Frequency spectrum blind sensing method based on covariance matrix decomposition
A covariance matrix and spectrum sensing technology, applied in transmission monitoring, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve the problems of decreased detection performance, unreliable detection performance, inaccurate theoretical thresholds, etc. Noise Uncertainty, Determining Simple Effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
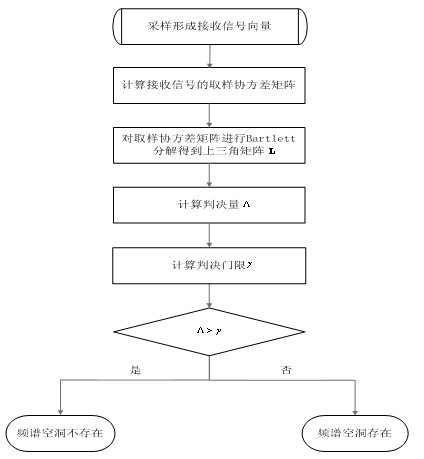
[0021] The blind spectrum sensing method based on covariance matrix decomposition firstly samples the covariance matrix of the received signal vector Do Bartlett decomposition to get an upper triangular matrix ; then use The quotient of the sum of the squares of the off-diagonal elements and the sum of the squares of the diagonal elements is used as the statistical decision quantity for spectrum hole detection. When the judgment quantity is greater than a certain threshold value, it is determined that the spectrum hole does not exist. On the contrary, when the When the decision amount is smaller than the threshold, it is determined that a spectrum hole exists. Its specific steps are expressed as:
[0022] 1) collect The received signal of the root receiving antenna is sampled to form received signal vector , ;in: Indicates the first Antenna's No. sampled signal, superscript T Indicates the transpose operation;
[0023]2) Calculate the sampling covariance m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com