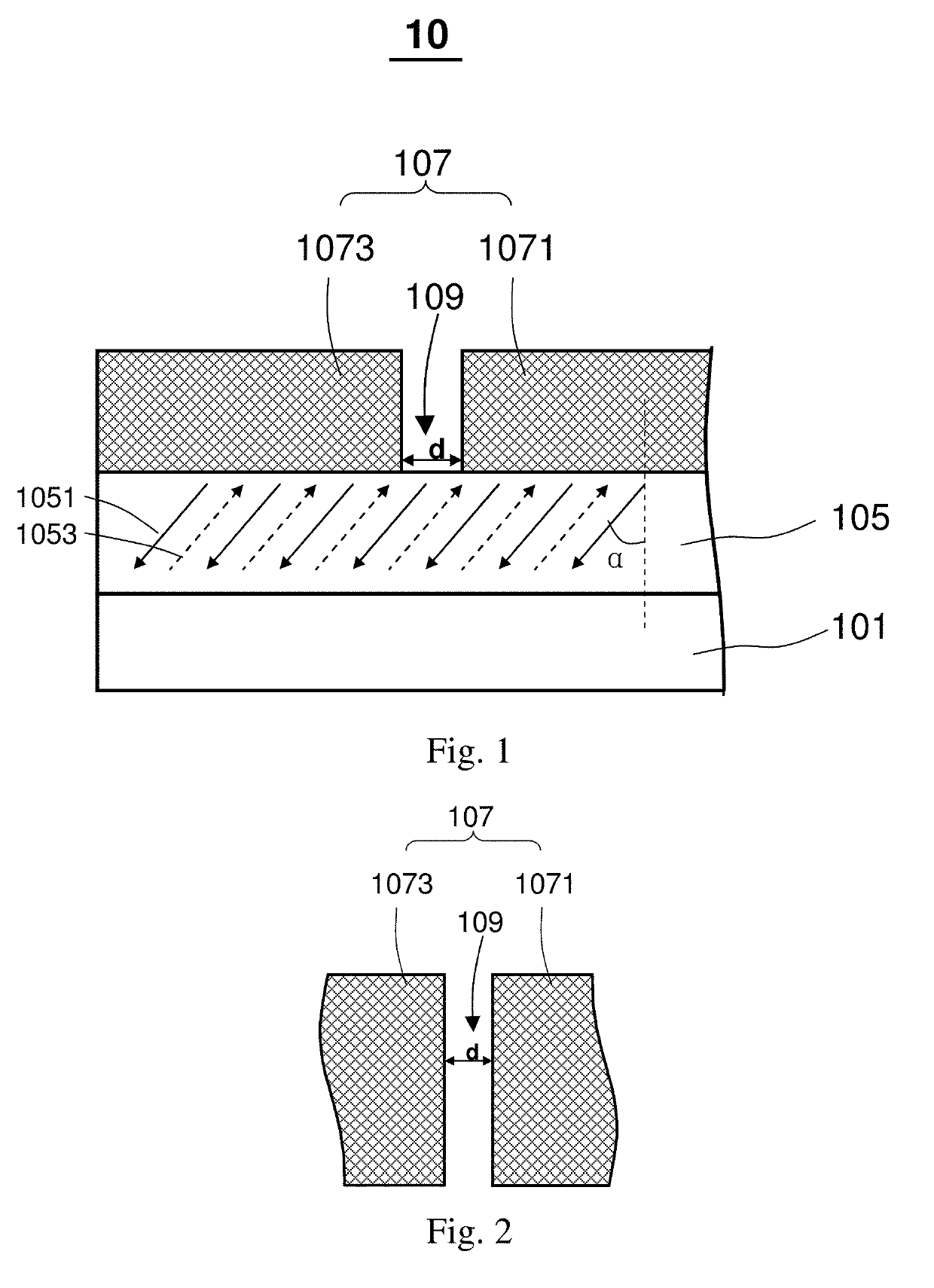
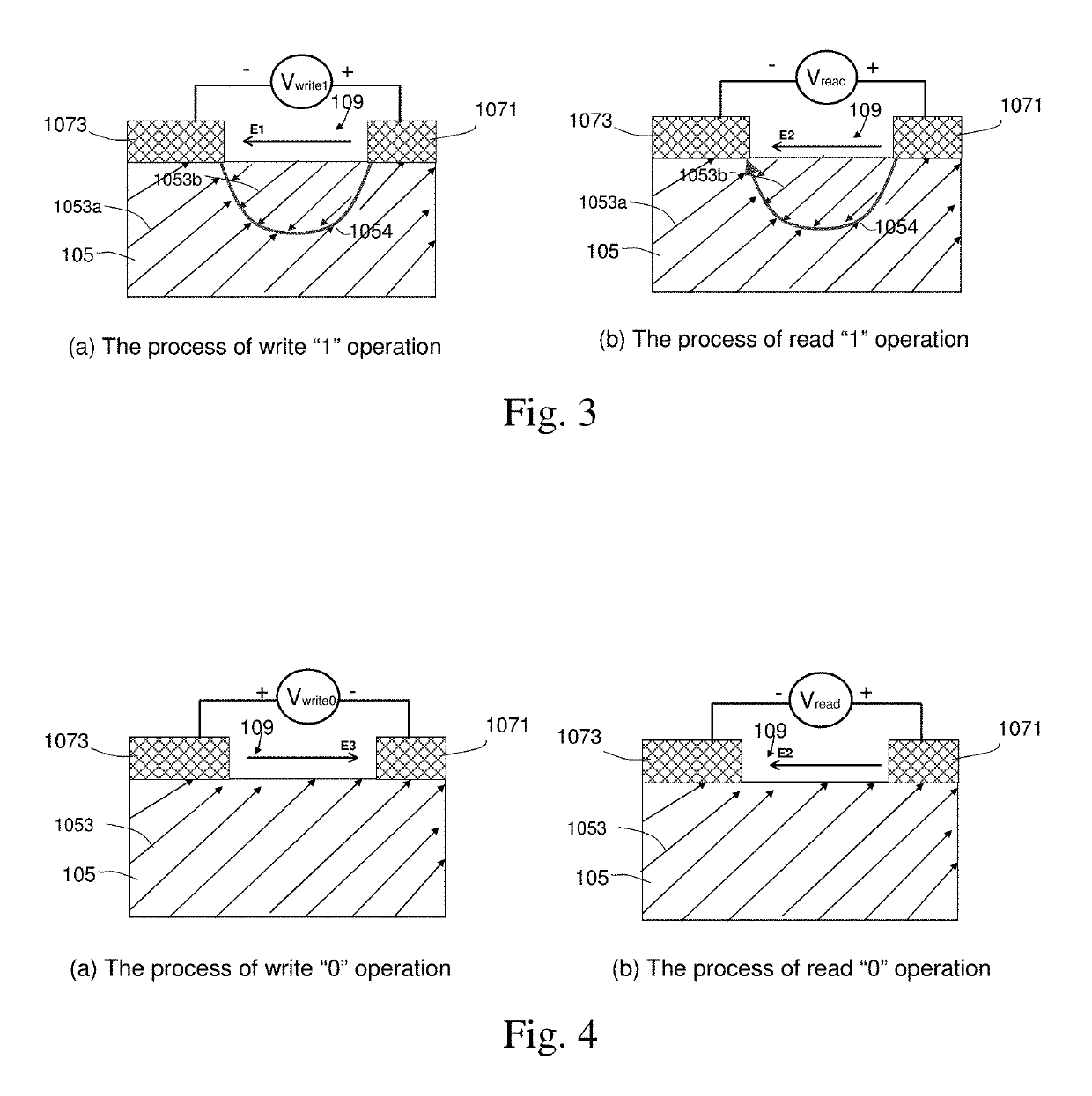
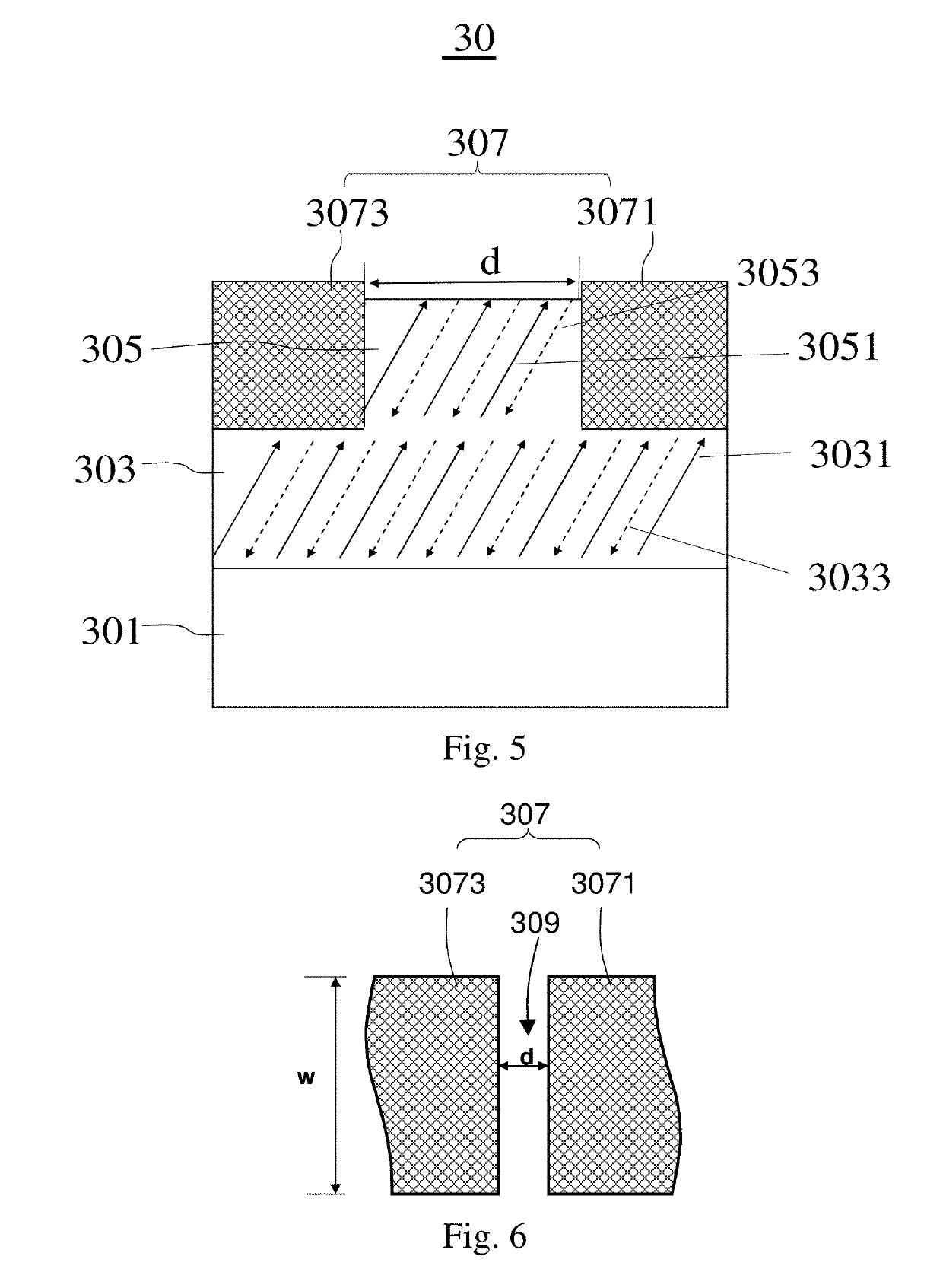
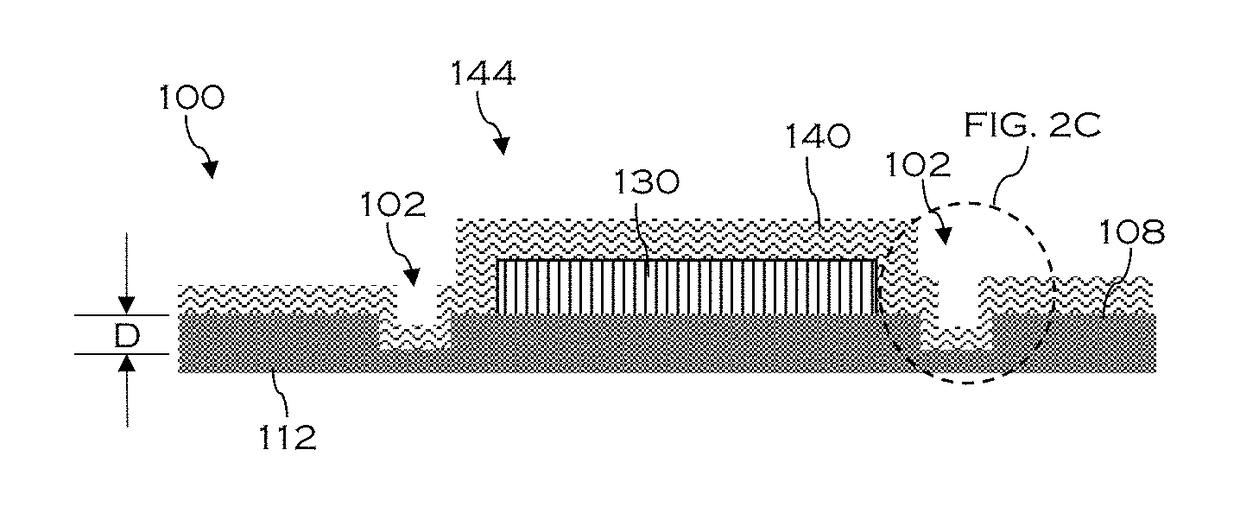
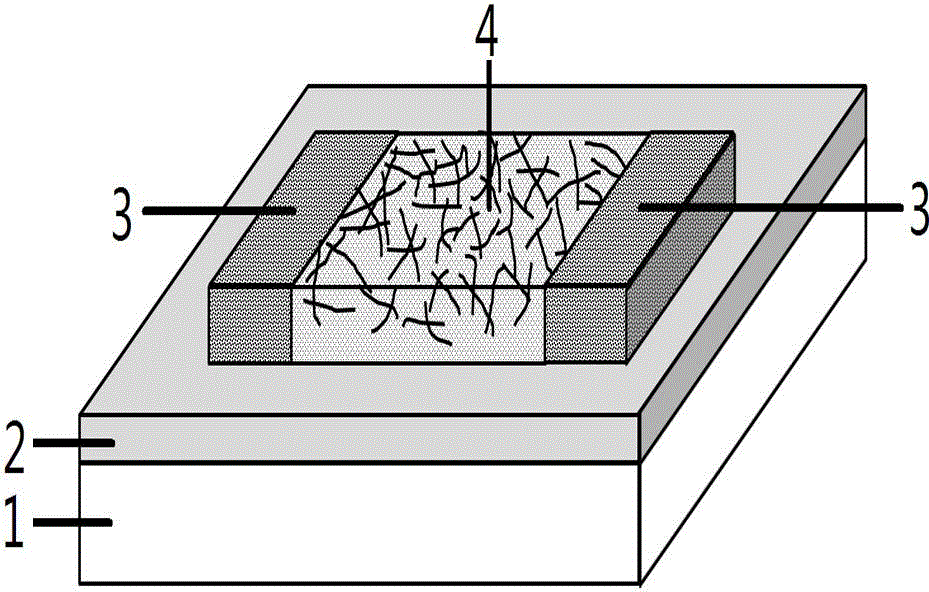
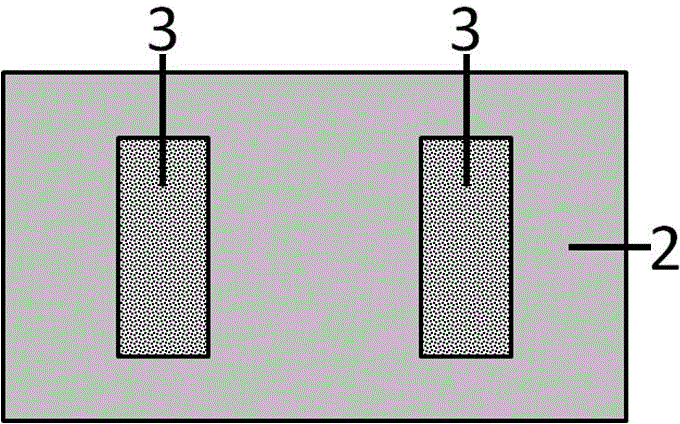
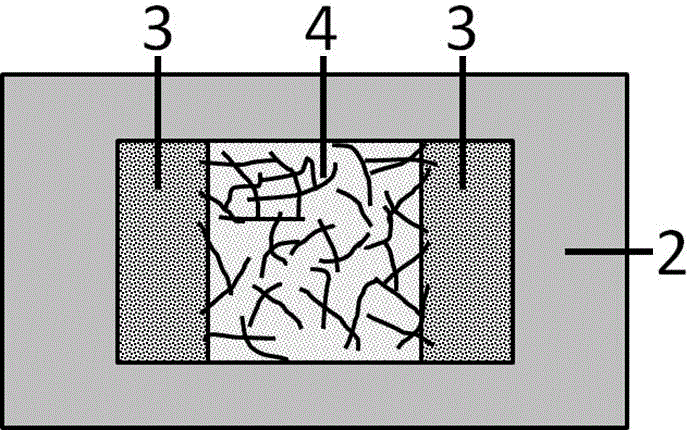
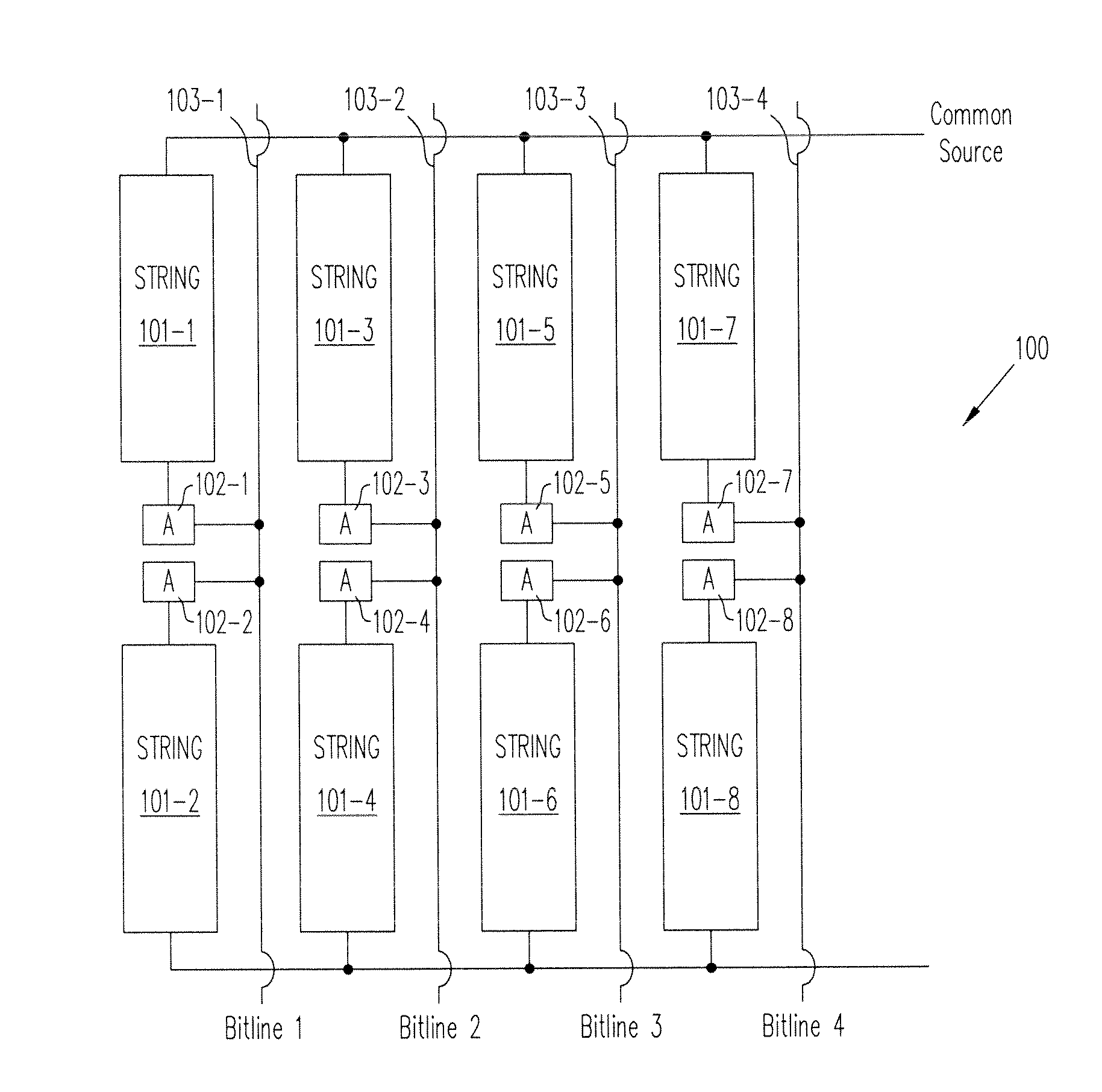
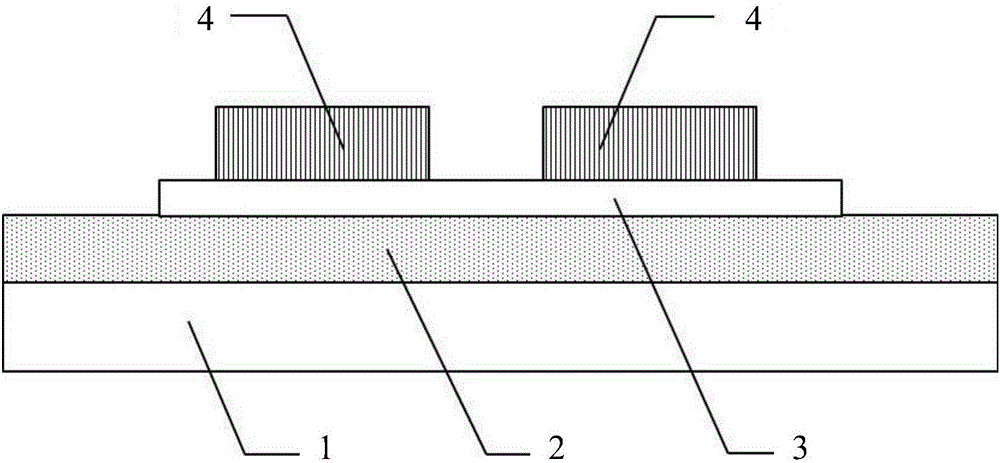
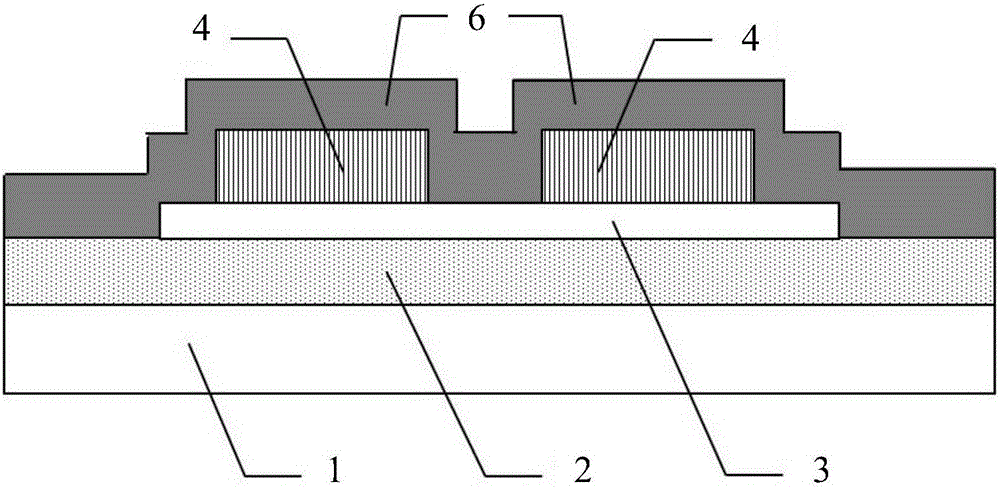
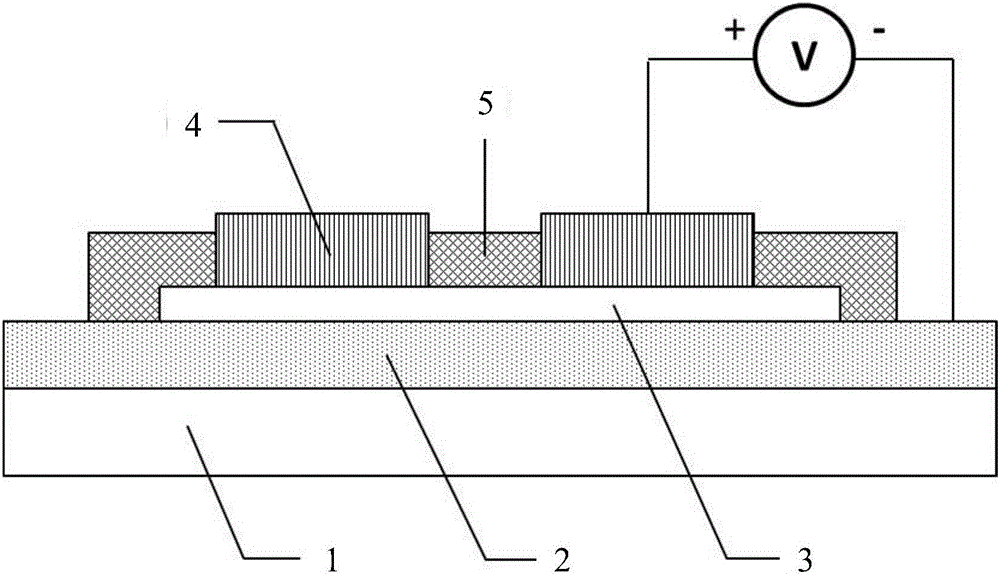
Patents
Literature
32 results about "Thin-film memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thin-film memory is a high-speed variation of core memory developed by Sperry Rand in a government-funded research project. Instead of threading individual ferrite cores on wires, thin-film memory consisted of 4 micrometre thick dots of permalloy, an iron-nickel alloy, deposited on small glass plates by vacuum evaporation techniques and a mask. The drive and sense lines were then added using printed circuit wiring over the alloy dots. This provided very fast access times in the range of 670 nanoseconds, but was very expensive to produce.
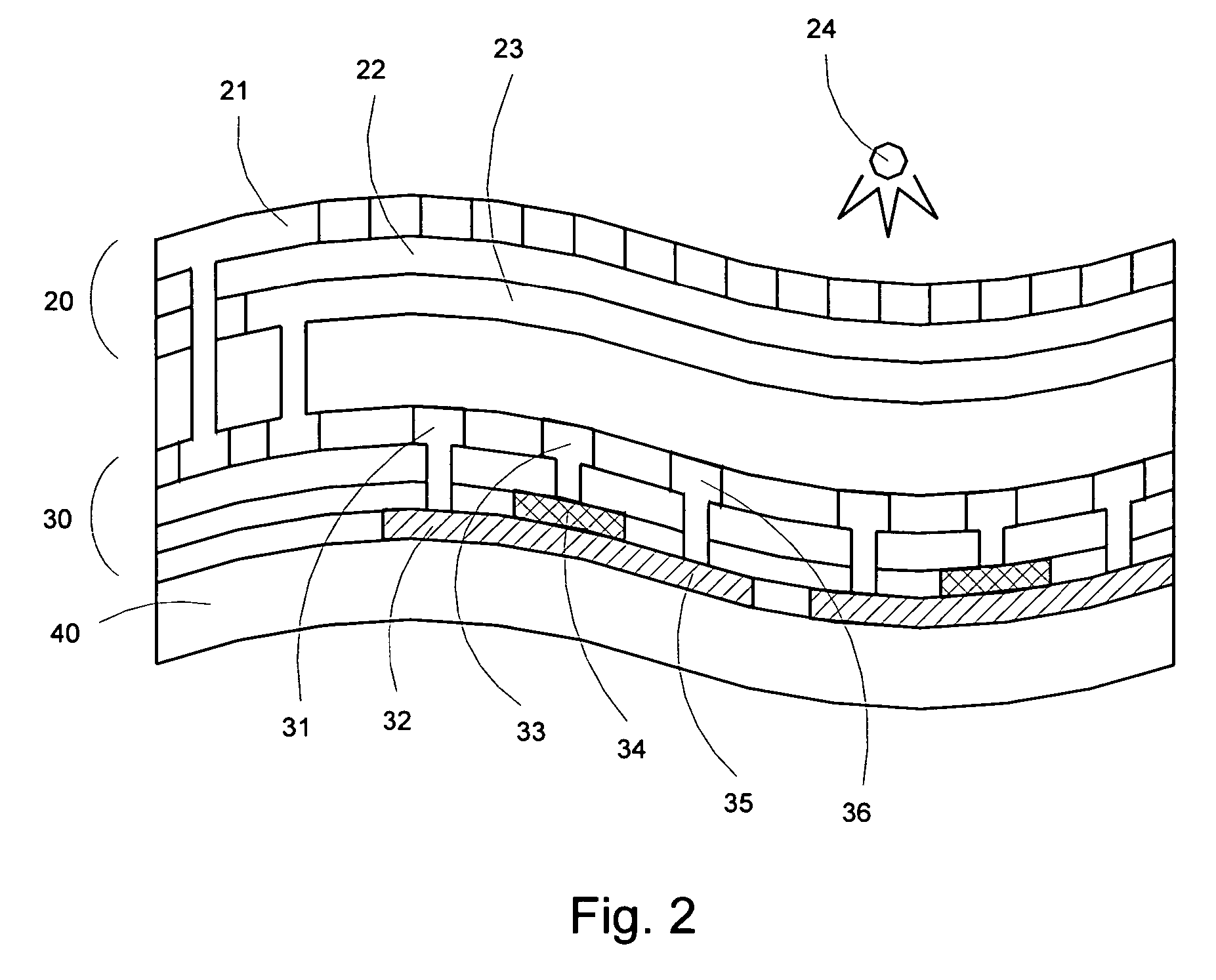
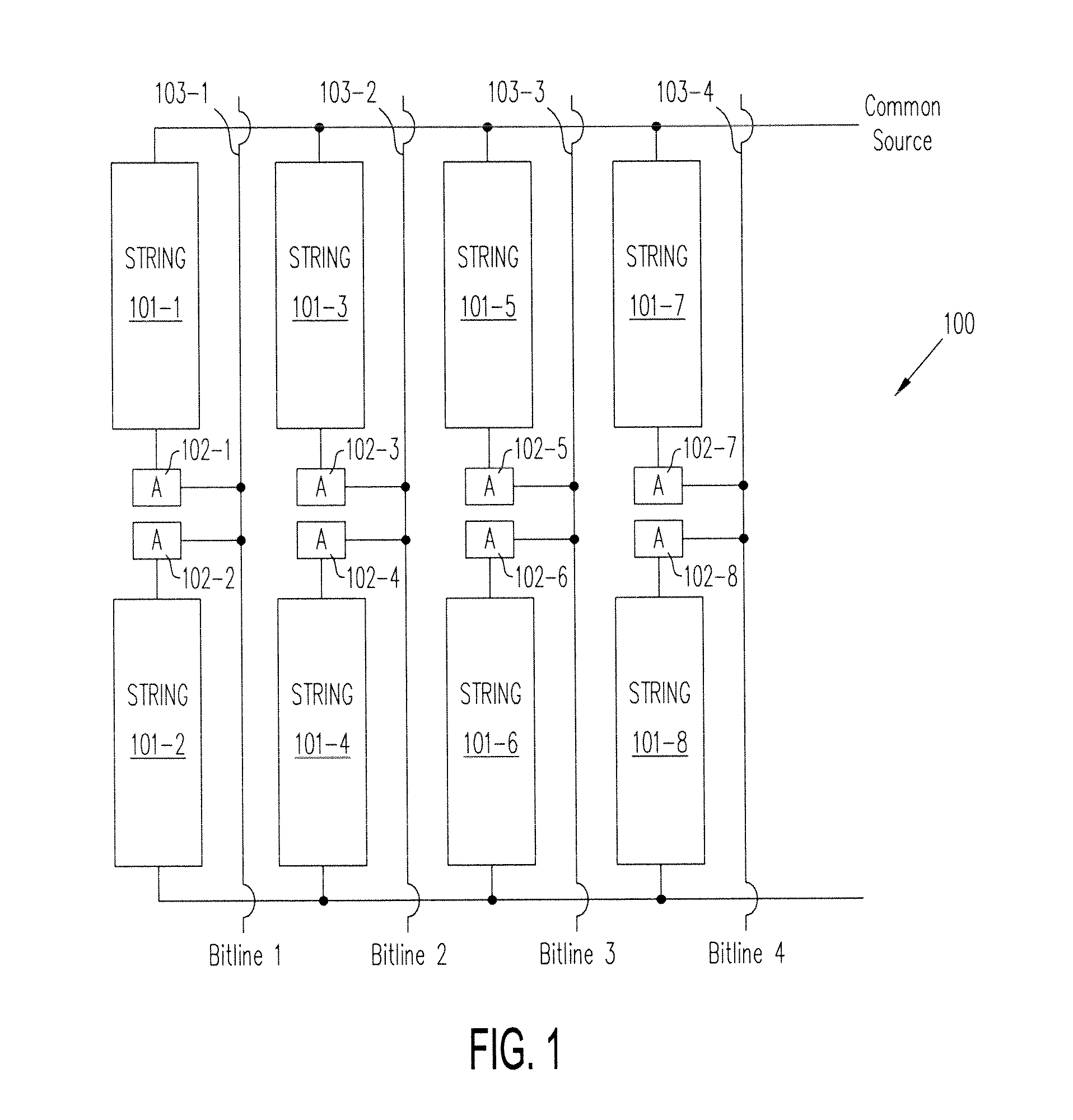
Thin film memory, array, and operation method and manufacture method therefor
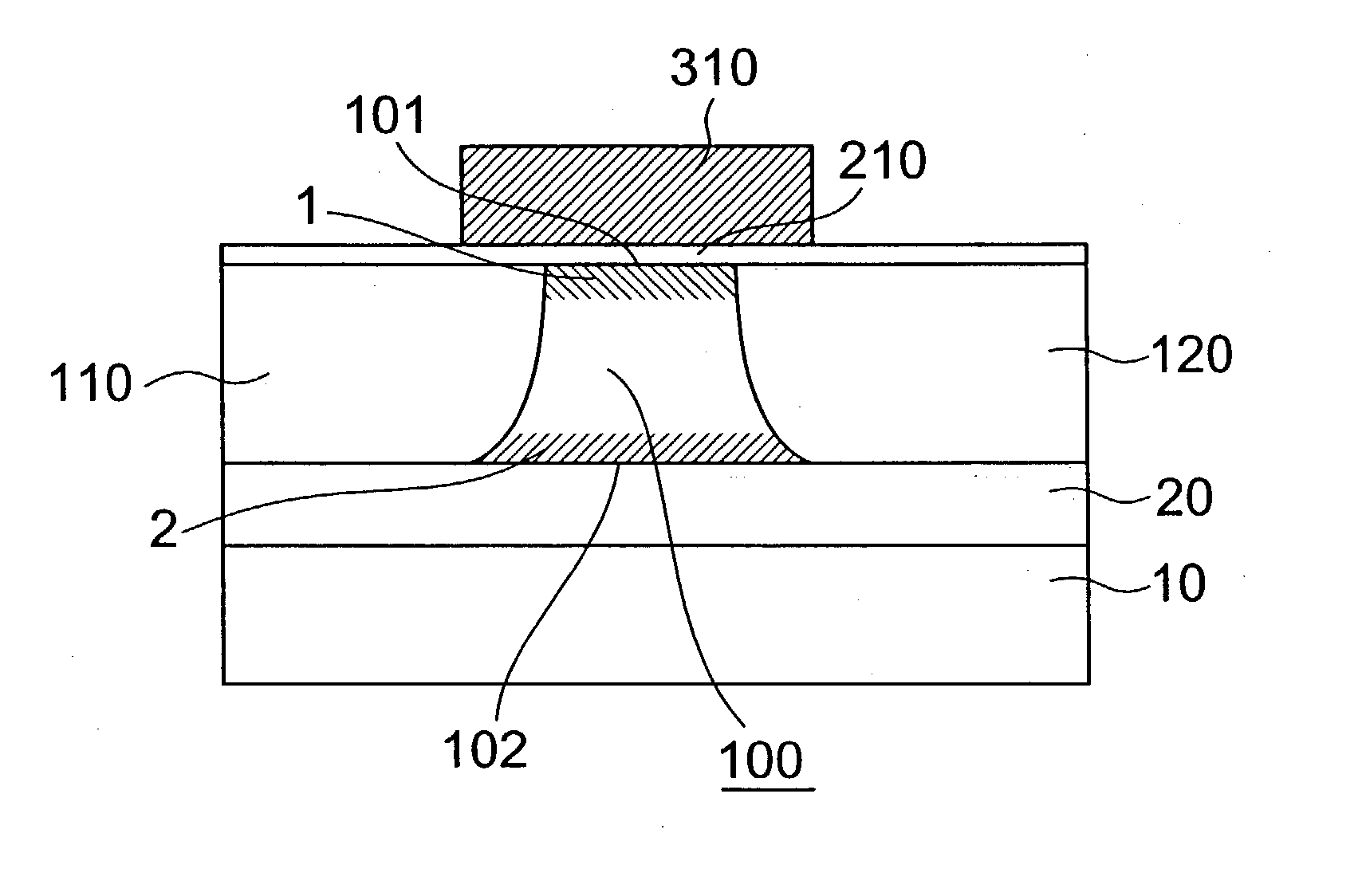
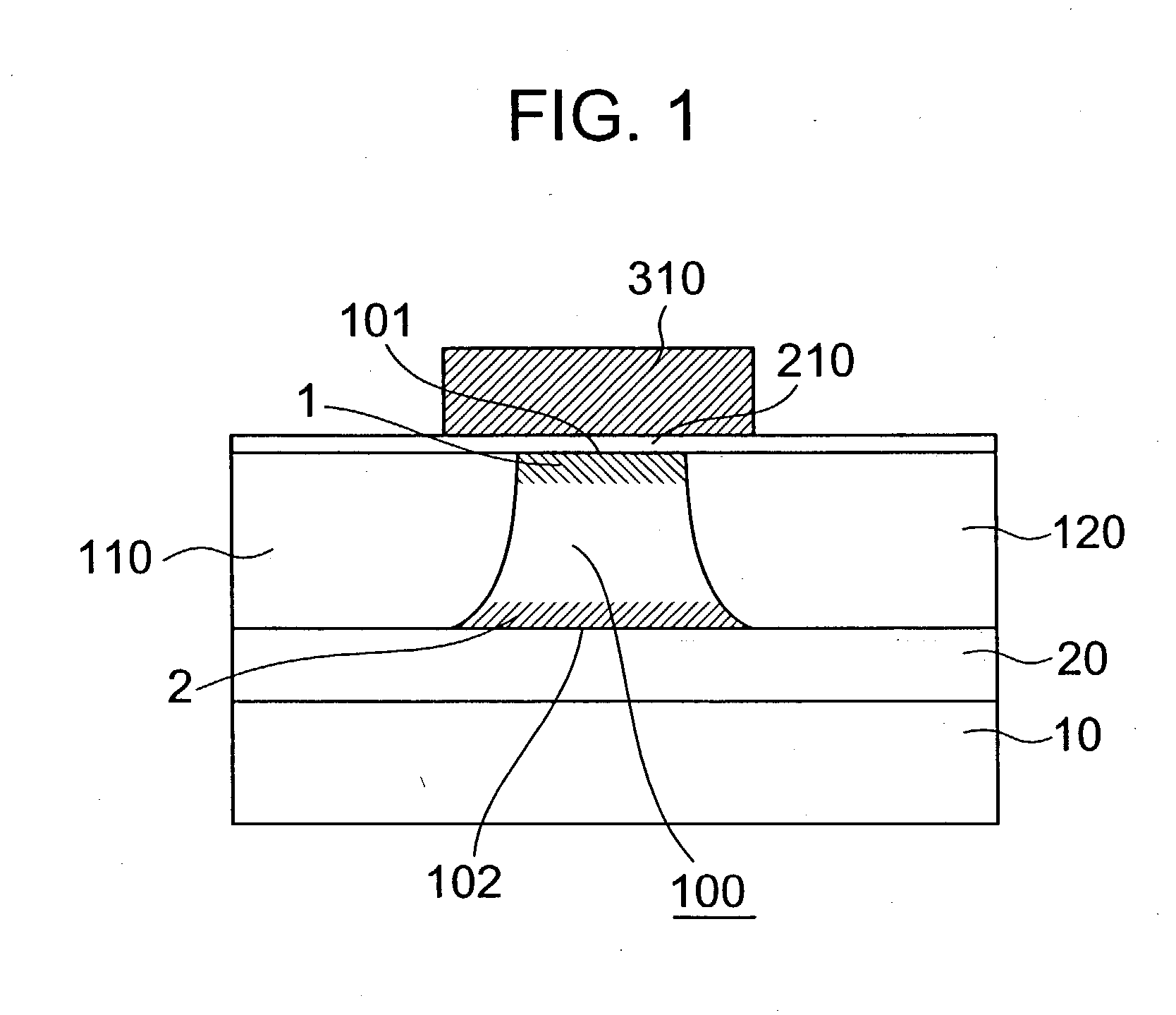
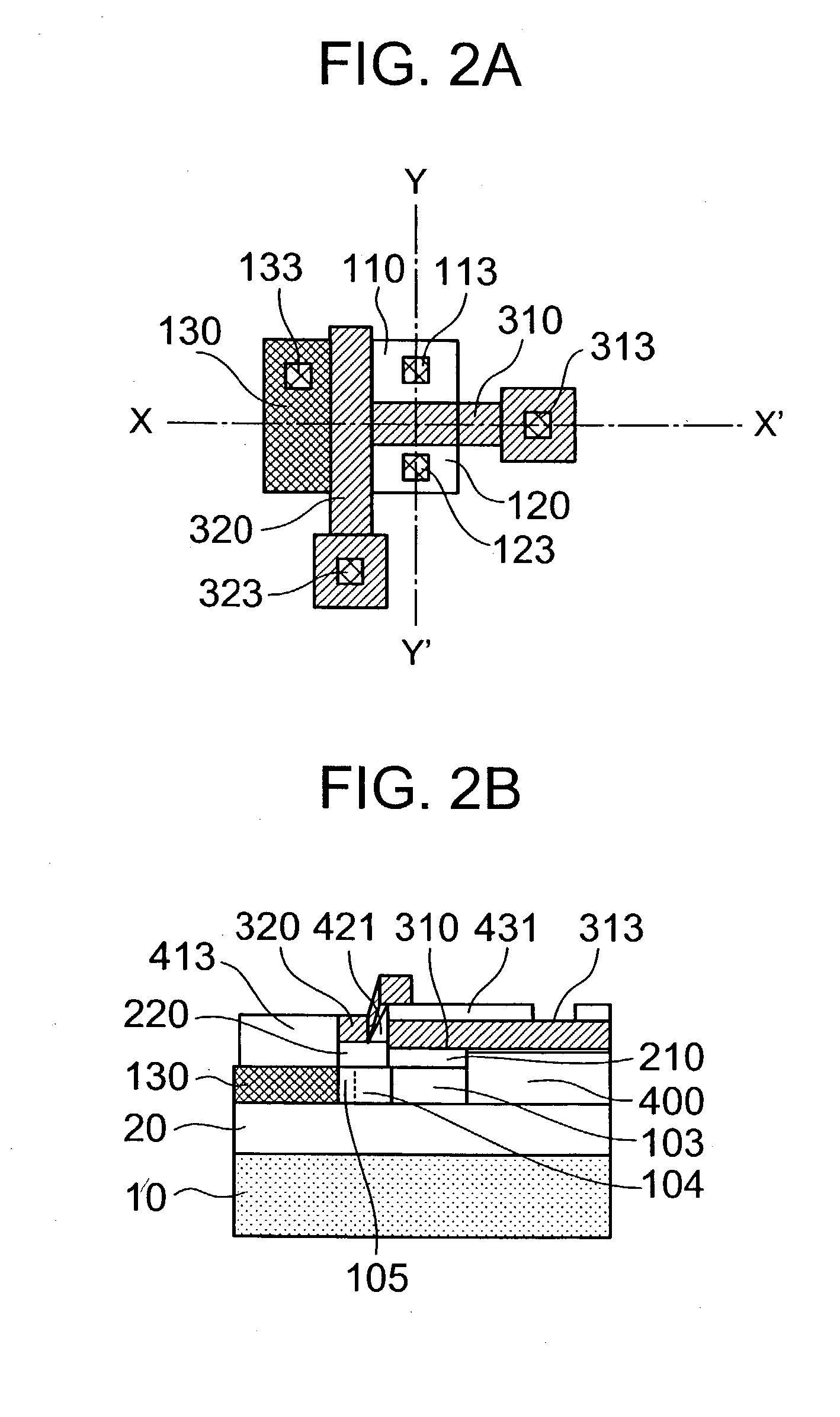
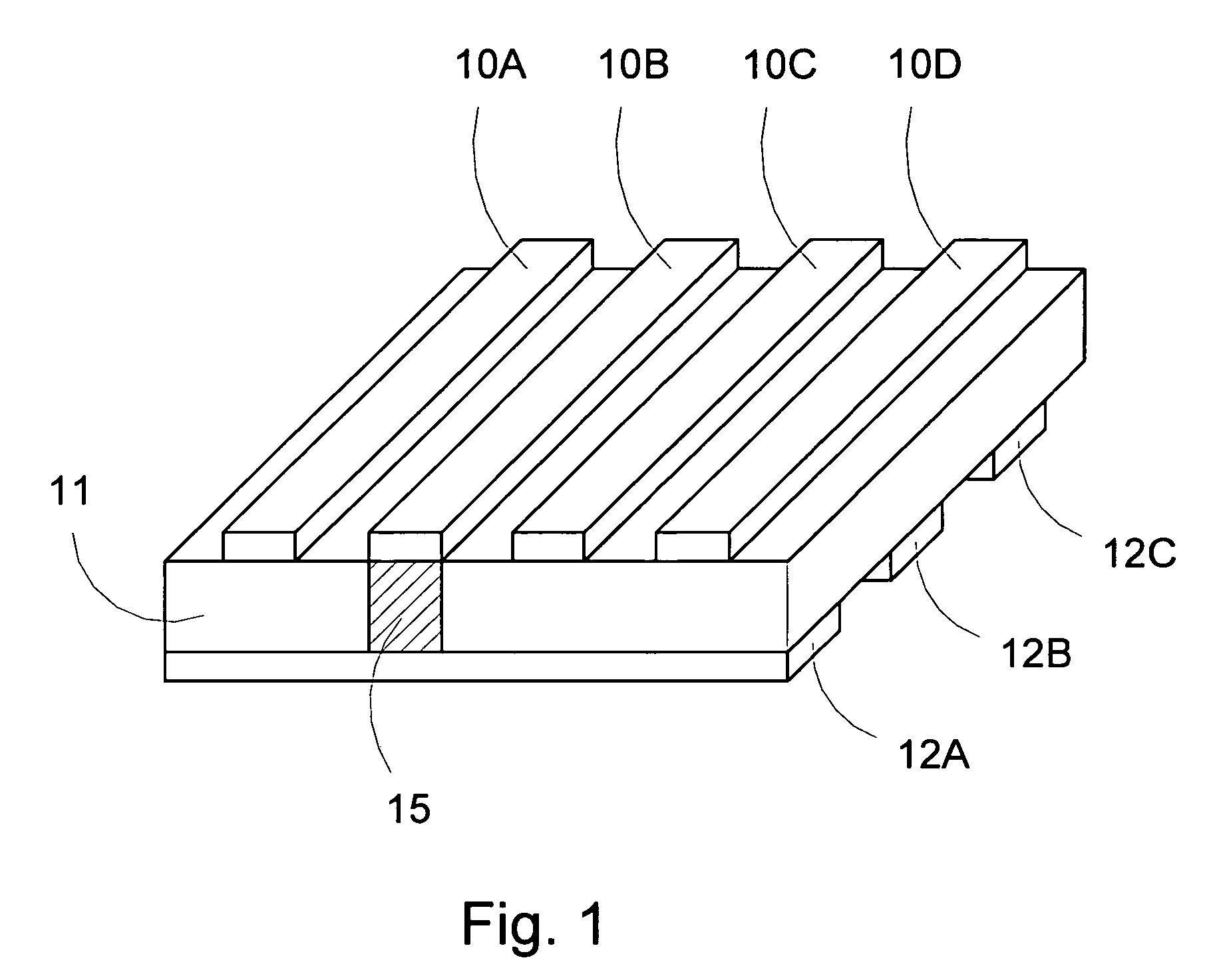
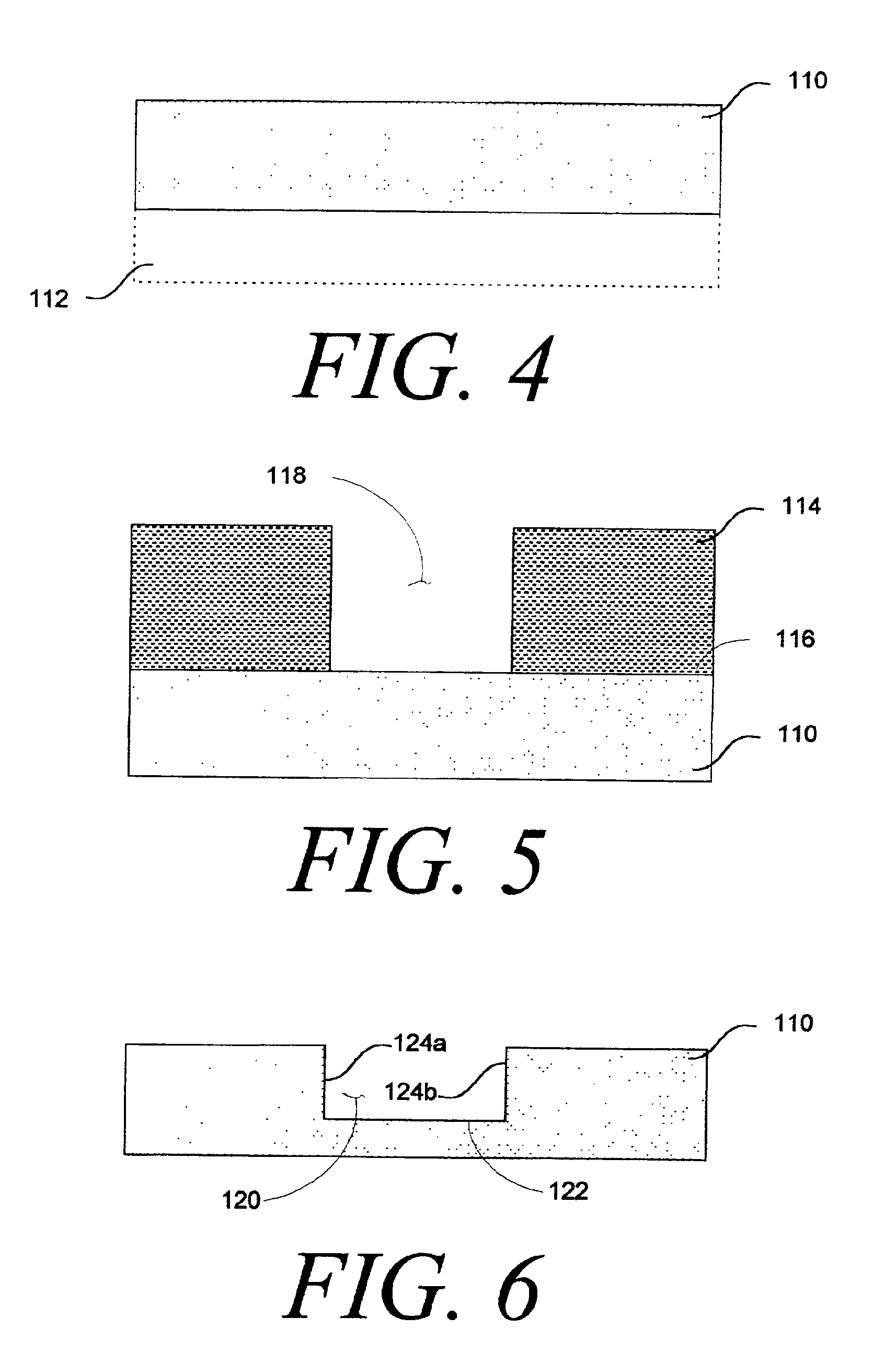
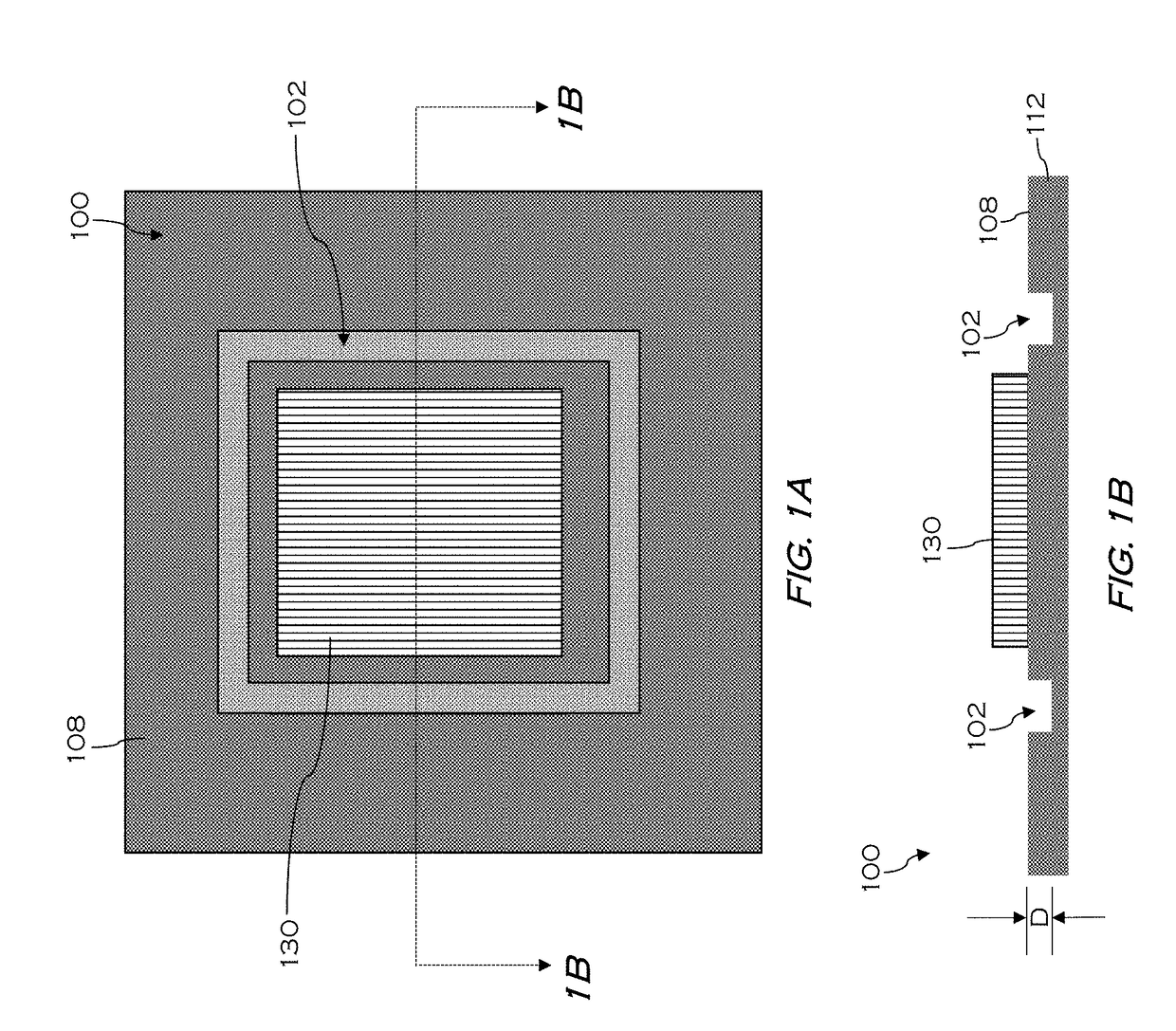
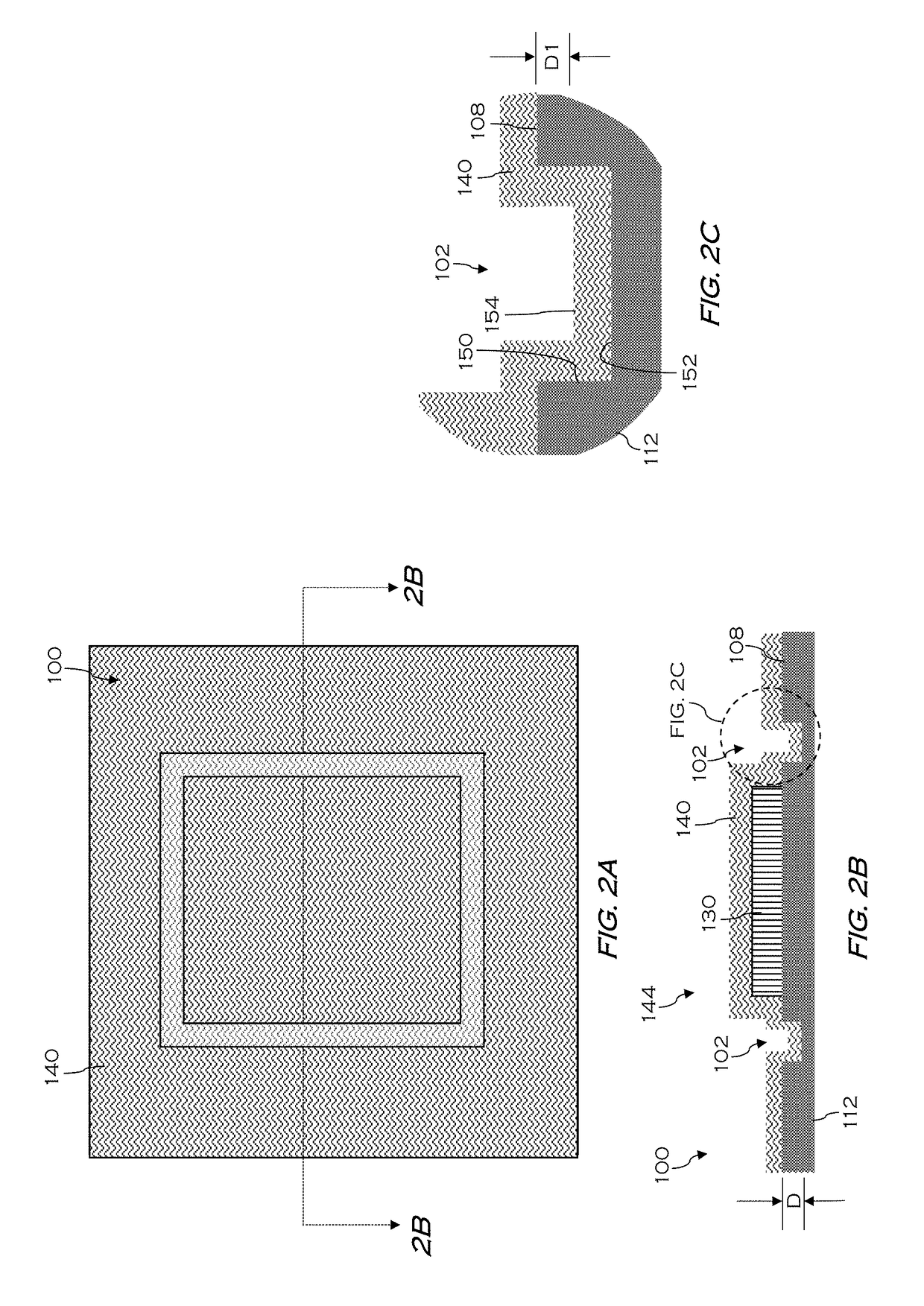
A memory cell which is formed on a fully depleted SOI or other semiconductor thin film and which operates at low voltage without needing a conventional large capacitor is provided as well as a memory cell array. The semiconductor thin film is sandwiched between first and second semiconductor regions which face each other across the semiconductor thin film and which have a first conductivity type. A third semiconductor region having the opposite conductivity type is provided in an extended portion of the semiconductor thin film. From the third semiconductor region, carriers of the opposite conductivity type are supplied to and accumulated in the semiconductor thin film portion to change the gate threshold voltage of a first conductivity type channel that is induced by a first conductive gate voltage in the semiconductor thin film between the first and second semiconductor regions through an insulating film.
Owner:HAYASHI YUTAKA +1
Ferroelectric or electret memory circuit
InactiveUS6878980B2Reducing and avoiding effect of fatigueSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOligomerThin-film memory
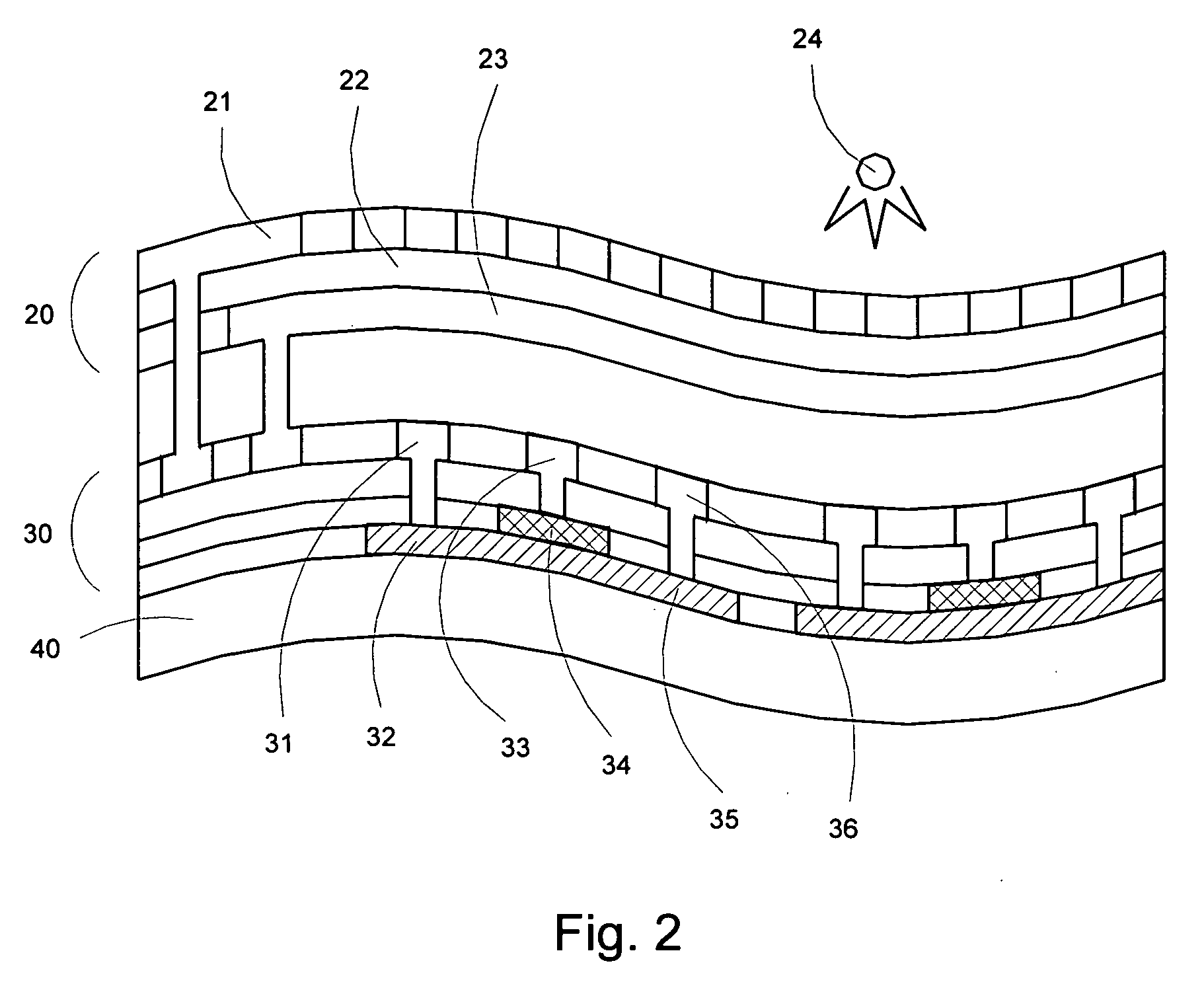
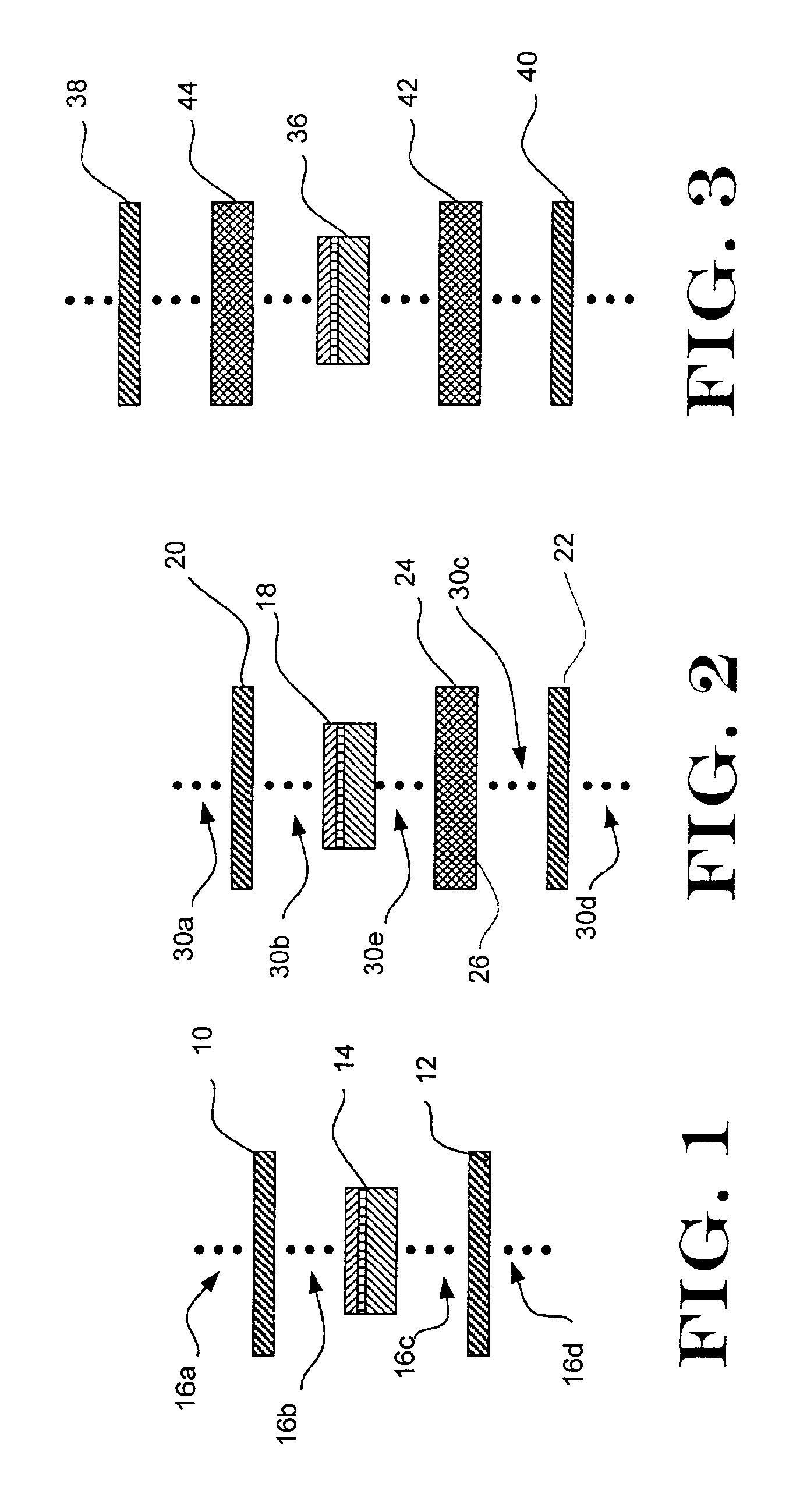
A ferroelectric or electret memory circuit, particularly a ferroelectric or electret memory circuit with improved fatigue resistance, including a ferroelectric or electret memory cell with a polymer or oligomer memory material contacting first and second electrodes, at least one of the electrodes is comprised of at least one functional material capable of physical and / or chemical bulk incorporation of atomic or molecular species contained in either the electrode or the memory material and displaying a propensity for migrating in the form of mobile charged and / or neutral particles between an electrode and a memory material, something which can be detrimental to both. A functional material with the above-mentioned properties shall serve to offset any adverse effect of a migration of this kind, leading to an improvement in the fatigue resistance of the memory cell. The memory circuit being used in a matrix-addressable memory device where the memory cells are formed in distinct portions in a global layer of a ferroelectric or electret thin-film memory material, particularly a polymer material.
Owner:THIN FILM ELECTRONICS ASA
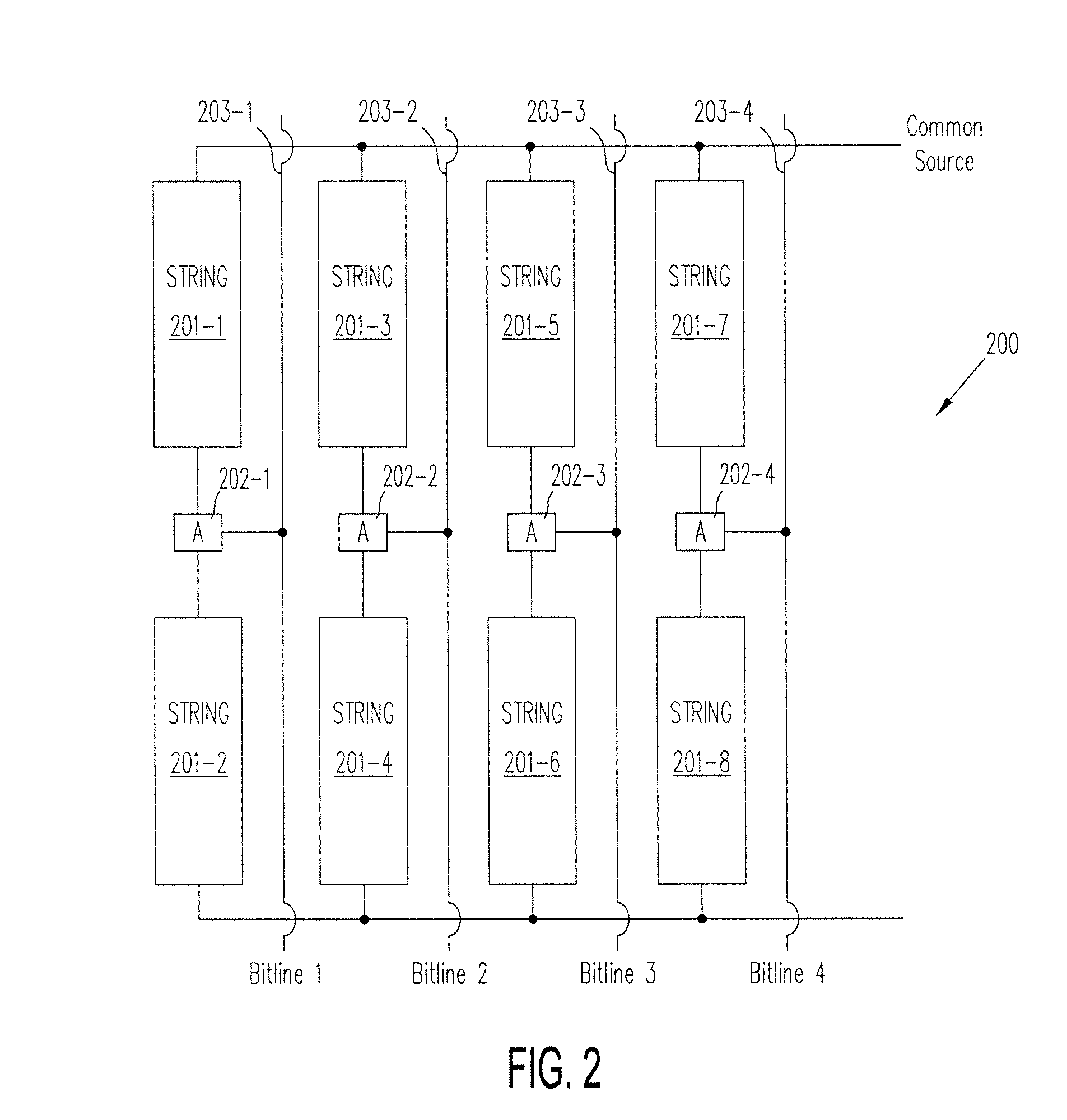
Thin film memory, array, and operation method and manufacture method therefor
A memory cell which is formed on a fully depleted SOI or other semiconductor thin film and which operates at low voltage without needing a conventional large capacitor is provided as well as a memory cell array. The semiconductor thin film is sandwiched between first and second semiconductor regions which face each other across the semiconductor thin film and which have a first conductivity type. A third semiconductor region having the opposite conductivity type is provided in an extended portion of the semiconductor thin film. From the third semiconductor region, carriers of the opposite conductivity type are supplied to and accumulated in the semiconductor thin film portion to change the gate threshold voltage of a first conductivity type channel that is induced by a first conductive gate voltage in the semiconductor thin film between the first and second semiconductor regions through an insulating film.
Owner:HAYASHI YUTAKA +3
Methods of forming magnetic shielding for a thin-film memory element
InactiveUS7166479B2Reduce undesirable fieldsEnhance the desirable magnetic fieldsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin-film memoryMagnetic memory
A monolithically formed ferromagnetic thin-film memory is disclosed that has local shielding on at least two sides of selected magnetic storage elements. The local shielding preferably extends along the back and side surfaces of a word line and / or digital lines of a conventional magnetic memory. In this configuration, the local shielding not only may help reduce externally generated EMI, internally generated cross-talk and other unwanted fields in the magnetic bit region, but may also help enhance the desired magnetic fields in the bit region.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Thin film non volatile memory device scalable to small sizes
InactiveUS20060151616A1Highly repeatableHighly stableNanoinformaticsDigital storageThin-film memoryEngineering
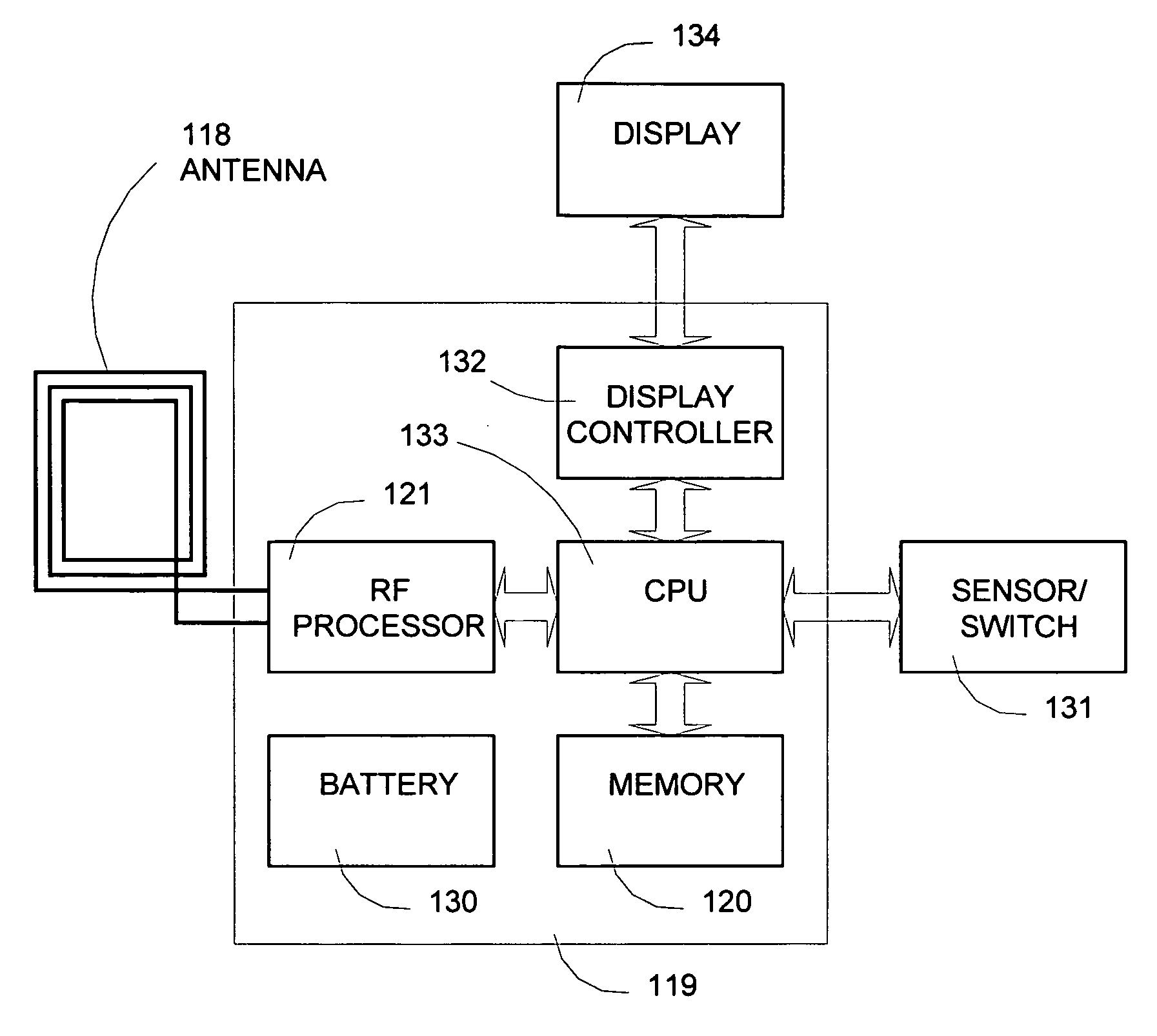
A thin film non volatile memory scalable to small sizes and its fabrication process are disclosed. The thin film memory comprises a thin film transistor control circuitry fabricated on a flexible substrate, together with an optoelectronic cross bar memory comprising a photoconducting material. The thin film non volatile memory can be used in RFID communication tag with the control circuitry further comprises wireless communication circuitry such as an antenna, a receiver, and a transmitter.
Owner:TERECIRCUITS CORP
Thin film memory device having local and external magnetic shielding
InactiveUS6872993B1Reduce undesirable fieldOvercome disadvantagesTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThin-film memoryMagnetic memory
A monolithically formed ferromagnetic thin-film memory is disclosed that has local shielding on at least two sides of selected magnetic storage elements. The local shielding preferably extends along the back and side surfaces of a word line and / or digital lines of a conventional magnetic memory. In this configuration, the local shielding not only may help reduce externally generated EMI, internally generated cross-talk and other unwanted fields in the magnetic bit region, but may also help enhance the desired magnetic fields in the bit region.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method to fabricate a thin film non volatile memory device scalable to small sizes
InactiveUS20060152960A1Highly repeatableHighly stableSolid-state devicesDigital storageThin-film memoryControl circuit
A thin film non volatile memory scalable to small sizes and its fabrication process are disclosed. The thin film memory comprises a thin film transistor control circuitry fabricated on a flexible substrate, together with an optoelectronic cross bar memory comprising a photoconducting material. The thin film non volatile memory can be used in RFID communication tag with the control circuitry further comprises wireless communication circuitry such as an antenna, a receiver, and a transmitter.
Owner:TERECIRCUITS CORP
Large current-readout ferroelectric single-crystal thin film memory as well as method of preparing the same and method of operating the same
Disclosed is a non-destructive large current-readout ferroelectric single-crystal thin film memory as well as a method of preparing the ferroelectric memory and a method of operating the ferroelectric memory. The large current-readout ferroelectric single-crystal thin film memory comprises a ferroelectric storage layer, which is a ferroelectric single-crystal storage layer. The non-destructive readout ferroelectric memory has a greatly increased read current in an on-state, and moreover, the data retention performance and data endurance performance are improved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Once write film storage
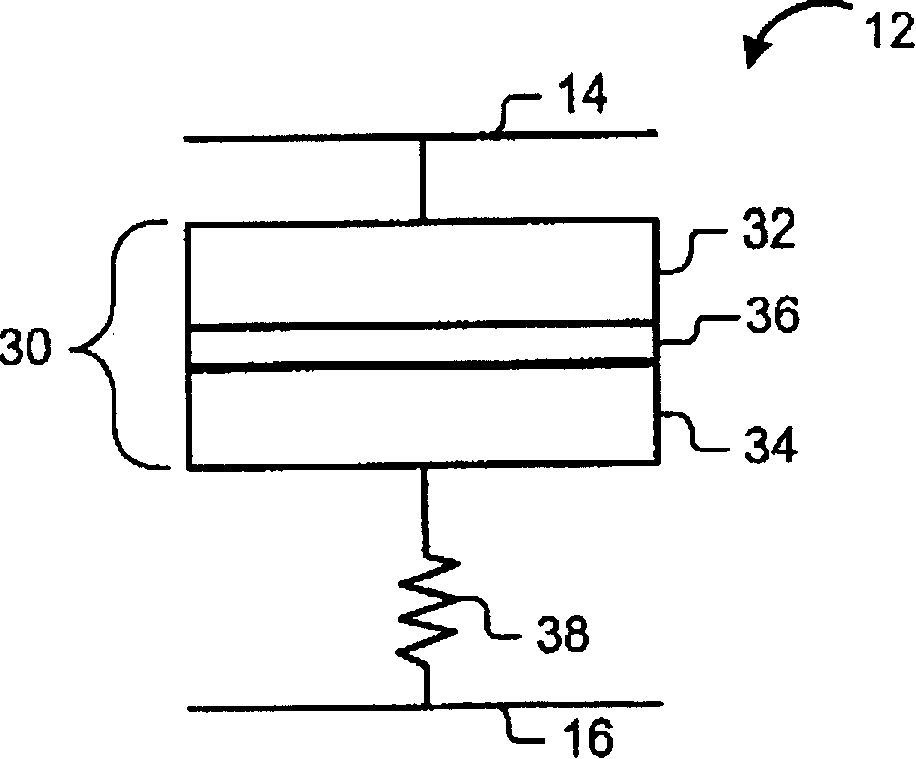
A data storage device (8, 210, 310) includes a group of memory cells (12, 110, 312) and write-once operations may be performed by damaging the thin-film barriers (36) of at least some of the memory cells (12, 110, 312). The data storage device (8, 210, 310) may be a Magnetic Random Access Memory ('MRAM') device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
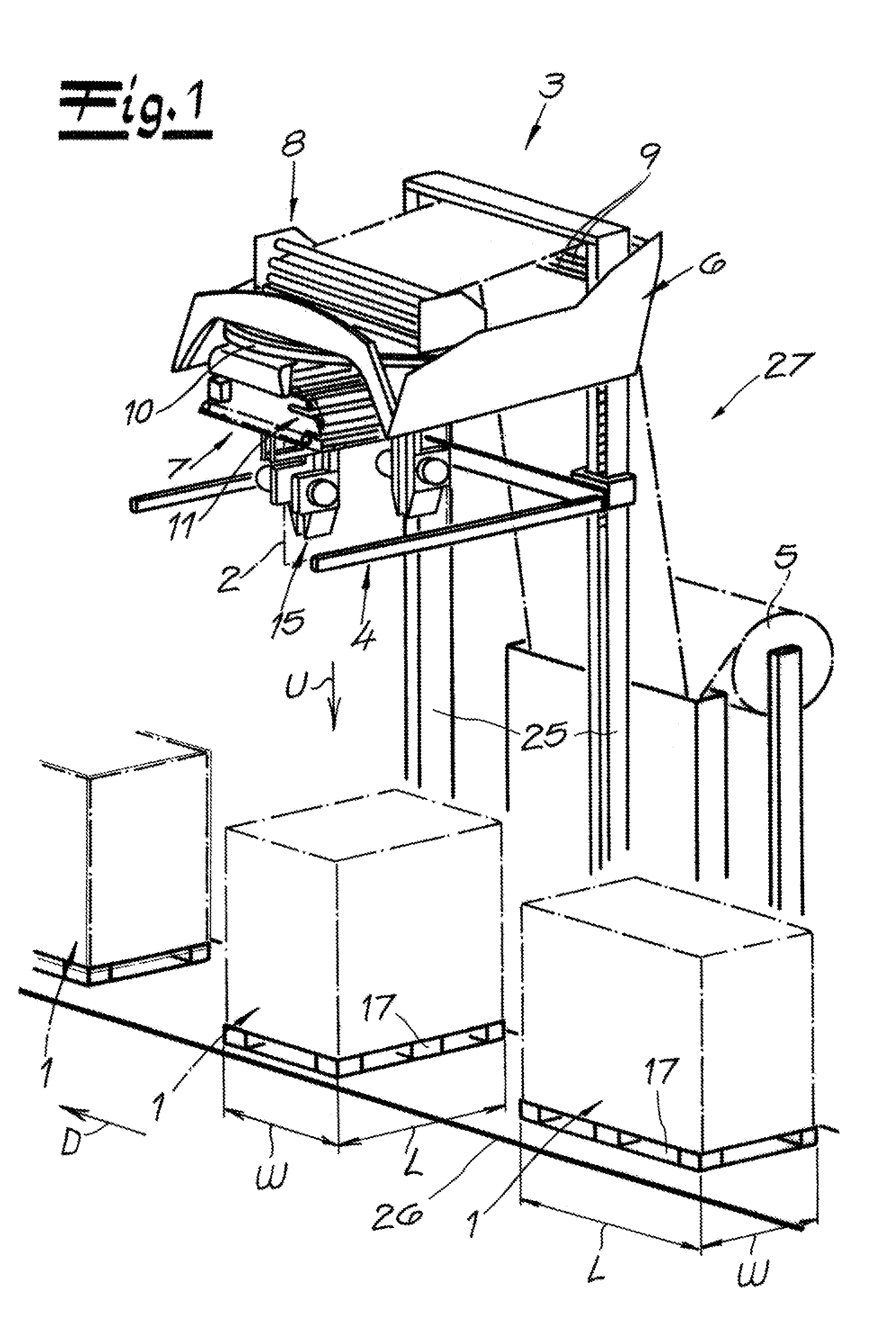
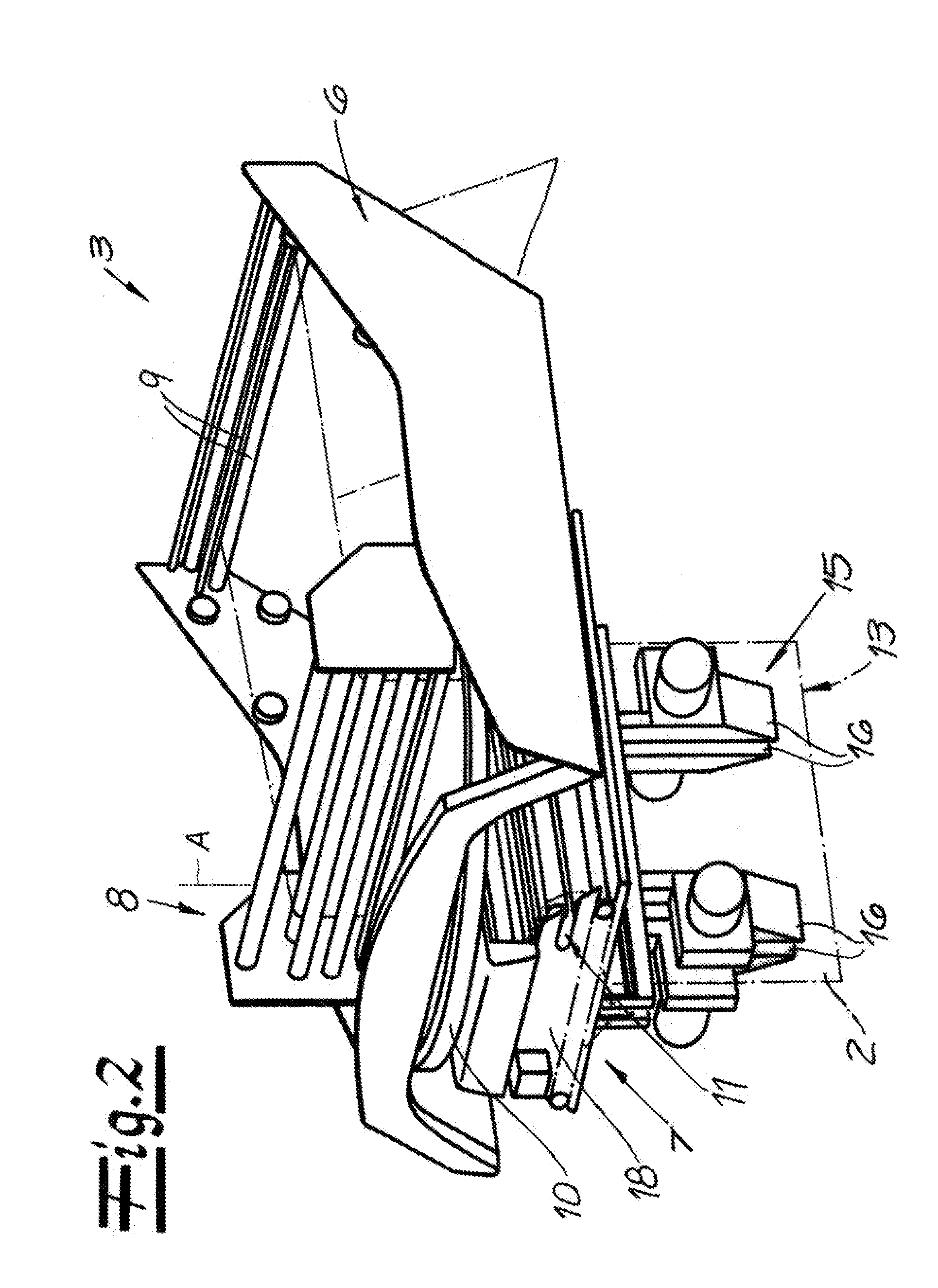
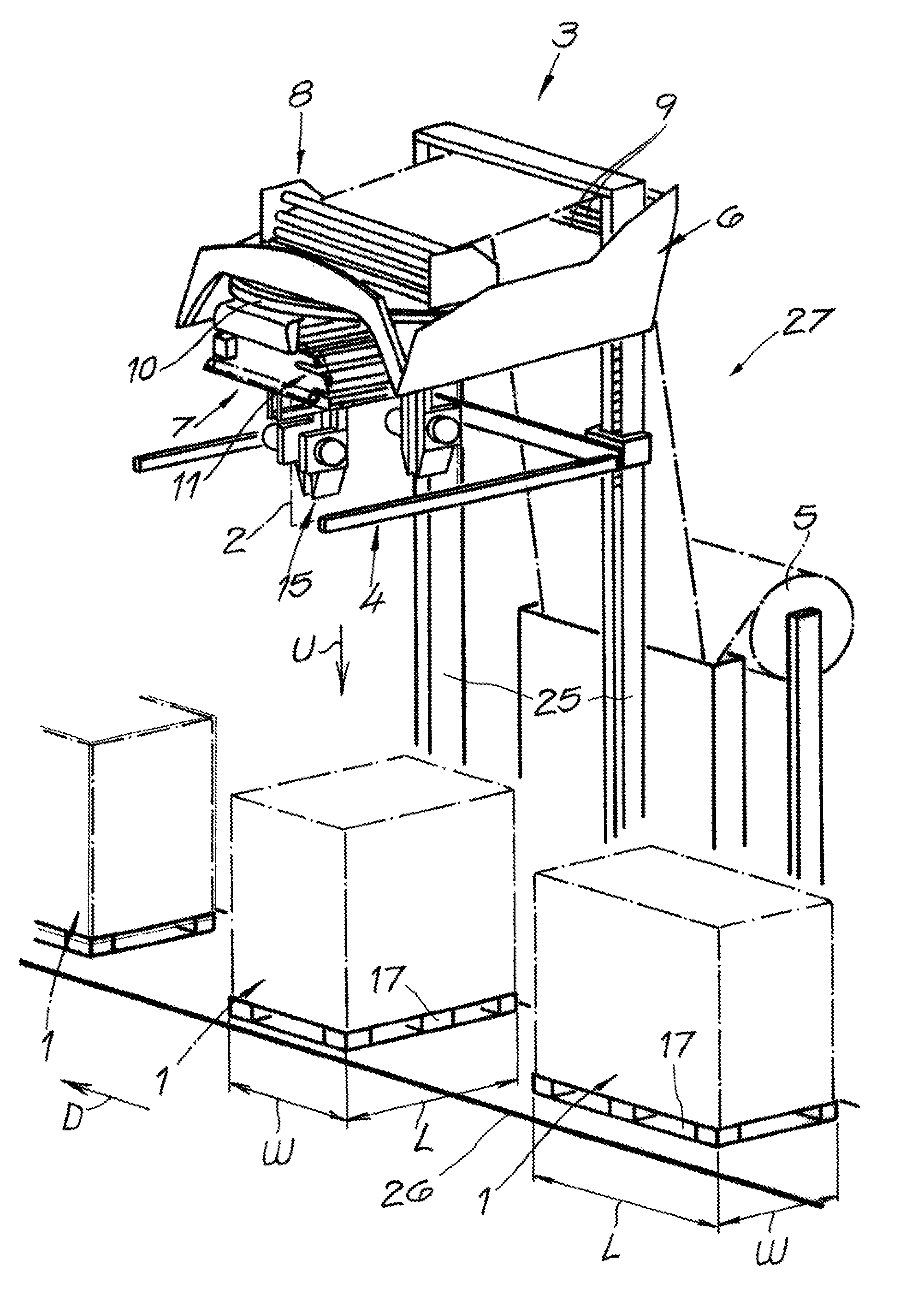
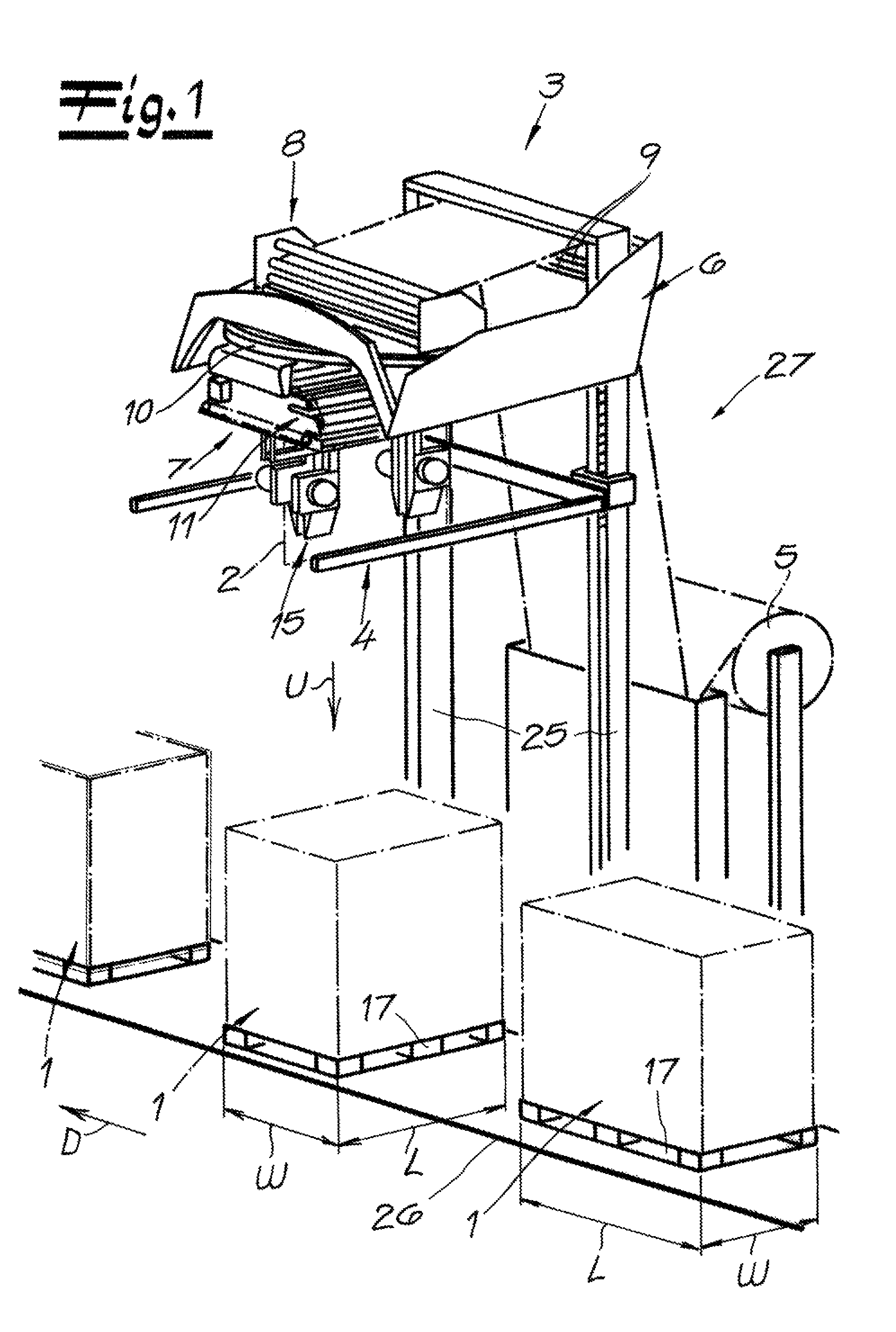
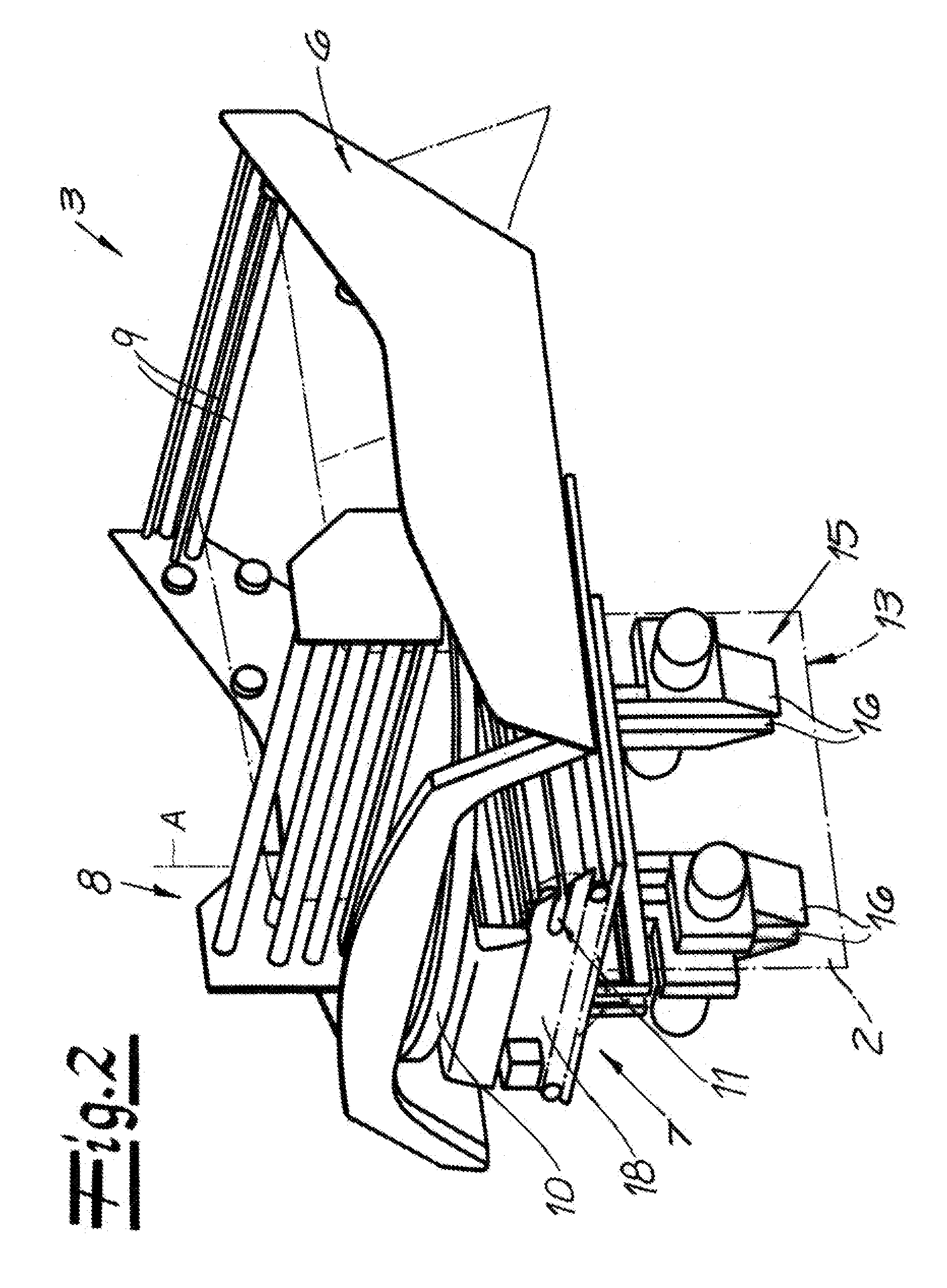
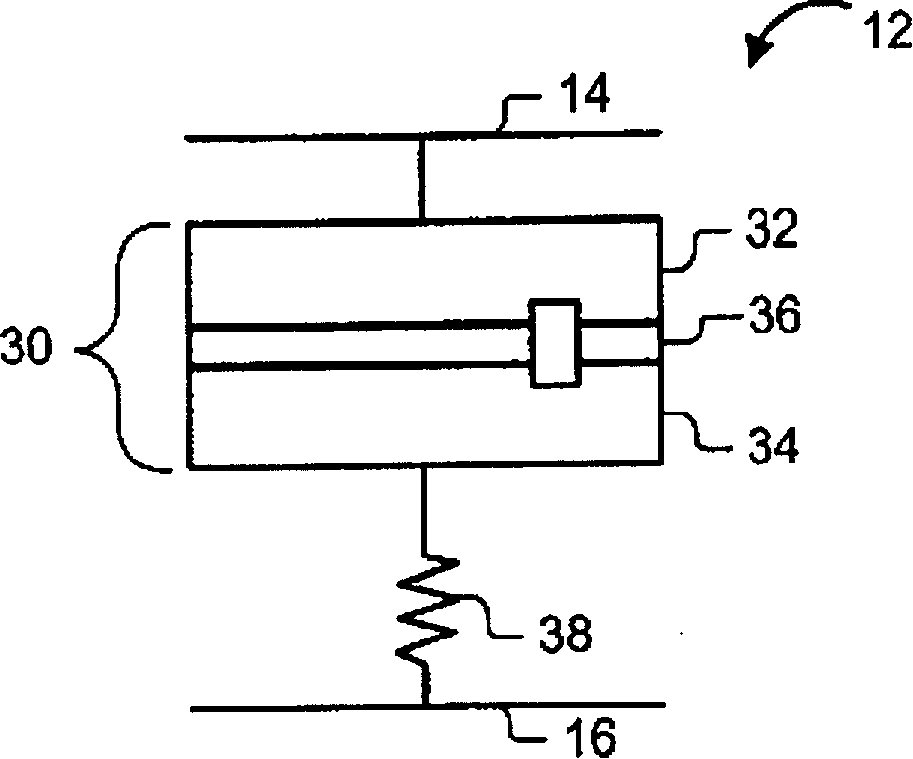
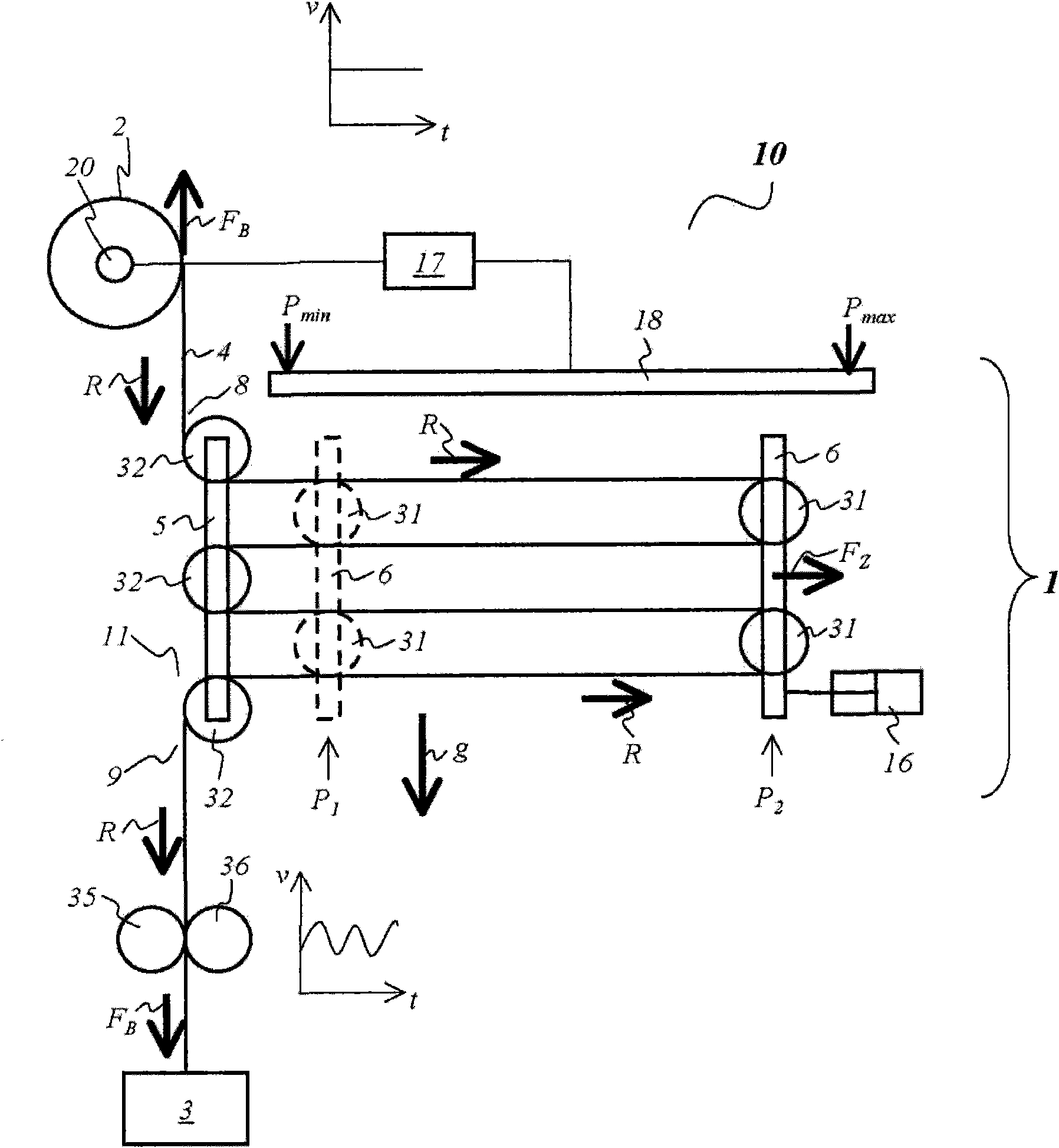
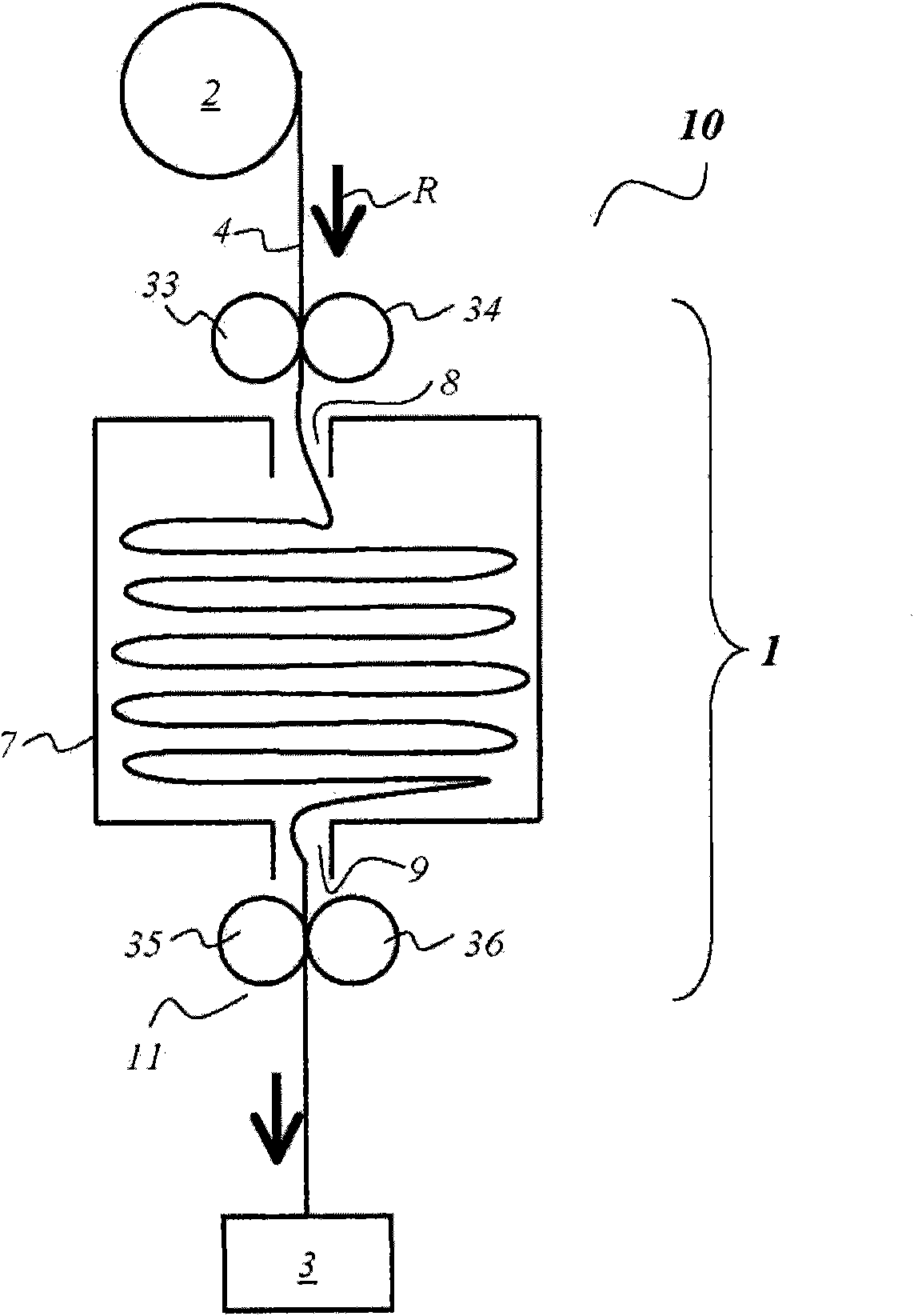
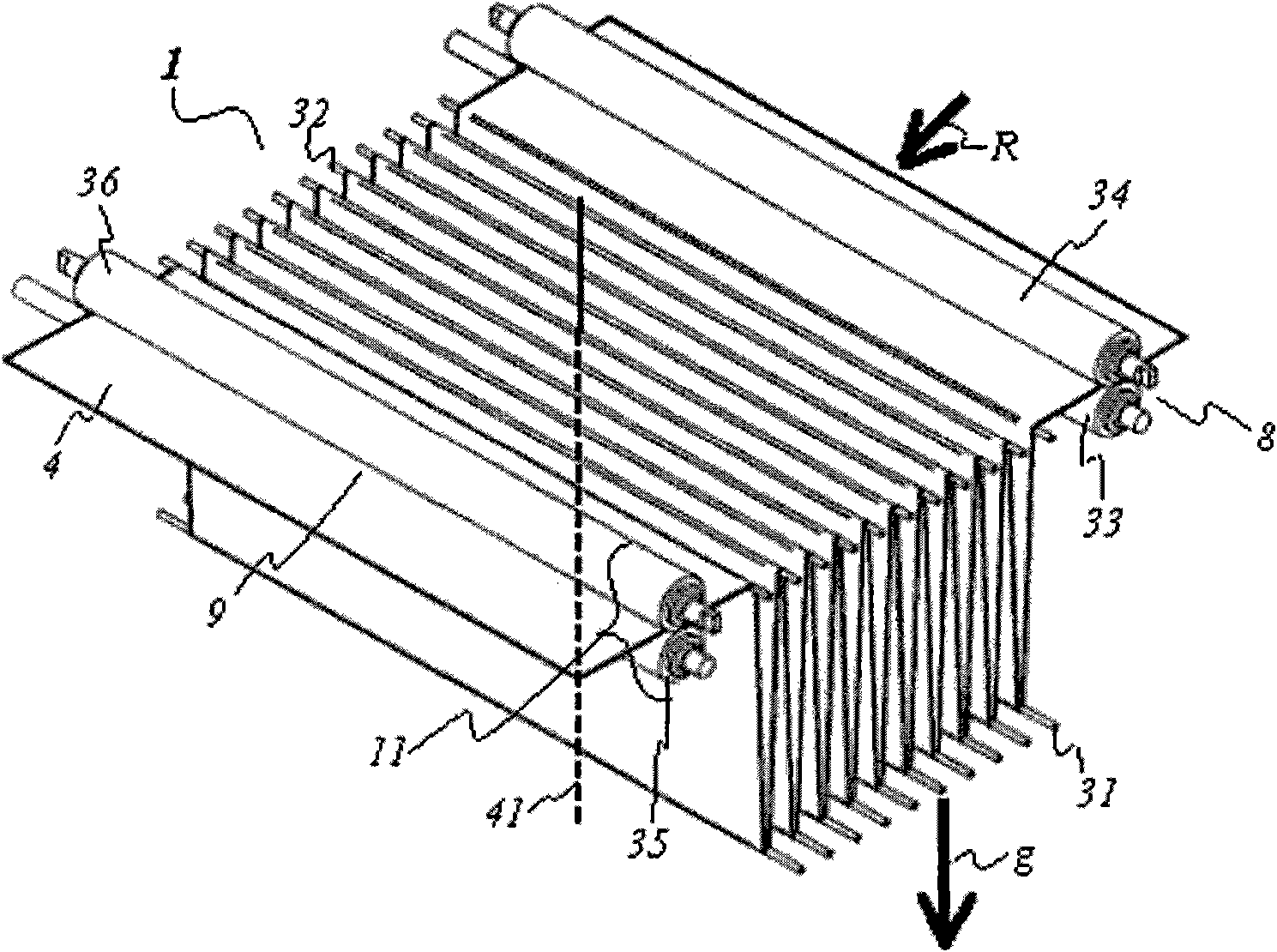
Film storage device, device and method for producing containers
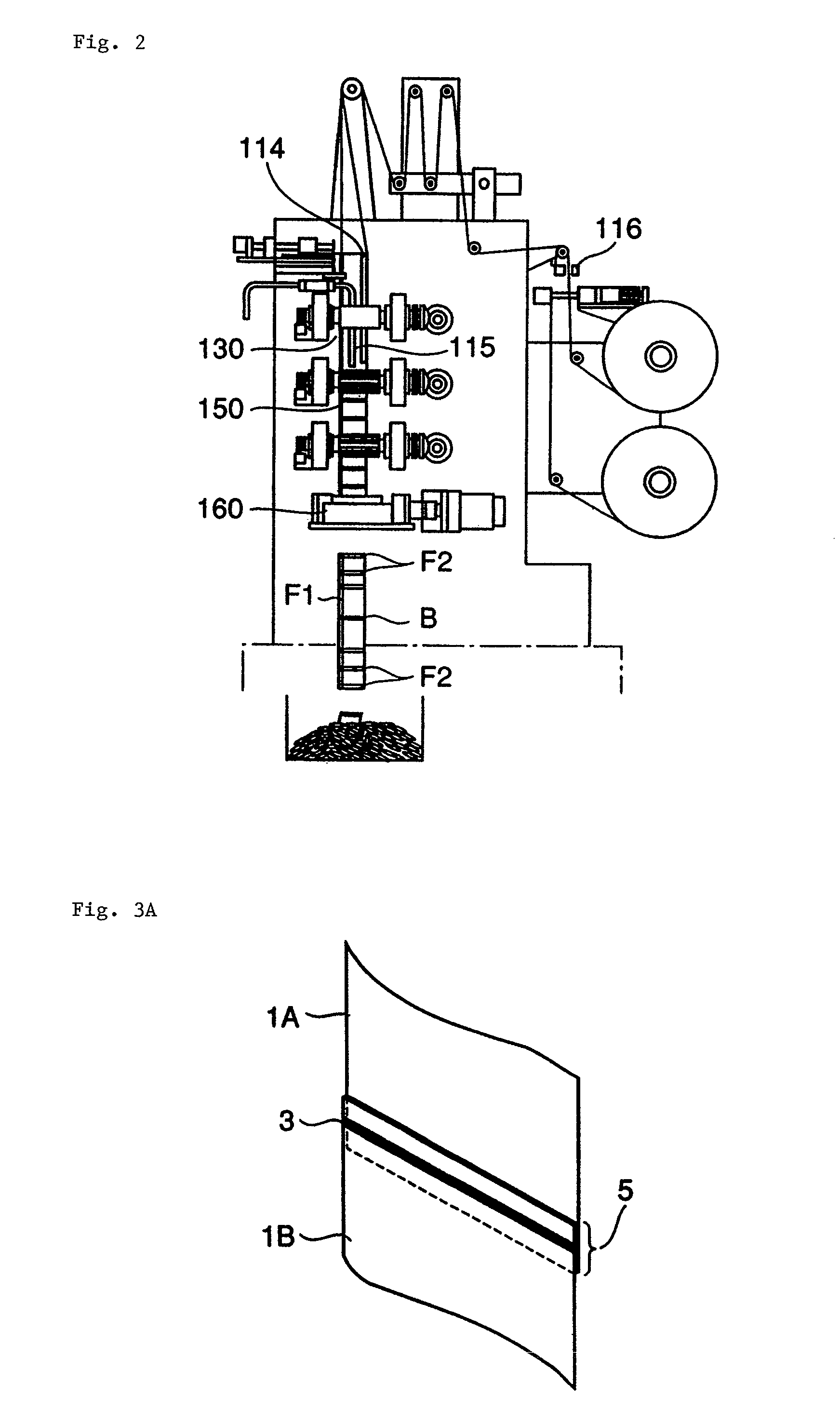
Film storage device, device and method for producing containers, the film storage device (1) is used for storing a part of a continuous foil (4), the device (10) and method are used for producing containers packaged by the continuous foil (4). The film storage device (1) has an inlet (8) assigned to drive and pressure rollers (33, 34) that are driven using adjustable rotational speed. An outlet (9) is assigned to other drive and pressure rollers (35, 36) that are driven using another adjustable rotational speed. The continuous foil (4) is guided between the drive and pressure rollers (33, 34) (35, 36). Movable foil guiding systems (5, 6, 31, 32) are arranged for adjusting an amount of part of the continuous foil (4) in cooperation with the drive and pressure rollers (33, 34) (35, 36) and gravitational force (g).
Owner:KRONES AG
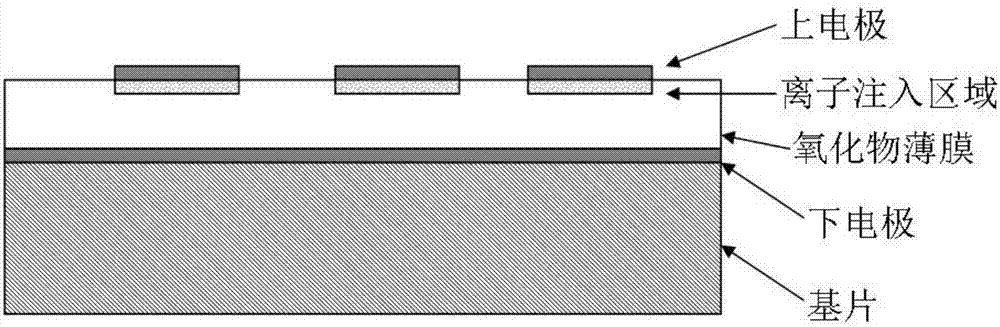
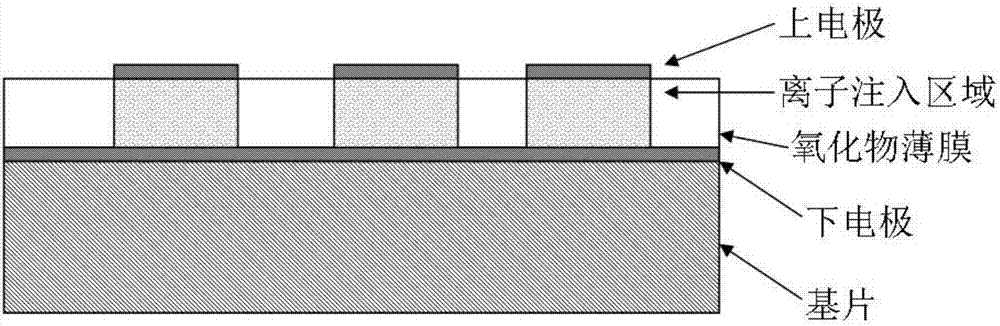
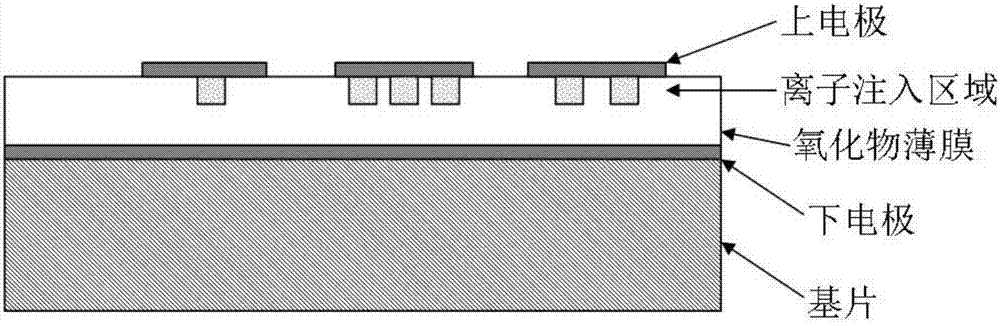
Resistive thin-film memory and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106910822AStrong process controllabilityImprove consistencyElectrical apparatusThin-film memoryControllability
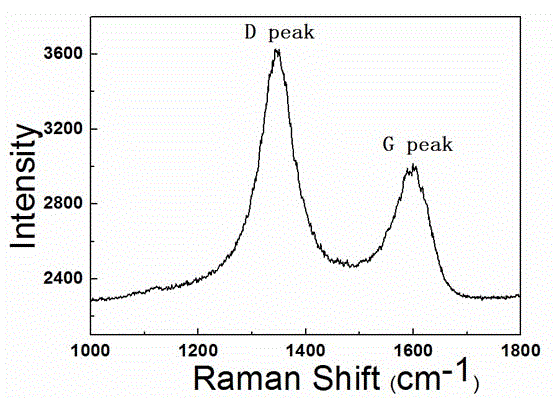
The invention belongs to the electronic thin film and component technical field and relates to a resistive thin-film memory and a preparation method thereof. According to the resistive thin-film memory and the preparation method thereof of the invention, regions of ion implantation are controlled, so that defects can be introduced into pattern regions which are consistent with photolithographic masks; the growth of a conductive filament which plays a key role in resistive behaviors is controlled in a predetermined range, so that the controllability of the resistive performance of resistive units and the consistency of the performance of different resistive units can be greatly improved; and the shape, size, number and position of the ion implantations can be controlled, so that other functions can be realized in non implantation regions. With the resistive thin-film memory and the preparation method thereof of the invention adopted, the performance of the resistive units can be well adjusted, the resistive performance of the resistive units can be improved, at the same time, the consistency of the different resistive units on the same thin film can be improved, and a conductive filament type resistive memory which is excellent in controllability performance, simple in production process and good in consistency can be prepared.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
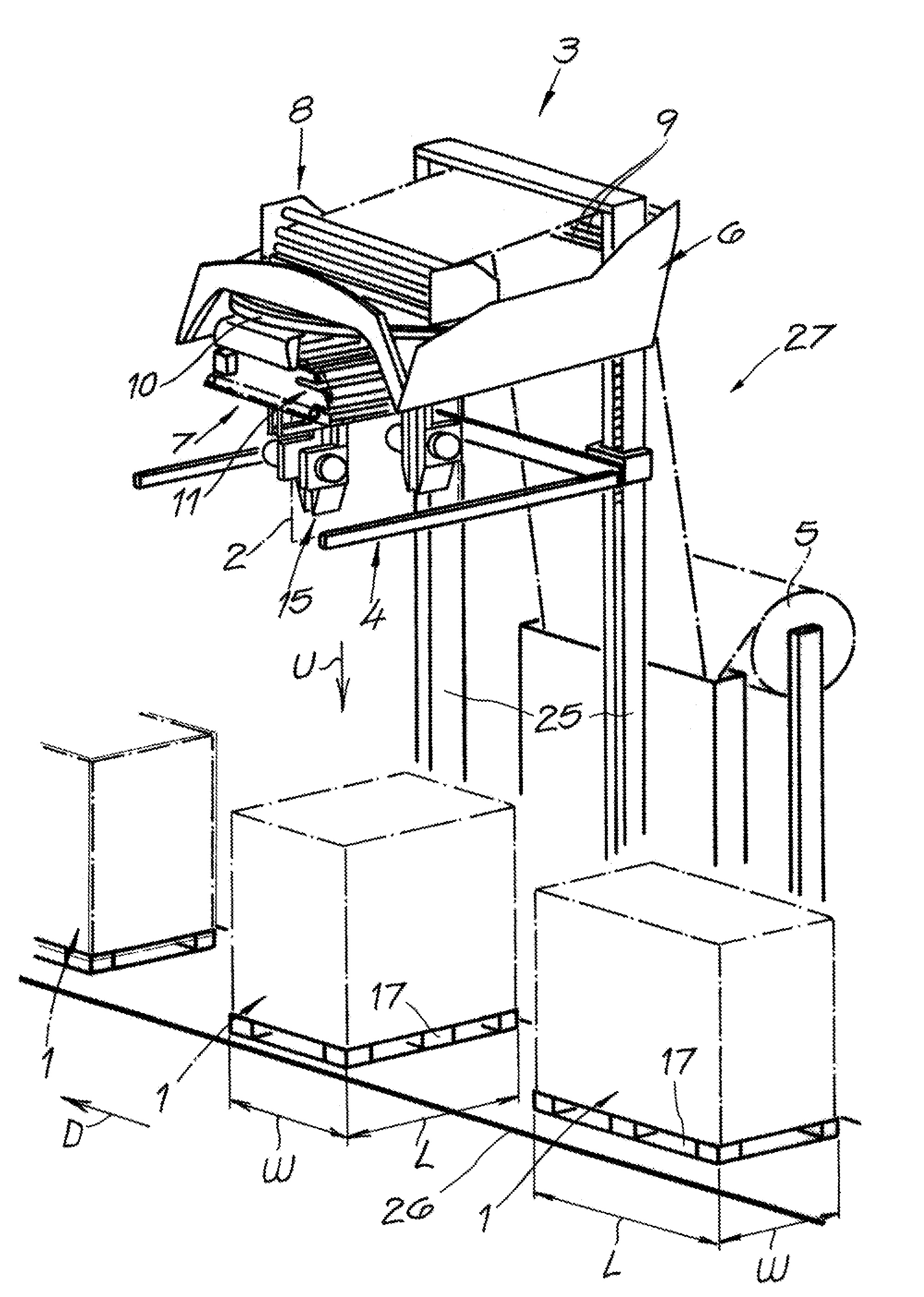
Method and apparatus for wrapping a foil around a stack of objects
ActiveUS20110258970A1Simple, less complicated, rapid, and operationally reliableSimple and less complex designPackaging cigaretteWrapper folding/bending apparatusThin-film memoryMechanical engineering
An apparatus for wrapping a film around each of a sequence of objects passing sequentially through a wrapping station has a supply of the film adjacent the station, a feed head at the station having a base, a support carried on the base and rotatable relative thereto about a vertical axis, and a feeder on the base for pulling the film off the supply and feeding it to the support. A film storer carried on the support is operable to take in and store a length of film fed to the support by the feeder. A pull-down device in the station is vertically displaceable below the feed head.
Owner:MSK VERPACKUNGS SYST GMBH
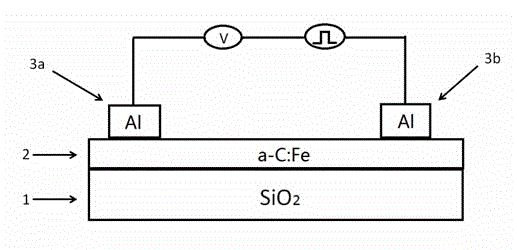
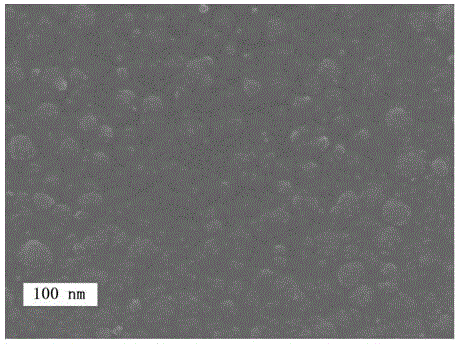
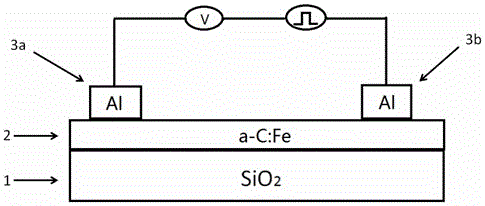
Aluminum/iron-doped amorphous carbon film/aluminum nano-thin-film memory resistor storage device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103985816ASimple structureStable structureElectrical apparatusHigh resistanceEnvironmental resistance
The invention discloses an aluminum / iron-doped amorphous carbon film / aluminum nano-thin-film memory resistor storage device and a manufacturing method thereof. According to the method, a quartz glass substrate serves as a substrate, an iron-doped amorphous carbon film is prepared through a pulsed laser deposition method, then two aluminum layers are evaporated on the amorphous carbon film through a vacuum hot evaporating method to serve as electrodes, a voltage trigger is connected, and the memory resistor storage device is prepared. Under room temperature, the memory resistor storage device is in a high resistance state or a low resistance state, the resistance switching phenomenon is extremely obvious, writing can be conducted through simple pulse voltage, and reading is achieved by detecting the resistance states. The aluminum / iron-doped amorphous carbon film / aluminum nano-thin-film memory resistor storage device has the advantages of being high in writing speed and repeatability, simple in structure, stable, resistant to vibration, concise in process, free of pollution to the environment, low in raw material price, easy to recycle and the like.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
Thin film non volatile memory device scalable to small sizes
InactiveUS7334737B2Highly repeatableHighly stableNanoinformaticsDigital storageThin-film memoryEngineering
Owner:TERECIRCUITS CORP
Large current-readout ferroelectric single-crystal thin film memory as well as method of preparing the same and method of operating the same
Disclosed is a non-destructive large current-readout ferroelectric single-crystal thin film memory as well as a method of preparing the ferroelectric memory and a method of operating the ferroelectric memory. The large current-readout ferroelectric single-crystal thin film memory comprises a ferroelectric storage layer, which is a ferroelectric single-crystal storage layer. The non-destructive readout ferroelectric memory has a greatly increased read current in an on-state, and moreover, the data retention performance and data endurance performance are improved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Energy storage device with encapsulation anchoring
InactiveUS20170301895A1Easy to anchorEasy to packFinal product manufactureCell electrodesThin-film memoryCoupling
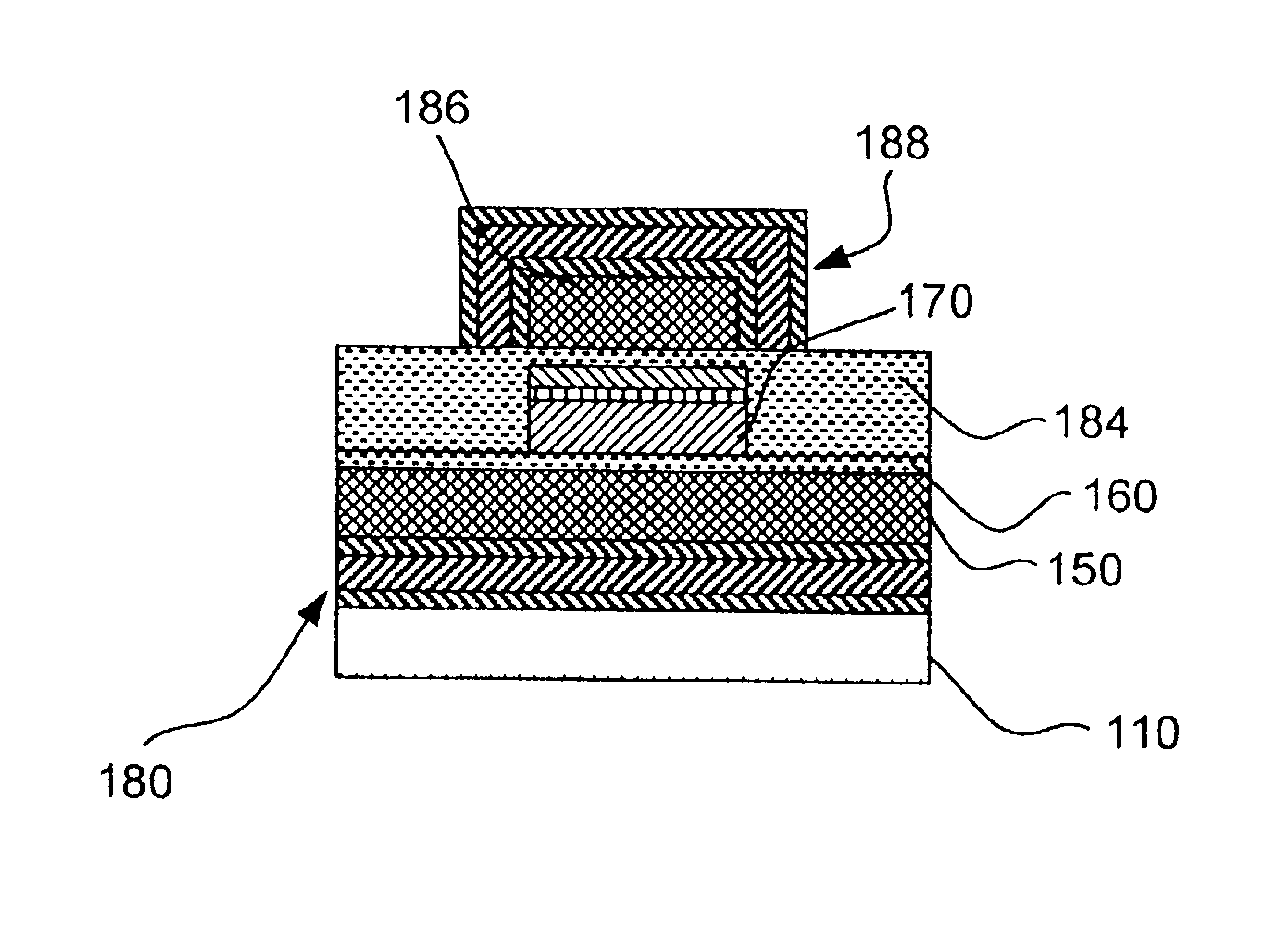
Approaches herein provide improved encapsulation of an energy storage device. In one approach, a thin film storage device stack is formed atop a first side of a substrate, and an encapsulant is formed over the thin film storage device stack. A recess formed in the substrate adjacent the thin film storage device stack provides an anchoring point for the encapsulant. In some approaches, the recess is provided partially through a depth of the substrate, and has a geometry to promote physical coupling between the encapsulant and the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Packaging apparatus
InactiveUS7934361B2Increase productivityWrapping material feeding apparatusWrapper twisting/gatheringThin-film memoryMechanical engineering
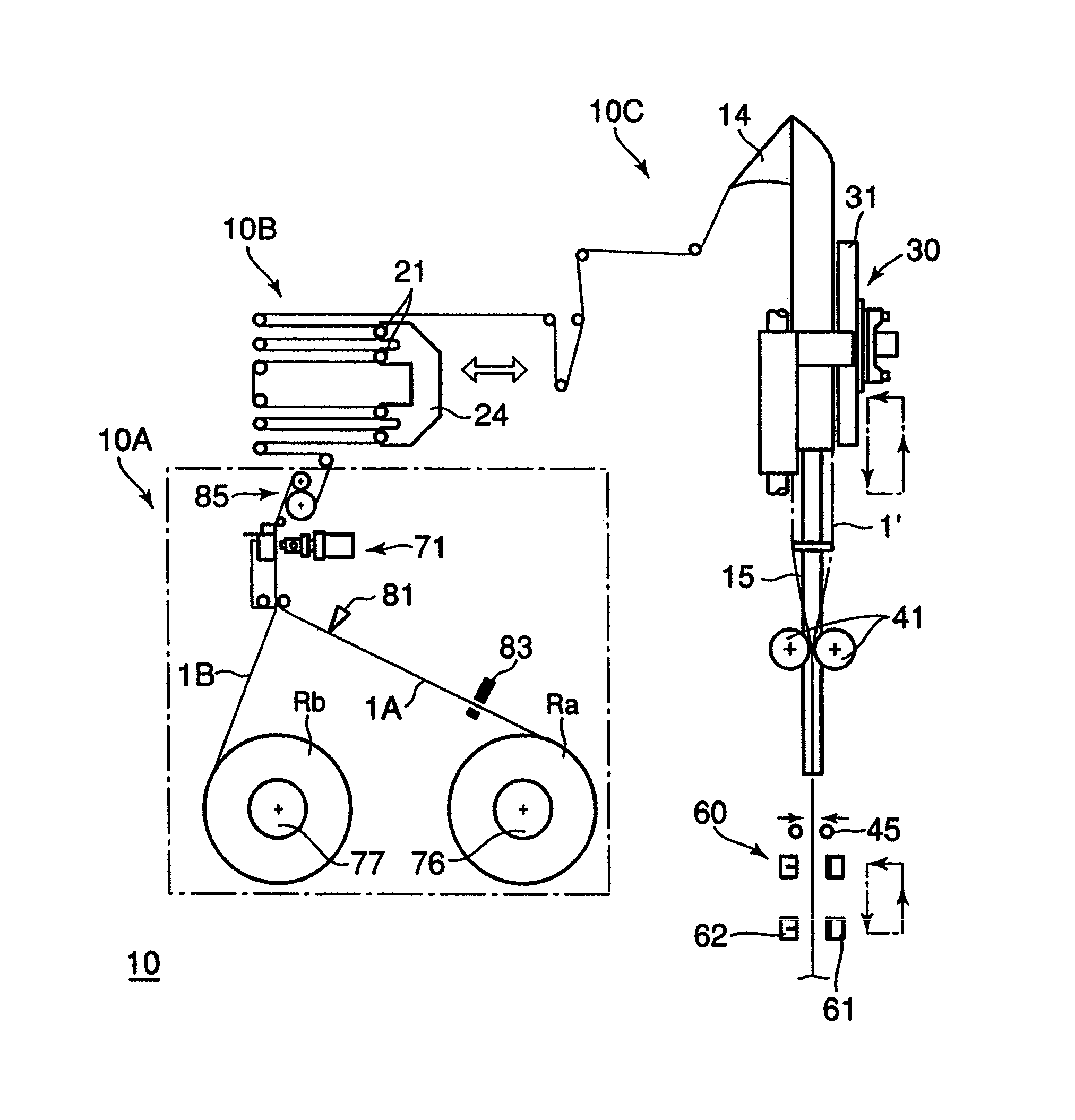
There is provided a packaging apparatus including a mechanism for joining a film from a film roll and a film from another film roll to each other. The packaging apparatus is capable of preventing a joint of the films from suffering a thermal sealing failure thereby increasing production efficiency. Package apparatus (10) includes film supply mechanism (10A) for joining and supplying films (1A, 1B) and packaging mechanism (10C) for producing package bags from the film. Film accumulator (10B) for guiding and holding the film in a meandering fashion is disposed between film supply mechanism (10A) and packaging mechanism (10C). Some of accumulating rollers (21) of film accumulator (10B) are movable to a predetermined position depending on the size of package bags to be manufactured. The length of the film from a position in which the films are joined to each other to a position in which the film is horizontally sealed is changed to prevent the joint between the films from being placed in the position in which the film is horizontally sealed.
Owner:ORIHIRO ENGINEERING CO LTD
Flexible resistive random access memory and preparation method
InactiveCN106920877AHigh mechanical strengthImprove bending strengthElectrical apparatusGraphicsThin-film memory
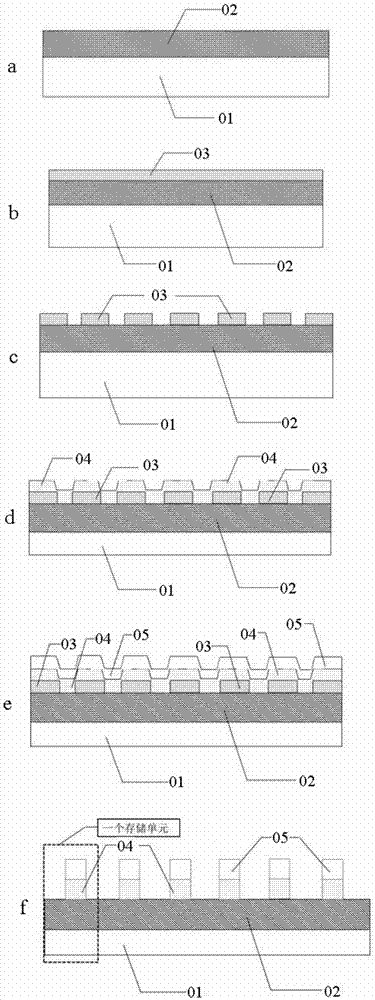
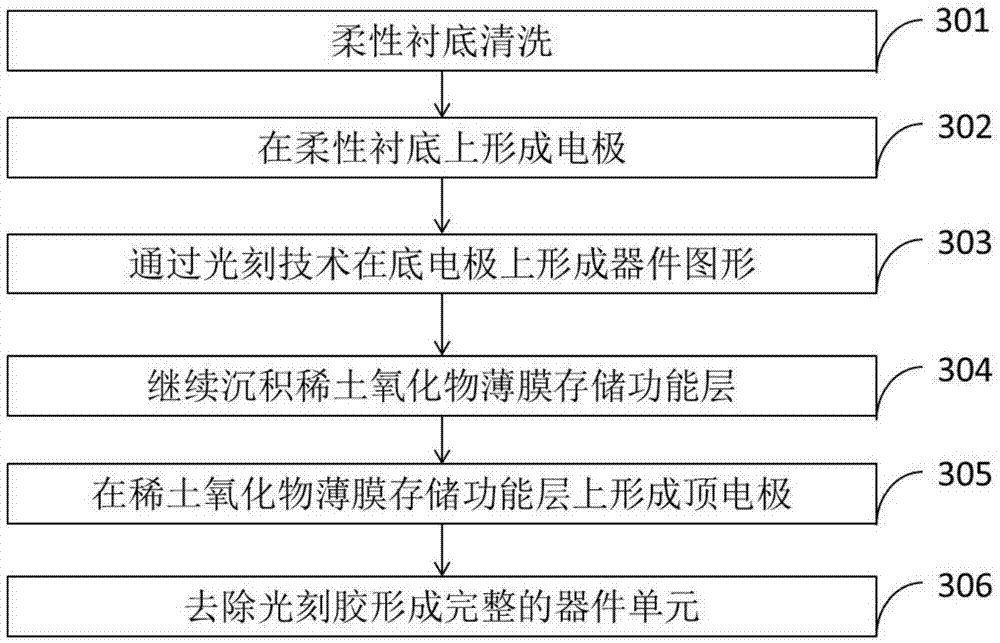
The invention discloses a flexible resistive random access memory and a preparation method. The flexible resistive random access memory comprises a bottom electrode, a memory functional layer and a top electrode which are prepared on a flexible substrate in sequence, wherein the bottom electrode, the memory functional layer and the top electrode form a sandwich structure; and the material of the memory functional layer is rare earth oxide. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) forming a bottom electrode layer on the flexible substrate; (2) forming a pattern required by the memory device on the bottom electrode through a photoetching process; (3) forming a rare earth oxide thin film memory functional layer on the pattern; (4) forming a top electrode layer on the memory functional layer; and (5) removing photoresist to form a complete device unit. The flexible resistive random access memory disclosed by the invention has the advantage of maintaining memory performance stability when the flexible resistive random access memory is bent for a certain radius and bent for multiple times, so that the flexible resistive random access memory is applicable to a flexible memory technology.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
Organic thin-film memory doped with carbon nano tubes
InactiveCN104934536AImprove performanceReduce manufacturing difficultySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricInsulation layer
The invention belongs to the field of microelectronic technologies, and particularly relates to an organic thin-film memory doped with carbon nano tubes. The memory is characterized in that silicon is taken as a substrate gate electrode, the substrate surface oxidizes to form a silicon dioxide insulation layer which acts as a gate dielectric layer, two metal electrodes, which are a source electrode and a drain electrode, are deposited on the insulation layer, a certain distance is reserved between the two electrodes, an organic thin film doped with the carbon nano tubes is deposited between the two electrodes so as to act as a conductive path, and the organic thin film is in contact with the electrodes at the two ends. Storage and erasing of data are realized through applying positive / negative voltage to the substrate (a back gate), and the stored data is read through measuring current of the source electrode and the drain electrode at zero gate voltage. The organic thin-film memory doped with the carbon nano tubes is simple in structure and easy to manufacture and integrate.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Non-volatile memory devices with thin-film and mono-crystalline silicon transistors
InactiveUS20160099355A1Efficient driveFast of stored dataTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineThin-film memory
A non-volatile memory device combines thin-film transistor-based memory cells with bulk mono-crystalline silicon transistors, which can more efficiently drive bit lines for fast sensing of the stored data in the thin-film memory cells.
Owner:SCHILTRON
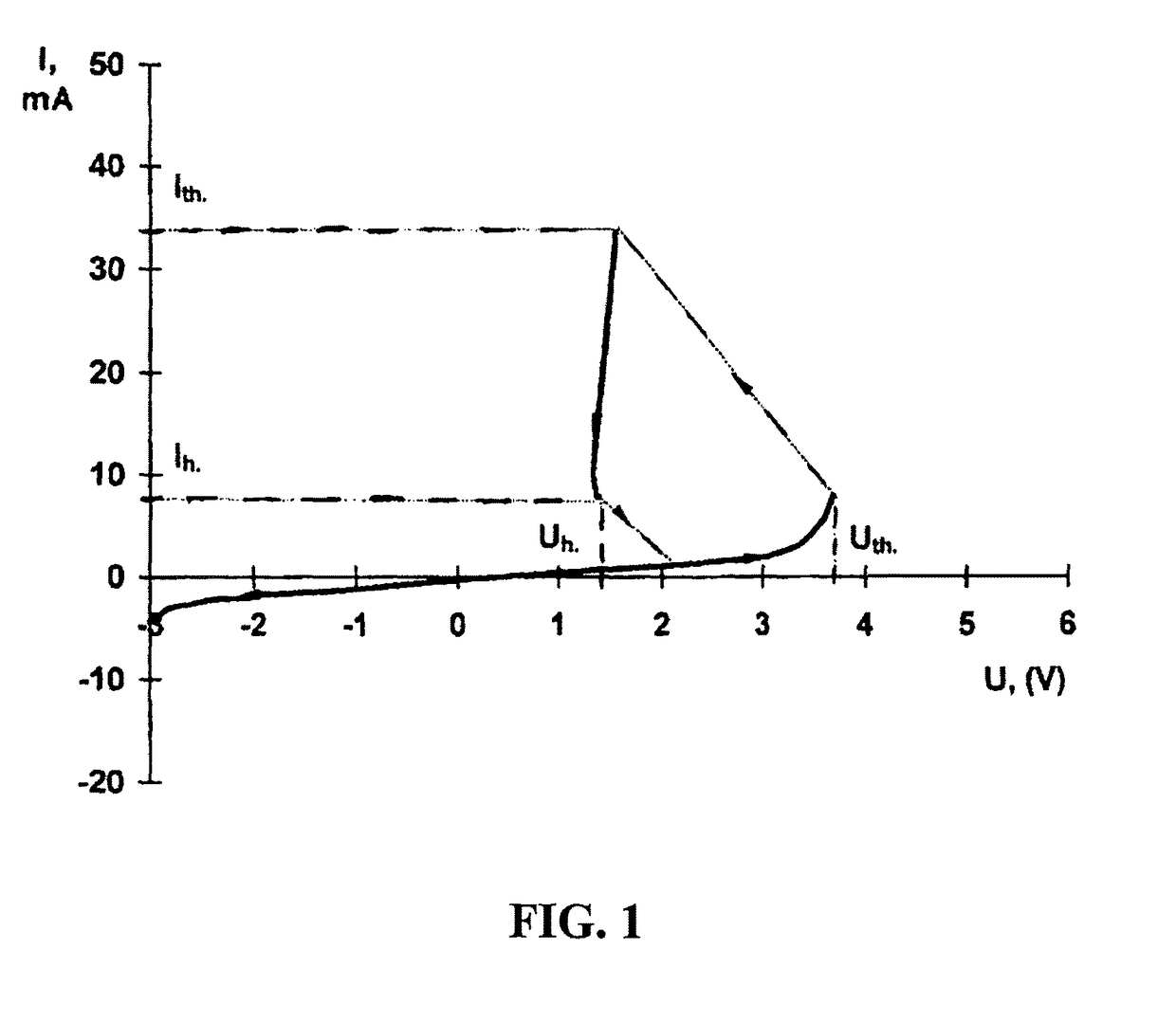
Semiconductor memory devices for use in electrically alterable read only memory (ROM) and semiconductor thin film devices (spintrons and spin-orbitrons)
ActiveUS9865811B2Improve superconductivityImproved Impedance StabilityElectrical apparatusDielectricHigh resistance
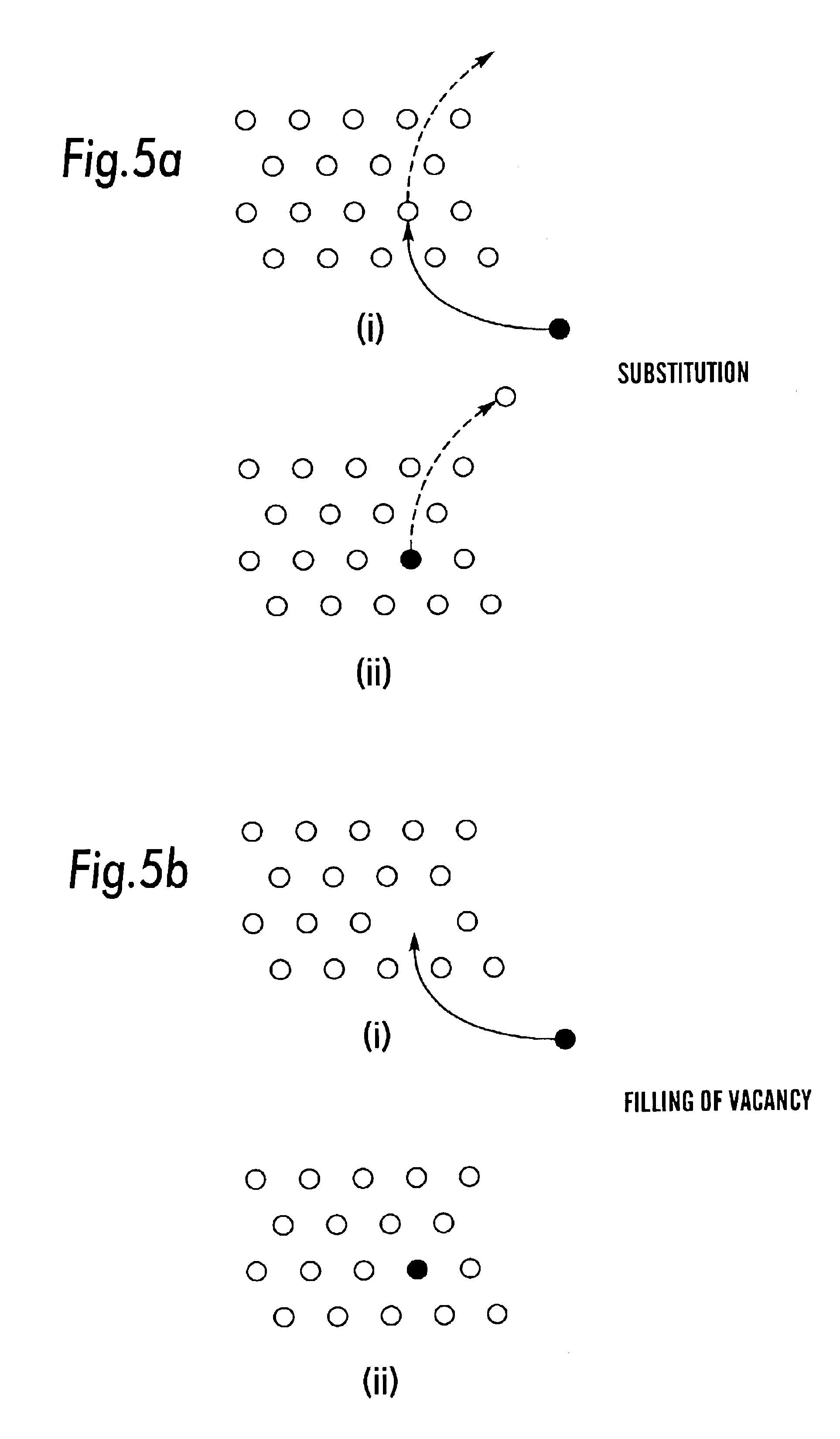
An electrically alterable thin film memory device or non-volatile trigger which can be switched from a high resistance state to a low resistance state. The device increases the concentration of electrically active impurities at correspondent electrodes to which respect impurities would electro migrate during a large number of set-reset cycles. The device comprises a layered structure with memory layers formed on an interface of two regions as the result of the mutual mixing and migration of their constituents. One region contains an electrically active donor impurity. A thin layer of dielectric is placed in the other region. Each of the memory layers includes an interface of chalcogenide films.
Owner:TROYAN EUGENIY
Method to fabricate a thin film non volatile memory device scalable to small sizes
InactiveUS7335551B2Highly repeatableHighly stableSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing technologyThin-film memory
Owner:TERECIRCUITS CORP
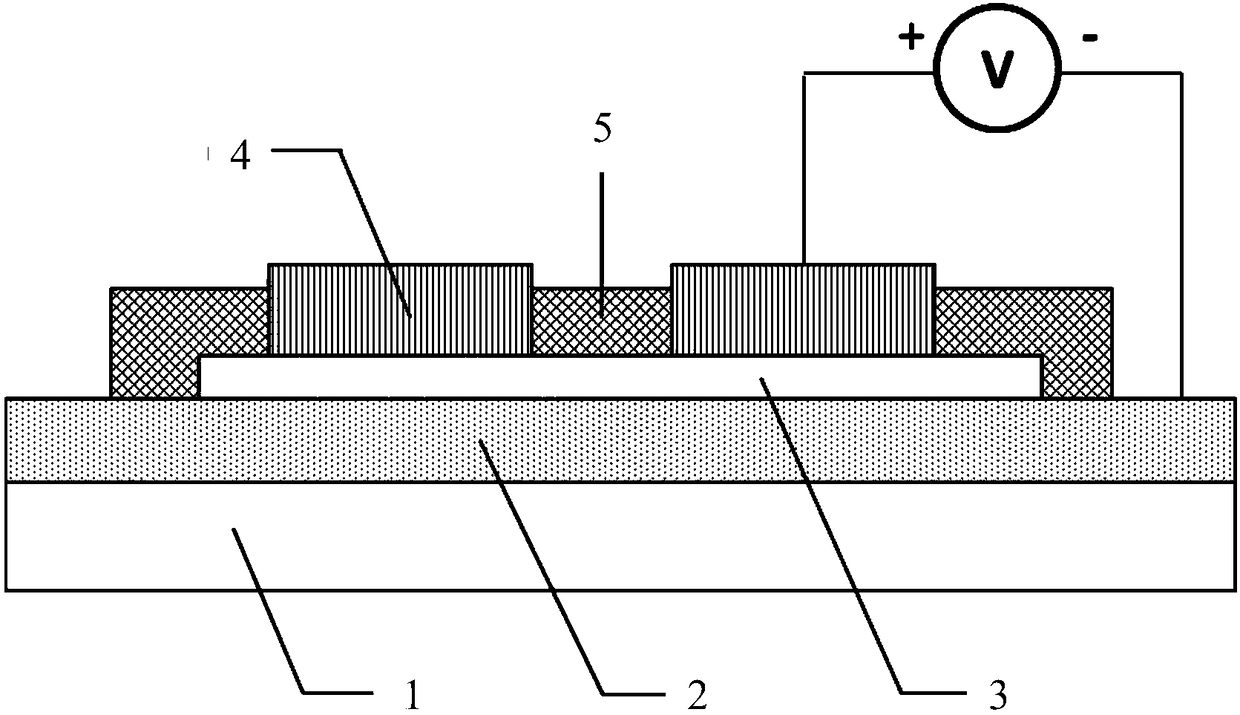
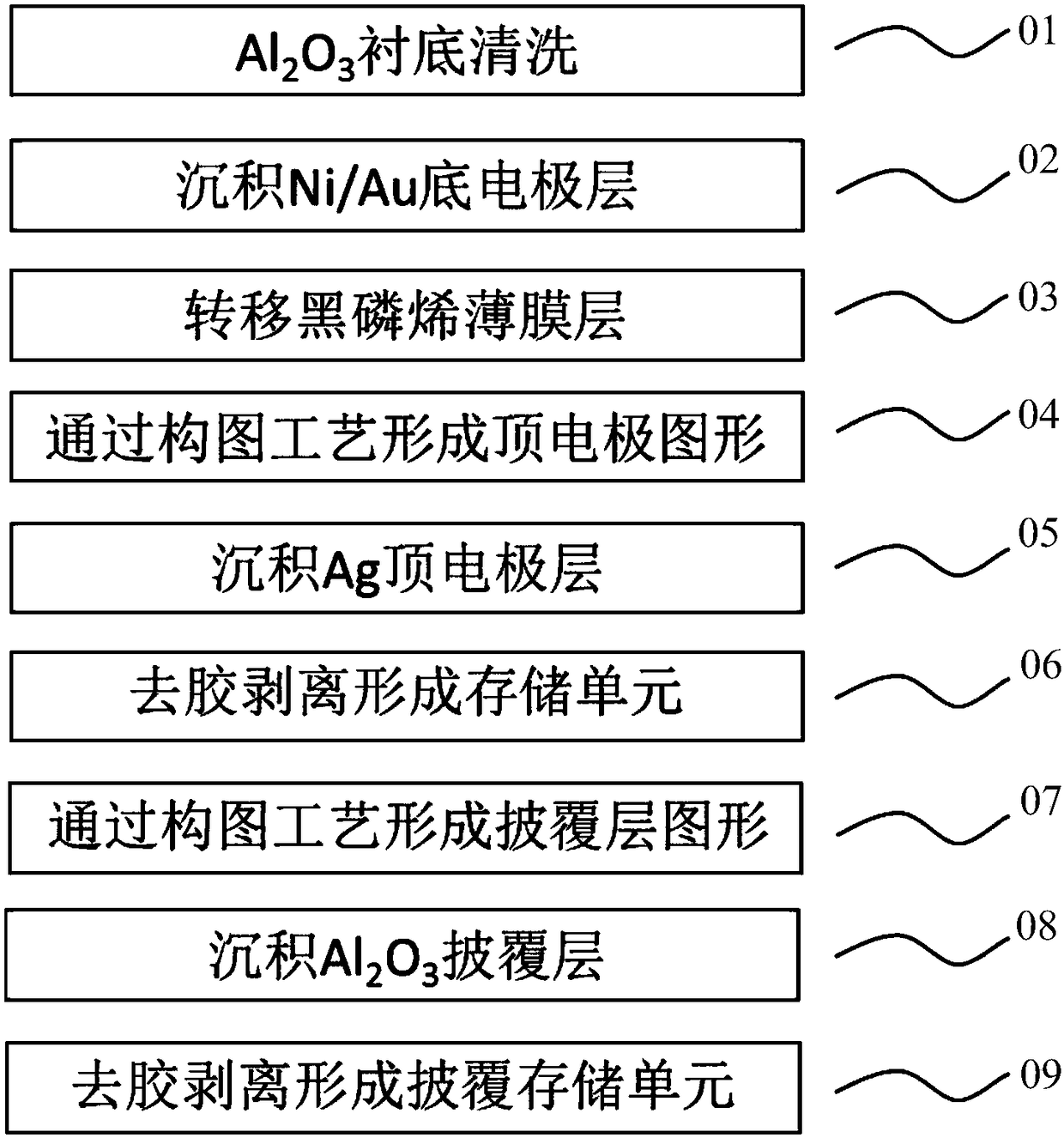
Black phosphorene film memory and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106783854AFast transitionStable reading and writing voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesThin-film memoryComposition process
The present invention relates to a black phosphorene film memory and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the black phosphorene film memory comprises the following steps: (1) cleaning a substrate; (2) forming a bottom electrode on the substrate; (3) forming the black phosphorene film layer on the bottom electrode; (4) forming the graph of a top electrode on the black phosphorene film layer through a composition process; (5) forming the top electrode on the black phosphorene film layer, and obtaining a memory unit; (6) forming the graph of a cladding layer at the upper side of the memory unit through the composition process; and (7) finally forming the cladding layer to allow the cladding layer to coat the part of the black phosphorene film layer without being coated with the top electrode, and obtaining the memory. The black phosphorene film memory is rapid in the transforming speed and stable in read-write voltage.
Owner:GRIMAT ENG INST CO LTD
A kind of aluminum/iron-doped amorphous carbon film/aluminum nano film memristor storage device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103985816BRealize switchingResistive switching phenomenon is obviousElectrical apparatusHigh resistanceEnvironmental resistance
The invention discloses an aluminum / iron-doped amorphous carbon film / aluminum nano-thin-film memory resistor storage device and a manufacturing method thereof. According to the method, a quartz glass substrate serves as a substrate, an iron-doped amorphous carbon film is prepared through a pulsed laser deposition method, then two aluminum layers are evaporated on the amorphous carbon film through a vacuum hot evaporating method to serve as electrodes, a voltage trigger is connected, and the memory resistor storage device is prepared. Under room temperature, the memory resistor storage device is in a high resistance state or a low resistance state, the resistance switching phenomenon is extremely obvious, writing can be conducted through simple pulse voltage, and reading is achieved by detecting the resistance states. The aluminum / iron-doped amorphous carbon film / aluminum nano-thin-film memory resistor storage device has the advantages of being high in writing speed and repeatability, simple in structure, stable, resistant to vibration, concise in process, free of pollution to the environment, low in raw material price, easy to recycle and the like.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
Method and apparatus for wrapping a foil around a stack of objects
ActiveUS9126703B2Simple, less complicated, rapid, and operationally reliableSimple and less complex designPackaging cigaretteWrapper folding/bending apparatusThin-film memoryEngineering
An apparatus for wrapping a film around each of a sequence of objects passing sequentially through a wrapping station has a supply of the film adjacent the station, a feed head at the station having a base, a support carried on the base and rotatable relative thereto about a vertical axis, and a feeder on the base for pulling the film off the supply and feeding it to the support. A film storer carried on the support is operable to take in and store a length of film fed to the support by the feeder. A pull-down device in the station is vertically displaceable below the feed head.
Owner:MSK VERPACKUNGS SYST GMBH
A kind of black phosphorene thin film memory and its preparation method
ActiveCN106783854BFast transitionStable reading and writing voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesThin-film memoryComposition process
The present invention relates to a black phosphorene film memory and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the black phosphorene film memory comprises the following steps: (1) cleaning a substrate; (2) forming a bottom electrode on the substrate; (3) forming the black phosphorene film layer on the bottom electrode; (4) forming the graph of a top electrode on the black phosphorene film layer through a composition process; (5) forming the top electrode on the black phosphorene film layer, and obtaining a memory unit; (6) forming the graph of a cladding layer at the upper side of the memory unit through the composition process; and (7) finally forming the cladding layer to allow the cladding layer to coat the part of the black phosphorene film layer without being coated with the top electrode, and obtaining the memory. The black phosphorene film memory is rapid in the transforming speed and stable in read-write voltage.
Owner:GRIMAT ENG INST CO LTD
Method of forming a one-time-programming (OTP) bit
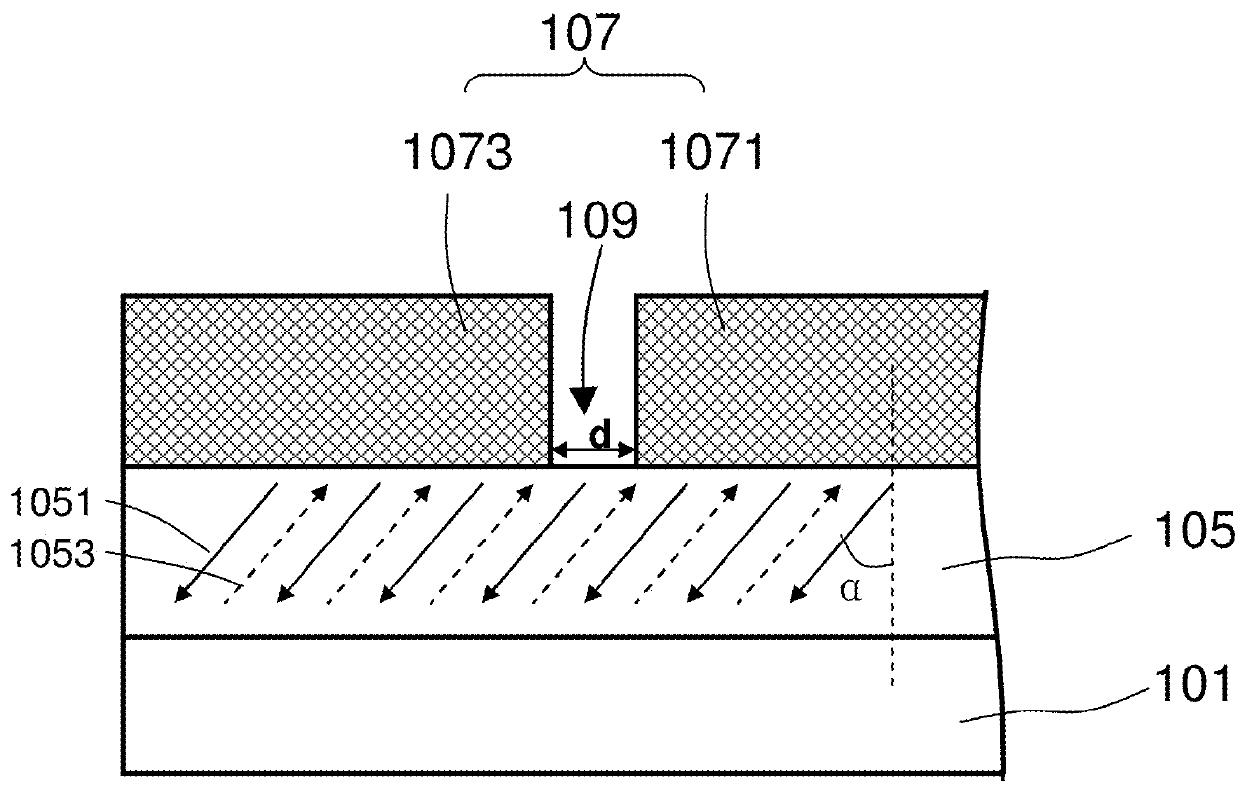
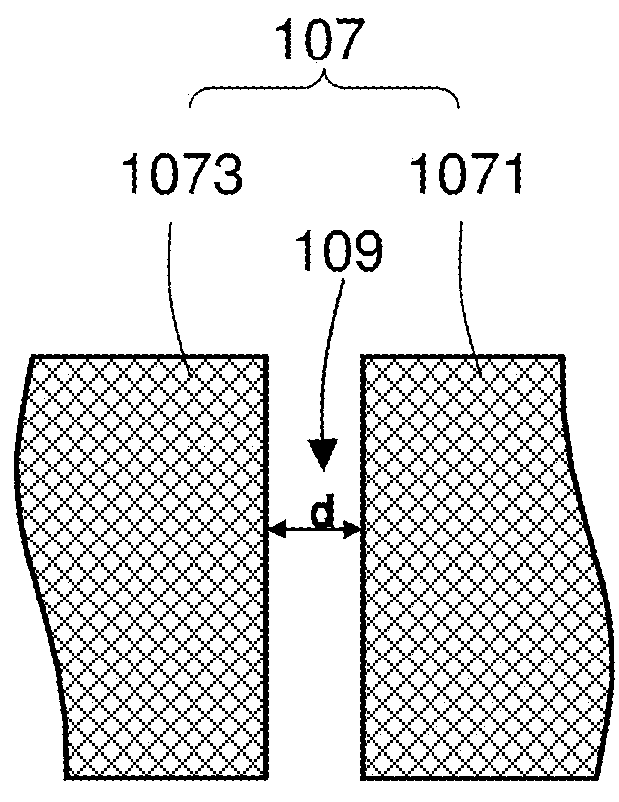
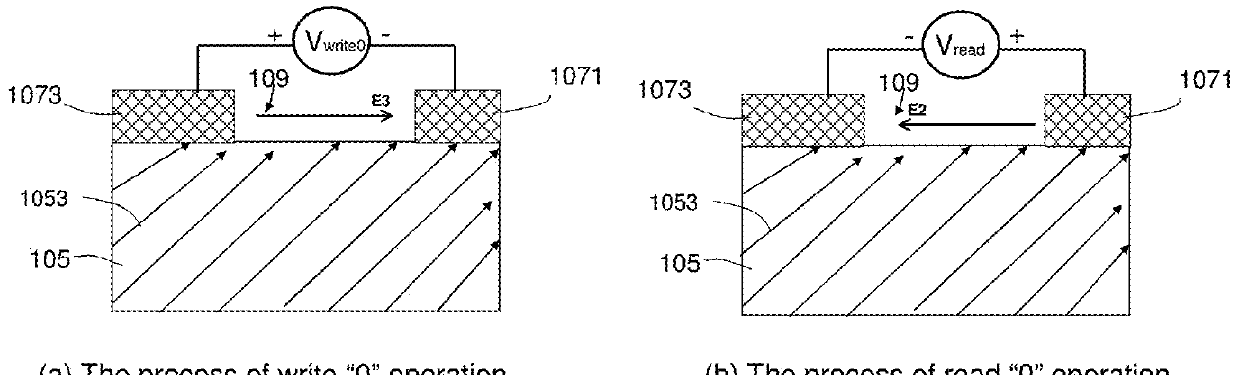
ActiveCN113724769AFix known issuesLow breakdown voltageMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesComputer architectureThin-film memory
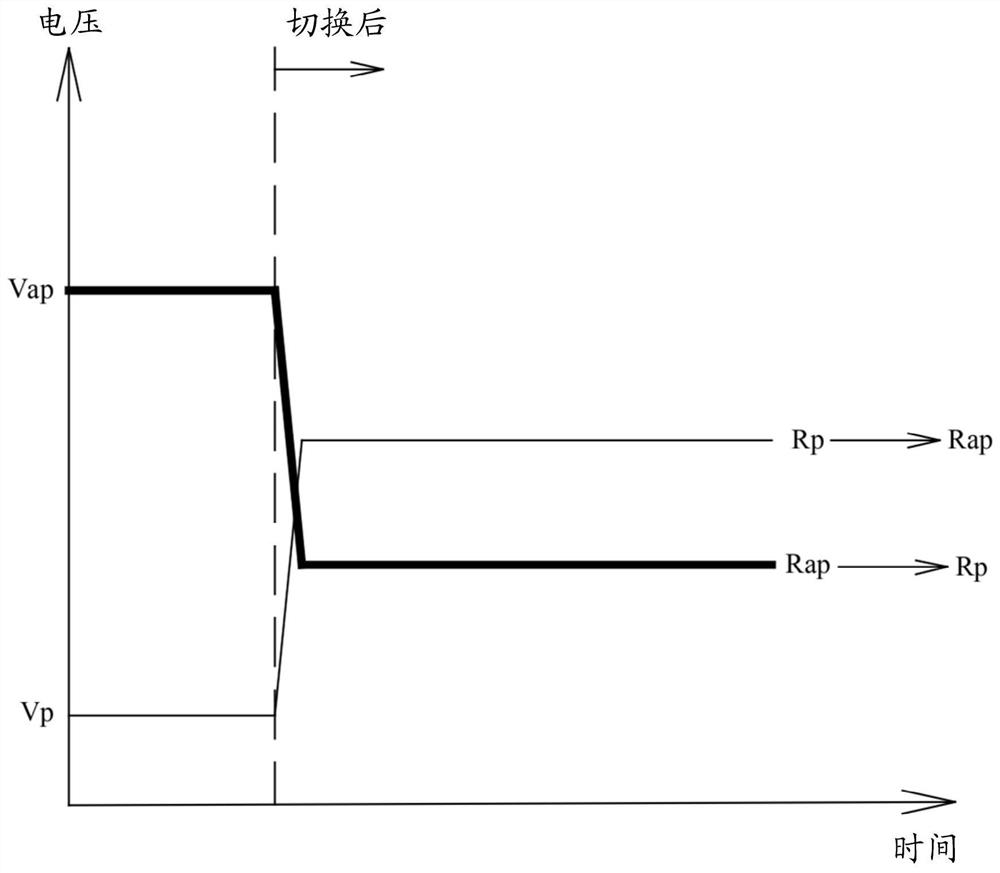
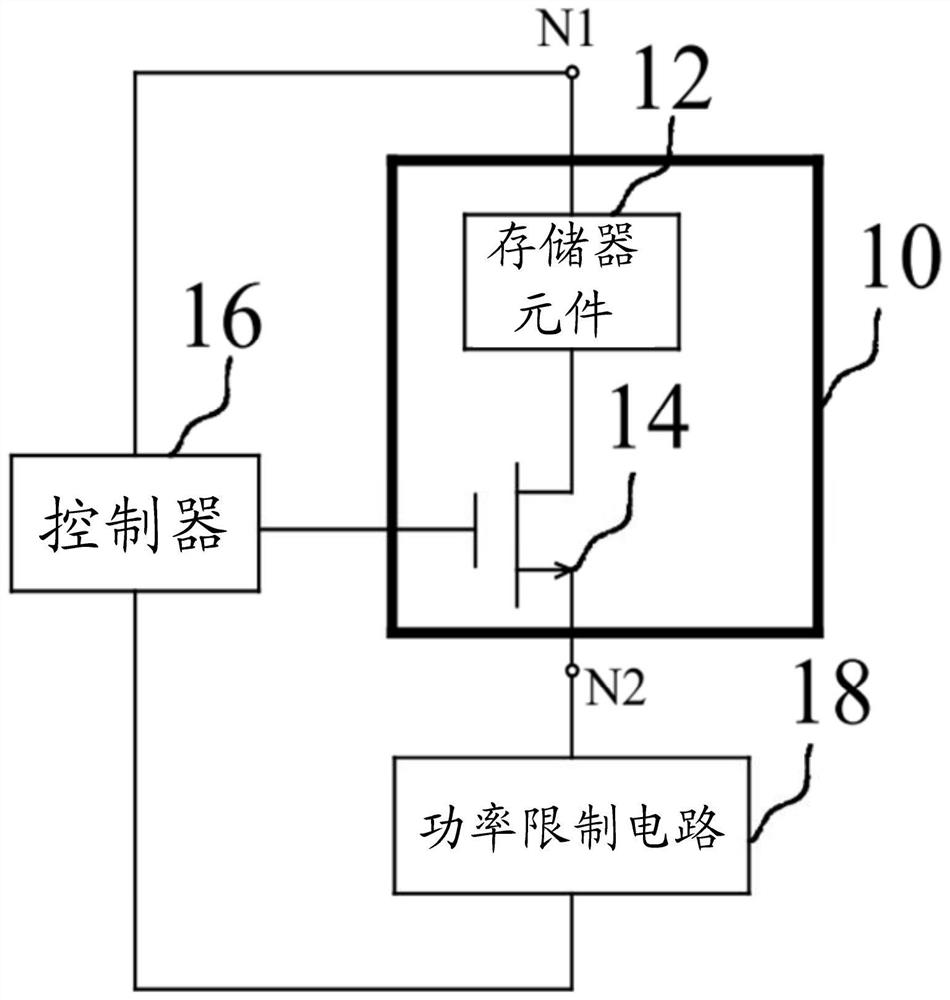
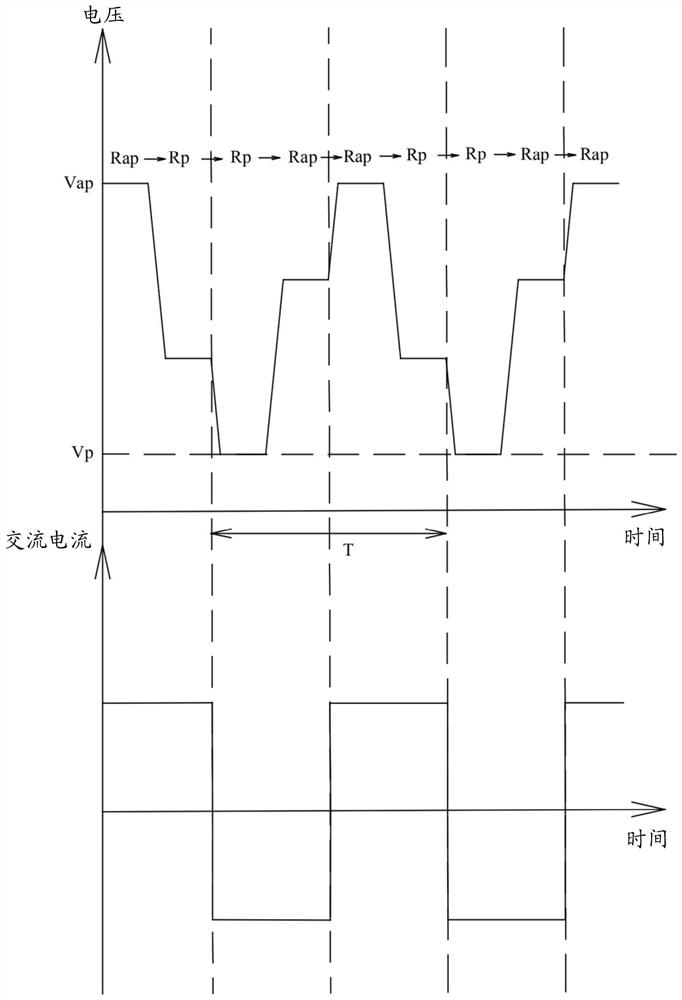
Disclosed is a method of forming a one-time-programming (OTP) bit. In the method of forming a one-time-programming (OTP) bit, a thin-film memory device is provided, which includes at least one memory element and a transistor, and the memory element is coupled to the transistor in series. Then, an alternating current is applied to the memory element and the transistor, the power applied to the memory element is constrained, and the transistor is turned on to change the resistance of the memory element for a plurality of cycles of the alternating current until the resistance of the memory element is irreversibly changed.
Owner:NS POLES TECH CORP
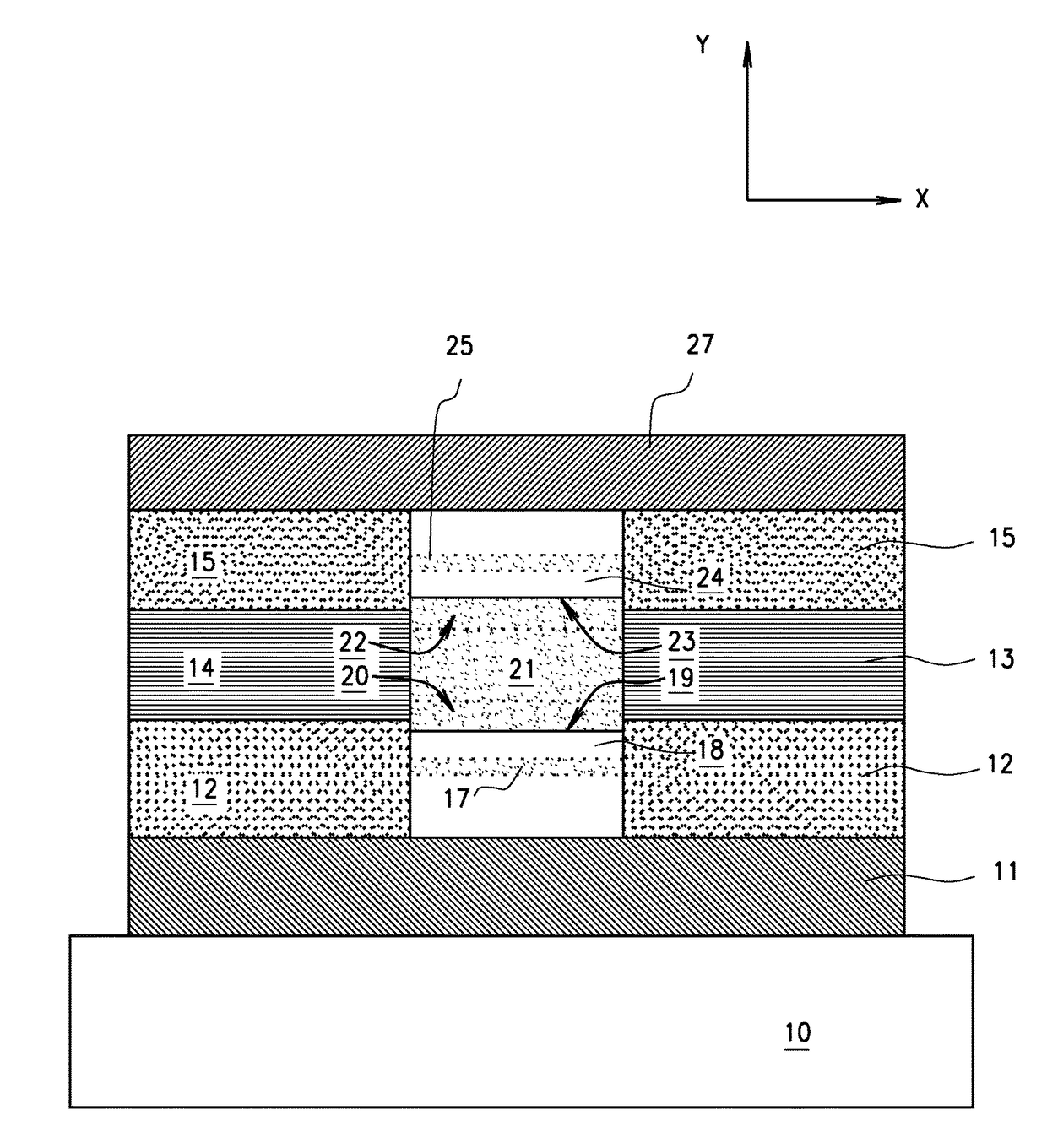
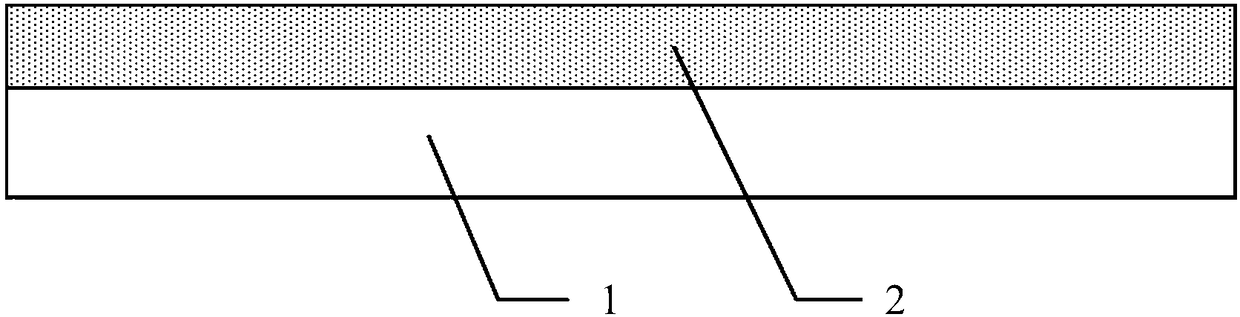
Thin film memory device having a variable resistance
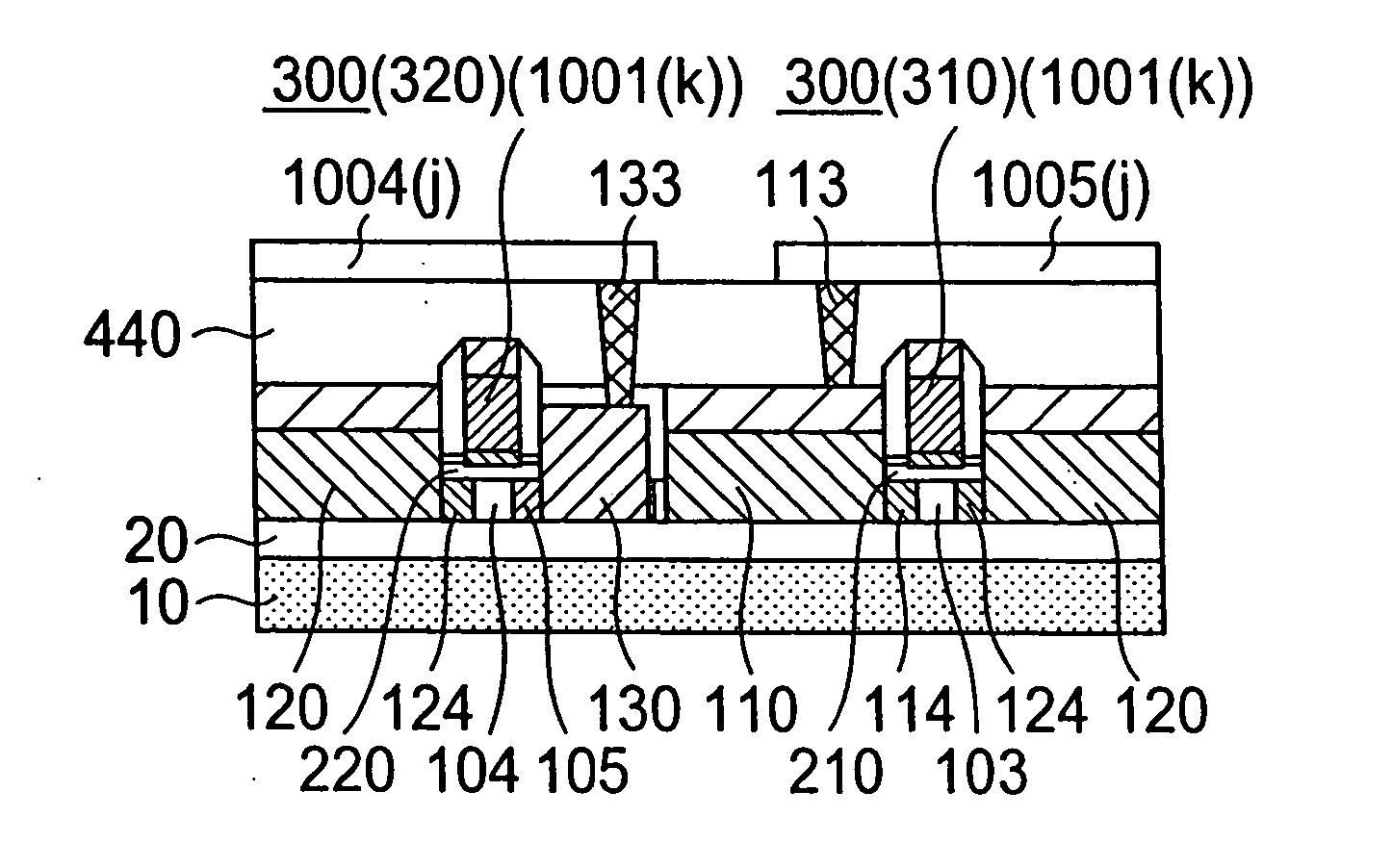
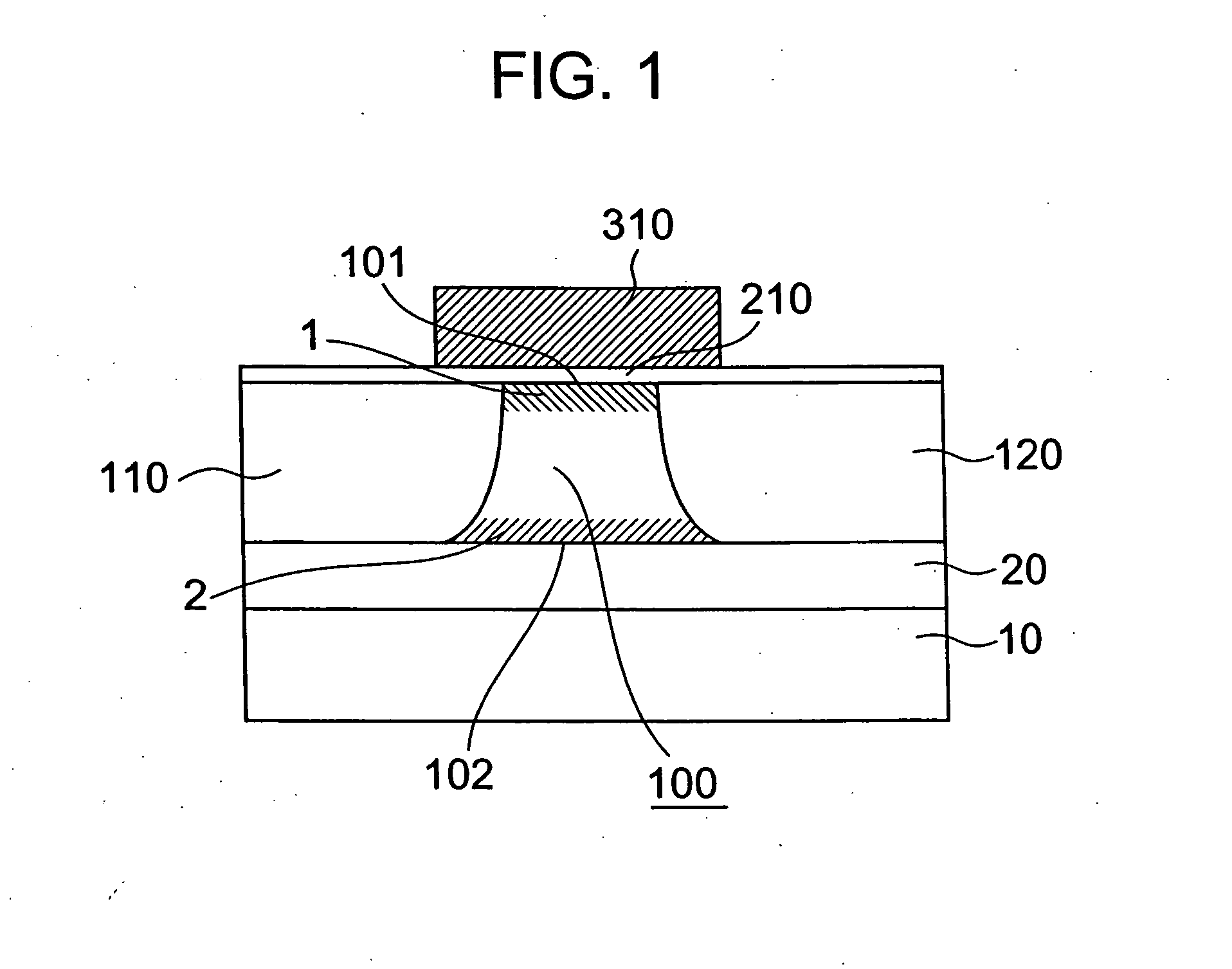
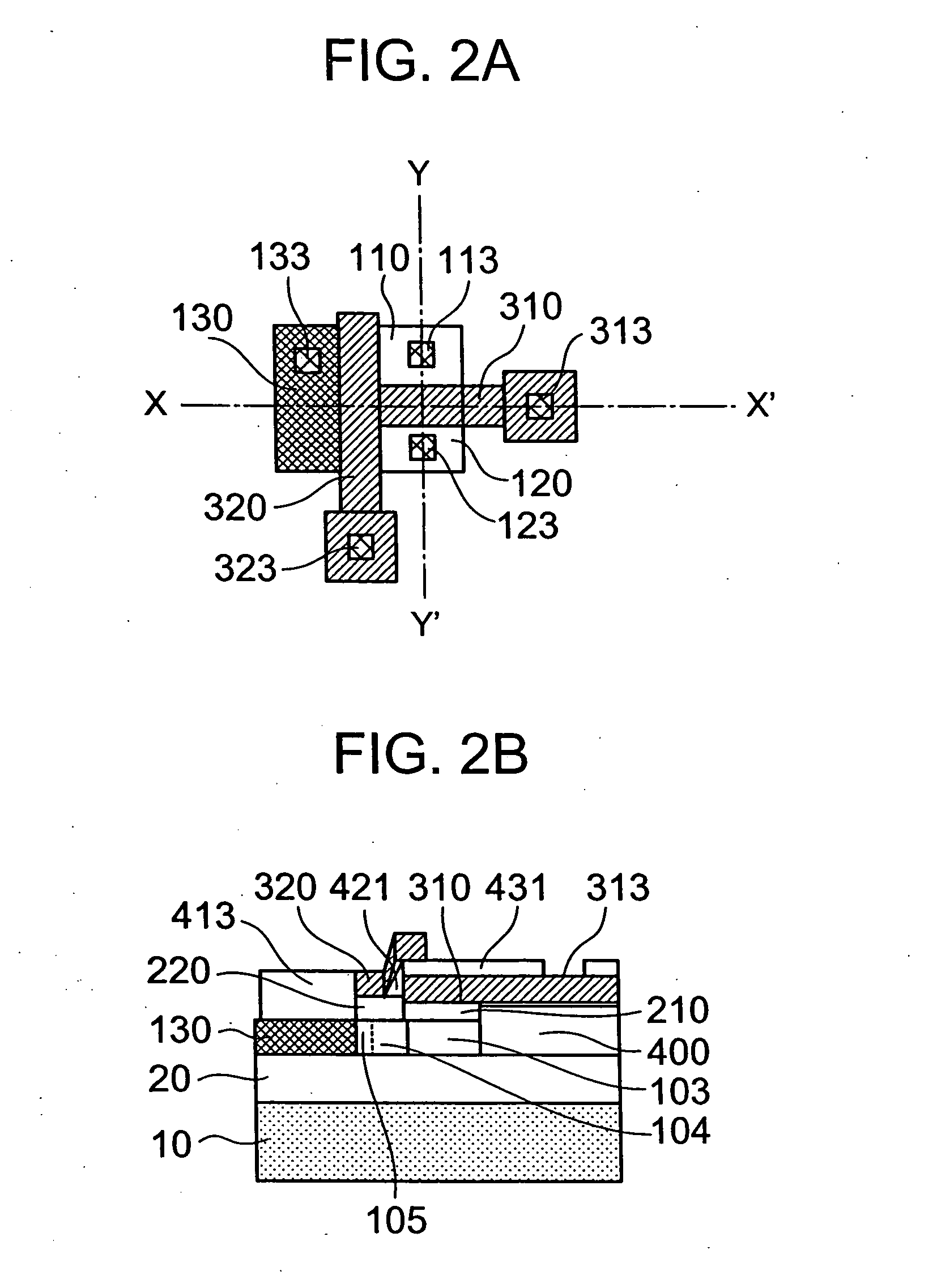
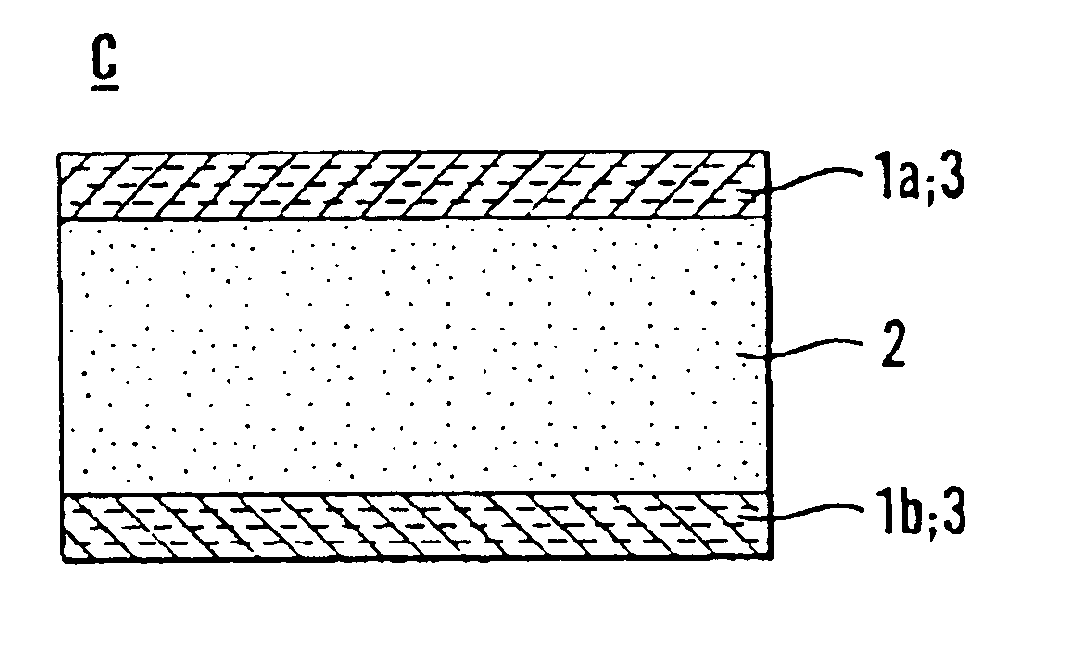
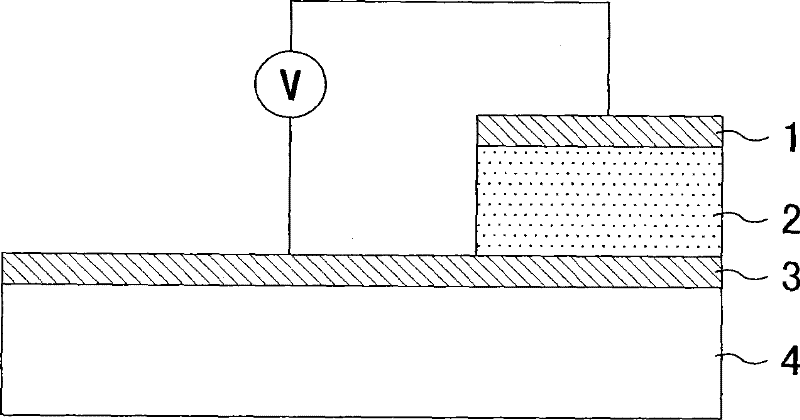
InactiveCN1938781BEasy to operateImprove manufacturing yieldElectrical apparatusRead-only memoriesThin-film memoryCharging order
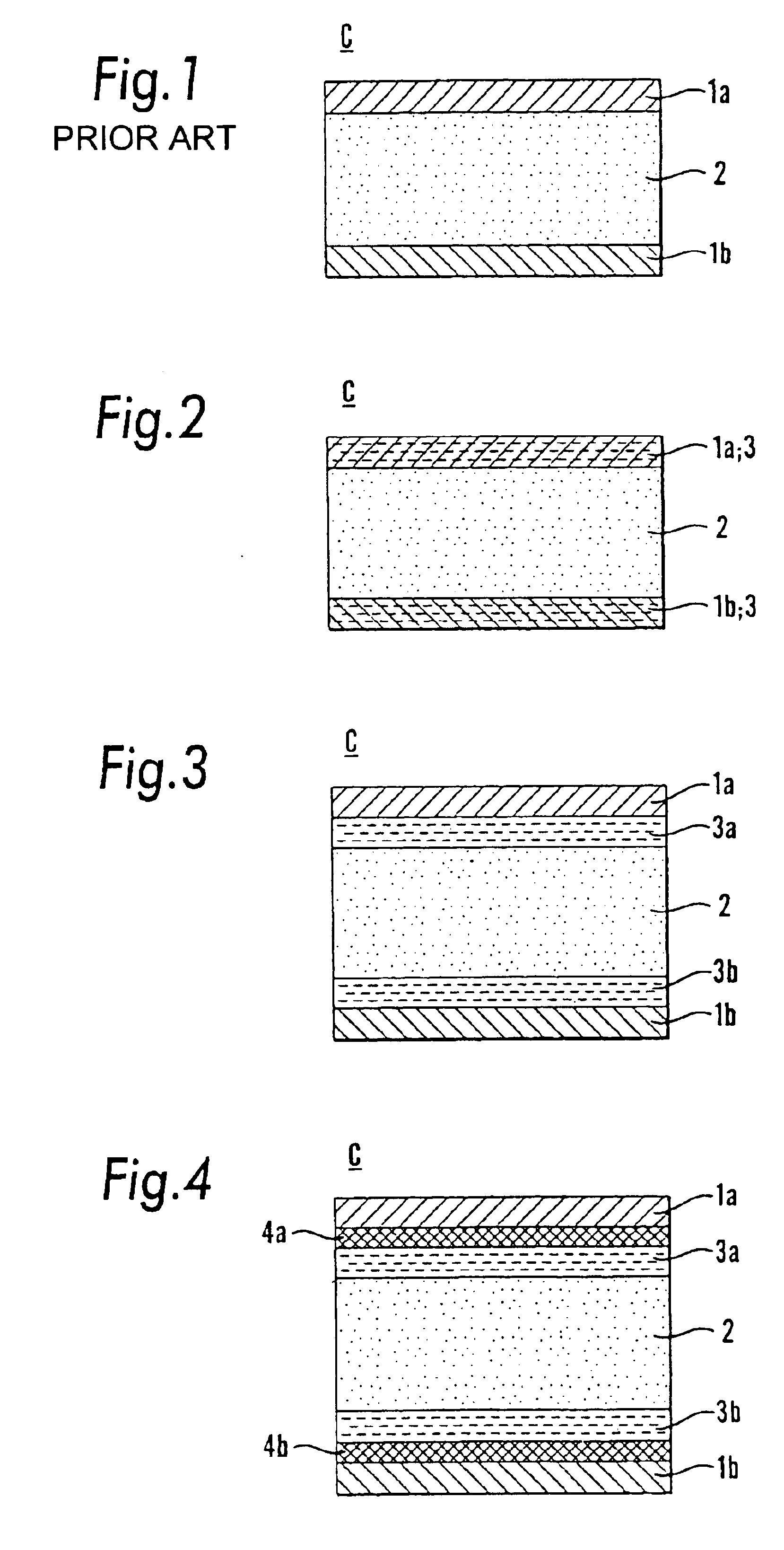
A thin film storage device includes a first electrode (3), a first variable resistance thin film (2), and a second electrode (1). The first electrode (3) is formed over a surface of a substrate (4). The first variable resistance thin film (2) is formed over a surface of the first electrode (3). The second electrode (1) is formed over a surface of the first variable resistance thin film (2). The first variable resistance thin film (2) comprises a material whose resistance in a bulk state changes in accordance with at least one of a lattice strain and a change of charge-order.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Once write film storage
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Film storage device, device and method for producing containers
The device (1) has an inlet (8) assigned to drive and pressure rollers (33, 34) that are driven using adjustable rotational speed. An outlet (9) is assigned to other drive and pressure rollers (35, 36) that are driven using another adjustable rotational speed. A continuous foil (4) is guided between the drive and pressure rollers. Movable foil guiding systems (31, 32) are arranged for adjusting an amount of part of the continuous foil in cooperation with the drive and pressure rollers and gravitational force (g). An independent claim is also included for a method for manufacturing a barrel.
Owner:KRONES AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com