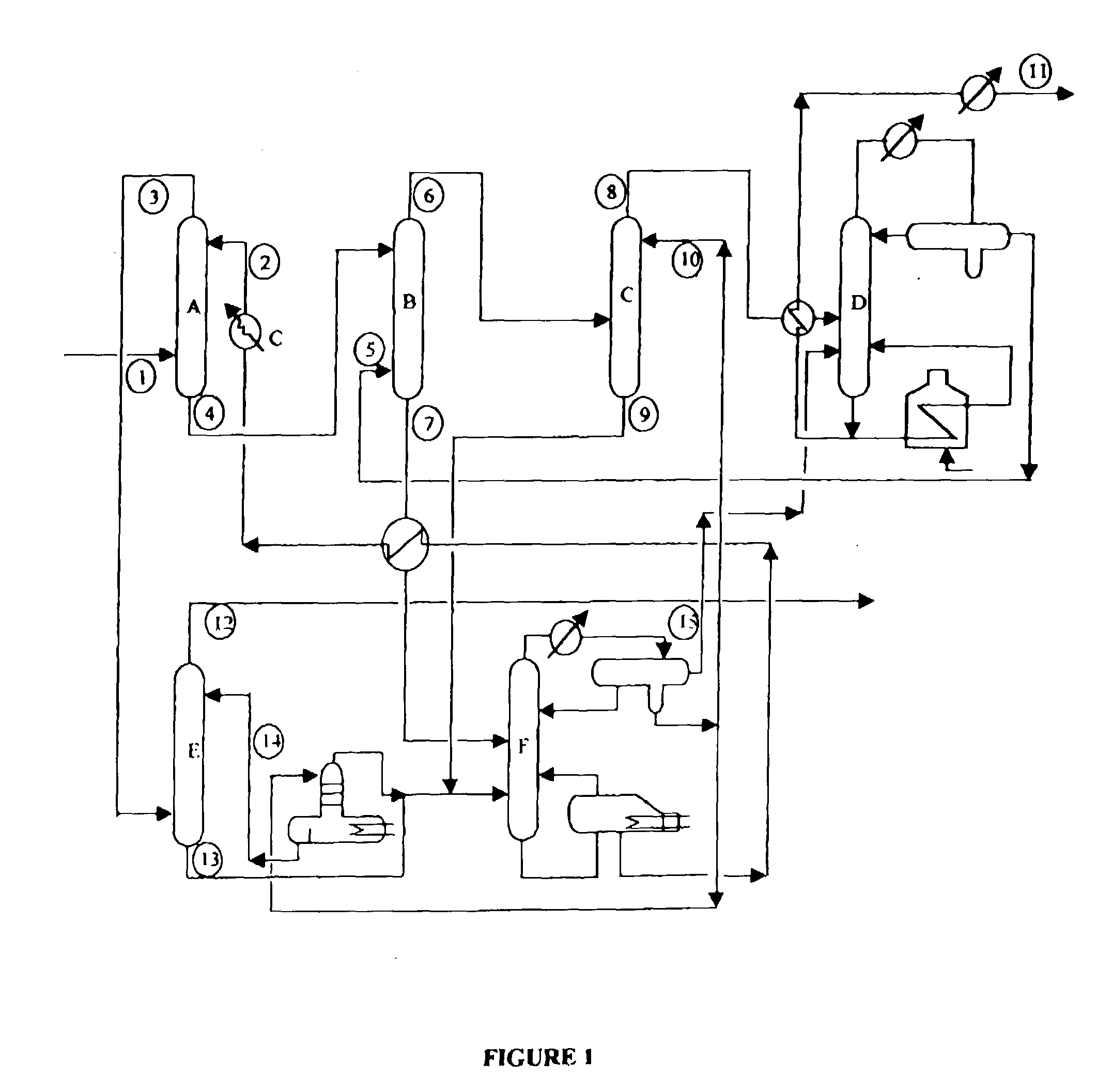
Process for extraction of aromatics from petroleum streams
a petroleum stream and aromatic technology, applied in the field of improved extraction of aromatics from petroleum streams, can solve the problems of high capital cost of process compared to solvent extraction, affecting hydrogen yield, and occasional failure of atf produced by this process, so as to reduce operating cost, save capital cost, and save utilities.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
[0060] For the extraction step the model mixture of propyl benzene-decane with 6.0 wt. % propyl benzene, was admixed with an equal weight of NMP p 20% sulpholane at 40.degree. C. Two liquid phases under equilibrium were formed. Each phase, as separated, made solvent-free and analysed. The extract phase contained 2.2 wt % propyl benzene, while its concentration reduced to 4.8 wt. % in the raffinate phase with 94.5 wt. % yield.
example 3
[0061] 3.3 kgs / hr of heavy naphtha fraction (100-200.degree. C.) from Assam crude, containing 30.2 wt. % aromatic is fed to packed extractor-A. It as counter-currently contacted with the selective solvent (NMP+10% water) at 40.degree. C. entering the column at a rate of 7.7 kgs / hr. The extract phase produced at a rate of about 8.6 kgs hr. 4.1 kgs hr of extract phase produced as above containing 0.54 kgs / hr of total hydrocarbons is fed it packed extractor-B and counter currently contacted with C.sub.6-C.sub.7 paraffinic petroleum fraction entering at a rate of 6.1 kgs / hr. Phase produced at a rate of 7.0 kgs / hr from the top of extractor-B contains 0.49 kgs / hr of NMP. The phase is water washed and fractionated shielding 0.55 kgs / hr of naphtha extract containing 77.2 w of aromatics. The recovered C.sub.6-C- paraffinic petroleum fraction is circulated back to extractor-B The bottom of the extractors contains 3.15 kgs / hr of lean solvent and 0.011 kgs / hr of naphtha hydrocarbons. 2.3 kgs / hr...
example 4
[0062] 2.0 kgb / hr of gas oil fraction (240-400.degree. C.) from Assam crude, containing 39.2 wt. % aromatic is fed to packed extractor-A. It was counter-currently contacted with the selective solvent (NMP+10% water) at 40.degree. C. entering the column at a rate of 7.4 kgs / hr. The extract phase produced at a rate of about 8.2 kgs / hr. 4.7 kgs / hr of extract phase produced as above containing 0.377 kgs / hr of total hydrocarbons is fed to packed extractor-B and counter currently contacted with C.sub.6-C.sub.7 paraffinic petroleum fraction entering at a rate of 6.8 kgs / hr Phase produced at a rate of 7.6 kgs / hr from the top of extractor-B contains 0.56 kgs / hr of NMP. The phase is water washed and fractionated yielding 0.345 kgs / hr of gas oil extract containing 86.9 wt % of aromatics. The recovered C.sub.6-C.sub.7 paraffinic petroleum fraction is circulated back to extractor-B. The bottom of the extractor-B contains 4.07 kgs / hr of lean solvent and 0.02 kgs / hr of gas oil hydrocarbons. 1.38 k...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com