Magnetic stacks with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy for spin momentum transfer magnetoresistive random access memory
a random access memory and magnetic anisotropy technology, applied in the field of spin momentum transfer magnetoresistive random access memory (mram), can solve the problems of difficulty in reading operations in the stt mram and low mr of mtjs made using pma materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
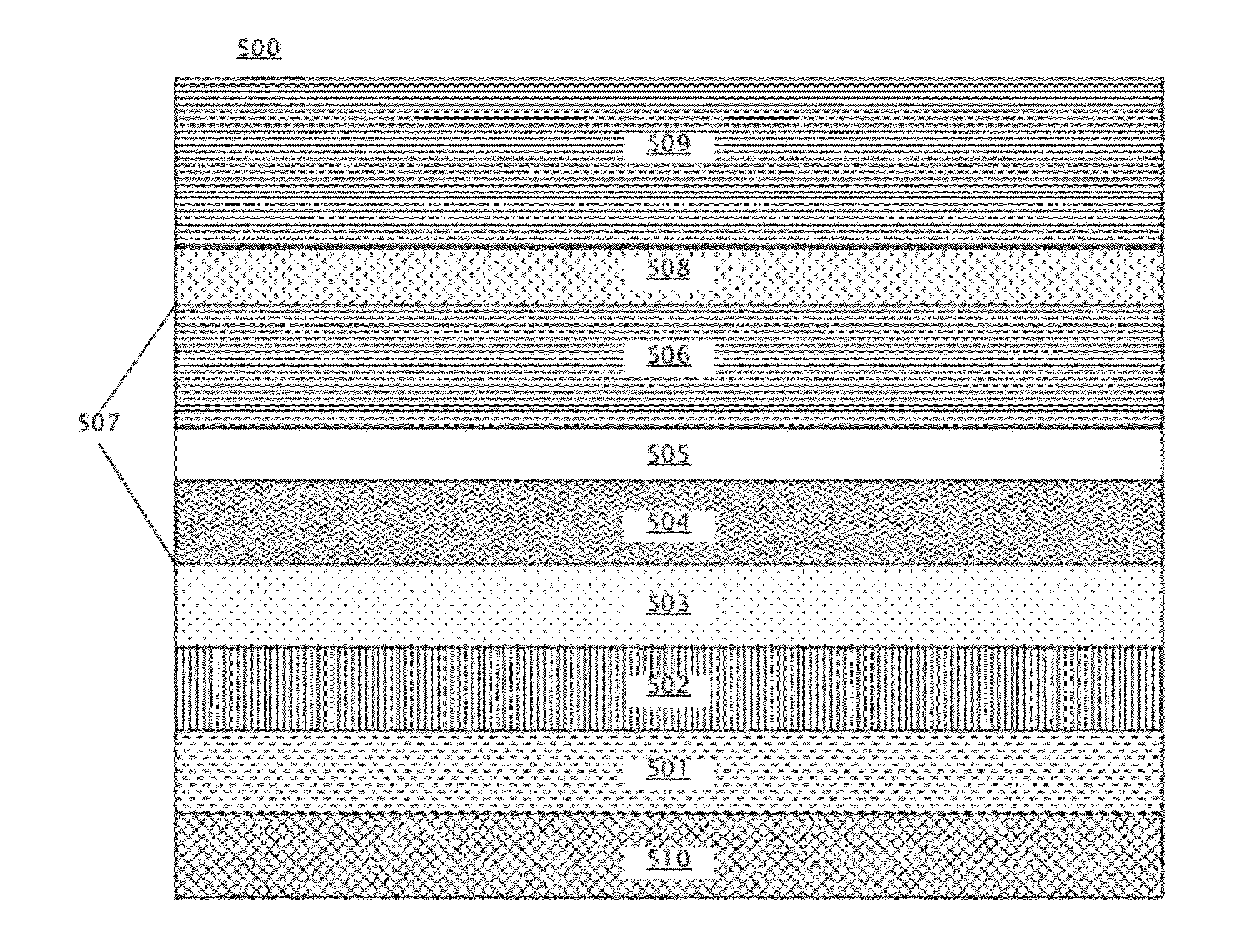
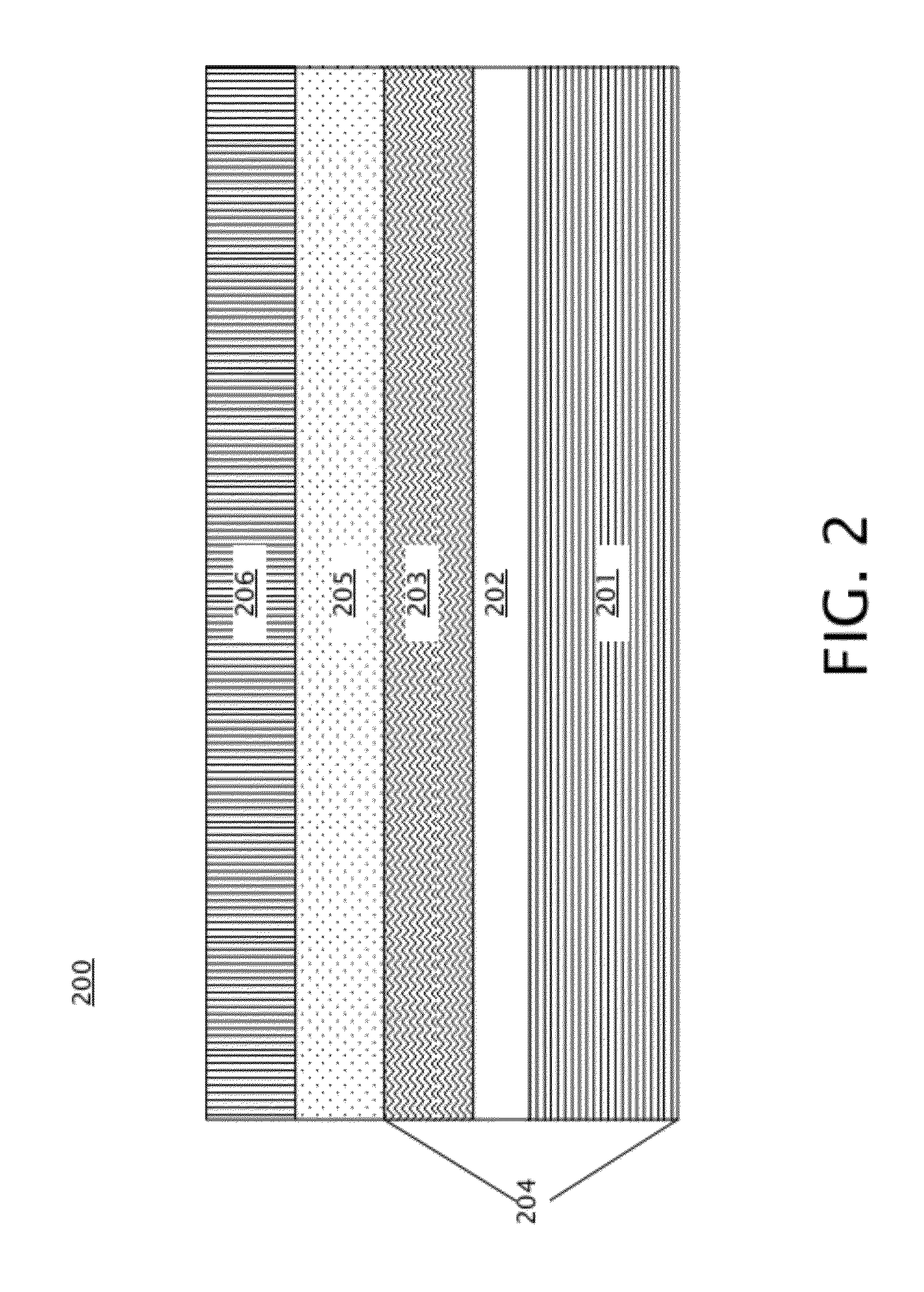
[0018]Embodiments of PMA magnetic stacks for STT MRAM are provided, with exemplary embodiments being discussed below in detail. The PMA magnetic stacks form MTJs that exhibit a high MR and a reduced fixed layer dipolar field thus commensurately reduced free layer loop offset through inclusion of one or more of a composite fixed layer, a synthetic antiferromagnetic (SAF) structure in the fixed layer, and a dipole layer. A composite fixed layer includes three layers: a dusting layer, a spacer layer, and a reference layer. A fixed layer SAF structure includes a SAF spacer located between two layers of magnetic material that are anti-parallelly coupled through the SAF spacer. The magnetization of the two layers of magnetic material in the SAF structure may be adjusted such that they are aligned opposite to one another, reducing the overall fixed layer dipole field. A dipole layer is located on the opposite side of the free layer from the tunnel barrier, and may be magnetized in a direct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com