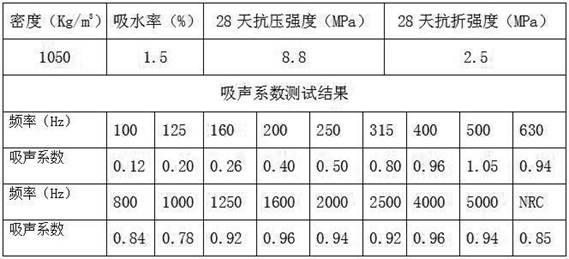
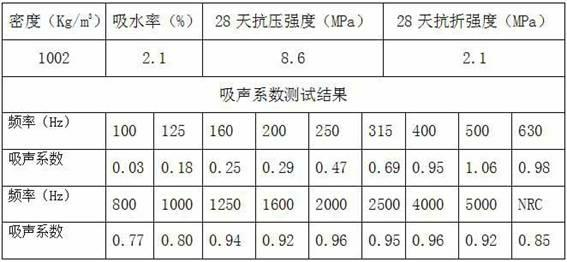
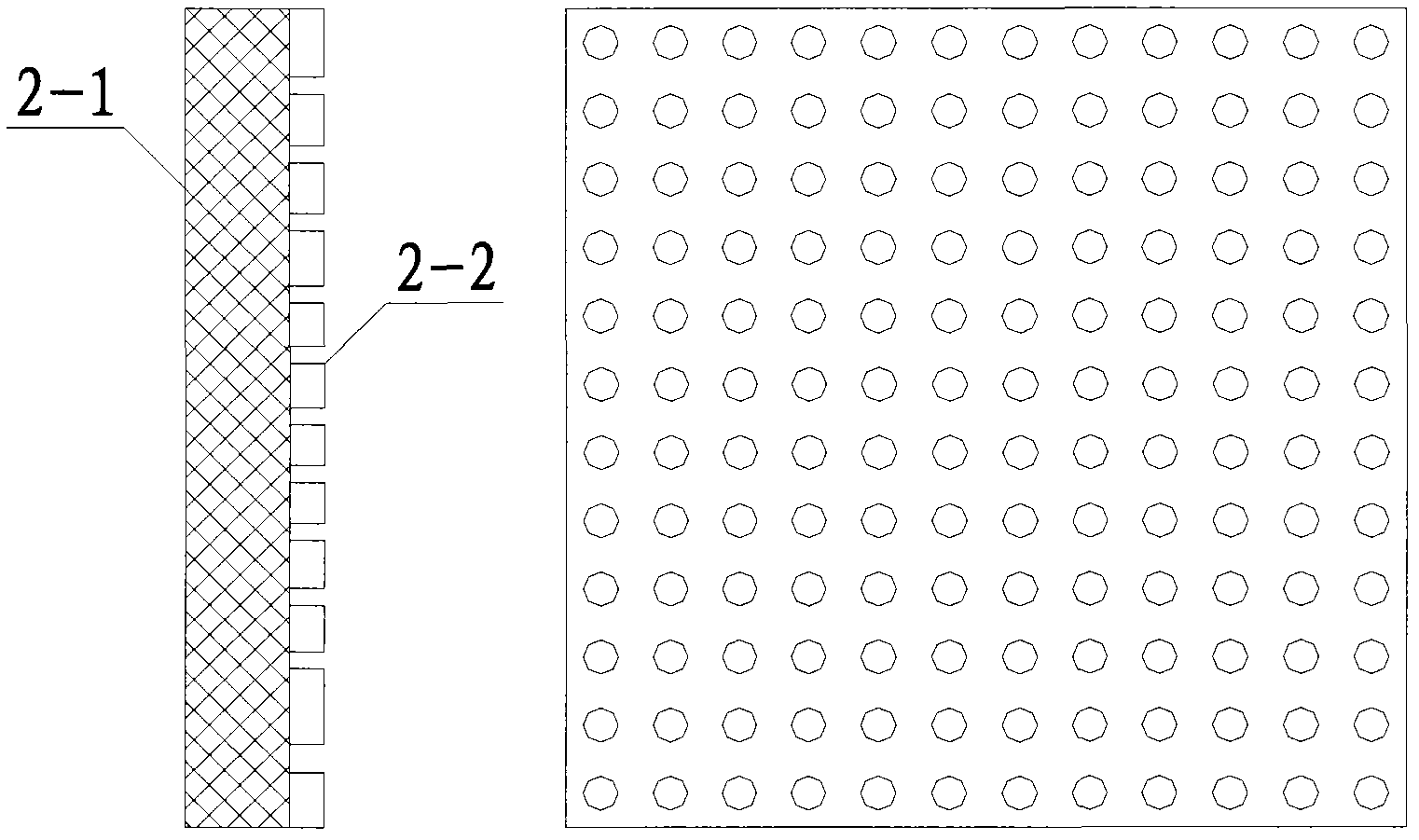Patents
Literature
377results about How to "Improve sound absorption performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
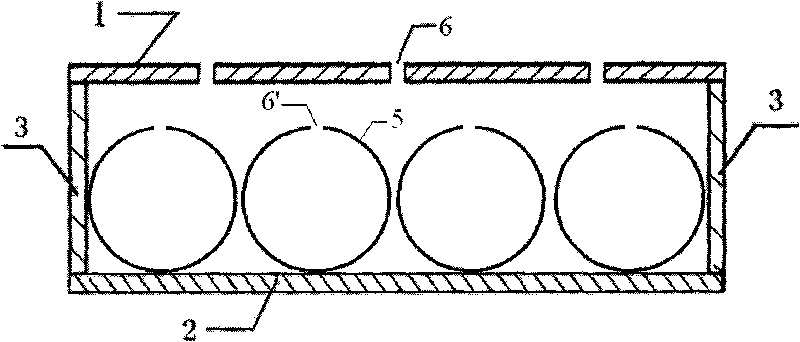
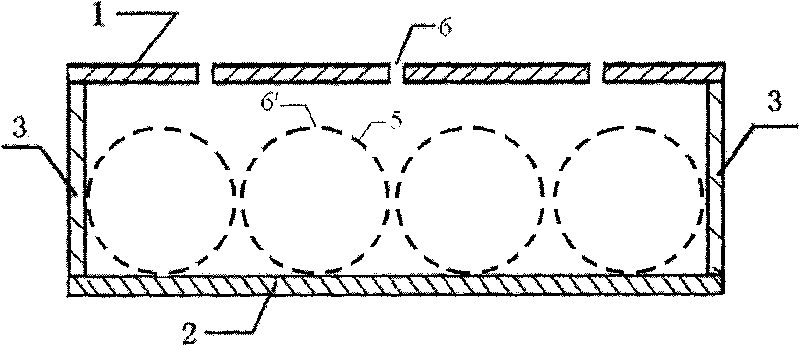
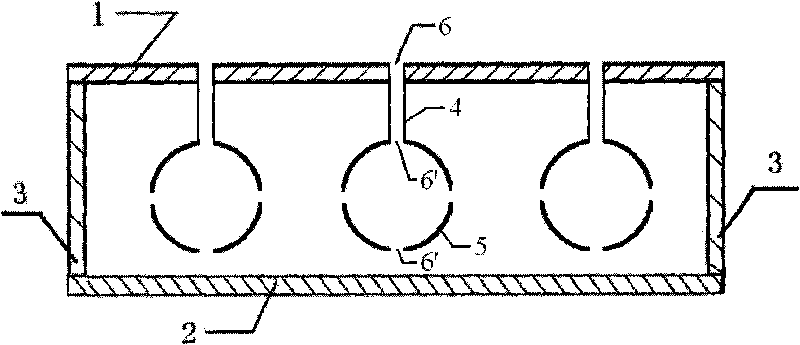
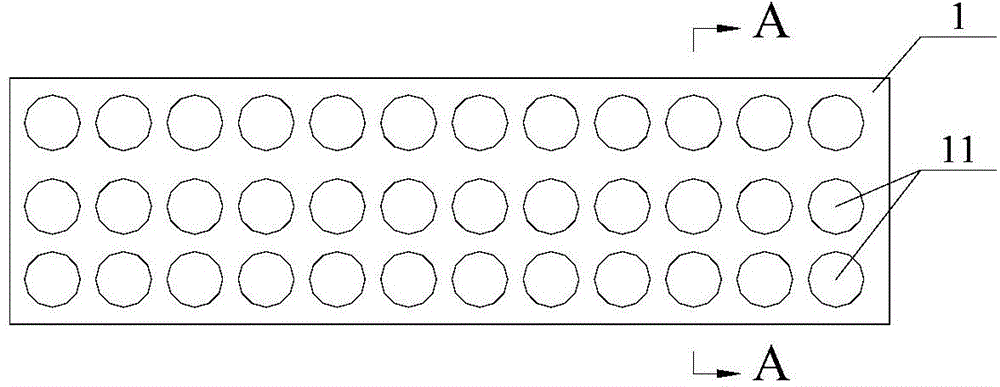
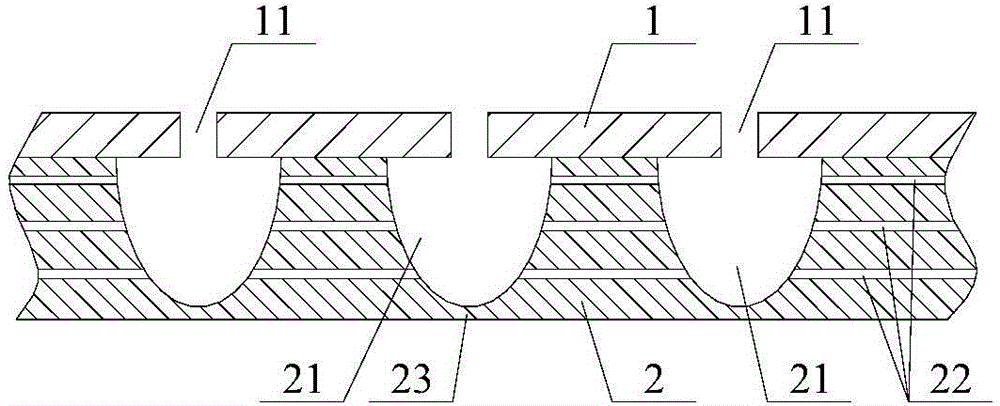
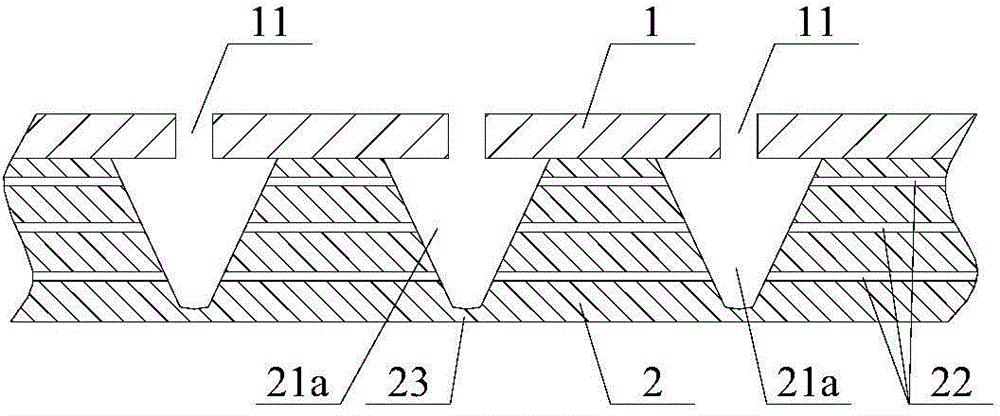
Composite sound absorbing device with built-in resonant cavity
ActiveCN101727894AIncrease sound resistanceIncrease acoustic reactanceSound proofingSound producing devicesResonant cavityResonance
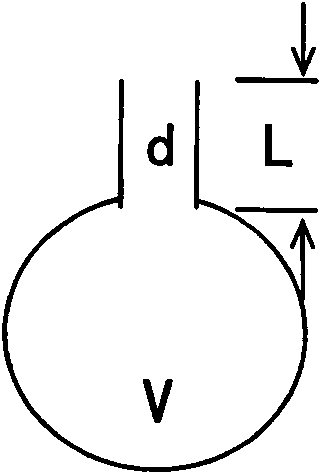
The invention relates to a composite sound absorbing device with a built-in resonant cavity. The device comprises a perforated plate with a plurality of first holes, a back plate and a side plate, wherein a sealed cavity is formed by the perforated plate, the back plate and the side plate. The device is characterized in that at least one or more resonant cavities are placed in the sealed cavity; the resonant cavity is provided with at least one or more second holes; at least one of the second holes is communicated with the sealed cavity; the volume V of the resonant cavity is equal to 10mm3-1*1,010mm3, and the thickness of the wall of the cavity is 0.05 to 10 mm; and the aperture d, of the second hole on the cavity is equal to 0.05 to 100 mm, and the perforated percentage sigma, is 0.01 to 30 percent. The device forms acoustic scattering in the sealed cavity through the resonant cavity; and the second hole increases the acoustic resistance and the multi-cavity coupling resonance. The device has a flexible design and contributes to improving sound absorbing effect and expanding the sound absorbing frequency band.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
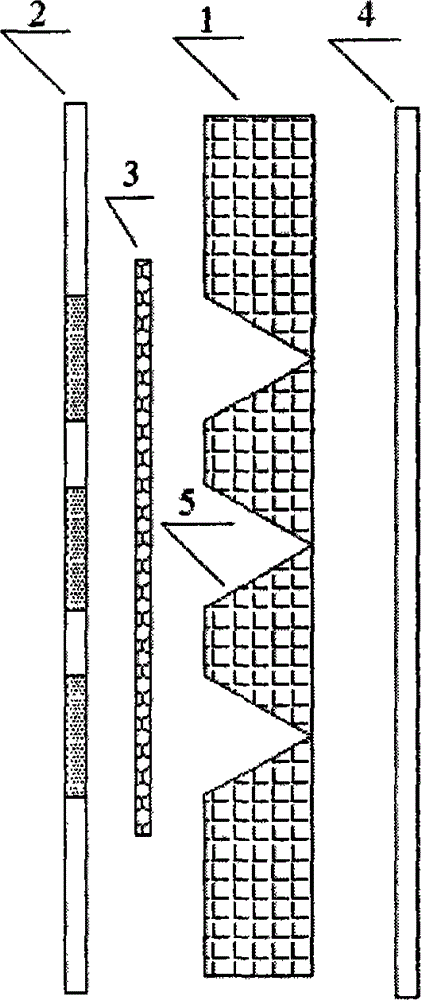
Multiple helmholtz resonator parallel cellular sandwich wood sound absorption plate
InactiveCN101962980AOvercome wasteStrong pressure resistanceCovering/liningsLayered productsCell cavityHelmholtz resonator
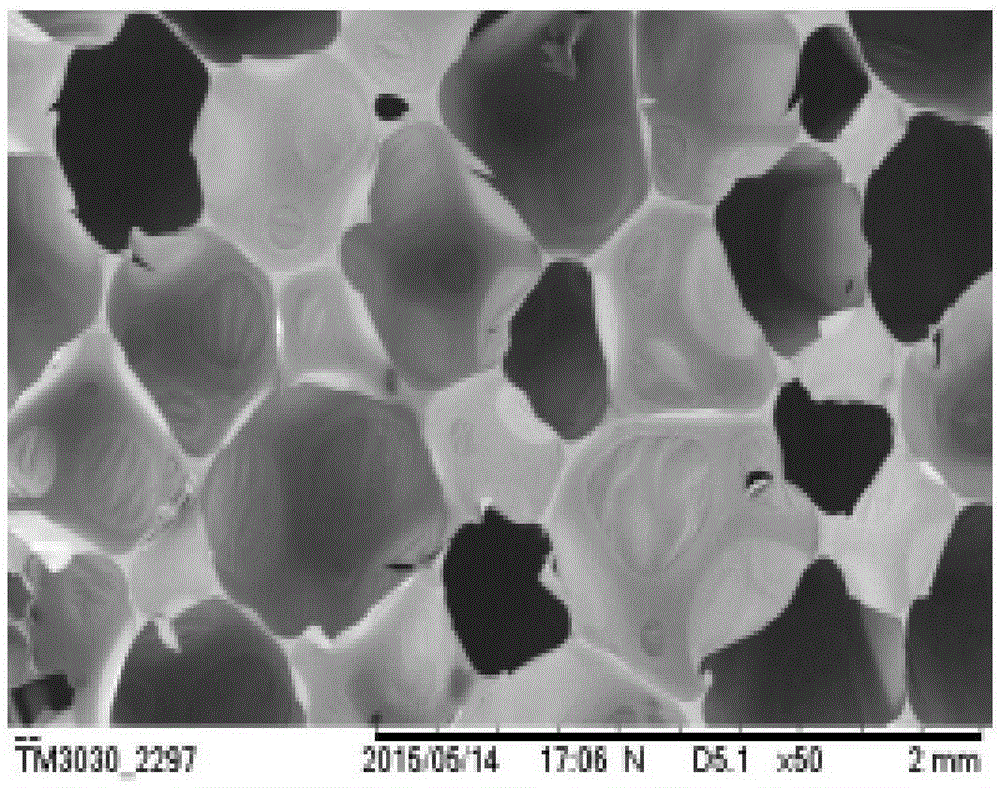
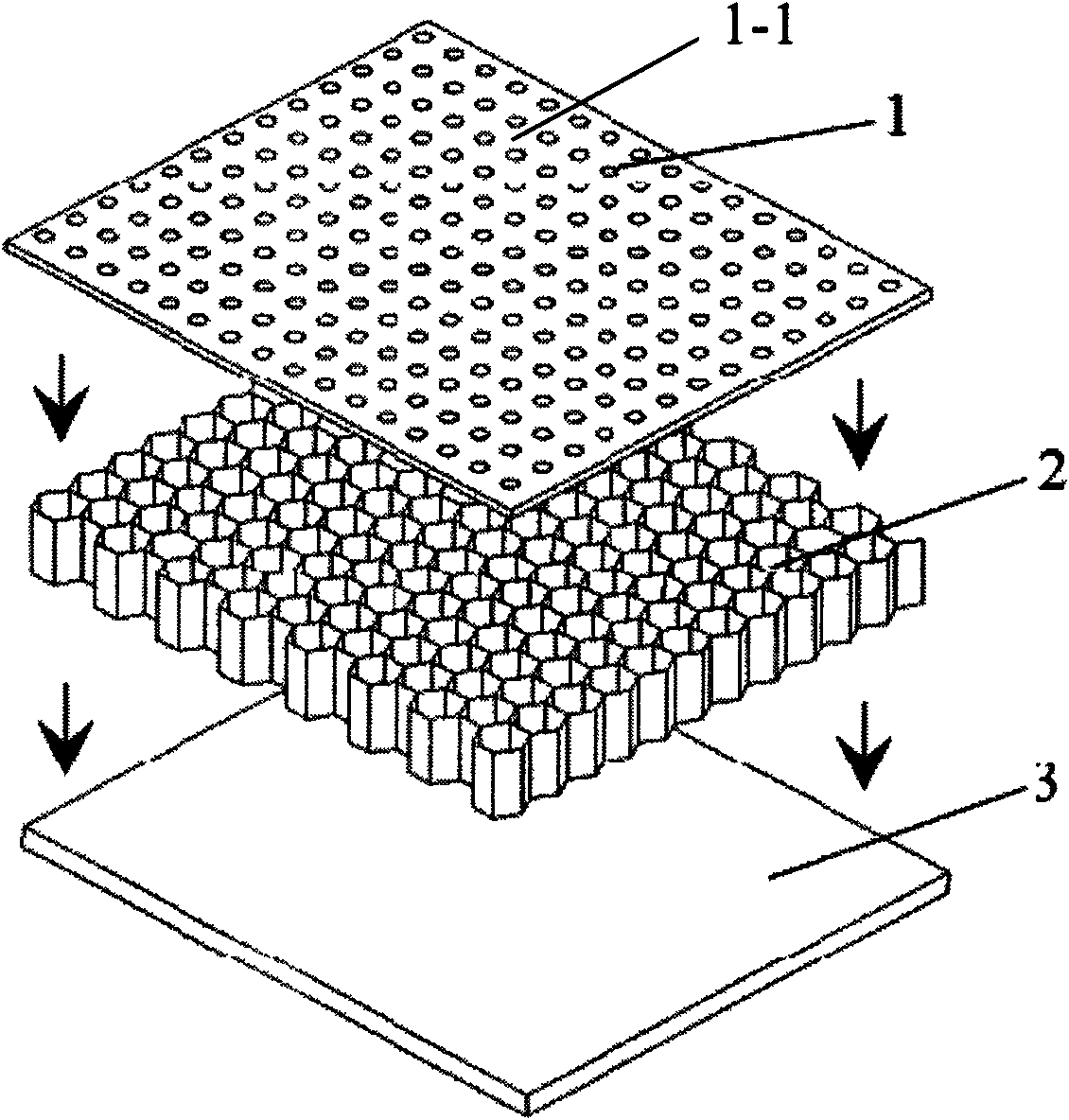
The invention relates to a multiple helmholtz resonator parallel cellular sandwich wood sound absorption plate, belonging to the field of sound absorption technologies. The invention solves the problems of small chamber volume ratio, narrow sound absorption frequency band and poor sound absorption effect in the traditional sound absorption panels. Technical essential is characterized in that a sandwich layer is a cellular sandwich layer; the cellular sandwich layer is formed from splicing a plurality of cylinder bodies with hexagonal cross sections; an inner cavity of each hexagonal cylinder body is a cell cavity chamber; the chamber volume ratio of the sandwich layer is larger than 90%; the area of perforation shape surrounded by contour lines of each perforation is less than a half of the hexagonal area of corresponding sandwich layer; and each small through hole on a panel is communicated with the cell cavity chamber at the corresponding position of the sandwich layer. The invention has wider sound absorption frequency band and better medium high frequency sound absorption performance, and the sanding wave tube method sound absorption coefficients respectively reach 0.8, 0.9 and 0.7 at 500Hz, 1000Hz and 2000Hz. In addition, the invention also has the characteristics of light weight, high ratio of strength to weight, good decorative effect, and the like; and wood resources can be saved, preparation process is simple, and cost is low.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
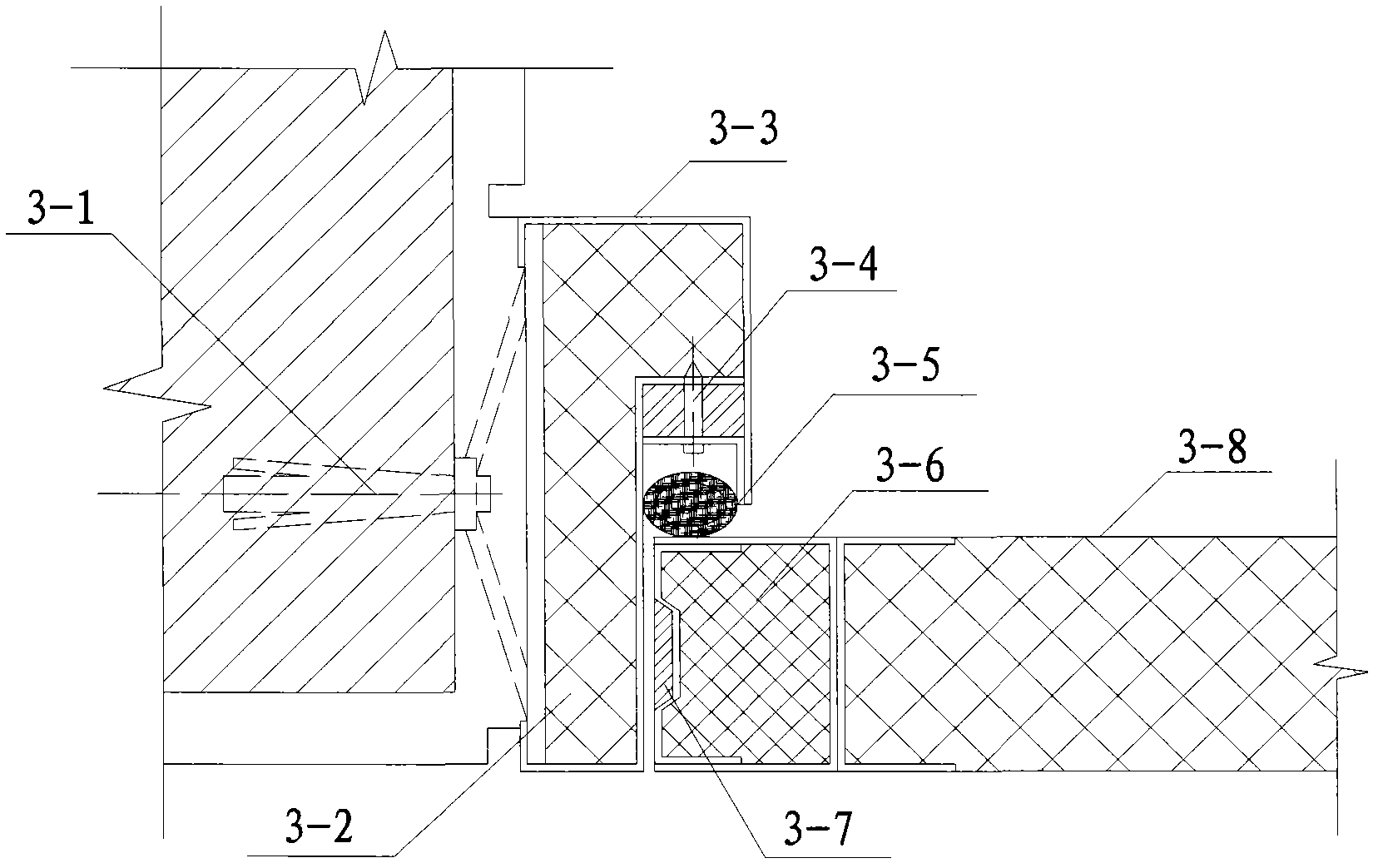
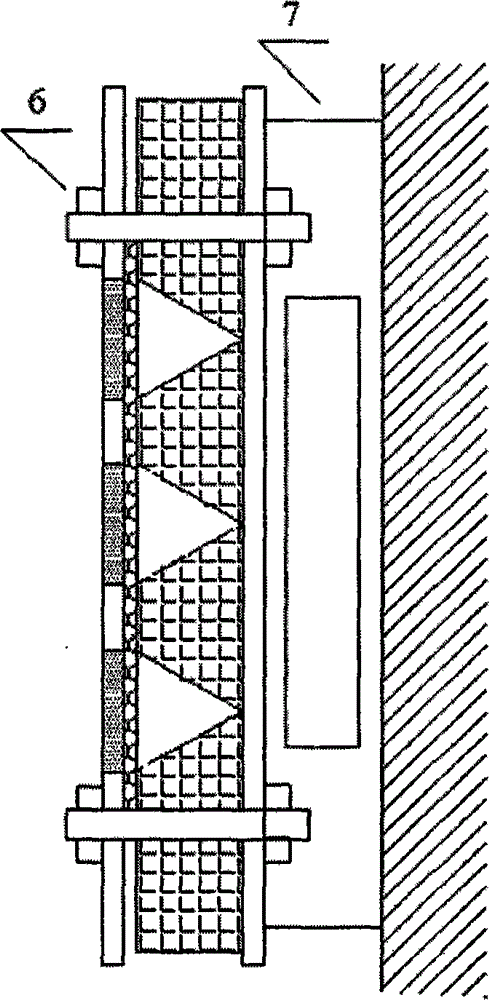
Noise reduction structure of main noise resources of urban indoor substation
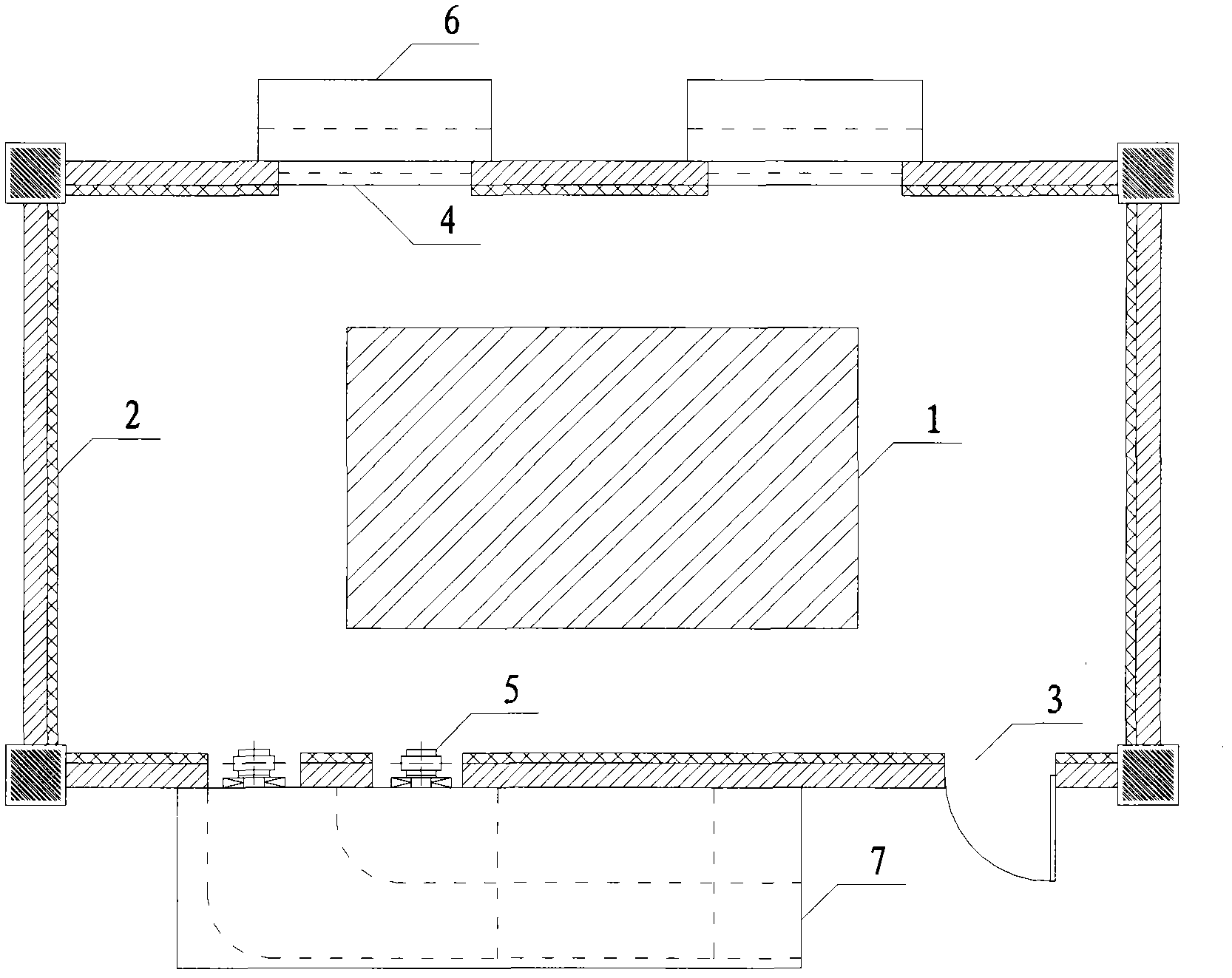
The invention relates to a noise reduction structure of main noise resources of an urban indoor substation, belonging to the technical field of noise pollution control in environmental engineering. The noise reduction structure is mainly used for reducing the noise resources of the urban indoor substation, including noise radiated by a main transformer and a reactor 1. The noise reduction structure comprises a wall perforated plate resonance sound absorption structure 2, a sound isolation door 3, a ventilating shutter 4, a low-noise axial flow fan 5, an air intake silencer 6 and an air exhaust silencer 7, wherein the wall perforated plate resonance absorption structure 2 is located inside the wall and comprises a perforated gypsum plate and acrylic cotton; the sound isolation door 3 is filled with glass coated intermediate glass cotton fiber, and the gap of a door frame is filled with sealing strips; the ventilating shutter 4 and the low-noise axial flow fan 5 are used for ventilating and dissipating heat to ensure the safe and stable operation of the main transformer and the reactor; the air intake silencer 6 is installed on the outer part of the ventilating shutter 4, the upper part is a lighting sound-isolating window cover, and the lower part is an air flow channel covering the sound absorption material; and the air exhaust silencer 7 is installed outside a ventilating fan hole, and the interior is an air flow channel covering the sound absorption material.
Owner:CEEC JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER DESIGN INST +1
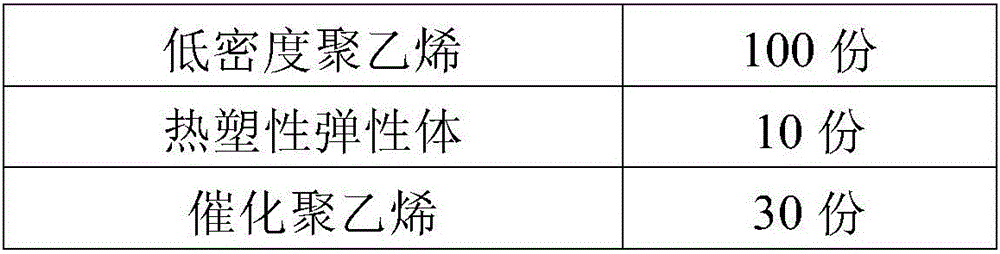
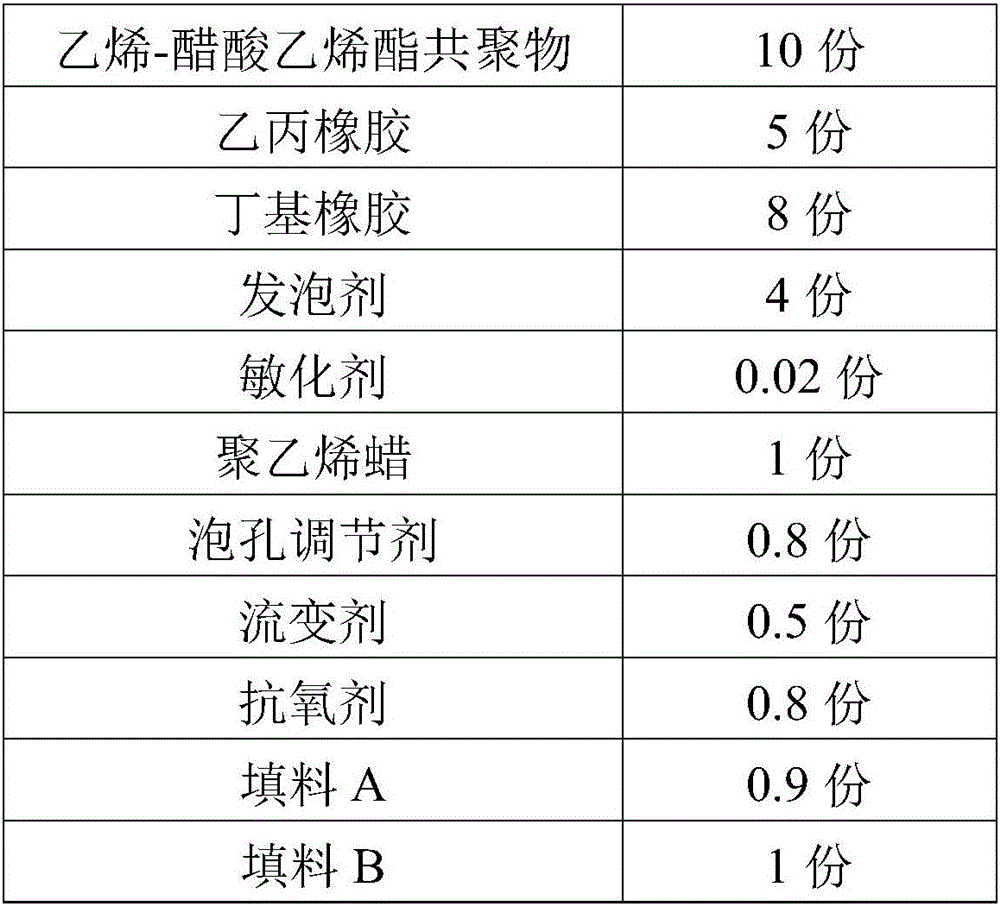
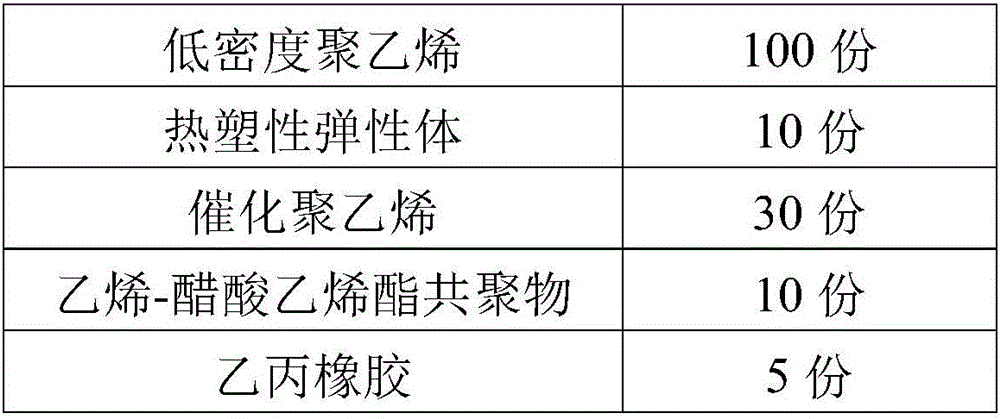
Sound absorption and thermal insulation polyolefin foamed sheet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106046483AHigh densityImprove uniformitySynthetic resin layered productsThermal insulationPolyolefin
The invention discloses a sound absorption and thermal insulation polyolefin foamed sheet and a preparation method thereof. The foamed sheet comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 110-140 parts of component A, 20-170 parts of component B, 1-20 parts of foaming agent, 0.01-8 parts of cell regulator and 0.1-20 parts of filler, wherein the component A consists of 100 parts of polyethylene and 10-40 parts of polyethylene copolymer; and the component B consists of 10-30 parts of thermoplastic elastomer, 10-80 parts of polyolefin resin and 0-60 parts of rubber. The method comprises the following steps: weighing the polyethylene resin, the thermoplastic elastomer, the polyolefin resin, the rubber, the foaming agent, the cell regulator and the filler according to the weight parts; and performing mixing granulation, sheet extrusion, irradiation crosslinking and free foaming to obtain the foamed sheet. In the invention, the prepared foamed material integrates the sound absorption and thermal insulation functions, the opening rate reaches 5-70%, the sound absorption coefficient reaches 0.2-0.5, and the heat conductivity coefficient reaches 0.026-0.035.
Owner:HUBEI XIANGYUAN NEW MATERIAL TECH INC
Composite resonance sound absorption device of tube bundle perforated plate
ActiveCN101645263AEffective absorptionIncrease sound resistanceSound producing devicesBroadbandEngineering
The invention relates to a composite resonance sound absorption device of a tube bundle perforated plate, comprising a sealed cavity composed of a perforated plate, a back plate and a lateral plate; the perforated plate is penetrated with superfine seams and voids; a tube bundle is formed by arraying N pieces of tubes which are placed in the sealed cavity, and one end of each tube penetrates intothe perforated plate or is inserted into the perforated plate by a transient joint to be connected with the perforated plate, and the other end thereof is an open or sealed end; the diameter of the tube is equal to that of the void; the external surface of the perforated plate is coated with a layer of porous sound absorption material; and N is less than or equal to the number of 6 of the voids. The invention combines the resonance sound absorption structure, superfine seam sound absorption structure and porous sound absorption material of the tube bundle perforated plate, uses the sound absorption theory of dissipating and absorbing through tube cavity coupling resonance and superfine seam resonance as well as porous sound absorption material to add acoustic resistance, intensify sound absorption, increase sound quality, lead the resonance absorption peak to move to low frequency, expand sound absorption frequency band, enhance sound absorption coefficient and realize the aim of broadband sound absorption.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Regenerated permeable concrete material prepared by using all components of construction waste and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107226643AGood water permeabilityImprove sound absorption performanceSolid waste managementPaving gutters/kerbsNational standardCompressive strength
The invention discloses a regenerated permeable concrete material prepared by using all components of construction waste and a preparation method thereof. The regenerated permeable concrete material is divided into a concrete base and a concrete facing. The method comprises the following steps: performing crushing and separation on construction waste to obtain construction waste coarse aggregate, construction waste fine powder and construction waste fine aggregate, preparing the concrete facing from the construction waste coarse aggregate and construction waste fine powder, and preparing the concrete base from the construction waste fine aggregate. The method can utilize all the components of the construction waste, and the utilization ratio is 100%. The prepared regenerated permeable concrete has the advantages of favorable permeation coefficient, favorable acoustical absorption coefficient and higher compression strength. The permeable system prepared from the regenerated permeable concrete material can satisfy the national standard on construction of sponge cities. The manufacturing cost is greatly lowered. The regenerated permeable concrete can be widely used in municipal construction.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Indoor thermal insulation construction method for city architecture ''cave dwelling type'' environment
InactiveCN101168978AMeet thermal insulation requirementsGuaranteed uptimeCovering/liningsSolid waste managementFloor slabEnvironmental effect
The invention relates to an insulation construction method for a city building, in particular to an indoor insulation construction method for cave dwelling type environment of the city building, and solves the problem that no mature indoor insulation construction method exists at present. The method comprises the construction working processes of substrate treatment, wall surface construction, ceiling construction, bathroom wall surface construction, and floor slab floor construction; through high-performance insulation material and unique construction technology, the invention performs the insulation treatment to the four indoor walls, the four walls of the bathroom, and the ceiling and the floor, can enable the indoor environment to form an insulation environment similar to an inner liner of a thermos bottle, can maintain the indoor temperature fluctuation within a very small fluctuation range, creates a cave dwelling type indoor environment with cool summer and warm winter, not only effectively prevents the cold and hot bridge phenomenon, but also meets the heat insulation requirement in a house, and achieves an energy-saving effect. On one hand, the invention technically guarantees the effective operation of family heat metering, on the other hand, the environmental effect created by the invention is basically similar to the thermal environment of the cave dwelling.
Owner:太原思科达科技发展有限公司
Concrete acoustic material and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102603247AImprove sound absorption performanceImprove mechanical propertiesSpecific gravityWaterproofing
The invention discloses a concrete acoustic material and a manufacturing method of the concrete acoustic material. The concrete acoustic material comprises 100 parts of cement, 120-180 parts of ceramsite, 0-1 part of polycarboxylate water reducer, 0-1.2 parts of silane waterproofing agent, 0-0.5 parts of polyester fiber, 0-0.3 parts of emulsion powder and 10-30 parts of water. The manufacturing method of the concrete acoustic material comprises the steps of burdening, molding, grouting, compression molding and demolding and maintaining. Compared with the prior art, the concrete acoustic material has the advantages that the mechanical property is high, the compression strength is more than 8MPa, the breaking strength is more than 2MPa; the specific gravity is light and is between 900-1100kg / m<3>; the sound suction frequency band is wide, the noise reduction coefficient is 0.85, can be more than 0.92 especially in the mid-high frequency band being more than 1250Hz, and is more than 1.04 in the frequency band being 500Hz. The concrete acoustic material not only can be applied to occasions such as high-speed railways, subways or urban railway systems, also can be used for building occasions with high noise reduction requirement, is convenient to construct and is safe and reliable.
Owner:LIUZHOU HANXIMING BUILDING MATERIAL DEV
Sound-absorbing radiation protective paint and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101831211AImprove sound absorptionGood radiation protectionRadiation-absorbing paintsLow speedHydroxyethyl cellulose
The invention relates to a sound-absorbing radiation protective paint, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 30 to 38 percent of porous modified starch, 5.0 to 9.5 percent of styrene-acrylic latex emulsion, 33 to 41 percent of barite, 0.5 to 1 percent of iron oxide, 0.25 to 1 percent of sodium polycarboxylate dispersant, 0.01 to 1 percent of brightening agent, 1.0 to 6 percent of titanium white, 0.5 to 1 percent of defoamer, 0.01 to 1 percent of mildew preventive, 13 to 18 percent of water, 0.4 to 1 percent of ethylene glycol, 0.3 to 1 percent of film-forming auxiliary agent, 0.005 to 1 percent of anti-freeze agent, 0.5 to 1 percent of graphite, 1 to 3 percent of hydroxyethyl cellulose and 0.20 to 1 percent of thickening agent. A preparation method of the sound-absorbing radiation protective paint comprises the steps of: (a) premixing, namely stirring 1 / 2 water, the sodium polycarboxylate dispersant, 1 / 2 defoamer, the mildew preventive, the thickening agent, the hydroxyethyl cellulose and the brightening agent at low speed to form colloidal solution; (b) dispersing and grinding, namely adding the titanium white, the barite, the graphite and the iron oxide into the colloidal solution and stirring the solution at high speed to prepare uniform sizing agent; (c) paint mixing, namely adding crylic acid emulsion, the film-forming auxiliary agent and the anti-freeze agent into the sizing agent, uniformly stirring the sizing agent, then dividing the porous modified starch into 1 to 5 parts, and adding the porous modified starch by 1 to 5 times into the mixture for low-speed and uniformly stirring the mixture; and (d) packaging the resulting product.
Owner:谢绍何
Anti-noise fiber material cushion and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101685630AImprove sound absorption performanceLight in massLayered productsNon-woven fabricsCushionRefrigerated temperature
The invention discloses an anti-noise fiber material cushion and a preparation method thereof. The material cushion is formed by overlapping at least two layers comprising an ultrathin fiber sound absorption material layer and an ultra-micro perforation sound absorption plate material layer, and the thickness of the material cushion is between 2 and 8 mm; the ultra-micro perforation sound absorption plate material layer is an ultrathin PVC paper board with the porosity of 0.2 to 3 percent; the ultrathin fiber sound absorption material layer is formed by overlapping 1 to 10 layers of fiber sound absorption materials with thickness of 0.2 to 2 millimeters; and the ultrathin fiber sound absorption material consists of a main fiber material and an auxiliary material. The anti-noise fiber material cushion has good noise reduction effect within a full audio frequency range, and particularly has quite obvious sound absorption performance of the noise under a high frequency; the noise is reduced by 2 to 8dB; and the anti-noise fiber material cushion is widely applied to the industrial fields of air conditioners, refrigerators, washing machines, automobiles, spaceflights and the like, and has quite important potential application value on noise reduction, energy conservation, consumption reduction and improvement of market competitiveness of products with higher noise requirements.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUAZHI ENERGY SAVING TECH
Mute environment-friendly paint and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to mute environment-friendly paint and a preparation method thereof. The mute environment-friendly paint consists of filler, an odor-eliminating latex, an assistant, pigment, a flame retardant and water, wherein the filler comprises a wood fiber, diatomite, expanded perlite and hollow glass microspheres; the expanded perlite is open pore expanded perlite with 14-120 meshes; and the average grain diameter of the odor-eliminating latex is 0.15-0.5mu m. The preparation method of the mute environment-friendly paint comprises three steps of premixing, dispersing and grinding and adjusting paint. The prepared mute environment-friendly paint has the advantages of favorable mute effect, safety, environmental protection, capability of adjusting the indoor air temperature, simple and convenient construction, favorable decorative effect and the like as well as favorable market prospect.
Owner:中科力川(北京)建设工程有限公司
Cellulose-reinforced polyurethane/epoxy resin interpenetrating polymer network hard composite foam material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105348473AHigh compressive strengthGood sound absorptionInterpenetrating polymer networkIsocyanate compound
The invention discloses a cellulose-reinforced polyurethane / epoxy resin interpenetrating polymer network hard composite foam material and a preparation method thereof, relates to a foam material and a preparation method thereof and aims at solving the problems that existing polymer formed through mutual interpenetrating of two types of polymer, namely polyurethane and epoxy resin, is poor in sound absorption property and low in mechanical property. The sound absorption property of the composite foam material ranges from 80% to 92%, and the composite foam material is prepared from polyether polyol, isocyanate, water, a foaming agent, foam stabilizer, initiator, hydrosol of nano-crystalline cellulose with the mass percentage being 1%, chain extender, a cross-linking agent and epoxy resin. The preparation method comprises the steps of firstly, mixing the polyether polyol, the foam stabilizer, the initiator, the foaming agent, the chain extender and the water with cellulose obtained after pretreatment, then adding the epoxy resin and the cross-linking agent, and obtaining a mixture; then mixing the isocyanate with the mixture, conducting stirring till bubbles are generated, leaving the mixture standing still, obtaining a foamed mixture, finally, conducting curing on the foamed mixture at the room temperature, and then conducting curing at the high temperature.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Array type silencer
InactiveCN101275700AIncrease the circulation areaShorten the lengthPipe elementsRigid pipesEngineeringNoise reduction
The invention discloses an array type muffer, the technical problems to be solved are to advance the silencing ability. The array type muffer is provided with an absorbing body in the tube, wherein the absorbing body is a tube provided with sound absorption material inside, the axis of the tube is arranged along the airflow direction in parallel, and the tube is fixedly arranged in the air pipe through the bracket. Compared with the existing technology, in the same length of the muffer, the absorption surface of the unit cross area is increased, the absorption property is advanced, the noise reduction effect is good, which ensures that in the same noise reduction effect, the length and the volume of the muffer are reduced, the air flow area of the unit cross area is increased, the flow velocity of the absorbing body is reduced, the air noise is reduced, the pressure loss is small, thereby reducing the pressure of the system fan, reducing the cost of the air system. The whole muffer is decomposed into each small absorbing body and the parts for installing the bracket, which is convenient for the transportation and installment.
Owner:方庆川 +1
Composite sound absorption structure
InactiveCN104616647AEffective sound absorptionPlay the role of energy consumptionSound producing devicesAcoustic absorptionEngineering
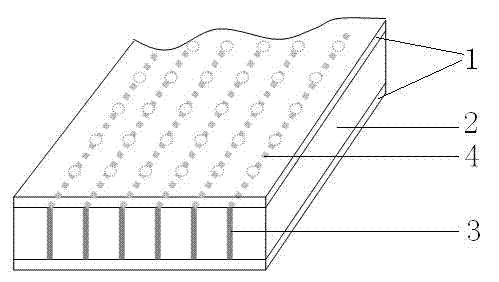
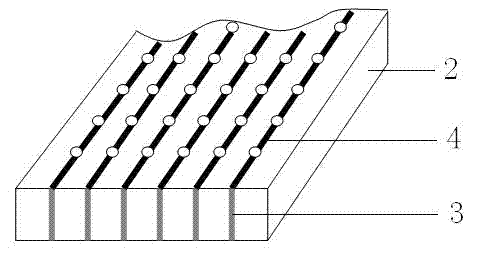
The invention relates to the sound absorption technical field, particularly to a composite sound absorption structure. A sound absorption plate of the composite sound absorption structure comprises a micro perforation plate and a plate base body; the micro perforation plate is provided with a plurality of through sound absorption holes; the plate base body is provided with a plurality of sound absorption empty chambers; a communication channel is formed between every two adjacent sound absorption empty chambers; the surface of the plate base body, which is provided with the sound absorption empty chambers, is attached to the micro perforation plate; every sound absorption hole formed in the micro perforation plate is communicated with the corresponding sound absorption empty chamber formed in the plate base body; an empty chamber is formed between a structural base body of the composite sound absorption structure and the plate base body of the sound absorption plate. Compared with the prior art, the micro perforation plate, the sound absorption empty chambers and the communication channel formed between every two adjacent sound absorption empty chambers can effectively participate in energy consumption and sound absorption, meanwhile the resonance effect is achieved through the empty chamber formed between the composite sound absorption plate and the structural base body, and accordingly the sound absorption effect of the composite sound absorption structure can be particularly significant and meanwhile the sound absorption structure can be separately and independently machined, the manufacturability is good, and the production cost can be controlled.
Owner:BEIJING MUNICIPAL INST OF LABOUR PROTECTION
Cup-shaped noise reduction and sound absorption member
ActiveCN102926334AImprove sound absorptionAchieve Impedance MatchingNoise reduction constructionWoolEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of a sound barrier acoustic member, and specifically relates to a cup-shaped noise reduction and sound absorption member of a sound barrier. The cup-shaped noise reduction and sound absorption member is composed of a plurality of cup-shaped noise reduction and sound absorption member units, wherein a panel of each unit is composed of a plurality of rectangular arrays and trapezoidal transverse bars; each rectangular array is composed of a plurality of uniformly distributed reflector cups with a paraboloid-shaped acoustic construction; diffraction holes are formed in the bottom of each reflector cup; a rectangular connecting groove is respectively arranged in the longitudinal center on the upper surface and the lower surface of a back plate of each unit; the connecting groove and the rectangular connecting grooves of other sound absorption member units in the same position form a square cavity during installation, wherein a square steel pipe is embedded in the cavity as a connecting piece for clamping two adjacent cup-shaped noise reduction and sound absorption member units; a sound insulation plate is mounted in a tubular cavity which is formed by connecting the panel and the back plate; support frames are arranged on the transverse bars inside the cavity; and spaces divided by the support frame are filled with sound absorption wools and gauzes. The cup-shaped noise reduction and sound absorption member has stronger sound absorption ability, and the low-frequency sound absorption ability is improved.
Owner:秦皇岛耀华装备集团股份有限公司
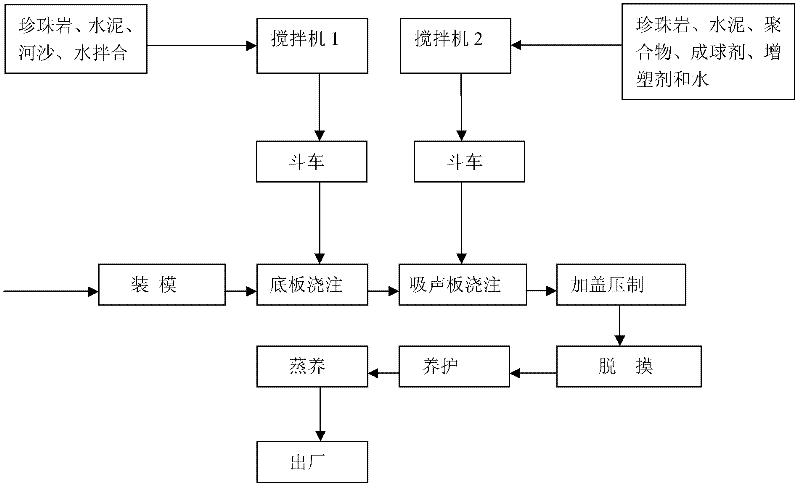
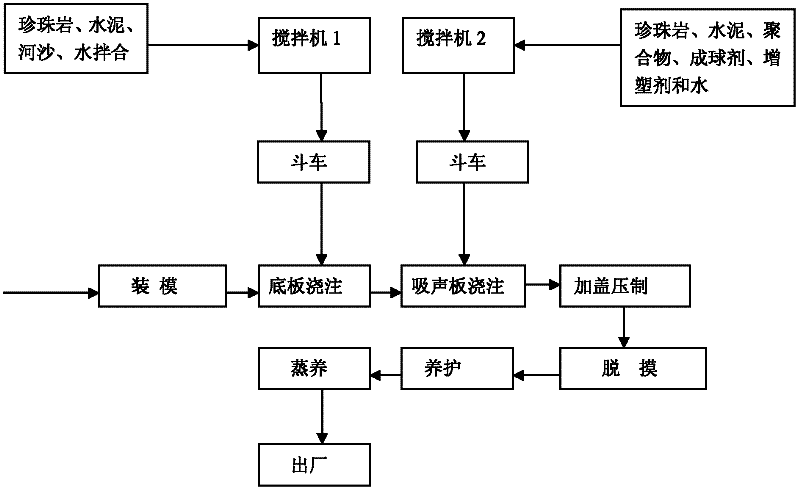
Porous perlite sound absorption material
The invention discloses a porous perlite sound absorption material used for building a sound absorption wall, characterized in that the porous perlite sound absorption material is prepared by the following procedures: blending and pelletizing the materials, pouring a soleplate, pouring a sound absorption plate, pressing, demolding, curing and vapor curing at 40 DEG C, and the like; the material is composed of the following ingredients in mass ratio: 1 part of perlite, 6 parts of 425 cement, 0.3 parts of high early strength cement, 0.1 part of polymer emulsion, 0.1 part of pelletizing agent, 0.01 part of plasticizer and 0.1 part of other accessory ingredients. The sound absorption material using perlite as aggregate disclosed by the invention has the advantages of excellent sound absorption effect, large anti-bending and anti-pressing strength, high sound absorption coefficient and wide sound absorption frequency band, and the sound absorption material has such excellent functions as fire resistance, moisture resistance, durability and innocuity, and the like, so that the sound absorption material has an extensive application prospect.
Owner:四川昊龙高科轨道交通新材料科技股份有限公司
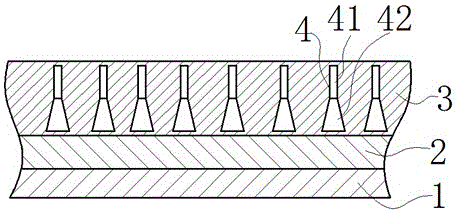
Noise reduction sound absorption layer
ActiveCN104485096AIncrease the barrier to spreadAchieve resistive sound absorption effectSound producing devicesFiberResonance
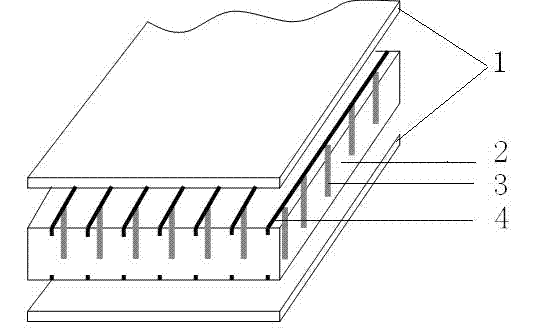
The invention provides a noise reduction sound absorption layer. The sound absorption layer comprises a keel and a sound absorption component, wherein the component comprises a micro-perforated panel 2, non-woven fabrics 3, a bi-component fiber mat 1 and a back plate 4, which are sequentially arranged along the direction from a noise source to a wall. The sound absorption principle of the noise reduction sound absorption layer couples the effects of bi-component resistive sound absorption and dual-layer resonance sound absorption; low-frequency noise of a substation transformer and a high-voltage reactor is effectively absorbed, and thus the target of reducing sensitive points on the boundary of a transformer substation and sensitive points out of the transformer substation is achieved.
Owner:STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER +3
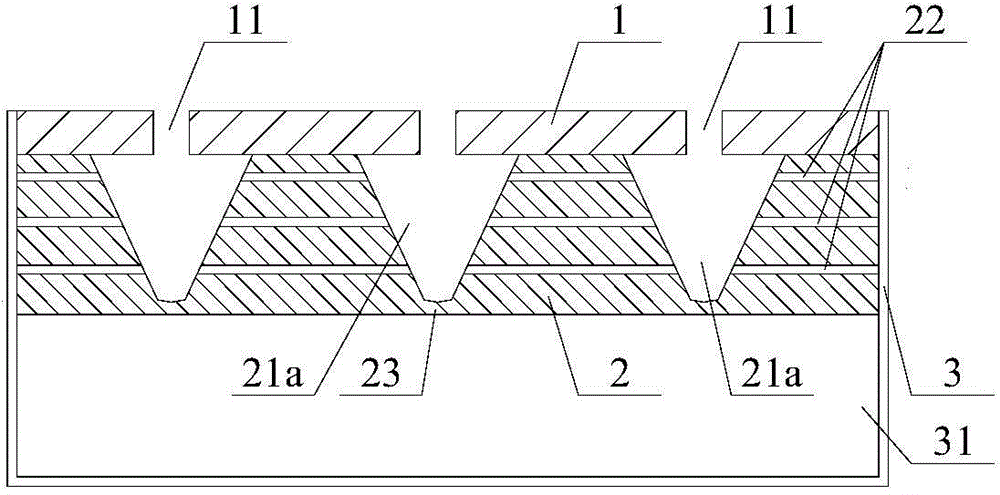
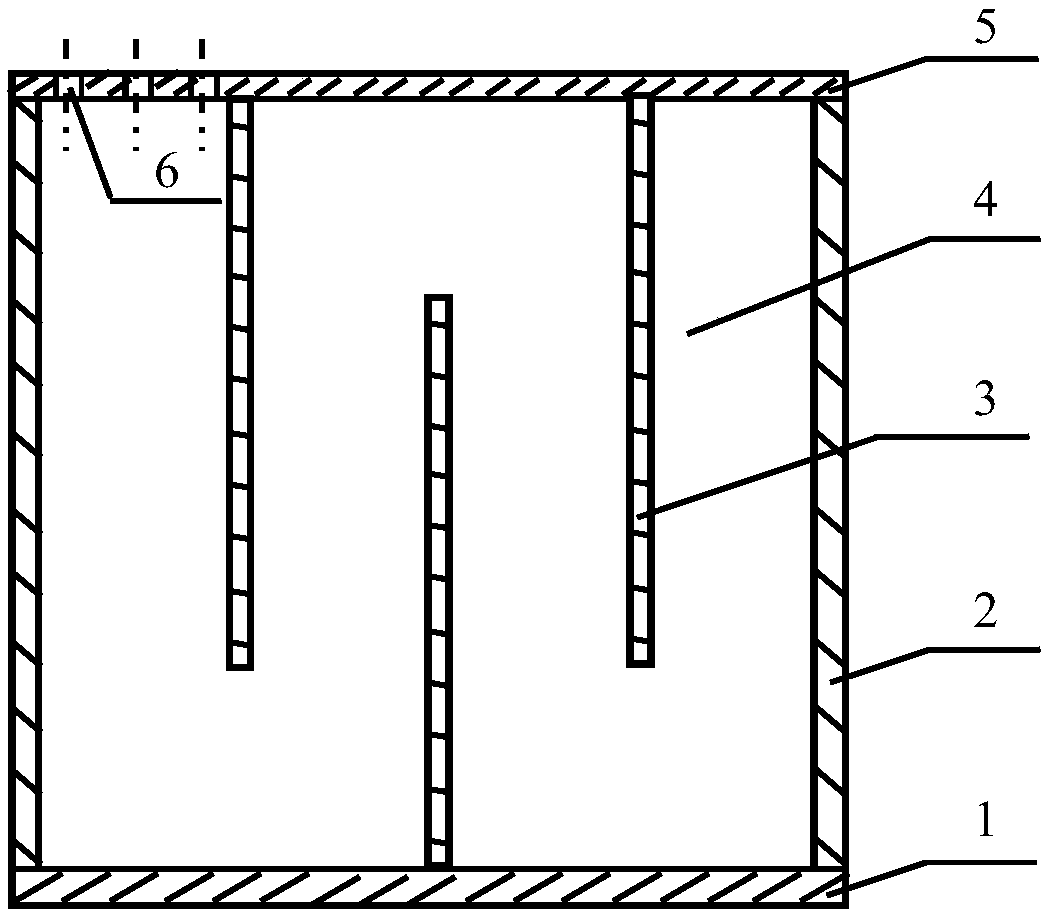
Broad-band sound absorption structure with zigzag cavity and microperforated board
InactiveCN109559728AImprove sound absorption performanceBroaden the sound absorption bandwidthSound producing devicesActive noise controlRear quarterNoise control
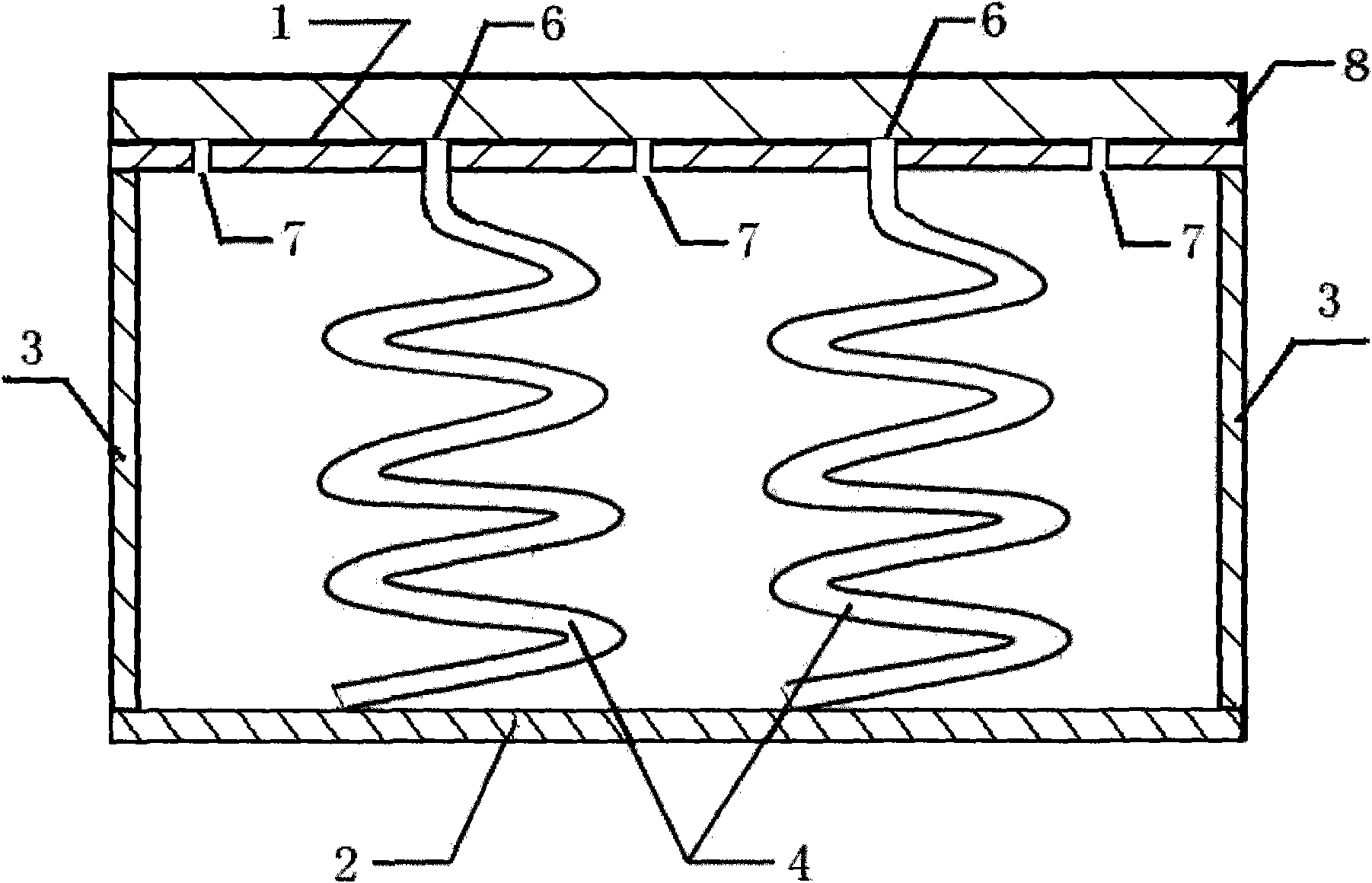
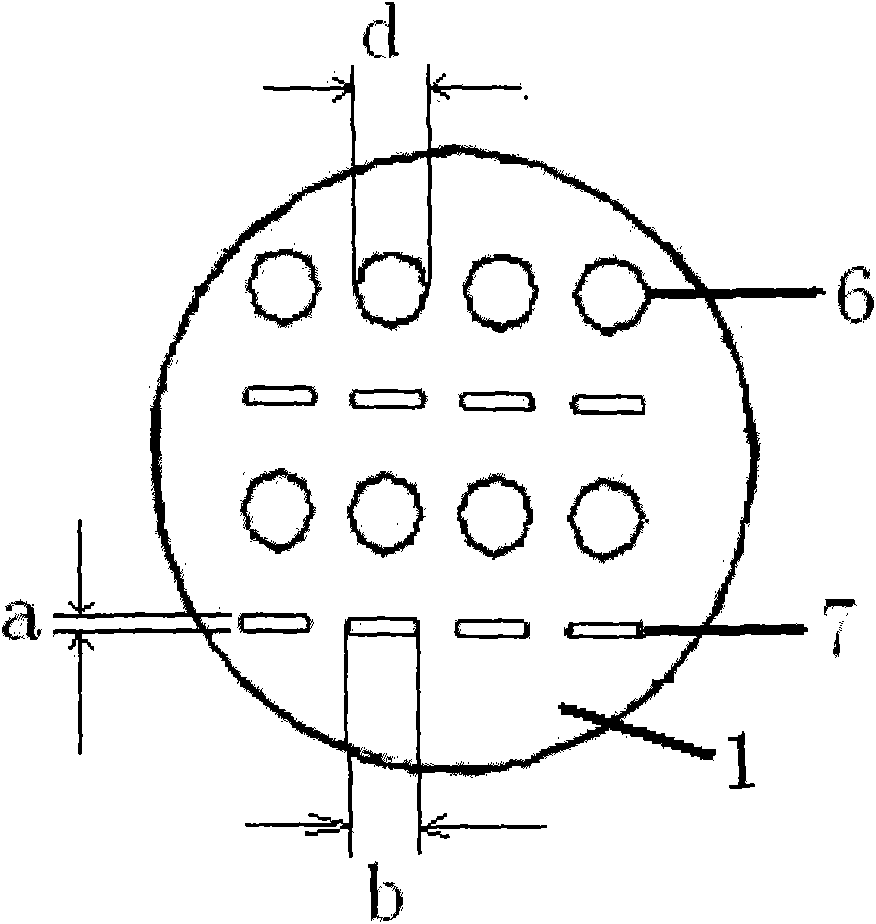
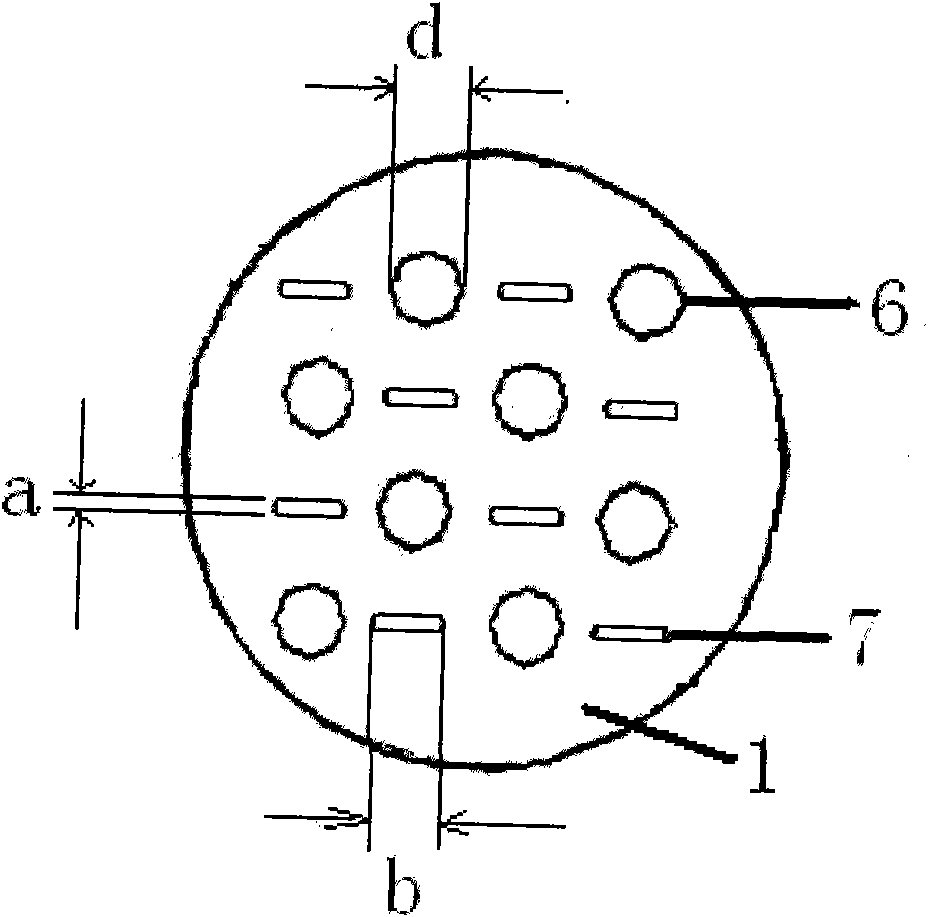
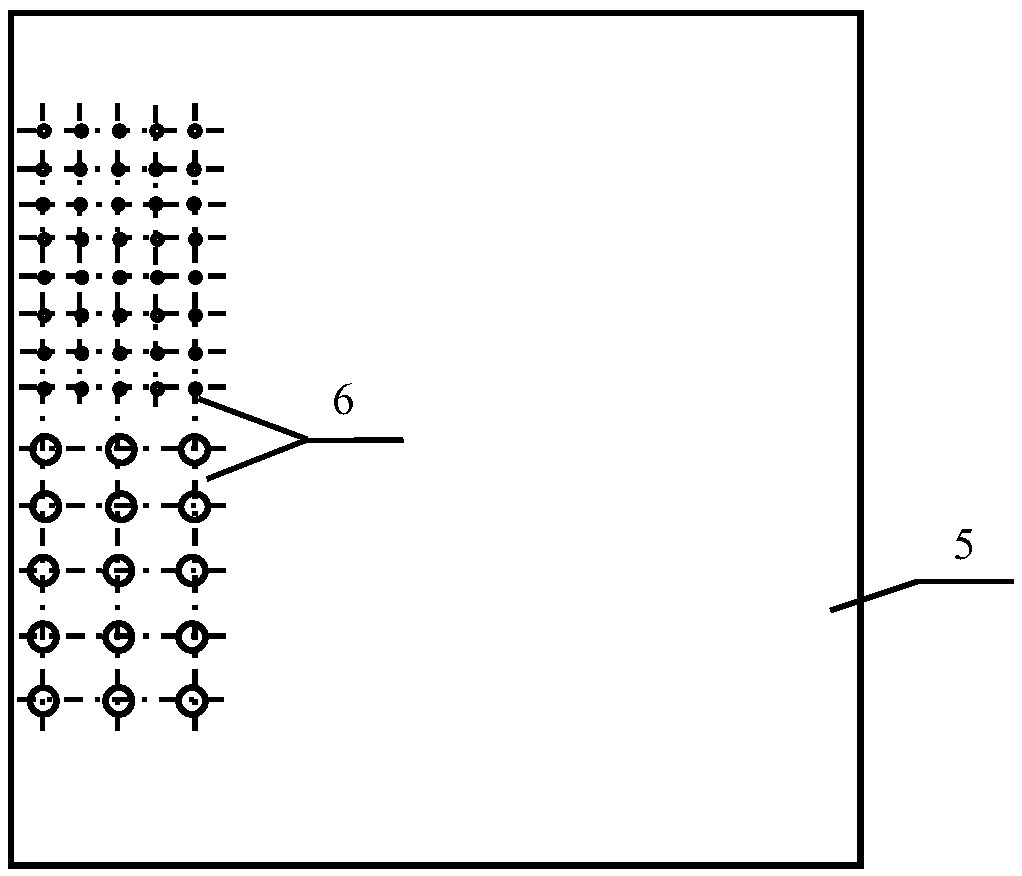
The invention belongs to the field of noise control, and in particular relates to a broad-band sound absorption structure with a zigzag cavity and a microperforated board. The structure comprises a bottom board 1, side walls 2, partition plates 3, a cover board 5, and microperforated holes 6, wherein the side walls 2 are tightly connected with the bottom board 1 and the cover board 5, so that an integral sound absorption back cavity is formed; the partition plates 3 are arranged in the sound absorption back cavity, and separate the integral back cavity into the zigzag cavity 4 alternately in sequence with the bottom board 1; the partition plates 3 are sequentially distributed in the back cavity at certain intervals and are closely connected with the side walls 2, and the distance and the number of the partition plates are adjustable, and the intervals between the adjacent partition plates are equal or similar; gaps are reserved between the partition plates 3 and the cover board 5, andthe height of the gaps can be the same or similar to the intervals among the partition plates; and the microperforated holes 6 of one or more different sizes are arranged in the cover board 5. For thebroad-band sound absorption structure, under the condition that the thickness of the back cavity of the microperforated board is not increased, the low-frequency sound absorption coefficient of a composite sound absorption structure is improved, the sound absorption frequency band of the structure is also effectively broadened, in addition, the structure is simple, the preparation cost is low, the application value is high, and the application range is wide.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
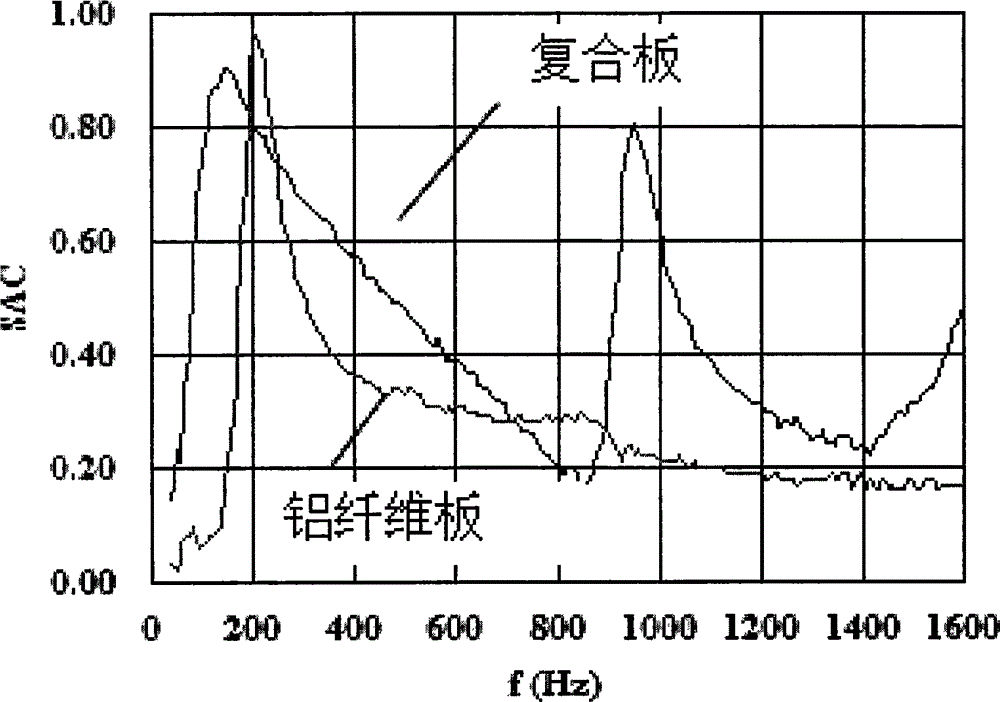
Z-direction enhanced underwater sound absorption sandwich composite material and preparation method for same
ActiveCN102930862ASolve the carrying capacitySolve the problem of sound absorption performanceSynthetic resin layered productsSound producing devicesVacuum assistedOperability
The invention discloses a Z-direction enhanced underwater sound absorption sandwich composite material and a preparation method for the same. The composite material comprises composite material panels, a sound absorption core material and enhancement structures, wherein the enhancement structures are arranged in the thickness direction of the sound absorption core material, namely a Z direction, between the upper and lower panels. The whole structure of the Z-direction enhanced underwater sound absorption sandwich composite material is formed by a vacuum assisted forming process. Compared with an ordinary sound absorption sandwich composite material, the Z-direction enhanced underwater sound absorption sandwich composite material has the advantages that flat compression strength is greatly strengthened, a compression modulus is improved by more than one order of magnitude, bending rigidity is doubled, sound absorption performance is improved by 10 to 85 percent, and sound absorption performance under high water pressure is improved by 50 to 85 percent; and the forming process has the advantages of high operability, high quality consistency, suitability for the formation of a large-sized composite material component, and the like.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
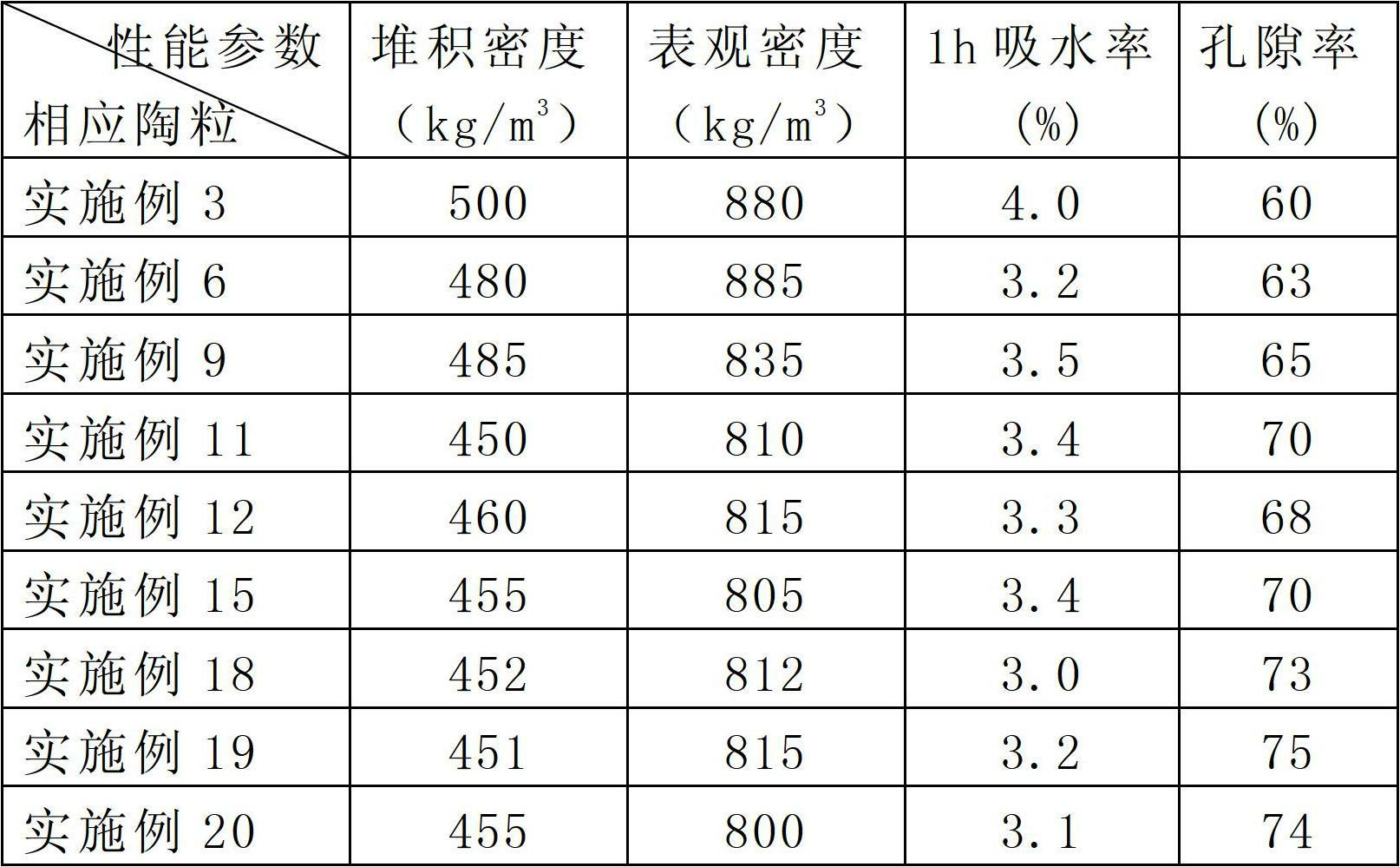
Efficient sound-absorbing ceramsite
InactiveCN102633491AImprove the sound absorption coefficientLightweight and high strengthCeramic materials productionCeramicwarePorositySludge
The invention relates to an efficient sound-absorbing ceramsite, belonging to the technical field of a building material. Aiming to solve the problems that city pollution can not be well solved, product properties are poor, the poor sound-absorbing effects are poor and the production cost is high in the prior art by mainly using the shale as ceramsite, can be solved, The invention provides the efficient sound-absorbing ceramsite, which is prepared from raw materials mainly consisting of raw materials of 60-80% of sludge, 5-20% of the shale, 5-20% of coal ash and 1.0-10% of additive. The efficient sound-absorbing ceramsite provided by the invention has the properties of wide sound-absorbing frequency band, fire resistance, good durability, freezing resistance, seismic resistance, high sound-absorbing coefficient, high porosity, light weight, high strength, heat resistance, anti-permeability and the like. The efficient sound-absorbing ceramsite further can be used for preparing a road barrier and a metro sound-absorbing material and has wide application prospect. Furthermore, the efficient sound-absorbing ceramsite provided by the invention mainly uses city sludge, so that not only can the problem of the city sludge be solved well, but also the overuse of a natural resource of the shale is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FANGYUAN BUILDING MATERIALS TECH
Refrigerator and wind way plate thereof
InactiveCN105180562AImprove silent qualityImprove sound absorption performanceLighting and heating apparatusDomestic refrigeratorsHelmholtz resonatorEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of household appliances, and discloses a refrigerator and a wind way plate thereof. The wind way plate comprises an outer side plate, an inner side plate and a surrounding plate, wherein the outer side plate and the inner side plate are oppositely arranged; the surrounding plate is respectively connected with the outer side plate and the inner side plate to define a sound absorption cavity; and the inner side plate is provided with multiple sound absorption holes communicated with the sound absorption cavity at intervals. The wind way plate comprises the inner side plate, the outer side plate and the surrounding plate to define the sound absorption cavity; the sound absorption holes are formed in the inner side plate, and are all communicated with the sound absorption cavity; and as the sound absorption holes are correspondingly communicated with the sound absorption cavity to form multiple Helmholtz resonators connected in parallel to form an excellent sound absorption system, compared with the prior art, the wind way plate can effectively improve the sound absorption effect, reduce the refrigerator wind way noise and promote the refrigerator silence quality.
Owner:HEFEI MIDEA REFRIGERATOR CO LTD +1
Viscoelasticity composite sound insulating board
InactiveCN105109122AWith mechanical strengthTo achieve the purpose of vibration reduction and sound absorptionSynthetic resin layered productsVehicle componentsElastomerPolyolefin
The invention discloses a viscoelasticity composite sound insulating board. The sound insulating board comprises a damping layer (1), a sound insulating layer (2) and a sound absorption layer (3) which are sequentially arranged. One side of the damping layer (1) is attached to the surface of a shell of an underwater moving body, and the damping layer (1) is made of isotropous polyurethane or macromolecule resin. The sound insulating layer (2) is made of polyolefin elastomers or glass fibers. The sound absorption layer (3) is made of photosensitive resin, and closed cavities (4) are arranged in the sound absorption layer (3) in an array mode. According to the viscoelasticity composite sound insulating board, the damping layer can achieve the purposes of reducing vibration and absorbing noise; the sound insulating layer achieves a reinforcing effect, so that the entire composite sound insulating board has certain mechanical strength integrally, and meanwhile the sound insulating capacity of the multi-layer structure in a low-middle frequency band is adjusted; the sound absorption layer absorbs outside noise, reflection echoes are reduced, and due to the fact that the cavities are formed in the sound absorption layer, the sound absorption effect is further enhanced. By means of the viscoelasticity composite sound insulating board, low-frequency noise of underwater ships can be effectively absorbed, and the structure is simple.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Sound-absorption needled non-woven composite and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103818084AImprove sound absorptionGood sound absorptionSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationPolyesterHot pressing
The invention discloses a preparation method for a sound-absorption needled non-woven composite. The preparation method comprises the following steps: A, opening porous polyester fibers, carding and netting; B, inputting the fiber net into a needling machine for reinforcing by needling, winding, cutting, and preparing fabric, wherein the thickness of the fabric is 4-40 mm and the surface density of the fabric is 40-500 g / m<2>; C, laminating 2-6 layers of the fabric, conducing hot pressing for combining, and then cooling, wherein the temperature for the hot pressing is 100-120 DEG C. The invention further discloses the sound-absorption needled non-woven composite. After hot pressing for combining, the sound-absorption performance of the sound-absorption needled non-woven composite is significantly improved; besides, the sound-absorption needled non-woven composite is light, thin, high in strength and low in production cost.
Owner:DANYANG YUSHENG TEXTILE NEW MATERIAL
Compound damping foam rubber material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106543500AImprove sound absorption performanceOptimizing the Ratio of Raw RubberRubber materialSound energy
The invention provides a compound damping foam rubber material. The material is prepared from rubber, reinforcing filling and addition agents, wherein the addition agents comprise a vulcanizing agent, a dispersant, an anti-scorching agent, an anti-ageing agent, an accelerant, a secondary accelerant and a softening agent; the rubber is selected from at least two of silicone rubber, nitrile butadiene rubber, butadiene rubber, isoprene rubber and ethylene propylene rubber; and the addition agents also comprise a foaming agent. The compound damping foam rubber material provided by the invention has the advantages of light weight, cost reduction, good transformer oil resisting performance, good electric insulating performance and the like; a pore structure generated by foaming and the rubber material have a viscoelastic damping synergistic effect to enhance sound energy dissipation and improve noise-reduction performance of the compound damping foam rubber material; and the compound damping foam rubber material can be used as a sound-absorption and noise-reduction material to be applied to vibration absorption and noise reduction of a transformer body, and has remarkable economic and social benefits.
Owner:STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER +3
Low-cost ecological ceramic material having a plurality of sound absorbing structures and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110342956AHigh open porosityImprove sound absorption performanceSound proofingCeramic materials productionPorosityWater vapor
The invention discloses a low-cost ecological ceramic material having a plurality of sound absorbing structures. The low-cost ecological ceramic material having the plurality of sound absorbing structuresis prepared from the following components: 22% to 27% offly ash, 13% to 18%ofcoal gangue, 8% to 12% ofred mud, 40%to 45% ofshale, 5%to 10% offeldspar, 0.2%to 2% of foaming agent, 0.5%to 3% of binder, 7%to 12% of pore forming agent, and 0% to 1% ofsurfactant; a variety of pore structures are arranged, and water vapor in the environment is absorbed to adjust the humidity of the air. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the low-cost ecological ceramic material.A perforated plate sound absorbing structure, a microperforated resonance sound absorbing structure, and a thin plate resonance sound absorbing structure are formed by three pore-forming methods of mechanical punching, pore forming agent, and foaming agent respectively, the open porosity of the material is increased, the high-frequency sound absorption effect is improved, the plurality of sound absorbing structures improve the sound absorption effect of the low and medium frequency, the preparation material islow in cost, and the environment-friendly effect is conformed.
Owner:SHANXI TIANHE NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Composite sound absorption plate
InactiveCN104616648AEffective sound absorptionEffective energy consumptionSound producing devicesMicro perforated plateAcoustic absorption
The invention relates to the sound absorption technical field, particularly to a composite sound absorption plate. The composite sound absorption plate comprises a micro perforation plate and a base body which are arranged in an attached mode; the micro perforation plate is provided with a plurality of through sound absorption holes; the base body is provided with a plurality of sound absorption empty chambers; a communication channel is formed between every two adjacent sound absorption empty chambers; the surface of the base body, which is provided with the sound absorption empty chambers, is attached to the micro perforation plate; every sound absorption hole formed in the micro perforation plate is communicated with the corresponding sound absorption empty chamber formed in the base body. Compared with the prior art, the micro perforation plate, the sound absorption empty chambers and the communication channel formed between every two adjacent sound absorption empty chambers can effectively participate in energy consumption and sound absorption, the energy consumption effect is achieved through the resonance sound absorption principle of the micro perforation plate and the sound absorption empty chambers, and accordingly the sound absorption effect of the structure can be particularly significant and meanwhile the sound absorption structure is located on the base body and the micro perforation plate and accordingly the separated independent machining can be performed, the manufacturability is good, and the production cost can be controlled.
Owner:BEIJING MUNICIPAL INST OF LABOUR PROTECTION
Preparation method for composite sound absorption material
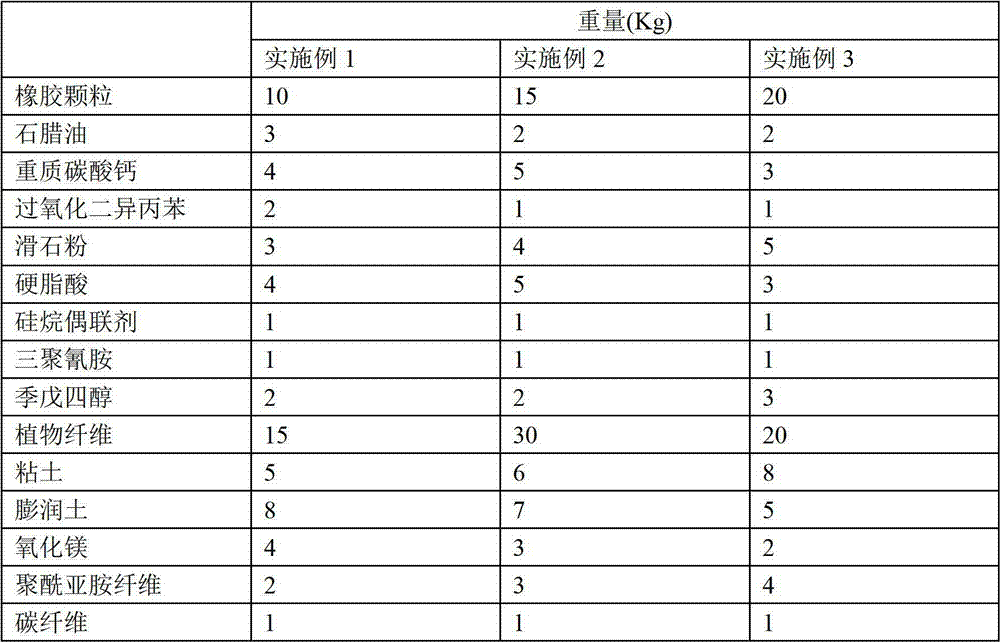
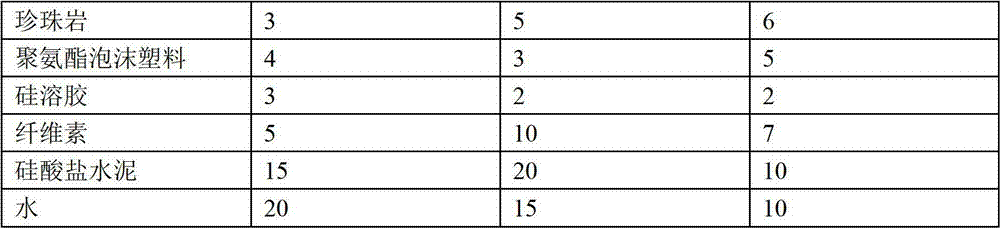
The invention provides a preparation method for a composite sound absorption material, which belongs to the technical field of building materials. The material is prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 10 to 20 parts of rubber particles, 2 to 3 parts of paraffin oil, 3 to 5 parts of heavy calcium carbonate, 1 to 2 parts of dicumyl peroxide, 3 to 5 parts of talc powder, 3 to 5 parts of stearic acid, 1 part of a silane coupling agent, 1 part of melamine, 2 to 3 parts of pentaerythritol, 15 to 30 parts of plant fibers, 5 to 8 parts of clay, 5 to 8 parts of bentonite, 2 to 4 parts of magnesia, 2 to 4 parts of polyimide fibers, 1 part of carbon fibers, 3 to 6 parts of perlite, 3 to 5 parts of polyurethane foam, 2 to 3 parts of silica sol, 5 to 10 parts of cellulose, 10 to 20 parts of silicate cement and 10 to 20 parts of water. The composite sound absorption material provided by the invention has good sound absorption and sound insulation effects.
Owner:苏州市德莱尔建材科技有限公司
Sound-insulation noise-reduction water-based wood primer
InactiveCN104403555AGood sound absorption performance and fire performanceDense paint filmFireproof paintsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsEmulsionCorrosion
Owner:广州益景春环保材料科技有限公司
Performance testing method for wideband perforated plate
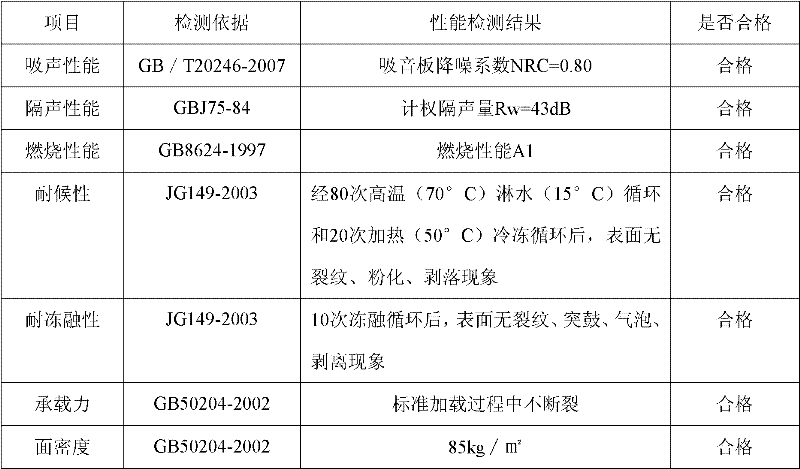
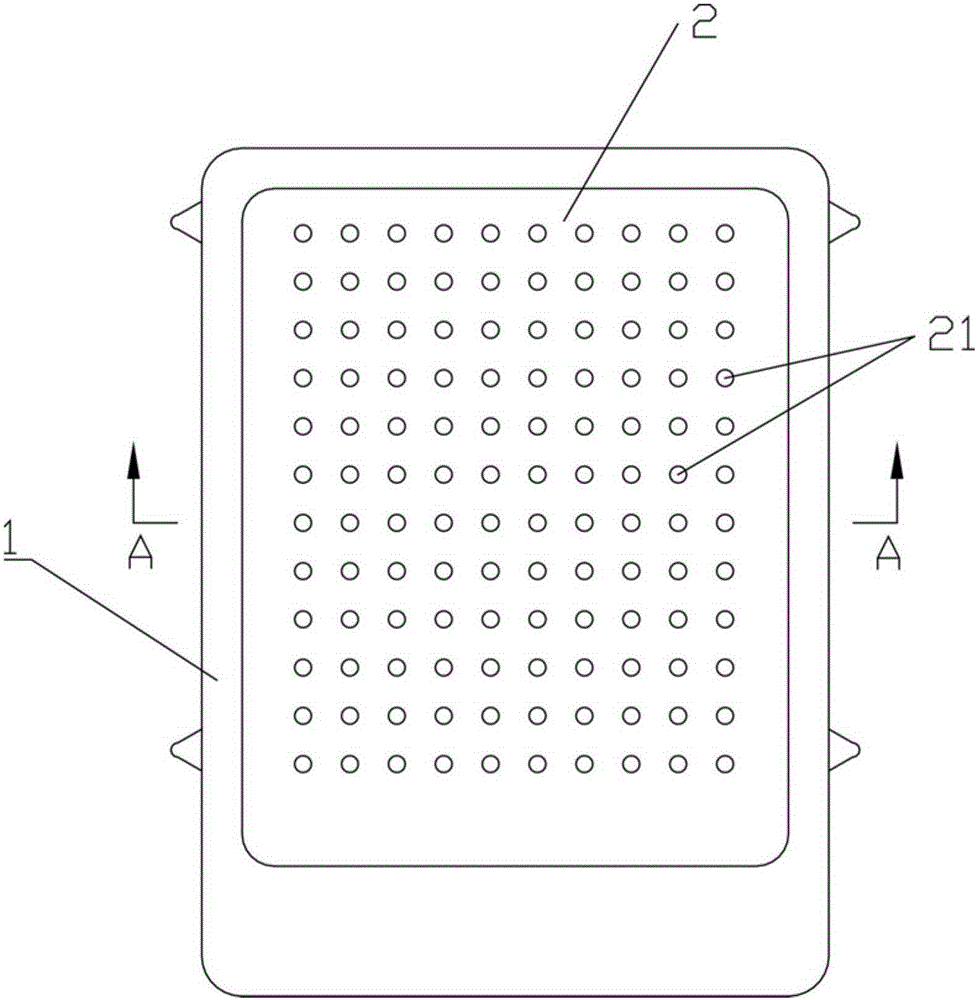
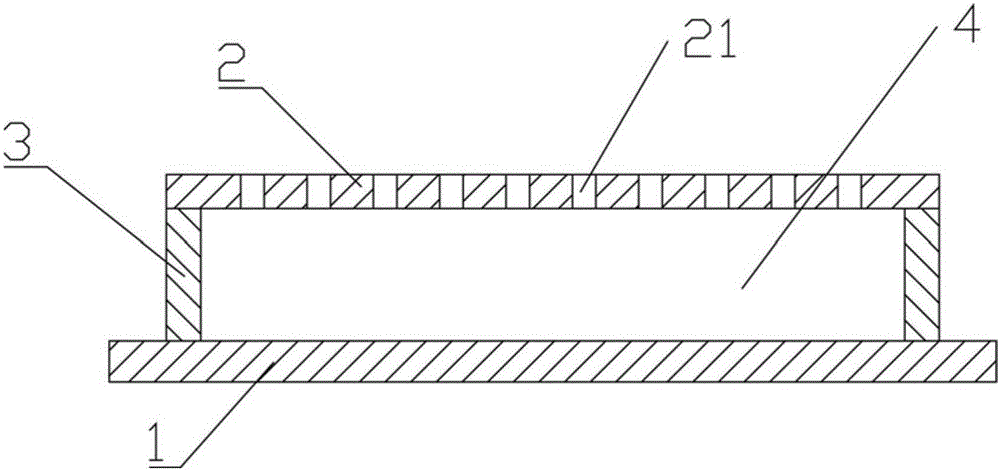
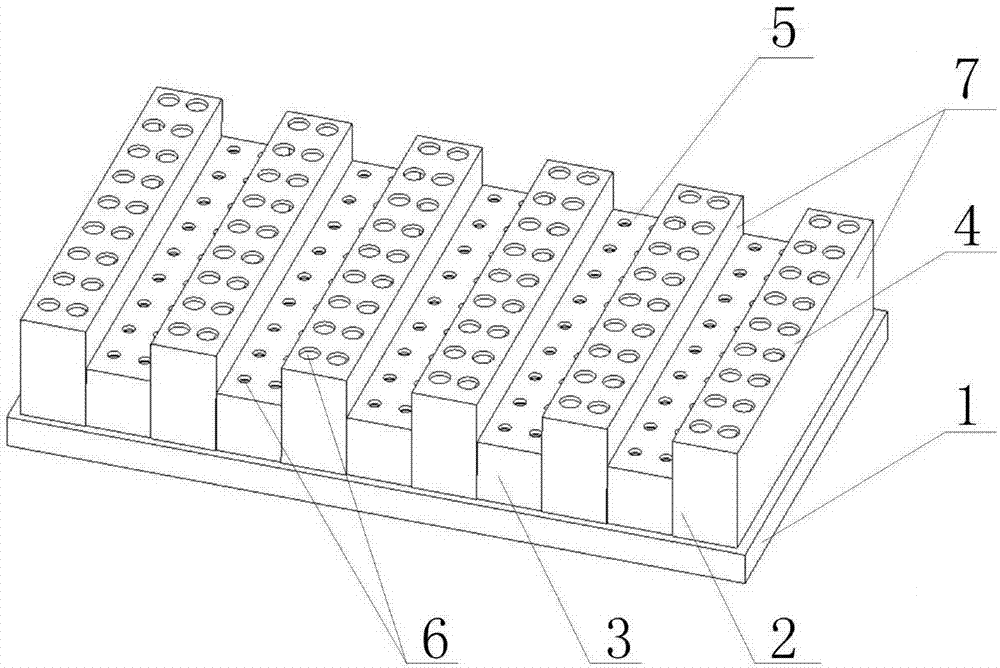
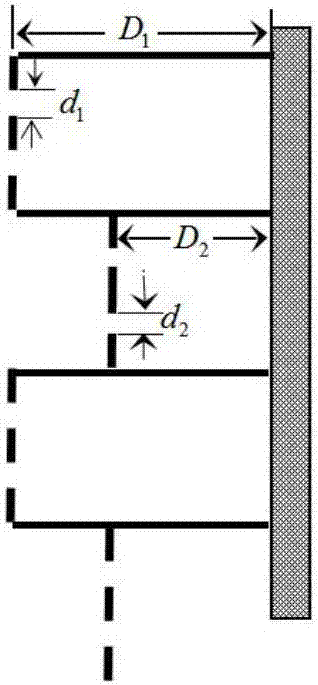
ActiveCN107039028AImprove sound absorption performanceSimple test methodAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSustainable transportationEngineeringAcoustics
The invention discloses a wideband perforated plate which comprises a back plate. The back plate is provided with a plurality of first hollow chambers and a plurality of second hollow chambers. A second hollow chamber is arranged between each two adjacent first hollow chambers. The first hollow chamber comprises a pore plate A, and the second hollow chamber comprises a pore plate B. The pore plate A and the pore plate B are sound absorbing plates with a plurality of pores. The distance between the pore plate A and the back plate is larger than that between the pore plate B and the back plate. The wideband perforated plate can effectively enlarge a sound absorbing band width and realizes high sound absorbing performance. Furthermore the performance testing method according to the invention has advantages of simple operation and high practicability.
Owner:郭辰曦
Waterborne polyurethane thermal-insulating sound-absorbing coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104789107AExtend your lifeLow shrinkagePolyurea/polyurethane coatingsSolventAbsorption effect
The invention discloses waterborne polyurethane thermal-insulating sound-absorbing coating and a preparation method thereof. The waterborne polyurethane thermal-insulating sound-absorbing coating comprises a polyurethane prepolymer, N-hydroxymethyl acrylamide, phthalic acid dibutyl ester, a zirconium-aluminic acid ester coupling agent, rutile titanium dioxide, methylsilicone oil, a mixed solvent and a sound-absorbing material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving every 1 kg by weight of N-hydroxymethyl acrylamide in 2 kg of 50-70% ethanol in volume concentration, mixing with the polyurethane prepolymer in a reaction kettle, enabling the components to react for 1 hour at 80-150 DEG C, and adding the zirconium-aluminic acid ester coupling agent to continuously react for 2-5 hours; subsequently adding the phthalic acid dibutyl ester, rutile titanium dioxide, methylsilicone oil, mixed solvent and sound-absorbing material, and uniformly mixing, thereby obtaining a waterborne polyurethane thermal-insulating sound-absorbing coating product. The waterborne polyurethane thermal-insulating sound-absorbing coating can insulate heat and absorb sound, and is good in chemical resistance, good in temperature resistance, good in weather resistance, long in film service life, free of toxicity or smell, safe and environment-friendly and good in sound absorption effect.
Owner:GUANGXI CHAOXING SOLAR ENERGY TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com