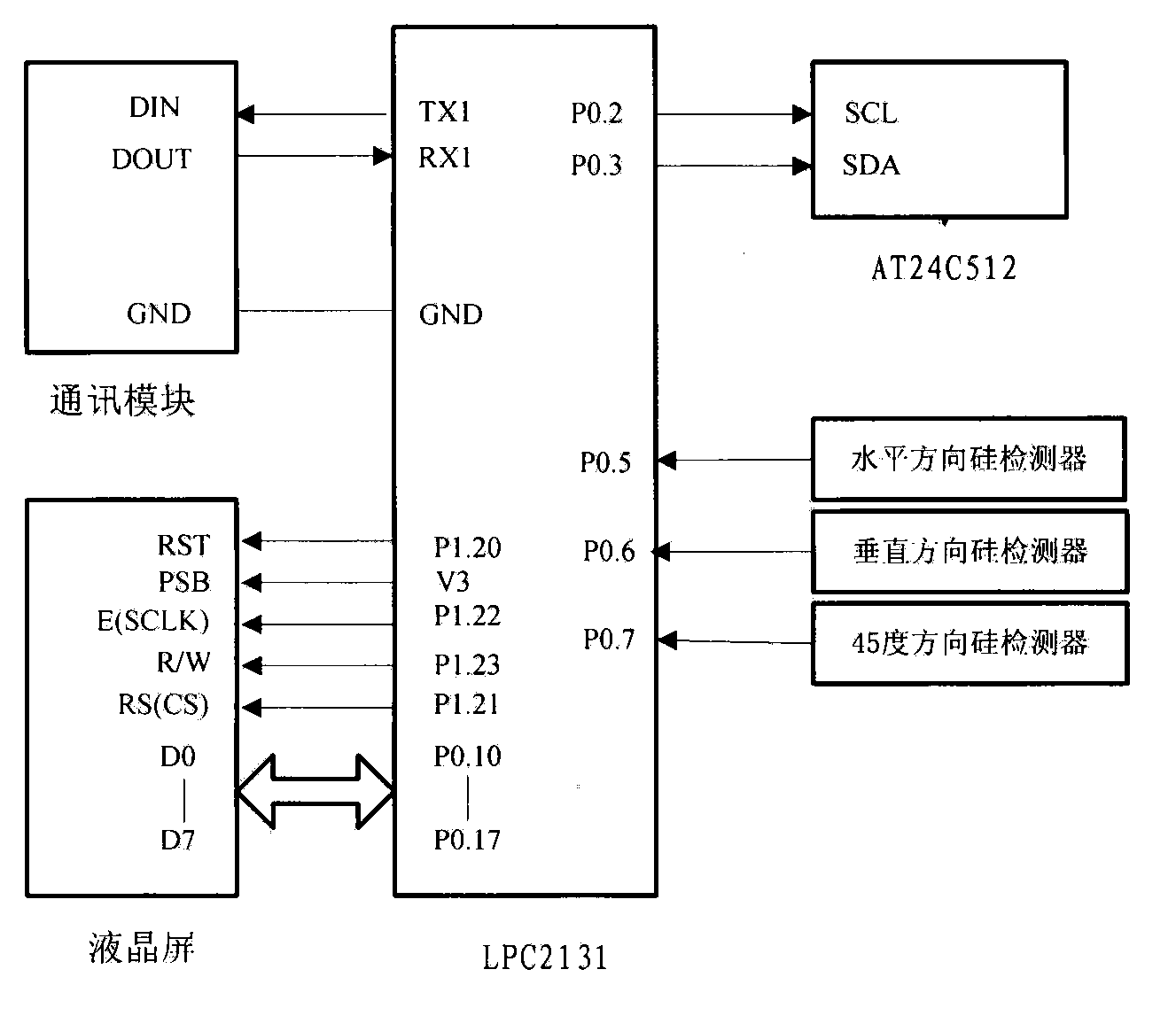
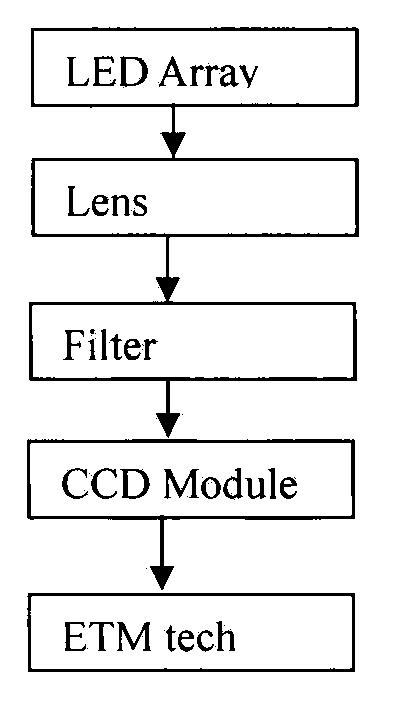
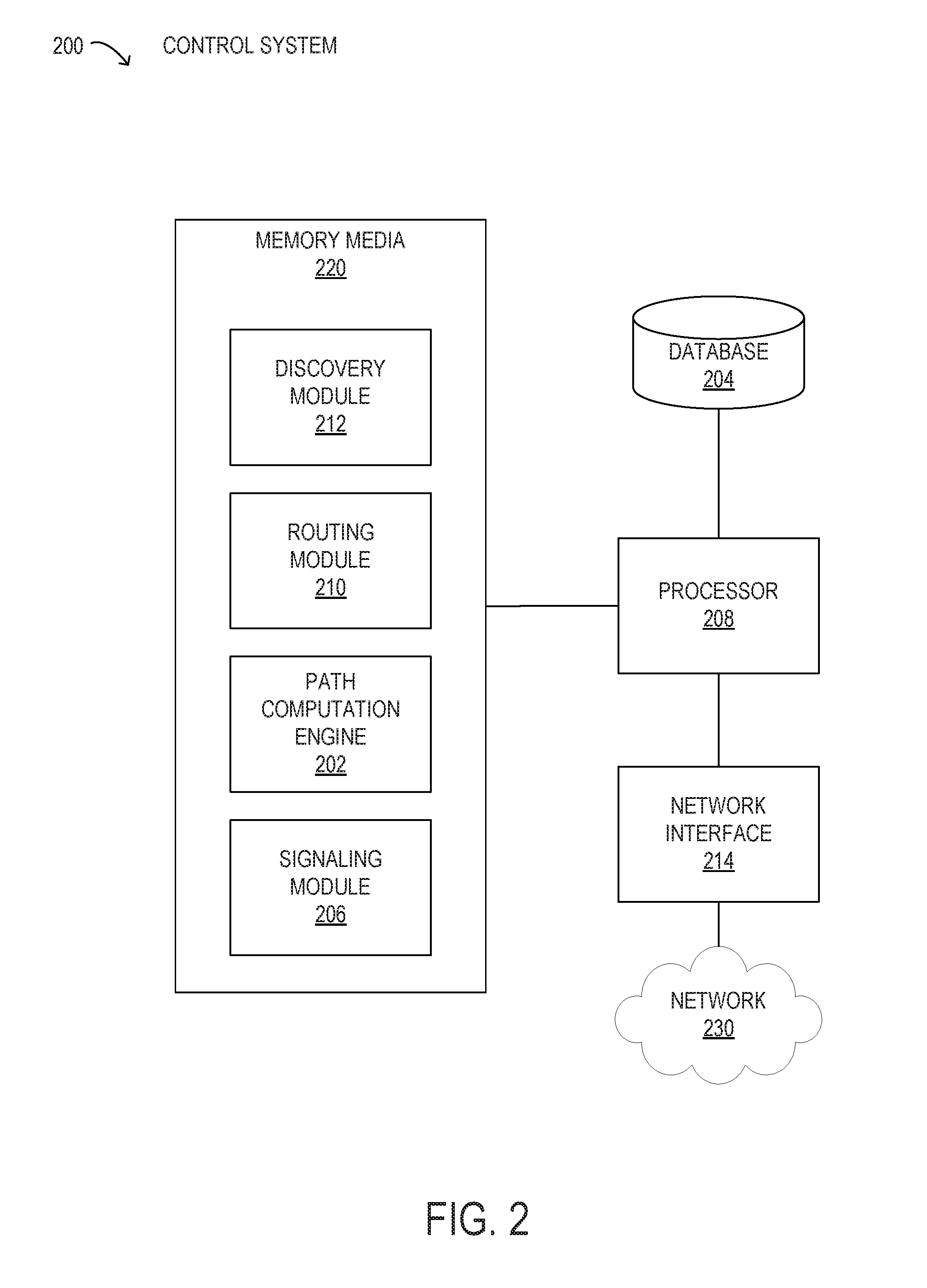
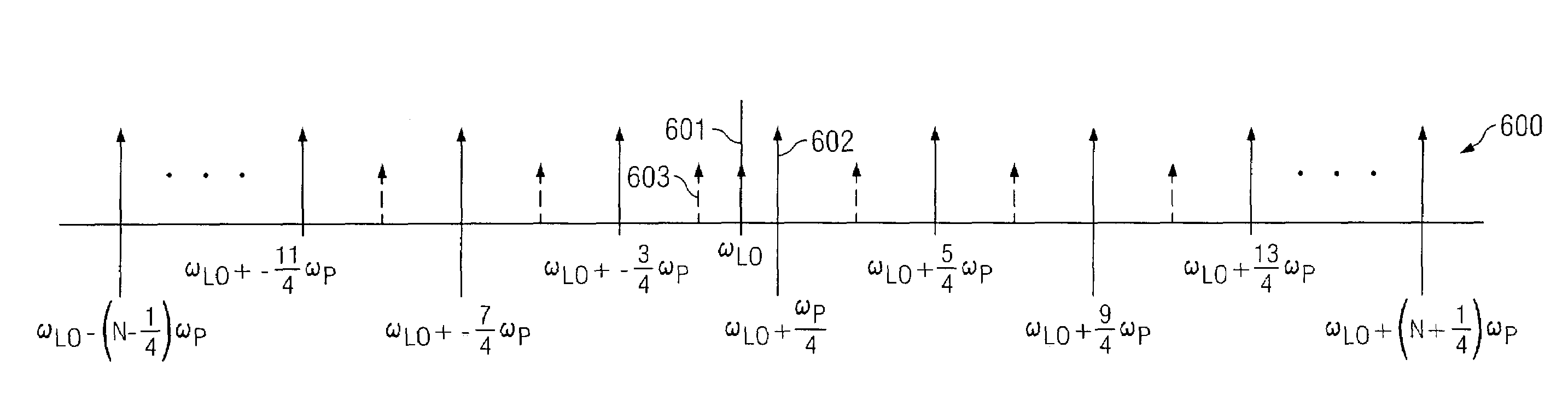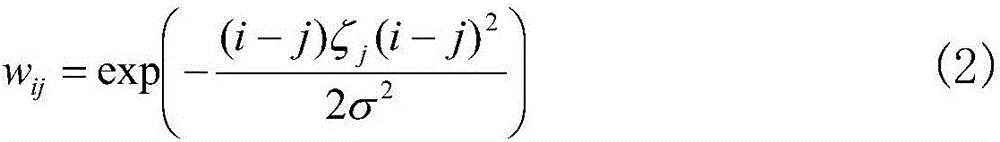Patents
Literature
55 results about "Spectral inversion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods and apparatuses for dealing with spectrum inversion
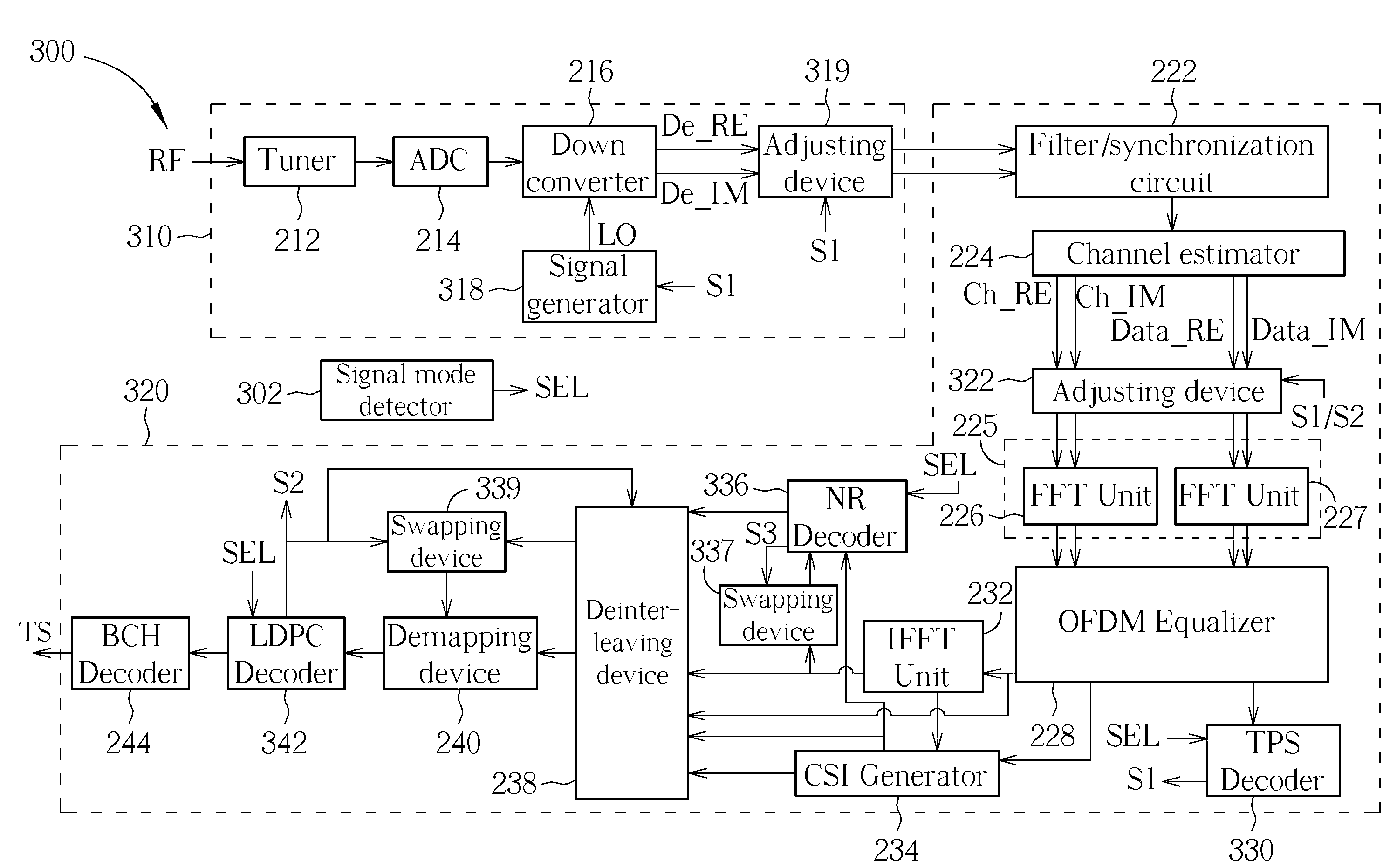
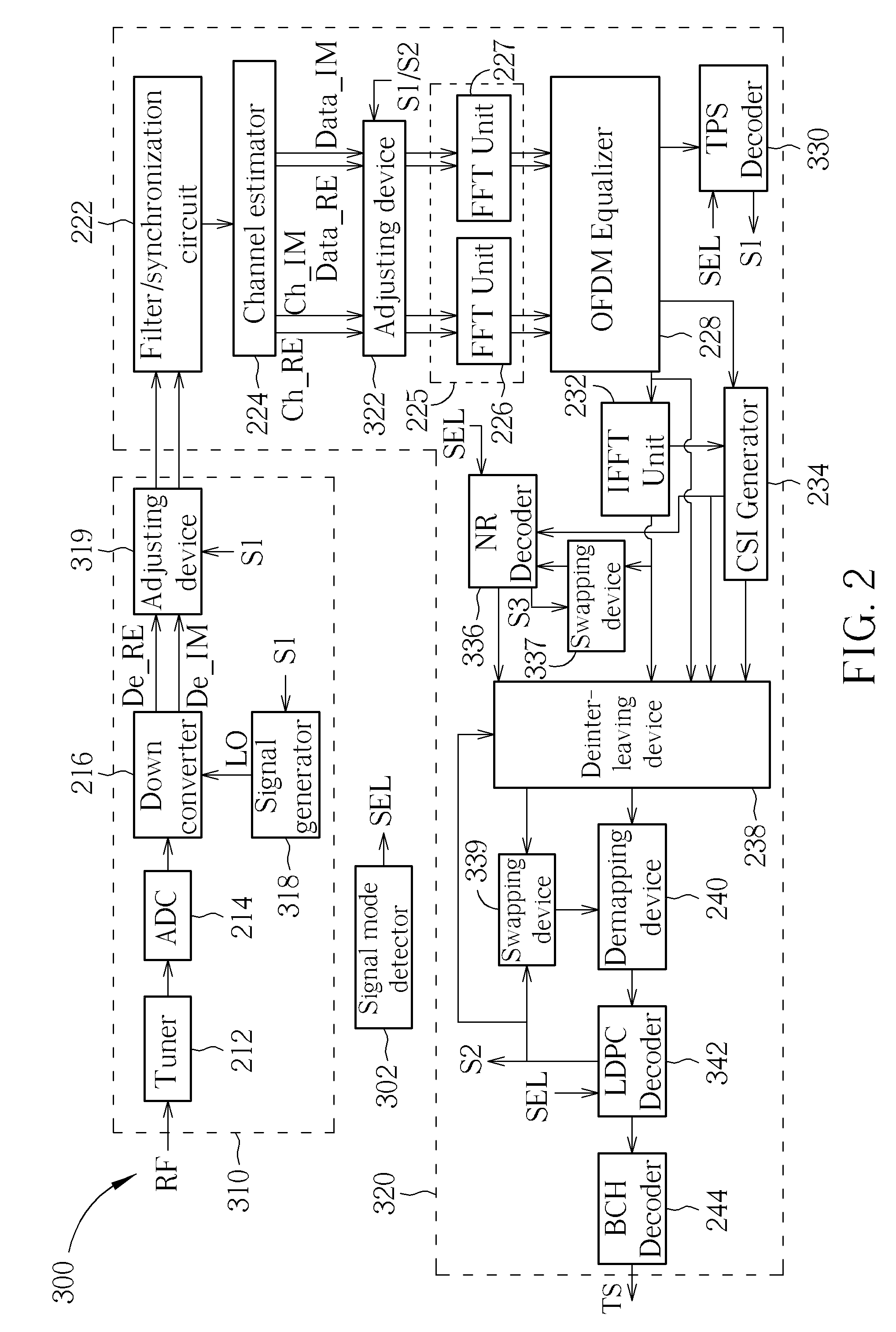
An apparatus of processing a time domain synchronous orthogonal frequency-division-multiplexing (TDS-OFDM) signal is provided. The apparatus includes a receiving block and a demodulating block. The receiving block receives the TDS-OFDM signal, and generates a down-converted signal according to the received TDS-OFDM signal. The demodulating block is coupled to the receiving block, and demodulates the down-converted signal to generate a transport stream. The demodulating block has a transmission parameter signaling (TPS) decoder implemented for performing a TPS decoding operation to generate a TPS decoding result and verifying a spectrum direction of the received TDS-OFDM signal according to the TPS decoding result.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
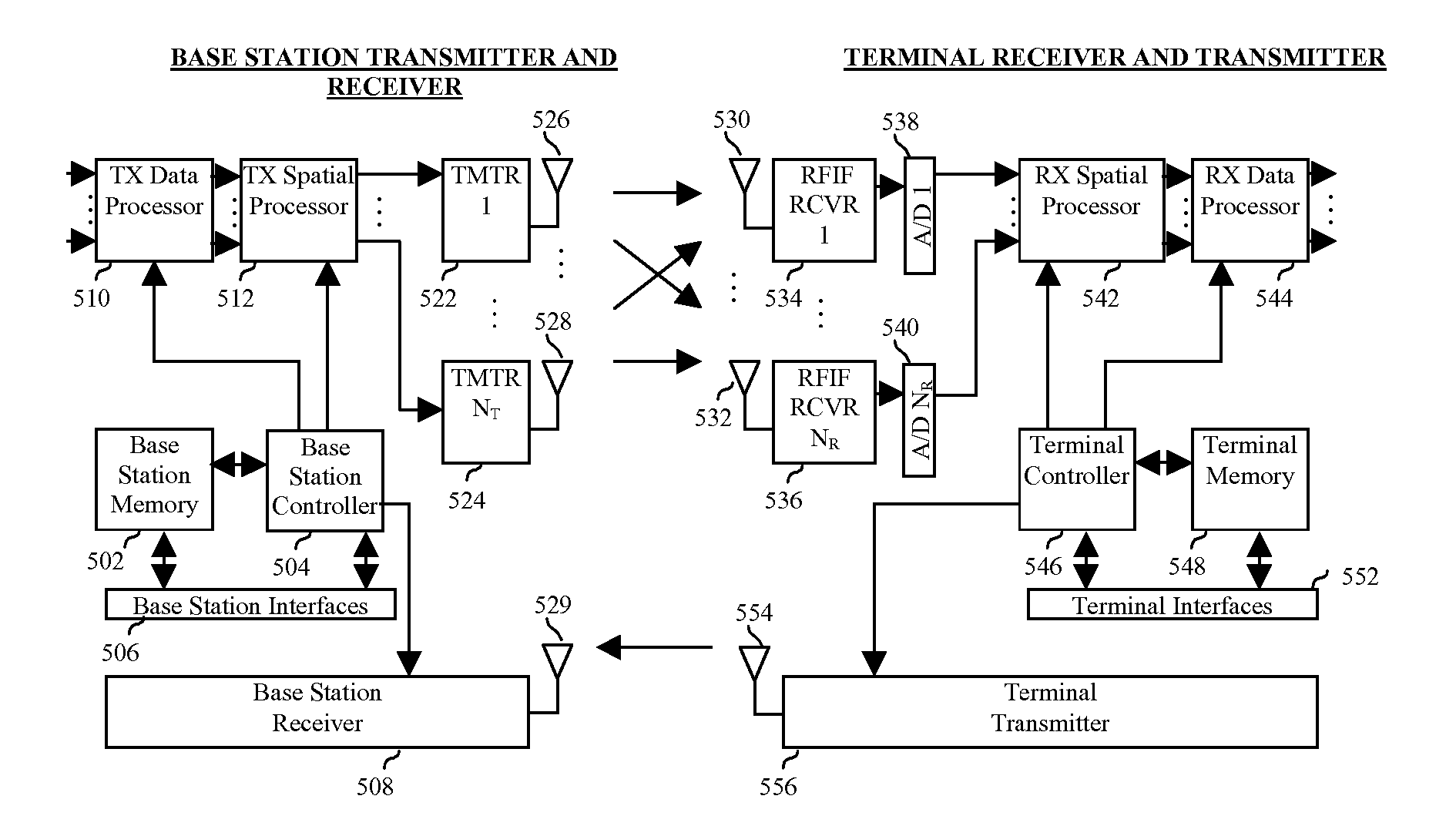
Method and system for communications with reduced complexity receivers
InactiveUS20070243839A1Spatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityFrequency spectrumEngineering
The invention provides a new method and system for low complexity, low cost, small component size, and low power communications. The system provides a digital sub-sampling receiver for multiple-antenna wireless receivers, with reduced number of analog RF / IF chains (or one chain) after a fixed number of receive antennas. The system provides a generator of transmit signals / sequences which are preconditioned by the operation of the system to compensate for spectral effects of ultra-low-rate sub-sampling, in that sequences preserve orthogonality under spectral repetition, spectral translation and spectral inversion. The system provides a management device to provide adaptation in transmit signals / waveforms / patterns as a function of channel and data source variations, such that communication data rates and capacities are maximized. The system can efficiently operate in multi-user multi-channel communication systems. The method implemented by the invention is split in its operation across the transmitter of the transmitting device and the receiver of the receiving device.
Owner:KOSTIC ZORAN
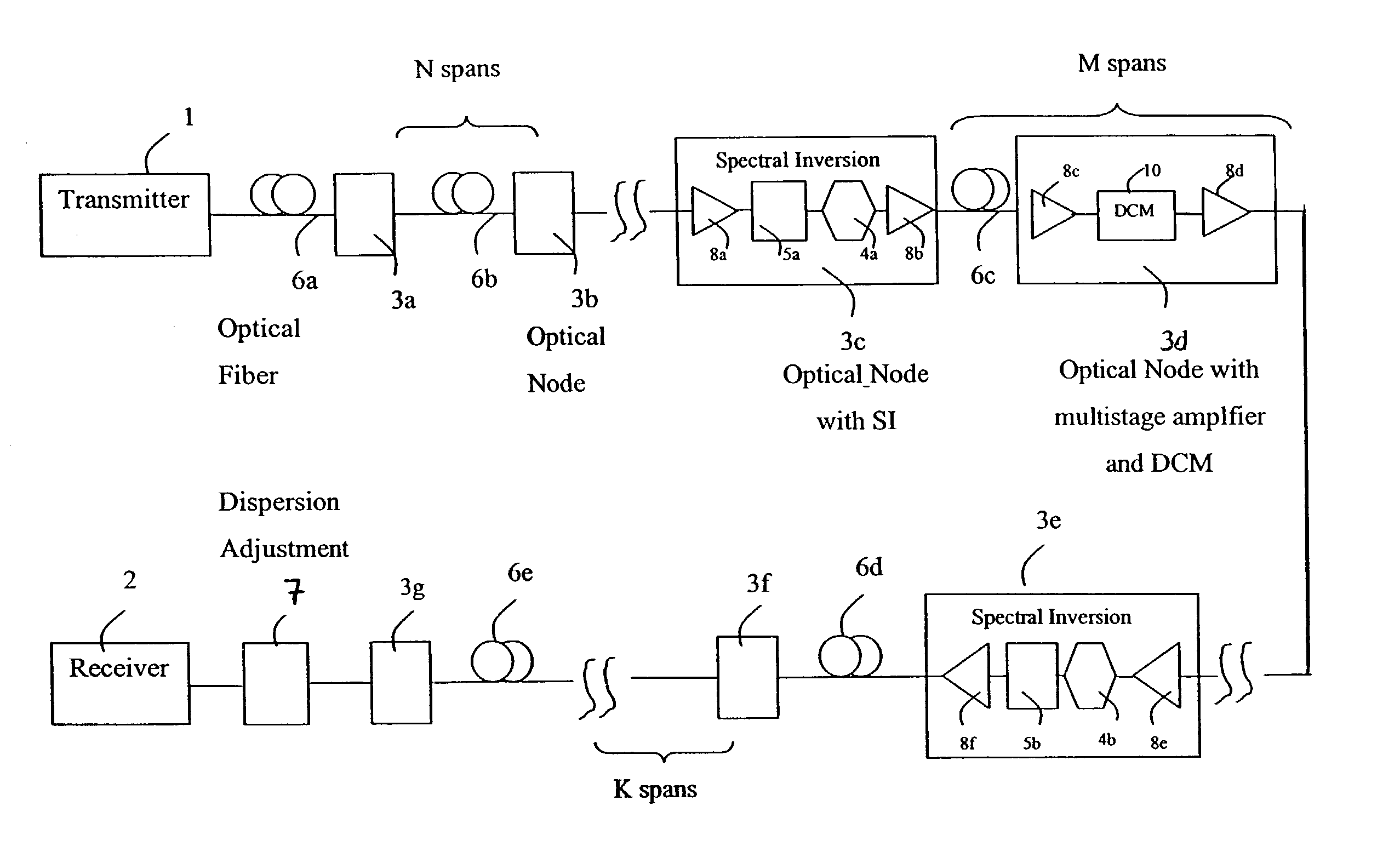
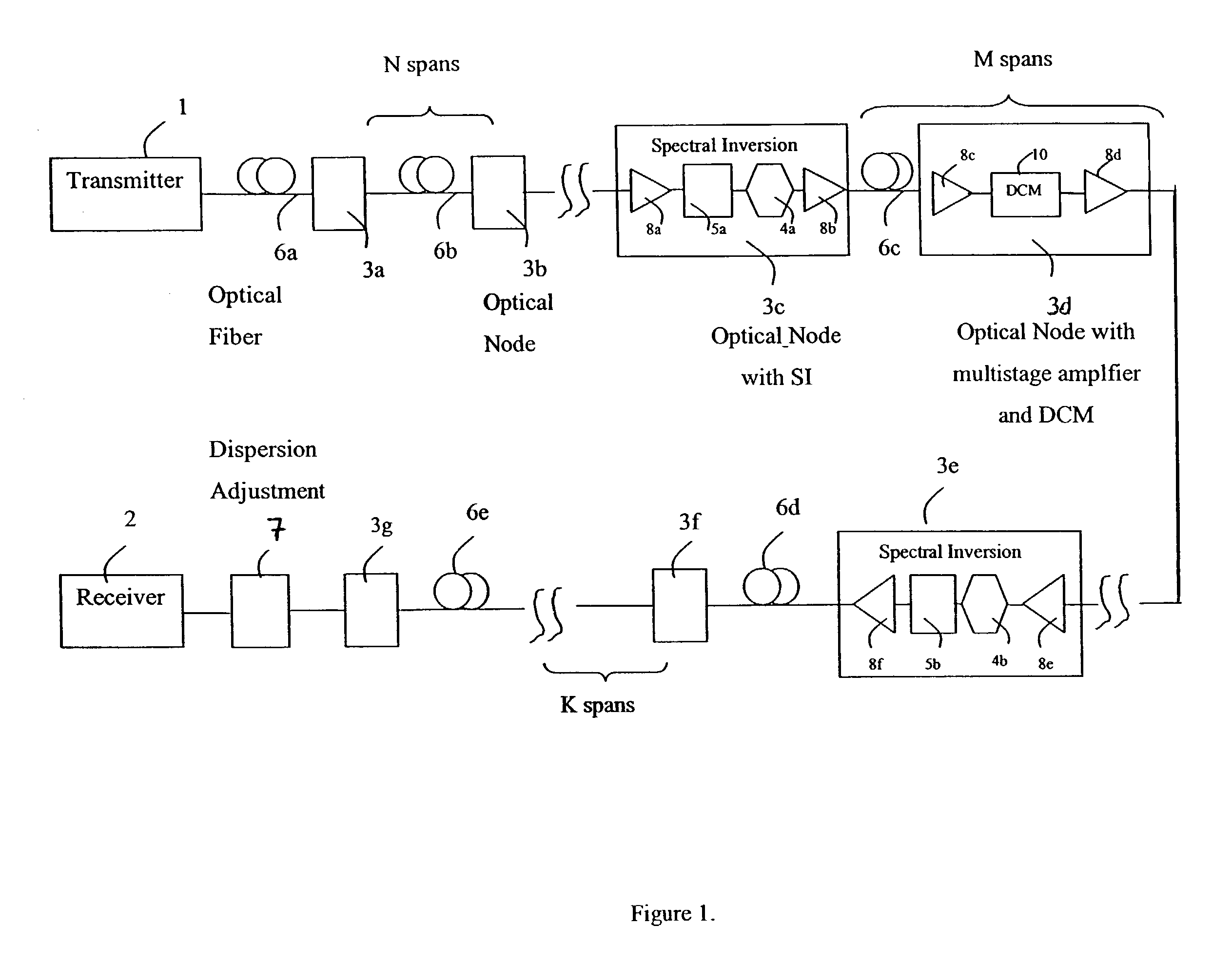
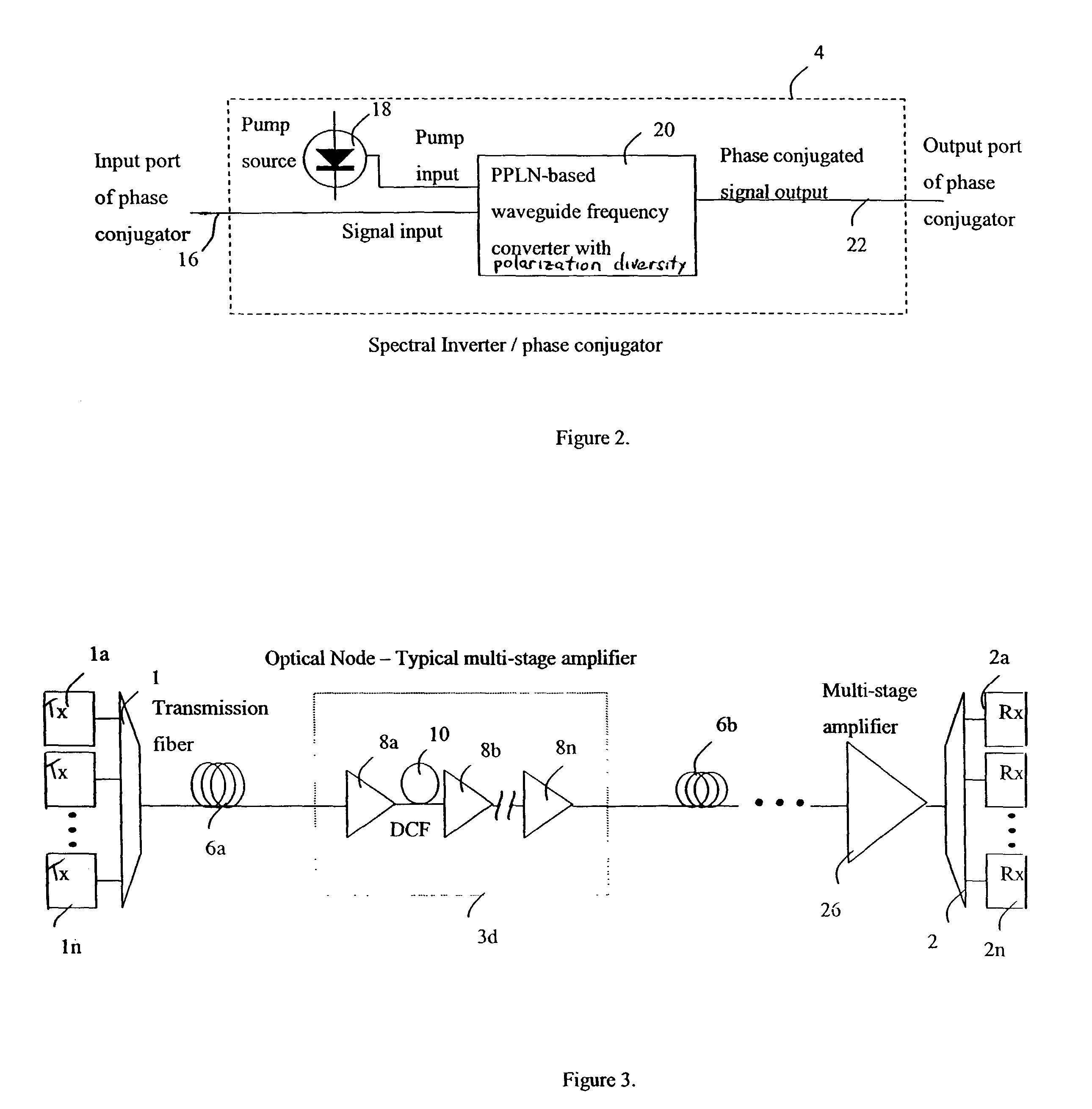
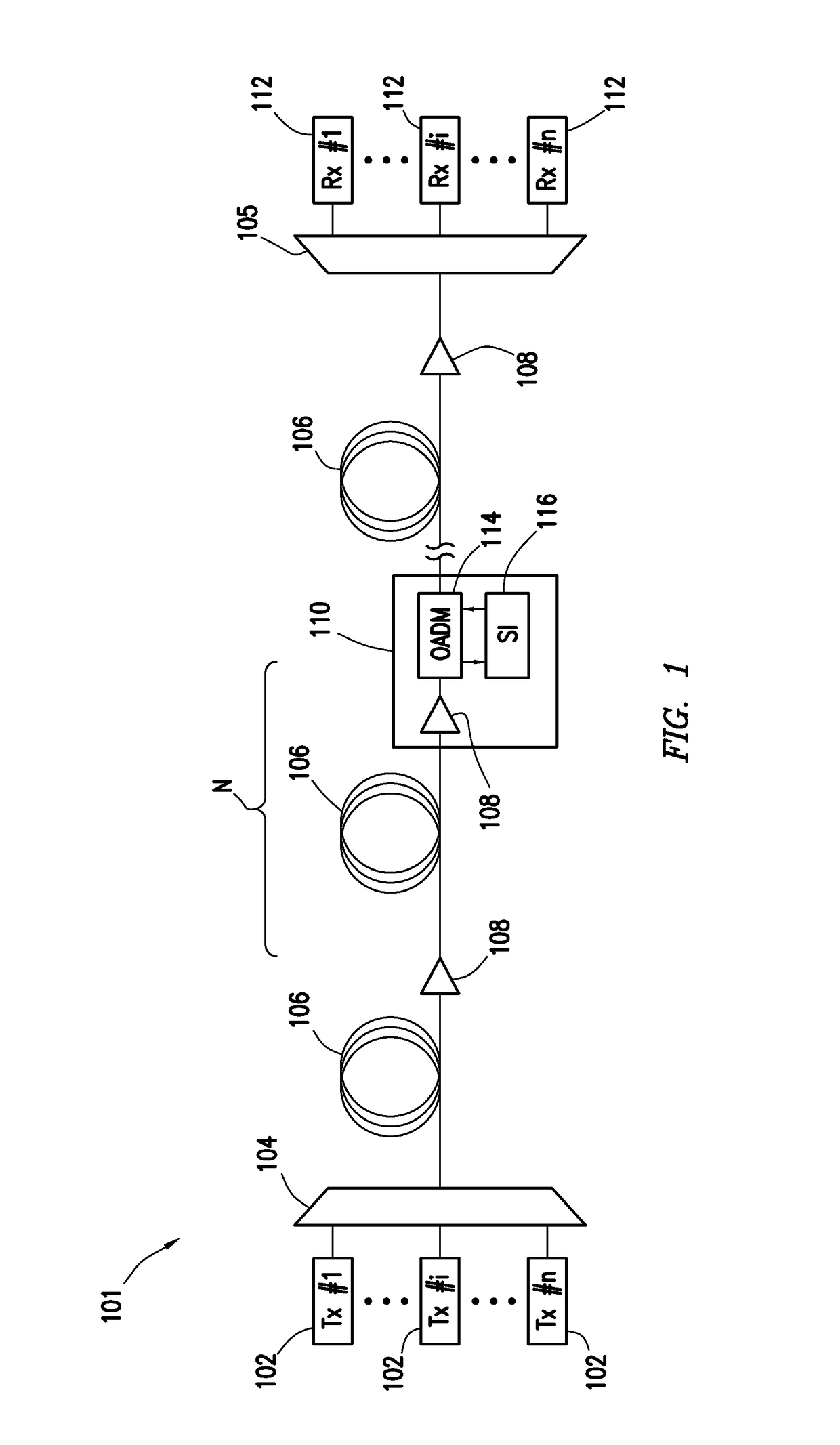
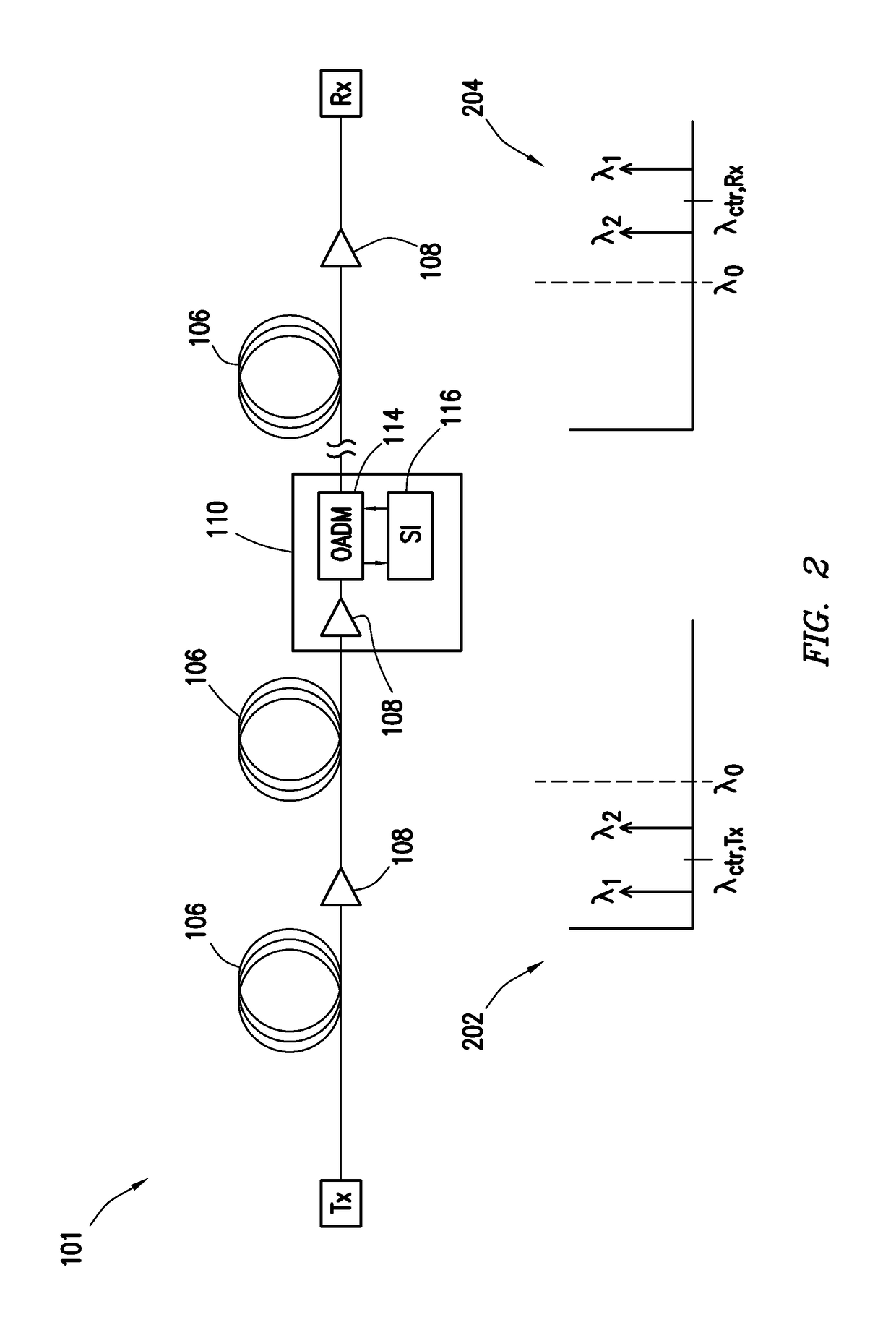
Spectral inversion and chromatic dispersion management in optical transmission systems
InactiveUS20030118347A1Adequate cancellationImprove performanceElectromagnetic transmissionFrequency spectrumAudio power amplifier
A system and method for improving performance of optical fiber networks. The combination of optical spectral inversion and dispersion management enhances performance in optical fiber transmission by controlling the effect of fiber nonlinearities. An optical fiber link, which includes a number of segments or spans, each with a length of fiber and an optical node (typically consisting of at least an amplifier), is provided with at least one spectral inverter, or an optical phase conjugator, connected in the link. Additionally, each span is provided with an amount of dispersion compensation, such as a length of appropriately chosen fiber, to compensate for dispersion as well as other distortion from dispersion's interplay with fiber nonlinear effects. Additional dispersion adjustment is provided in association with the spectral inverter. The location of the spectral inverter (or inverters) and the amount of appropriate dispersion compensation are designed along with other transmission parameters for optimized system performance.
Owner:SPECTRALANE
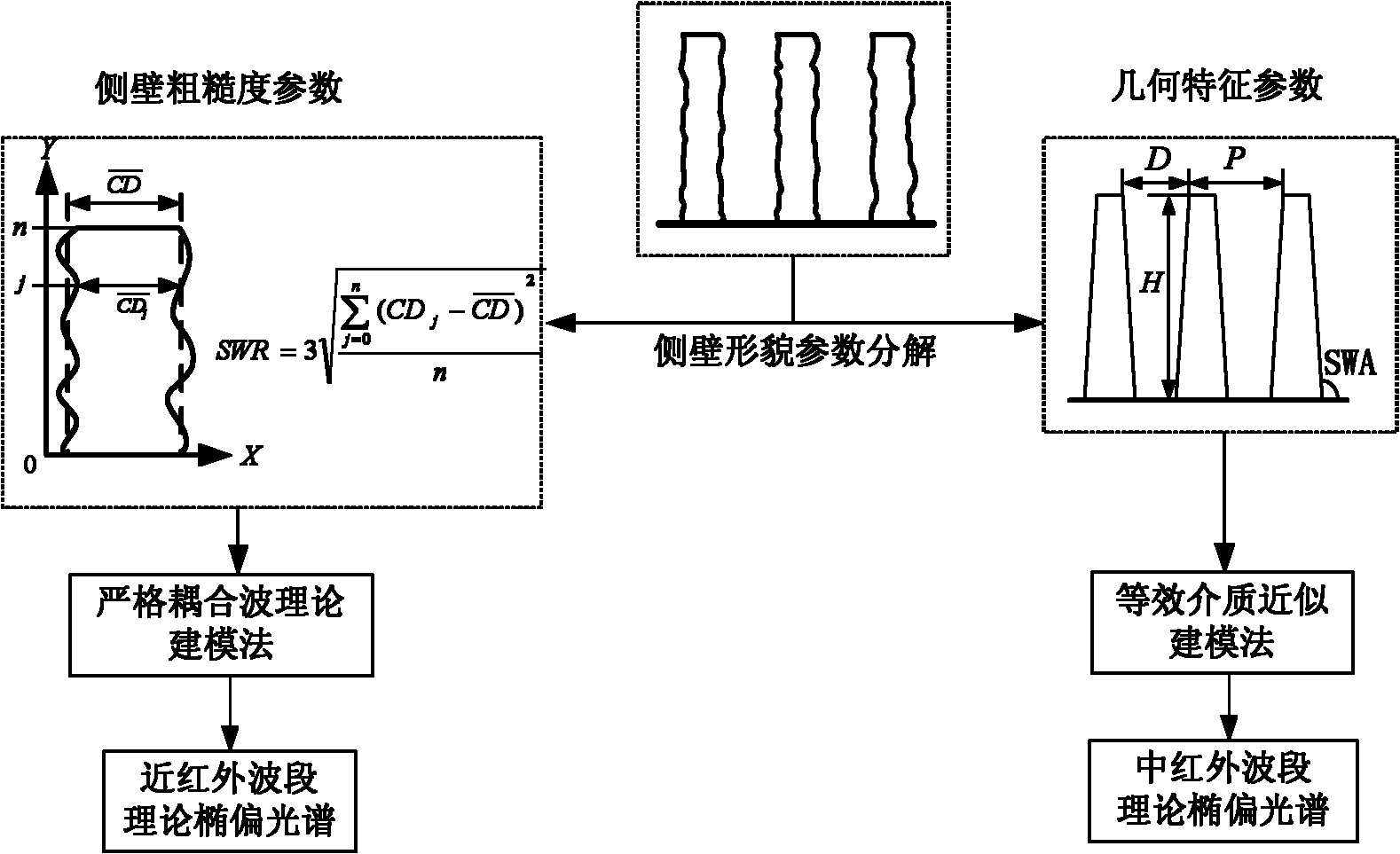
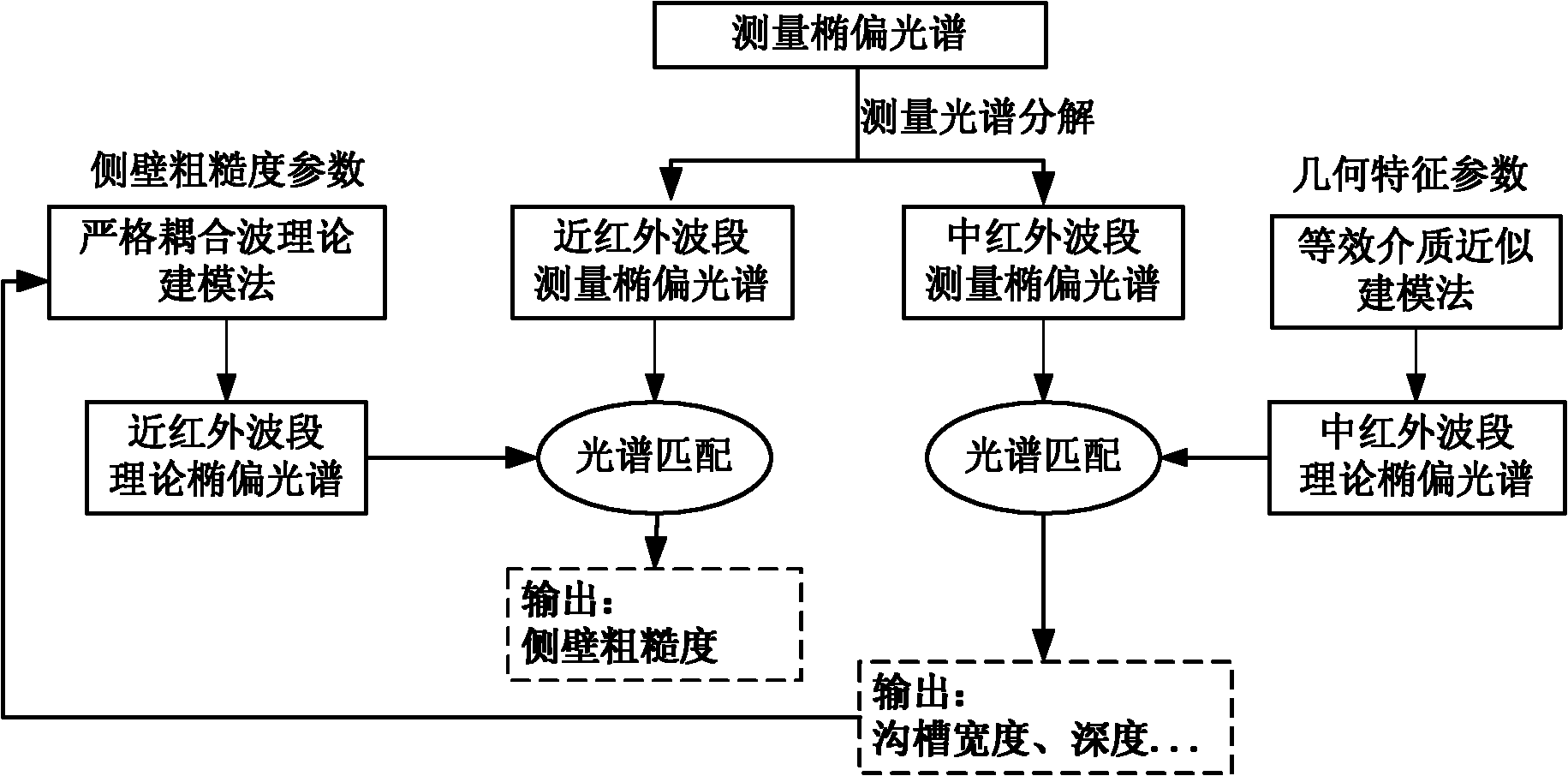
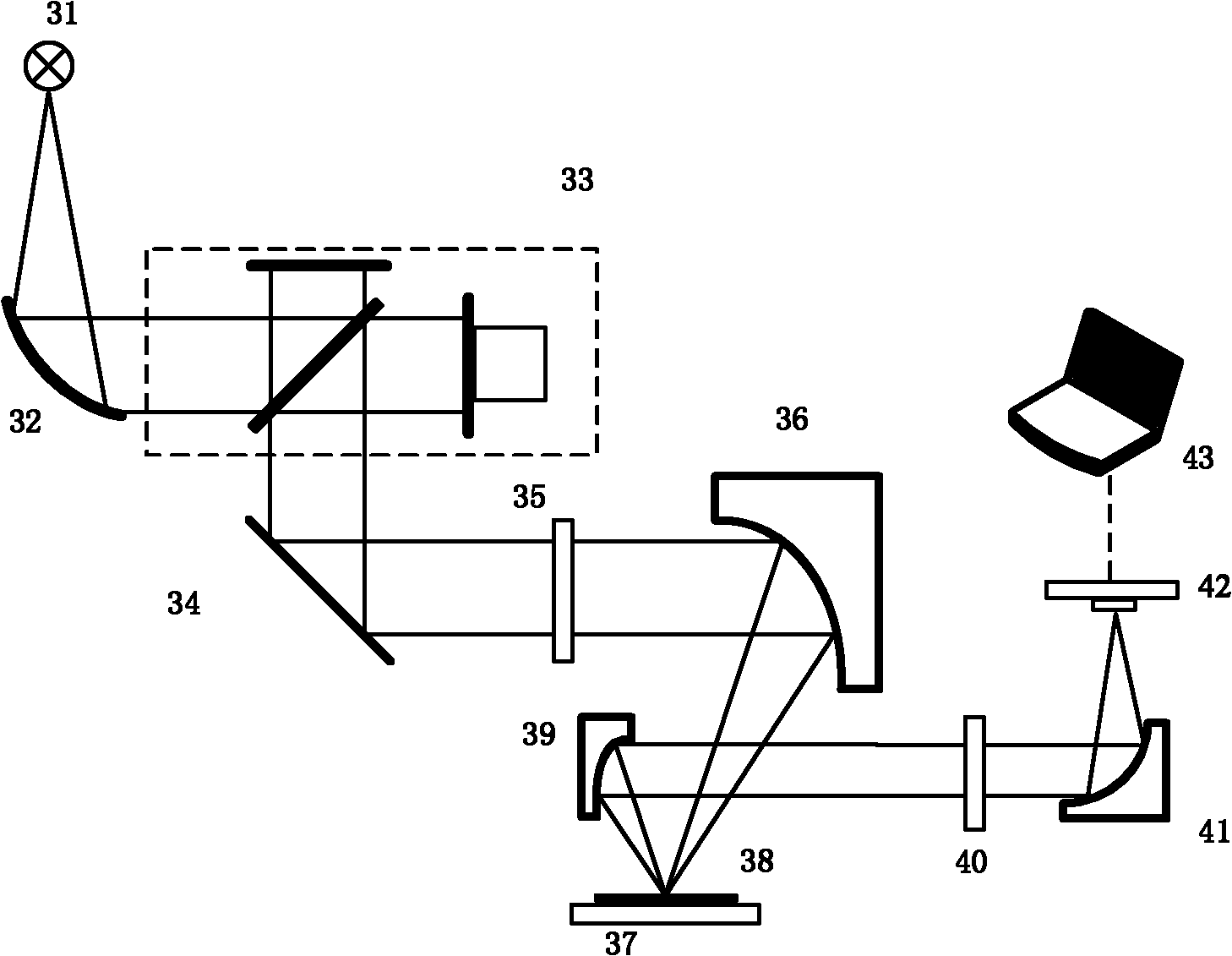
Method and device for rapidly measuring sidewall appearance of micro-nano deep groove structure
ActiveCN102082108ARealize onlineQuick measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementUsing optical meansMicro nanoMiddle infrared
The invention discloses a method and device for rapidly measuring sidewall appearance of a micro-nano deep groove structure, which can simultaneously and rapidly measure the parameters of the sidewall appearance of the micro-nano deep groove structure, such as line width, groove depth, sidewall angle, sidewall roughness and the like. The method comprises the steps of: projecting elliptical polarized lights, which is obtained by polarizing light beams with the wavelengths ranging from near infrared waveband to middle infrared waveband, onto the surface of a structure to be measured; collecting zero-level diffraction signals on the surface of the structure to be measured, and calculating to obtain a measured infrared spectroscopic ellipsometry of the micro-nano deep groove structure; calculating theoretical spectroscopic ellipsometries in the near infrared waveband and the middle infrared waveband respectively by using a wavelength allocation modeling method, matching the theoretical spectroscopic ellipsometries with the infrared spectroscopic ellipsometry measured in the experiment by using a stepwise spectral inversion method, and sequentially extracting the groove structure parameter and the roughness parameter. The device comprises an infrared light source, first, second, third and fourth off-axis parabolic mirrors, a Michelson's interferometer, a planar reflector, a polarizer, a sample bench, an analyzer, a detector and a computer; and the method is a noncontact, nondestructive low-cost method for rapidly measuring the sidewall appearance.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
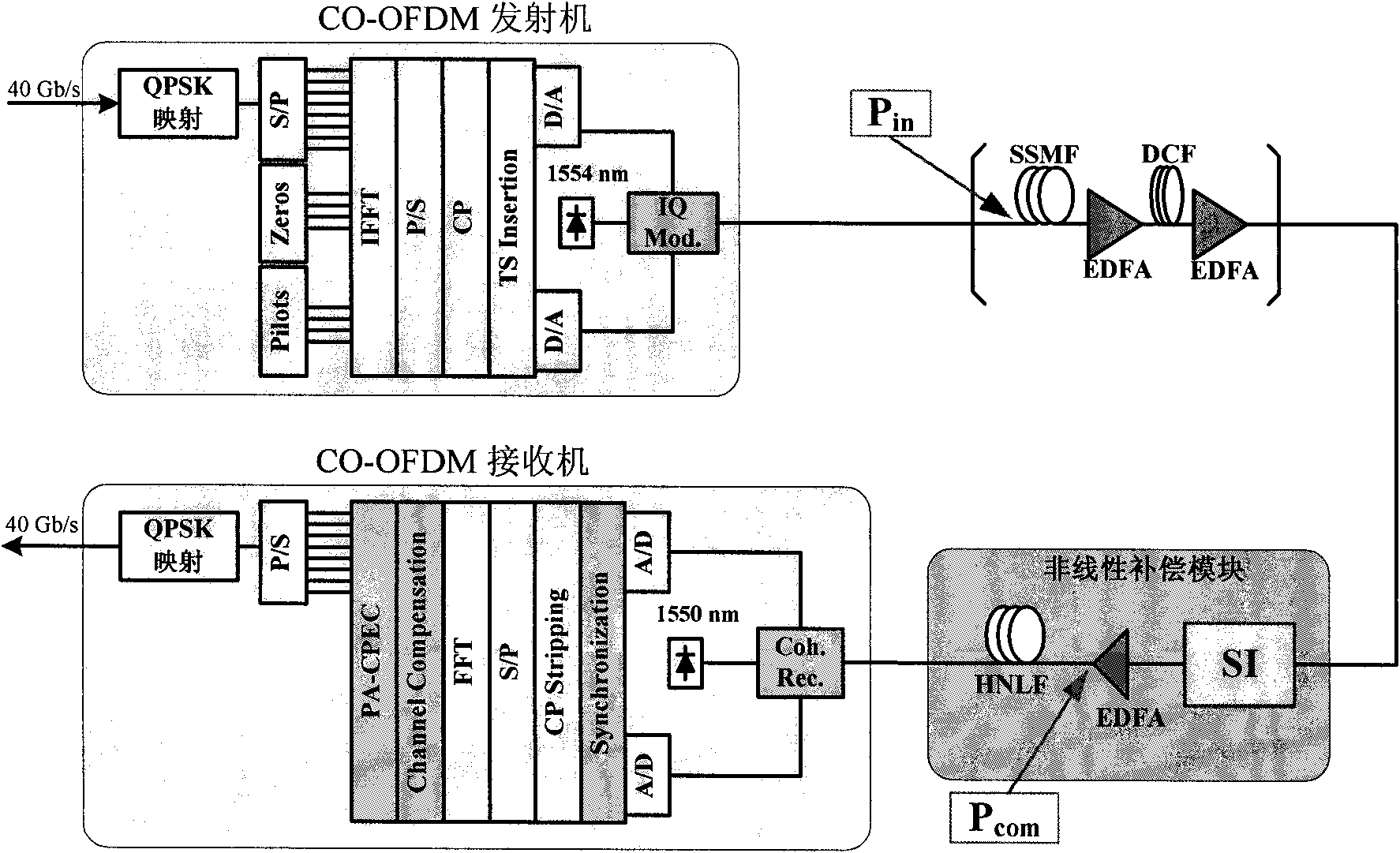
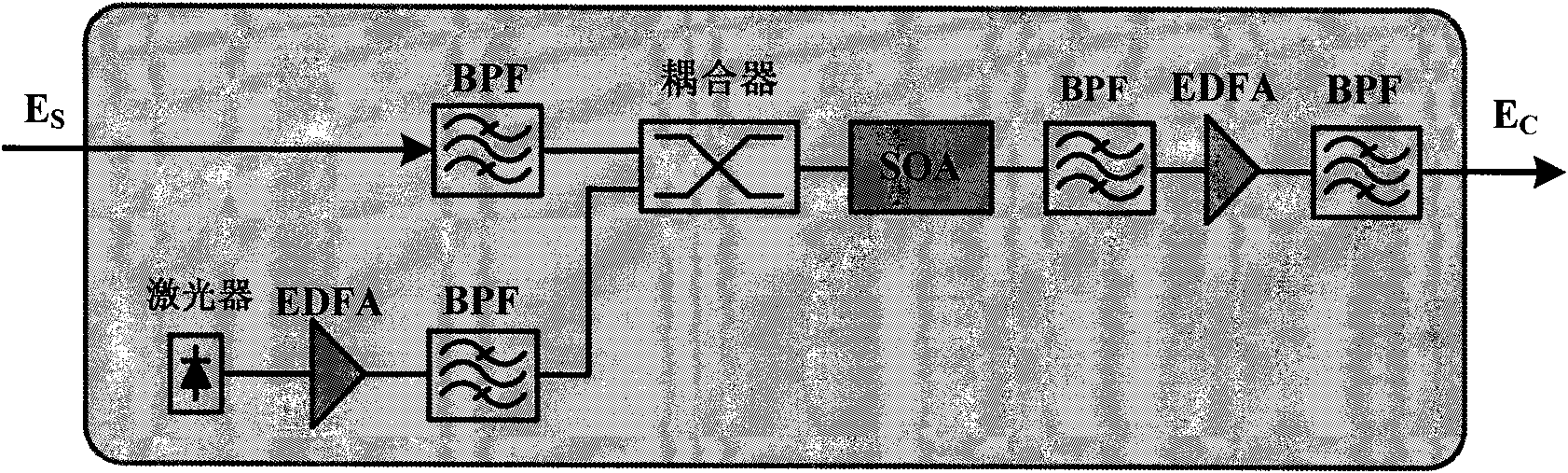
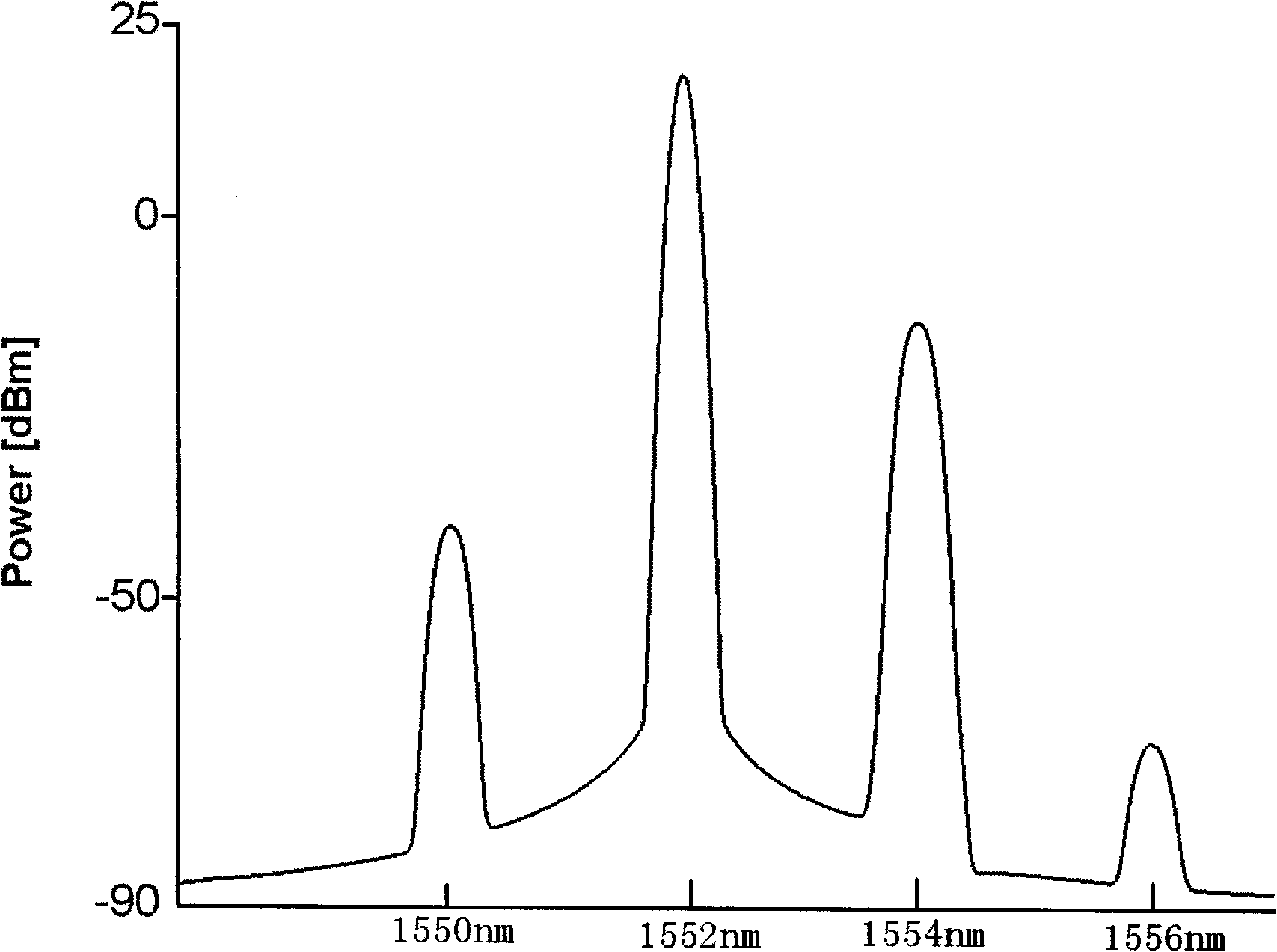
SI (Spectrum Inversion)-based nonlinear fiber damage compensation method and device in OFDM system
The invention relates to SI (Spectrum Inversion)-based nonlinear fiber damage compensation method and device in an O-OFDM (Optical-Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) system, belonging to the field of optical communication and applied to the O-OFDM system for nonlinear fiber damage compensation. The whole compensation module is arranged in front of a receiver of the O-OFDM system and comprises an SI unit and an HNLF (Highly Non-Linear Fiber) which has a certain length and is arranged behind the SI unit, wherein SI is realized by an SOA (Semiconductor Optical Amplifier) based on FWM (Four Wave Mixing) effect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Data aided detection of spectrum inversion
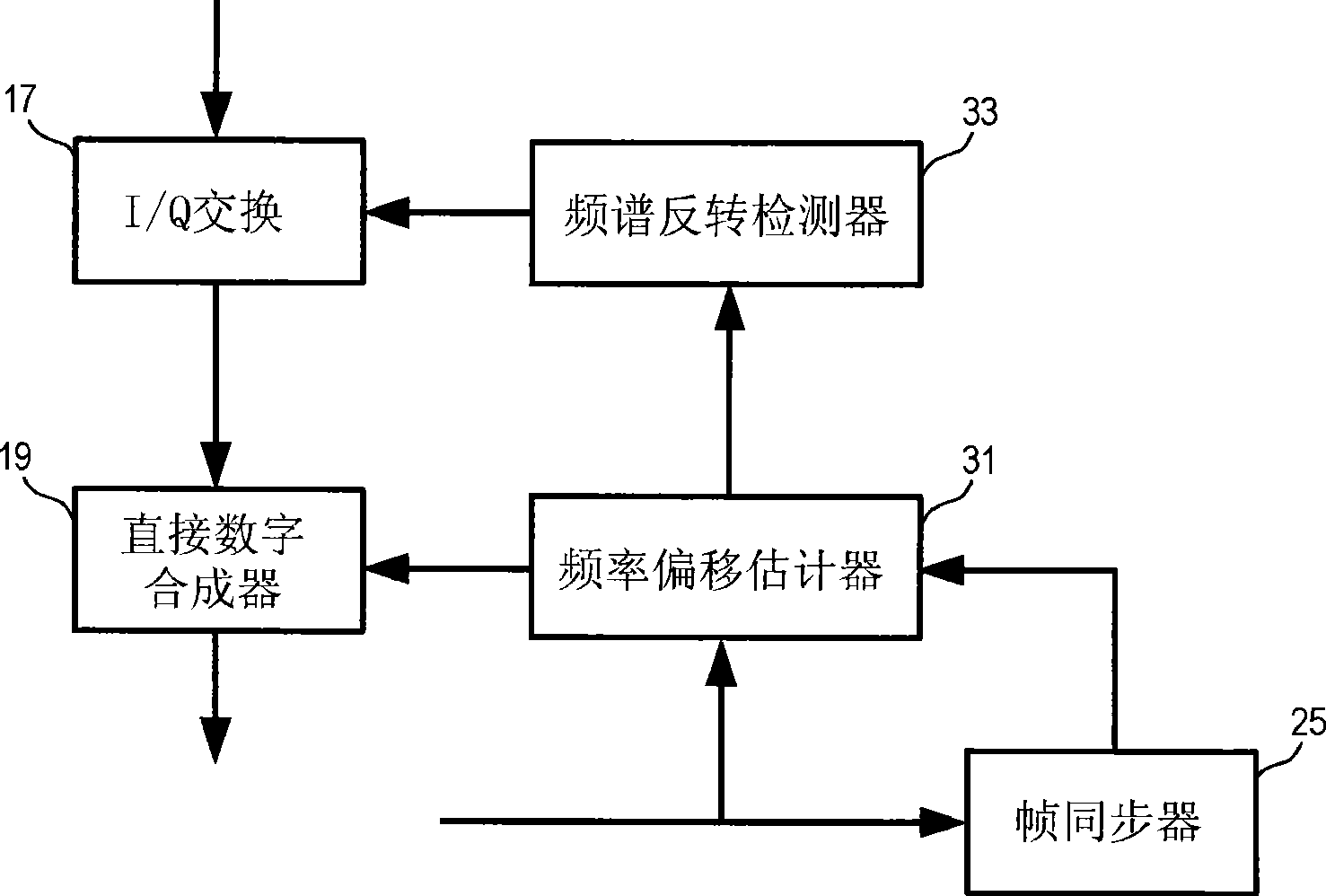
The invention provides methods and apparatuses to detect spectrum inversion based on estimated frequency offset in carrier signal. In one embodiment, a receiver includes an I / Q swap module to output an in-phase component and a quadrature-phase component; a frequency offset estimator to determine an offset in carry frequency of the in-phase and quadrature-phase components; and a spectrum inversiondetector coupled to the frequency offset estimator and the I / Q swap module. The spectrum inversion detector is configured to signal the I / Q swap module to swap the in-phase component and the quadrature-phase component when an absolute value of the offset in carry frequency is above a predetermined threshold.
Owner:MONTAGE TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method and system for communications with reduced complexity receivers
InactiveUS7564910B2Spatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityFrequency spectrumEngineering
The invention provides a new method and system for low complexity, low cost, small component size, and low power communications. The system provides a digital sub-sampling receiver for multiple-antenna wireless receivers, with reduced number of analog RF / IF chains (or one chain) after a fixed number of receive antennas. The system provides a generator of transmit signals / sequences which are preconditioned by the operation of the system to compensate for spectral effects of ultra-low-rate sub-sampling, in that sequences preserve orthogonality under spectral repetition, spectral translation and spectral inversion. The system provides a management device to provide adaptation in transmit signals / waveforms / patterns as a function of channel and data source variations, such that communication data rates and capacities are maximized. The system can efficiently operate in multi-user multi-channel communication systems. The method implemented by the invention is split in its operation across the transmitter of the transmitting device and the receiver of the receiving device.
Owner:KOSTIC ZORAN
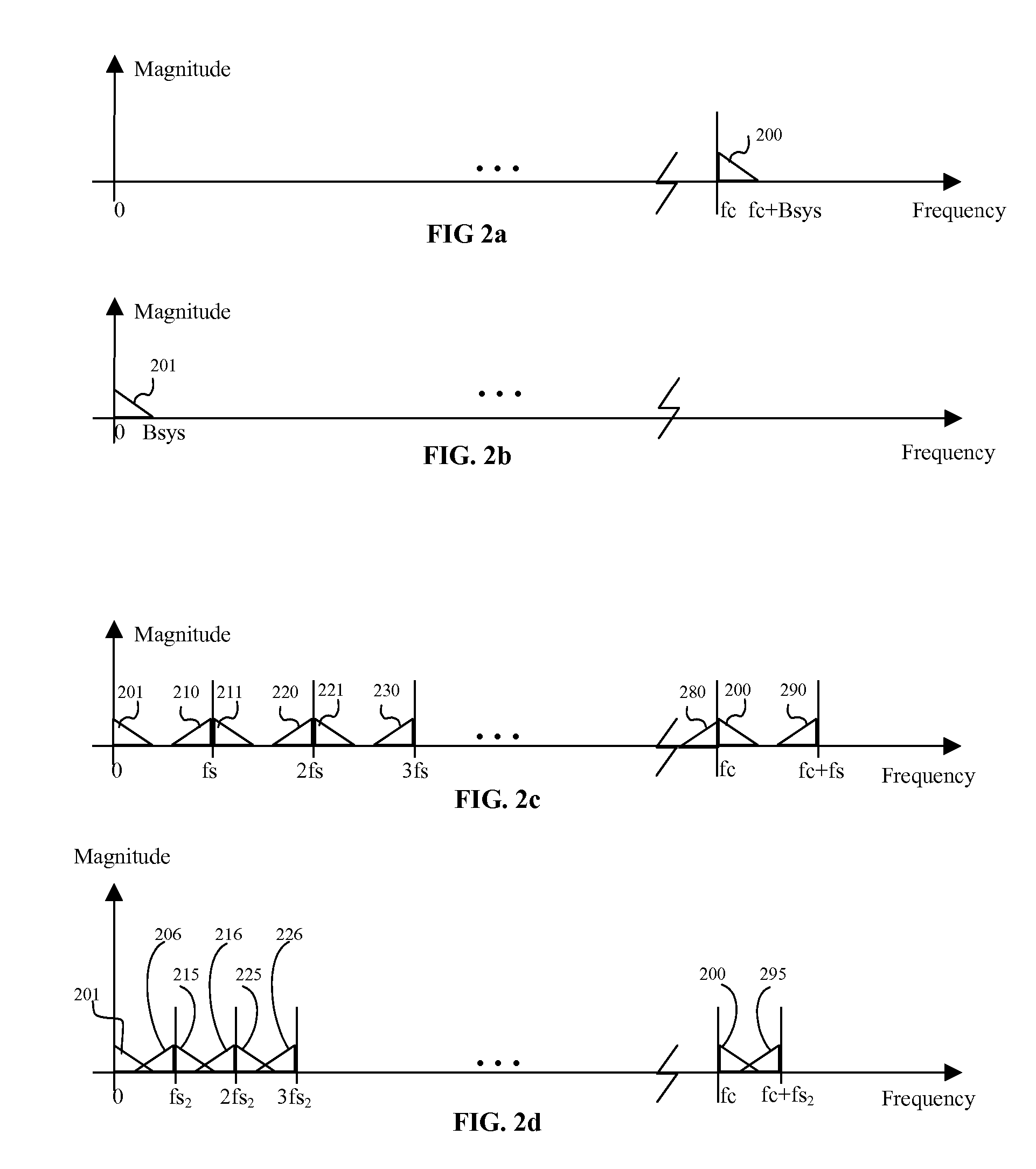
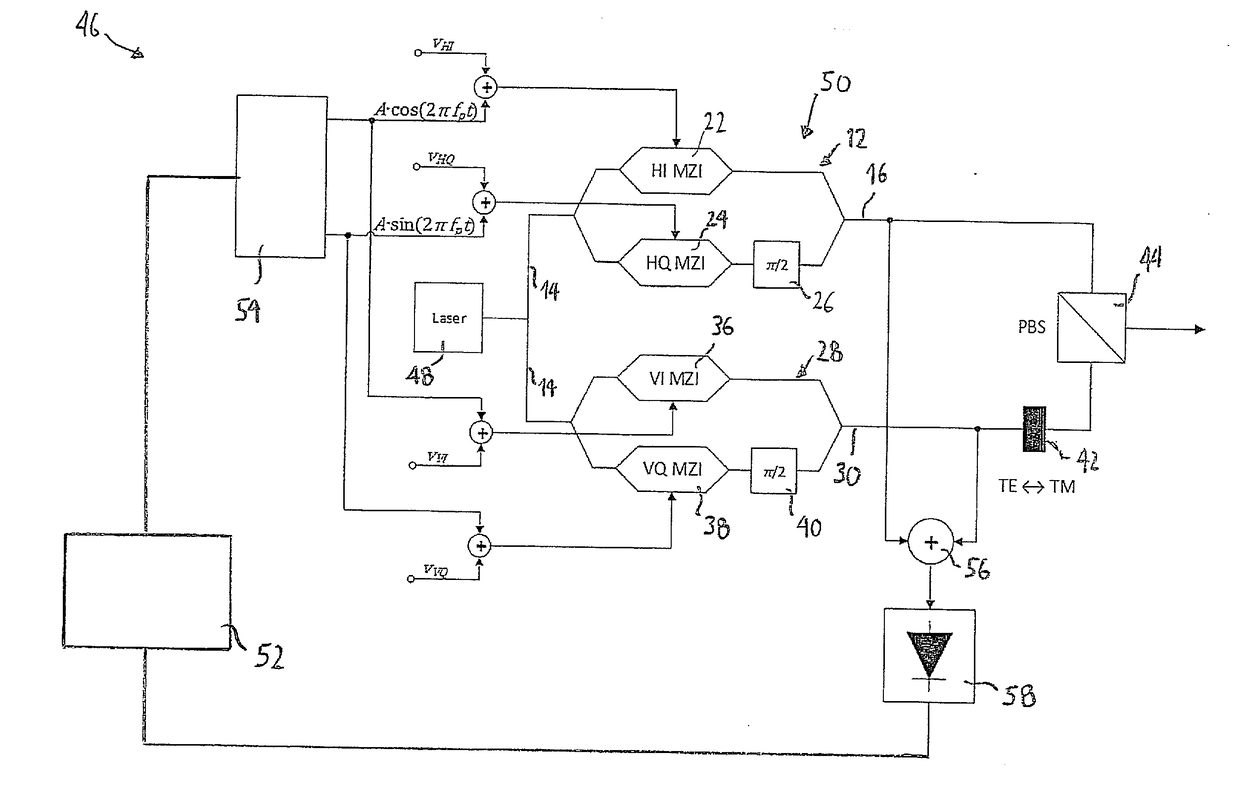
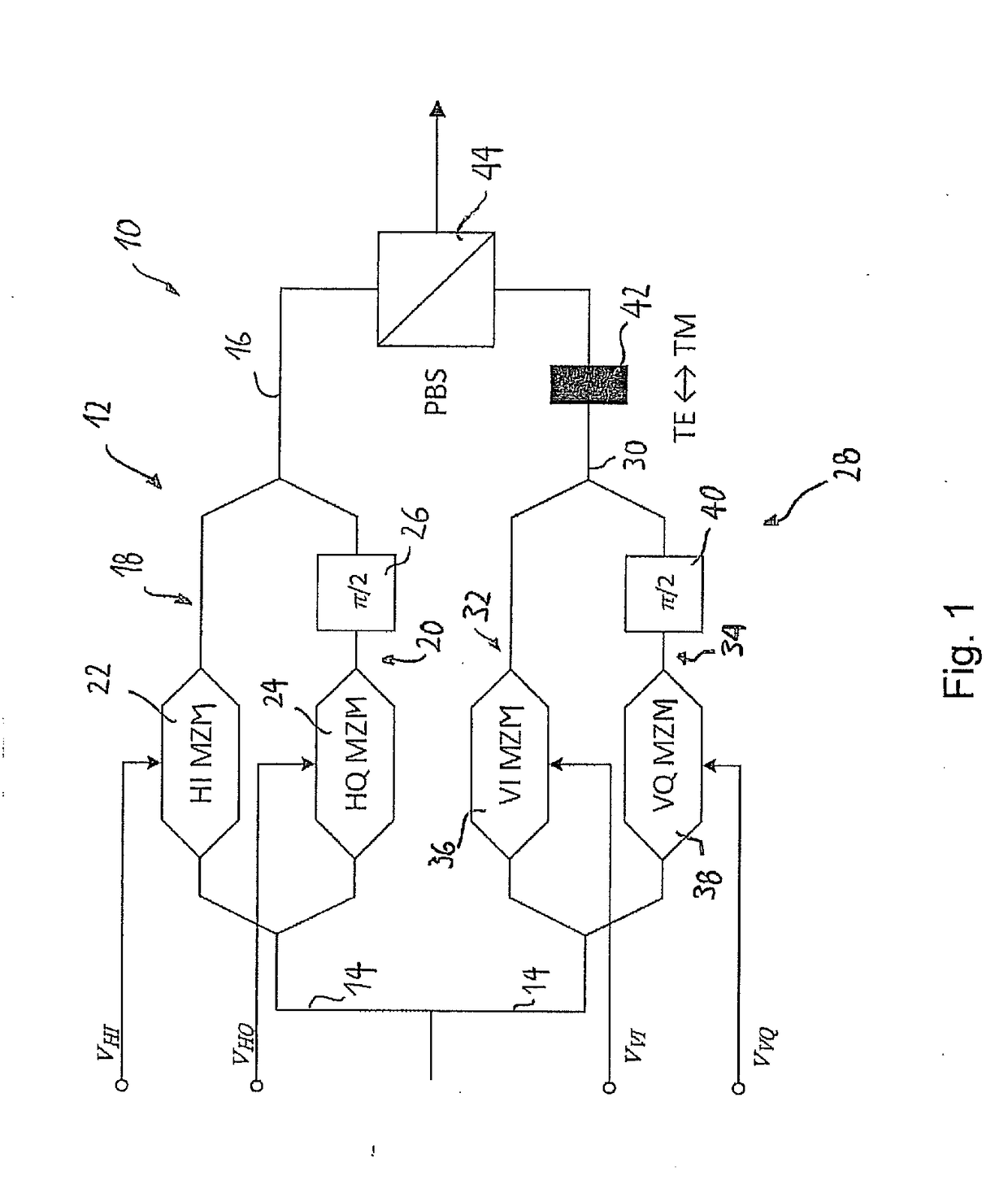
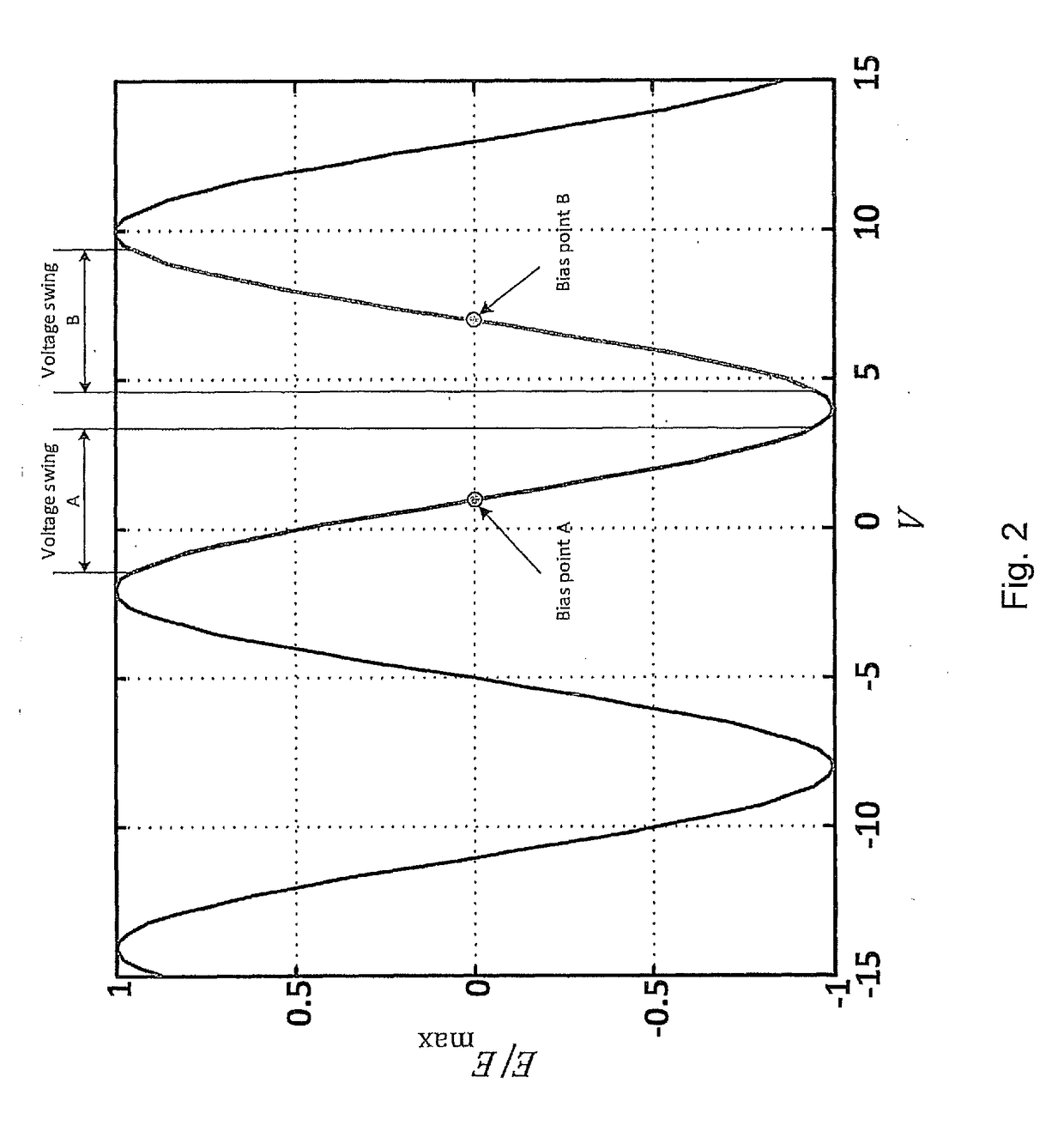
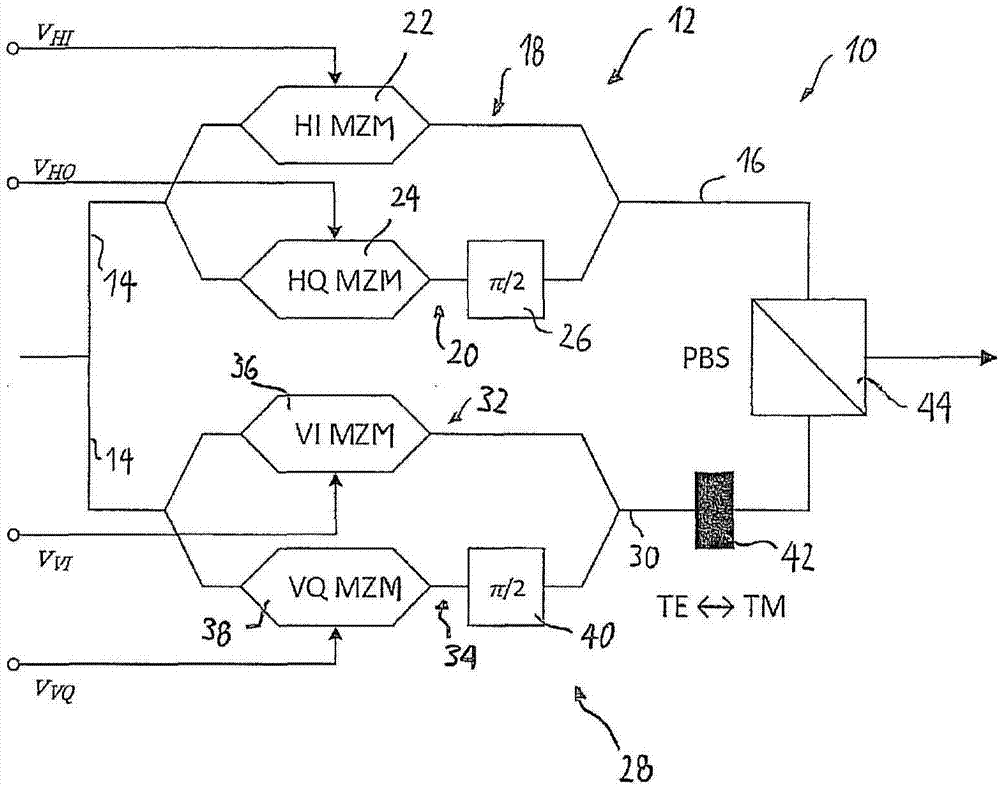
Spectral inversion detection for polarization-division multiplexed optical transmission
ActiveUS20170264389A1Efficient and reliableEfficient and reliable processingPolarisation multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersMultiplexingFrequency spectrum
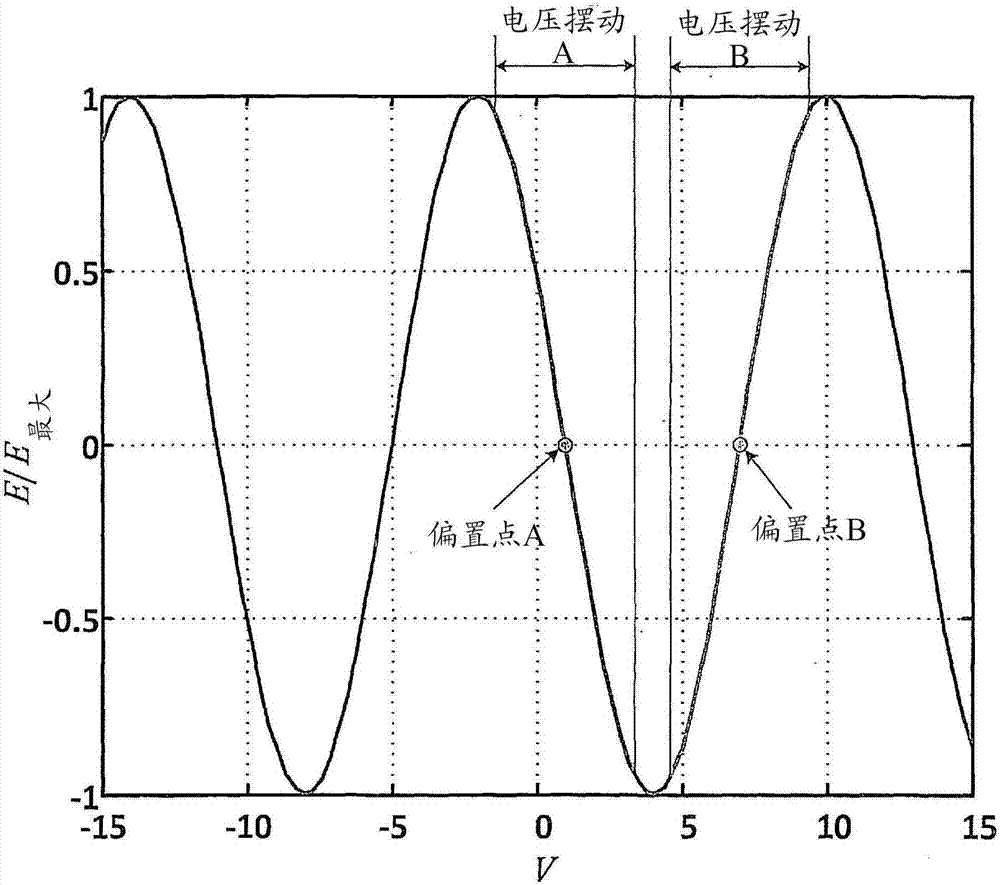
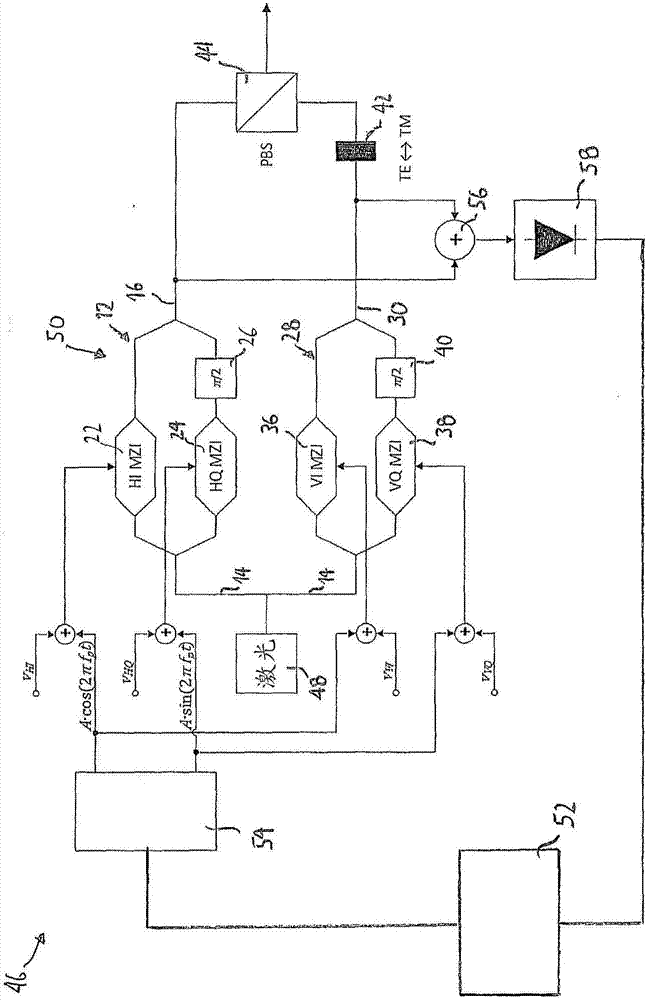
Disclosed herein is a modulator (50) for polarization-division multiplexing (PDM) transmission. The modulator (50) comprises first and second DP-MZMs (12, 28) associated with first and second polarizations, each DP-MZM (12, 28) having an input for an in-phase and a quadrature driving signal for modulating the in-phase and quadrature components of an optical signal according to respective transfer functions, and a detector (58) suitable for detecting light comprising at least a portion of the light outputted by the first DP-MZM (12) and a portion of the light outputted by the second DP-MZM (28). The modulator (50) is adapted to superimpose a first pilot signal on one of the in-phase and quadrature driving signals of the first DP-MZM (12) and on one of the in-phase and quadrature driving signals of the second DP-MZM (28), and a second pilot signal on the respective other of the in-phase and quadrature driving signals of the first and second DP-MZMs (12, 28). Further, the first and second pilot signals are chosen such that the signal detected by said detector (58) is indicative as to whether the slopes of the transfer functions are different for the in-phase and quadrature components of one of the first and second DP-MZMs (12, 28) and identical for the other of the first and second DP-MZMs (12, 28).
Owner:XIEON NETWORKS SARL
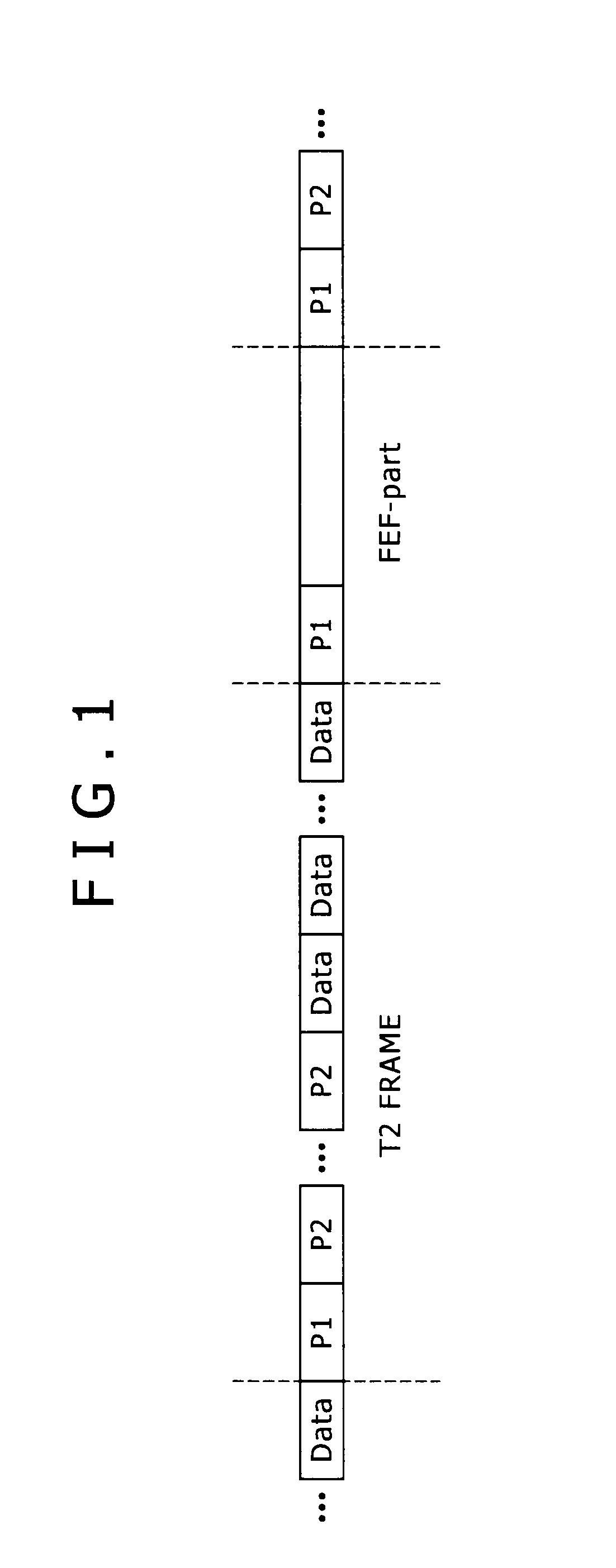
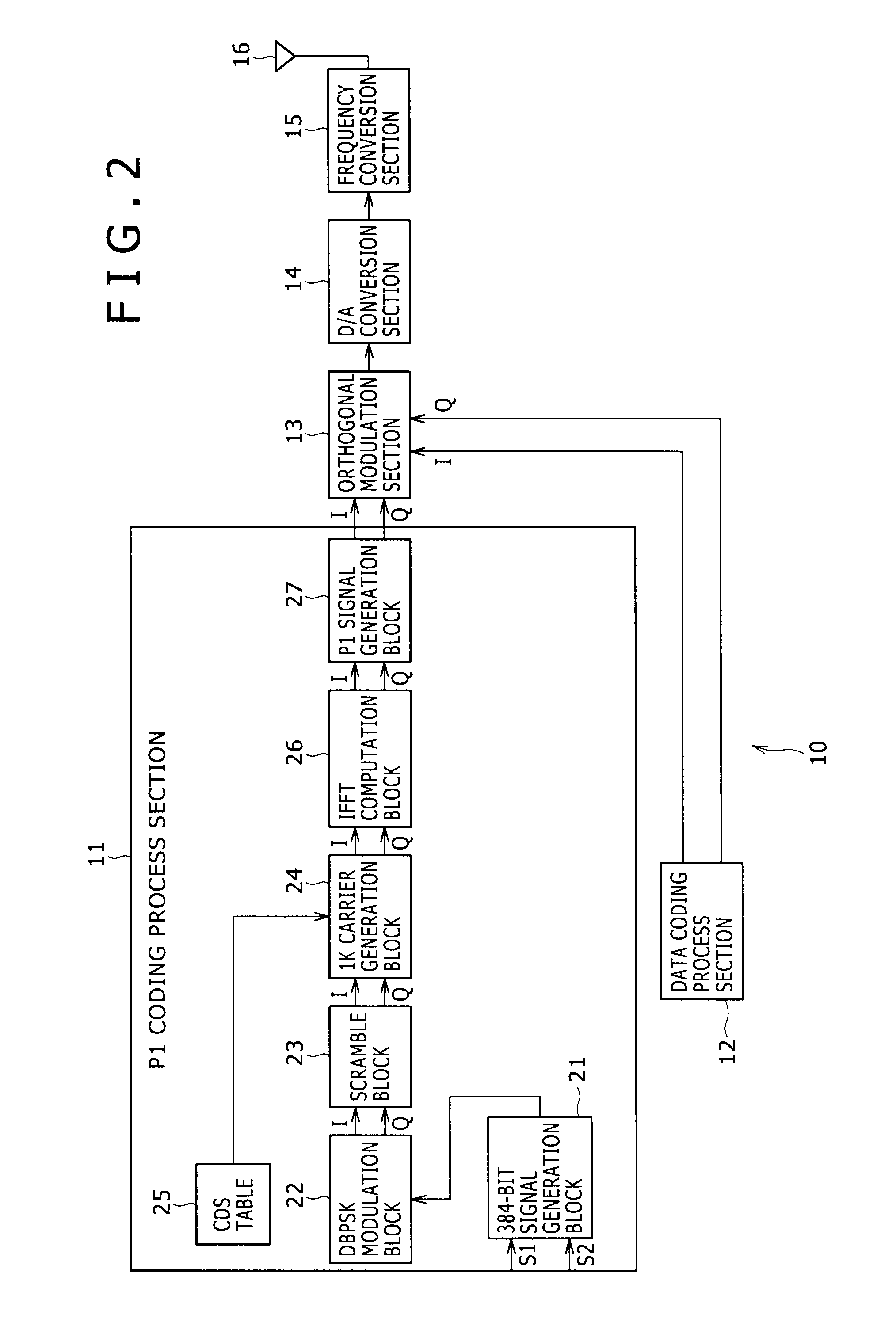
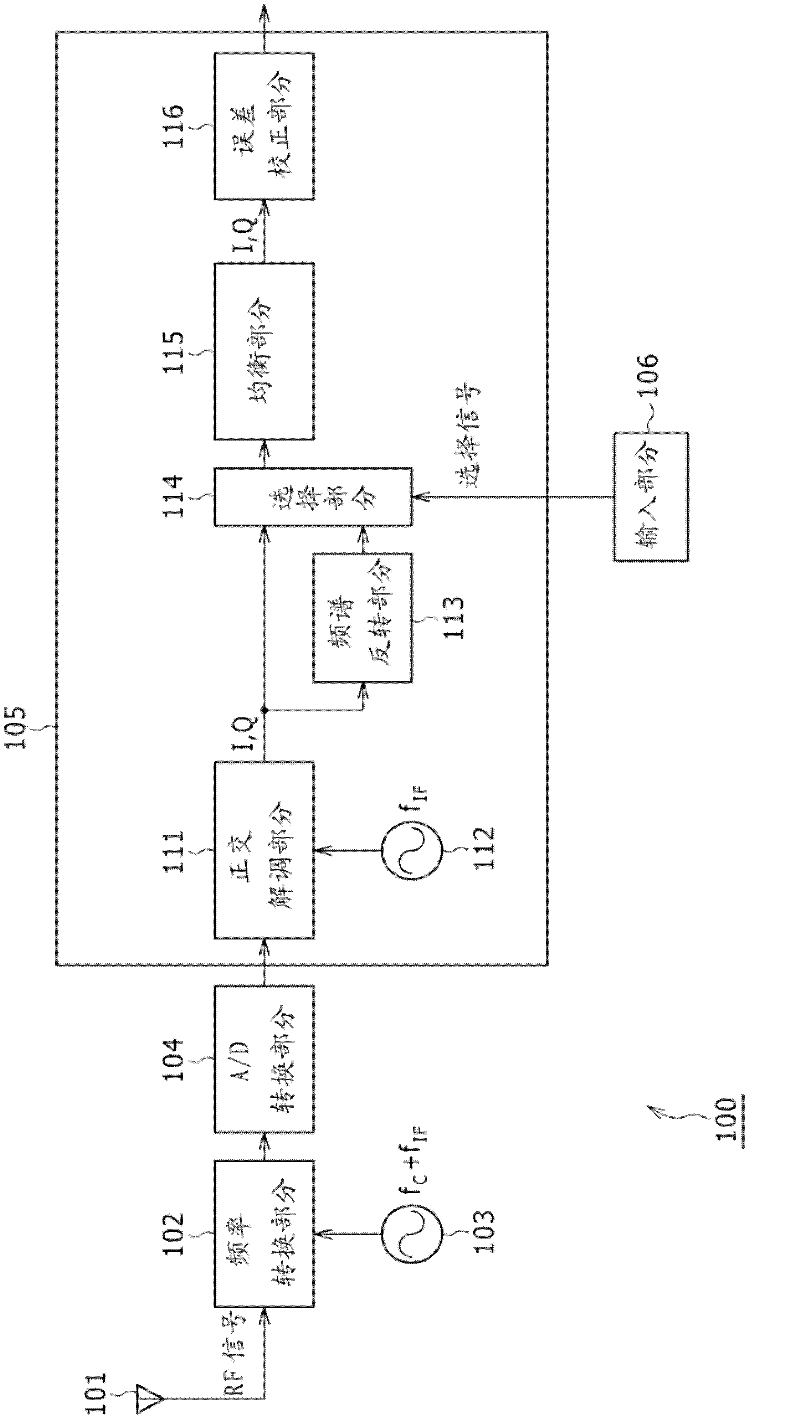
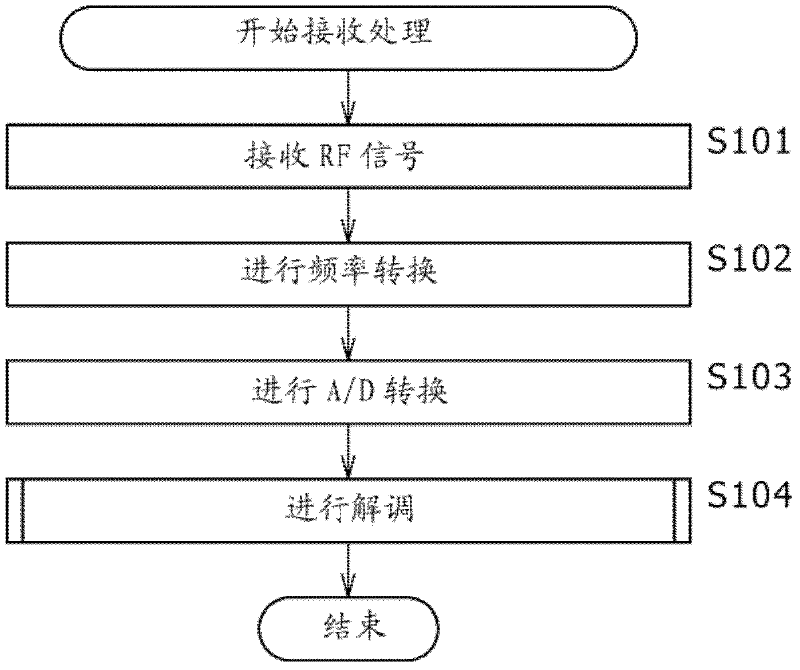
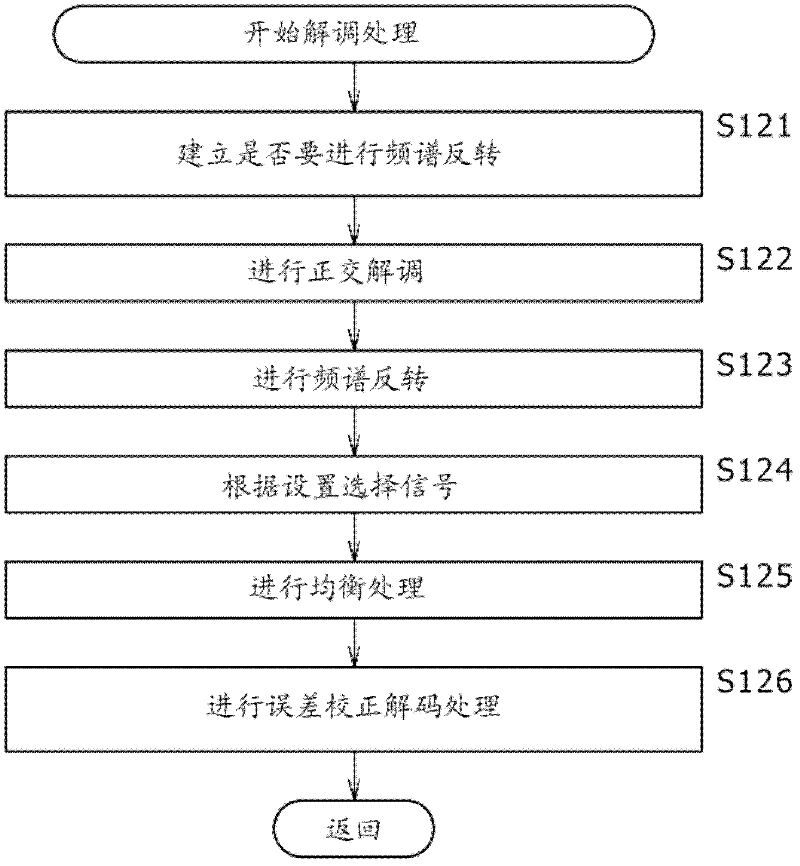
Reception apparatus, reception method, reception program, and reception system
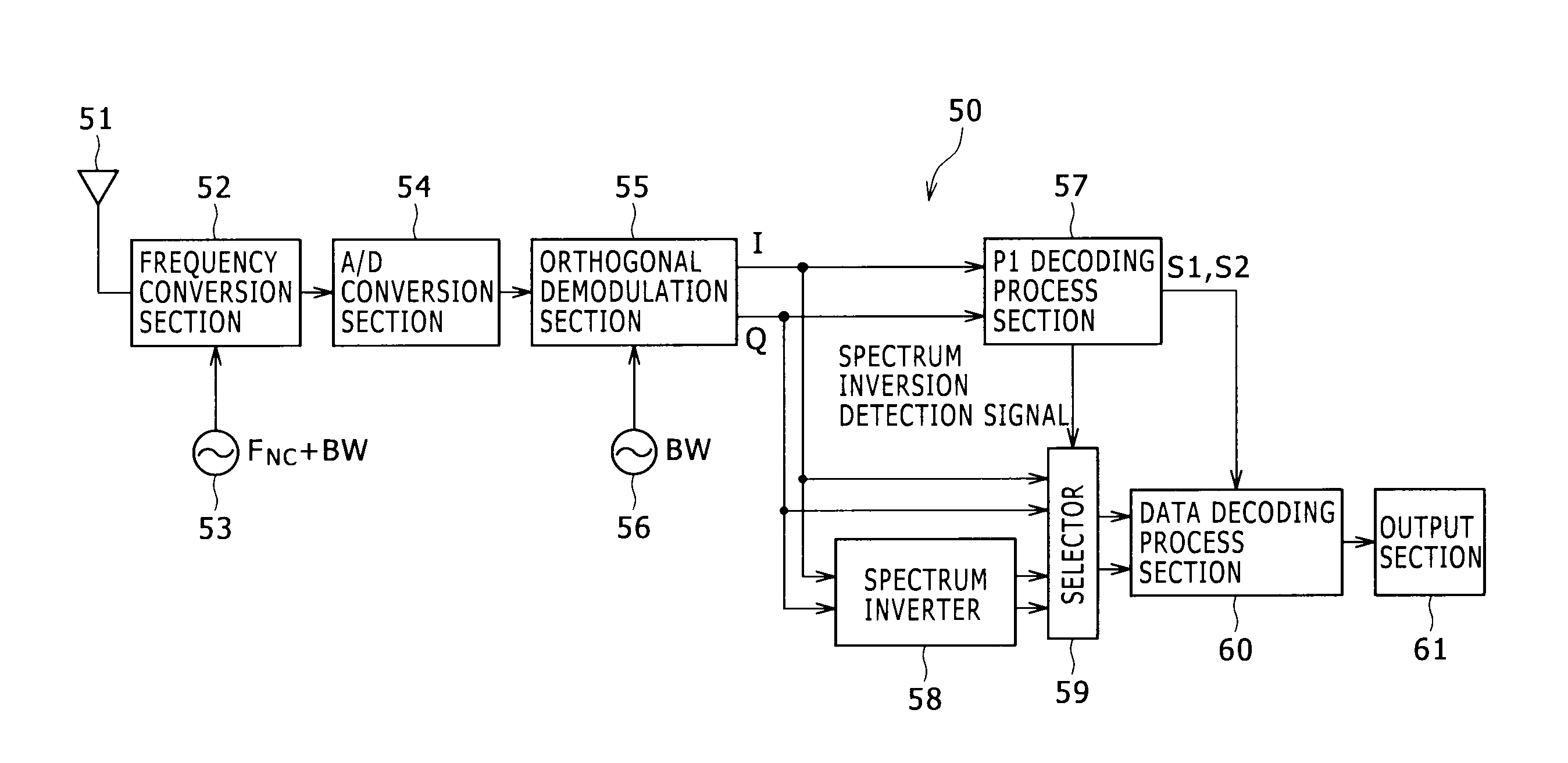
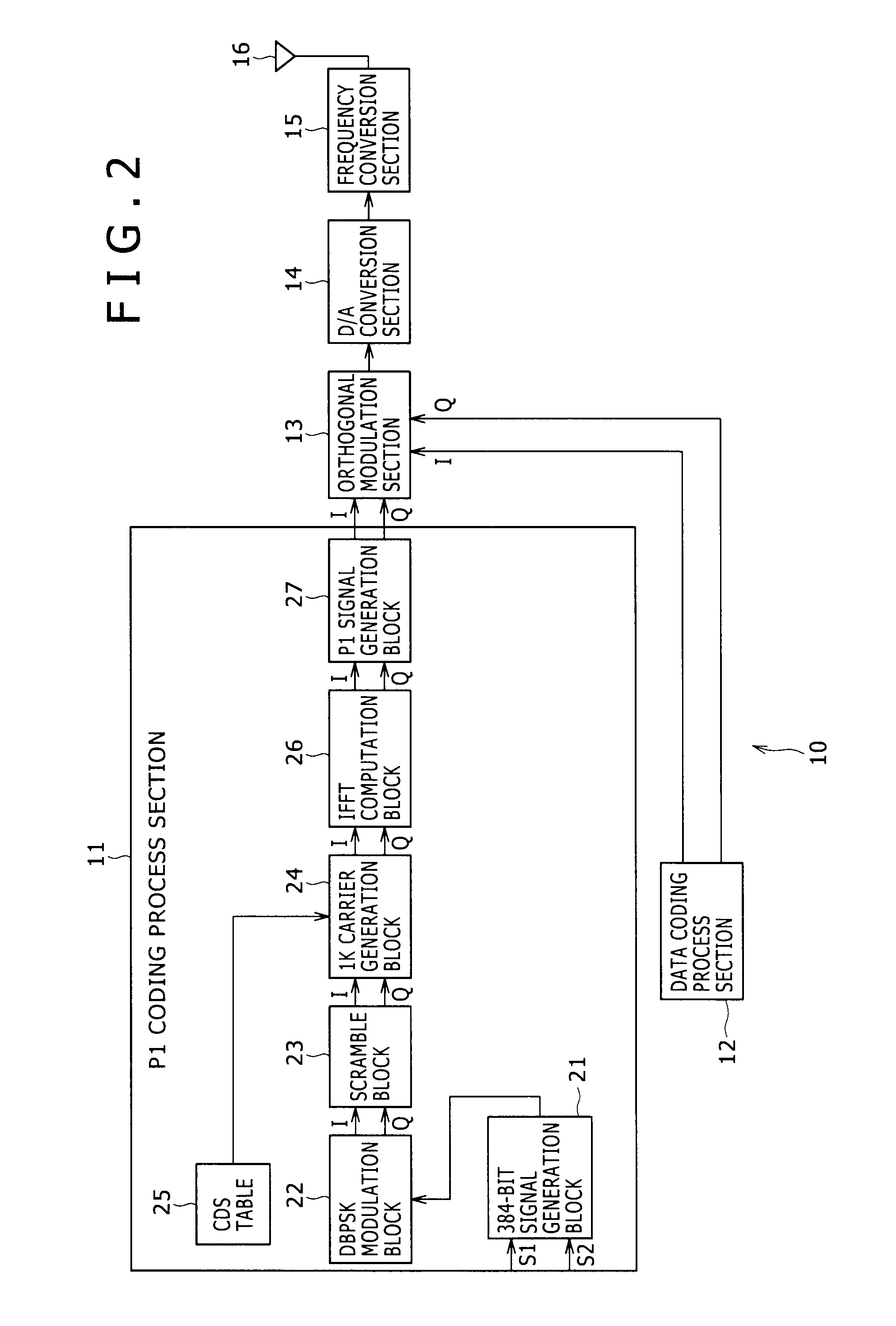
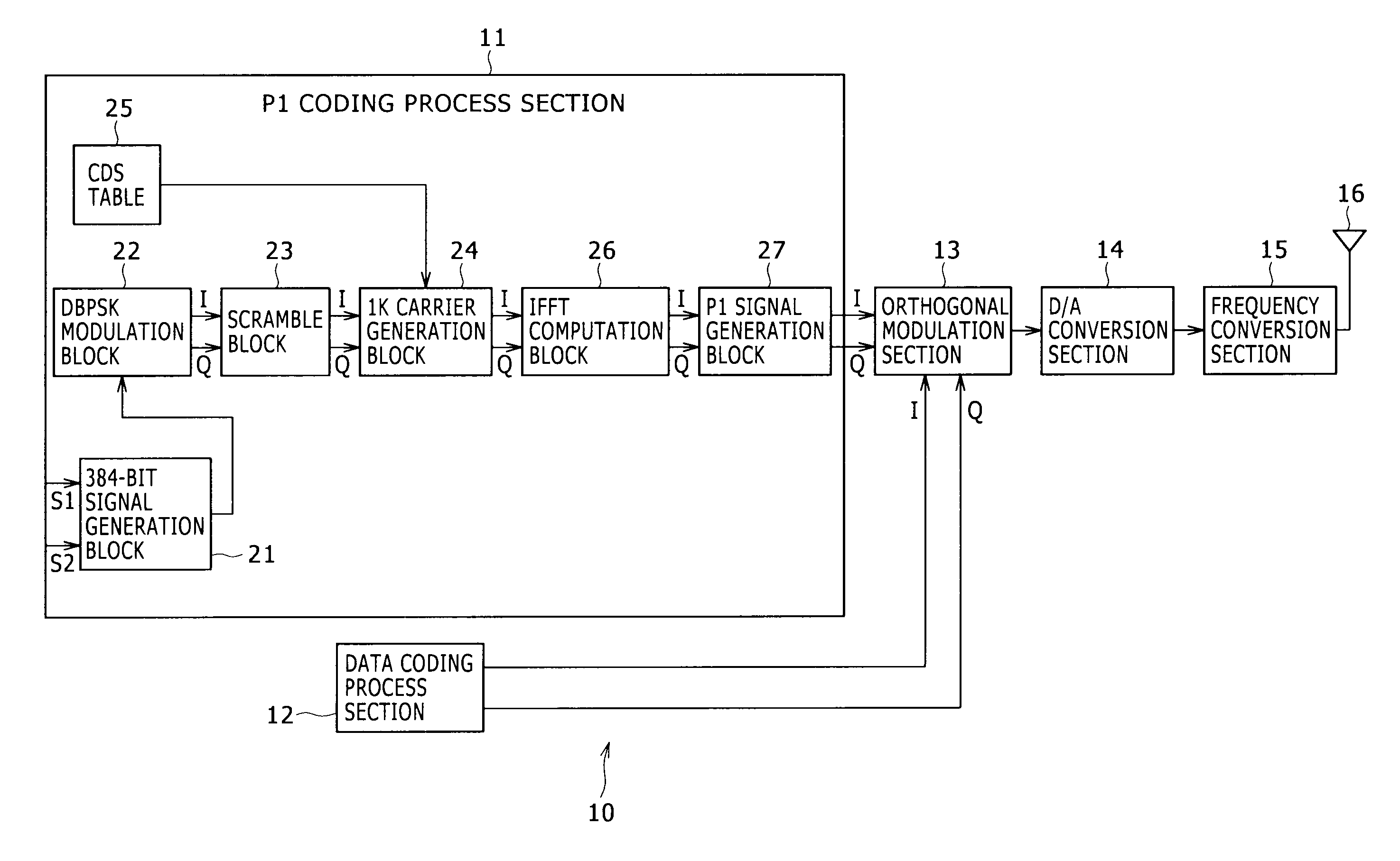
ActiveUS8537939B2Accurate demodulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationDigital videoFrequency spectrum
Disclosed herein is a reception apparatus including: a spectrum inversion detection section configured to detect the occurrence or absence of spectrum inversion in a received signal complying with the Digital Video Broadcasting-Terrestrial 2 standard known as DVB-T2, using a P1 signal constituting the received signal; a spectrum inversion section configured to perform a spectrum inversion process on the received signal if the occurrence of the spectrum inversion is detected at least by the spectrum inversion detection section; and a demodulation section configured to demodulate the received signal having undergone the spectrum inversion process if the occurrence of the spectrum inversion is detected by the spectrum inversion detection section, the demodulation section further demodulating the received signal yet to undergo the spectrum inversion process if the absence of the spectrum inversion is detected by the spectrum inversion detection section.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Reception apparatus, reception method, reception program, and reception system
ActiveUS20110142098A1Accurate demodulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationDigital videoFrequency spectrum
Disclosed herein is a reception apparatus including: a spectrum inversion detection section configured to detect the occurrence or absence of spectrum inversion in a received signal complying with the Digital Video Broadcasting-Terrestrial 2 standard known as DVB-T2, using a P1 signal constituting the received signal; a spectrum inversion section configured to perform a spectrum inversion process on the received signal if the occurrence of the spectrum inversion is detected at least by the spectrum inversion detection section; and a demodulation section configured to demodulate the received signal having undergone the spectrum inversion process if the occurrence of the spectrum inversion is detected by the spectrum inversion detection section, the demodulation section further demodulating the received signal yet to undergo the spectrum inversion process if the absence of the spectrum inversion is detected by the spectrum inversion detection section.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
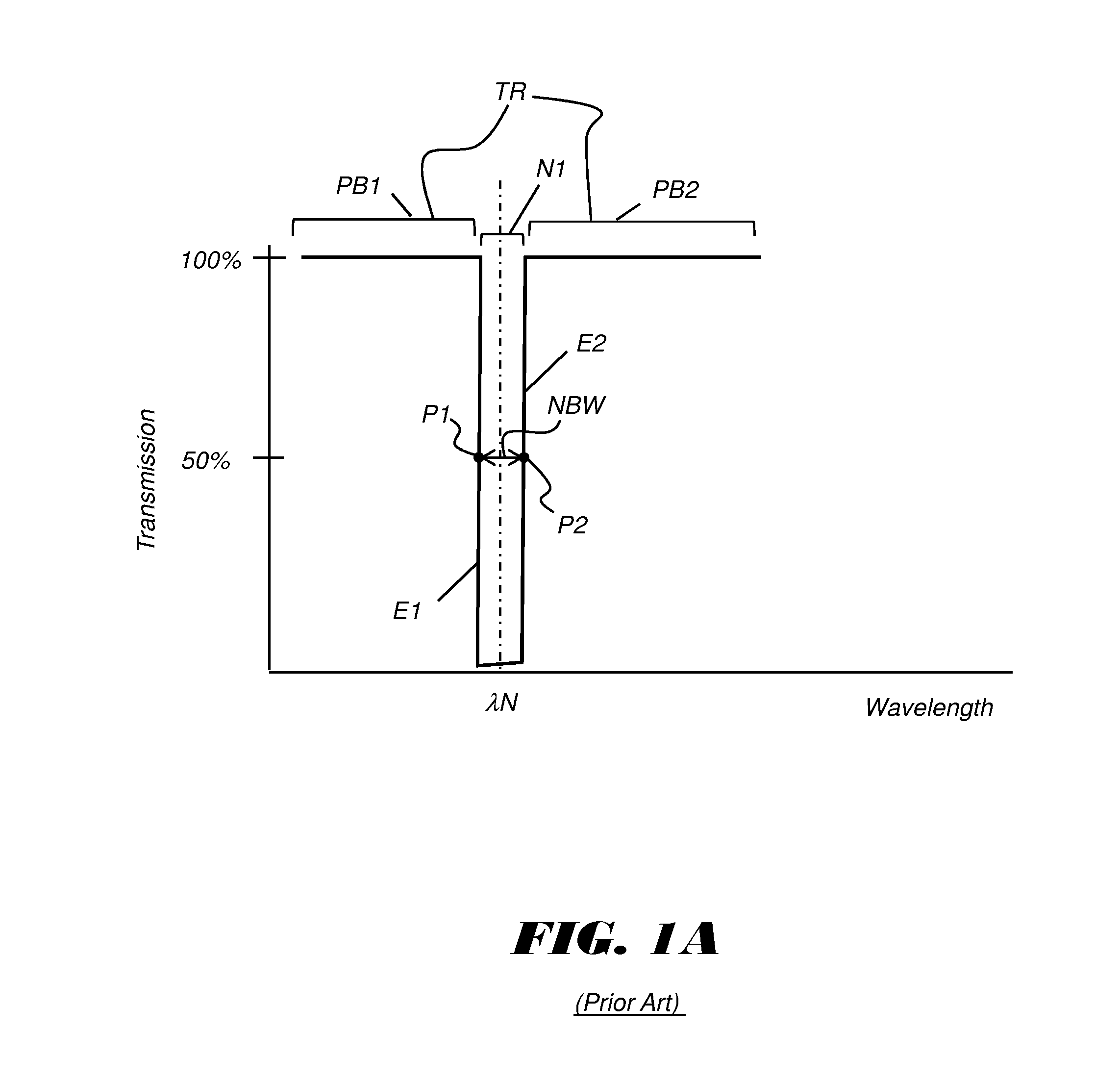
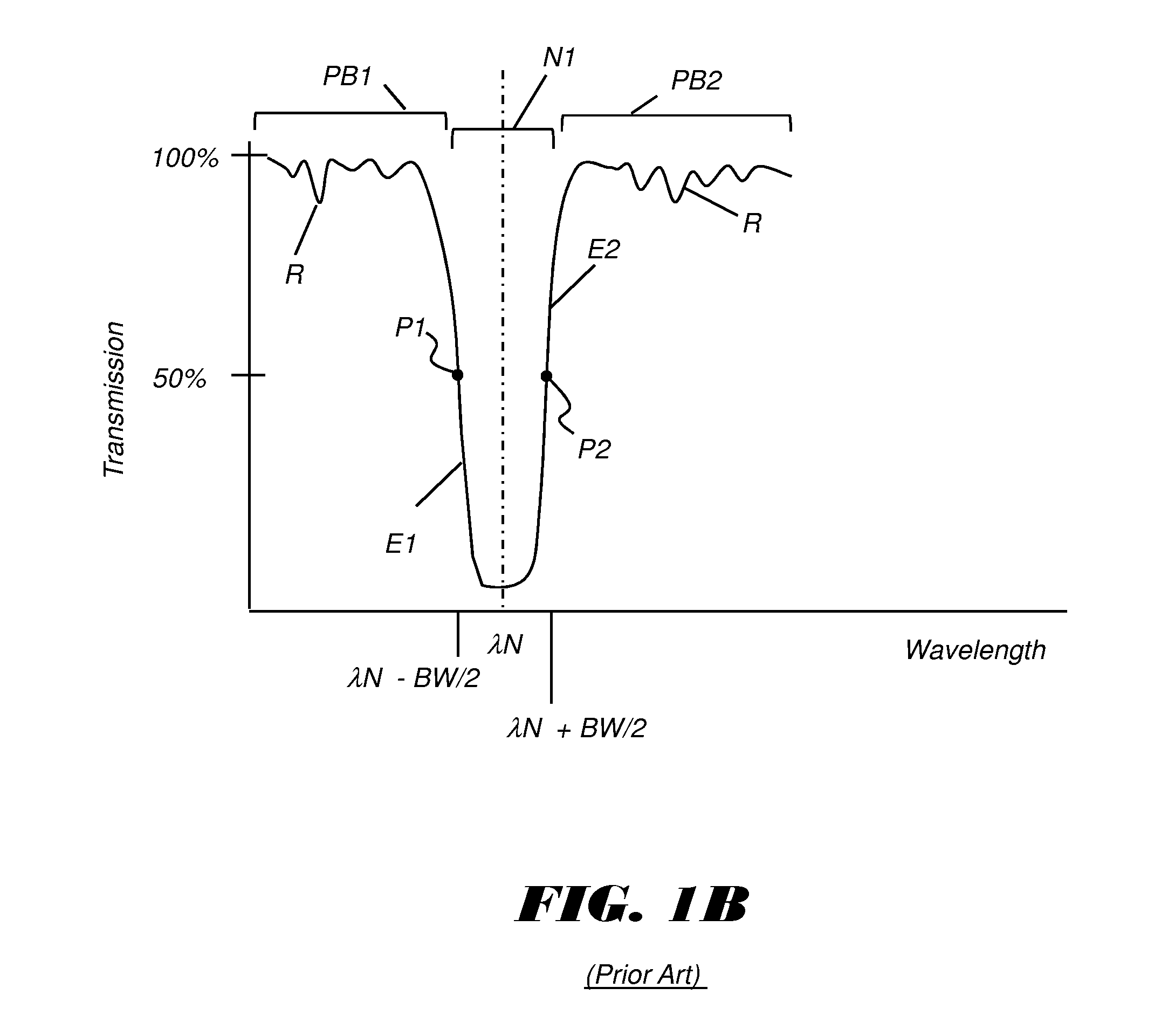
Notch filter system using spectral inversion
An optical filter apparatus transmits less than 5% of light within a notch spectral range about a central line wavelength with a notch bandwidth, and transmits more than 90% of light within a transmission spectral range that extends over an adjacent pass band of longer and shorter wavelengths and excludes the notch. The apparatus has a first thin film interference filter and a second thin film interference filter in the path of incident light reflected from the first filter. The first and second thin film interference filters are each treated to transmit light of the notch spectral range and reflect light of the transmission spectral range and each have thin film layers formed on a substrate, including first layers having a first refractive index, and second layers having a higher second refractive index. The notch bandwidth at full width half transmission is less than 5% of the central line wavelength.
Owner:SEMROCK
Signal processing apparatus, signal processing method and program
InactiveCN102457354AAppropriate treatmentBaseband system detailsForward error control useFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
A signal processing apparatus is disclosed which includes: a detection section configured such that based on a result of the error correction of a signal generated by a single carrier system, the detection section detects the presence or absence of spectrum inversion in the signal; and a selection section configured such that if the detection section detects the spectrum inversion, the selection section selects the spectrally inverted signal as the signal subject to the error correction, and that if the detection section does not detect the spectrum inversion, then the selection selects the spectrally uninverted signal as the signal subject to the error correction.
Owner:SONY CORP
Systems and methods of using IQ modulation for calibration or measurement
InactiveUS7397865B2High signal accuracyImprove accuracyNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency spectrumImage resolution
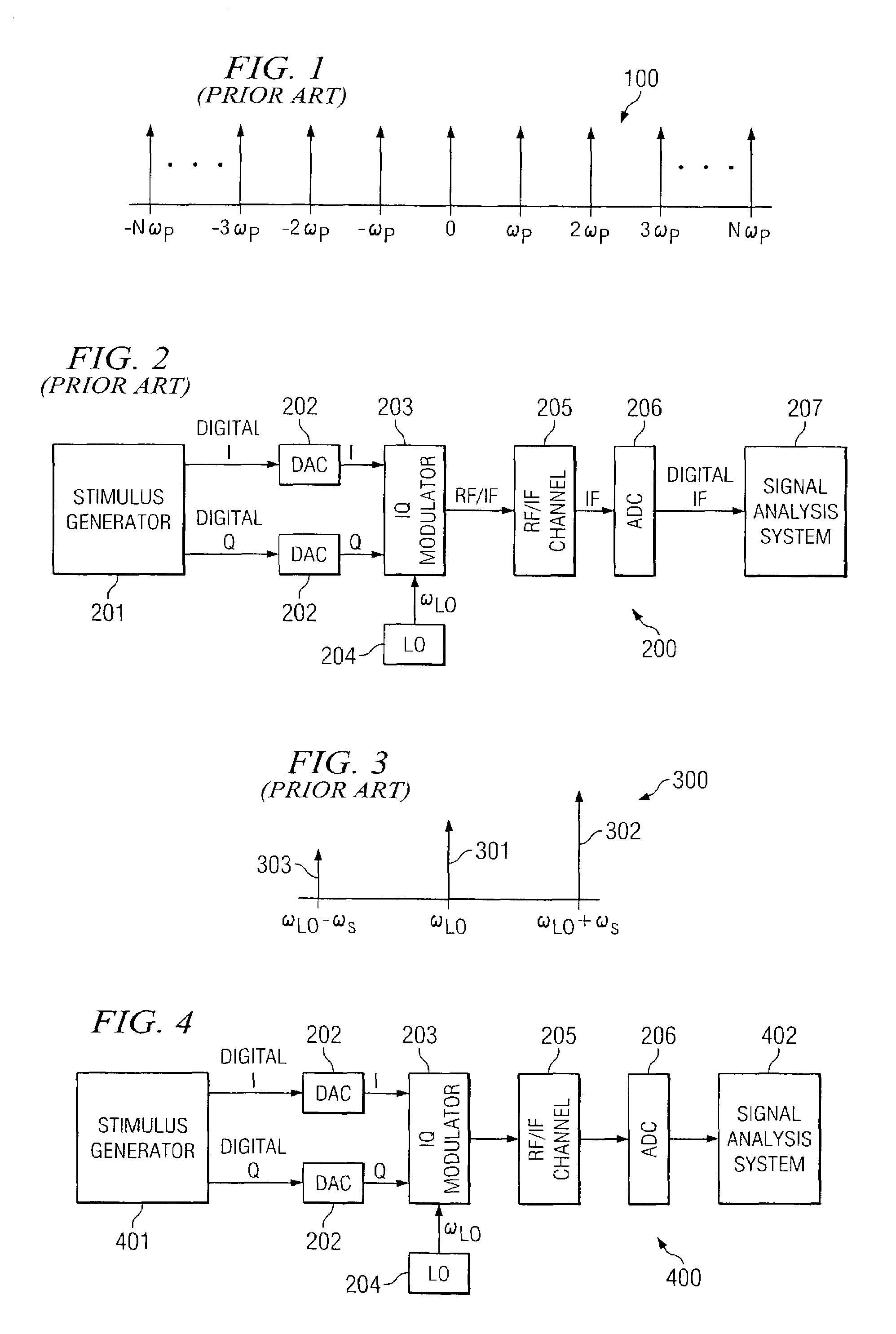
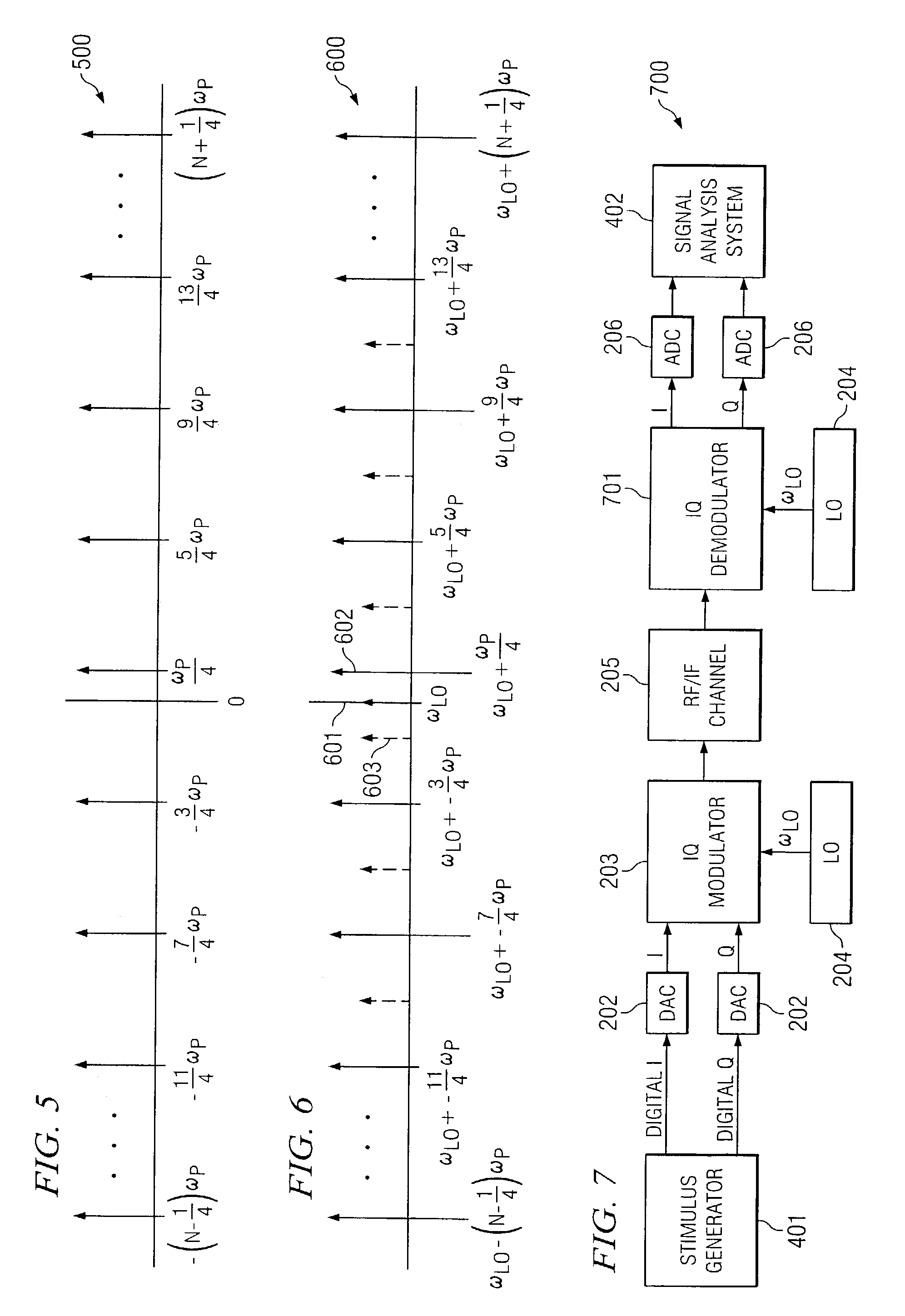
A system analyzer may generate an estimated frequency response of a device, system, communication medium, or combination thereof by utilizing a stimulus signal that is robust against IQ modulator impairments. A stimulus generator may be used to generate a plurality of discrete tones according to a frequency spacing and a frequency offset. The frequency spacing and the frequency offset cause spectrally inverted spurs (generated by impairments of the IQ modulator) to occur at frequencies other than frequencies of said modulated signal that are associated with said plurality of discrete tones. Additionally, by implementing a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) to possess a frequency resolution equal to the frequency offset, there is no leakage of power associated with the spectrally inverted spurs into frequency bins of the DFT associated with the desired frequency components. Likewise, leakage between the desired frequency components and leakage associated with the local oscillator may be avoided.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method and device for field rapid detection on content of nitrogen and phosphorus substances in eutrophic water
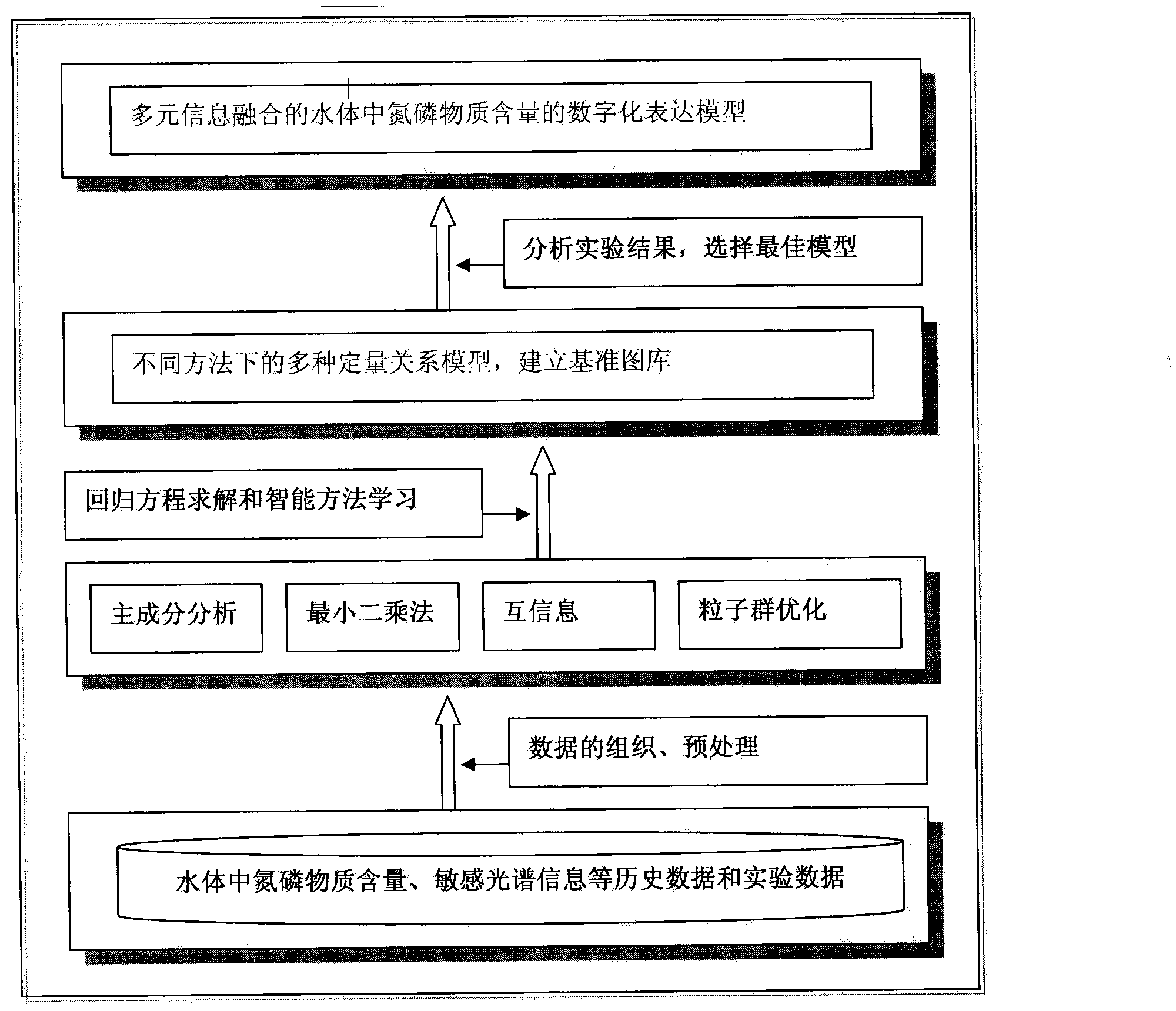
InactiveCN103674835AImprove universalityImprove accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsChemical oxygen demandSignal on
The invention relates to a real-time, convenient and reliable method for field rapid detection on the content of nitrogen and phosphorus substances in eutrophic water, and a low-cost field detection device mounted in an ocean wireless measurement and control network or an aquaculture Internet of Things. A simulation study on spectral inversion of the content of nitrogen and phosphorus substances in water is carried out, and the effect of spectral signals on chromatic aberration is fused effectively. On the basis, a relatively complete sample set of spectral characteristic information of eutrophication characterization parameters, such as soluble organic matters, chemical oxygen demand, total nitrogen and total phosphorus, is established as a reference image library; the reference image library contains prominent features, such as gray levels, image borders, outlines, surfaces and spectral lines. Finally, obtained images (including spectral information images) are compared with the reference image library and analyzed, sequentially, chromatic aberration of water eutrophication can be inversed and simulated, and the total content of nitrogen and phosphorus substances can be deduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
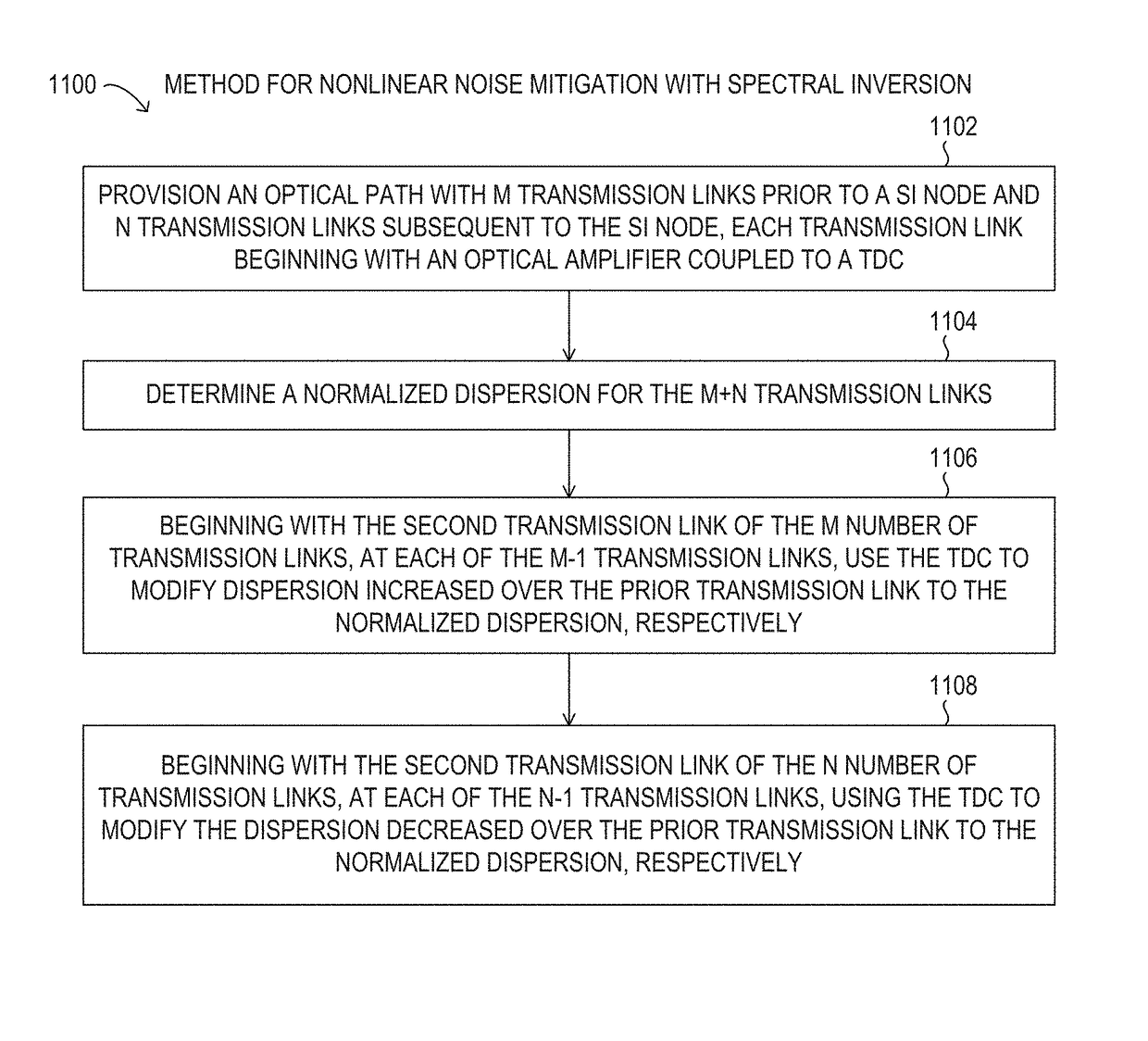
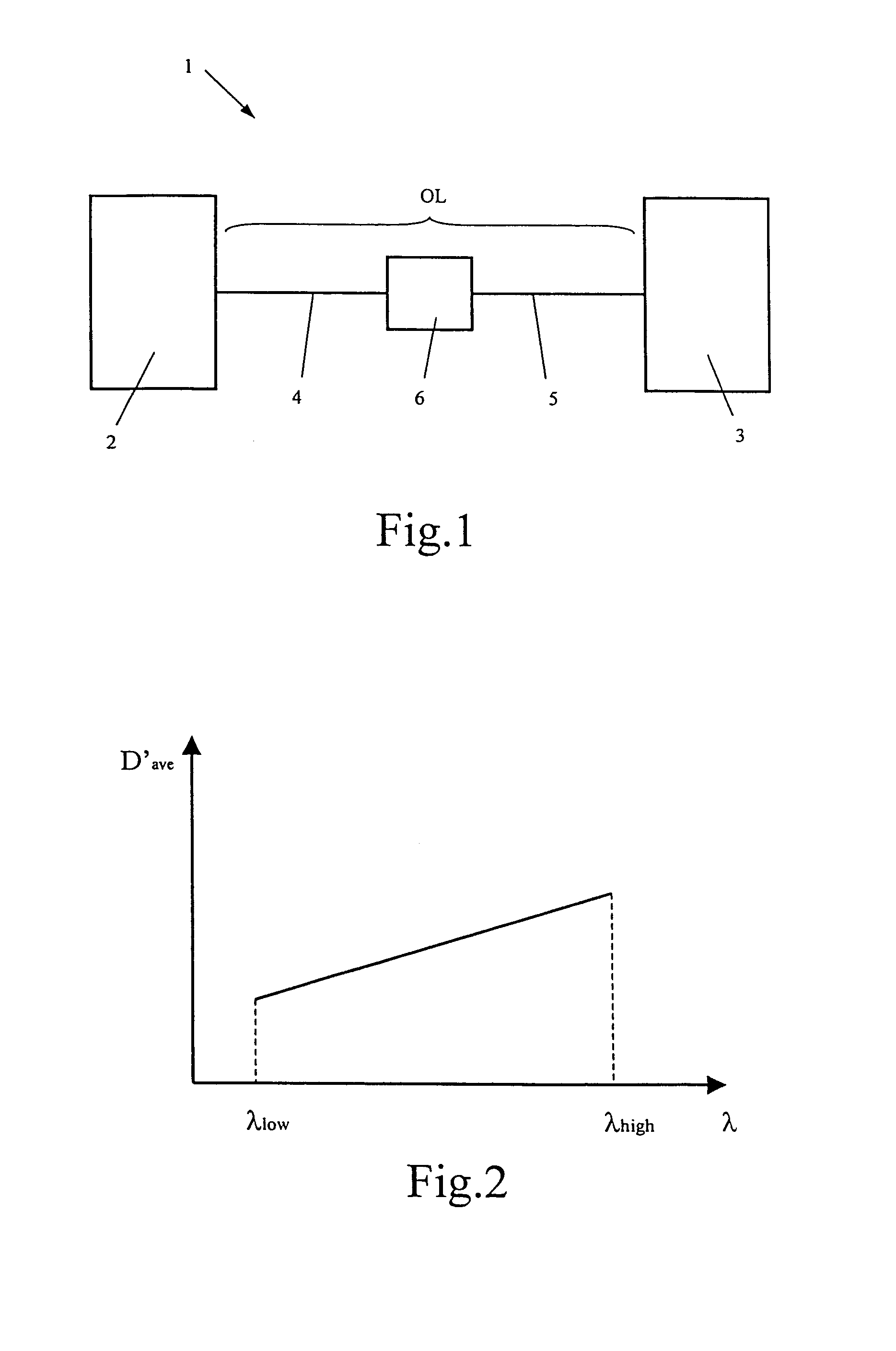
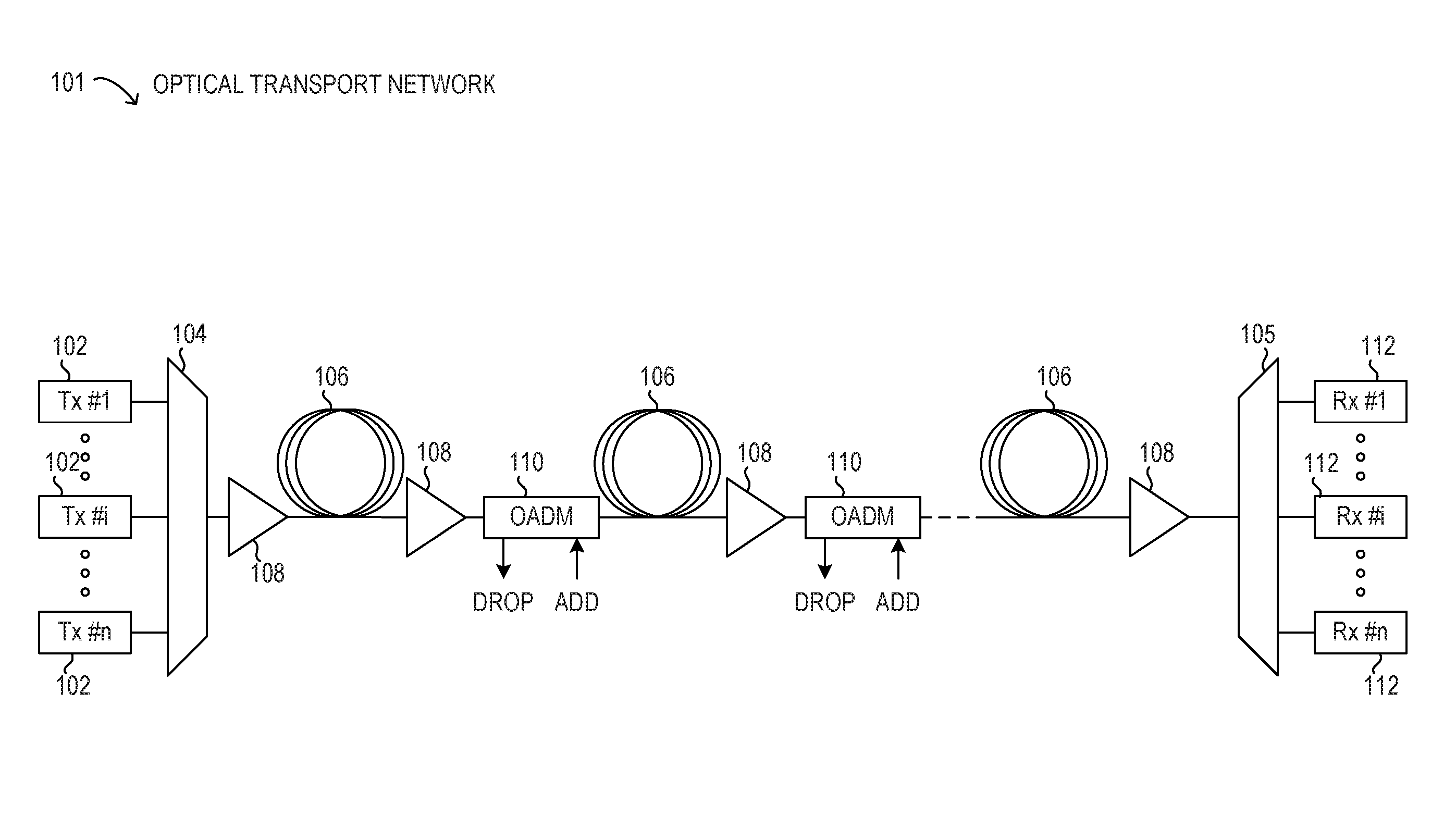
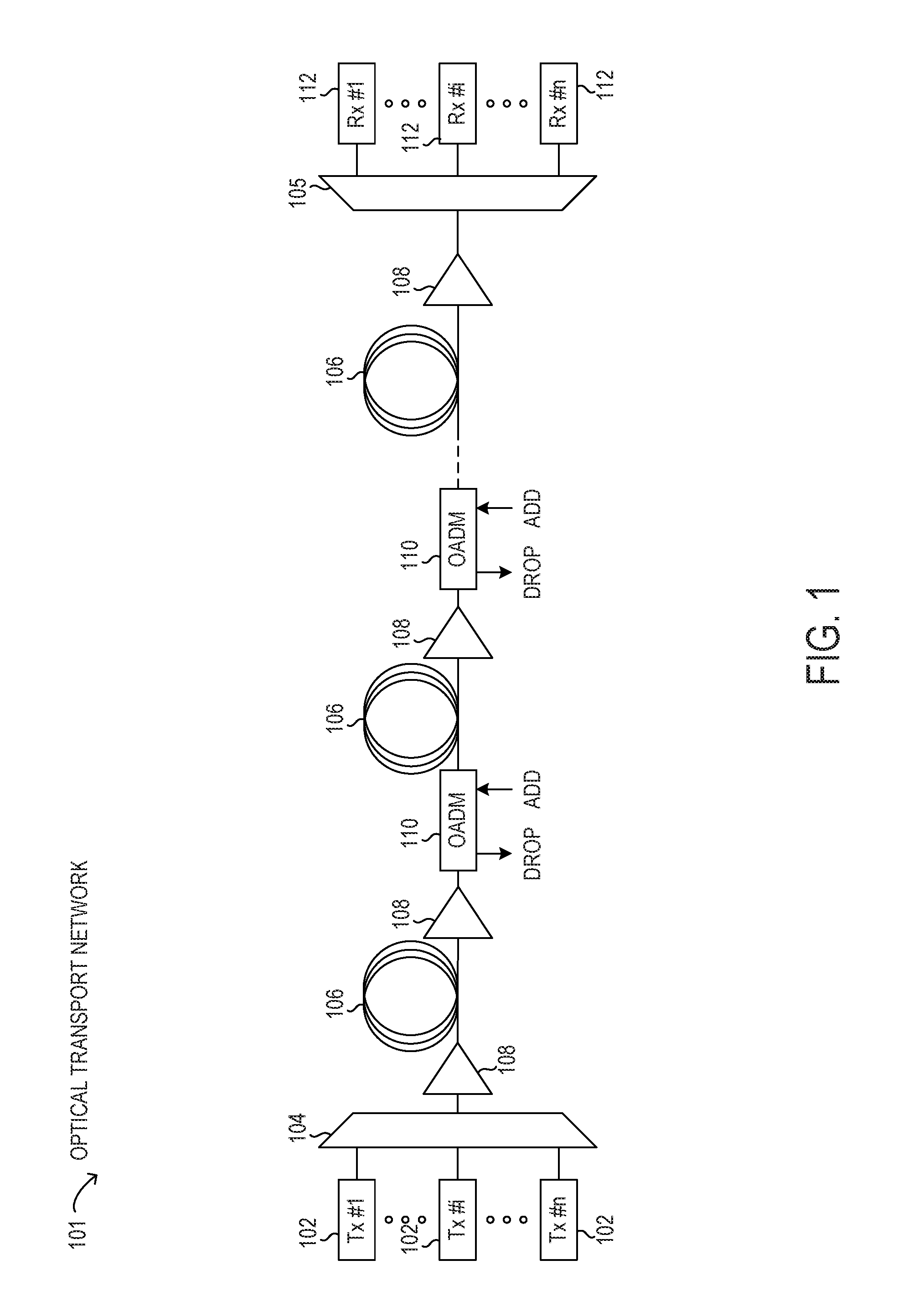
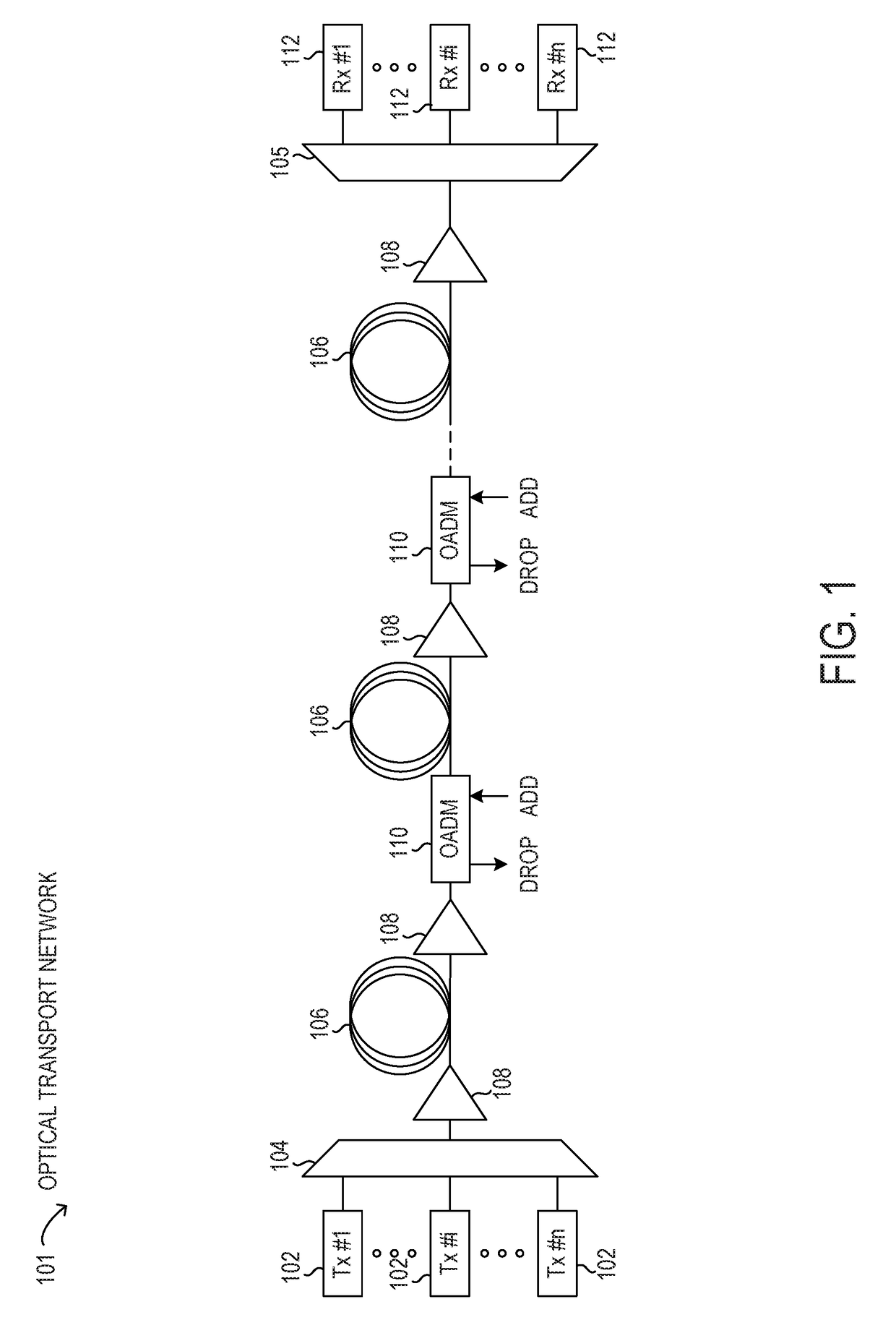
Nonlinear noise mitigation with spectral inversion in optical transport networks
ActiveUS9838123B1Mitigating nonlinear noiseElectromagnetic network arrangementsDistortion/dispersion eliminationFrequency spectrumTransport network
Methods and systems may mitigate nonlinear noise (NLN) penalties for optical paths using spectral inversion in optical transport networks. Using a tunable dispersion compensator with an optical amplifier at each span in an optical path, the dispersion along the optical path may be modified to a normalized dispersion for each span. In this manner, the dispersion associated with NLN accumulation may be balanced by NLN compensation to reduce overall NLN levels for the optical path.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
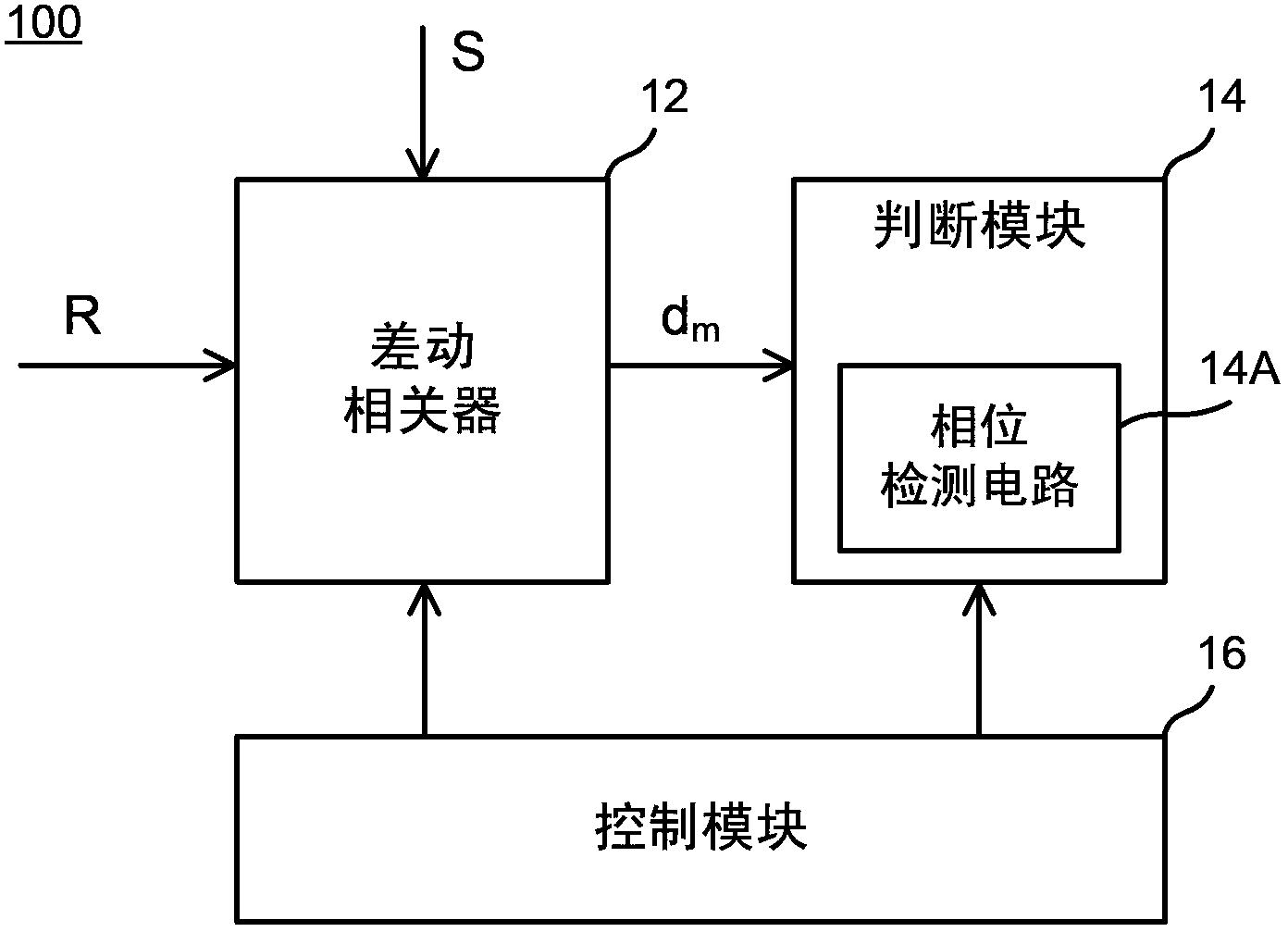
Apparatus and method for detecting spectrum inversion
InactiveUS8824528B2Simple structureEnsure proper implementationReceivers monitoringModulated-carrier systemsFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
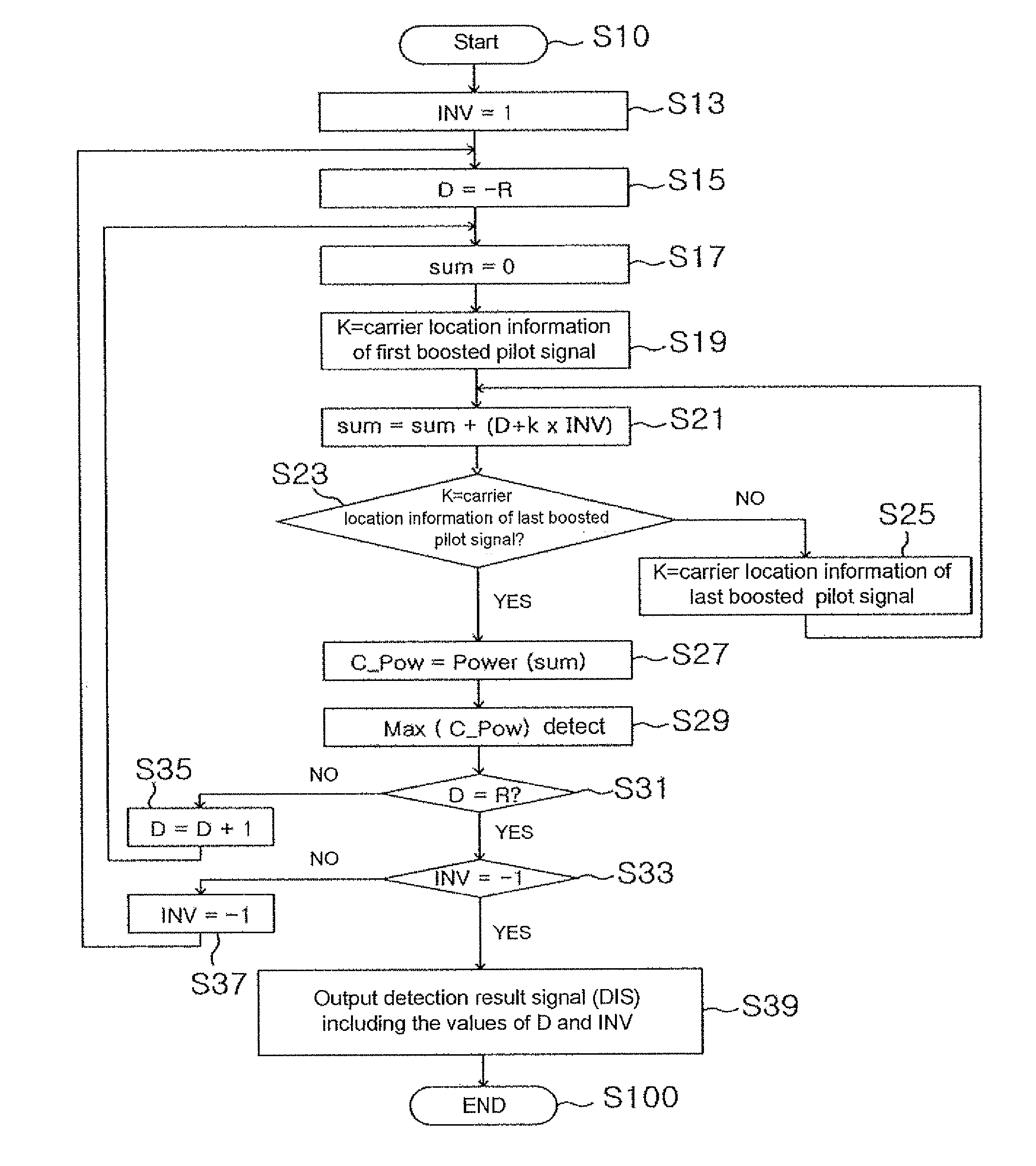
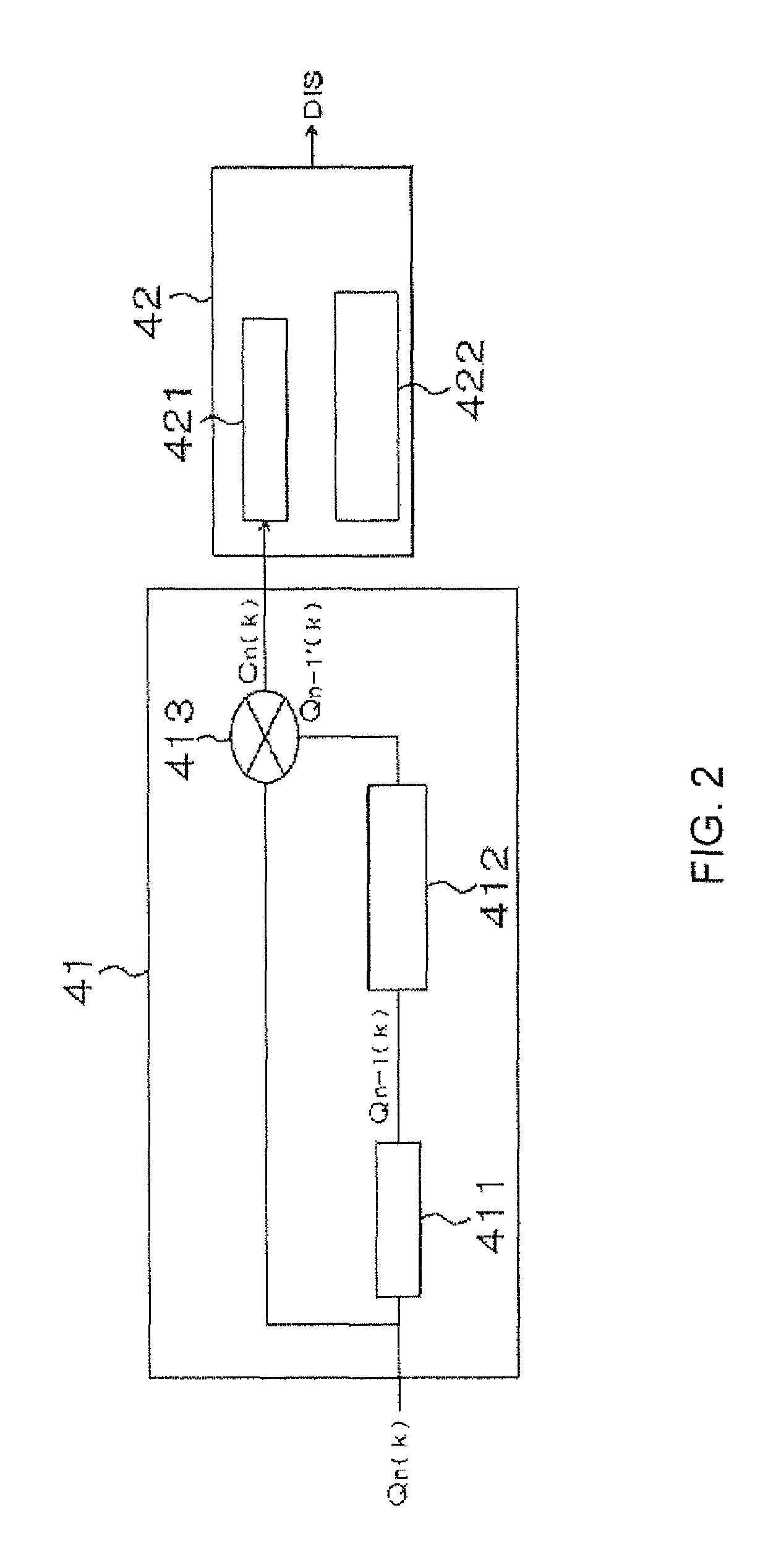
The present invention relates to a spectrum inversion detection apparatus which includes a differential correlation value computing portion, utilized to use a present and previous time axial symbols to compute differential correlation values individually corresponding to carriers; and a controlling portion, utilized to use the differential correlation values, when a spectrum inversion status flag is not at a spectrum inversion state, to compute a correlativity value of the each integer frequency displacement thereby, and when spectrum inversion status flag is at the spectrum inversion state, to determine a maximal correlativity value among all the computed correlativity values, and to decide a spectrum inversion status flag of the computed correlativity value which is determined as the maximal correlativity value thereby utilizing as a detection result signal to output.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICON KOREA INC
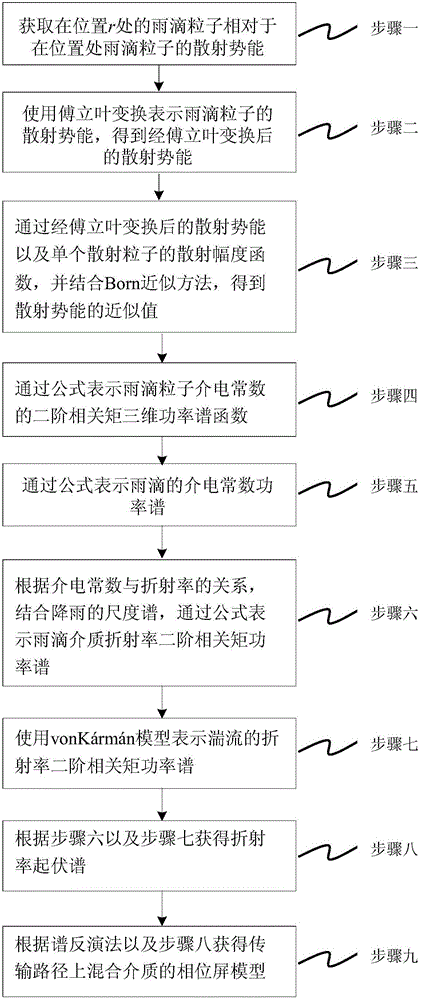
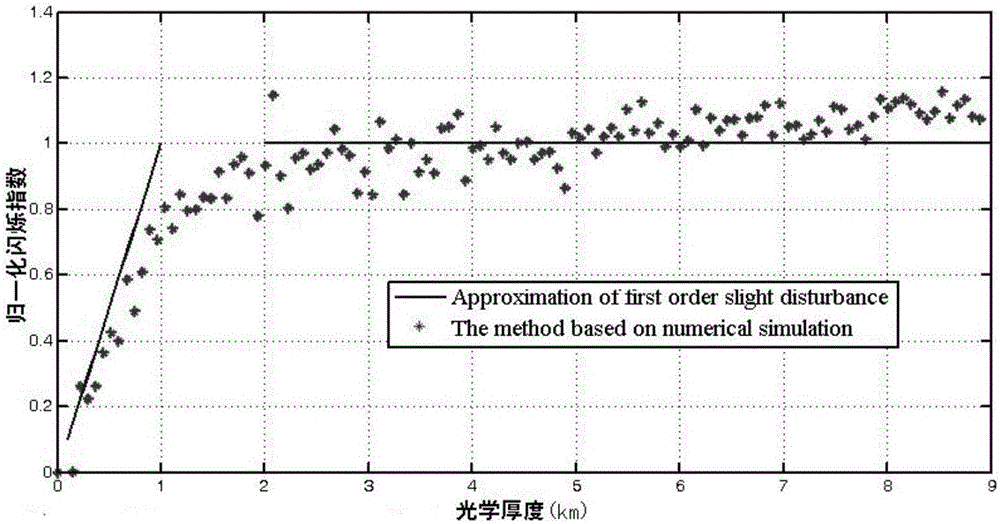
Phase screen modeling method for discrete raindrop media based on spectral inversion method
ActiveCN106644104AMeeting the Needs of Virtual TrialsOptical measurementsConstant powerFourier transform on finite groups
The invention relates to a phase screen modeling method for discrete raindrop media based on a spectral inversion method, and belongs to discrete raindrop medium phase screen modeling field. In order to overcome the shortcomings that the description of light field information is incomplete in a phase screen model of discrete raindrop media, the requirements of a virtual test is not satisfied, and the phase disturbance of raindrops to the light field is not considered, the invention proposes a phase screen modeling method for discrete raindrop media based on the spectral inversion method, the phase screen modeling method including the steps of obtaining scattering potential energy of raindrop particles; obtaining the scattering potential energy after Fourier transform; obtaining an approximate value of the scattering potential energy through the scattering potential energy after Fourier transform; expressing a second-order correlation moment three-dimensional power spectral function of a dielectric constant of the raindrop particles by a formula; expressing a dielectric constant power spectrum of the raindrops by a formula; expressing a second-order correlation moment power spectrum of a medium refractive index of the raindrops by a formula; and obtaining a phase screen model of mixed media on a transmission path according to the spectral inversion method. The invention is applicable to a simulation model of laser transmission in rain.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
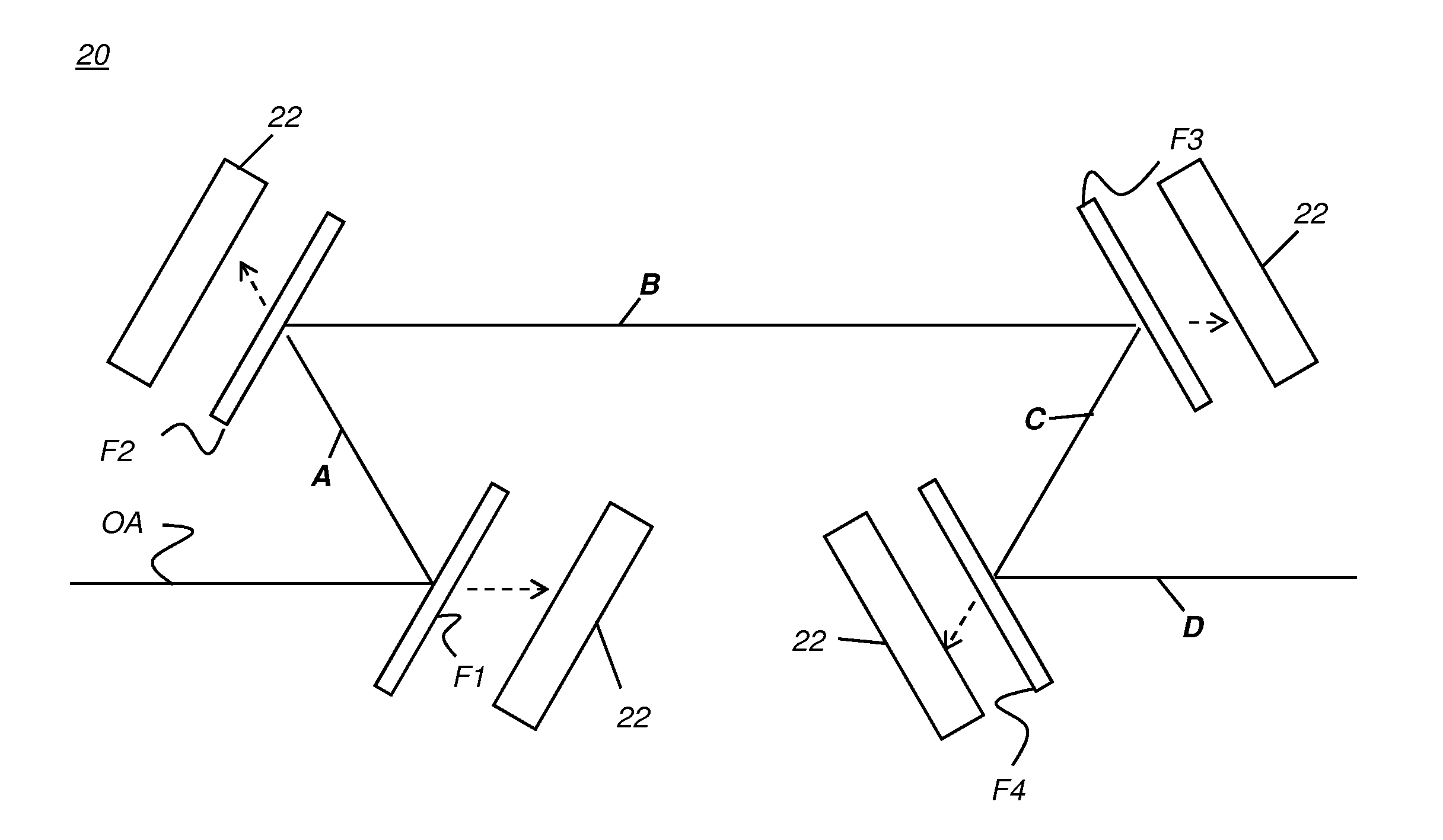
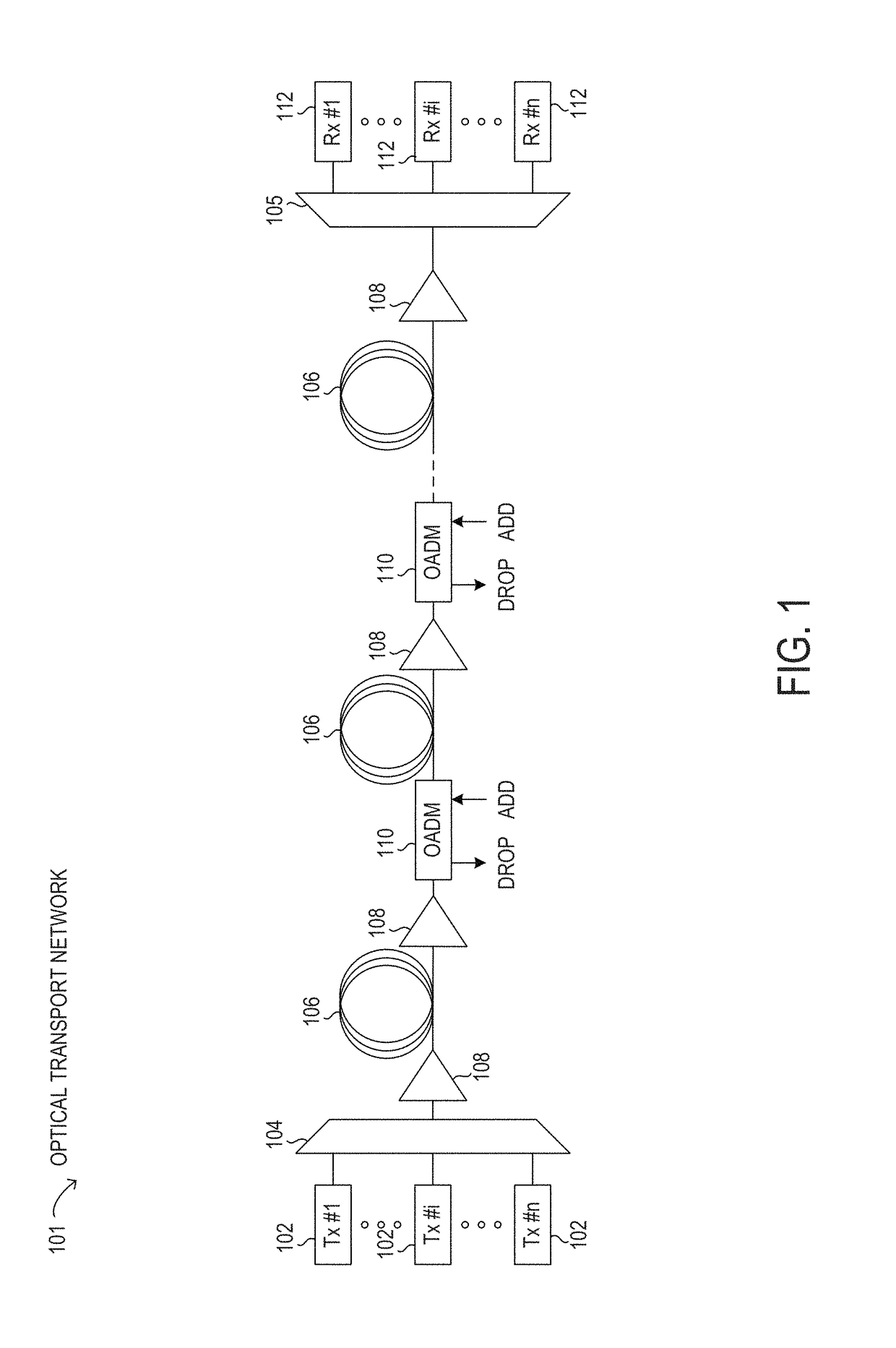
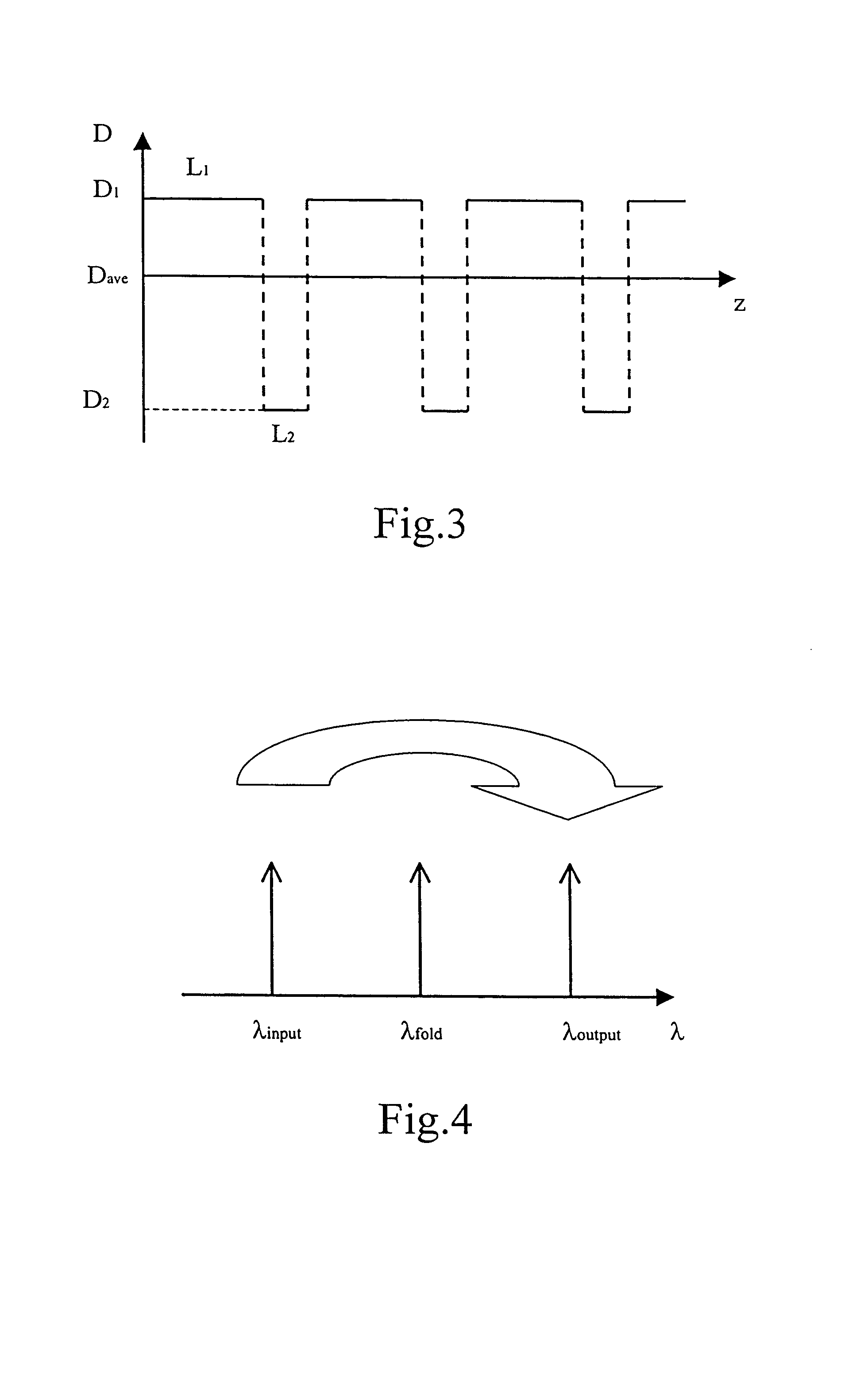
Wavelength division multiplexing optical transmission system using a spectral inversion device
ActiveUS7187868B2Low reception errorEasy to implementWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersTransfer systemEngineering
A WDM system includes a transmission station, a receiving station, a first optical path and a second optical path. The first optical path includes a first section and a second section, the second section being capable of compensating at least partially the dispersion accumulated by a series of optical channels along the first section. The series of channels includes at least a first plurality of channels having an average dispersion of the same sign in the first optical path. The system also includes at least a first conversion device, capable of inverting the spectrum and modifying the wavelength of at least the first plurality of channels, to produce a second plurality of channels having an average chromatic dispersion of the same sign in the second optical path.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
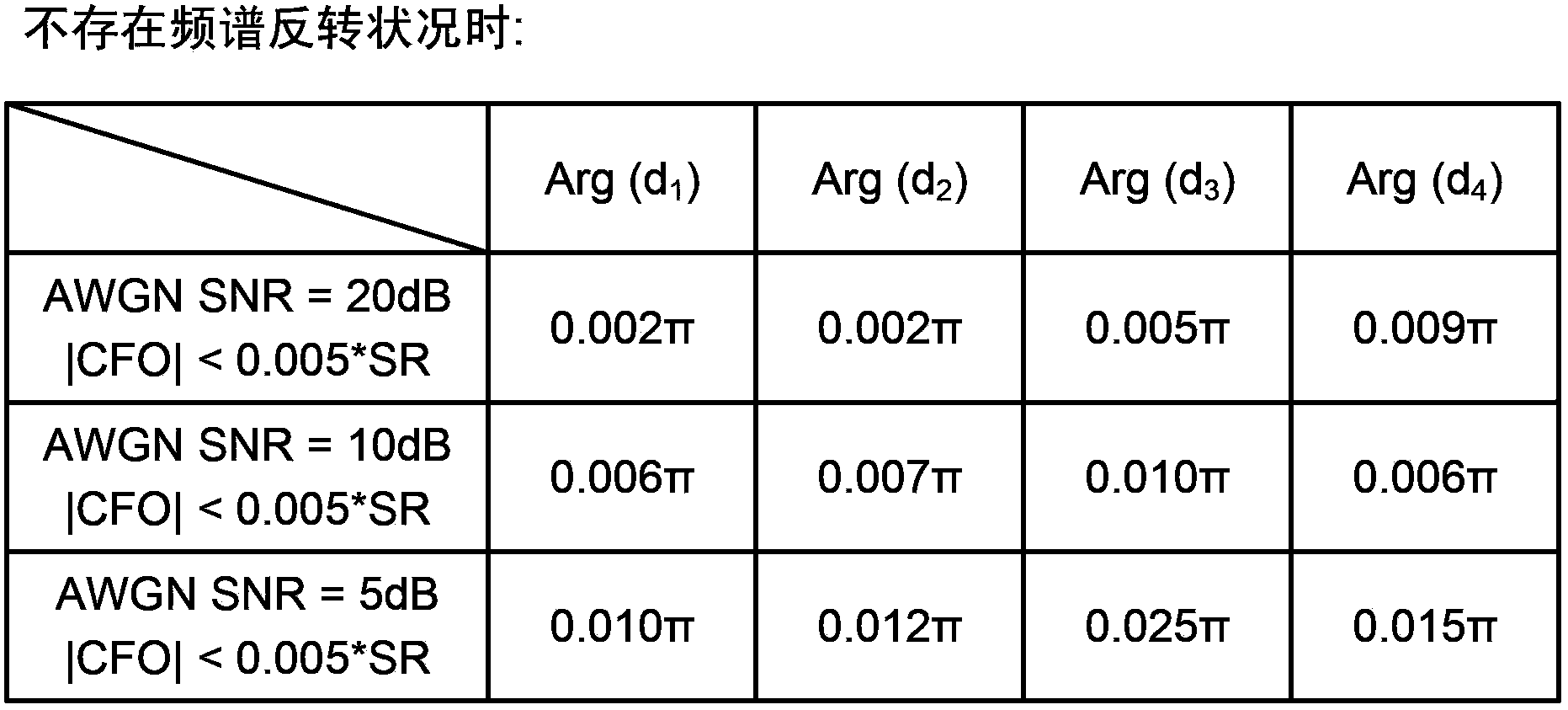
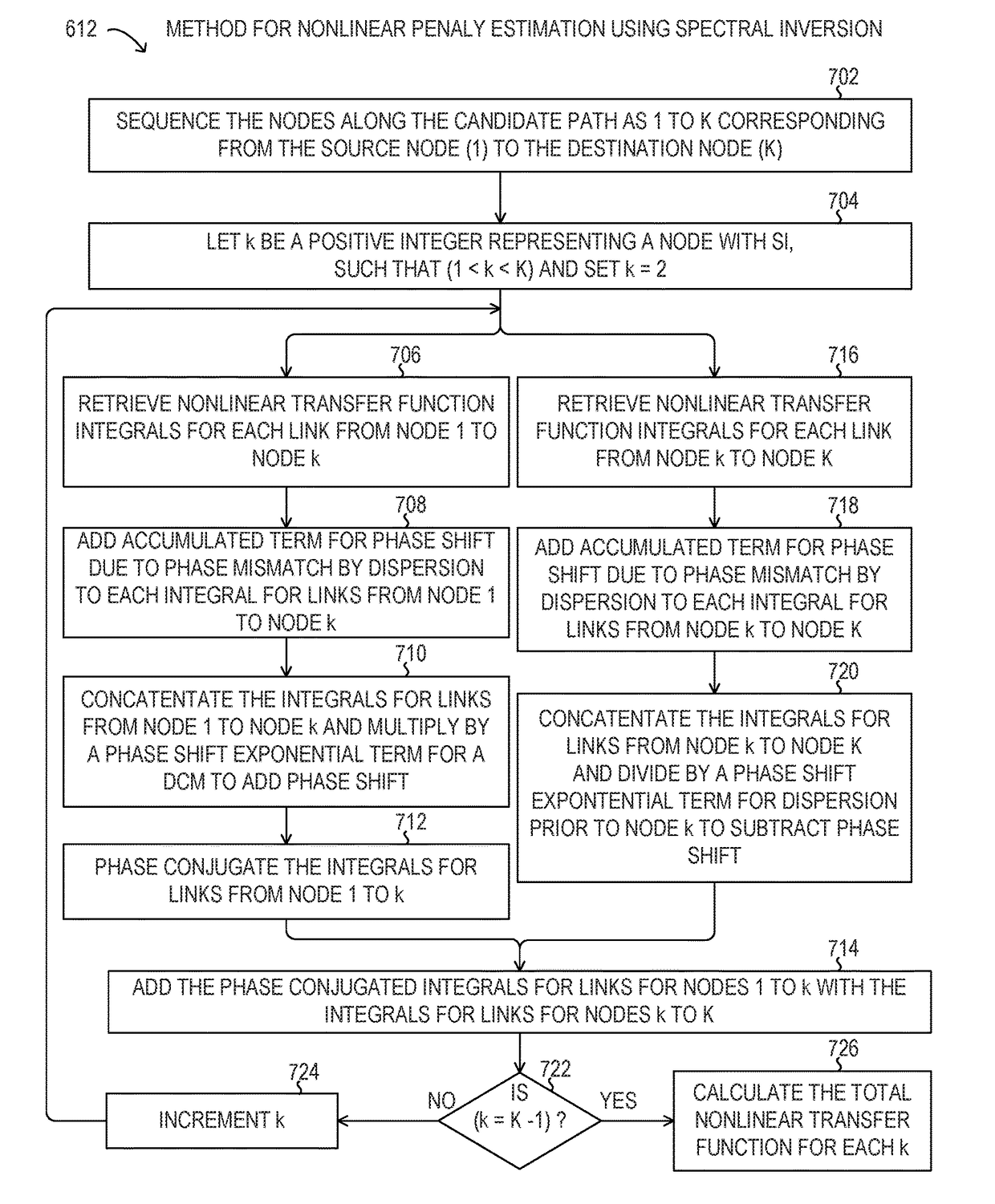
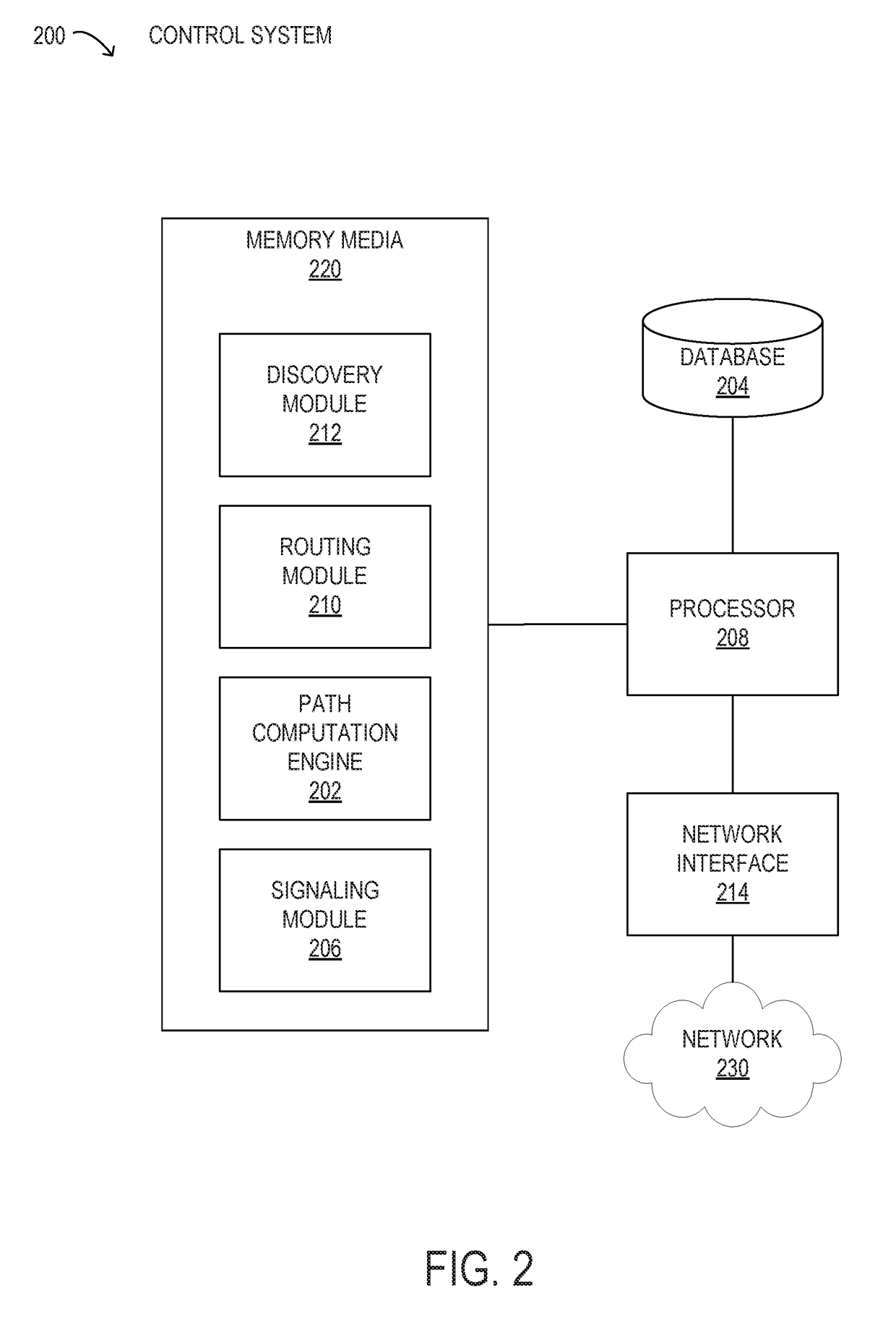
Nonlinear penalty estimation using spectral inversion in optical transport networks
ActiveUS20160316283A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexFrequency spectrumComputer science
Methods and systems may estimate nonlinear penalties for optical paths using spectral inversion in optical transport networks. Certain values of nonlinear transfer functions for nonlinear penalty estimation may be pre-calculated for optical paths between given nodes. When an optical path computation for using spectral inversion between a given source node and a given destination node is desired, the pre-calculated values may be concatenated for improved computational efficiency.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
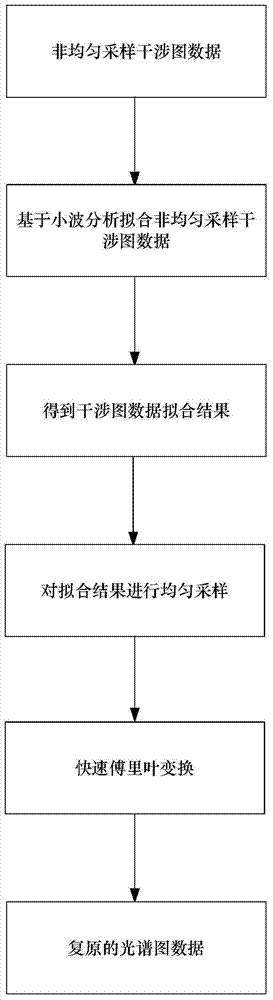
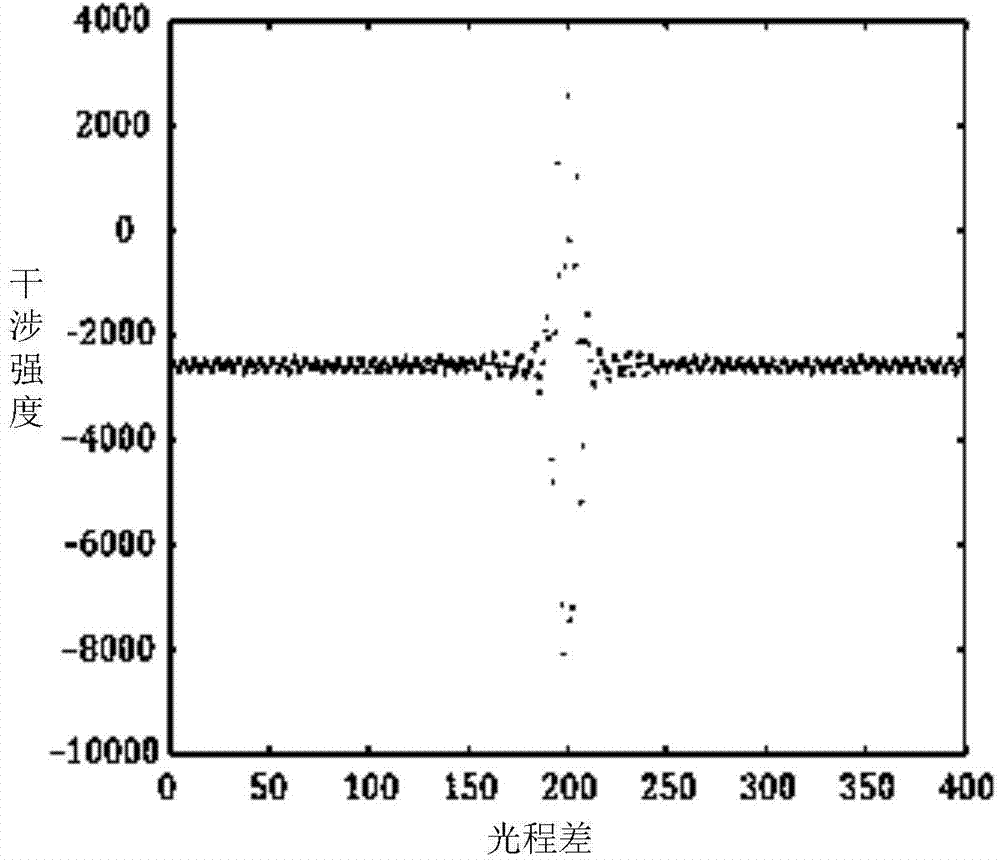
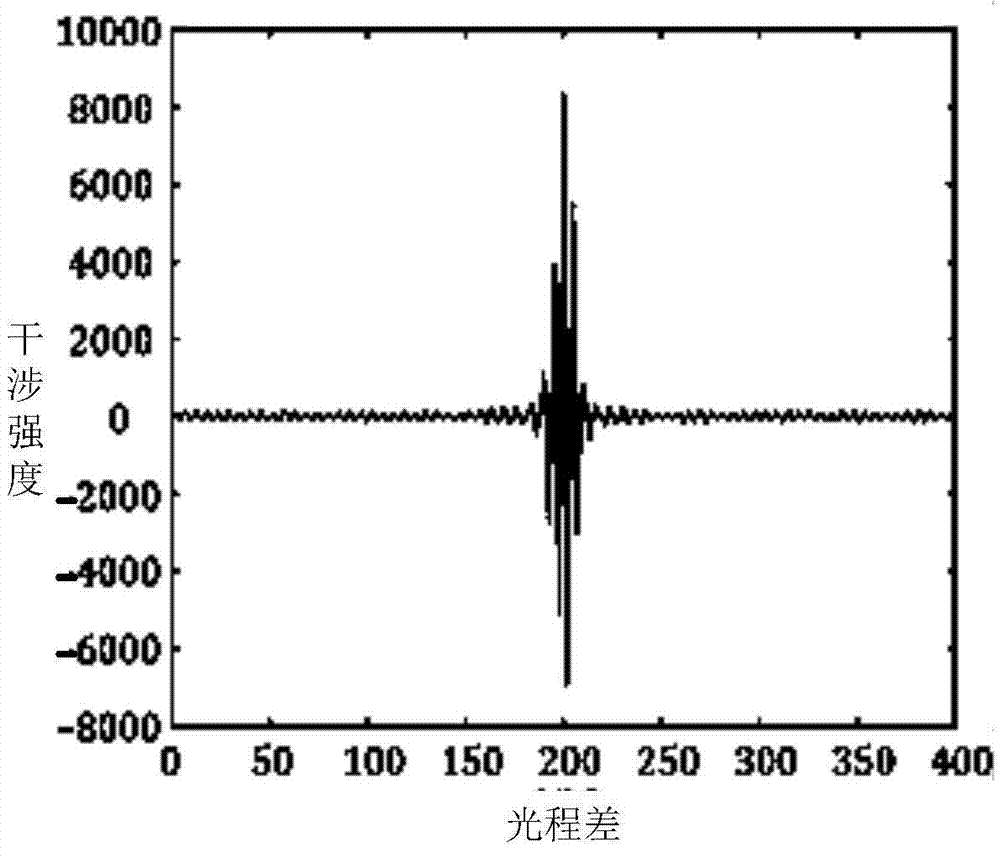
Method for restoring interference pattern data spectra based on wavelet analysis
ActiveCN103578086AFit fineImprove performanceImage enhancementInterferometric spectrometrySpectral patternFast Fourier transform
The invention discloses a method for restoring interference pattern data spectra based on wavelet analysis. The method comprises the steps of applying the fitting interpolation method based on the wavelet analysis to non-uniform sampling interference pattern reconstruction, and conducting spectral inversion; firstly applying the fitting method based on the wavelet analysis to conduct fitting on non-uniform sampling interference data to obtain a fitted interference data curve, and then conducting uniform interpolation sampling to obtain uniformly-sampled interference data; conducting the FFT on the uniformly-sampled interference data on the basis of the interference spectroscopy theory to obtain a resorted spectral pattern. According to the result of a simulation experiment, it can be seen that the method is more suitable for the characteristics that the interference data change severely at the positions with zero optical path difference and change slowly at the positions with larger optical path differences, and the interference data curve is better fitted. After the uniform sampling, the FFT is carried out to obtain the spectral inversion pattern. The method has the advantages of being capable of exquisitely fitting the interference pattern data, better reflecting the characteristics of the interference pattern data and being lower in fitting error.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and device for eliminating spectrum inversion, and receiver
ActiveCN102195918AEliminates the effect of inversionReduce time consumptionError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsFast Fourier transformFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a method for eliminating spectrum inversion. The method comprises the following steps of: detecting whether a received signal has a spectrum inversion problem or not; if the received signal has the spectrum inversion problem, checking whether a frequency point index value FFT_IDX of fast Fourier transform is 0 or not; if the frequency point index value FFT_IDX is 0, adopting an orthogonal inphase frequency domain signal of the 0th sub-carrier of the received signal as an inphase orthogonal frequency domain signal of the 0th sub-carrier of an output signal; and if the frequency point index value FFT_IDX is not 0, adopting the orthogonal inphase frequency domain signal of the (N-FFT_IDX)th sub-carrier of the received signal as the inphase orthogonal frequency domain signal of the (N-FFT_IDX)th sub-carrier of the output signal, wherein N is the number of sampling points of the fast Fourier transformer, and the frequency point index value FFT_IDX is an integer ranged from 0 to N-1.
Owner:ALICORP
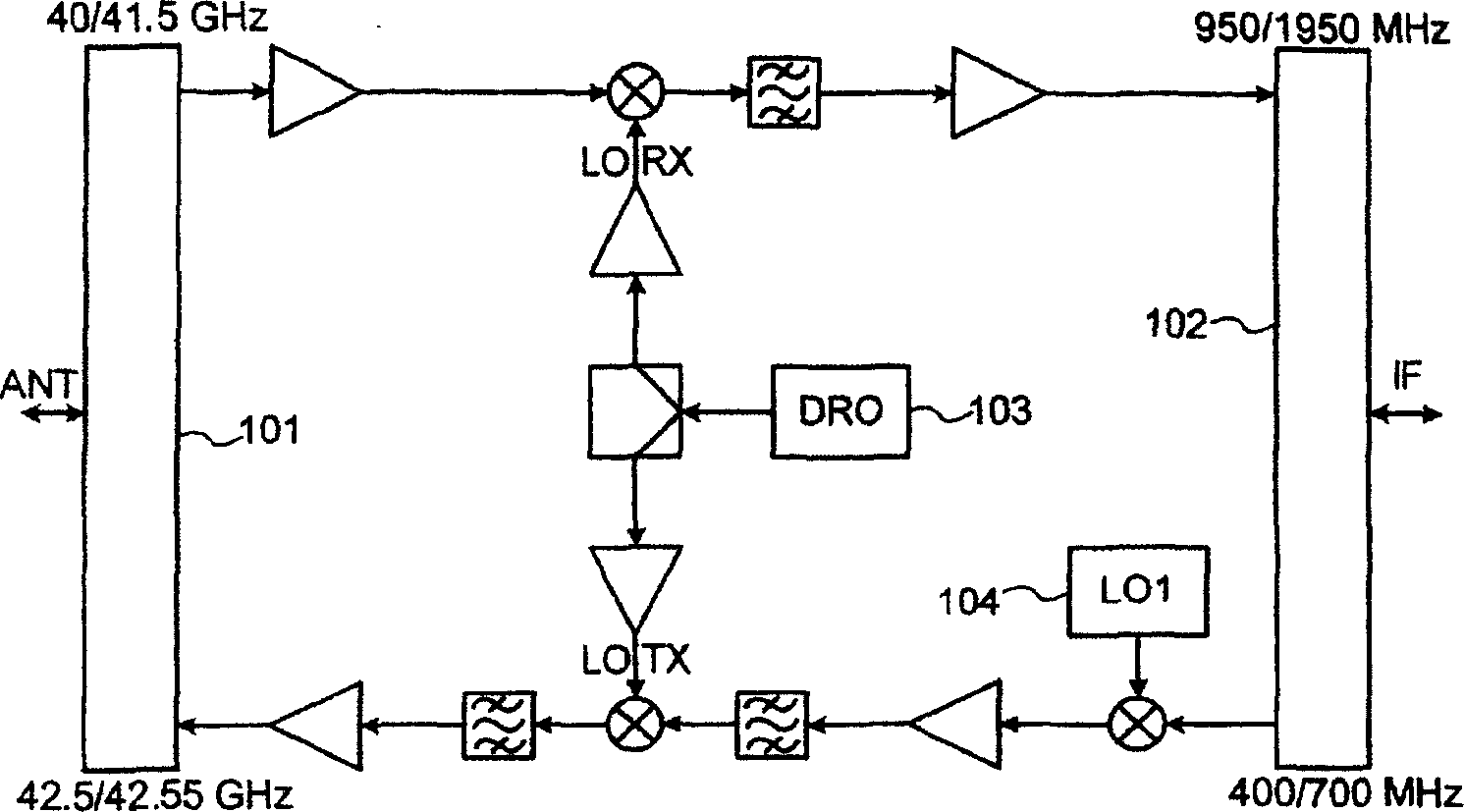
Vhf adapter for cable network
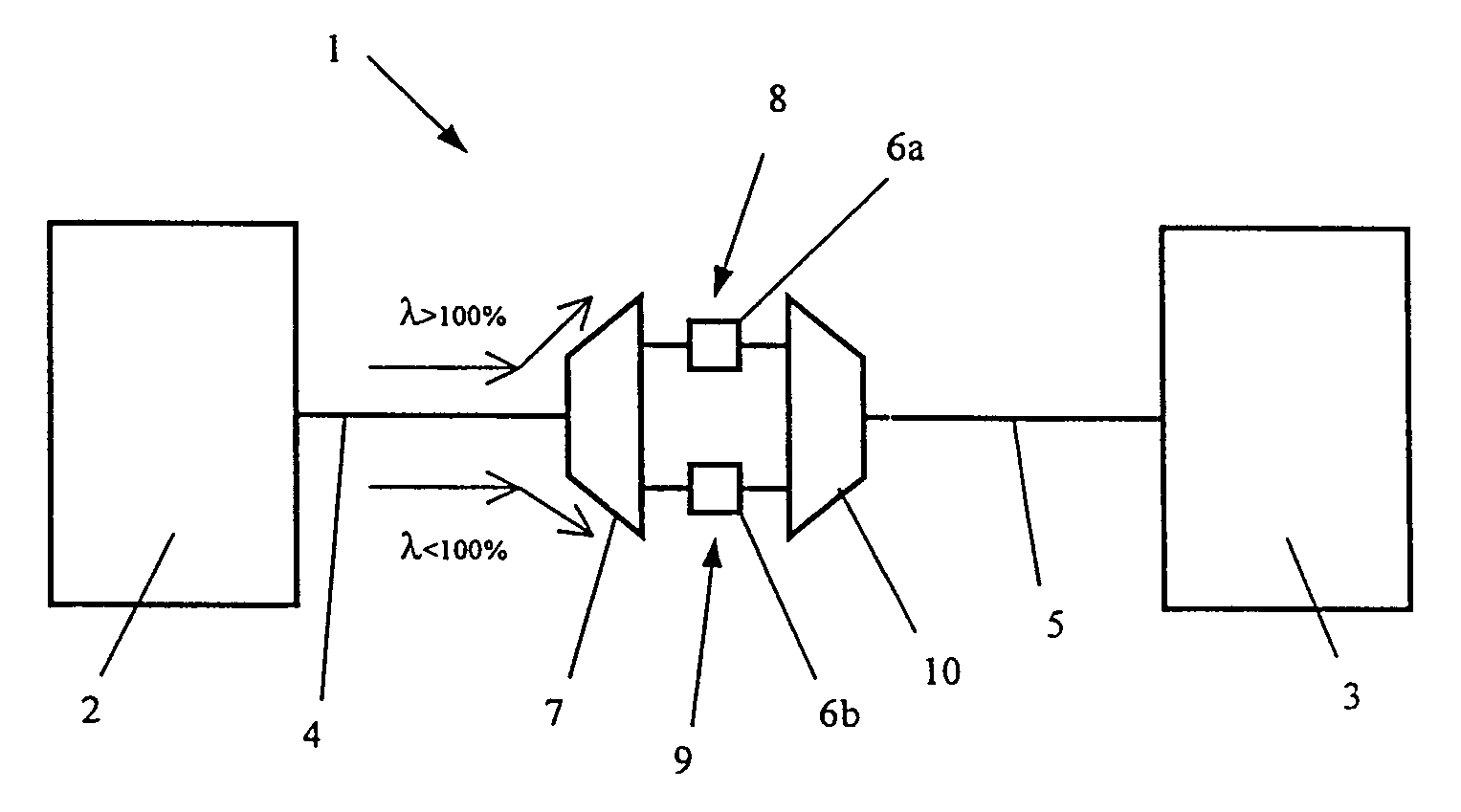
InactiveCN1669216AAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTransmissionFrequency spectrumIntermediate frequency
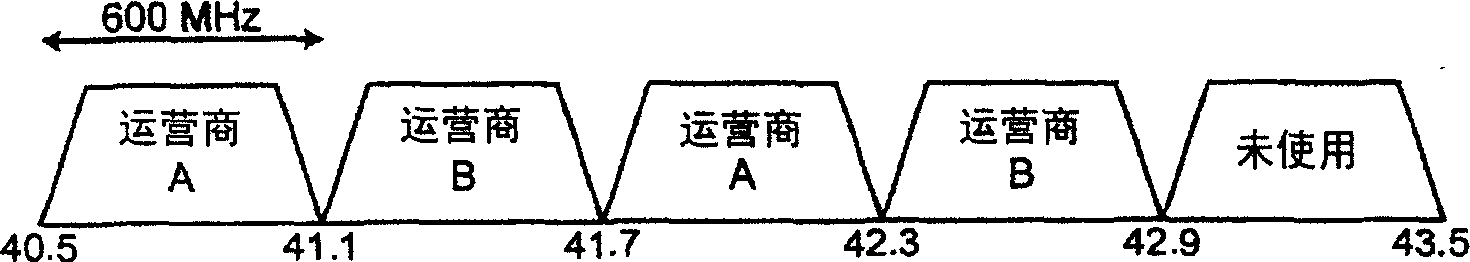
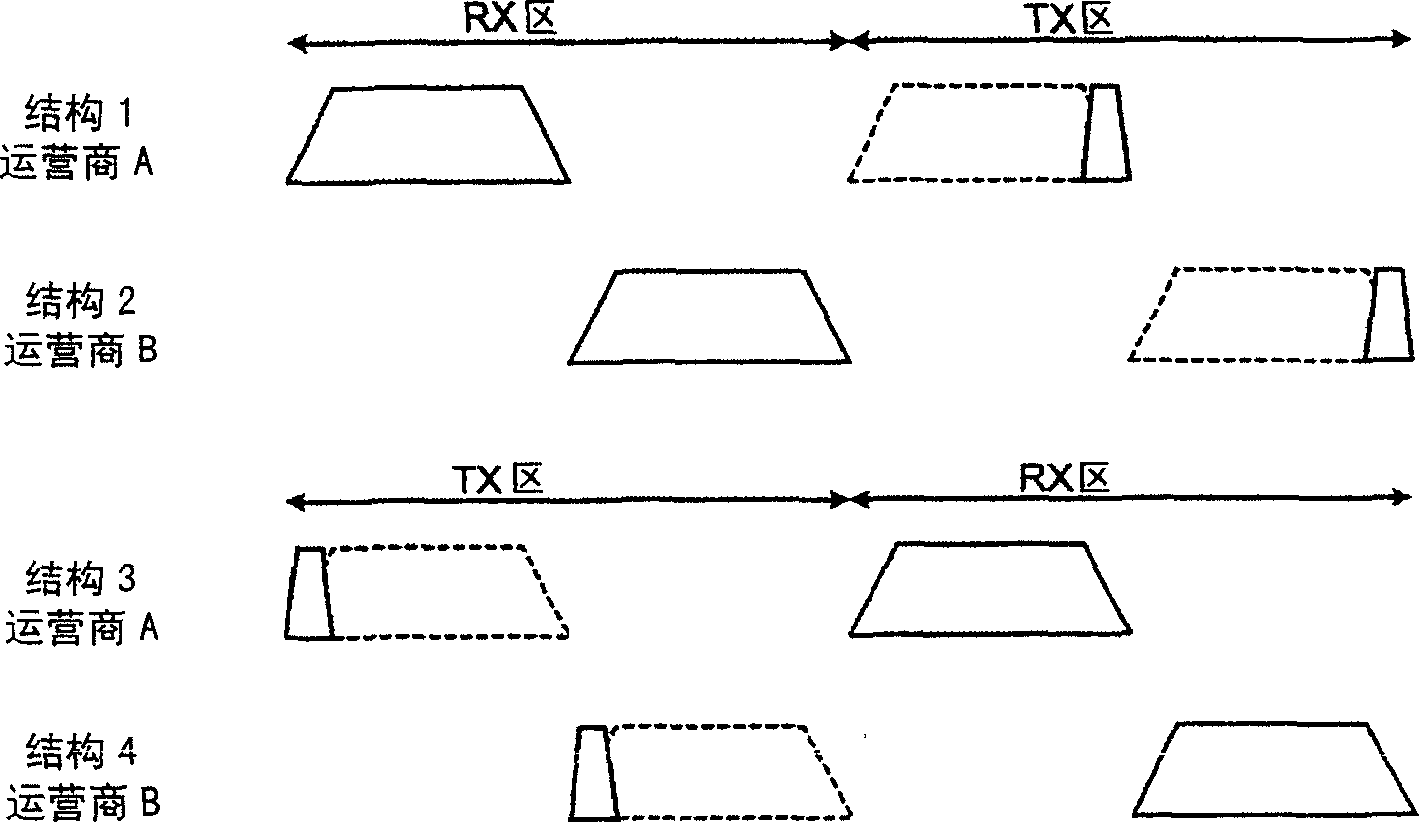
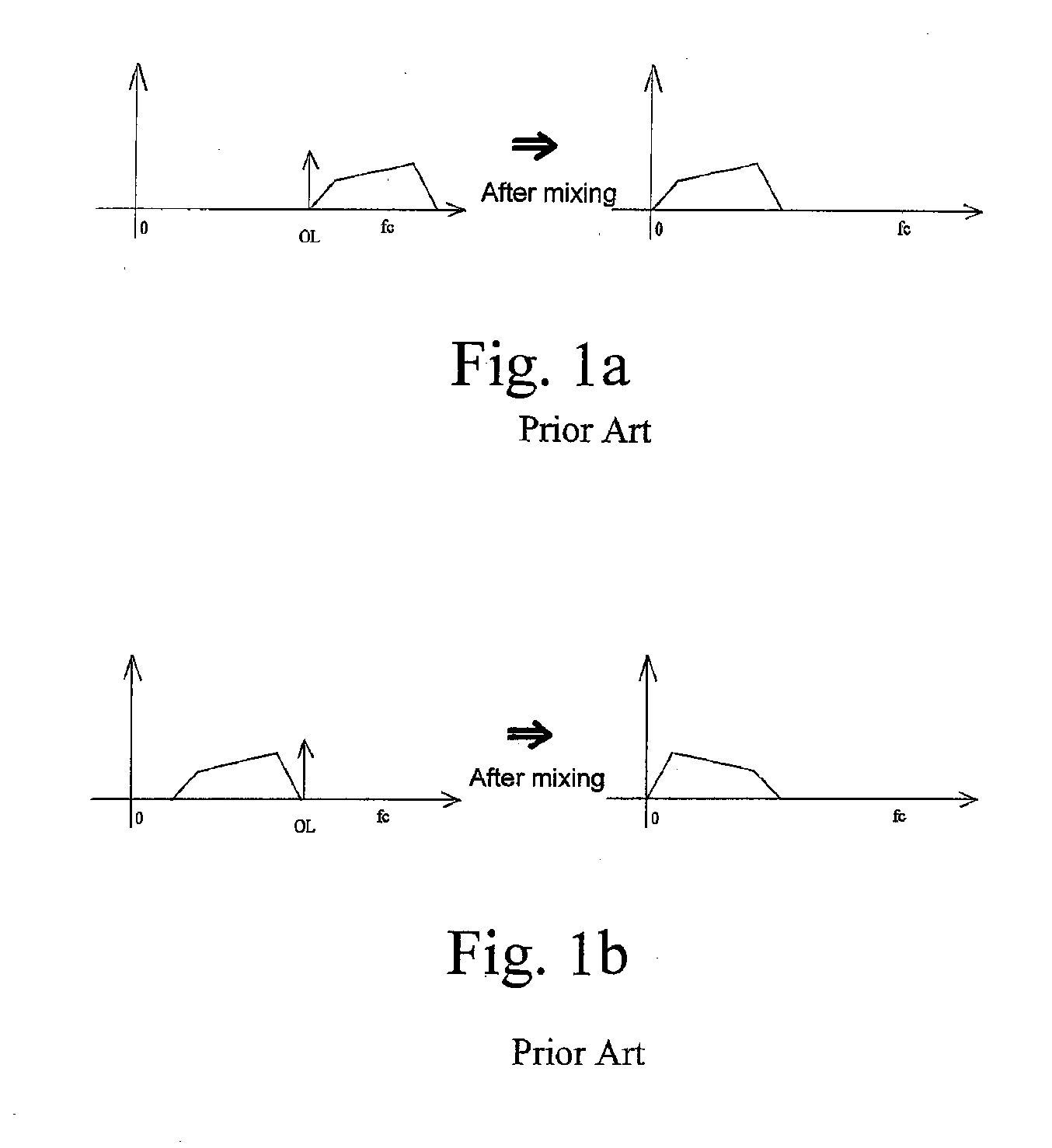
The invention relates to VHF adapters for cable networks of the ODU type. It consists in using two conversion chains, up and down, in which a very stable single reference oscillator (403) drives means (404, 405, 410, 423) of generating the VHF and IF local frequencies common to these two conversion chains. A very selective surface wave filter (417) makes it possible to reject the frequency of the local oscillator at the level of the first intermediate frequency. It makes it possible to obtain a DOCSIS compatible millimetre MWS ODU whose frequency stability and spectral purity satisfy the constraints of the cable standard without undertaking spectral inversion of the signals transmitted and received.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
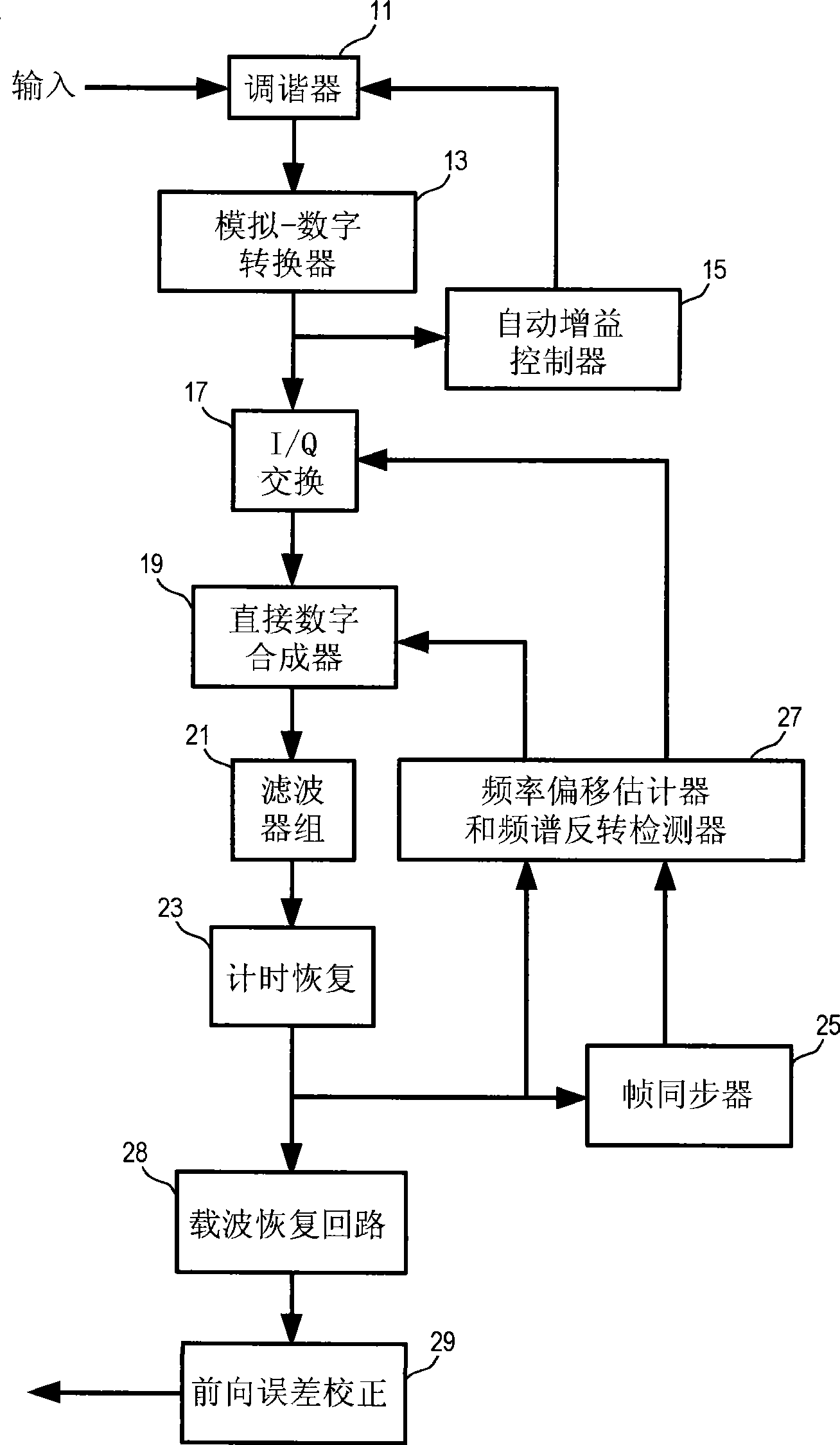
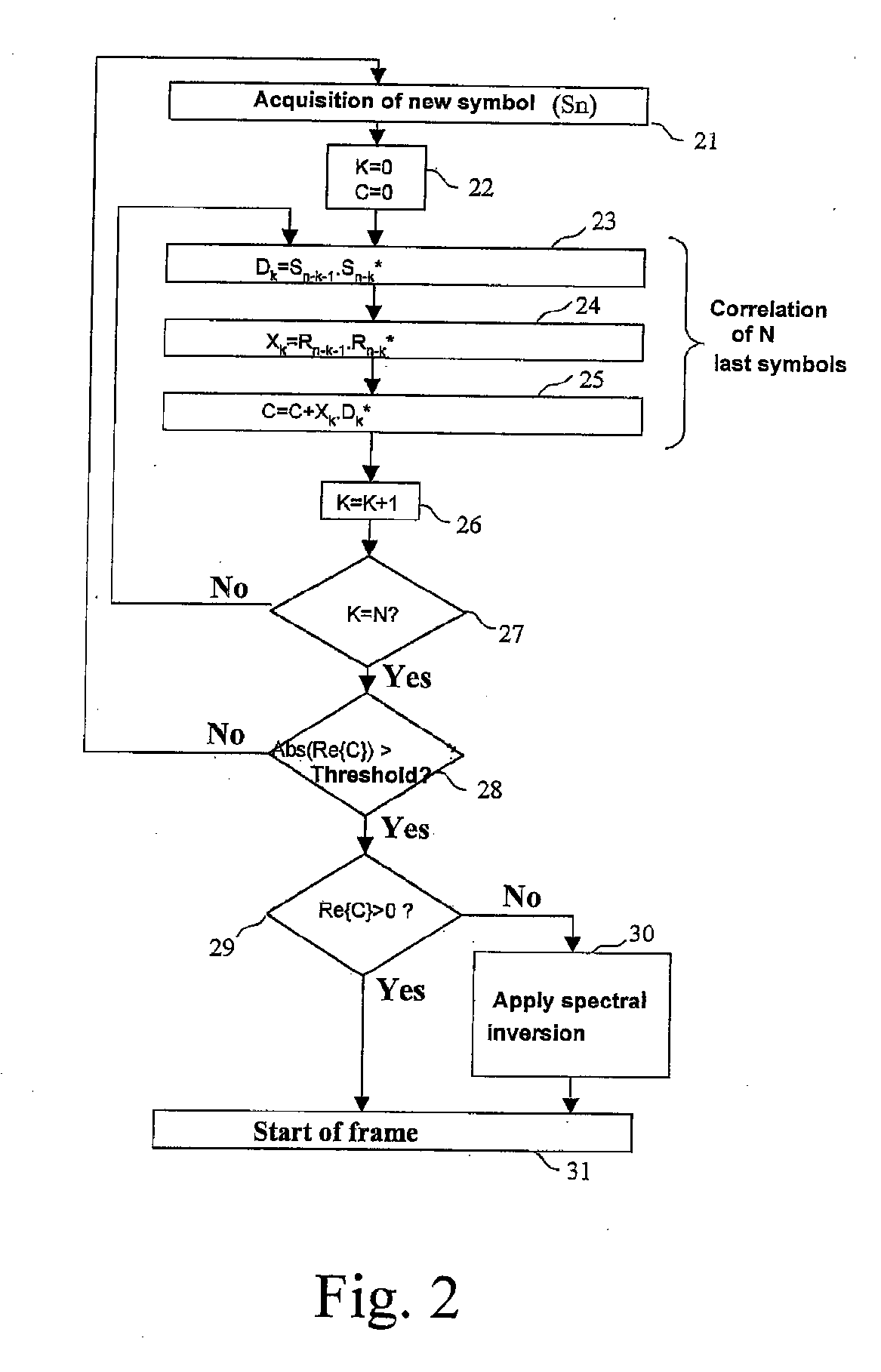
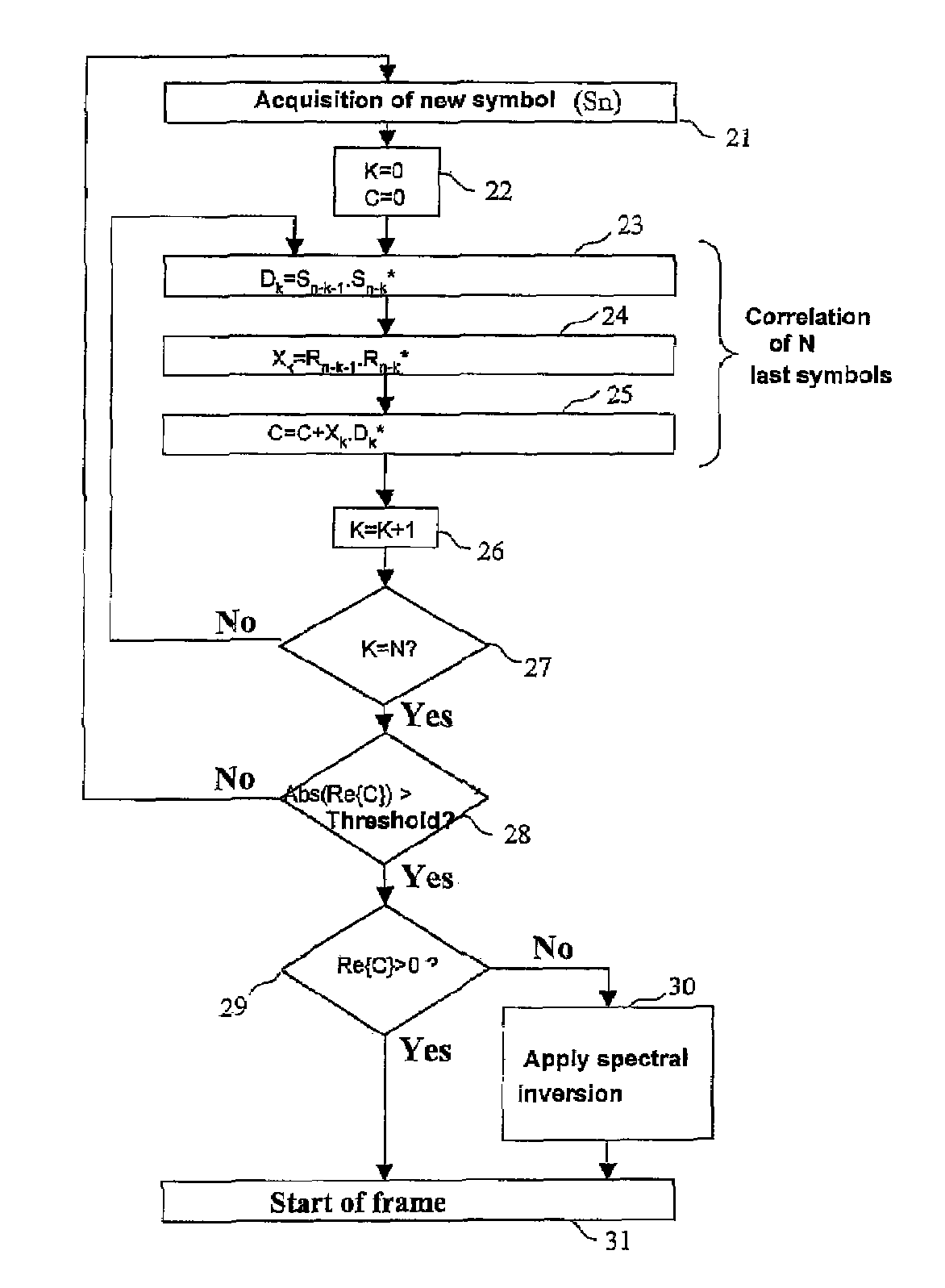
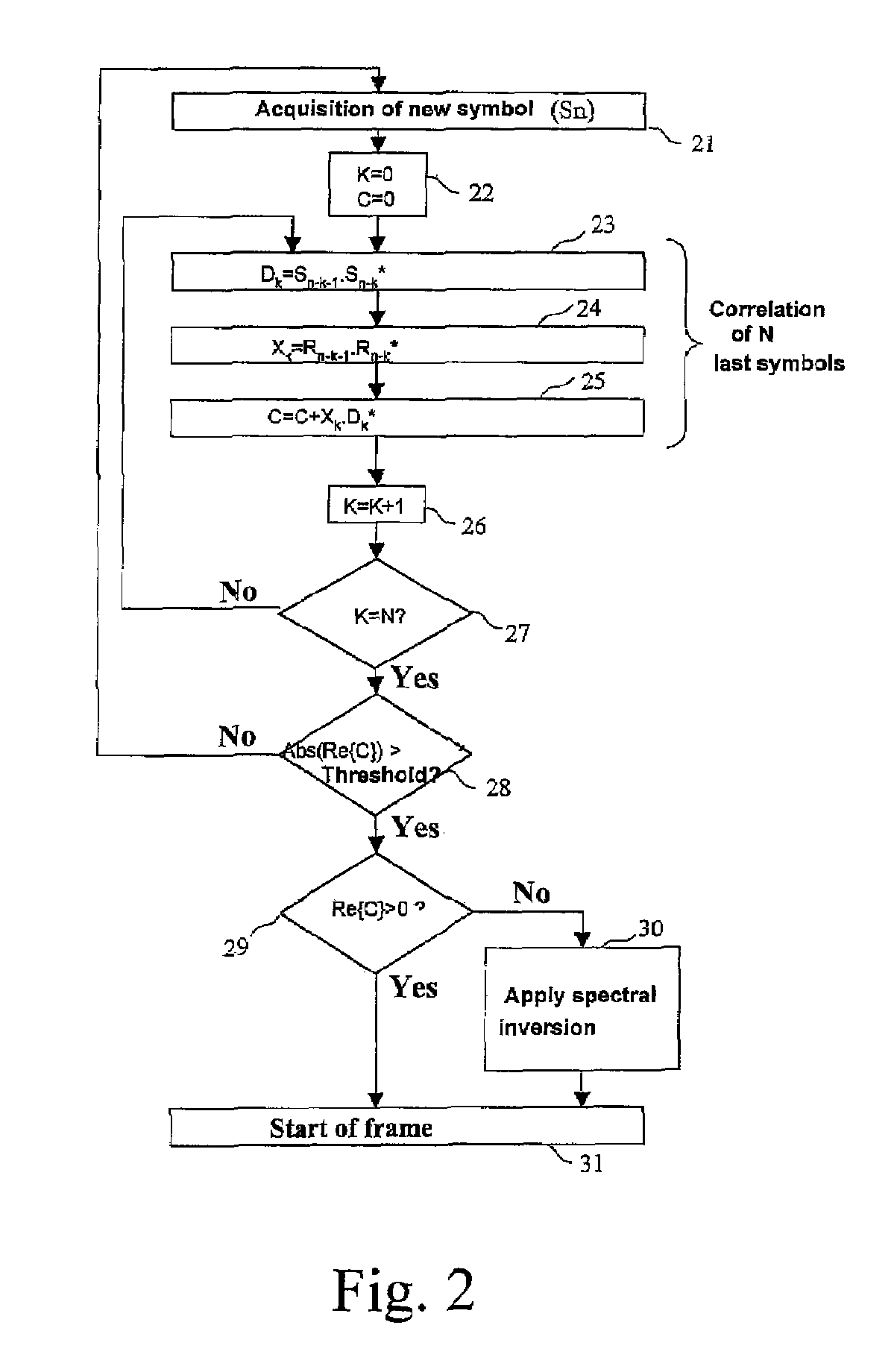
Process for automatic correction of the spectral inversion in a demodulator and device to implement the process
ActiveUS20070002975A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
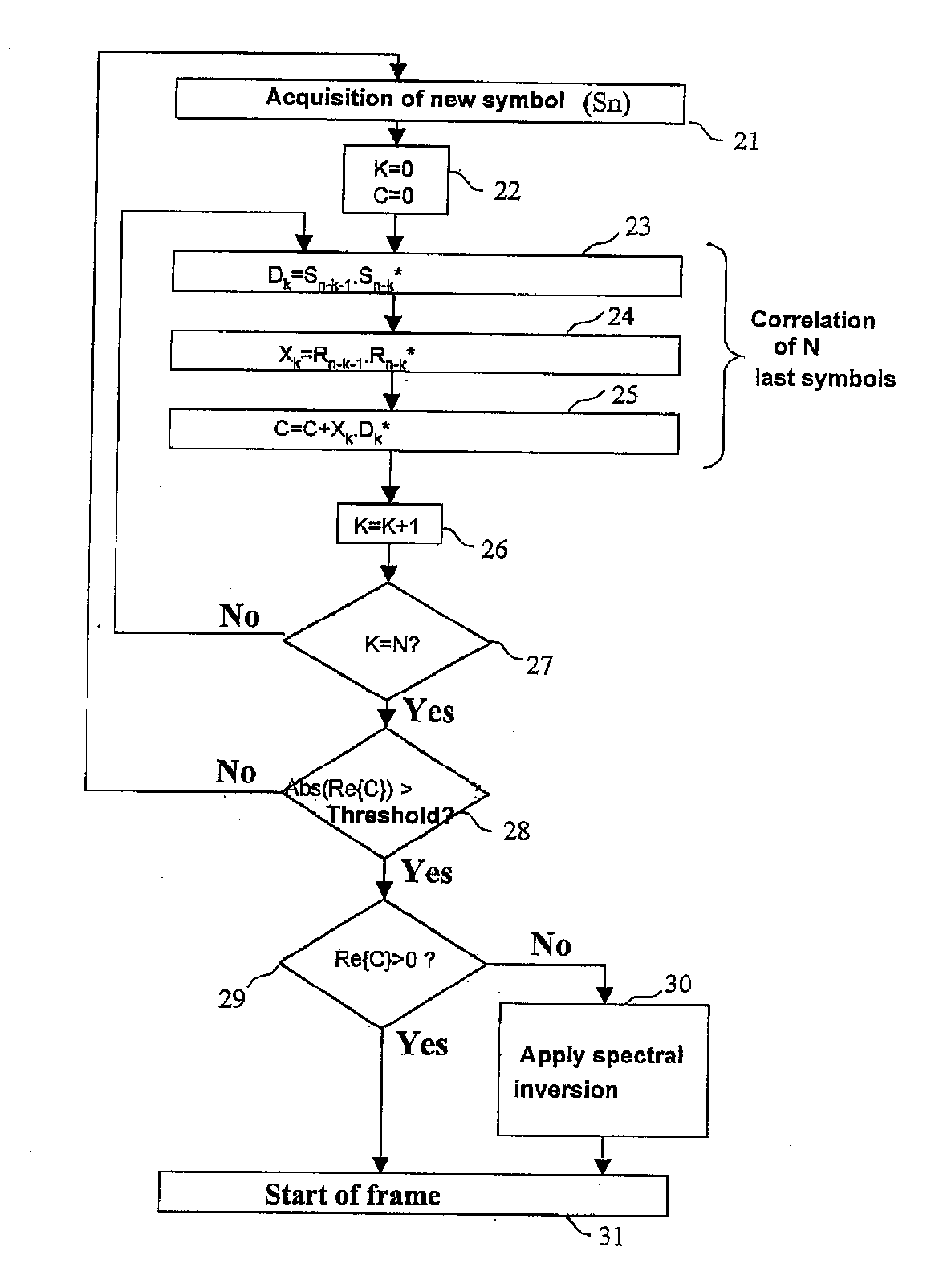
A process of correction of the spectral inversion for a receiver in a digital communication system: the process allows the reception in the receiver of a training sequence presumably known according to a modulation of type π / 2 BPSK or MDP2. The process includes the following steps: Demodulating of the training sequence; Calculating of the differential correlation on a set of N received samples (Rn) and presumably sent (Sn) to generate a result; Using the result to detect the beginning of the frame and to order a spectral inversion in the chain of reception of the aforementioned receiver before launching the detection of the beginning of the frame. A receiver to process automatically the spectral inversion is also described.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Process for automatic correction of the spectral inversion in a demodulator and device to implement the process
ActiveUS7697636B2Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
A process of correction of the spectral inversion for a receiver in a digital communication system: the process allows the reception in the receiver of a training sequence presumably known according to a modulation of type π / 2 BPSK or MDP2. The process includes the following steps: Demodulating of the training sequence; Calculating of the differential correlation on a set of N received samples (Rn) and presumably sent (Sn) to generate a result; Using the result to detect the beginning of the frame and to order a spectral inversion in the chain of reception of the aforementioned receiver before launching the detection of the beginning of the frame. A receiver to process automatically the spectral inversion is also described.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
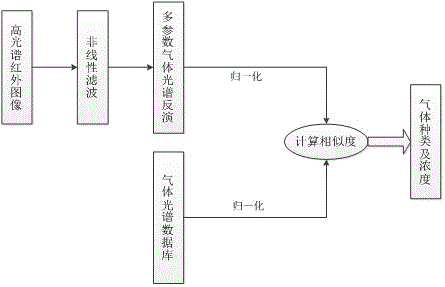
Gas detection method based on hyperspectral infrared image processing
ActiveCN106018316AReduce noiseReduce image noiseMaterial analysis by optical meansNonlinear filterDirect component
The invention discloses a gas detection method based on hyperspectral infrared image processing. The gas detection method based on the hyperspectral infrared image processing comprises the following steps of (a), collecting the infrared spectral data of a target area by adopting a hyperspectral infrared imaging system; (b), reducing the noise of the infrared spectral data and image noise of each wave band by utilizing a nonlinear wave filter; (c), calculating the infrared absorption spectral curve of a gas by adopting a gas spectral inversion algorithm; (d), carrying out normalization on the spectral data processed in step (b) and special data obtained through calculation in step (c), so as to reduce the influence of a direct component in a spectral line, and afterwards, judging the type and the concentration of the gas by adopting a feature weighting based generalized angular similarity measuring method. According to the gas detection method based on the hyperspectral infrared image processing, the noise of the infrared spectral data and the image noise of each wave band are reduced by utilizing the nonlinear wave filter; afterwards, the noise reduction, the dimensionality reduction and the spectral inversion operation are carried out on a collected hyperspectral image; the processed hyperspectral image is compared with data in a gas infrared absorption spectrum library; thus, the type of the gas can be identified and the concentration of the gas can be estimated.
Owner:HUBEI JIUZHIYANG INFRARED SYST CO LTD
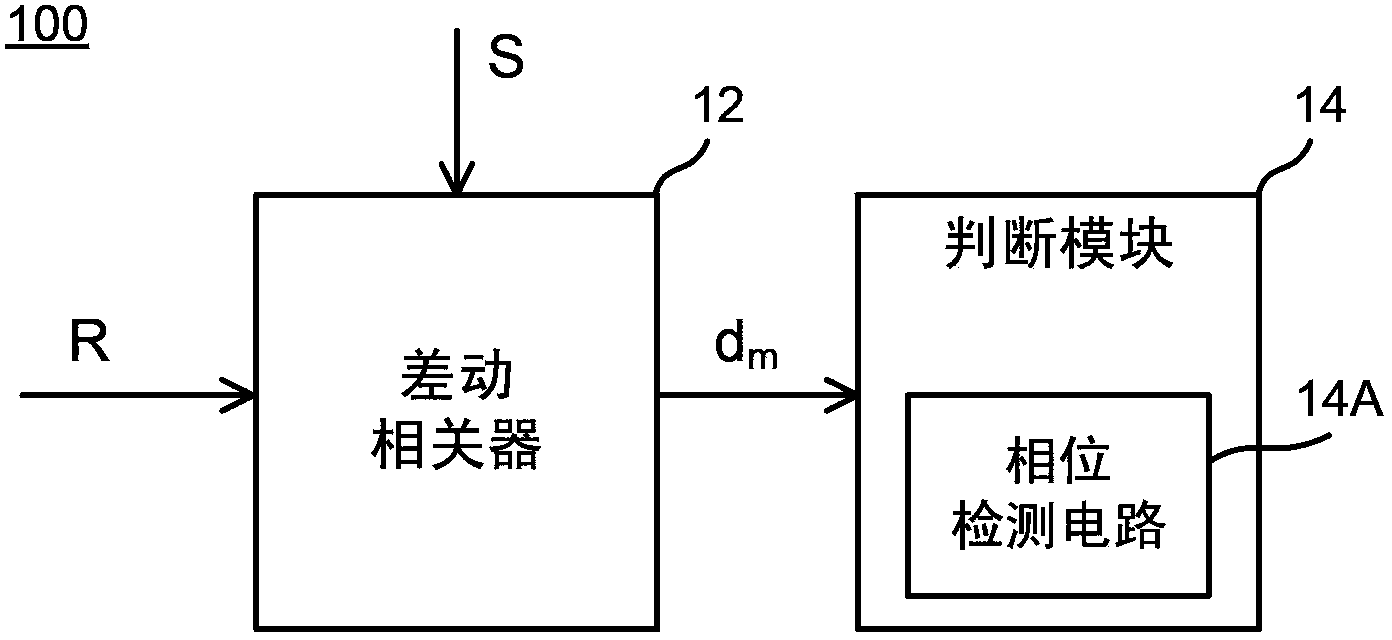
Frequency spectrum inversion judging device and frequency spectrum inversion judging method
The invention provides a frequency spectrum inversion judging device which comprises a differential motion correlator and a judging module. The differential motion correlator is used for applying odd-order differential motion correlation operation on an input signal and a known signal so as to generate a differential motion relevant result. When the input signal is judged as a target signal corresponding to the known signal, the judging module judges whether frequency spectrum inversion exists in the input signal according to the phase of the differential motion relevant result.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Nonlinear penalty estimation using spectral inversion in optical transport networks
ActiveUS9912435B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringNODALFrequency spectrum
Methods and systems may estimate nonlinear penalties for optical paths using spectral inversion in optical transport networks. Certain values of nonlinear transfer functions for nonlinear penalty estimation may be pre-calculated for optical paths between given nodes. When an optical path computation for using spectral inversion between a given source node and a given destination node is desired, the pre-calculated values may be concatenated for improved computational efficiency.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Mineral content spectrum inversion method based on deep neural network
ActiveCN109978162AAdd depthAvoid falling intoColor/spectral properties measurementsNeural architecturesNerve networkNetwork model
The invention belongs to the technical field of geological exploration, and particularly relates to a mineral content spectral inversion method based on a deep neural network. According to the mechanism and inversion characteristics of the rock mineral spectrum, a neural network model capable of rapidly and accurately inverting the mineral content of the surface rock soil is established, and the mineral content of the surface rock soil can be determined, analyzed and evaluated by using hyperspectral data.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY
Spectral inversion detection for polarization-division multiplexed optical transmission
ActiveCN107005310APolarisation multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency spectrumIn-phase and quadrature components
Owner:XIEON NETWORKS SARL
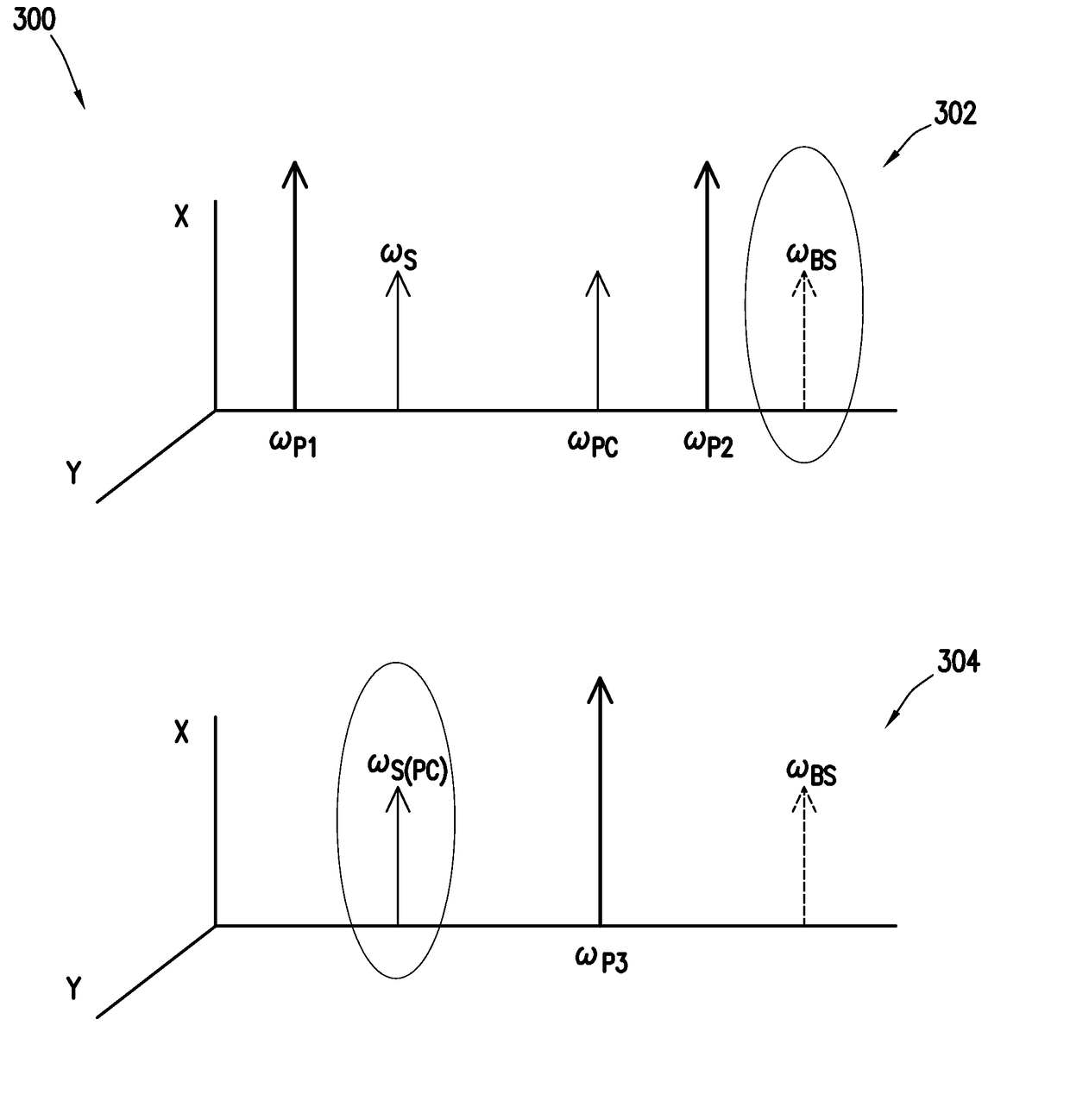
Wavelength shift elimination during spectral inversion in optical networks
Methods and systems are provided for wavelength shift elimination during spectral inversion in optical networks. The method includes receiving an input optical signal, and generating a combined optical signal by combining, by Bragg scattering, the input optical signal having an input wavelength with a first pump signal having a first wavelength. The method further includes converting the combined optical signal into an output optical signal, by phase-conjugation, using a second pump signal having a second wavelength. The output optical signal has the same wavelength as the input optical signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com