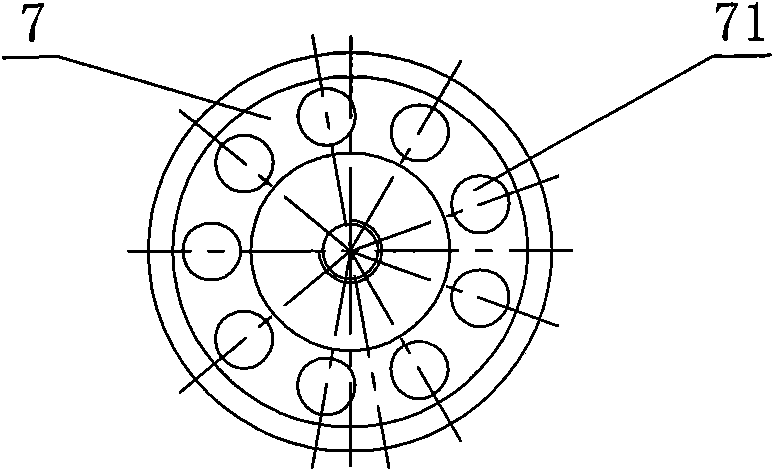
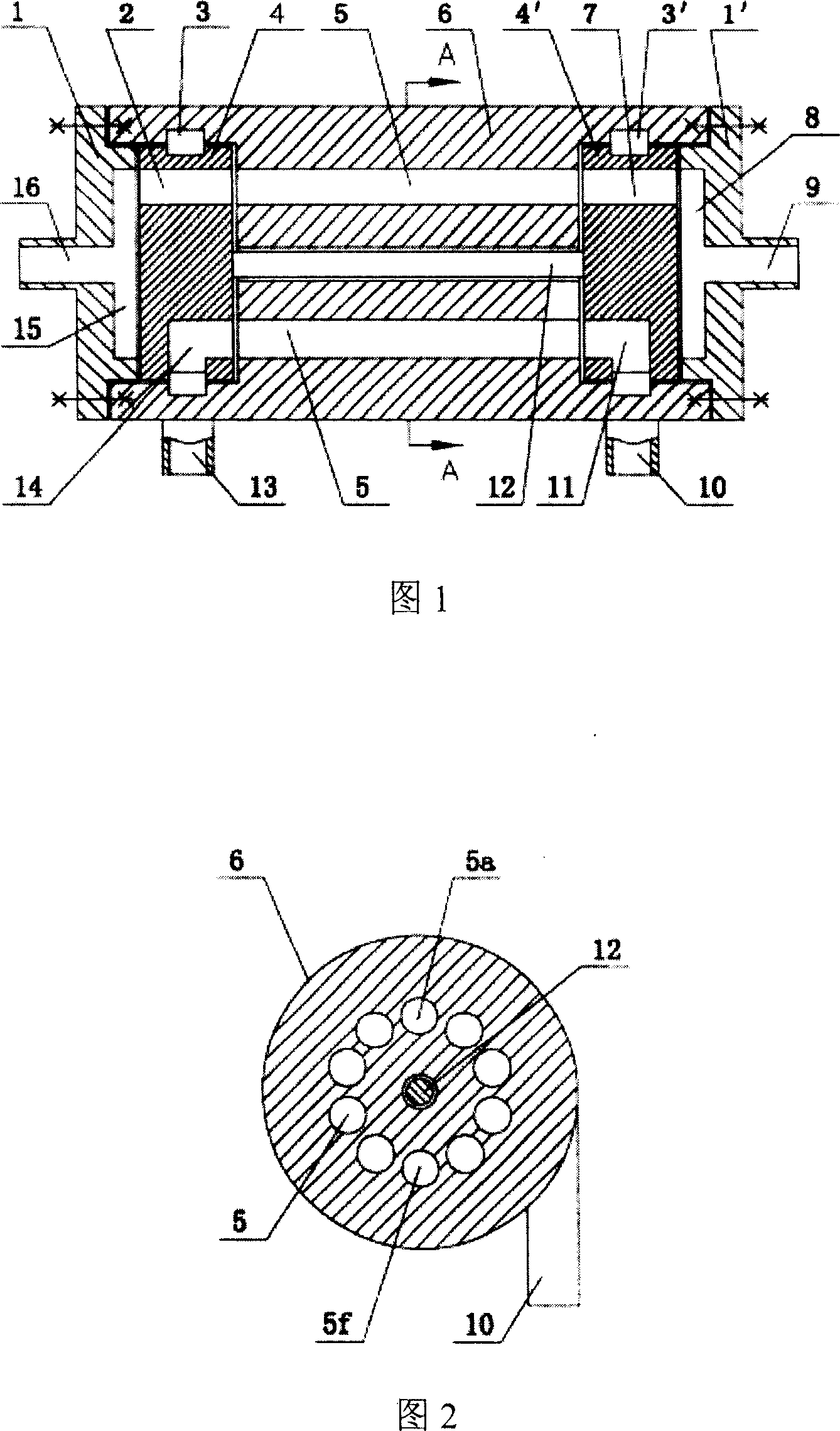
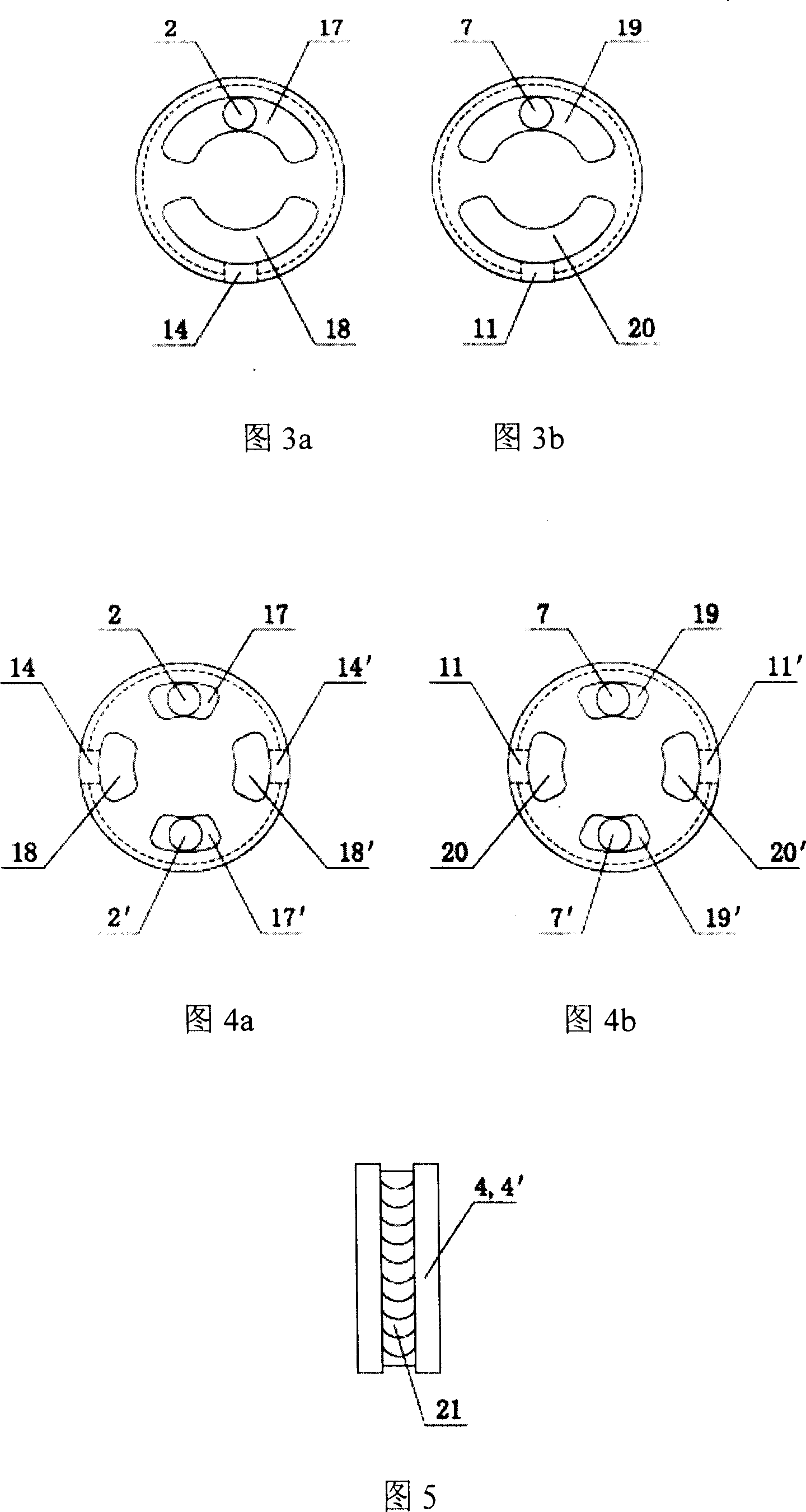
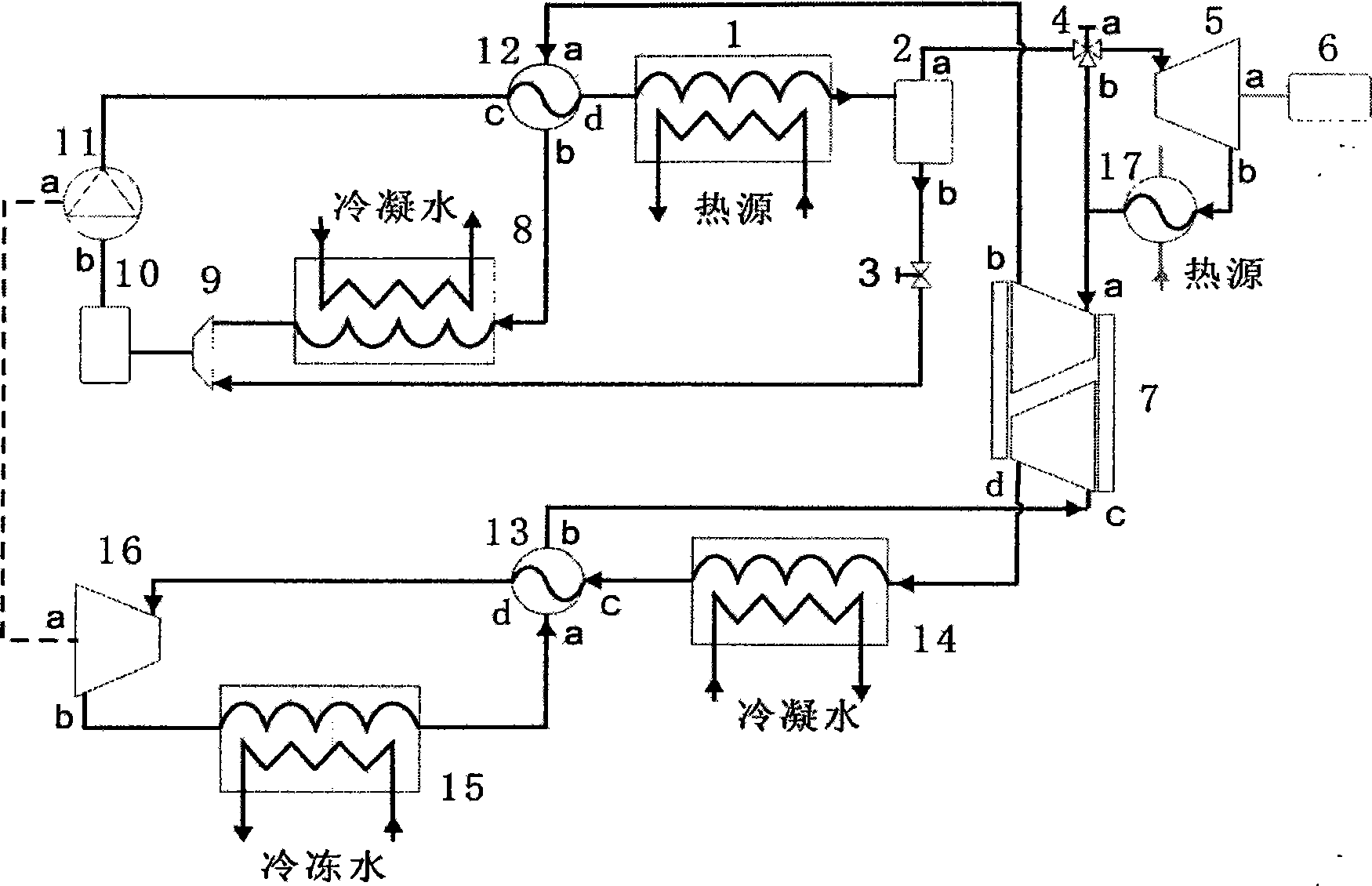
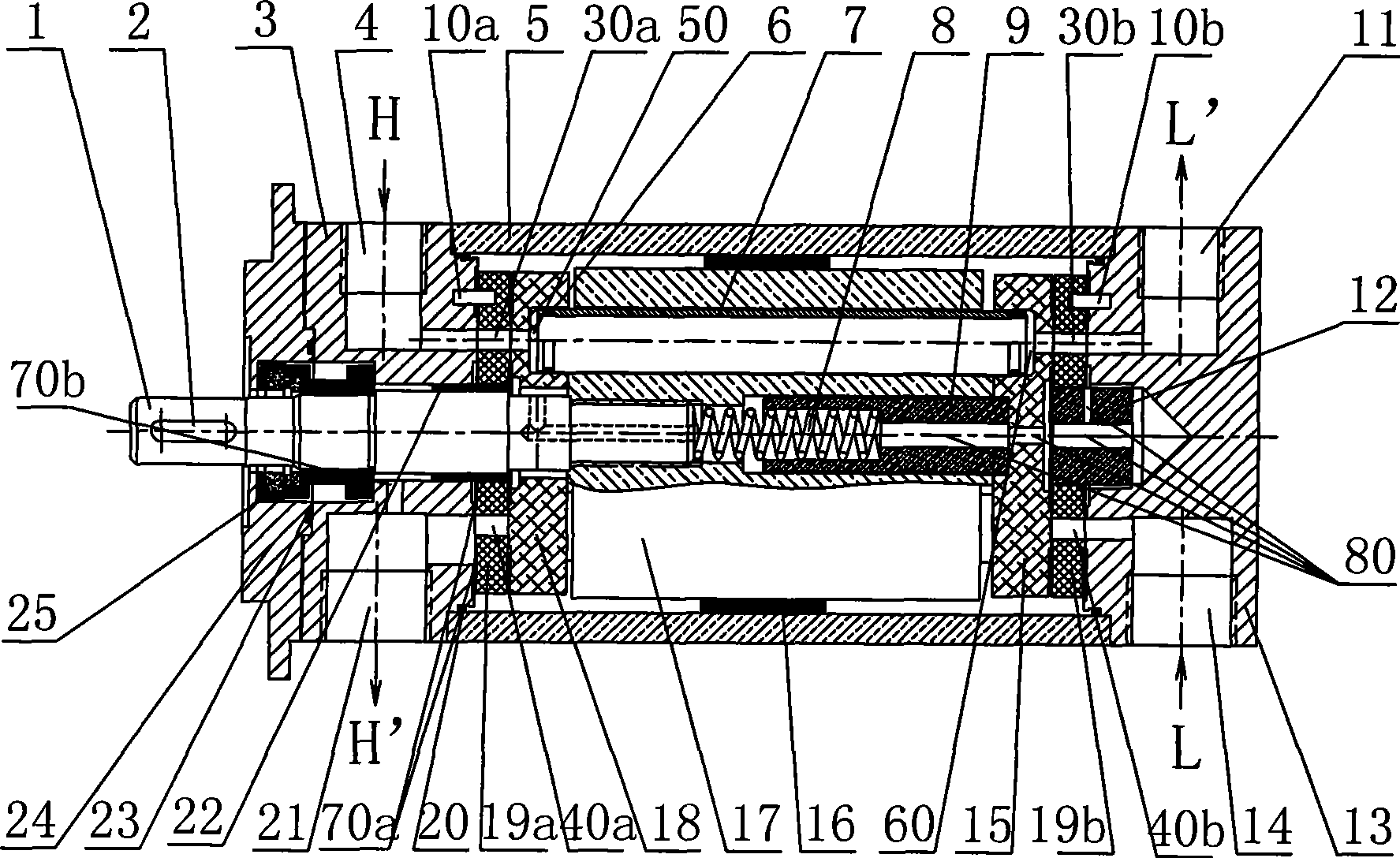
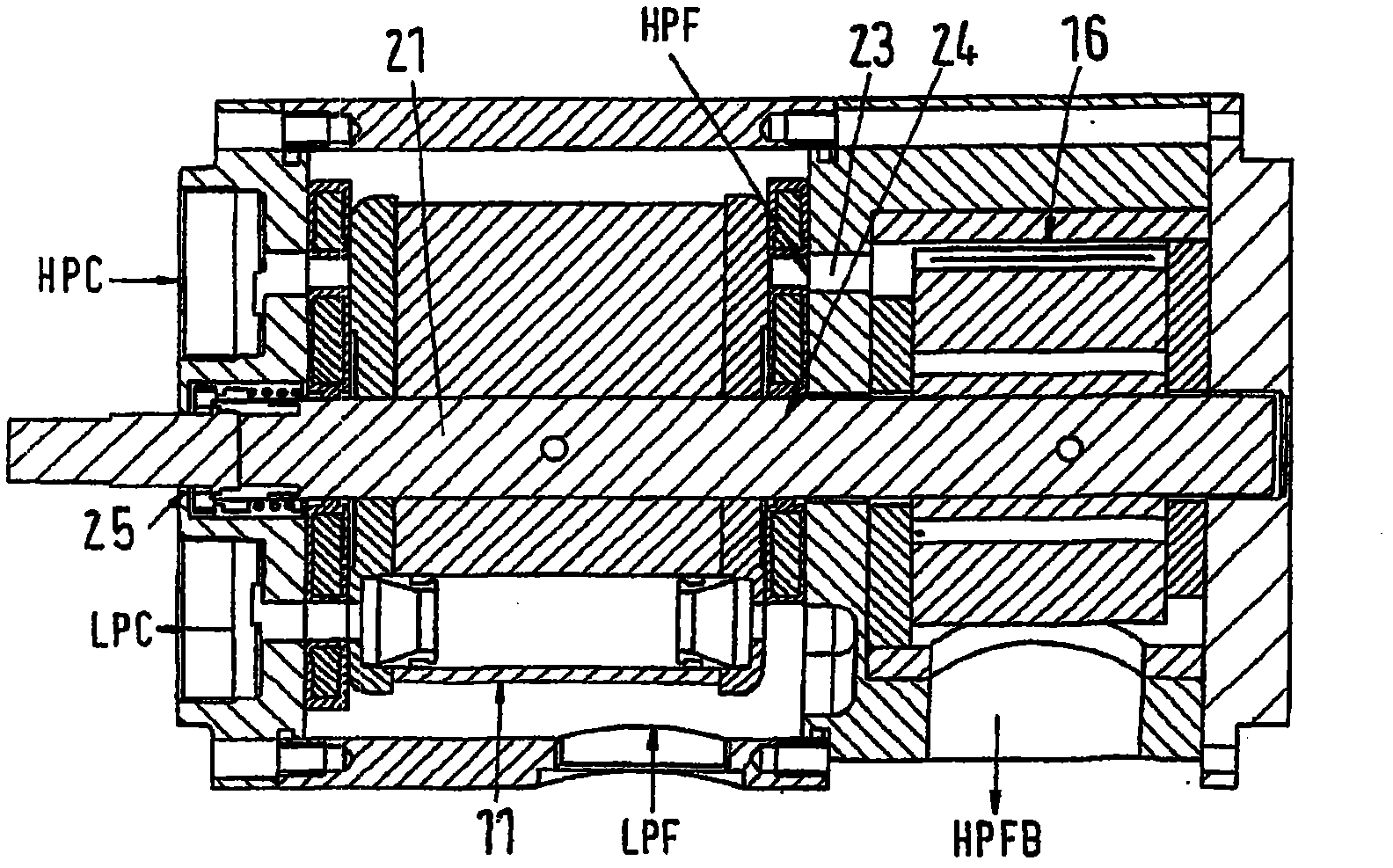
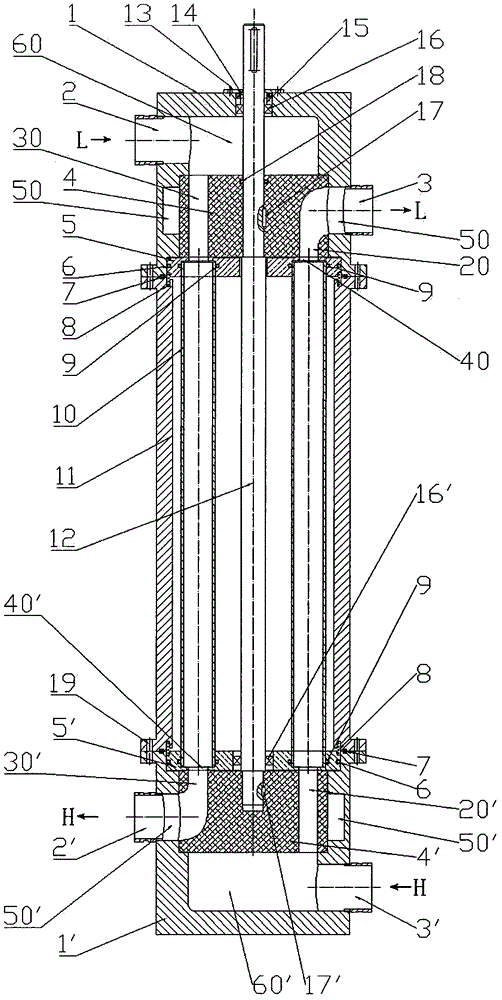
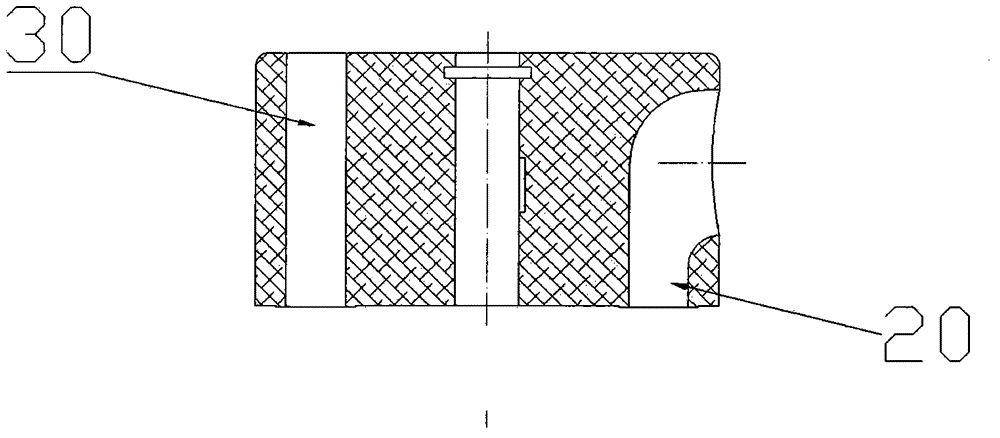
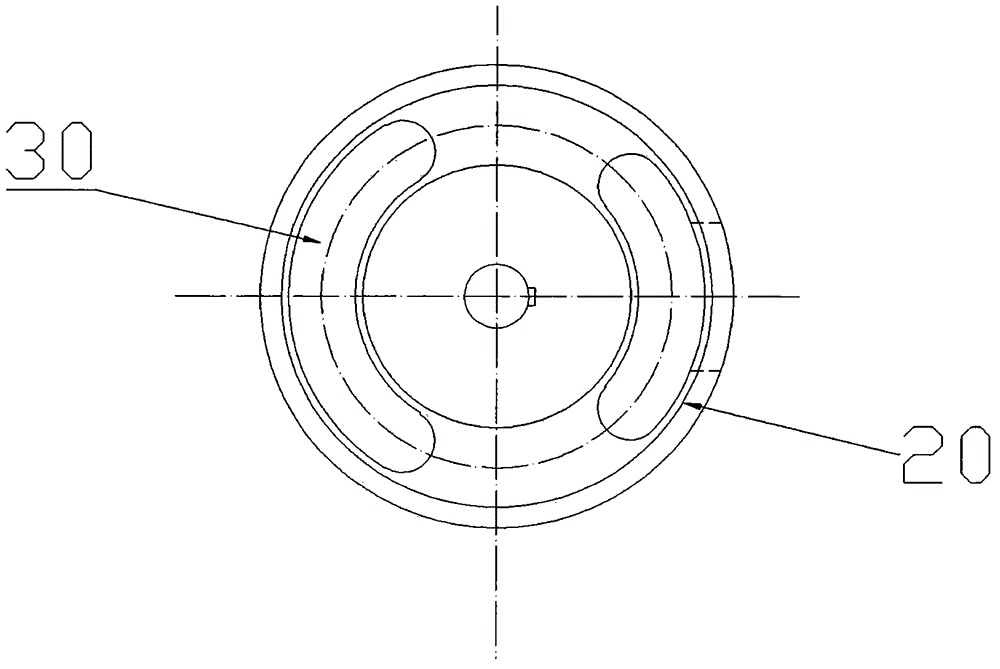
Patents
Literature
138 results about "Pressure exchanger" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
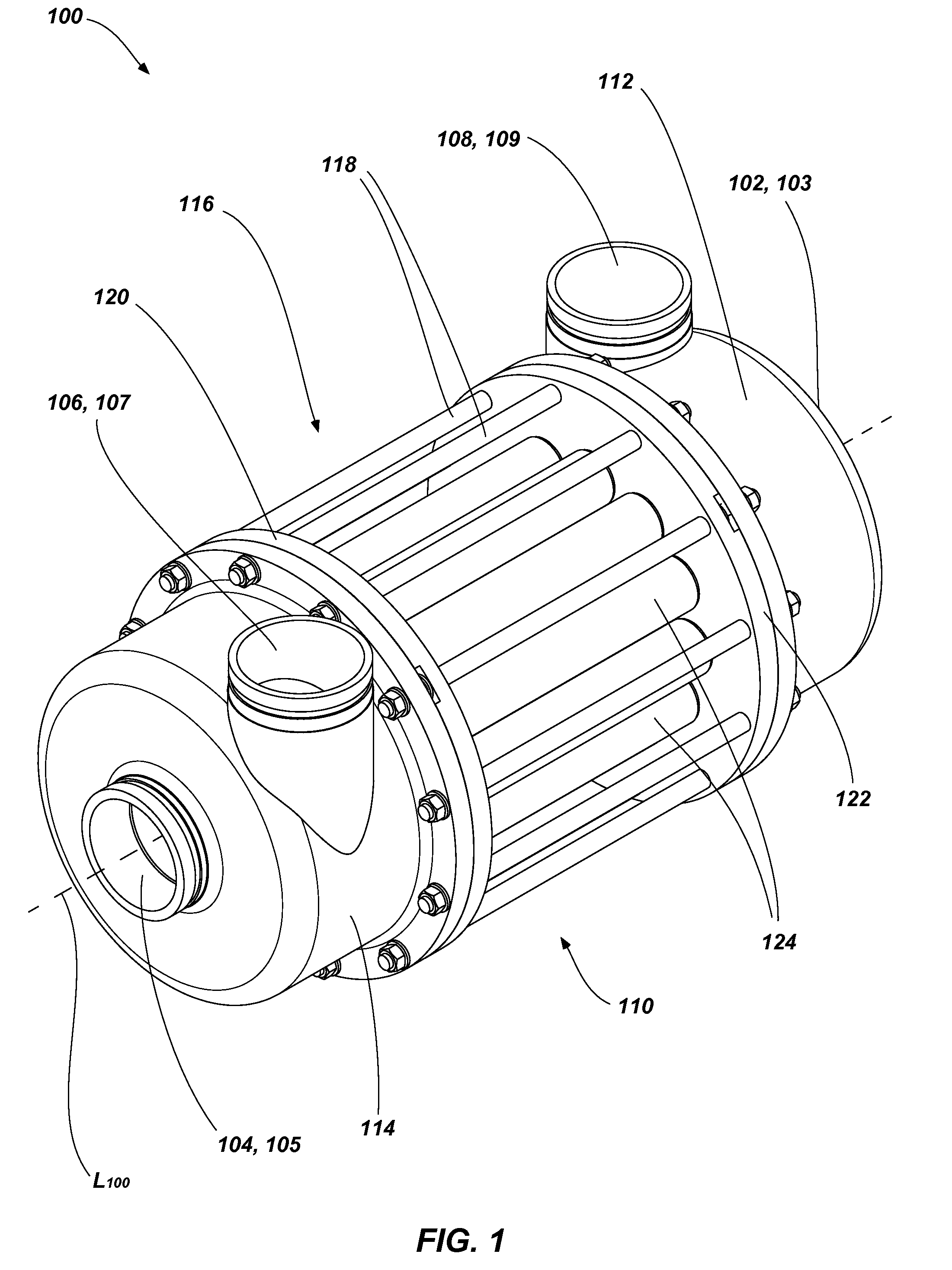
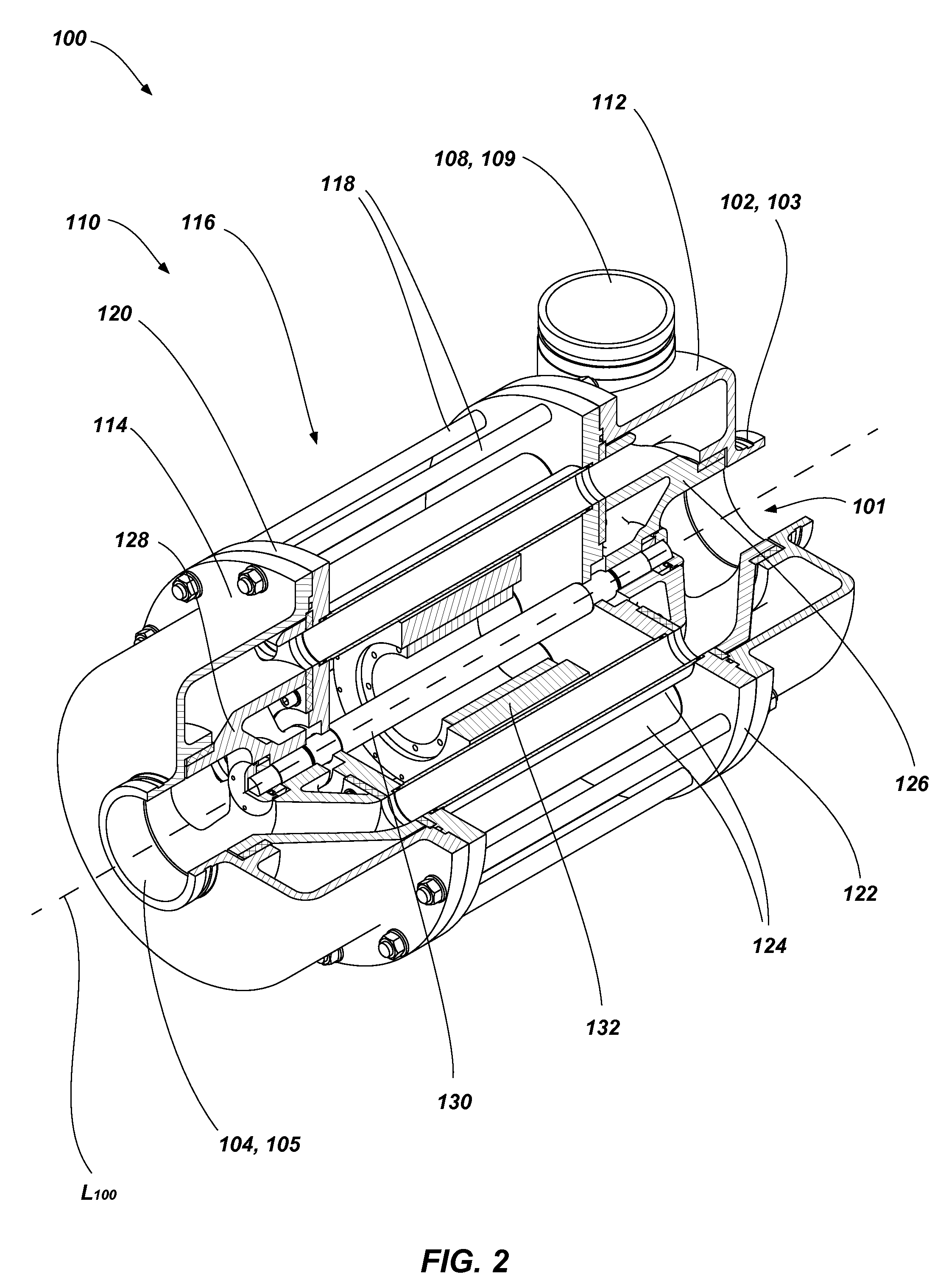
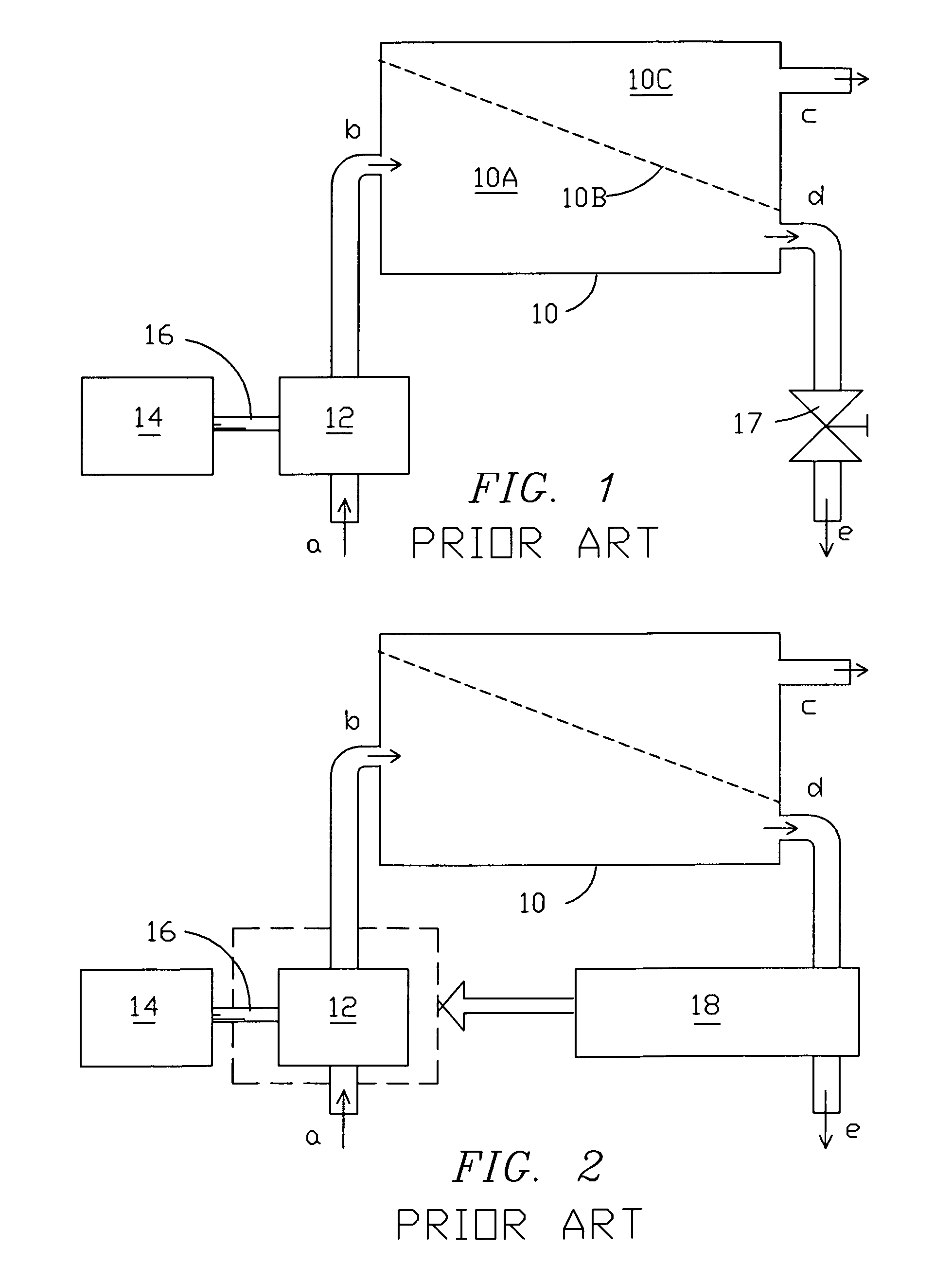
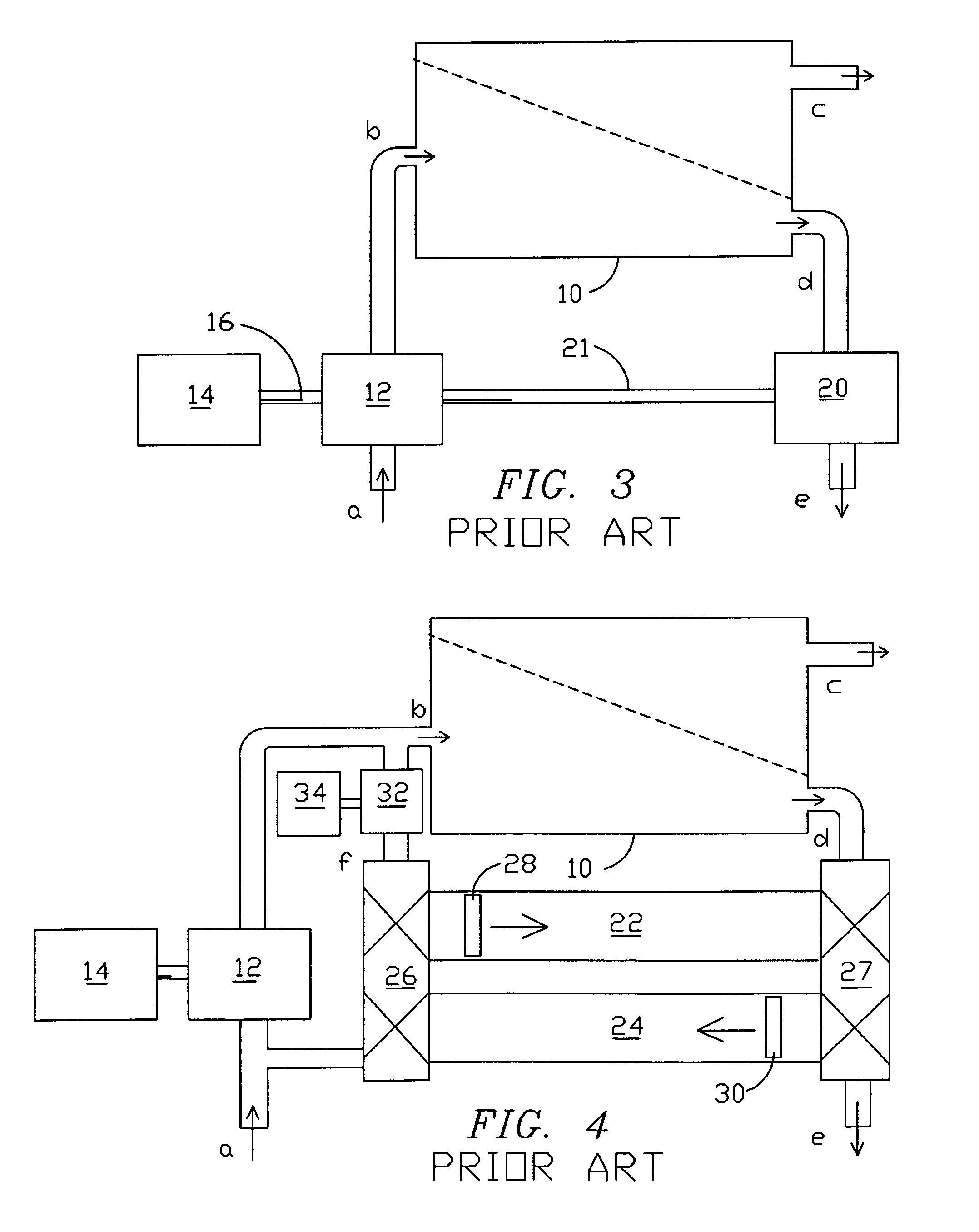
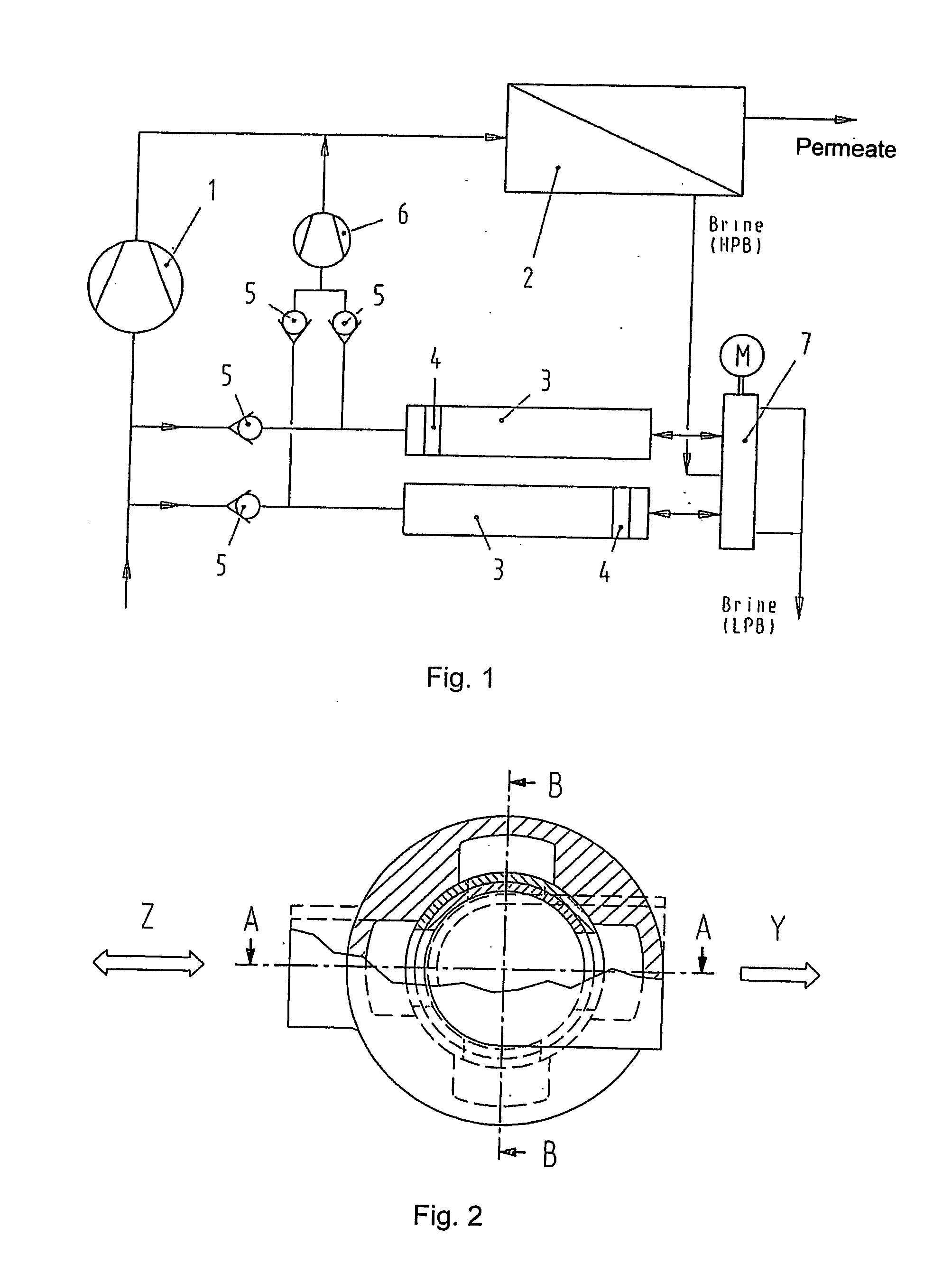
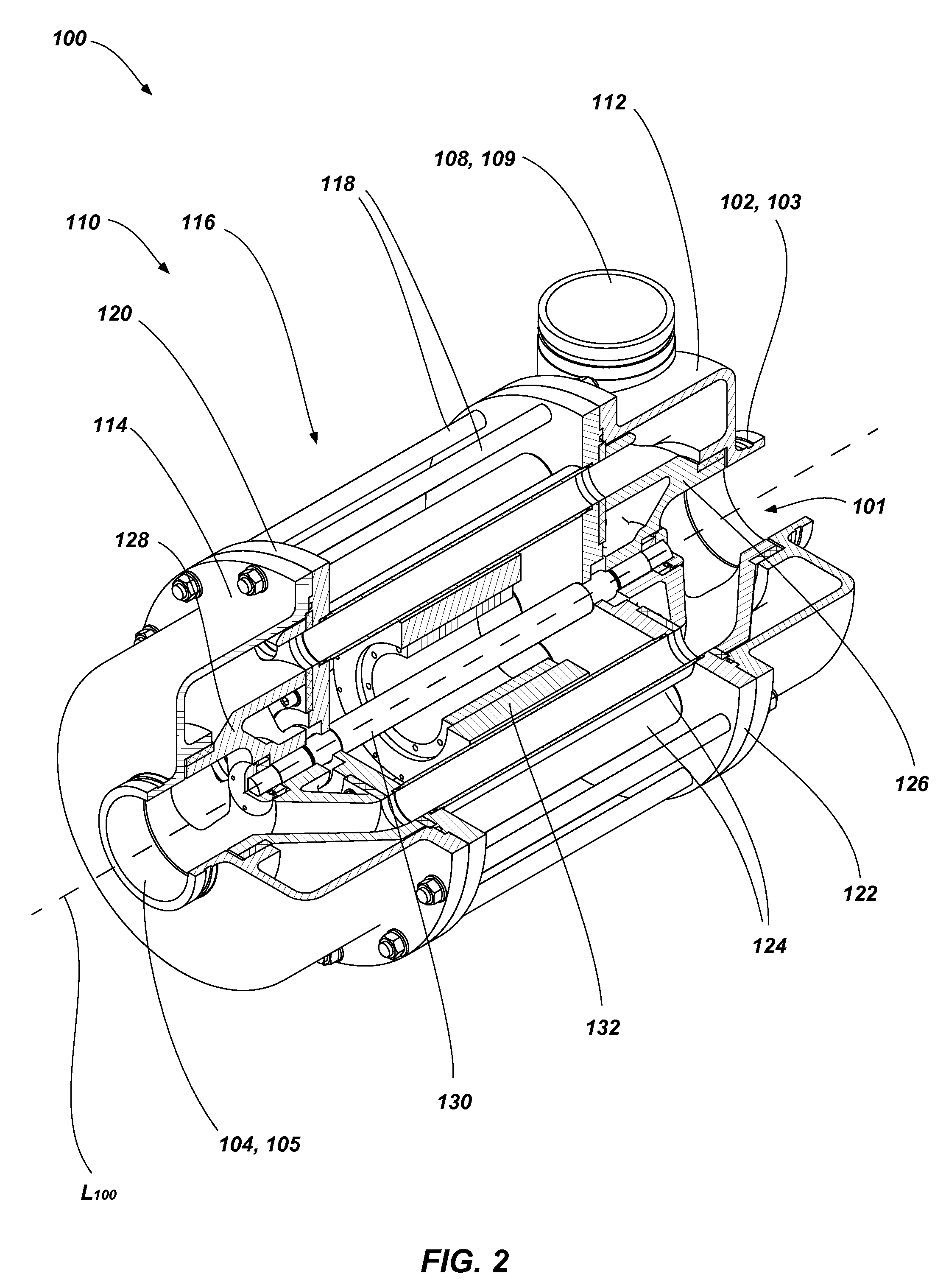
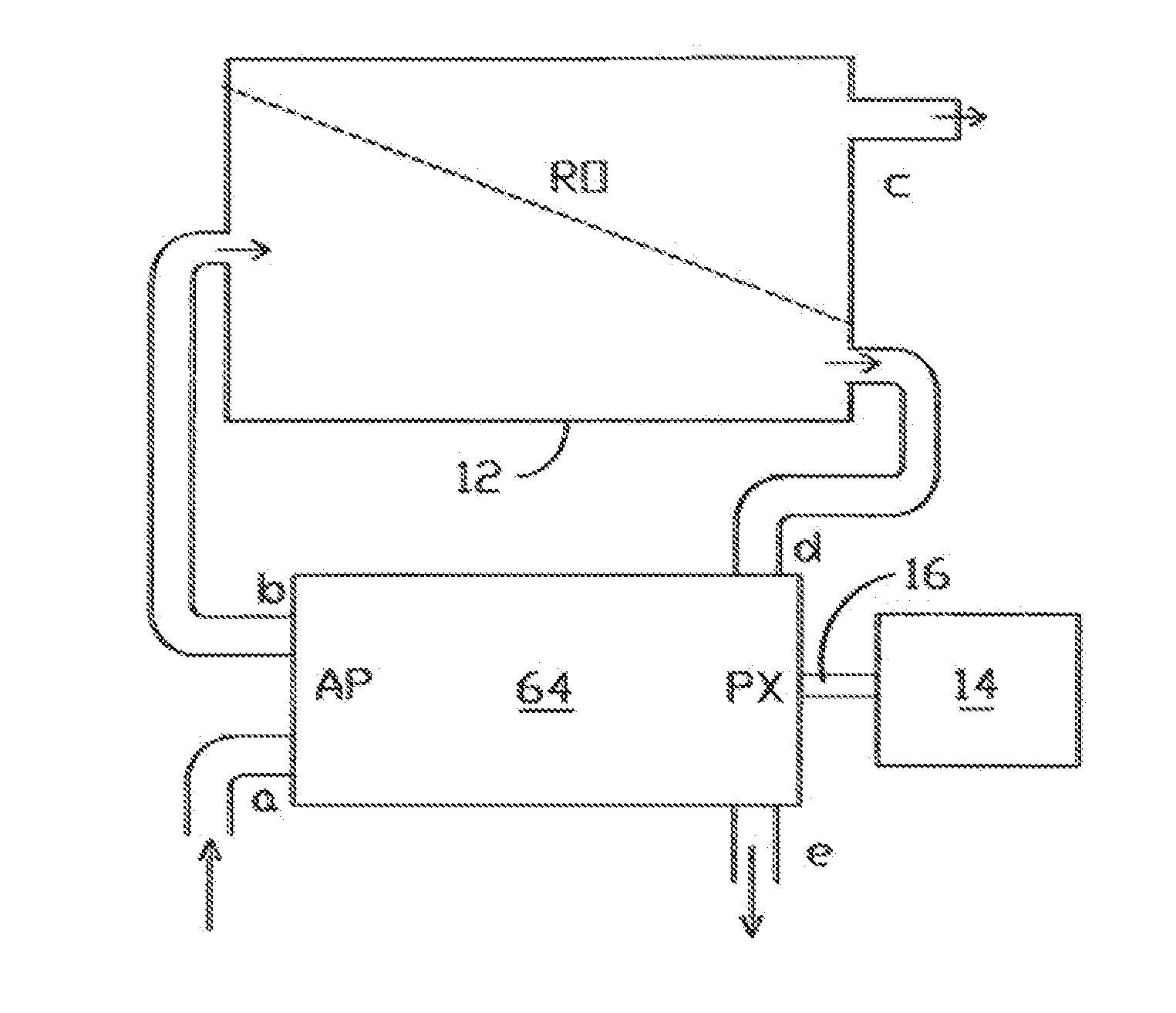
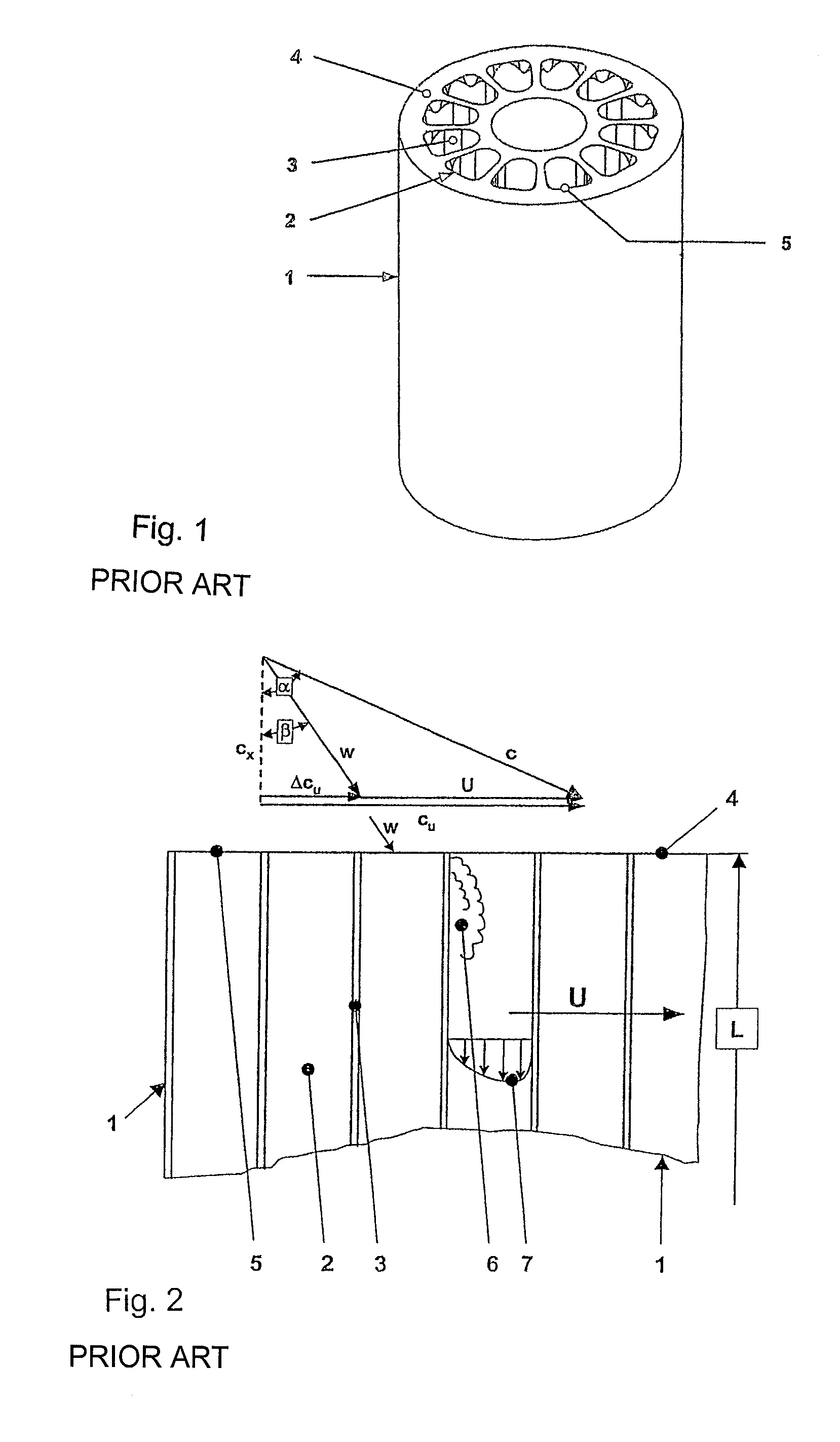
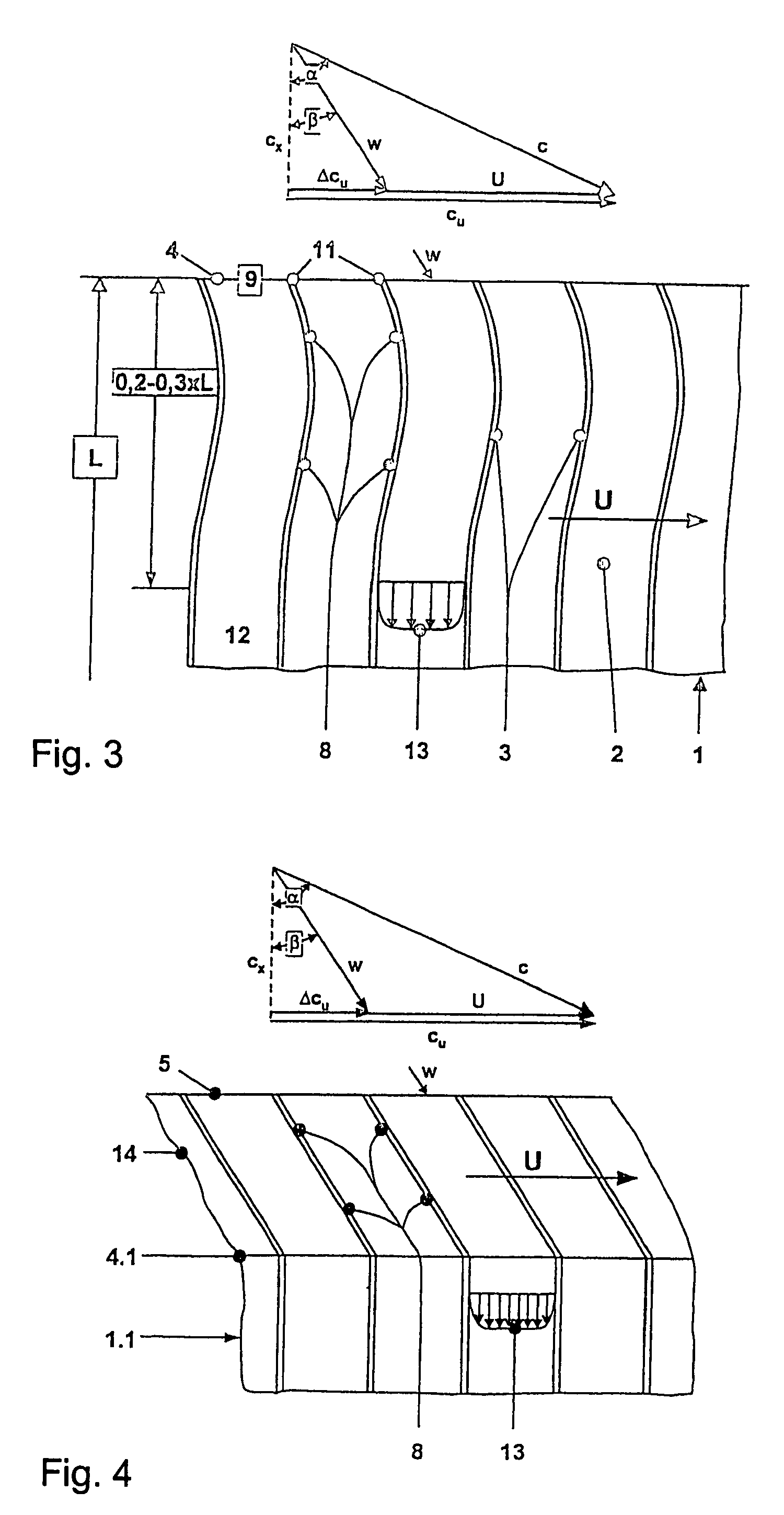
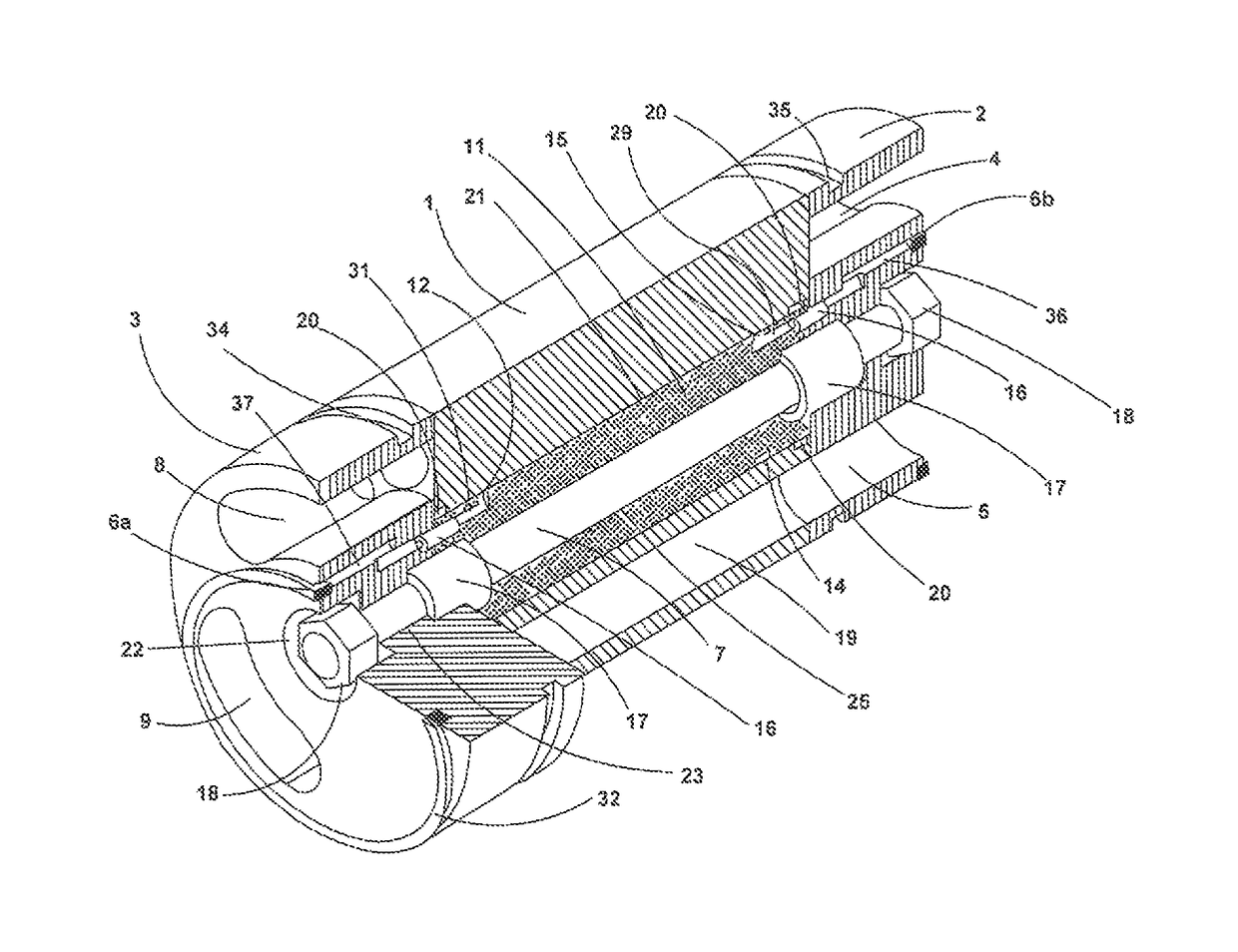
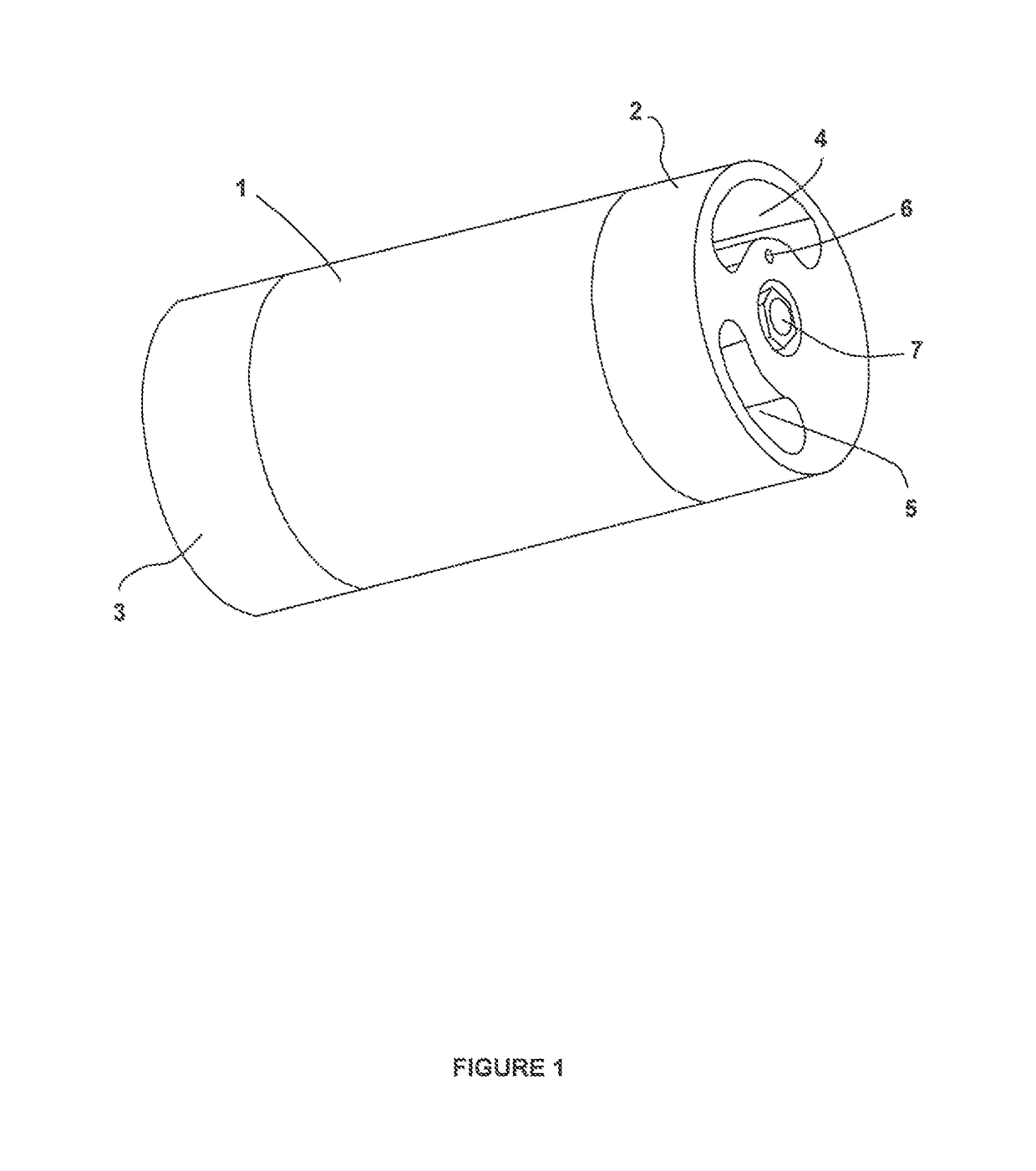
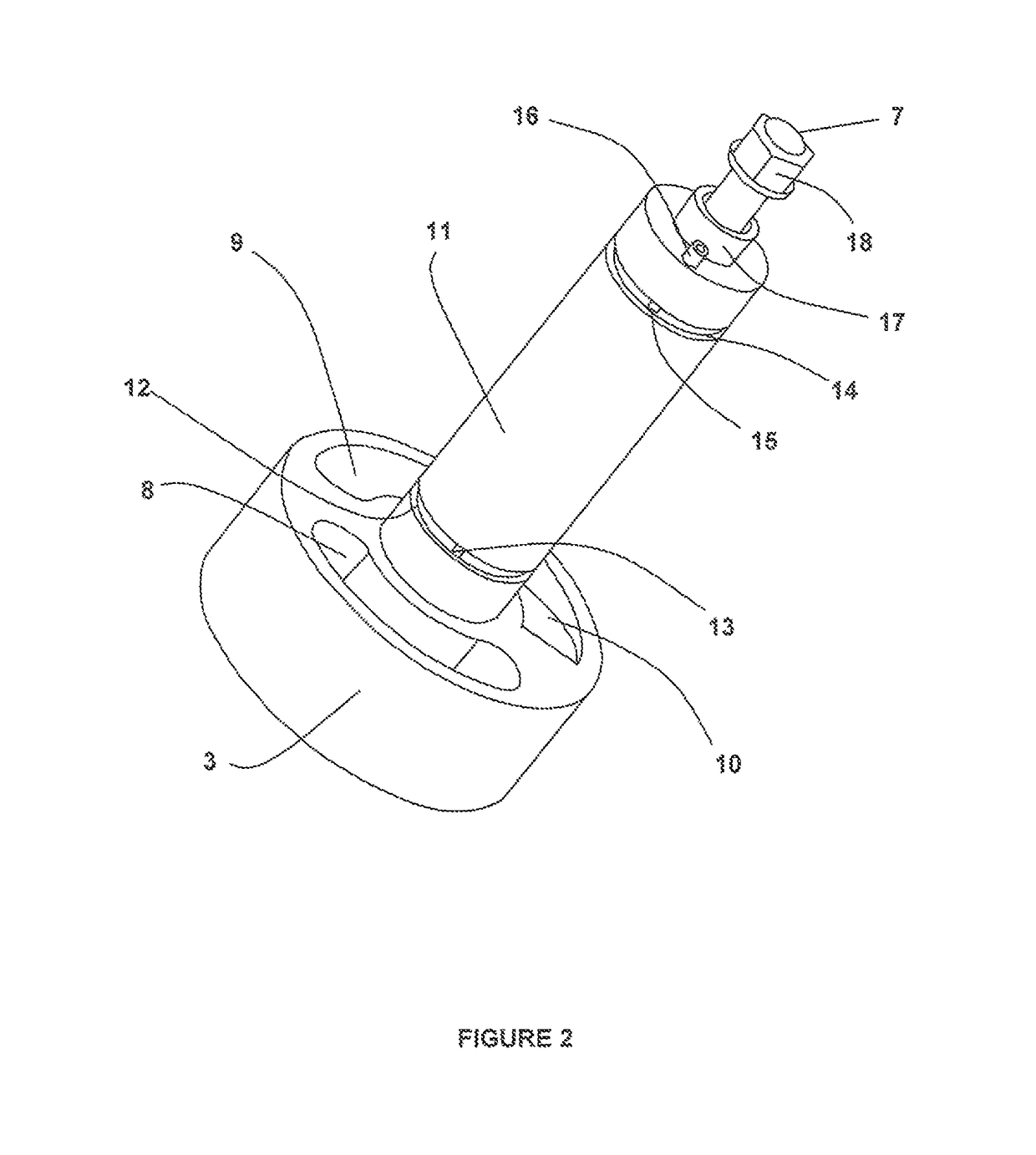
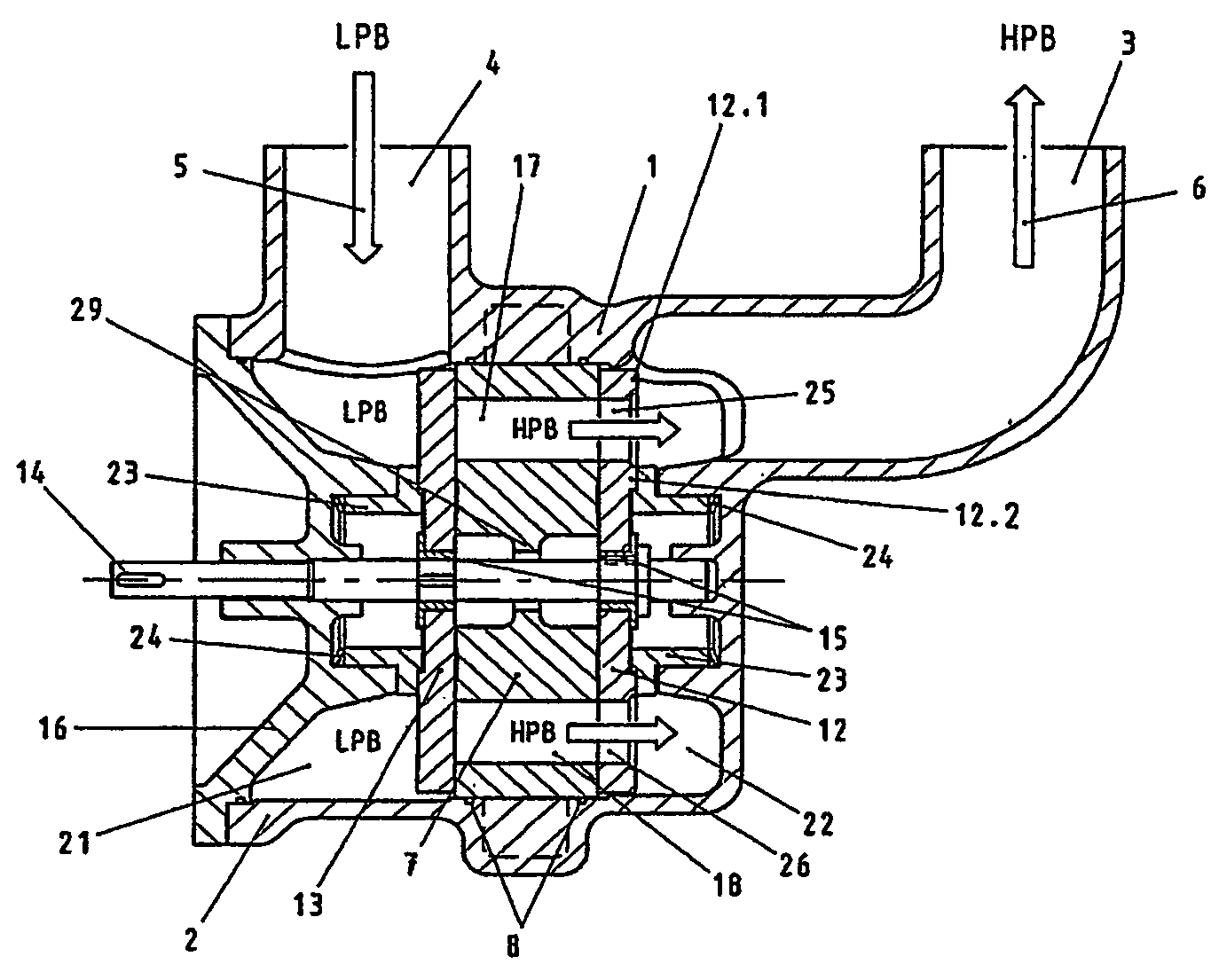
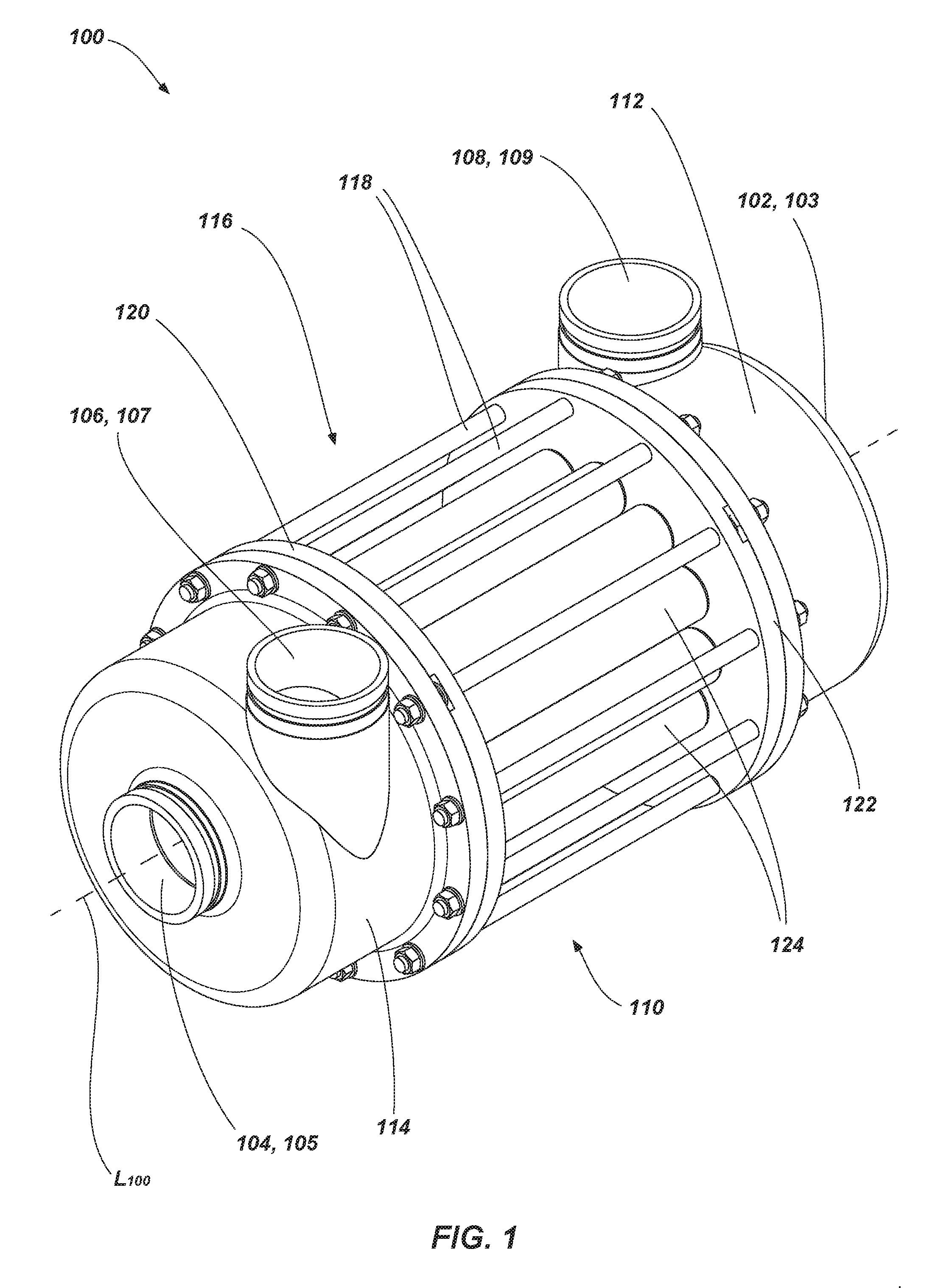
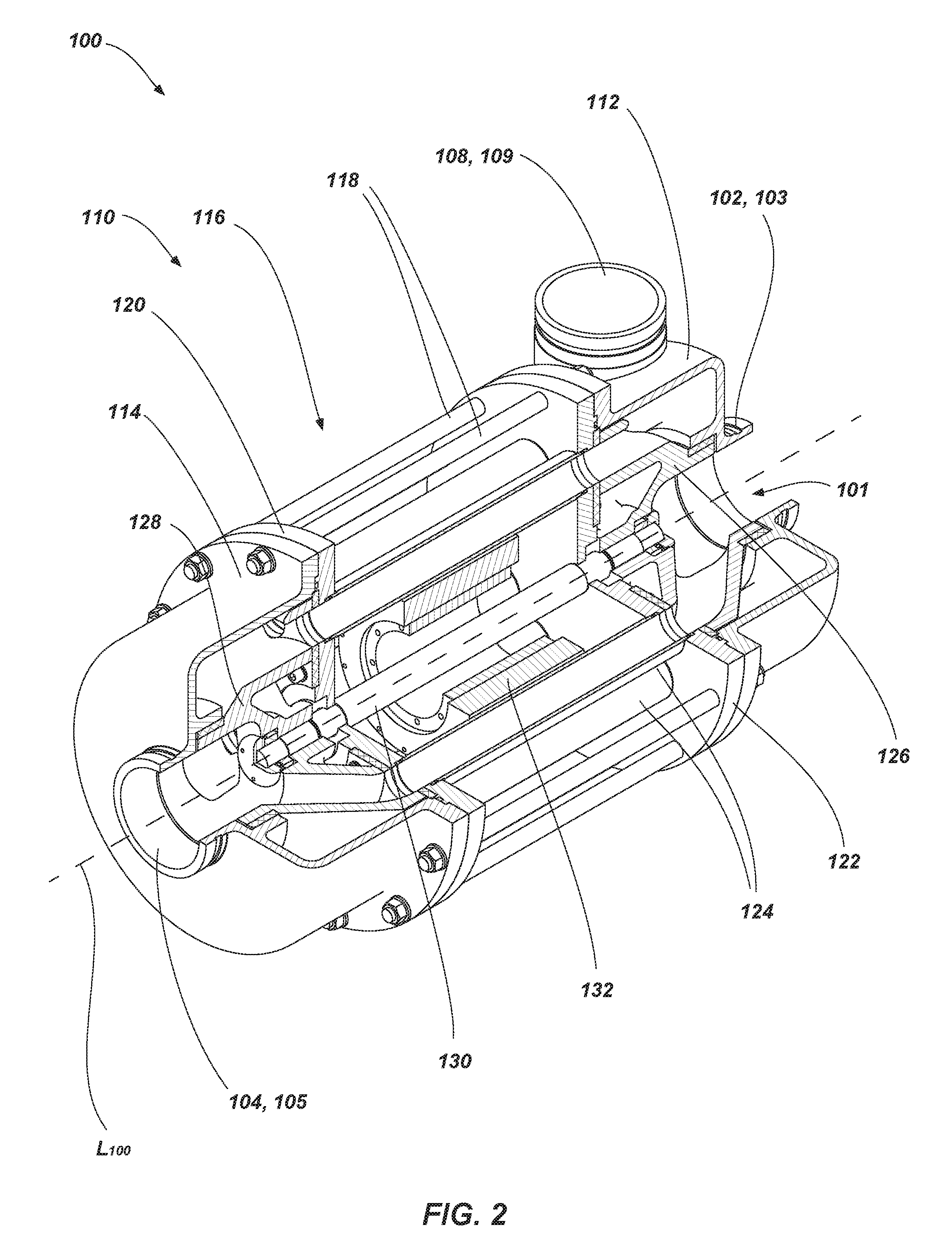
A pressure exchanger transfers pressure energy from a high pressure fluid stream to a low pressure fluid stream. Many industrial processes operate at elevated pressures and have high pressure waste streams. One way of providing a high pressure fluid to such a process is to transfer the waste pressure to a low pressure stream using a pressure exchanger. One particularly efficient type of pressure exchanger is a rotary pressure exchanger.
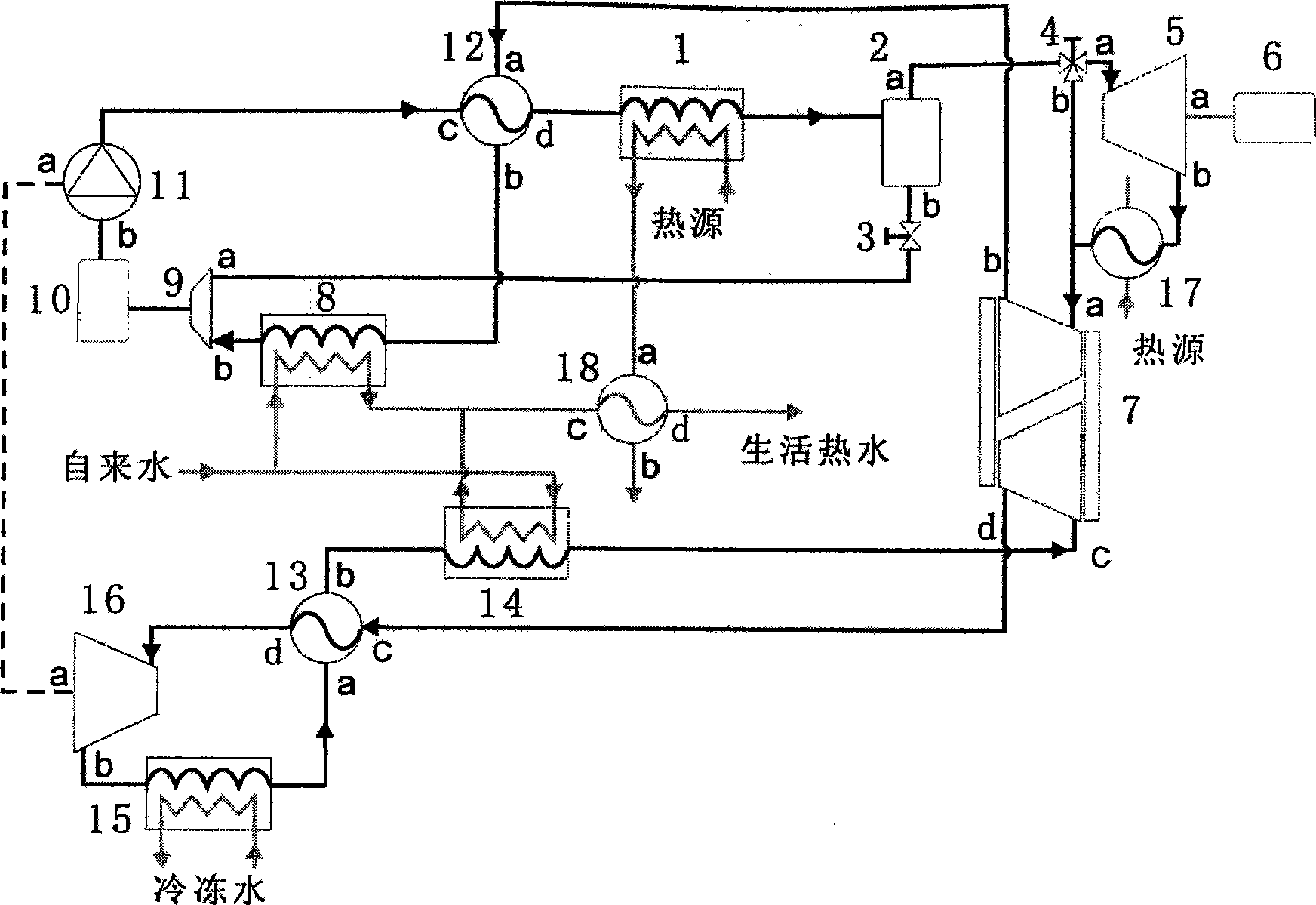
Fully integrated NF-thermal seawater desalination process and equipment
InactiveUS20060157410A1High yieldEffectively and efficiently dealGeneral water supply conservationReverse osmosisDistillationEngineering
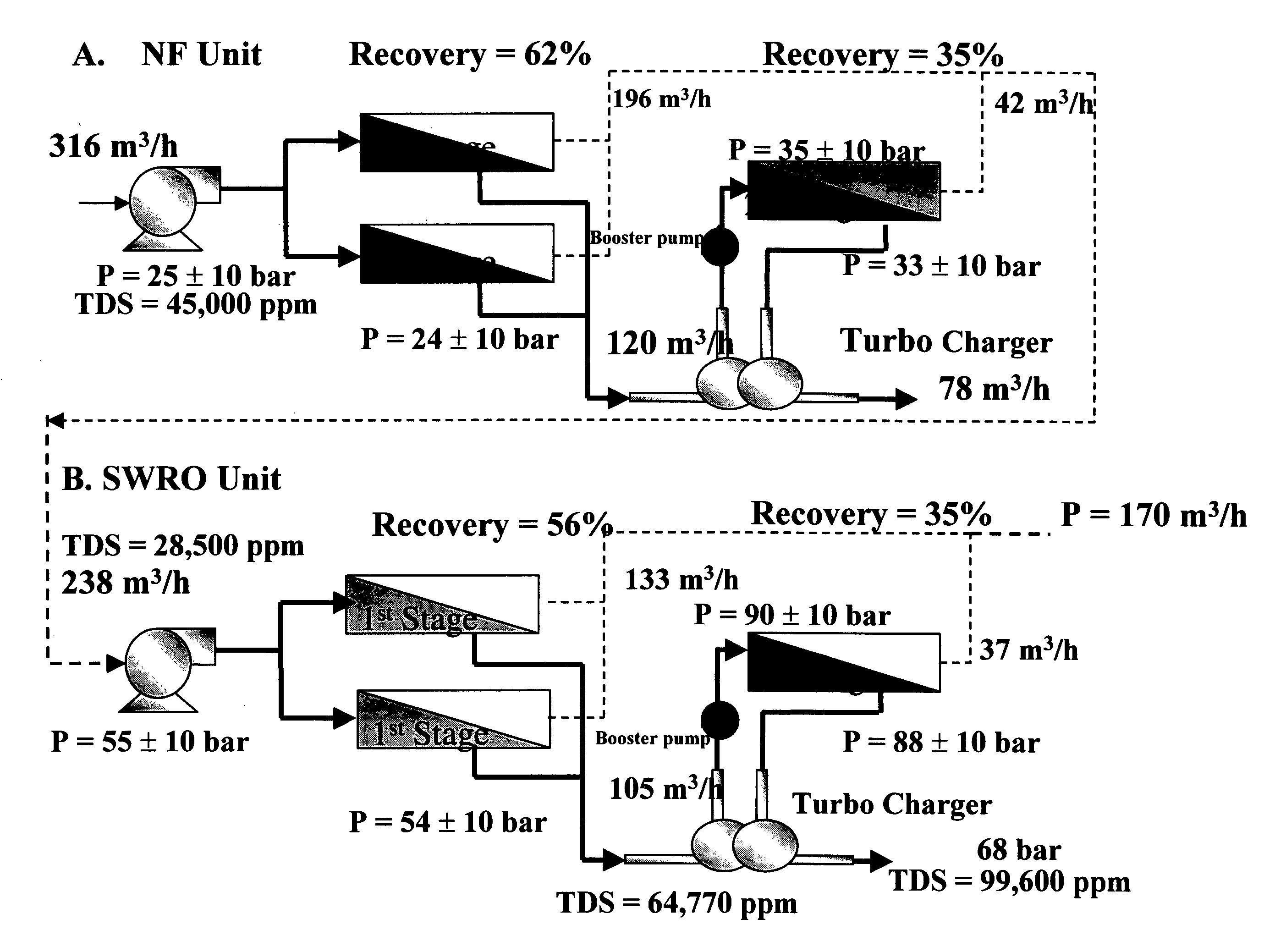
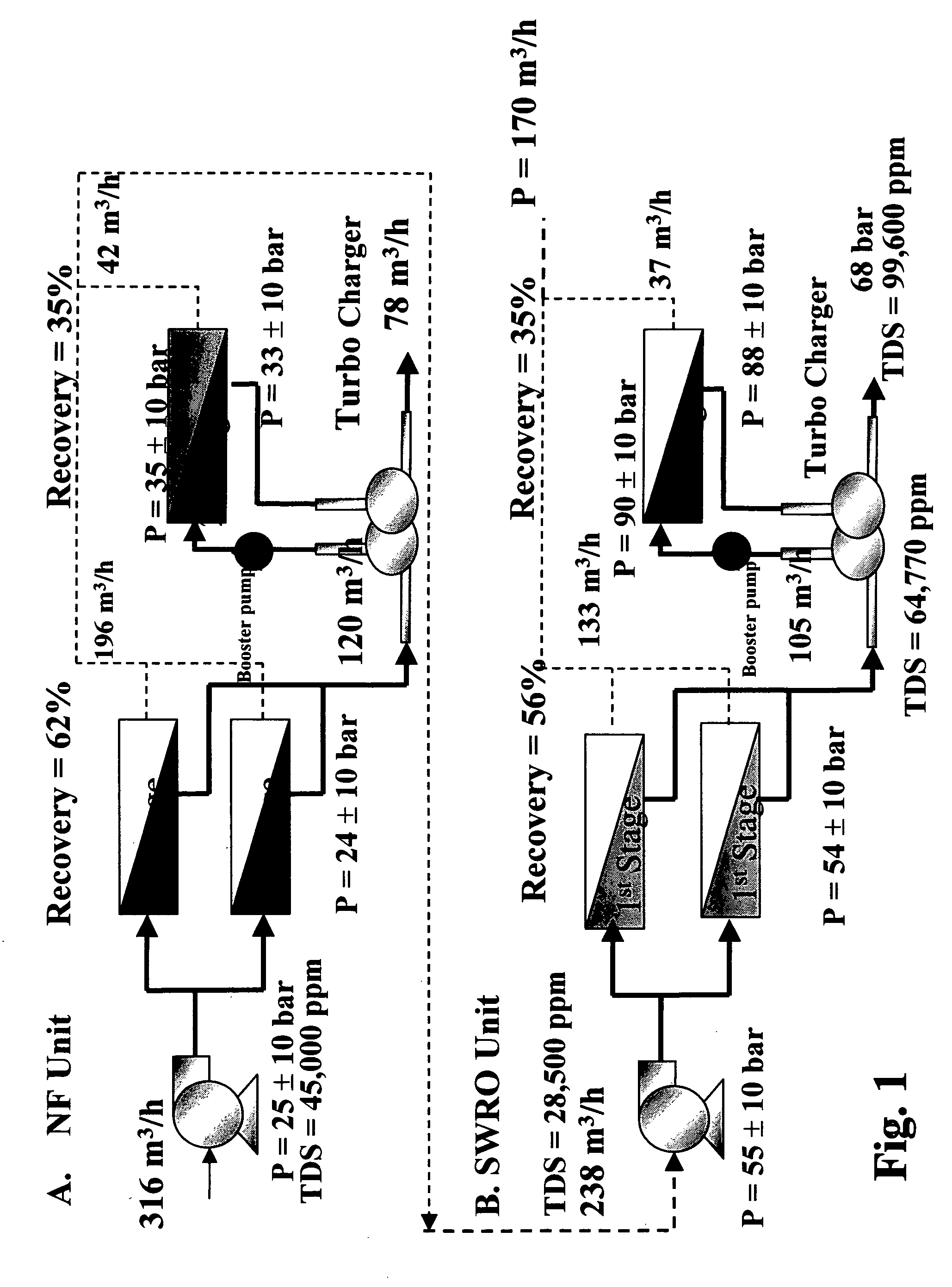
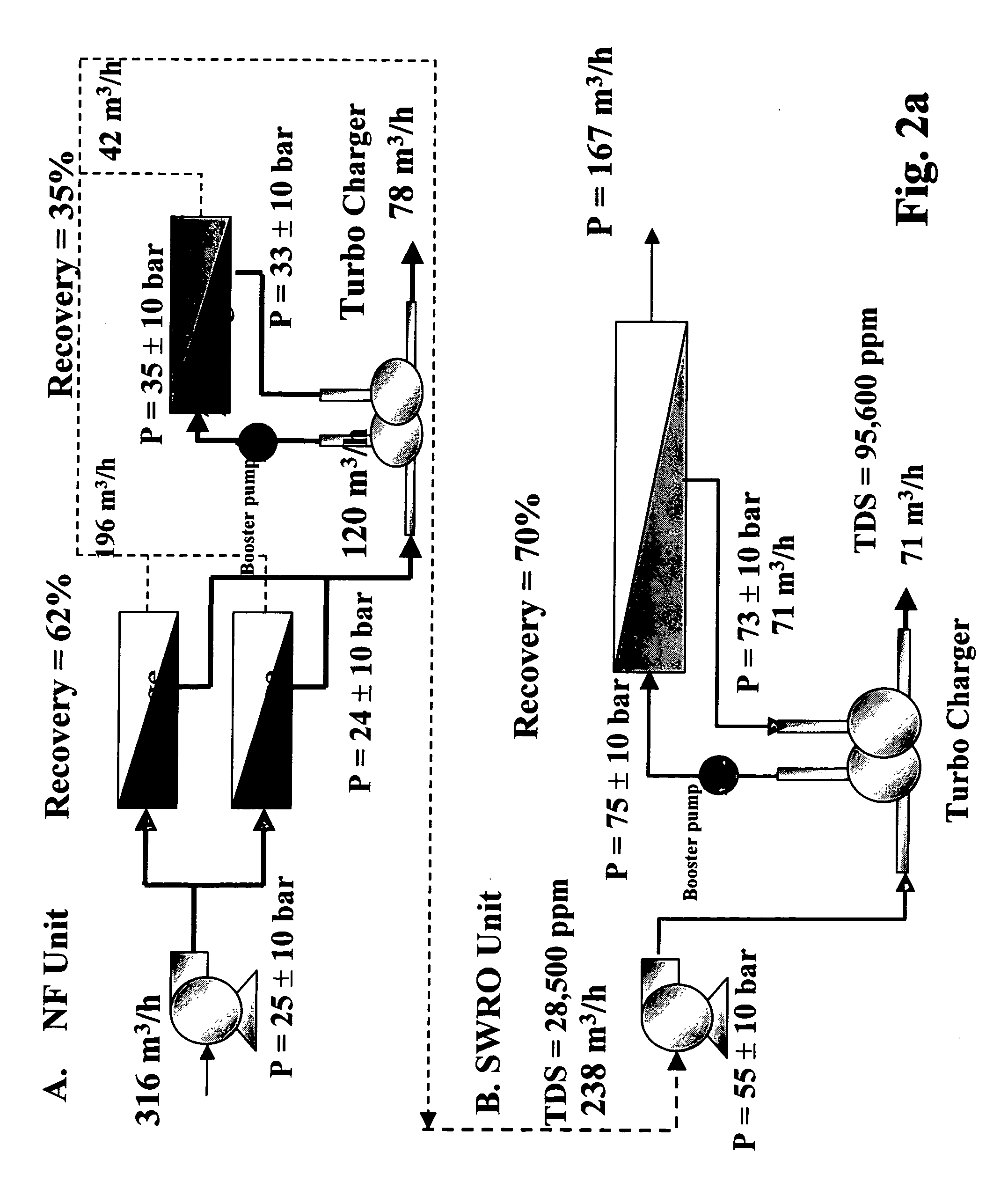
An optimal thermal seawater desalination process is disclosed, which combines two or more substantially different water pretreatment processes in a unique manner and in a special configuration, hereto unknown to prior desalination arts, to produce a high yield of high quality fresh water, including potable water. In this process a two stage NF membrane pretreatment unit (NF2) with an energy recovery turbo charger (TC) device in between the stages or equipped with an energy recovery pressure exchanger (PX) is synergistically combined with at least one thermal desalination unit to form a dual hybrid of NF2-Thermal (FIG. 4 ), or alternatively the two stage NF2 unit is synergistically combined with a two stage SWRO unit (SWRO2) with an energy recovery TC in between the stages or combined with one stage SWRO (SWRO1) equipped with an energy recovery TC or PX system and the reject from the SWRO2 or SWRO1 unit is made make-up to a thermal unit to form a tri-hybrid of NF2-SWRO2 reject-Thermal (FIG. 5 ). In both the cases of di- or trihybrids the thermal unit is equivalent to a multistage flash distillation (MSFD) or multieffect distillation (MED) or vapor compression distillation (VCD) or thermal reheat (RH) evaporator. Typically a process of this invention using the two stage NF2 initial pretreatment step will perform a semi-desalination step by reducing feed TDS by about 35 to 50%, but most important, especially to the thermal seawater desalination process, it removes the water recovery limiting, scale forming hardness ions of Ca++ and Mg++ by better than 80% and their covalent anions of sulfate to better than 95% and bicarbonate to about 65%. The removal of scale forming hardness ions, especially SO4=, and bicarbonates allowed for the operation of thermal unit in the above hybrids at top brine temperature (TBT) much greater than its present TBT limit by the singular conventional process of 120° C. for MSFD and operation of MED or VCD or RH unit at TBT much higher than their present TBT limit of 65-70° C., with many advantages gained by this process over prior art sweater desalination processes. The process of this invention exceeds all prior thermal seawater desalination arts in efficiency, including water yield, product water recovery ratio and unit water cost as well as in energy consumption per unit product which is equivalent or less than other efficient prior art seawater thermal desalination processes. By this process, an NF product recovery ratio of 75 and 80% or better is achieved from the high salinity Gulf sea (TDS≈45,000 ppm) and about an equal product recovery ratio is also obtained from the SWRO or thermal unit when it is operated on NF product for a total water recovery ratio in excess of 52% for seawater
Owner:SALINE WATER CONVERSION CORP SWCC
Pressure exchanger
ActiveUS7306437B2Increase capacityIncrease momentumRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsGeneral water supply conservationCavitationMomentum
Owner:ISOBARIC STRATEGIES INC
Speed-regulated pressure exchanger
InactiveUS20070137170A1Efficient operating stateMinimal mixing lossPump componentsGas turbine plantsMechanical engineeringPressure exchanger
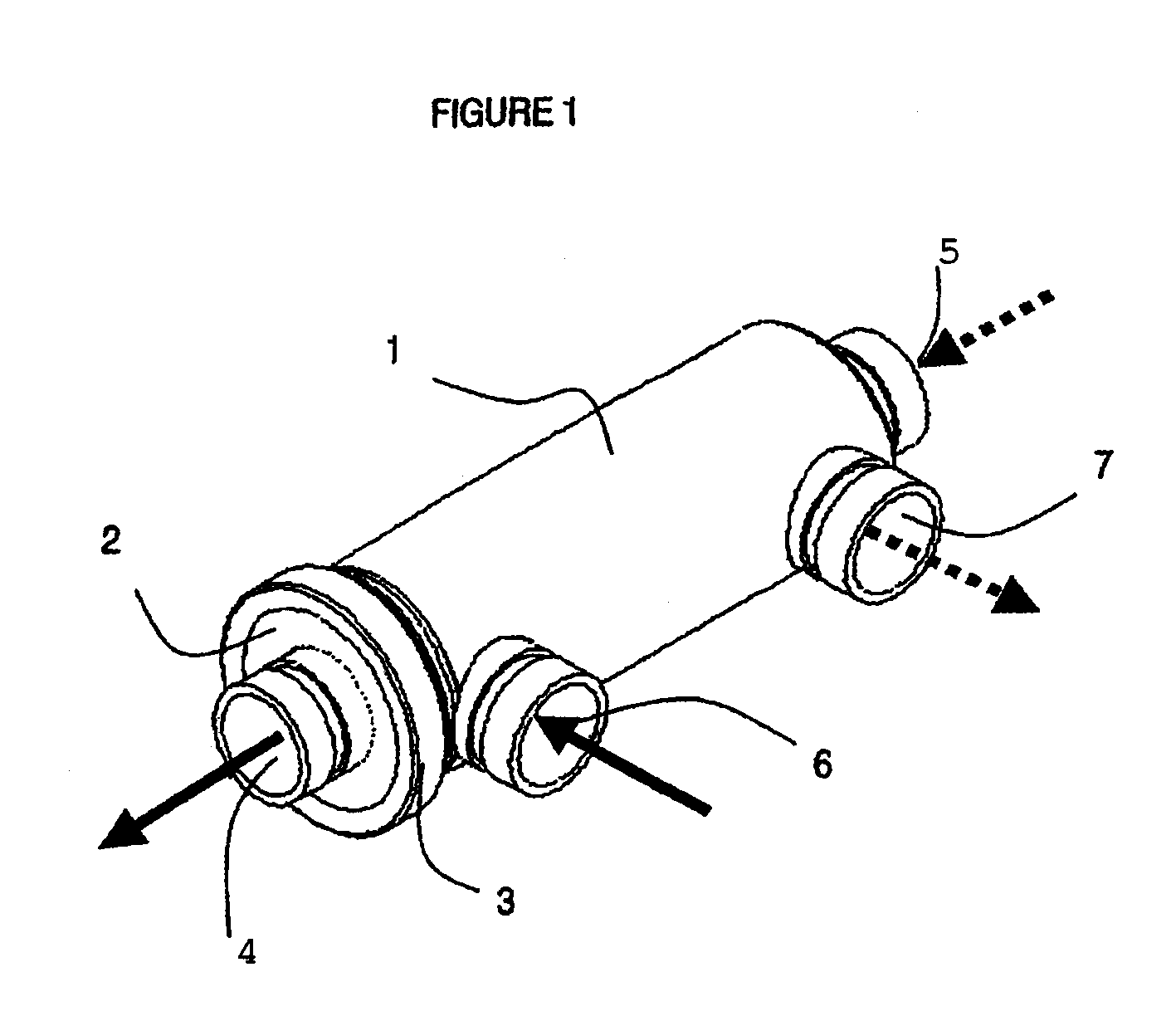
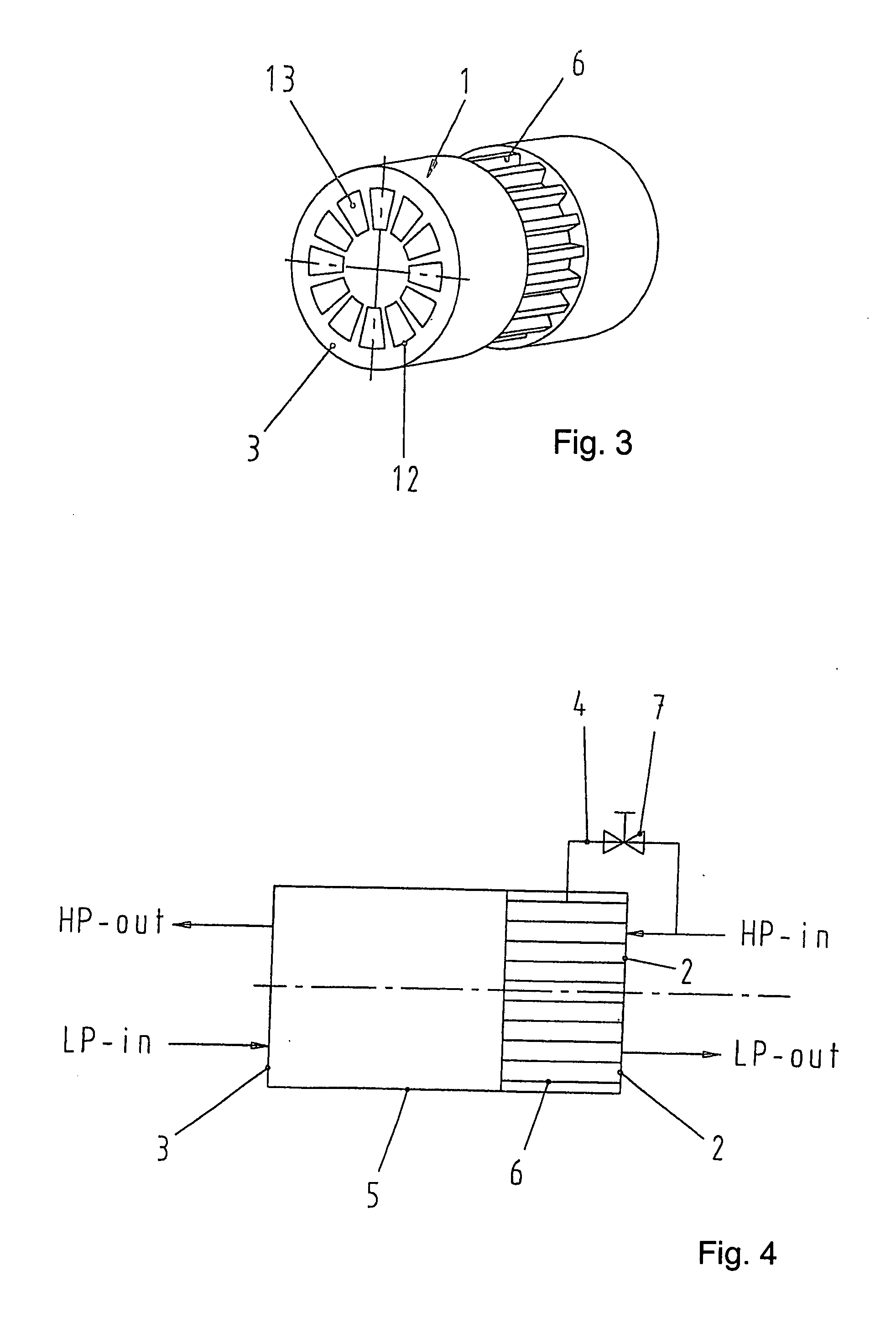
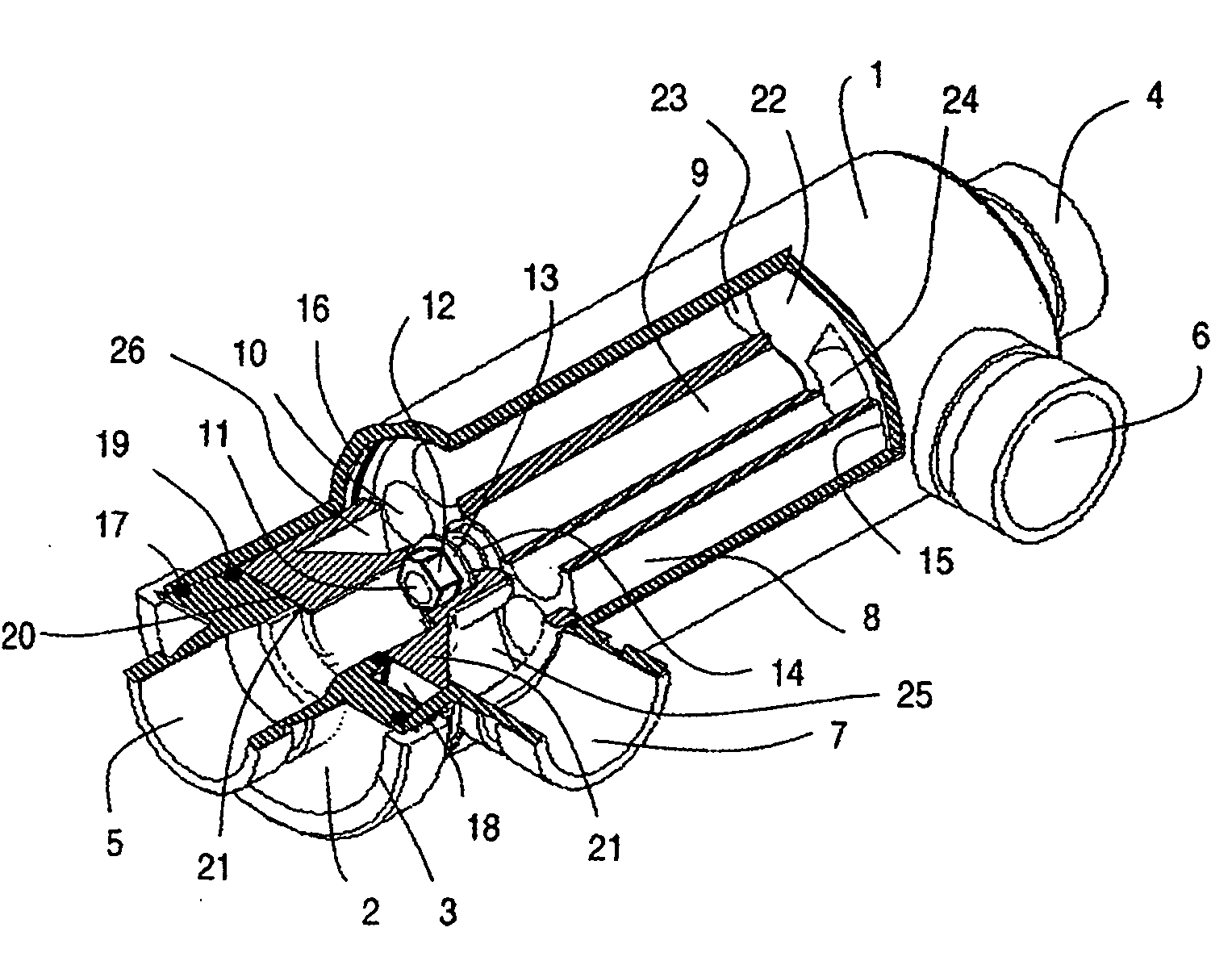
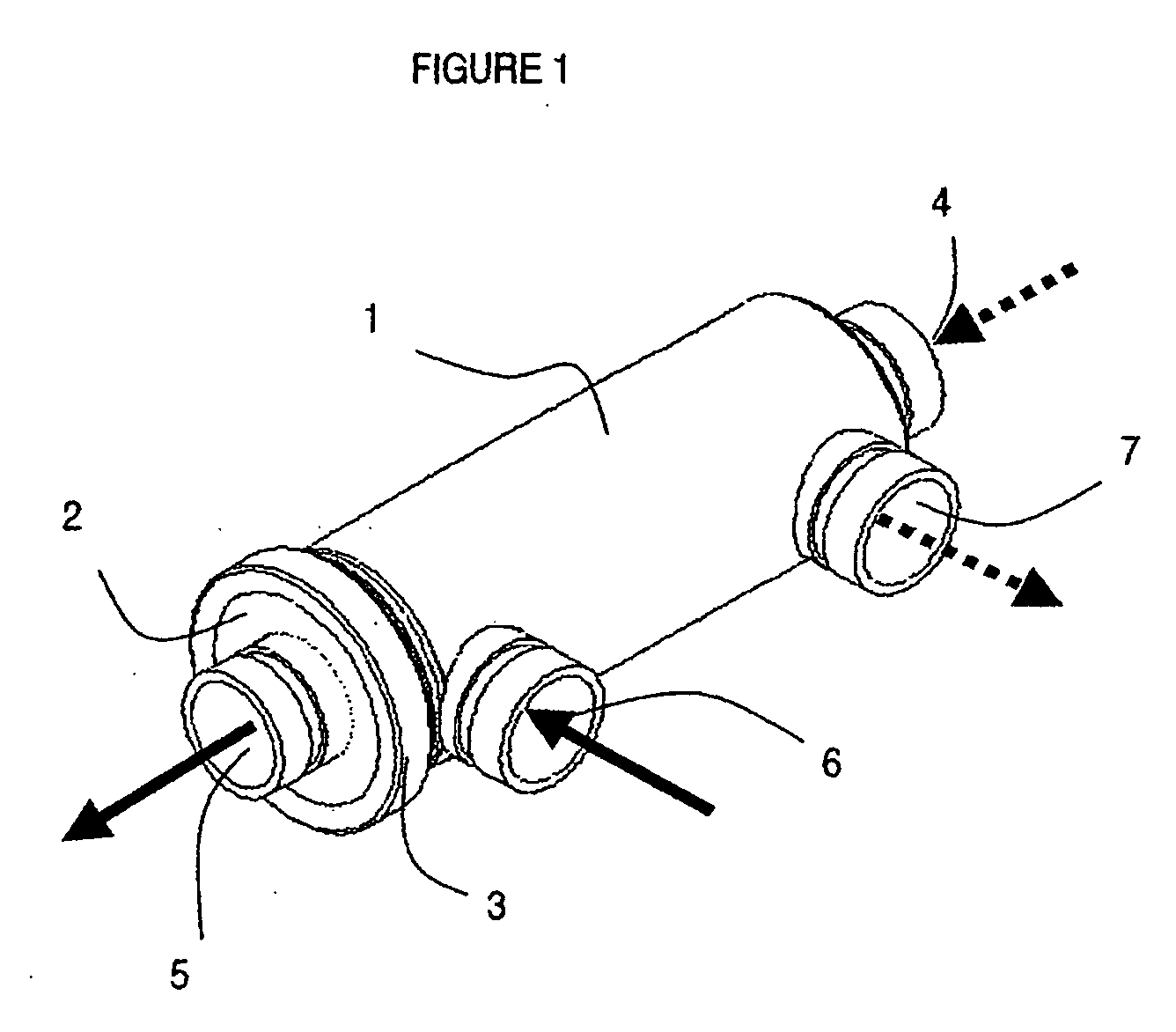
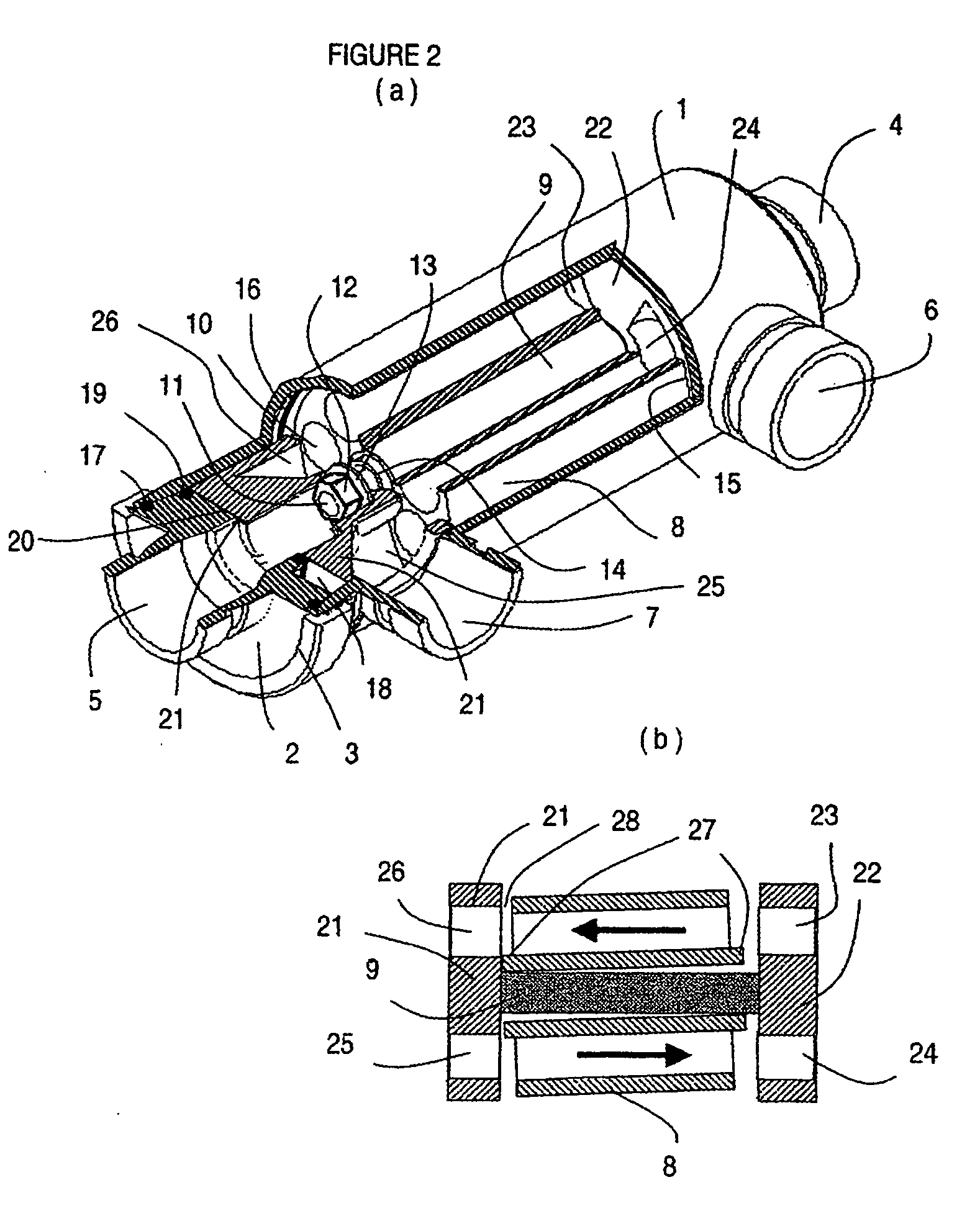
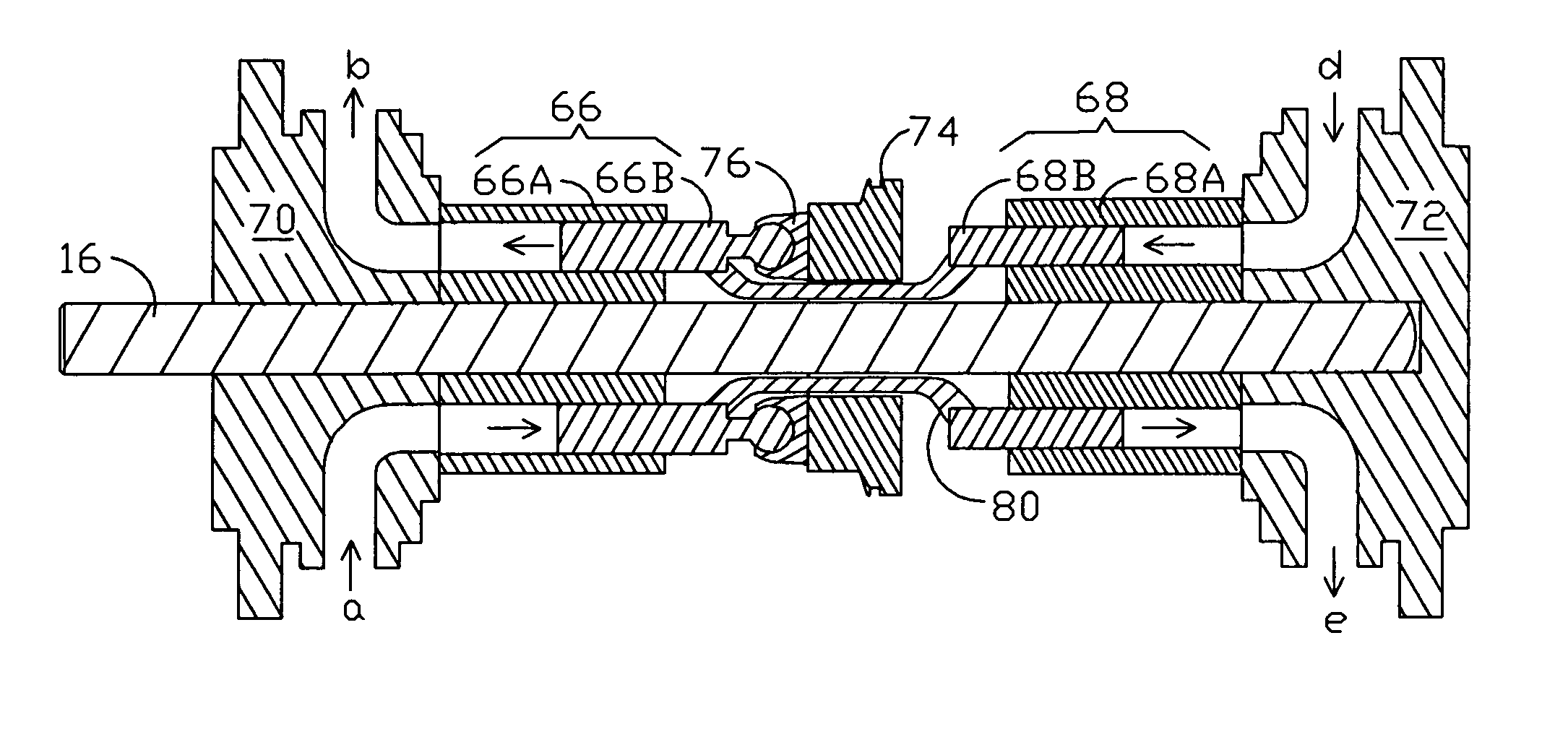
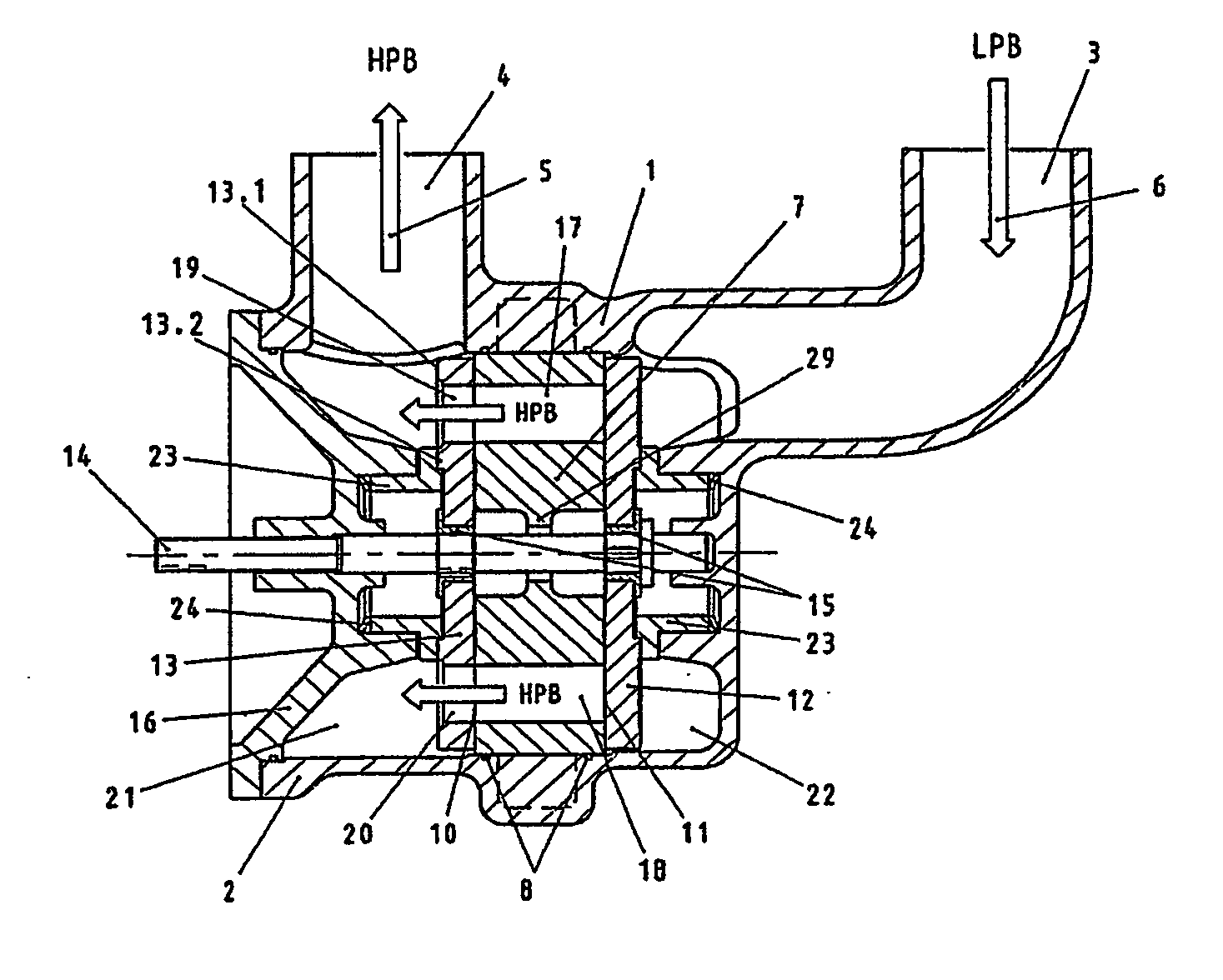
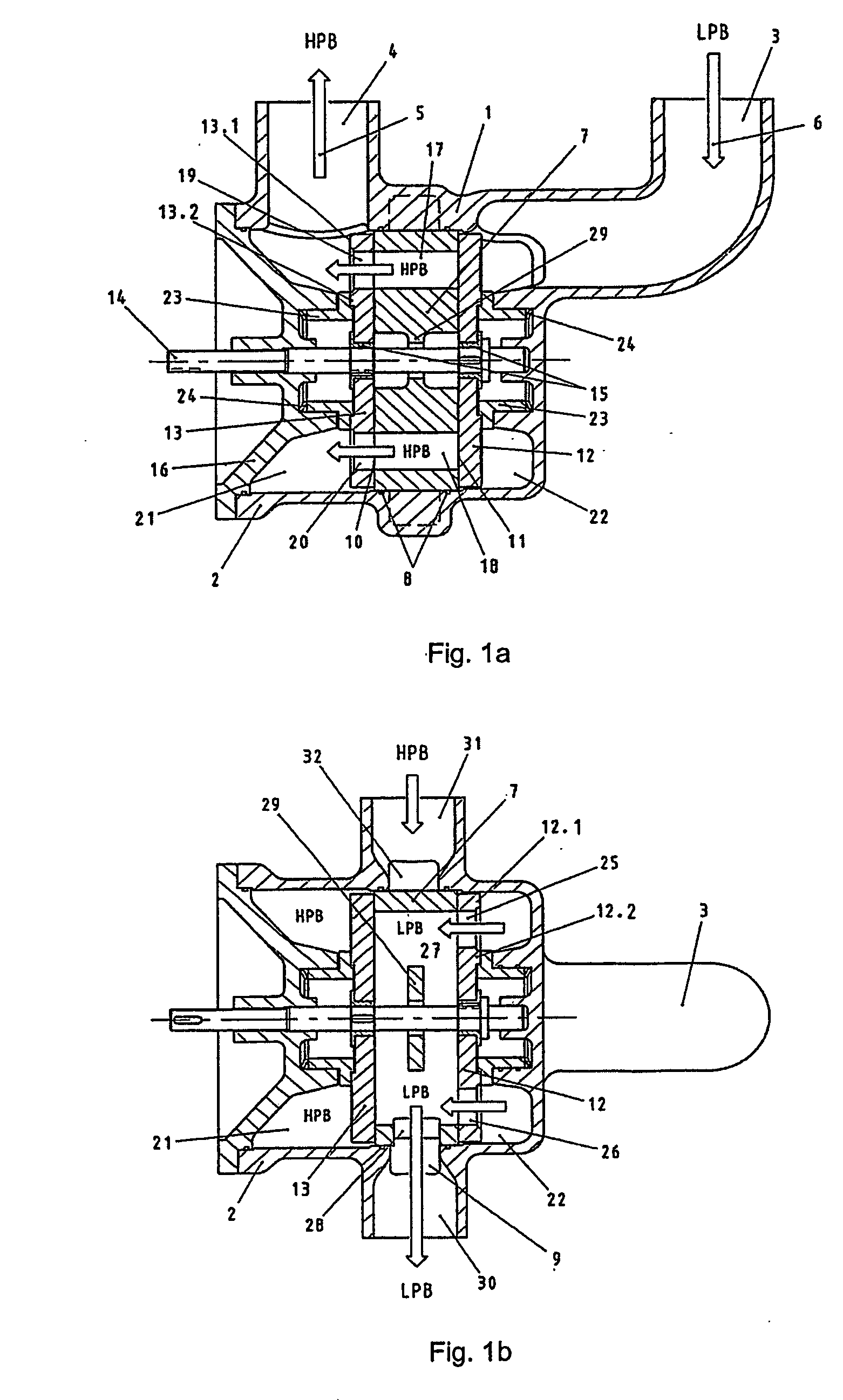
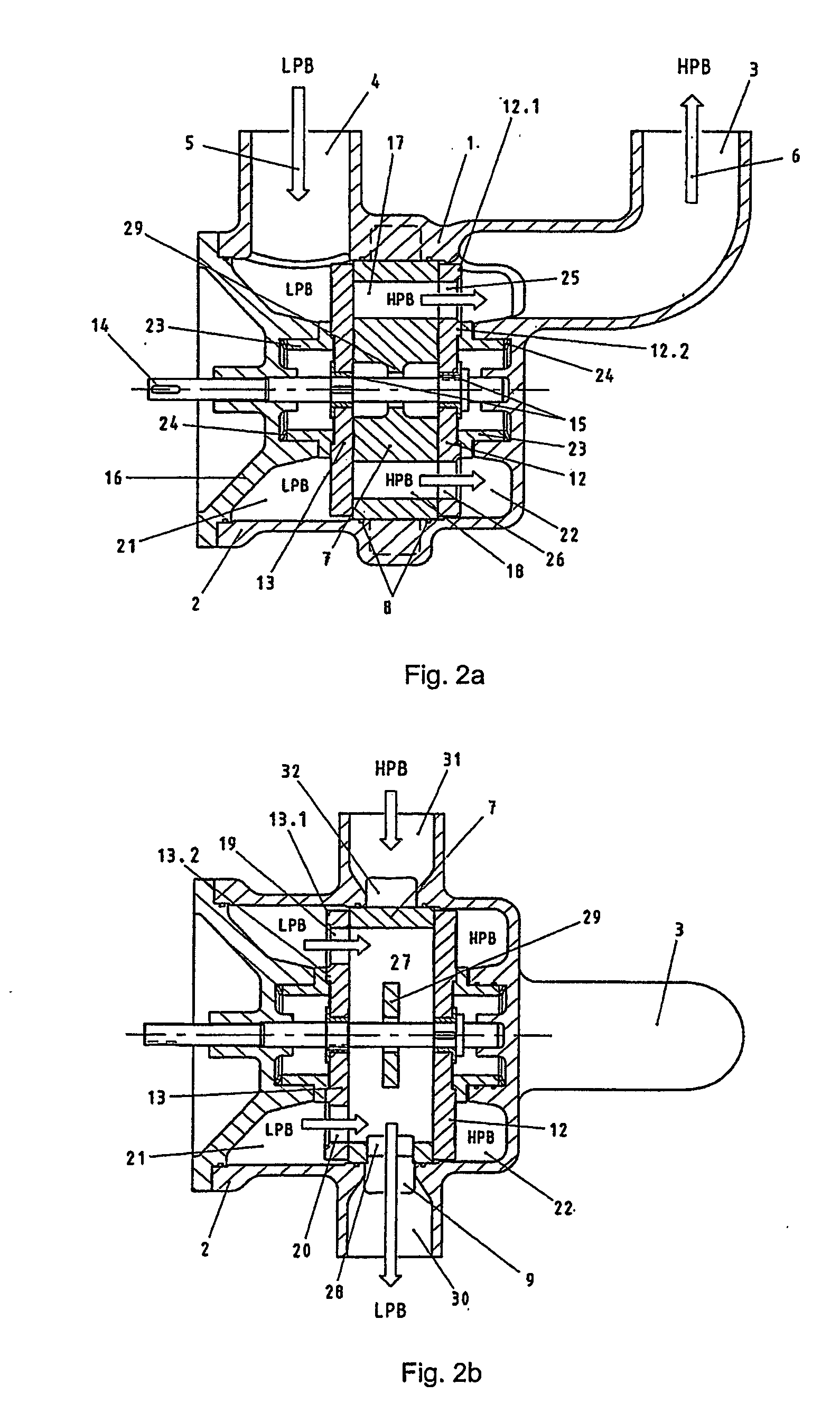
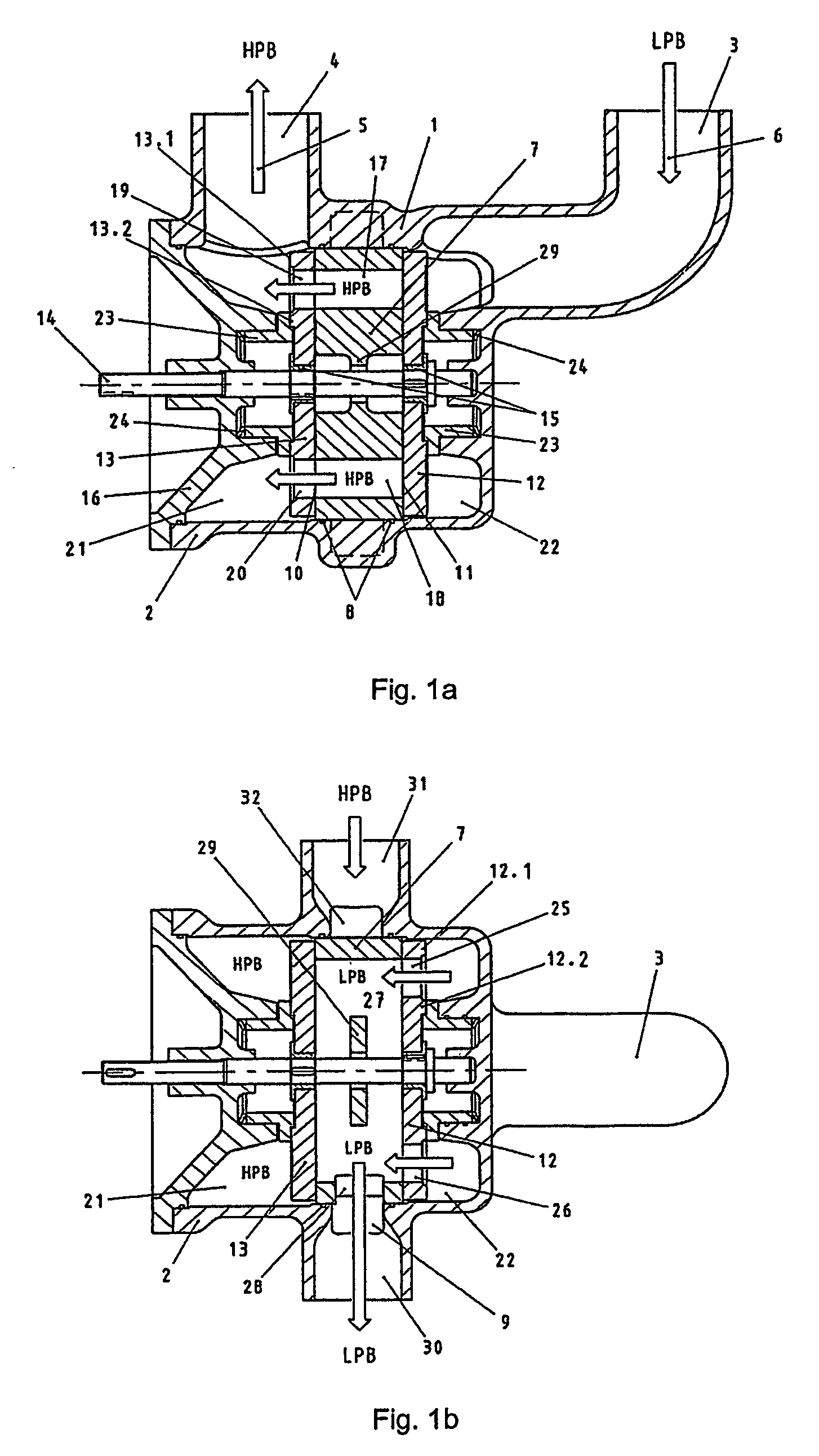
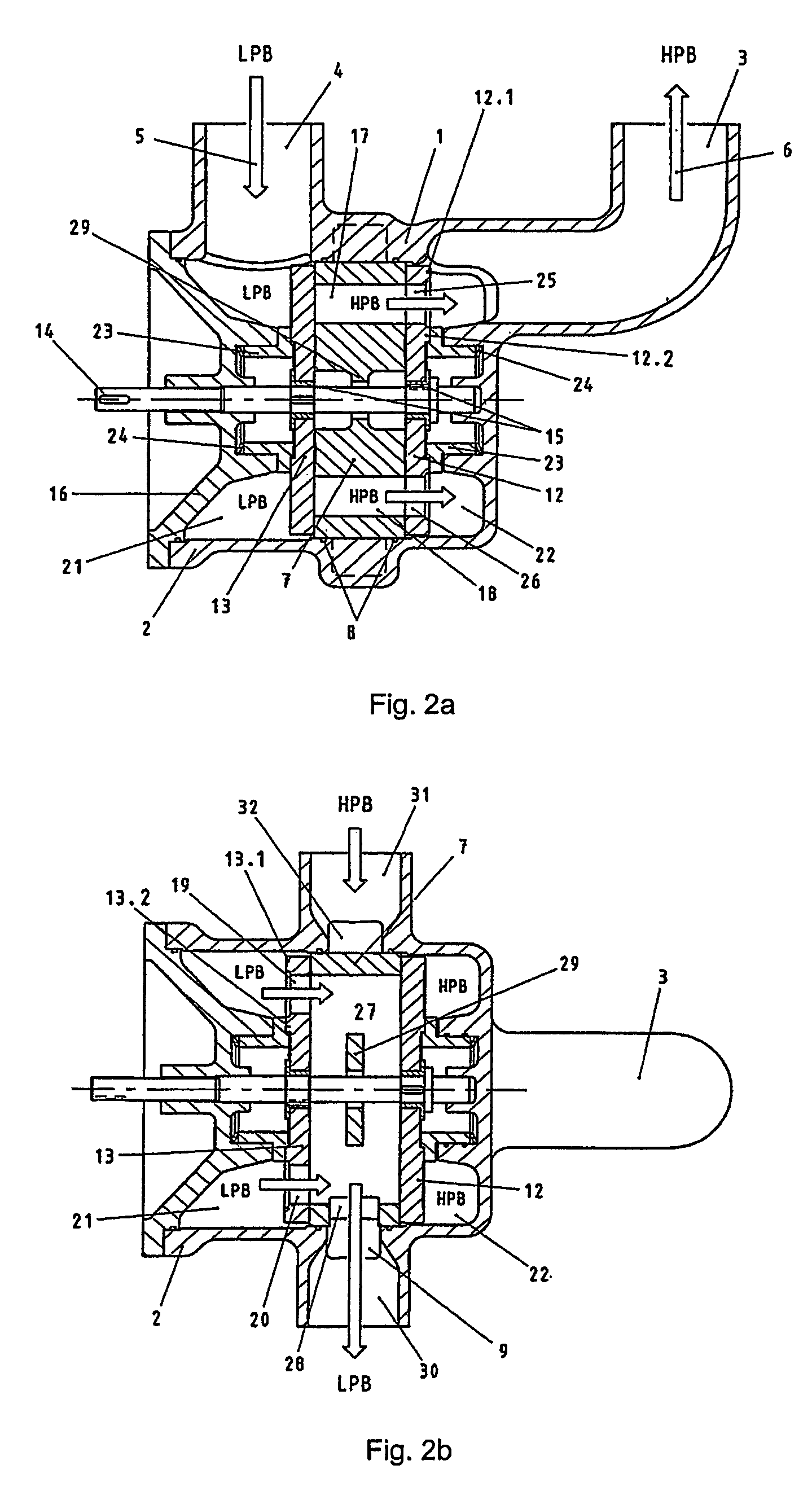
A pressure exchanger for transferring pressure from a higher pressure liquid in a first liquid system to a lower pressure liquid in a second liquid system having a housing (8) with inlet and outlet connection openings (10-10.3) for each liquid and a rotor (1) arranged in the housing for rotation about a longitudinal axis. The rotor has a plurality of through channels (13) arranged around the longitudinal axis with openings (12) on axial end faces (2, 3) of the rotor. The rotor channels (13) are connected to the connection openings (10-10.3) through flow openings (11-11.3) in the housing such that during rotation of the rotor high pressure liquid and low pressure liquid are alternately supplied to the respective systems. A predominantly axially extending flow transition is formed between the flow openings (11-11.3) in the housing and the openings (12) of the rotor channels (13), and the flow openings in the housing form part of curved cavities (19) with each cavity (19) simultaneously covering several rotor channel openings (12) and having a shape which equilibrates the liquid flow speed in the vicinity of the housing flow openings (11-11.3). External surfaces (5-5.3) of the rotor (1) have an energy converting or energy transmitting configuration (6), and a partial flow (TS) of high pressure and / or flow energy impinging on the configuration (6) produces rotation of the rotor (1). A regulator (7) the varies the amount of the partial flow (TS) and the rotational speed of the rotor (1) and controls the rotational speed of the rotor for substantially shock-free admission of the mass flow into the rotor channels (13).
Owner:KSB AG
Combined axial piston liquid pump and energy recovery pressure exchanger
InactiveUS7799221B1Improve welfareMinimize the numberMembranesGeneral water supply conservationReciprocating motionEnergy recovery
A pumping machine, that can serve a system as the sole main pump for pressurizing a primary liquid flow, incorporates, in a single machine, a rotor-drum type AP (axial piston) pump and a PX (pressure exchanger) that recovers energy from a secondary liquid flow such as the brine discharge from an RO seawater desalination system, with benefits including fewer moving parts and small machine size along with lower capital and operating costs. A single rotor-drum containing the cylinders and pistons is located between two end blocks, one or both configured with manifold passageways, ports and sliding valves. A swash-plate at one end reciprocates the pistons axially when the rotor-drum is rotated. Two working chambers, primary and secondary, are formed at opposite ends of a single piston in each cylinder, thus enabling the single rotor-drum to function as a primary liquid-pressurizing axial pump (AP) with sliding valves at the primary end enabling primary liquid pumping, and as a secondary outflow-driven pressure exchanger (PX) recovering energy from pressure drop in the secondary liquid flow and thus contributing work to primary pumping, saving energy and reducing operating costs.
Owner:OCEAN PACIFIC TECH
Pressure exchanger
ActiveUS20060032808A1Improve flow capacityIncrease momentumRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsGeneral water supply conservationCavitationMomentum
A pressure exchanger for transferring pressure energy from a relatively high-pressure fluid stream to another relatively low-pressure fluid stream is provided. A ducted rotor is positioned on a central axle between two end covers inside a pressure vessel with a coaxial inlet and outlet pair that is in communication with a pair of low pressure ports having inclination forming an inlet tangential velocity vector in the direction of rotor rotation and an outlet tangential velocity vector in opposite direction imparting a rotational momentum on rotor. A pair of high-pressure ports is adapted for flow without inclination and imparts no momentum to rotor and flow can be varied without impacting the rotor's RPM. The end covers have a sloped surface following a flat sealing area that increases the clearance in the direction of rotation causing increased outflow during depressurization and lower duct pressure before duct is exposed to low pressure port and furthermore causing increased inflow during the pressurization phase before duct is exposed to the high pressure port, which will dissipate pressure energy as opposed to producing cavitation or pressure waves with result wear and noise.
Owner:ISOBARIC STRATEGIES INC
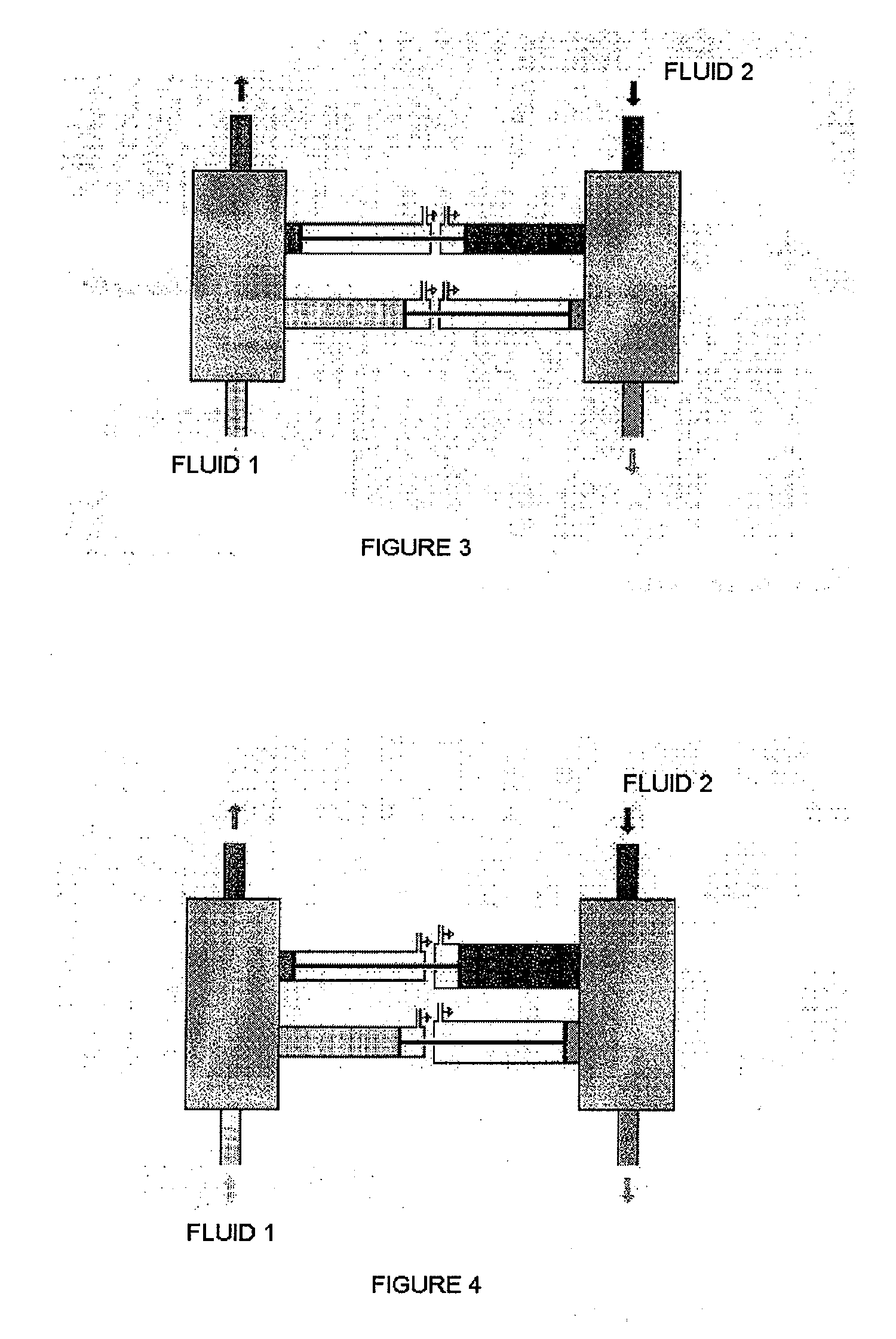
Fluid exchanger devices, pressure exchangers, and related methods
ActiveUS20140048143A1Scale upSpecific water treatment objectivesWater/sewage treatmentRotary valveEngineering
Exchanger devices include a plurality of fixed exchange ducts and a rotating valve assembly for directing flow to and from the plurality of exchange ducts. Methods of exchanging pressure between fluid streams may include directing fluids through an exchange device and pressurizing a fluid in the plurality of exchange ducts of the exchanger device.
Owner:FLOWSERVE PTE LTD
Liquid excess pressure energy recovery device
ActiveCN101865191AImprove energy recovery efficiencyStrong ability to adapt to changing working conditionsFluid-pressure actuator componentsHigh energyDrive shaft
The invention provides a liquid excess pressure energy recovery device. The device comprises a drive motor and a rotating assembly, wherein the rotating assembly comprises a rotating ring used for seal, a drive shaft, a rotor and a driven shaft; the rotor is provided with one or more flow channels which are parallel to the axial direction of the drive shaft; and a pressure exchanger is also provided with a fixed assembly, wherein the fixed assembly comprises a mechanical sealing cover, a static ring used for mechanical seal, a fixed valve plate, a floating valve plate, a shell, a compression spring, an outer end cover and a bolt. The liquid excess pressure energy recovery device of the invention has an energy recovery rate over 90 percent, has much higher energy recovery rate compared with pressure energy utilization devices such as a Francis pump, a Pelton turbine and the like which have the energy recovery rate of between 30 and 70 percent and need converting mechanical energy intermediately, has higher adaptability to working condition changes, and can also keep the energy recovery rate over 90 percent when the conditions such as flow rate, temperature and the like change.
Owner:SUNUP ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
Double-dial coupled type pressure exchanger for sea water or brine reverse osmosis desalination system
InactiveCN1994905AReduce rotation speedIncrease the processing load of a single machineGeneral water supply conservationSeawater treatmentSaline waterCoupling
The invention discloses a double-rotary disc coupling typed pressure exchanger of seawater or bitter saline water reverse osmosis desalination system, which comprises the following parts: cylinder, left rotary disc, right rotary disc, left end lid, right end lid and middle axle. The invention increases single set disposing load of pressure exchanger, which reduces rotary speed to flow working liquid continuity and stability.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
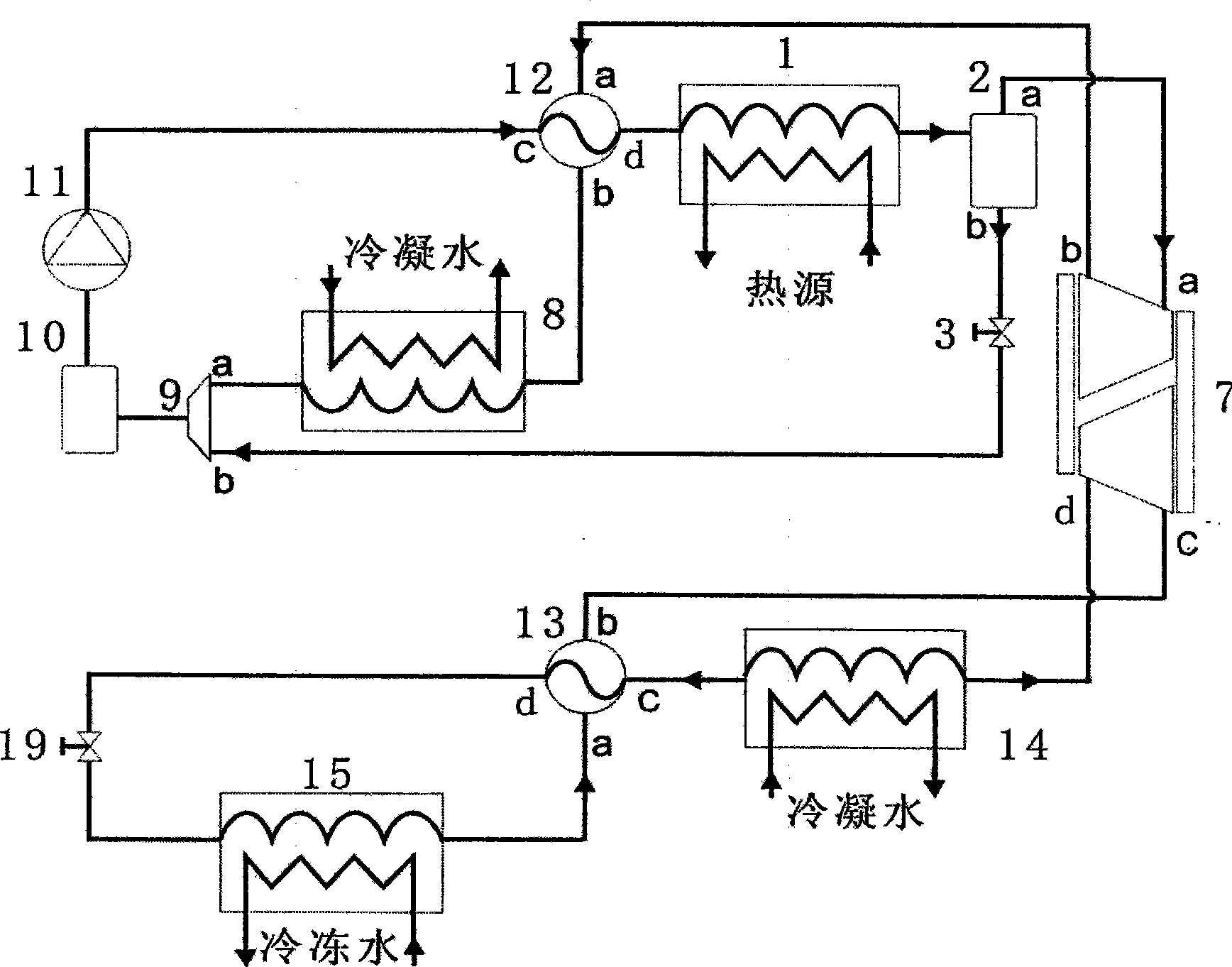
Heat-driven refrigeration and power generation integration apparatus
InactiveCN101458000AWorking fluid selection is not limitedOptimizationCompression machines with non-reversible cycleSteam engine plantsVapor liquidThermal energy
The invention provides a device integrating functions of heat-driven refrigeration and power generation which comprises a heat energy engine and a refrigerator. The heat energy engine comprises a circulating pump, a steam generator, a vapor liquid separator, a two-way valve, a three-way valve, a turbine, a generator, a pressure exchanger, a first vapor-liquid heat exchanger, a first condenser, a unit with two mixing canterns, a reservoir and a reheater. The heat energy engine utilizes heat energy to generate high pressure vapor to drive the compression refrigeration and promote the turbine and the generator to generate power. The refrigerator comprises an evaporator, a second vapor-liquid heat exchanger, a pressure exchanger, a second condenser and an expander. The shaft power output of the expander of the refrigerator is used for driving the circulating pump. Working media of the heat energy engine and the refrigerator can be the same or not. Non-azeotropic working media can be adopted for improving the efficiency. The heat driven-refrigeration and power generation integrated device can use a low grade heat source and can be regulated into individual cold supplying system, a cooling and power combined system or an electricity heat and chilled water congenerating system. The heat driven-refrigeration and power generation integrated device has the advantages of high efficiency, small investment, short installation period, low maintaining fee, etc.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Split-chamber pressure exchangers
InactiveUS20100014997A1Lower performance requirementsComplicatesPiston pumpsPositive-displacement liquid enginesEngineeringChamber pressure
The invention relates to split-chamber pressure exchangers. Split-chamber pressure exchangers are characterized in that the pressure exchange chambers and the pistons thereof are split in two. Each fluid passes through the corresponding chamber thereof, such that said fluids cannot be mixed. The cross sections of the chambers can be varied in order to vary the transmitted pressure. The reverse line operation can be established and synchronized using a U-shaped tube with telescopic sides and a fixed base filled with fluid or diametrically opposed curved lines, and multiple arrangements can be used. Split-chamber pressure exchangers can be used as surface or well pumping systems and the pumping fluid used can differ from the fluid to be pumped. Different levels of any material can be exploited at any storage site using a chamber with elastic walls filled with fluid and attached to the bottom. Electric power can be generated by centrifuging the pre-pumped fluid.
Owner:PREXTOR SYST
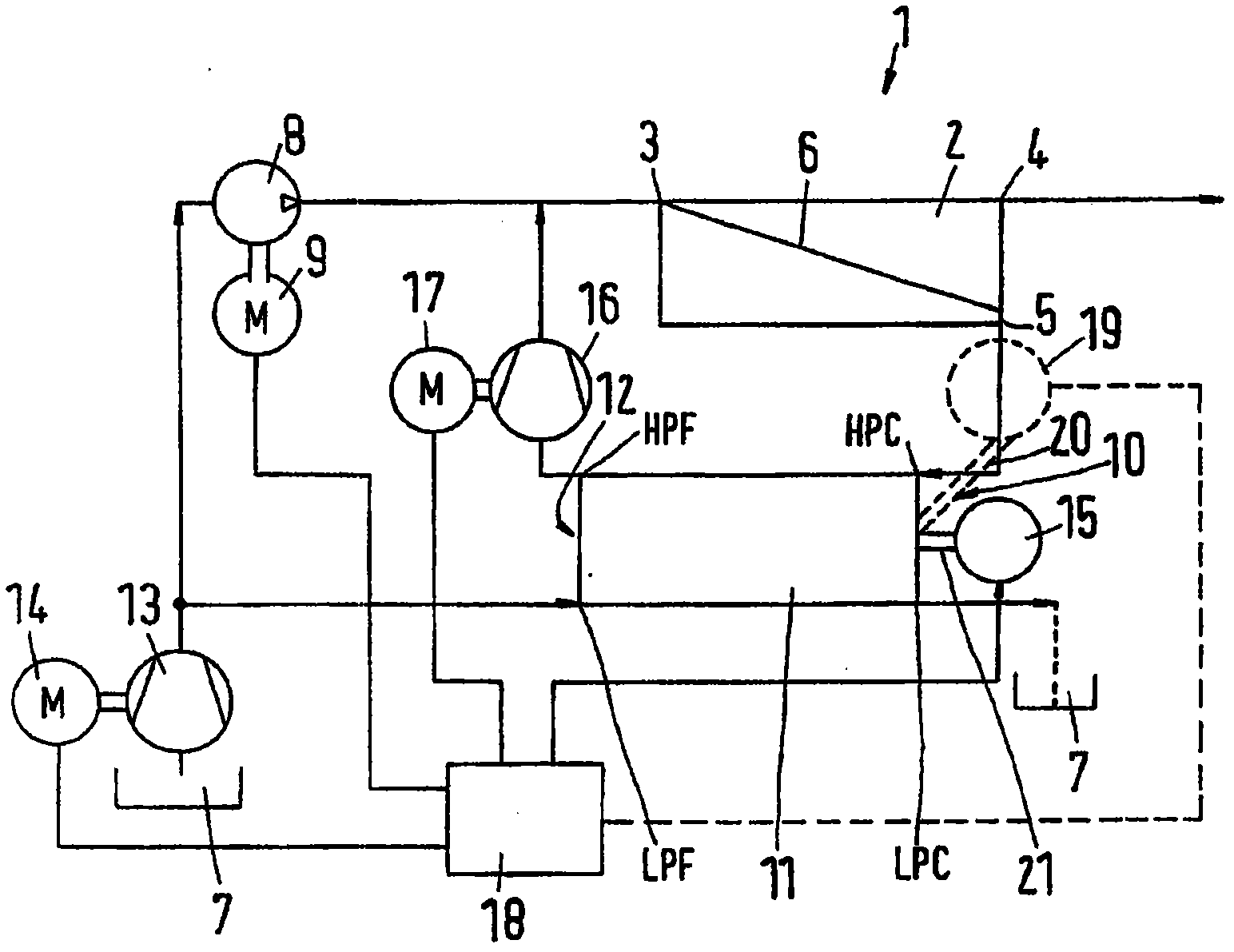
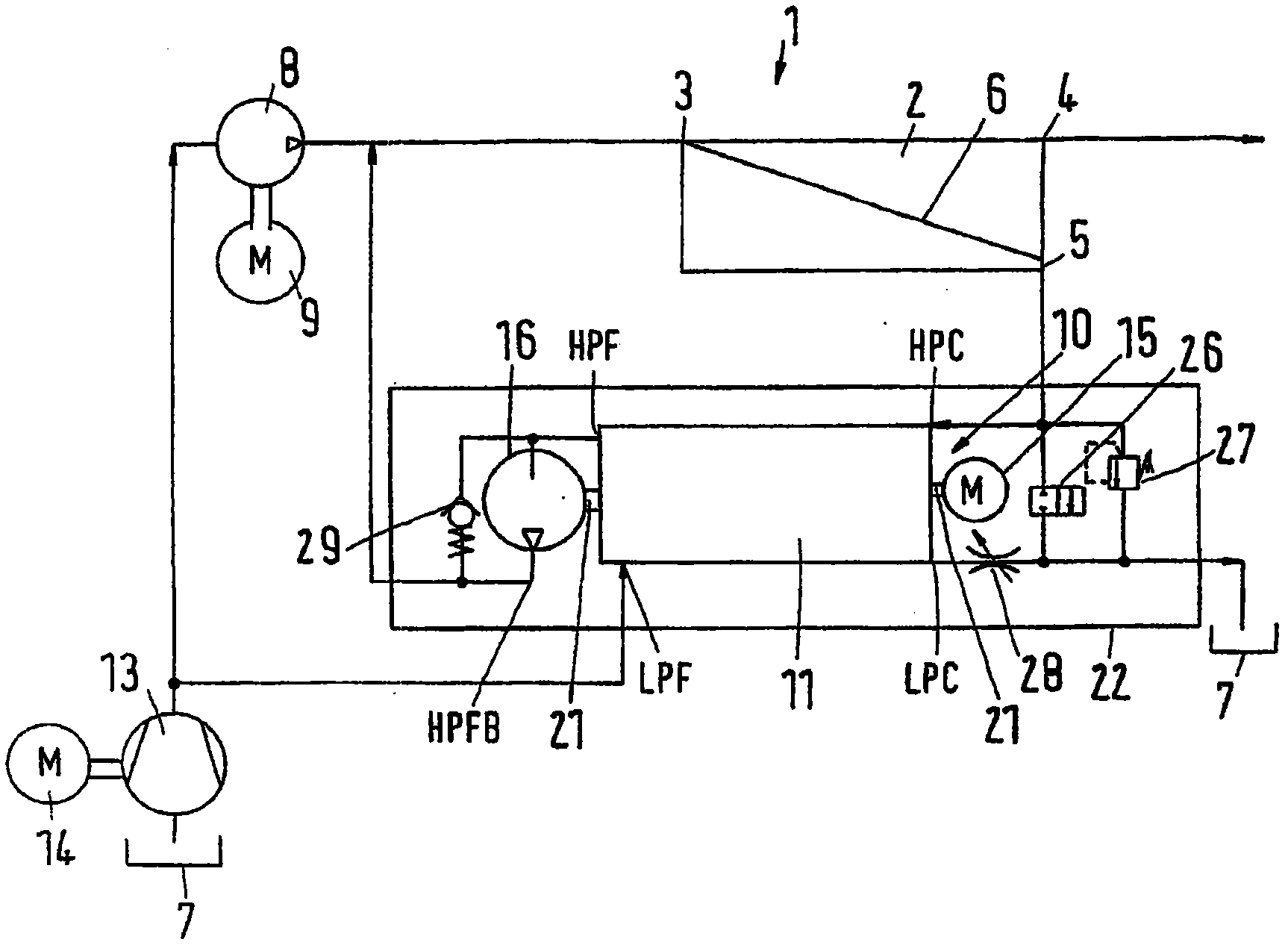
Pressure exchanger system
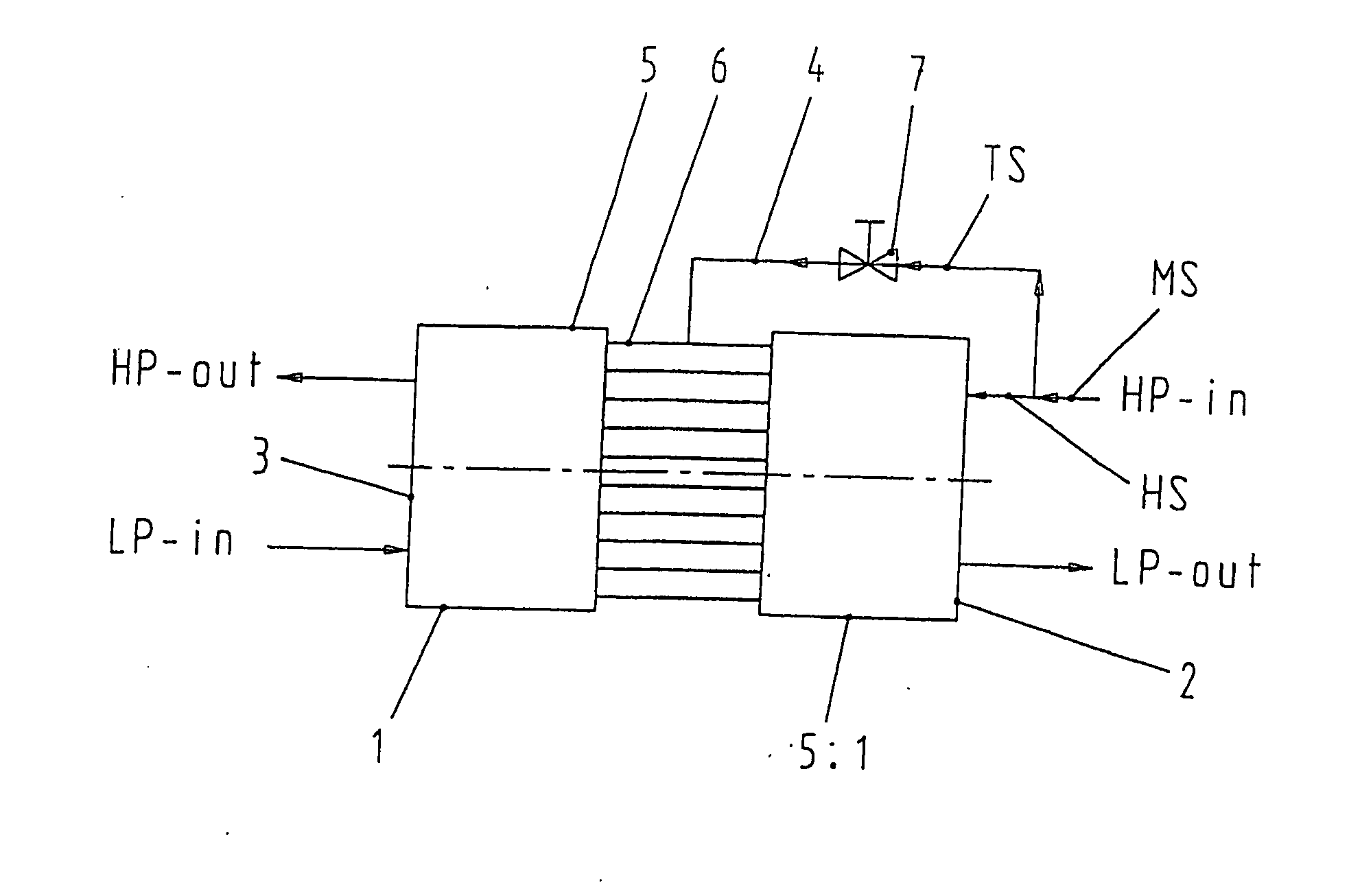
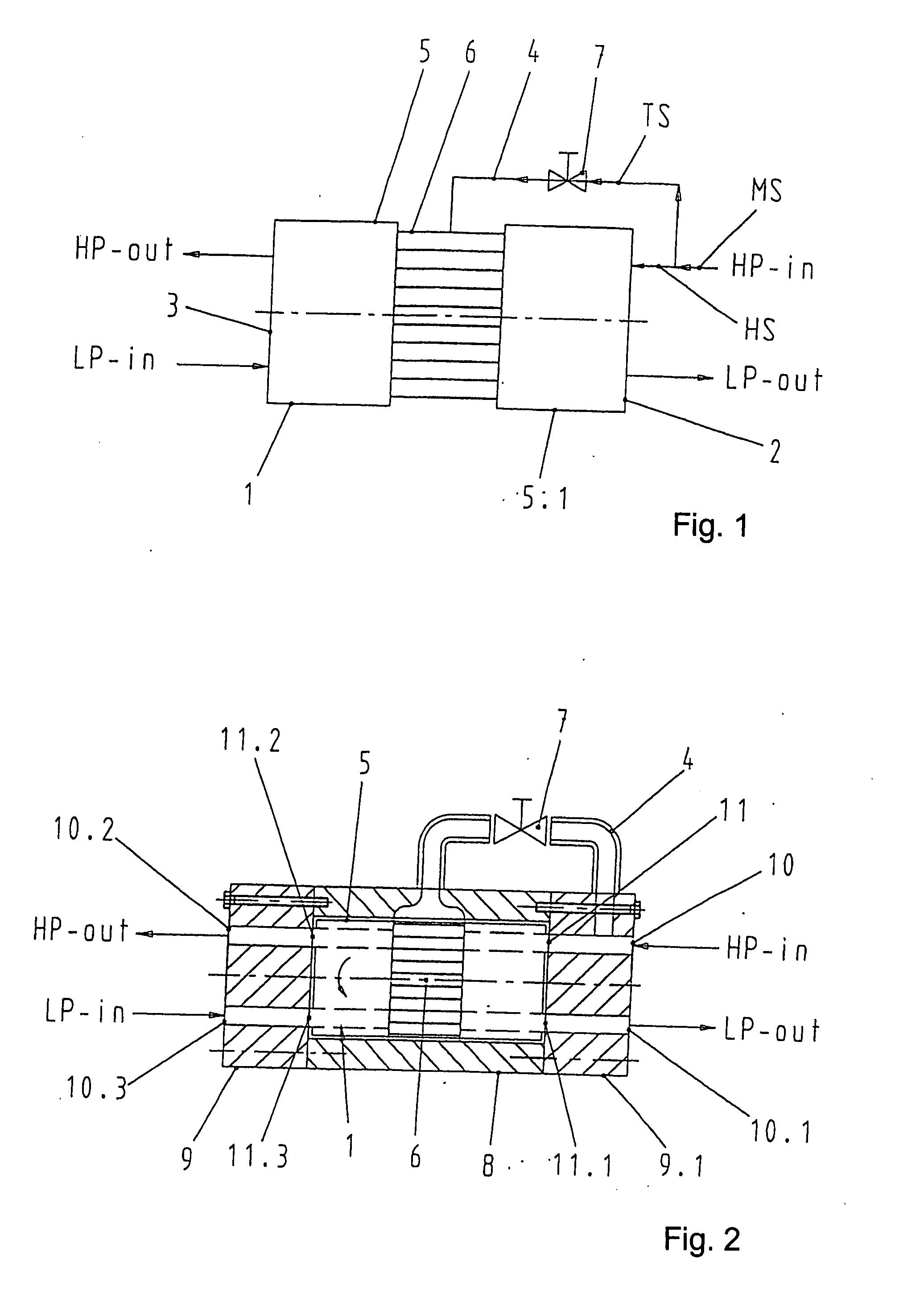
InactiveUS7168927B2Guaranteed uptimeIncrease loadPump componentsFluid-pressure convertersHigh energyEngineering
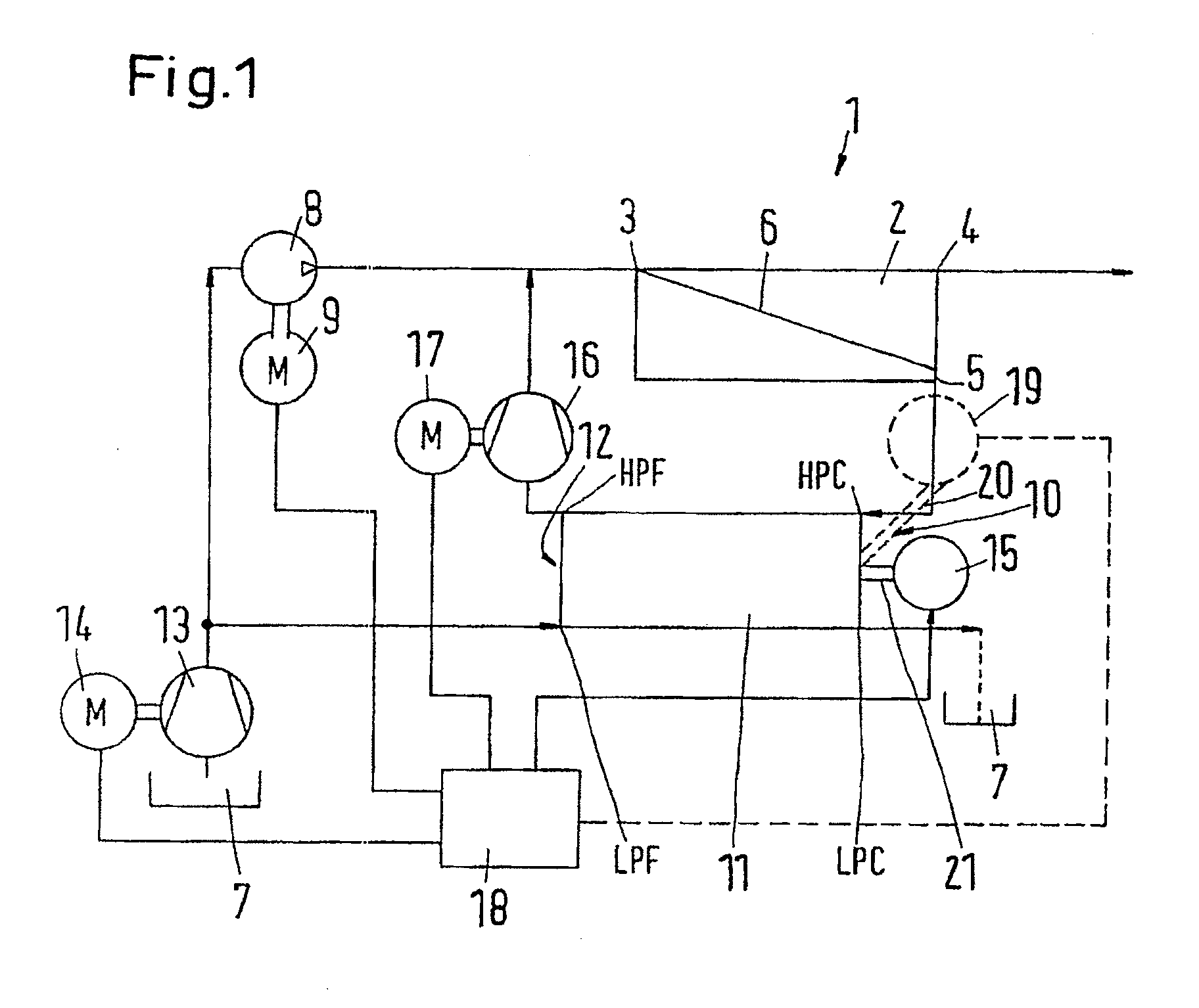
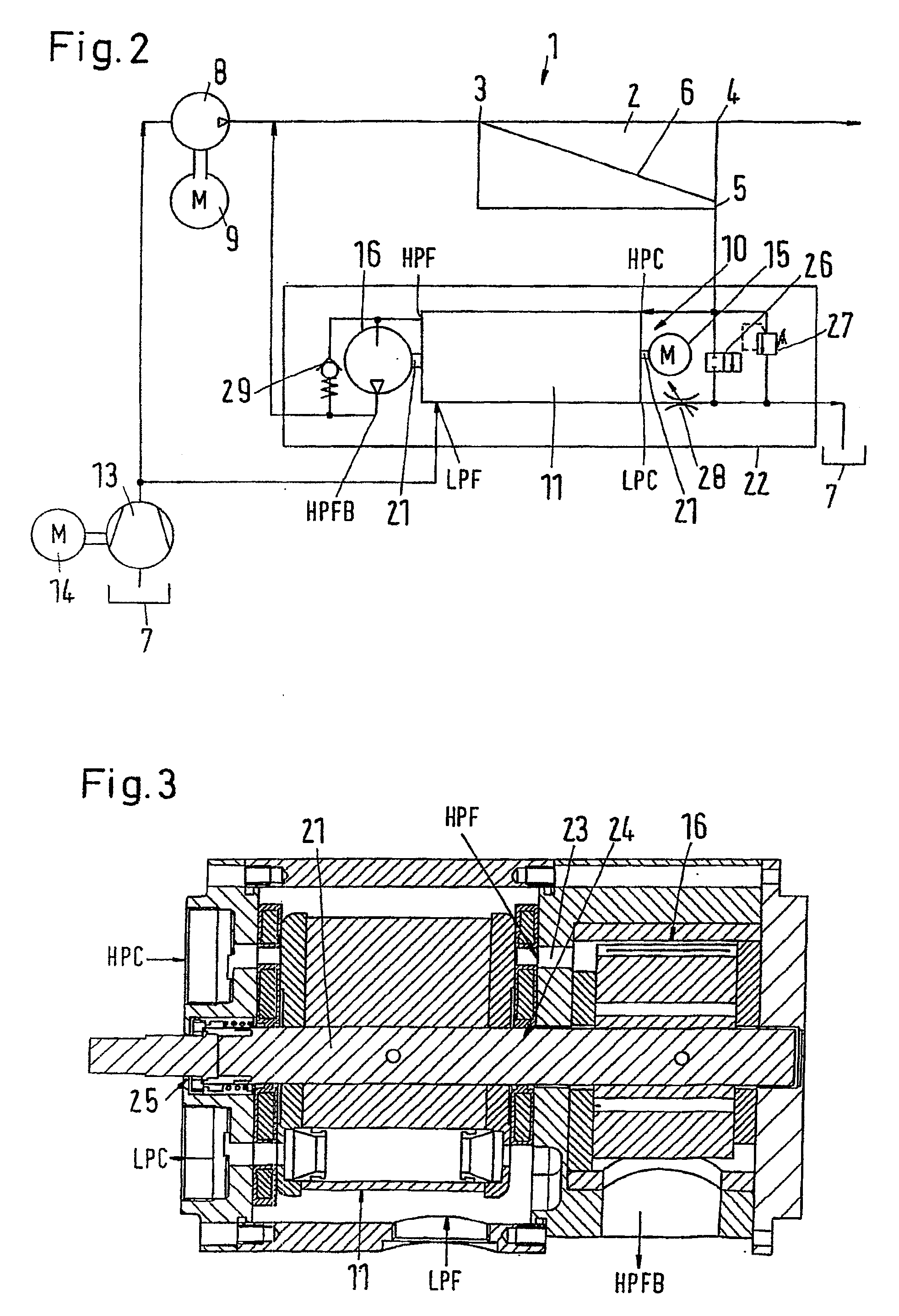
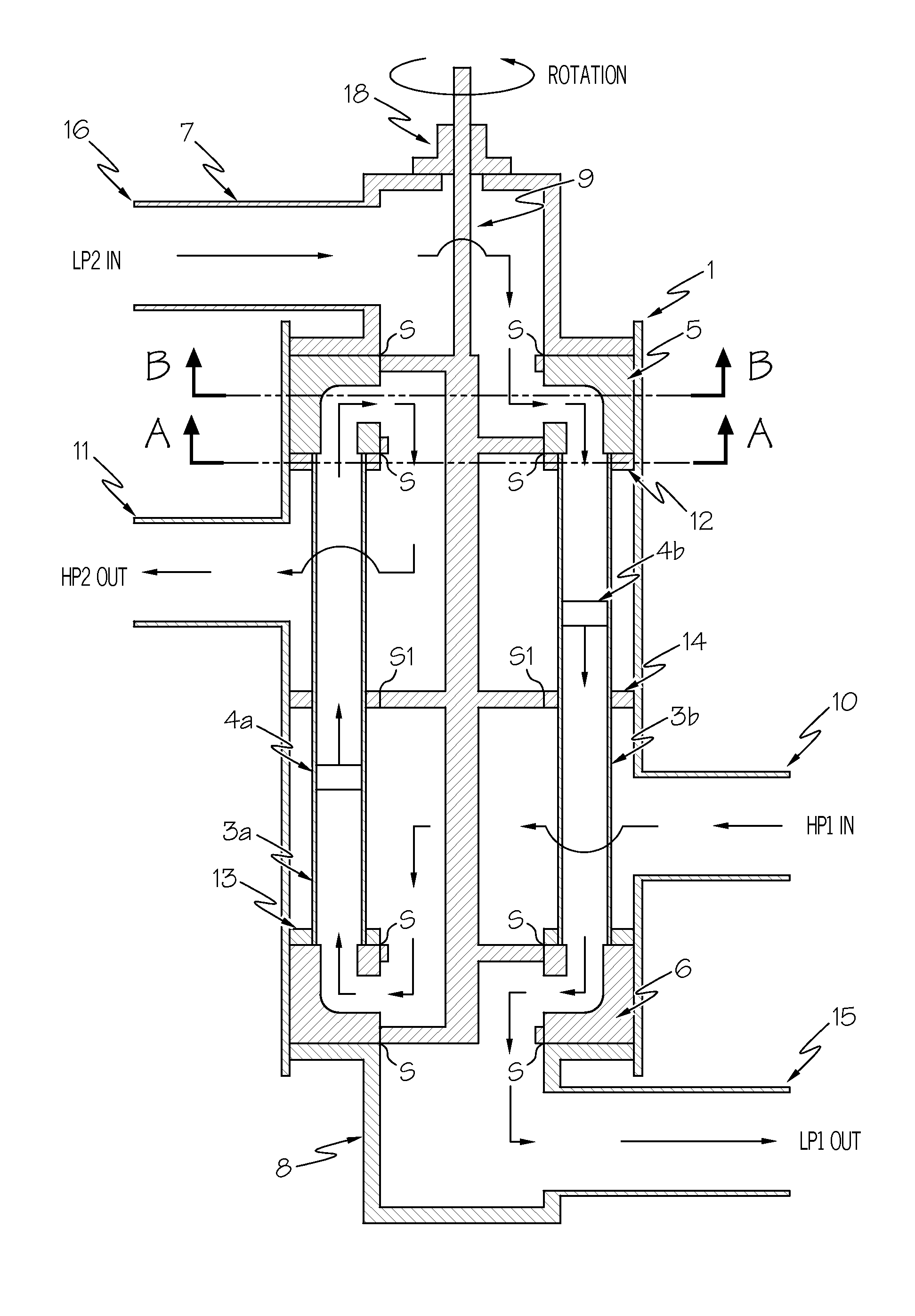
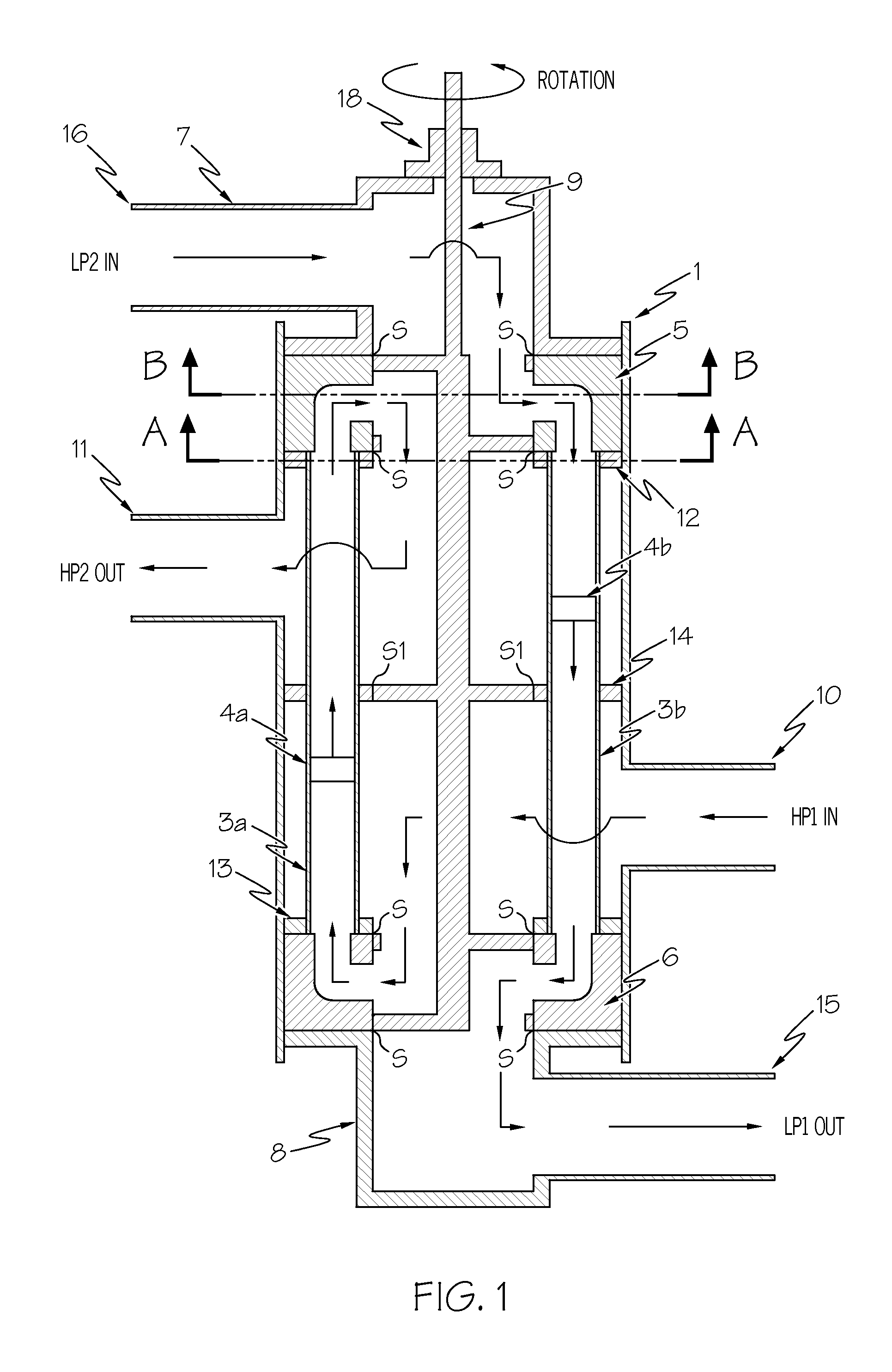
A pressure exchanger system having at least two tubular chambers, in which a plurality of reversing valves reverse the flow paths of fluid flows through the at least two tubular chambers. At least one driven reversing valve alternately reverses the flow paths between a supply source, which supplies a high-energy high-pressure fluid, and the tubular chambers. In reversing the liquid flows and shutting off previously open flow paths, the driven reversing element in the reversing valve executes a discontinuous or variable movement sequence.
Owner:KSB AG
Axial piston machine
ActiveUS7988428B1Reduce operating costsEasy to deployMembranesPositive displacement pump componentsMotor driveReciprocating motion
A pressure pump in a primary liquid flow is combined with a pressure exchanger for energy recovery from a secondary liquid flow. A motor-driven rotor portion, including two (primary and secondary) rotatable drum-type cylinder assemblies, is disposed between end blocks configured with input / output ports and cavities forming sliding synchronous reversing valves. Interconnected piston assemblies, including at least one primary piston and one secondary piston, are reciprocated axially by a central angled swash-plate in a progressive sequential manner by rotation of the rotor portion. The combination machine can be optimized for beneficial deployment in a reverse osmosis seawater desalination system to provide unusual simplicity, high efficiency energy recovery from the brine discharge flow and low overall operating cost.
Owner:OCEAN PACIFIC TECH
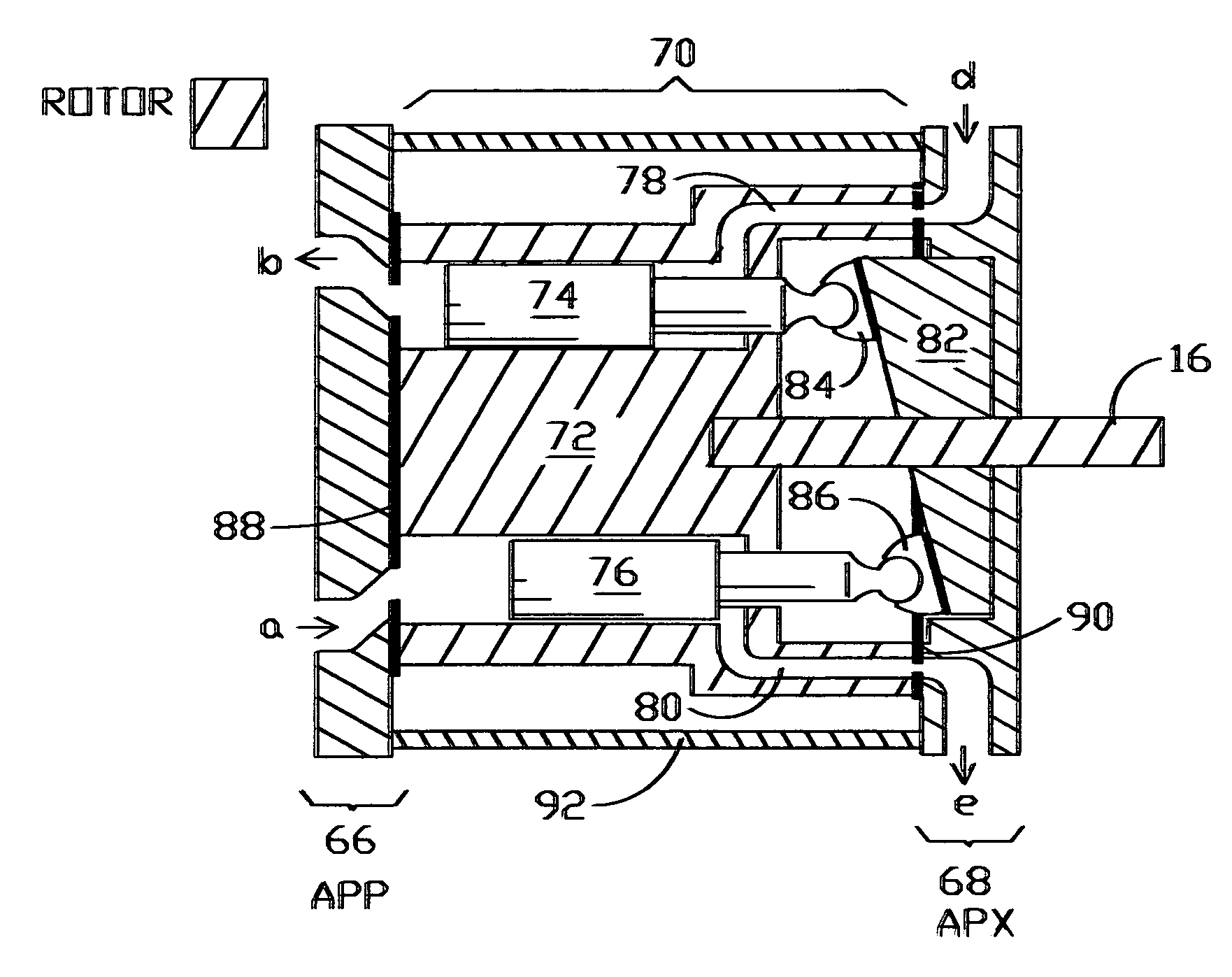
Pressure exchanger for transmitting pressure energy from a first liquid stream to a second liquid stream
ActiveUS20110008182A1Guaranteed uptimeAdditional exchangePump componentsPump controlDrive motorEngineering
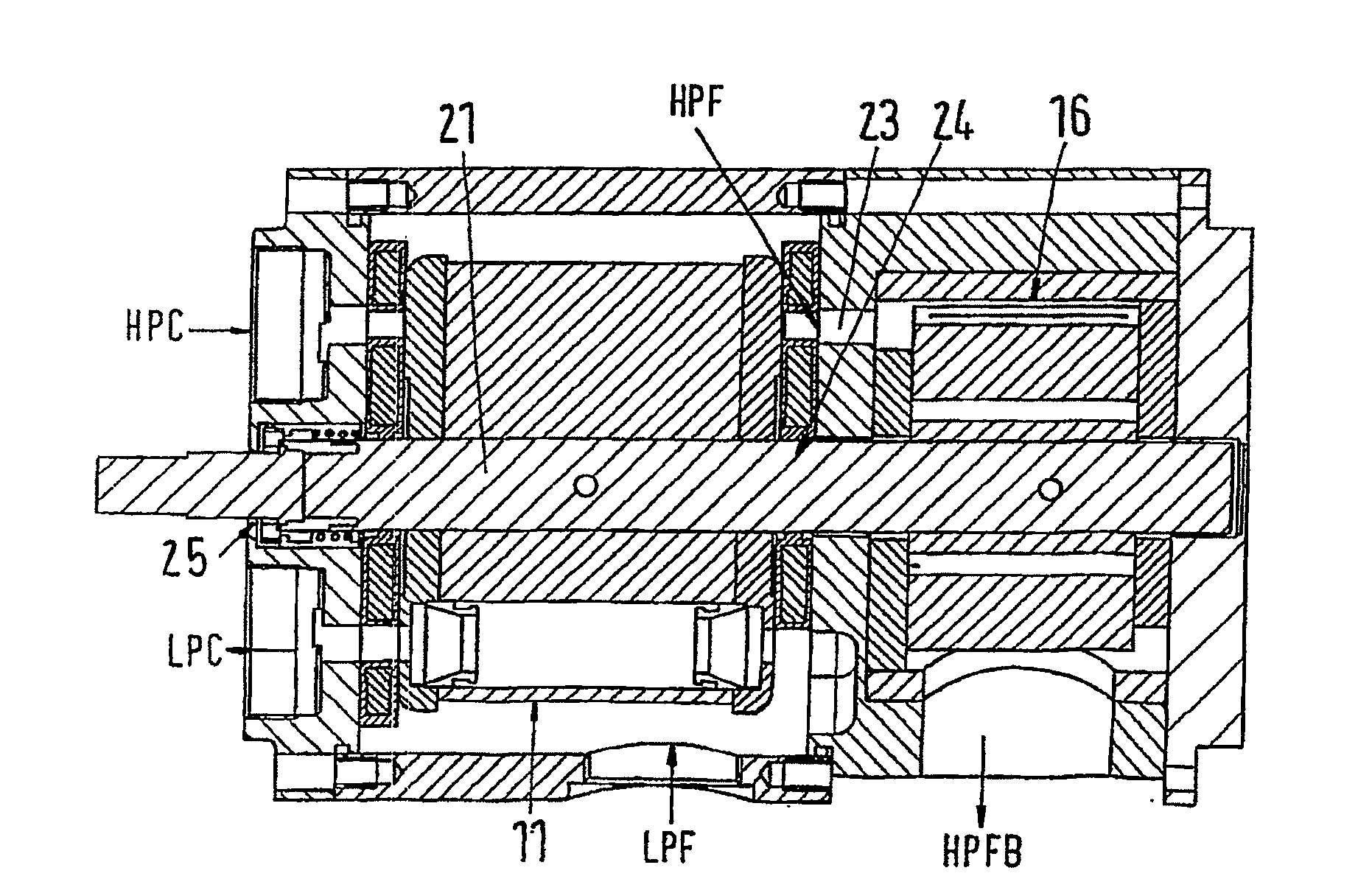
A pressure exchanger for transmitting pressure energy from a first fluid flow to a second fluid flow includes a housing having an entry and an exit for the first fluid flow and an entry and an exit for the second fluid flow. A rotor arranged in the housing includes a multitude of channels which extend radially distanced to a rotation axis of the rotor. The rotor is arranged to the entries and exits in a manner such that the channels, on rotation of the rotor, in each case in an alternating manner, connect the entry for the first fluid flow to the exit for the second fluid flow, and the entry for the second fluid flow to the exit for the first fluid flow, and with a drive motor via which the rotor may be driven in rotation, and with setting means for changing the rotational speed of the rotor.
Owner:GRUNDFOS MANAGEMENT AS
Pressure exchanger system
InactiveUS20050166978A1Guaranteed uptimeIncrease loadPump componentsFluid-pressure convertersHigh energyEngineering
A pressure exchanger system having at least two tubular chambers, in which a plurality of reversing valves reverse the flow paths of fluid flows through the at least two tubular chambers. At least one driven reversing valve alternately reverses the flow paths between a supply source, which supplies a high-energy high-pressure fluid, and the tubular chambers. In reversing the liquid flows and shutting off previously open flow paths, the driven reversing element in the reversing valve executes a discontinuous or variable movement sequence.
Owner:KSB AG
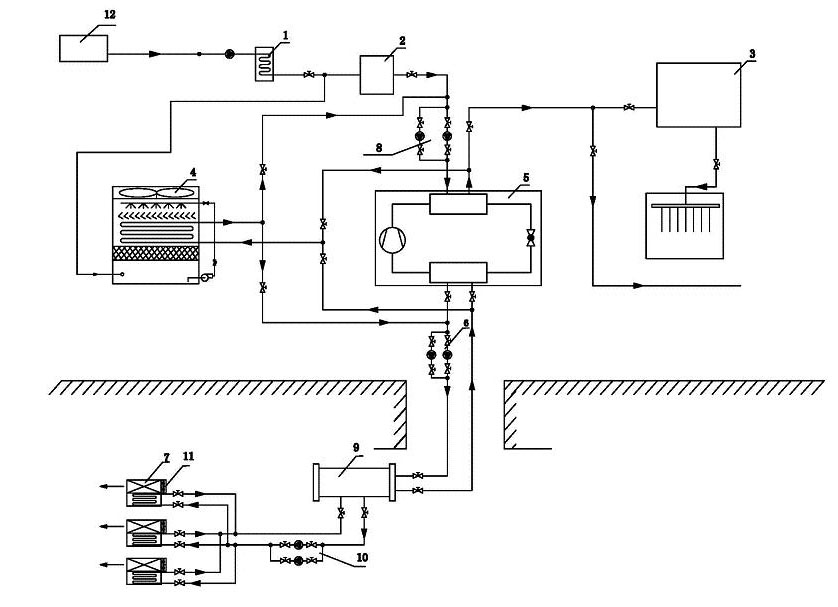
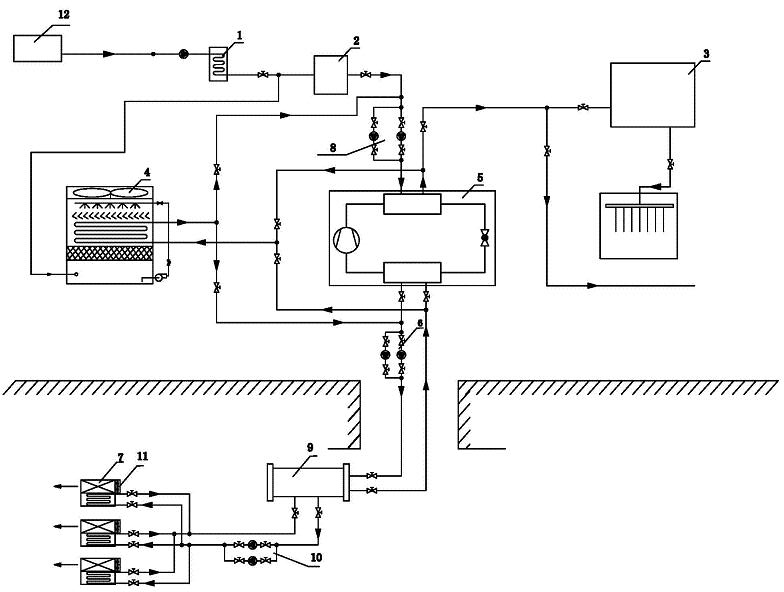
Heat-radiating, recovering and cooling system for mine
ActiveCN102121392AMeet the requirements of energy saving and environmental protectionGood well cooling effectTunnel/mines ventillationCooling towerSoftened water
The invention discloses a heat-radiating, recovering and cooling system for a mine. The system comprises an enclosed cooling tower, a thermal energy recovering device, a thermal energy recovering device water circulating pump, a pressure exchanger, a pressure exchanger water circulating pump, a refrigerating and cooling device, a fan and an underground cooling unit water circulating pump, whereinall components adopt modular designs. The system integrates the advantages of centralized refrigeration and distributed refrigeration, so that a good underground cooling effect can be achieved. Meanwhile, a thermal energy recovery technology is adopted, so that all thermal energy produced by a refrigerator is recovered and utilized, the recovered thermal energy can be used for supplying hot waterfor bathing to the ground as well as heat in office areas in winter, and a boiler can be fully eliminated. A water treatment system of the system can be used for producing purified water or softened water by using waste water drained by a sewage treatment plant, and the produced water can be recycled by the system, so that the requirements for energy conservation and environmental protection are met.
Owner:DALIAN EAST REFRIGERATION EQUIP
Valve unit for pressure exchanger installations
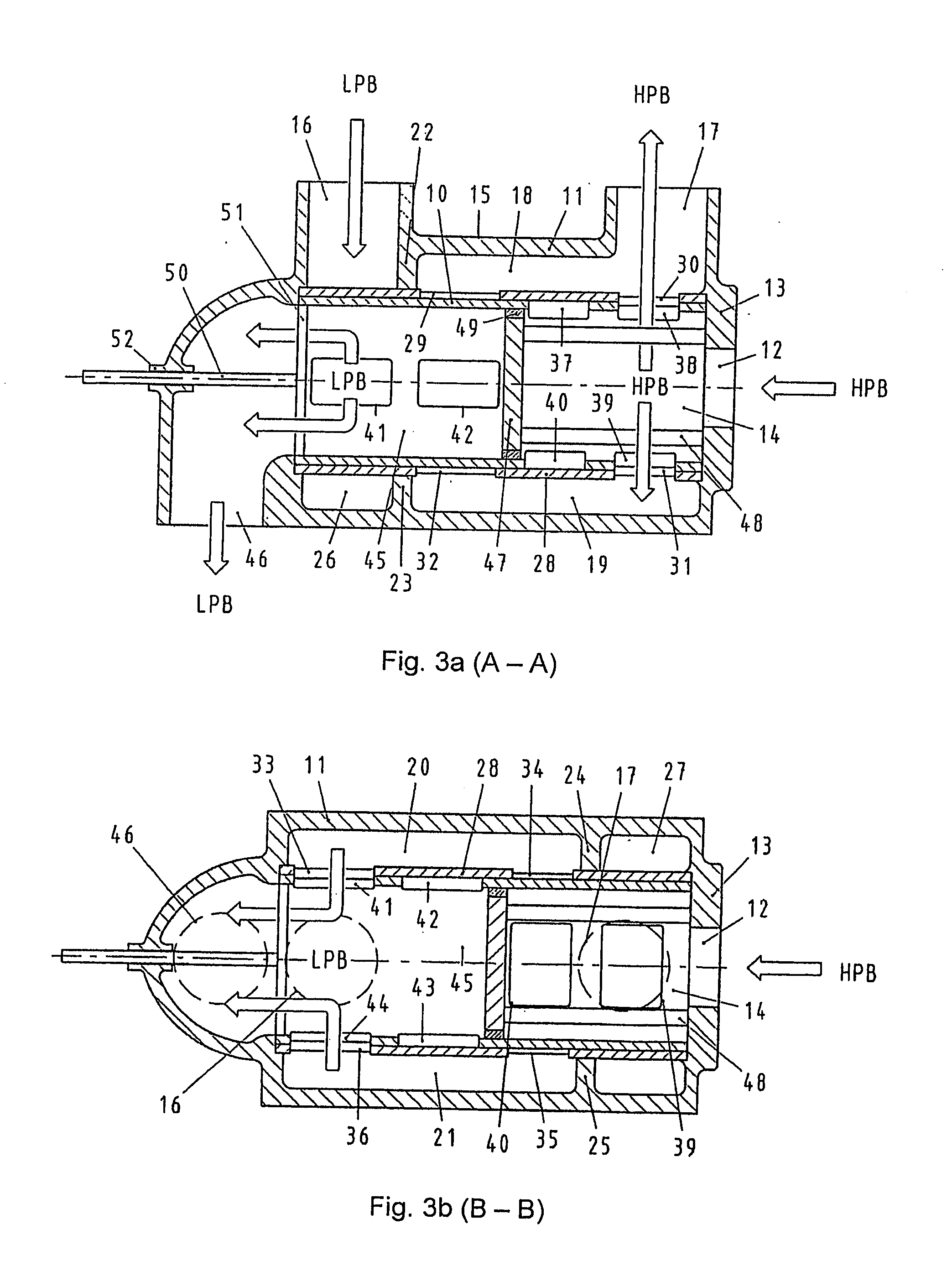
A valve for switching over liquid paths, particularly for pressure exchanger installations with tubular pressure exchanger chambers (3) through which an alternating flow occurs, in which a rotatable control element (10, 10.1) having a plurality of flow paths is mounted in a housing (11), which in turn comprises a plurality of connection opening (12, 16, 17, 46) connected to a first pipe system and to an end of at least one pressure exchanger. Another end of the pressure exchanger is connected to a second pipe system through a valve. A motorized drive shaft (50) rotates the control element so as to alternately connect the control element flow paths to openings inside housing (11). Oncoming flow to the control element may come from an axial direction or from a radial direction, and outgoing flow from the control element occurs in the axial direction.
Owner:KSB AG
Fluid exchanger devices, pressure exchangers, and related methods
ActiveUS9435354B2Specific water treatment objectivesFluid-pressure convertersEngineeringFluid exchange
Exchanger devices include a plurality of fixed exchange ducts and a rotating valve assembly for directing flow to and from the plurality of exchange ducts. Methods of exchanging pressure between fluid streams may include directing fluids through an exchange device and pressurizing a fluid in the plurality of exchange ducts of the exchanger device.
Owner:FLOWSERVE PTE LTD
Combined Axial Piston Liquid Pump and Energy Recovery Pressure Exchanger
ActiveUS20110006006A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityMembranesGeneral water supply conservationReciprocating motionEngineering
Owner:OCEAN PACIFIC TECH
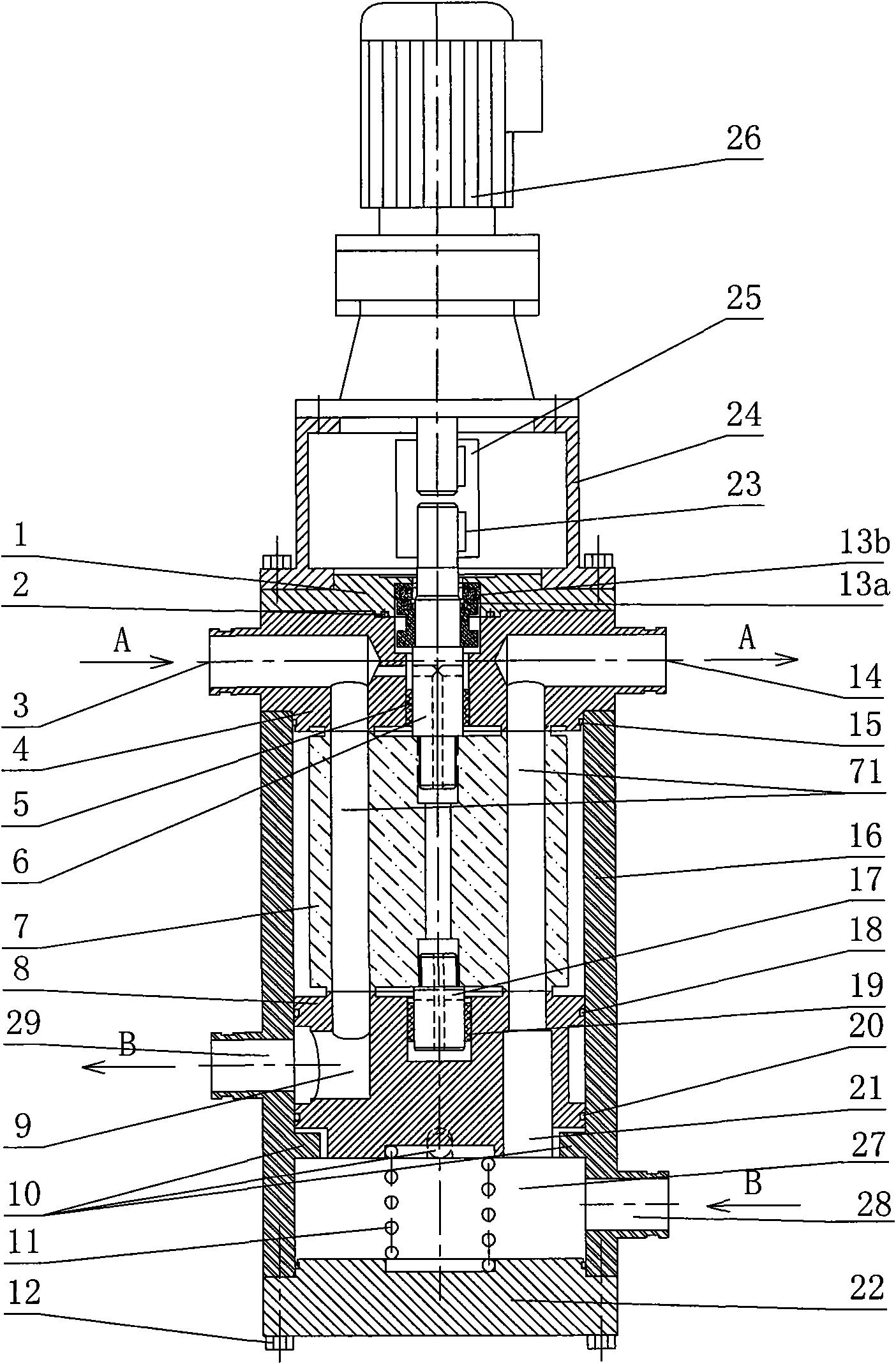
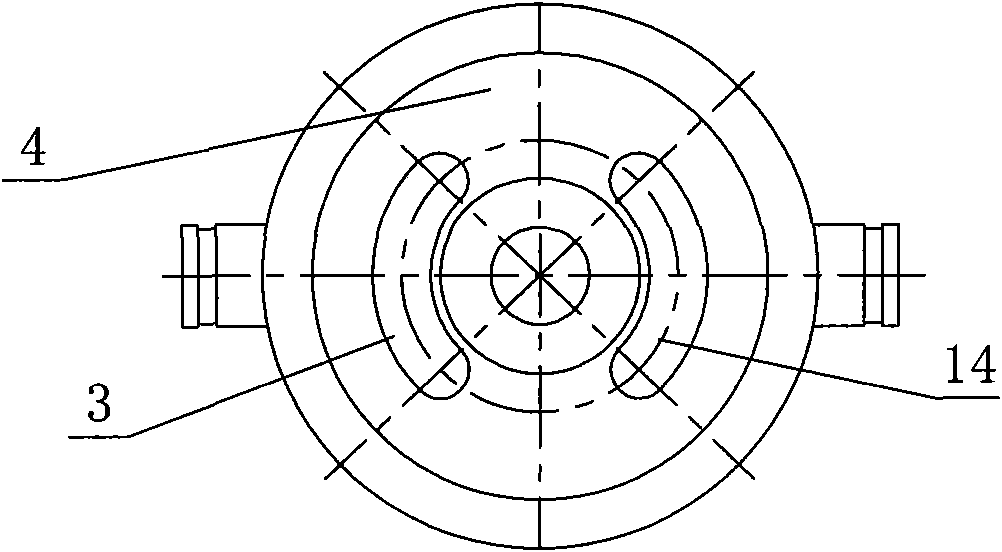
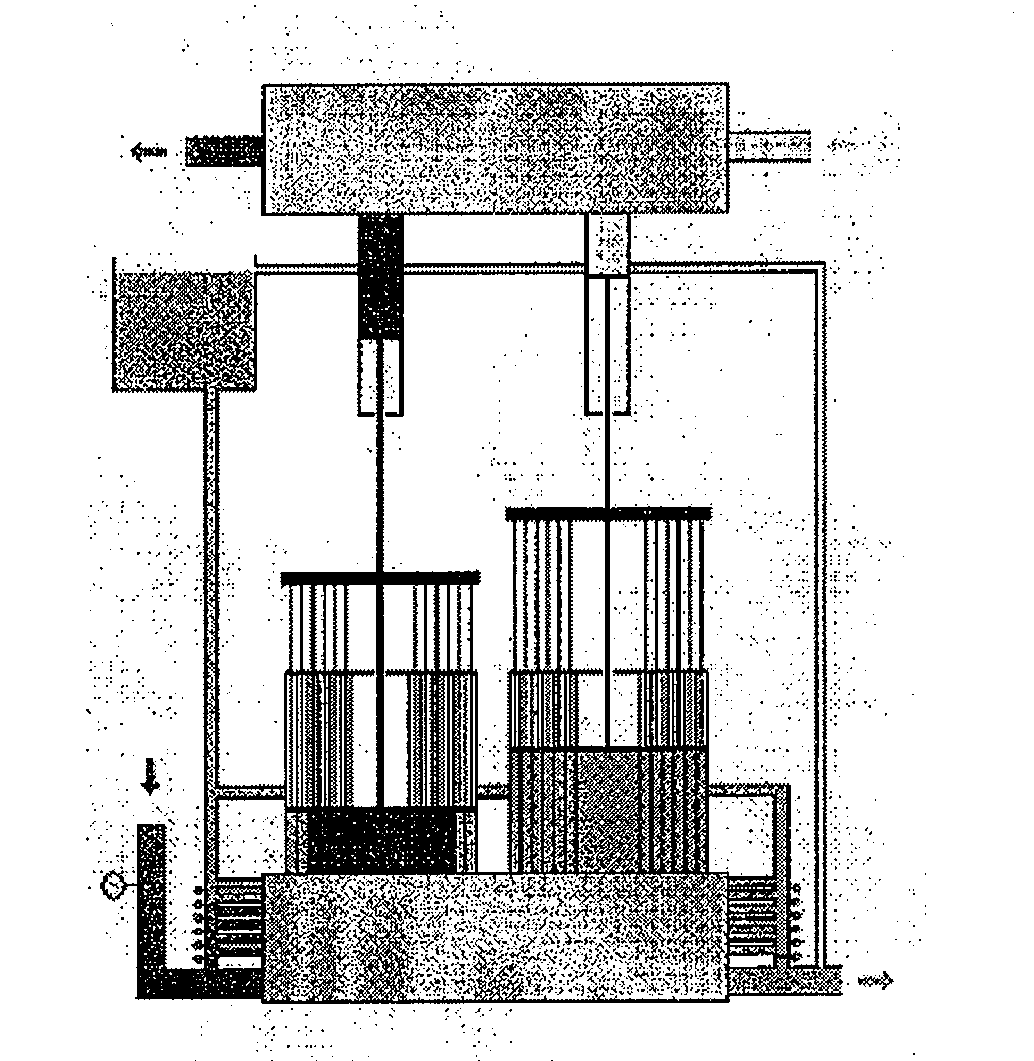
Pressure exchanger
ActiveCN101440828AImprove energy recovery efficiencySimple structureFluid-pressure convertersMachines/enginesControl systemDrive shaft
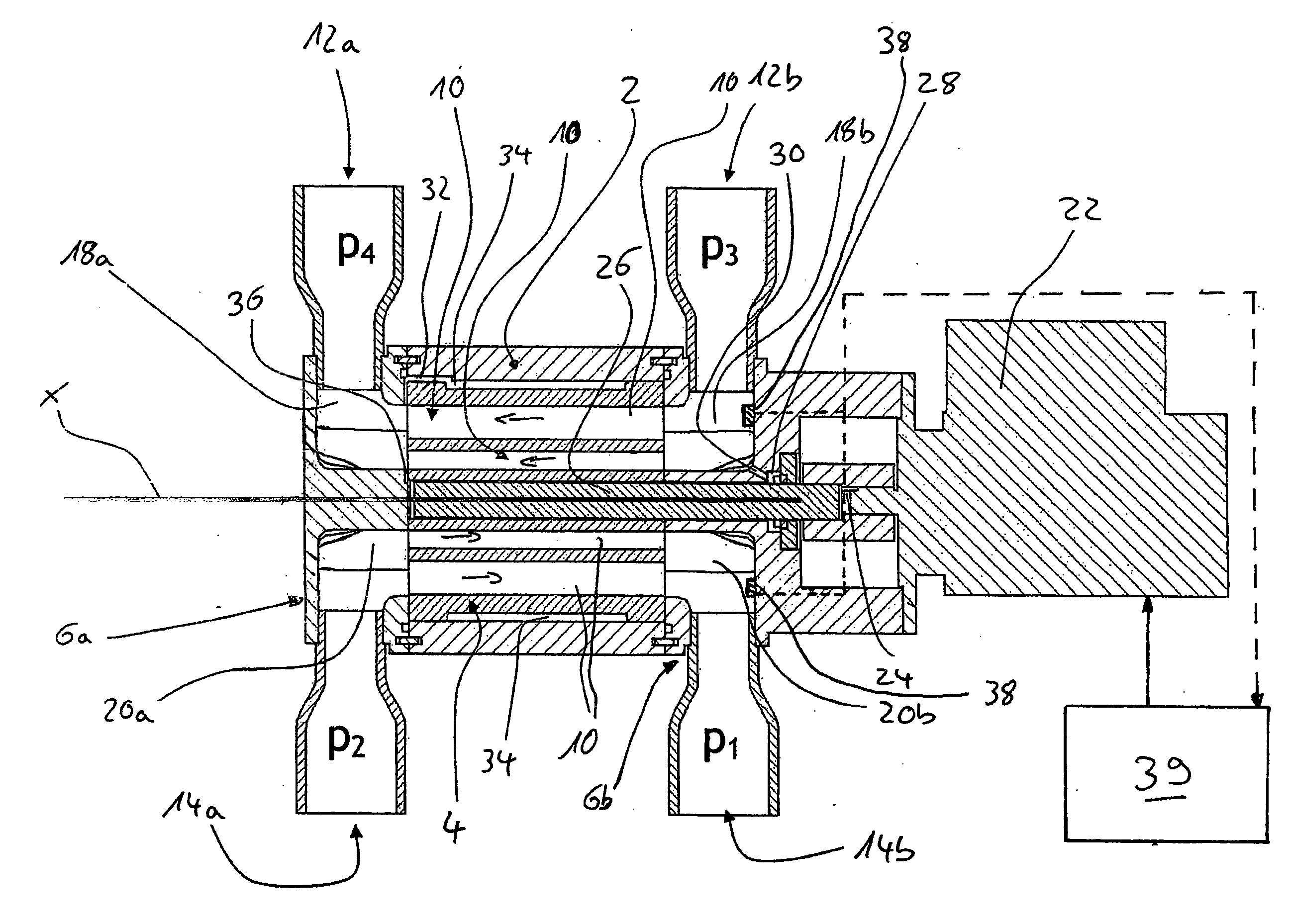
The invention provides a pressure exchanger, which comprises a rotating component. The rotating component comprises a driving shaft, a rotor, a left thrust disk and a right thrust disk positioned on two sides of the rotor respectively, a spring, and a compaction bar acted by the spring to thrust the right thrust disk to the right; the pressure exchanger is also provided with a non-rotating component which comprises a shaft seal cover, a left end cap provided with a relatively high-pressure fluid inlet and a relatively low-pressure fluid outlet, a left port plate arranged on the left side of the left thrust disk, a right port plate arranged on the right side of the right thrust disk, a right end cap provided with a relatively low-pressure fluid inlet and a relatively high-pressure fluid outlet, and a shell. The pressure exchanger has higher energy recovery efficiency, needs no complex valve control system, basically has no fluid pressure and fluctuation of flow in a used system, hardlyhas leakage on a thrust face and a sealing face, has less leakage and higher volume efficiency than a pressure exchanger in clearance fit, and is convenient to produce efficient miniature, medium andlarge-sized pressure exchangers.
Owner:杭州帕尔水处理科技有限公司
Channel form for a rotating pressure exchanger
InactiveUS7815421B2Reduced mixing lossAvoid developmentPump componentsFlexible member pumpsEngineeringMechanical engineering
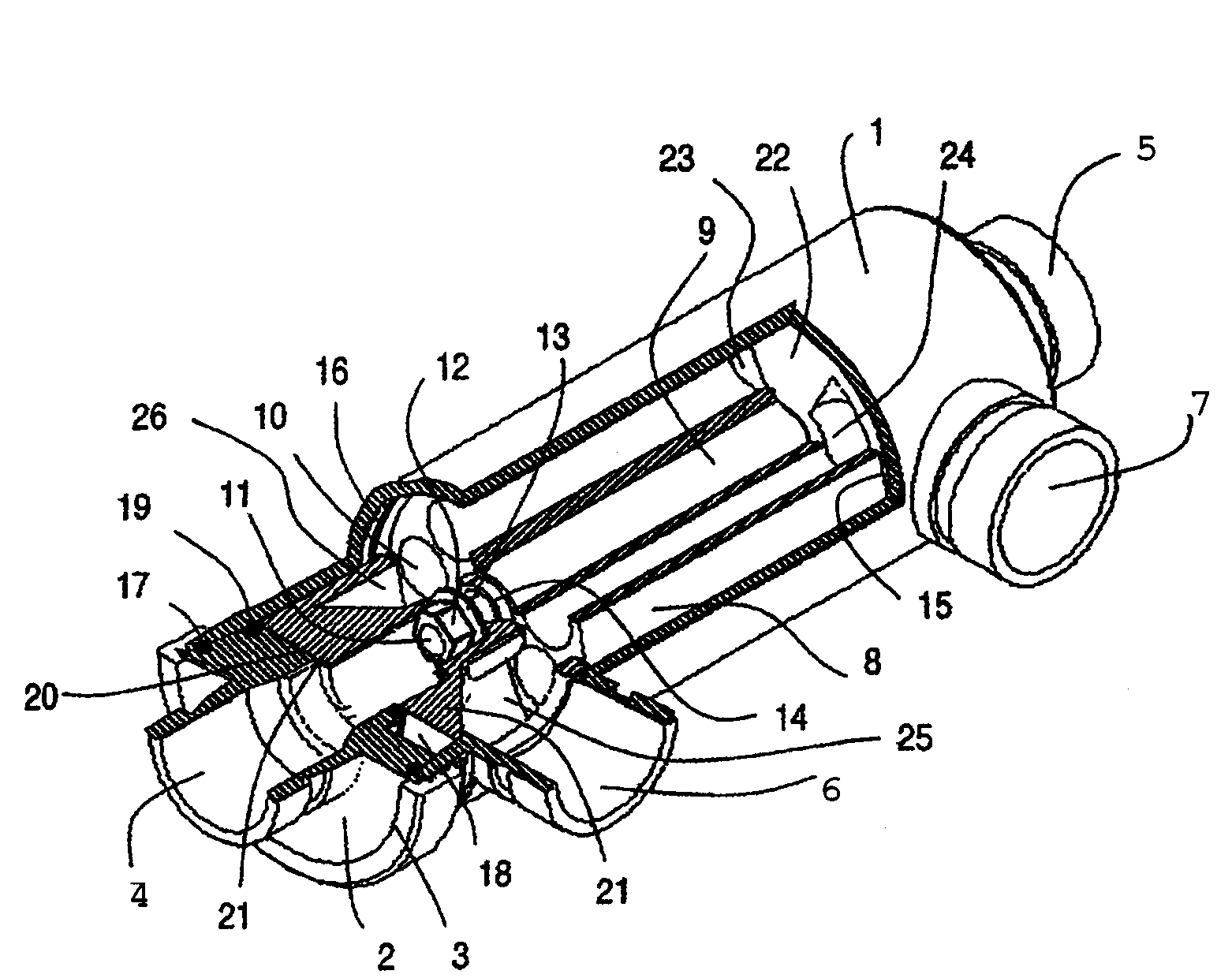
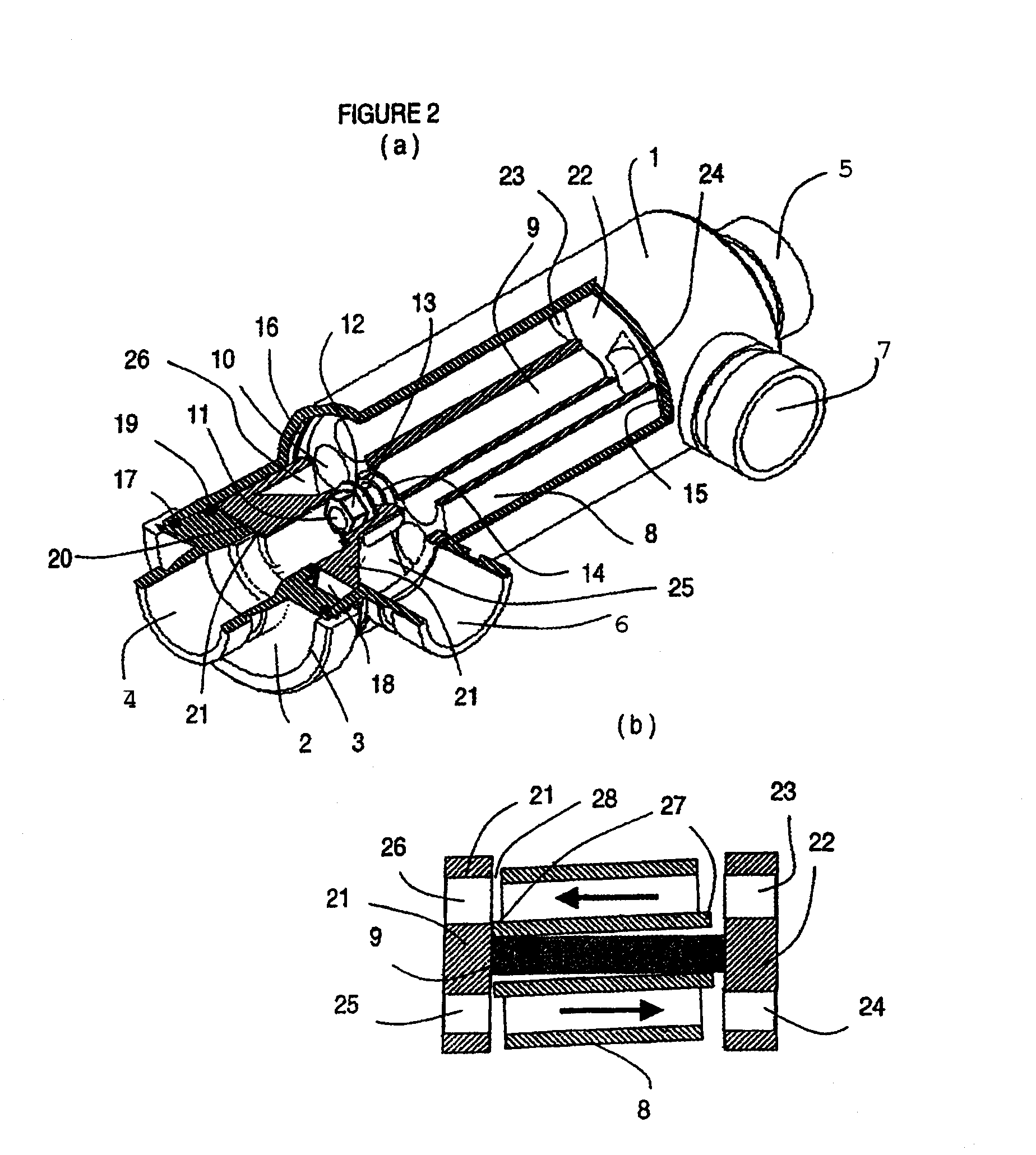
A pressure exchanger transferring pressure energy from a liquid in a first liquid system to a liquid in a second liquid system, having a housing with inlet and outlet connection openings for each liquid and a rotor arranged in the housing for rotation about a longitudinal axis. Through rotor channels are arranged around the rotor longitudinal axis with openings on each axial end face of the rotor. The rotor channels are arranged for connection through opposing flow openings facing the housing to the connection openings of the housing. During rotor rotation high pressure liquid and low pressure liquid are alternately introduced into the respective systems. Liquid flowing to the rotor through the openings generates a circumferential force (cu) for driving the rotor, and starting at or following the openings a flow guiding configuration formed as a rotor channel flow diverting contour is arranged in the rotor channels.
Owner:KSB AG
Flow-reversing valve
InactiveUS20060060245A1Little strengthImprove sealingValve members for heating/coolingMultiple way valvesLine tubingDrive shaft
A valve for switching fluid paths, particularly for pressure exchanger installations with tubular chambers through which fluid flows in an alternating manner, including a rotatable closing element (12, 13) provided with a motorized drive shaft (14) and arranged inside a housing (2) having a plurality of connections (3, 4) for connecting lines leading to a pipe system and to a respective end of at least one pressure exchanger. Another end of each pressure exchanger is connected through a valve arrangement to a second pipe system. A splitter (7) provided with a plurality of overflow paths (17, 18, 27) is arranged inside the housing (2); mouths of the overflow paths are located on two axial end faces (10, 11) and on the circumference of the splitter (7), and a rotatable, disk-shaped control element (12, 13) is arranged in a sealing manner at each end face of the splitter (7).
Owner:KSB AG
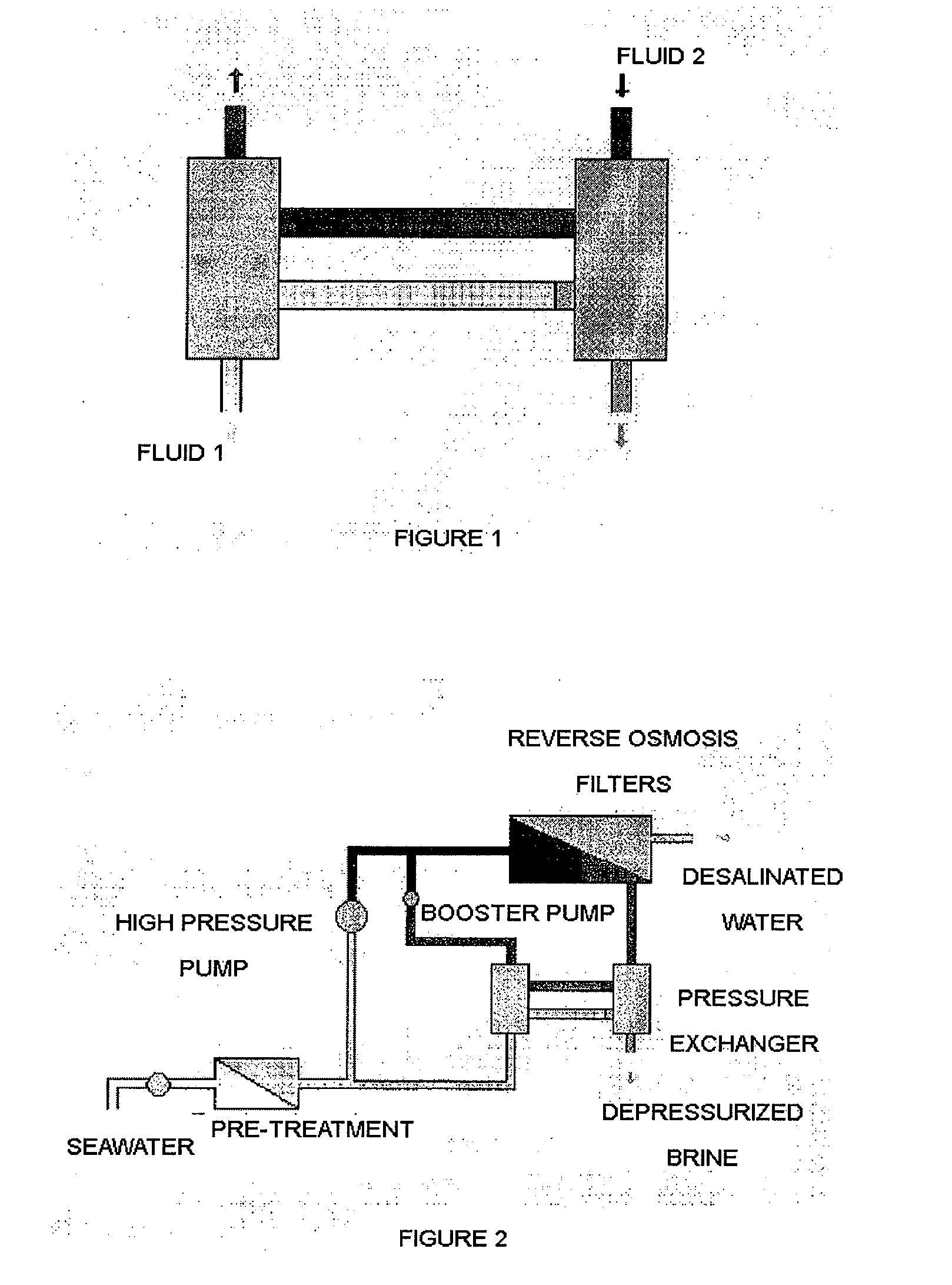
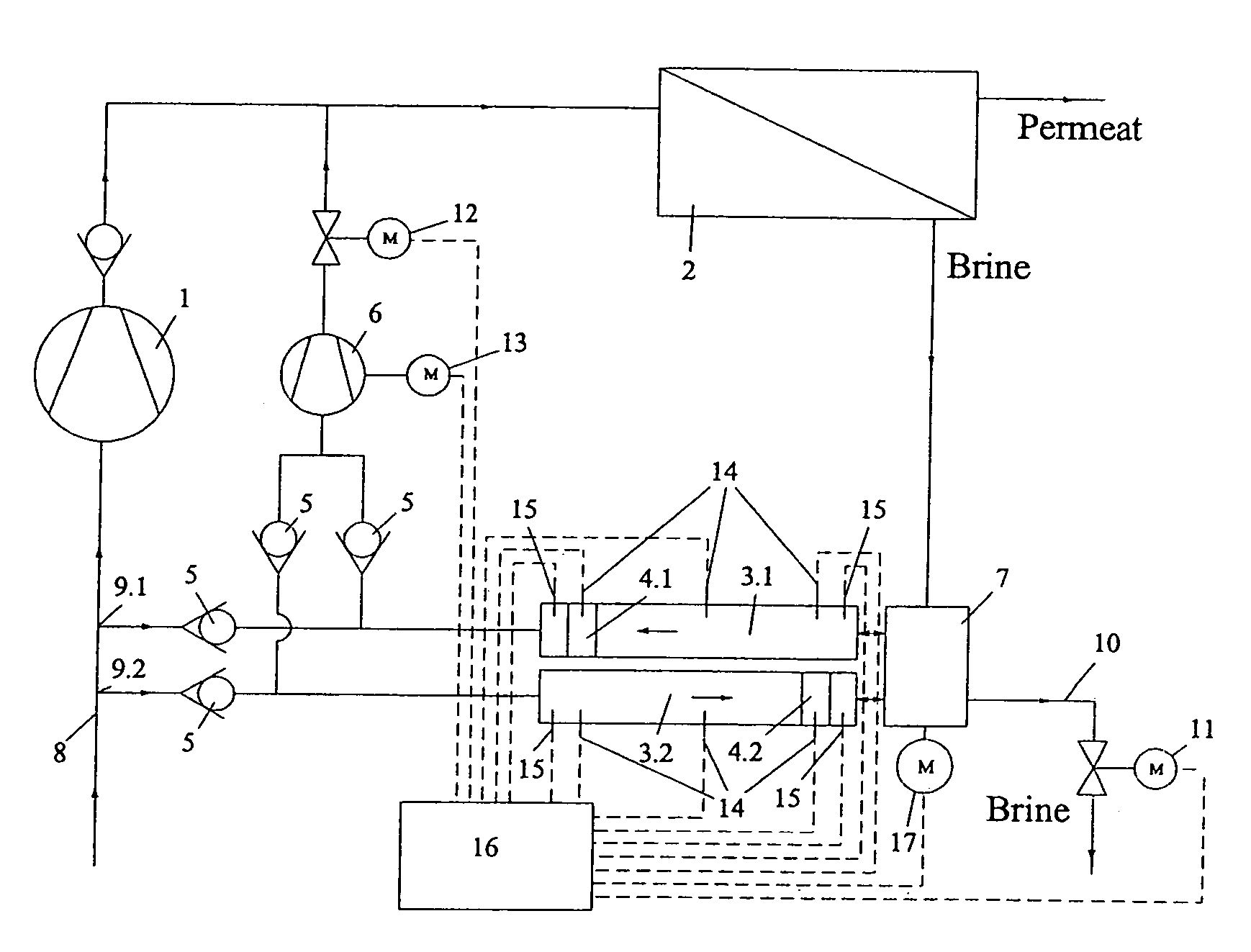
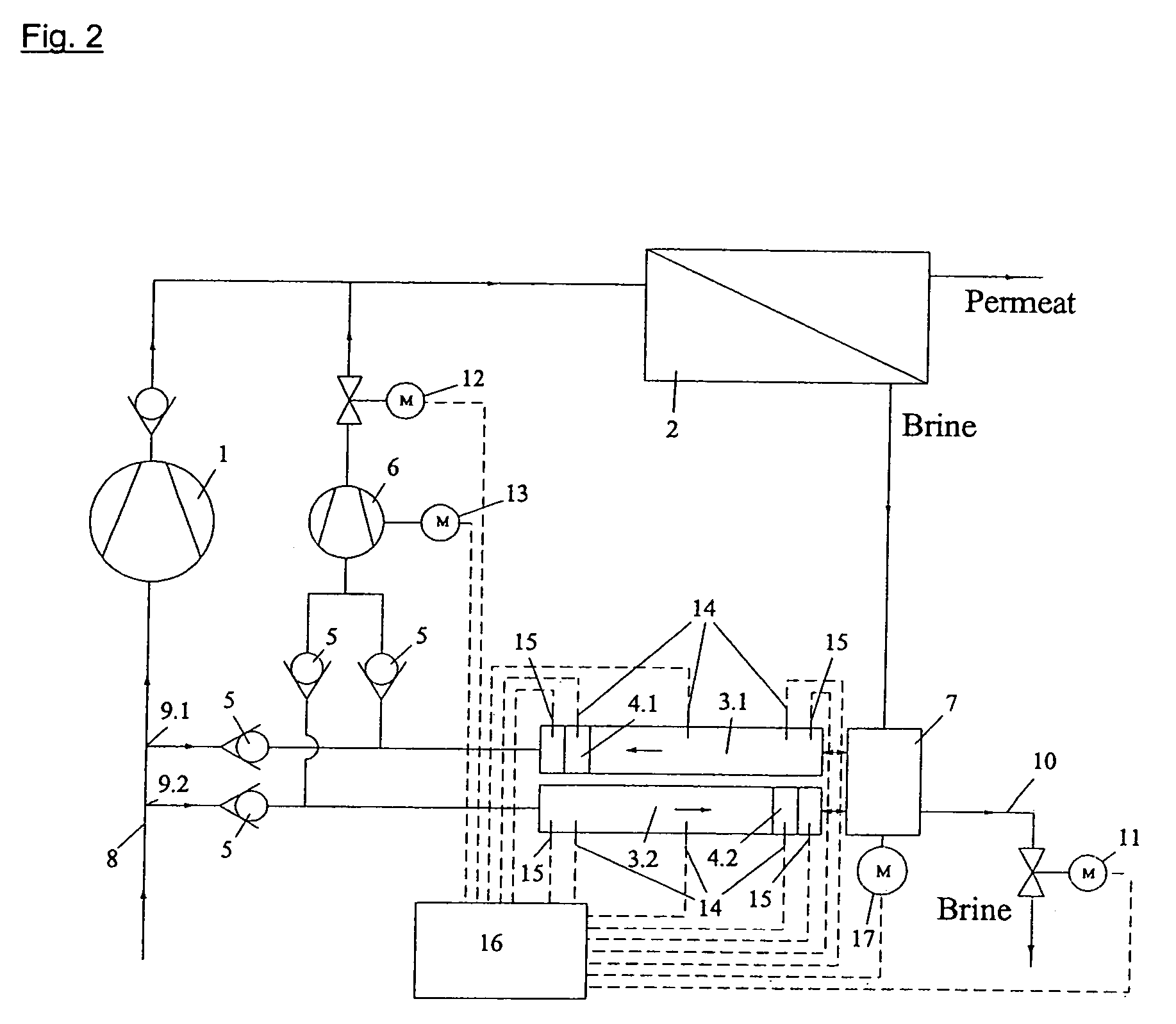
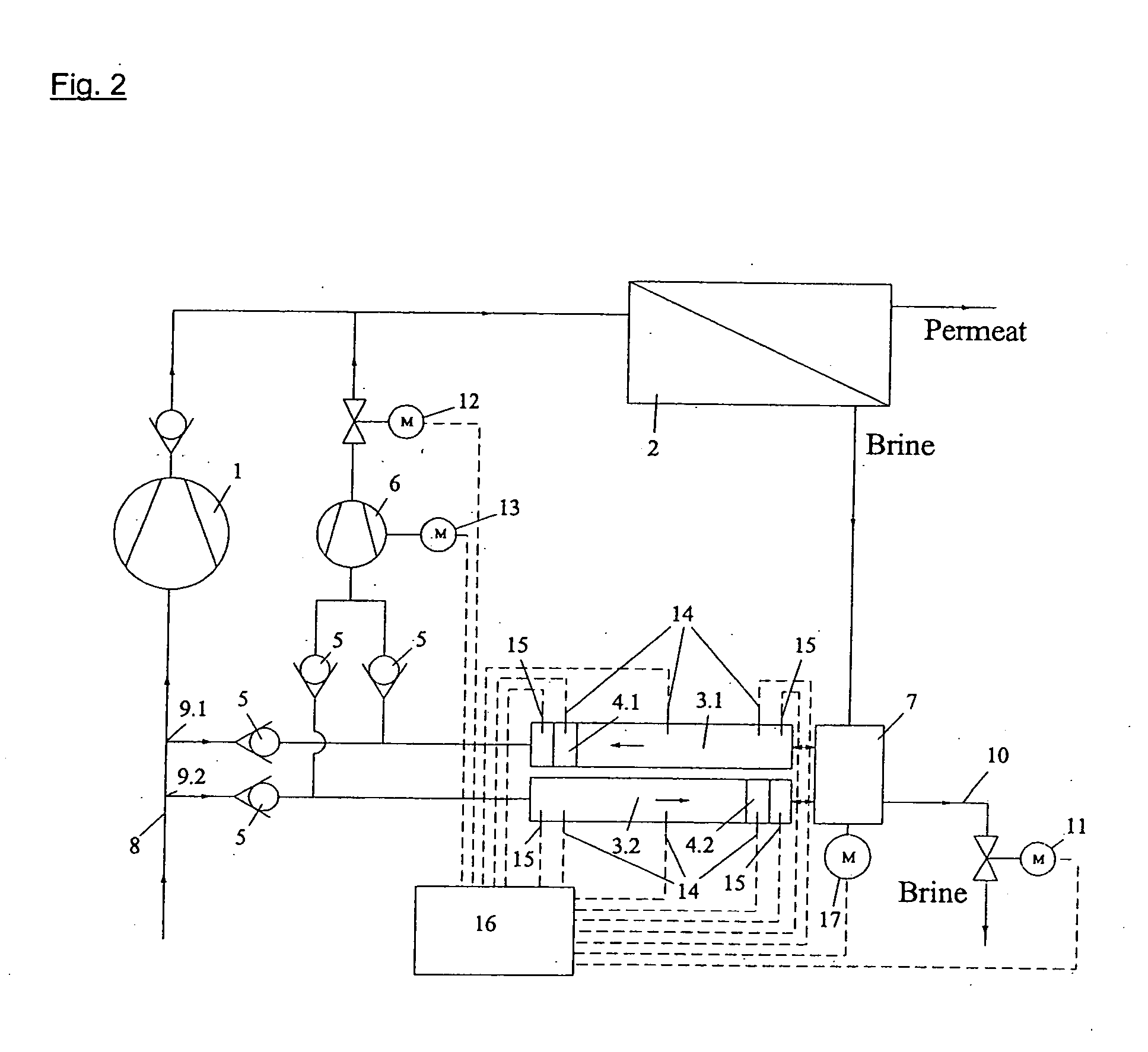
Reverse osmosis system
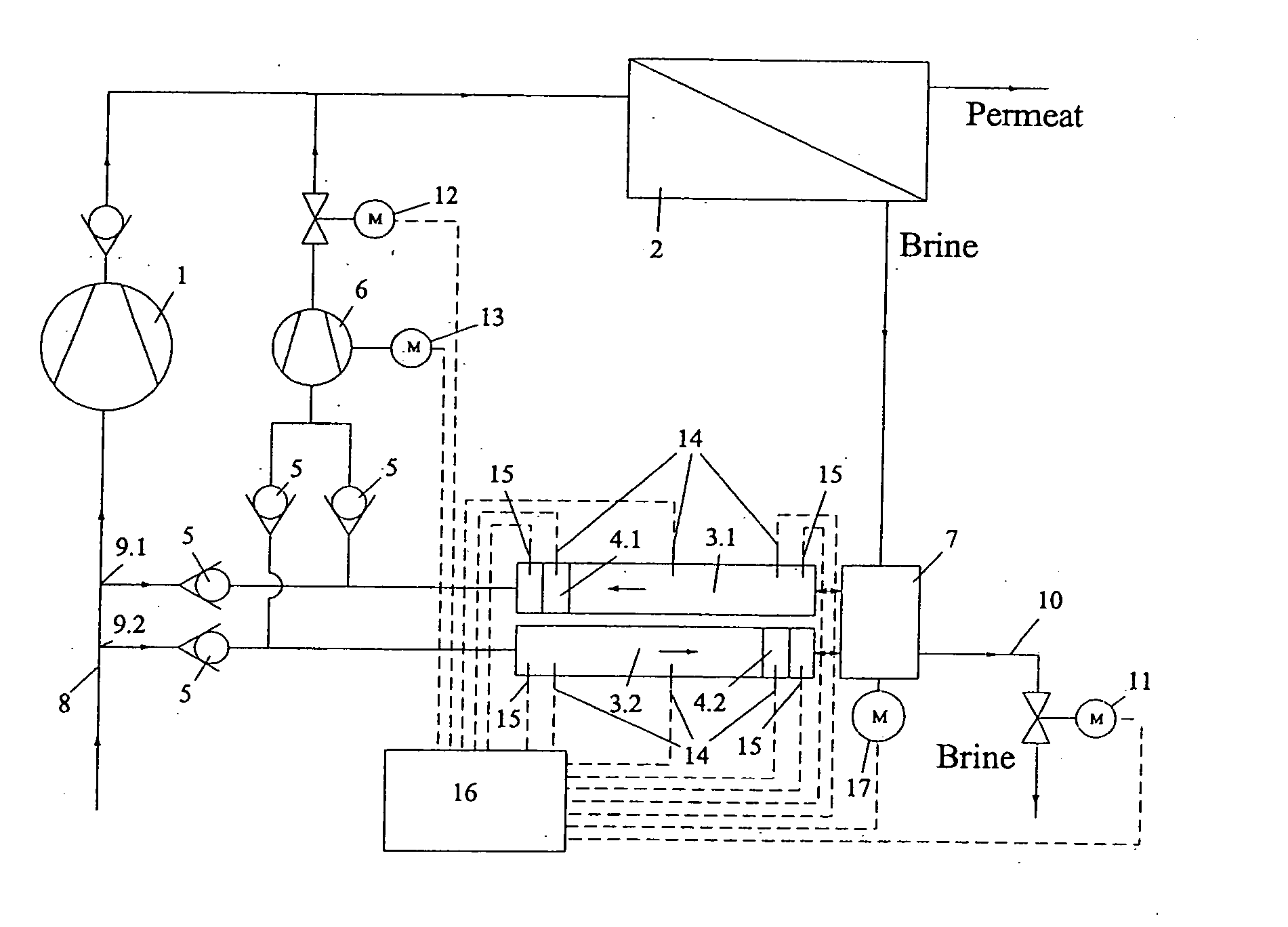
ActiveUS20110203987A1Avoid differential pressureConstant feed performanceMembranesGeneral water supply conservationReverse osmosisEngineering
The invention concerns a reverse osmosis system (1) with a membrane unit (2) comprising an inlet (3), a permeate outlet (4) and a concentrate outlet (5), a high-pressure pump (8) that is connected to the inlet (3), a pressure exchanger (11) connected on its concentrate side (10) to the concentrate outlet (5), and a booster pump between the pressure exchanger (11) and the inlet (3). It is endeavoured to make the energy consumption as small as possible. For this purpose, the booster pump is made as a displacement pump.
Owner:DANFOSS AS
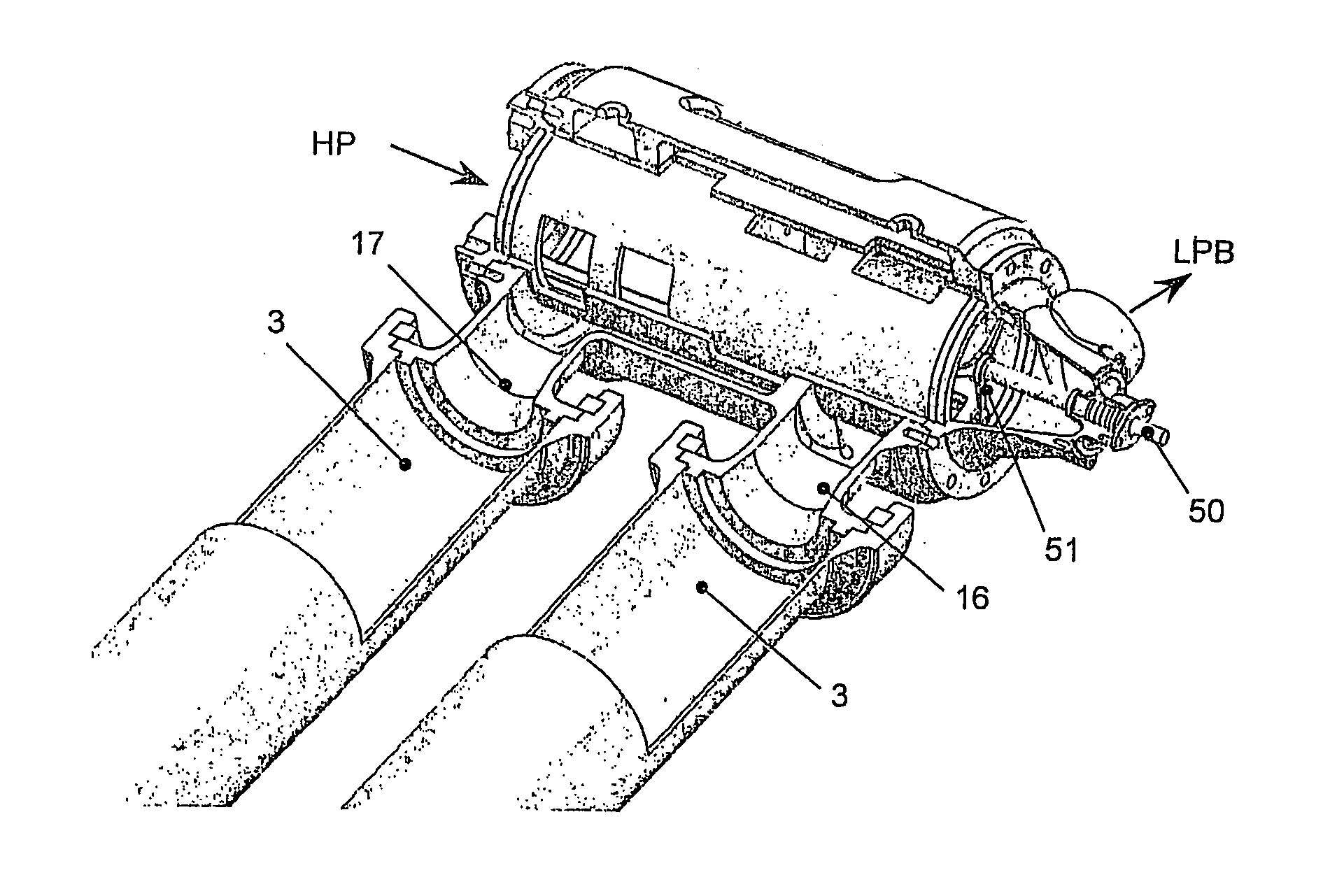
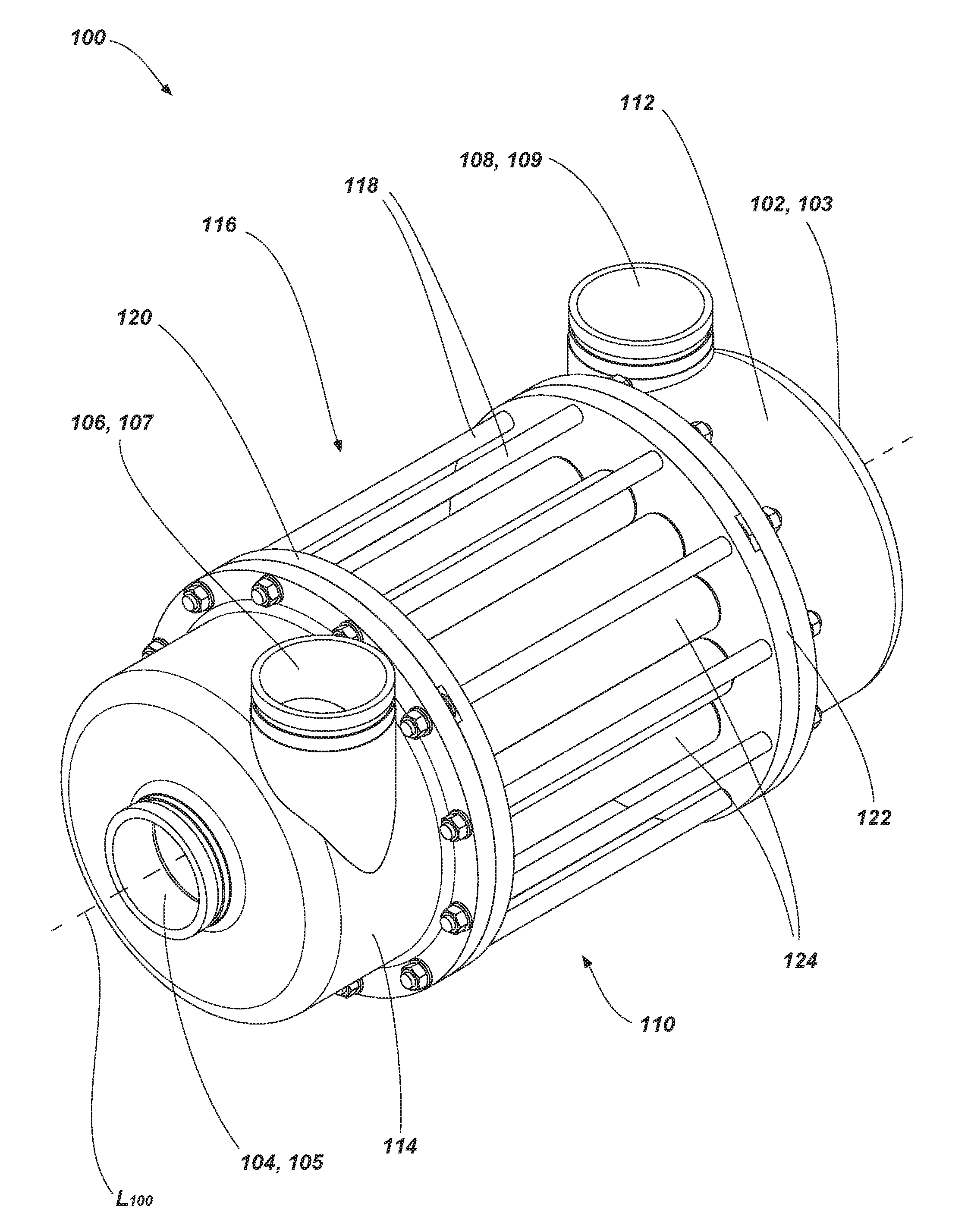
Rotor positioning system in a pressure exchange vessel
ActiveUS10125796B2Positive displacement pump componentsCombustion enginesMechanical engineeringPositioning system
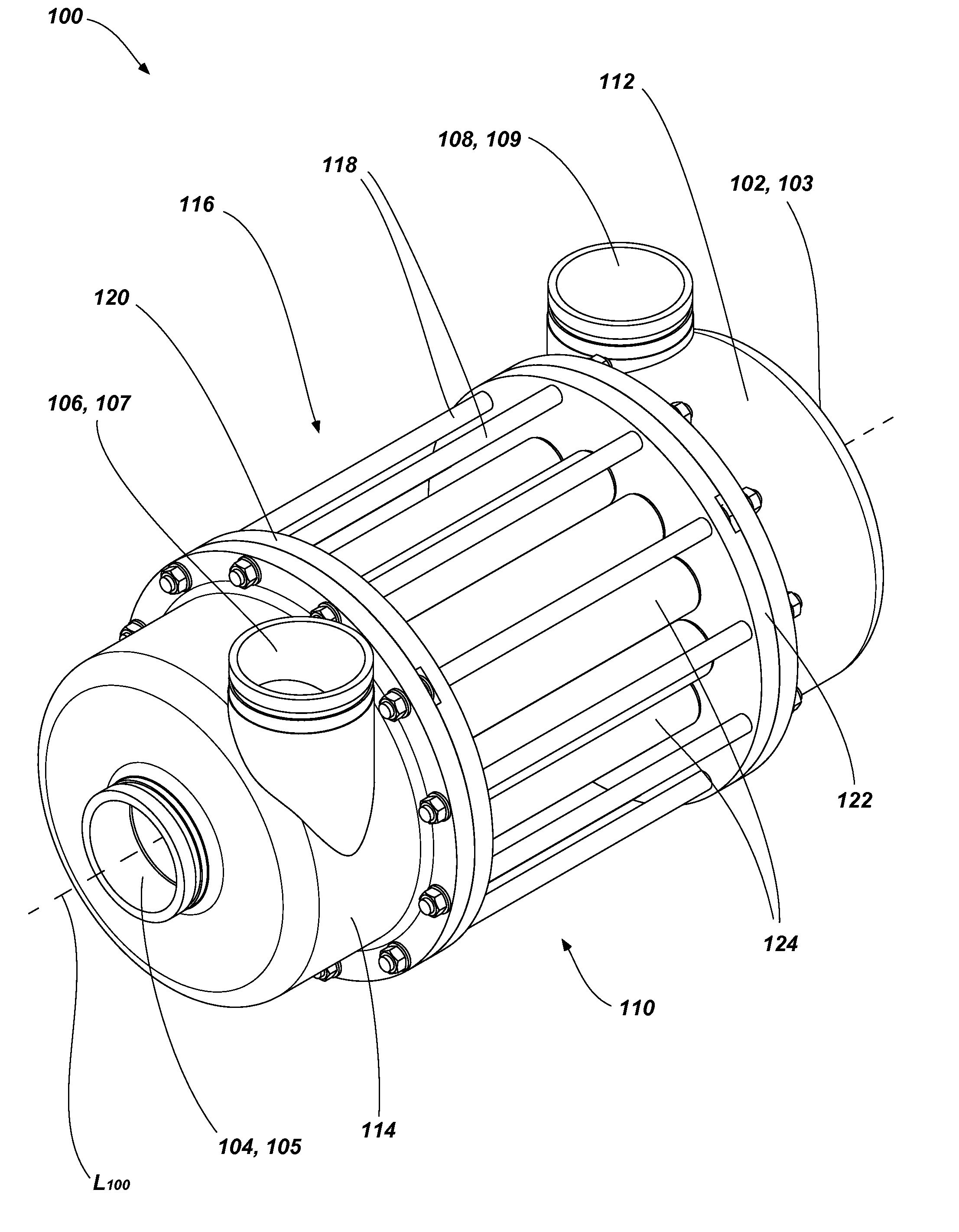
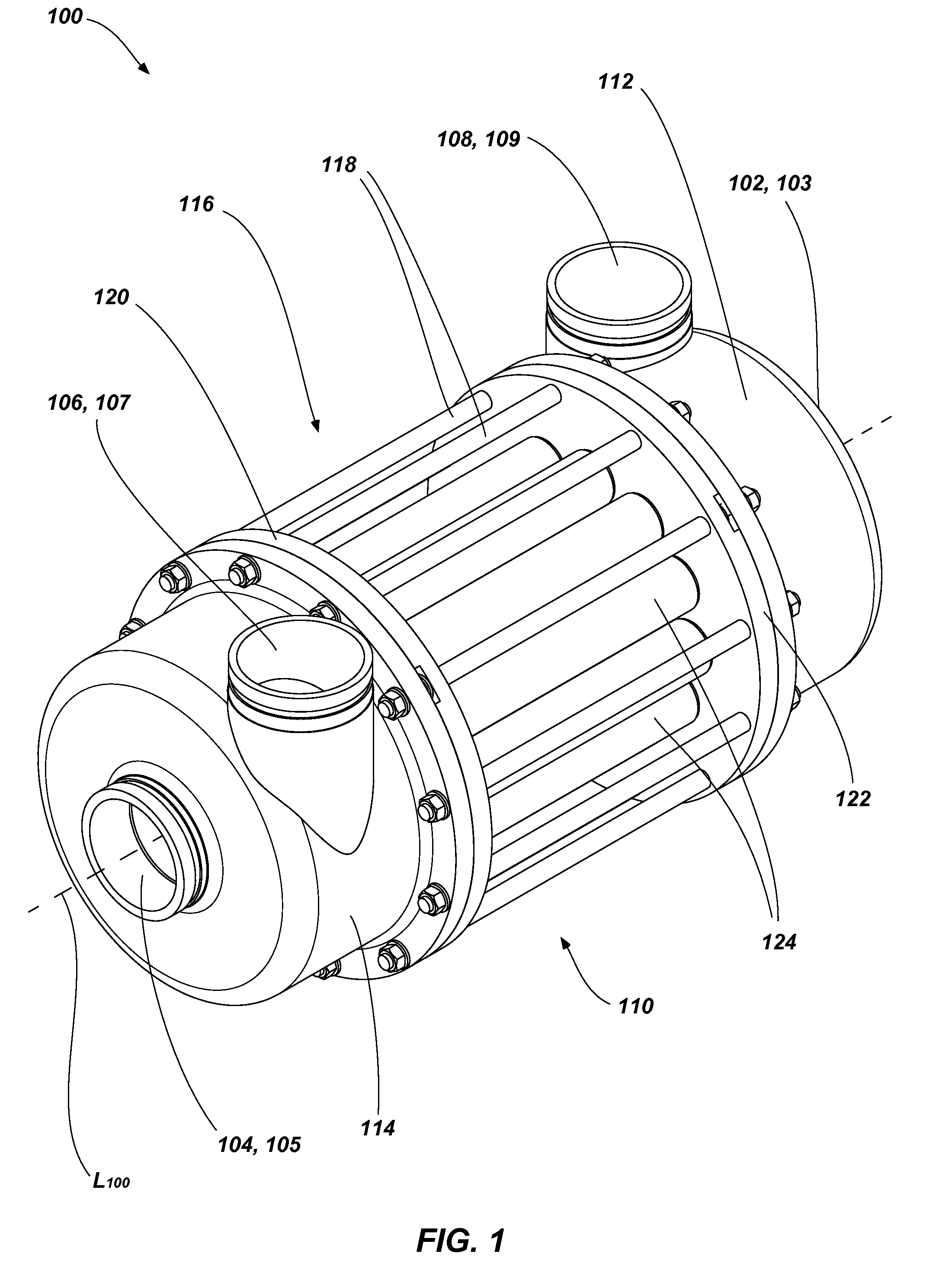
A rotor positioning system for rotary pressure exchangers with a rotor with a central bore accommodating an axle affixed to end covers in each end having at least one pair of high and low pressure ports in communication with opposing end cover ports through coaxial rotor ducts.
Owner:ISOBARIC STRATEGIES INC
Flow-reversing valve
A valve for switching fluid paths, particularly for pressure exchanger installations with tubular chambers through which fluid flows in an alternating manner, including a rotatable closing element (12, 13) provided with a motorized drive shaft (14) and arranged inside a housing (2) having a plurality of connections (3, 4) for connecting lines leading to a pipe system and to a respective end of at least one pressure exchanger. Another end of each pressure exchanger is connected through a valve arrangement to a second pipe system. A splitter (7) provided with a plurality of overflow paths (17, 18, 27) is arranged inside the housing (2); mouths of the overflow paths are located on two axial end faces (10, 11) and on the circumference of the splitter (7), and a rotatable, disk-shaped control element (12, 13) is arranged in a sealing manner at each end face of the splitter (7).
Owner:KSB AG
Pressure exchanger
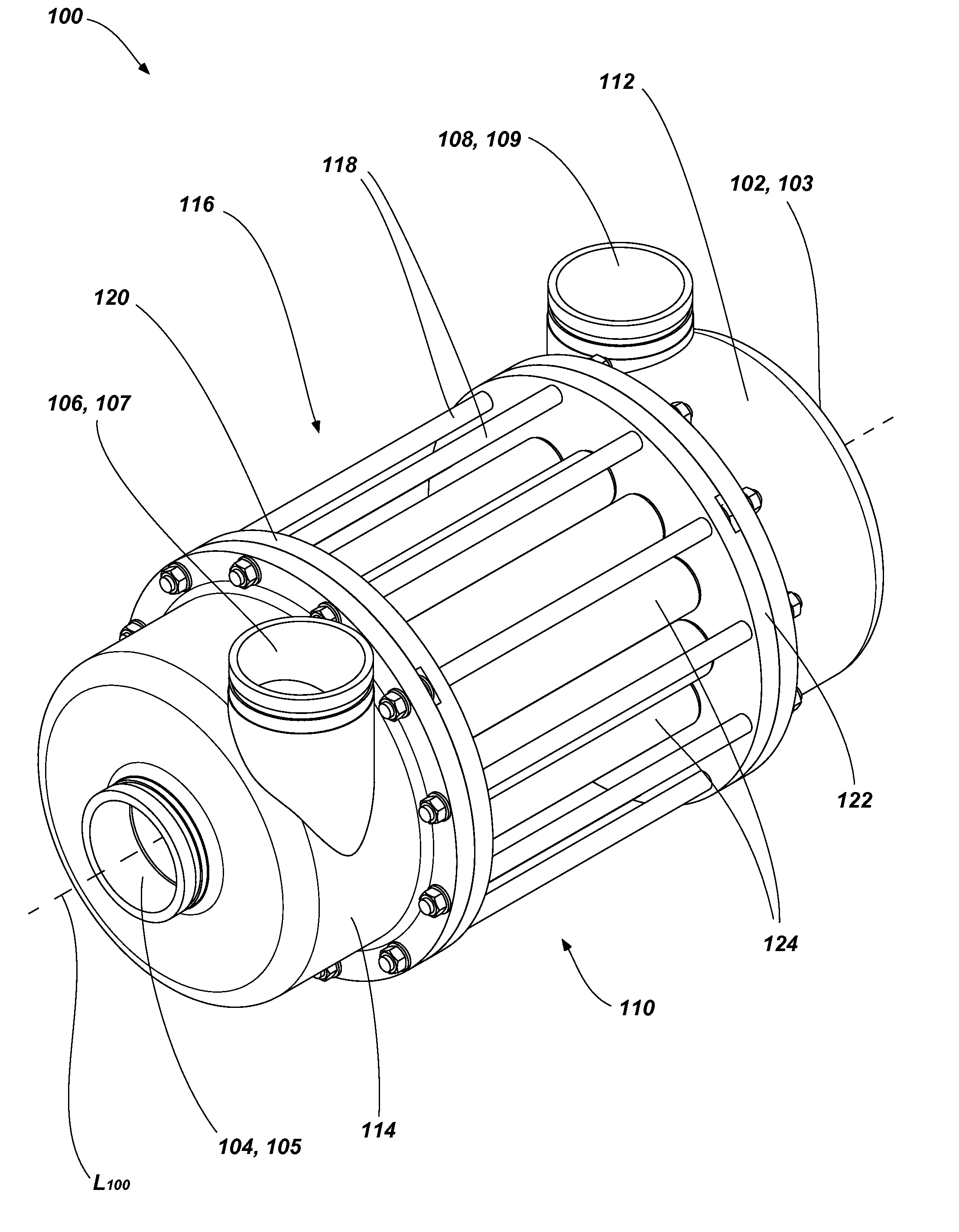
ActiveUS8622714B2Reduce complexityEasy to operatePump componentsGas turbine plantsEngineeringDistributor
A pressure vessel provided with a first port acting as a high pressure inlet of a first stream and a second port acting as a high pressure outlet. A rotatable valve element is located in the center of the machine. In operation, a fluid stream is introduced to the machine at high pressure where it then passes through the open ports of the valve element and into flow distributor causing upward displacement of a first duct piston, resulting in pressurization and flow of a second fluid. At the same time the second fluid is introduced to the machine at low pressure and flows into the pressure exchange duct, causing downward displacement of a second duct piston and resulting in flow of the first fluid below the duct piston, which then flows into the lower flow distributor, into the valve element, and then out of the pressure vessel.
Owner:FLOWSERVE HLDG
Valve unit for pressure exchanger installations
InactiveUS7600535B2Easy to controlSettling tanks feed/dischargeMultiple way valvesDrive shaftEngineering
A valve for switching over liquid paths, particularly for pressure exchanger installations with tubular pressure exchanger chambers (3) through which an alternating flow occurs, in which a rotatable control element (10, 10.1) having a plurality of flow paths is mounted in a housing (11), which in turn comprises a plurality of connection opening (12, 16, 17, 46) connected to a first pipe system and to an end of at least one pressure exchanger. Another end of the pressure exchanger is connected to a second pipe system through a valve. A motorized drive shaft (50) rotates the control element so as to alternately connect the control element flow paths to openings inside housing (11). Oncoming flow to the control element may come from an axial direction or from a radial direction, and outgoing flow from the control element occurs in the axial direction.
Owner:KSB AG
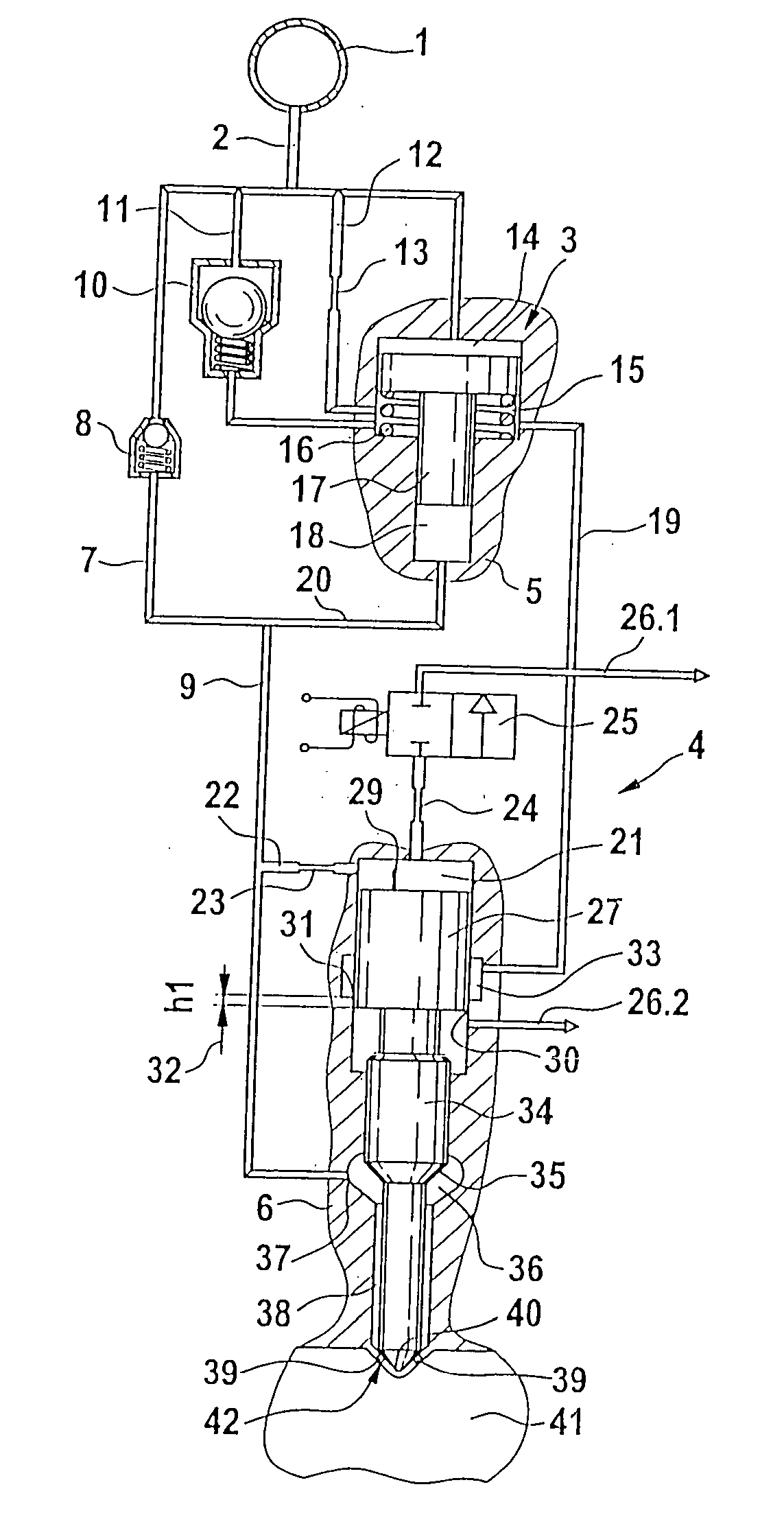
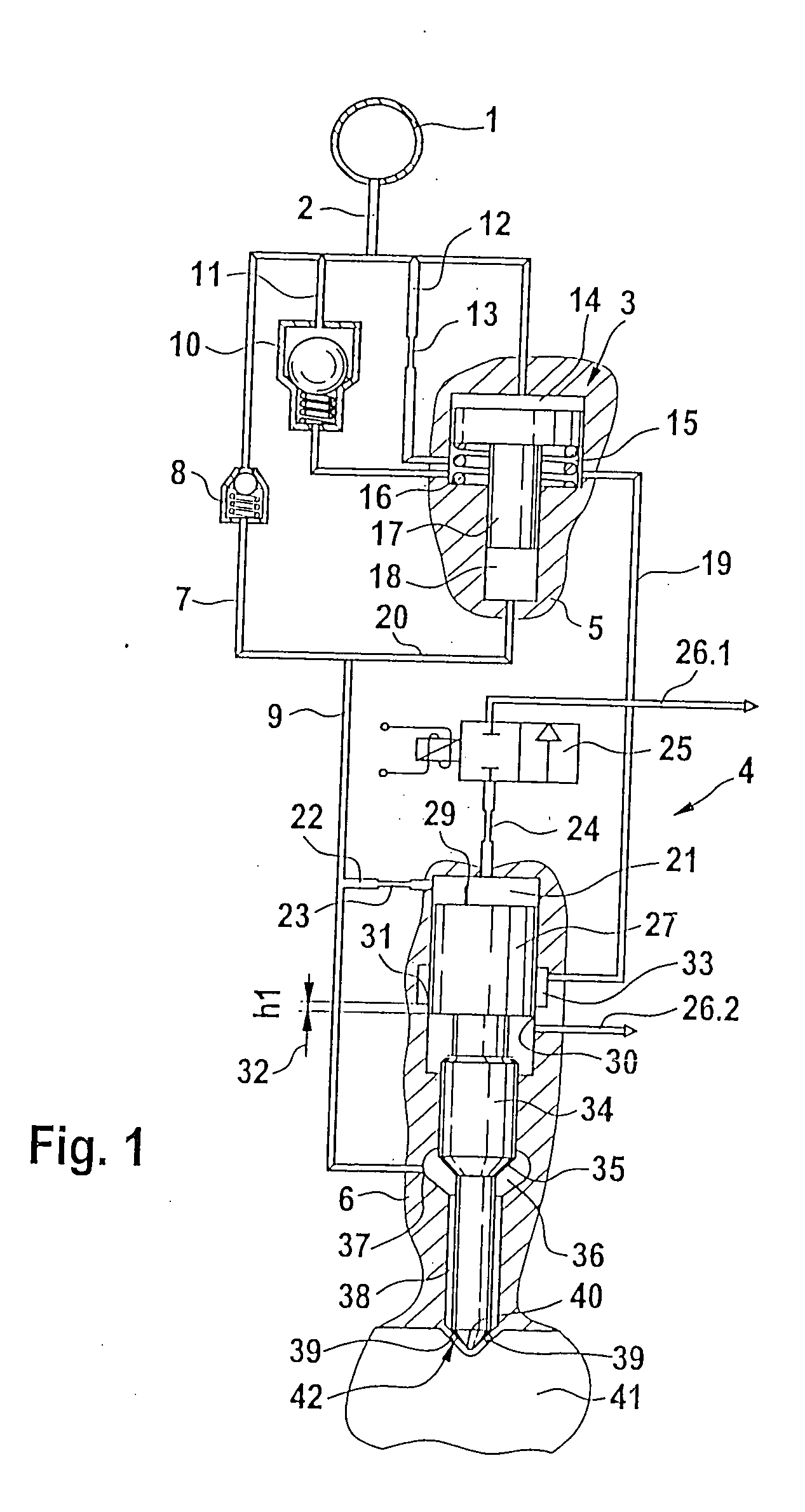
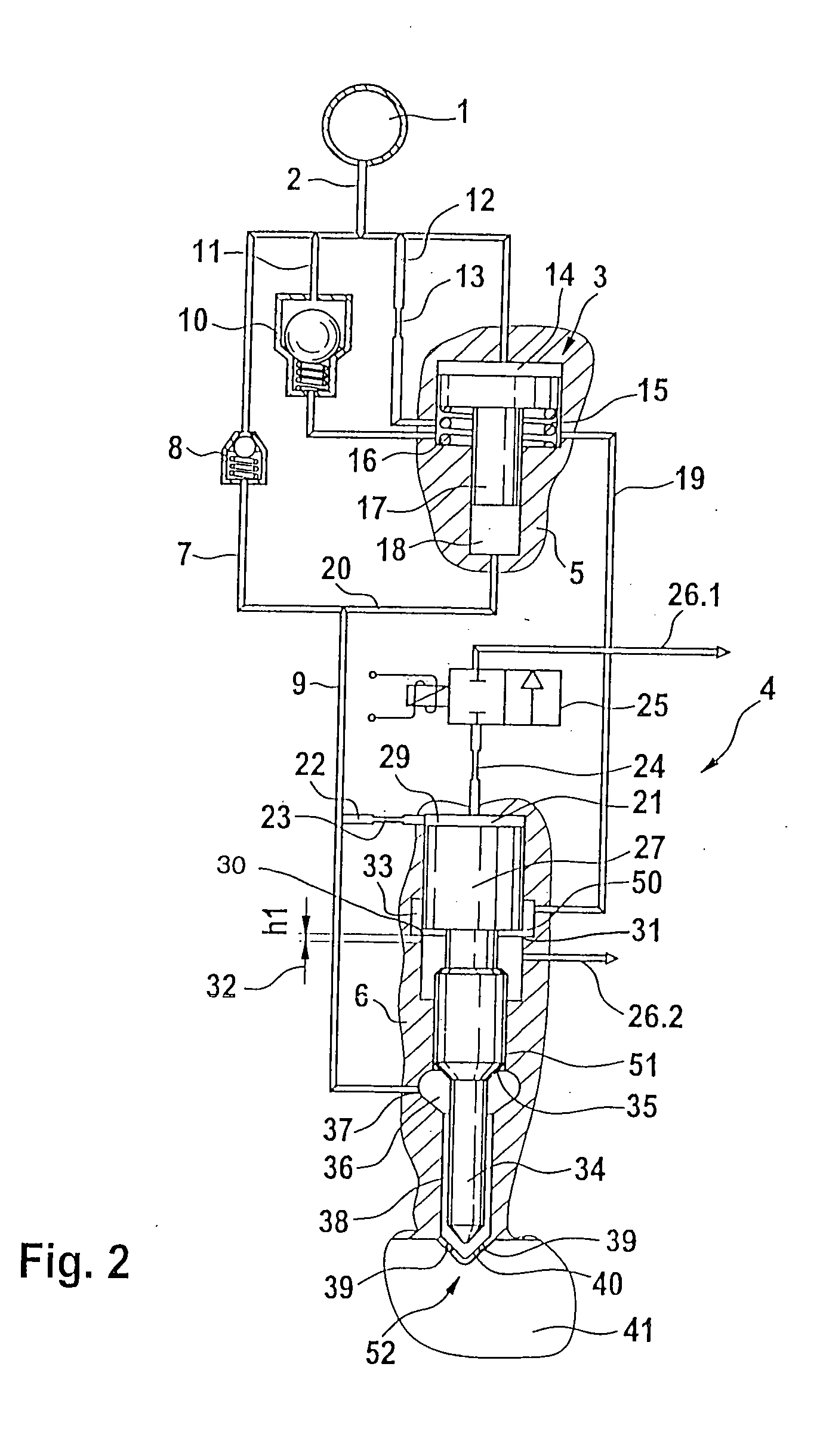
Control of a pressure exchanger by displacement of an injection valve member
A device for injecting fuel into a combustion chamber of an internal combustion engine, including an injector body which contains an injection valve element which can be actuated through pressurization / pressure relief of a control chamber by means of a control valve. A pressure booster having a piston unit that divides a working chamber from a control chamber of the pressure booster acts on a compression chamber that communicates with a nozzle chamber encompassing the injection valve element. A pressurization or pressure relief of the control chamber of the pressure booster occurs as a function of the stroke motion of the injection valve element.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Fluid exchanger devices, pressure exchangers, and related methods
ActiveUS20160377096A1Specific water treatment objectivesWater/sewage treatmentRotary valveFluid exchange
Exchanger devices include a plurality of fixed exchange ducts and a rotating valve assembly for directing flow to and from the plurality of exchange ducts. Methods of exchanging pressure between fluid streams may include directing fluids through an exchange device and pressurizing a fluid in the plurality of exchange ducts of the exchanger device.
Owner:FLOWSERVE PTE LTD
Reverse-osmosis apparatus
ActiveCN102138007AControl speedReduce delivery volumeMembranesGeneral water supply conservationReverse osmosisPressure exchanger
The present invention relates to a reverse-osmosis apparatus (1) having a diaphragm unit (2) which has an inlet (3), a permeate outlet (4) and a concentrate outlet (5), a high-pressure pump (8) which is connected to the inlet (3), a pressure exchanger (11), of which the concentrate side (10) is connected to the concentrate outlet (5), and a boosting pump between the pressure exchanger (11) and the inlet (3). The aim is to consume as little energy as possible. To this end, provision is made for the booster pump to be in the form of a positive-displacement pump (16).
Owner:DANFOSS AS
Rotation type energy recovery device
ActiveCN104791333AReduce volumeSimple structureEngine sealsFluid-pressure actuator componentsControl powerMotor drive
The invention provides a rotation type energy recovery device. The rotation type energy recovery device comprises a rotation assembly and a non-rotation assembly. The rotation assembly comprises a drive shaft, a movable ring, an upper flow distribution rotor and a lower flow distribution rotor, wherein the drive shaft is sleeved with the movable ring, and the movable ring is used for mechanical seal. The non-rotation assembly comprises a mechanical seal cover, a static ring, an upper end cover, an upper antifriction bearing, an upper thrust collar, a spring ring, a pressure exchange tube, a shell, a lower thrust collar, a lower antifriction bearing and a lower end cover, wherein the static ring is used for mechanical seal and is matched with the movable ring, the upper antifriction bearing is installed in the upper end cover, the pressure exchange tube is axially parallel to the drive shaft, and the lower antifriction bearing is installed in the lower thrust collar. The rotation type energy recovery device adopts motor drive, rotation flow distribution and self-tight seal, achieves efficient and stable pressure and energy exchange, solves the technical problem that a pressure exchanger in the prior art can not handle large or ultra-large flow, and meanwhile can replace a valve control power exchanger energy recovery device for large or ultra-large rated flow exchange processing and have stable and continuous flow and pressure.
Owner:丁武龙
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com