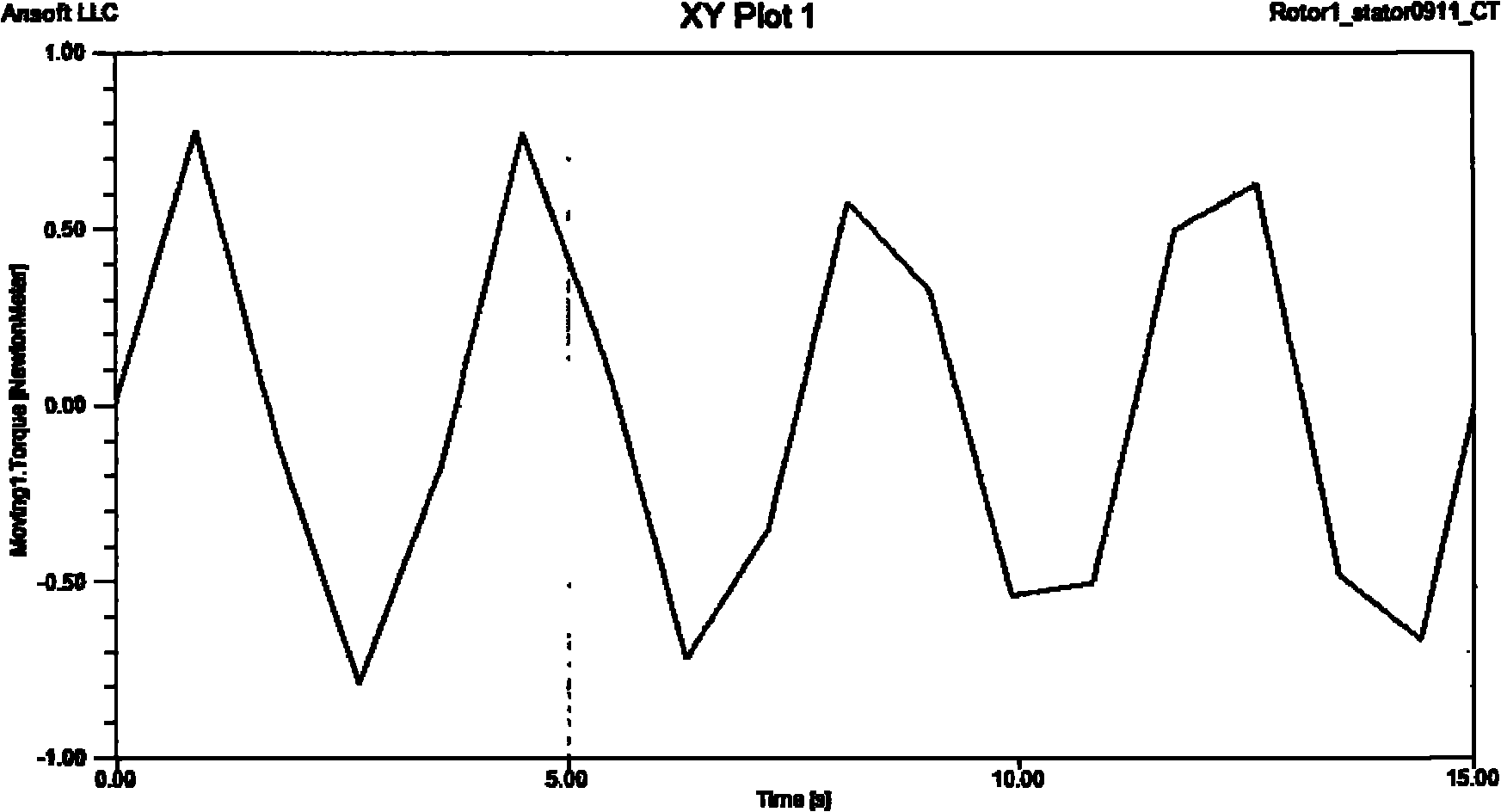
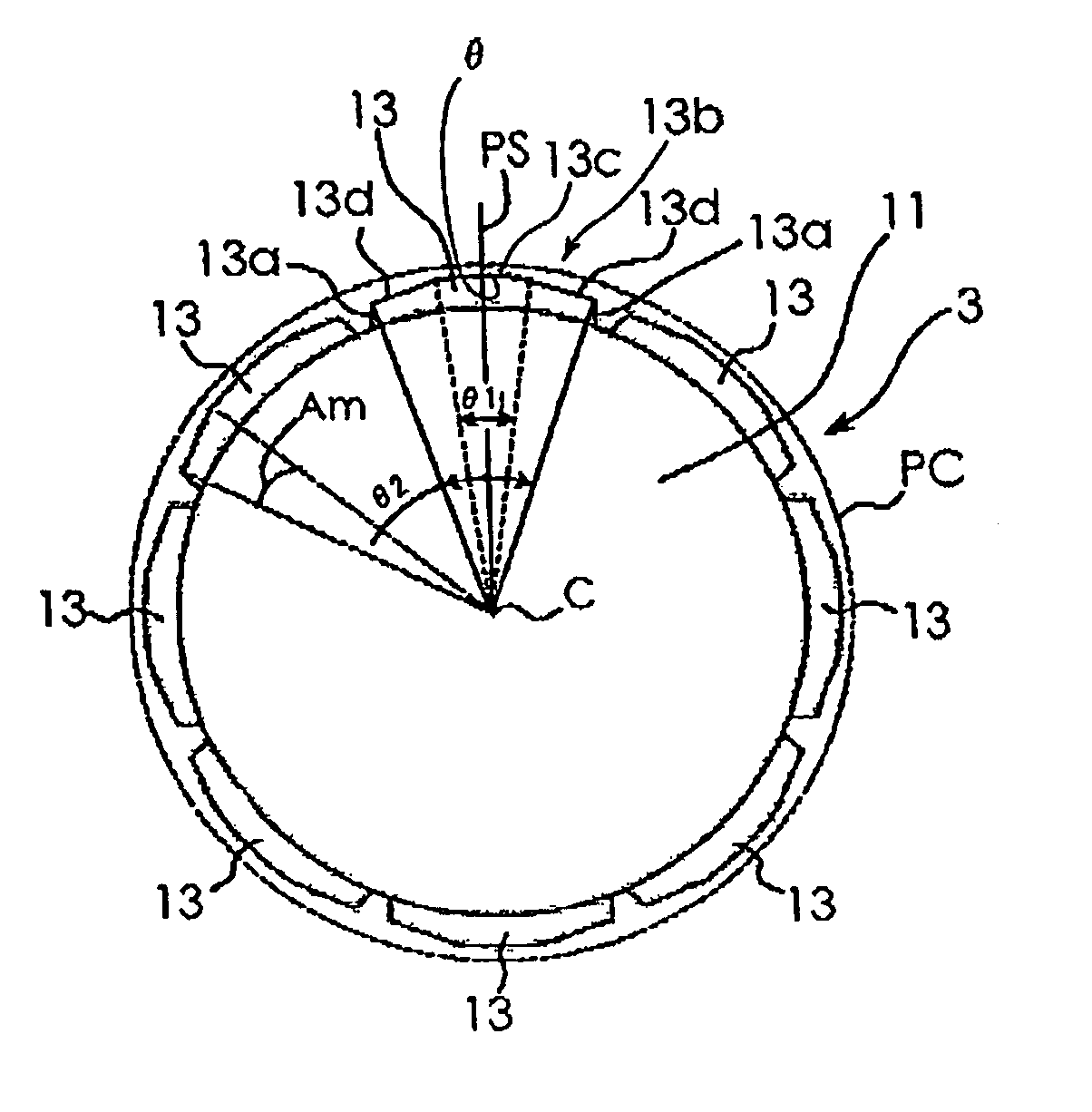
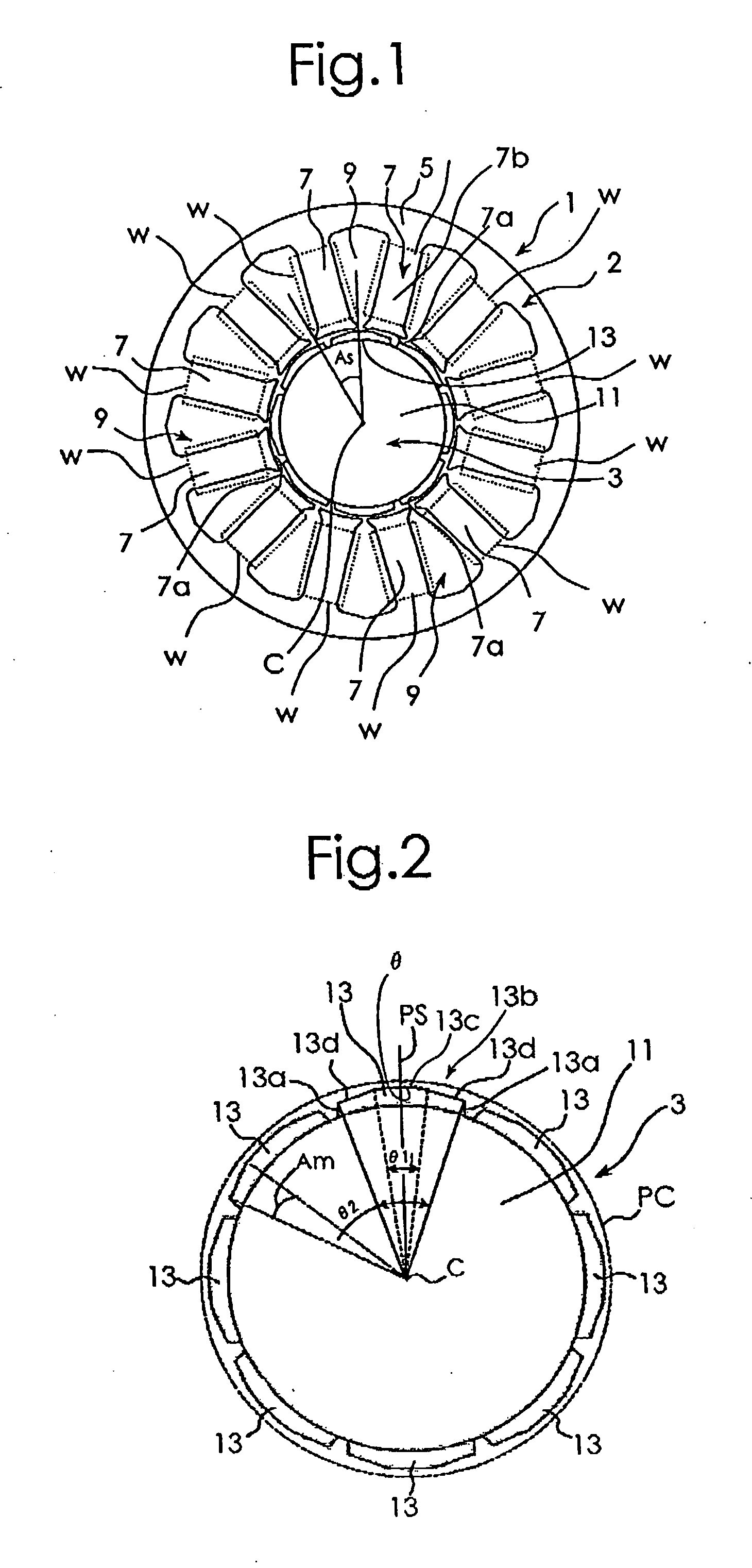
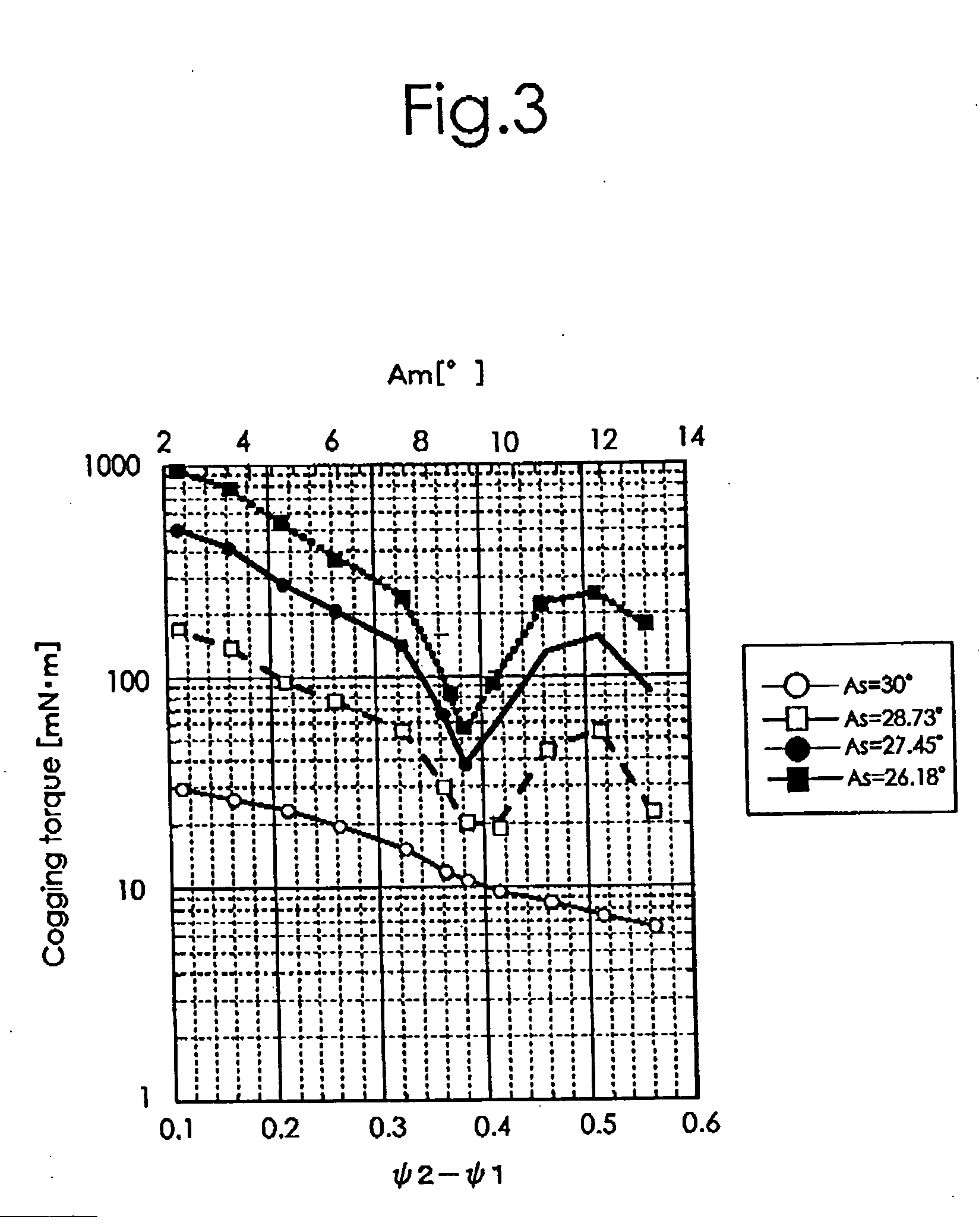
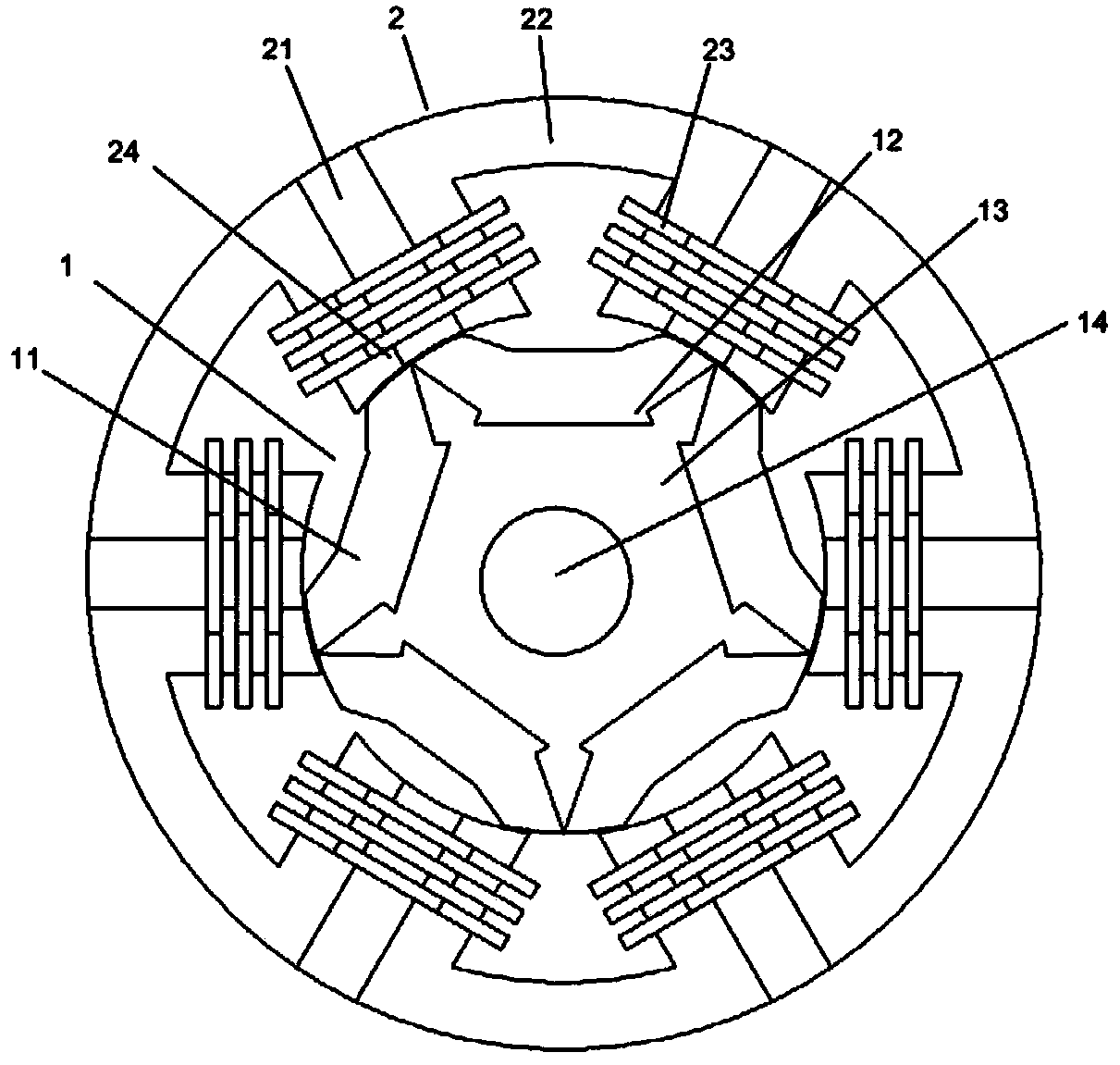
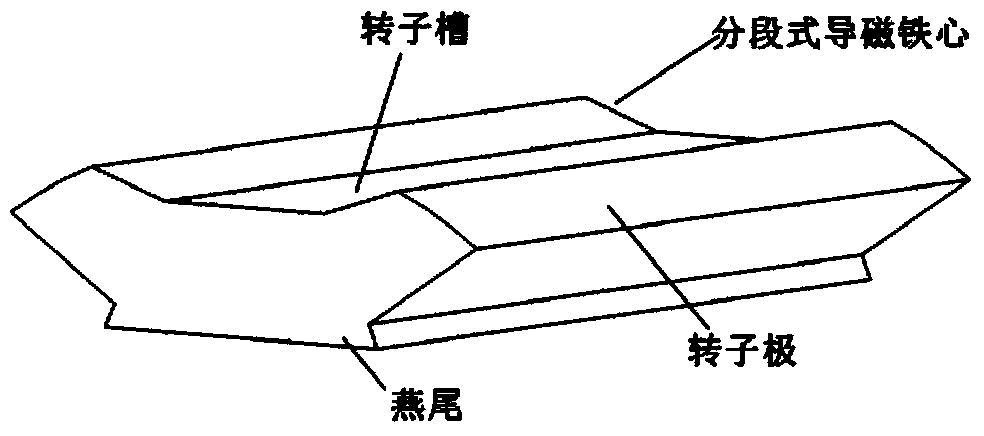
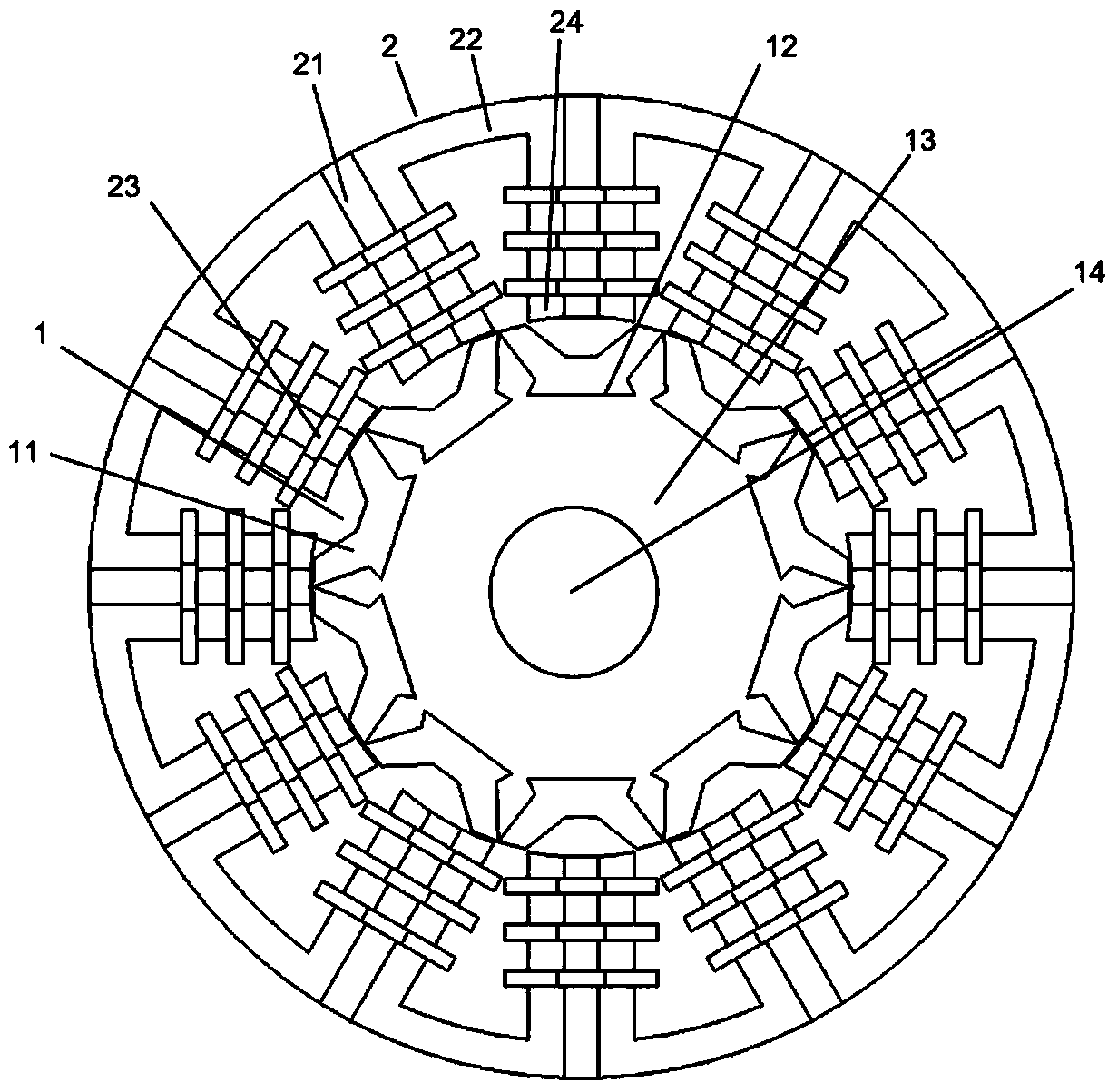
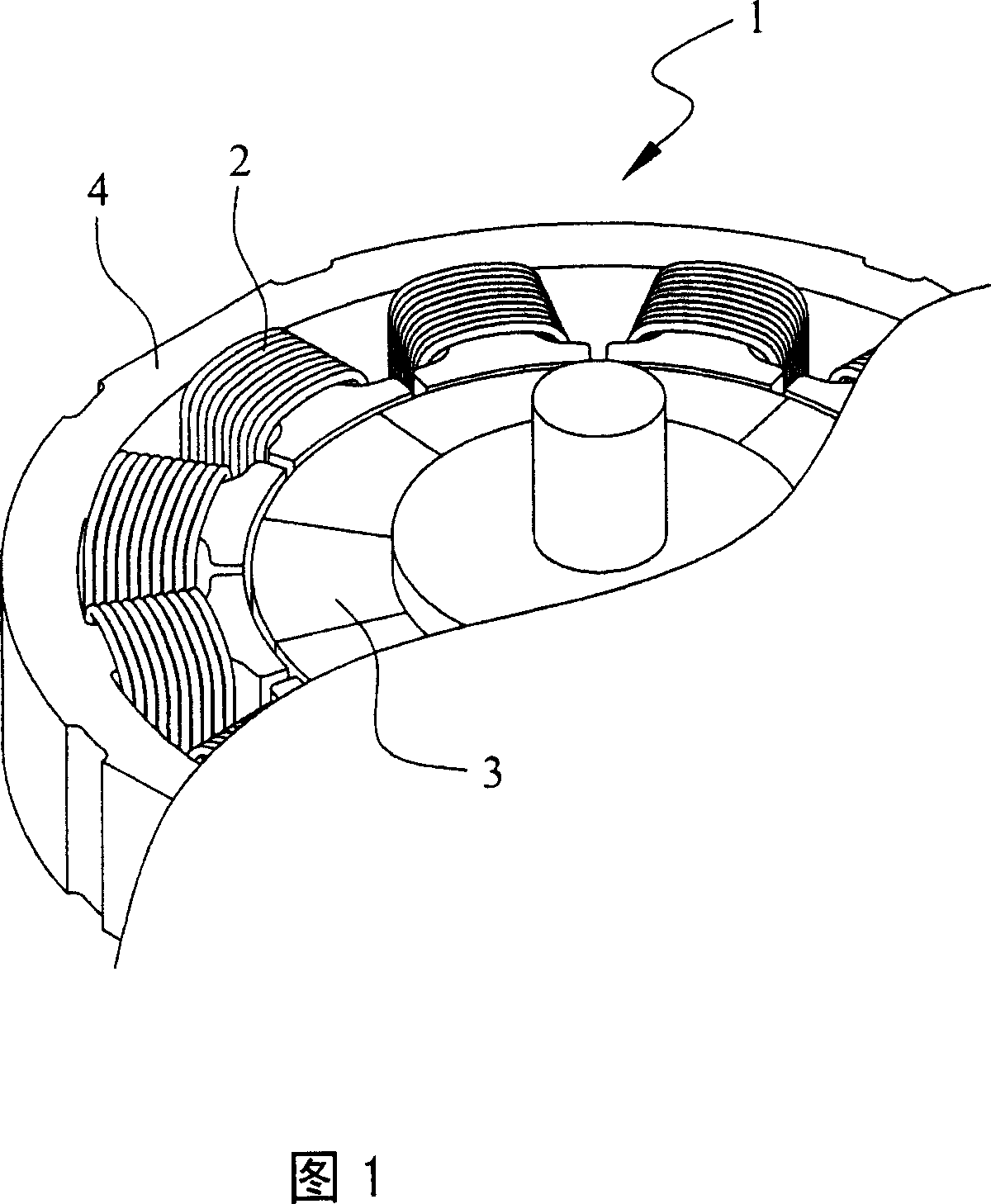
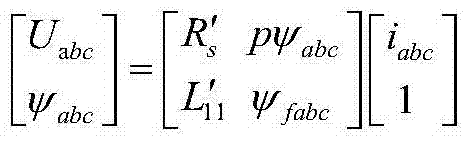Patents
Literature
193results about How to "Reduce cogging torque" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
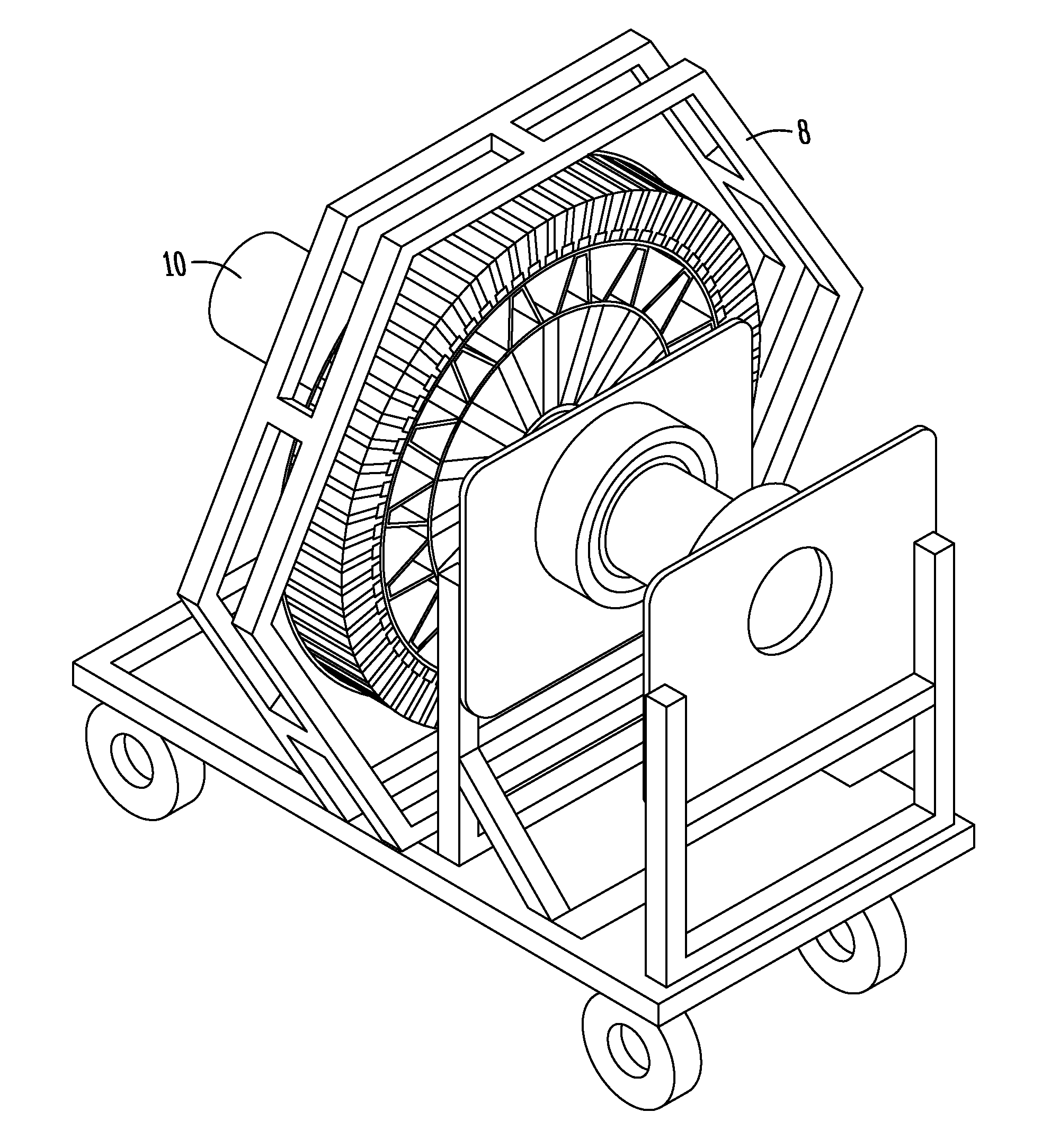
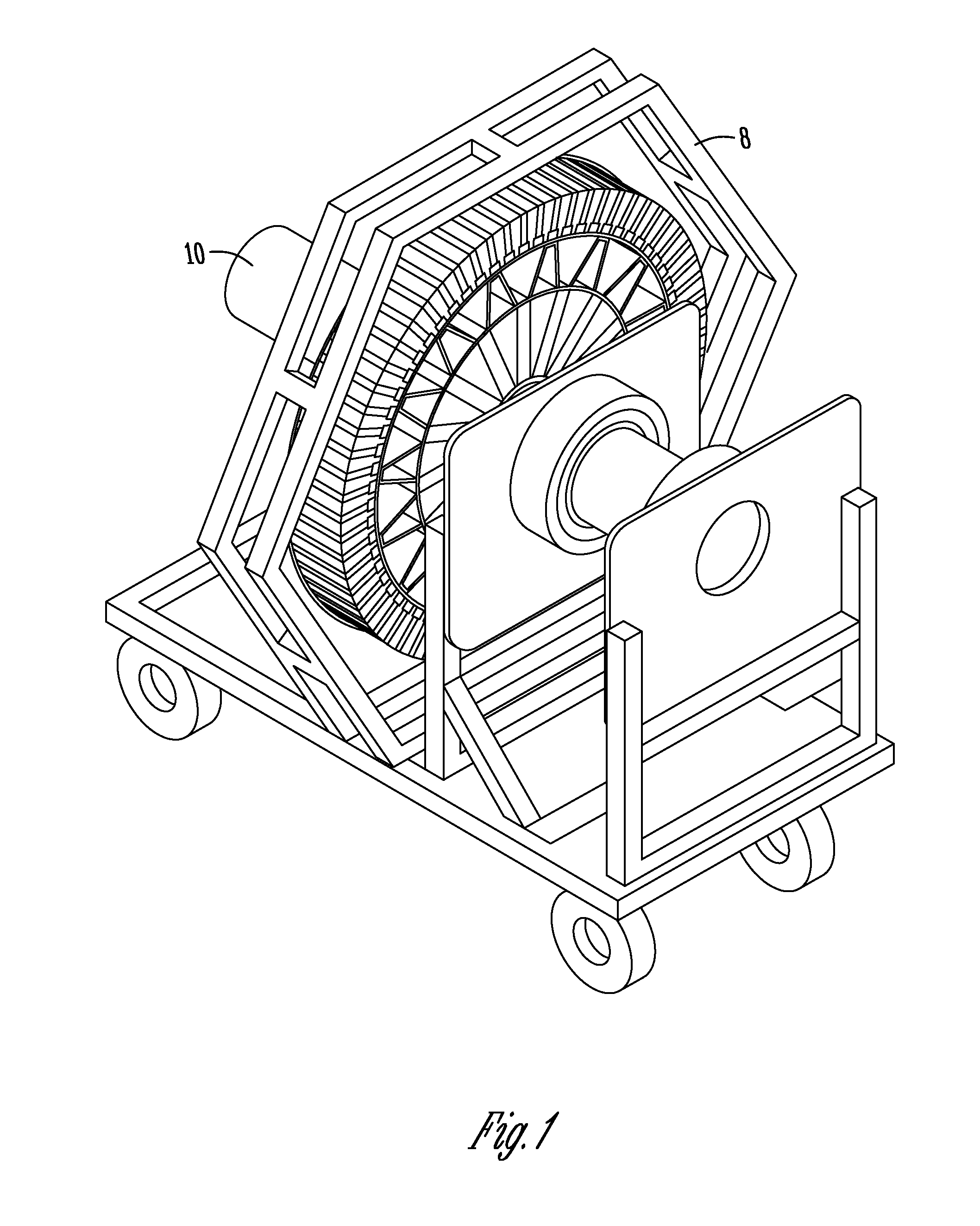
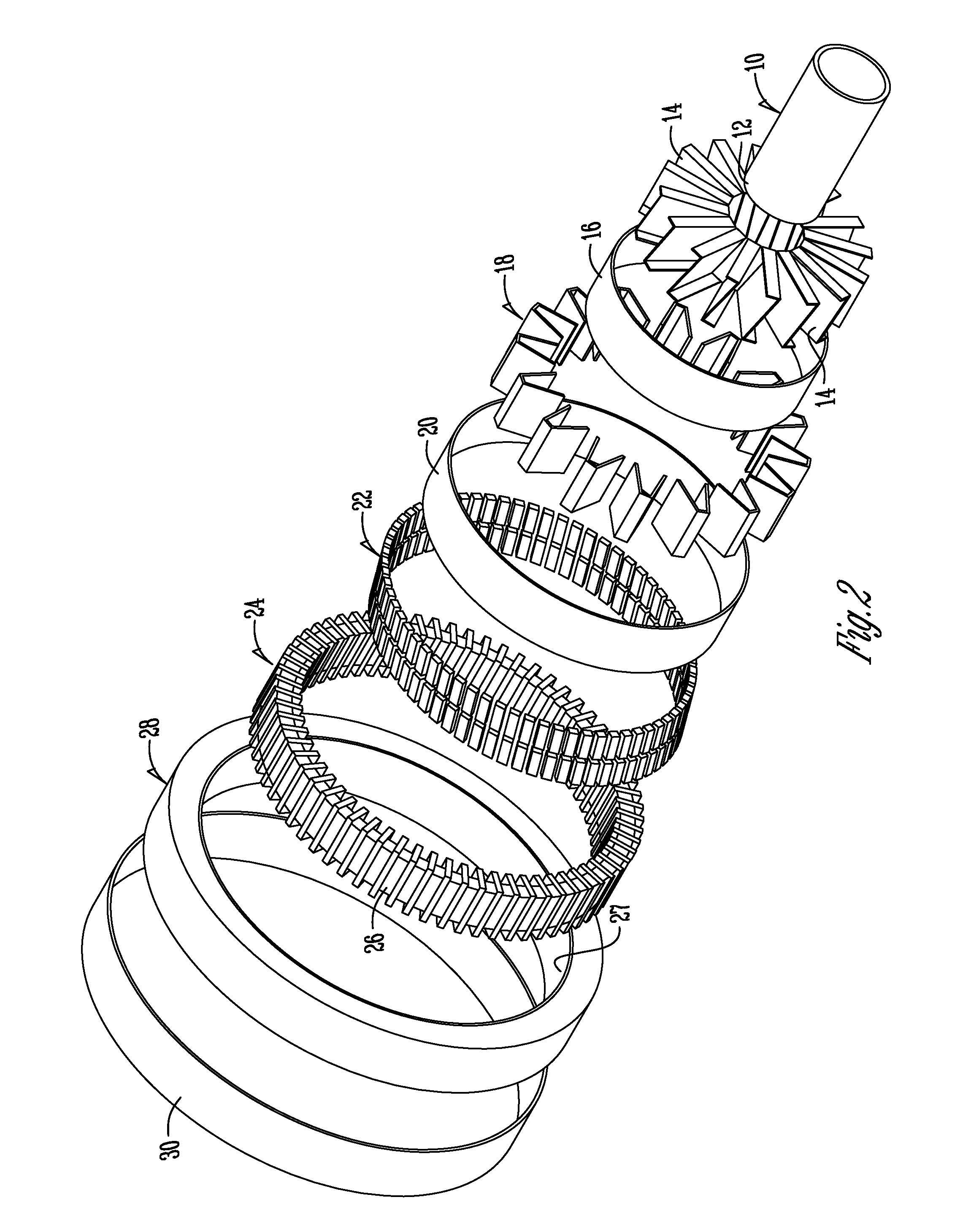
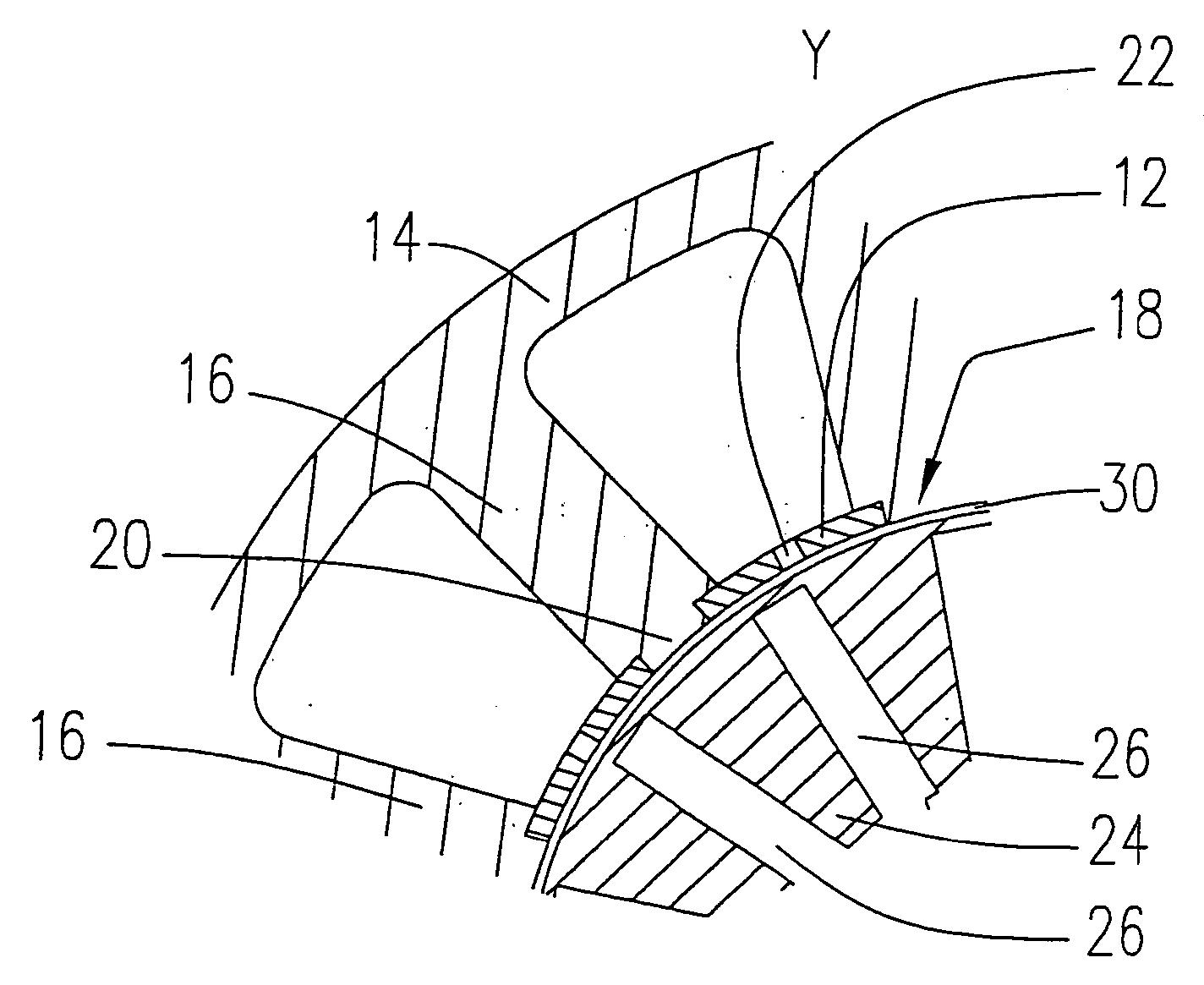
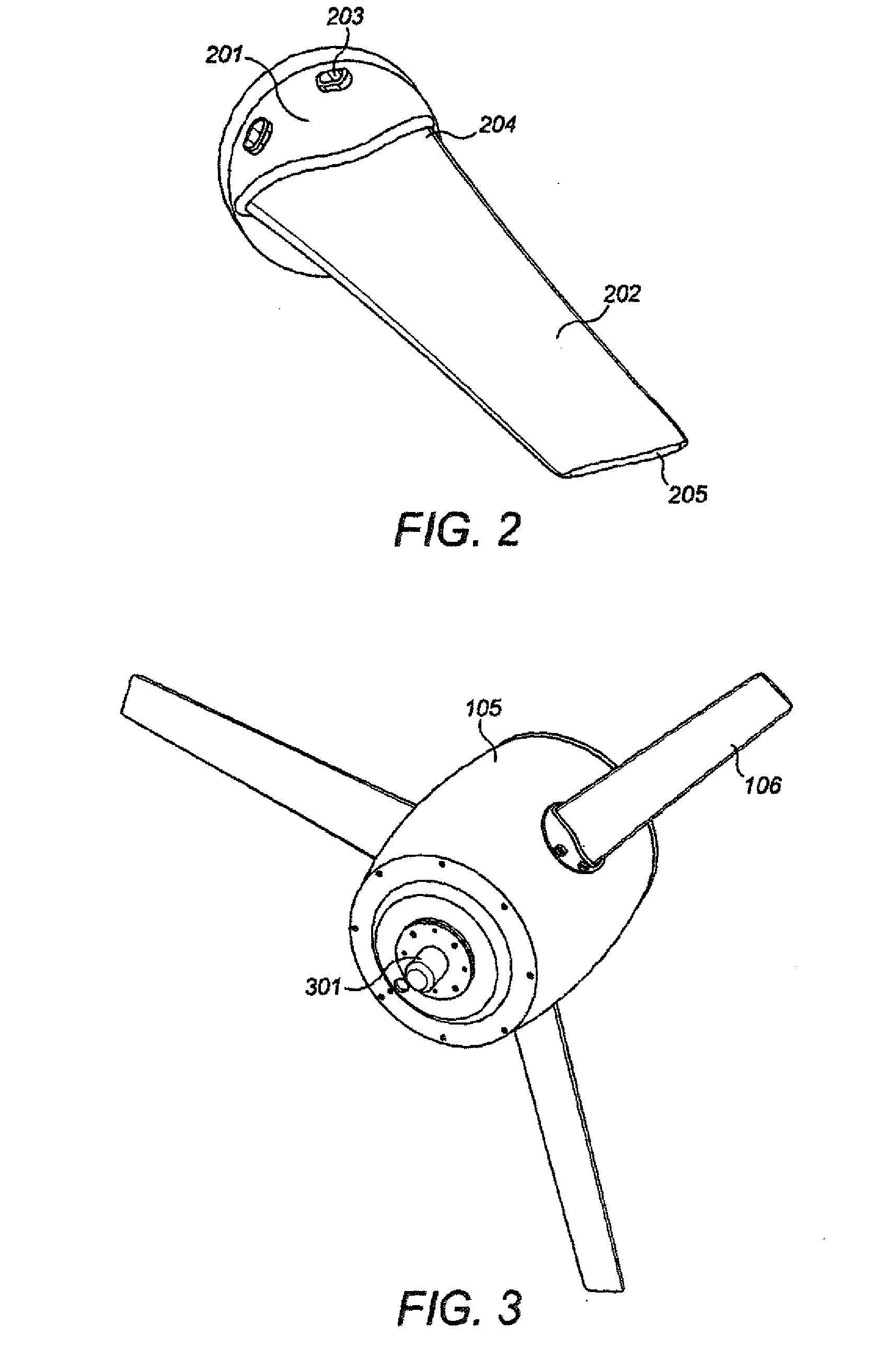
Direct drive wind turbine and blade assembly
Owner:TODOROF BILL
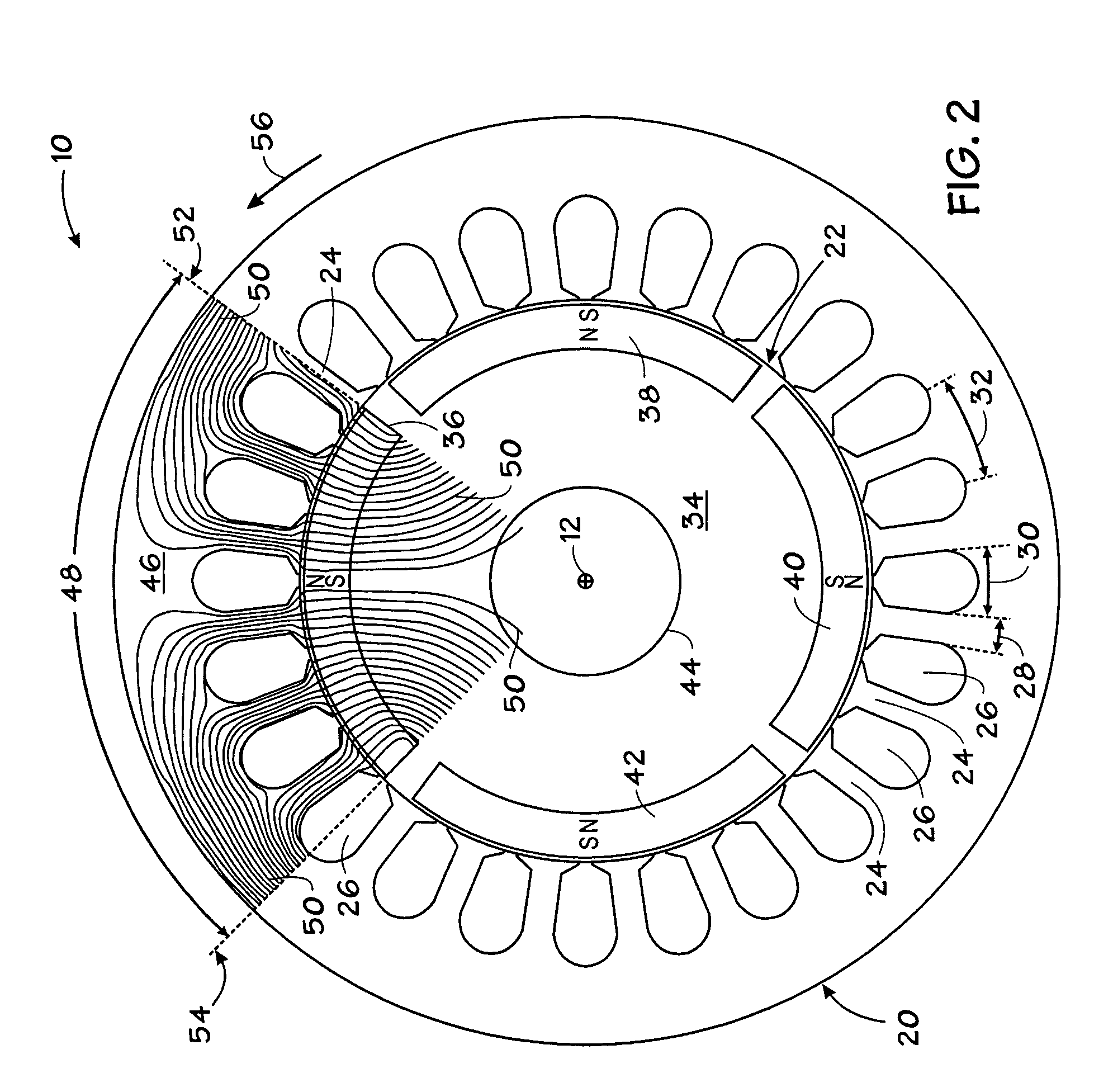
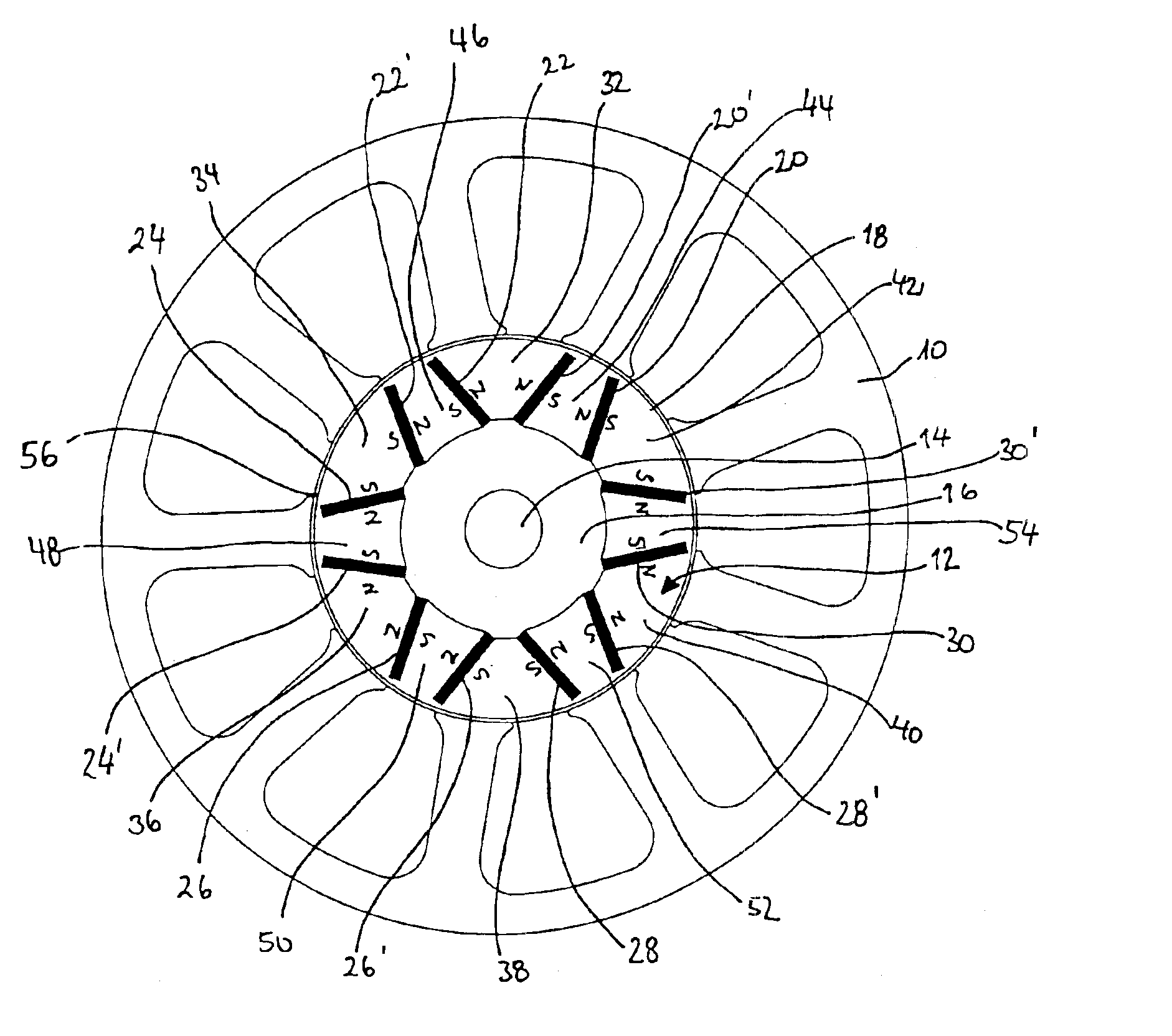
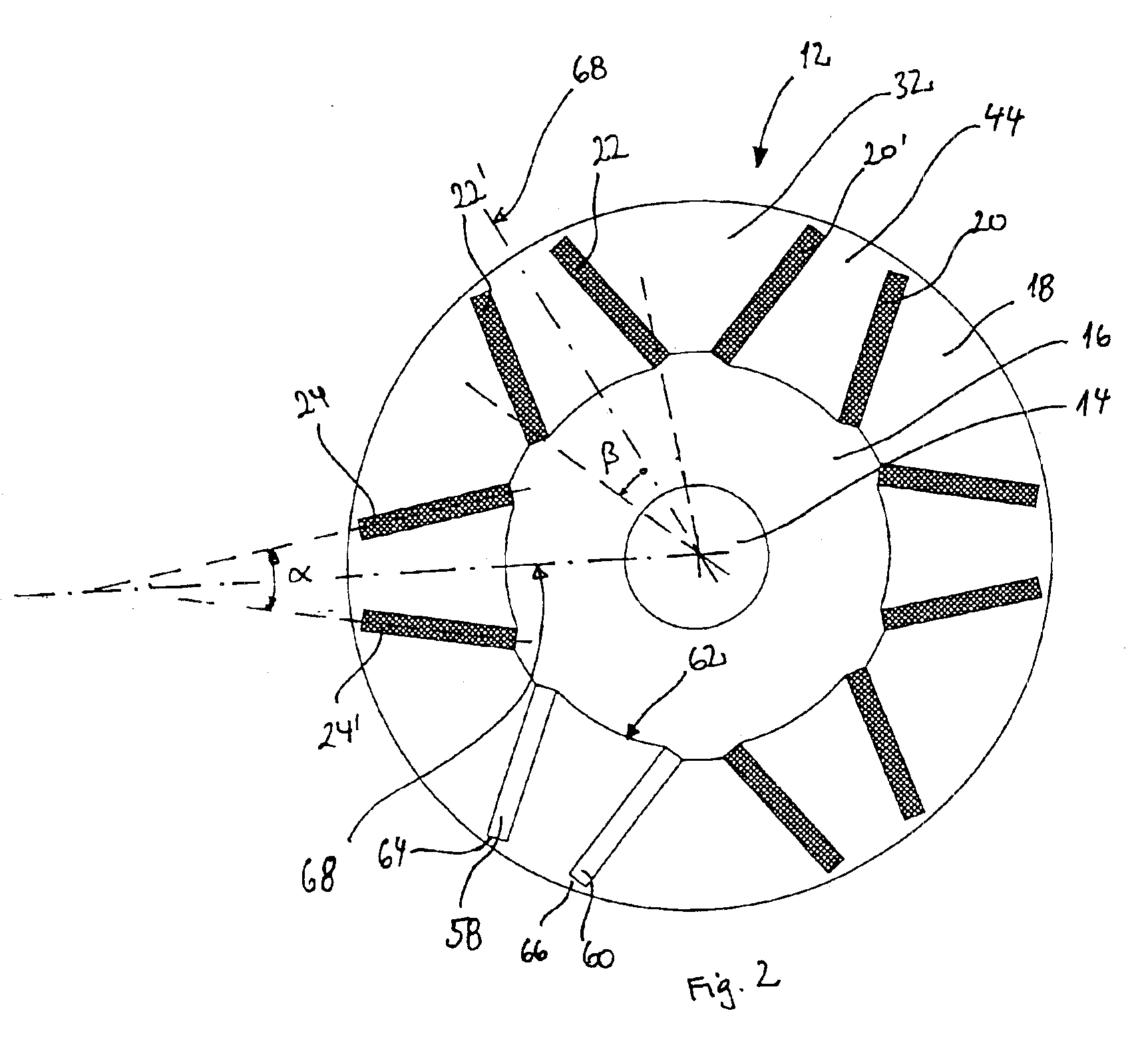
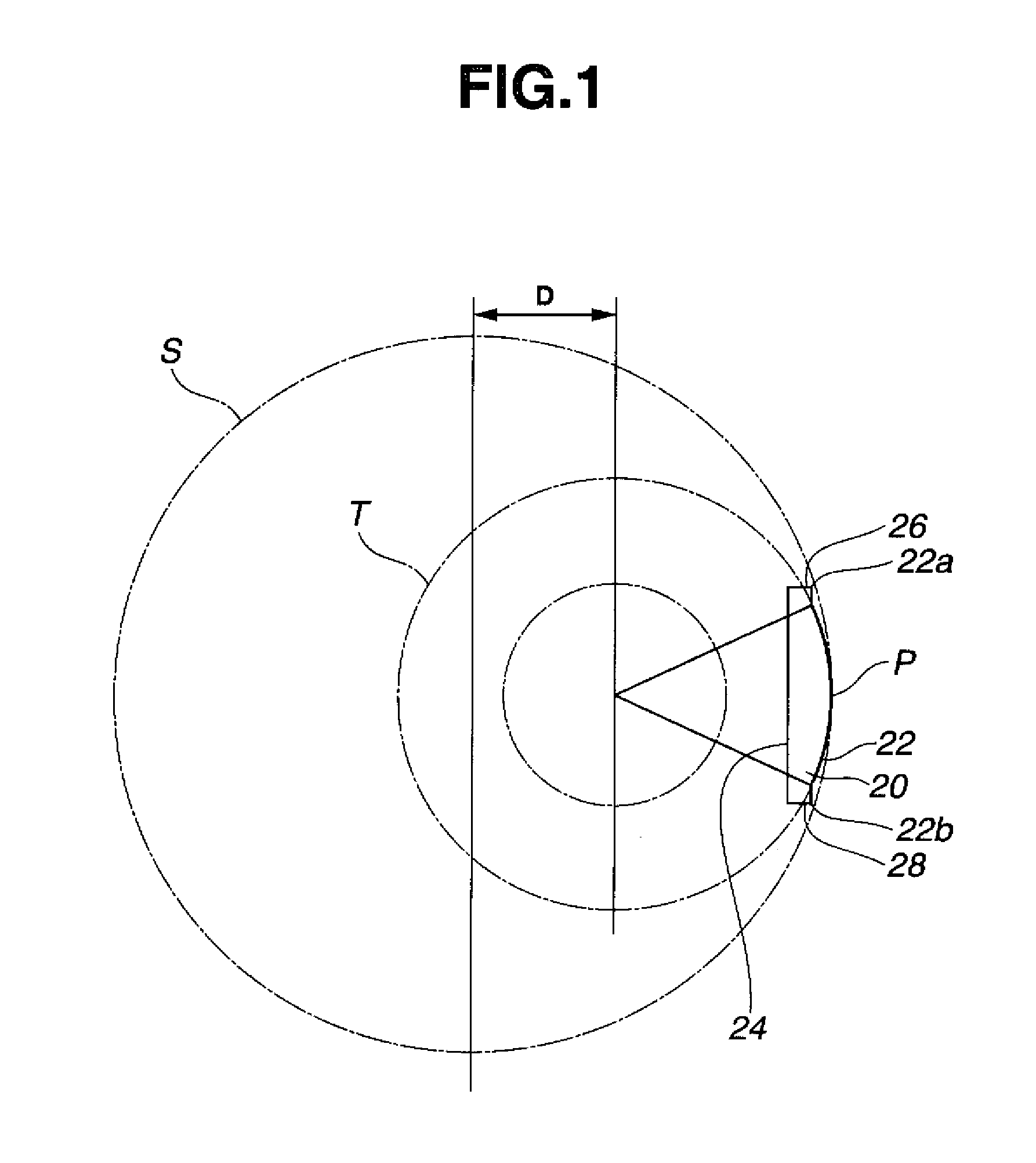
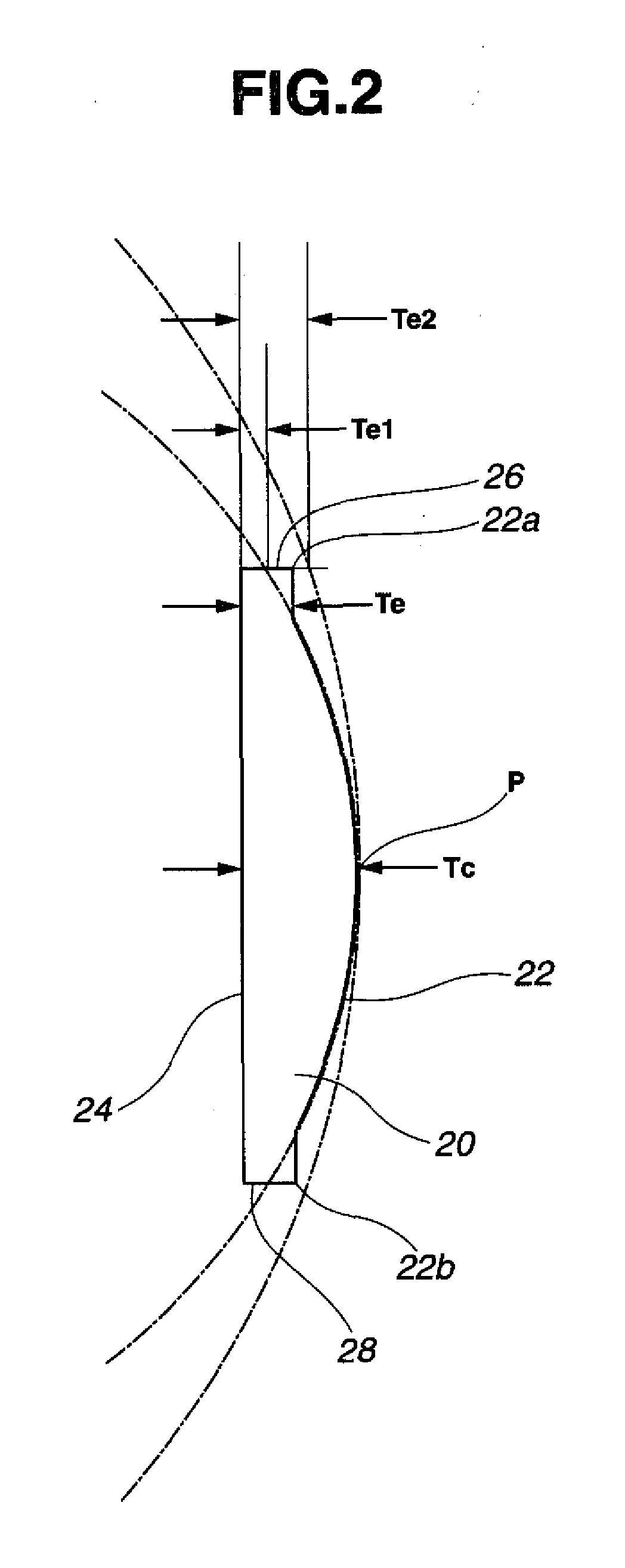
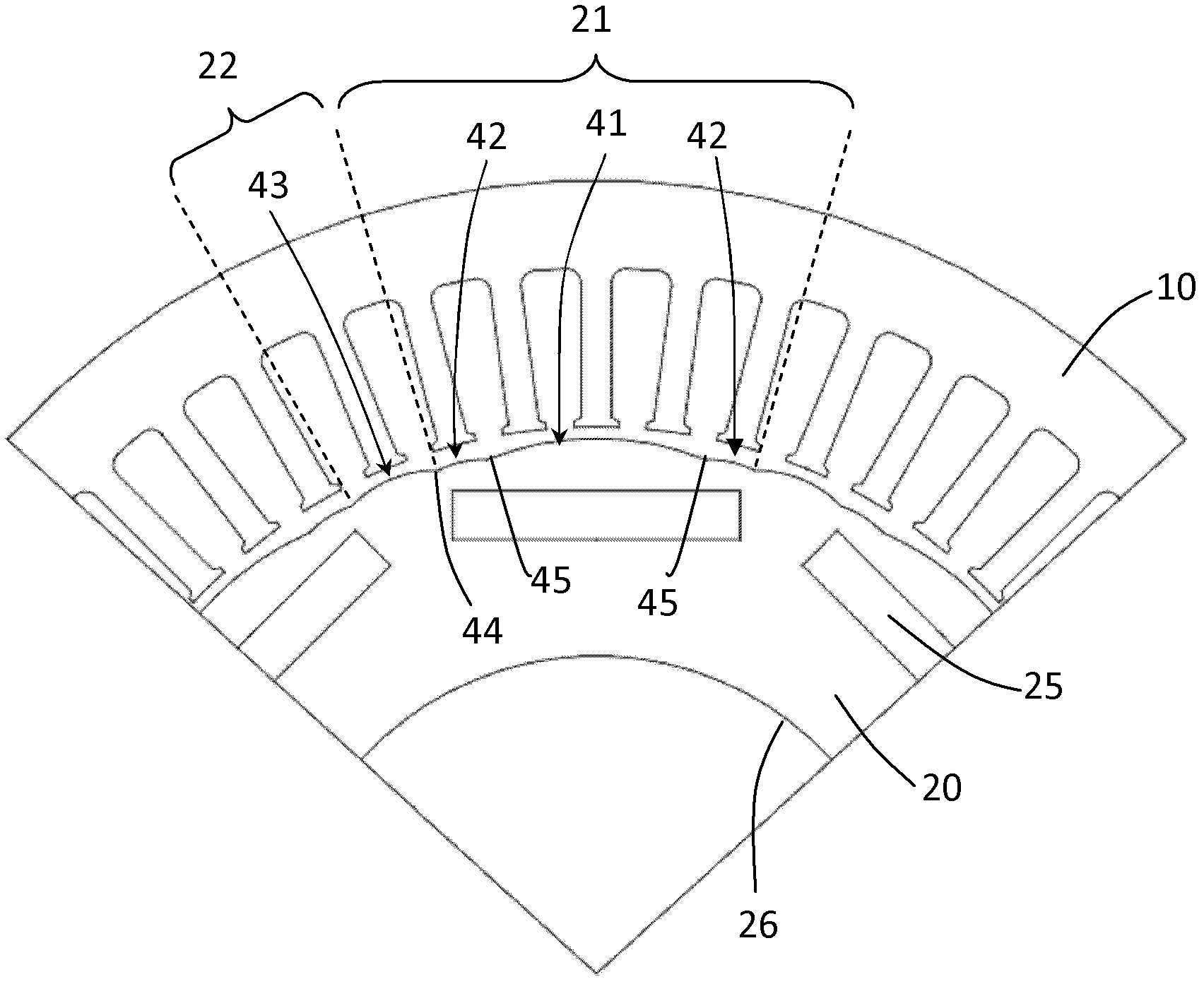
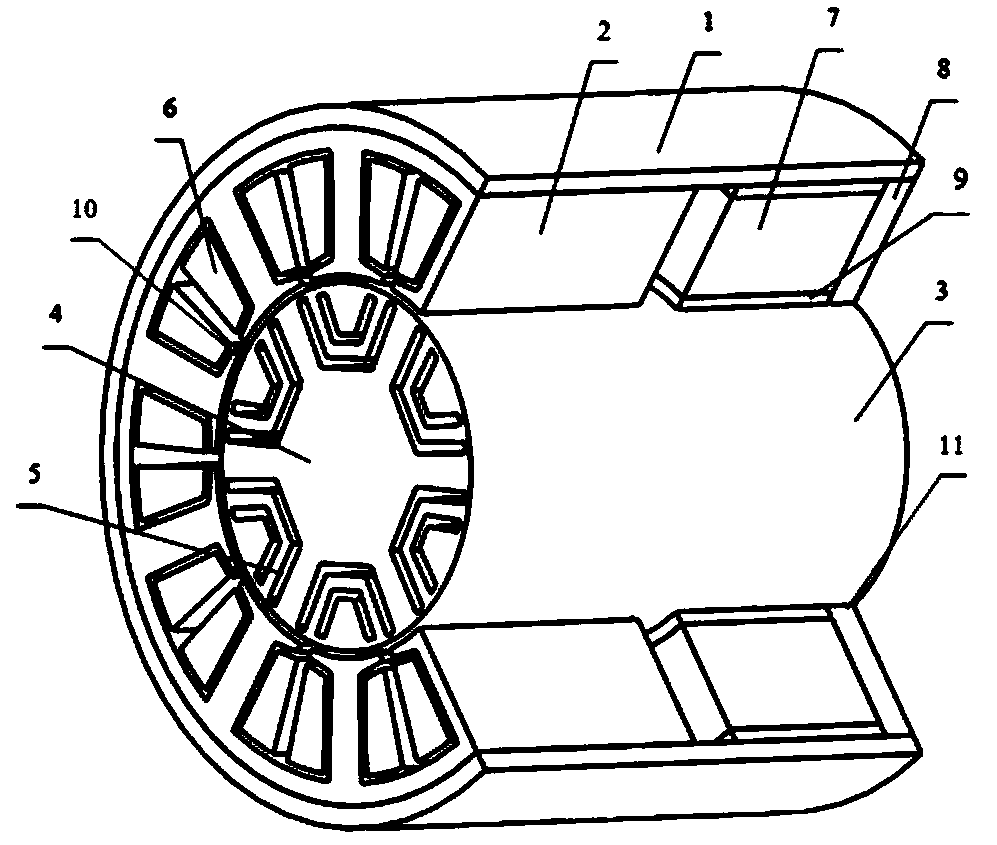
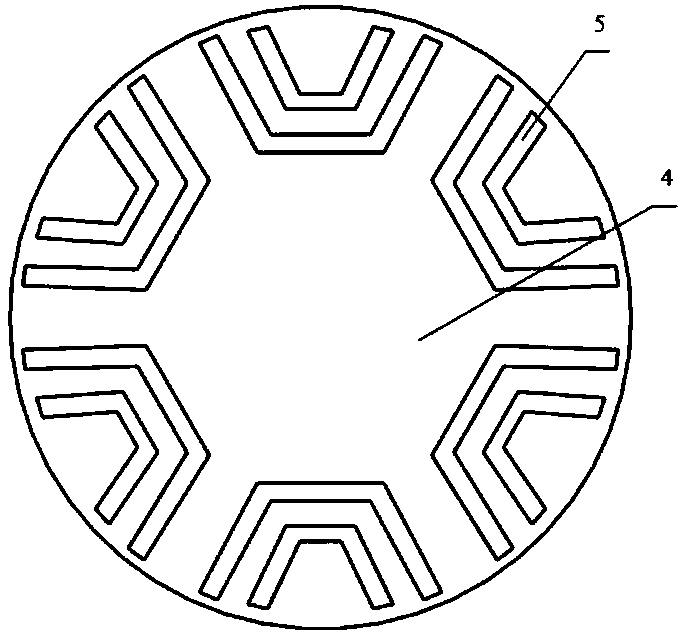
Stator arrangement for an electric machine, a method for the manufacture of a stator arrangement and a direct current motor
InactiveUS20060108890A1Minimizes problemPrevent materialWindingsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineConductor Coil
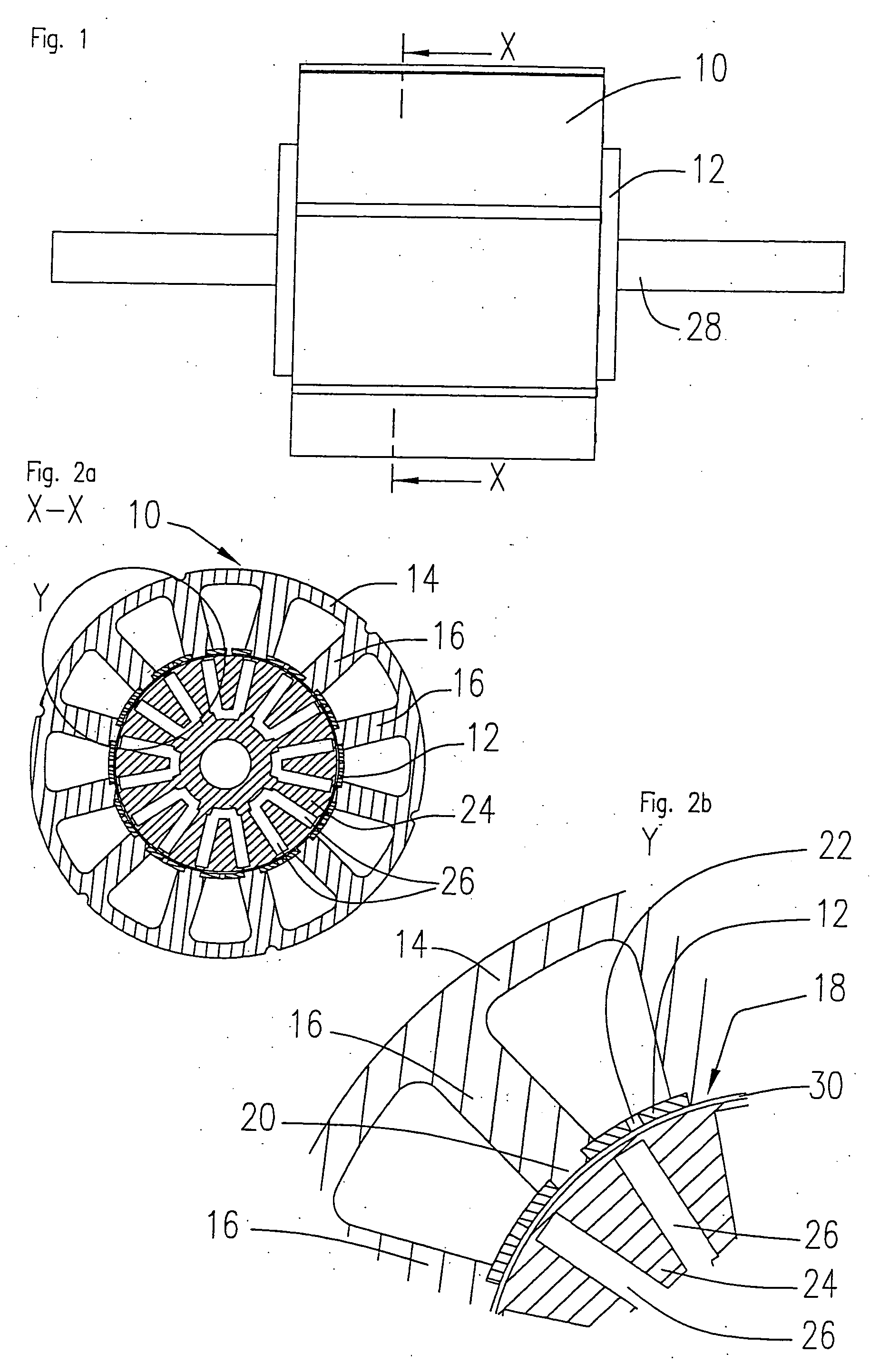
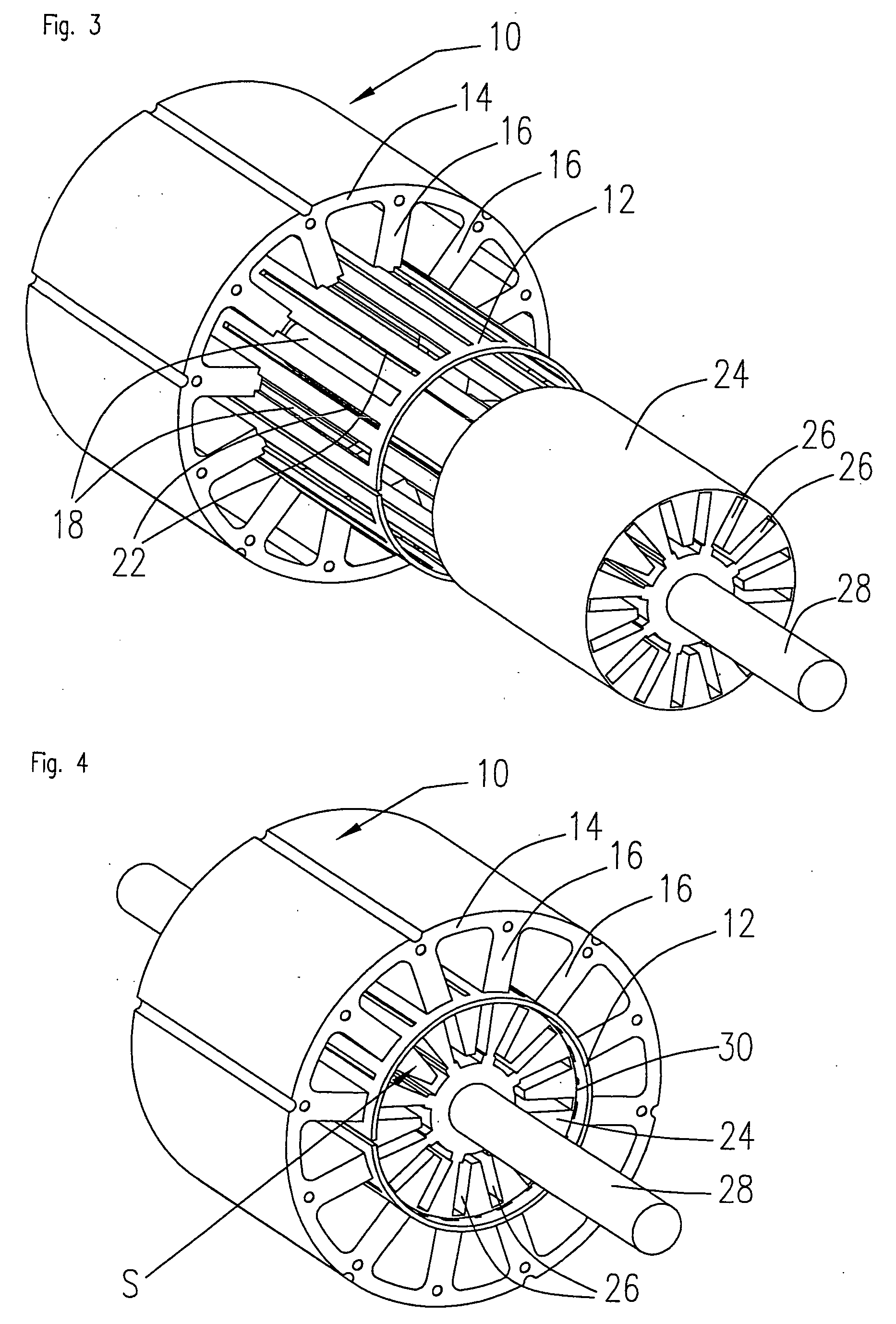
The invention relates to a stator arrangement for an electric machine, particularly a DC motor, comprising a stator body having a stator back yoke ring and a number of stator teeth between which stator slots to receive stator windings are formed, the stator teeth extending radially from the stator back yoke ring and stator poles being formed at the free ends of the stator teeth, the stator teeth being coupled to a sleeve, which extends coaxially to the stator body, at their free ends. The invention also relates to a method for the manufacture of a stator arrangement of this kind and a direct current motor that employs such a stator arrangement.
Owner:MINEBEA CO LTD
Cogging reduction in permanent magnet machines
ActiveUS7385328B2Reduce cogging torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsLeading edgePermanent magnet motor
A permanent magnet motor having a rotor and a stator and configured such that when the leading edge of each pole of the rotor aligns with a stator tooth the trailing edge of that pole is generally not aligned with a stator tooth.
Owner:BALDOR ELECTRIC COMPANY
Rotor punching structure for permanent-magnet servo motor
ActiveCN104882981AImprove back EMF waveformReduce additional stray lossMagnetic circuit rotating partsPunchingCoupling
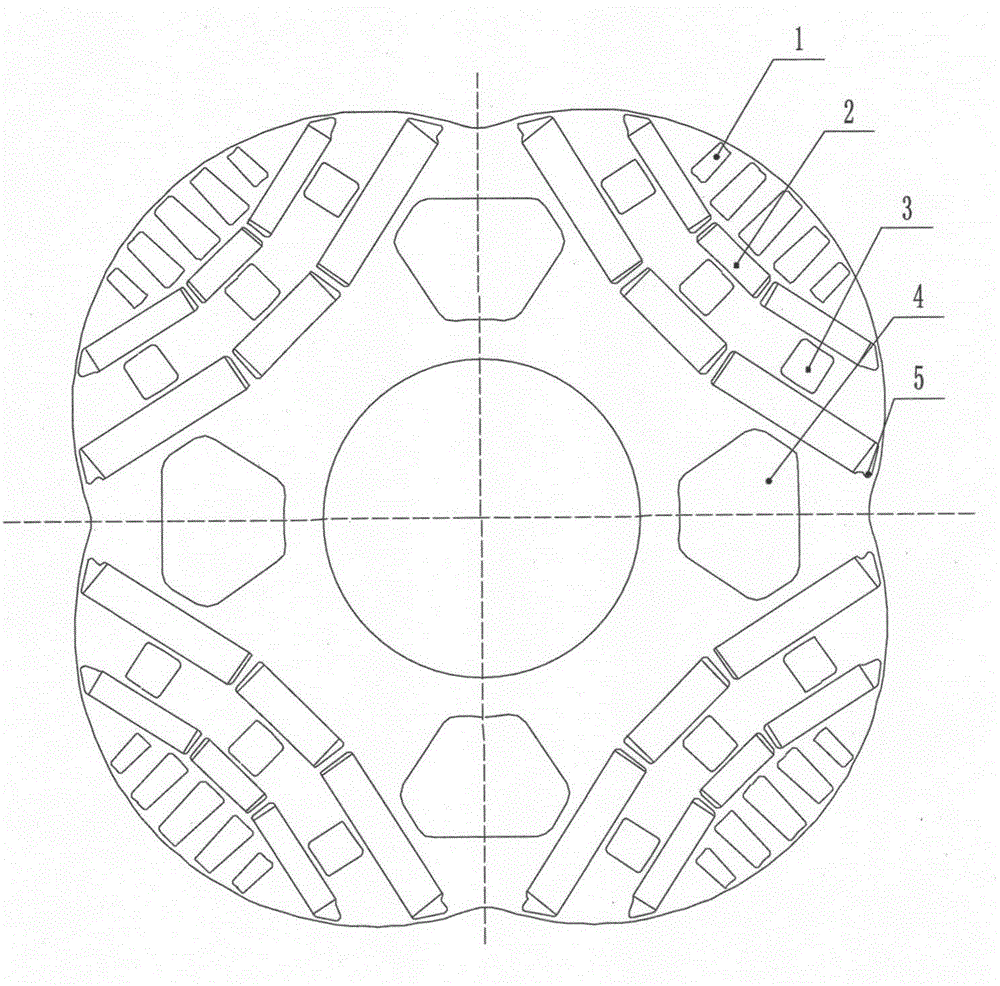
The invention provides a rotor punching structure for a permanent-magnet servo motor, and the structure comprises a rotor punching body. The peripheral surface of the rotor punching body is provided with permanent magnet tanks, and the interior of each permanent magnet tank is provided with a permanent magnet in an embedded manner. The external circle of the rotor punching body above the permanent magnet tanks is not concentric with the internal circle of a stator. The rotor punching body above the permanent magnet tanks is provided with magnetic isolation holes which are arranged horizontally, and the rotor punching body below the permanent magnet tanks is provided with an axial cooling channel. The permanent magnet tanks are radially arranged in a layered manner, and magnetic isolation tanks are respectively disposed between the adjacent permanent magnet tanks. Magnetic isolation bridges are disposed among the magnetic isolation tanks and the permanent magnet tanks. Through the improvement of the rotor punching structure and the control of the direction of a magnetic field, the nonlinear impact, caused by the coupling of quadrature-axis and direct-axis magnetic circuits, on motor parameters is reduced, and the space of a rotor punching is used fully for placing permanent magnets as many as possible. Moreover, the capability of resistance to demagnetizing and the overbearing capability of the permanent-magnet servo motor are improved, and the operation performance of the permanent-magnet servo motor is effectively improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MOTOR SYST ENERGY SAVING ENG TECH RES CENT +2
Turbine generator
InactiveUS20140284932A1More buoyantReduce size and weightDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesAc-dc conversionElectric energyRotational axis
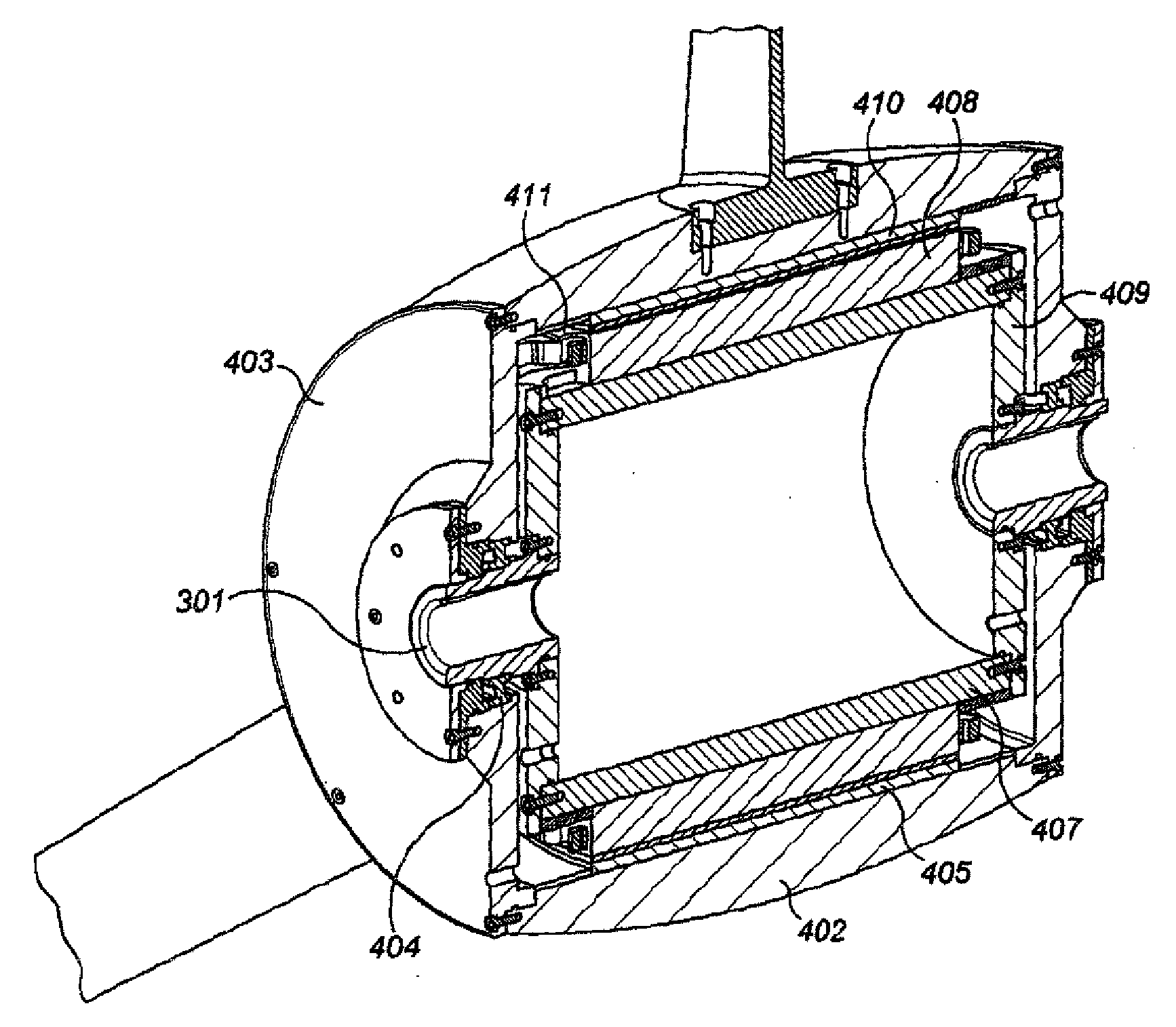
The invention relates to the generation of electricity from flowing fluid and in the preferred embodiment to a horizontal axis turbine and generator assembly. The present invention is applicable to water turbines and the invention is described in relation to this application. It is however to be appreciated that it is applicable to wind turbines. The present invention provides turbine generator for generating electrical power from flowing fluid comprising a rotatable hub having an external surface and a rotational axis arranged, in use, parallel to the direction of the flow, a plurality of blades mounted on the external surface of the hub and extending radially outwards from the hub; a plurality of magnets mounted on a surface inside the rotatable hub said surface arranged to rotate with the rotatable hub thereby forming a rotor of an electrical generator, and a plurality of non-rotating coils fixed to a stationary cylindrical core within the periphery of the rotatable hub, said coils and core thereby forming a stator of the electrical generator.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
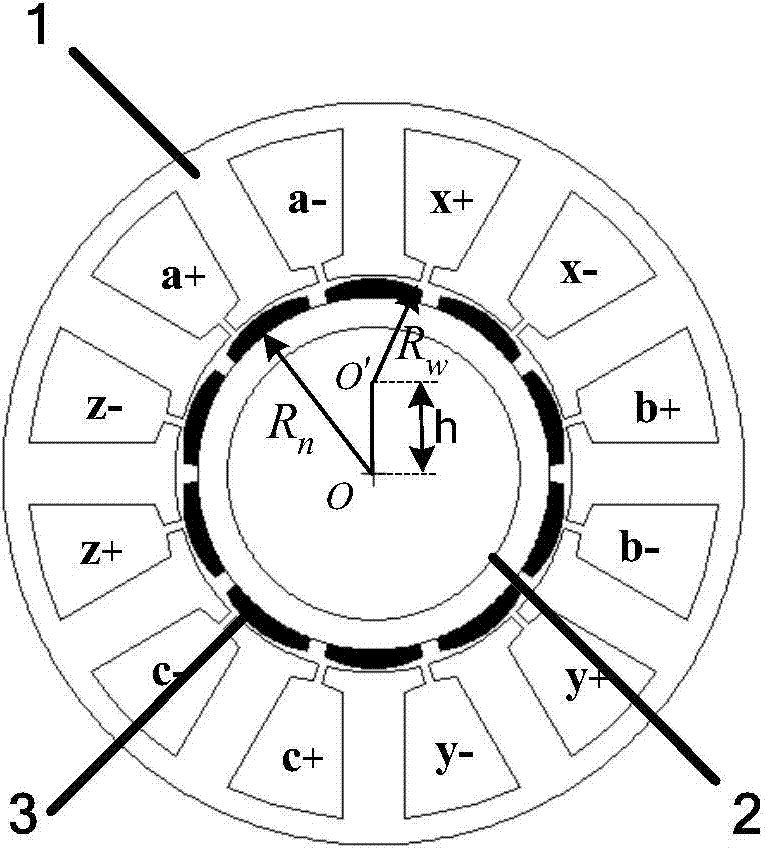
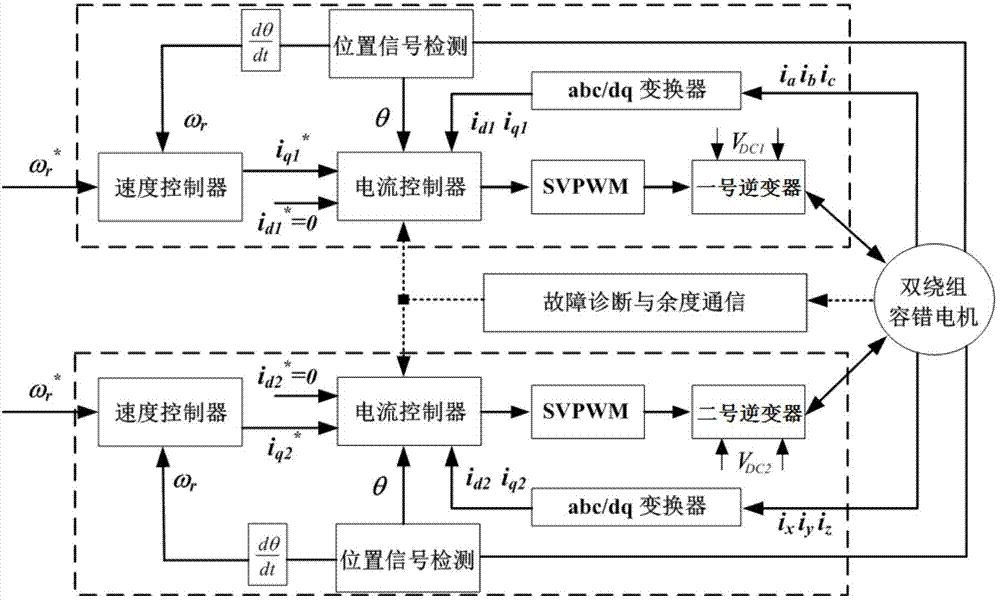
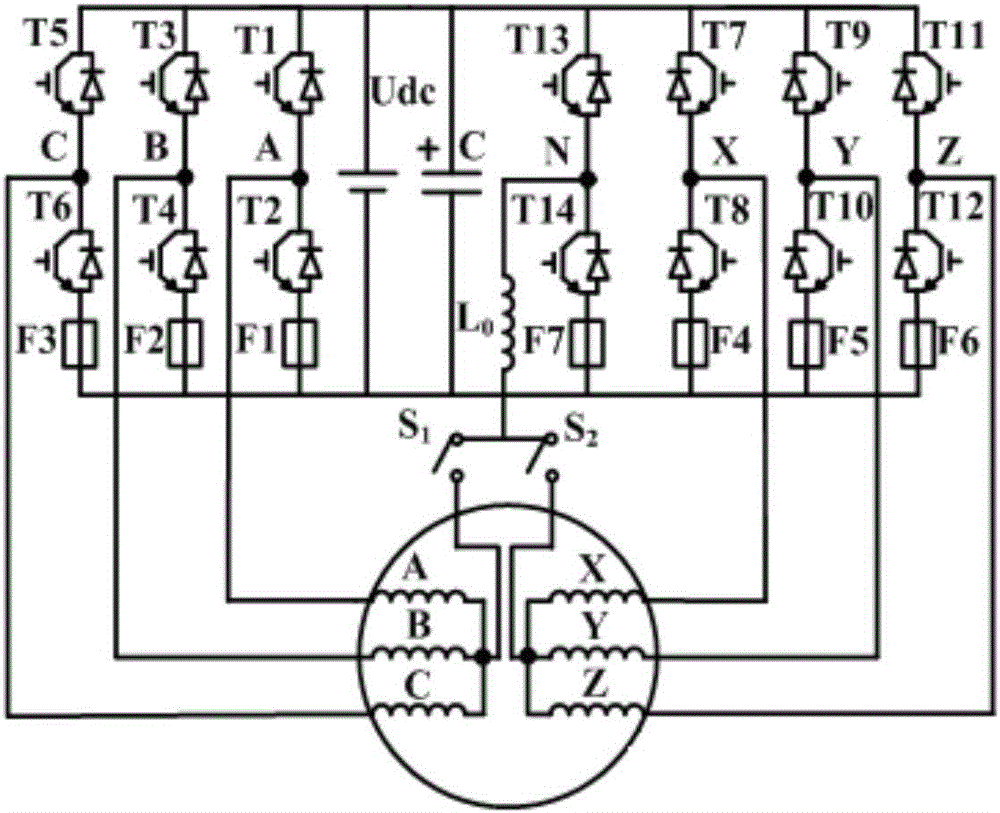
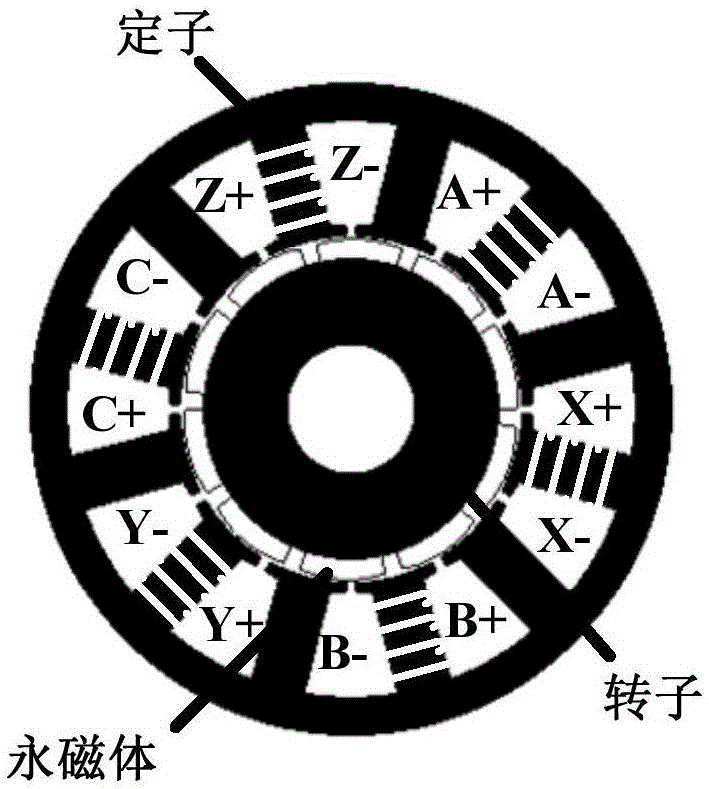
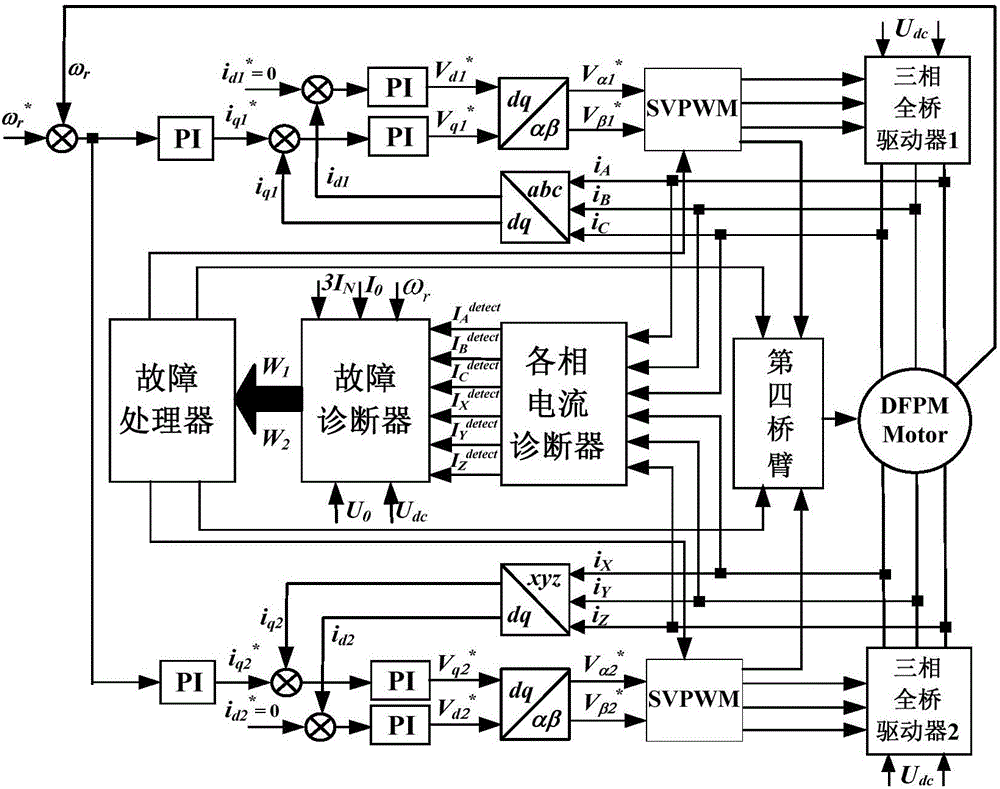
Control method for drive system of duplex-winding permanent magnet fault tolerant motor
ActiveCN104506113AReduce cogging torqueHigh sine degree of air gap magnetic field distributionAC motor controlPermanent magnet rotorFault tolerance
The invention discloses a control method for a drive system of a duplex-winding permanent magnet fault tolerant motor. The duplex-winding permanent magnet fault tolerant motor consists of a slot stator 12 and a polar meter pasting type permanent magnet rotor, wherein the stator comprises two sets of symmetrical armature windings in three-phase centralized tooth-separating winding, which are independent with one another. The control method comprises the following steps: establishing a mathematical model of the drive system of the duplex-winding permanent magnet fault tolerant motor, realizing control on the motor through a speed controller, a current controller, a SVPWM and an inverter in sequence according to the established model as well as the acquired and given motor signal; increasing a fault diagnosing and redundancy communicating function to respectively diagnose and process the winding broken circuit or short circular faults of the control system. The control method is simple and easy to implement, has high reliability and strong fault tolerance, can be used for realizing the fault-tolerant control on the system broken circuit of the short circuit fault very well, and is suitable for aerospace and military situations with high reliability and high performance requirements.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
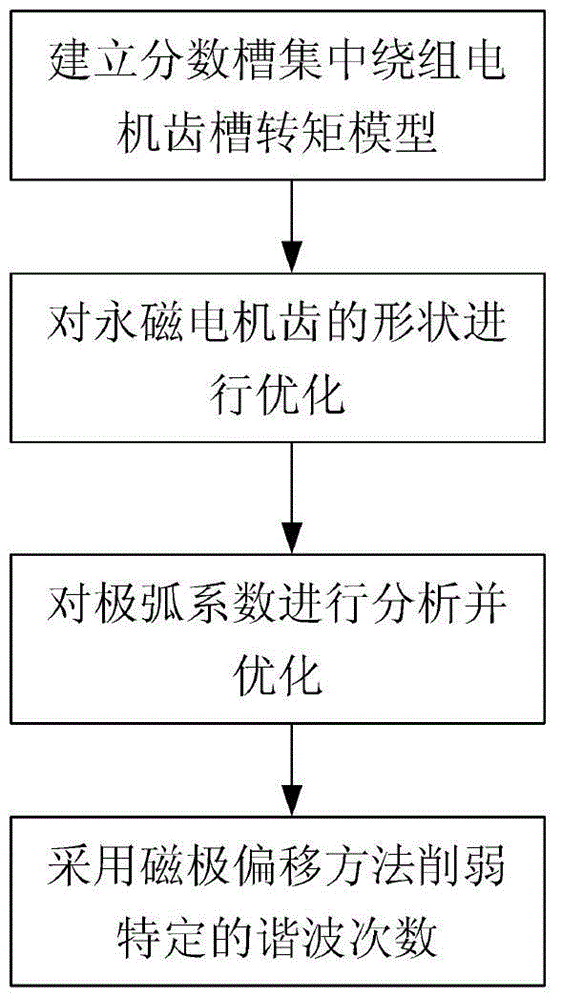
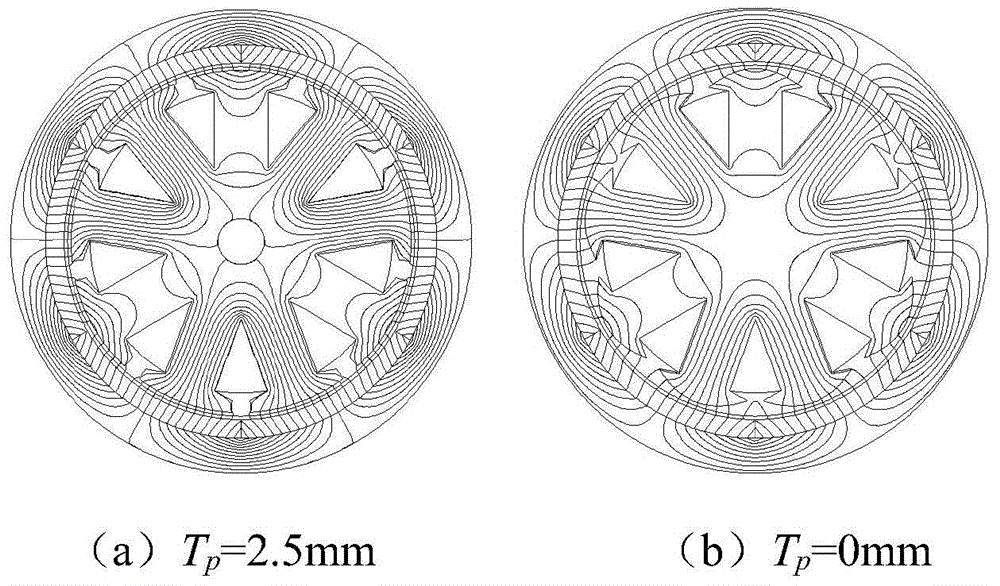
Method for weakening cogging torque of permanent magnet synchronous generator
ActiveCN104617720AReduce cogging torqueReduce starting torqueManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesWind energy generationElement modelPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention belongs to the permanent magnet synchronous generator technology field, and particularly relates to a method for weakening cogging torque of a permanent magnet synchronous generator. The method for weakening the cogging torque of the permanent magnet synchronous generator includes: firstly, optimizing the shape of a permanent magnet motor tooth so as to reduce the cogging torque; then, optimizing a pole arc coefficient; next, using a magnet pole shifting method to reduce a harmonic component of the cogging torque so as to achieve the purpose of reducing the cogging torque; finally, combining the above three steps so as to minimize the cogging torque, building a finite element model of the permanent magnet synchronous generator, and performing analysis and finite element verification on a provided cogging torque suppression method. The method for weakening the cogging torque of the permanent magnet synchronous generator has the advantages of reducing the cogging torque of the permanent magnet synchronous generator on the premise of slightly influencing other properties of the permanent magnet synchronous generator by changing the shape of the tooth and using an optimal pole arc coefficient method and a magnetic pole shifting method in combination, and then reducing starting resistance torque of a direct drive permanent magnet synchronous wind generator, and improves usage rate of wind energy.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Rotor assembly for an electrical machine and permanent magnet motor comprising such a rotor assembly
InactiveUS6927519B2Low cogging torqueEasy to changeMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPermanent magnet motorEngineering
Rotor assembly for an electrical machine, wherein a body of generally cylindrical shape having an inner opening for coaxially mounting the body on a shaft, permanent magnets embedded in said body, wherein at least one of the permanent magnets is split in at least two magnet sections which extend from about the inner opening towards the outer periphery of the body and are inclined towards a plane, which extends in a radial direction of the body.
Owner:MINEBEAMITSUMI INC
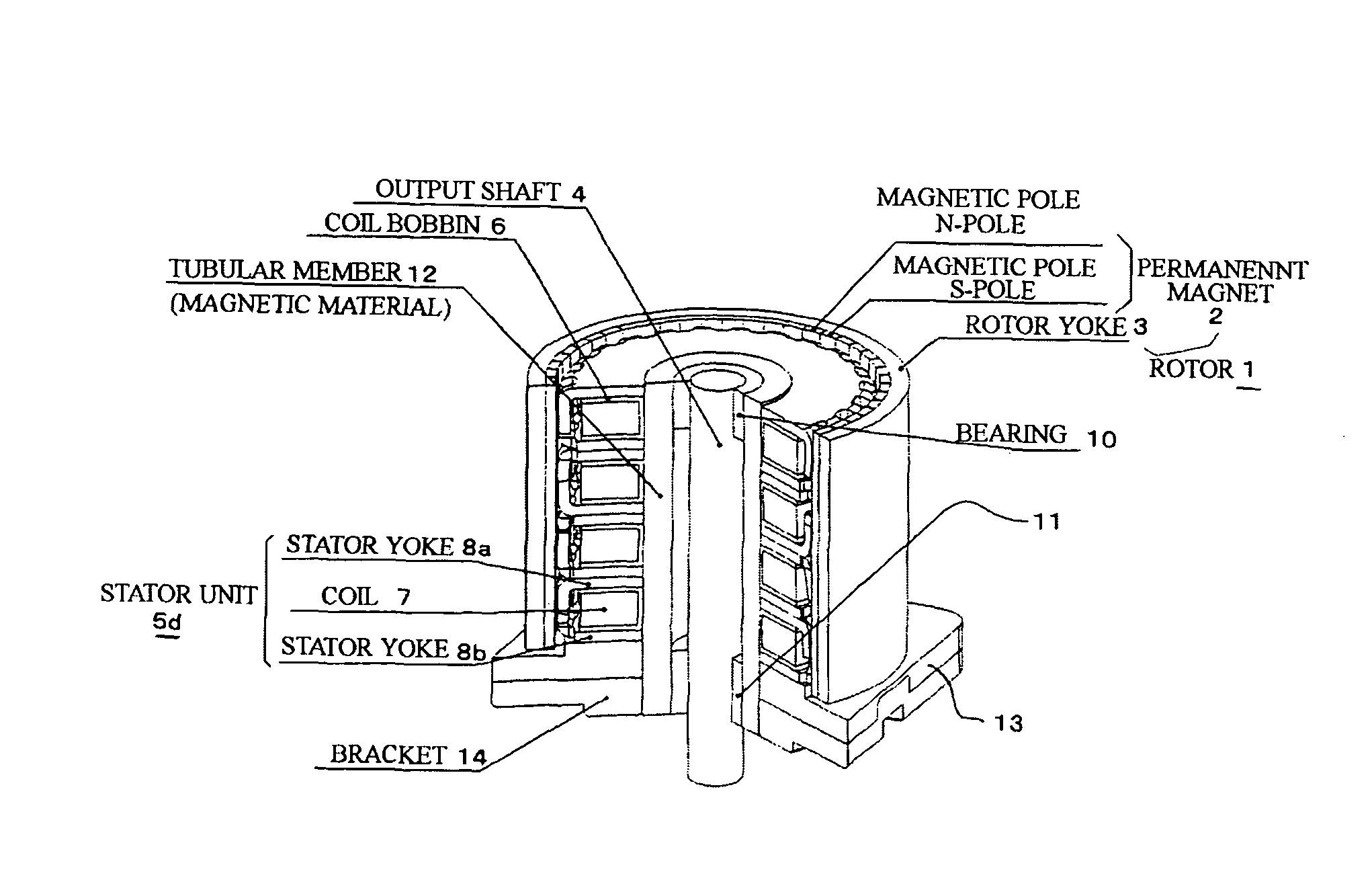
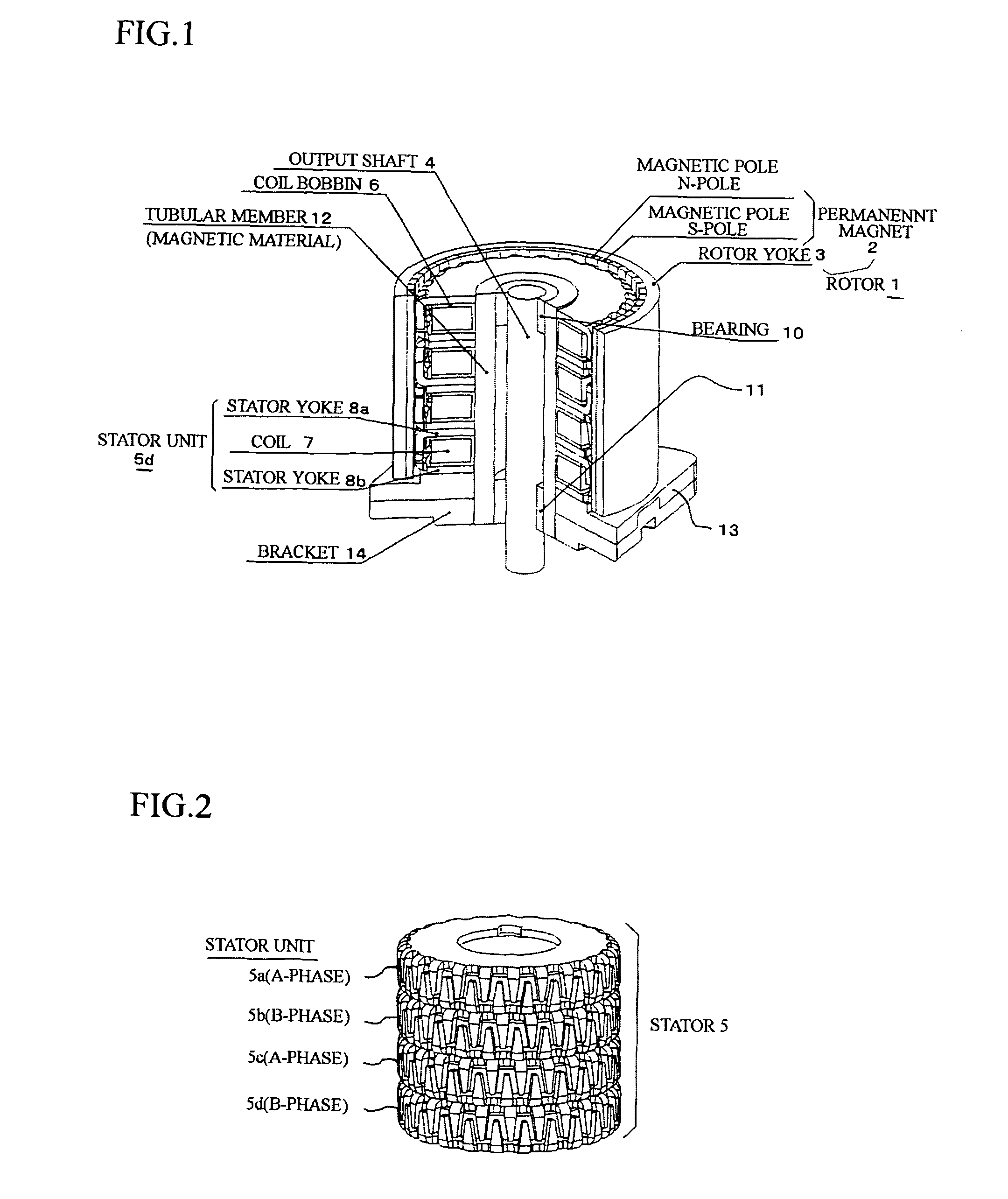
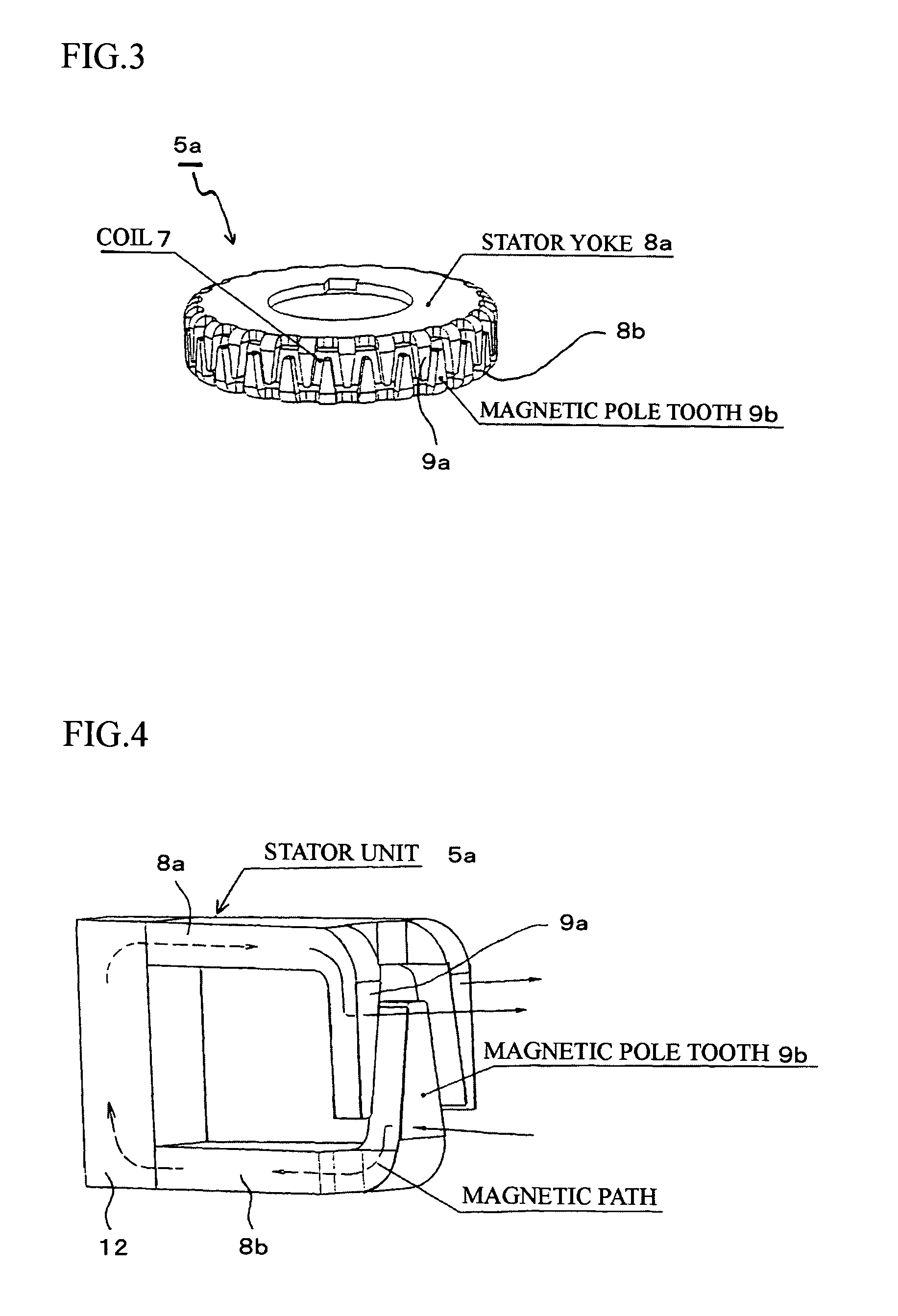
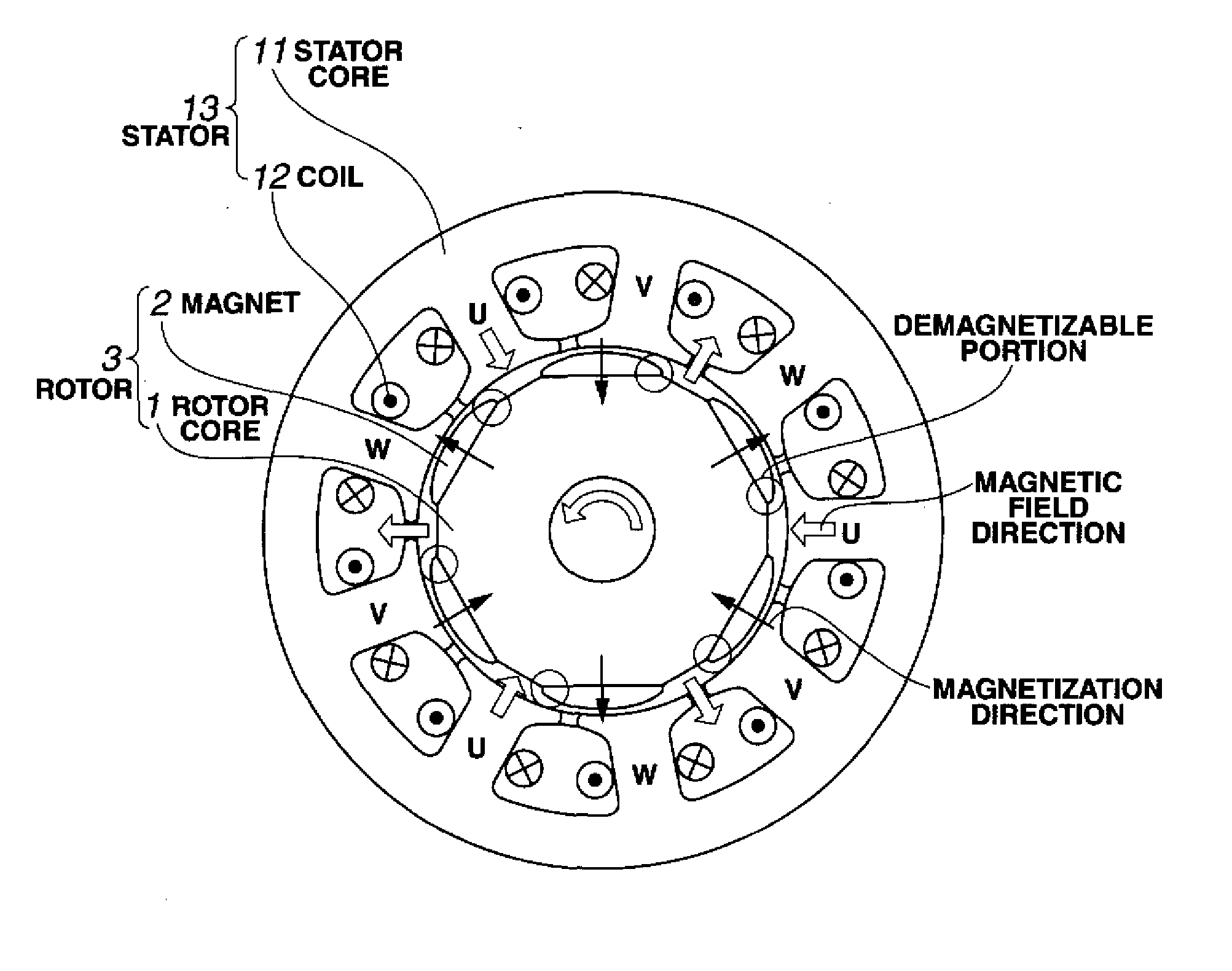
Permanent magnet type rotary machine
InactiveUS7898123B2Small sizeReducing cogging torqueMagnetic circuit stationary partsAsynchronous induction clutches/brakesPhase differenceMagnetic poles
The permanent magnet type rotary machine is capable of reducing cogging torque caused by variation of amounts of magnetic flux in magnetic circuits. The permanent magnet type rotary machine comprises: a stator constituted by stator units, which are coaxially stacked and in each of which a coil is sandwiched between stator yokes; and a rotor including a permanent magnet having magnetic poles, which respectively face magnetic pole teeth of the stator yokes, the rotor being rotatably supported by an output shaft. The stator units in one phase is divided into n (n is an integer one or more), and magnetic centers of at least one pair of the magnetic pole teeth of the adjacent stator yokes, which are vertically arranged, are shifted with a prescribed phase difference so as to mutually cancel their cogging torque.
Owner:SHINANO KENSHI
Electric motor and apparatus for manufacturing electric motor
ActiveUS20060163967A1Long processEfficient punchingMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsMagnetic anisotropySheet steel
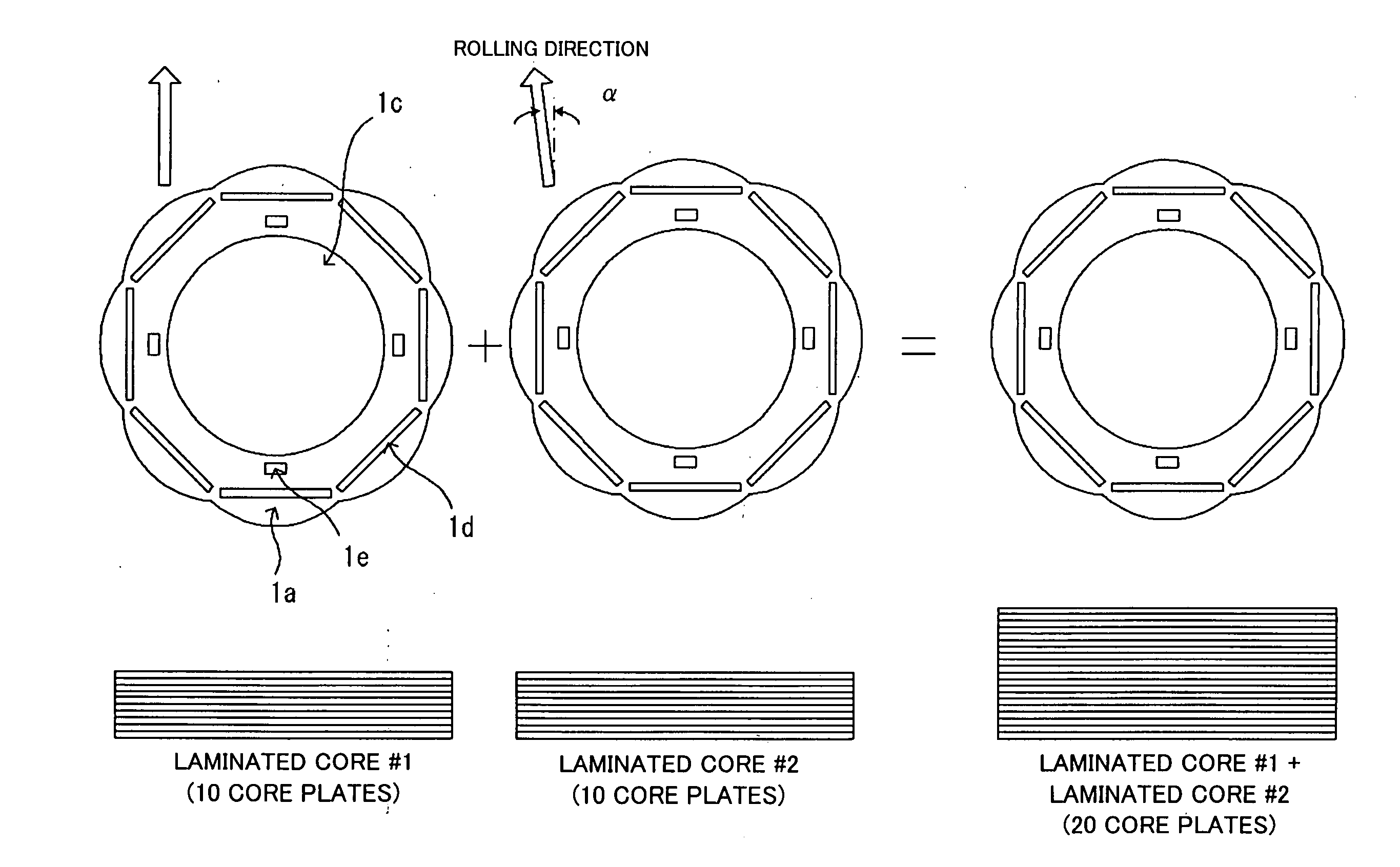
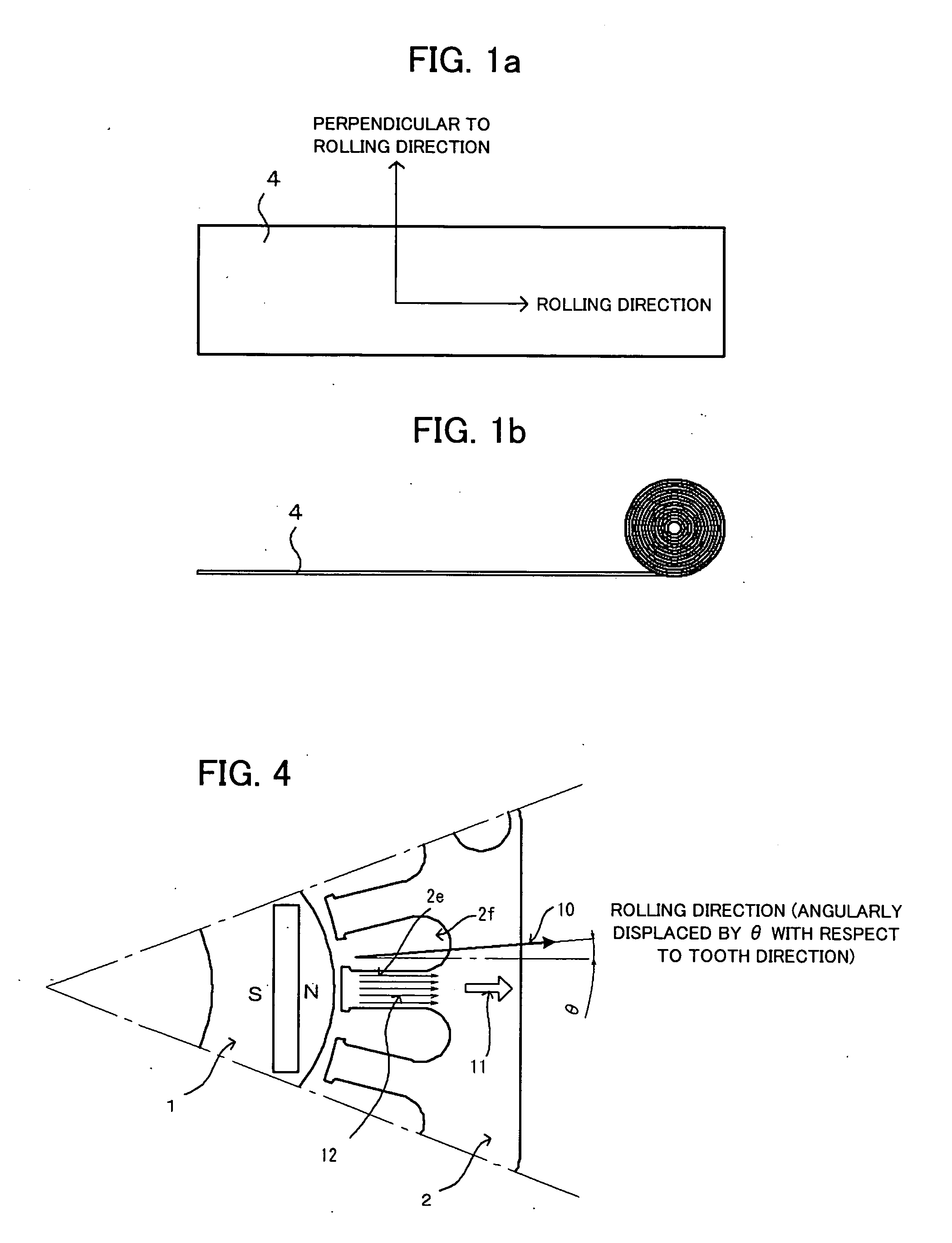
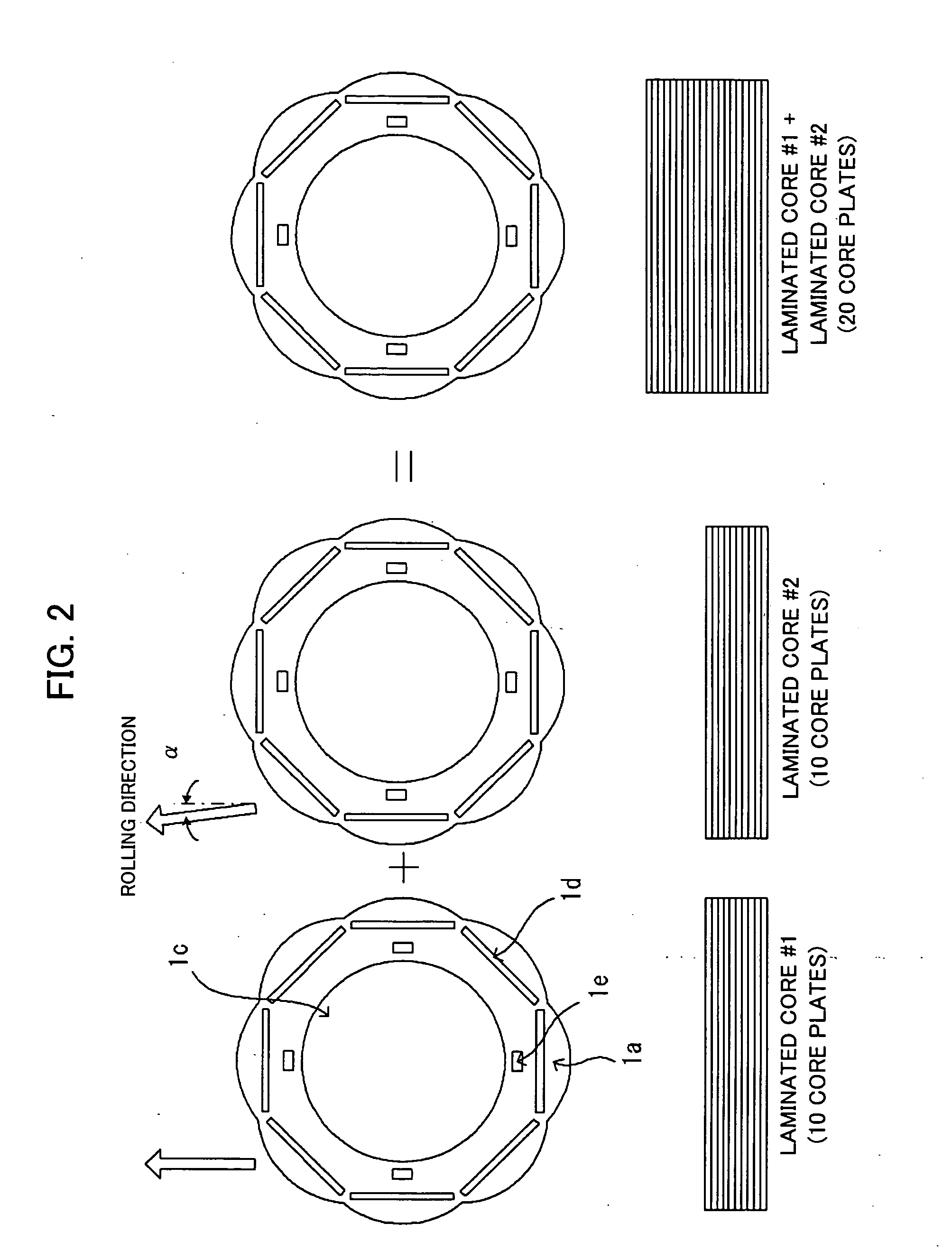
A motor capable of reducing cogging torque depending on teeth of a stator, and a motor manufacturing apparatus for manufacturing this motor. The angles of rolling directions of cores stacked are set so that the phase difference between the phases of cogging torques produced on the cores is 180° so that the cogging torques produced on the cores cancel each other to reduce the total cogging torque in the motor. The motor comprises a laminated core formed by stacking a plurality of cores made from a rolled electromagnetic sheet steel. The cores forming the laminated core have rolling directions different from each other by a specified machine angle determined depending on the number of slots and / or the number of poles, where the specified machine angle is an angle which produces a phase difference of 180° between the phases of cogging torques produced due to magnetic anisotropy of the cores and the arrangement of teeth depending on the number of slots and / or poles of the motor.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Radial Anisotropic Magnet Manufacturing Method, Permanent Magnet Motor Using Radial Anisotropic Magnet, and Iron Core-Equipped Permanent Magnet Motor
ActiveUS20090007417A1Small sizeIncrease productionMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnetsMagnetic anisotropyMagnetic poles
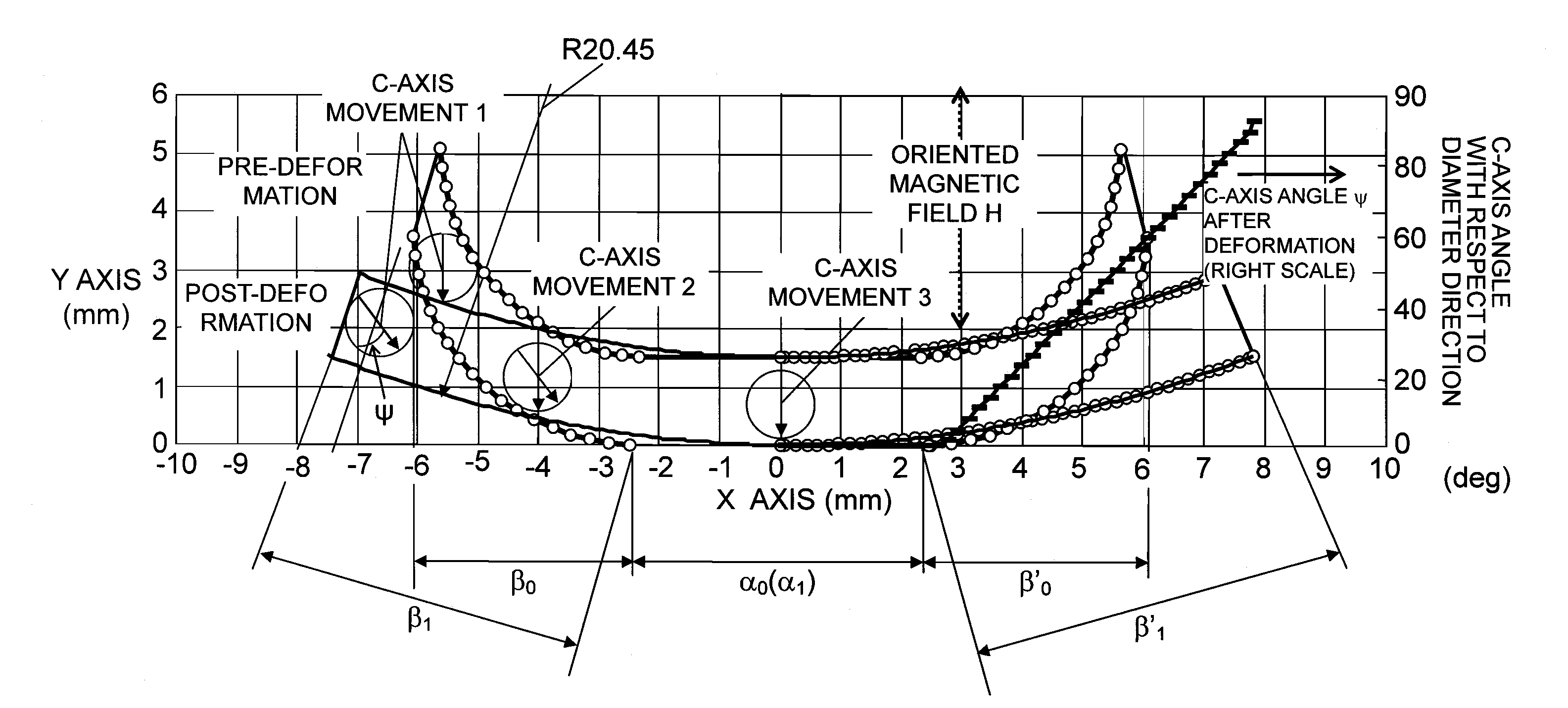
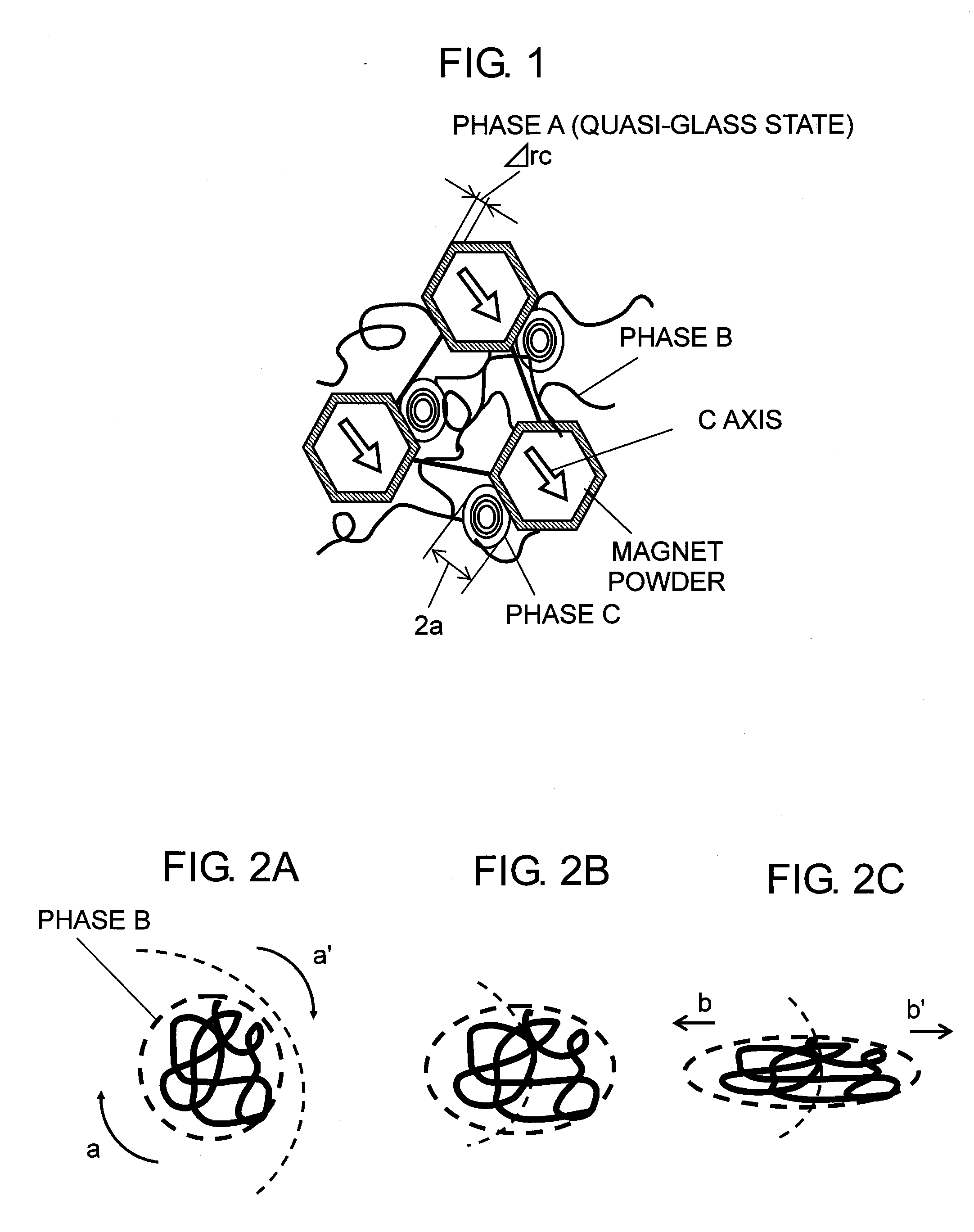
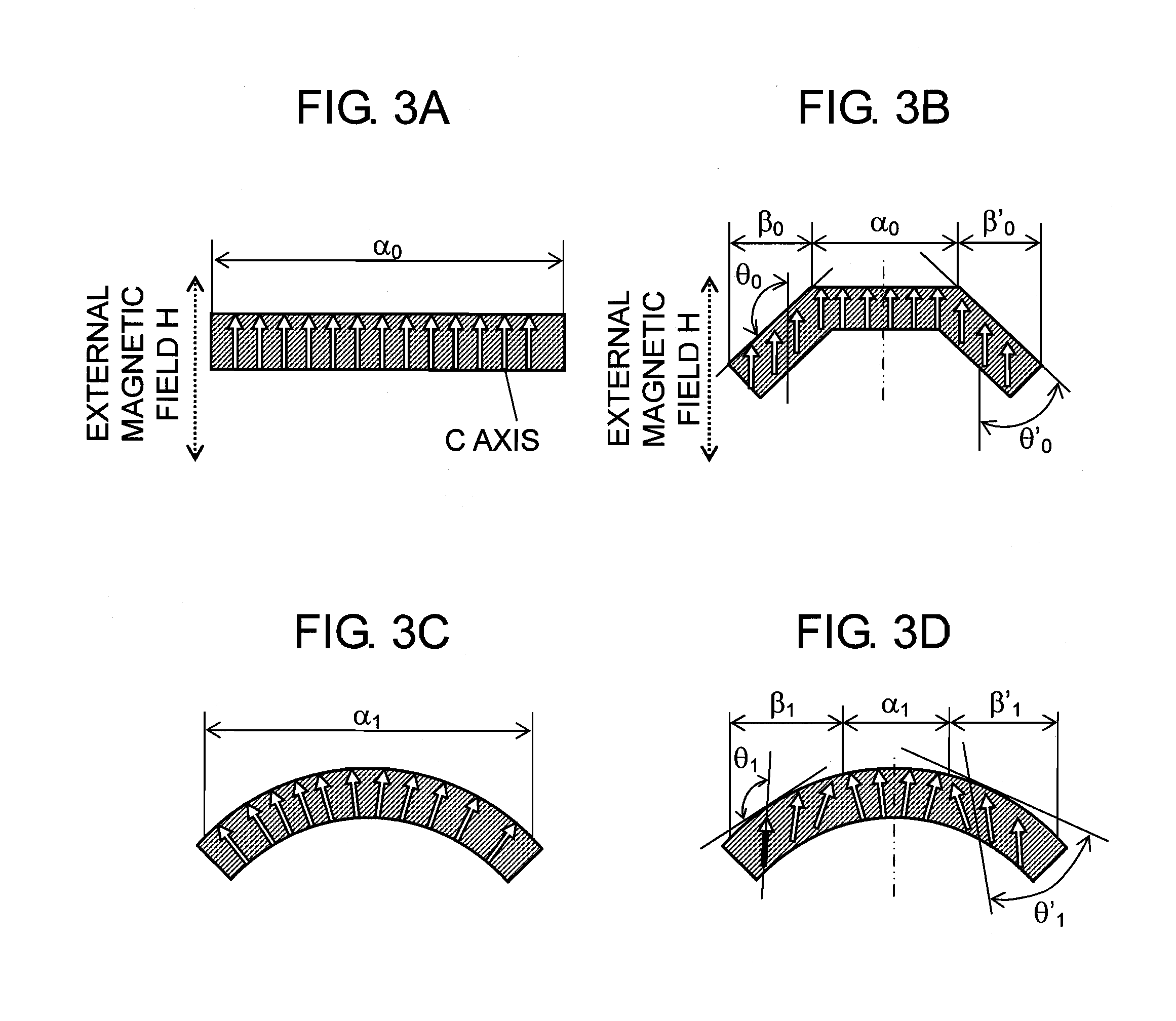
In order to improve tranquility and controllability of an iron core-equipped permanent magnet motor with an improvement of a maximum energy product (BH)max by improving a shape compatibility of a radial anisotropic magnet, there is provided a radial anisotropic magnet manufacturing method of fixing magnet powder in a net shape so as to maintain a magnetic anisotropic (C-axis) angle of a magnet with respect to a tangential line and for performing a deformation with a flow so as to have a predetermined circular arc shape or a predetermined annular shape. Particularly, by performing a deformation with a viscous flow or an extension flow, a deformability of the magnet is improved, and thus a shape compatibility with respect to a thickness is improved. AC-axis angle θ with respect to a tangential direction is controlled at an arbitrary position and an arbitrary angle so as to reduce cogging torque without separating a magnetic pole into segments.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN102420475AReduce cogging torqueEasy to manufacture and assembleMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machine detailsPermanent magnet synchronous motorMagnetic poles
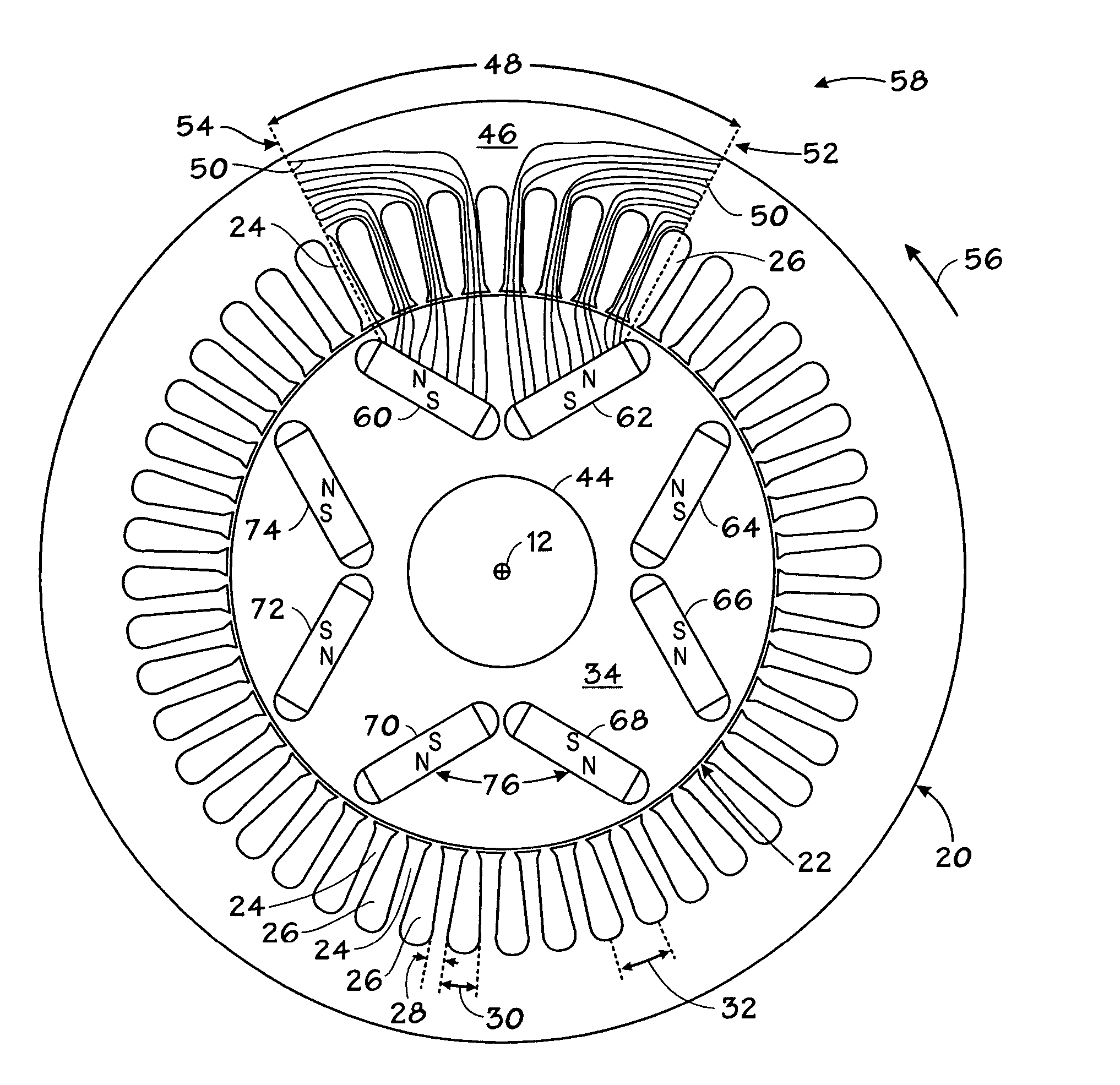
A purpose of the present invention is providing a permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor structure which has high air gap flux density and is easy to generate back electromotive force with a sine wave. In a permanent magnet synchronous motor, a circumferential surface of the rotor is uniformly provided with a plurality of magnetic steel grooves which are independently enclosed and do not contact mutually. Every two magnetic steel grooves are arranged to form a V shape, an opening of the V shape faces excircle of the rotor, and a tip of the V shape faces a rotor center. Each magnetic steel groove is provided with magnetic steel. In each group of V-shaped magnetic steel grooves, two magnetic steel facing the excircle of the rotor core have a same magnetic pole, and magnetic poles of magnetic steel facing the excircle of the rotor core in two adjacent groups of V-shaped magnetic steel grooves are opposite with the magnetic pole of the two magnetic steel. The excircle of the rotor goes down toward the center with depth delta and smooth transition at a crossing position of axes, which means that air gap width at the crossing position is less than air gap width at a straight axis position by delta. Through improving the rotor, the permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor has high mechanical strength and a large salient pole ratio, and weakened magnetism speed expansion is facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN SANTROLL ELECTRIC SCI & TECH
Permanent magnet rotary motor
InactiveUS20050258698A1Reduce torqueIncreased torque densityMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesTorque density
There is provided a permanent magnet rotary motor that can maintain higher torque density and can also reduce cogging torque more greatly than a conventional permanent magnet rotary motor. A pair of end surfaces of each of permanent magnets used for a rotor are substantially parallel to a virtual plane that extends in the radial direction of a rotor core while passing through the centers of a stator core and an arc surface. Then, the length of the arc surface in the peripheral direction of a rotor core and inclinations of inclined surfaces are so determined that a pole arc ratio Ψ1 of the arc surface and a pole arc ratio ψ2 of a magnetic pole surface in each permanent magnet satisfy the relation of P / 2N≦Ψ2−Ψ1≦1.38×P / 2N.
Owner:SANYO DENKI CO LTD
Three-phase four-leg structure-based double-winding permanent magnet fault-tolerant electric driving system and control method
ActiveCN106470008AWith magnetic isolationWith thermal isolationAC motor controlMathematical modelStructure based
The invention discloses a three-phase four-leg structure-based double-winding permanent magnet fault-tolerant electric driving system and a control method. A double-winding permanent magnet fault-tolerant motor stator in the system is composed of two sets of evenly-distributed three-phase windings which are independent from each other, wherein the two sets of evenly-distributed three-phase windings spatially differ from each other by an electric angle of 60 degrees; an armature winding concentrated tooth spaced winding mode is adopted to form the two sets of three-phase windings; and according to the driver, two sets of independent three-phase half-bridge driving circuits are adopted, and a direct-current bus-bar and a bridge leg circuit are used in a shared manner. The three-phase four-leg structure-based double-winding permanent magnet fault-tolerant electric driving system of the invention has a motor winding open-circuit fault diagnosis function and a motor winding short-circuit fault diagnosis function, can quickly obtain the type of a fault through diagnosis and locate the fault, and carry out corresponding fault-tolerant control according to a fault diagnosis result and an established post-fault mathematical model and based on acquired signals in the operation of a motor. The three-phase four-leg structure-based double-winding permanent magnet fault-tolerant electric driving system and the control method of the invention have the advantages of simplicity, high feasibility, high reliability and high fault-tolerant capability. With the three-phase four-leg structure-based double-winding permanent magnet fault-tolerant electric driving system and the control method adopted, the problem that a double-winding permanent magnet fault-tolerant motor continues to operate after one-phase and multi-phase open-circuit or short-circuit faults occur can be solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Permanent magnet and permanent magnet rotating machine
ActiveUS20080055032A1Reduce torqueReduce demagnetizationMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnetsMagnetCentral region
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Built-in permanent magnet motor
ActiveCN103187844ASuppression of the air gap magnetic fieldImprove the problem of excessive cogging torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsHarmonicPermanent magnet motor
The invention discloses a built-in permanent magnet motor. Main polar faces and interpolar faces of a rotor of the motor are formed by connecting a plurality of arcs of eccentric circles not concentric with the circle center of the rotor, so that an air gap is adjusted, and a purpose of reducing a cogging torque of the motor is achieved, and higher harmonic during motor operation is reduced according to regular hierarchic air gap thickness variation. According to the motor, quadrature-axis inductance of the motor is increased in a mode of adopting the air gap thickness of the specific interpolar face and keeping the preset widths of the interpolar faces, so that a reluctance torque of the motor is increased, and torsion of the motor is increased.
Owner:ADLEE POWERTRONIC
Like pole type inductor motor hiding salient pole
InactiveCN103683771AEliminate cogging saliency effectReduce cogging torqueAsynchronous induction motorsFriction lossInductor
The invention provides a like pole type inductor motor hiding a salient pole. A motor stator core is formed by overlying of silicon steel sheets, three-phase armature windings are wound on the teeth of the stator core symmetrically, annular exciting windings are arranged between the armature windings and motor end caps, and the center lines of the exciting windings coincide with the center line of the stator core. A motor rotor is divided into two parts, the surface of the rotor part corresponding to the exciting windings is smooth, and the inner portion of a rotating shaft has no tooth socket; the surface of the rotor part corresponding to the armature windings is smooth, and magnetic separating grooves are formed in the inner portion of a rotating shaft in the axial direction. A main magnetic flux path in the motor is restrained through the magnetic separating grooves in the inner portion of the rotating shaft, a salient pole effect is formed on the motor rotor, and unidirectional alternating air-gap fields are established in air gaps. Through the adoption of a hiding salient pole structure, the cogging torque of the motor is lowered, the torque pulsation in the motor running process is reduced, the wind path structure of the motor is improved, wind friction loss in high-speed running of the motor is reduced, and the running efficiency of the motor is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Rotor of permanent magnet motor
ActiveCN103259356ASimple manufacturing processHigh mechanical strengthMagnetic circuit rotating partsLine segmentMagnet
The invention discloses a rotor of a permanent magnet motor. The rotor comprises a rotor core with a plurality of installation grooves and permanent magnets installed in the installation grooves. The rotor core is provided with a central hole and a plurality of sections of cylindrical surfaces, a magnetic bridge is connected between adjacent cylindrical surfaces, the outside surface of each magnetic bridge is much closer to the central hole of the rotor core relative to the cylindrical surfaces, the outside surface of each magnetic bridge is outwards concave from the installation grooves to form a groove in the magnetic bridge, and the widths of the grooves are smaller than that of those of the installation grooves. Compared with the prior art, the rotor of the permanent magnet motor has the advantages that the magnetic bridges and the grooves are arranged to allow a motor with the rotor to obtain low cogging torque, reversed electromotive force tending to the sine and low load torque pulsation. The rotor has the advantages of being simple in manufacturing process, high in mechanical strength, low in noise and high in demagnetization-resistance performance due to appropriate multi-section arc or the line-section magnetic bridges, and the rotor is applicable to motors of roller washing machines.
Owner:GUANGDONG WELLING ELECTRIC MACHINE MFG +1
Motor
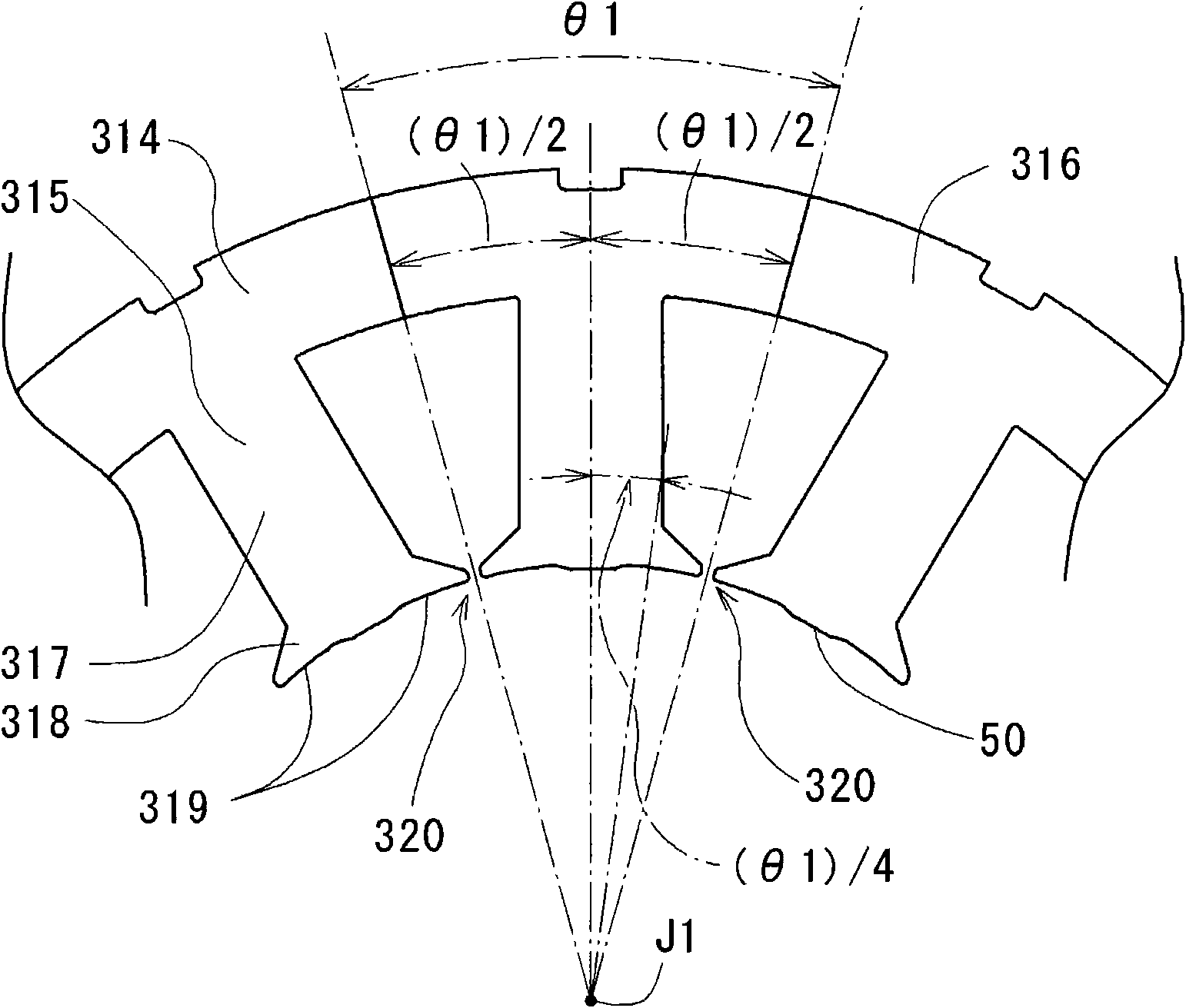
InactiveCN101978574AReduce rotational torqueReduce cogging torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsRotor magnetsEngineering
A protrusion (50) is arranged on an opposing surface (319) of a teeth portion (315) to protrude toward a rotor magnet (23). The protrusion (50) is arranged substantially at the center of the opposing surface (319) in the circumferential direction. Thus, the fundamental wave of the waveform of a cogging torque generated by the slot opening (320) has a phase inverse to the phase of the waveform of a cogging torque generated by the protrusion (50). Thus, the cogging torque generated by the slot opening (320) is reduced by the cogging torque generated by the protrusion (50).
Owner:NIDEC CORP
Rare-earth Permanent Magnet-Forming Sintered Body, and Rare-earth Permanent Magnet obtained by Magnetizing said Sintered Body
ActiveUS20180336981A1Reduce cogging torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnetsRare earthThree dimensional shape
This invention provides for a rare-earth permanent magnet-forming sintered body having an integral sintered structure of magnet material particles containing a rare-earth substance. The integral sintered structure is formed in a three-dimensional shape having: a cross-section with a shape defined by a radially outer-side arc-shaped surface having a first curvature radius, a radially inner-side arc-shaped surface having a second curvature radius less than the first curvature radius and having an arc shape concentric with the outer-side arc-shaped surface; and a first end face and a second end face each of which is a radially-extending face along a virtual radial line extending from a curvature center of the arc shapes; and an axial length extending in a direction perpendicular to the cross-section.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Rotor skewed pole structure for permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN105262302AReduce cogging torqueEasy to assembleSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnet synchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous generator
The invention relates to a rotor skewed pole structure for a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The rotor skewed pole structure is a multi-section rotor skewed pole structure formed by laminating a plurality of rotor punched sheets together, wherein each rotor punched sheet comprises installation holes and magnet grooves; the installation holes and the magnet grooves are respectively arranged in an area of the rotor punched sheet near the edge at equal intervals; the installation holes of the adjacent rotor punched sheets are staggered and aligned; and the magnet groove is used for installing a magnet. According to the rotor skewed pole structure for the permanent magnet synchronous motor disclosed by the invention, additional tools and moulds are unnecessary; only one set of punching mould is used; the specially-designed punched sheets are specially combined, such that the skewed pole can be realized; and the cogging torque is effectively reduced.
Owner:DIBAISHI MOTOR TECH SUZHOU CO LTD
High-power density permanent magnet servo motor and stator structure therefor
InactiveCN105680581AEnsure inner circle is smoothReduce cogging torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsRotor magnetsHigh pressure
The invention relates to a stator structure of a high power density motor, comprising a stator tooth core, a stator yoke core and a winding, the stator tooth core is wound with the winding, and is connected with the stator yoke iron The cores are spliced and connected, and filled with a filler in a vacuum and high pressure environment; after splicing, the head end of the stator tooth core forms a ring with a gap. The present invention also relates to a high power density servo motor, comprising the above-mentioned stator structure, a rotor and its rotor magnetic steel, the magnetic steel is attached to the outer surface of the rotor iron core, and the outer surface of the magnetic steel adopts an eccentric structure; the rotor Located inside the stator structure and coaxial with the stator; the air gap between the stator structure and the rotor is a non-uniform air gap. The invention can not only ensure the inner circle of the stator iron core is smooth, reduce the cogging torque of the motor, but also improve the slot full rate of the motor.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELECTRICGROUP CORP
Combined motor stator component and sleeve used for wet operation pump and assembly method thereof
InactiveCN102723793AReduce wall thicknessReduce air gapMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsStator coilEngineering
The invention relates to a combined motor stator component and sleeve used for a wet operation pump. The combined motor stator component and sleeve comprises a stator component and a sleeve, wherein the stator component comprises a stator iron core, a stator coil and a pole piece; a plurality stator teeth distributed at intervals extend integrally from the periphery of the stator iron core, one end of the pole piece is connected with the stator teeth in a matching way, the sleeve is integrally injected on the other end of the pole piece, and one or more positioning parts is / are arranged on the end face or the side face of a non-injection sleeve of the pole piece. The invention further relates to an assembly method of the combined motor stator component and sleeve, wherein the pole piece is placed and located in an injection mold, the sleeve is obtained by injection on the pole piece, then the other end of the pole piece is connected in a matching way with the stator teeth to obtain the combined motor stator component and sleeve for the wet operation pump. According to the invention, the pole piece is stably positioned in the injection mold to guarantee the injection molding effect of the sleeve.
Owner:CHANGZHOU XINYA ELECTROMOTOR
Low-cogging-torque flux switching permanent magnet motor
InactiveCN103825380AReduce cogging torqueGuaranteed induced potential amplitudeMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machinePermanent magnet motor
The invention discloses a low-cogging-torque flux switching permanent magnet motor which comprises a stator of a salient pole structure and a rotor of an embedded structure. The stator is provided with 6n U-shaped stator magnetic-conducting iron cores. Adjacent side edges of every two adjacent U-shaped stator magnetic-conducting iron cores form one stator tooth. A permanent magnet is embedded in each stator tooth. The permanent magnets are magnetized in the tangential direction, and the magnetizing directions of every two adjacent permanent magnets are opposite. The rotor of the embedded structure comprises 5n embedded U-shaped rotor magnetic-conducting iron cores, a rotor block and a rotor shaft, wherein the rotor block and the rotor shaft are made of non-magnetic-conducting materials, the embedded U-shaped rotor magnetic-conducting iron cores are embedded in the rotor block, adjacent side edges of every two adjacent embedded U-shaped rotor magnetic-conducting iron cores form one rotor electrode, and n is a positive integer. The rotor of the embedded structure of the motor has the advantages of being easy to manufacture, solid and durable. The number of used silicon steel sheets is reduced, it is guaranteed that the motor outputs average output torque, and the cogging torque and the torque pulsation of the motor are effectively lowered at the same time.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Motor stator device
InactiveCN101009439ADoes not affect rigidityIncrease floor areaMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesEngineeringTooth part
The invention provides a motor stator device that comprises a stator, several loops and a rotor. Several tooth parts are set in the stator, and a locating slot is set between the adjacent two tooth parts of the stator wall, every locating slot is distributed with a tooth; every loop surrounds the tooth part of the stators; the rotor is set in inner of the stator for loop to generate electromagnetic attraction when electrified to make rotor rotating; it can increase the fill in ratio of wire, usage efficiency and decrease the rotating torque, but the rigidity will not be effected.
Owner:JAGUAR PRECISION IND +1
Permanent magnet type synchronous motor
ActiveCN101001038AReduce cogging torqueReduce the magnetic forceMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic tension forceSynchronous motor
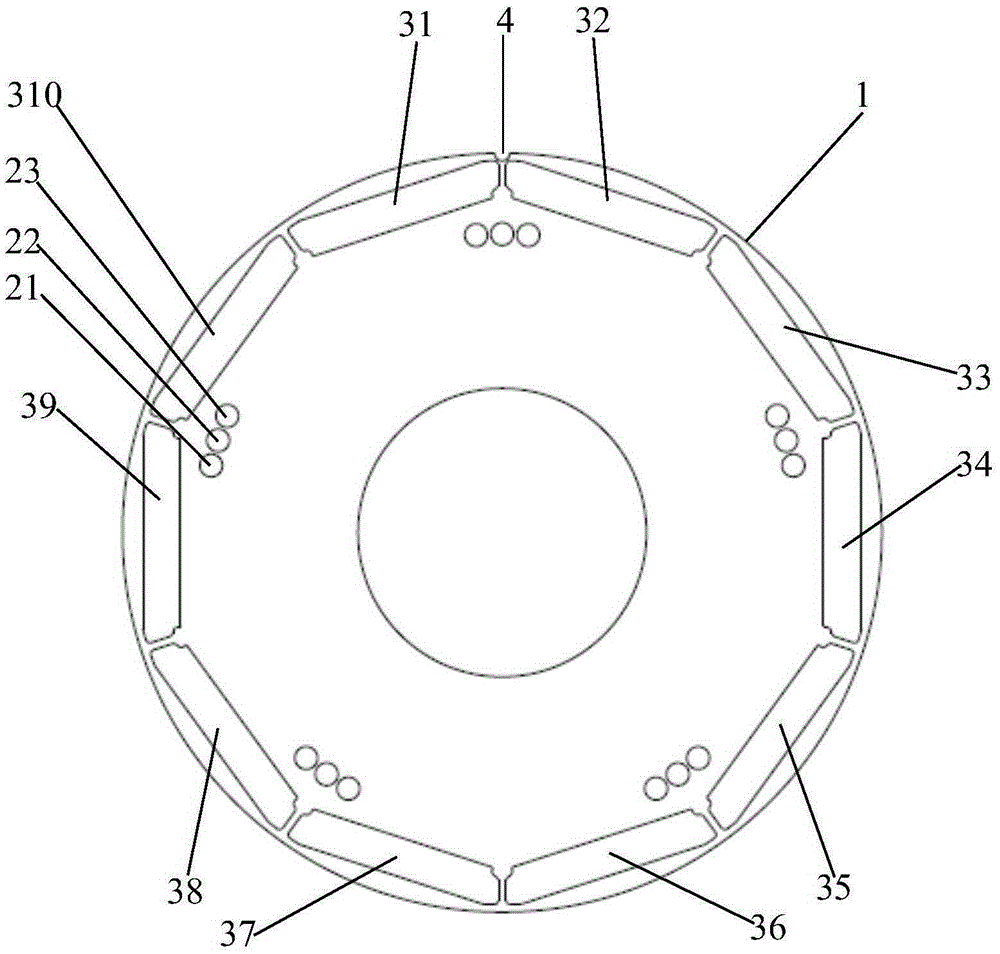
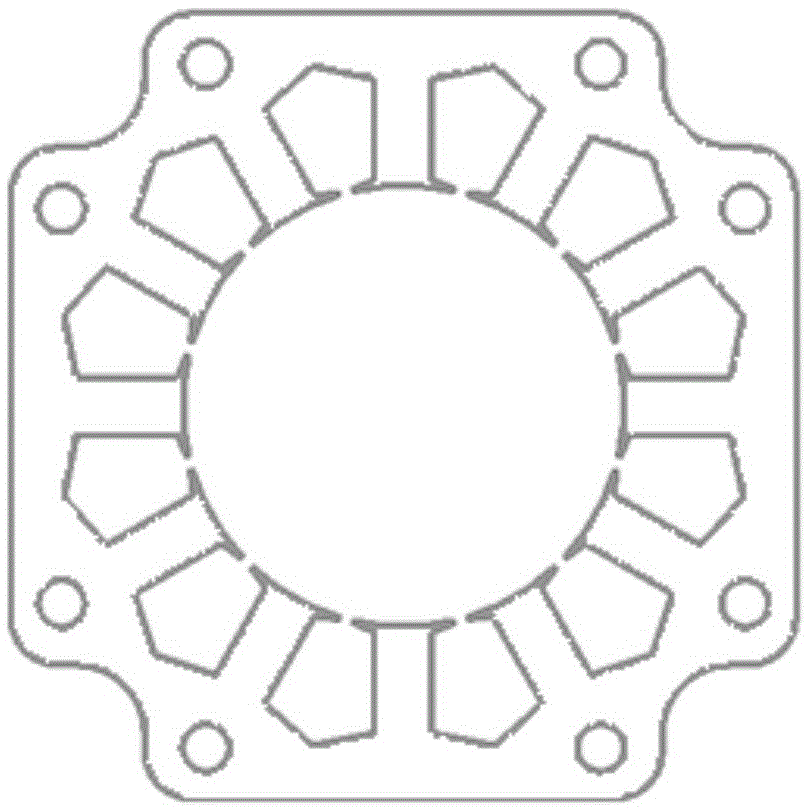
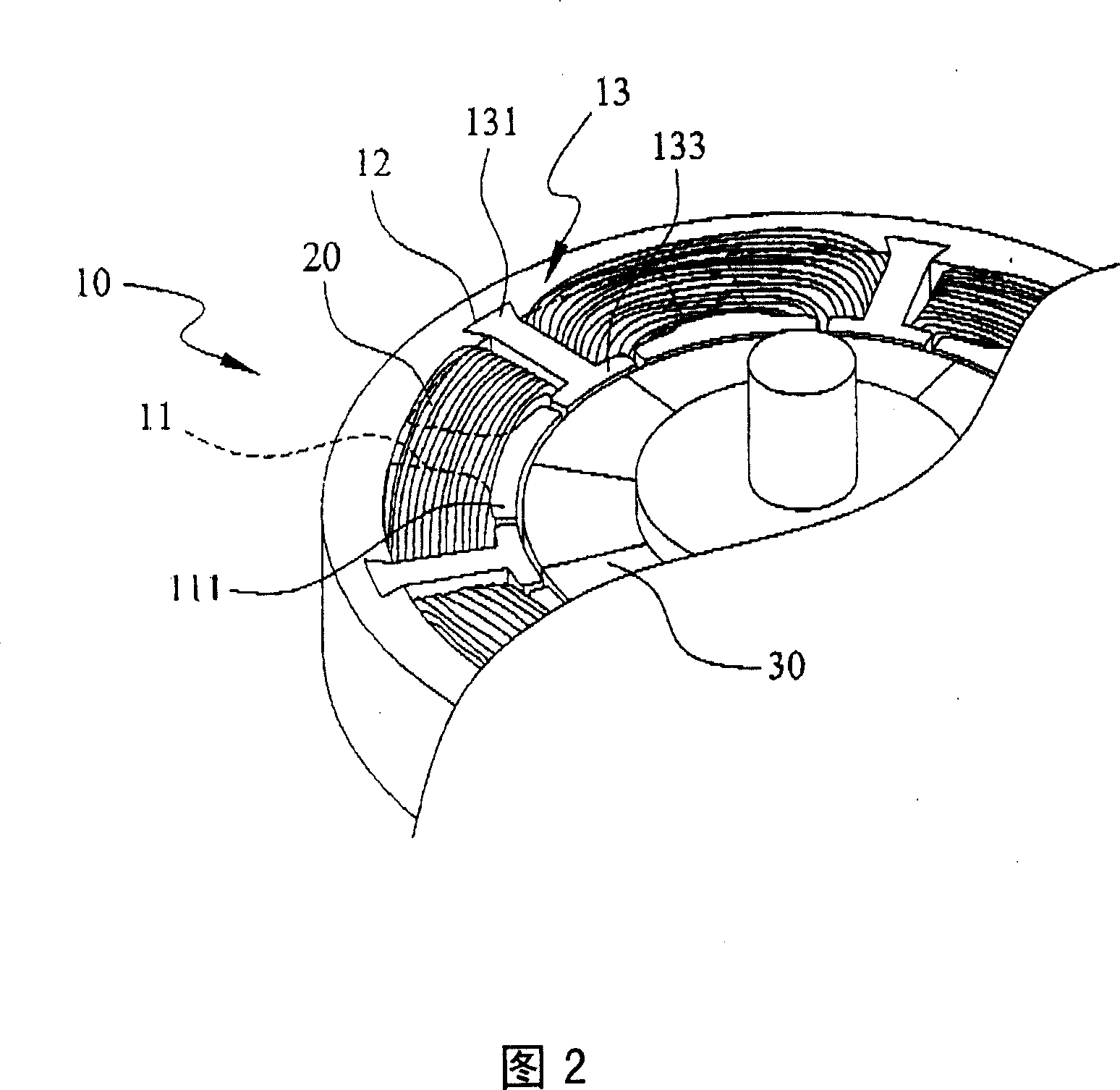
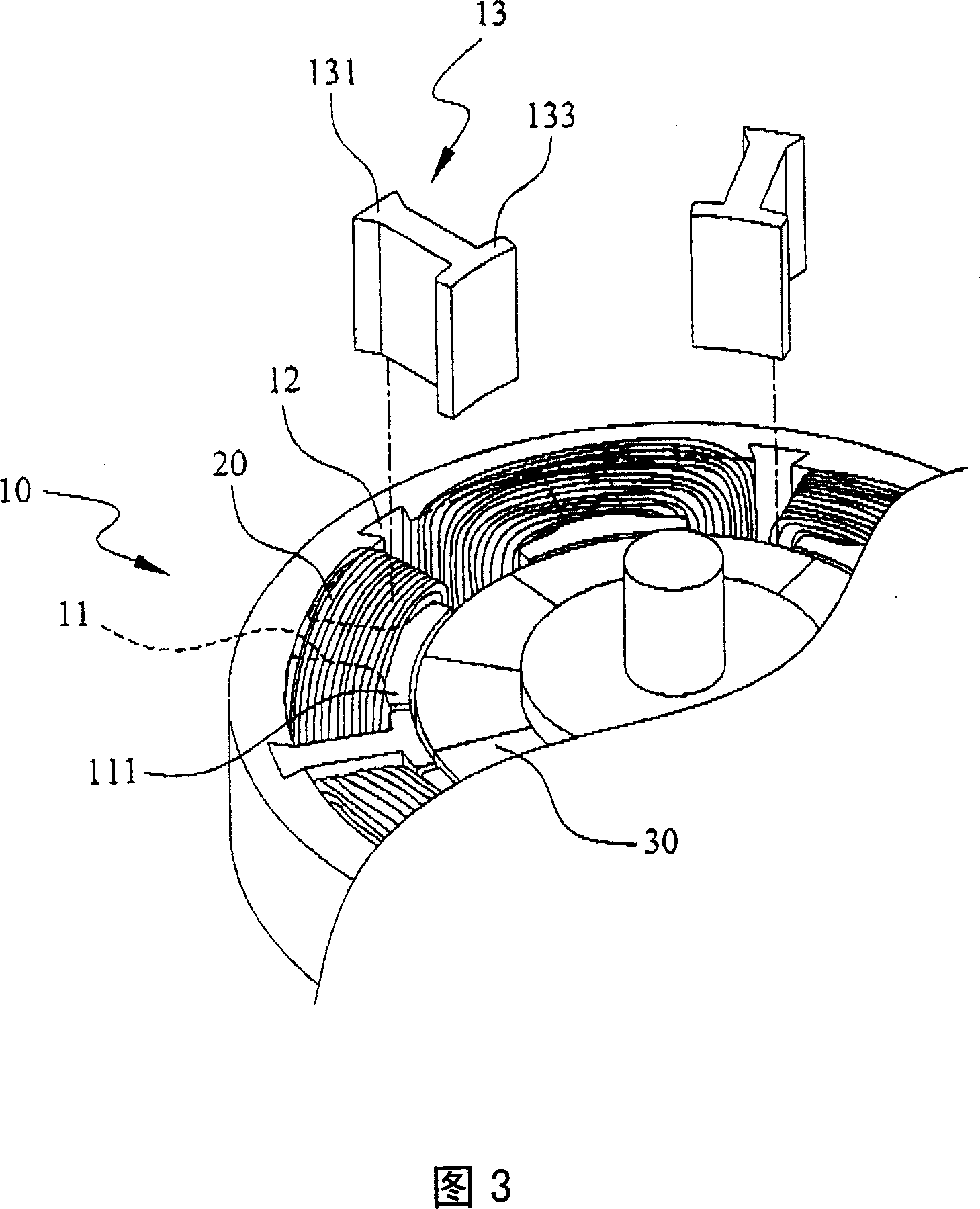
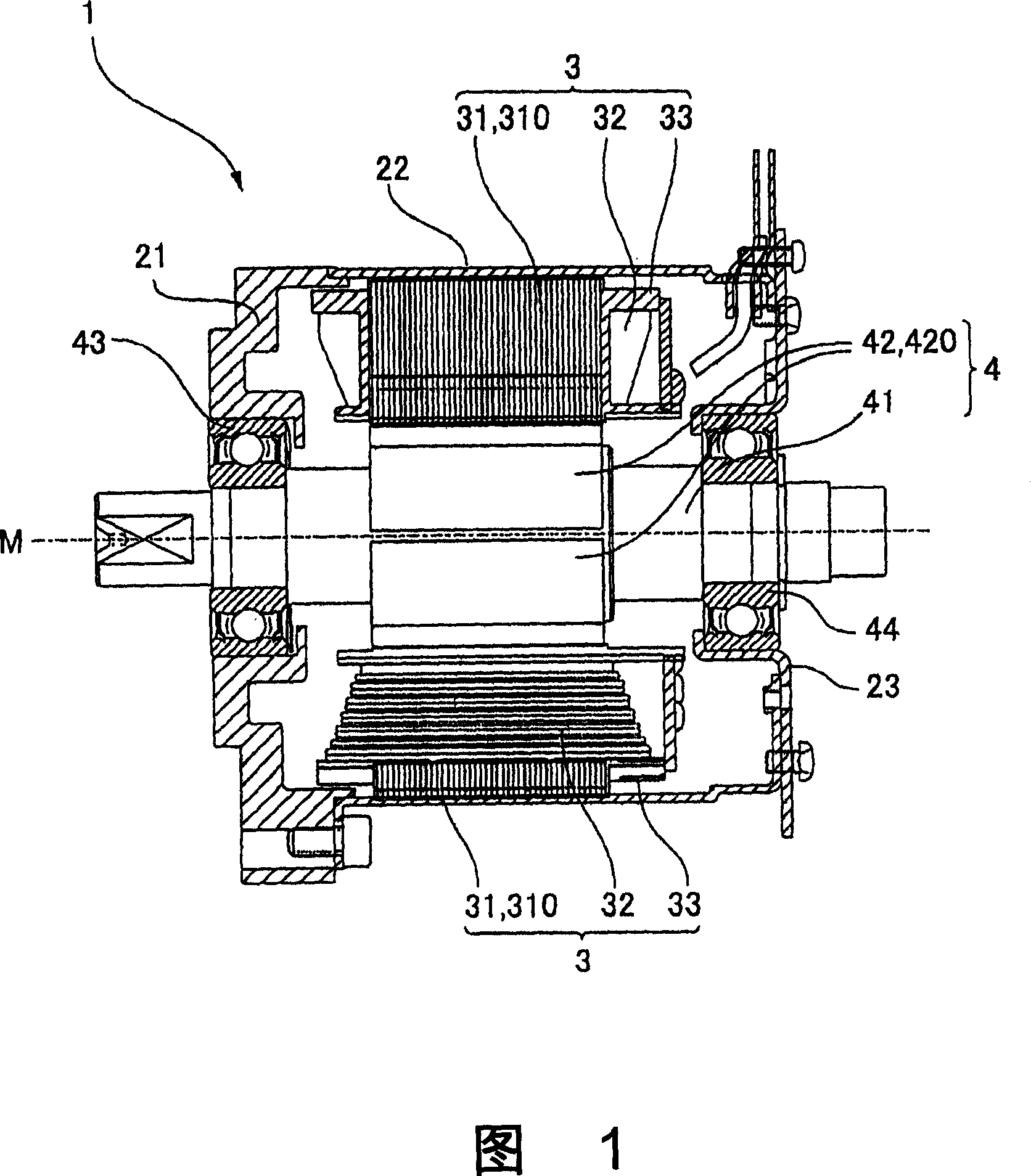
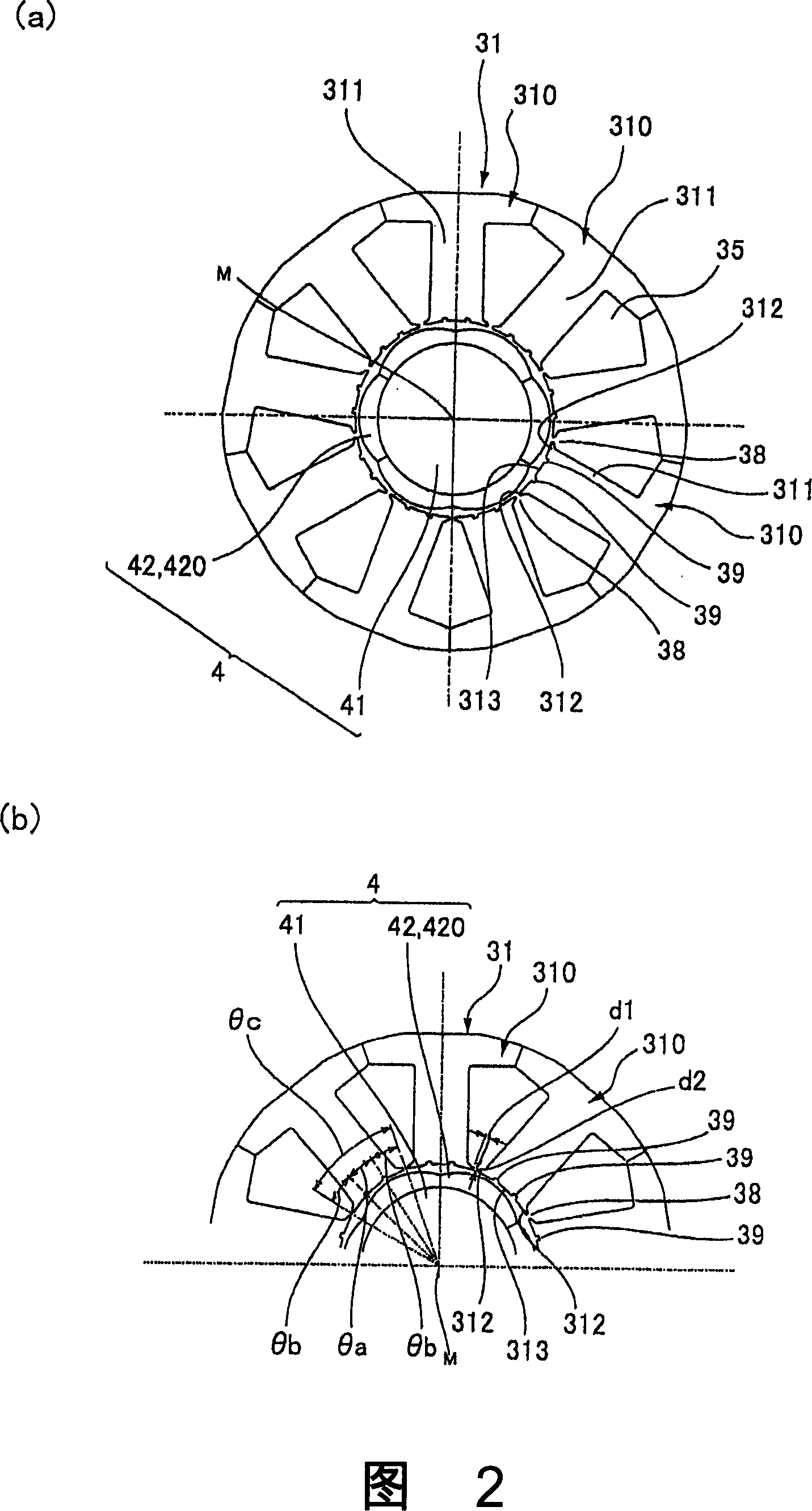
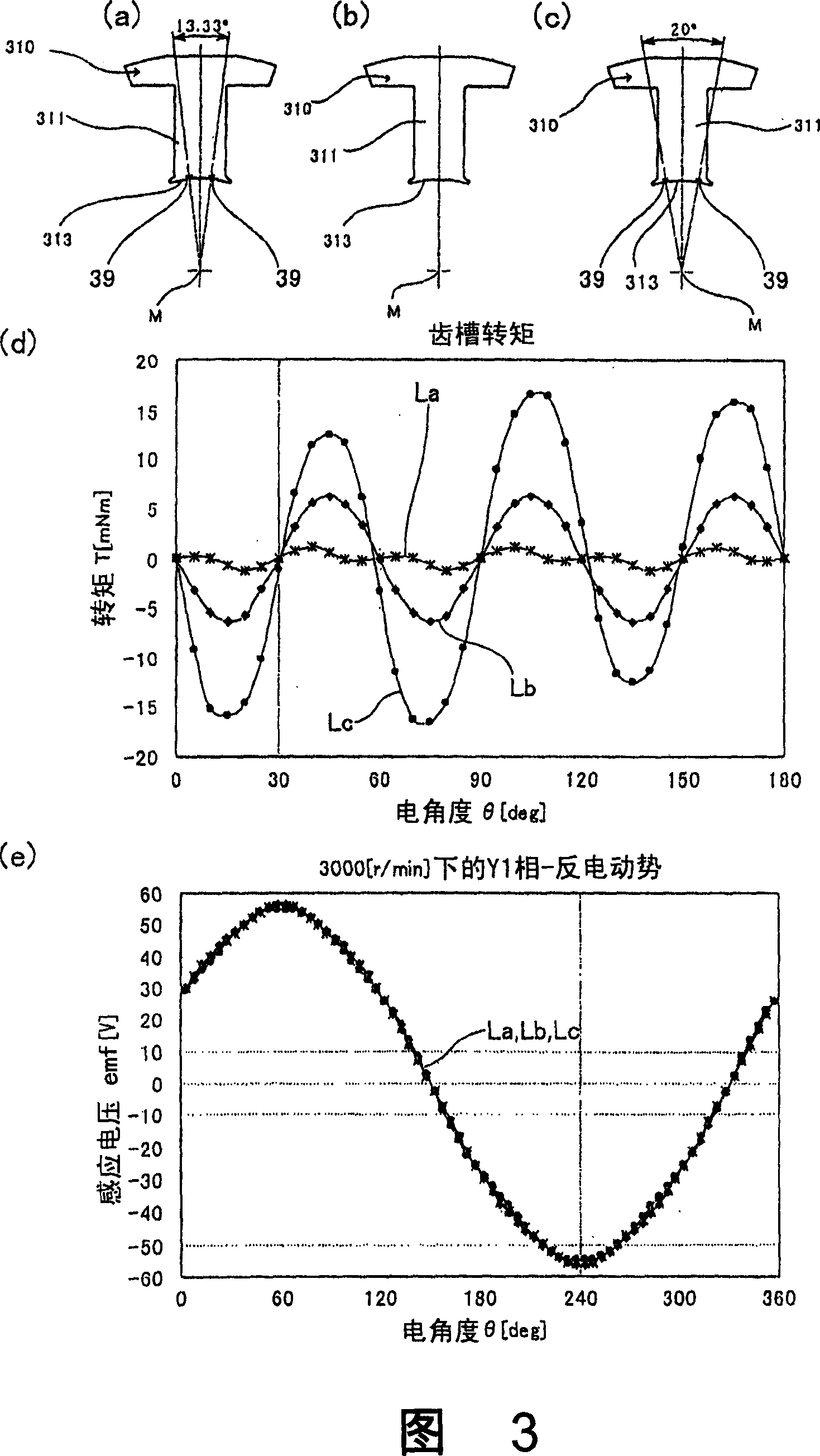
The invnetion provides a permanent magnet synchronous motor, capable of preventing the magnetic force of a stator core from being reduced, and reducing the torque of a tooth space. In a motor (1), a stator core (31) comprises of a plurality of divided iron cores (310), a stator (4) has a divided permanent-magnet (420) mounted in the circumferential direction of a revolving shaft (41). In the divided iron cores (310), a gap (38) is formed between the front ends of the adjacent teeth (311), an auxiliary slot (39) is formed on the front end face (313), for dividing the the front end face (313) in the circumferential direction based on a equal angle.
Owner:SANKYO SEIKI MFG CO LTD
Spindle motor, disk drive, and method of fabricating a stator core
InactiveCN101202474AImprove efficiencyBulk recordingMagnetic circuit stationary partsRecord information storageSheet steelStator coil
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Motor rotor and method of manufacturing same
ActiveCN108964310AReduce cogging torqueReduce torque rippleMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesElectric machineElectrical polarity
The invention relates to a motor rotor and a method of manufacturing the same. The motor rotor (2000) includes a rotor yoke (250) and a plurality of magnetic pole modules (200) disposed on the rotor yoke (250); each magnetic pole module (200) includes a substrate (210), a case (240) and a pair of magnetic pole units (220, 230) with opposite polarities accommodated in an accommodation space formedby the substrate (210) and the case (240); the magnetic pole units (220, 230) in each magnetic pole module (200) are spaced apart from each other by a first distance along the circumferential direction of the rotor yoke (250); and the plurality of magnetic pole modules (200) are mechanically fixed to the rotor yoke (250) through pressing bars (280) and fasteners ( 270). With the motor rotor of themotor rotor of the invention, generator performance (cogging torque and torque ripple), the protection of the magnetic poles, and the mechanical fixation of the magnetic poles can be shared.
Owner:BEIJING GOLDWIND SCI & CREATION WINDPOWER EQUIP CO LTD
Brushless motor
InactiveUS20170288517A1Increase effective magnetic fluxReduce air gapMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsBrushless motorsEngineering
A brushless motor including a toothed part with a tooth main body and a tip part. Protruding slant parts are formed on both sides of the tooth tip part. A tip surface is formed on the inner diameter of the tip part to face a magnet. A groove part is recessed in the center of the tip surface and extends in the axial direction. A depth d of the groove part satisfies 0<d≦(Lx−Rt) / 3. A width Wg of the groove part satisfies Wt>Wg≧Wt / 2 (Lx: distance between rotor center and a tooth / slant intersection X; X: intersection between an extension line P of a circumferential side surface of the tooth main body and an extension line Q of a slope of the slant part; Rt: radius of the inner diameter of the tooth tip surface; Wt: width of the tooth main body).
Owner:MITSUBA CORP
Motor
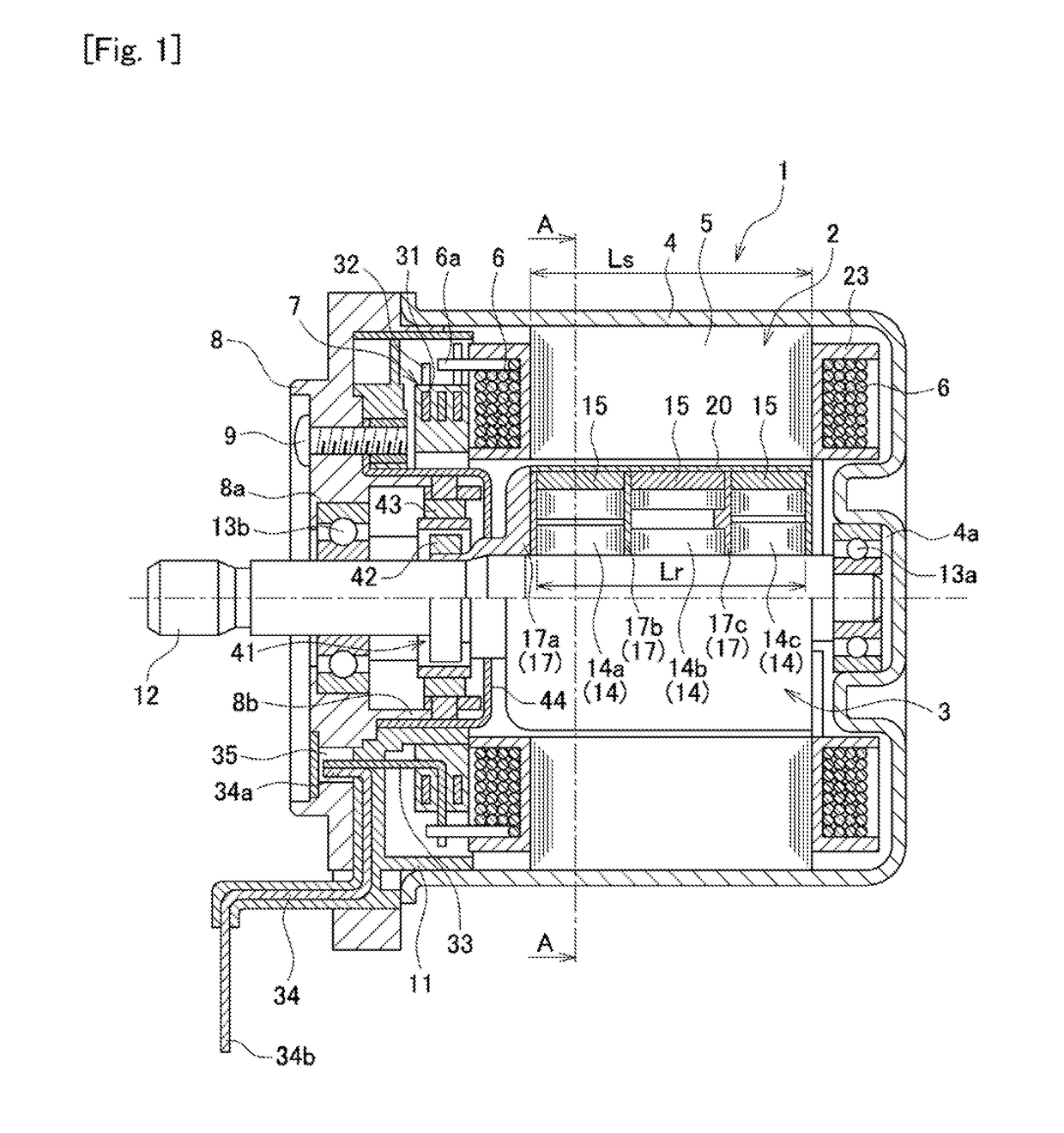
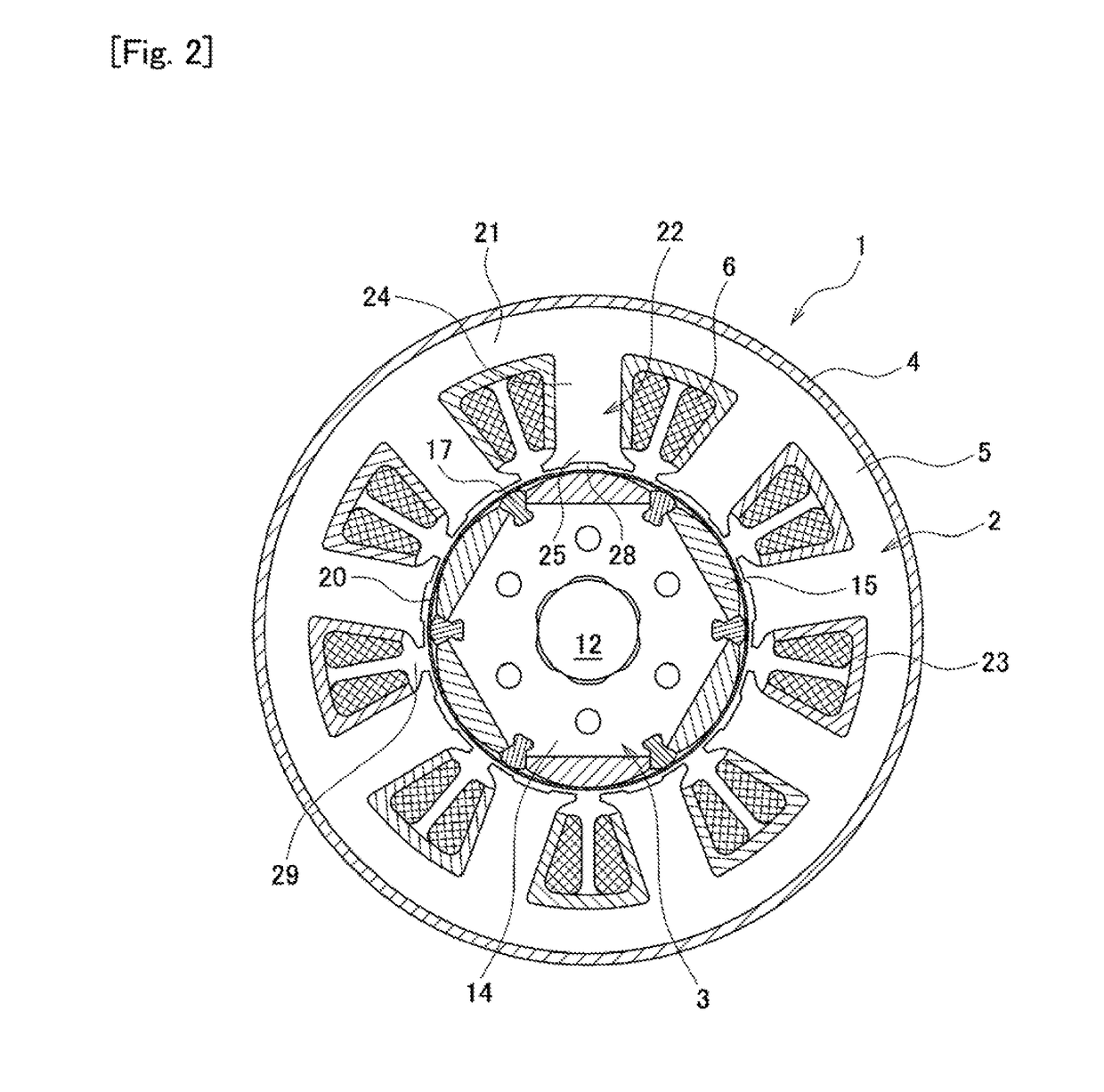
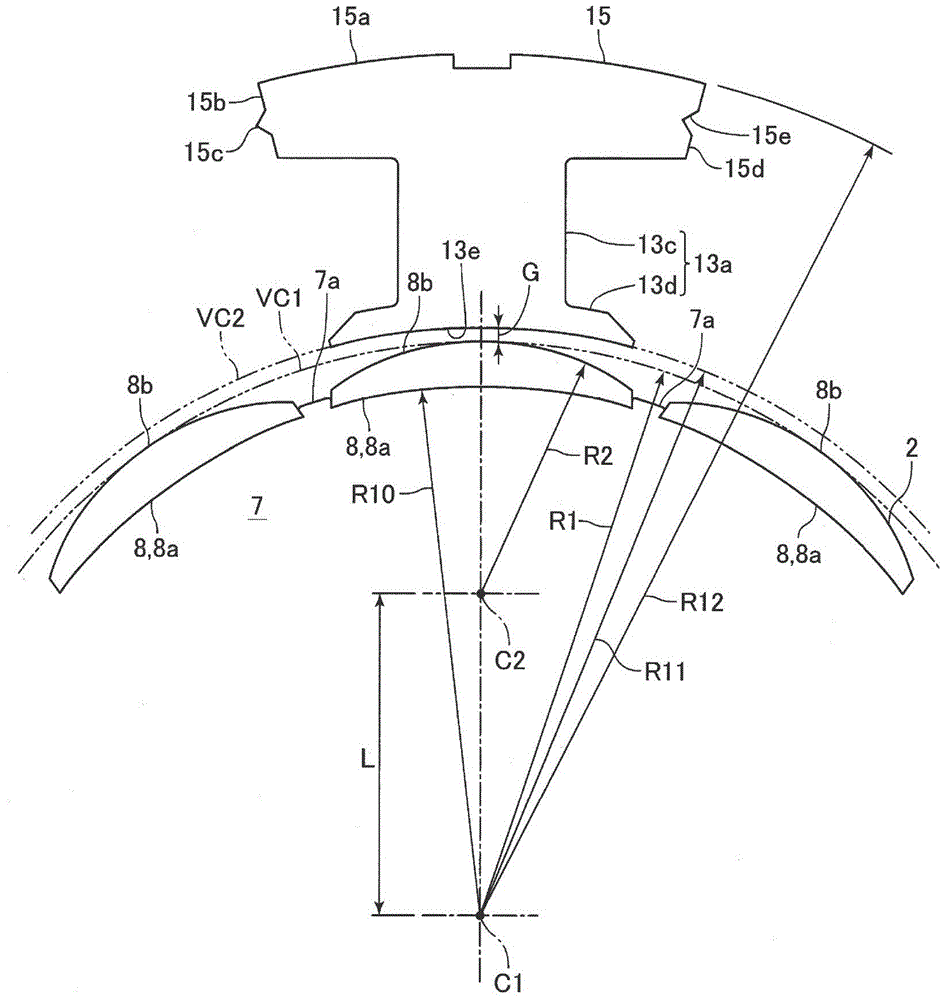
InactiveCN105048748ASmall torqueReduce cogging torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesPhysics
The utility model discloses a motor. The number of bulged poles of a stator is twelve, and the number of magnetic poles formed on the peripheral surface of a rotor is ten. The motor not only can form an effective magnetic circuit, but also can reduce the cogging torque. In the motor, the stator (3) disposed at the radial peripheral side of the rotor (2) comprises a stator core (13) which is provided with twelve bulged poles (13a) bulging radially inwards. The rotor (2) comprises a plurality of permanent magnets (8) which are arranged in the peripheral direction in an adjacent manner, and are arranged opposite to tail end faces (13e) of the bulged poles (13a), wherein there are gaps between the permanent magnets (8) and the tail end faces (13e) of the bulged poles (13a). The number of the magnetic poles on the peripheral surface of the rotor (2) is ten. The tail end faces (13e) of the bulged poles (13a) form a concave curved surface through smooth connection surfaces, and surfaces (8b), opposite to the tail end faces (13e) of the bulged poles (13a), of the permanent magnets (8), form a convex curved surface. In the motor, the ratio R1 / R2 of the radius R1 of an imaginary circle contacting with a part of surfaces (8b) of the permanent magnets (8) to the curvature radius R2 of each of the surfaces (8b) of the permanent magnets (8) is from 0.4 to 0.55.
Owner:NIDEC SANKYO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com