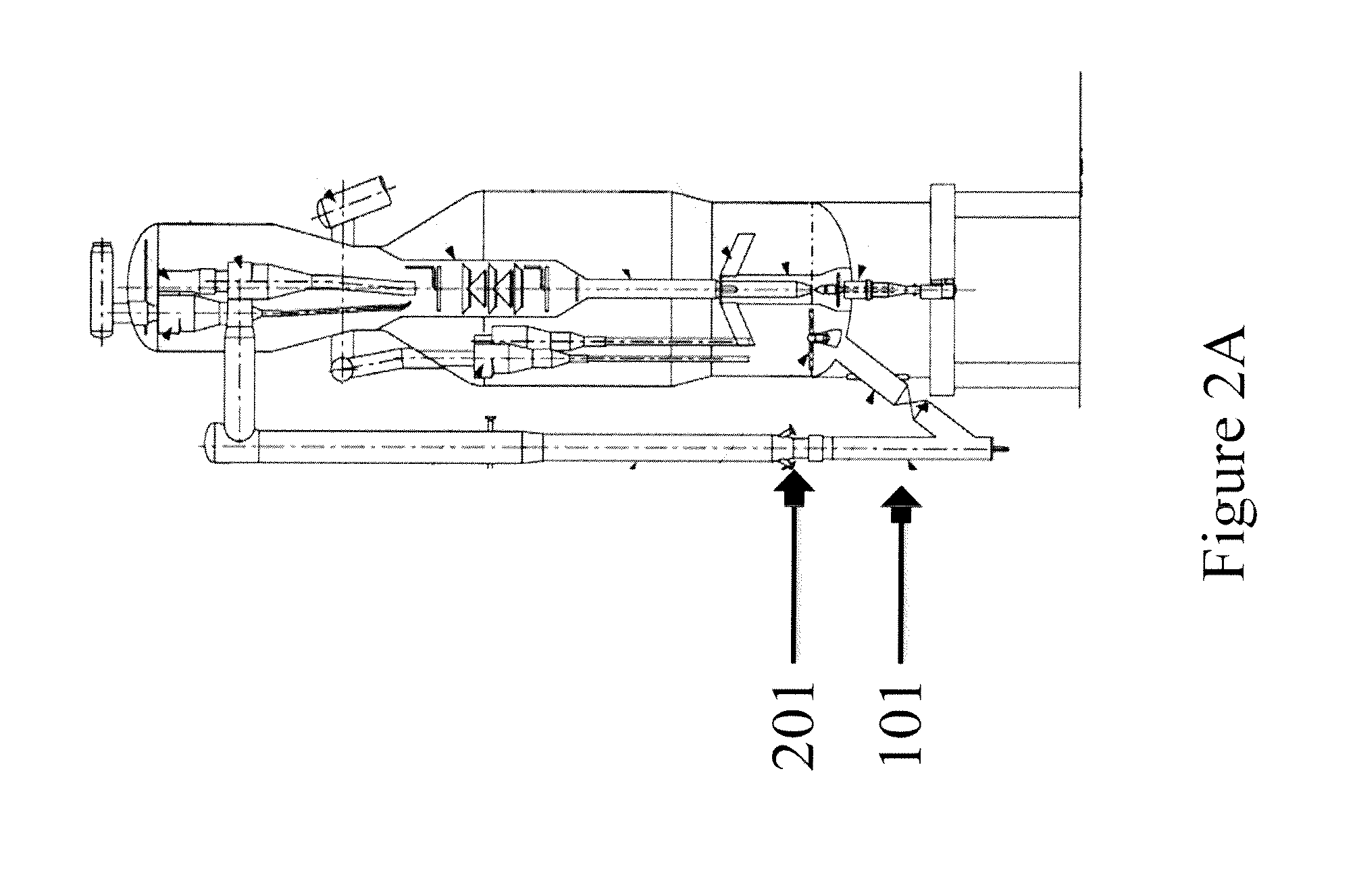
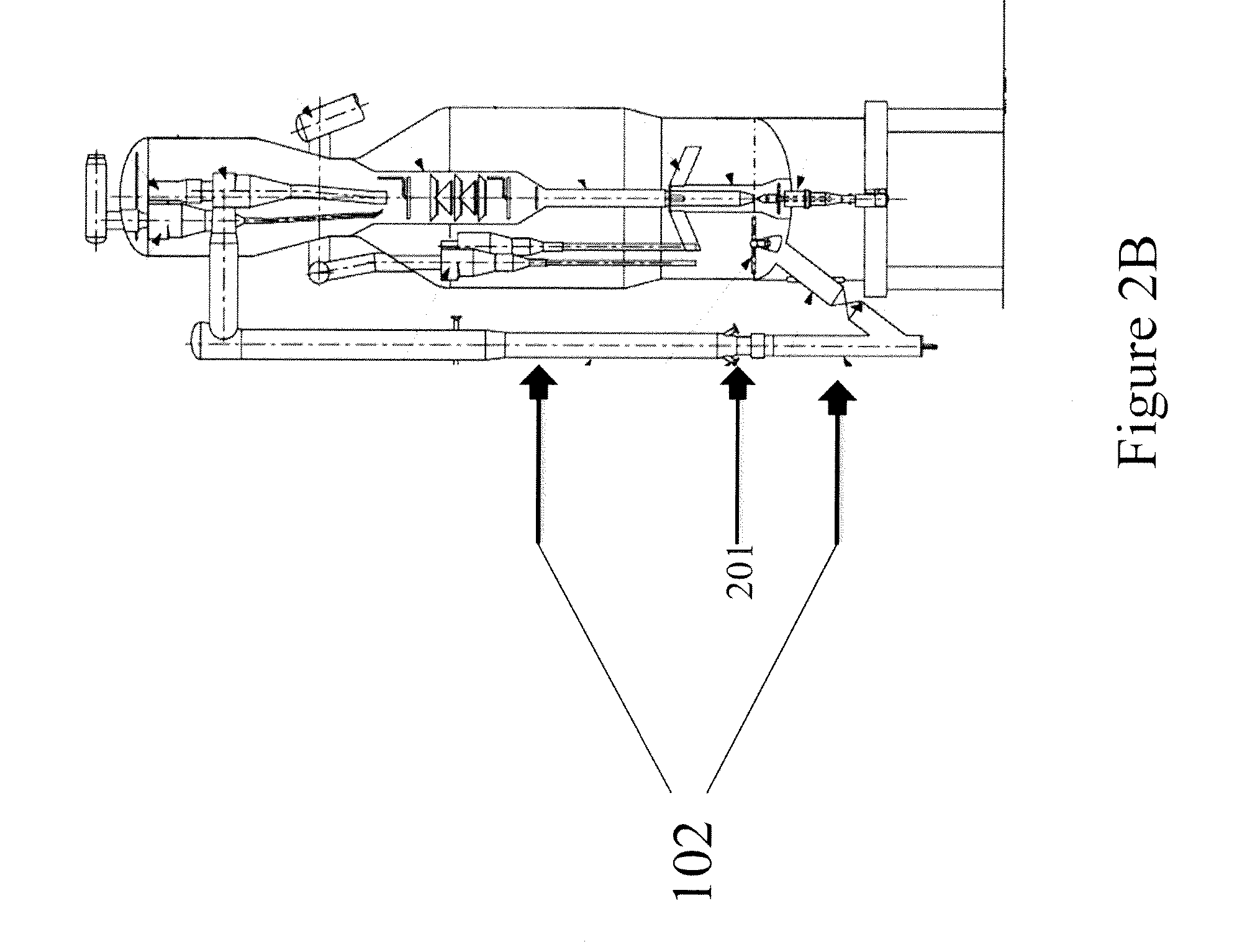
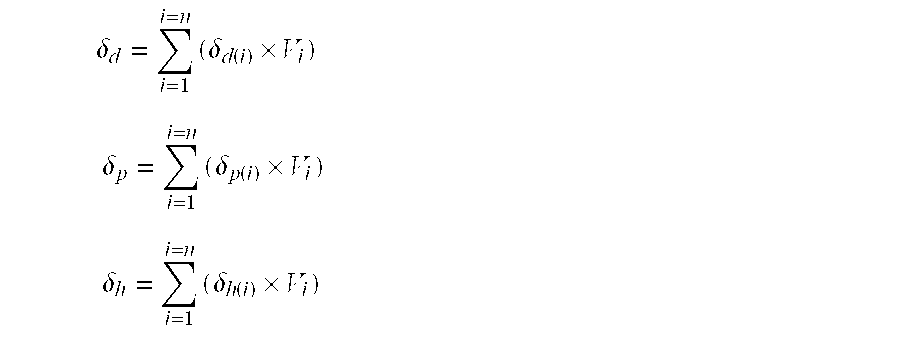Patents
Literature
145 results about "Distillates petroleum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Petroleum distillates are hydrocarbon solvents produced from crude oil. These solvents include mineral spirits, kerosene, white spirits, naphtha, and Stoddard solvent. Petroleum distillates are good for removal of heavy oil and grease, tar, and waxes.
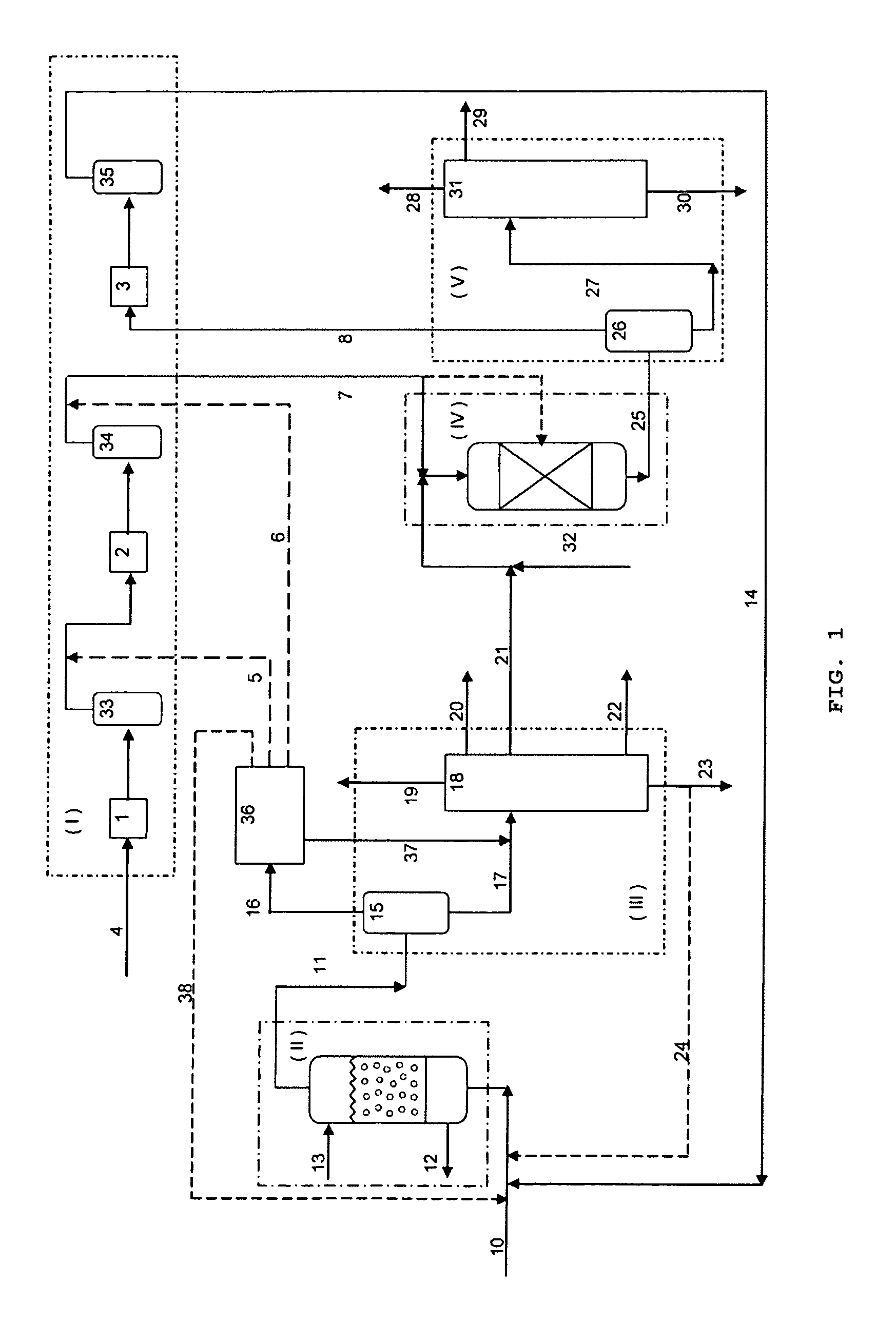
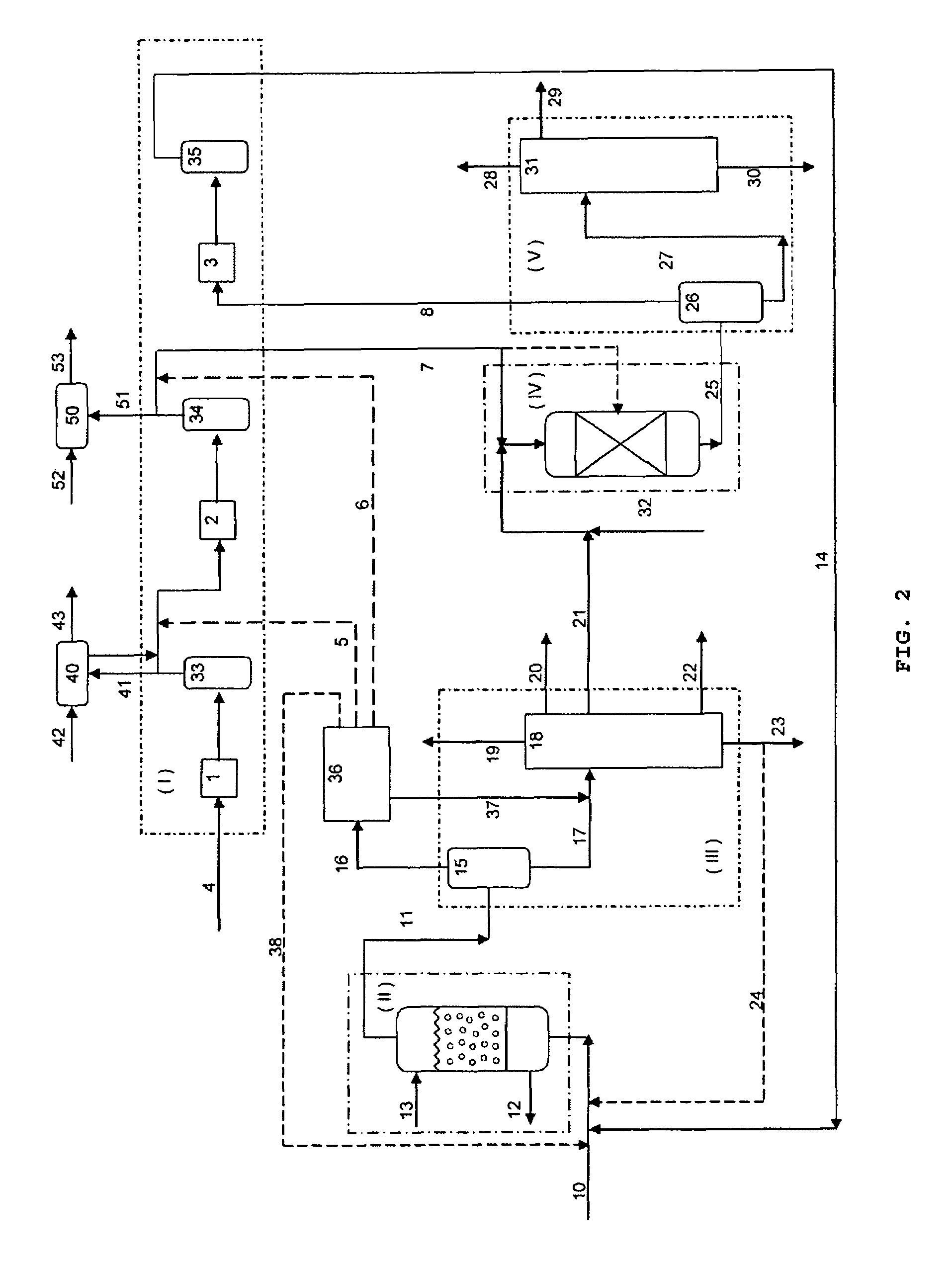
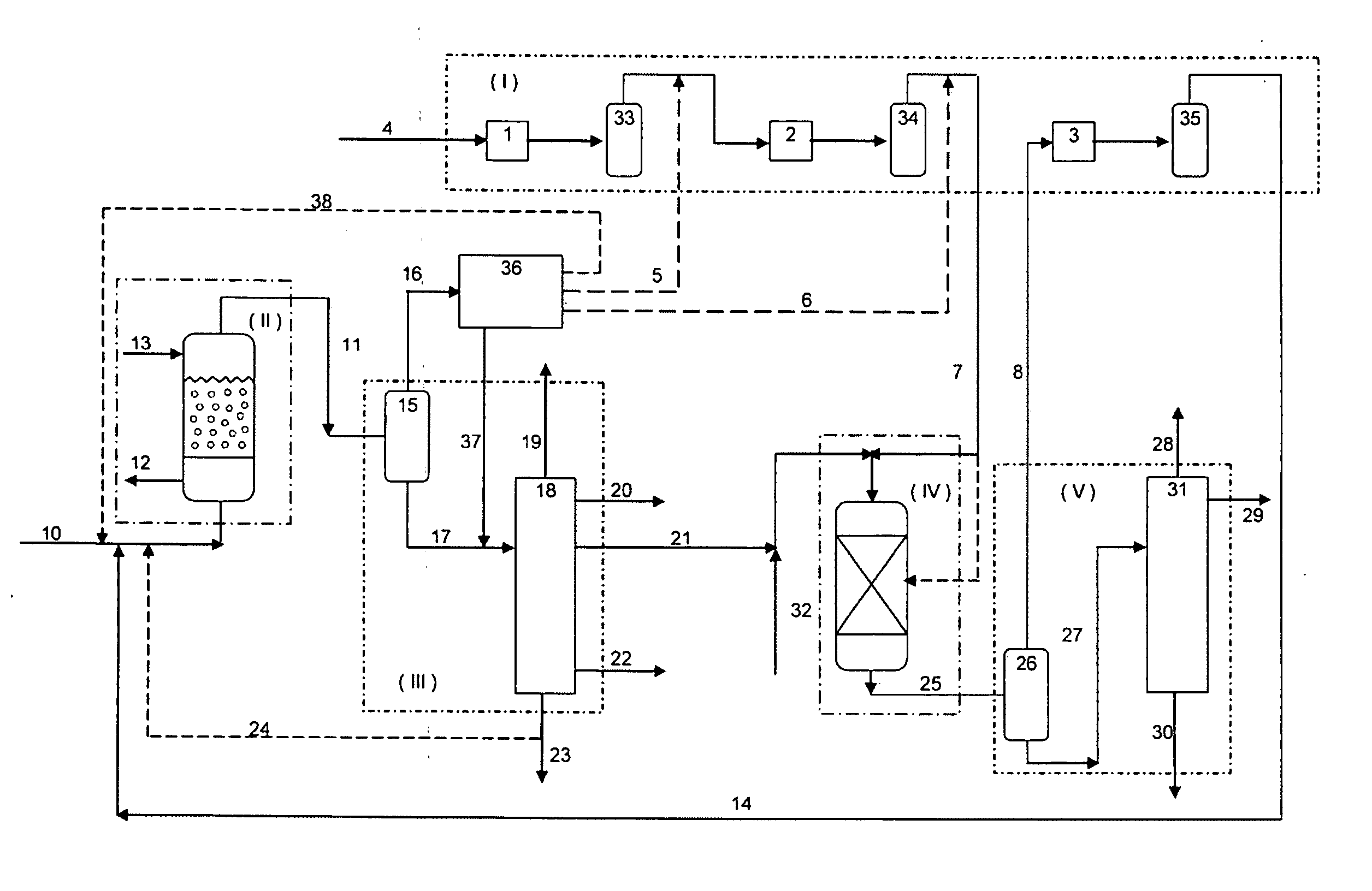
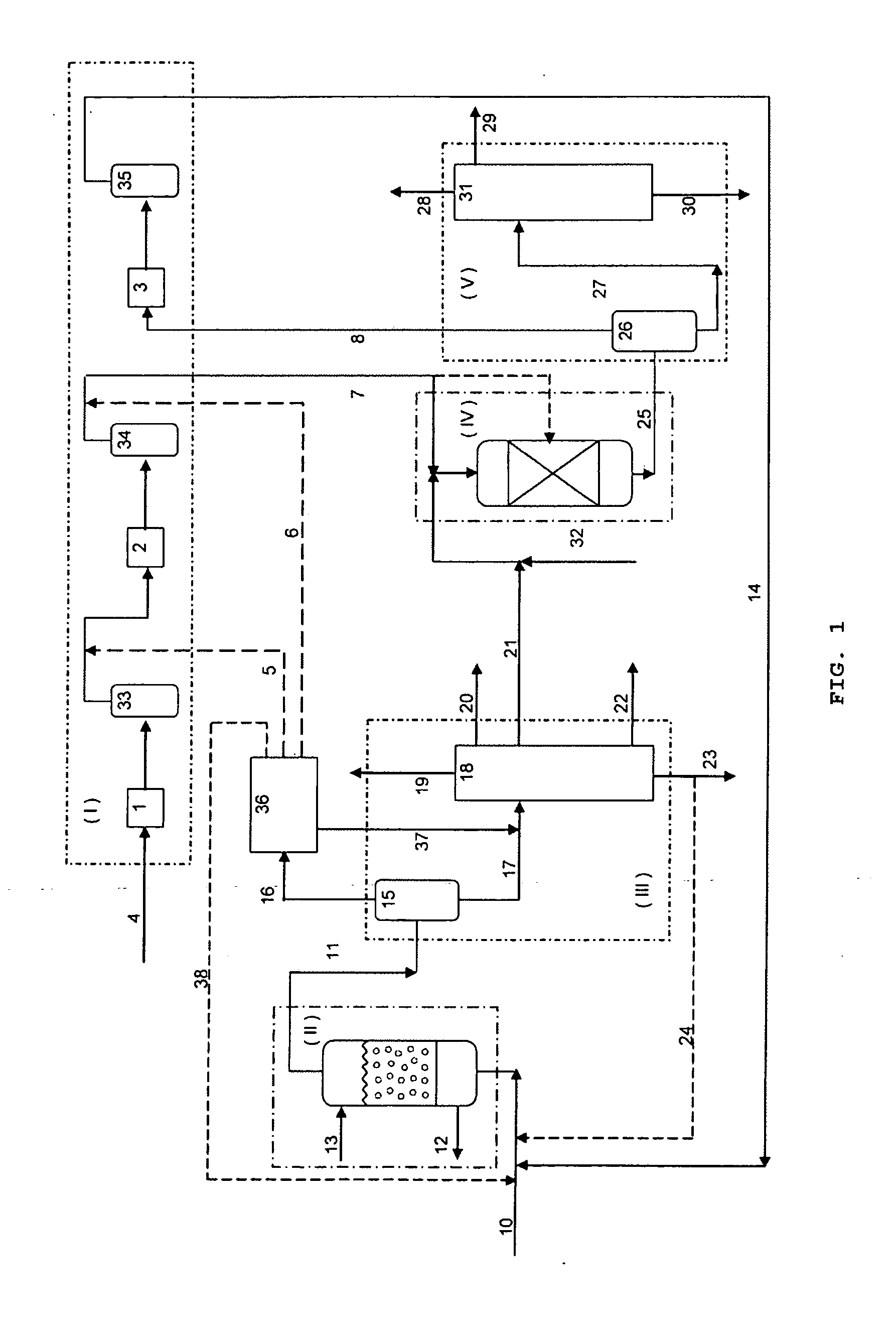
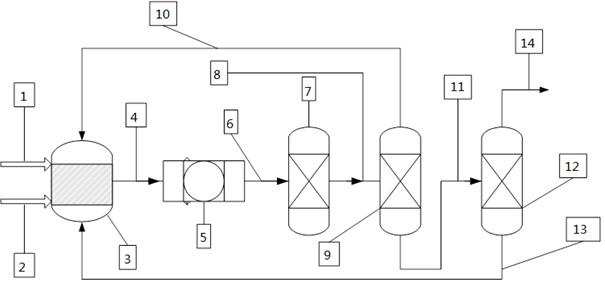
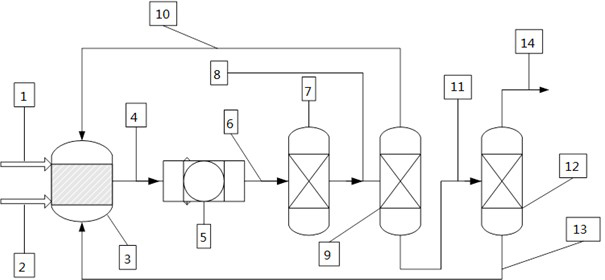
Catalytic multi-stage process for hydroconversion and refining hydrocarbon feeds
InactiveUS6190542B1Improve distillation yieldQuality improvementCatalyst activation/preparationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionLiquid productDistillates petroleum
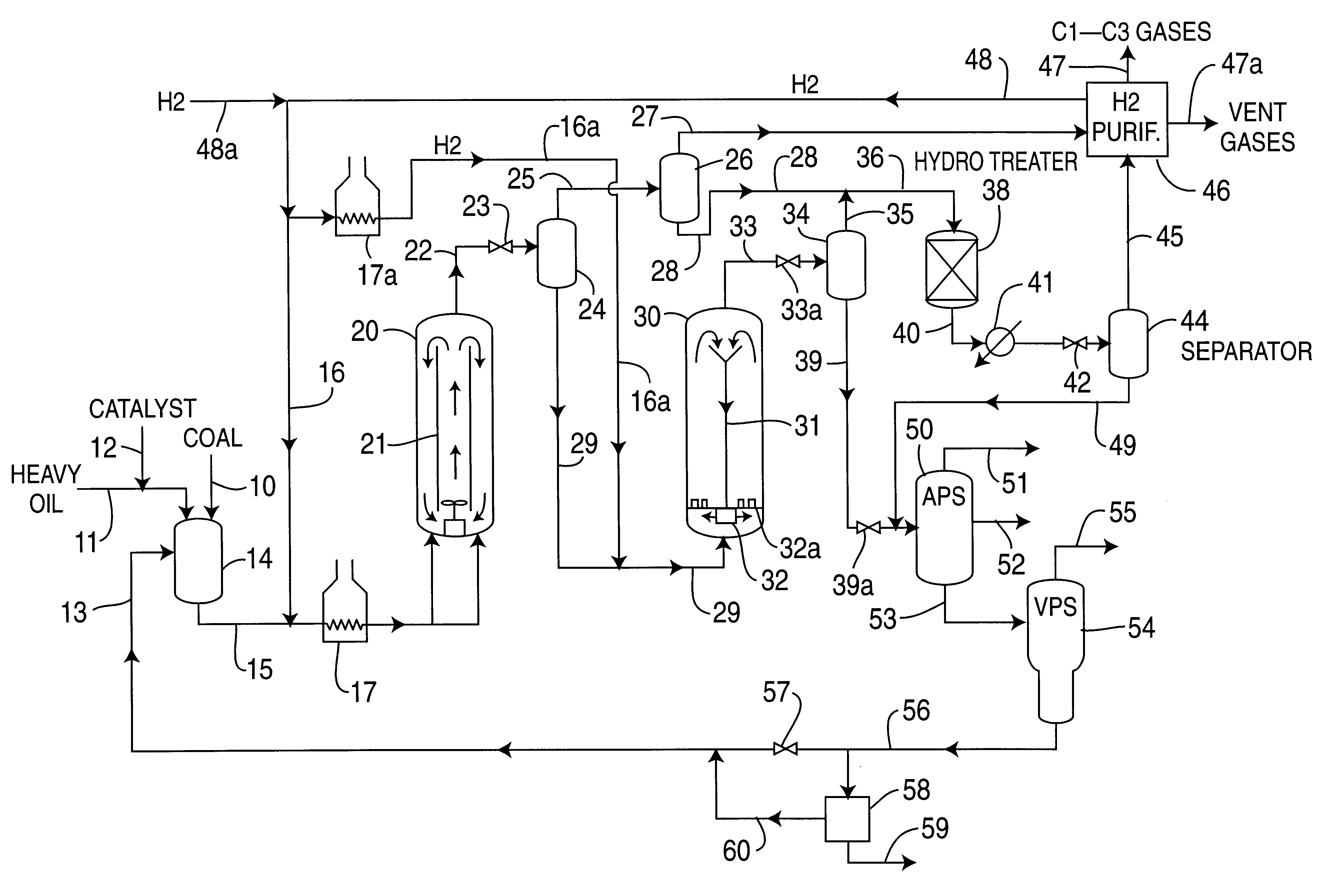
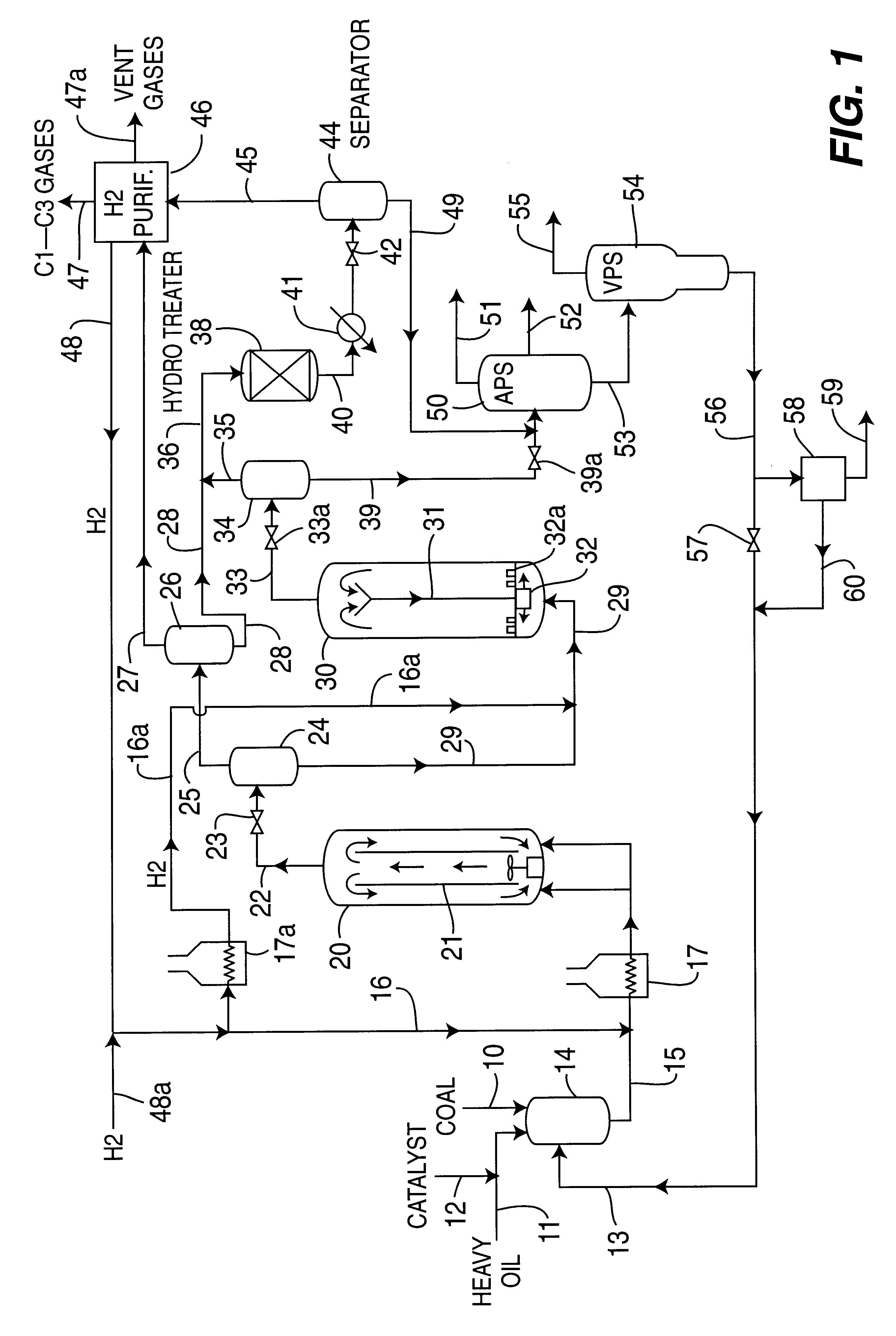
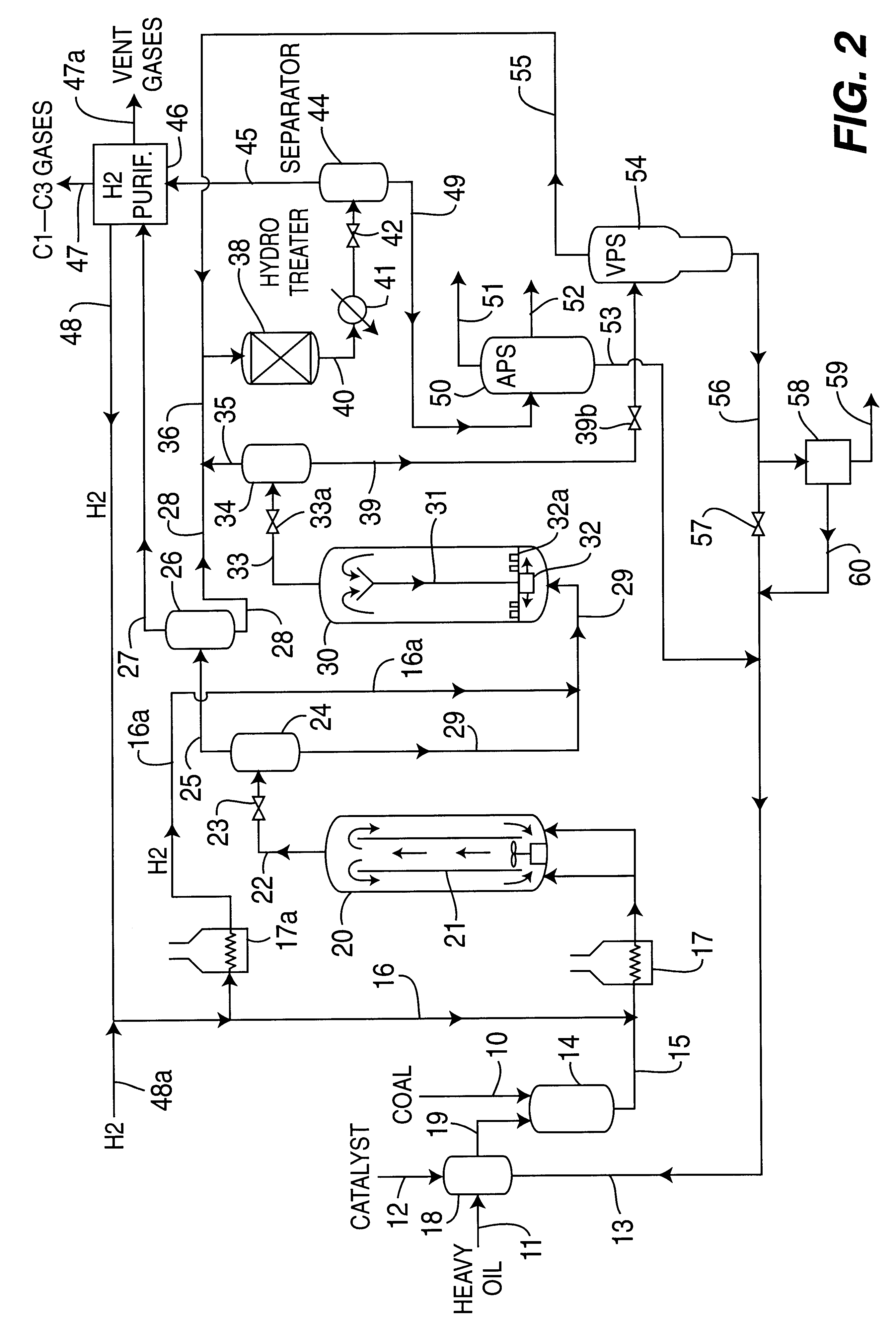
A multi-stage catalytic hydrogenation and hydroconversion process for heavy hydrocarbon feed materials such as coal, heavy petroleum fractions, and plastic waste materials. In the process, the feedstock is reacted in a first-stage, back-mixed catalytic reactor with a highly dispersed iron-based catalyst having a powder, gel or liquid form. The reactor effluent is pressure-reduced, vapors and light distillate fractions are removed overhead, and the heavier liquid fraction is fed to a second stage back-mixed catalytic reactor. The first and second stage catalytic reactors are operated at 700-850.degree. F. temperature, 1000-3500 psig hydrogen partial pressure and 20-80 lb. / hr per ft.sup.3 reactor space velocity. The vapor and light distillates liquid fractions removed from both the first and second stage reactor effluent streams are combined and passed to an in-line, fixed-bed catalytic hydrotreater for heteroatom removal and for producing high quality naphtha and mid-distillate or a full-range distillate product. The remaining separator bottoms liquid fractions are distilled at successive atmospheric and vacuum pressures, low and intermediate-boiling hydrocarbon liquid products are withdrawn, and heavier distillate fractions are recycled and further upgraded to provide additional low-boiling hydrocarbon liquid products. This catalytic multistage hydrogenation process provides improved flexibility for hydroprocessing the various carbonaceous feedstocks and adjusting to desired product structures and for improved economy of operations.
Owner:HEADWATERS CTL
Production of biological diesel oil by integrated hydrogenation
InactiveCN101029245AAchieve reliabilityAchieve economyBiofuelsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionDistillates petroleumBiodiesel
Production of biological diesel oil by integrated hydrogenation is carried out by mixing straight-run diesel oil with soya-bean, hydrogenation refinery reacting at 3.0-8.0MPa and 250-400degree and under existence of catalyst and converting vegetable oil into biological diesel oil. It's simple and cheap.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Methods of hydrotreating a mixture made up of oils of animal or vegetable origin and of petroleum cuts with quench injection of the oils on the last catalyst bed
ActiveUS20080173570A1Low costReduce use costCatalytic crackingHydrocarbon oil crackingDistillates petroleumVegetable oil
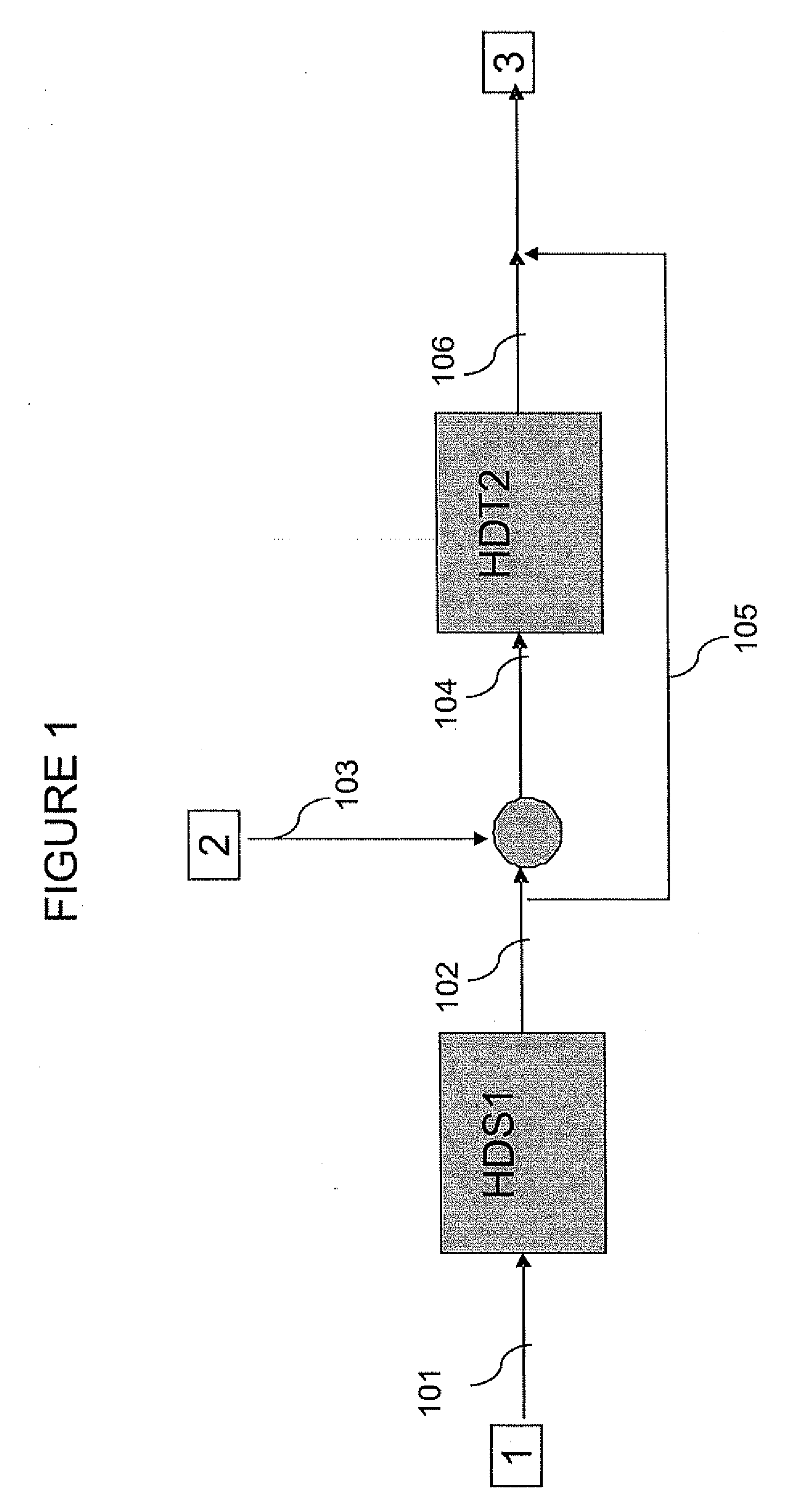
A hydrotreating method uses two catalyst beds with the introduction, on the last catalyst bed, of oils of animal or vegetable origin for co-treating a mixture made up of oils of vegetable or animal origin and of petroleum cuts (gas oil cuts (GO) and middle distillates) in order to produce gas oil effluents meeting specifications with an improved cetane number. The first catalyst bed is dedicated to only the deep desulfurization reactions (HDS1) of a petroleum type feed. The effluents of the first catalyst bed having an effluent sulfur content below or equal to 50 mg / kg are separated into two streams. The first stream, which is predominant, is sent to the gas oil pool. The second stream is mixed with oils of vegetable or animal origin. The resultant oil-petroleum cut mixture is then subjected to a milder hydrotreatment (HDT2). The effluents obtained at the outlet of the second catalyst bed can optionally be mixed with the predominant stream from the first bed. The process economy, the tolerance to the specifications relative to oils of animal or vegetable origin and the quality of the products obtained are thus greatly improved.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Method and apparatus for measuring the properties of petroleum fuels by distillation
InactiveUS20070050154A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityChemical property predictionMaterial thermal analysisBoiling pointDistillation
It is a purpose of this invention to accurately measure the properties of petroleum and petroleum fractions from a small volume of sample oil in a short period of time with less cost and energy for the analysis by vaporizing and distilling the respective components contained in the sample to be measured by a distillation apparatus. The components in the sample oil are first separated and vaporized by the distillation apparatus and the boiling point distribution of the respective components is measured. The property estimation means is equipped with a property estimation model for evaluating the property estimate value outputted from the property estimation model. The method is incorporated into standard or otherwise any distillation test apparatus to provide accurate measure of the thermodynamic and transport properties of undefined multicomponent mixtures such as crude oil, petroleum fractions, gas condensates and the like.
Owner:KWAIT UNIV
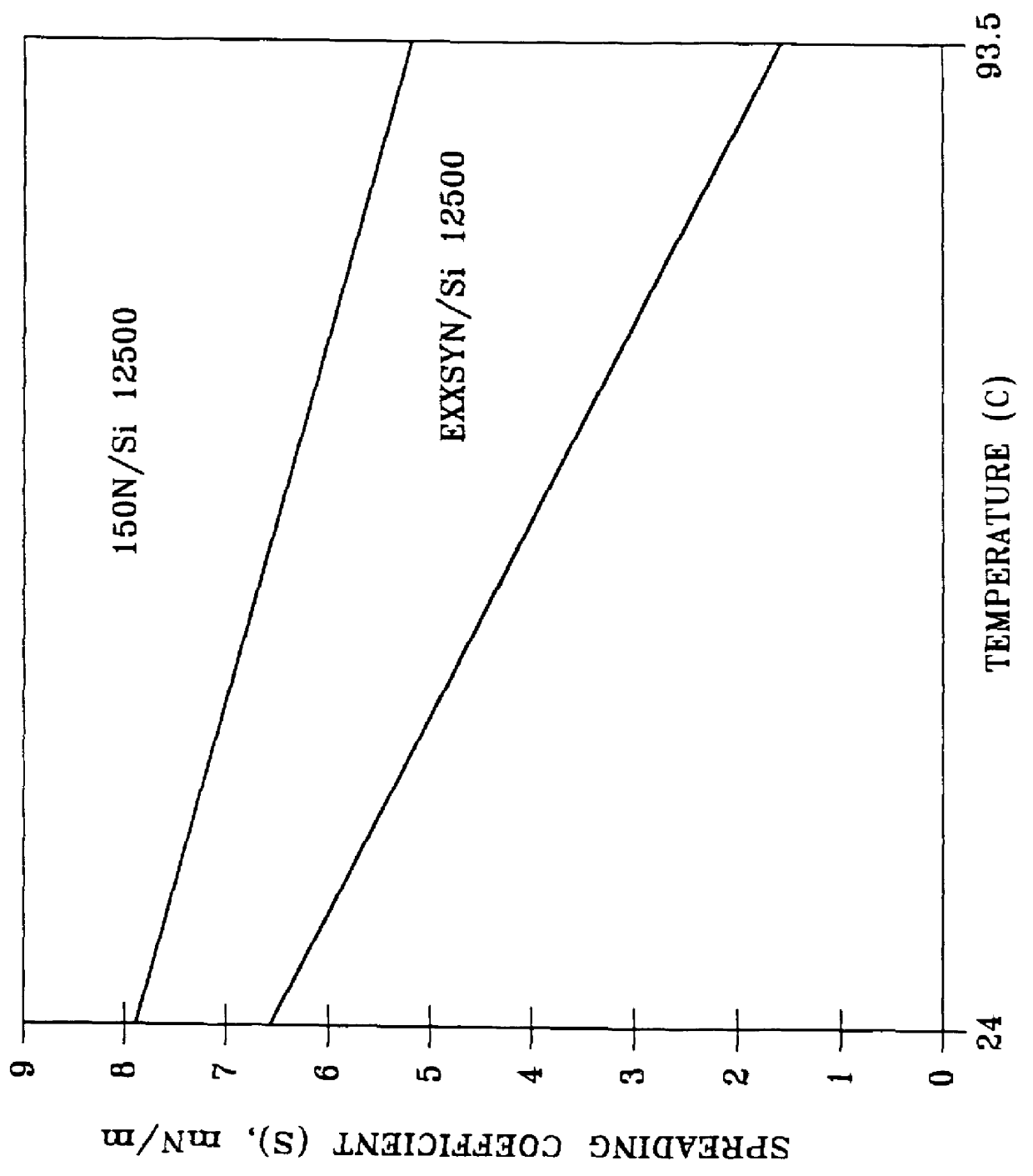
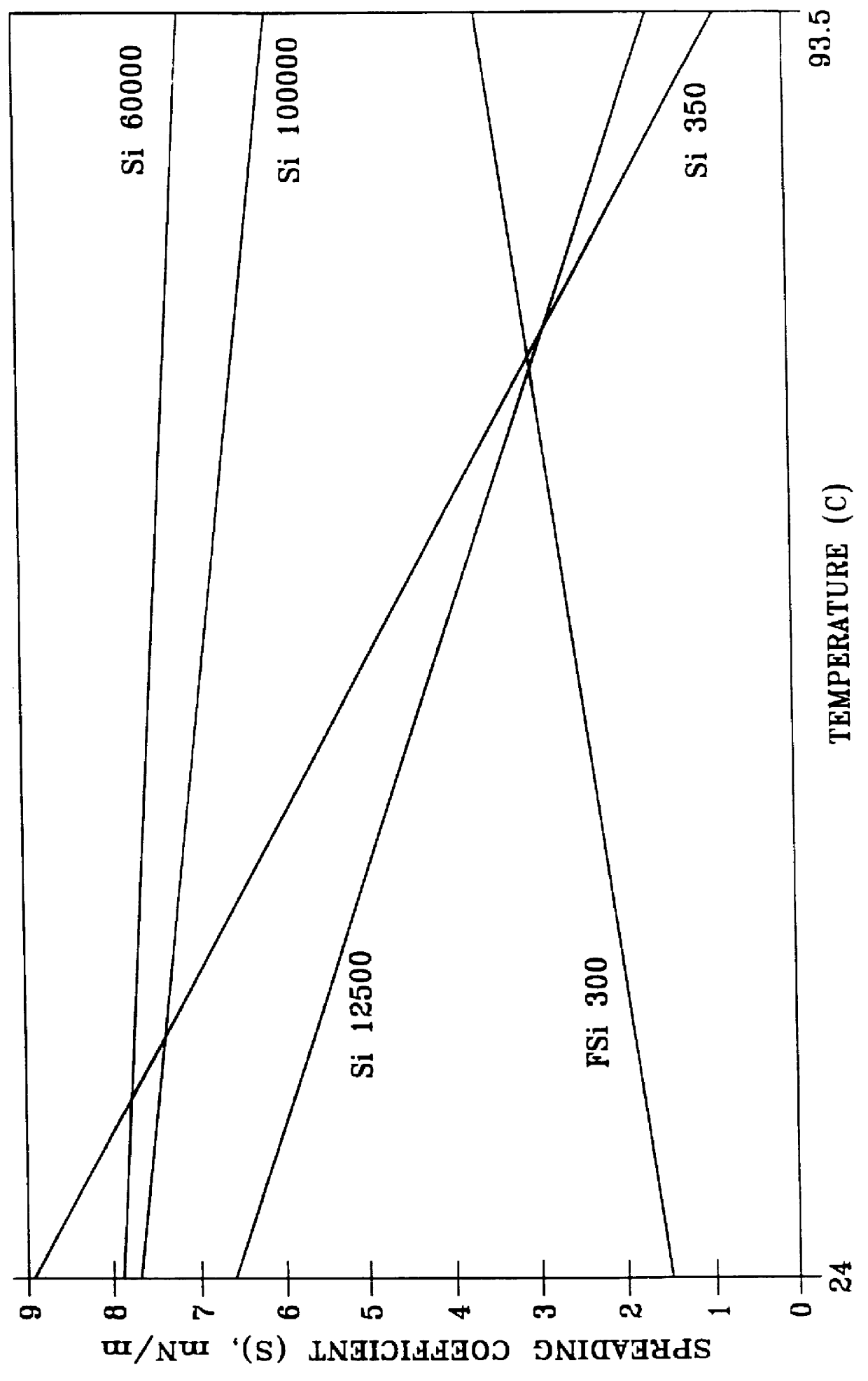
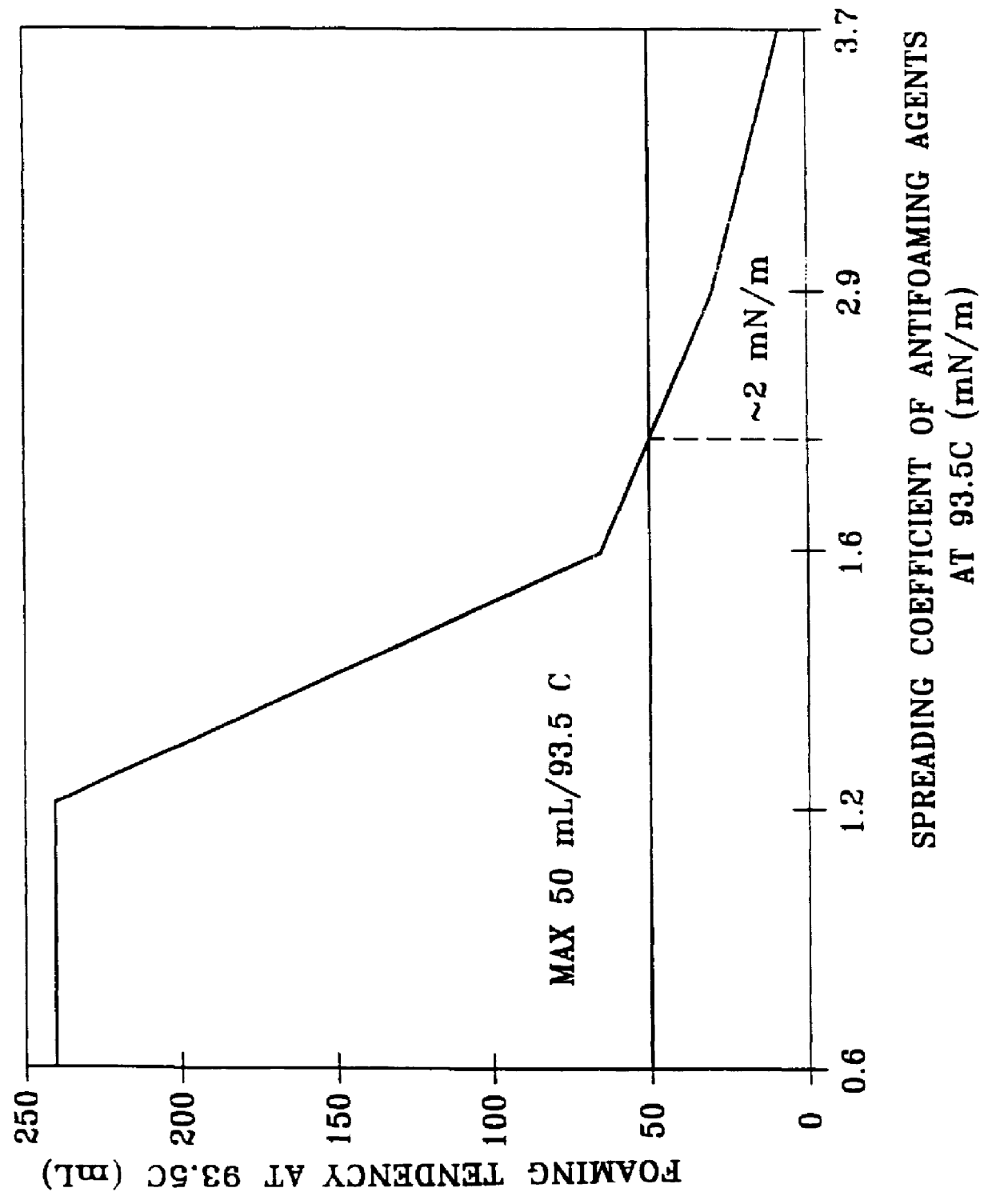
Method for reducing foaming of lubricating oils
Foaming of a lube oil comprising a base stock derived from wax isomeration and an additive package is effectively reduced to within specification limits of 50 ml / ml over a temperature range of from at least 24 DEG C. to 93.5 DEG C. by adding to the oil an effective amount of an antifoamant exhibiting a spreading coefficient of at least about 2 mN / m. This has been found to be particularly effective in reducing foaming of lube oils containing a mixture of a wax isomerate oil and a petroleum oil fraction. Antifoamants typically used with conventional lube oils containing one or more petroleum fraction base stocks, but which do not exhibit a spreading coefficient of at least 2 mN / m with the wax isomerate containing oil, have been found not to be effective in reducing the foaming of the oil.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
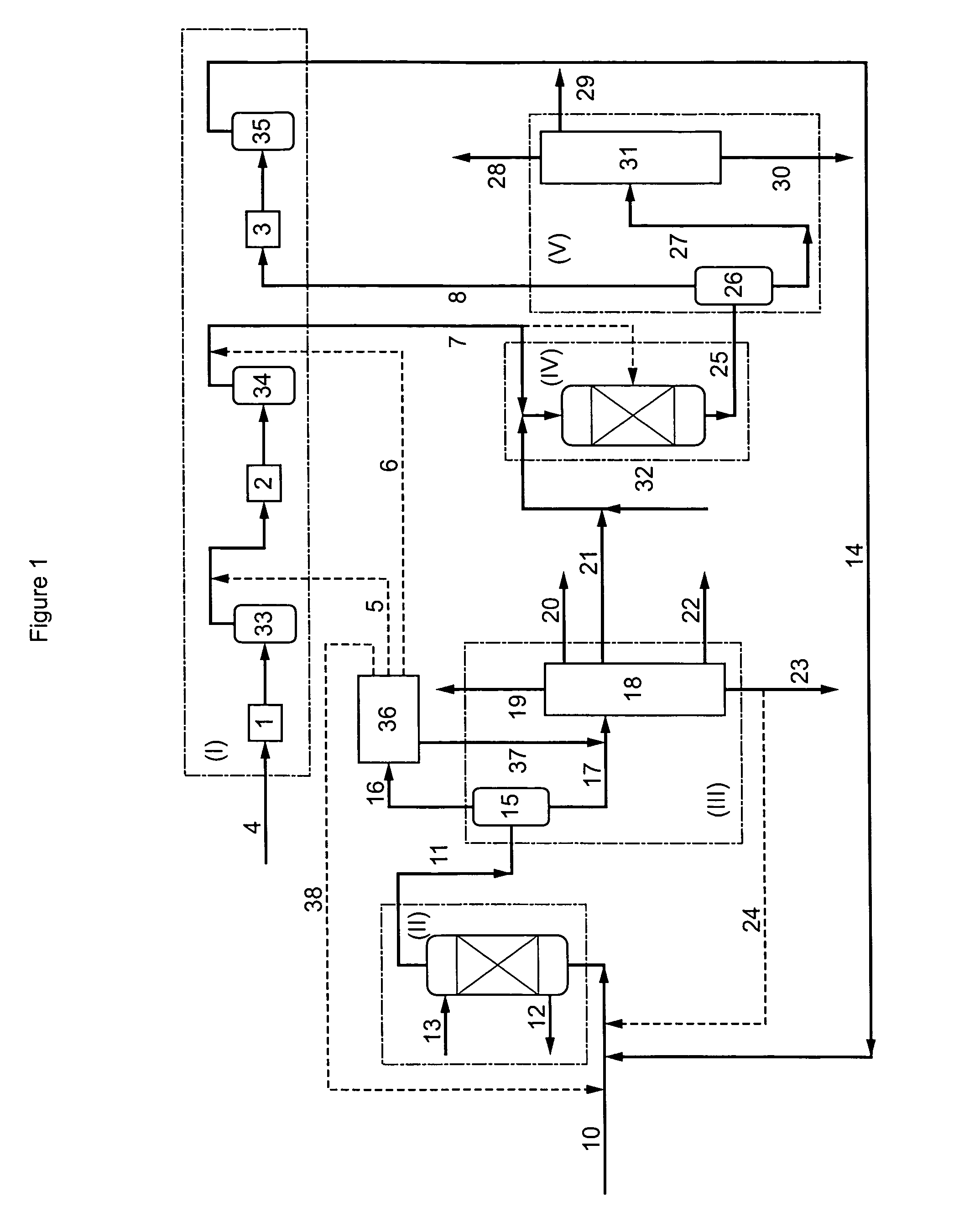
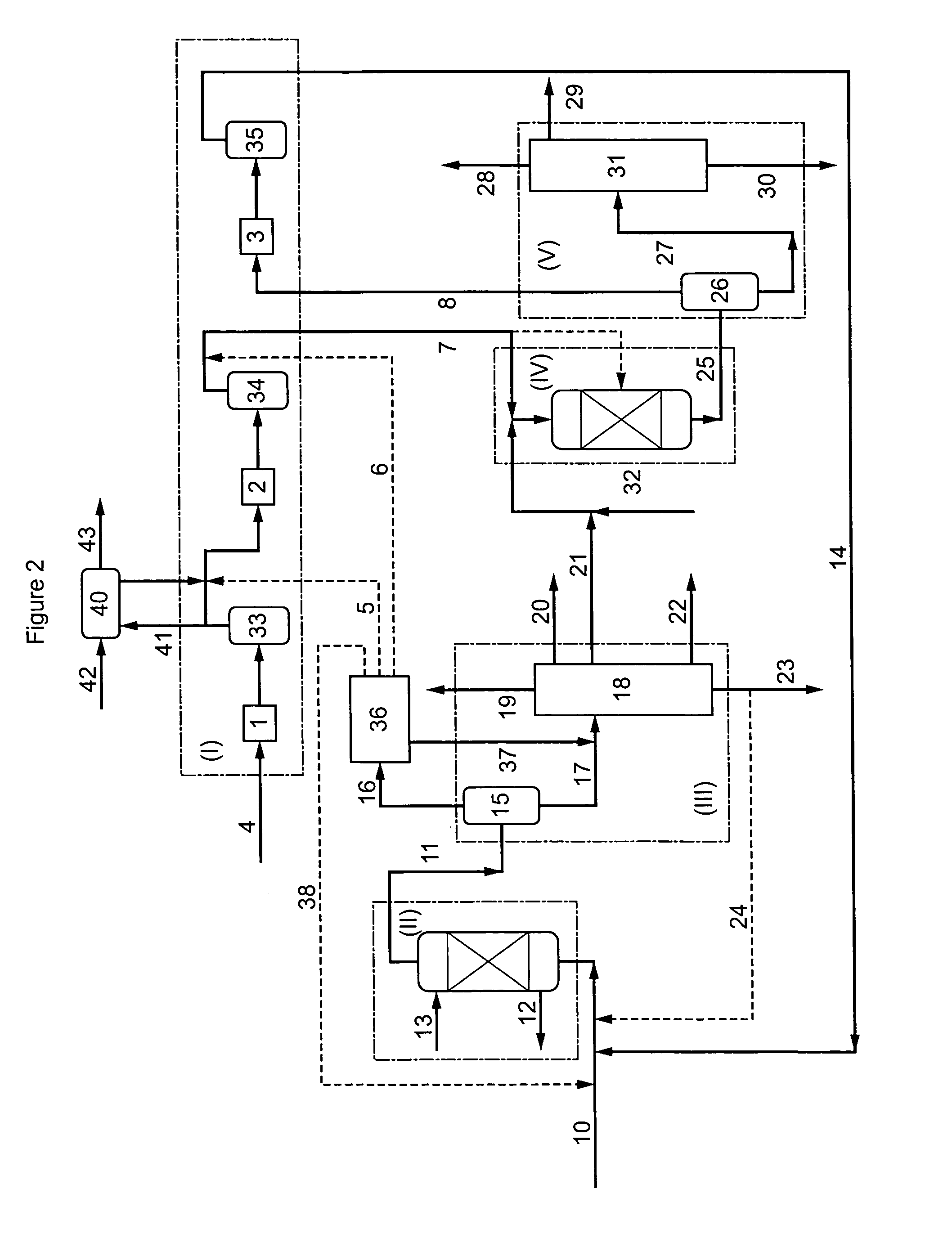
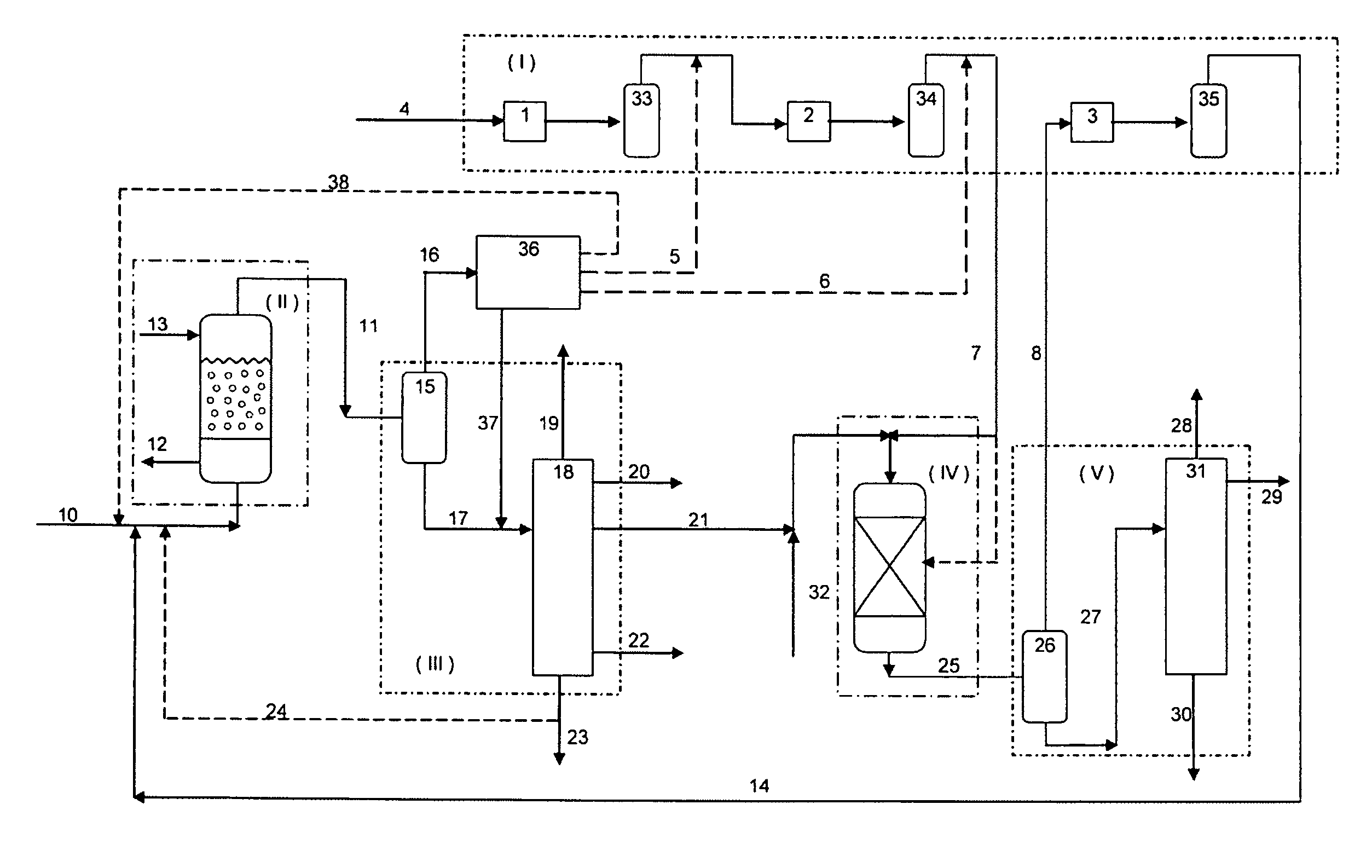
Process and installation for conversion of heavy petroleum fractions in a fixed bed with integrated production of middle distillates with a very low sulfur content
InactiveUS20080093262A1Low investment costEasy to useHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionHydrocarbon oil crackingDistillates petroleumNaphtha
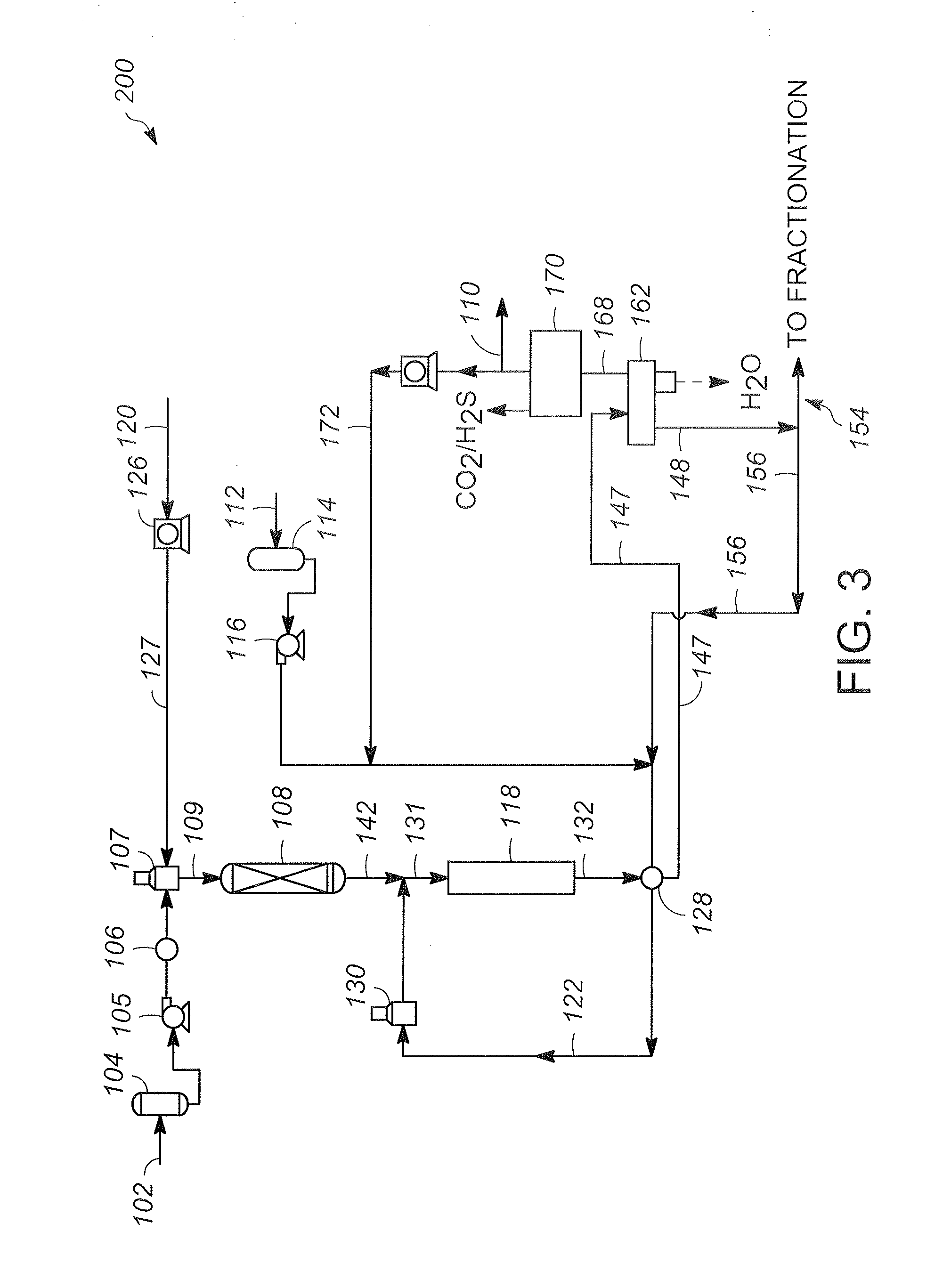
This invention relates to a process and an installation for treatment of a heavy petroleum feedstock, of which at least 80% by weight has a boiling point of greater than 340° C., whereby the process comprises the following stages:(a) Hydroconversion in a fixed-bed reactor operating with an upward flow of liquid and gas, whereby the net conversion in products boiling below 360° C. is from 10 to 99% by weight;(b) Separation of the effluent obtained from stage (a) into a gas containing hydrogen and H2S, a fraction comprising the gas oil, and optionally a fraction that is heavier than the gas oil and a naphtha fraction;c) Hydrotreatment by contact with at least one catalyst of at least the fraction comprising the gas oil obtained in stage (b);d) Separation of the effluent obtained at the end of stage (c) into a gas containing hydrogen and at least one gas oil fraction having a sulfur content of less than 50 ppm, preferably less than 20 ppm, and more preferably still less than 10 ppm,the hydroconversion stage (a) being conducted at a pressure P1 and the hydrotreatment stage (c) being conducted at a pressure P2, the difference ΔP=P1−P2 being at least 2 MPa, the hydrogen supply for the hydroconversion (a) and hydrotreatment (c) stages being ensured by a single compression system with n stages.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Process to produce low sulfur catalytically cracked gasoline without saturation of olefinic compounds
ActiveUS20090145807A1Reduce sulfur contentLow sulfurTreatment with plural serial stages onlyTreatment with hydrotreatment processesDistillates petroleumHydrogen
The invention relates to a process for the desulfurization of a gasoline fraction with high recovery of olefins and reduced loss of Research Octane Number (RON). A petroleum fraction is contacted with hydrogen and a commercially available hydrodesulfurization catalyst under mild conditions with to remove a first portion of the sulfur present, and is then contacted with an adsorbent for the removal of additional sulfur.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Process and installation for conversion of heavy petroleum fractions in a boiling bed with integrated production of middle distillates with a very low sulfur content
ActiveUS7704377B2Low costTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyCoke ovensDistillates petroleumNaphtha
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Process and installation for conversion of heavy petroleum fractions in a boiling bed with integrated production of middle distillates with a very low sulfur content
ActiveUS20070209965A1Low investment costOptimizing operating pressureTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyCoke ovensDistillates petroleumNaphtha
This invention relates to a process and an installation for treatment of a heavy petroleum feedstock, of which at least 80% by weight has a boiling point of greater than 340° C., whereby the process comprises the following stages: (a) hydroconversion in a boiling-bed reactor operating with a rising flow of liquid and gas, conversion in % by weight of the fraction having a boiling point of greater than 540° C. being from 10 to 98% by weight; (b) separation of the effluent obtained from stage (a) into a gas containing hydrogen and H2S, a fraction comprising the gas oil and optionally a fraction that is heavier than gas oil and a naphtha fraction; c) hydrotreatment by contact with at least one catalyst of at least the fraction comprising the gas oil obtained in stage (b); d) separation of the effluent obtained at the end of stage (c) into a gas containing hydrogen and at least one gas oil fraction having a sulfur content of less than 50 ppm, preferably less than 20 ppm, and more preferably less than 10 ppm, the hydroconversion stage (a) being conducted at a pressure P1 and the hydrotreatment stage (c) being conducted at a pressure P2, the difference ΔP=P1−P2 being at least 3 MPa, hydrogen supply for the hydroconversion (a) and hydrotreatment (c) stages being ensured by a single compression system with n stages.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Process for preparing fraction oil hydrogenation treatmnt catalyst
InactiveCN1458232APromote formationModulation of surface propertiesHydrocarbon oils refiningDistillates petroleumActive component
The preparation process of fraction oil hydrogenation treatment catalyst includes assistant adding modification of gamma-alumina precursor and subsequent conventional preparation process. The fraction oil hydrogenation treatment catalyst includes gamma-alumina precursoe prepared through carbonation process, aluminum nitrate process, aluminum sulfate process or aluminum chloride process; F an / or Bas assistant and W and Ni as active component. Compared with available technology, the present invention has the advantages of simple preparation process, low cost, low power consumption, and excellent catalyst performance. The catalyst of the present invention is suitable for hydrogenation treatment of 130-390 deg.c fraction oil.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
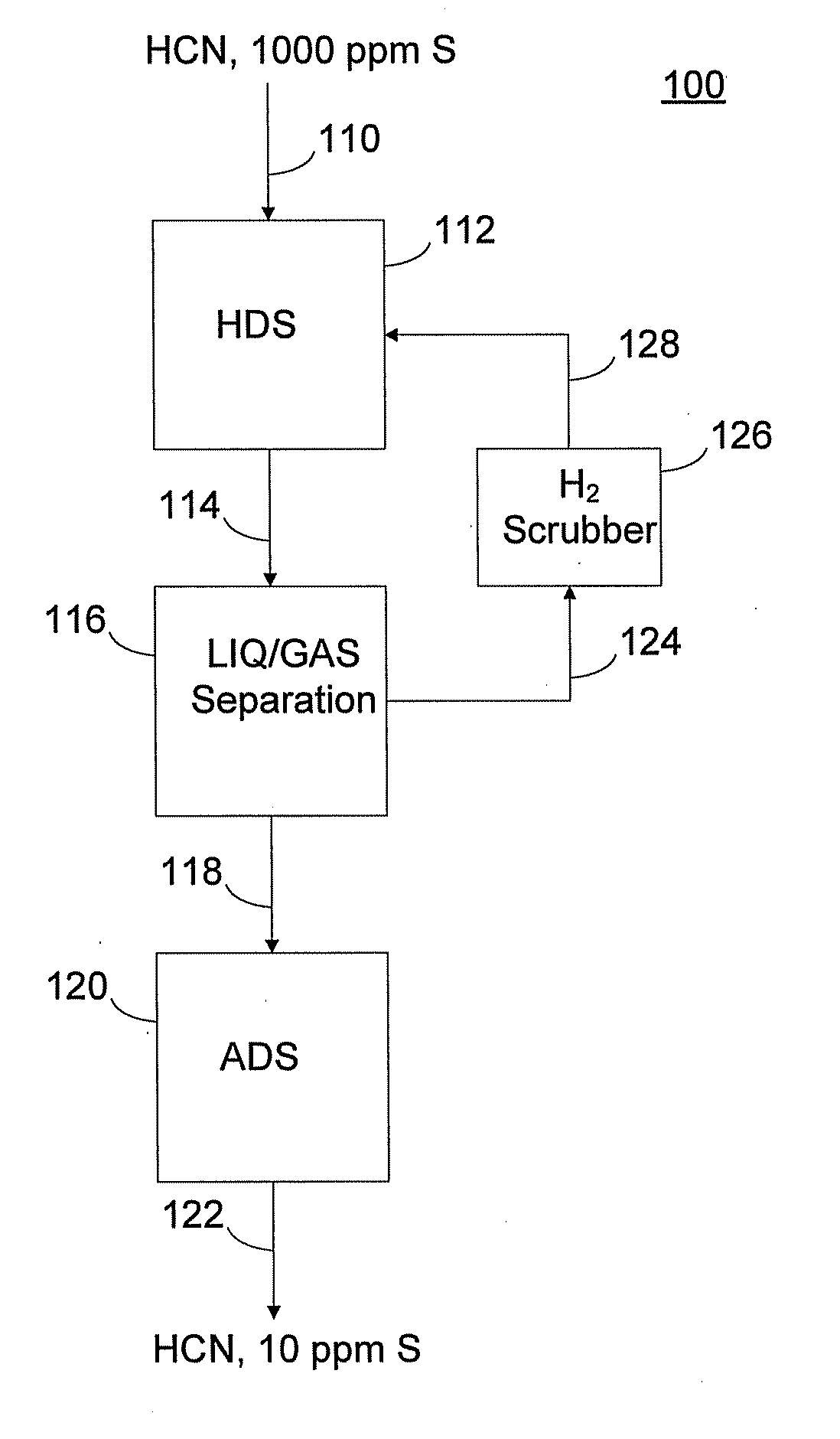
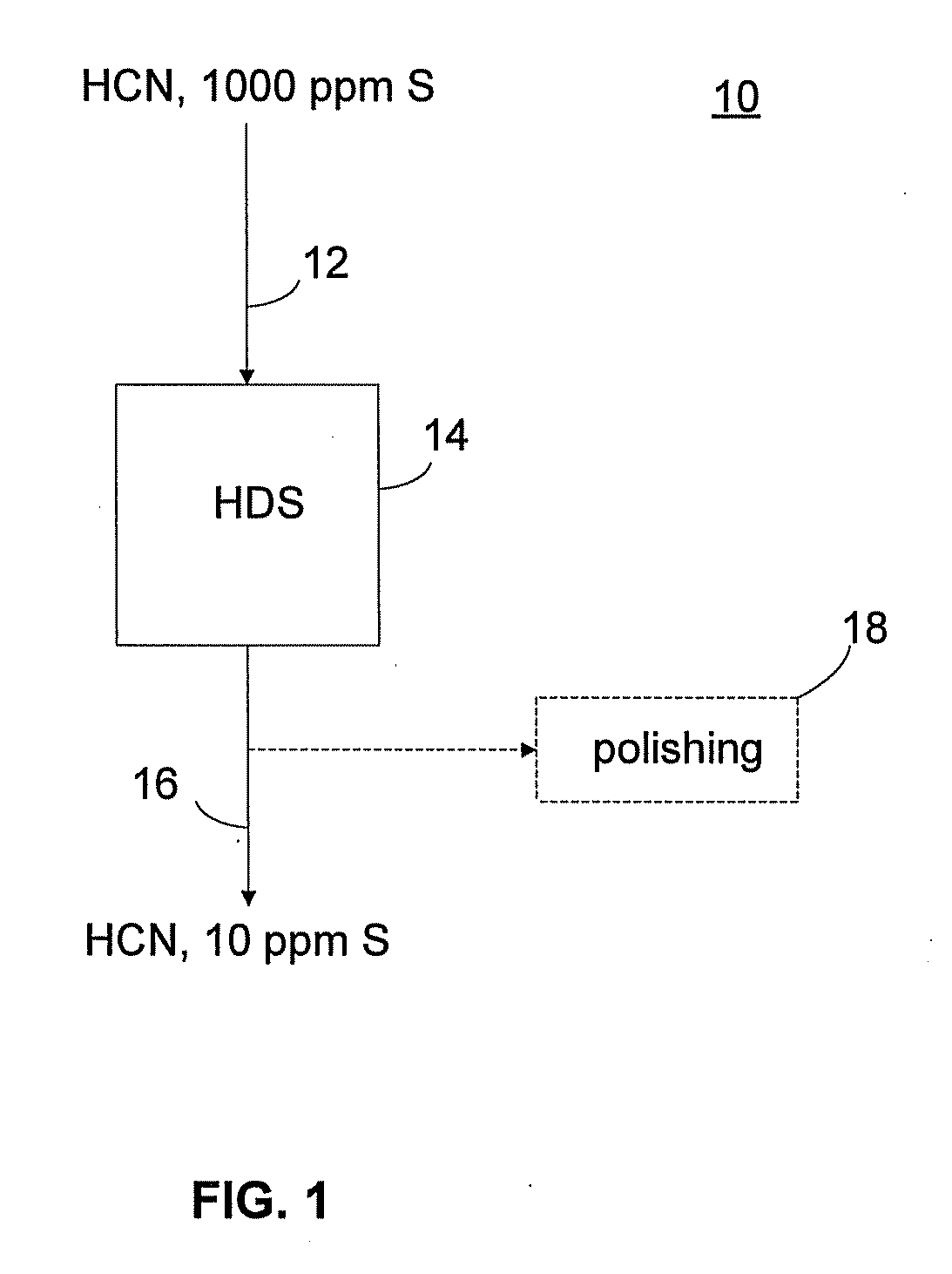
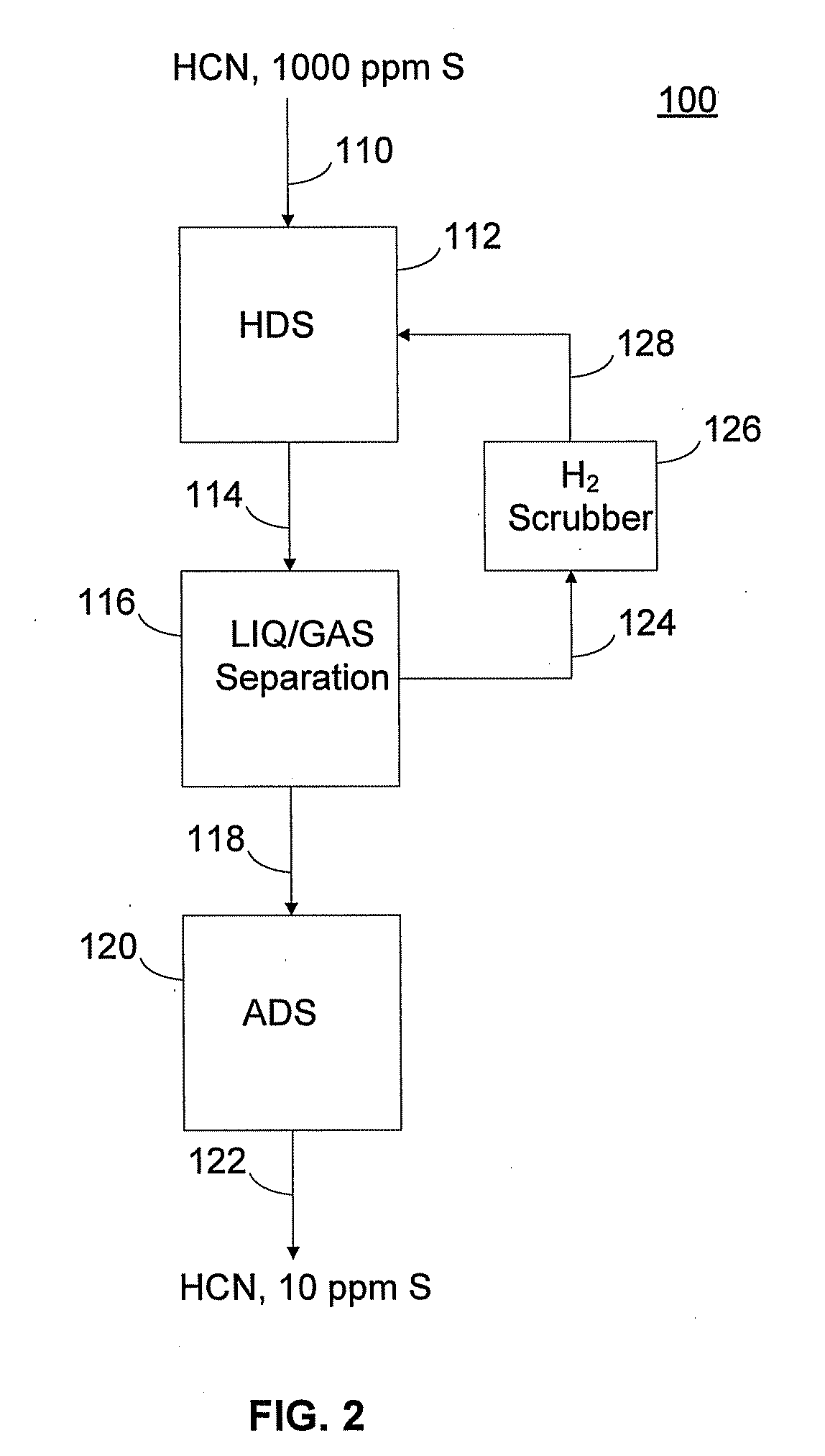
Method and apparatus for stripping sulfur-containing compounds from hydrocarbon feed stock in hydrorefining of petroleum distillates
InactiveUS7001503B1Reduce contentSimple structureHydrocarbon oil crackingTreatment with hydrotreatment processesDistillates petroleumHydrogen
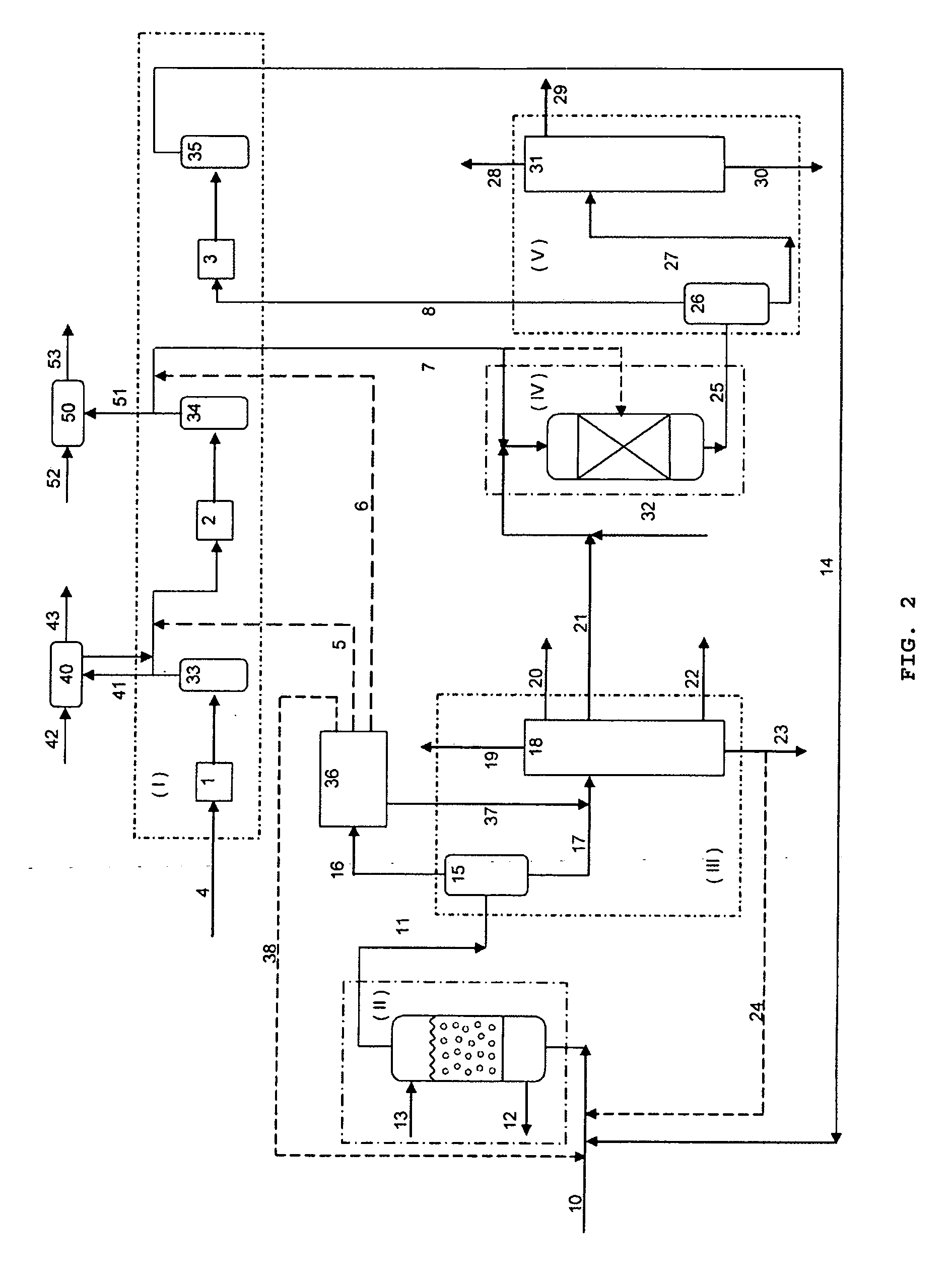
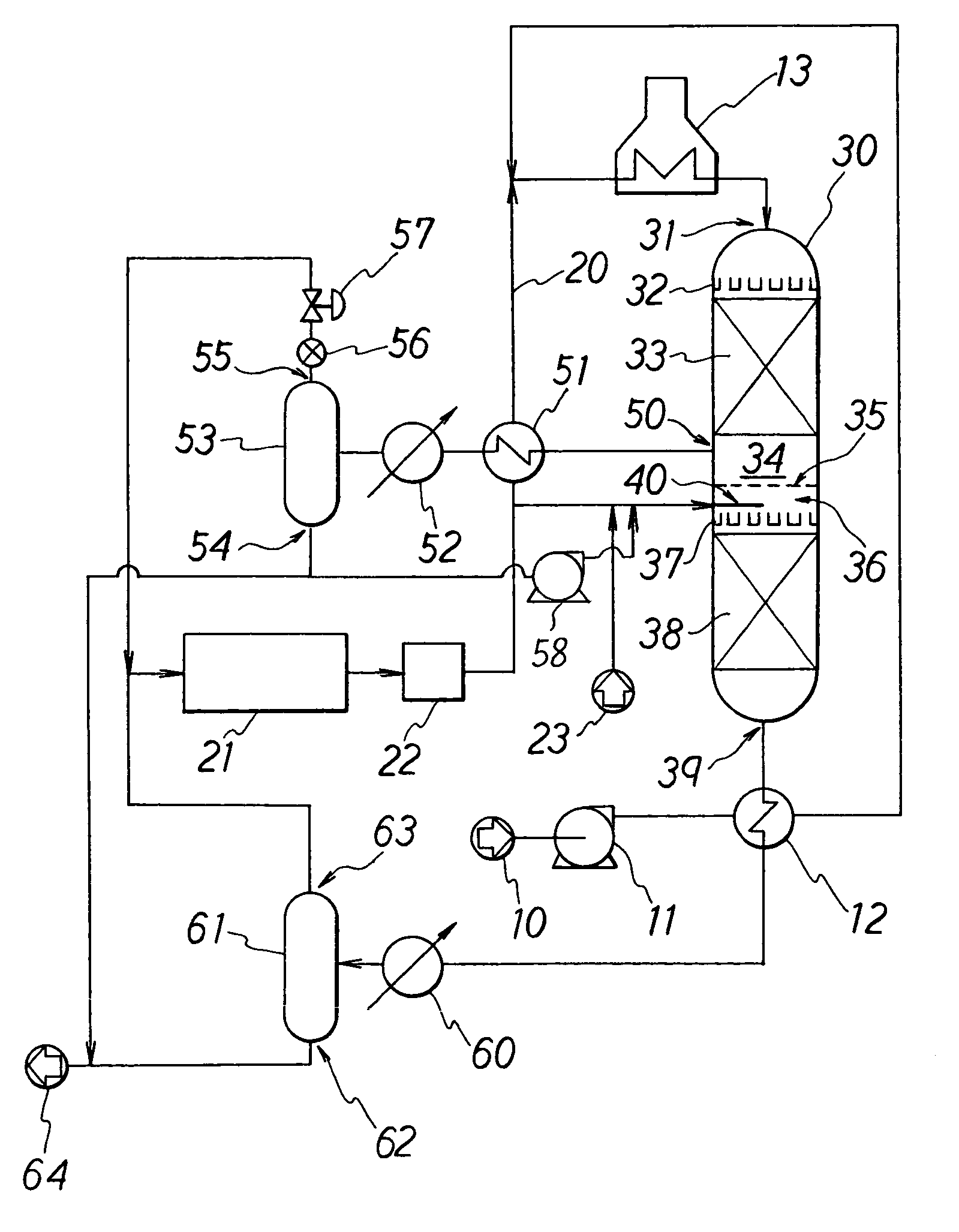
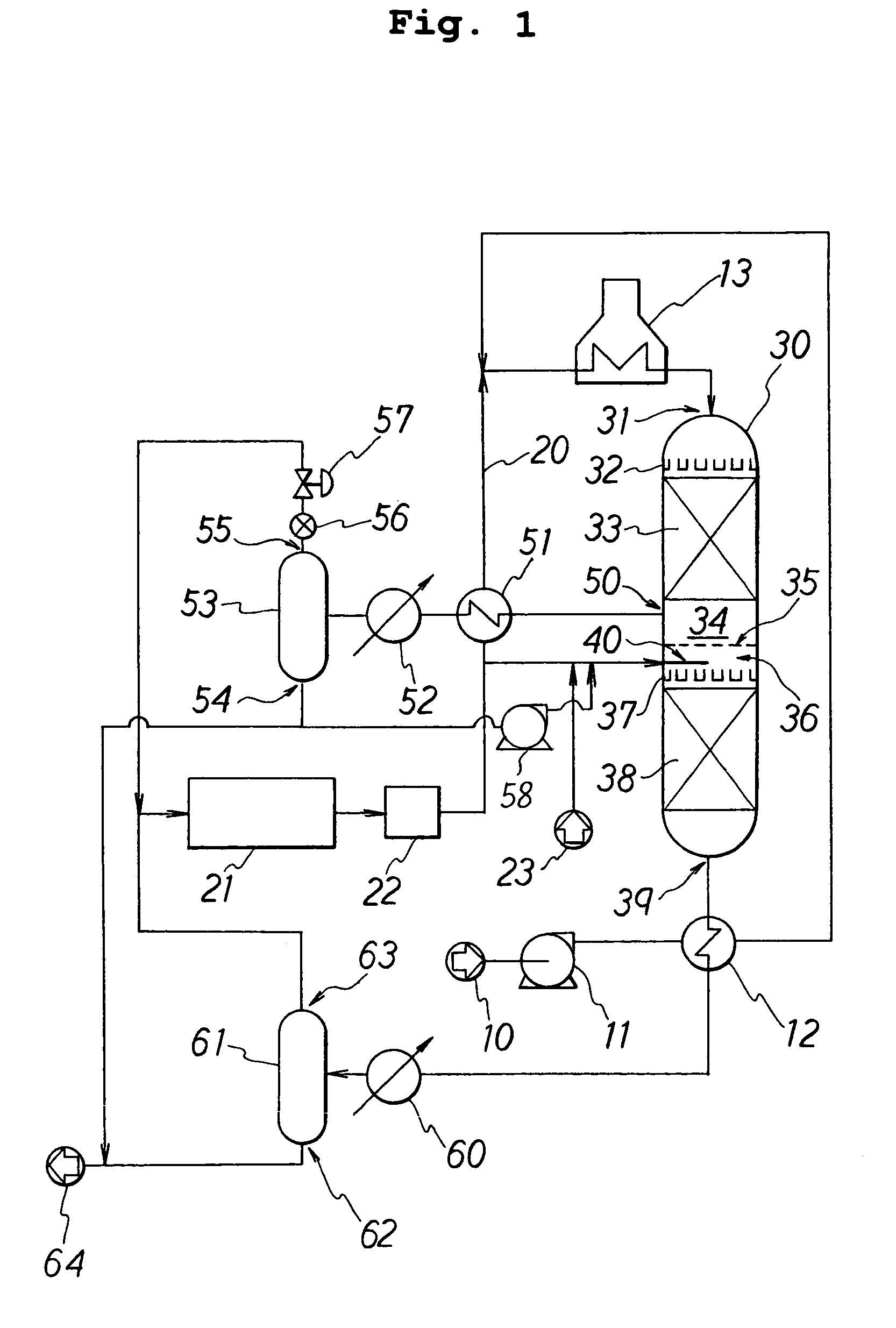
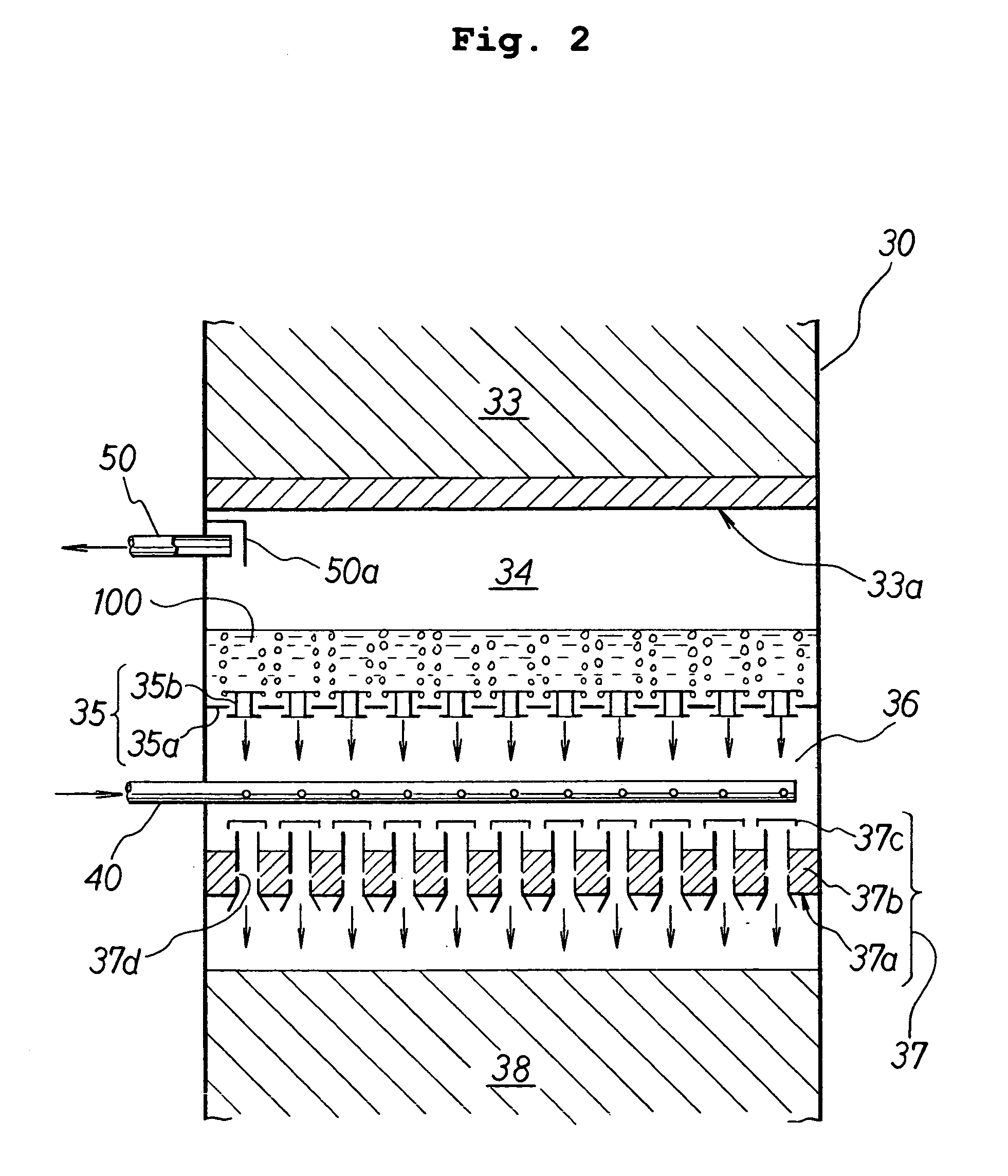
A unit for hydrorefining of hydrocarbon crude oil comprising sulfur-containing compounds comprises first catalyst layer 33 and second catalyst layer 38, top space 34 for separating vapor component and liquid component, bottom space 36, and valve tray 35 that divides top space 34 and bottom space 36. Hydrogen released from hydrogen nozzle 40 placed in the bottom space is passed through liquid component that has accumulated in the valve tray and stripping of liquid components is performed. Hydrogen released from hydrogen nozzle 40 is again introduced, to second catalyst layer 38 as a cocurrent with the stripped liquid component. By stripping, it is possible to reduce the sulfur content, the nitrogen content and reduce the aromatic content of the hydrocarbon crude oil when compared to the conventional method. Since the hydrorefining unit has a simple structure, the unit can be easily made by modifying existing units.
Owner:JAPAN ENERGY CORP +1
Catalytic conversion process for producing ethylene and propylene using low-density oil fraction
InactiveCN1566272AExtended service lifeHigh yieldCatalytic crackingChemical recyclingDistillates petroleumReaction zone
The invention discloses a catalytic conversion process for producing ethylene and propylene using low-density oil fraction which comprises, contacting lightweight petroleum distillate containing rich olefin with heated five-membered ring high silicon zeolite catalyst, reacting under catalytic conversion condition, thus separating the reaction product and catalyst to be produced, leading out the resultant from the main reaction zone and further separating, then loading the catalyst into regenerator after stripping for carbon burning reproduction at the presence of oxygen-containing gas, finally loading the heated regenerated catalyst into pre-reaction zone for recycling.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Process for Producing Hydrorefined Gas Oil, Hydrorefined Gas Oil, and Gas Oil Composition
InactiveUS20080308459A1Increase cetane numberSufficient efficiencyTreatment with hydrotreatment processesRefining by aromatic hydrocarbon hydrogenationDistillates petroleumMolecular sieve
A process of the present invention for producing a hydrotreated gas oil has a step for obtaining a product oil having a total aromatic content of 3% by volume or less by hydrogenating a hydrotreated oil including 95% by volume or more of fraction having a boiling point range of 150-380° C., a sulfur content of 2-15 ppm by mass, a total aromatic content of 10-25% by volume, and a naphthene of 20-60% by volume in the presence of a hydrogenation catalyst; and a step for obtaining, by hydrogenating the above-described product oil in the presence of a hydrogenation catalyst containing a crystalline molecular sieve component, a product oil satisfying the conditions that the content of petroleum fraction having a boiling point range of lower than 150° C. is 16% by volume or less, and the sum of the total aromatic content and the total naphthene content is 80% or less relative to the sum of these in the hydrotreated oil.
Owner:IKI HIDESHI +3
Method for producing anti-evolving-gas additive of transformer oil and its using method
InactiveCN1438299AReduce pollutionEasy to dehydrateHydrocarbon oils refiningDistillates petroleumDistillation
The invention is a producing method of anti-gas yeilding additive of transformer oil. At first, it uses petroleum distillation, boiling point 250-500 deg.C, as raw material, adopts any one or more of the hydrogenation catalyzer; Co-Mo, Ni-Mo, W-Ni and Mo-Co-Ni to make hydrogenation process; secondly, and at constant pressure distils the produced oil after the hydrogenation process to get the distillation, boiling point 280-360 deg.C, so as to get the additive; the usage: adding the additive to common transformer oil, concocting to get super-high transformer oil.
Owner:克拉玛依市金龙特种油品公司
Method for preparing low-polymerization-degree polyformaldehyde dialkyl ether from petroleum fractions and application
ActiveCN102173984AHigh CN valueApparent output ratioOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationDistillates petroleumChemical industry
The invention belongs to the technical fields of energy chemical industry and clean diesel components and in particular relates to a method for preparing low-polymerization-degree polyformaldehyde dialkyl ether from main raw materials such as a petroleum C4 component, an alkadiene-removed petroleum C5 component, a catalytic cracking light petroleum 30-90-DEC C fraction low-carbon monoolefine and the like. The structural general formula of the low-polymerization-degree polyformaldehyde dialkyl ether is CnH2n+1O(CH2O)mCnH2n+1, wherein m is an integer from 1 to 5; and n is an integer from 2 to 5. The low-polymerization-degree polyformaldehyde dialkyl ether prepared by the method has a higher CN value, can be applied to diesel fuel widely and effectively without high polymerization degree andhas a relatively simple preparation process. The byproducts petroleum C4 and C5 in the petroleum cracking ethylene process and the catalytic cracking petroleum 30-90-DEC C light fraction serve as theraw materials, so production cost is greatly saved by using low-carbon olefin in the raw materials, a good technical route is provided for comprehensive utilization of a large number of byproducts inthe petroleum cracking process, and remarkable economic significance is achieved.
Owner:DONGFANG HONGSHENG NEW ENERGY APPL TECH RES INST +1
Process for extraction of aromatics from petroleum streams
InactiveUS20040182750A1Lower cost of capitalReduce operating costsTreatment with plural serial refining stagesRefining with two or more solventsDistillates petroleumNaphtha
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method for preparing heteropoly acid/ordered mesic porous silicon oxide catalyst, and its application
InactiveCN1947840APrevent elutionGood dispersionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRefining to eliminate hetero atomsAlcoholHeteropoly acid
A heteropoly acid / ordered meso-porous silicon oxide catalyst used for removing the S-contained benzothiophenium compounds from the fractional oil of petroleum is prepared through such steps as dissolving heteropoly acid in the mixture of absolute alcohol and distilled water, adding ethyl n-silicate, magnetic stirring to obtain solution A, dissolving the polyoxyethene-polyoxypropene-polyoxyethene triblock copolymer in the mixture of absolute alcohol and distilled water to obtain solution B, slowly adding B to A, magnetic stirring to obtain sol, culturing it at 38-42 deg.C for 6-8 days, pulverizing, and calcining in N2.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of initiating solvent for direct liquefy of coal
ActiveCN1865399AOperational flexibilityImprove hydrogenation performanceLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionDistillates petroleumDistillation
The invention discloses a preparing method of coal direct liquefied initial solvent, which comprises the following steps: adopting oil distillate with distillation range at 220-538 deg.c, specific gravity at 1.01-1.10 g per cm3 and condensed-nuclei aromatics content over 70 percent; preparing coal direct liquefied initial solvent with distillation range at 220-480 deg.c, specific gravity at 0.95-0.99 g per cm3 and condensed-nuclei aromatics content over 80 percent through catalytic hydrogenation course. The method possesses excellent hydrogen supplying property and fitful viscosity, which can satisfy the direct liquefied need for coal slurry.
Owner:CHNA ENERGY INVESTMENT CORP LTD +1
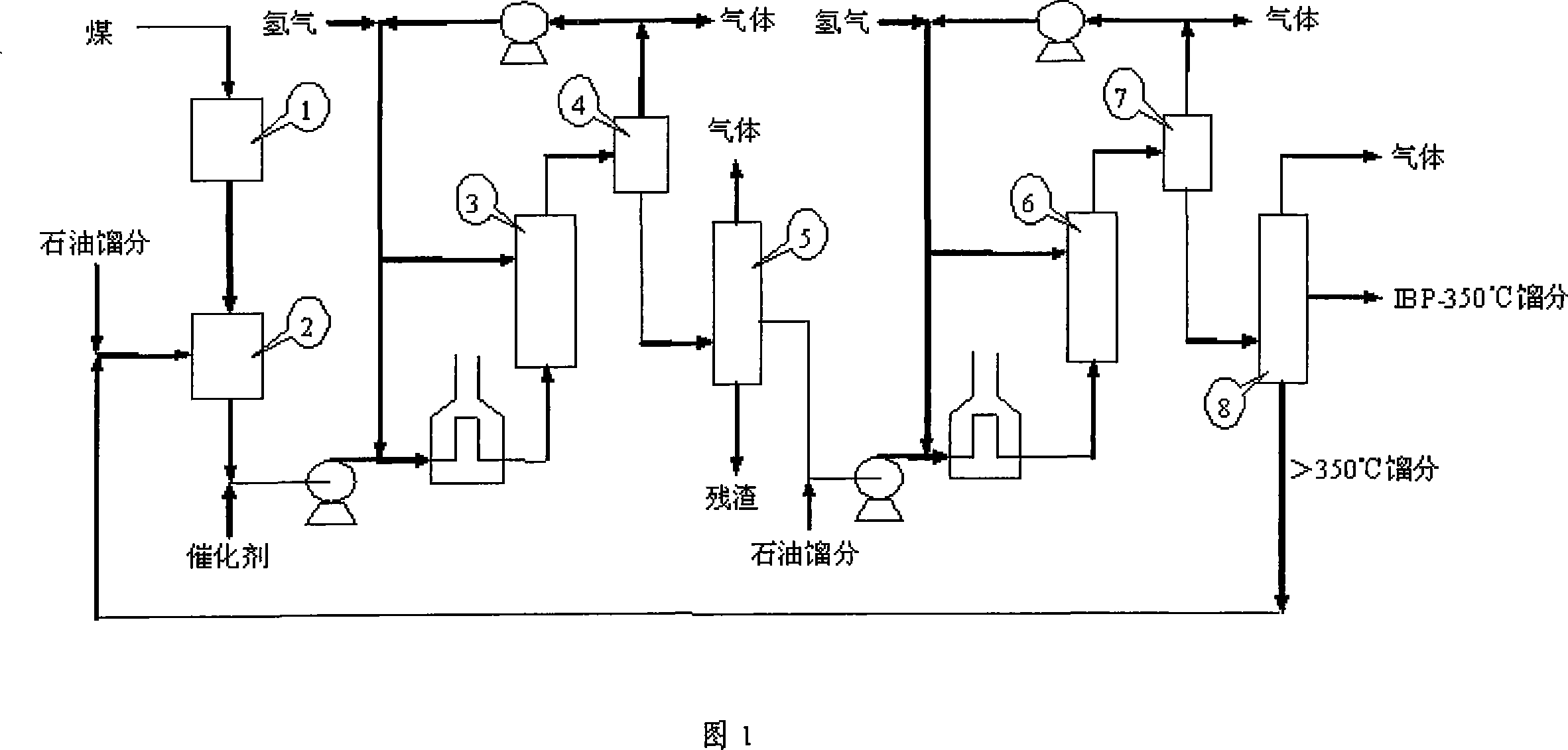
Coal and stone oil joint processing method for producing high quality engine fuel
ActiveCN101220287AHigh yieldEasy to optimizeLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionTreatment with hydrotreatment processesDistillates petroleumOil processing
The invention relates to a method which can combine coal and petroleum to produce good quality fuel of a motor, which comprises the following steps: (1) the coal powder and the solvent oil are prepared into coal slurry; (2) the coal slurry is subject to hydrocracking reaction; (3) the oil products of the step (2) are subject to hydrogenation reaction after experiencing solid removal; (4) the liquefied whole fraction produced by the step (3) is subject to fractionation to get three fractions, that is, naphtha fraction, diesel fraction and fraction oil higher than 350 DEG C; (5) the diesel fraction of the step (4) is subject to depth hydrofining; (6) the high cetane value diesel produced in the process of petroleum and the products produced by the step (5) are mixed according to the needed ratio, thus obtaining motor fuel with good quality; wherein, the solvent oil of the step (1) comprises the petroleum fraction oil. The method can fully transfer heavy oil, maintain high coal slurry concentration and improve the yield of motor fuel with good quality. .
Owner:CHNA ENERGY INVESTMENT CORP LTD +1
Method for producing high-octane gasoline by hydrocracking distillate oil of low-grade petroleum
InactiveCN101962570AFix low octaneSolve the problem of low cetane number of diesel productsTreatment with hydrotreatment processesDistillates petroleumSolvent
The invention relates to a method for producing high-octane gasoline by hydrocracking distillate oil of low-grade petroleum, which belongs to the technical field of petroleum refining. The method is as follows: carrying out hydrocracking ring opening and cracking reaction on distillate raw materials including straight-run distillate oil produced by atmospheric and vacuum distillation one-time processing production of the petroleum, light cycle oil produced by a catalytic cracking device, the distillate oil produced by a delayed coking device, light deasphalted oil which removes asphalt in solvent and the like of low-grade petroleum in the presence of hydrogen partial pressure and a bifunctional catalyst, and then producing blended components of the high-octane gasoline which is rich in mononuclear aromatics and the research octane number RON of 80-96, wherein the distillation range of the distillate raw materials is 160-450 DEG C. The invention provides a brand new way for upgrading the quality of the gasoline and diesel to the standard which is equivalent to European Union IV (the sulfur content in the finished product gasoline is below 50ppm, and the sulfur content in the diesel is below 50ppm) and European Union V (the sulfur content in the finished product gasoline is below 10ppm, and the sulfur content in the diesel is below 30ppm).
Owner:孙雪 +2
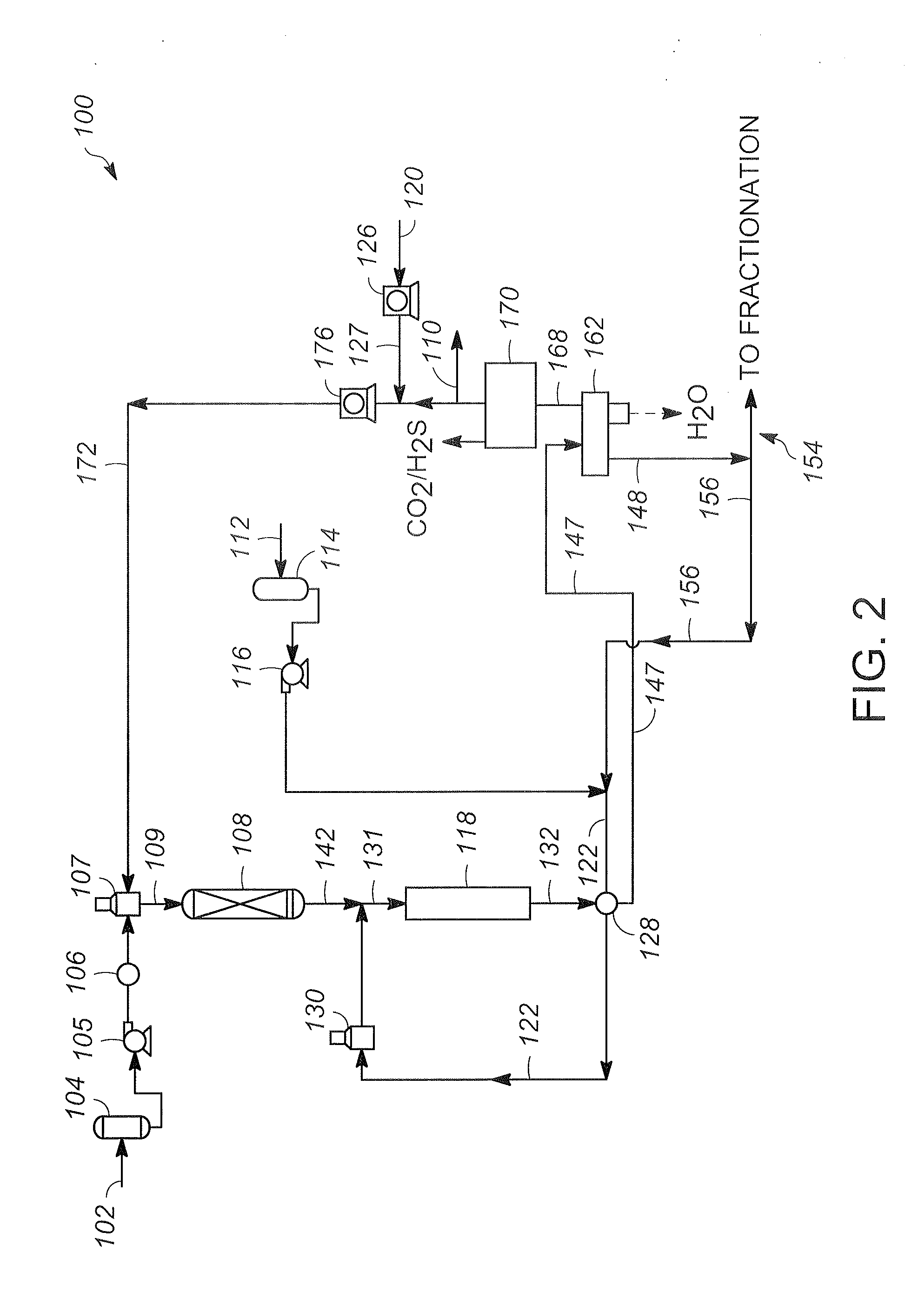
Methods for co-processing biorenewable feedstock and petroleum distillate feedstock
Methods for co-processing a biorenewable feedstock and a petroleum distillate feedstock are provided. The petroleum distillate feedstock containing sulfur is reacted with hydrogen gas in the presence of a hydrotreating catalyst thereby forming an effluent mixture comprising hydrogen sulfide. A combined feed comprising the effluent mixture, optionally a recycle liquid, and the biorenewable feedstock is contacted with hydrogen gas in a reaction zone with a deoxygenation catalyst under reaction conditions to provide a reaction product comprising a hydrocarbon fraction. The combined feed comprises greater than 50 weight percent biorenewable feedstock.
Owner:UOP LLC
Solvent oil hydrogenation and quality change method
ActiveCN1769391AHigh yieldLow viscosityTreatment with hydrotreatment processesDistillates petroleumHydrogenation catalysis
The invention relates to a method of hydrogenation to improve quality of solvent oil. The invention takes one or more petroleum fractions from petrol, coal oil, diesel oil as raw materials, contactly reacting with hydrogenation catalysis containing ª
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalysis, oxidation sweetening method for distillate oil of petroleum
A catalytic oxidation and desulfidation method for petroleum distillate oil includes using car bon material or / and carbon material carried with transition metal as catalyst, carrying out reaction under action of at least one type of peroxide and at least one type of acid and generating peroxyacid and hydroxy free radical to concert sulfur compound contained in oxidized petroleum distillate oil on the reaction.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Hydrogenation dearomatization catalyst containing molecular screen
A hydrogenation dearomatization catalyst containing molecular sieve consists of alumina 20.0í½80.0wt% and lucinite molecular sieve 0.5í½50.0wt%. It takes at least one Fe, Co and Ni metal of ó° family and Mo and W metal of ó÷B family as active component. It can be used for hydrogenation refining of petroleum distillate and hydrogenation dearomatization hydrocarbon of diesel oil.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
Distillate hydrogenation catalyst and its preparation method
ActiveCN1769382ASuitable for saturation reactionsIncreased saturation activityHydrocarbon oils refiningDistillates petroleumMolecular sieve
The invention discloses the hydrotreatment catalyst and preparing method. The catalyst contains the 1wt%-10wt% organic auxiliary agent, using the inorganic refractory oxide compound containing the Y-molecular screen as carrier, and using the metals in the VIB and VIII as active metal componemt. The method comprises the following steps: using the inorganic refractory oxide compound containing the Y-molecular screen as carrier, after soaking the catalyst carrier in the active metal and organic auxiliary agent, drying at the 200íµ, and getting the catalyst. The said catalyst can be used for hydrotreating process of fraction of petroleum, especially for hydrodesulphurization and hydrodenitrification process of middle distillate oil.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
System and process for reacting a petroleum fraction
InactiveUS20090314686A1Facilitate converting pitchLow hydrogen purityHydrocarbon oils treatment control/regulationCatalytic naphtha reformingDistillates petroleumHydrogen
In one exemplary embodiment, a system for reacting a first feed can include a petroleum fraction having at least about 90%, by volume, with a boiling point of at least about 300° C. The system can include a bubble column reactor. The bubble column reactor, in turn, can include a first inlet for the first feed and a second inlet for a second feed including a gas rich in hydrogen. In addition, the petroleum fraction may be in counter-current flow with respect to the gas rich in hydrogen inside the bubble column reactor.
Owner:UOP LLC
Methods to increase gasoline yield
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
Process for the demercaptanization of petroleum distillates
InactiveUS20020130062A1Eliminate useHigh mercaptan selectivityRefining with oxygen compoundsRefining to eliminate hetero atomsActivated carbonDistillates petroleum
The demercaptanizaiton of petroleum distillates can be carried out by sorption of the mercaptan with activated carbon and oxidation of the sorbed mercaptan to disulfide at between approximately 20.degree. C. to 55.degree. C. The activated carbon used in the process is commercially readily available. Its surface area typically ranges from between approximately 500 to 1500 m.sup.2 / g and has substantial percentage of the pores in the 10 to 100 Angstrom range.
Owner:DS2 TECH
Method of optimizing heavy crude pipeline transportation
InactiveUS20070175512A1Contribution can be suppressedOther chemical processesLiquid carbonaceous fuelsDistillates petroleumHeavy crude oil
Heavy crude transportation optimization method wherein at least one solvent consisting of a petroleum cut is added to said crude. According to the method, the polar component δp of the Hildebrand parameter of the solvent is increased, and the contribution of hydrogen bond δh of the Hildebrand parameter of the solvent is controlled, by adding a predetermined amount of at least one specific additive.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Petroleum sulfonate compounded system for oil displacement and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102604620AHigh content of active ingredientsGood solubility and dispersibilityDrilling compositionSal ammoniacChemistry
The invention relates to a compound adjustment method of petroleum sulfonate, which provides a petroleum sulfonate compounded system for oil displacement, which ensures that lamination does not occur when a product is laid within 30 days at normal temperature and a preparation method of the petroleum sulfonate compounded system. The system takes petroleum distillate oil as raw material, takes gaseous sulfur trioxide, liquid sulfur trioxide or fuming sulfuric acid as sulfonating agent, takes petroleum sulfonate, the active matter content of which is larger than 28 percent, formed by neutralizing ammonia or sodium hydroxide as a base, and is formed by adding dodecyl benzene sulfonic acid, heavy alkyl benzene sulfonic acid, alpha-olefin sulfonic acid, alkali or water. The system comprises the following components by mass: 40 to 90 percent of petroleum sulfonate, 0 to 20 percent of dodecyl benzene sulfonic acid, 0 to 20 percent of heavy alkyl benzene sulfonic acid, 0 to 10 percent of alpha-olefin sulfoacid, 0 to 30 percent of alkali and 0 to 40 percent of water. By adopting the technical scheme, the adaptability of petroleum sulfonate products in an oil field is improved, the product stabilizing capacity is enhanced, and the production process of the petroleum sulfonate is simplified.
Owner:胜利油田中胜环保有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com