Solvent pulping of biomass
a biomass and solvent technology, applied in the direction of continuous pulping process, inorganic base pulping, pretreatment with water/steam, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, increased cod pollution, and need for significant amounts of purchased power for electricity, and achieve high level of solvent recovery, high efficiency and effective manner
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
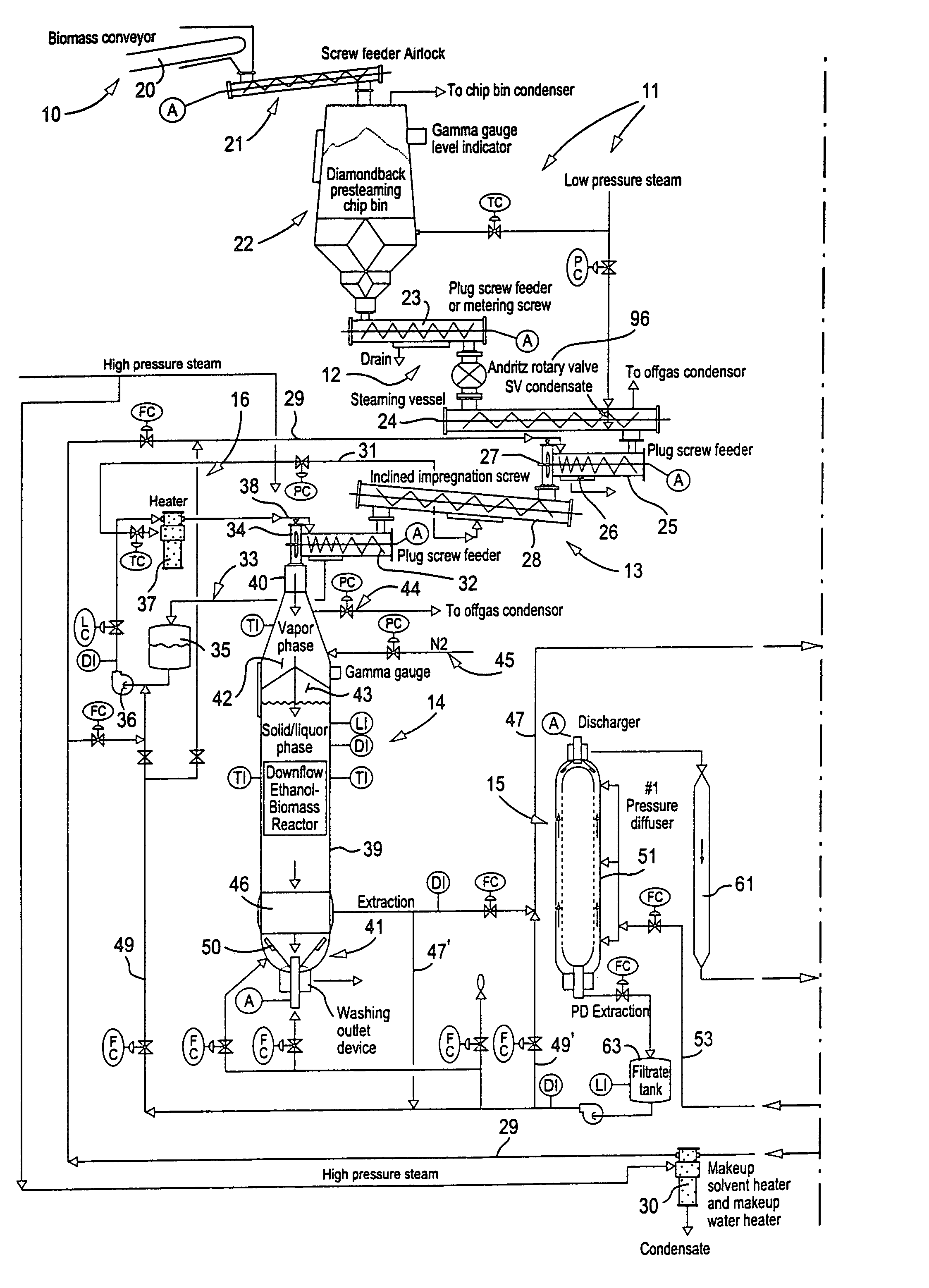
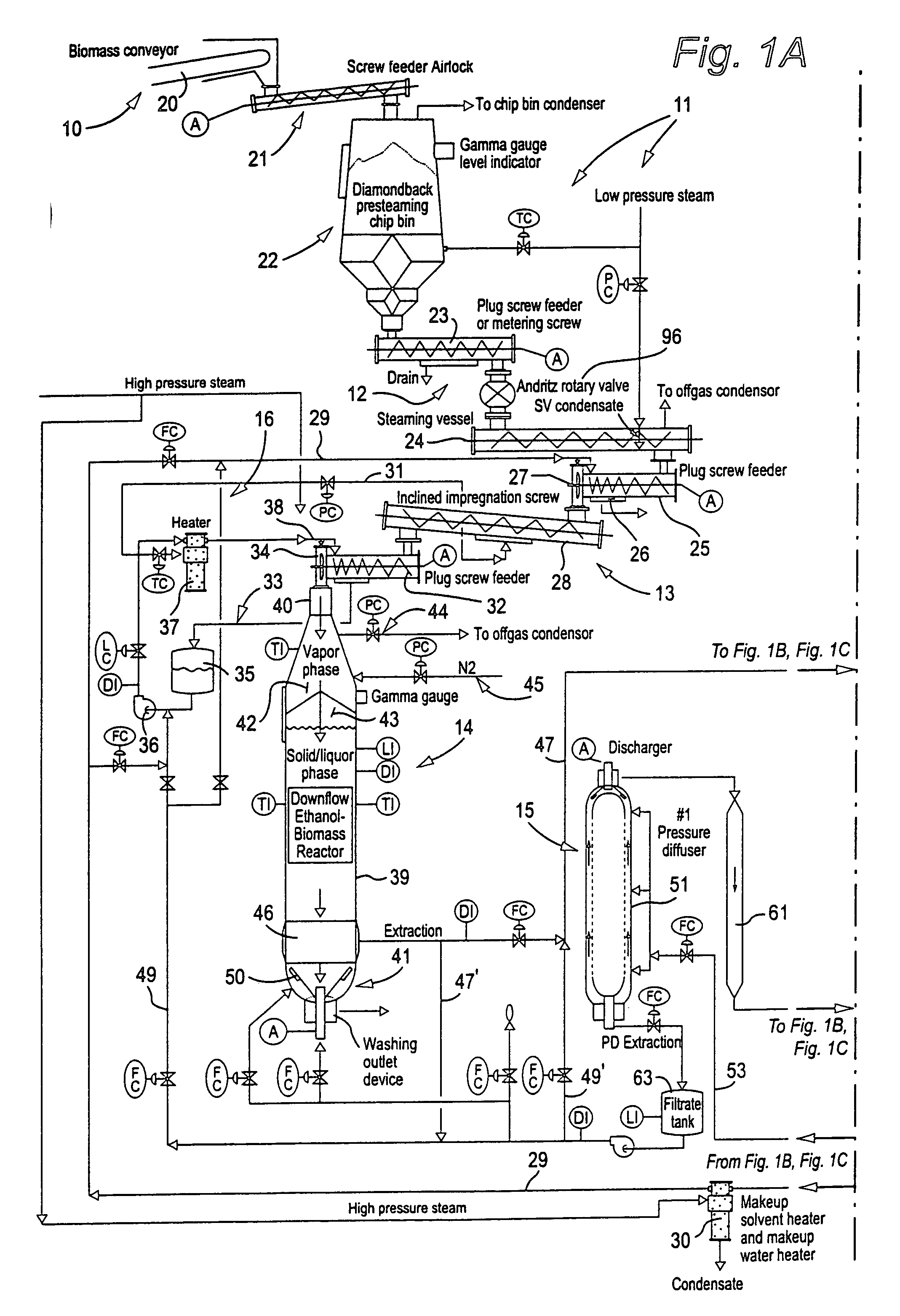
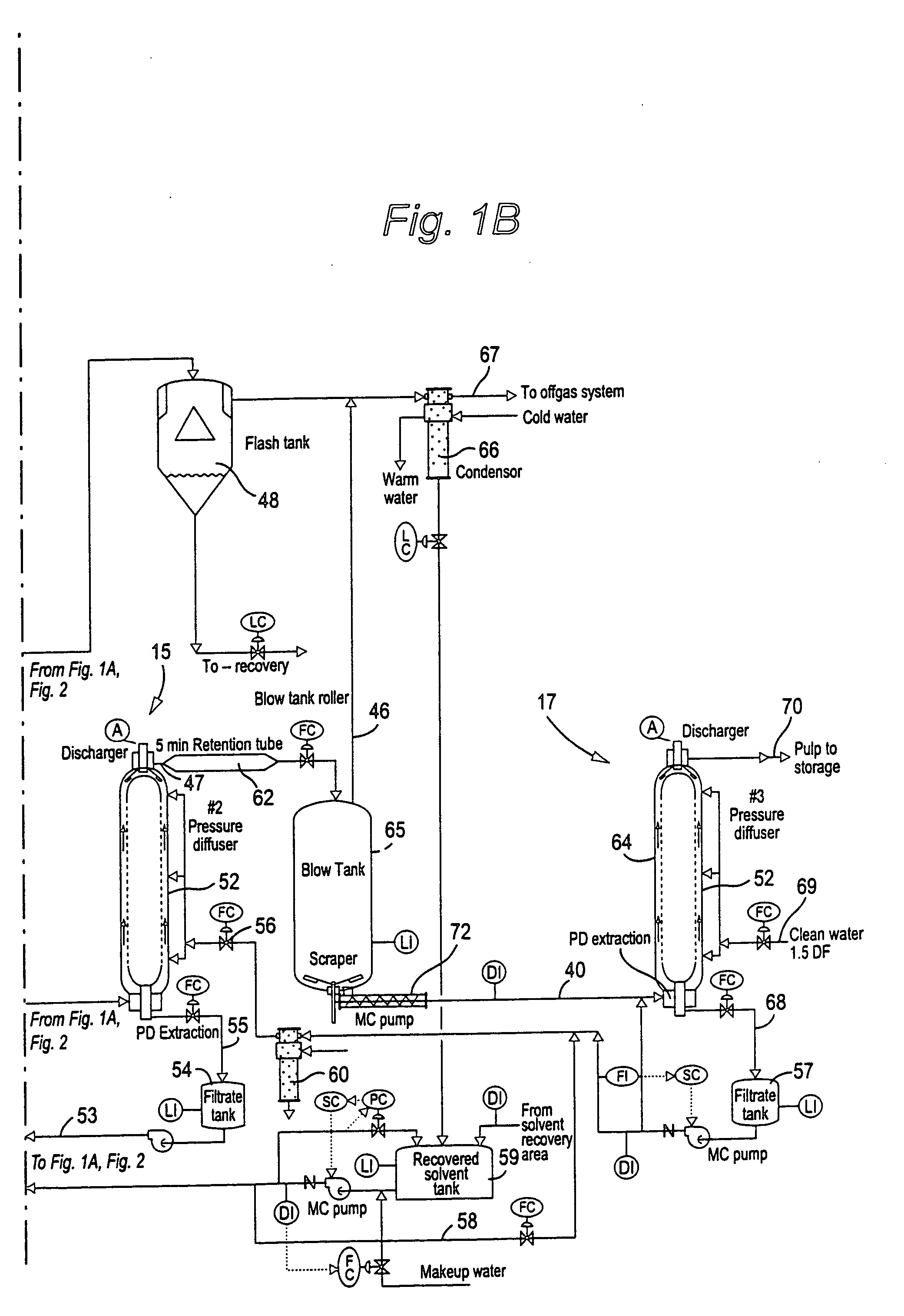
[0024] FIGS. 1A, 1B and 1C schematically illustrate one exemplary form (and variations) a system can take for practicing an advantageous solvent pulping method according to the invention. FIGS. 2, 1B and 1C schematically illustrate another exemplary form (and variations) a system can take for practicing an advantageous solvent pulping method according to the invention. FIGS. 3, 4, 6 and 7 illustrate other embodiments (for example, possible changes to FIGS. 1A, 1B, 1C and 2, or separate systems) that may be utilized according to the present invention. FIG. 5 schematically illustrates another exemplary form a system can take for practicing an advantageous solvent pulping method according to the invention.
[0025] In FIGS. 1A, 1B, 1C, 2, 3, 4, 6 and 7, many of the components are similar (e.g., components 23 and 94--plug or compression screw feeders, components 24 and 98--steaming vessel or inclined steaming vessel, components 25 and 102--plug or compression screw feeders, components 28 a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com