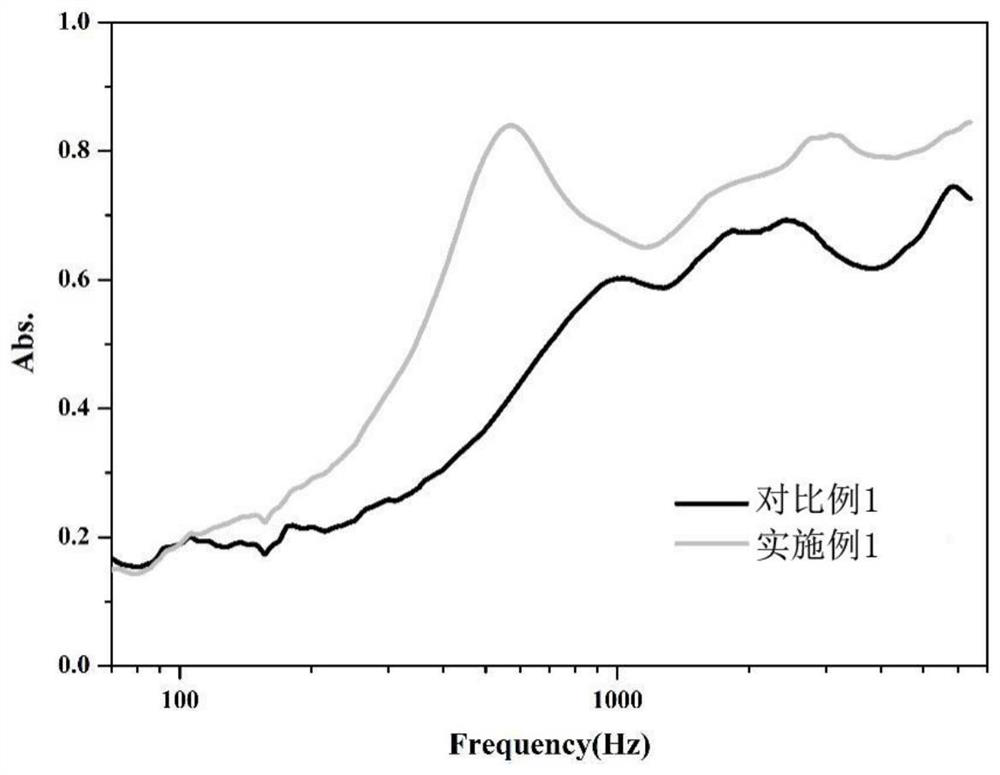
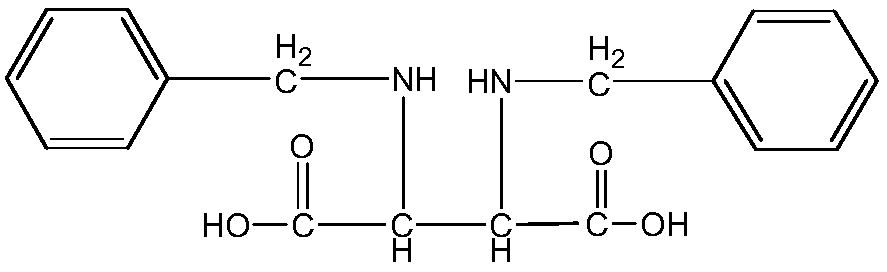
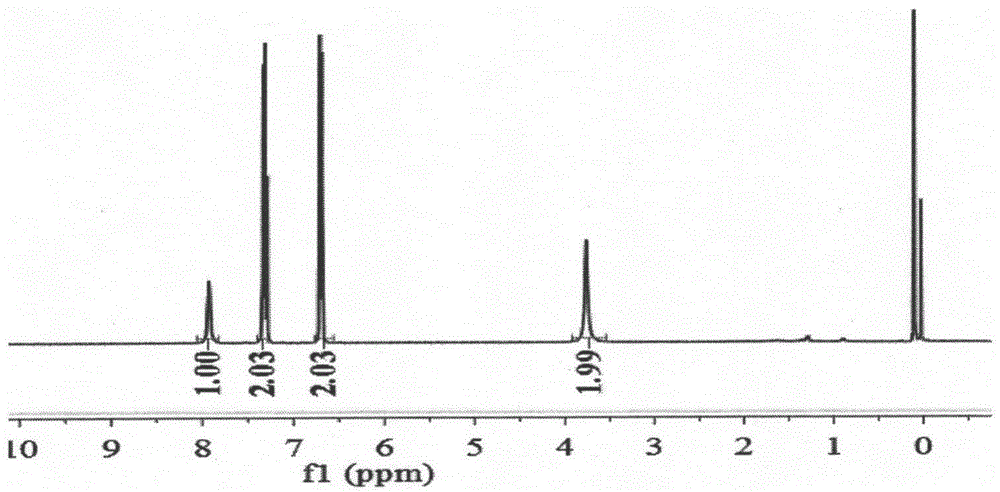
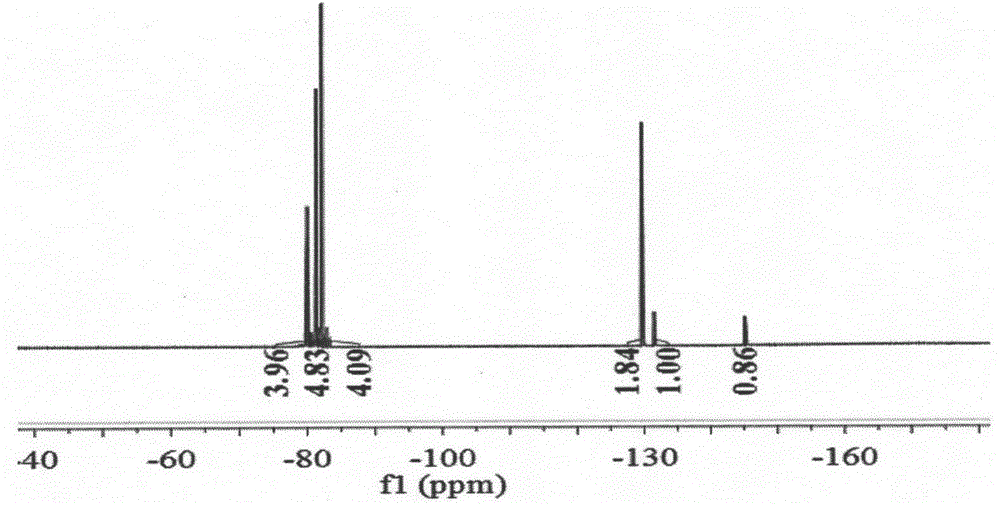
Patents
Literature
33results about How to "Improve conversion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Heat dissipating protective sheets and encapsulant for photovoltaic modules
InactiveUS20100288333A1Improve conversionPrevent decrease in efficiencyPV power plantsHeat-exchange elementsEngineeringPhase-change material
A photovoltaic module that resists or reduces unwanted increases in temperature of the photovoltaic cells encapsulated within the module is provided. This is accomplished by incorporating materials into module components that operate to direct heat away from the solar cells that are within the modules. One or more phase change materials are incorporated into the polymer layer of the backsheet that is position closest to the solar cells. Thermally conductive materials may be incorporated into the layers and / or module components closer to the outside of the module. These materials can be used separately or in conjunction with each other.
Owner:MADICO INC
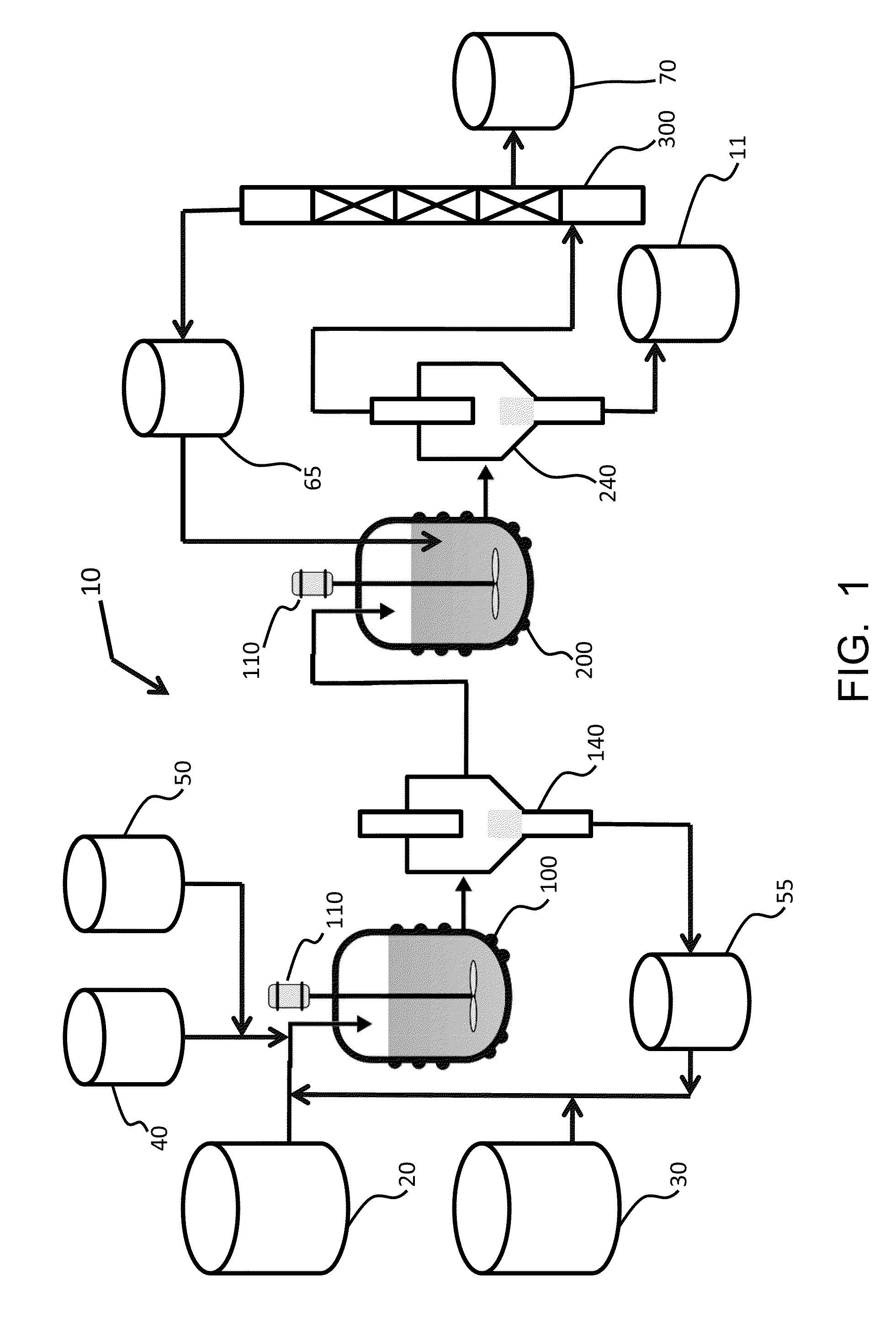
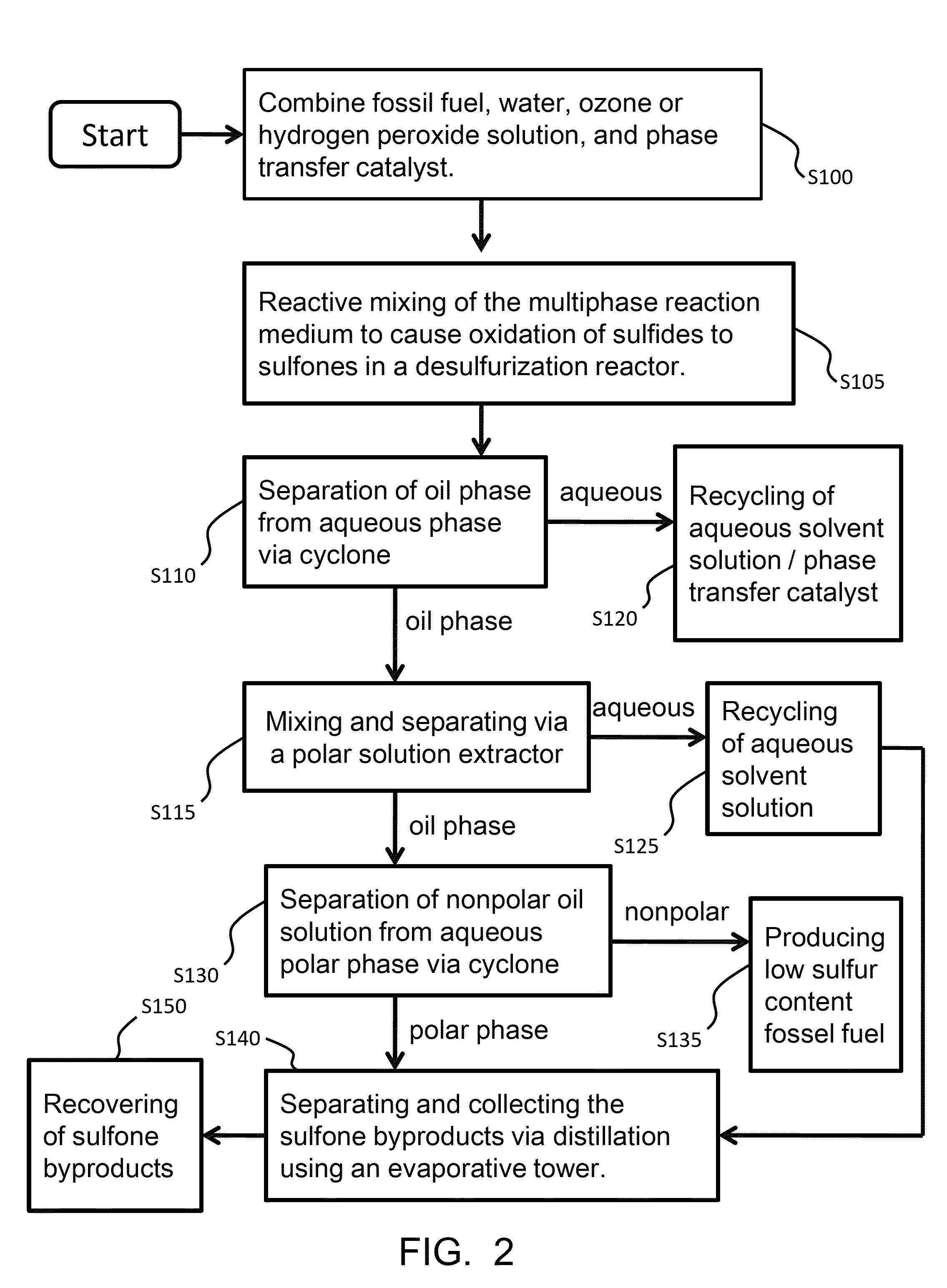
Mixing-assisted oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuel using quaternary ammonium salt and portable unit thereof
InactiveUS20120018350A1High yieldImprove conversionRefining with metalsRefining with oxygen compoundsFossil fuelPhase-transfer catalyst
The desulfurization of fossil fuels is provided by the combination of fossil fuels with an aqueous mixture of ozone or hydrogen peroxide and a Tetraoctylphosphonium salt phase transfer catalyst, and the mixture is then subjected to reactive mixing to form oxidize sulfur compounds in the fuel. The polar oxidized sulfones species are removed via another mixing step. The desulfurization device can be in the form of a portable device which provides for continuous mixing-assisted desulfurization for the removal of sulfur containing compounds from fossil fuels such as diesel fuel.
Owner:LIN HSIN TUNG +2
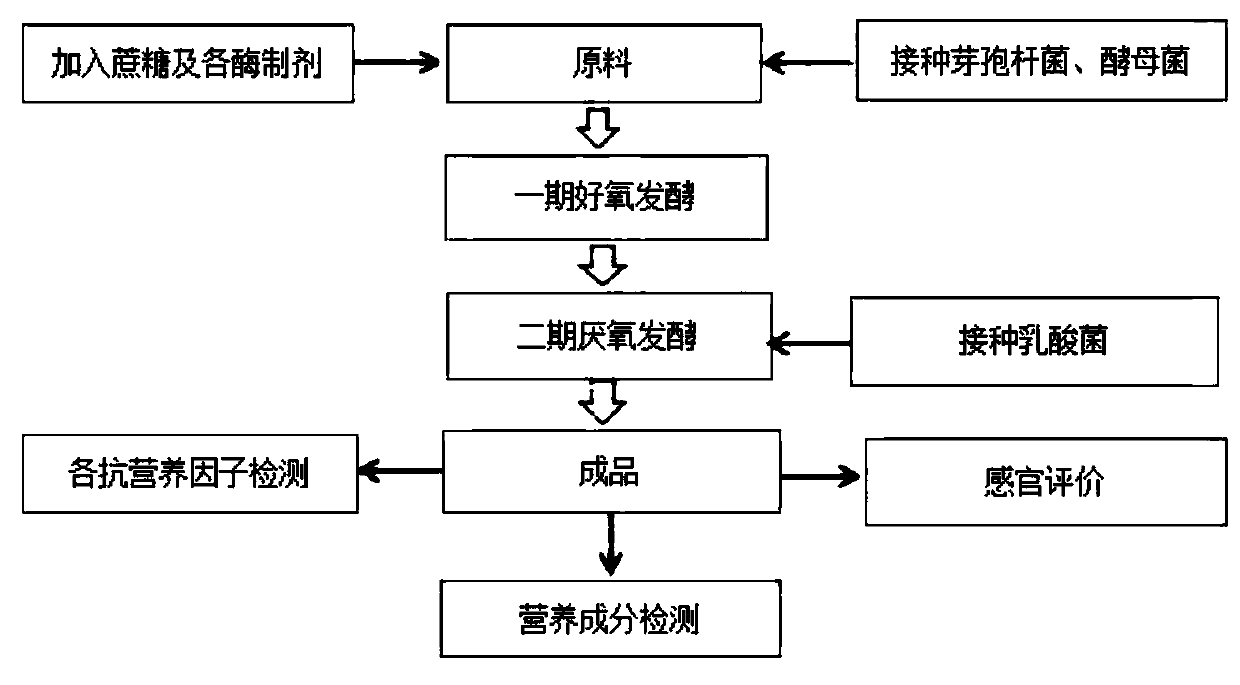
High-efficiency and low-cost fermentation feed processing method based on bean dregs and application
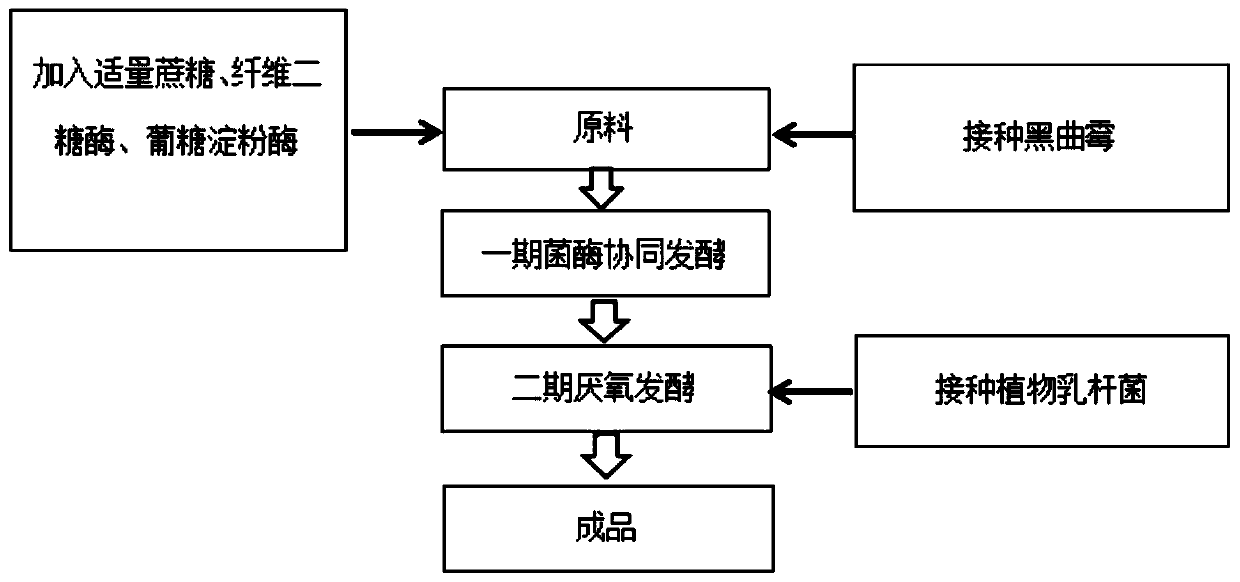
The invention belongs to the field of biological feed, and relates to a high-efficiency and low-cost fermentation feed processing method based on bean dregs and application; the processing method comprises the steps of activating a strain to obtain fermentation seed liquid of bacillus, yeast and lactic acid bacteria; mixing the bean dregs with bran or rice bran, then adding sucrose, adding cellulase, cellobiase, glucoamylase, xylanase, mannanase and beta-glucanase, mixing to obtain a primary aerobic fermentation medium, inoculating the bacillus fermentation seed liquid and the yeast fermentation seed liquid for primary aerobic fermentation, obtaining a primary fermentation mixture after fermentation, and then inoculating the lactic acid bacteria fermentation seed liquid for anaerobic fermentation under sealed conditions to obtain a finished product; an bacteria-enzyme cooperative fermentation and aerobic and anaerobic step-by-step fermentation mode is adopted, the fermentation is completed, the conversion degree of soybean peptide is high, the removal rate of trypsin inhibitor is 85% or above, each mycotoxin is lower than the feed hygiene limit standard of China; the feed is good in palatability, and favored by animals, and the economic efficiency is high.
Owner:浙江康星生物科技有限公司
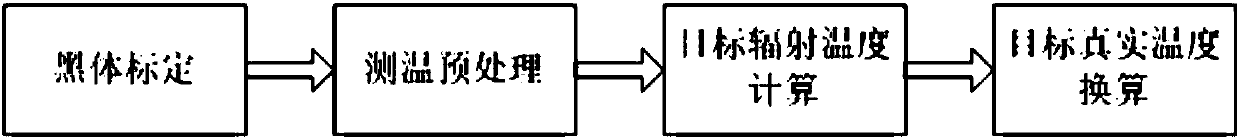
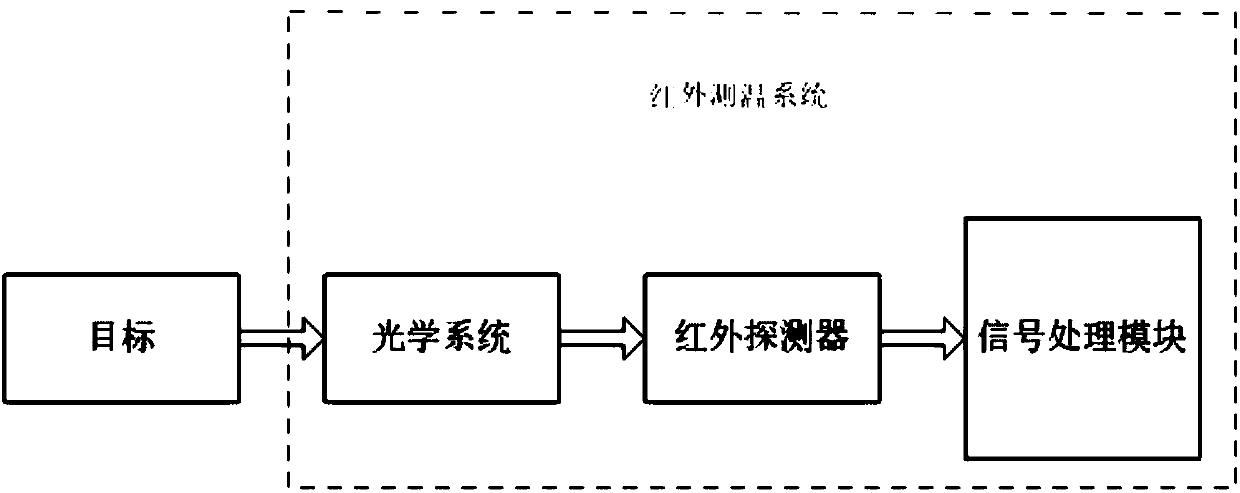
Method for improving temperature measurement precision of thermal infrared imager
InactiveCN107741276AImprove temperature measurement accuracyImprove conversionRadiation pyrometryBlack bodyRadiation temperature
The invention relates to a method for improving the temperature measurement precision of a thermal infrared imager. The method comprises the steps that a high-precision black body is adopted to calibrate the thermal infrared imager, wherein the calibration aims to test the whole system to find the relation between the temperature of the black body and the gray value of an image and describe the relation with a lookup table; the radiation temperature of an object is calculated by using the gray value of the image; the radiation temperature is converted into the real temperature. Compared with atraditional fitted curve black body calibration temperature measurement method, in the method, the black body calibration is conducted by using the difference value lookup table, the temperature measurement pretreatment is adde, the conversion of the radiation temperature is added, and the real temperature value of the target object is obtained; meanwhile, the influences of target reflected radiation, backgrounds and atmospheric radiation on the temperature measurement are reduced, and the temperature measurement precision is improved. The method is suitable for the application field where temperature measurement and detection are conducted by using an infrared detector in electrical equipment detection, fire situation detection, petroleum pipeline detection and the like.
Owner:LUOYANG INST OF ELECTRO OPTICAL EQUIP OF AVIC
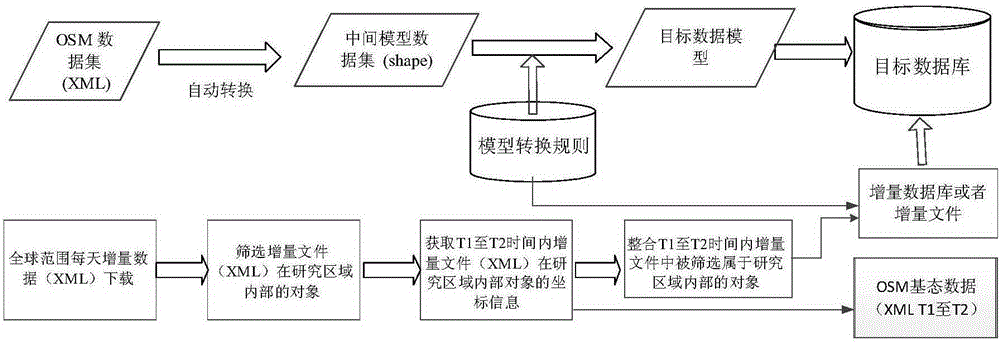
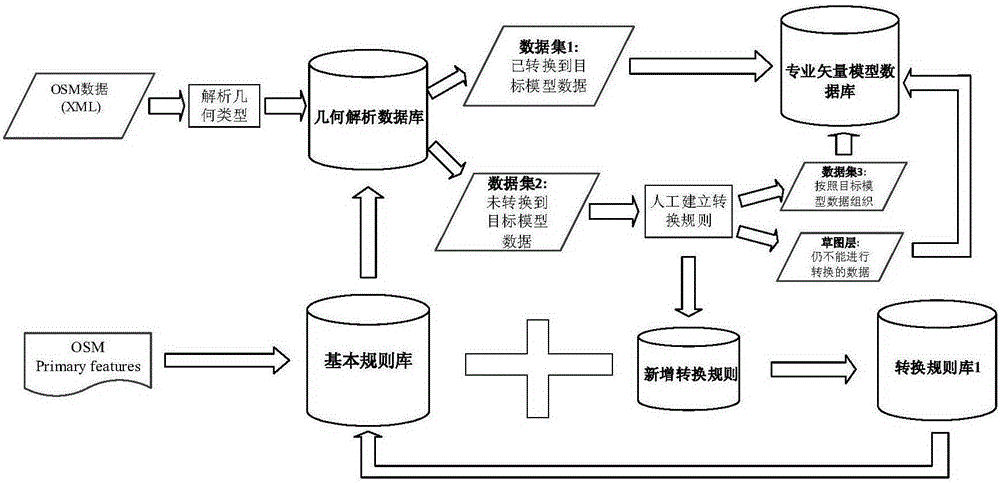
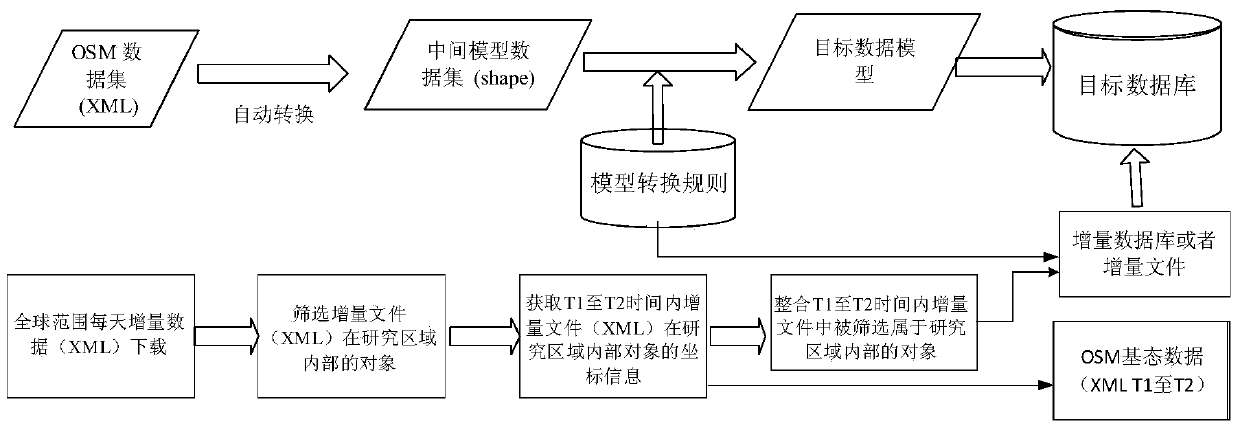
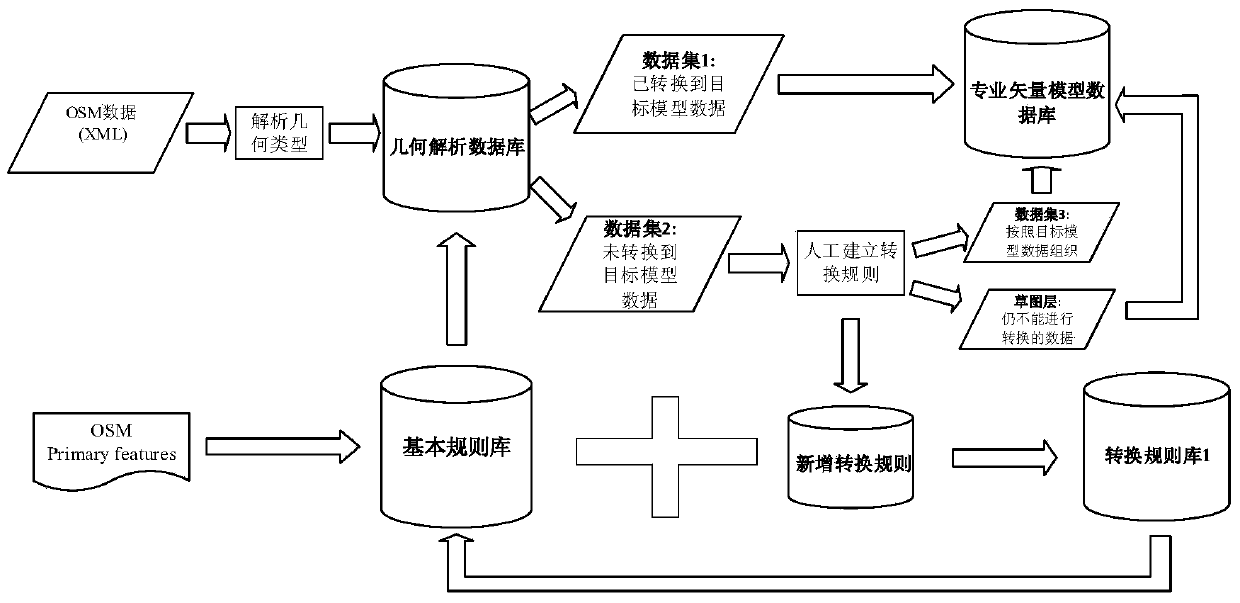
Method for model automatic conversion from OSM (OpenStreetMap) data to professional GIS vector data and dynamic integration of OSM incremental data
ActiveCN105183825AAchieve automatic full conversionLow costGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsGeographic spaceChange Type
The present invention discloses a method for model automatic conversion from OSM data to professional GIS vector data and dynamic integration of OSM incremental data. The method comprises: downloading XML OSM vector data expressed by node, way and relation, and converting the OSM vector data into a user vector data model by using a rule repository to obtain basic state data sometime and somewhere; by using OSM daily global change data, screening incremental data of a research zone by calculating a topological relationship between a change object considering a version evolution process and an object in a Diff file; determining a change type of the object after integration by applying an incremental data integration method which considers an evolution process of a change type between adjacent versions to multi-version incremental data; and finally updating original OSM basic state data by using the obtained incremental data. The method can obtain overseas geospatial vector data of our country efficiently and cost-effectively and maintain the up-to-date state of the data.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
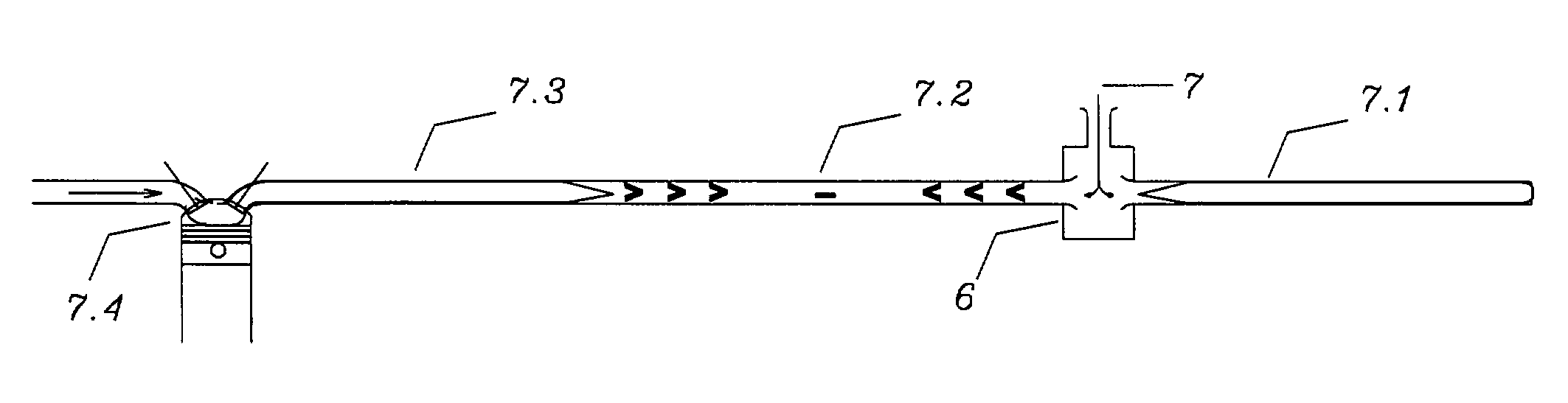
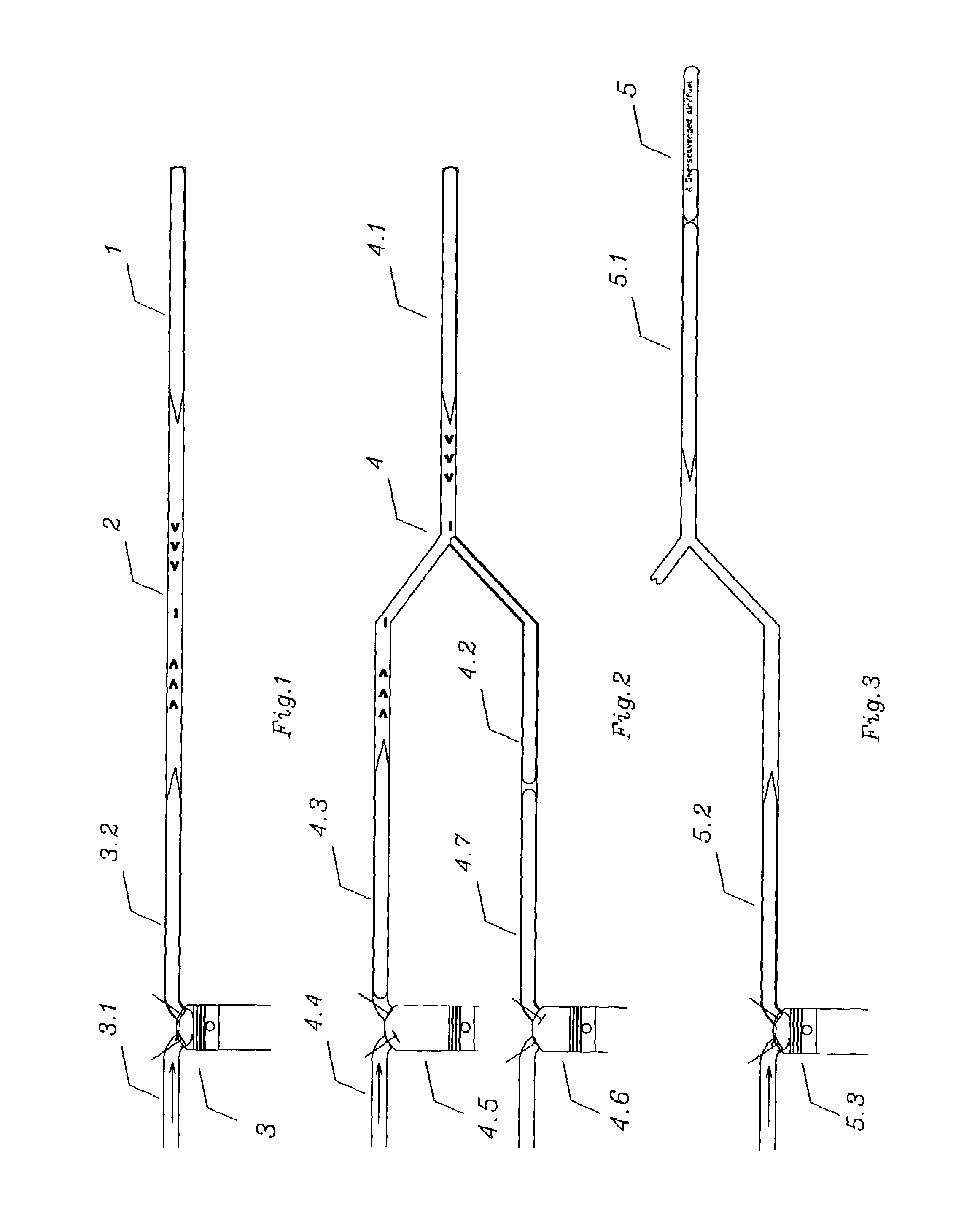
Induction exhaust system
InactiveUS6964161B2Improve conversionIncrease efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelAmount of substanceDirect combustion
A induction exhaust system, for an internal combustion engine, capable of the multi step processes of 1) scavenging the chamber of exhaust gases and free radicals, 2) breaking the scavenge vacuum wave behind each energetic exhaust pulse, releasing said free radicals and the overscavenged air fuel vacuumed from the intake manifold during valve overlap, and 3) induction of such free radicals, unburned fuel, and fresh matter including atmospheric air. Such multi step process 1) relatively improves the fuel efficiency of such engines by reducing the wasted potential energy normally expelled by exhaust systems; unburned fuel, sound pressure energy, waste heat energy, energy rich free radicals formed by incomplete combustion, and energy rich catalytic converter products rich in potential energy that can be further combusted via induction, 2) increases catalytic converter efficiency by forcing unburned air fuel and free radicals to make multiple passes through such converter, thereby increasing residency time, 3) reduces emissions of undesirable compounds and free radicals via induction, 4) improves relative effective octane rating of fuel used by creating a unique composition of matter that acts to refract and reflect sonic detonation shock waves, disrupting and disbursing them, reducing detonation, thereby improving combustion efficiency, and 5) allows a new means to direct combustion process products and / or remove undesirable products, and / or introduce desirable matter into a combustion chamber, allowing further alteration of such unique composition of matter layered on top of such engine's prime mover combustion surface, and 6)including an adaptive means to dynamically optimize its function.
Owner:CAMPBELL MONTY ALLEN
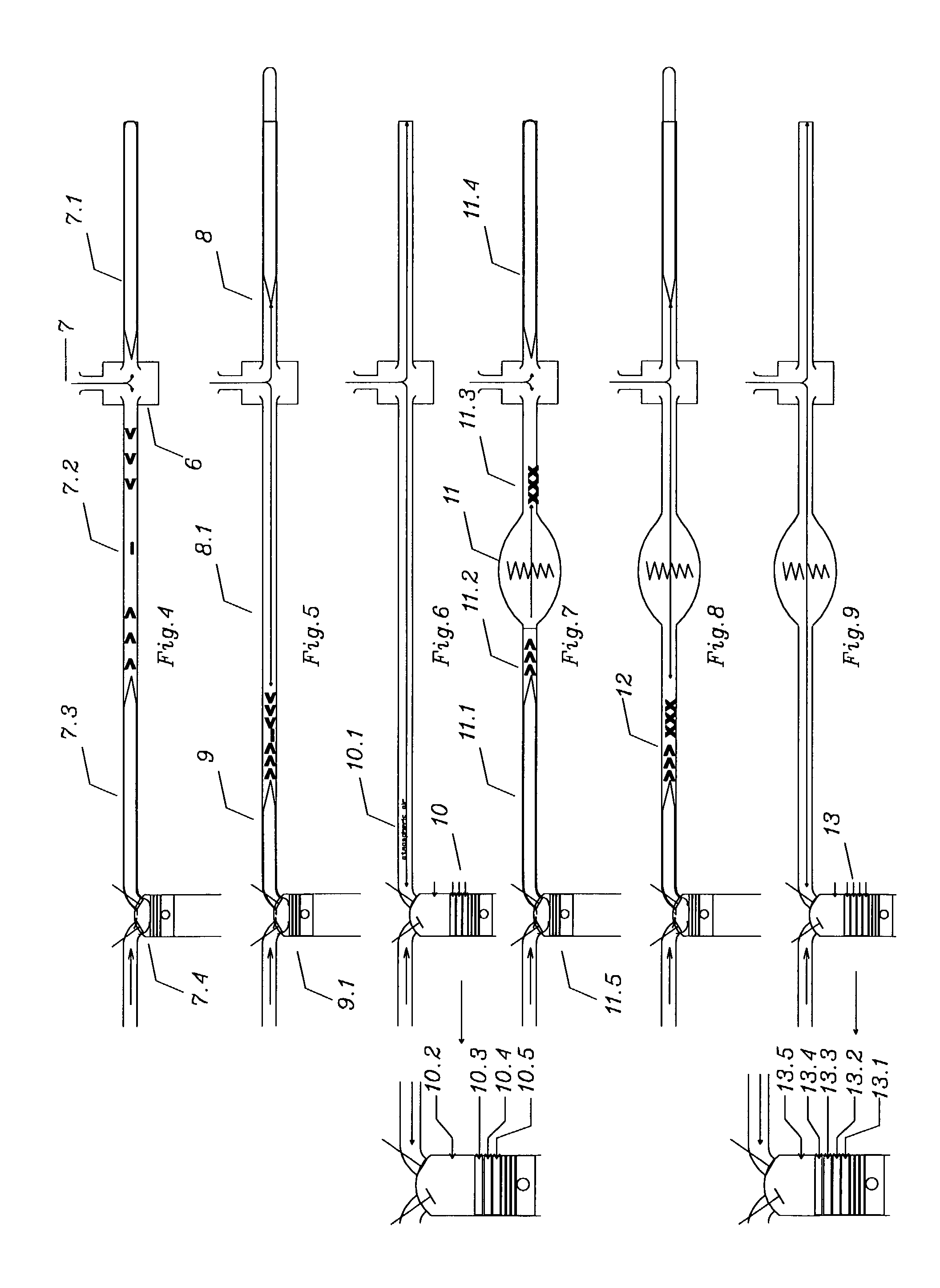
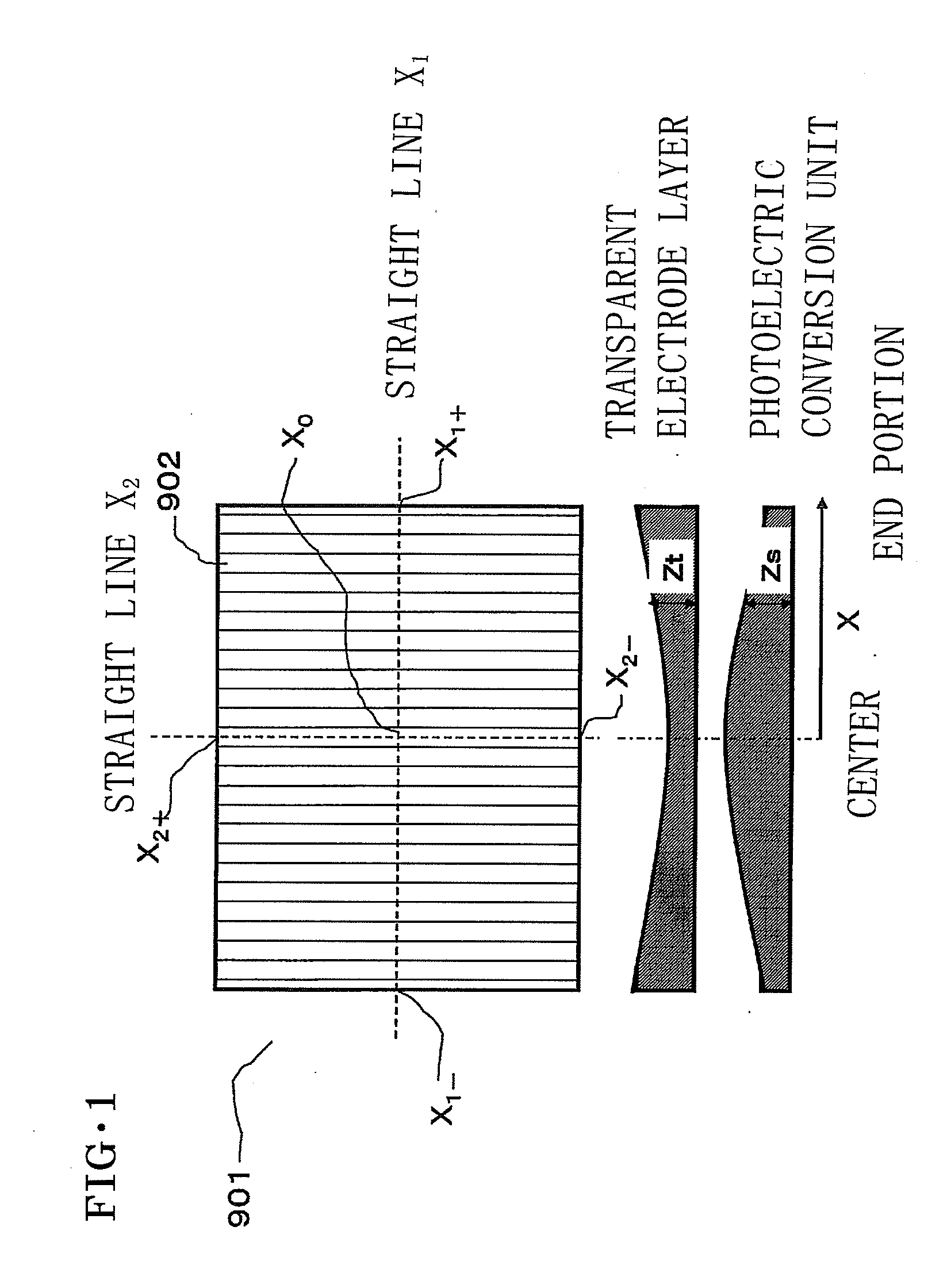
Thin film photoelectric conversion device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110061715A1Current be improveImprove conversionPV power plantsFinal product manufactureLine segmentEngineering
Provided is a thin film photoelectric conversion device with maximized output characteristic, by improving an uneven current value of a photoelectric conversion cell caused by an uneven film thickness and an uneven film quality of a photoelectric conversion semiconductor layer, which may be generated in scaling up an integrated-type thin film photoelectric conversion device. The thin film photoelectric conversion device includes: a substrate, a transparent electrode layer, a photoelectric conversion unit, and a back electrode layer. An increasing rate ΔZt of the film thickness Zt of the transparent electrode layer along X and an increasing rate ΔZs of the film thickness Zs of the photoelectric conversion unit along X have different signs, whereas one line segment in a parallel direction to a main surface of the substrate is taken as X″.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
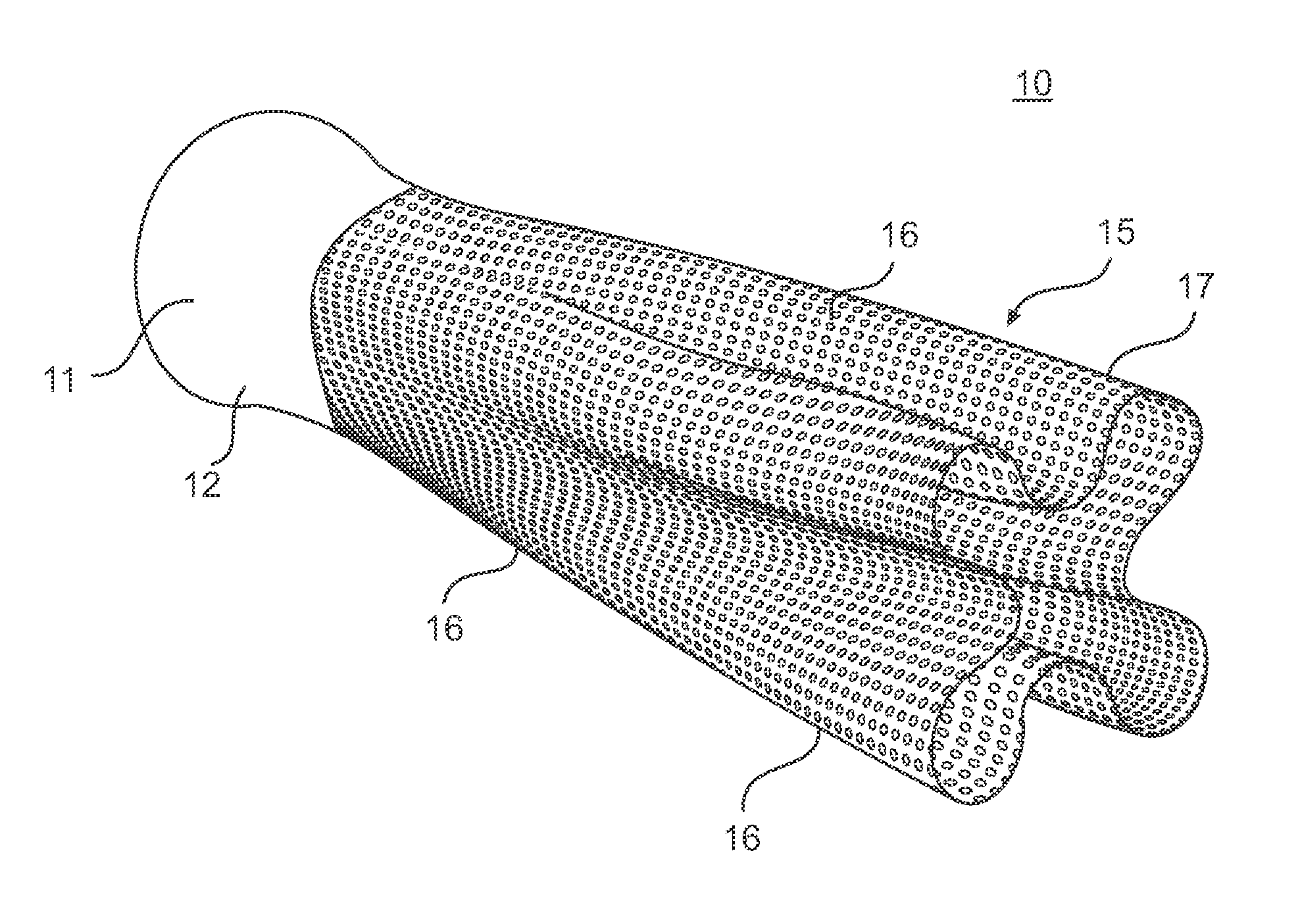
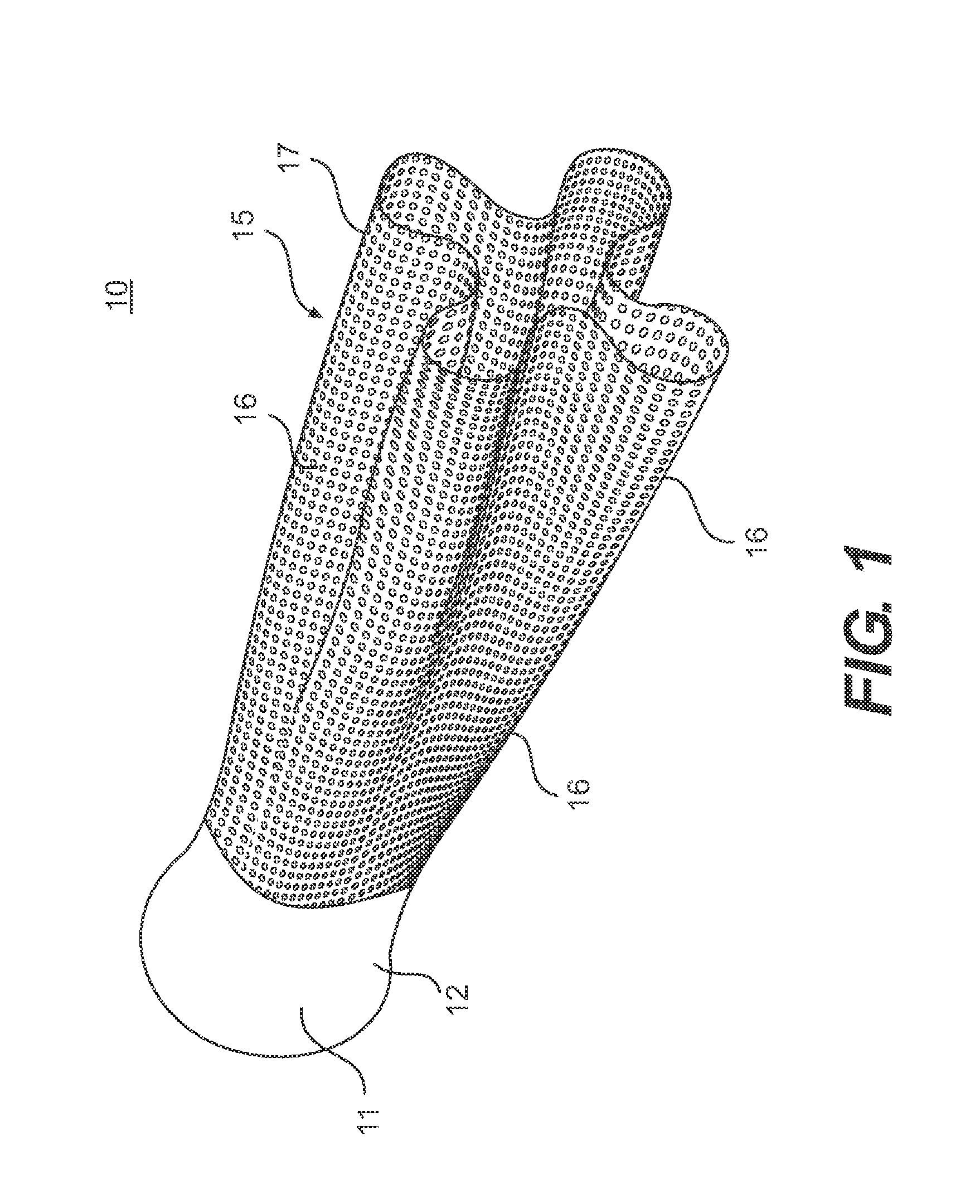
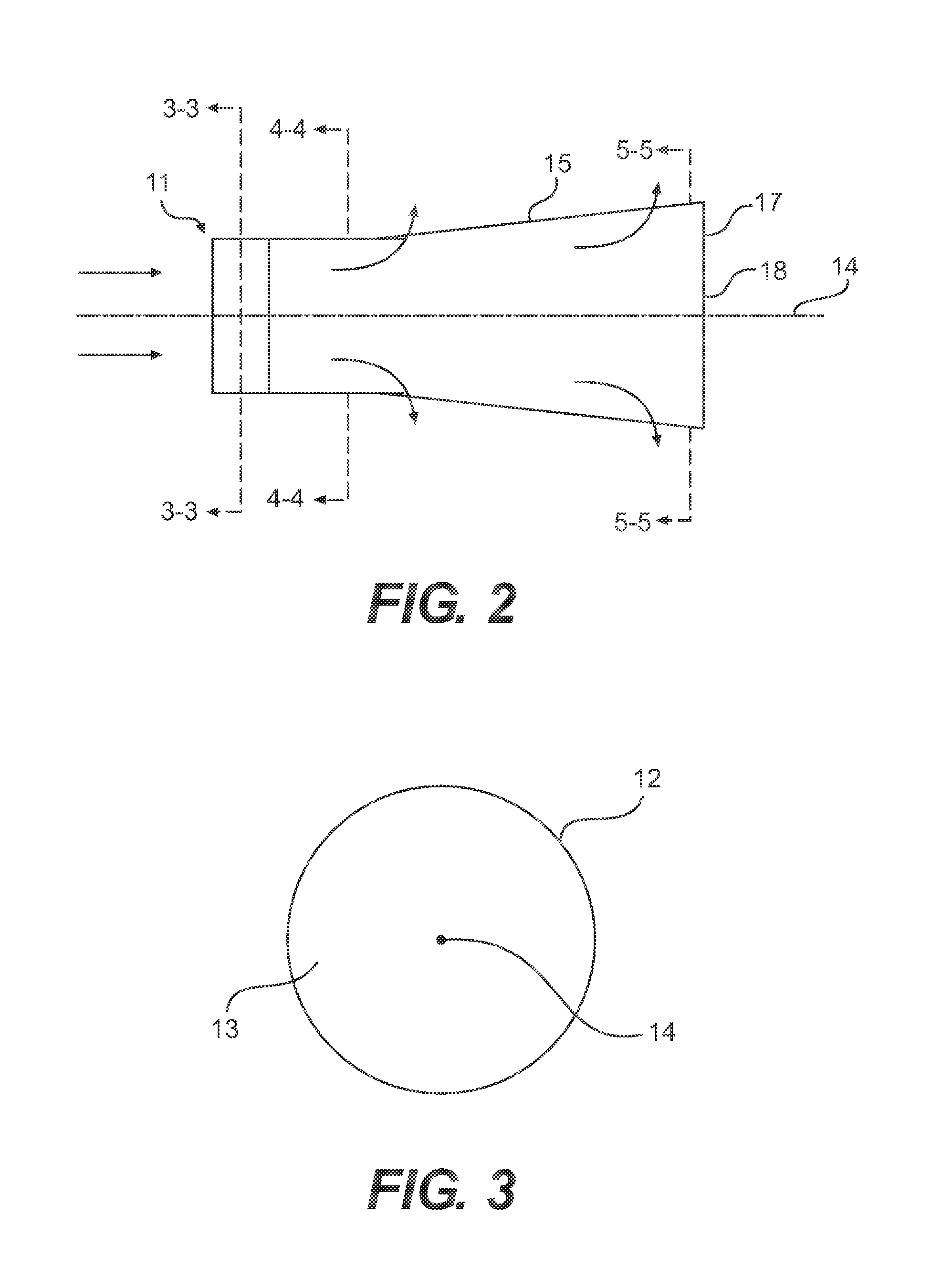
Pre-converter device for cleaning exhaust gas for an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7384609B2Improve conversionSpeed up the conversion processCombination devicesExhaust apparatusExhaust fumesEngineering
A catalytic converter device for cleansing exhaust gas emitted from an internal combustion engine is disclosed. The catalytic converter device includes an elongated body having a longitudinal axis. An inlet area is located at one end of the elongated body, wherein the exhaust gas enters the elongated body in the inlet area. A sleeve extends from the inlet area. The sleeve has a catalytic material formed thereon. The sleeve has an active surface for reacting with the exhaust gas, wherein the size of the active surface increases as a distance from the inlet area increases. The sleeve includes a plurality of openings formed therein and at least one depression.
Owner:BRP ROTAX
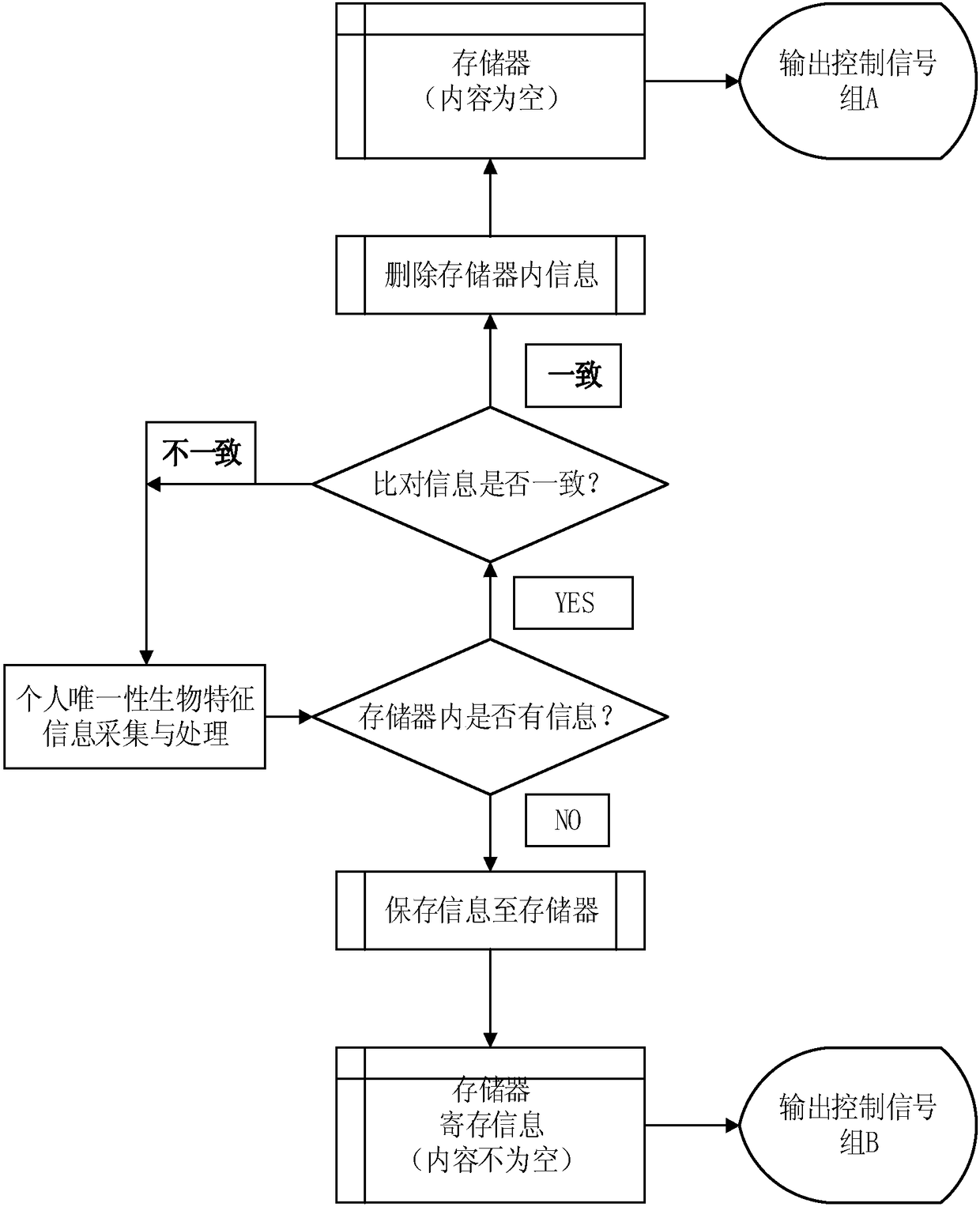
Minimalist method for ensuring safety of personal belongings and performing personal duties based on uniqueness of biological features and application of minimalist method
InactiveCN109147095ASimple logicThe program is minimalIndividual entry/exit registersEngineeringHuman body
The invention provides a minimalist method for ensuring safety of personal belongings and performing personal duties based on uniqueness of biological features. The method includes the following stepsthat solely by recognizing the biological features, locking and unlocking actions are sequentially achieved for ensuring the safety of the personal belongings; or, solely by recognizing the biological features, unlocking and locking actions are sequentially achieved for performing personal duties; or solely by recognizing the biological features, locking and unlocking actions are sequentially achieved for performing personal duties; or solely by recognizing the biological features, unlocking and locking actions are sequentially achieved for ensuring the safety of the personal belongings. Theuniqueness of the human body biological features is used for performing uniqueness operation of the 'open first and close after' or 'close first and open after', the operation is simple and convenient, and the method is characterized in that 'people who open a storage cabinet need to close the storage cabinet, and people who close the storage cabinet need to open the storage cabinet. According tothe method, only the biological feature information of a current user is stored, the hardware requirement is very low, the production cost is reduced, and the comfort level and the sense of security of the user are improved.
Owner:汤烈 +1
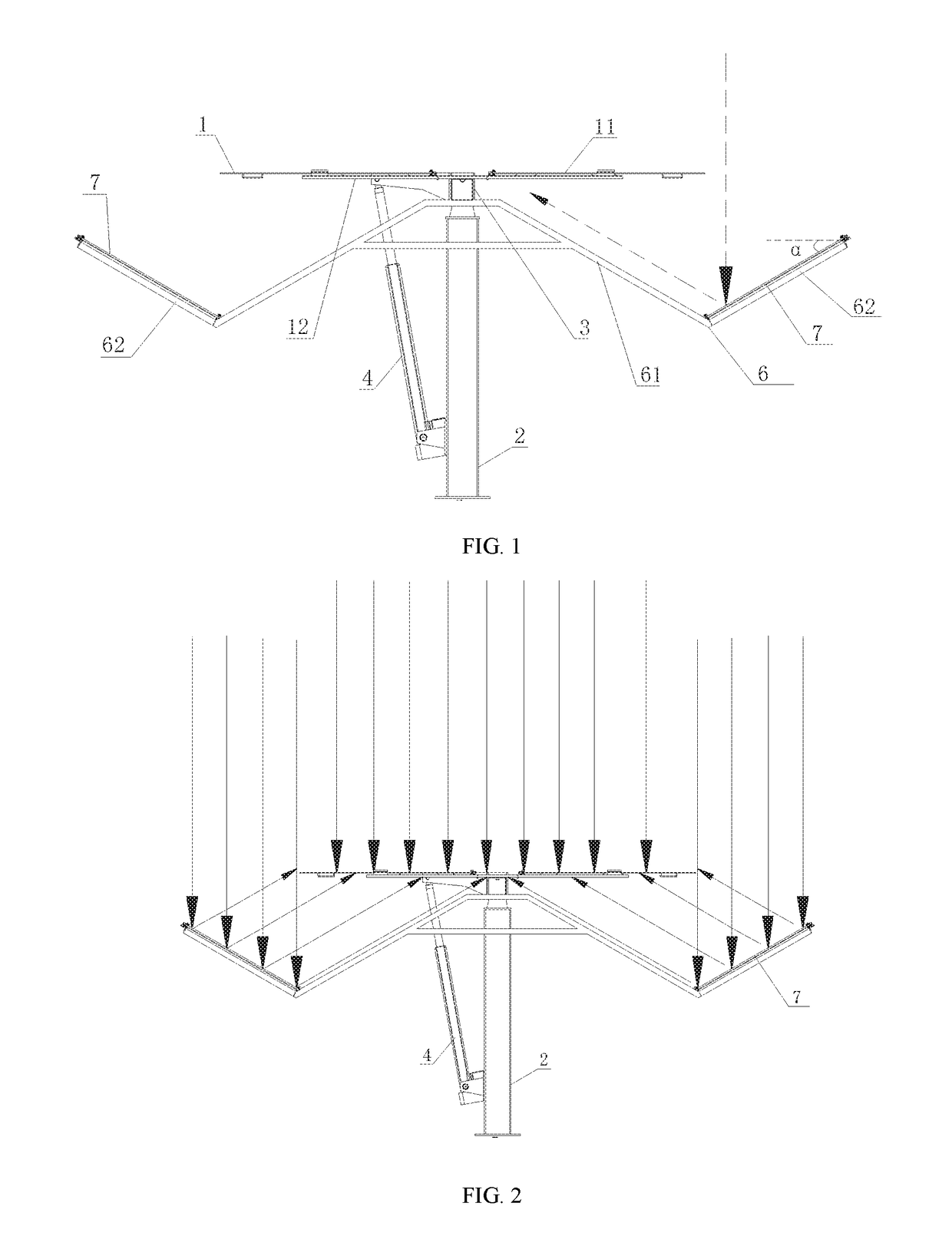
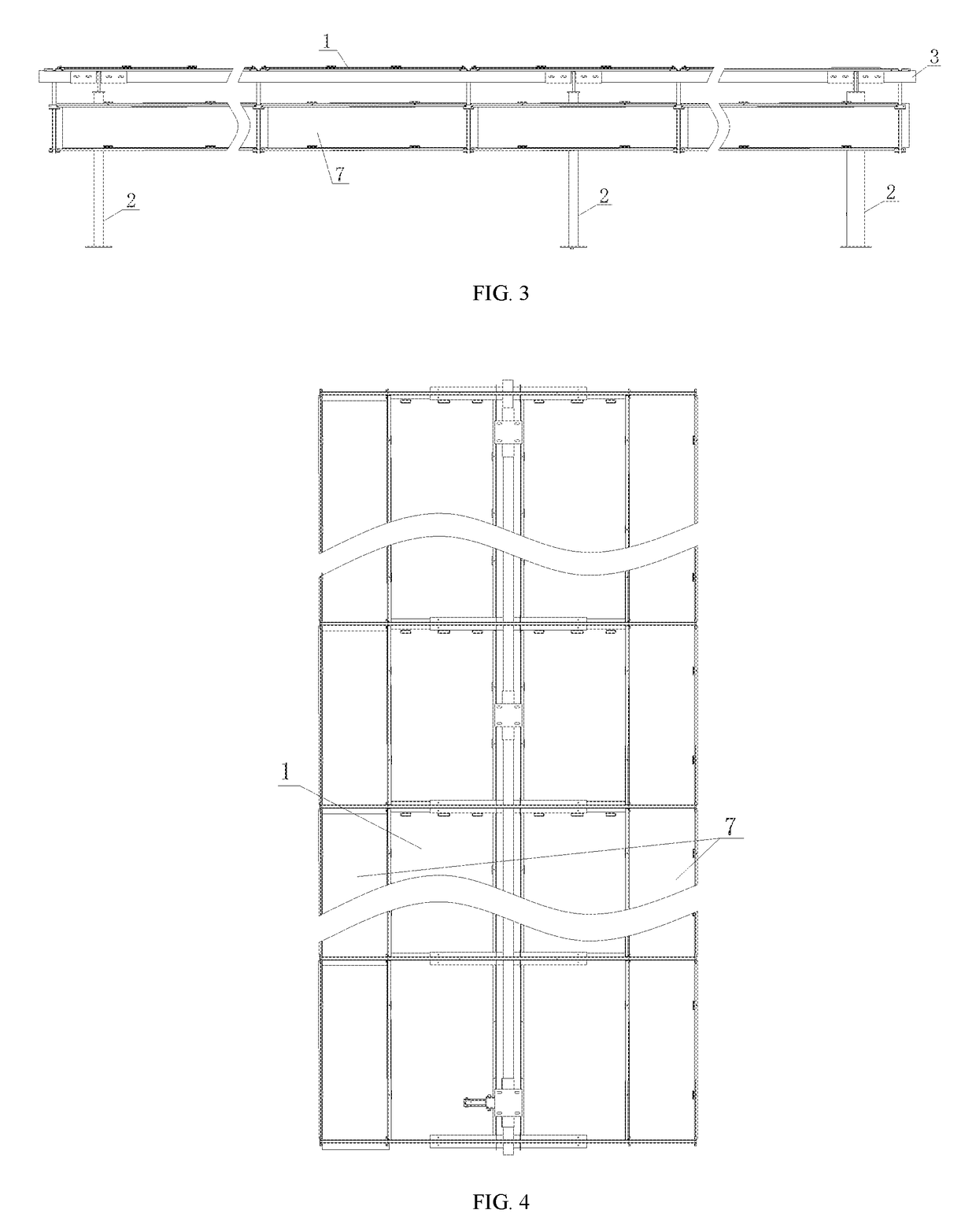
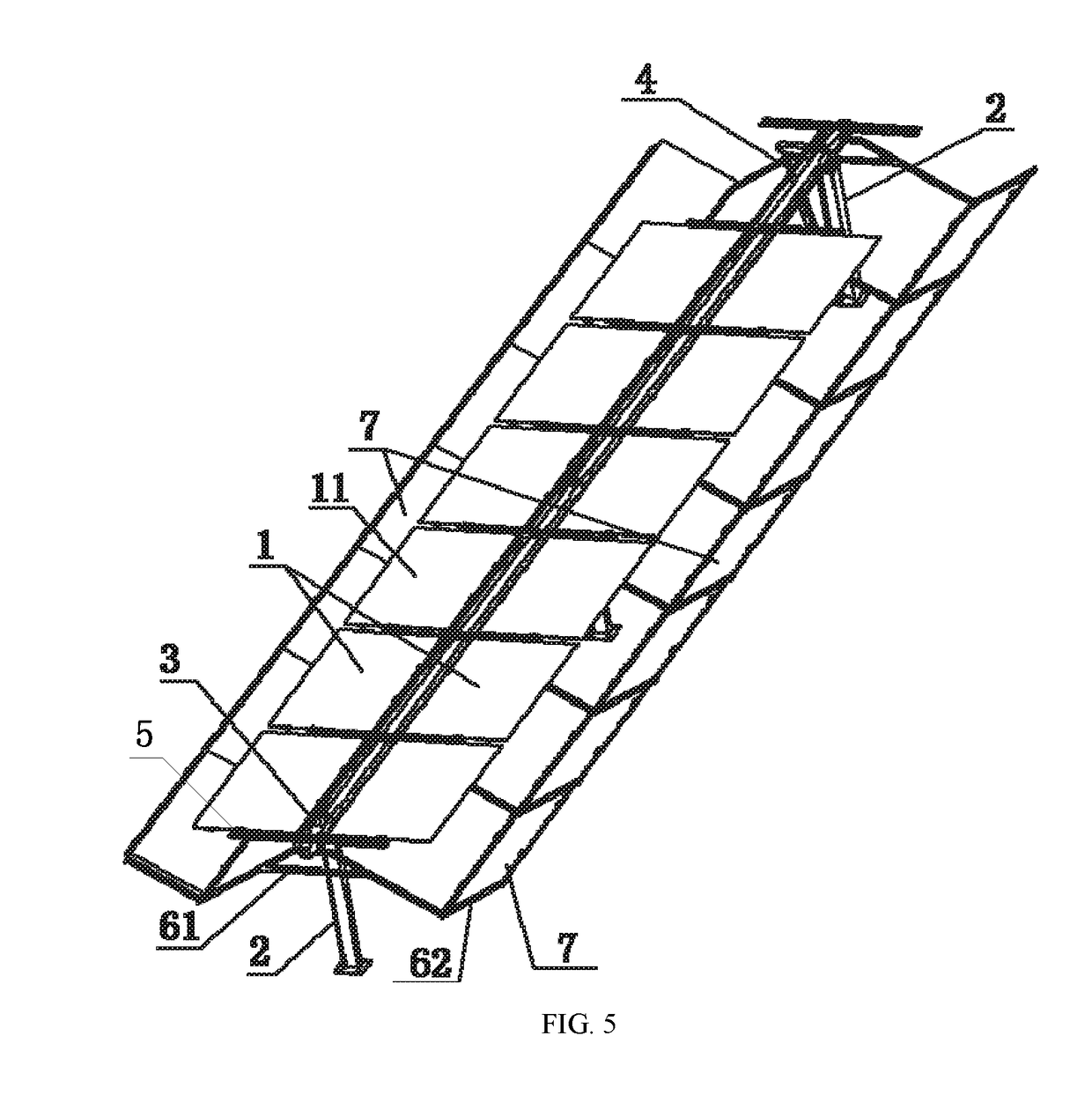
Horizontal single-axis tracking photovoltaic support with double-sided power generation
InactiveUS20190020302A1Improve conversionIncrease light intensityPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyAcute angleEngineering
The present invention provides a horizontal single-axis tracking photovoltaic support with double-sided power generation, suitable for installing a double-sided PV module with a toward-sun light absorption surface and a backward-sun light absorption surface, including: an upright post and a torque tube disposed on the upright post, the torque tube capable of being rotated around the upright post under the action of a driving device, a plurality of groups of crossbeams are disposed along a lengthwise direction of the torque tube, and the double-sided PV module is disposed on each group of the crossbeams, a light-reflecting-panel support is disposed at the torque tube, and a light-reflecting panel is disposed on the light-reflecting-panel support. The light-reflecting panel reflects sunlight onto the backward-sun light absorption surface, and an angle α between the plane where the light-reflecting panel is located and the plane where the double-sided PV module is located is an acute angle.
Owner:HANGZHOU PINNET TECH CO LTD
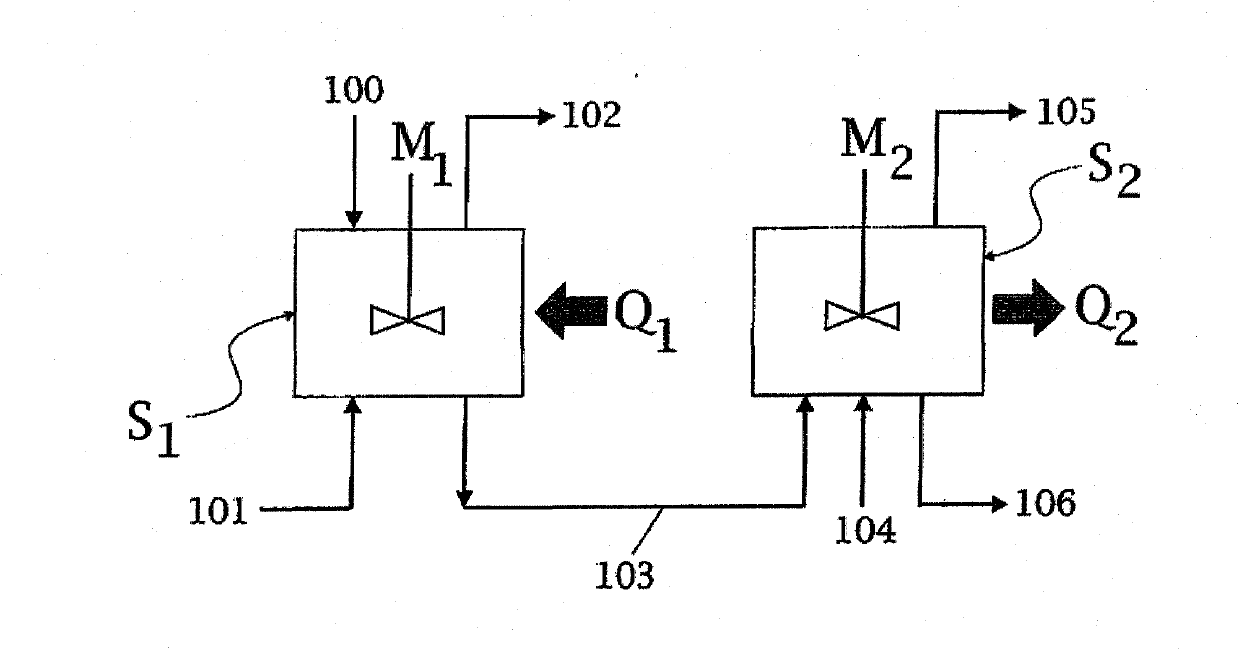
Process for producing high-quality melamine from urea
InactiveCN102015663ADelayed expansionSpeed up heat exchangeProcess control/regulationOrganic chemistryFluid phasePhysical chemistry
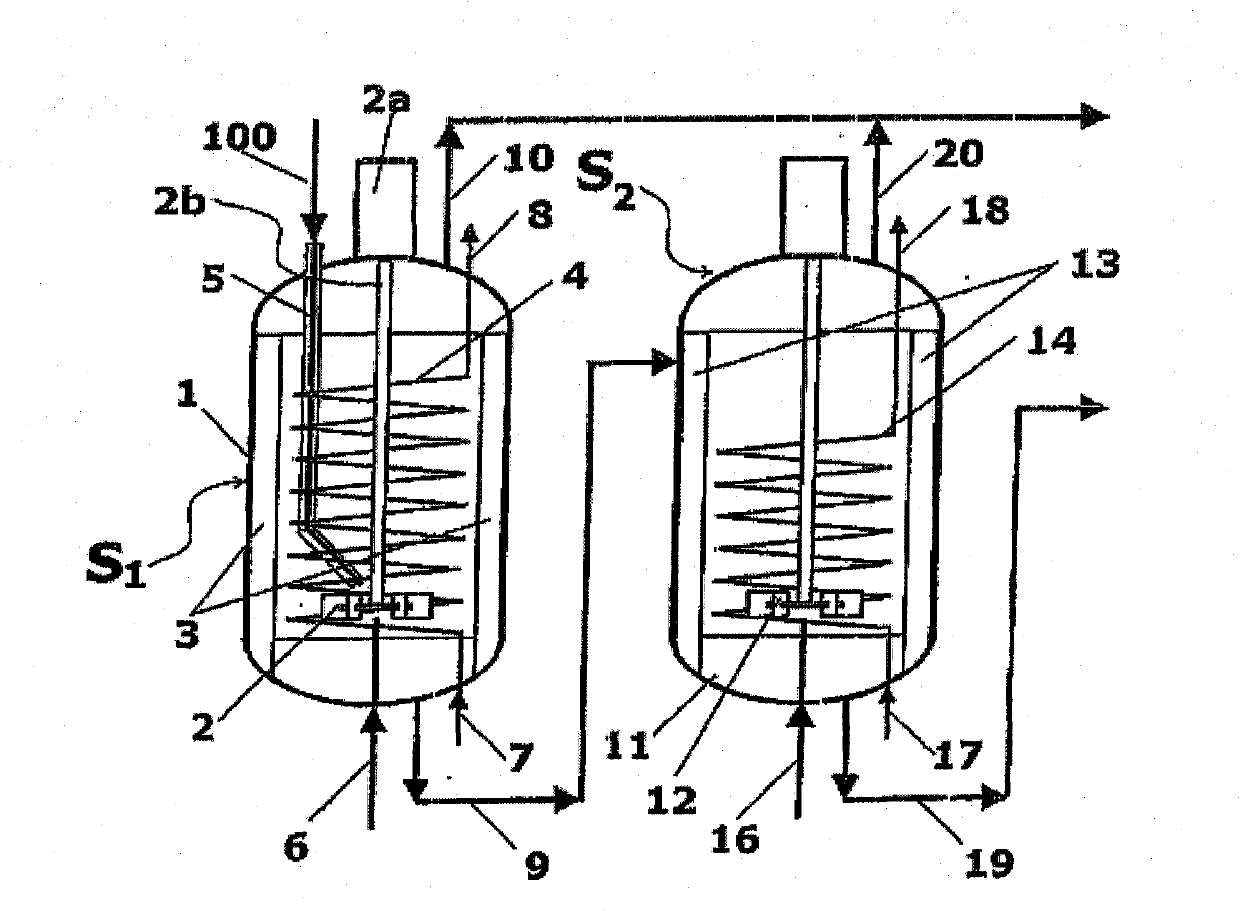
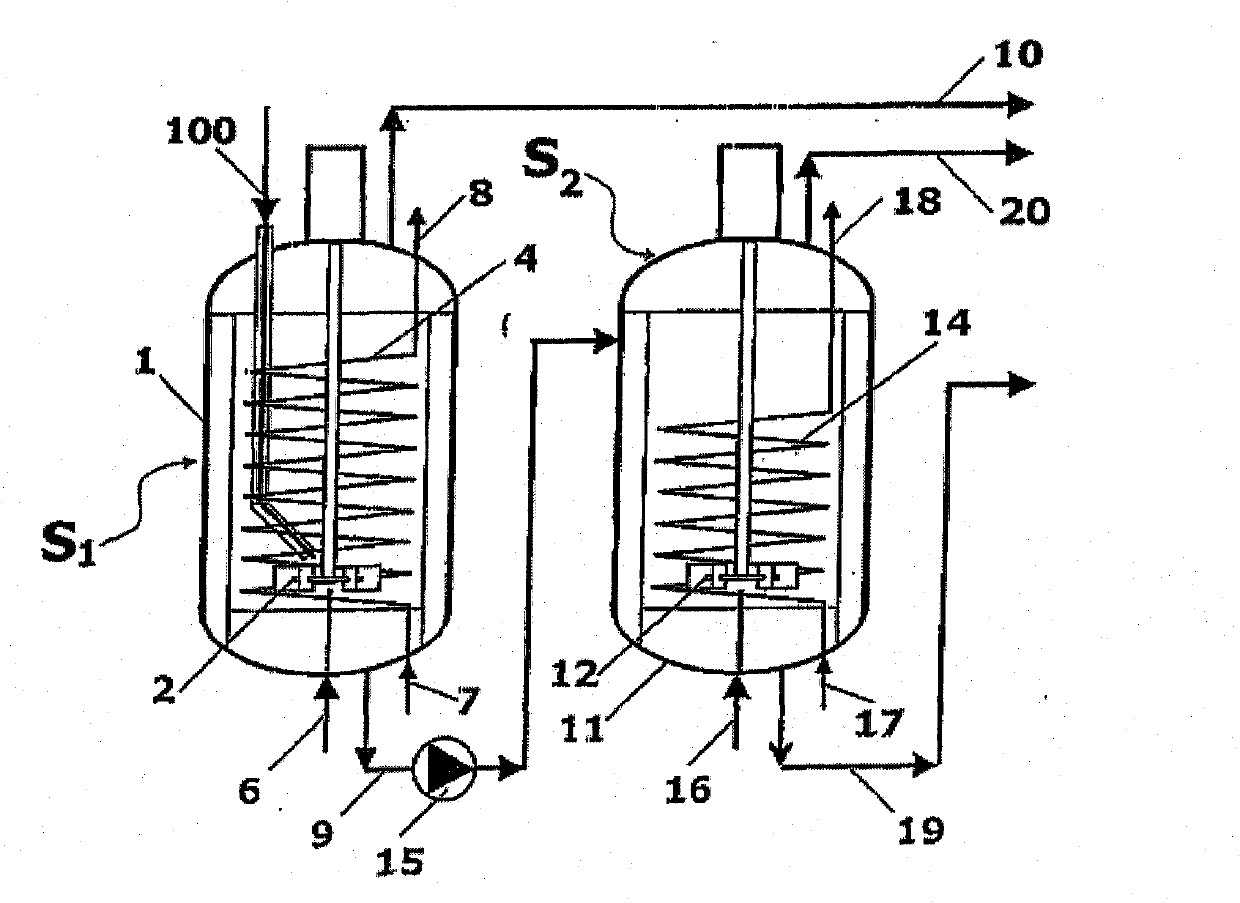
A process for high-pressure, liquid phase conversion of urea into melamine is disclosed, where molten urea is fed to a first reaction zone (S1 ) where the melamine melt is under mechanical agitation, and a heat input (Q1 ) is provided to maintain the endothermic reaction, and the liquid is then passed to a second reaction zone (S2) kept at a lower temperature and where further agitation is provided. Embodiments of plants adapted to carry out the process are also disclosed, including multiple stirred reactors in cascade and a single reactor with multiple internal compartments defining said first and second reaction zones.
Owner:UREA CASALE SA
Quick-response reversible-photoisomerization perfluorinated-ether-chain azobenzene and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN104926683ASolve the problem of green environmental protectionNon-bioaccumulativeOrganic chemistryTenebresent compositionsStructural formulaAniline
The invention discloses quick-response reversible-photoisomerization perfluorinated-ether-chain azobenzene and a preparation method therefor. The perfluorinated-ether-chain azobenzene has a structural formula shown in the description. The preparation method comprises the steps: dissolving p-phenylene diamine and perfluoroether acyl fluoride, which serve as starting compounds, in an organic solvent so as to prepare (4-perfluoroether amide)phenylamine; diazotizing the compound by a hydrochloride / nitrite system, and then, enabling the diazotized compound to react with an alkali solution of phenol so as to prepare 4-perfluoroether amide-4'-hydroxyazobenzene; and in an anhydrous organic solvent, enabling 4-perfluoroether amide-4'-hydroxyazobenzene to react with methacryloyl chloride or acryloyl chloride so as to prepare 4-perfluoroether amide-4'-methacrylate azobenzene or 4-perfluoroether amide-4'-acrylate azobenzene. The compound disclosed by the invention has the advantages of reversible photoisomerization, quick response and high isomerization degree; a fluorinated ether chain is free of biological accumulation compared with a perfluoroalkyl hydrocarbon chain; and the compound contains an active functional group, i.e., propenyl which can participate in addition reaction or polymerization reaction, so that the field of application is broad.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
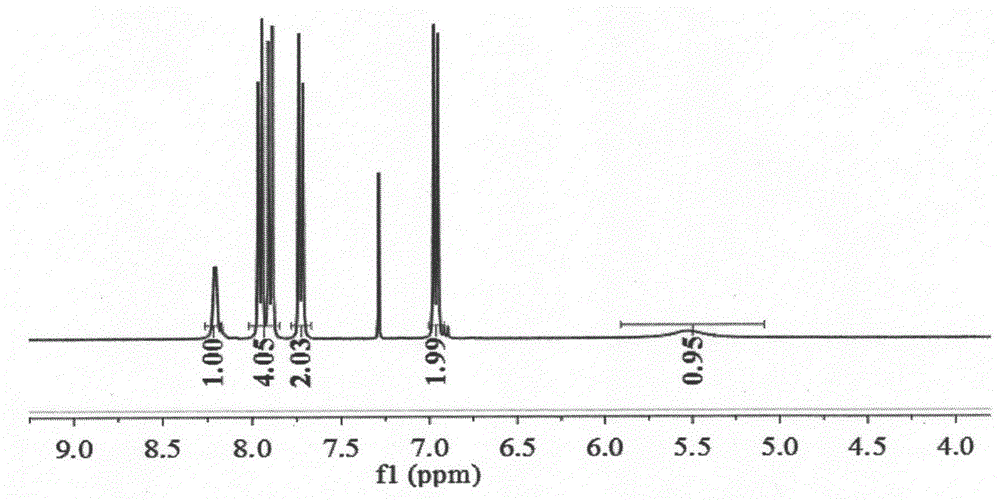
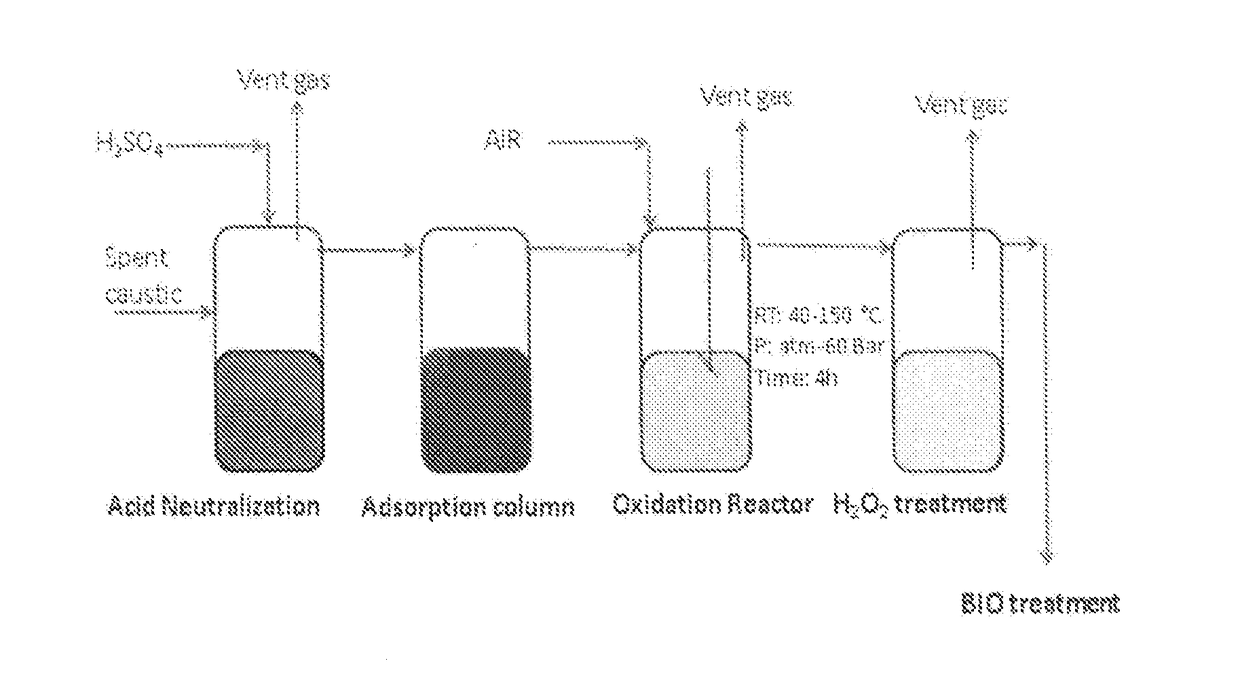
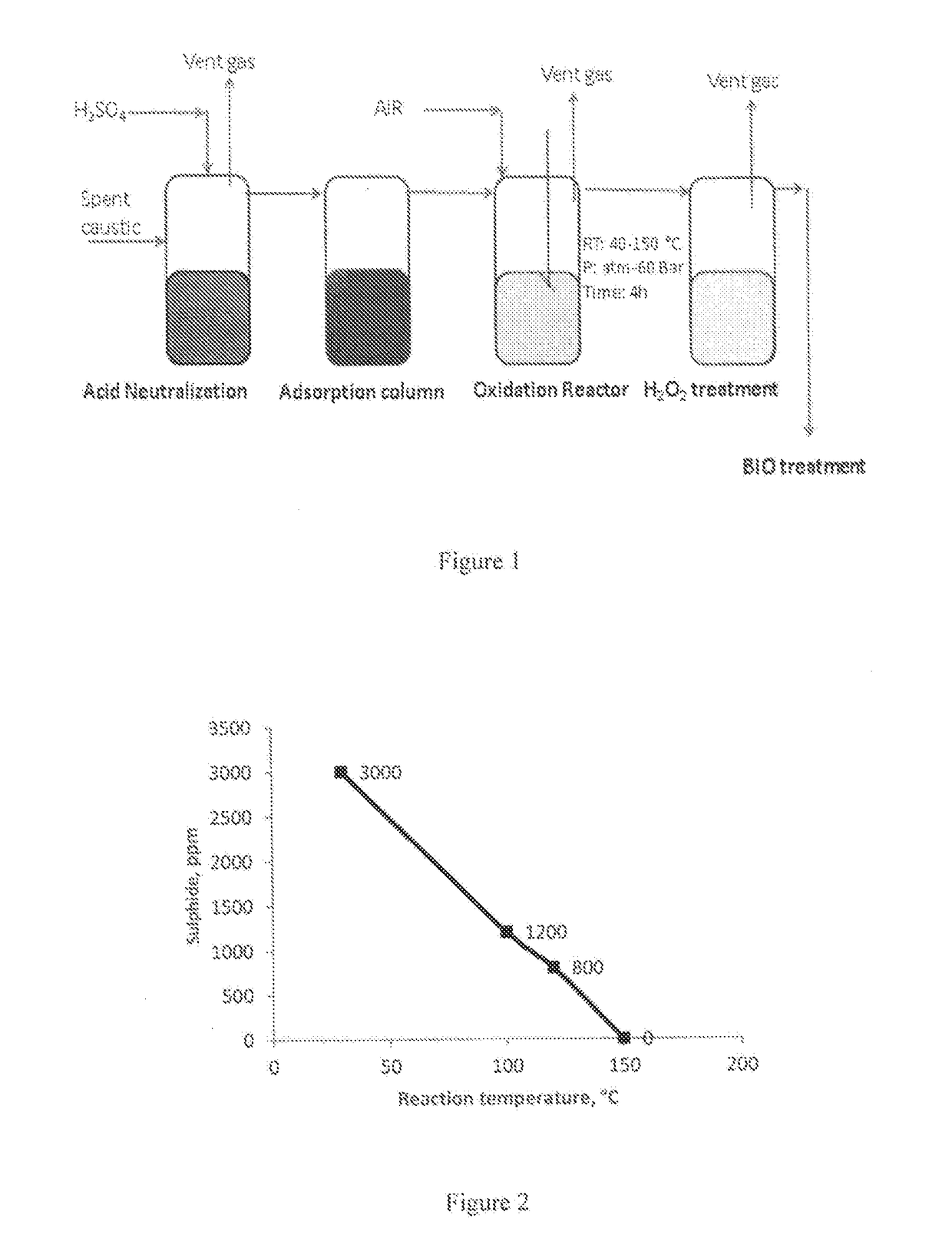
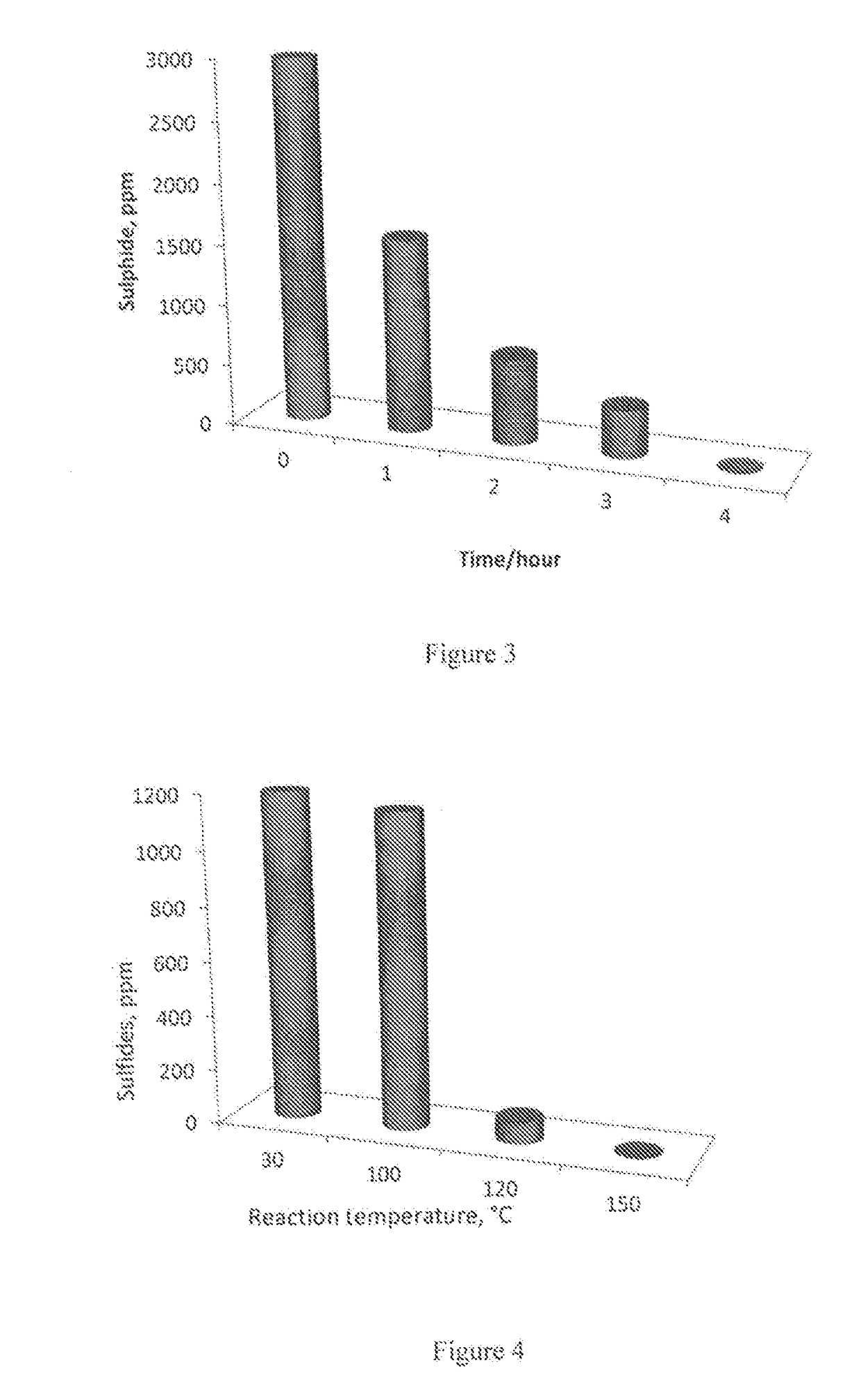
Removal of Sulfides in Spent Caustic Stream over Active Solid Phase Catalysts
ActiveUS20170174544A1Effective oxidationImprove conversionSludge treatment by oxidationMolecular sieve catalystsSolid phasesSulfide
The present subject matter relates to the development of active catalyst composite based on supported transition metal oxides, especially, Cu, Co that are effective in the removal sulfides in the diluted spent caustic. The process for the reduction of sulfides in spent caustic comprises of reacting various organic and inorganic sulfides with molecular oxygen in the presence of active catalyst at various reaction temperatures ranging ambient to 200° C. and pressures between atmospheric pressure to 60 bars. The process also relates to complete scheme for the removal of sulfides in spent caustic.
Owner:HINDUSTAN PETROLEUM CORP LTD
Fermentation method for effectively improving content of soy isoflavone glycoside in soybean dreg feed
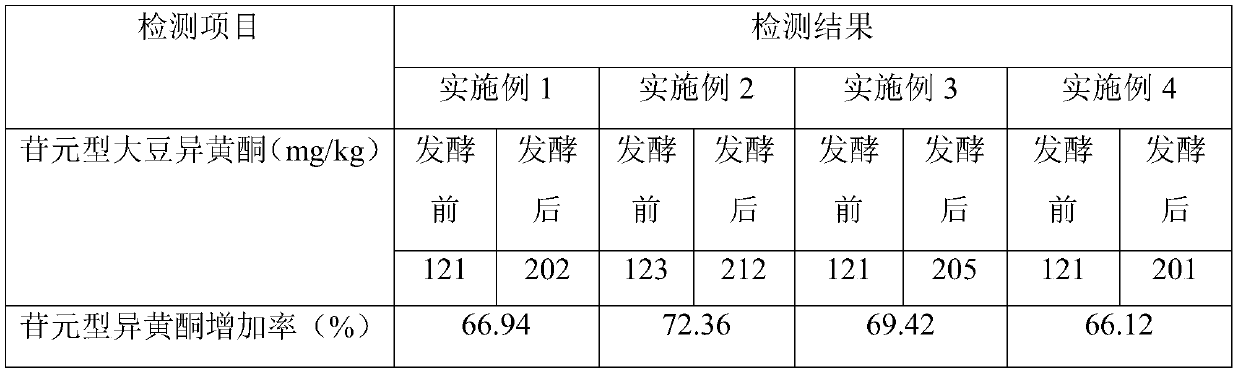
The invention belongs to the field of biological feed, and relates to a fermentation method for effectively improving the content of soy isoflavone glycoside in soybean dreg feed. The method includesthe steps that lactobacillus plantarum is activated and cultured to obtain a lactobacillus plantarum fermentation seed solution; then a proper amount of cellobiase, glucose amylase and cane sugar areadded into soybean dregs and uniformly mixed to obtain a first-stage fermentation culture medium; aspergillus niger powder is added into the first-stage fermentation culture medium, the water contentand fermentation temperature are adjusted for first-stage bacterial enzyme collaborative fermentation, and a first-stage fermentation mixture is obtained; then the lactobacillus plantarum fermentationseed solution is inoculated in the first-stage fermentation mixture and uniformly mixed so as to obtain a second-stage fermentation mixture; second-stage anaerobic fermentation is carried out under asealing condition, and a finished product is obtained after fermentation is completed. Bacterial enzyme collaborative fermentation and aerobic and anaerobic step-by-step fermentation are used, the cheap soybean dreg raw materials are used, fermentation is thorough, the conversion degree of aglycone type soy isoflavone is high, the economic benefit is good, the palatability is good, and animals like to eat the feed.
Owner:浙江康星生物科技有限公司
Synthetic method of 2-chloroethyl hydrazono methyl formate
InactiveCN109180535AHigh yieldImprove catalytic performanceOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAcetic anhydrideDouble phase
The invention discloses a synthetic method of 2-chloroethyl hydrazono methyl formate. According to the synthetic method, dimethyl carbonate, hydrazine hydrate, chloroacetaldehyde, methyl formate, p-nitrobenzaldehyde, acetic anhydride, pyrrole, pyridine, zinc chloride, and terephthalaldehyde are taken as main raw materials; dimethyl carbonate and hydrazine hydrate are subjected to oxidation reaction under the effect of catalyst AZO-CMP-1; chloroacetaldehyde and methyl formate addition substation is carried out so as to obtain the target product 2-chloroethyl hydrazono methyl formate; in oxidation reaction, the catalyst is a liquid solid double-phase catalyst system, and is extremely high in catalytic activity, selectivity, and recycling stability; high conversion degree is achieved; production separation purifying is easy; and product yield is high.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Depth detection device for water conservancy and hydropower
InactiveCN113819975AControl lifting speedImprove conversionMachines/enginesLevel indicatorsGear wheelElectric machine
The invention belongs to the technical field of detection devices and particularly relates to a depth detection device for water conservancy and hydropower. The device comprises a main body, wherein supporting blocks for supporting a roller are arranged at an upper end of the main body, the supporting blocks are connected through rotating shafts, and the rotating shafts of the supporting blocks are sleeved with the roller for sleeving a rope; connecting blocks for limiting and sliding the T-shaped sliding rod are arranged at two ends of the supporting block, the roller is connected with a speed regulating box through a rope, a motor is arranged at the speed regulating box and drives a rack mechanism to rotate through a main shaft, and the rack mechanism drives a first transmission gear mechanism to rotate through a second transmission gear mechanism; the first transmission gear mechanism drives the third gear mechanism to rotate through a connecting shaft, and the rotating speed of the third gear mechanism is controlled through the motor, so the lifting speed of the rope is controlled, stress difference caused by uneven speed is reduced, conversion of the extending distance of the rope is effectively improved, and detection precision is improved.
Owner:ECONOMIC RES INST OF STATE GRID GANSU ELECTRIC POWER
High-frequency ultrasonic transducer with curved focusing array and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105591020AIncrease horizontal resolutionImprove conversionPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device detailsRadianHigh frequency
The invention discloses a high-frequency ultrasonic transducer with a curved focusing array and a preparation method thereof. The high-frequency ultrasonic transducer comprises a curved substrate. The upper surface of the curved substrate is an annular member of which the radian is 60-180 DEG. The upper surface of the curved substrate is totally or partially covered by a curved focusing array. The bottom of the curved focusing array is a bottom electrode of which the height is 4[mu]m to 20[mu]m. The bottom electrode is provided with 16-225 parallelly arranged arc-shaped array elements on the bottom electrode. The bottom of each arc-shaped array element is a lead magnesium niobate-lead titanate thick film of which the height is 7[mu]m-100[mu]m, and the top is a gold electrode of which the height is 100nm-300nm. Furthermore the circle center of the arc-shaped array element is arranged in the central axis of the upper surface of the curved substrate. Through the high-frequency ultrasonic transducer and the preparation method thereof, the ultrasonic transducer with the lead magnesium niobate-lead titanate thick-film focusing array is prepared, and the high-frequency ultrasonic transducer with high resolution has a good application prospect.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of preparation method of high-efficiency spherical-like green phosphor for white LED
ActiveCN104371723BImprove consistencyDifficult to disperseEnergy efficient lightingLuminescent compositionsAdhesiveSlurry
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-efficiency spherical green fluorescent powder for white light LEDs (light-emitting diodes). The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing raw materials according to the stoichiometric proportion, weighing an adhesive which accounts for 0.5-5 wt% of the raw materials, and carrying out wet mixing on the raw materials in deionized water by using a ball mill to obtain a uniform powder slurry, and carrying out spray granulation on the powder slurry to obtain a highly dispersed spherical powder precursor; (2) carrying out first sintering on the powder precursor in an oxidizing atmosphere to form first sintering powder; and (3) mixing the first sintering powder with a fluxing agent, and carrying out second sintering in a reducing atmosphere to obtain the green fluorescent powder for white light LEDs. The green fluorescent powder for LEDs has the advantages of high crystallization degree, higher quantum efficiency and higher granule uniformity due to the spherical granular shale of the powder.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGCUN YUJI TECH
Method for improving urban organic garbage mixed anaerobic digestion directional hydrolytic acidification effect
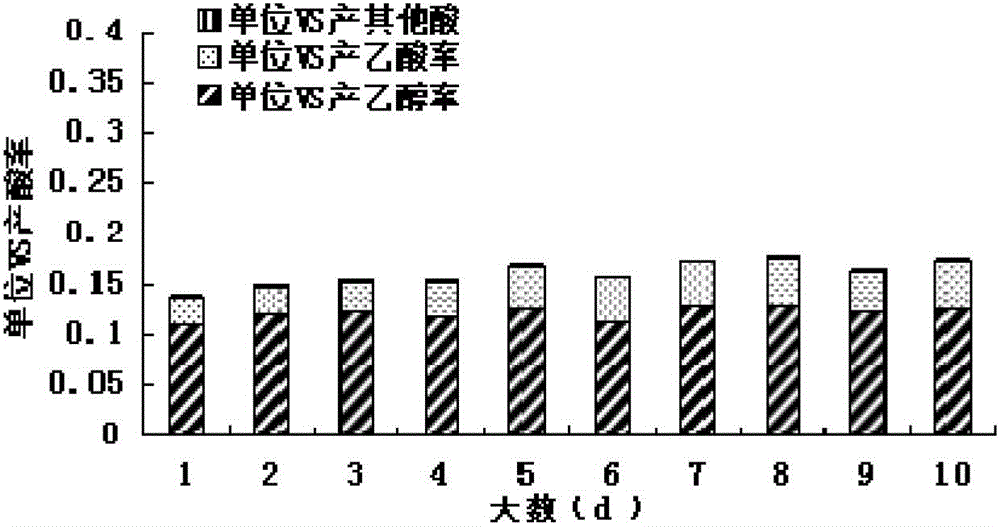
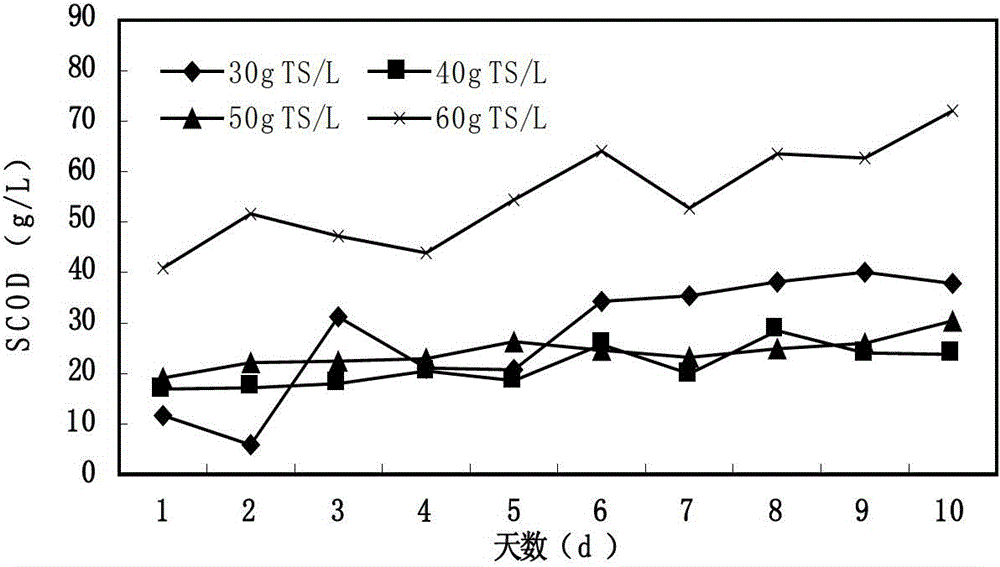
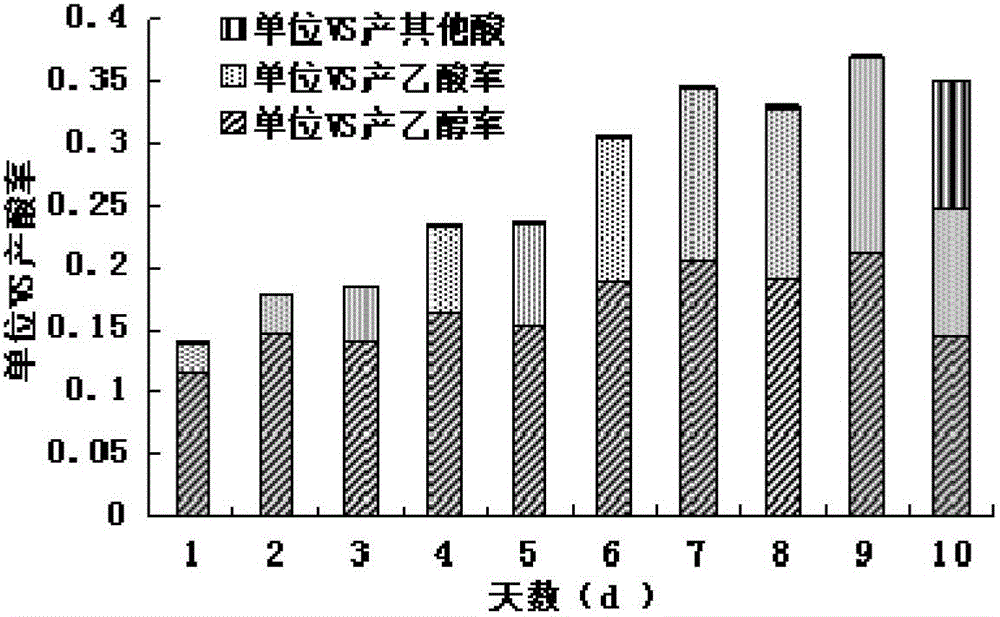
The invention discloses a method for improving an urban organic garbage mixed anaerobic digestion directional hydrolytic acidification effect. The method is characterized in that different urban raw organic biomass materials are mixed according to a certain proportion, inoculated by anaerobic sludge according to a certain proportion, and subjected to anaerobic digestion hydrolytic acidification treatment at a feed organic loading rate of 30-60TS / L, namely 25.8-51.6gVS / L, and at 35-55 DEG C; a pH value is controlled at 4.60-6.20; the content of organic acid in a product is obviously higher than that of a control group; and components of acid are controlled directionally, and mainly are alcohol and acetic acid. The method is simple in technology and high in operability; various biomass wastes are simultaneously treated by an anaerobic acidification technique; appropriate proportioning of the different raw materials contributes to element balance in a system, so that the yield of total organic acid is 72-216% higher than that of organic acid not subjected to directional acidification; alcohol and acetic acid account for 98% of total acid; and quality raw materials can be provided for organic acid production, and subsequent methanation treatment of organic acid directional control or two-phase anaerobic digestion.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for purification of D-pinitol from carob bean water extract
ActiveCN110862305AReduce contentSimple stepsEther separation/purificationFermentationFructoseSucrose hydrolysis
Belonging to the technical field of D-pinitol purification, the invention discloses a method for purification of D-pinitol from a carob bean water extract. The method for purification of D-pinitol includes the steps of: raw material pretreatment: adjusting the pH value of a raw material solution to acidic; sucrose hydrolysis conversion: adding sucrase into the raw material solution, and hydrolyzing and converting sucrose into fructose and glucose; fructose precipitation: removing fructose by precipitation method; glucose oxidation: oxidizing glucose into gluconic acid; and purification of D-pinitol: separating gluconic acid by chromatography, and conducting reduced pressure concentration on eluent to obtain high-purity D-pinitol. The invention aims to use a mild purification method to reduce impurities and remove blood sugar raising factors at the same time as many as possible step by step.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIANFENG HEALTH TECH
High-temperature thermal shock resistant ceramic material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-temperature thermal shock resistant ceramic material, which comprises the following steps: mixing ceramic powder with an organic binder to obtain a ceramic feed; and molding the ceramic feed, discharging glue, and sintering, thereby obtaining the product. Wherein the ceramic powder is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 31 to 53 parts of fused quartz, 25 to 45 parts of tabular corundum powder, 20 to 35 parts of aluminum oxide micro powder and 0.5 to 1.5 parts of silicon nitride micro powder. The ceramic material prepared by the method has good high-temperature thermal shock resistance.
Owner:SHANDONG RES & DESIGN ACADEMY OF IND CERAMICS
Solid catalyst useful for converting an alkylene oxide to an alkylene glycol
ActiveUS20090099393A1Improve catalytic hydration propertyImprove conversionOxygen-containing compound preparationCation exchanger materialsOxidePolystyrene
A solid (i.e., heterogeneous) catalyst useful for preparing an alkylene glycol from the corresponding alkylene oxide as well as a process for the catalytic hydration of an alkylene oxide to an alkylene glycol utilizing such a catalyst are provided. The catalyst of the present invention is based on an ion exchange resin including polystyrene crosslinked with from about 2 to about 10 weight (wt.) % divinyl benzene. The ion exchange resin further includes quaternary ammonium groups or quaternary phosphonium groups. The process includes reacting water and an alkylene oxide in at least one reactor under conditions to form an alkylene glycol, wherein the at least one reactor includes a catalyst based on an ion exchange resin that includes polystyrene crosslinked with from about 2 to about 10 weight (wt.) % divinyl benzene.
Owner:SD LIZENZVERWGMBH
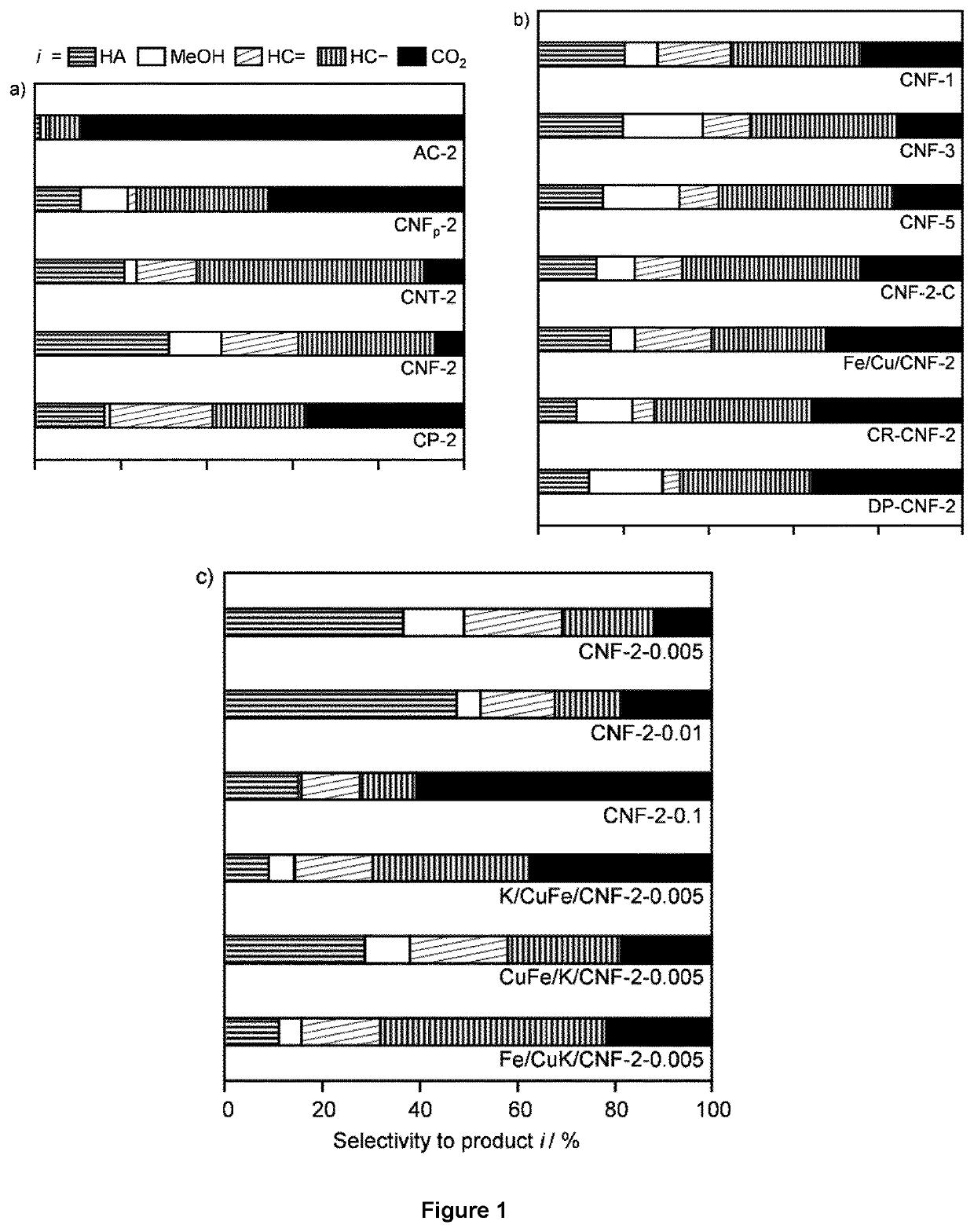
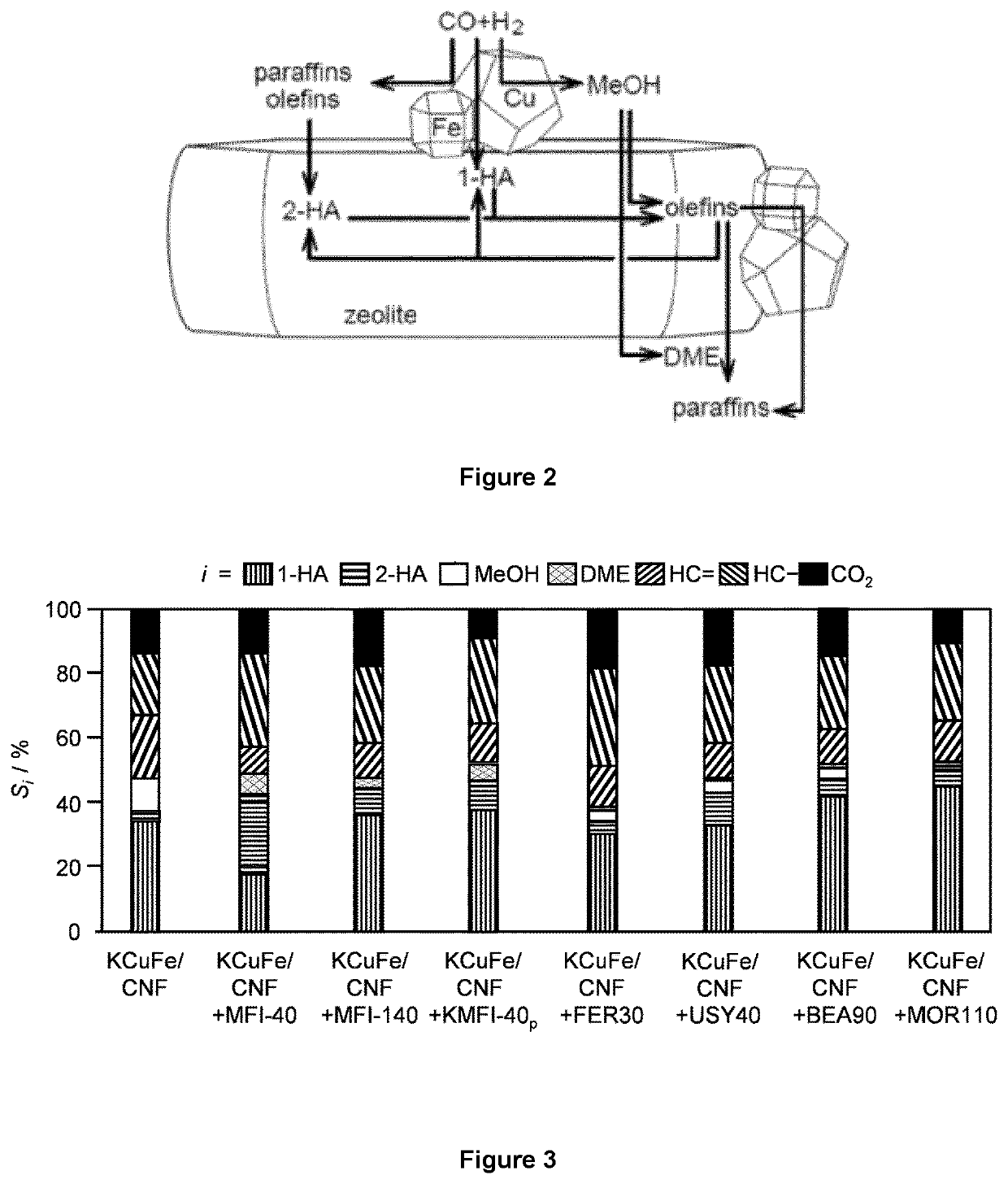
Process using catalytic composition for the conversion of syngas to higher alcohols
ActiveUS20220089516A1Improvement in co conversionImprove conversionOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationSyngasProcess engineering
The present disclosure relates to a process for converting syngas to C2+ alcohols, said process comprising the steps of providing a reactor, of providing a catalyst composition and one or more acidic materials within said reactor, of providing a feed stream comprising a mixture of H2 and CO; and of contacting said feed stream with said catalyst composition and said one or more acidic materials under reaction conditions to provide product stream. Said process is remarkable in that said catalyst composition comprises an active phase comprising CuFe deposited on a carbon-containing support, and the one or more acidic materials are one or more zeolites having a Si / Al molar ratio ranging between 2 and 200.
Owner:TOTAL SE +1
Method for processing low-grade potassium-containing rock
InactiveCN105063374AImprove conversionReduce recycling processProcess efficiency improvementMineralogyLow graded
Te invention belongs to the field of comprehensive potassium ore processing, and particularly relates to a method for processing low-grade potassium-containing rock. The method includes the steps that the low-grade potassium-containing rock is transferred into a grinding machine after being smashed; water is added at a temperature ranging from 100 DEG C to 700 DEG C for conducting mixing and grinding, wherein the amount of the added water is 1-5 times of the weight part of the potassium-containing rock; meanwhile, sodium salt is slowly added in the process of adding water for conducting grinding, wherein the amount of the added sodium salt is 0.2-1 time of the weight part of the low-grade potassium-containing rock; and after adding of the sodium salt is finished, the reaction temperature is kept, materials are stirred for 3-10 h, and a potassium-containing solution and fluosilicate are obtained through filtering. The method has the beneficial effects of being low in device requirement, cost and energy consumption, simple in process and high in potassium conversion rate.
Owner:铜仁市万山区盛和矿业有限责任公司
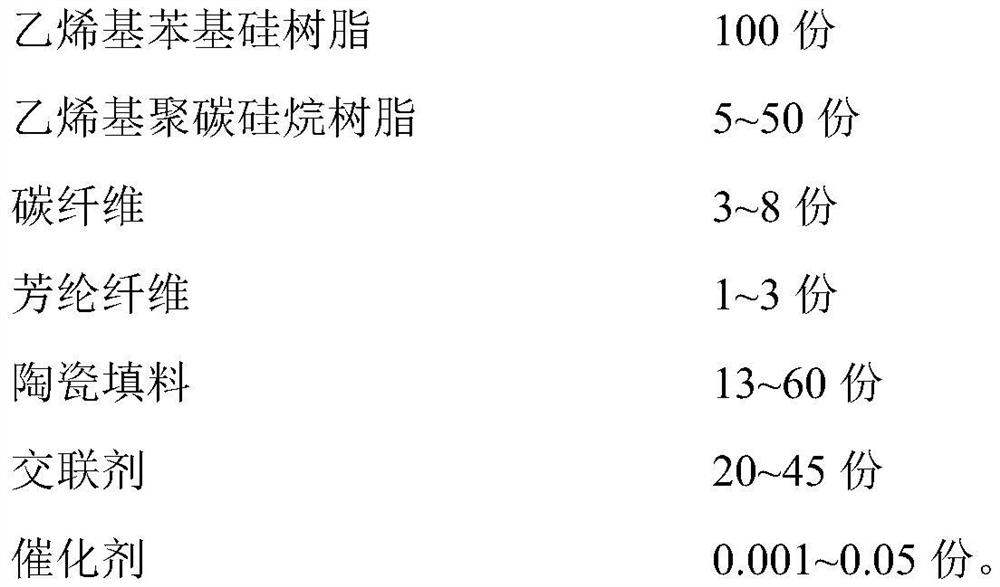
Polycarbosilane and polysiloxane resin-based ablation-resistant composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a polycarbosilane and polysiloxane resin based ablation-resistance composite material and a preparation method thereof. The polycarbosilance and polysiloxane resin based ablation-resistance composite material is prepared by mixing and solidifying the following raw materials in parts by weight: 100 parts of vinyl phenyl silicone resin, 5-50 parts of vinyl polycarbosilane resin, 3-8 parts of carbon fiber, 1-3 parts of aramid fiber, 13-60 parts of ceramic filler, 20-45 parts of crosslinking agent and 0.001-0.05 part of catalyst. Before material solidification, the sizingmaterial viscosity is small, the mobility is high, and thus multiple kinds of construction condition requirements can be met; compared with a material using polysiloxane matrix resin alone, the material has the advantages that after material solidification, the tensile strength is significantly improved, the adhesive property requirement is met, the ablation-resistance property of the material ismore excellent, and thus the material is a thermal protection material which has a good combination property.
Owner:山东山科瑞森新材料科技有限公司
A method for automatic model conversion from osm data to professional gis vector data and dynamic integration of osm incremental data
ActiveCN105183825BLow costKeep currentGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsChange TypeXML
The present invention discloses a method for model automatic conversion from OSM data to professional GIS vector data and dynamic integration of OSM incremental data. The method comprises: downloading XML OSM vector data expressed by node, way and relation, and converting the OSM vector data into a user vector data model by using a rule repository to obtain basic state data sometime and somewhere; by using OSM daily global change data, screening incremental data of a research zone by calculating a topological relationship between a change object considering a version evolution process and an object in a Diff file; determining a change type of the object after integration by applying an incremental data integration method which considers an evolution process of a change type between adjacent versions to multi-version incremental data; and finally updating original OSM basic state data by using the obtained incremental data. The method can obtain overseas geospatial vector data of our country efficiently and cost-effectively and maintain the up-to-date state of the data.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Polyimide sound absorption foam with spherical pit microstructure and preparation method of polyimide sound absorption foam
ActiveCN112126110AImprove conversionImprove sound absorption performanceSound producing devicesAir quality improvementActive agentSurface-active agents
The invention discloses polyimide sound absorption foam with a spherical pit microstructure and a preparation method of the polyimide sound absorption foam. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: S1, preparing a foaming white material containing a non-ionic surfactant, wherein the total part of the foaming white material is 250-450 parts by weight, the use amount of the non-ionicsurfactant for preparing the foaming white material is 75-125 parts by weight, the non-ionic surface active agent is composed of polyhydric alcohol and polysiloxane-polyether copolymer, and the massratio of polyhydric alcohol to polysiloxane-polyether copolymer is 0.8: 1 to 1.2: 1; S2, uniformly mixing the foaming white material containing the non-ionic surfactant with a foaming black material,and carrying out foaming molding to obtain a polyimide foam intermediate; and S3, demolding the foam intermediate, and curing the foam intermediate in a blast drying oven to finally obtain the polyimide sound absorption foam with a spherical pit microstructure. The prepared polyimide sound absorption foam can improve the reflection and absorption effects of sound waves in foam holes so as to enhance the sound wave consumption capacity of the material.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for preparing 1,3-bisbenzyl-2-imidazolidine-4,5-dicarboxylic acid
InactiveCN109651254AEase of industrial productionPreparation raw materials are non-toxic and environmentally friendlyOrganic chemistryChemical synthesisImidazolidine
The invention relates to the field of chemical synthesis, in particular to a method for preparing 1,3-bisbenzyl-2-imidazolidine-4,5-dicarboxylic acid. The method comprises the main step that cis-2,3-dibenzylamine succinic acid and dimethyl carbonate are used as raw materials for preparation under the catalytic function of zinc acetate. The method can effectively prevent environmental hazards caused by phosgene, has the advantages of high conversion degree, mild reaction conditions, few side reactions, easy separation and purification and the like, reduce the production cost and is more conducive to industrial production.
Owner:安徽泰格生物技术股份有限公司
Rapid response reversible photoisomerization perfluoroether chain-containing azobenzene and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104926683BSolve the problem of green environmental protectionNon-bioaccumulativeOrganic chemistryTenebresent compositionsStructural formulaP-Phenylenediamine
The invention discloses quick-response reversible-photoisomerization perfluorinated-ether-chain azobenzene and a preparation method therefor. The perfluorinated-ether-chain azobenzene has a structural formula shown in the description. The preparation method comprises the steps: dissolving p-phenylene diamine and perfluoroether acyl fluoride, which serve as starting compounds, in an organic solvent so as to prepare (4-perfluoroether amide)phenylamine; diazotizing the compound by a hydrochloride / nitrite system, and then, enabling the diazotized compound to react with an alkali solution of phenol so as to prepare 4-perfluoroether amide-4'-hydroxyazobenzene; and in an anhydrous organic solvent, enabling 4-perfluoroether amide-4'-hydroxyazobenzene to react with methacryloyl chloride or acryloyl chloride so as to prepare 4-perfluoroether amide-4'-methacrylate azobenzene or 4-perfluoroether amide-4'-acrylate azobenzene. The compound disclosed by the invention has the advantages of reversible photoisomerization, quick response and high isomerization degree; a fluorinated ether chain is free of biological accumulation compared with a perfluoroalkyl hydrocarbon chain; and the compound contains an active functional group, i.e., propenyl which can participate in addition reaction or polymerization reaction, so that the field of application is broad.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
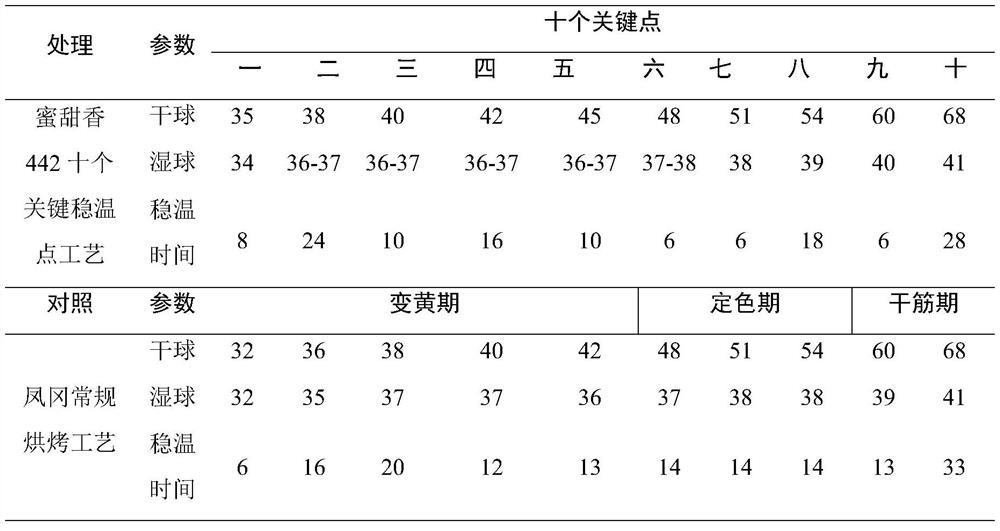
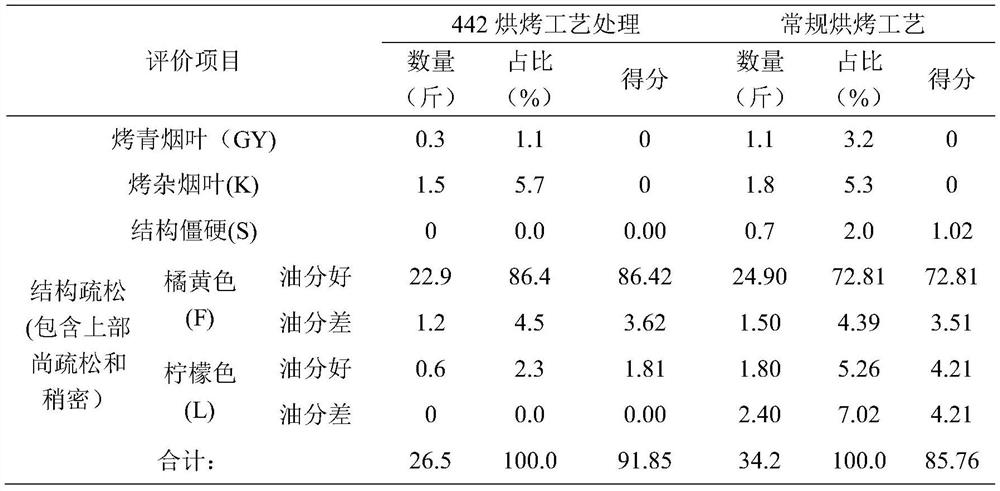
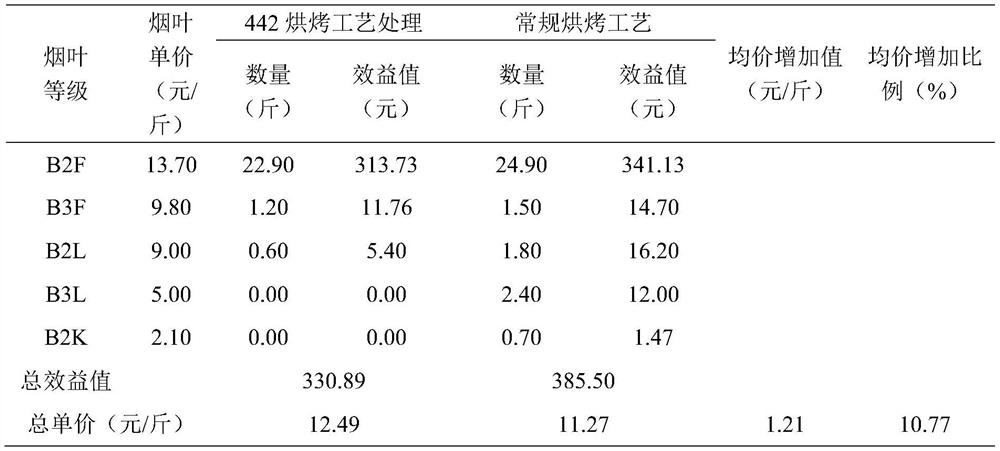
Curing process of ten key temperature-stabilizing points for a honey-sweet flavor tobacco leaf
ActiveCN109998144BReduce inefficient bake timeImprove conversionTobacco preparationHoney FlavorMacromolecular Substances
The invention discloses a baking process of ten key stable temperature points of honey-sweet-flavored tobacco leaves. Wet key points, full yellowing key points, soft and wilting key points, semi-dry key points of tobacco leaves, key points of main vein turning white, key points of aroma formation, key points of balanced color and key points of tobacco leaves drying Toasting, through this process, the macromolecular substances of the tobacco leaves can be fully degraded, a large number of small molecular substances (aroma precursor substances) are formed, and the tobacco leaves are fully softened and withered. In order to improve the softness of the tobacco leaves, increase the aroma and oil content of the tobacco leaves, and enhance the color of the tobacco leaves , providing a favorable safeguard against stiffness.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com