Image stitching method and device
An image stitching and image technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as inability to perform image stitching and inability to calculate images.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
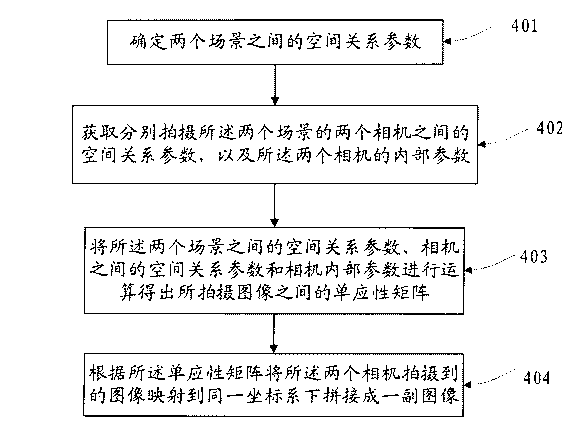
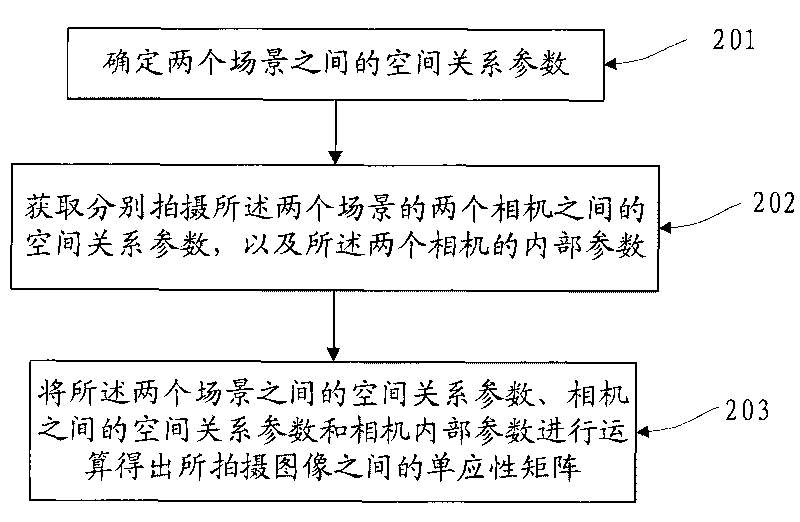
[0049] If two cameras shoot two scenes separately to obtain the images of the two scenes; or one camera shoots the two scenes separately to obtain the images of the two scenes, in order to stitch the two scenes together , it is necessary to calculate the homography matrix between two images. Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a method for calculating the homography matrix between cameras, such as figure 2 As shown, the method includes:
[0050]201. Determine the spatial relationship parameter between two scenes, the spatial relationship parameter can be expressed by a function, assuming that one of the scenes is represented by P 1 , another scenario P 2 , then the spatial relationship parameter can be passed through P 2 =f(P 1 )To represent;
[0051] 202. Obtain the spatial relationship parameters between the two cameras that shoot the two scenes respectively, and the internal parameters of the two cameras; the spatial relationship parameters are also called e...
Embodiment 2
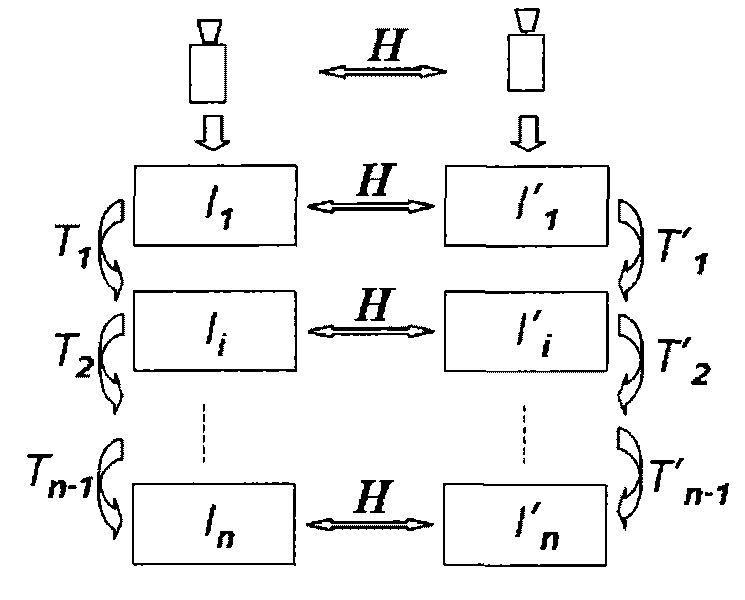
[0077] The application of the embodiment of the present invention is described below by taking the image of a large checkerboard as an example. First, make a Figure 6 As shown in the large checkerboard, there are two areas to be photographed surrounded by lines 1 and 2 in the large chessboard, and the sizes of these two areas to be photographed can be adjusted according to actual needs. The black grid or the white grid in the above-mentioned checkerboard are generally squares or rectangles of known size, because the size of the middle grid of the chessboard is known, so the positional relationship of the three-dimensional space of the two areas to be photographed can be known or solved (that is: two The spatial relationship parameters between scenes), that is to say, any pair of grids in the area to be photographed is selected, and the relative positional relationship between them is known or obtainable.
[0078] Secondly, the left and right cameras are used to simultaneously...
Embodiment 3
[0112] In this example, it is assumed that P 1 ,P 2 are two points in two scenes, and the spatial position relationship between the two scenes is: P 2 =f(P 1 ) = P 1 +b, and assume that K, K′ are the internal parameter matrices of the left and right cameras respectively, [R 1 t 1 ], [R 2 t 2 ] are the external parameters of the left and right cameras (together they can represent the spatial relationship between the cameras), and [R t] is the rotation matrix and translation vector of the right camera relative to the left camera.
[0113] Suppose P 1 ,P 2 , and the corresponding image coordinates are p 1 ,p 2 , then there is: P 1 ,P 2 The corresponding point in the camera coordinate system is P c1 ,P c2 , then there are:
[0114] P 1 = R 1 P c 1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com