Pedestrian navigation method based on inertia, magnetic heading and zero-speed correction
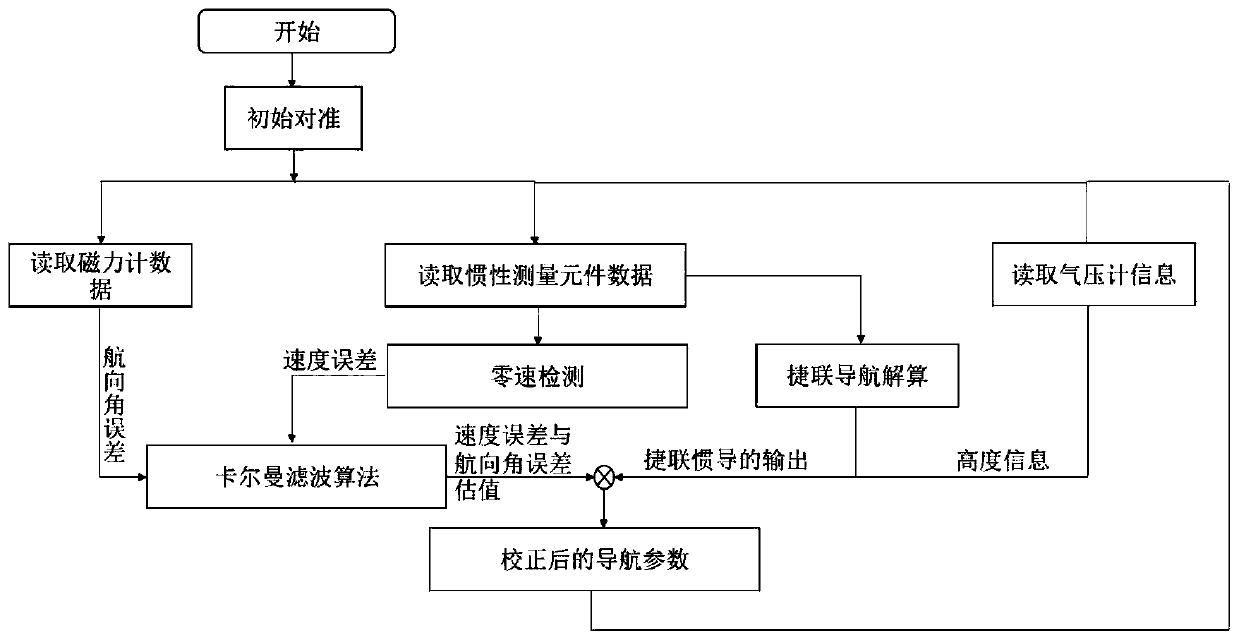
A zero-speed correction and pedestrian navigation technology, which is applied in directions such as navigation, navigation, and ground navigation through speed/acceleration measurement. Problems such as state transition matrix F matrix and observation matrix H matrix
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0167] Apply the above-mentioned pedestrian navigation method to the outdoor test, as follows:
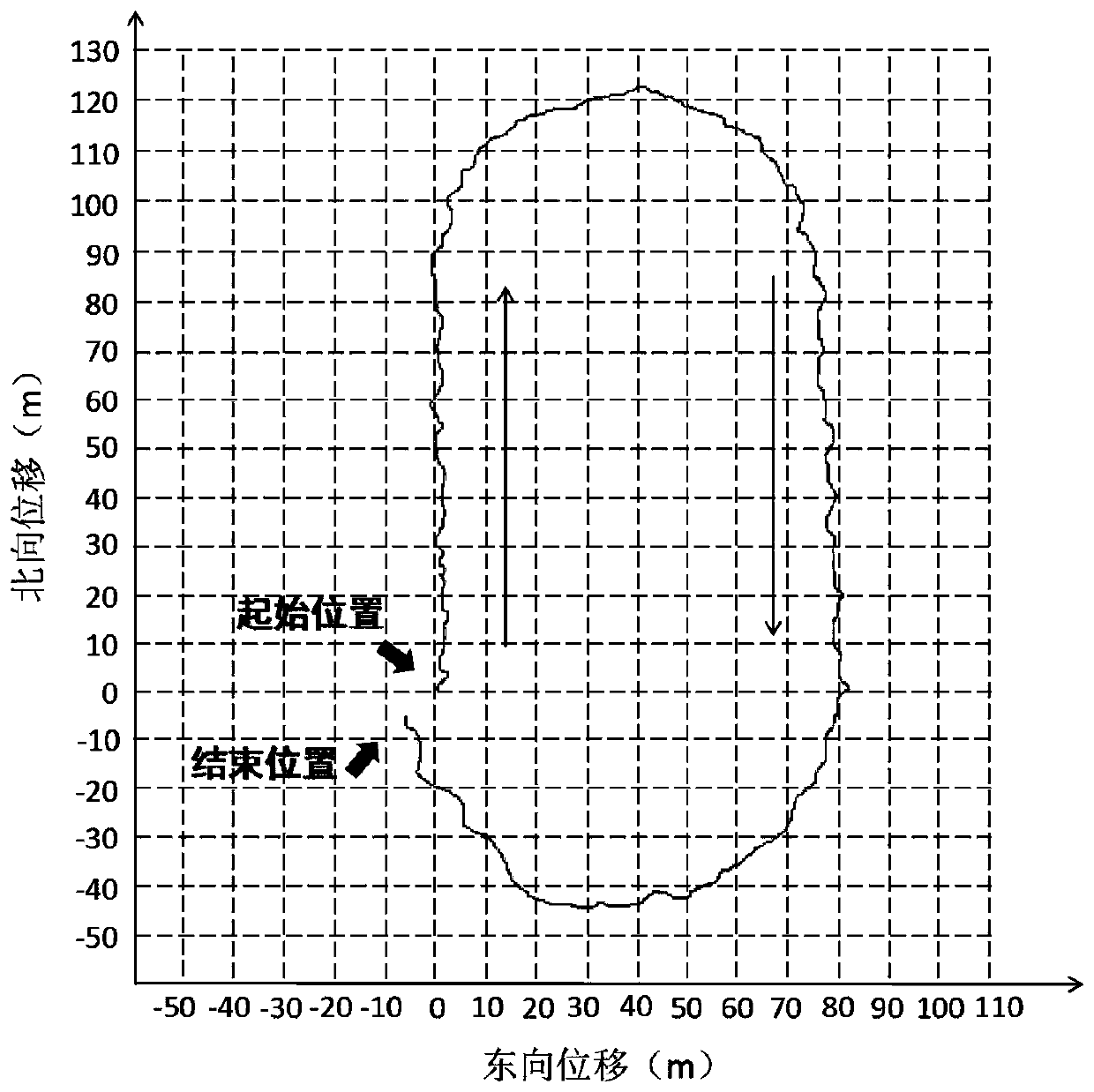
[0168] Such as figure 2 As shown, it is the plane displacement diagram of the outdoor walking experiment of the pedestrian navigation system, in which the thin black line represents the displacement curve of the pedestrian navigation system using zero-speed correction and magnetic heading assistance.
[0169] The outdoor experiment site is the new playground of our school. In a clockwise direction, along the innermost white line of the 400m runway, from the starting point shown in the picture, walk around the playground clockwise at a constant speed, and finally return to the starting position to complete the entire experiment The travel time is about 5 minutes and 37 seconds. Before starting to walk, first stand still at the starting position for 30 seconds to complete the initial alignment. Because the start position and end position of the experiment are the same, the positio...
Embodiment 2
[0174] The pedestrian navigation method described above was applied to indoor experiments, as follows:
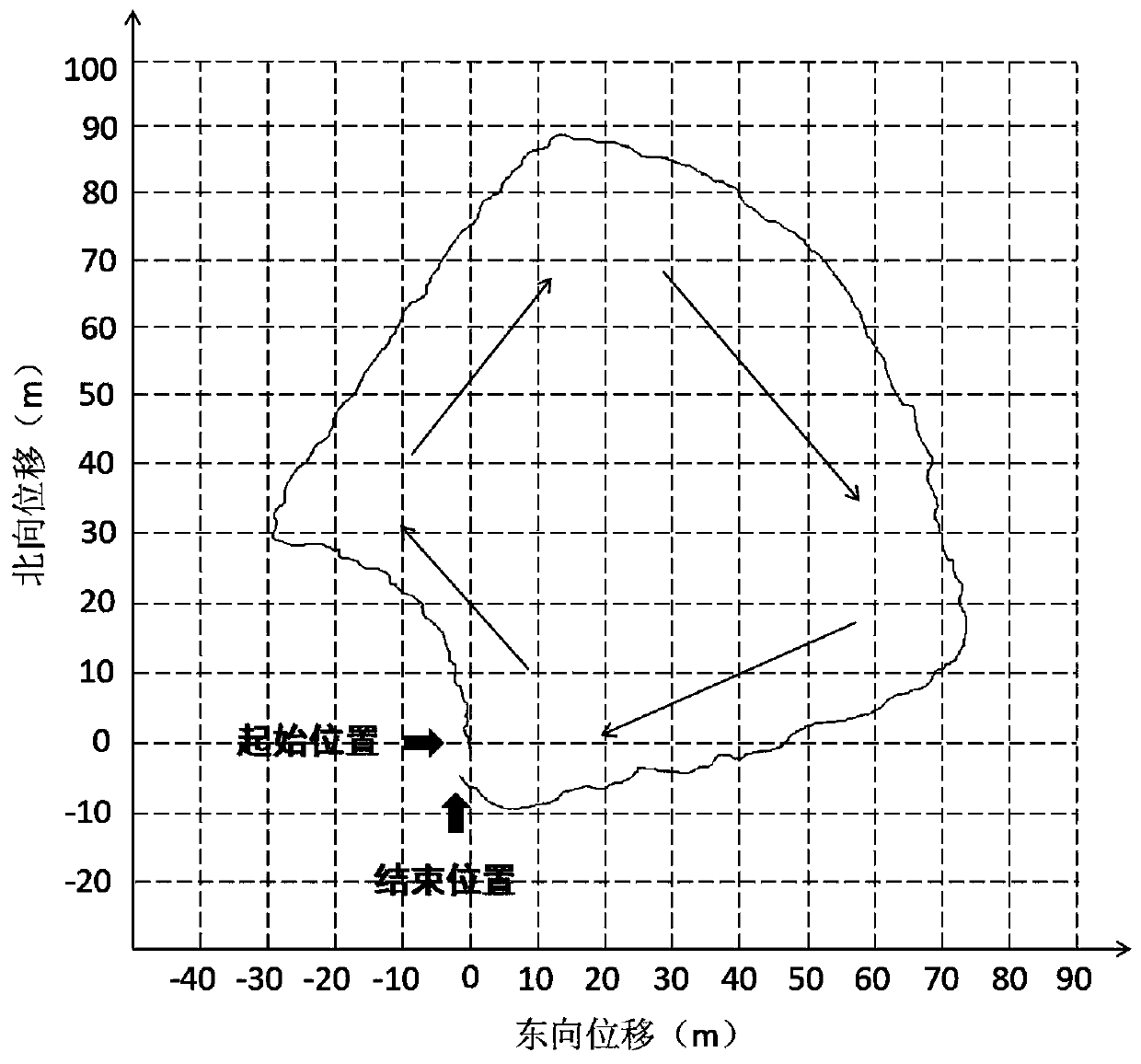
[0175] Such as image 3 As shown, the four areas of ABCD are connected by corridors, so walk clockwise along the wall at a constant speed, and finally return to the starting position. The walking time is about 4 minutes and 02 seconds. Before starting to walk, first stand still at the starting position for 30 seconds to complete the initial alignment. The thin black line represents the displacement curve of the pedestrian navigation system using zero speed correction and magnetic heading assistance.
[0176] Since the traditional satellite positioning system is not used, the closed indoor environment does not affect the work of the pedestrian navigation system.
[0177] The error distance and error proportion are shown in Table 2. Due to the shortened walking time, the final error distance and error proportion data are reduced to a certain extent compared with long-distan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com