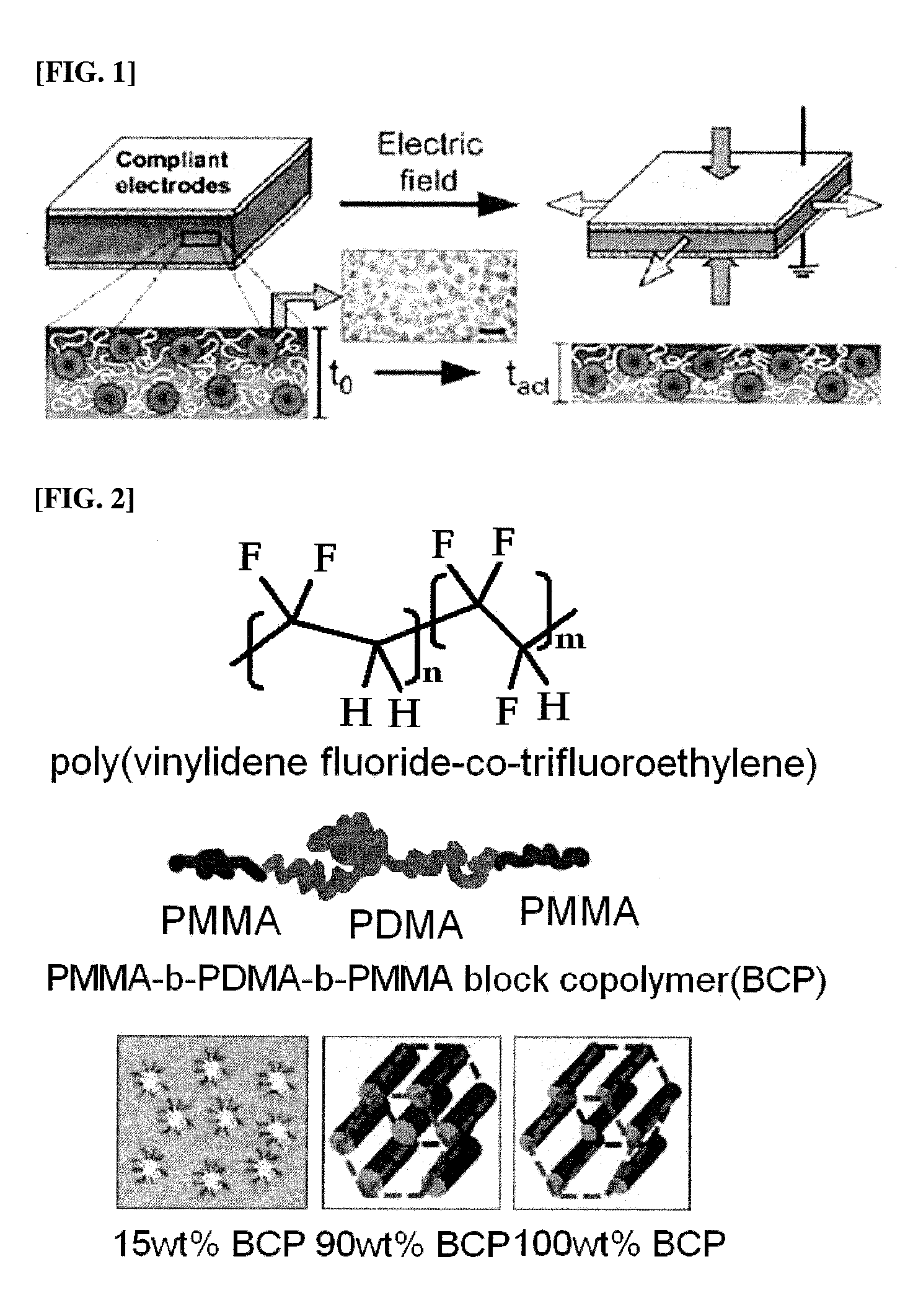
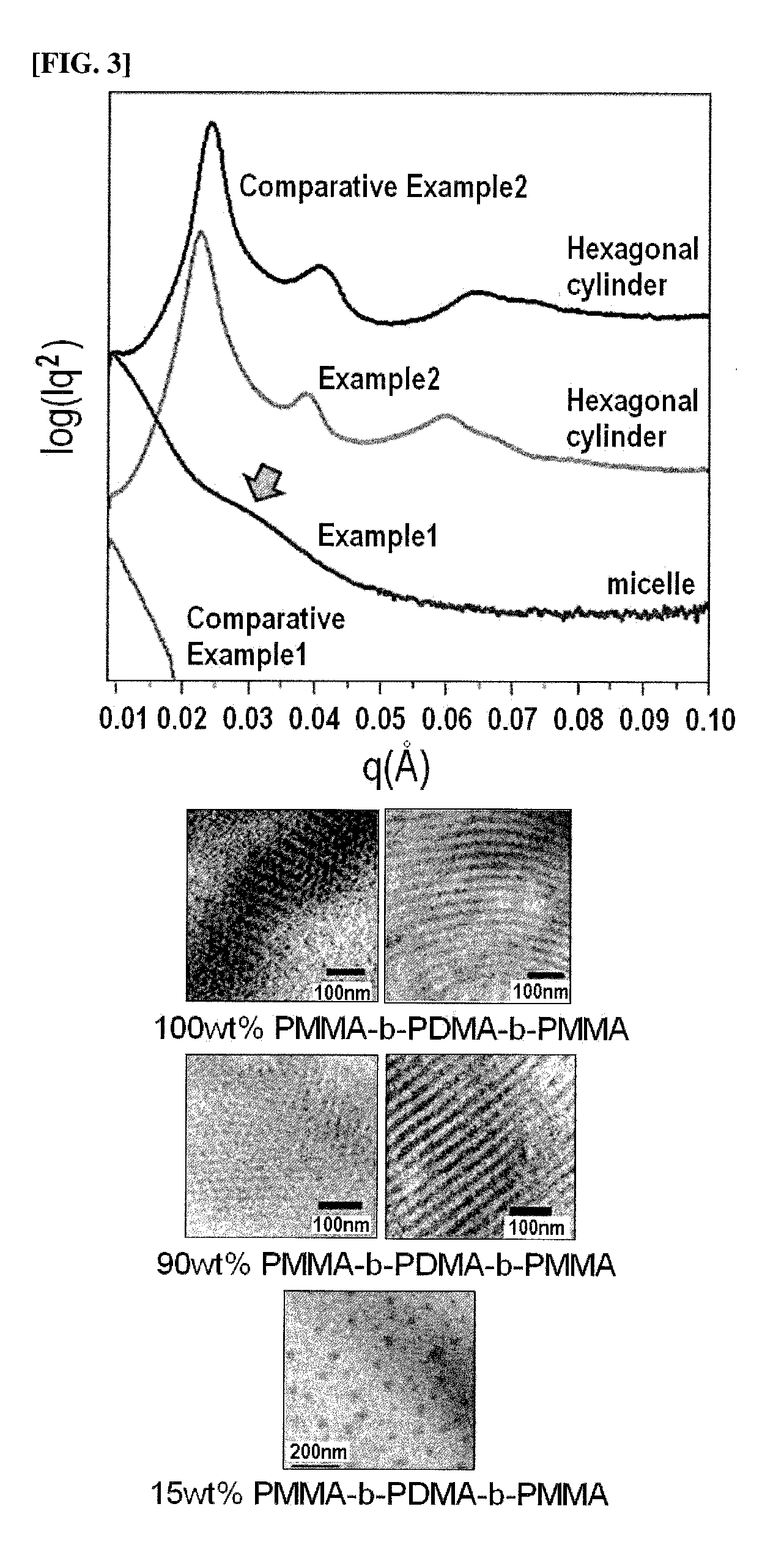
Patents
Literature
205 results about "Piezoelectric polymer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A piezoelectric polymer is a plastic material with groups of molecules linked as orderly crystallites.
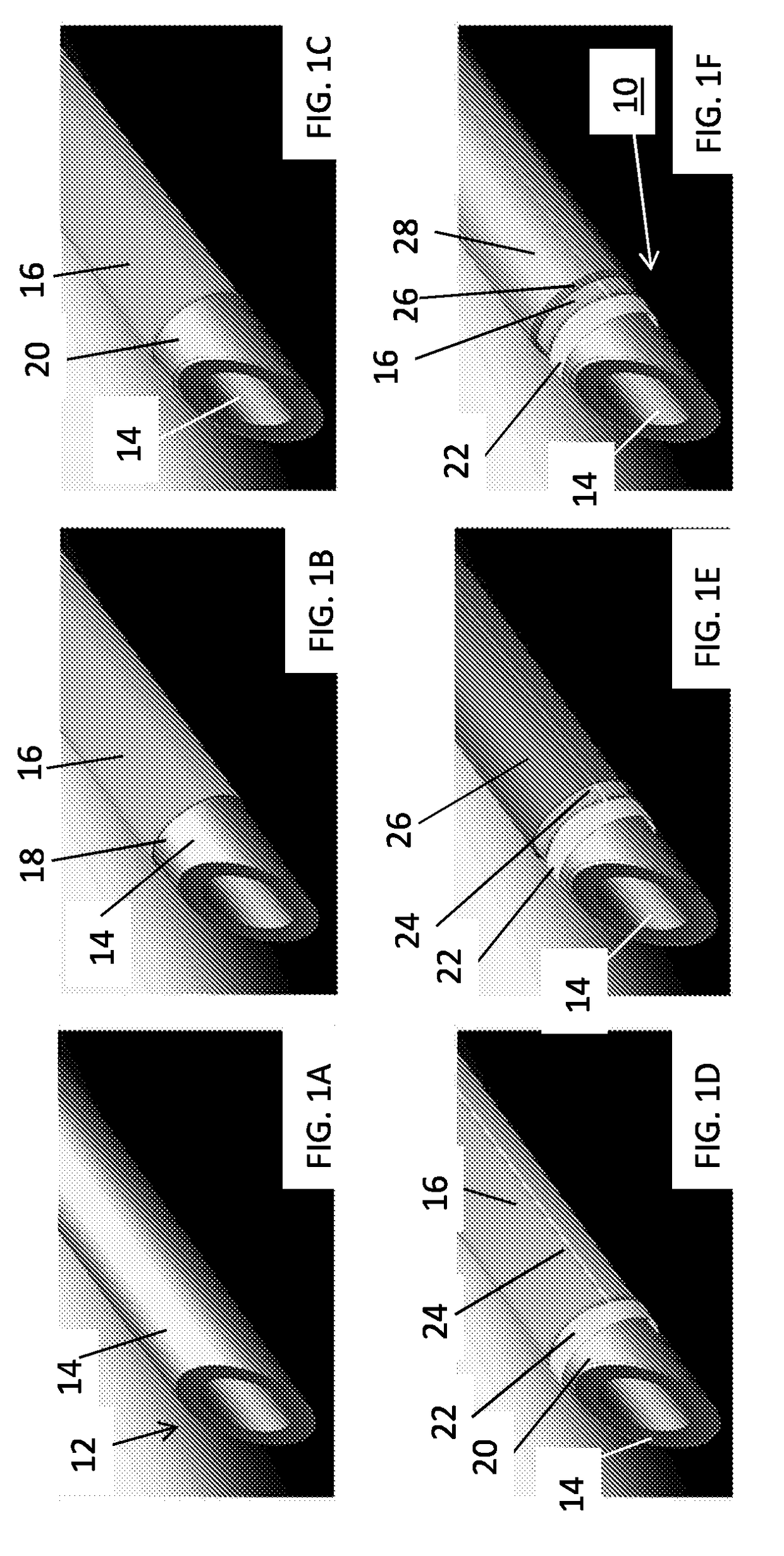
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors by active composite artificial muscle implants
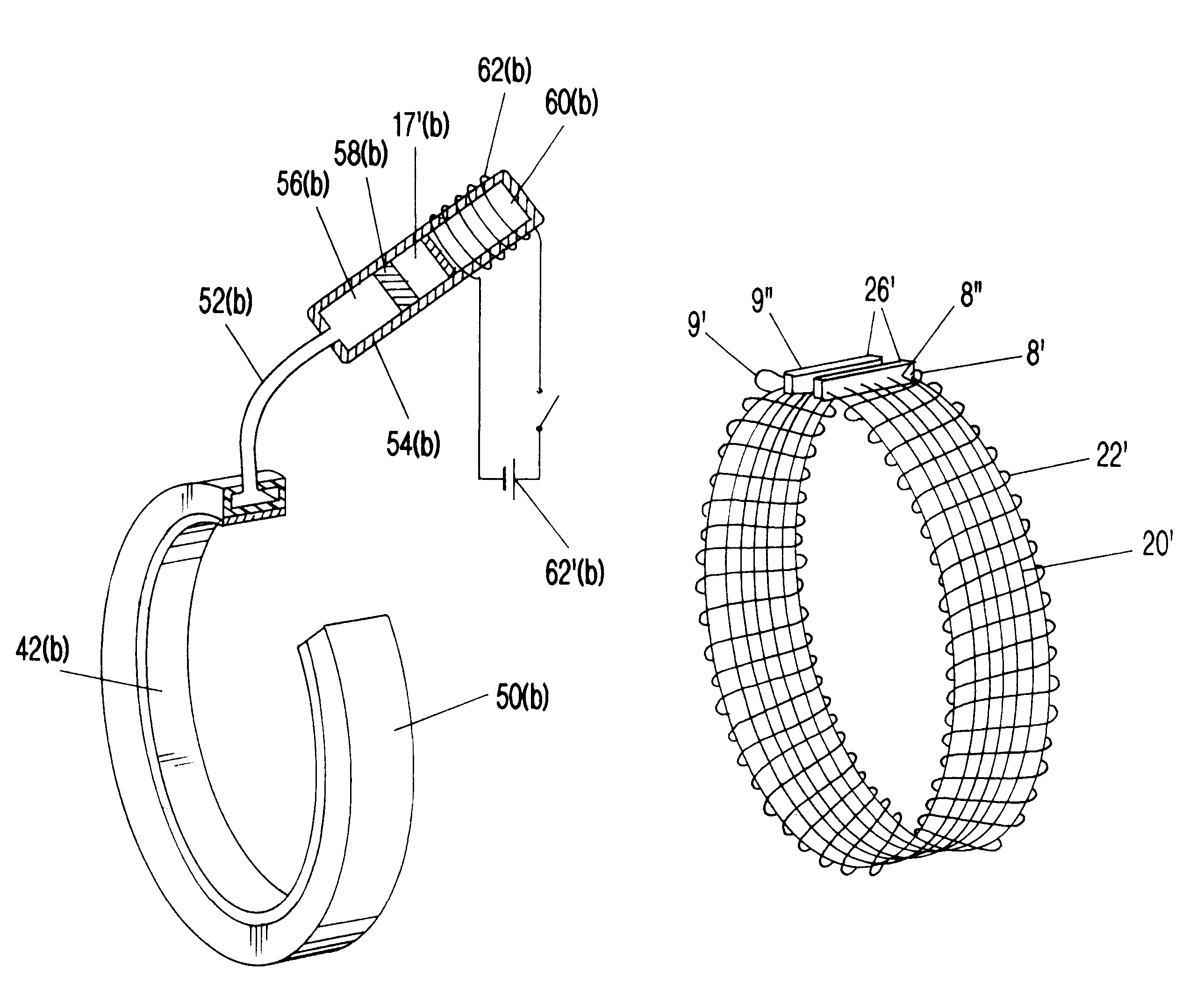
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors such as presbyopia, hyperopia, myopia, and stigmatism by using transcutaneously inductively energized artificial muscle implants to either actively change the axial length and the anterior curvatures of the eye globe. This brings the retina / macula region to coincide with the focal point. The implants use transcutaneously inductively energized scleral constrictor bands equipped with composite artificial muscle structures. The implants can induce enough accommodation of a few diopters, to correct presbyopia, hyperopia, and myopia on demand. In the preferred embodiment, the implant comprises an active sphinctering smart band to encircle the sclera, preferably implanted under the conjunctiva and under the extraocular muscles to uniformly constrict the eye globe, similar to a scleral buckle band for surgical correction of retinal detachment, to induce active temporary myopia (hyperopia) by increasing (decreasing) the active length of the globe. In another embodiment, multiple and specially designed constrictor bands can be used to enable surgeons to correct stigmatism. The composite artificial muscles are either resilient composite shaped memory alloy-silicone rubber implants in the form of endless active scleral bands, electroactive ionic polymeric artificial muscle structures, electrochemically contractile endless bands of ionic polymers such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN), thermally contractile liquid crystal elastomer artificial muscle structures, magnetically deployable structures or solenoids or other deployable structures equipped with smart materials such as preferably piezocerams, piezopolymers, electroactive and eletrostrictive polymers, magnetostrictive materials, and electro or magnetorheological materials.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ROBOTS
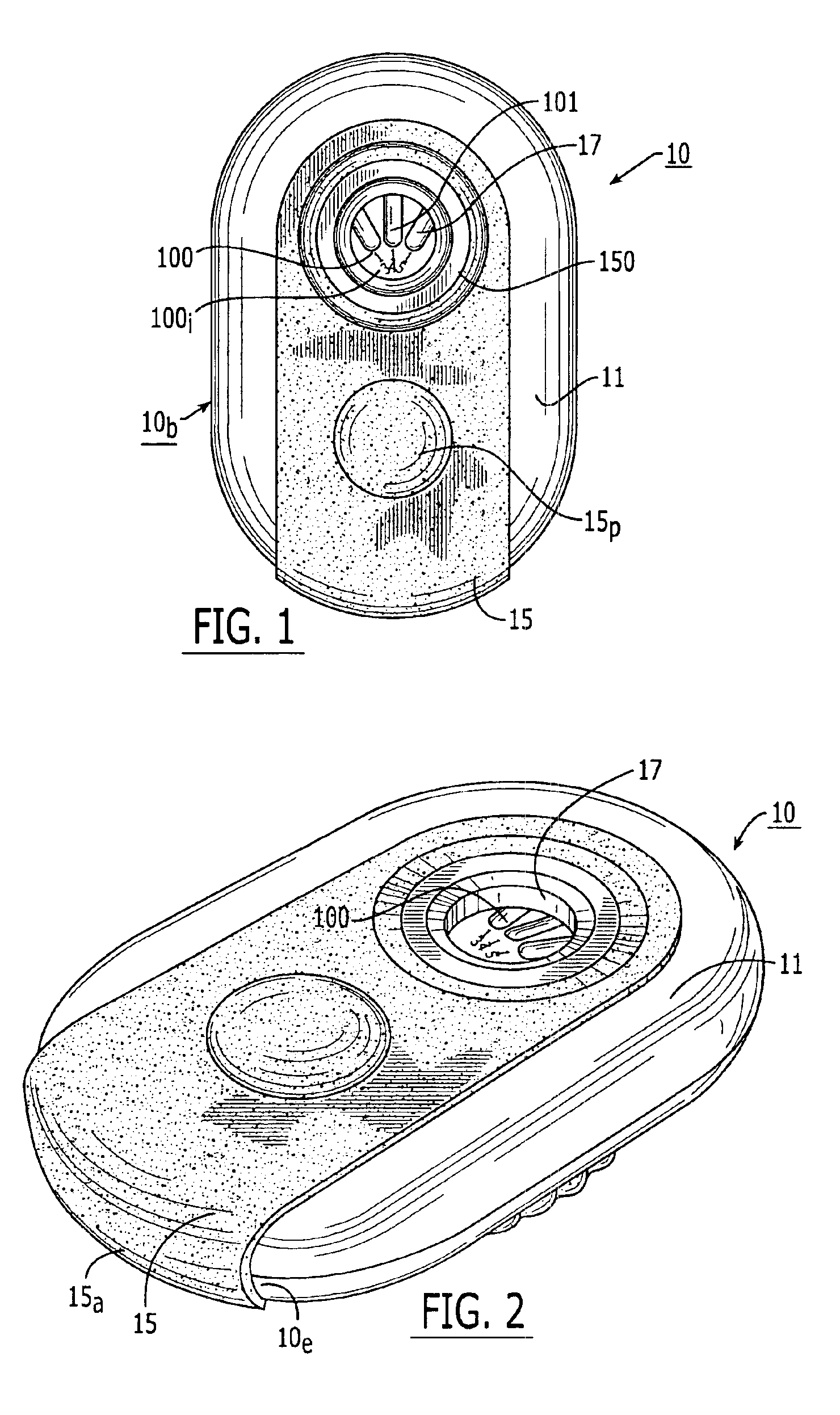
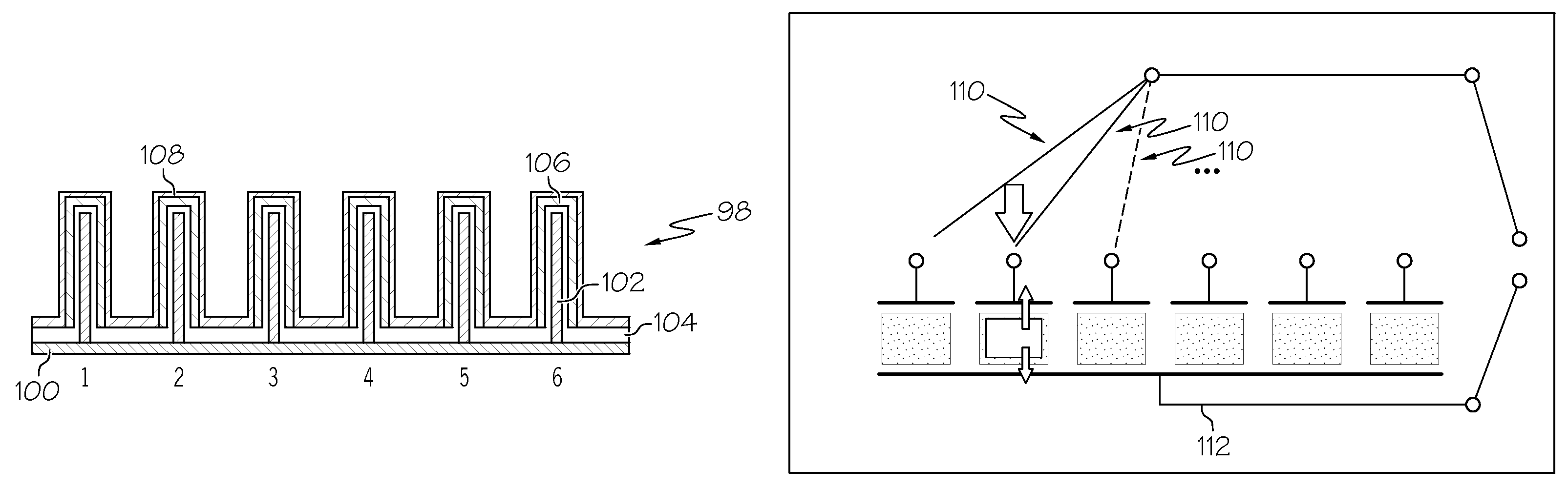
Dry powder inhalers, related blister devices, and associated methods of dispensing dry powder substances and fabricating blister packages
InactiveUS6889690B2Easy to optimizeLimit amount of resistanceSmall article dispensingLiquid surface applicatorsPowder InhalerInhalation
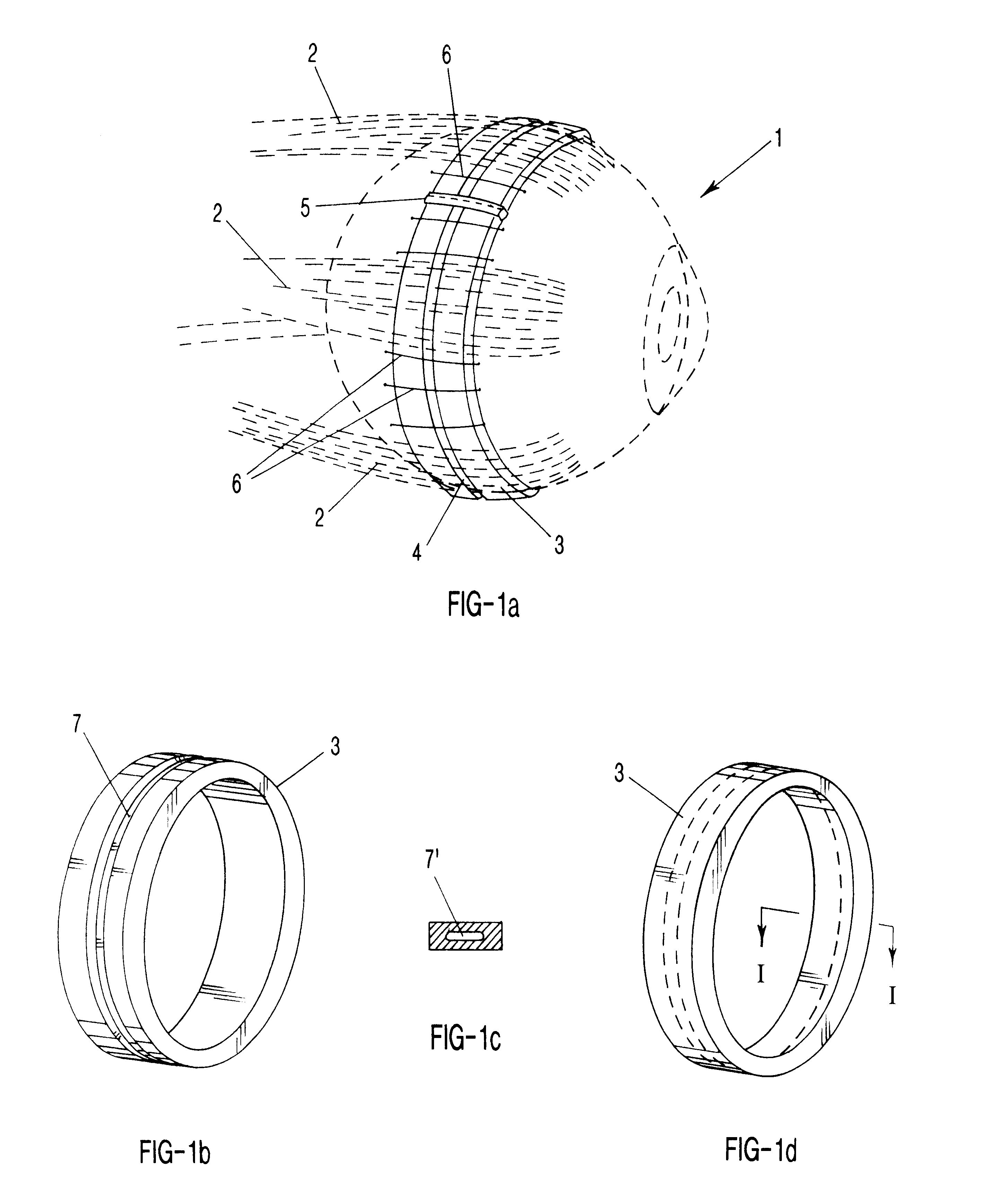
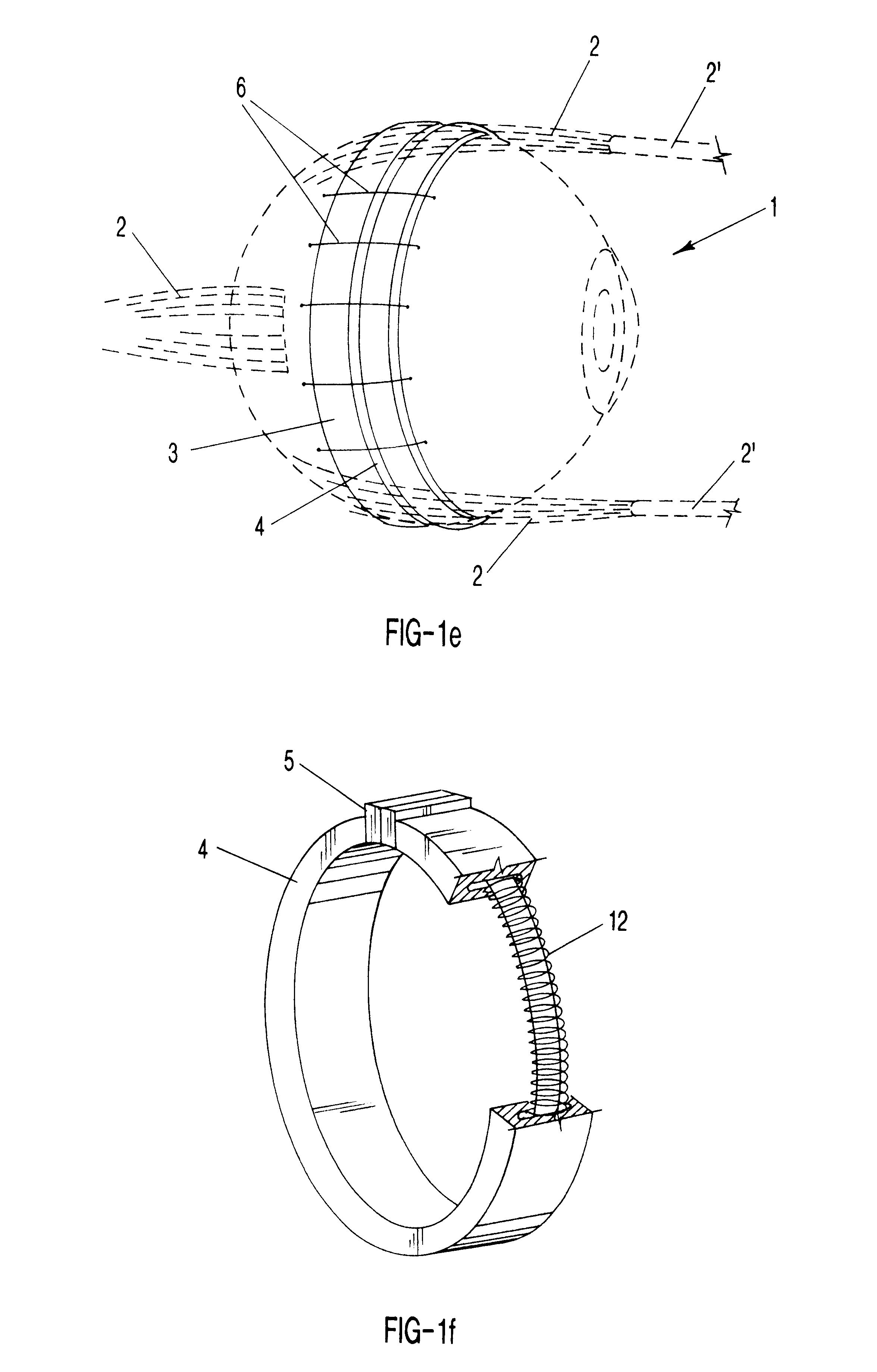
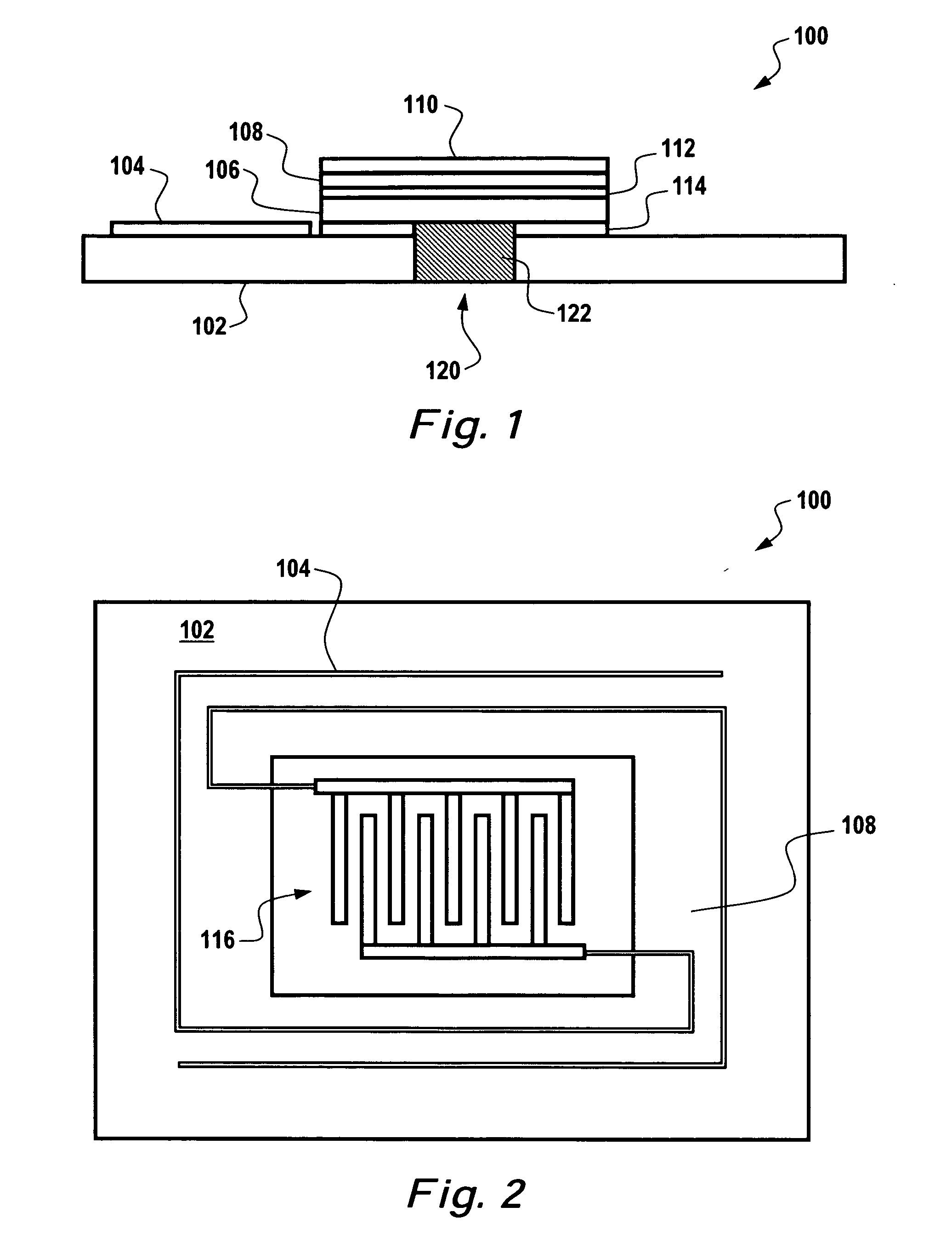
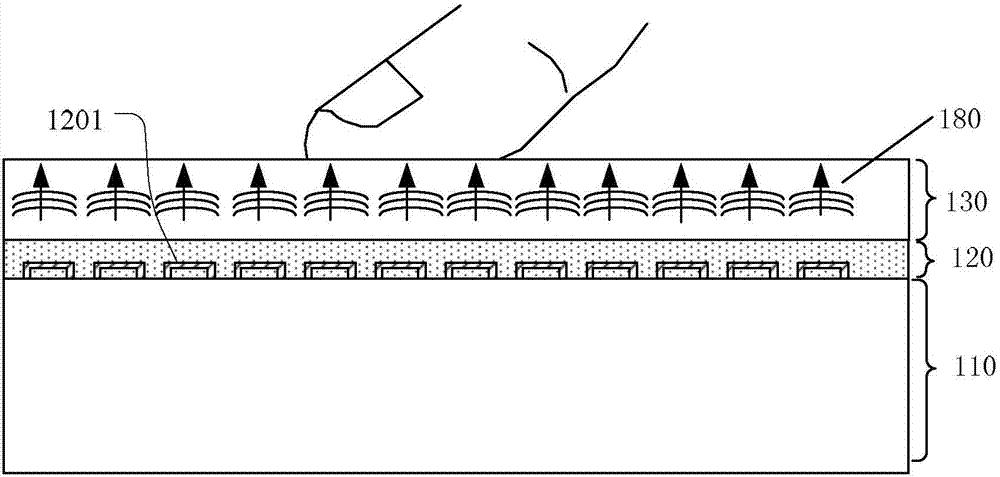
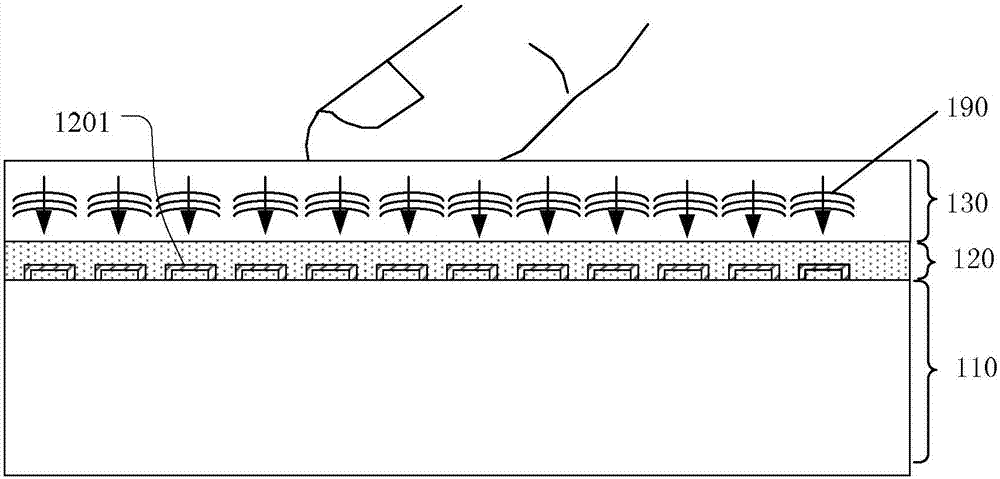
The present invention includes dry powder inhalers and associated multi-dose dry powder packages for holding inhalant formulated dry powder substances and associated fabrication and dispensing methods. The multi-dose package can include a platform body comprising at least one thin piezoelectric polymer material layer defining at least a portion of a plurality of spatially separated discrete elongate dry powder channels having an associated length, width and height; and a metallic material attached to selected portions of the piezoelectric polymer material including each of the regions corresponding to the elongate dry powder channels to, in operation, define active energy releasing vibratory channels. In operation, the elongate channels can be selectively individually activated to vibrate upon exposure to an electrical input.The dry powder inhaler includes an elongate body having opposing first and second outer primary surfaces with a cavity therebetween and having opposing top and bottom end portions and a multi-dose sealed blister package holding a plurality of discrete meted doses of a dry powder inhalable product located in the cavity of the elongate body. The inhaler also includes an inhalation port formed in the bottom end portion of the elongate body, the inhalation port configured to be in fluid communication with at least one of the discrete meted doses during use and a cover member that is pivotably attached to the elongate body so that it remains attached to the body during normal operational periods of use and moves to a first closed position to overlie the inhalation port at the bottom end portion of the body during periods of non-use and moves to a second open position away from the inhalation port during periods of use to allow a user to access the inhalation port.
Owner:ORIEL THERAPEUTICS INC
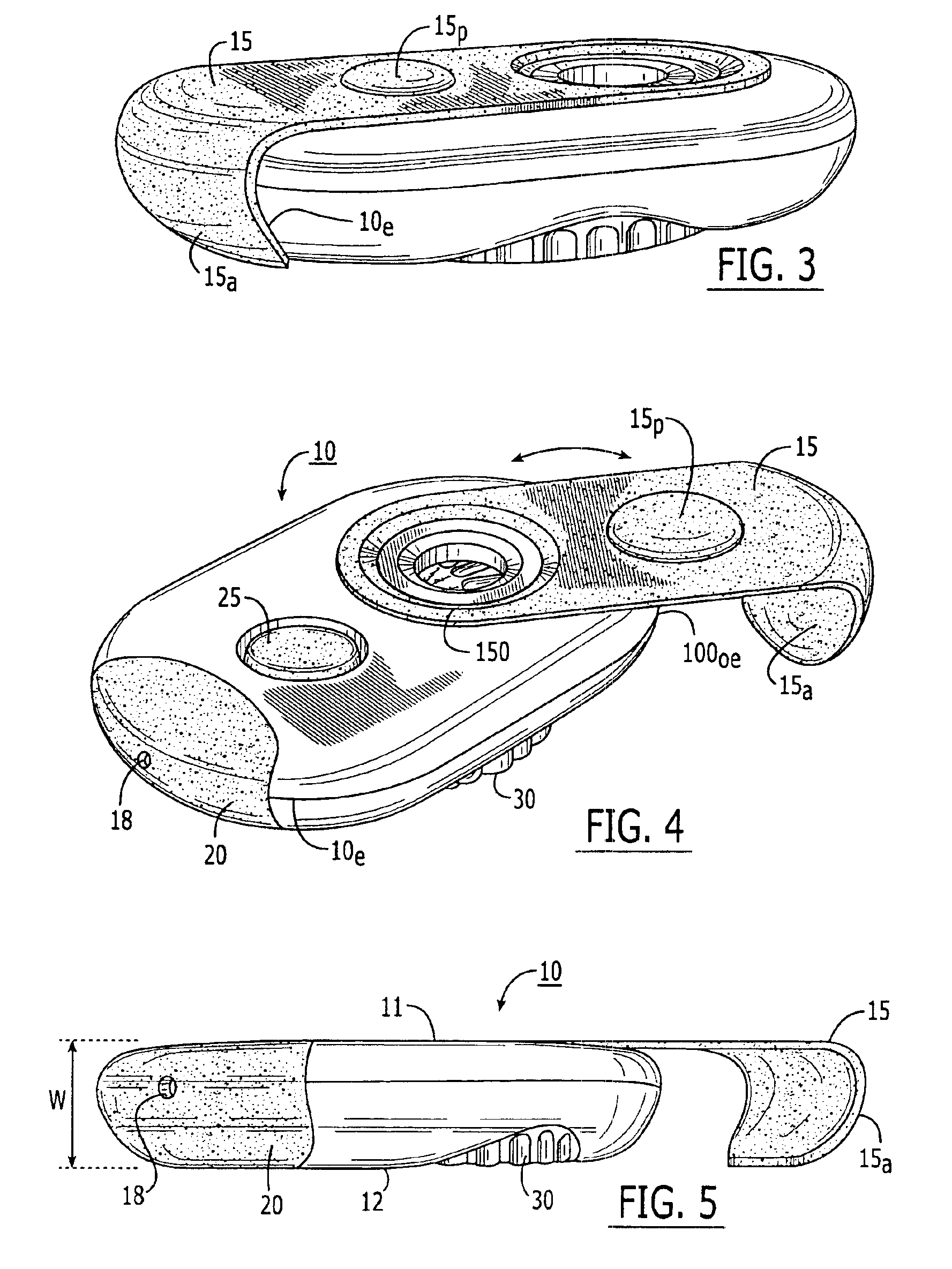
Dry powder inhaler devices, multi-dose dry powder drug packages, control systems, and associated methods
InactiveUS6971383B2Evenly dispersedFacilitate dispersion and releaseRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsPowder InhalerPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
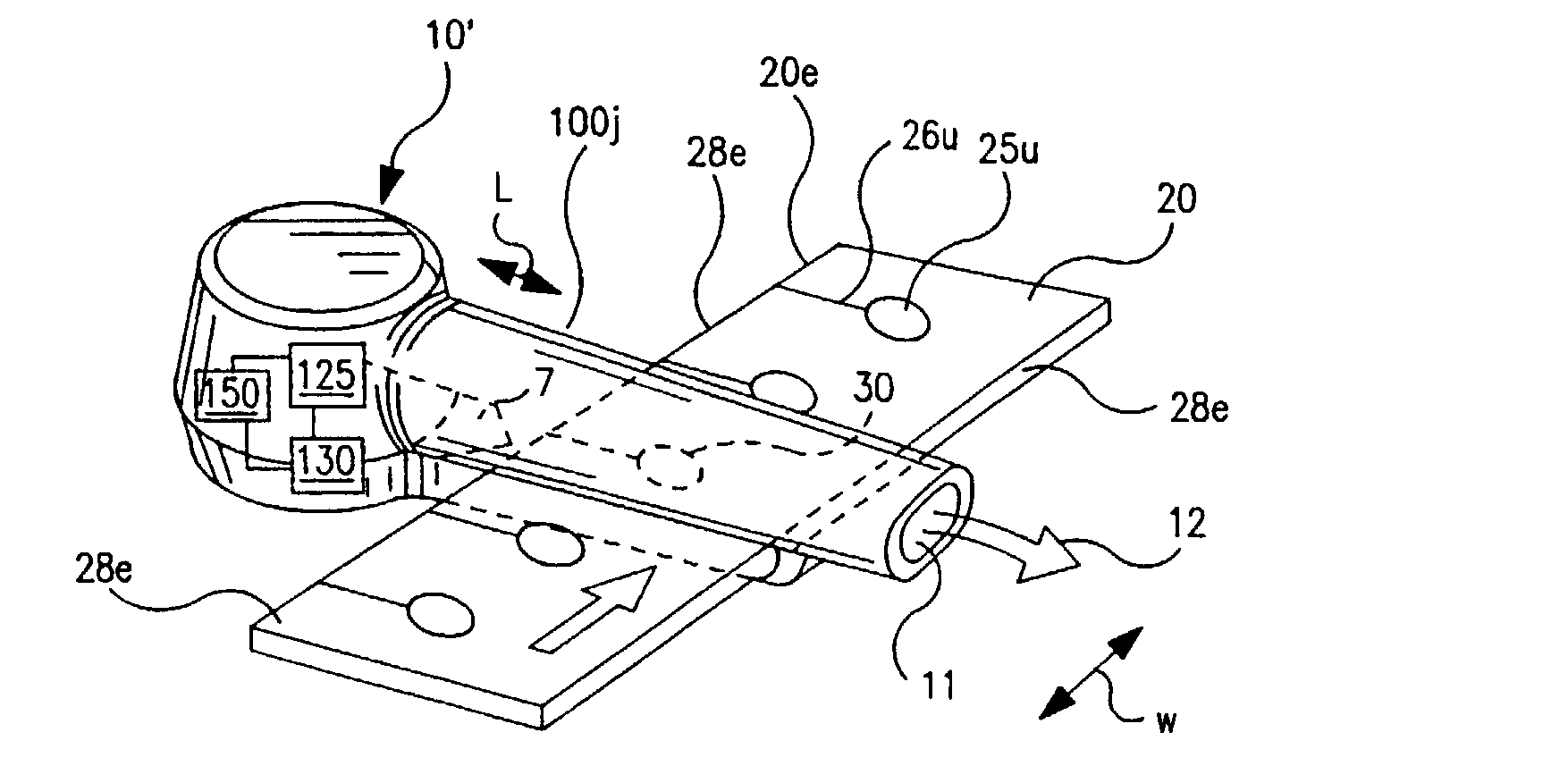
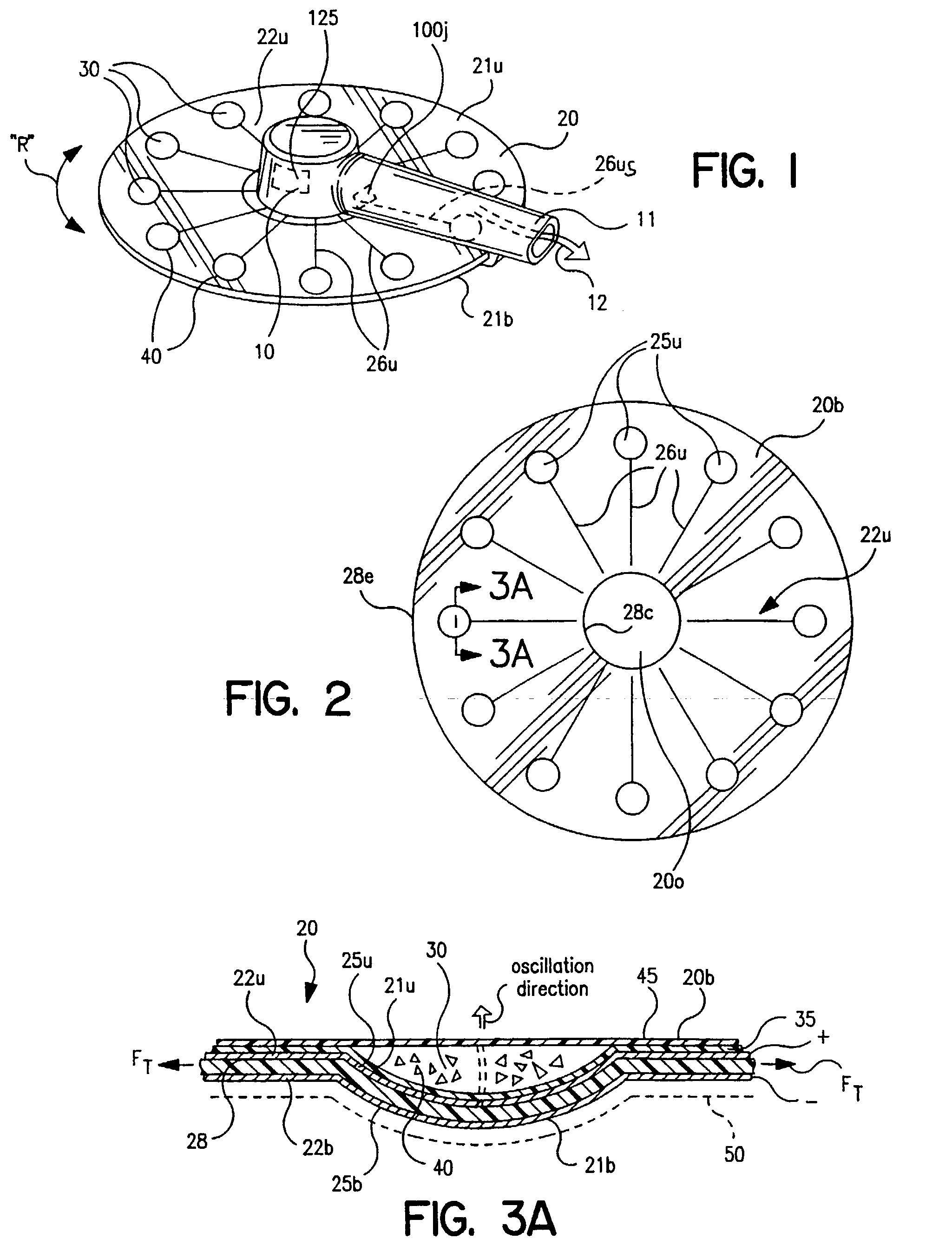
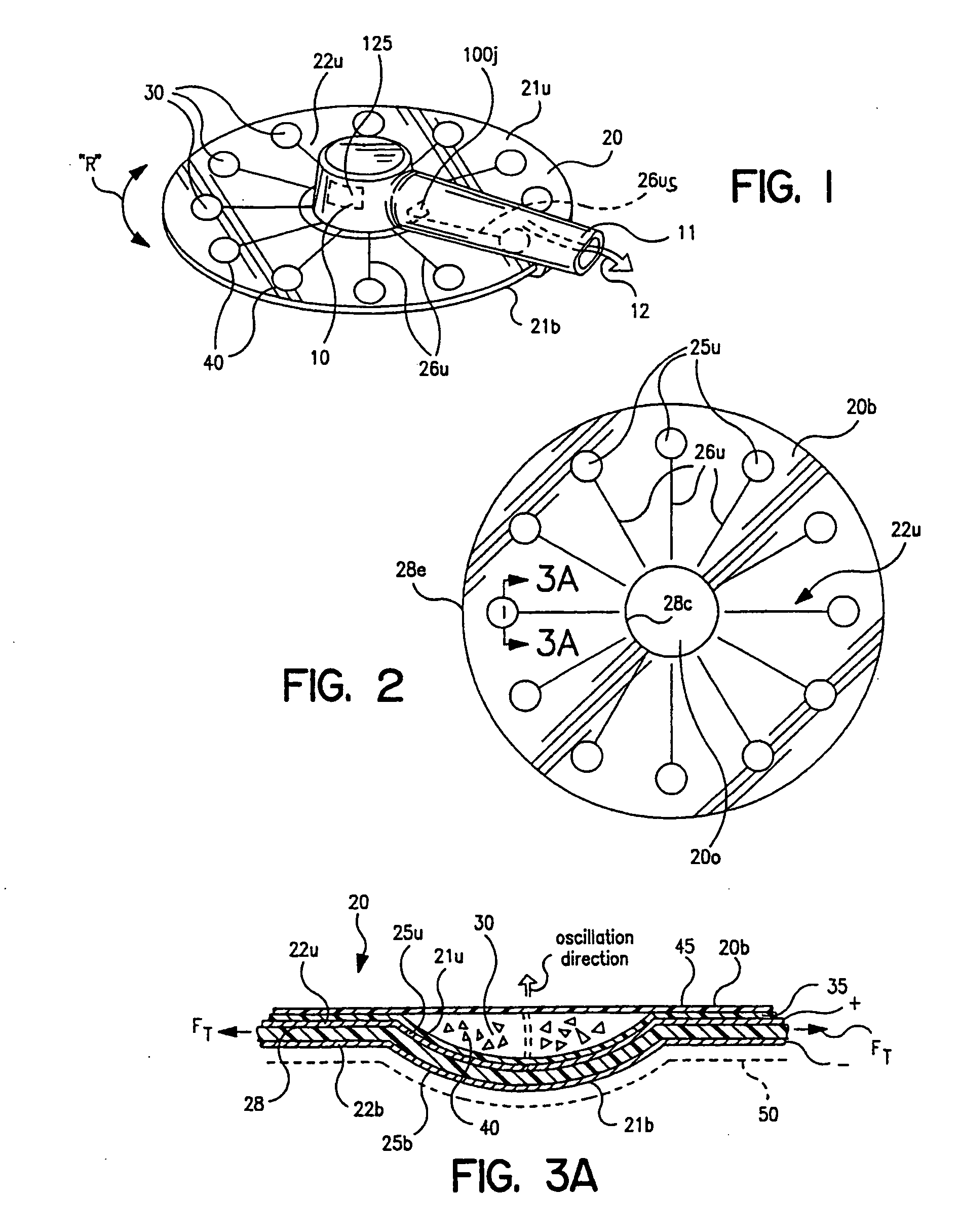
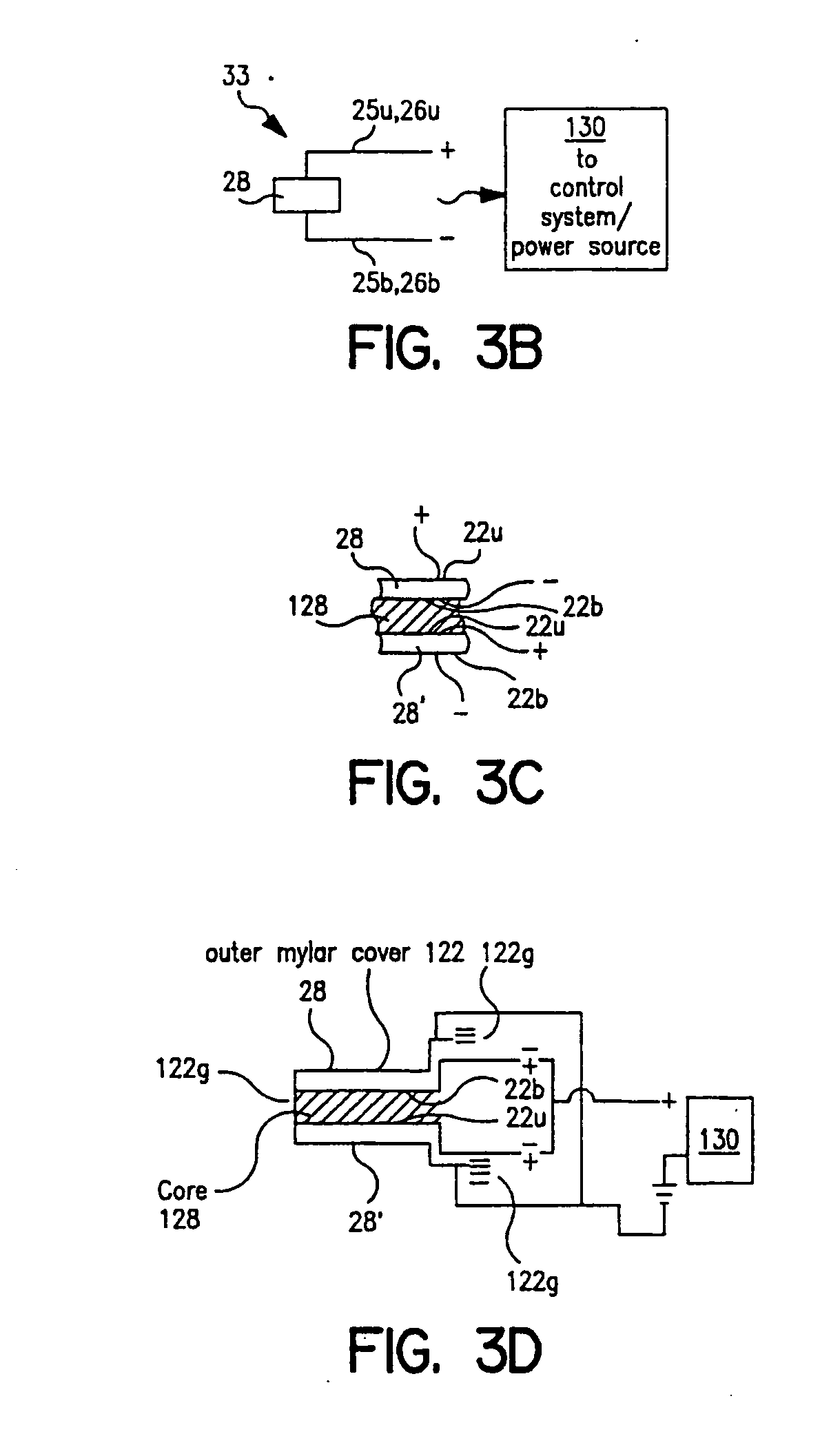
Dry powder inhalers (FIG. 1) with integrated active energy patient assist dispersal systems are configured with control systems which provide adjustable energy output responsive to the user's inspiratory capabilities and / or the flowability of the dry powder being administered. The multi-dose dry drug package (FIG. 2) a piezoelectric polymer substrate which flexes to deform and provide mechanical oscillation in a selected region of the package corresponding to the dry powder drug which is dispersed during inhalation by a user. Control system (FIG. 12) employs fuzzy logic to relate in response to a user's inspiratory effort.
Owner:ORIEL THERAPEUTICS INC
Implantable sensor for measuring physiologic information
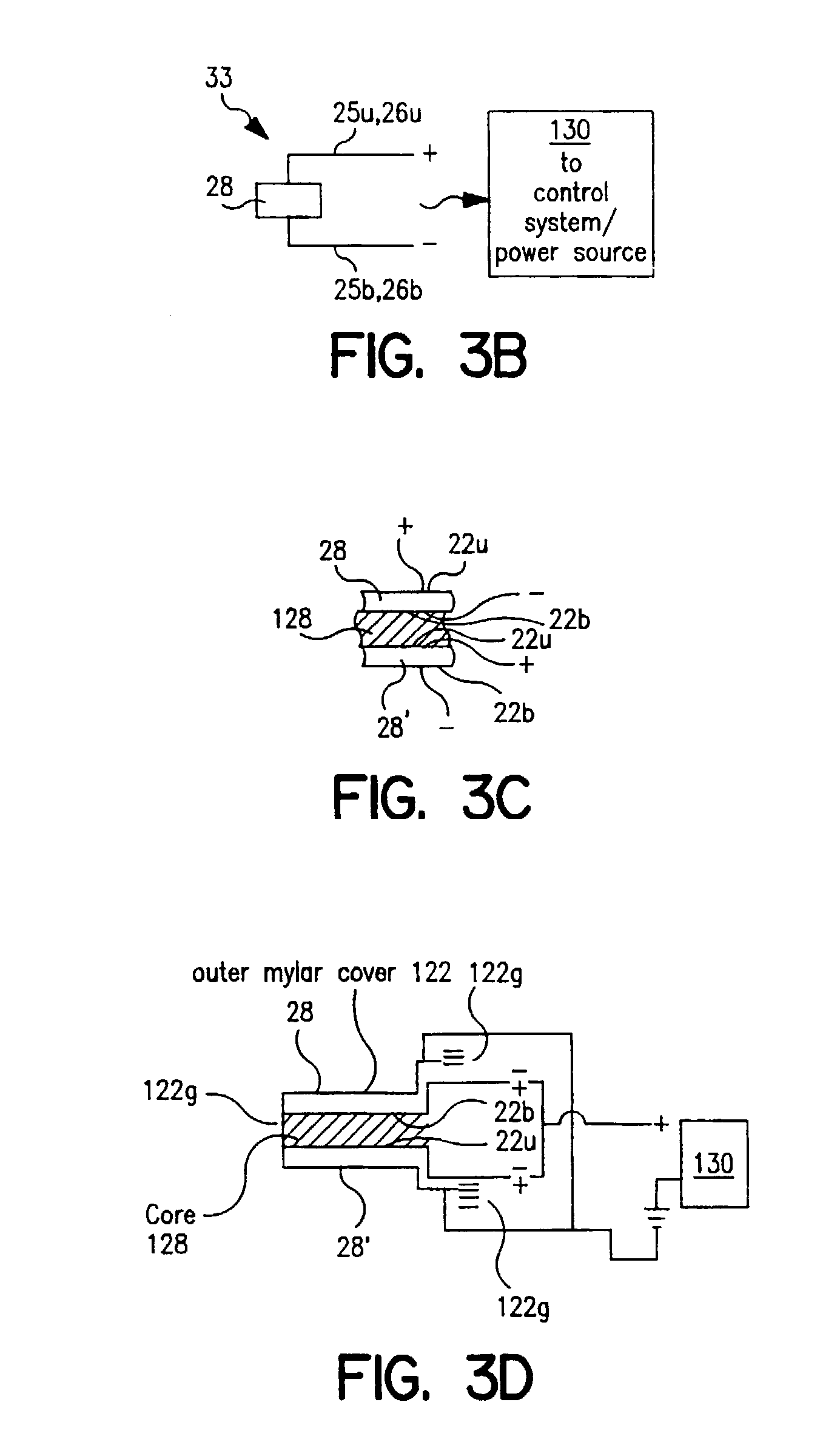
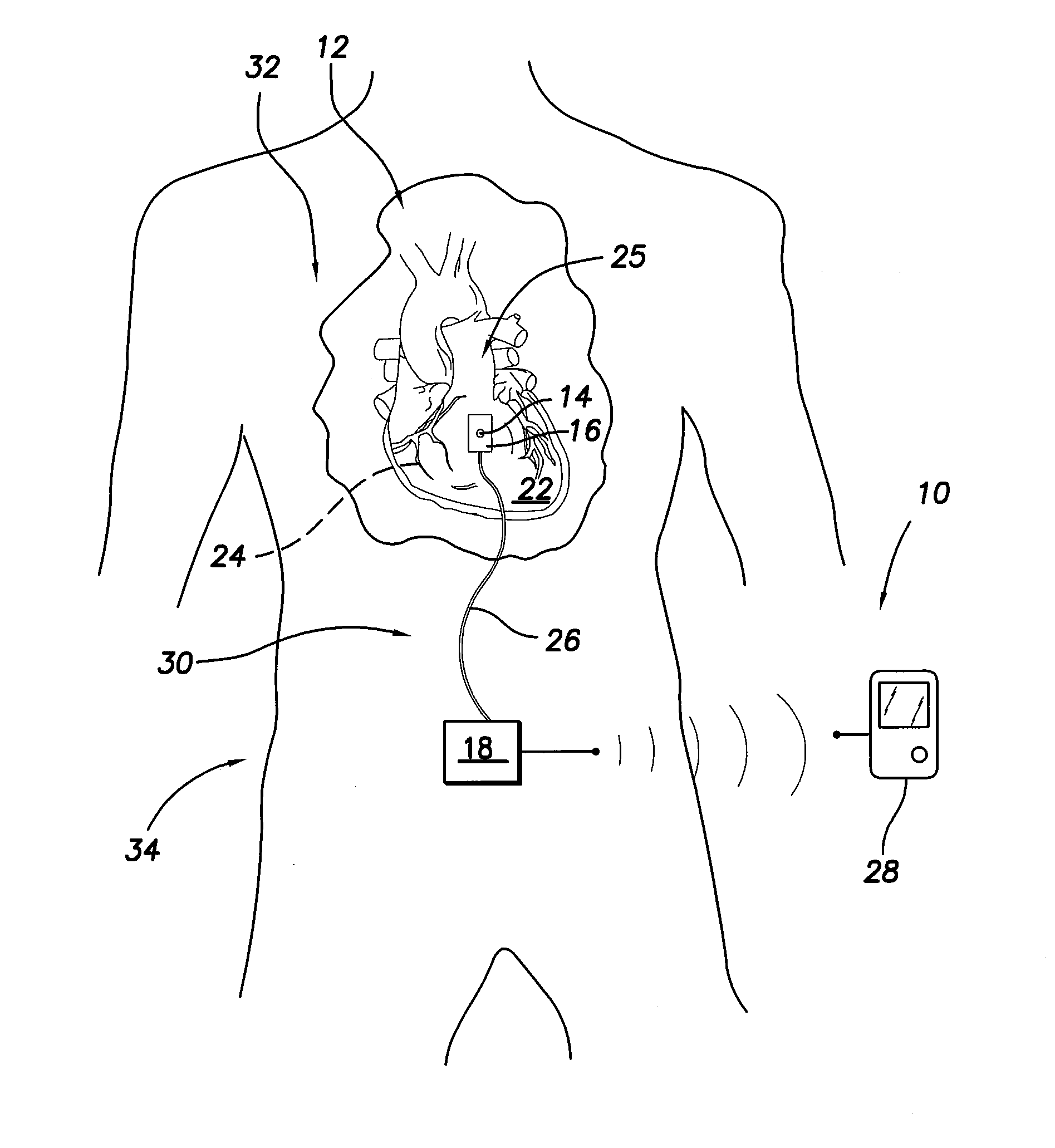
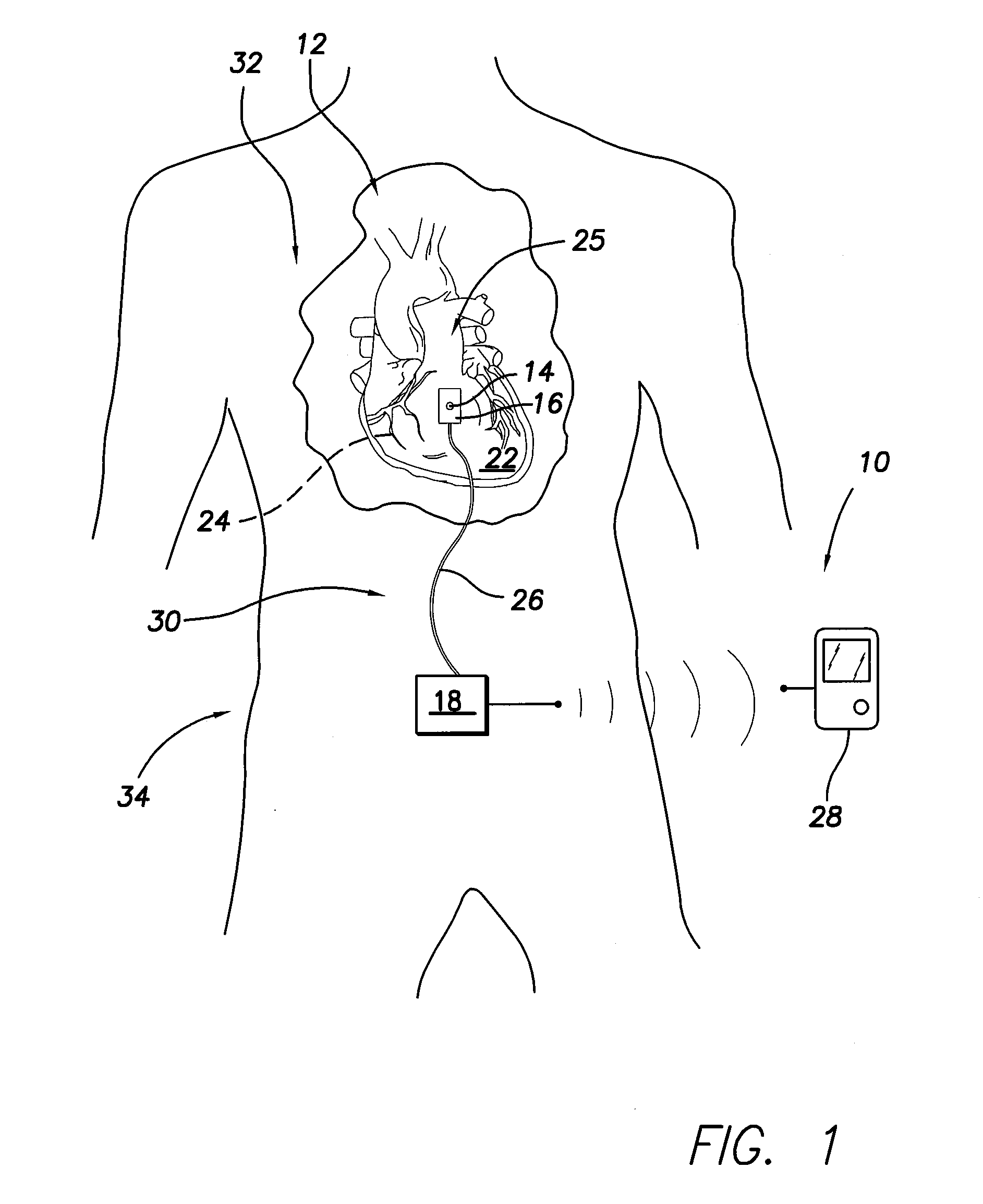
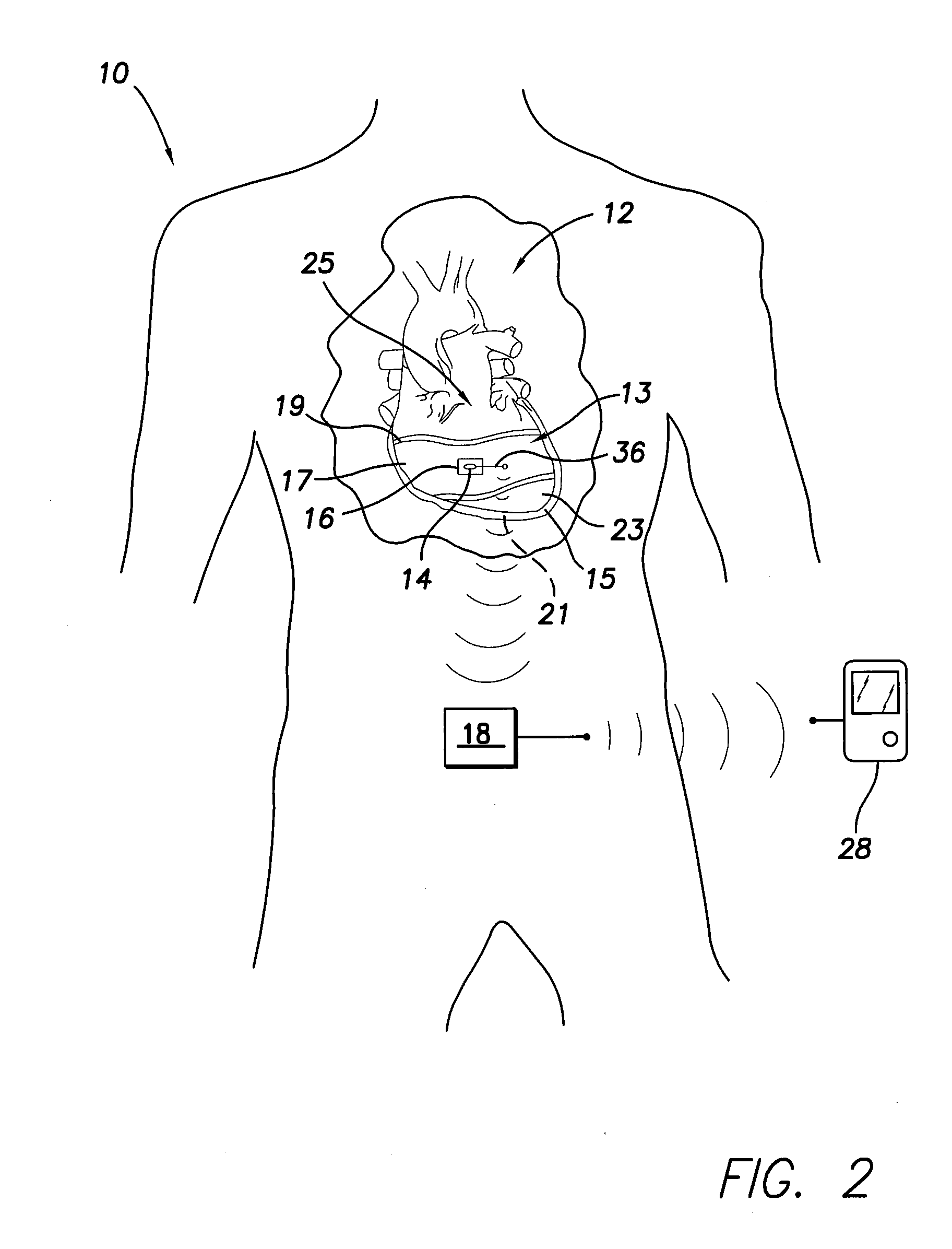
An implantable sensor is provided that includes a piezopolymer sensor element including a body having a plurality of layers of a piezopolymer, and an attachment device configured to hold the piezopolymer sensor element in direct contact with at least one of a bodily fluid and bodily tissue such that the piezopolymer sensor element is configured to bend in response to motion of the at least one of bodily fluid and bodily tissue. A pair of electrodes is attached to the piezopolymer sensor element and the electrodes are configured to collect an electrical charge that is generated within the piezopolymer sensor element due to the bending of the piezopolymer sensor element.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
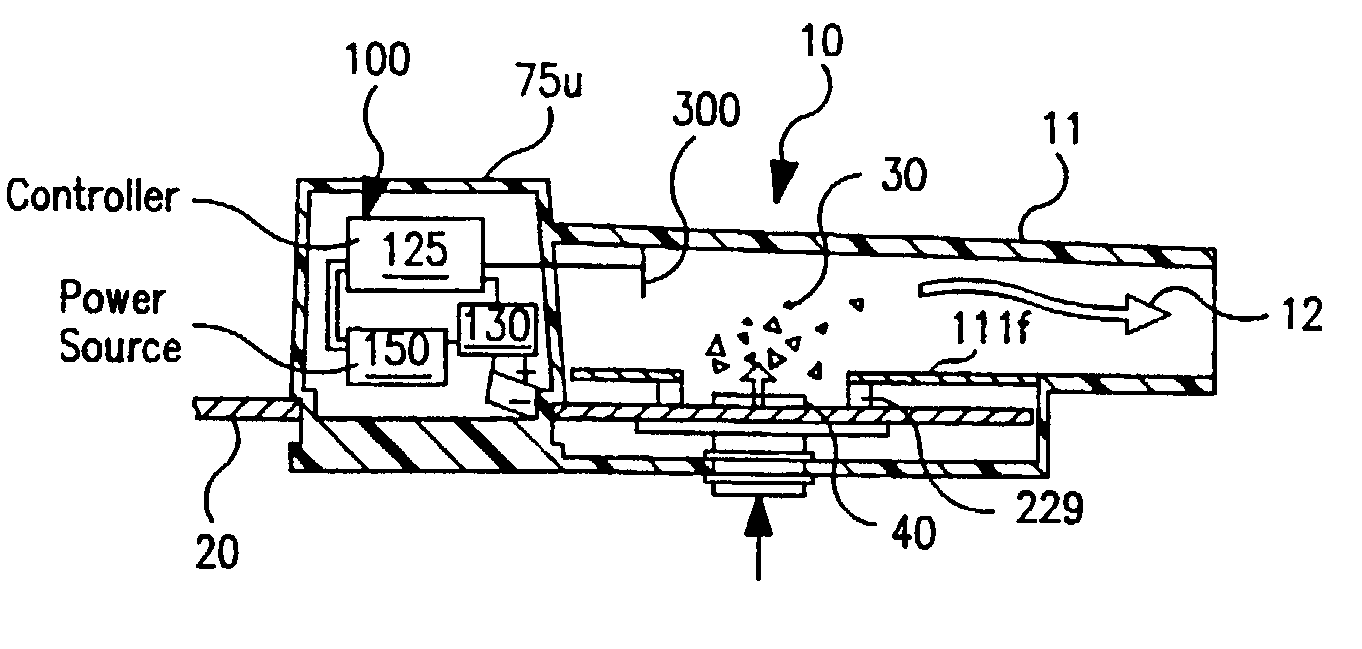
Dry powder inhaler devices, multi-dose dry powder drug packages, control systems, and associated methods
InactiveUS20040123864A1Evenly dispersedFacilitate dispersion and releaseRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsElectricityPowder Inhaler
Dry powder inhalers (FIG. 1) with integrated active energy patient assist dispersal systems are configured with control systems which provide adjustable energy output responsive to the user's inspiratory capabilities and / or the flowability of the dry powder being administered. The multi-dose dry drug package (FIG. 2) a piezoelectric polymer substrate which flexes to deform and provide mechanical oscillation in a selected region of the package corresponding to the dry powder drug which is dispersed during inhalation by a user. Control system (FIG. 12) employs fuzzy logic to relate in response to a user's inspiratory effort.
Owner:ORIEL THERAPEUTICS INC
Noise rejecting electronic stethoscope
InactiveUS20080137876A1Simple and rugged in designIncrease heightStethoscopeElectronic stethoscopeEngineering
An acoustic-electronic stethoscope that filters aberrant environmental background noise. The chest piece employs acoustic vents to inhibit resonant amplification of noise and contains a diaphragm design that focuses vibrational energy to a raised ring, which transfers and further focuses the energy to a piezoelectric polymer sensor with dual elements. The ensuing electrical signal is then preamplified with the low frequency sound, comprising predominantly background noise, filtered out. The stethoscope contains a binaural head set and output jack for down loading of data. Furthermore, areas normally subject to exposure and damage to water, such as the chest piece and headset, are water-tight.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
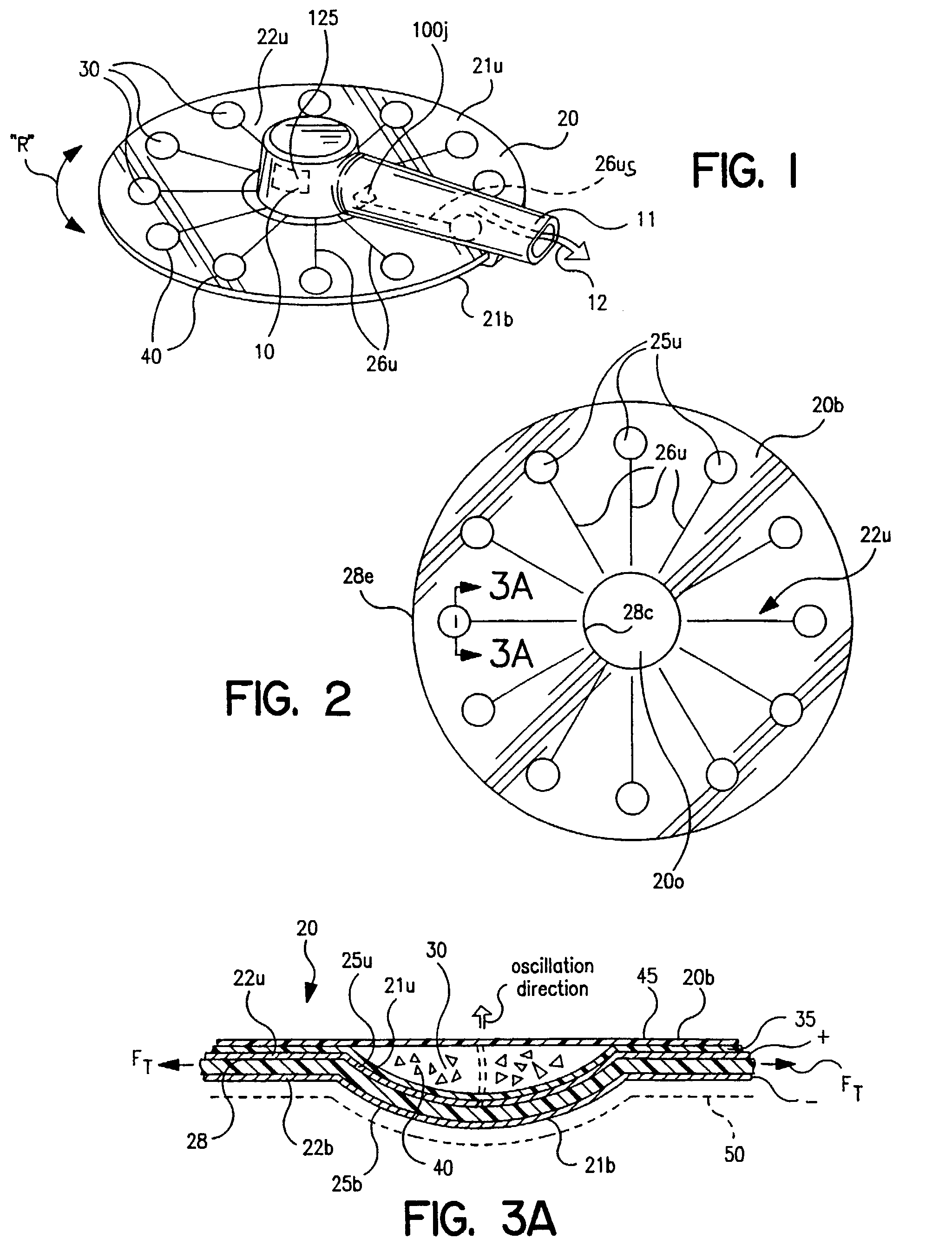
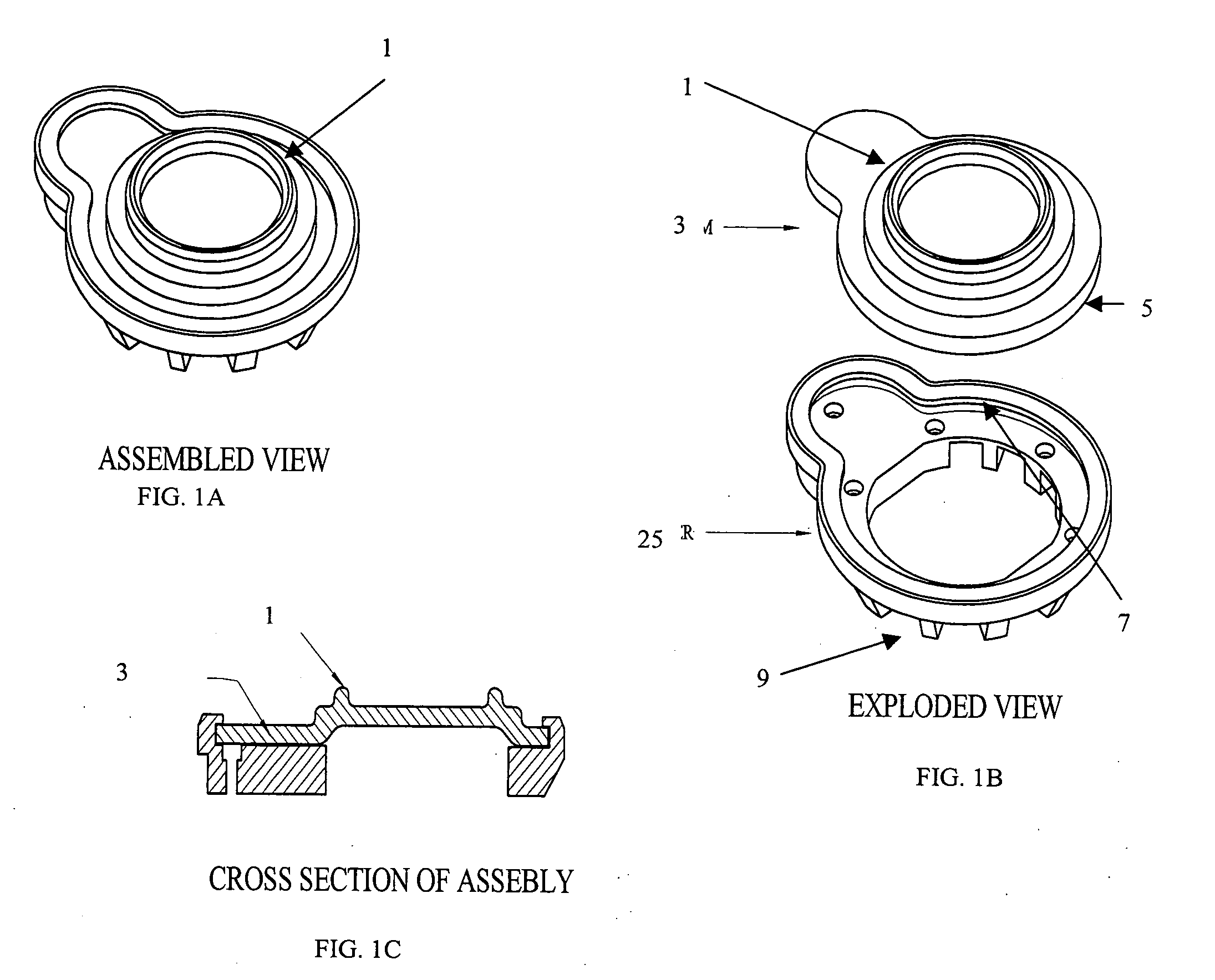
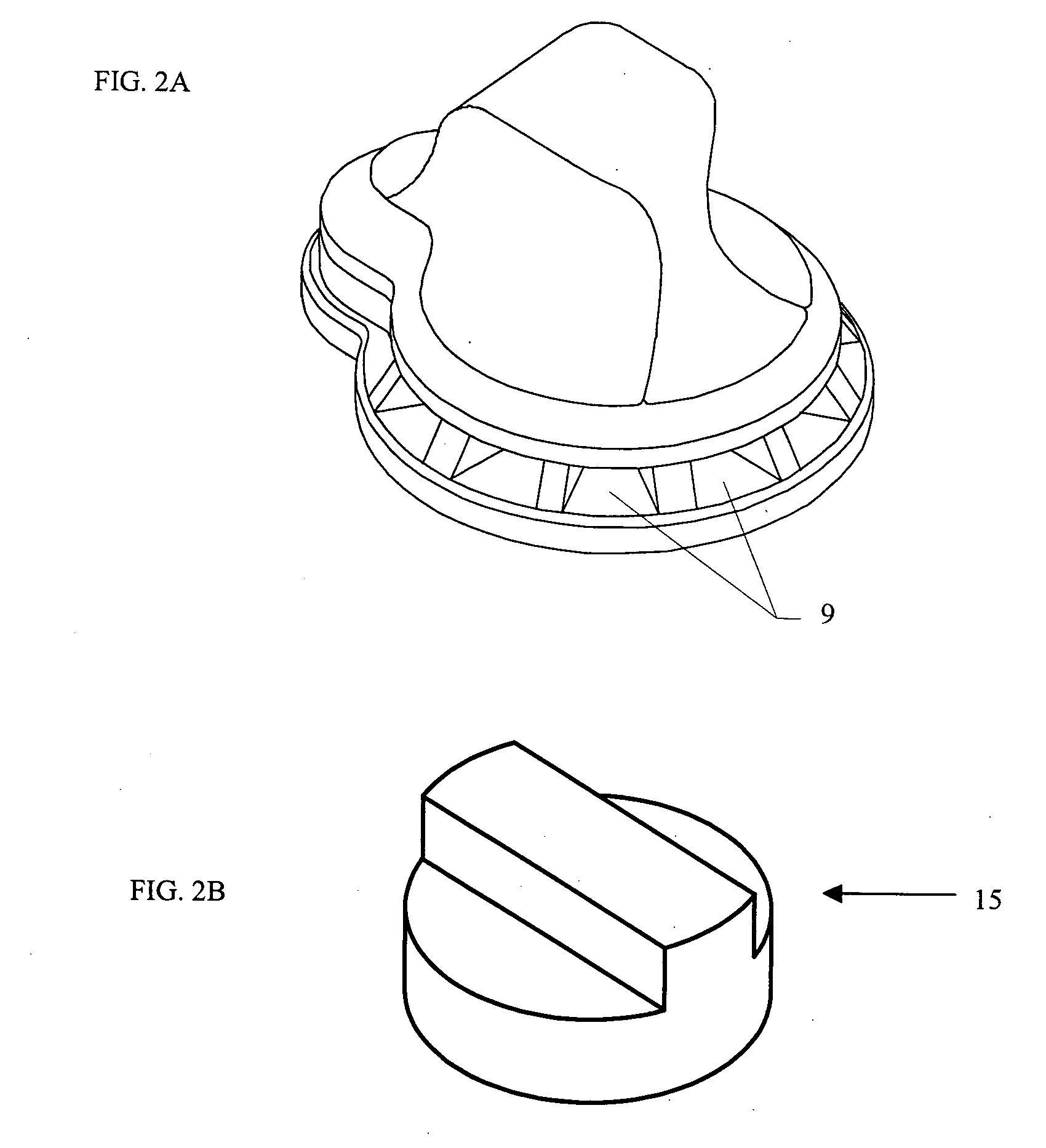
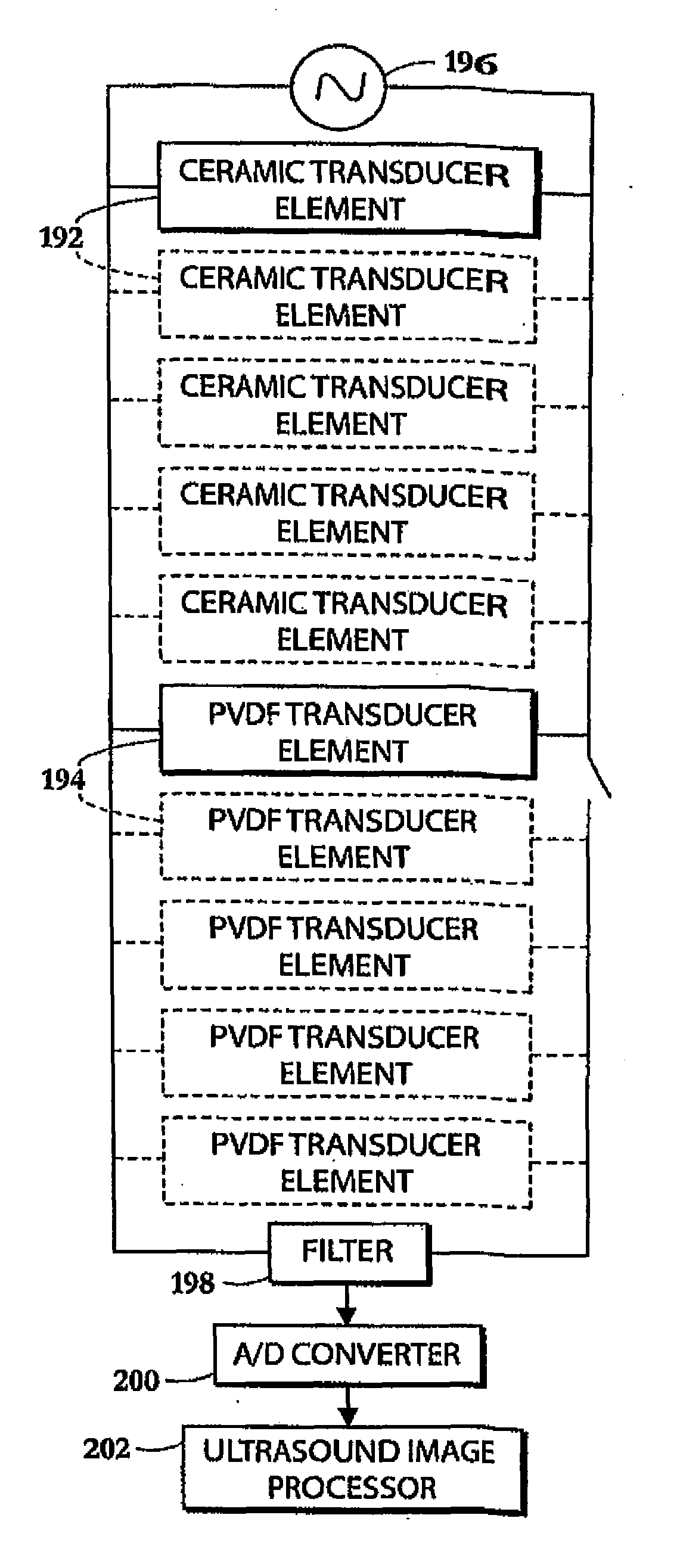
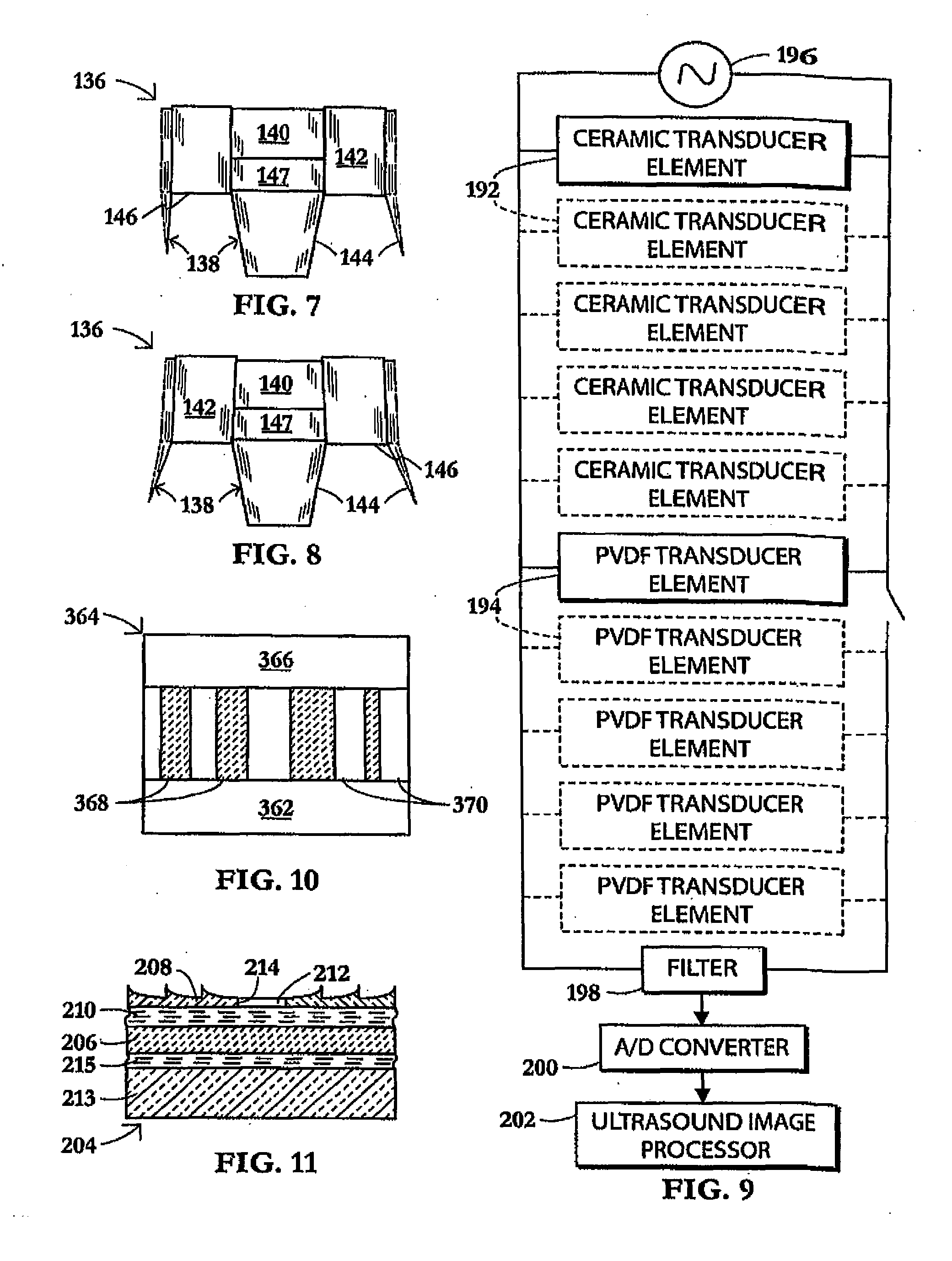
Dual-Mode Piezocomposite Ultrasonic Transducer
ActiveUS20130060140A1Easy to optimizeEasy to operateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyElectricityUltrasonic sensor
A compact, high power, dual mode, emitting and receiving ultrasound transducer and method for applying ultrasonic energy within a living subject and for monitoring the effects it induces in tissue comprises a set of piezoelectric polymeric transducer elements and a set of piezoelectric ceramic elements, bonded together. The polymeric transducer elements have electrodes enabling their use for low power diagnostic imaging interrogation of the tissue and the ceramic transducer elements have electrodes enabling their use for high power therapy applications.
Owner:MISONIX INC
Piezoelectric device of polymer
InactiveUS20130127299A1Material nanotechnologyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesOptoelectronicsGraphene
The present invention relates to a piezoelectric device of a multi-layered structure on which first electrodes and second electrodes are sequentially stacked on a piezoelectric polymer and single surfaces or both surfaces of piezoelectric polymer.In accordance with the present invention, the vibration response characteristics of the piezoelectric polymer can be improved by using the graphene or the composite thereof as a surface electrode material to the piezoelectric polymer; and, there are effects that the response characteristics of the piezoelectric device are excellent and the reliability thereof is excellent by forming a second electrode having an excellent conductivity and a protection electrode thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Touch and auditory sensors based on nanotube arrays
A sensor comprising: at least one sensor probe comprising: a pair of electrodes; a vertically aligned nanotube disposed between the pair of electrodes; optionally a piezoelectric polymer on the nanotube; and optionally, a field source for generating a field, the field source operatively connected to the pair of electrodes; whereby when the sensor probe is contacted, a change in the field occurs or electricity is generated. Methods of using the sensors are also described.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Dry powder inhaler devices, multi-dose dry powder drug packages, control systems, and associated methods
InactiveUS20060191534A1Evenly dispersedFacilitate dispersion and releaseRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsPharmaceutical formulationDecentralised system
Dry powder inhalers with integrated active energy patient assist dispersal systems are configured with control systems which provide adjustable energy output responsive to the user's inspiratory capabilities and / or the flowability of the dry powder drug being administered. The multi-dose dry drug package includes a piezoelectric polymer substrate (such as PVDF) which flexes to deform and provide mechanical oscillation in a selected region of the package corresponding to the dry powder drug dose in the exit flow path and is thus actively dispersed into the exit flow path of the inhaler during the user's inspiratory activity. Control systems employ fuzzy logic models of the flowability of particular drug formulations (also being able to compensate or allow for the particular type of excipient used) and / or adjust for the real-time measured inspiratory efforts of the user. Manufacturing process control systems can adjust certain parameters in response to a fuzzy logic model of the flowability of the dry powder and other conditions associated with the dry powder drug being produced and / or dispensed.
Owner:HICKEY ANTHONY J +1
Disk drive load arm structure having a strain sensor and method of its fabrication
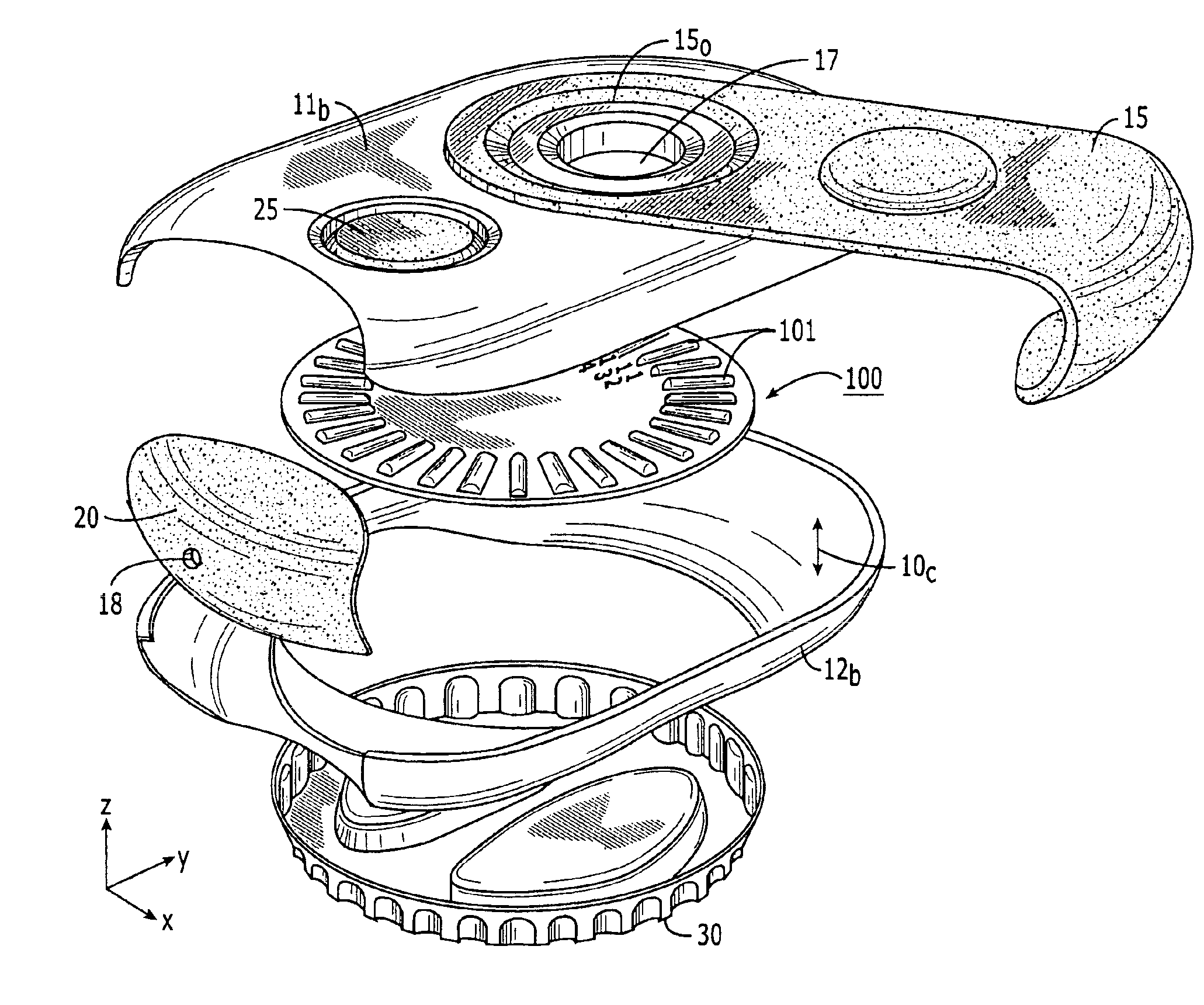
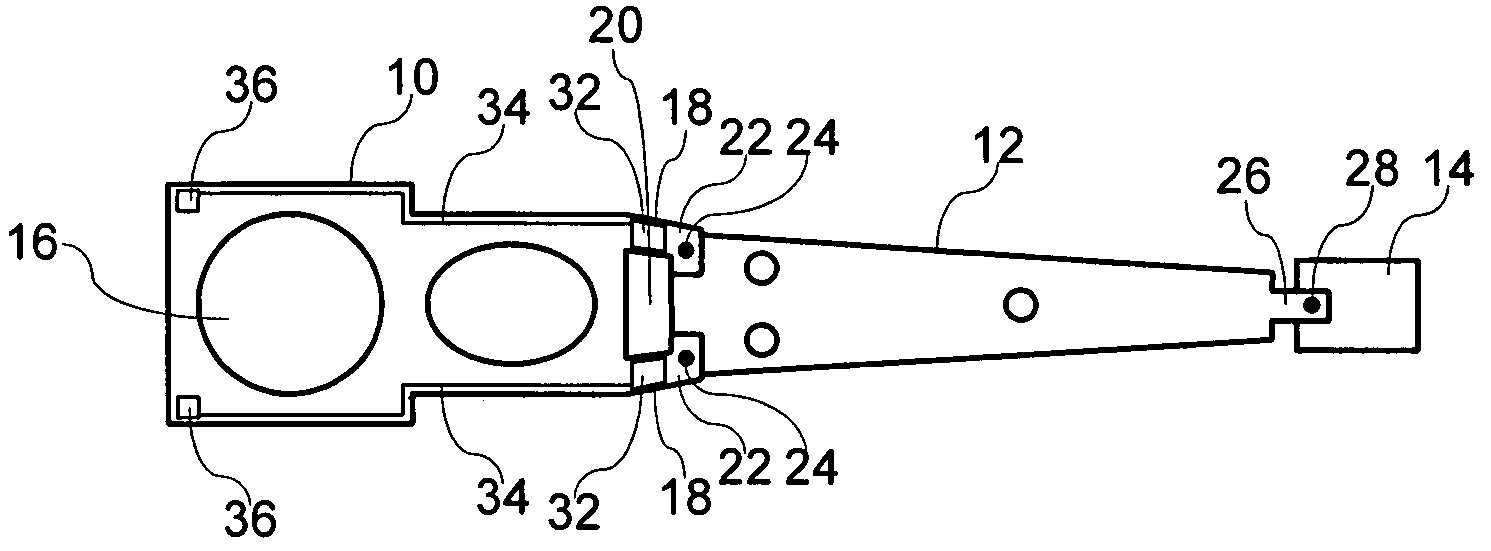
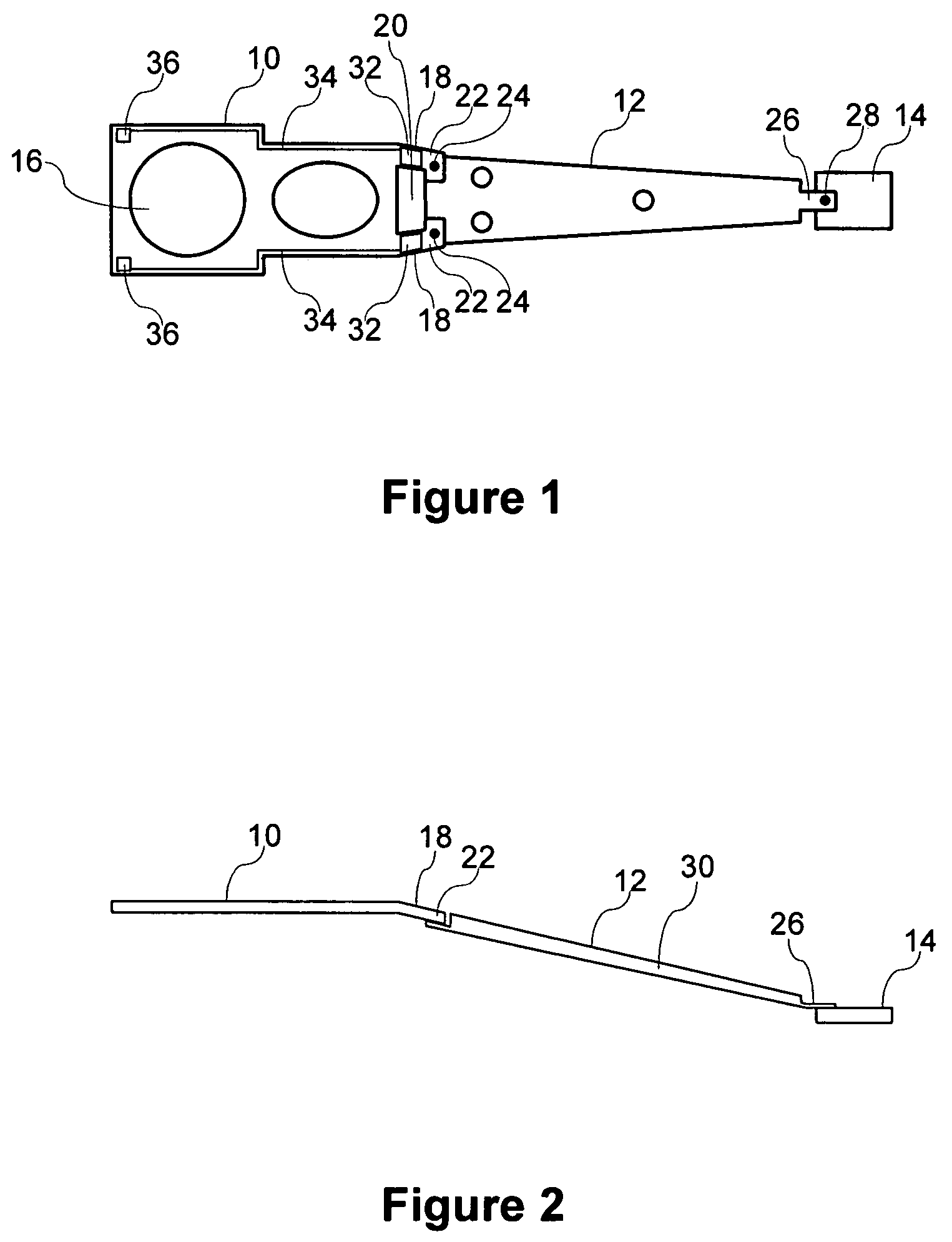
A load arm for a disk drive may include a base section that has an opening for receiving a spindle of a voice coil motor. The base section may have hinge arms that extend from the base section and terminate in tab portions. An arm section may be affixed to the tabs of the hinge arms of the base section such as by spot welding. A head suspension assembly may be affixed to a distal end of the arm section such as by spot welding. A sensor may be provided on a hinge arm of the base section. The sensor may comprise a piezoelectric polymer sensing element and an electrode formed over the piezoelectric polymer sensing element.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
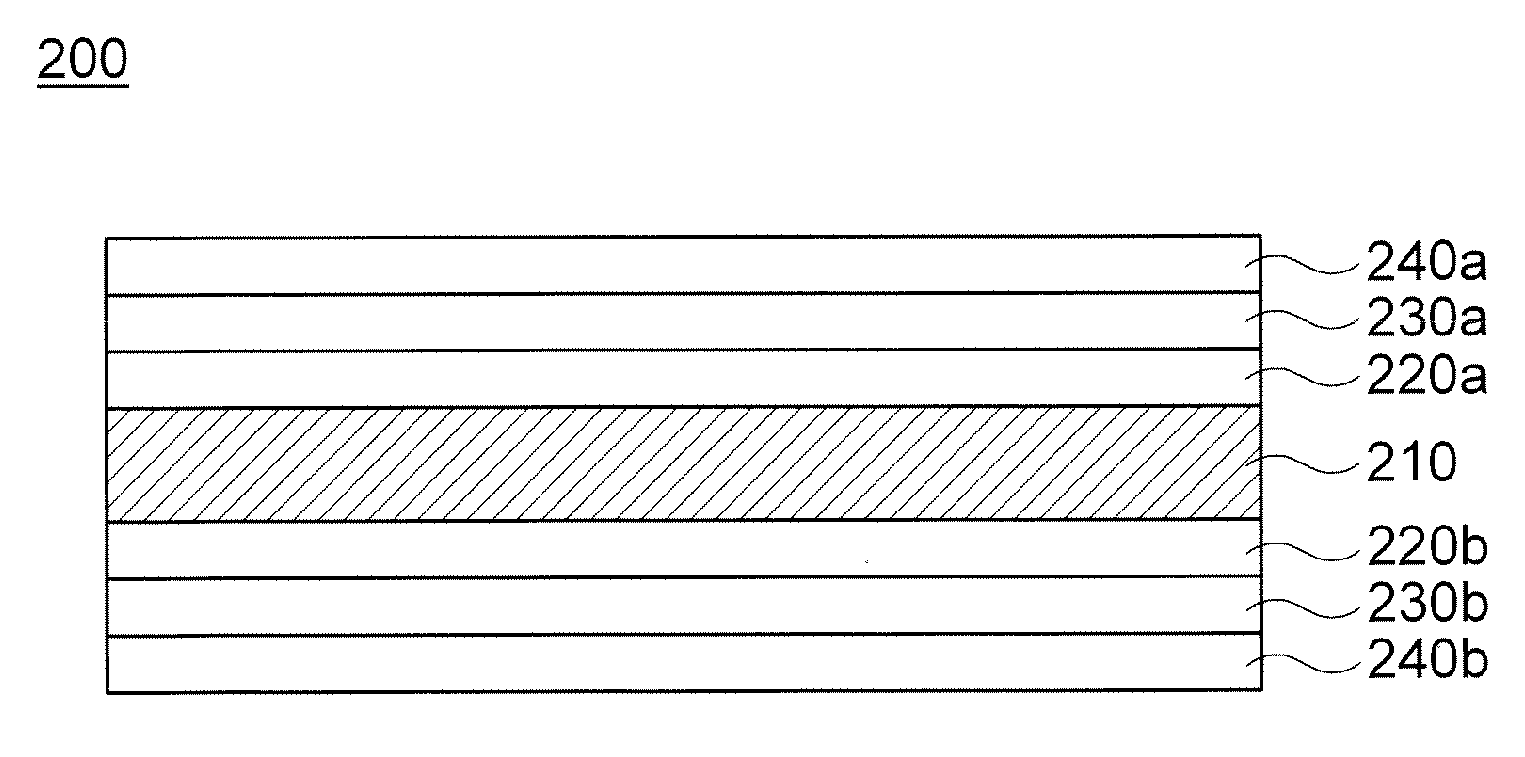
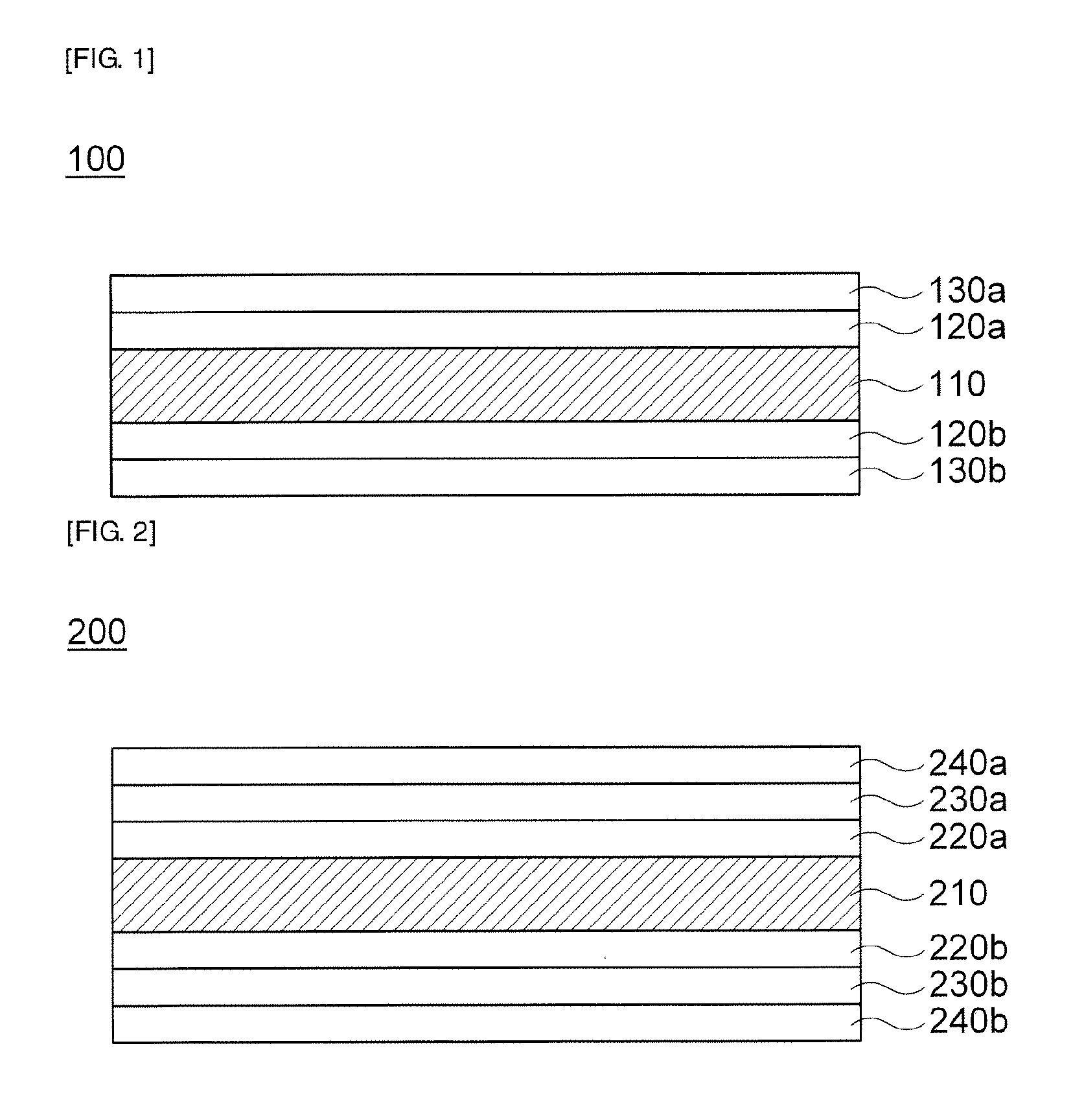
Piezoelectric polymer material and method for producing same
ActiveUS20120132846A1High constantExcellent transparency and dimensional stabilityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionCrystallinityMicrowave transmission
The invention provides a piezoelectric polymer material comprising a helical chiral polymer having a weight average molecular weight of from 50,000 to 1,000,000 and optical activity, the piezoelectric polymer material having: crystallinity as obtained by a DSC method of from 20% to 80%; a transmission haze with respect to visible light of 50% or less; and a product of the crystallinity and a standardized molecular orientation MORc, which is measured with a microwave transmission-type molecular orientation meter at a reference thickness of 50 μm, of from 40 to 700.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC +1
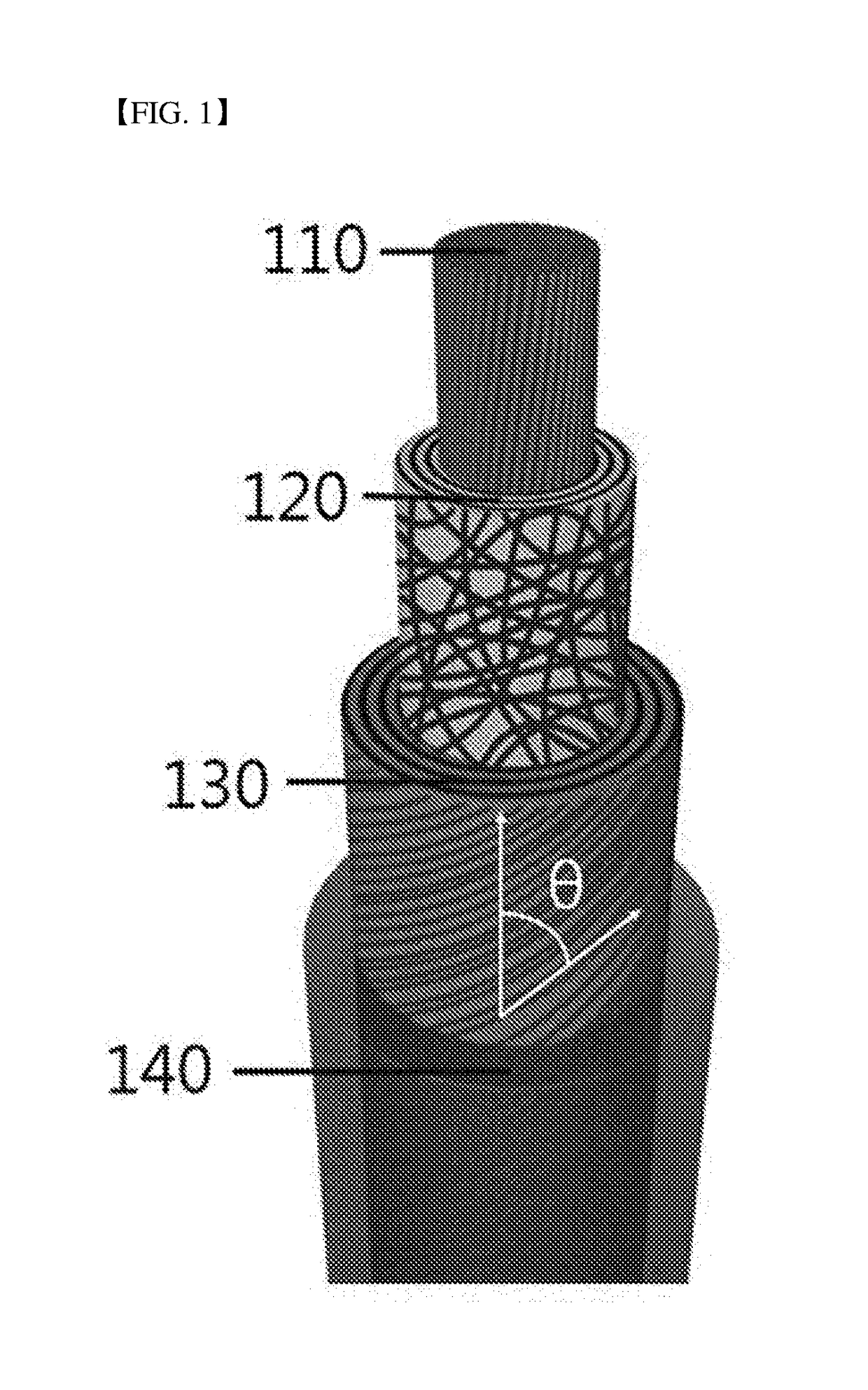
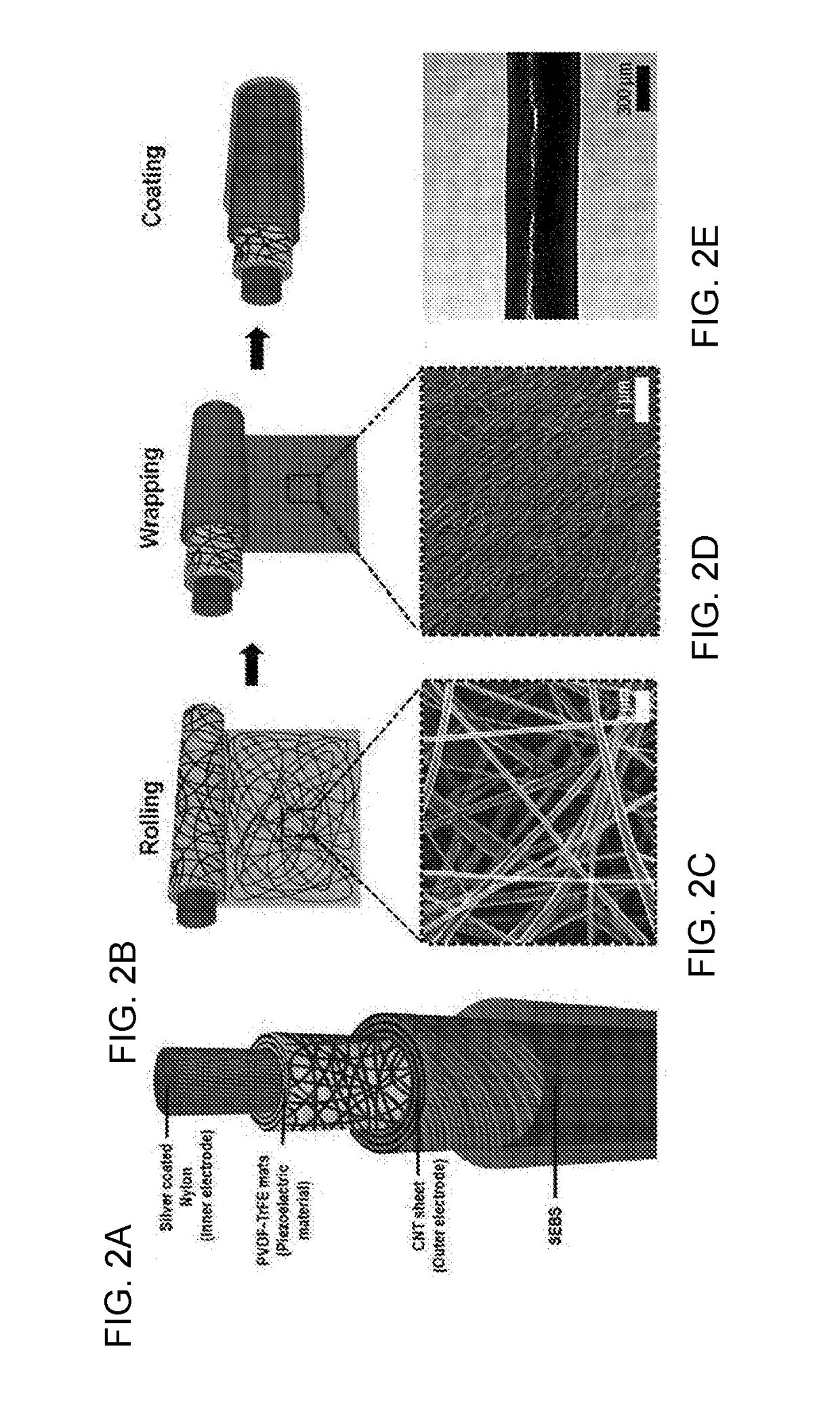
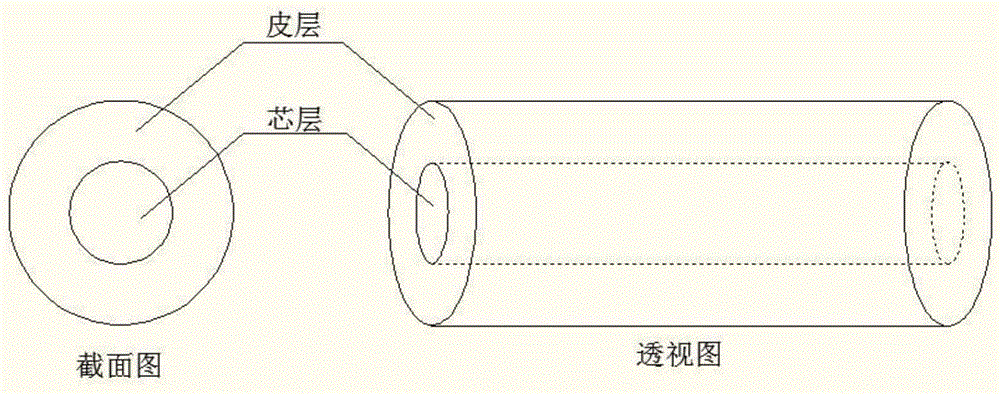
Piezoelectric fiber having excellent flexibility and elasticity, and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20170331027A1Good flexibilitySolving the Insufficiency of ElasticityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesFiberPliability
The present invention relates to a piezoelectric fiber having excellent flexibility, the piezoelectric fiber employs a conductive fiber member as an inner electrode, on which a piezoelectric polymer layer, an outer electrode and a coating layer are sequentially formed, thereby having excellent flexibility and sufficient elasticity to be sewed, woven, knotted or braided. Therefore, the piezoelectric fiber can be applied in power supplies for a variety of sizes and types of wearable electronic devices, portable devices, clothing, etc. In addition, since the piezoelectric fiber has excellent piezoelectricity and durability because of the above-described structure, it can effectively convert deformation or vibration caused by external physical force into electric energy, and thus can replace existing ceramic-based and polymer piezoelectric bodies, etc. Furthermore, an economical and simple method of manufacturing a piezoelectric fiber having excellent piezoelectricity is provided.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUNDATION HANYANG UNIV)
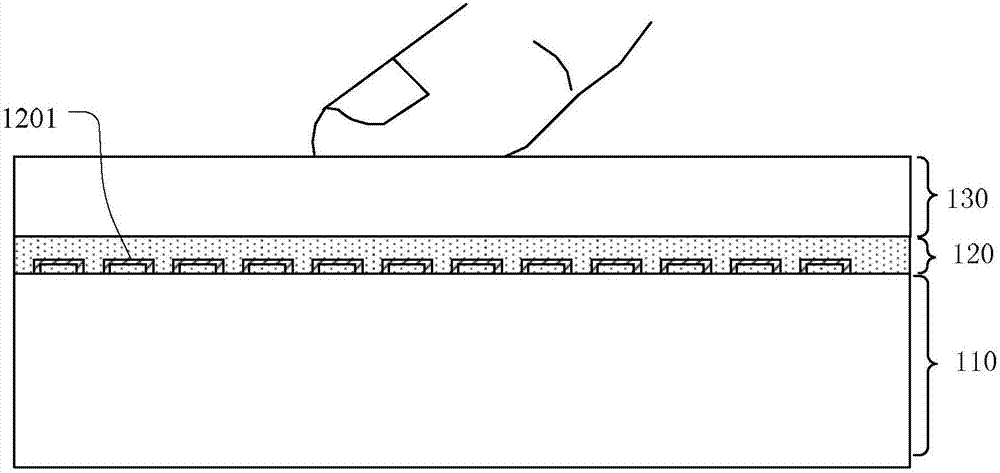
Artificial skin flexible tactile sensor measurement device
ActiveCN105738012AImprove flexibilityMultidimensionalForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesHuman bodyFiber
An artificial skin flexible tactile sensor measurement device belongs to the technical field of a tactile sensor. The artificial skin flexible tactile sensor measurement device is composed of a bionic epidermal tissue layer, a bionic dermal tissue layer, a bionic subcutaneous tissue layer and an artificial skin adhering base. The bionic subcutaneous tissue layer is uniformly applied on the outer surface of the artificial skin adhering base. The bionic dermal tissue layer is uniformly applied on the outer surface of the bionic subcutaneous tissue layer. The bionic dermal tissue layer is internally provided with three liquid core PVDF piezoelectric polymer fibers. The bionic epidermal tissue layer is uniformly applied on the outer surface of the bionic dermal tissue layer. The artificial skin flexible tactile sensor measurement device is mounted on the arm of a robot. The robot with tactile feeling can utilize the artificial skin flexible tactile sensor measurement device for obtaining a plurality of property characteristics of a target object, thereby finishing more complicated tasks by the robot through identifying the object. Furthermore the artificial skin flexible tactile sensor measurement device has wide application range in researching fields of sports, rehabilitation, human body biomechanics, etc.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Porous piezoelectric material with dense surface, and associated methods and devices
ActiveUS20170317269A1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesPolymer scienceThin membrane
A method for producing a porous piezoelectric polymer film with a dense surface, includes depositing a polymer solution onto a substrate to form a polymer film including a solvent; evaporating a portion of the solvent to form the dense surface away from the substrate; forming water droplets in interior of the polymer film; and substantially evaporating the water droplets and remaining solvent to form porous interior. A piezoelectric composition includes a piezoelectric material with a porous interior and a dense surface for interfacing with an electrode. A piezoelectric device includes a first electrode; a porous piezoelectric film with a dense surface and porous interior, wherein the porous piezoelectric film is deposited on the first electrode and the dense surface is away from the first electrode; and a second electrode deposited on the dense surface for, together with the first electrode, providing an electrical interface for the porous piezoelectric film.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Noise rejecting electronic stethoscope
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Disposable wireless pressure sensor
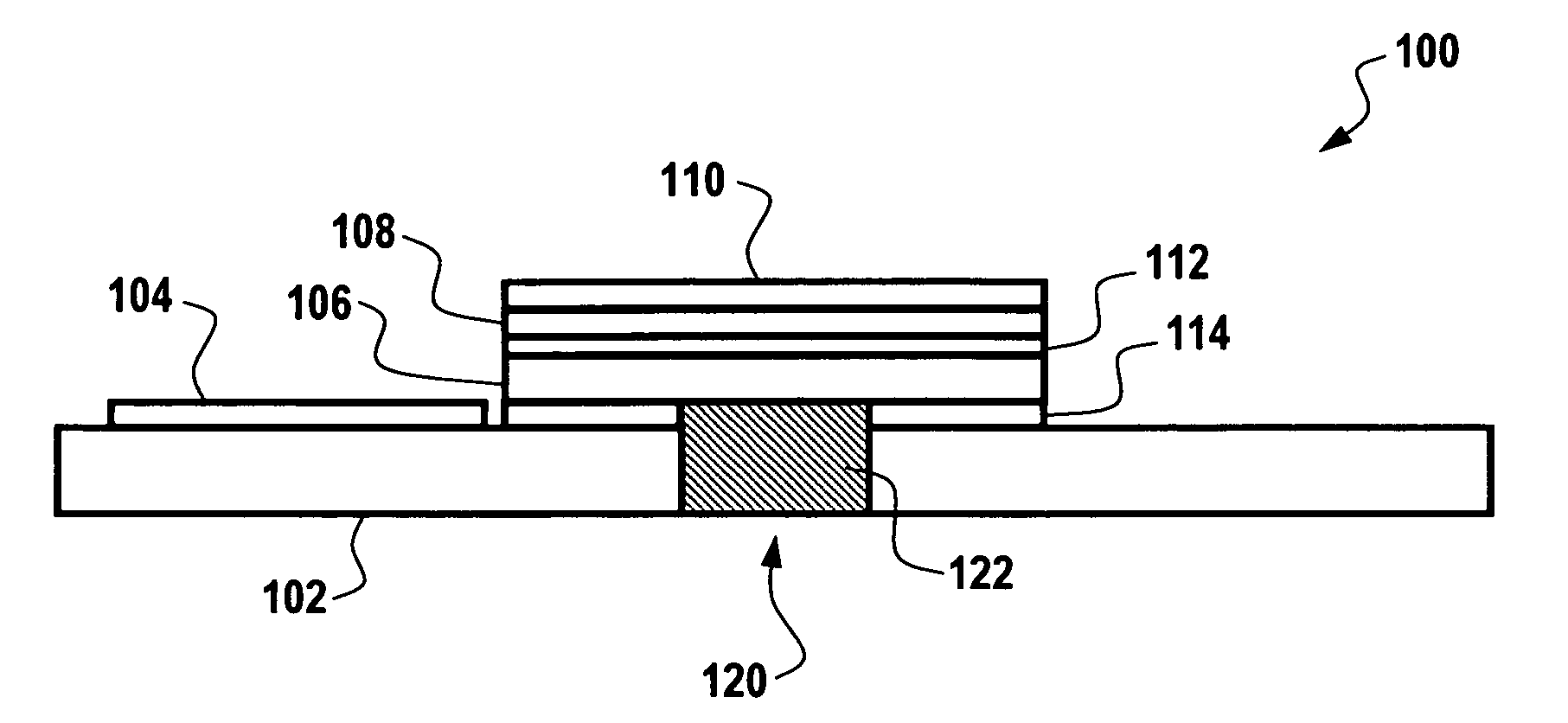
InactiveUS20060107749A1Low thermal conductivityFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsCatheterDielectricPolymer substrate
In general, a dielectric polymer substrate provided and an antenna formed upon the dielectric polymer substrate. A piezoelectric polymer layer (e.g., a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) piezoelectric film) can be formed above the dielectric polymer substrate. Additionally, an interdigital (IDT) layer can be configured upon the PVDF piezoelectric layer, thereby permitting the piezoelectric polymer layer and the IDT layer to detect pressure data and transmit the data to a receiver via the antenna.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
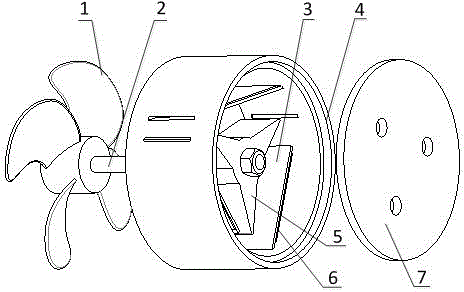
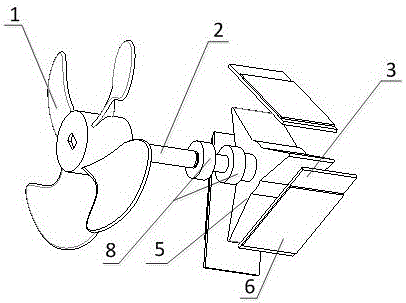
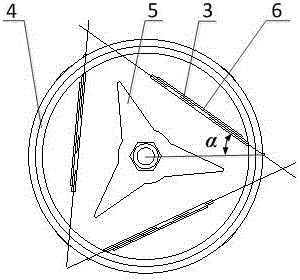
Wind energy collector based on flexible polymer piezoelectric material
InactiveCN106050570AReduce distractionsExtended service lifePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesFinal product manufactureElectricityRotational degrees of freedom
The invention relates to a wind energy collector based on a flexible polymer piezoelectric material. The wind energy collector comprises blades, a rotary shaft, flexible materials, a cylindrical shell, a rotary disc, piezoelectric films and a top cover, wherein the rotary shaft is fixed to the cylindrical shell through bearings and only has one degree of rotation freedom; one end of the rotary shaft is connected with the blades, and the other end of the rotary shaft is connected with the rotary disc; each flexible material and the corresponding piezoelectric film form a flexible piezoelectric polymer cantilever beam, and the multiple flexible piezoelectric polymer cantilever beams are evenly distributed on and fixed to the cylindrical shell; and the top cover is installed at the bottom of the cylindrical shell. The blades are driven to rotate by wind, the rotary shaft transfers the motion to the rotary disc, the rotary disc beats the flexible piezoelectric polymer cantilever beams periodically while rotating, and the piezoelectric films generate electric energy under vibration caused by beating and deformation recovery. The wind energy collector is simple in structure, high in energy collection efficiency, long in service life and suitable for a wide wind speed changing range, the requirements for a manufacturing process are low, and the wind energy collector can provide energy for micro-sensing network nodes.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
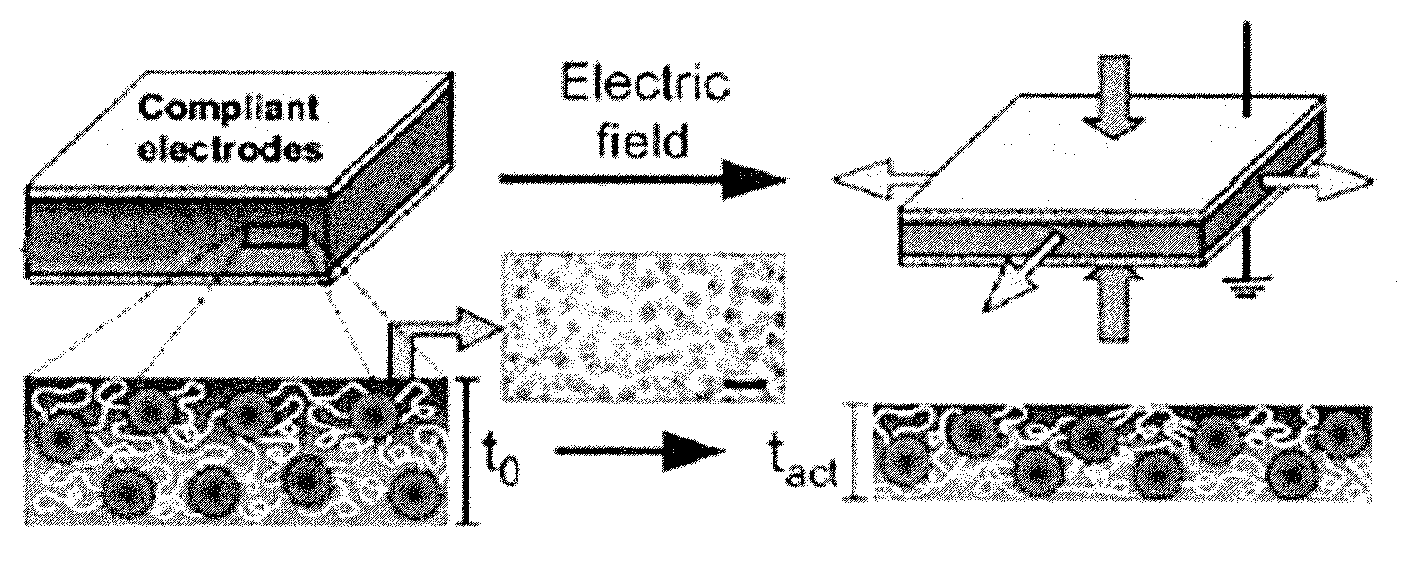
Polymer blend composition and tunable actuators using the same
ActiveUS20120248945A1Good compatibilityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityMechanical energy
The present invention relates to one of energy conversion devices, actuator and a dielectric layer used in the actuator. The present invention provides a polymer blend composition capable of easily controlling the ability of converting electrical energy to mechanical energy, which is prepared by blending a piezoelectric polymer with a flexible elastomeric block copolymer showing an effective miscibility therewith, and a tunable actuator using the same.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
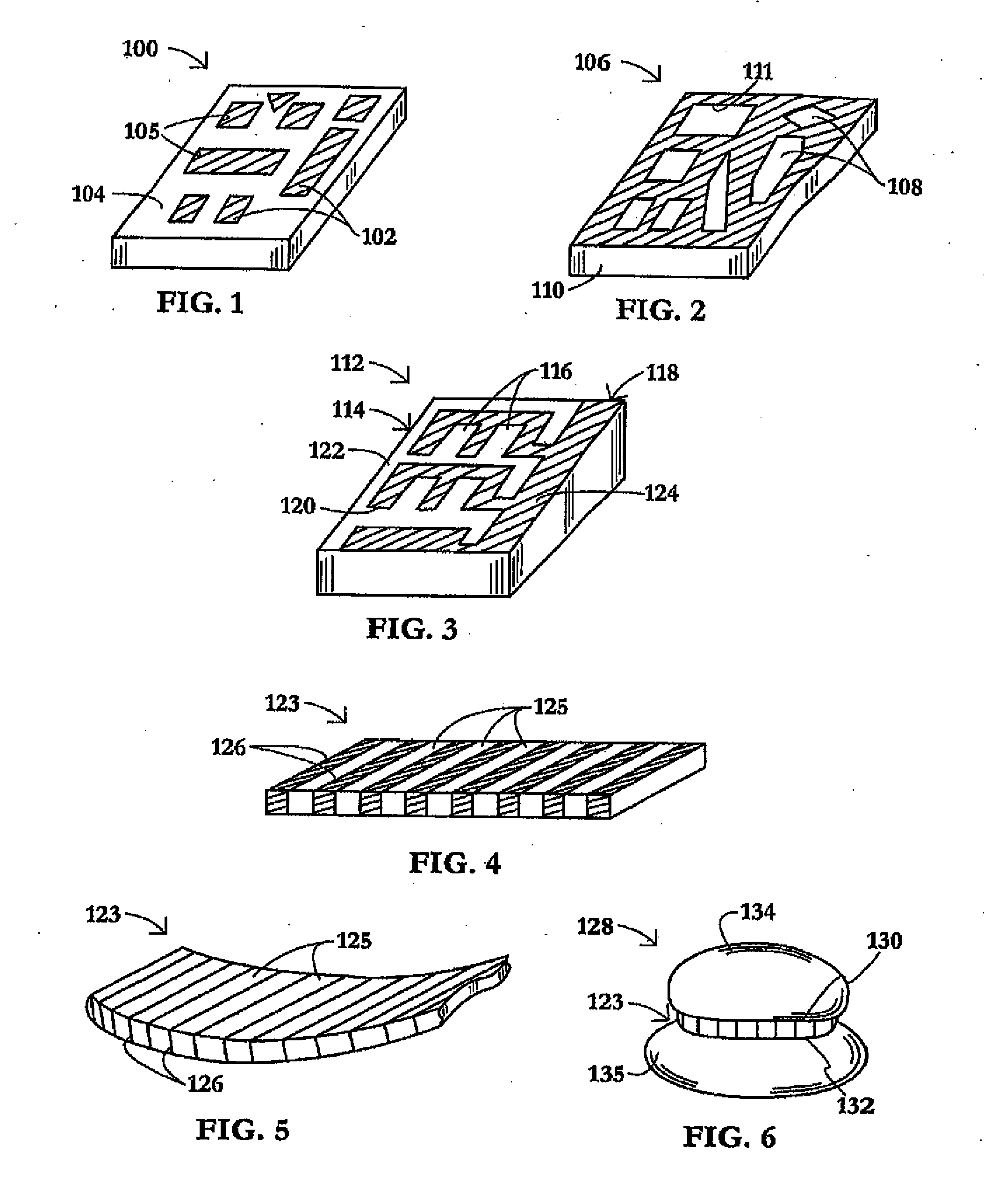
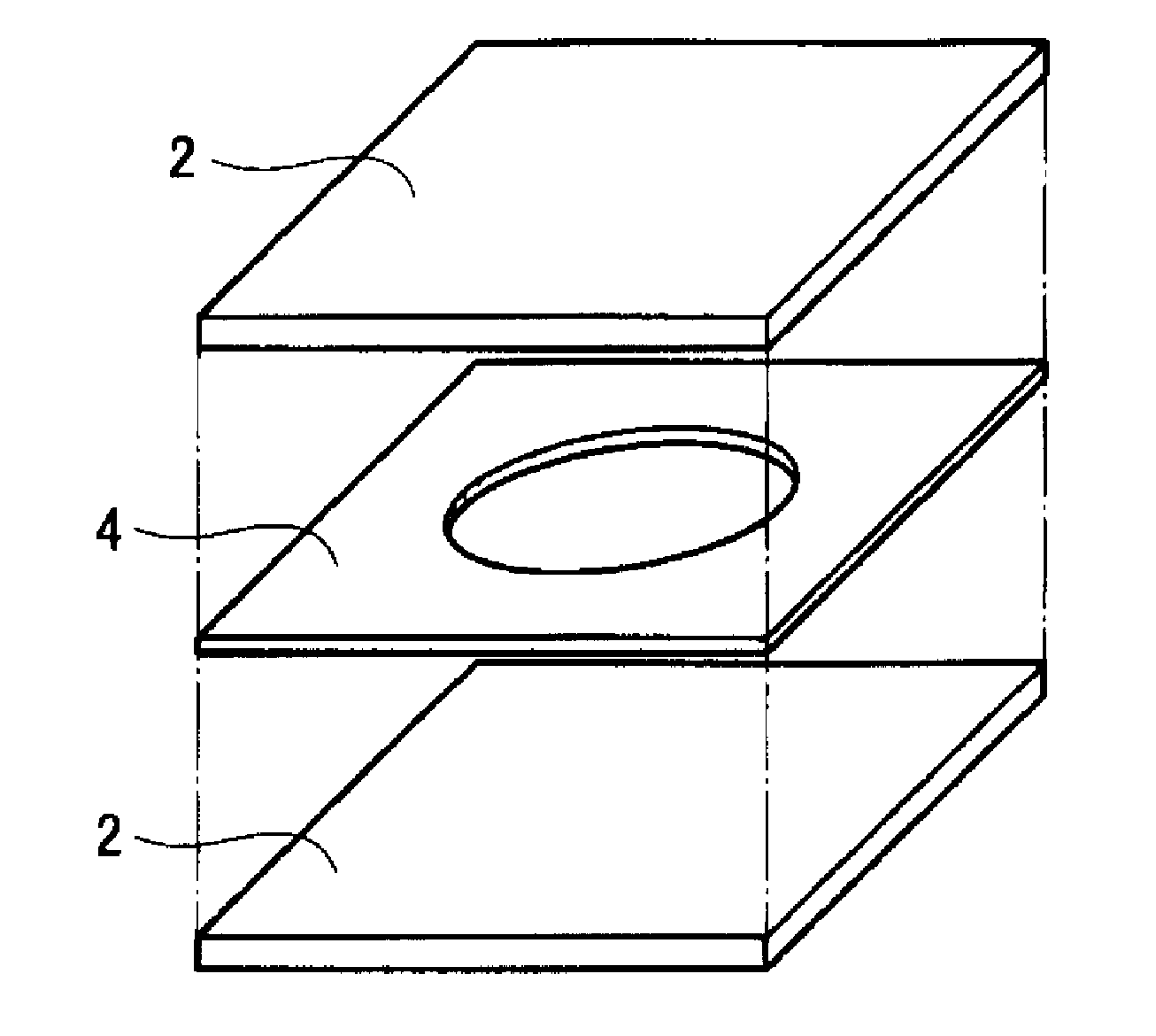
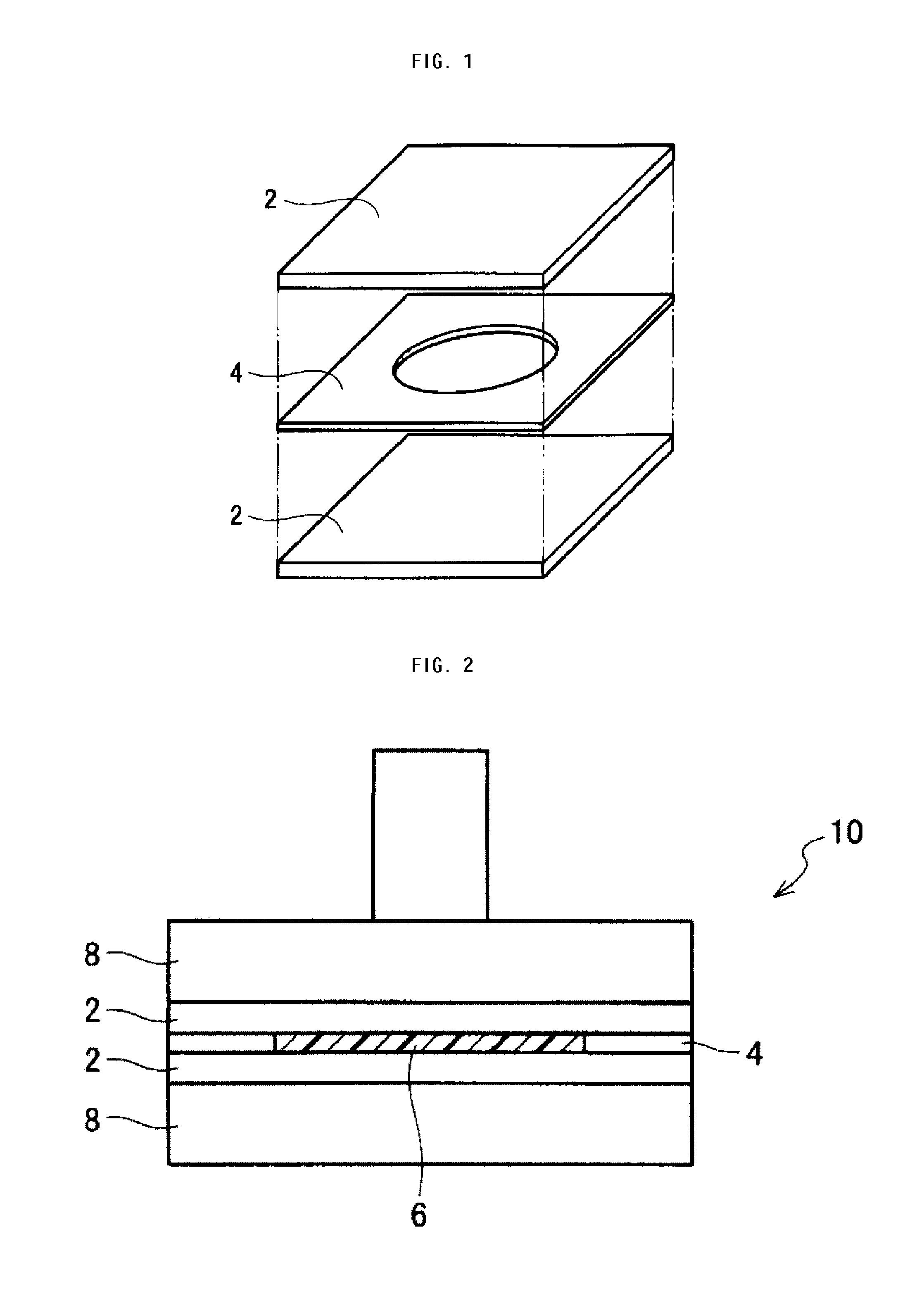
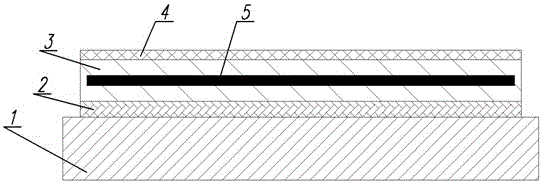
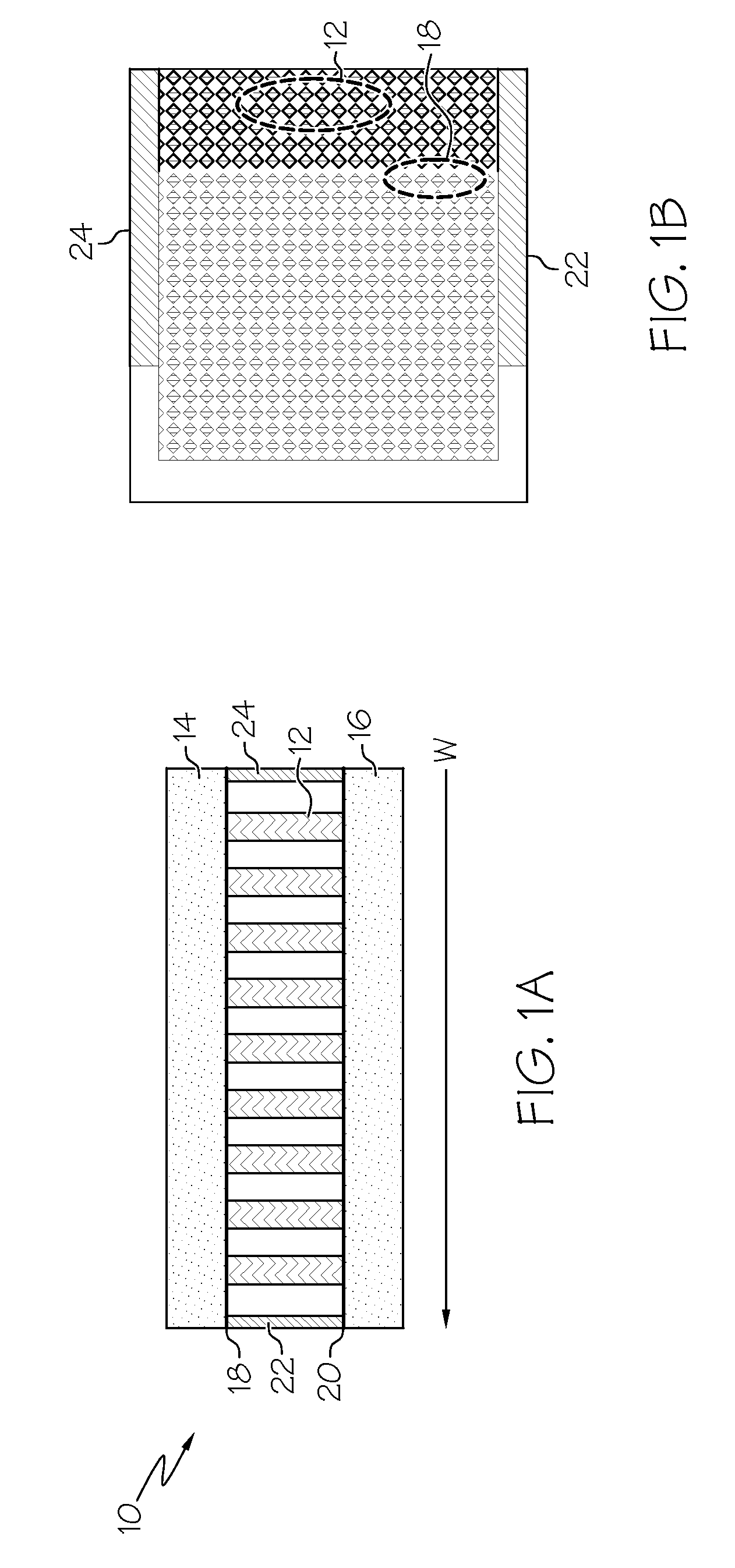
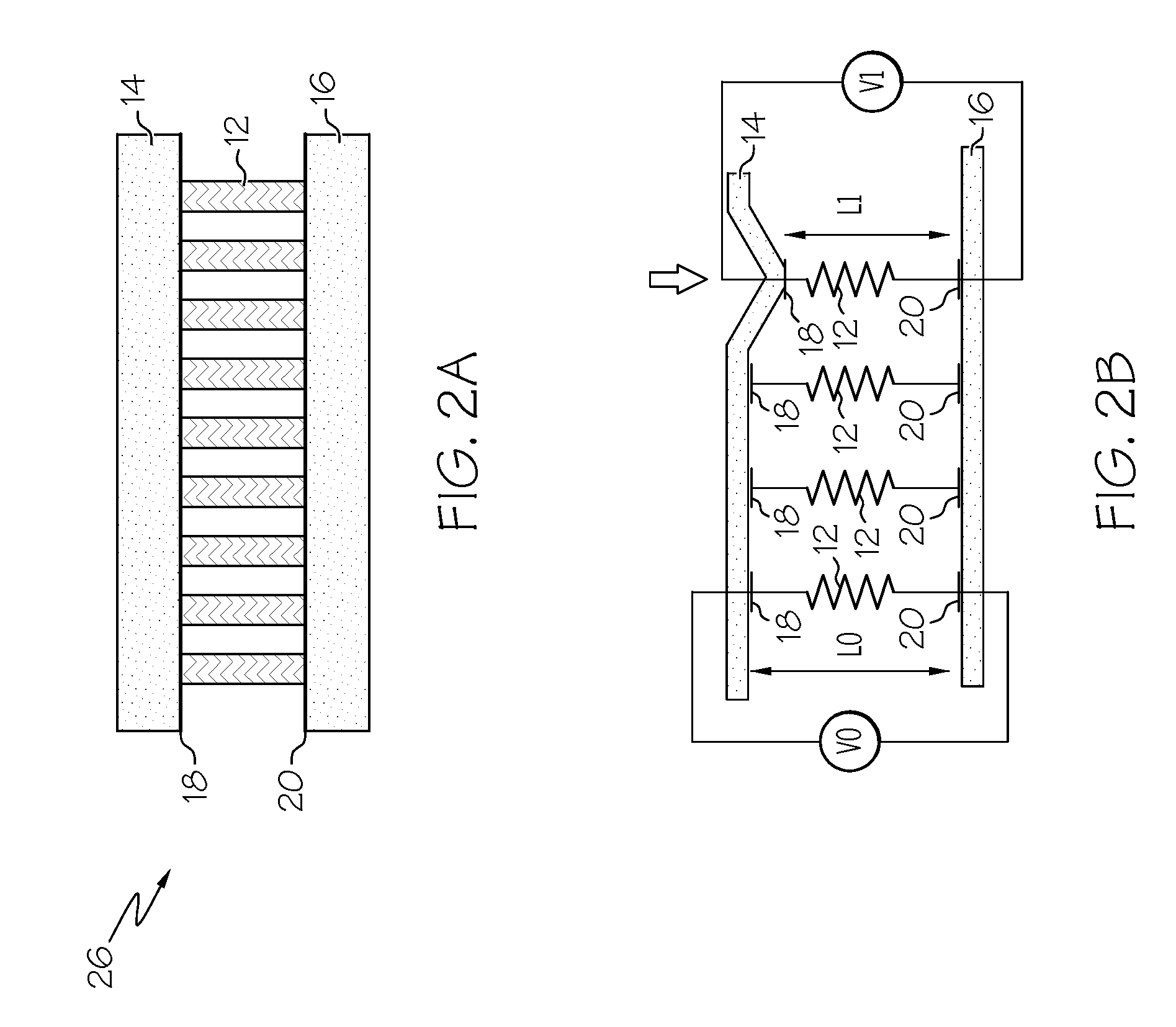
Piezoelectric polymer composite article and system
ActiveUS20070205701A1Resistive to oxidationMore cost efficientPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesConductive polymerPiezoelectric polymer
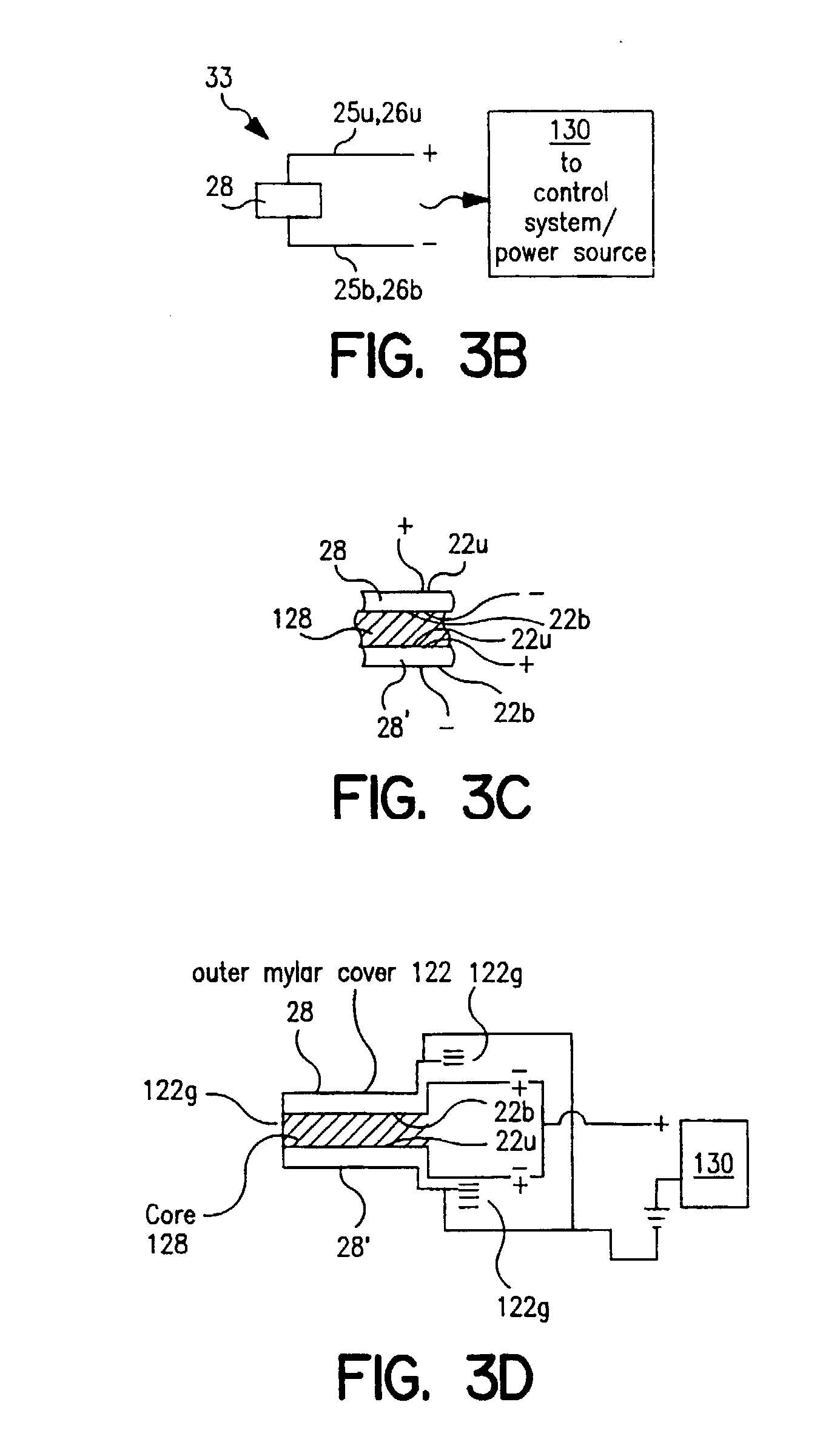
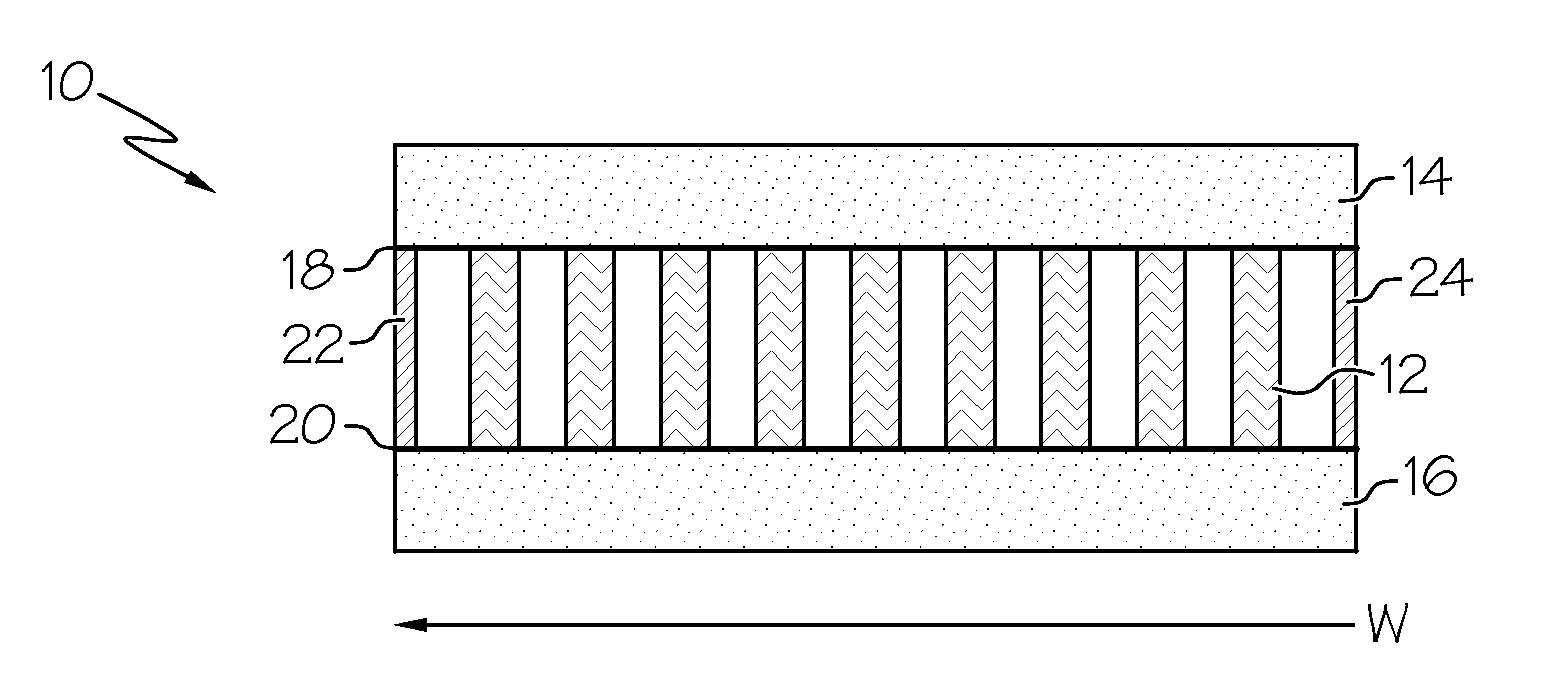
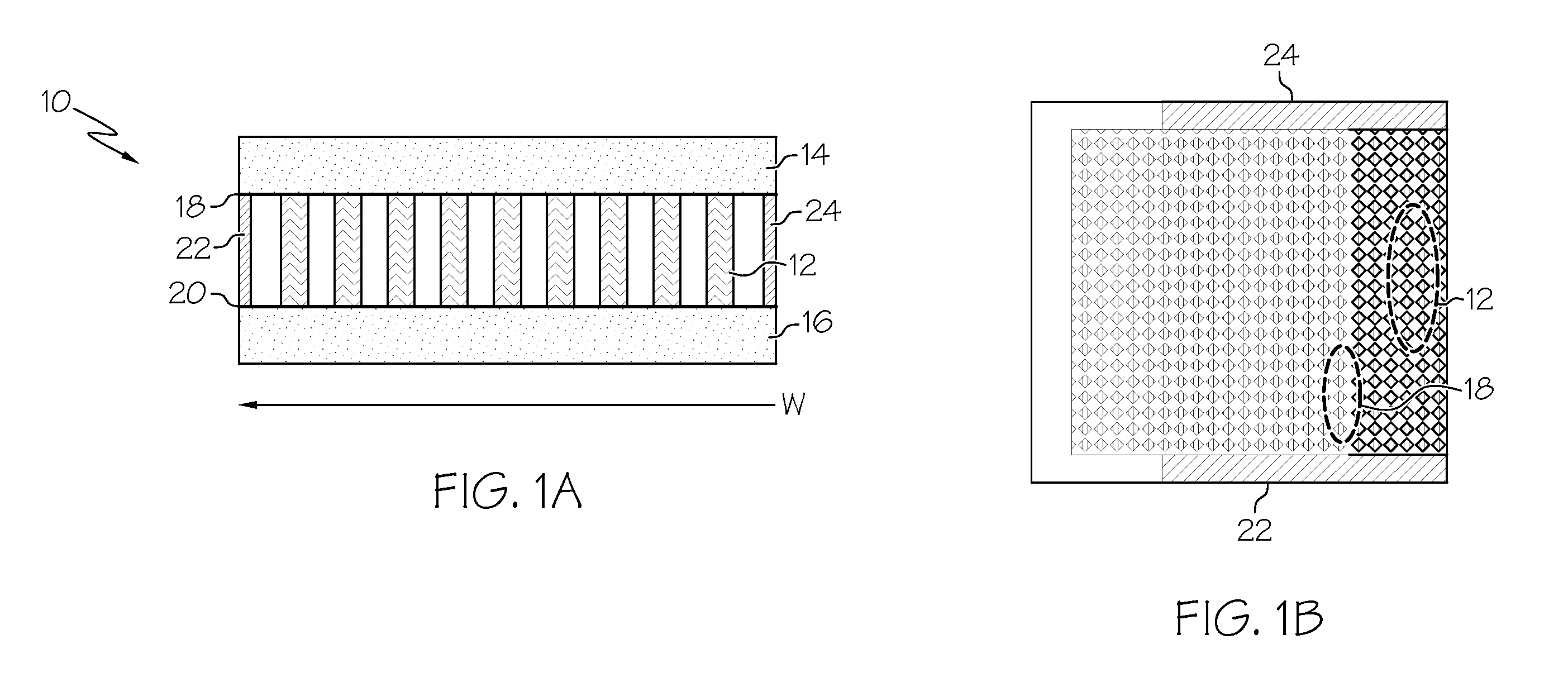
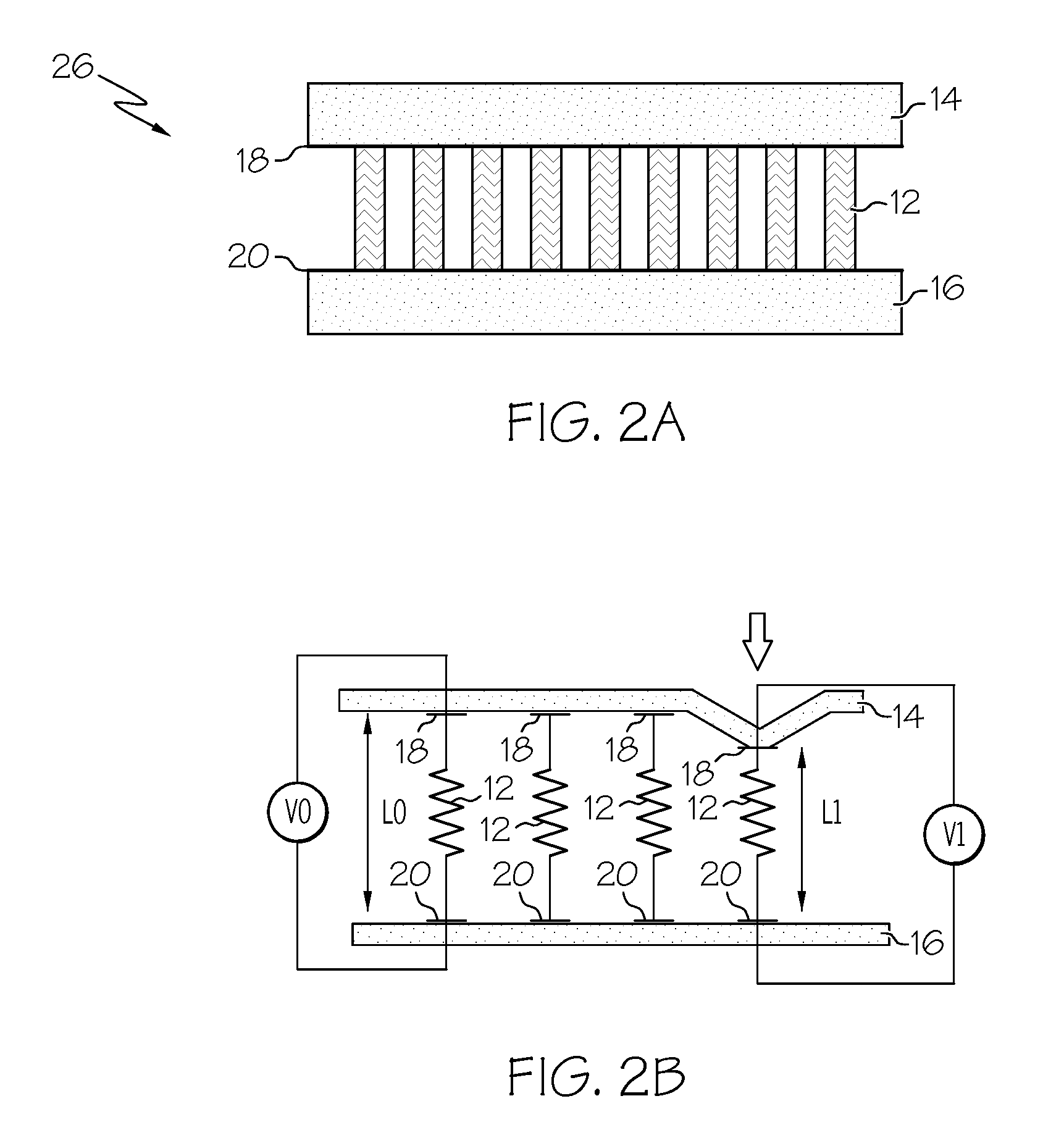
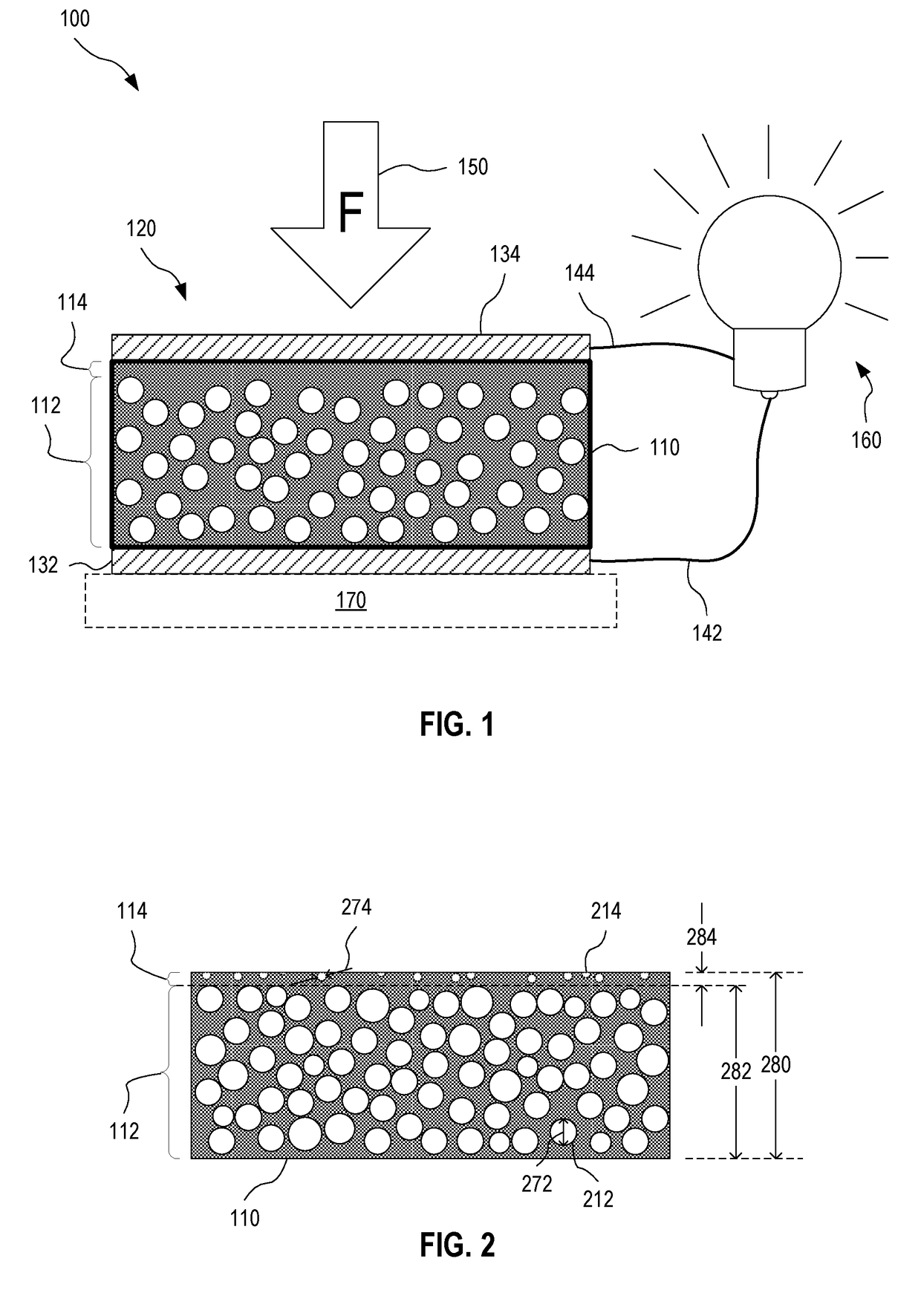
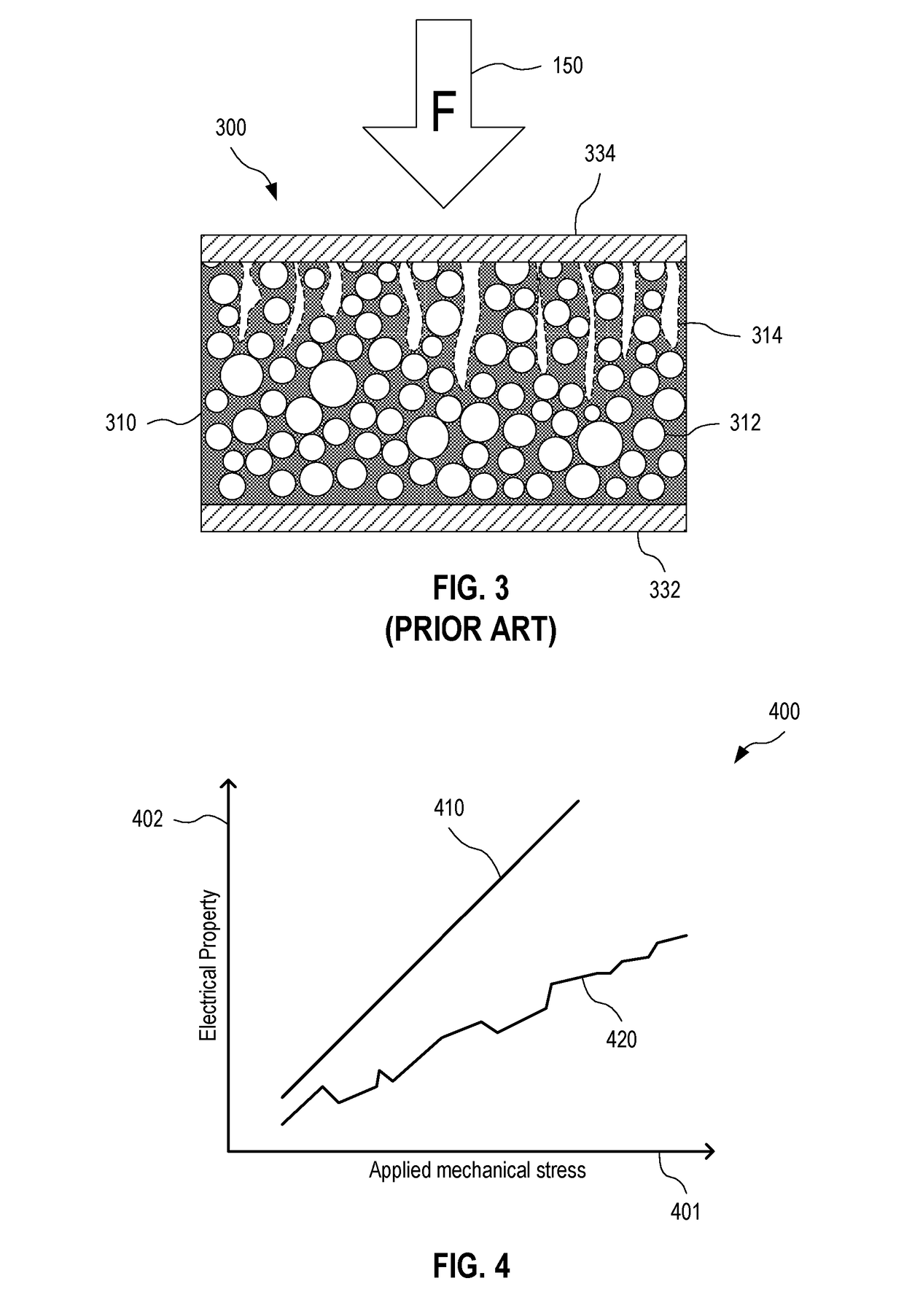
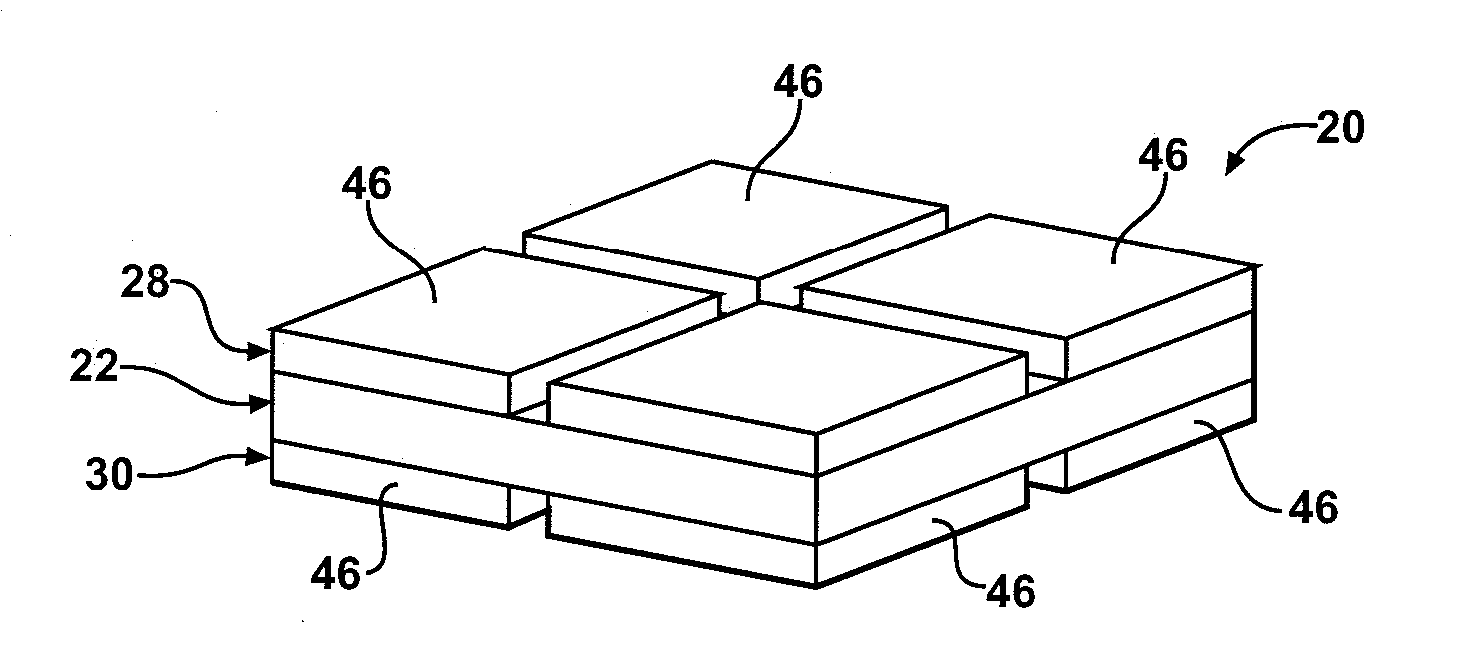
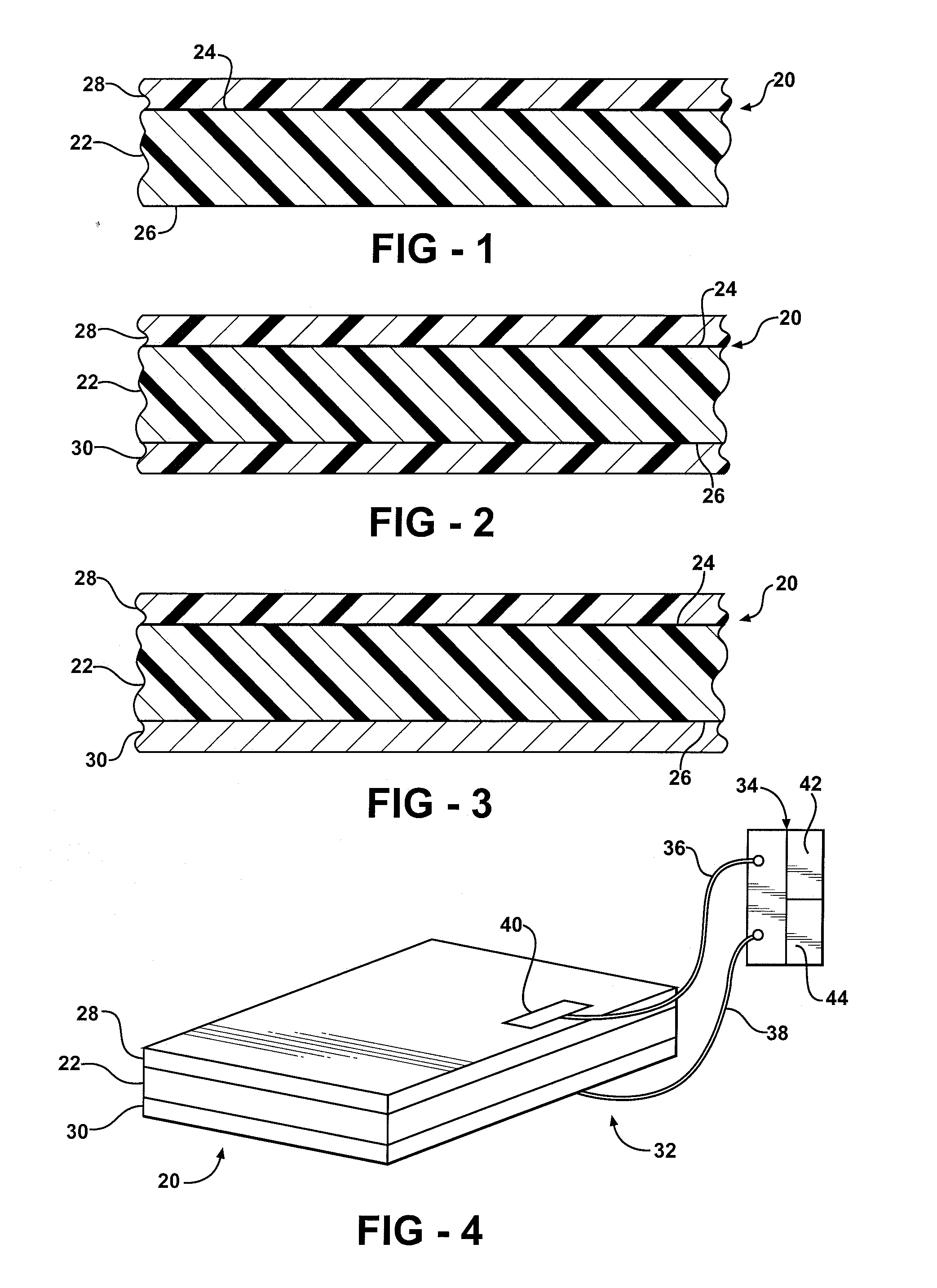
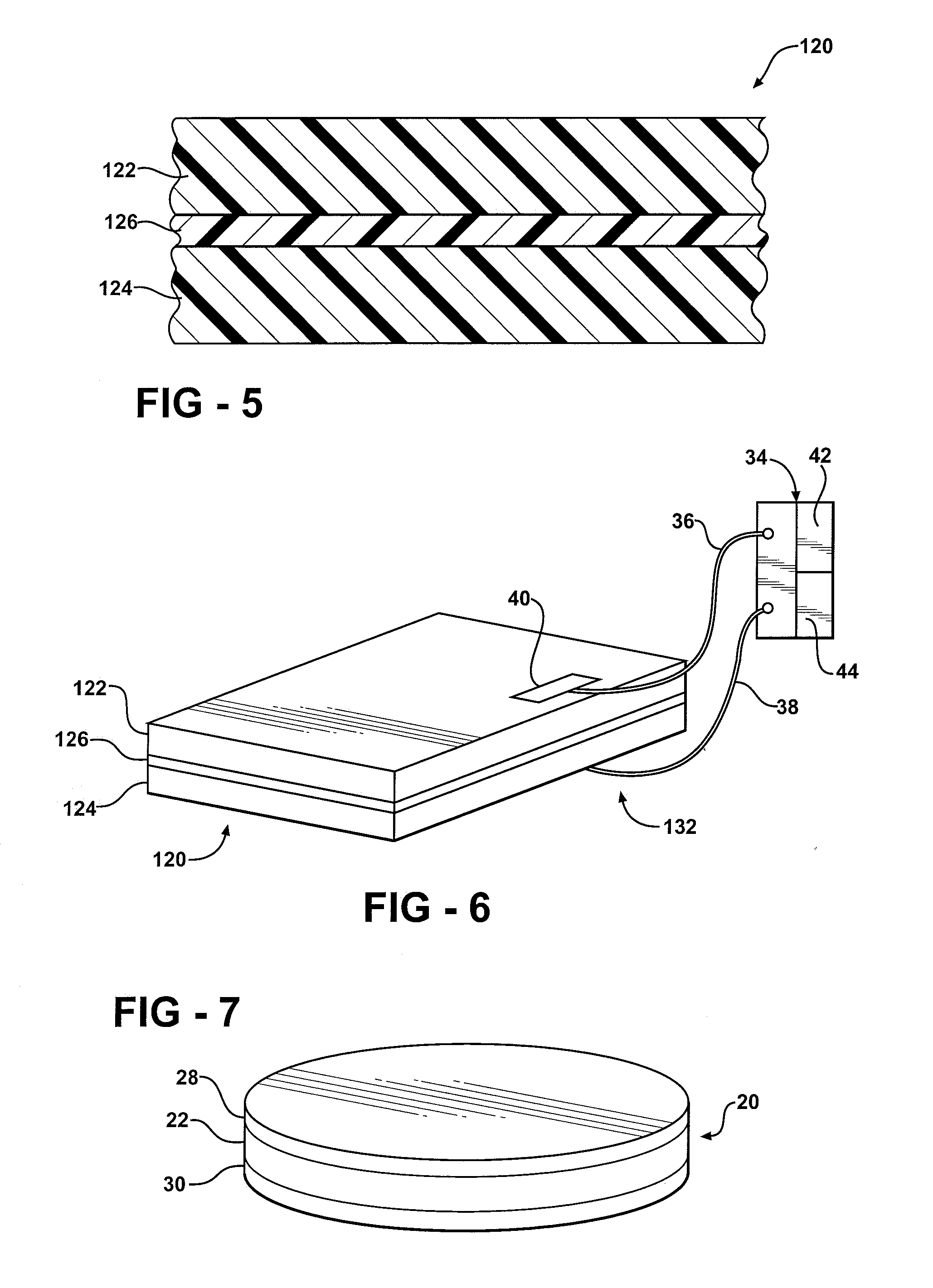
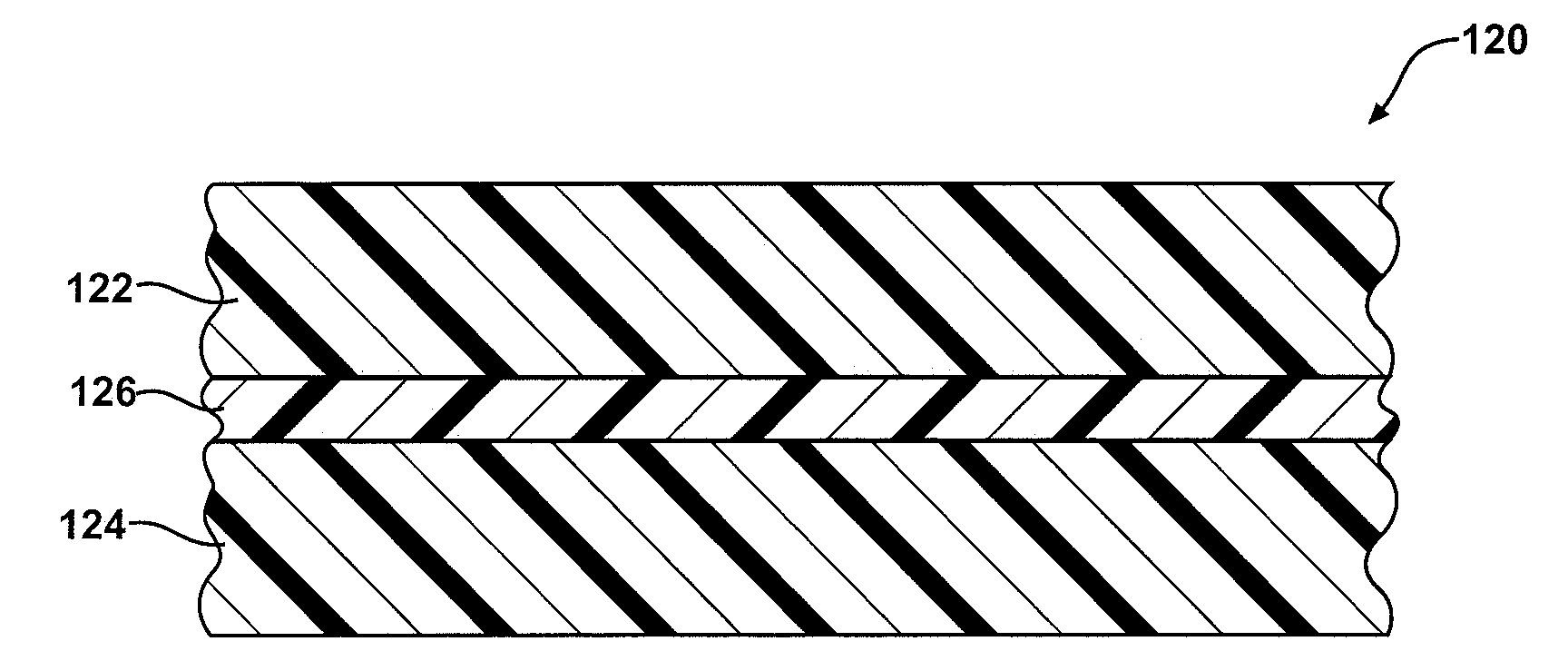
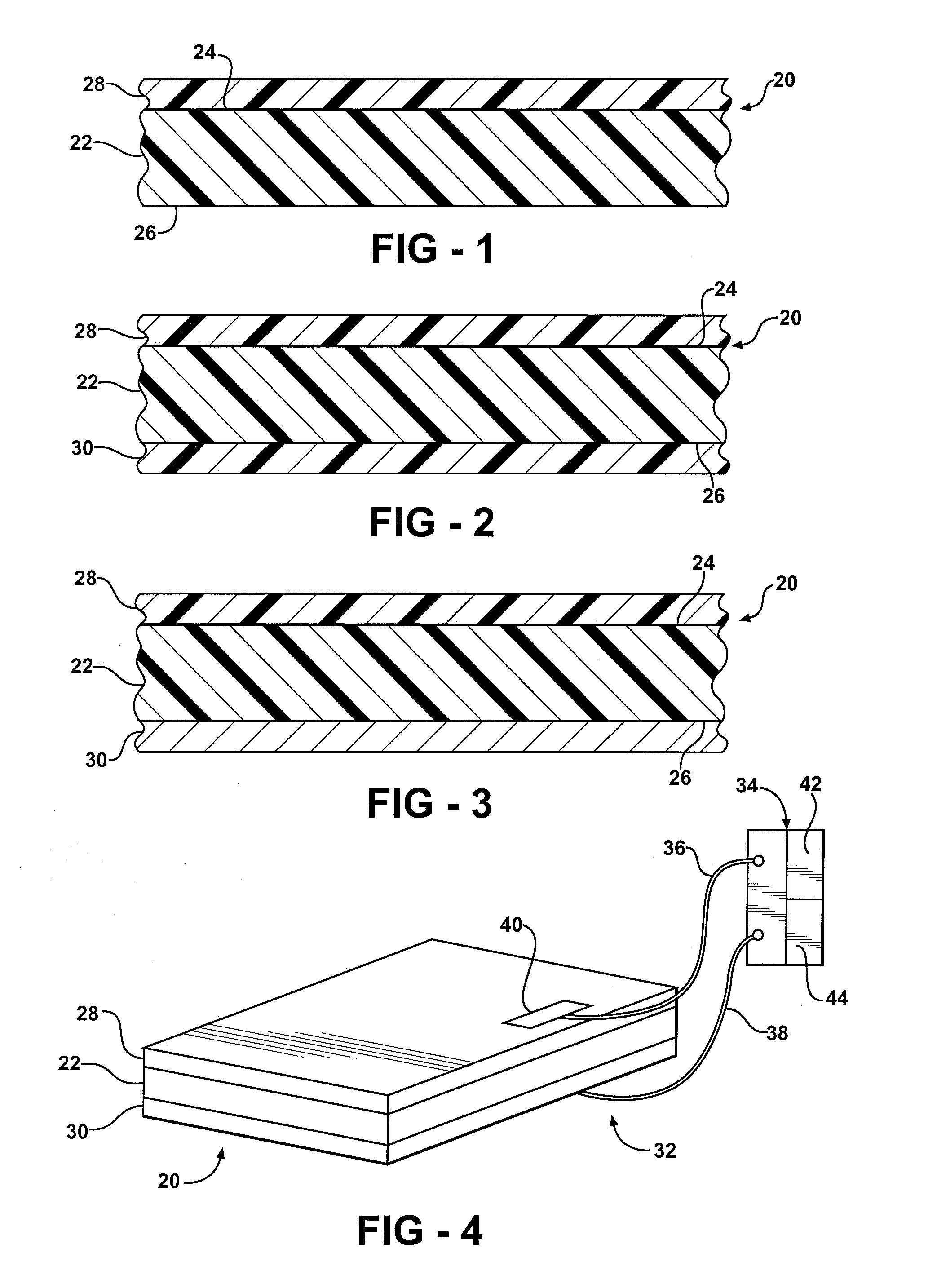
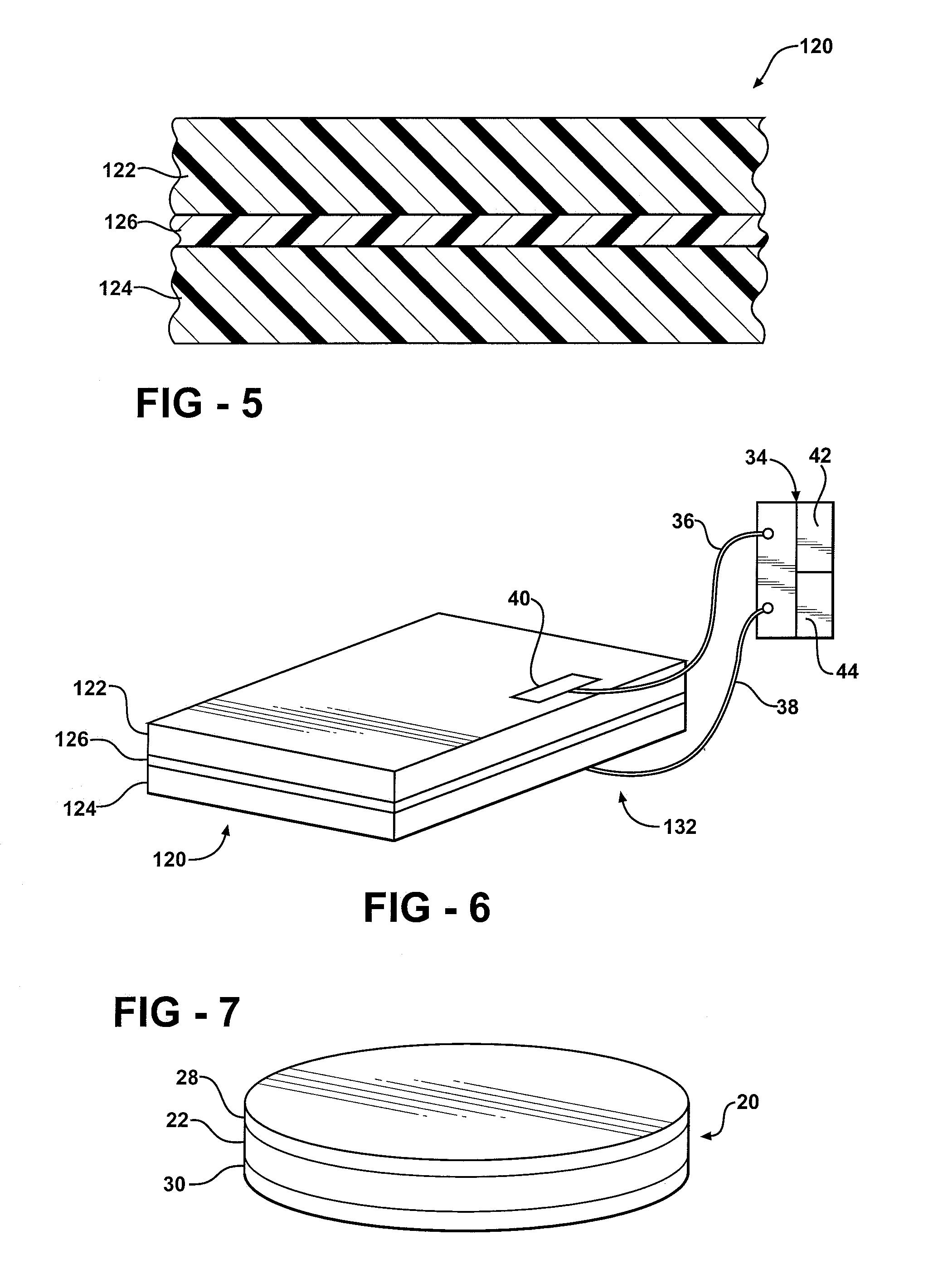
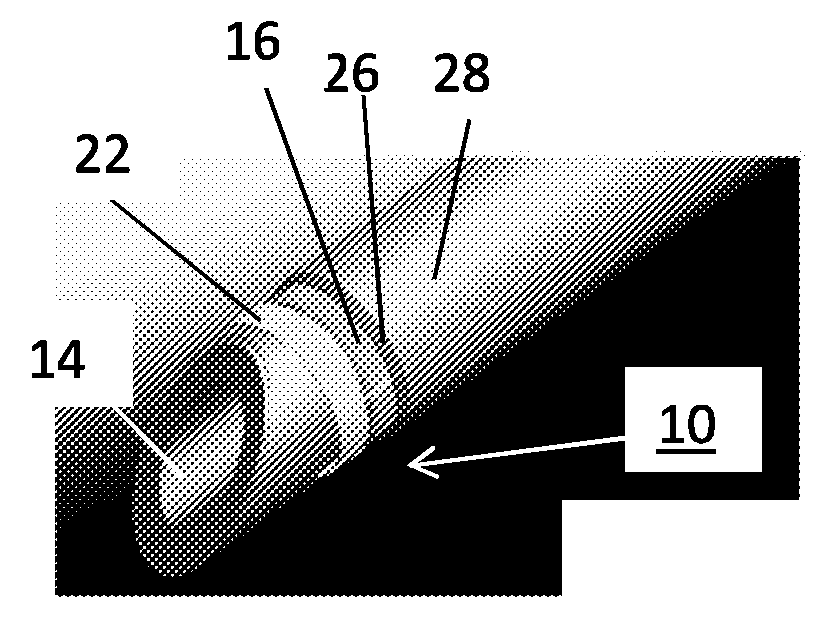
The subject invention provides composite articles (20, 120) and associated systems (32, 132). A first composite article (20) includes a piezoelectric layer (22) having a piezoelectric property. The piezoelectric layer (22) is sandwiched between a first conductive layer (28) and a second conductive layer (30). At least one of the conductive layers (28, 30) is a conductive polymer having an electrically conductive property. A second composite article (120) includes first and second piezoelectric layers (122, 124) having a piezoelectric property. The first and second piezoelectric layers sandwich an insulating layer (126). A first system (32) and a second system (132) each include a control device (34) electrically connected to the first composite article (20) or the second composite article (120), respectively. The control device (34) measures an electrical signal generated by the respective piezoelectric layers (22, 122, 124) and / or produces an electrical signal to actuate the respective piezoelectric layers (22, 122, 124).
Owner:BASF CORP
Piezoelectric polymer composite article and system
ActiveUS7443082B2Resistive to oxidationCost efficientPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesConductive polymerPiezoelectric polymer
The subject invention provides composite articles (20, 120) and associated systems (32, 132). A first composite article (20) includes a piezoelectric layer (22) having a piezoelectric property. The piezoelectric layer (22) is sandwiched between a first conductive layer (28) and a second conductive layer (30). At least one of the conductive layers (28, 30) is a conductive polymer having an electrically conductive property. A second composite article (120) includes first and second piezoelectric layers (122, 124) having a piezoelectric property. The first and second piezoelectric layers sandwich an insulating layer (126). A first system (32) and a second system (132) each include a control device (34) electrically connected to the first composite article (20) or the second composite article (120), respectively. The control device (34) measures an electrical signal generated by the respective piezoelectric layers (22, 122, 124) and / orproduces an electrical signal to actuate the respective piezoelectric layers (22, 122, 124).
Owner:BASF CORP
Touch and auditory sensors based on nanotube arrays
A sensor including at least one sensor probe including a pair of electrodes; a vertically aligned nanotube disposed between the pair of electrodes; optionally a piezoelectric polymer on the nanotube; and optionally, a field source for generating a field, the field source operatively connected to the pair of electrodes; whereby when the sensor probe is contacted, a change in the field occurs or electricity is generated. Methods of using the sensors are also described.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Ultrasonic sensor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN107203739AReduce manufacturing costImprove yieldPrint image acquisitionCMOSManufacturing cost reduction
The invention discloses an ultrasonic sensor and a manufacturing method thereof. The method comprises the steps of forming at least one ultrasonic transducer, forming a piezoelectric stack layer which comprises a piezoelectric layer, a firsts electrode and a second electrode which are respectively arranged on the first surface and the second surface of the piezoelectric layer, wherein the first layer and the second layer face each other; and forming an electric connection between the piezoelectric stack layer and a CMOS circuit, wherein the piezoelectric layer is composed of an organic piezoelectric polymer. According to the method, the piezoelectric layer is formed by the organic piezoelectric polymer, thereby reducing manufacture cost and improving sensor performance.
Owner:HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS
Piezoelectric polymer/metal composite nano-filament and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104790064AImprove refinementImprove power generation efficiencyFilament/thread formingConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsFiberPolymer dissolution
The invention relates to a piezoelectric polymer / metal composite nano-filament and a preparation method thereof. The piezoelectric polymer / metal composite nano-filament comprises conductive metal wire core layer and a piezoelectric polymer surface layer. The preparation method comprises the following preparation steps: at first, a polymer is dissolved in a single or compound solvent, then a solution is sprayed on the surface of a metal wire by electrostatic spinning to enable the solution to coat a polymer nano-fiber surface layer, and at last, the obtained fiber stands at room temperature till the solvent volatilizes. Through electrostatic spinning, a piezoelectric polymer is spun on the metal wire, so that the piezoelectric polymer directly coats the metal wire, the metal wire is directly used as an electrode during the packaging process, the refine and the power generation efficiency of a nanogenerator are improved, and the piezoelectric polymer / metal composite nano-filament has a high development prospect in the aspects of sensor, medicine, and energy conversion.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
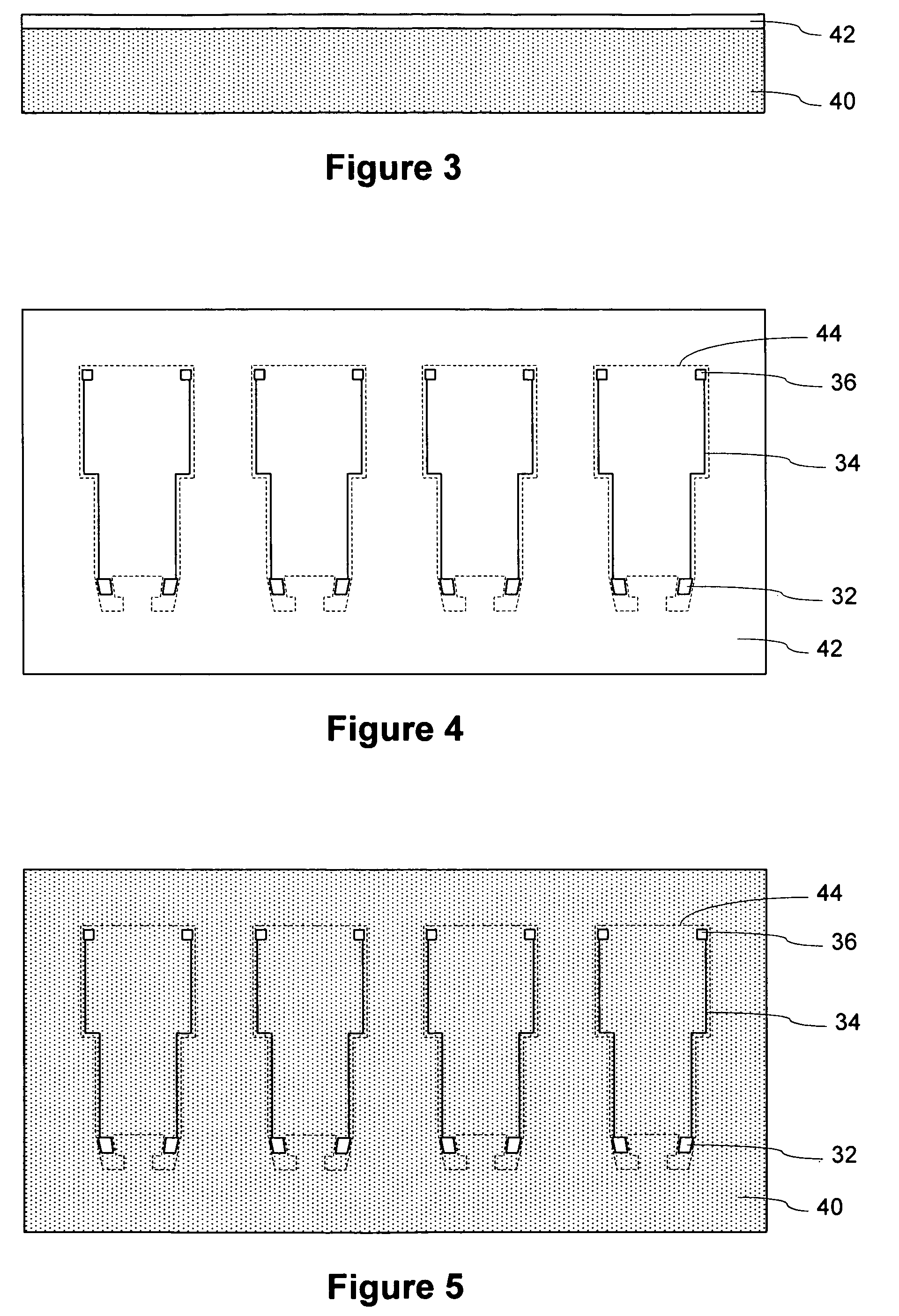
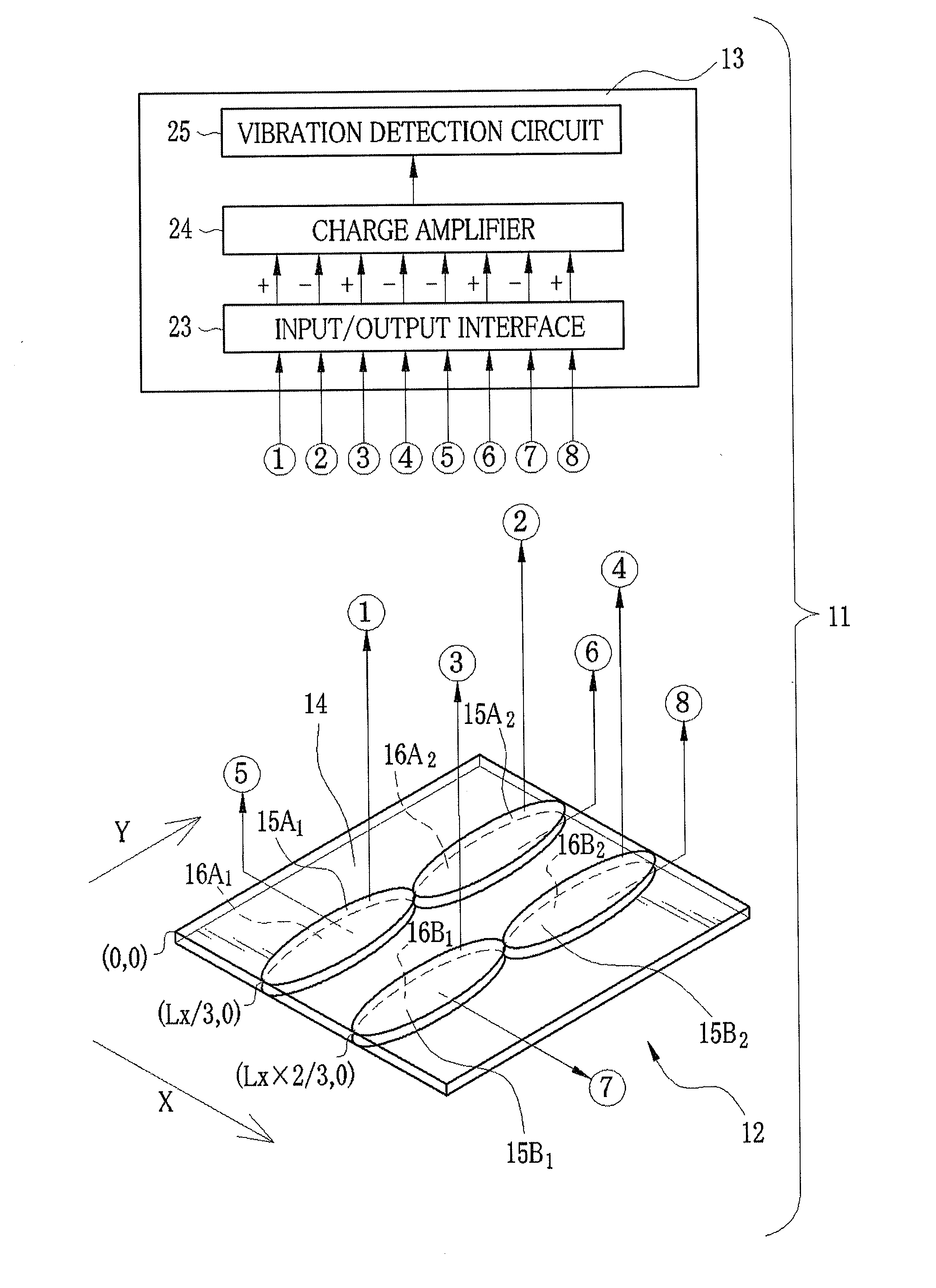
Vibration sensor film, vibration actuator film, vibration reduction film, and multilayer film using them
ActiveUS20100194243A1Improve accuracyReduce vibrationPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementEngineeringActuator
A vibration reduction system has a vibration reduction film and a control unit. The vibration reduction film is constituted of a vibration sensor film, an insulating layer, and a vibration actuator film that are stacked in this order. In each of the vibration sensor film and the vibration actuator film, two pairs of electrodes are formed on both surfaces of a piezoelectric polymer film into a pattern based on a particular mode of vibration. The electrodes of the vibration sensor film overlap with the electrodes of the vibration actuator film. In response to electric charge signals from the electrodes of the vibration sensor film, the particular mode of vibration is detected. By application of voltages into the electrodes of the vibration actuator film, a vibration of opposite phase is generated to counteract the detected vibration.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Polymer film optical fiber F-P cavity-based underwater shock pressure sensor and dynamic calibration experiment system thereof
InactiveCN102519663ASmall sizeTest dynamic matching error is smallFluid pressure measurement by optical meansSensor arrayFiber
The invention discloses a polymer film optical fiber F-P cavity-based underwater shock pressure sensor and a dynamic calibration experiment system of the sensor. The system adopts polymer film optical fiber F-P cavities to detect an underwater shock pressure, performs high-speed linear demodulation on an underwater shock sensor array which is formed by the polymer film ultra-short fiber F-P cavities by the three-wavelength light source excitation and random deterministic phase interval passive homodyne demodulation techniques, so as to achieve the effect of measuring an underwater shock pressure field. Besides, the method for dynamically calibrate the super-mini underwater shock pressure sensor having a plane structure is implemented by electromagnetic shock wave source excitation. The sensor is in parallel with the conventional sensing devices such as piezoelectric ceramics and piezoelectric polymer underwater shock pressure sensors or underwater ultrasonic sensors, and has not only a direct significance in measurement of shock pressures in strong electromagnetic interference environments but also an important significance in researches on underwater / ground shock pressure measurement and underwater ultrasonic sensor arrays.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
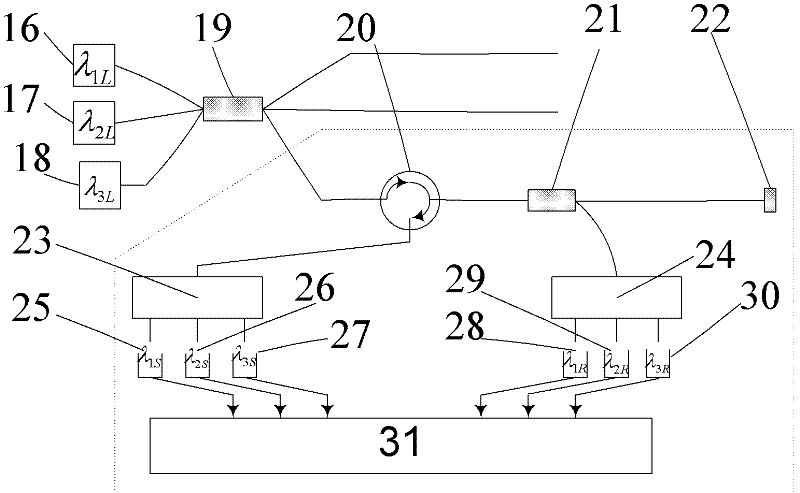
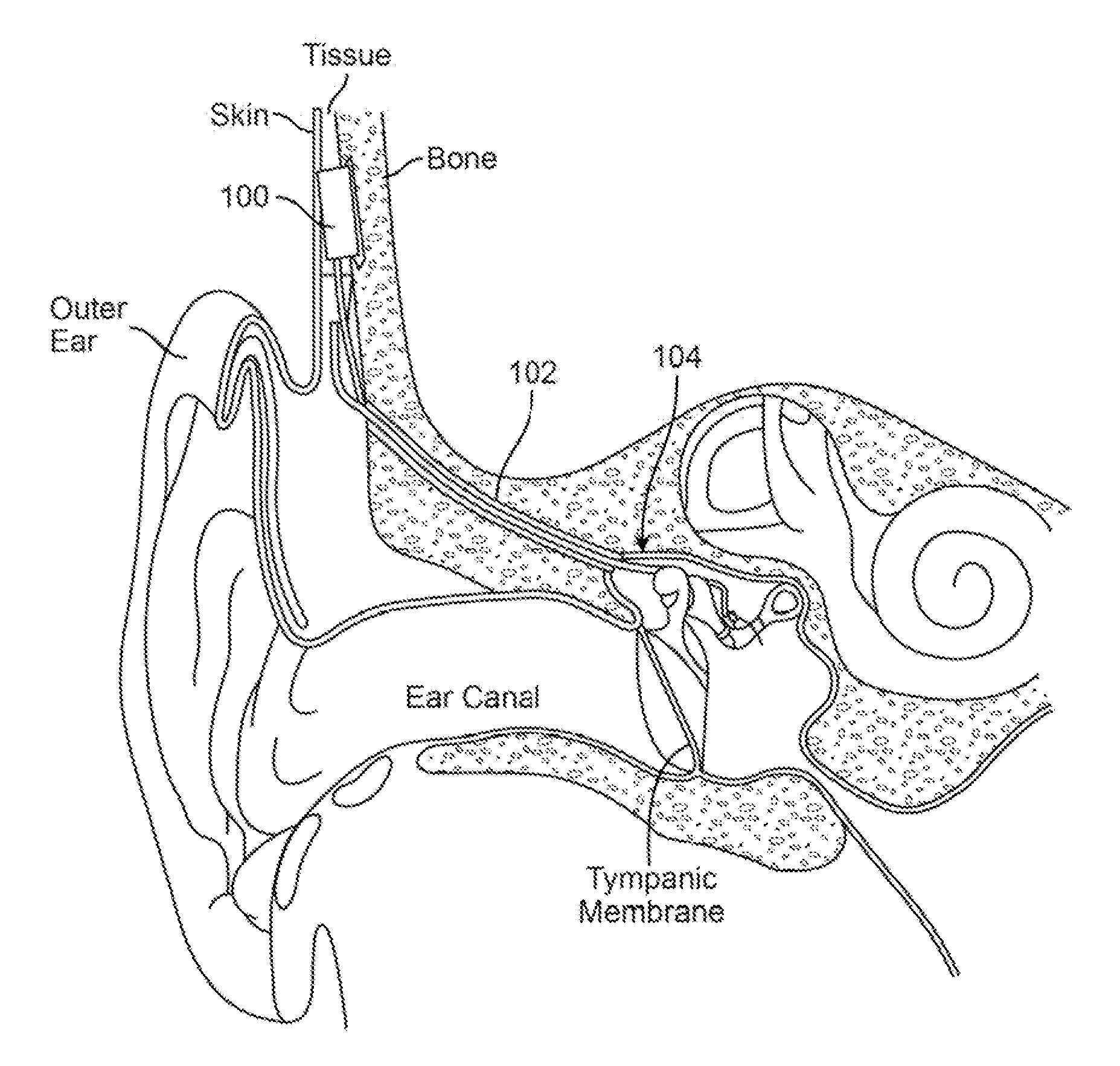
Implantable piezoelectric polymer film microphone
InactiveUS20120165597A1Reduce stiffnessReduce impactElectrotherapyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersElectricityEngineering
Implantable piezoelectric polymer film microphone apparatus and methods are described for use as an integral component of a hearing augmentation device system. The piezoelectric polymer film can be polyvinylidene fluoride (“PVDF”). Generally, a piezoelectric polymer film serves as the sensor that is well matched to tissue and which directly converts to an electrical signal by the piezoelectric effect vibration signals which are received through the tissue in which the piezoelectric polymer film microphone is implanted.
Owner:SOUNDMED LLC
Functional wound dressing capable of accelerating wound healing and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102861355ASimple preparation processLow costAbsorbent padsConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsWound healingWound dressing
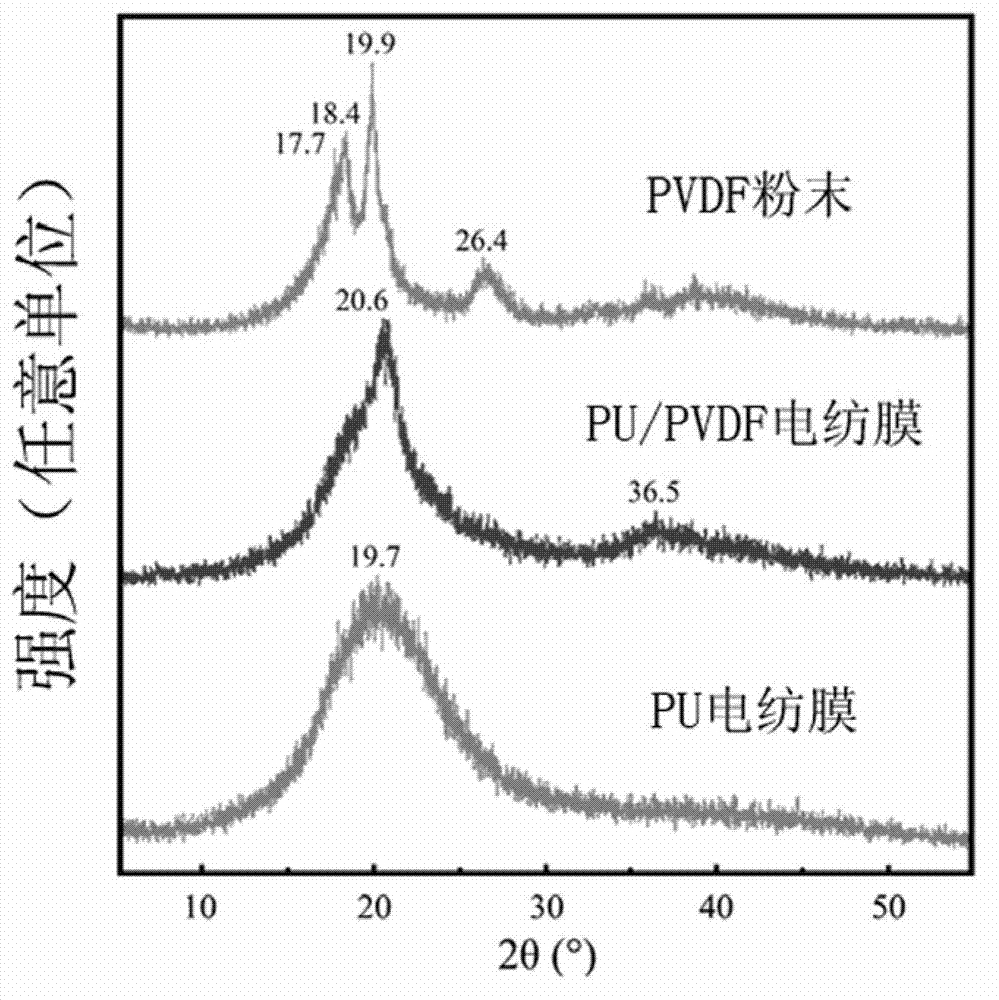
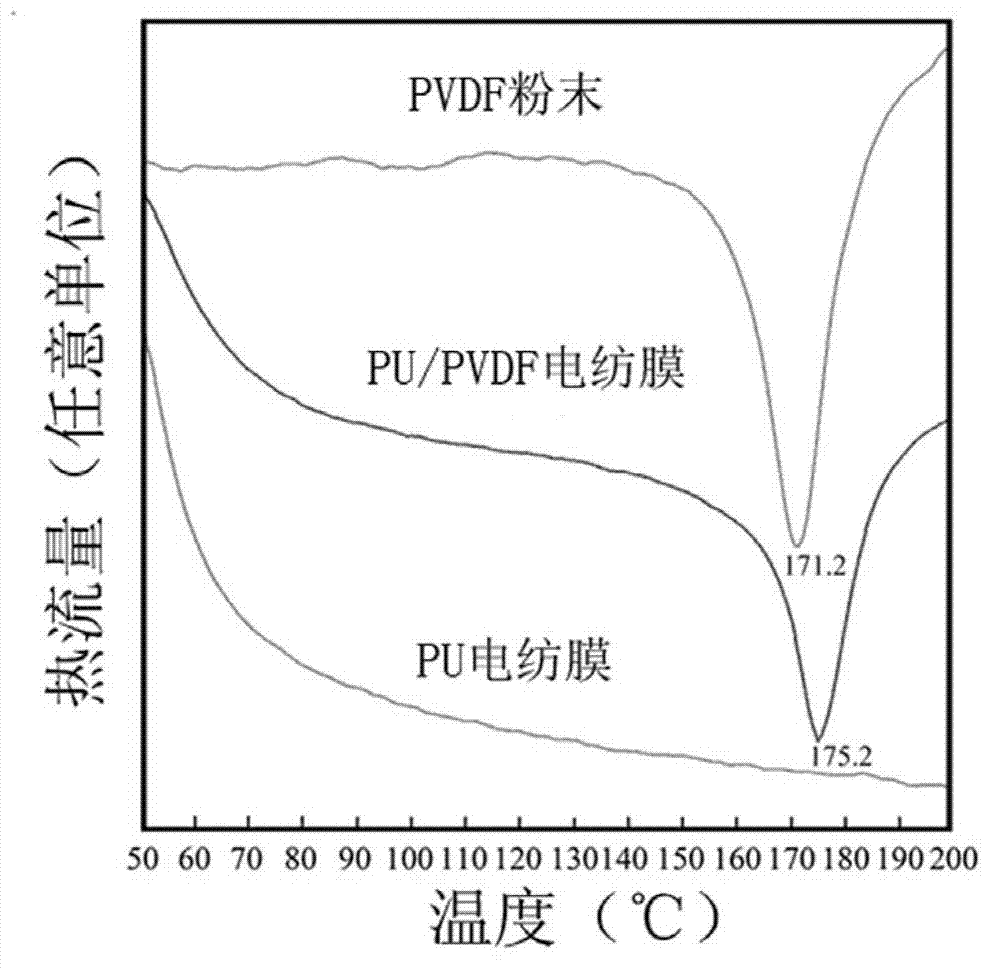
The invention relates to a functional wound dressing capable of accelerating wound healing and a preparation method thereof. The functional wound dressing is a polyurethane (PU) / polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) electric spinning membrane which is made of PU and PVDF in a mass ratio of 1:3-3:1, the functional wound dressing is prepared by using a method of electrostatic spinning, and the thickness of the PU / PVDF electric spinning membrane is 150-250 mum. The functional wound dressing can use electrical stimulatory effects produced by piezoelectric polymer PVDF to accelerate wound healing, has the advantages of being good in biocompatibility, simple and convenient to prepare, low in cost and the like, and is wide in market development prospects.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
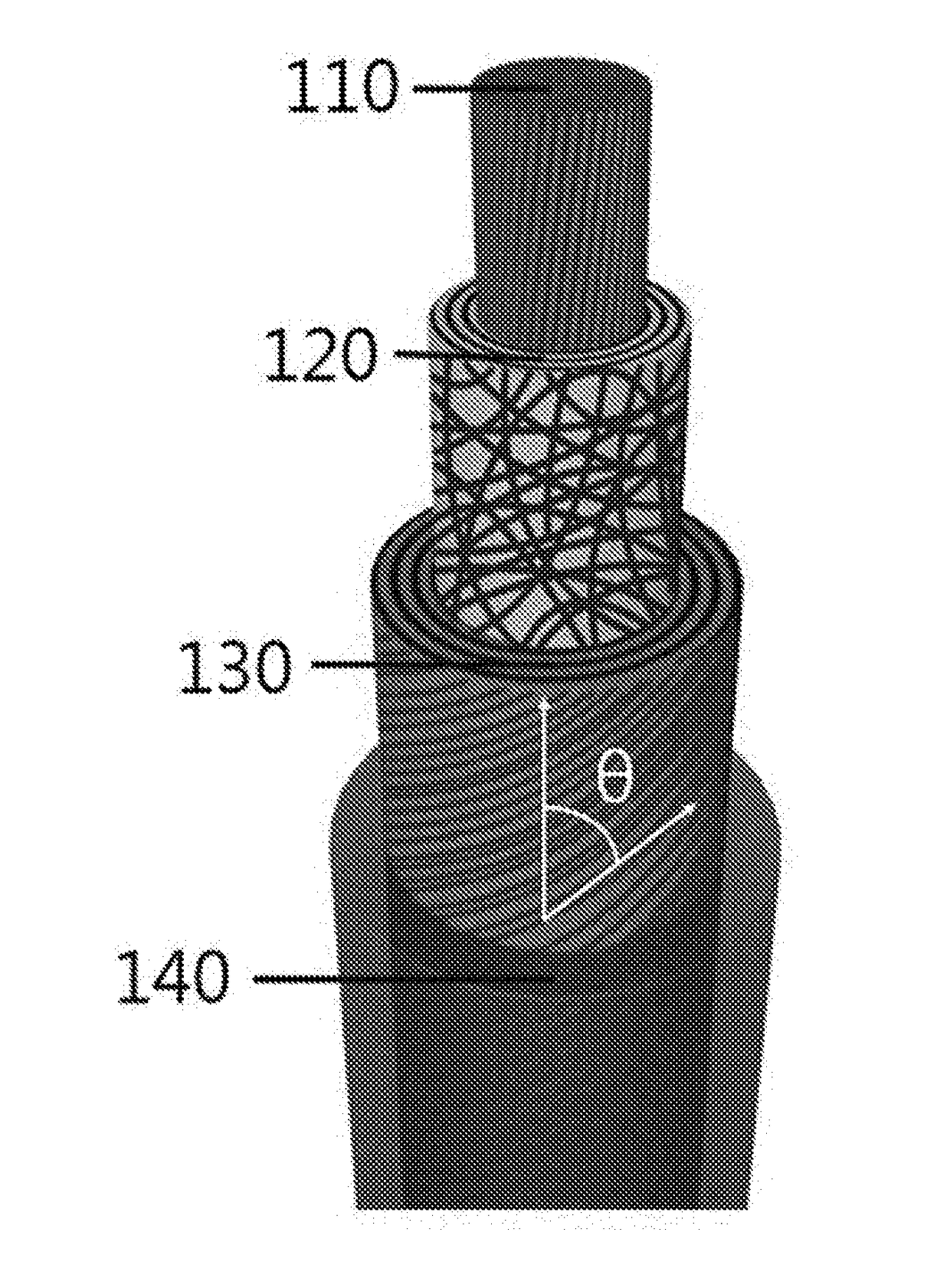
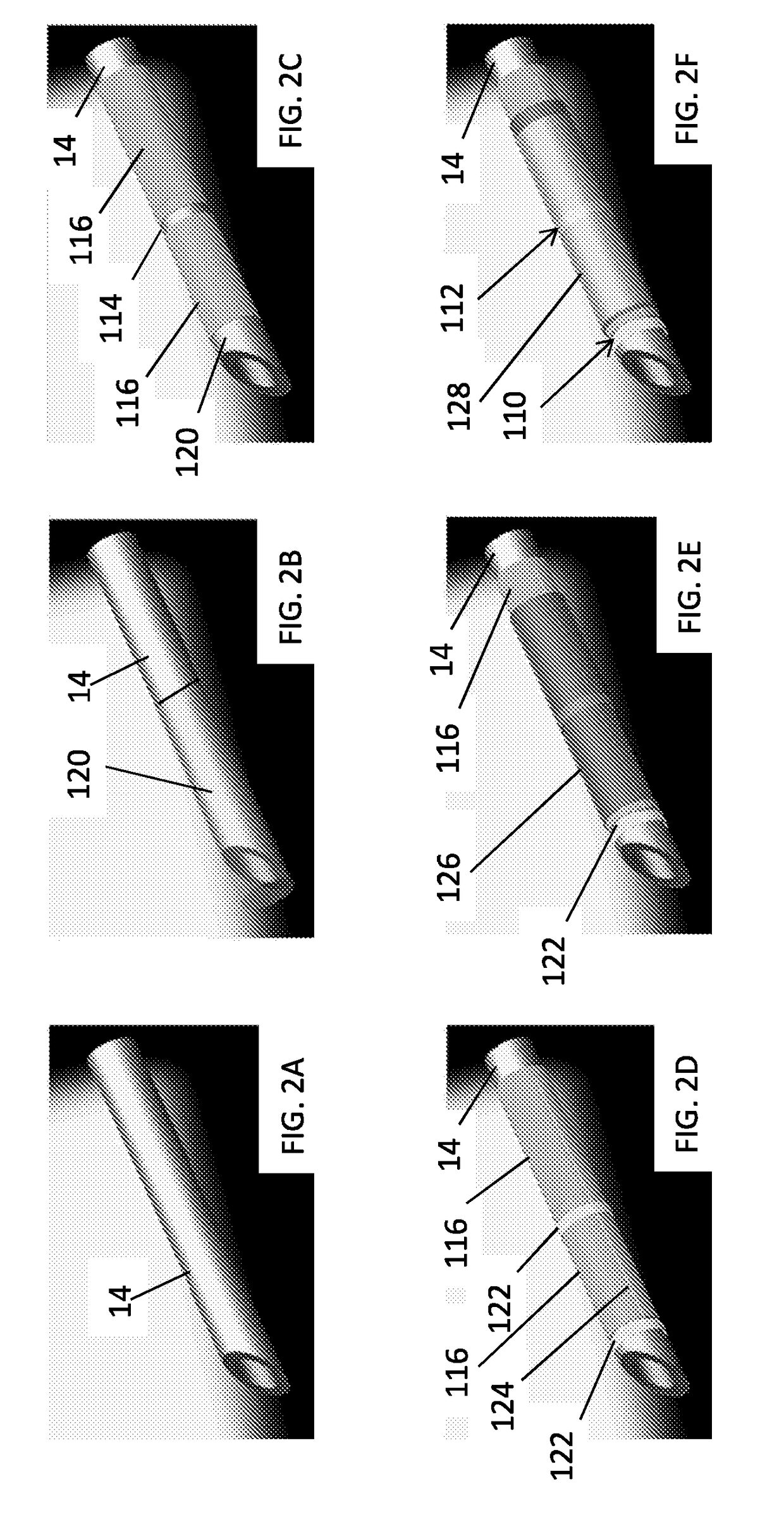
Needle with piezoelectric polymer sensors
ActiveUS20170172618A1Organ movement/changes detectionSurgical needlesElectricityElectrical connection
A medical device includes a conductive body (14) including a surface and a sensor (10) conformally formed on the surface and including a piezoelectric polymer formed about a portion of the surface and following a contour of the surface. The piezoelectric polymer is configured to generate or receive ultrasonic energy. Electrical connections (24) conform to the surface and are connected to an electrode in contact with the piezoelectric polymer. The electrical connections provide connections to the piezo electric polymer and are electrically isolated from the conductive body over a portion of the surface.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Dual-functional toughening-damping intercalation material and product prepared from same
ActiveCN103963398AIncrease dampingIncrease stiffnessSynthetic resin layered productsCarbon fibersResin-Based Composite
The invention relates to a dual-functional toughening-damping intercalation material applied to a carbon fiber strengthening lamination resin-based composite and a preparation method of the dual-functional toughening-damping intercalation material, as well as the integrated toughening-damping carbon fiber strengthening lamination resin-based composite prepared from the intercalation material, wherein the intercalation material having the dual-functions of toughening and damping is formed by compounding carrier materials such as non-woven fabrics with low surface density, and load carrying materials such as piezoelectric ceramic powder, piezoelectric polymer powder and other conductive auxiliary components; the intercalation material is placed between the laminations of the conventional carbon fiber lamination composite to obtain the composite which has high damping and high flexibility after the intercalation material is molded and cured. As the preparation method utilizes carriers, all functional components are distributed uniformly and the intercalation material is simple in a preparation technology; besides, being compatible with the conventional molding method of the composite, the preparation method is low in cost.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com