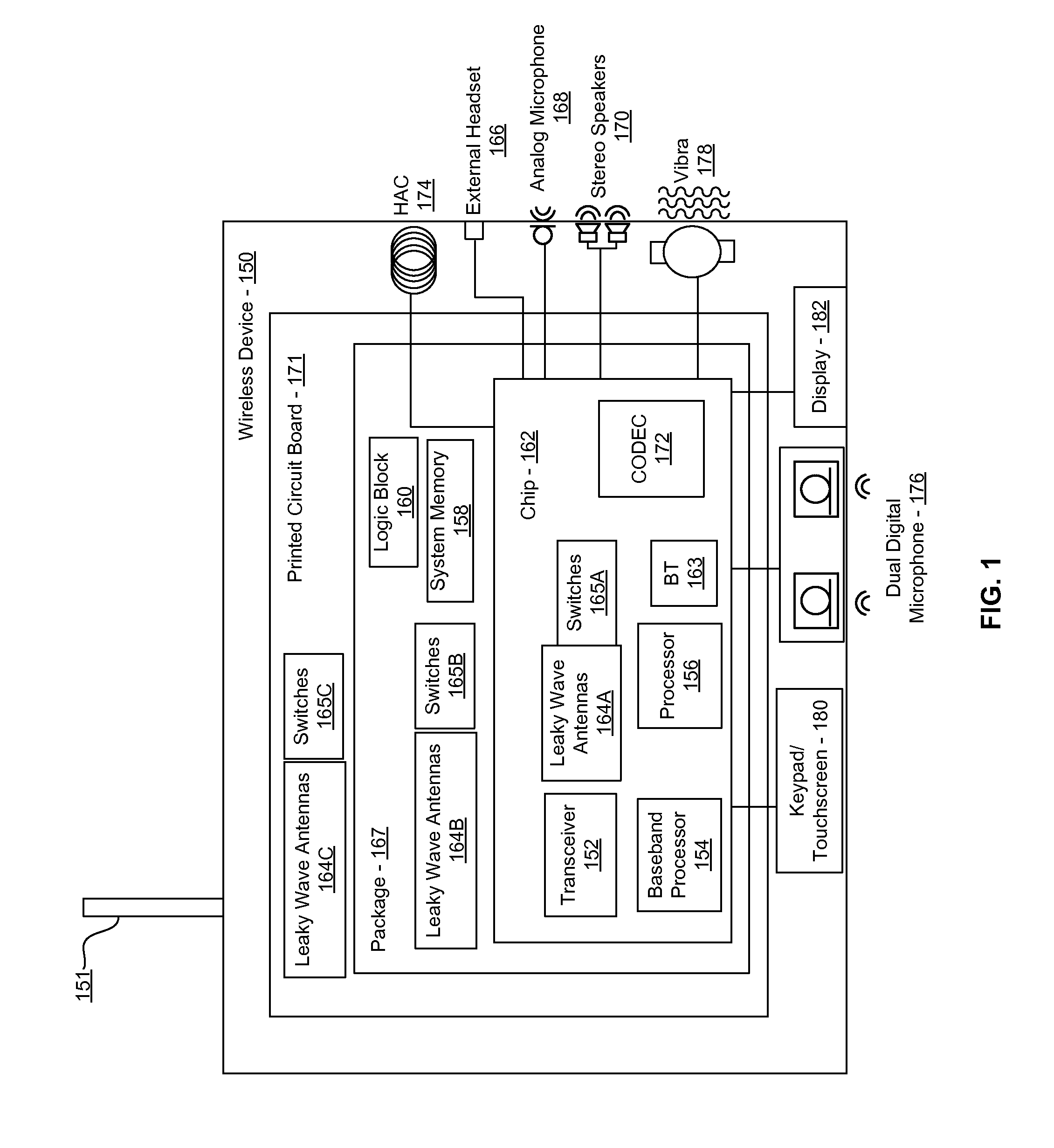
Method and system for a 60 ghz leaky wave high gain antenna
Methods and systems for a 60 GHz leaky wave high gain antenna are disclosed and may include communicating RF signals using one or more or more leaky wave antennas (LWAs) in a wireless device. The LWAs may be integrated in metal traces on a chip, a package, and / or a printed circuit board (PCB). The metal traces may supply voltage signals to one or more circuits on the chip, package, and / or PCB. The voltage signals may include DC bias voltages, and / or signals at a frequency that is lower than a resonant frequency of the LWAs. The LWAs may include microstrip or coplanar lines where a cavity height of the LWAs is dependent on a spacing between the lines. An angle of the wireless signals with a surface of the chip, package, and / or PCB may be dynamically configured. The LWAs may be configured via switches in the chip, package, and / or PCB.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Ultrasonic transducer, ultrasonic speaker, and method of controlling the driving of ultrasonic transducer
InactiveUS20050281419A1Decrease audible componentImprove directivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical vibrations separationUltrasonic sensorAlternating current
An electrostatic ultrasonic transducer includes a diaphragm having a conducting layer and a pair of first and second fixed electrodes opposed to the corresponding surfaces of the diaphragm, the pair of fixed electrodes having a plurality of through holes in corresponding positions, wherein a DC bias voltage is applied to the conducting layer of the diaphragm and an alternating current signal is applied between the first and second fixed electrodes to generate an ultrasonic wave. Part of the pair of fixed electrodes includes s driving fixed electrode for driving the ultrasonic transducer, and the other part includes a detecting fixed electrode for detecting the amplitude of the diaphragm. The ultrasonic transducer includes a control unit that controls the vibration of the diaphragm so that the amplitude is proportional to the input signal based on the amplitude of the diaphragm detected by the detecting fixed electrode.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method and system for communicating via leaky wave antennas within a flip-chip bonded structure
Methods and systems for communicating via leaky wave antennas (LWAs) within a flip-chip bonded structure are disclosed and may include communicating RF signals in a wireless device including one or more LWAs between a plurality of support structures, the structures being coupled via flip-chip bonding. Low-frequency signals may be communicated via flip-chip bonding contacts. The RF signals may be communicated perpendicular to a surface and / or at a desired angle from the surface of the structures, which may include at least one of: an integrated circuit, an integrated circuit package, and a printed circuit board. The LWAs may include microstrip and / or coplanar waveguides where a cavity height of the LWAs may be configured by controlling spacing between conductive lines in the waveguides. The low-frequency signals may include DC bias voltages. The RF signals may be communicated from a single LWA to a plurality of LWAs.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
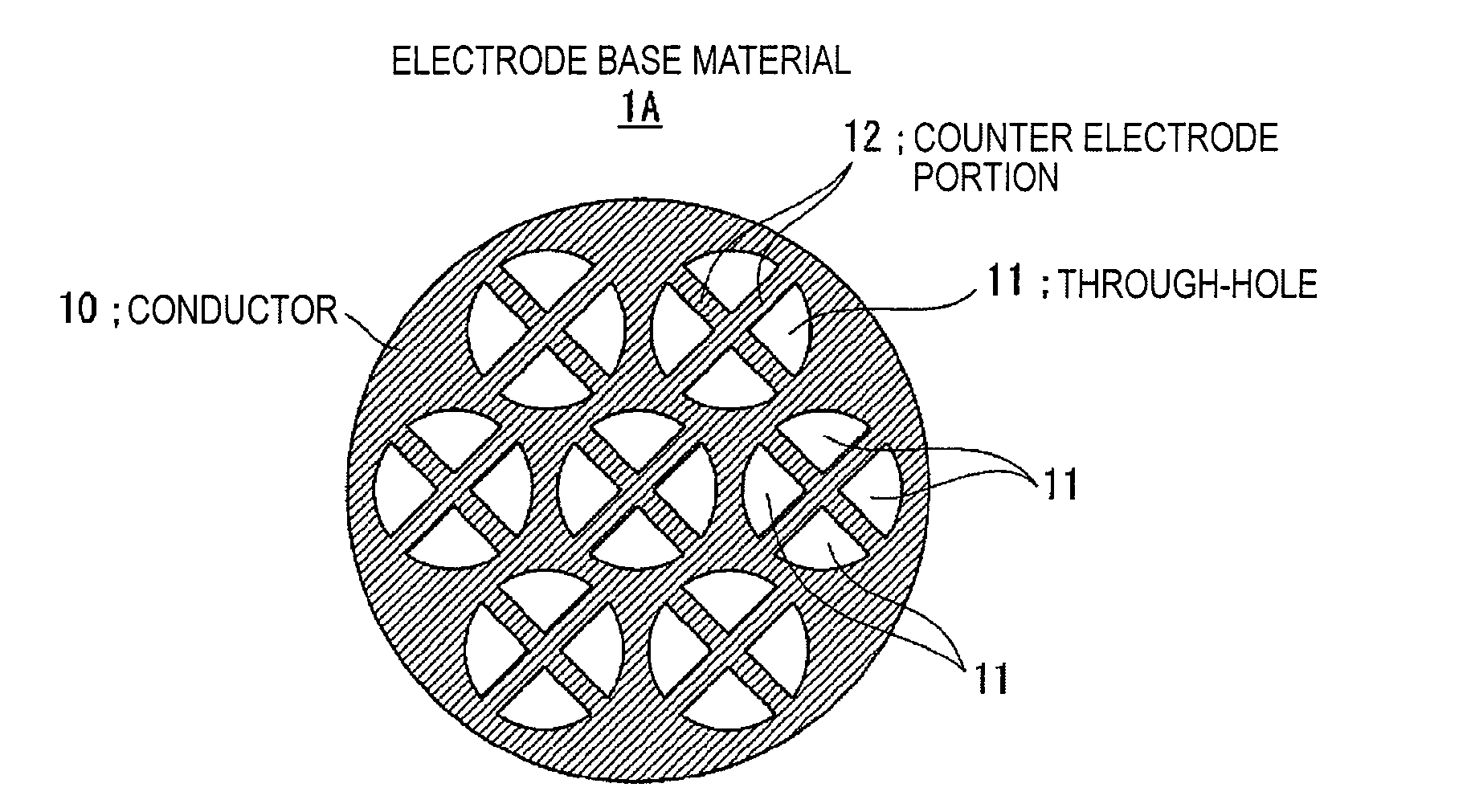
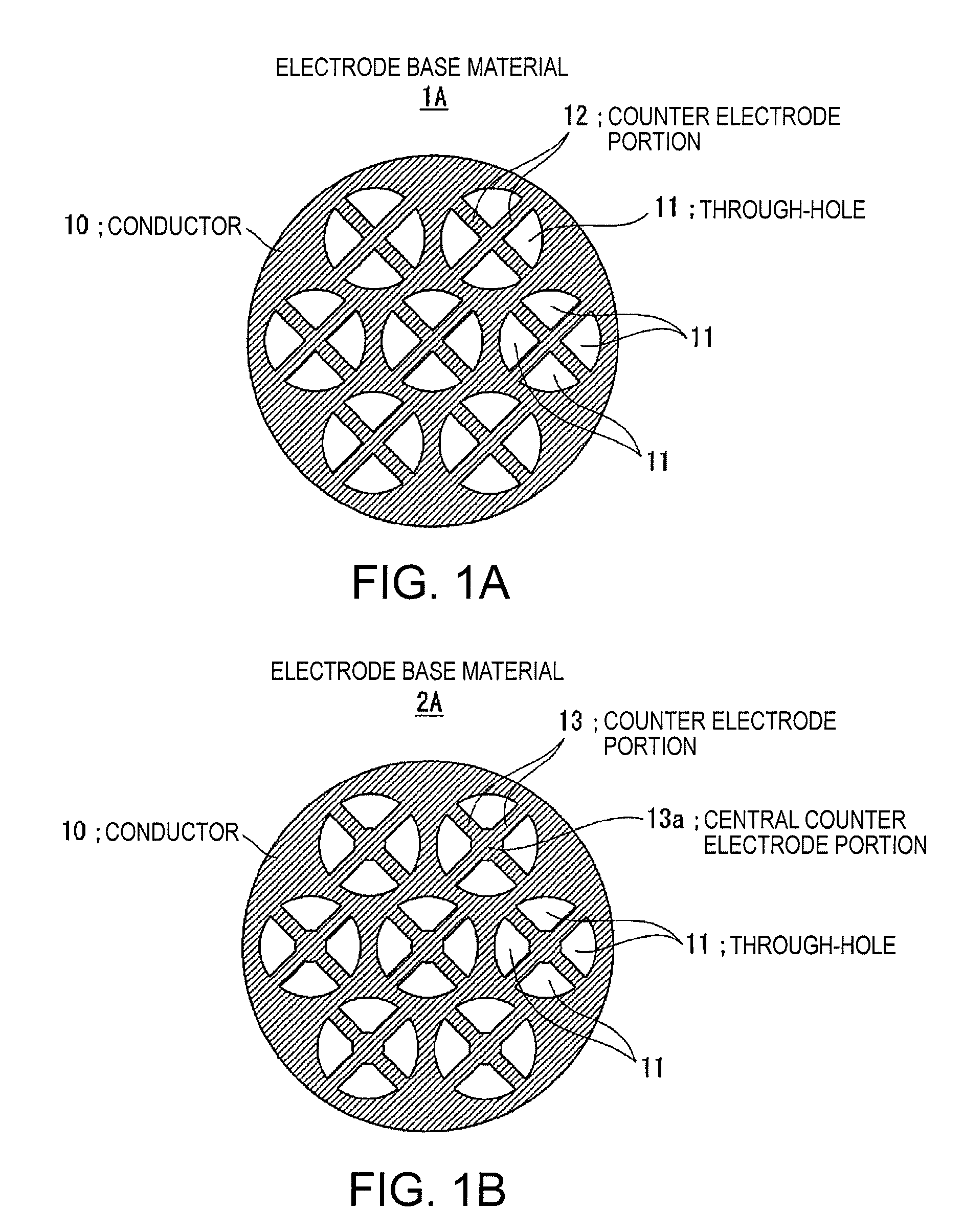
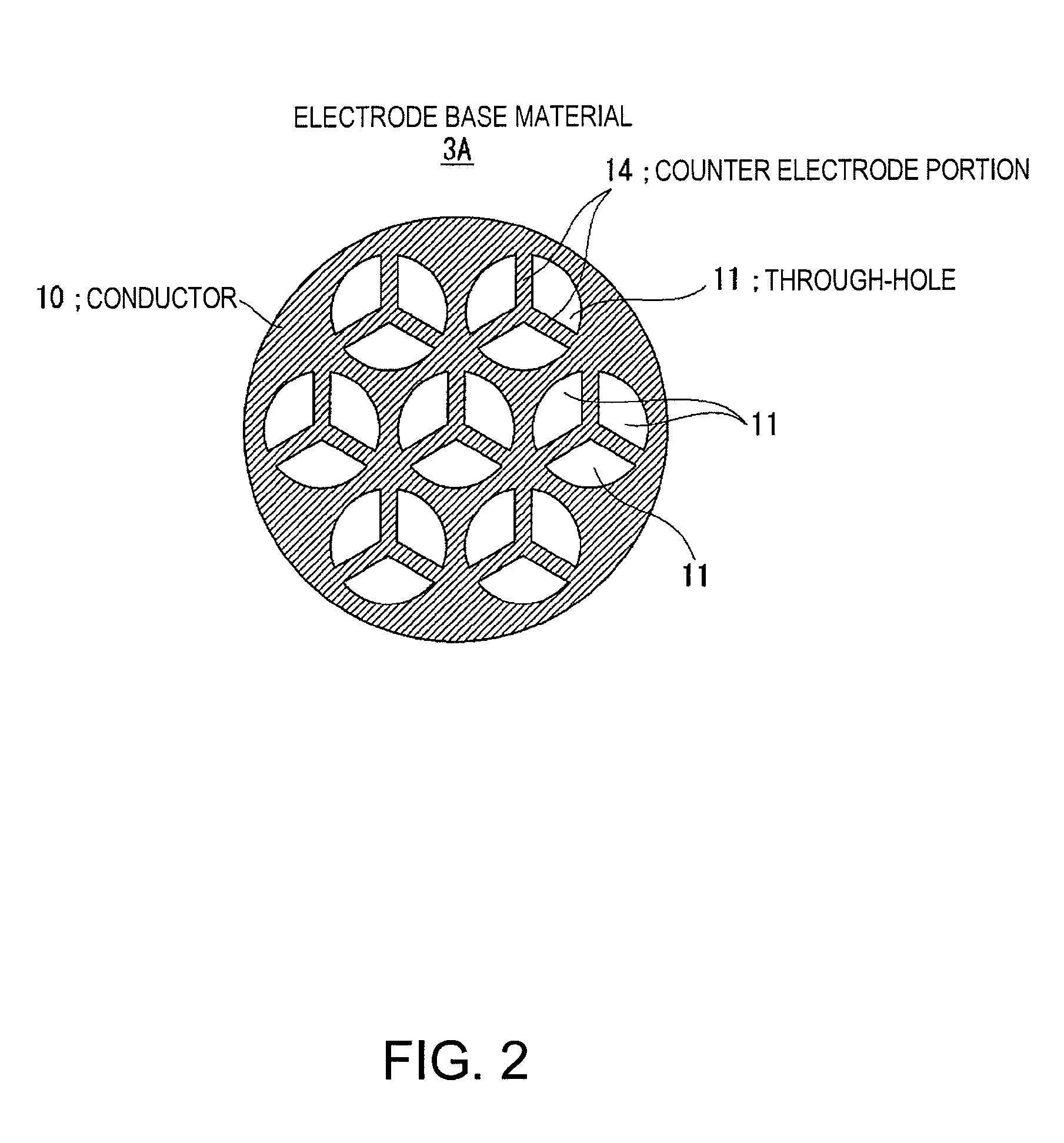
Electrostatic ultrasonic transducer, method of manufacturing electrostatic ultrasonic transducer, ultrasonic speaker, method of reproducing sound signal, and super-directivity sound system, and display device
InactiveUS20070195976A1Increase the output sound pressureEfficiently displacedElectrostatic transducersTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsVibrating membraneSignal wave
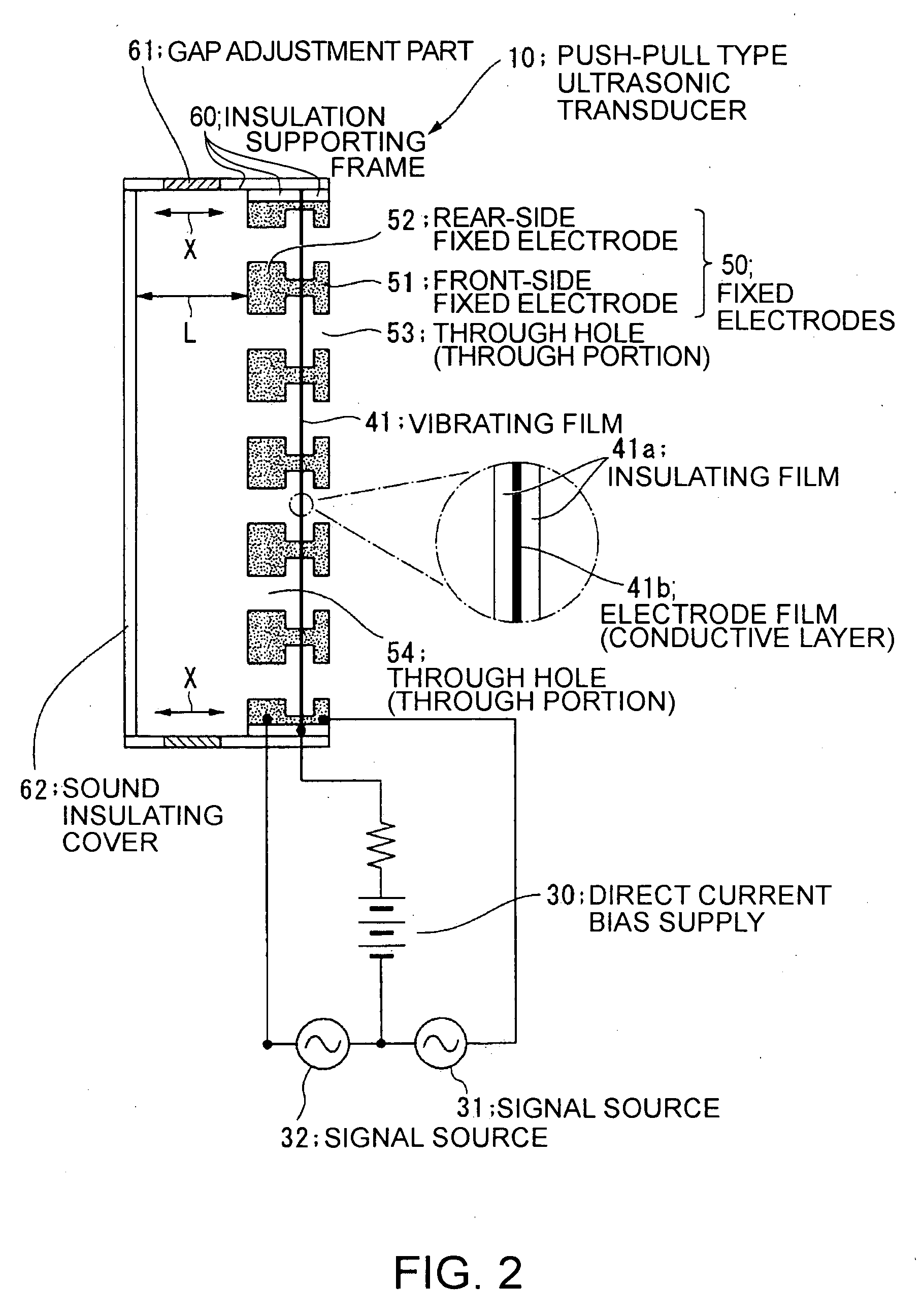
An electrostatic ultrasonic transducer includes a first electrode that has through-holes, a second electrode that has through-holes, and a vibrating membrane that is disposed such that the through-holes of the first electrode and the through-holes of the second electrode form a pair, interposed between a pair of electrodes composed of the first electrode and the second electrode, and having a conductive layer applied with a direct current bias voltage. The first electrode and the second electrode each have counter electrode portions that are formed in the through-holes to face the vibrating membrane, and a modulated wave, which is obtained by modulating a carrier wave in an ultrasonic frequency band with a signal wave in an audible frequency band, is applied between the pair of electrodes.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
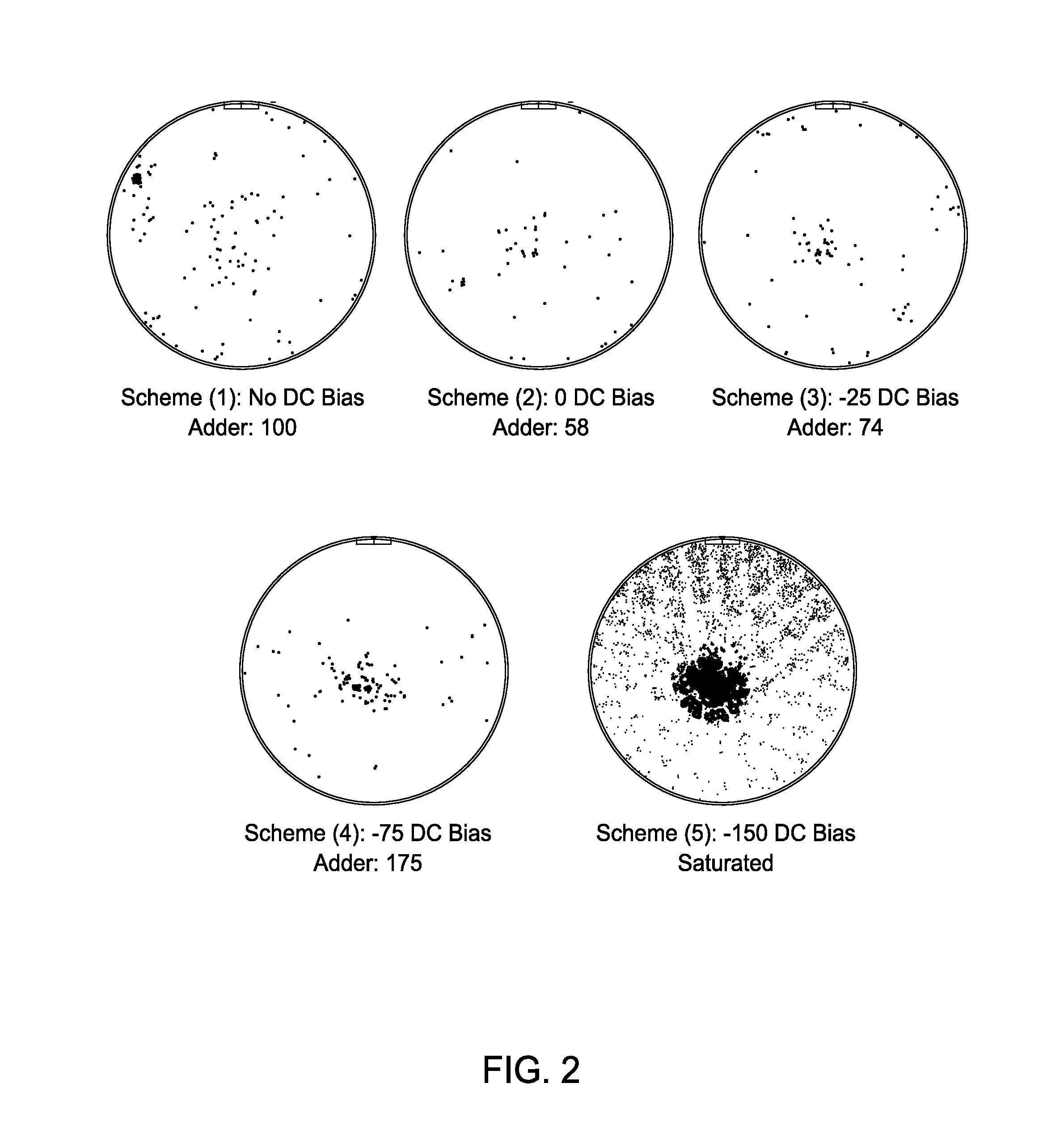
System and method for voltage-based plasma excursion detection
ActiveUS8502689B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma instabilityAudio power amplifier
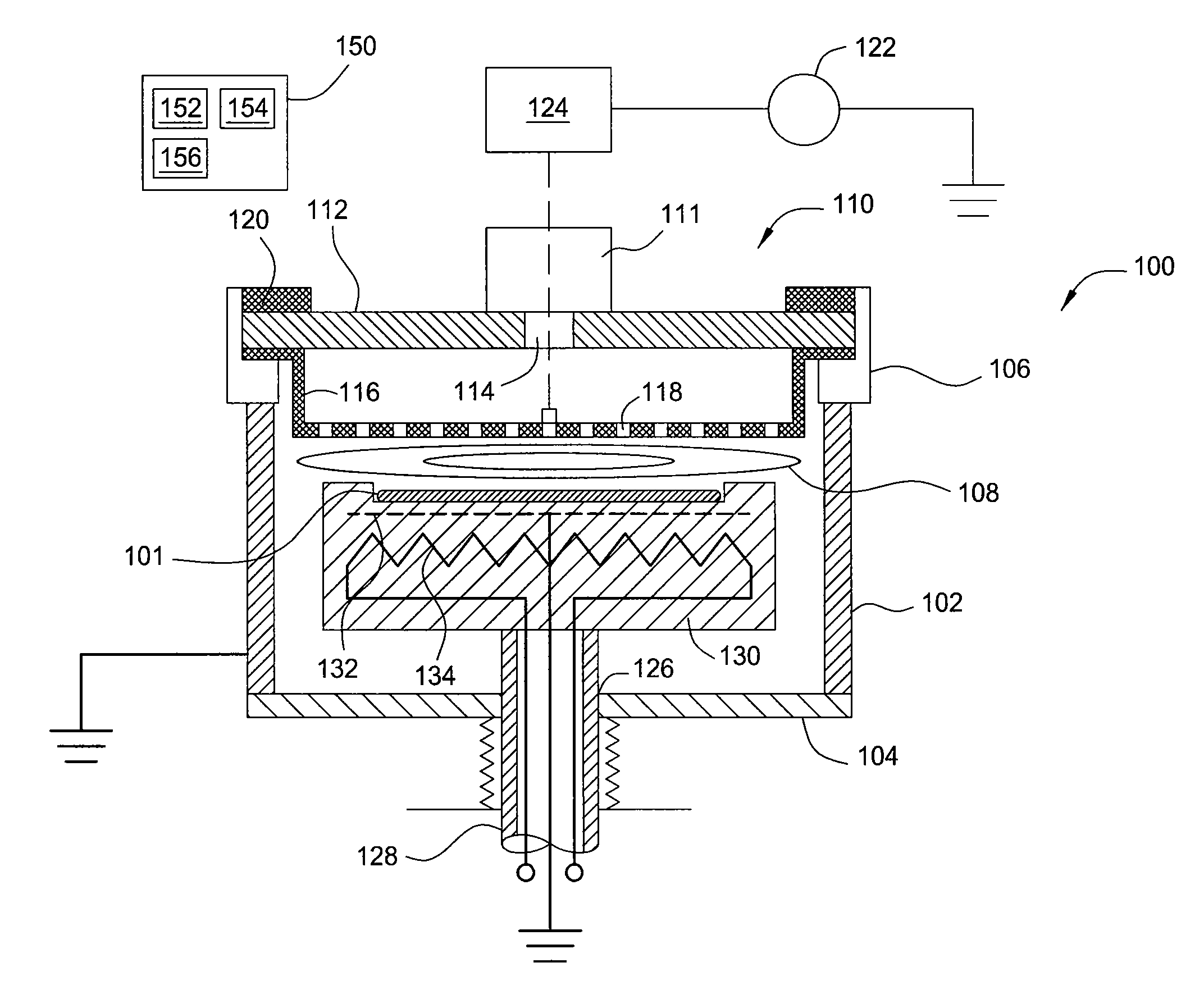
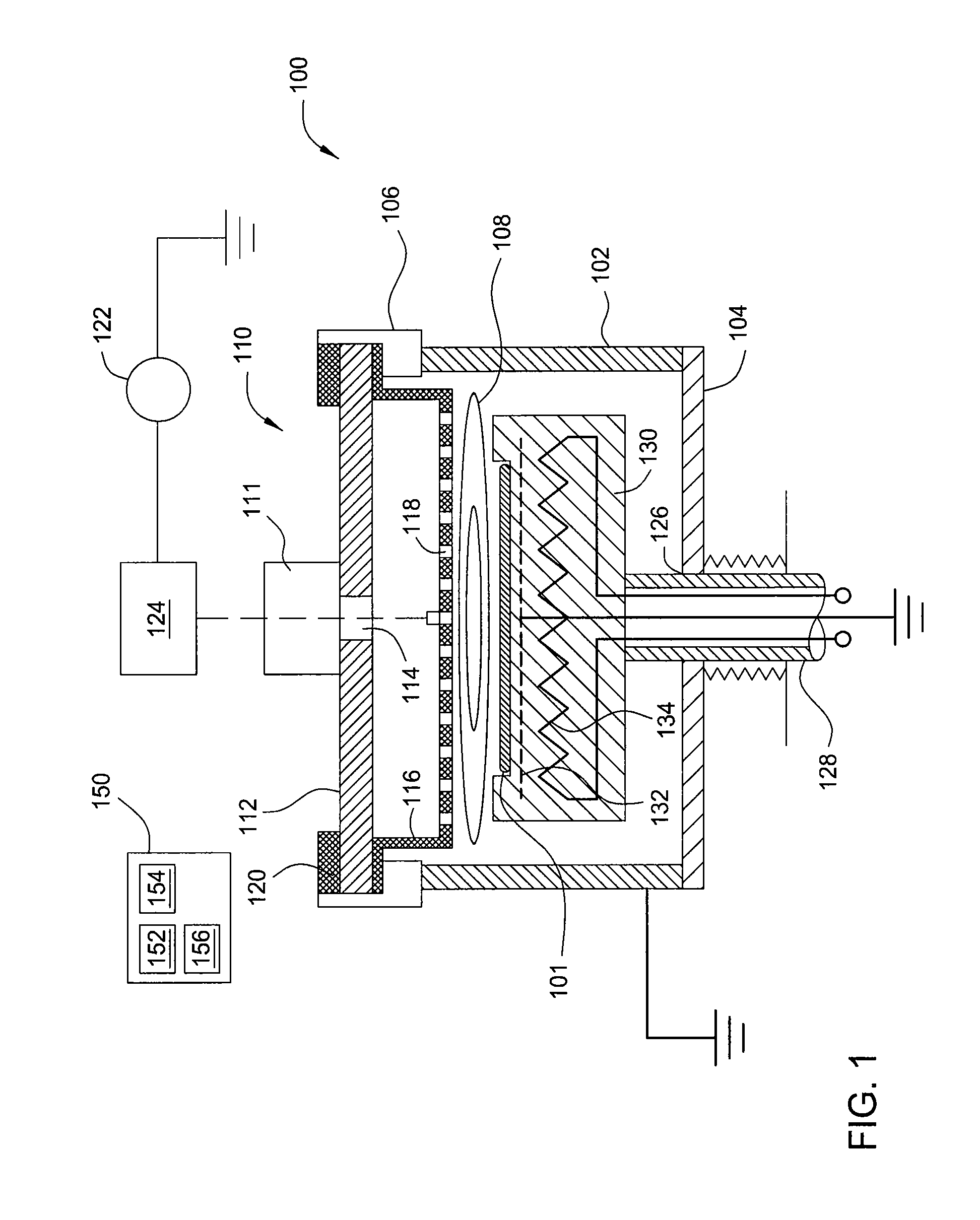
The present invention provides a system and method for the detection of plasma excursions, such as arcs, micro-arcs, or other plasma instability, during plasma processing by directly monitoring direct current (DC) bias voltage on an RF power electrode of a plasma processing chamber. The monitored DC bias voltage is then passed through a succession of analog filters and amplifiers to provide a plasma excursion signal. The plasma excursion signal is compared to a preset value, and at points where the plasma excursion signal exceeds the preset value, an alarm signal is generated. The alarm signal is then fed back into a system controller so that an operator can be alerted and / or the processing system can be shut down. In certain embodiments, multiple processing regions can be monitored by a single detection control unit.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
High-speed single-photon detector in telecommunication wavelength band
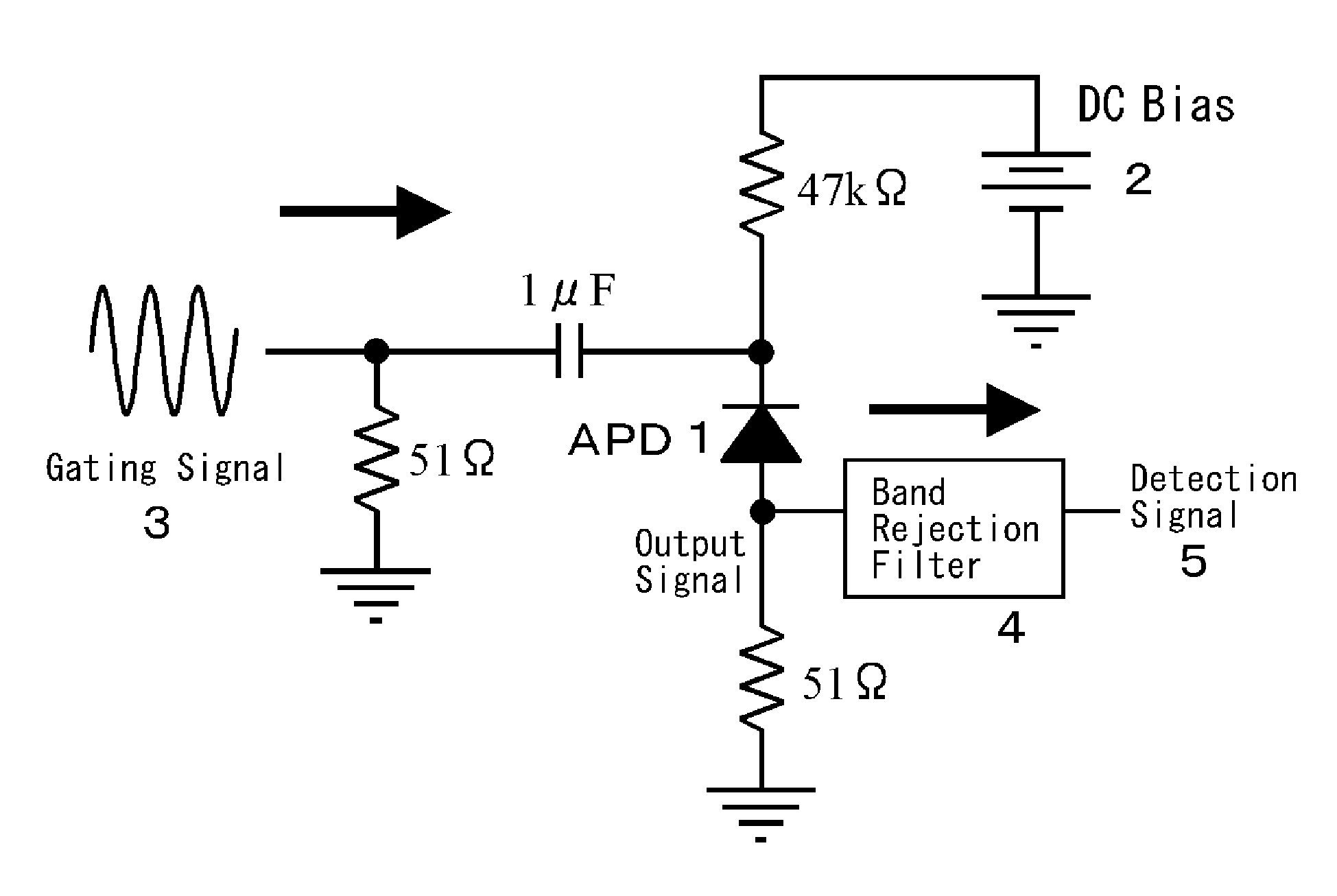
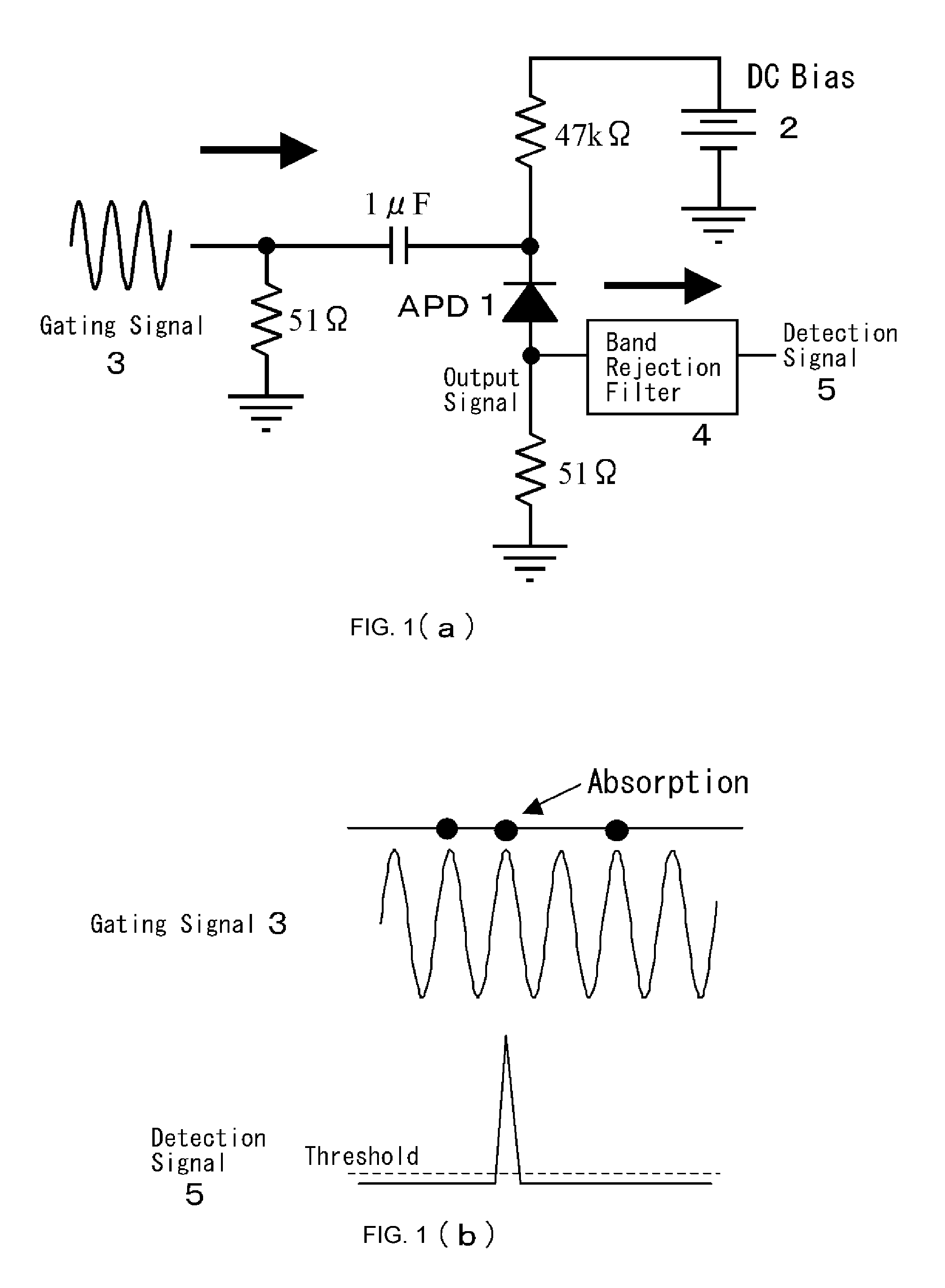
In order to operate a single photon detector in communication wavelength band at a high speed, a DC bias voltage 2 lower than the breakdown voltage is applied to an InGaAs / InP avalanche photodiode (APD) 1. A 500 MHz sine wave gating signal 3 is superimposed with the DC bias voltage 2 and applied to the APD 1 so as to exceed the breakdown voltage by about 4V in a fractional time of each period. The sine wave gating signal 3 passed through the APD 1 is substantially completely removed by a filter 4, thereby improving S / N and enabling to detect a single photon even if the avalanche multiplication time is shortened to reduce the after pulse and the detection period. As a result, it achieves to detect a single photon in the 1550 nm communication band at a high speed.
Owner:NIHON UNIVERSITY
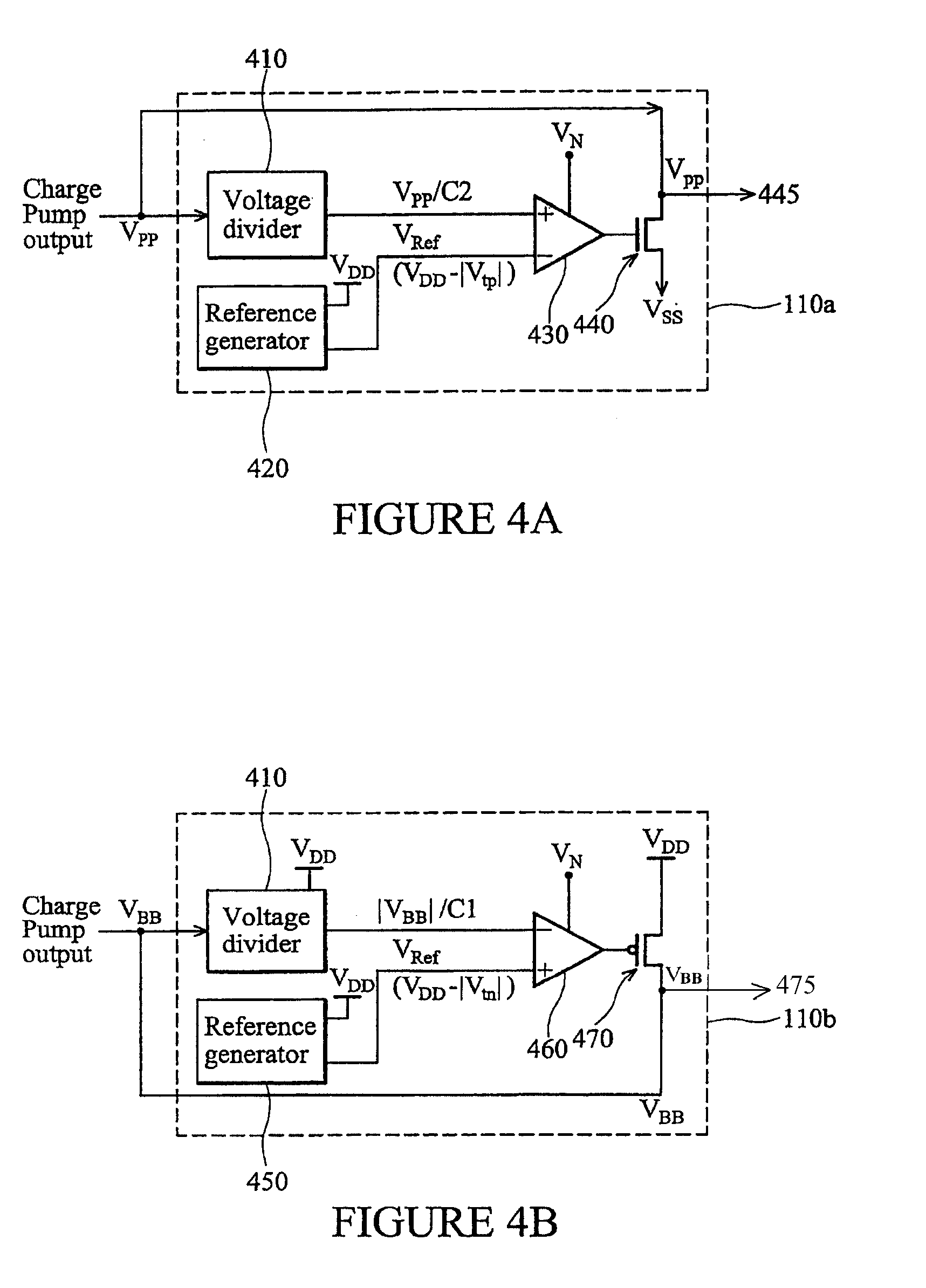
Back-bias voltage regulator having temperature and process variation compensation and related method of regulating a back-bias voltage
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
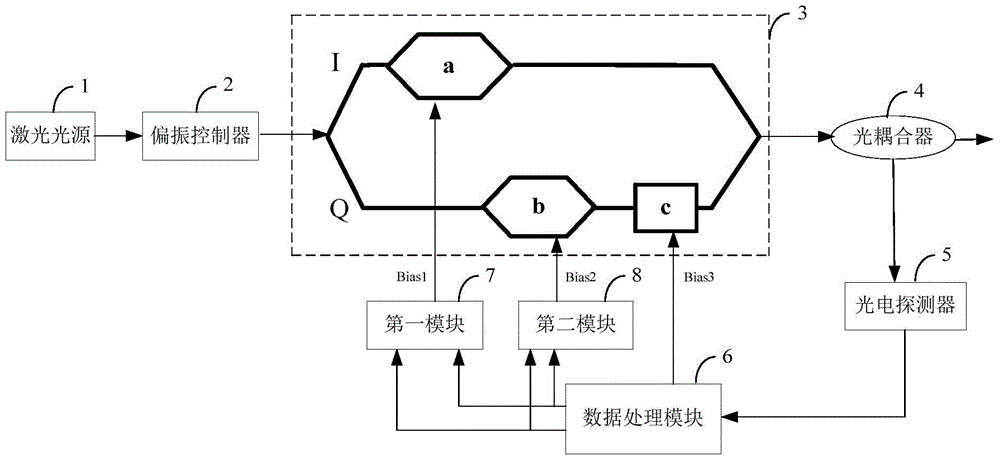
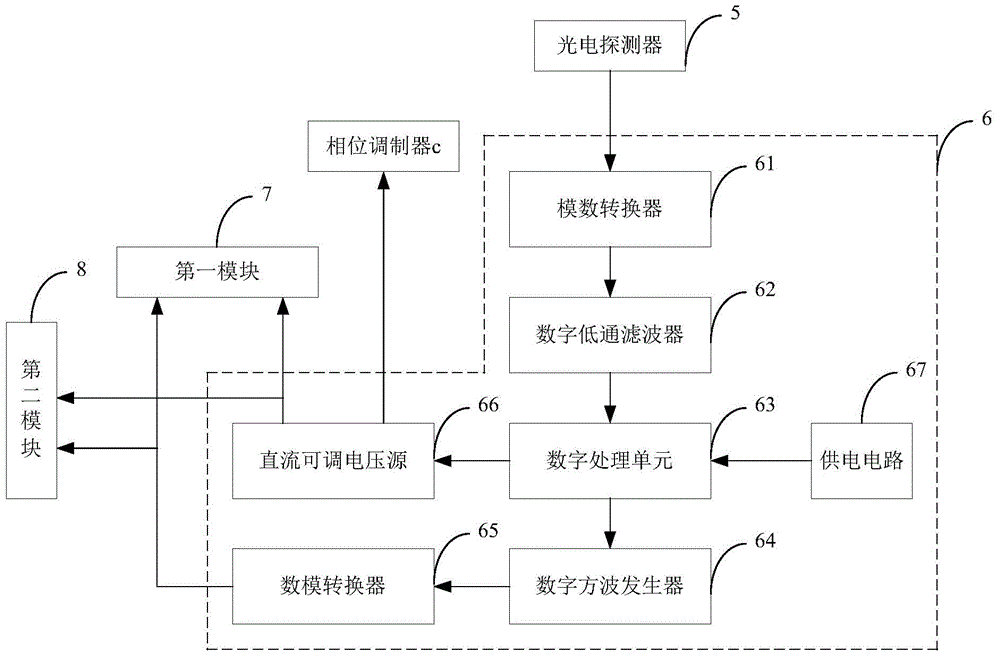
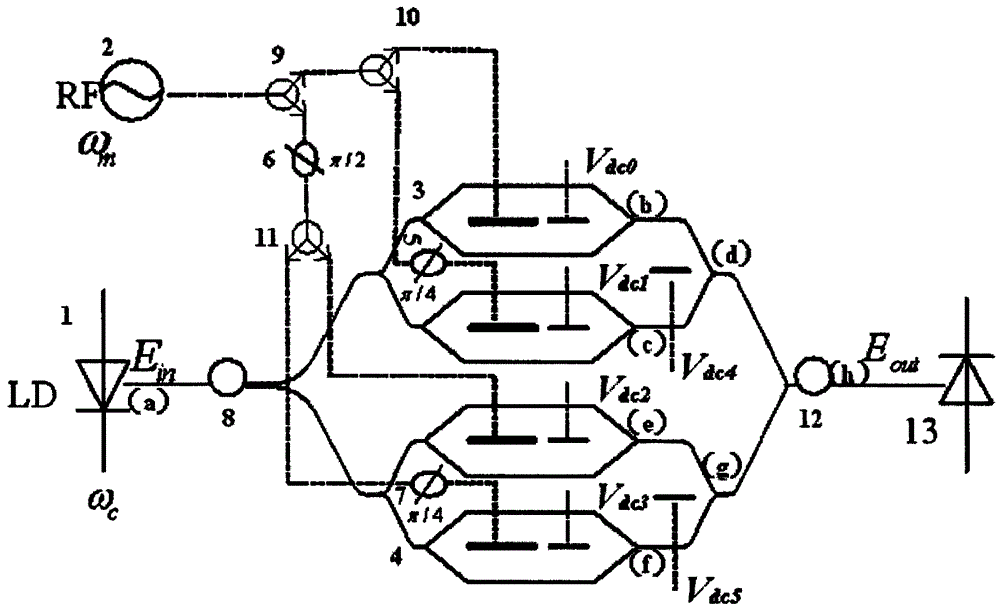
Control system and method of bias voltage of IQ optical modulator
ActiveCN104485997AGuaranteed OrthogonalityEasy Feedback ControlFibre transmissionEngineeringOptical coupler
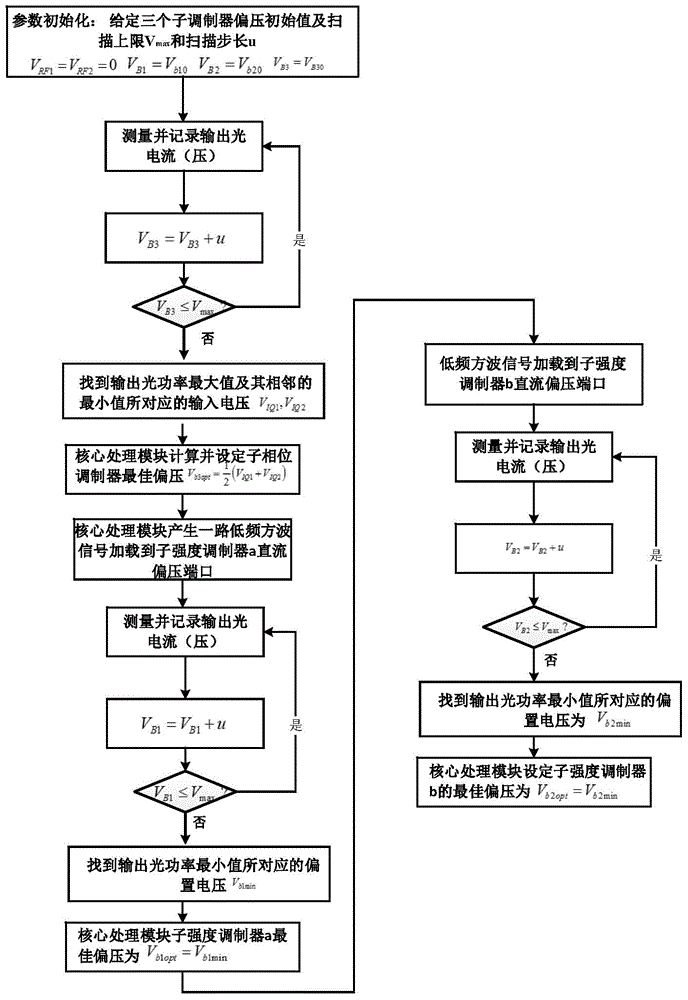
The invention discloses a control system of bias voltage of an IQ optical modulator and a control method of the bias voltage of the IQ optical modulator. The control system comprises a laser optical source, a polarization controller, the IQ optical modulator, an optical coupler, a photoelectric detector and a data processing module, which are connected in sequence, wherein the output of the IP optical modulator is divided by the optical coupler, and then is connected to the photoelectric detector; the output of the IP optical modulator is connected with the input of the data processing module; three outputs of the data processing module are respectively sent to the direct current bias voltage input ports of three subsidiary modulators of the IQ optical modulator. The control method comprises the steps of optimizing the bias voltage of a subsidiary phase modulator by measuring the maximum value and the adjacent minimum value of an output optical power, loading the minimum value of search optical power of a path of low-frequency square signal onto two subsidiary intensity modulators in sequence to optimize the bias voltages of the two subsidiary intensity modulators on that basis, and finally realizing the control and locking on each subsidiary modulator working point of the IQ optical modulator. By applying the control system and the control method, the perfect bias point of the IQ optical modulator can be rapidly and automatically controlled.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
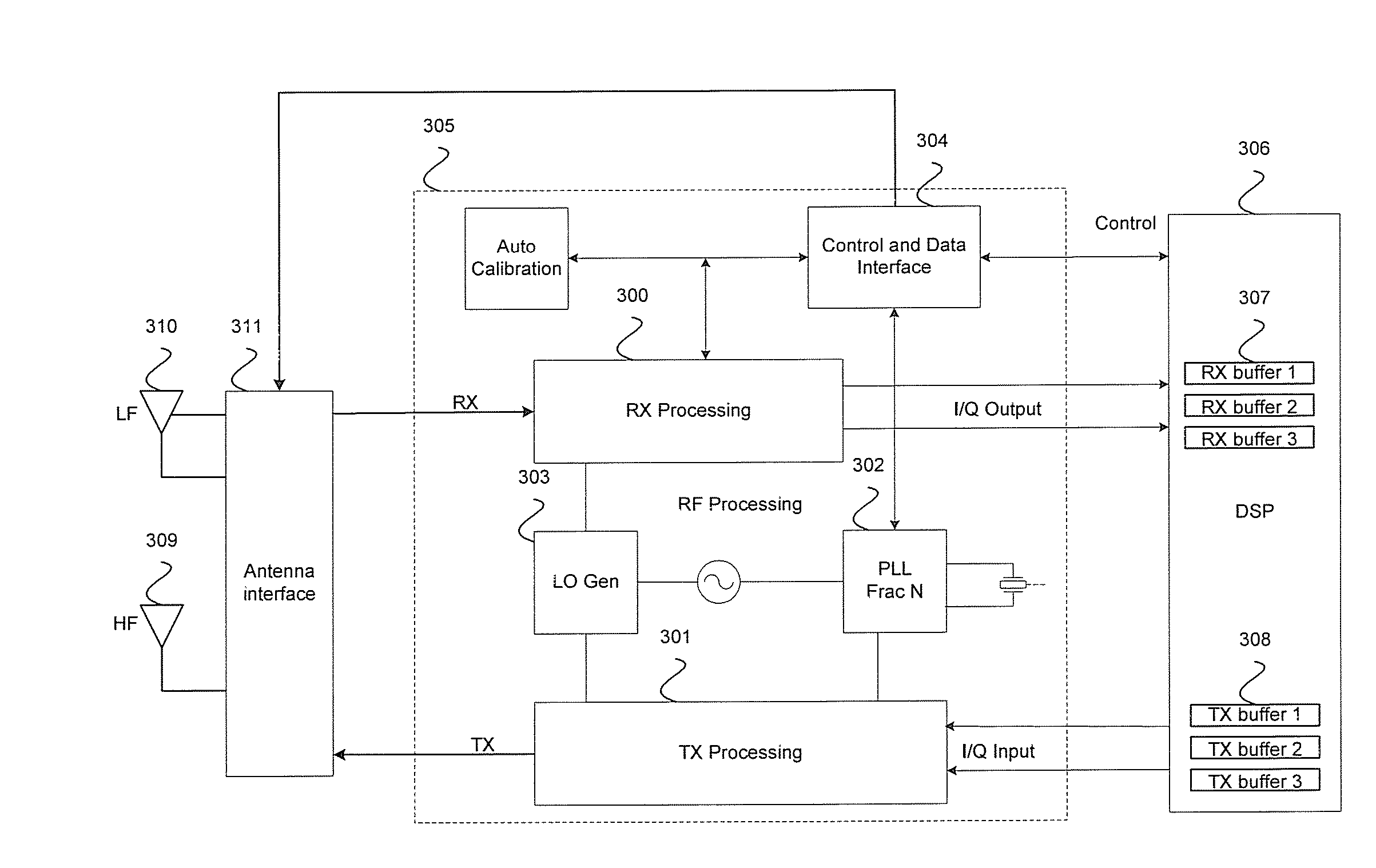
Method and System for Interfacing to a Plurality of Antennas
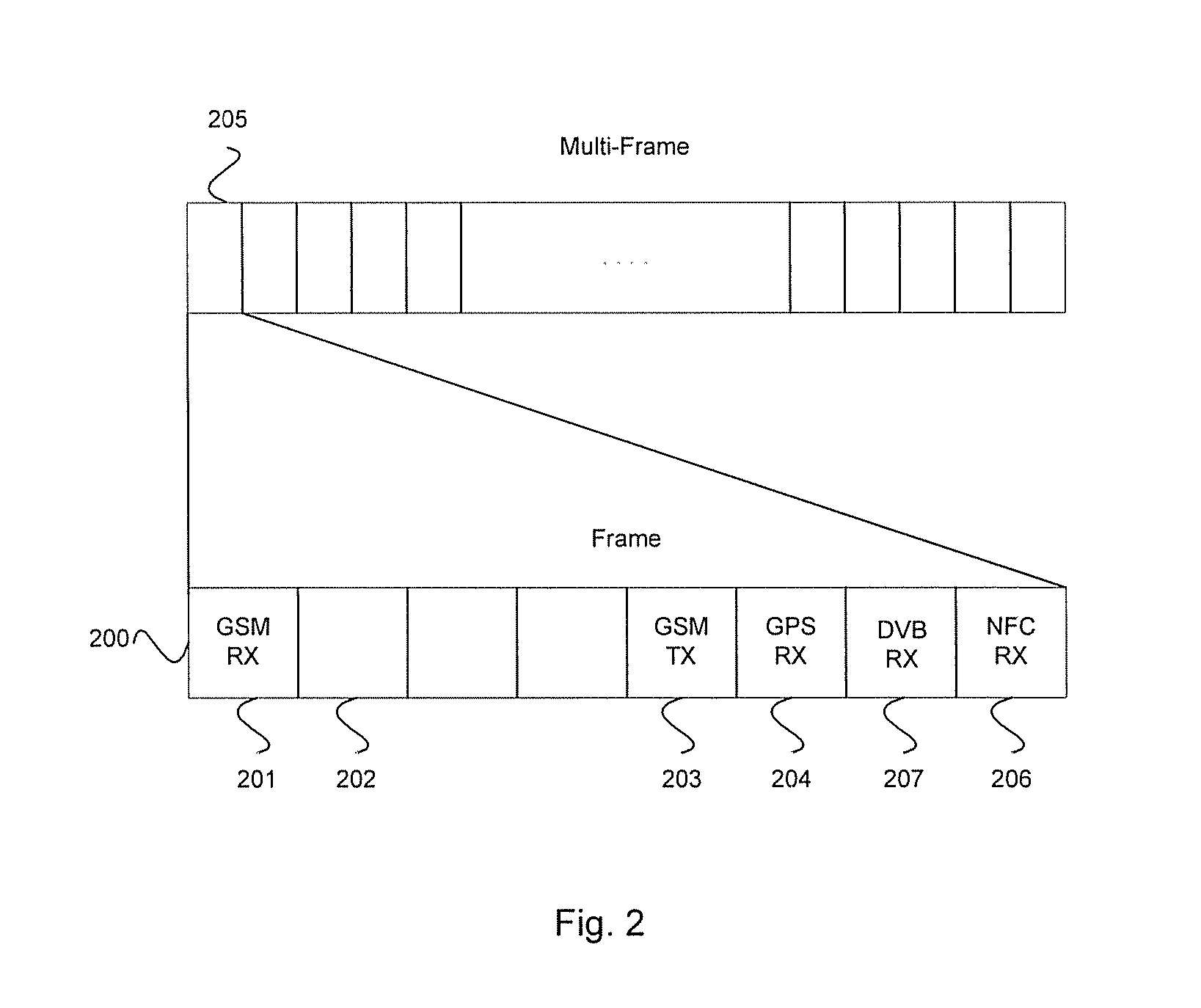
A method and system for interfacing to a plurality of antennas is provided. The method may comprise scheduling signals within different frequency ranges communicated from different antennas to use different timeslots in a TDM frame, such as a GSM frame. A plurality of antennas may be used, and at least one high frequency antenna may be adapted to operate at frequencies above 700 MHz and at least one low frequency antenna may be adapted to operate at frequencies below 700 MHz. The high frequency antenna may support WCDMA, HDSPA, HSUPA, GSM, GPRS, EDGE, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, GPS, and / or DVB communication. The low frequency antenna may support FM or NFC. NFC may be enabled by applying a DC bias voltage to the low frequency antenna. The method may also comprise dynamically tuning the antennas to frequency bands corresponding to particular communication protocols. The dynamic tuning may further comprise compensating the antennas for changes in frequency.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
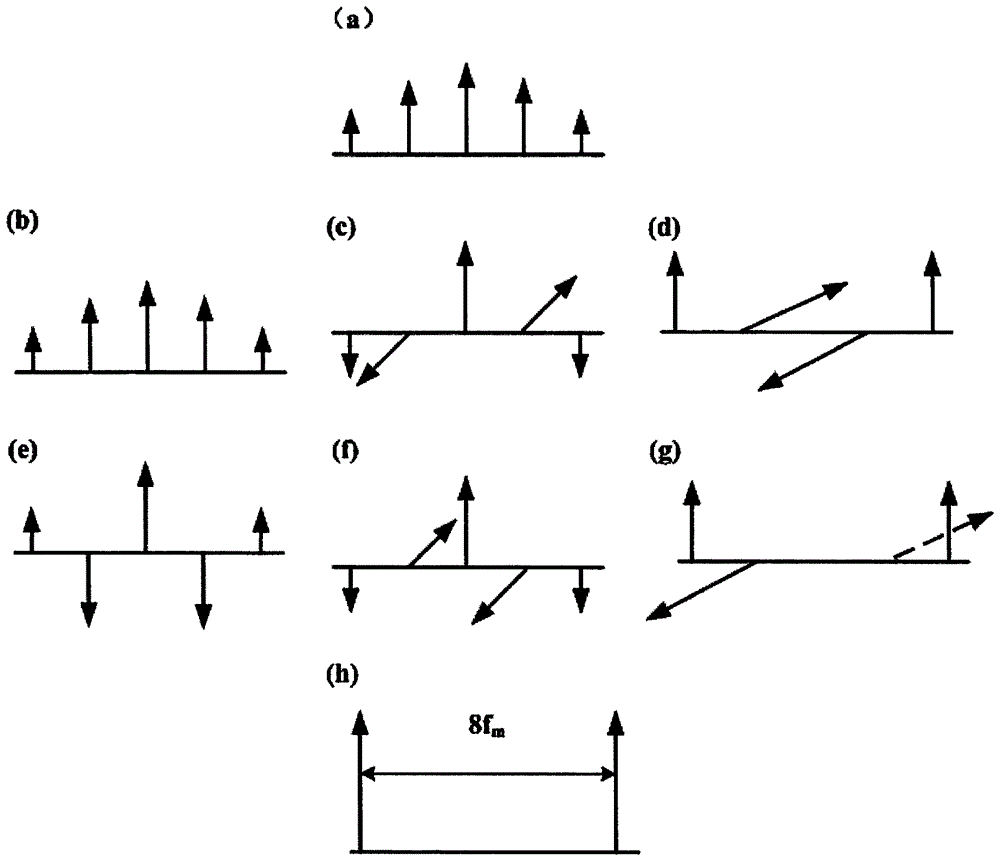
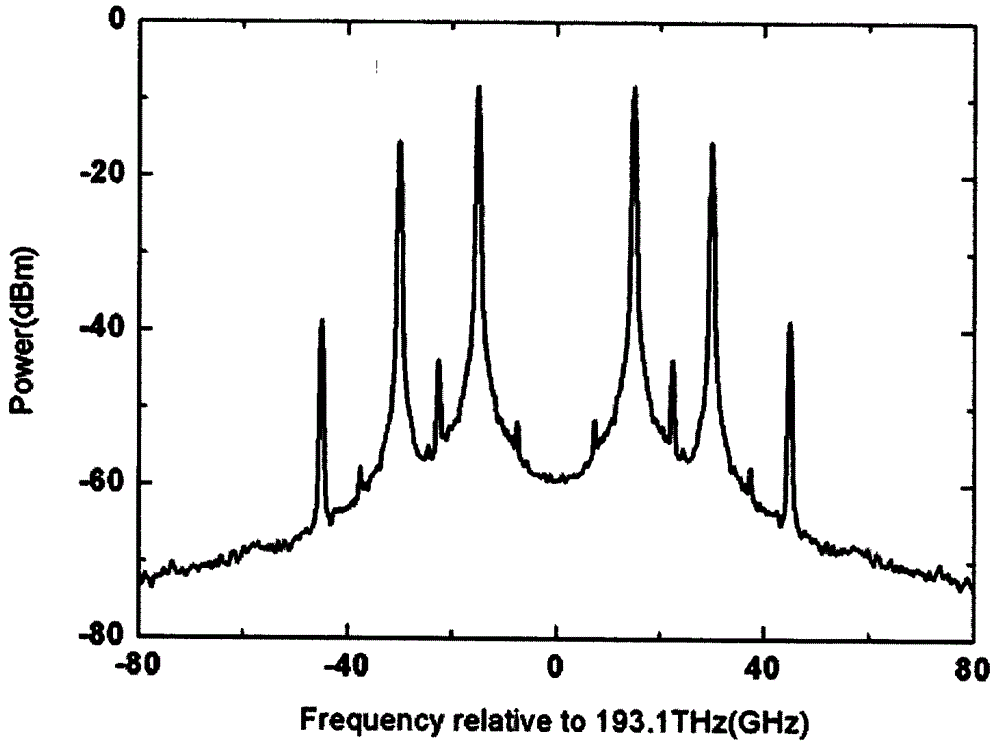
Device and method for generating eight frequency multiplication millimeter waves by utilizing Mach-Zehnder modulator
ActiveCN104022830AReduced frequency indexLow costModulated-carrier systemsRadio-over-fibreLocal oscillator signalLithium niobate
The invention discloses a device and method for generating eight frequency multiplication millimeter waves by utilizing a Mach-Zehnder modulator, and the device and method are mainly used for the generation of the optical millimeter waves in a radio over fiber (ROF) access network. The method is shown in attached figures: optical millimeter wave signals, the frequency of which is eight times as large as that of local oscillator signals, are generated by utilizing nonlinear characteristics and interference superposition characteristics of two parallelly-connected double-parallel lithium niobate Mach-Zehnder modulators (DPMZM) and under the condition of an appropriate DC bias voltage, thereby greatly reducing equipment frequency index required for generating high frequency / extremely high frequency signals, and reducing the system cost. According to the device and method, specific phase modulation index is not needed, and radio-frequency signals can be flexibly adjusted, so that the requirement for radio-frequency power is lowered; and meanwhile, stray sideband can be well restrained.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
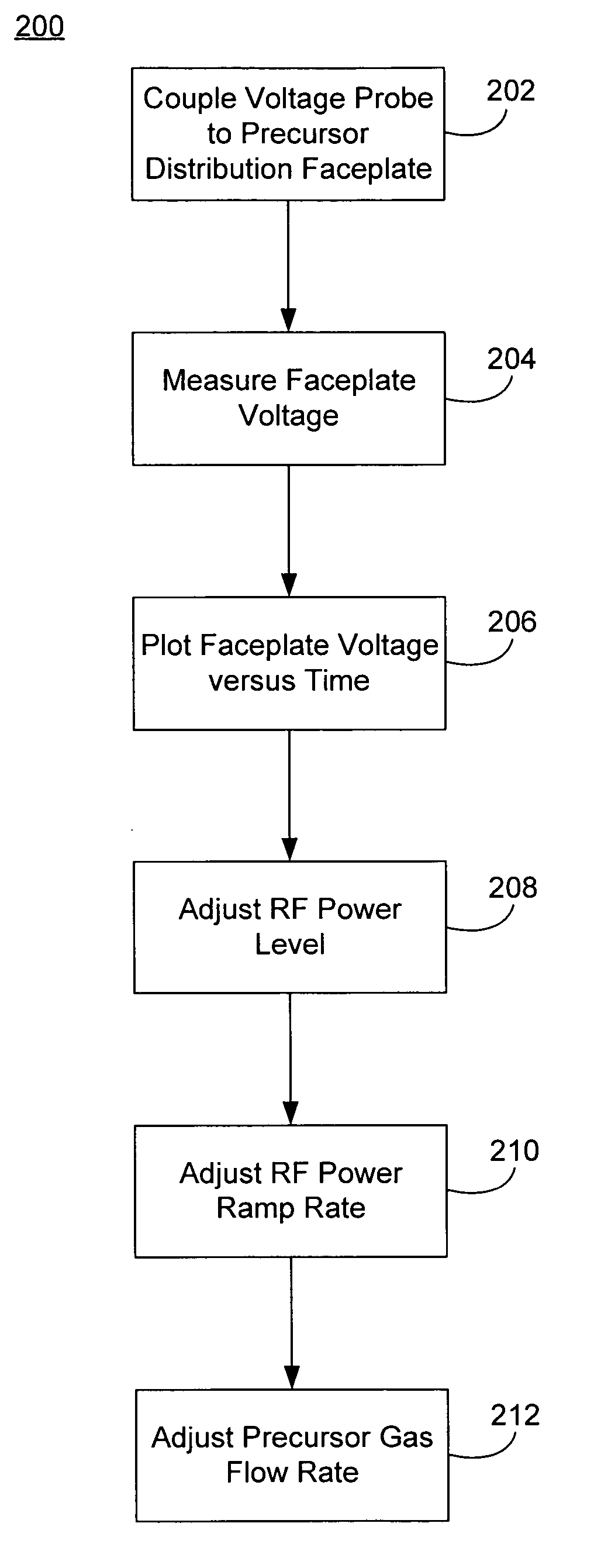
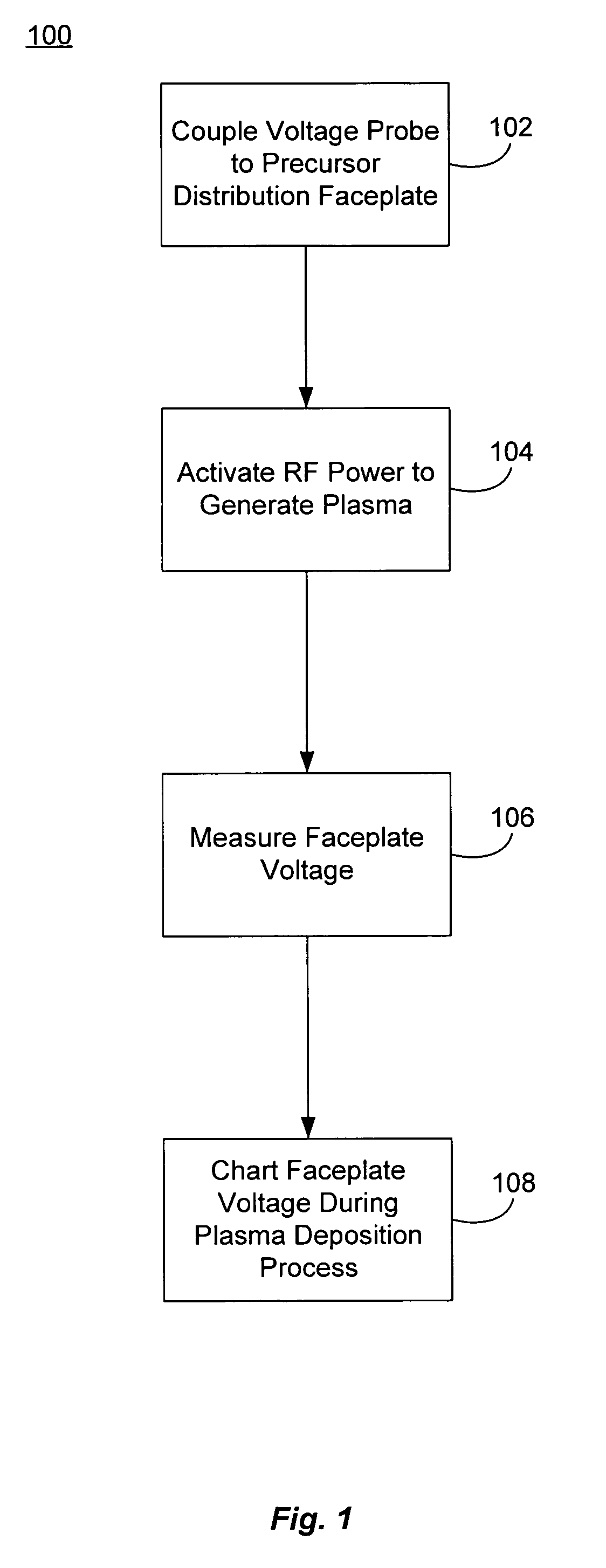
Non-intrusive plasma monitoring system for arc detection and prevention for blanket CVD films
InactiveUS20070042131A1Reduce arcingLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesMonitoring systemEngineering
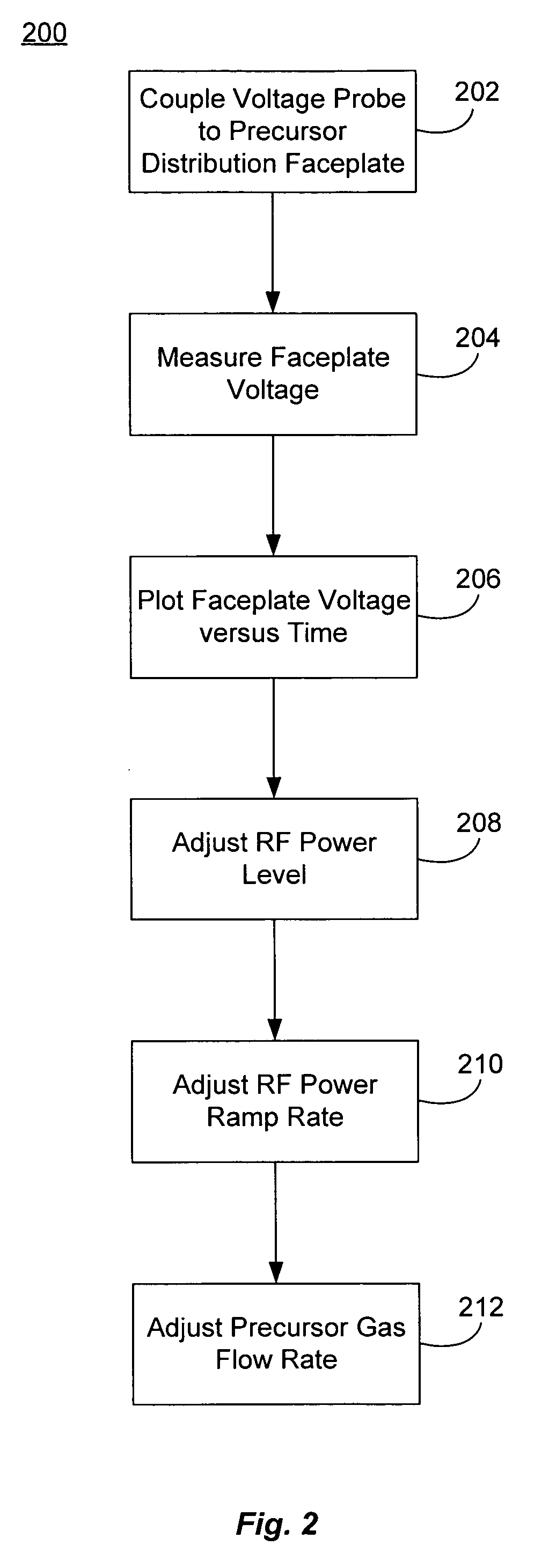
Methods and systems of diagnosing an arcing problem in a semiconductor wafer processing chamber are described. The methods may include coupling a voltage probe to a process-gas distribution faceplate in the processing chamber, and activating an RF power source to generate a plasma between the faceplate and a substrate wafer. The methods may also include measuring the DC bias voltage of the faceplate as a function of time during the activation of the RF power source, where a spike in the measured voltage at the faceplate indicates an arcing event has occurred in the processing chamber. Methods and systems to reduce arcing in a semiconductor wafer processing chamber are also described.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Microphone and Method for Calibrating a Microphone
ActiveUS20130136267A1Semiconductor electrostatic transducersElectrostatic transducer microphonesPull in voltageEngineering
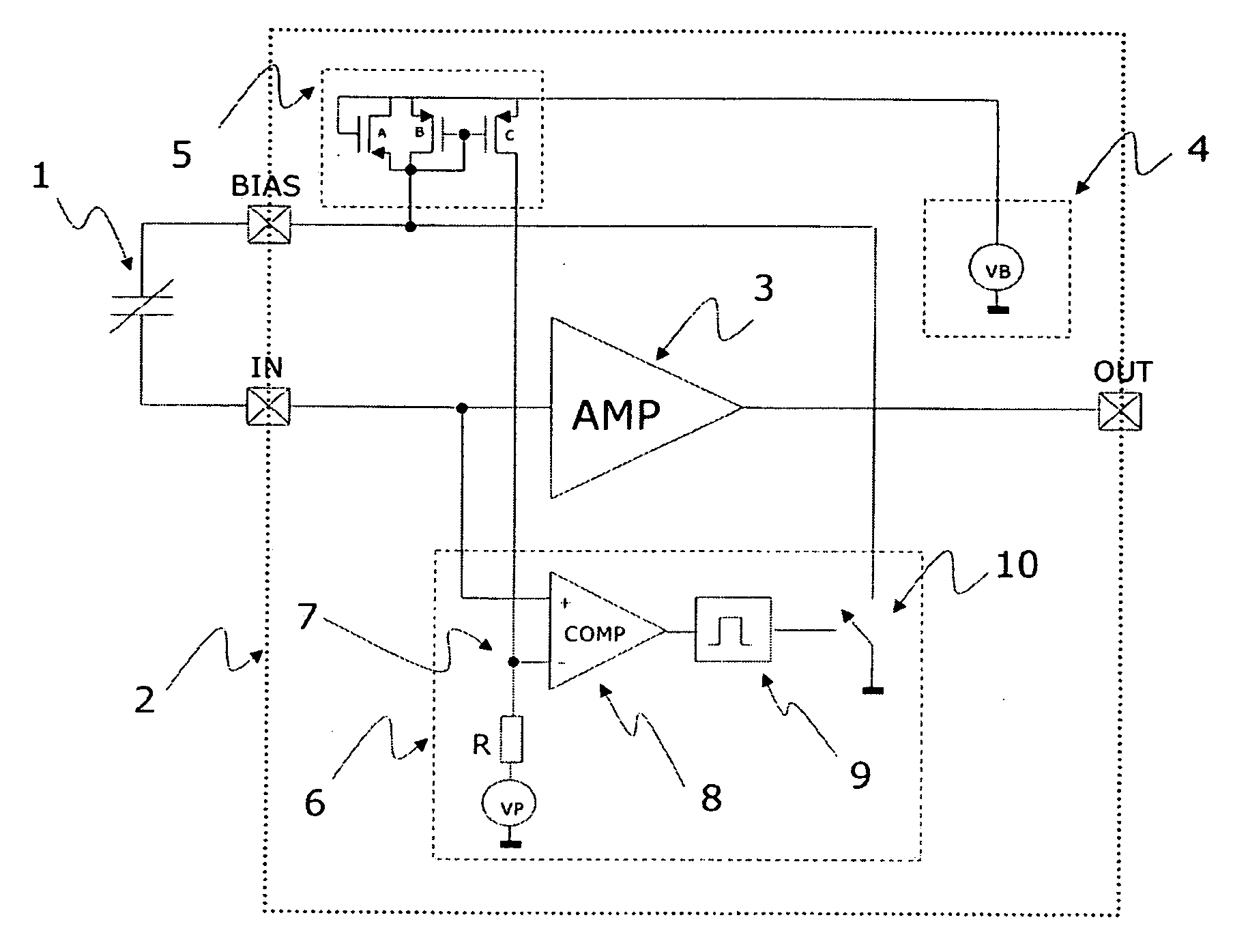
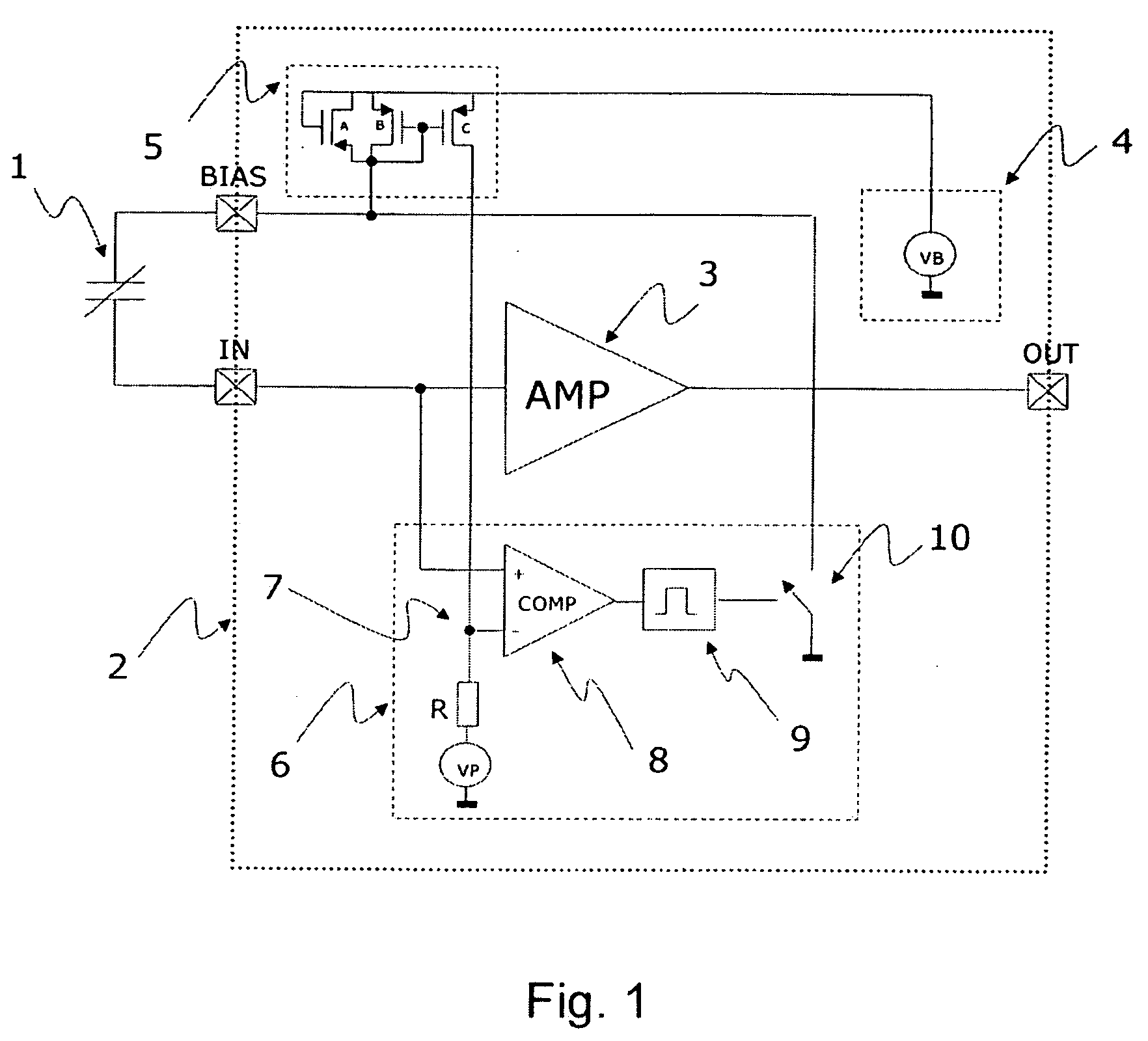
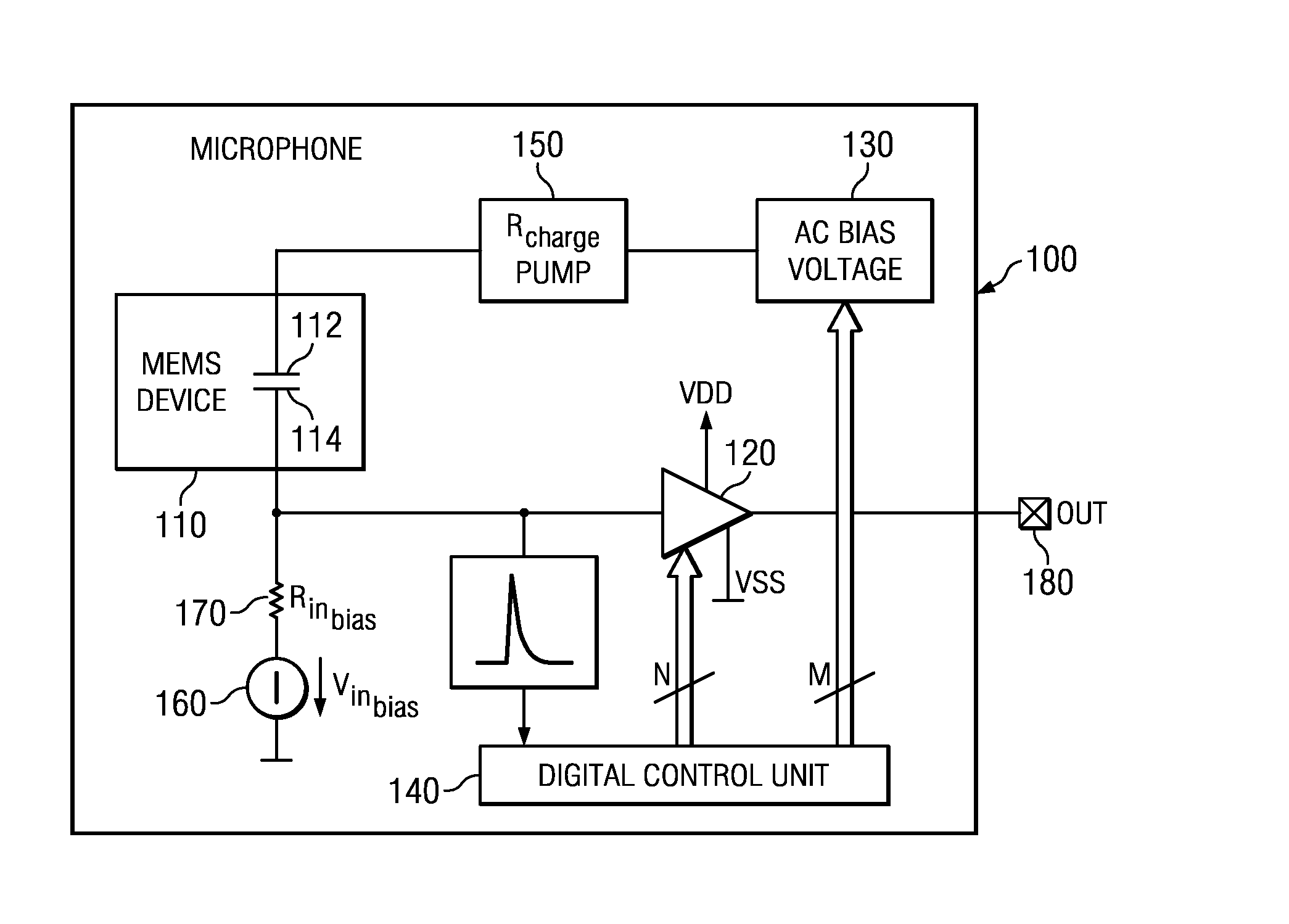
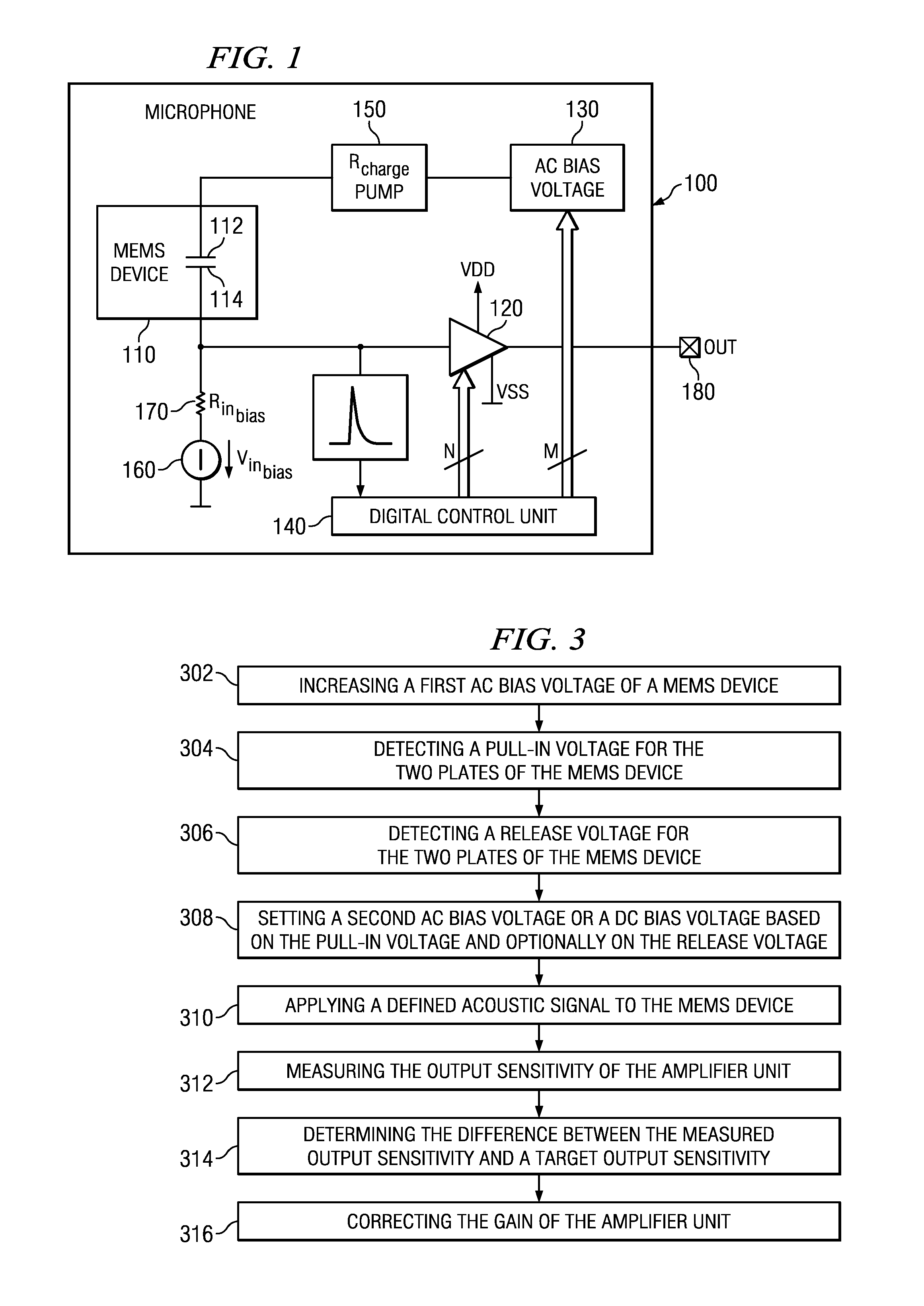
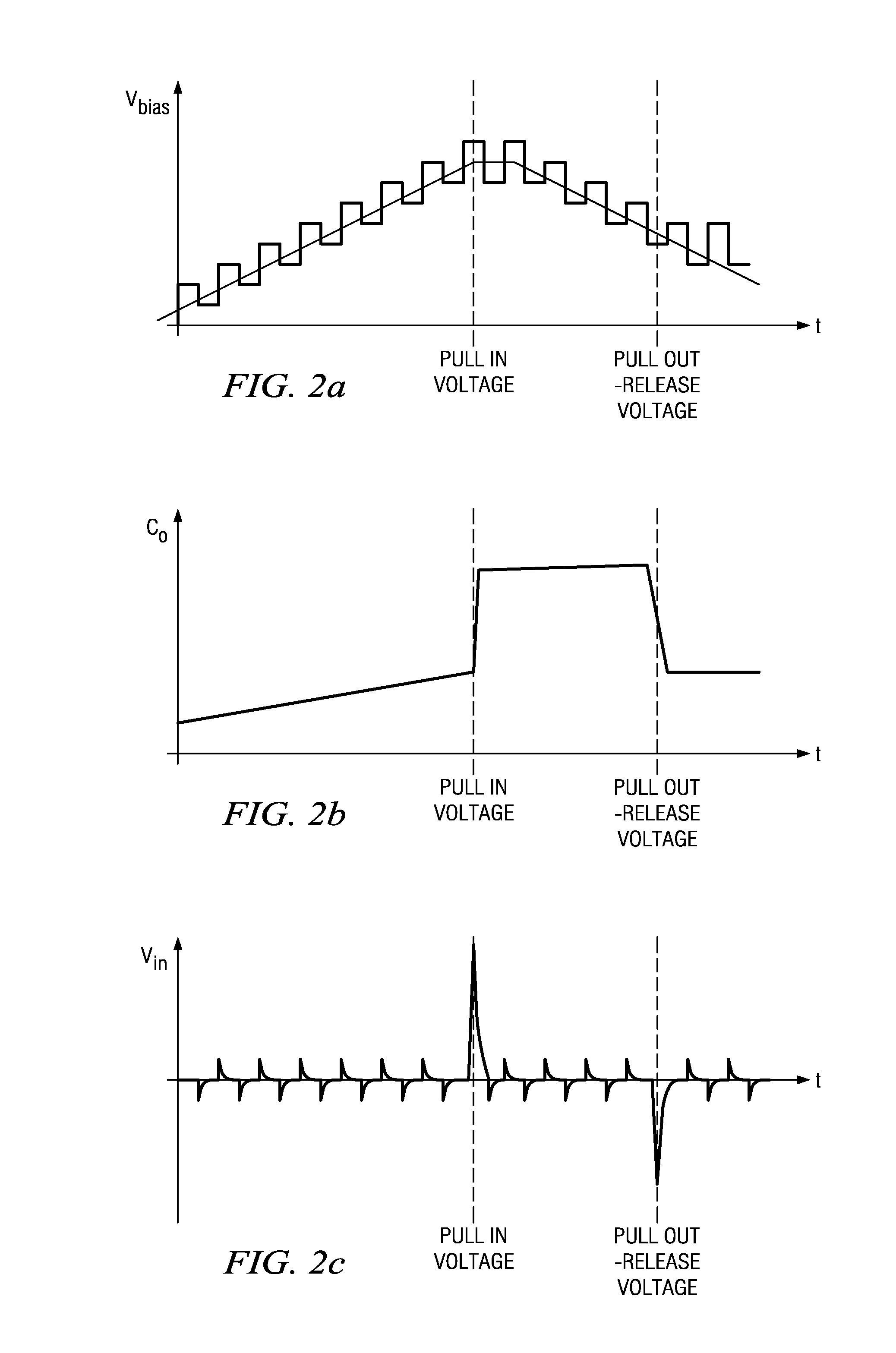
A microphone and a method for calibrating a microphone are disclosed. In one embodiment the method for calibrating a microphone comprises operating a MEMS device based on a first AC bias voltage, measuring a pull-in voltage, calculating a second AC bias voltage or a DC bias voltage, and operating the MEMS device based the second AC bias voltage or the DC bias voltage.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Electronic circuit for controlling a capacitive pressure sensor and capacitive pressure sensor system
ActiveUS20110056302A1Avoid disadvantagesHigh sensitivityFluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesFluid pressure measurement using capacitance variationCapacitive pressure sensorEngineering
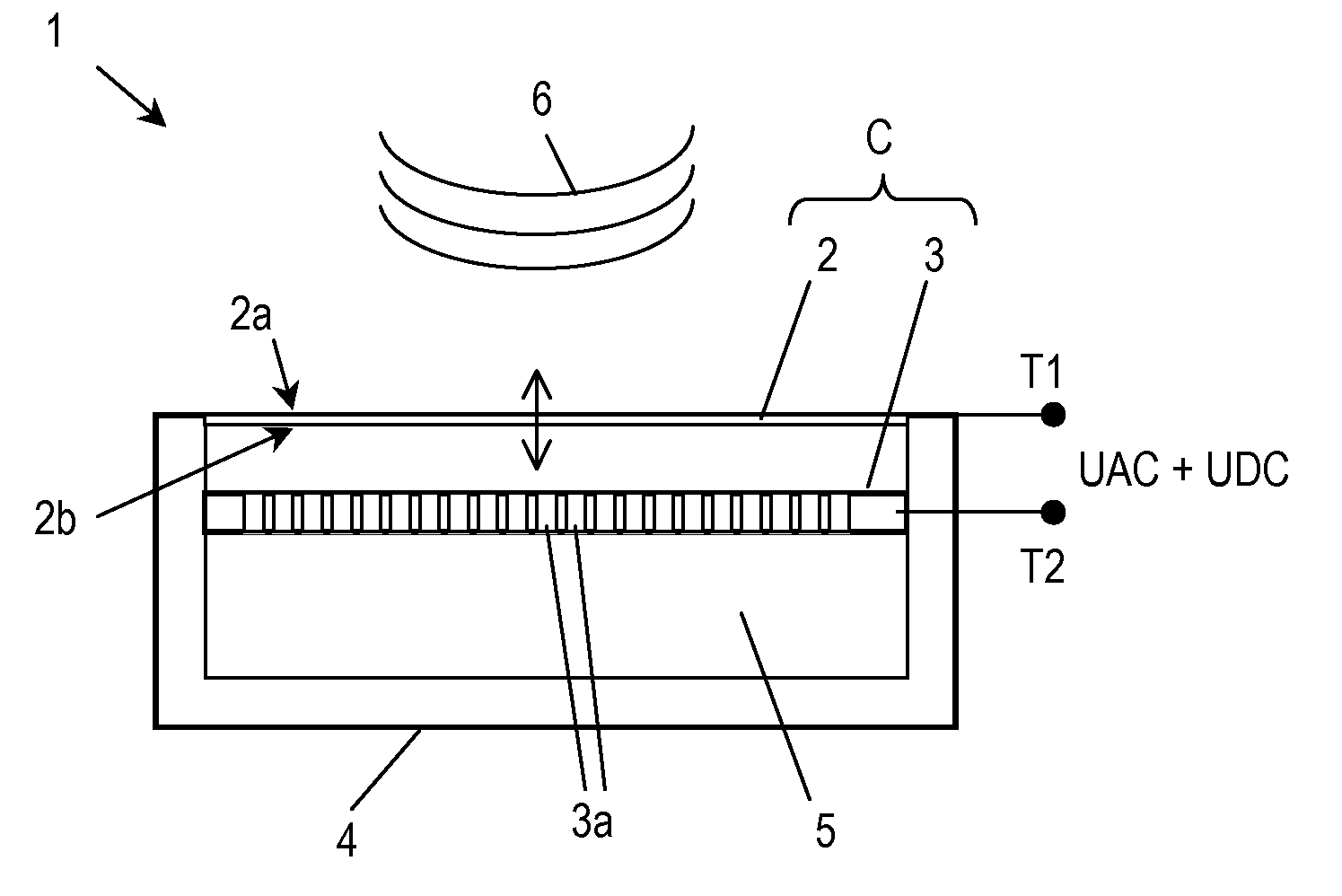
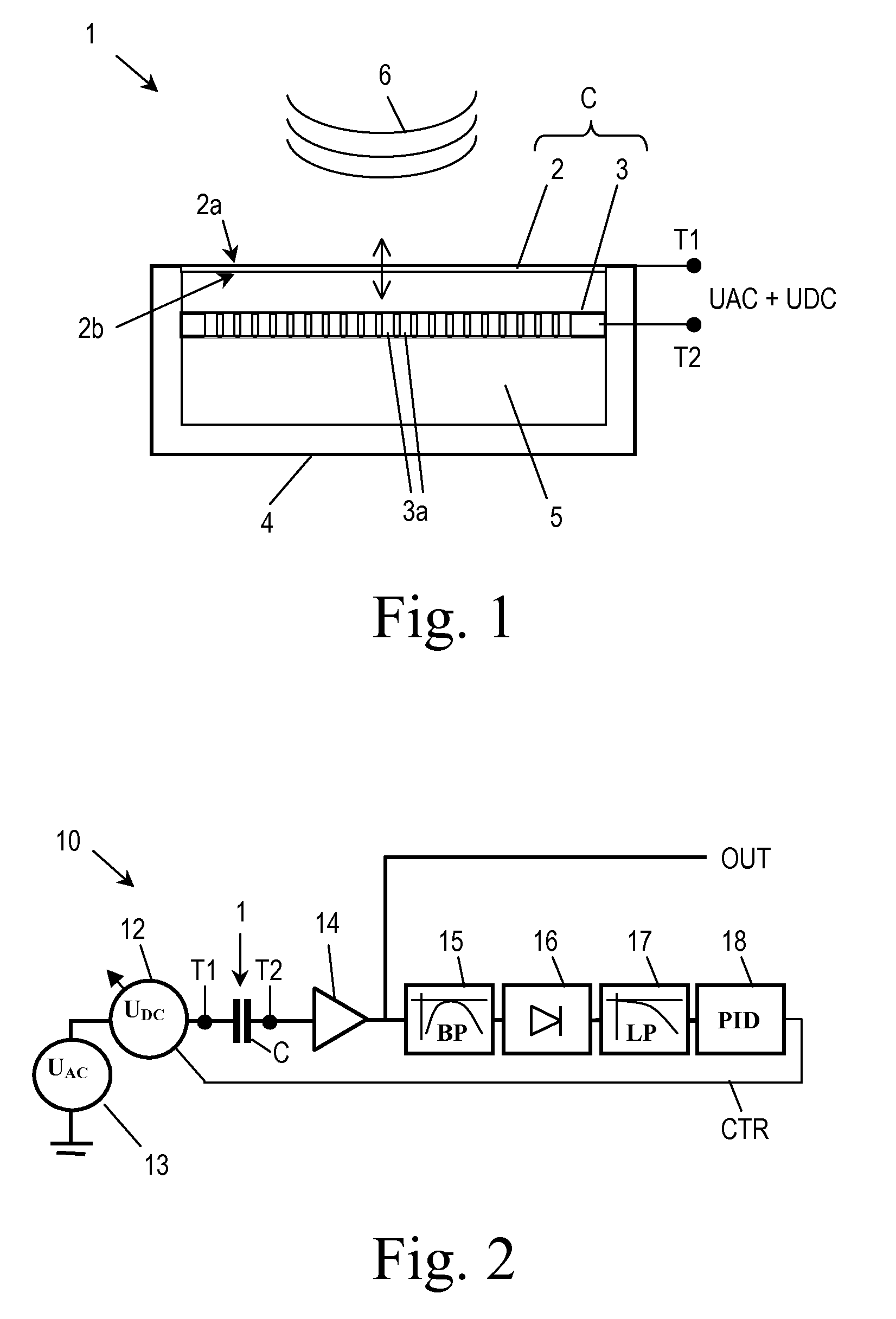
An electronic circuit (10) for controlling a capacitive pressure sensor (1), which capacitive pressure sensor (1) comprises a plate electrode capacitor (C) with a capacity that varies in dependence on pressure changes exerted on a deflectable diaphragm (2) forming one plate electrode of the capacitor (C), wherein the electronic circuit (10) comprises a DC voltage source (12) being adapted to generate a DC bias-voltage (UDC) to be applied across the electrodes of the capacitor (C), an AC voltage source (13) being adapted to generate an AC voltage signal (UAC) to be applied across the electrodes of the capacitor (C) and a controller (18) being adapted to receive an output signal (OUT) of the capacitor (C) and to control the DC voltage source (12) such that the DC bias-voltage (UDC) applied to the capacitor (C) adopts a value that maintains the capacity of the capacitor (C) at a desired value.
Owner:NXP BV
A calibrated microelectromechanical microphone
InactiveCN101155442ASemiconductor electrostatic transducersElectrostatic transducer microphonesVoltage generatorAudio power amplifier
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com