Smooth symmetrical surface rebuilding method based on single image
A symmetrical surface and smooth technology, which is applied in the field of image-based 3D solid model reconstruction system, can solve the problem that users are difficult to estimate the depth value, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
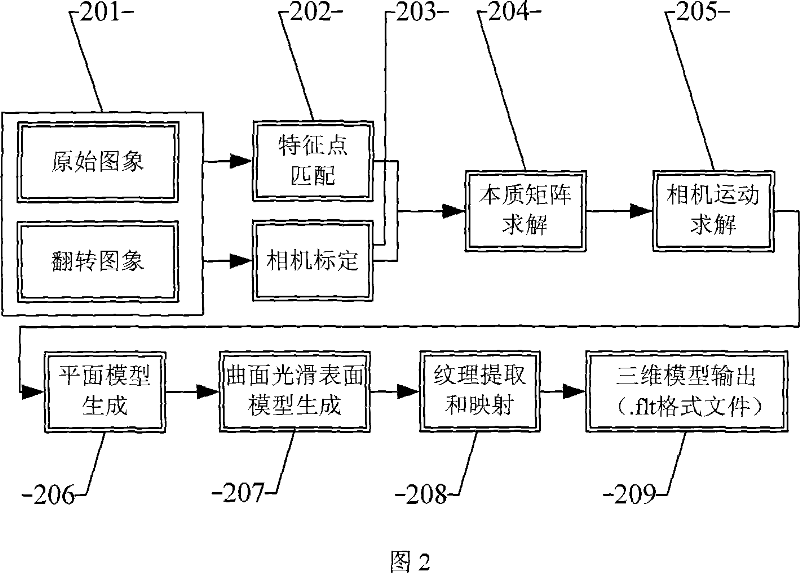
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
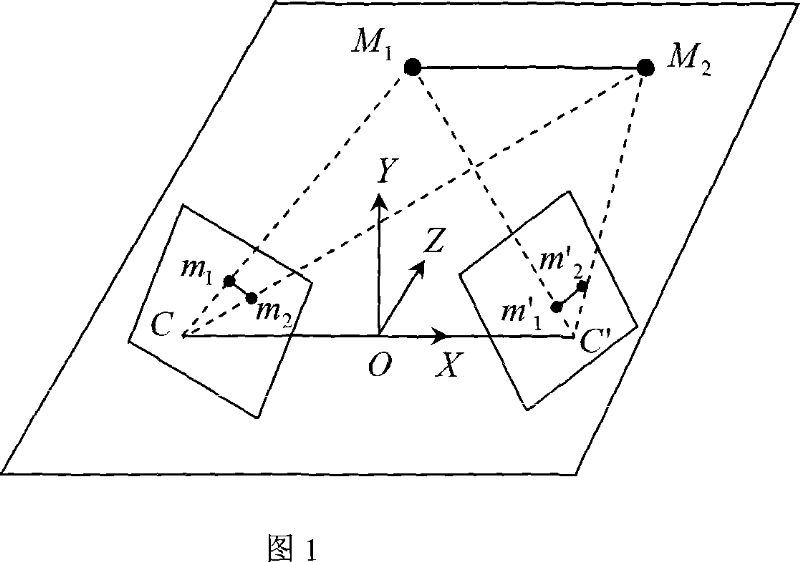
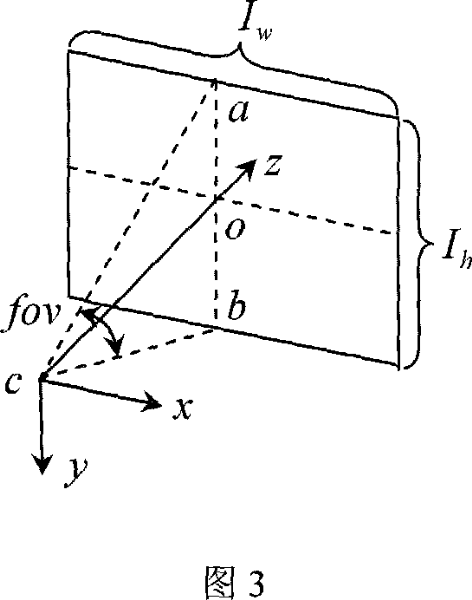
[0025] Referring to Fig. 1, the theory is proved: under the simplified perspective imaging model, the image of a mirror-symmetrical object flipped horizontally is equivalent to the image taken from another symmetrical position. This theory is the theoretical basis for subsequent steps. The specific process is as follows: using the traditional pinhole camera model, for any point in the world coordinate system M=[X, Y, Z] T After perspective projection, m=[u, v] is obtained in the image T It can be expressed as:
[0026] λ[u, v, 1] T =K[R|t][X, Y, Z, 1] T (1-1)
[0027] where λ is a non-zero scaling factor, (R, t) is the rotation and translation of the world coordinate system relative to the camera coordinate system, K is the camera intrinsic parameter matrix,
[0028] K = f 0 I w ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com