Patents
Literature
199results about "Electrical haptic/tactile feedback" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
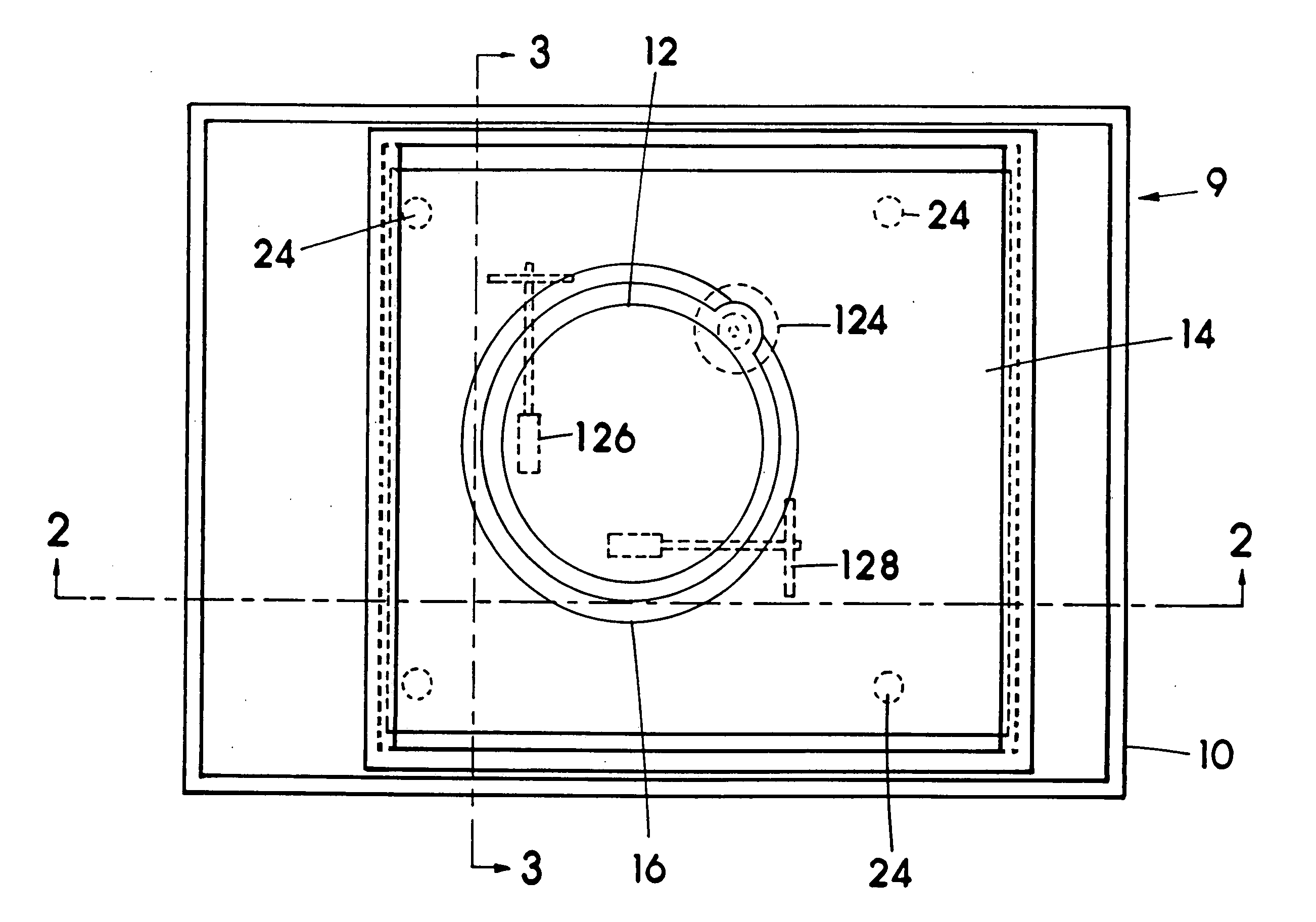
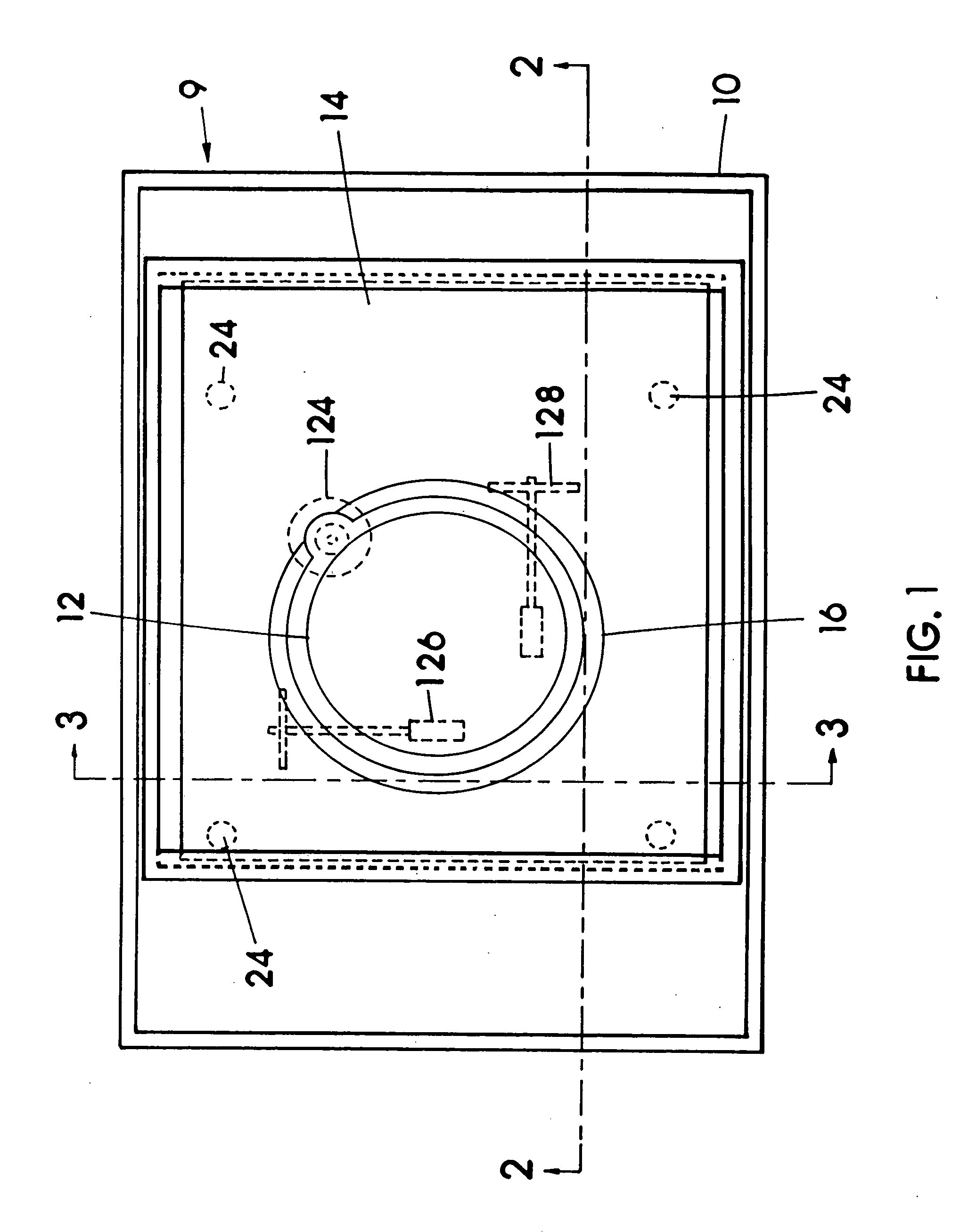
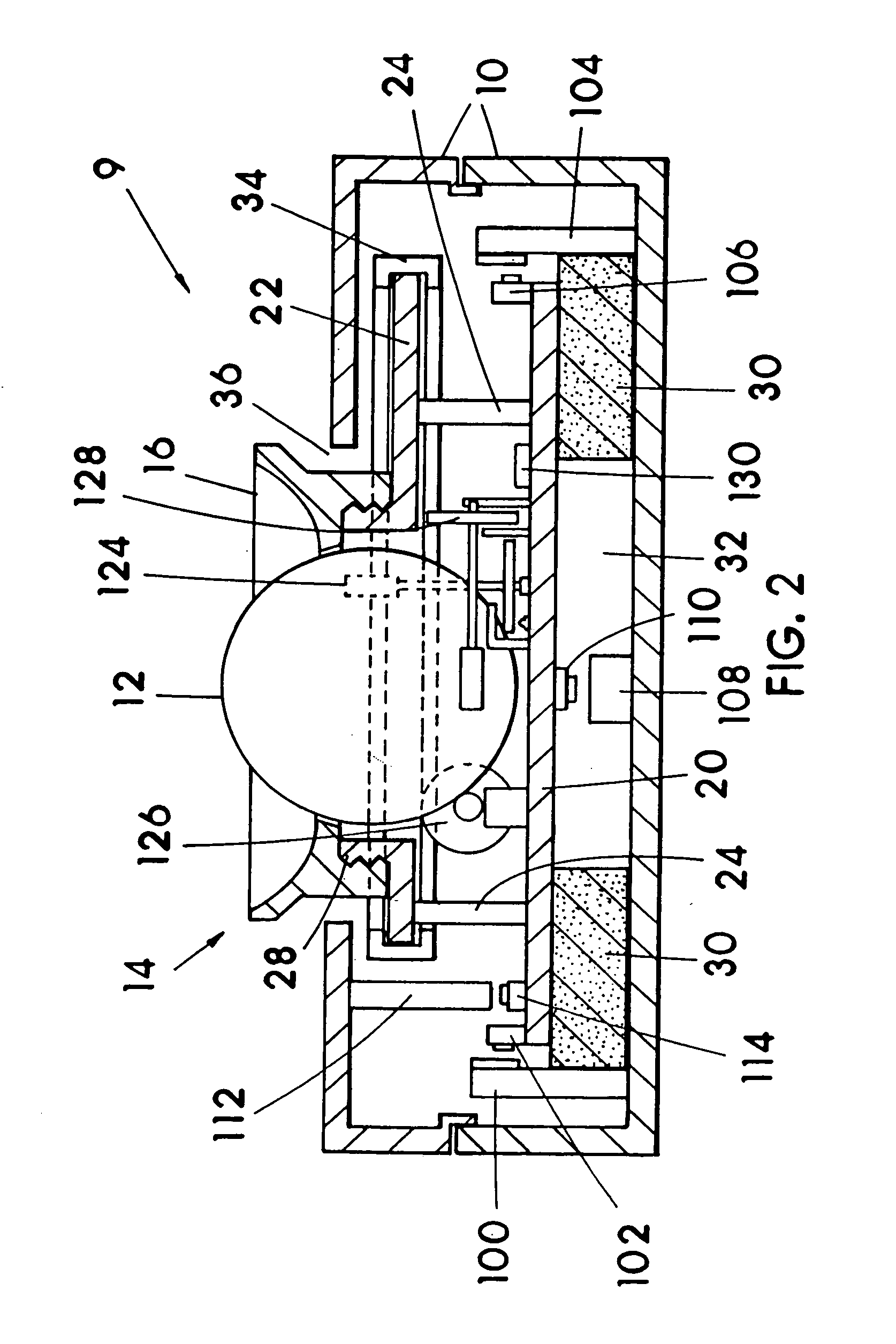
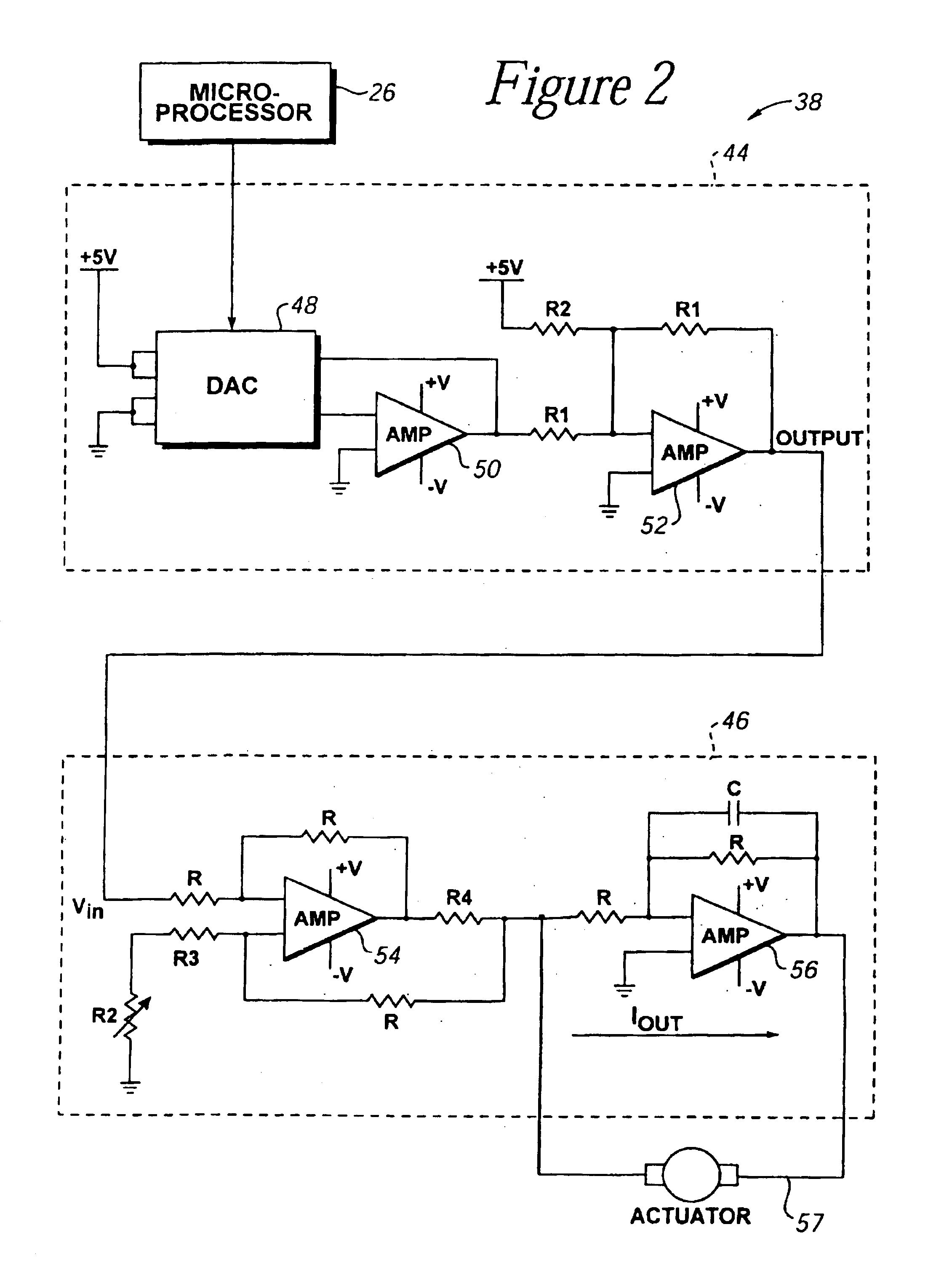
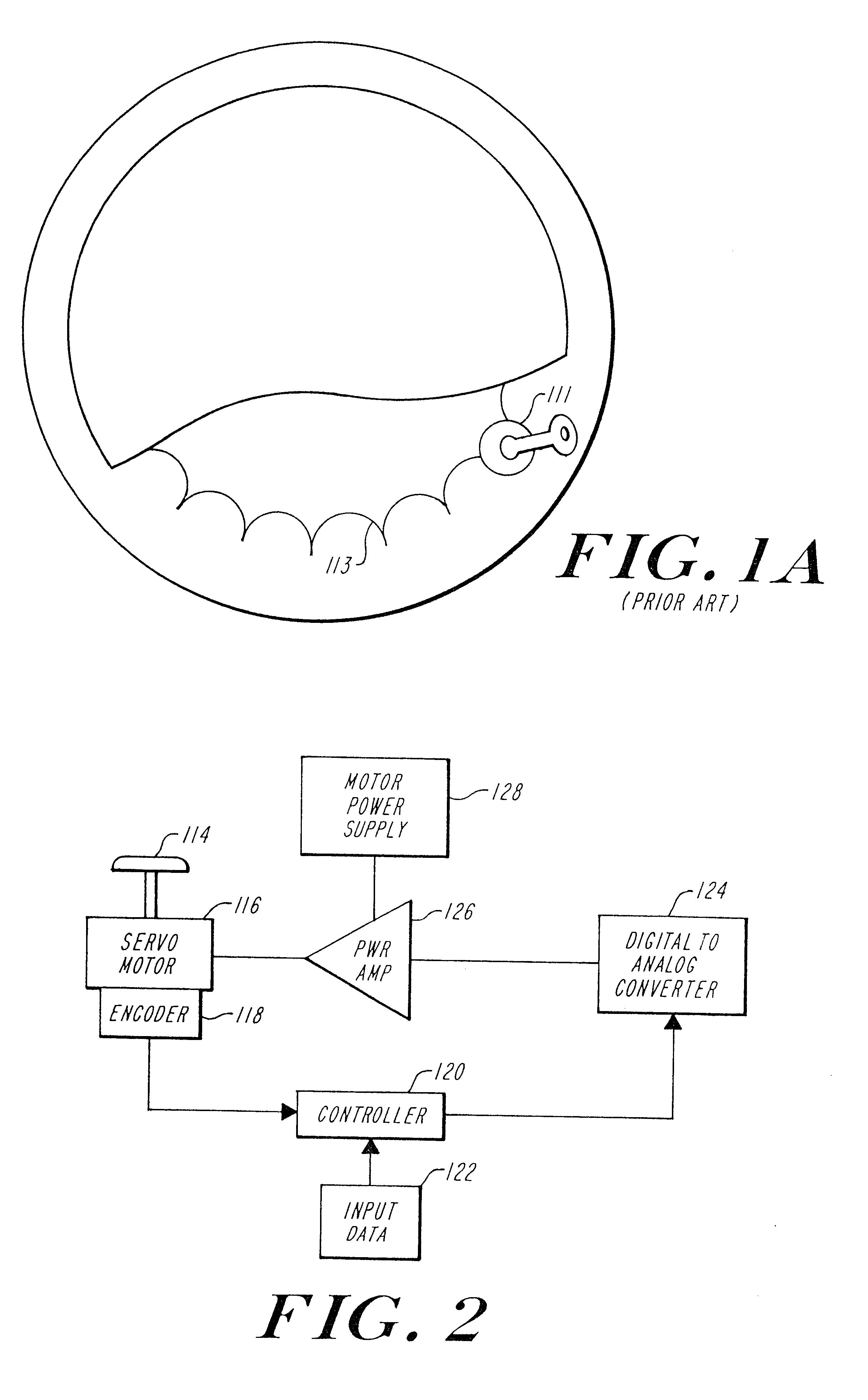
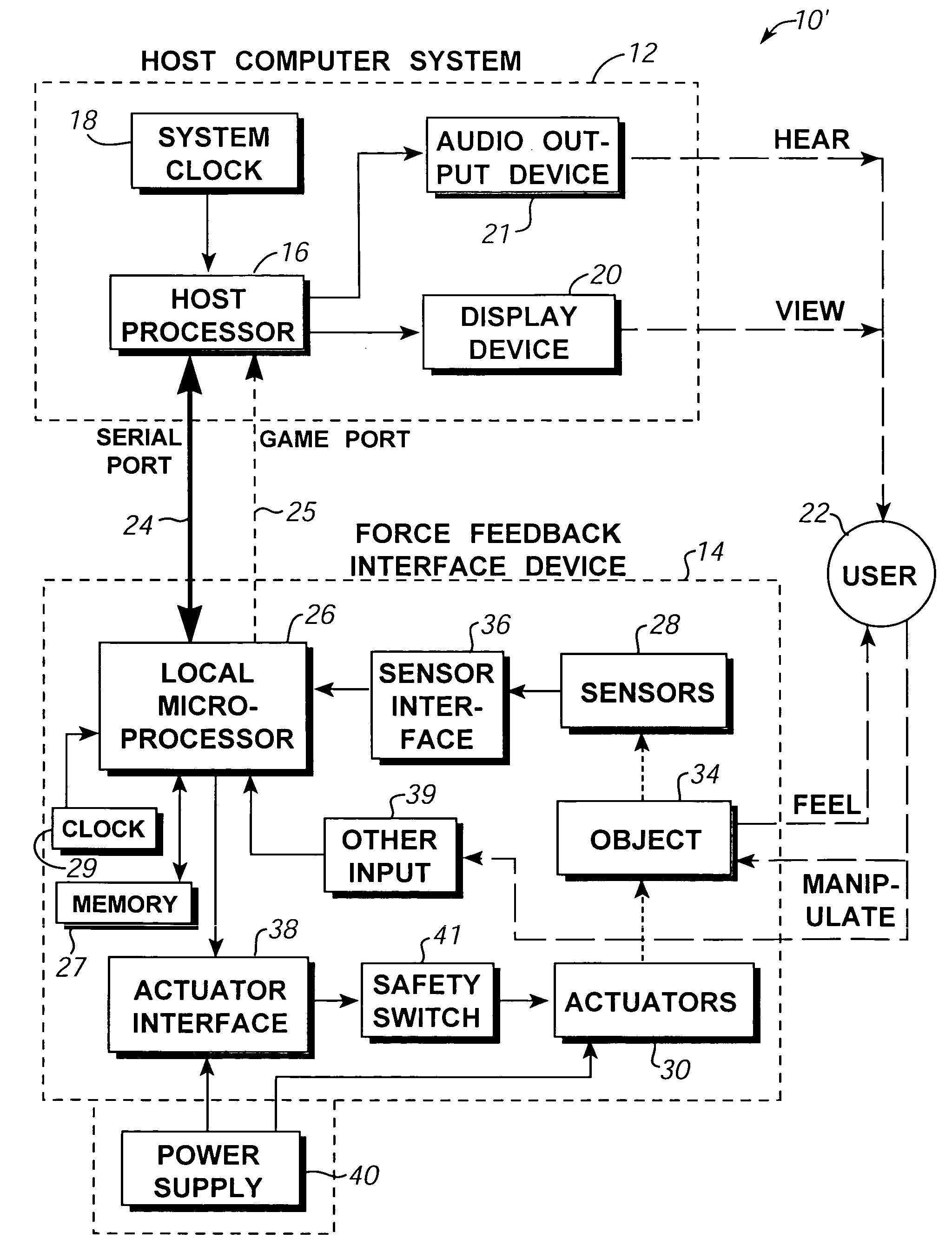
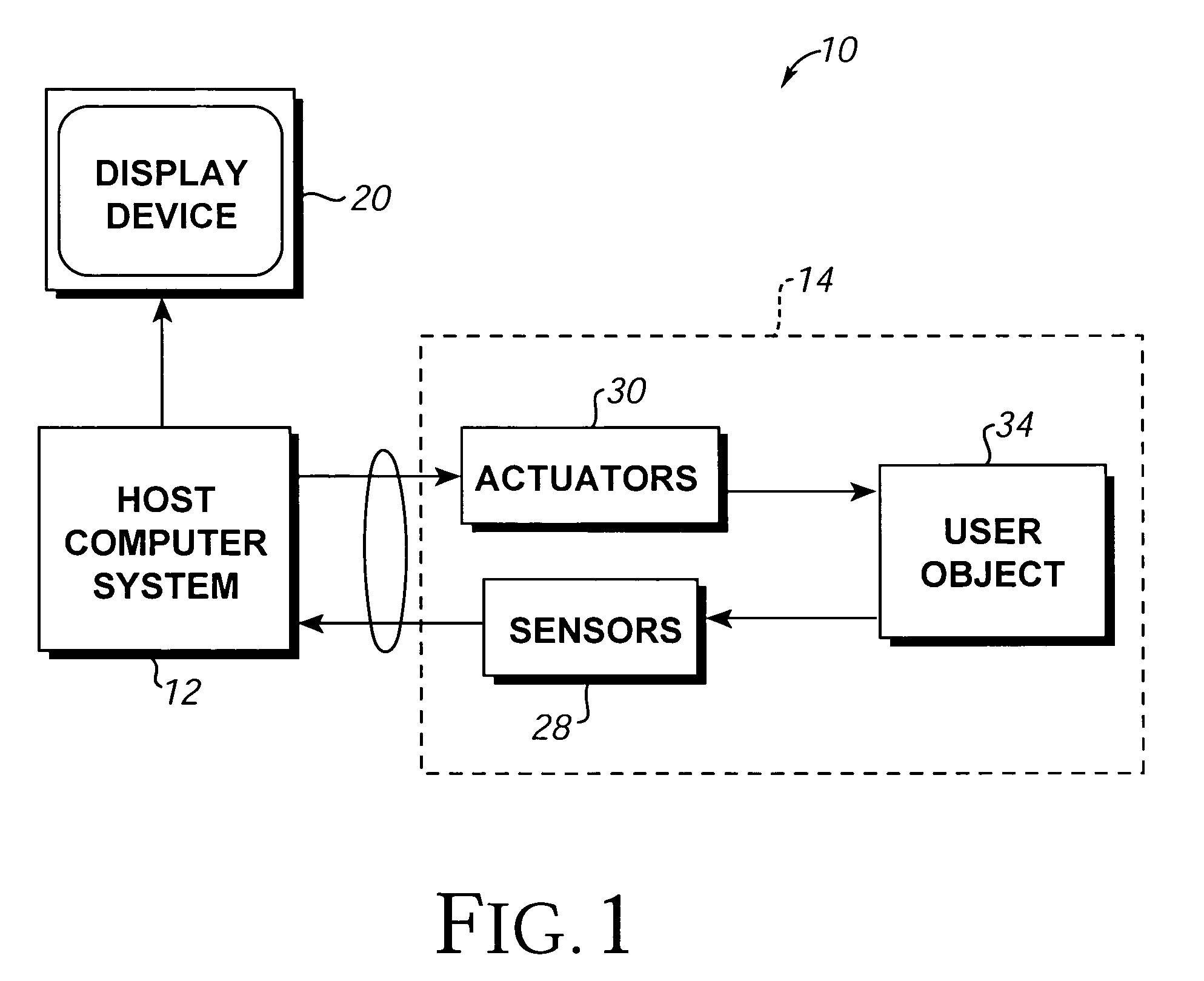
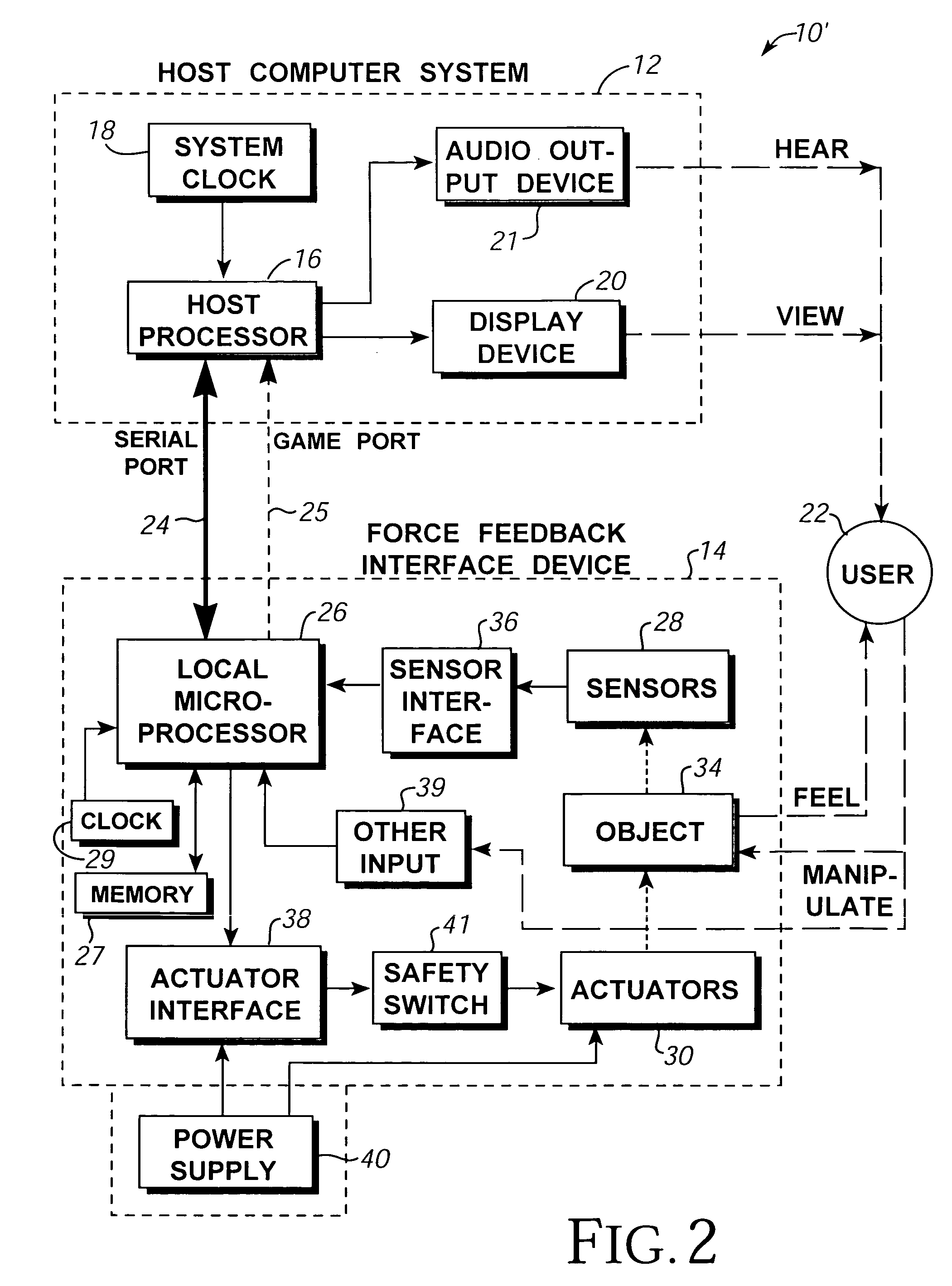
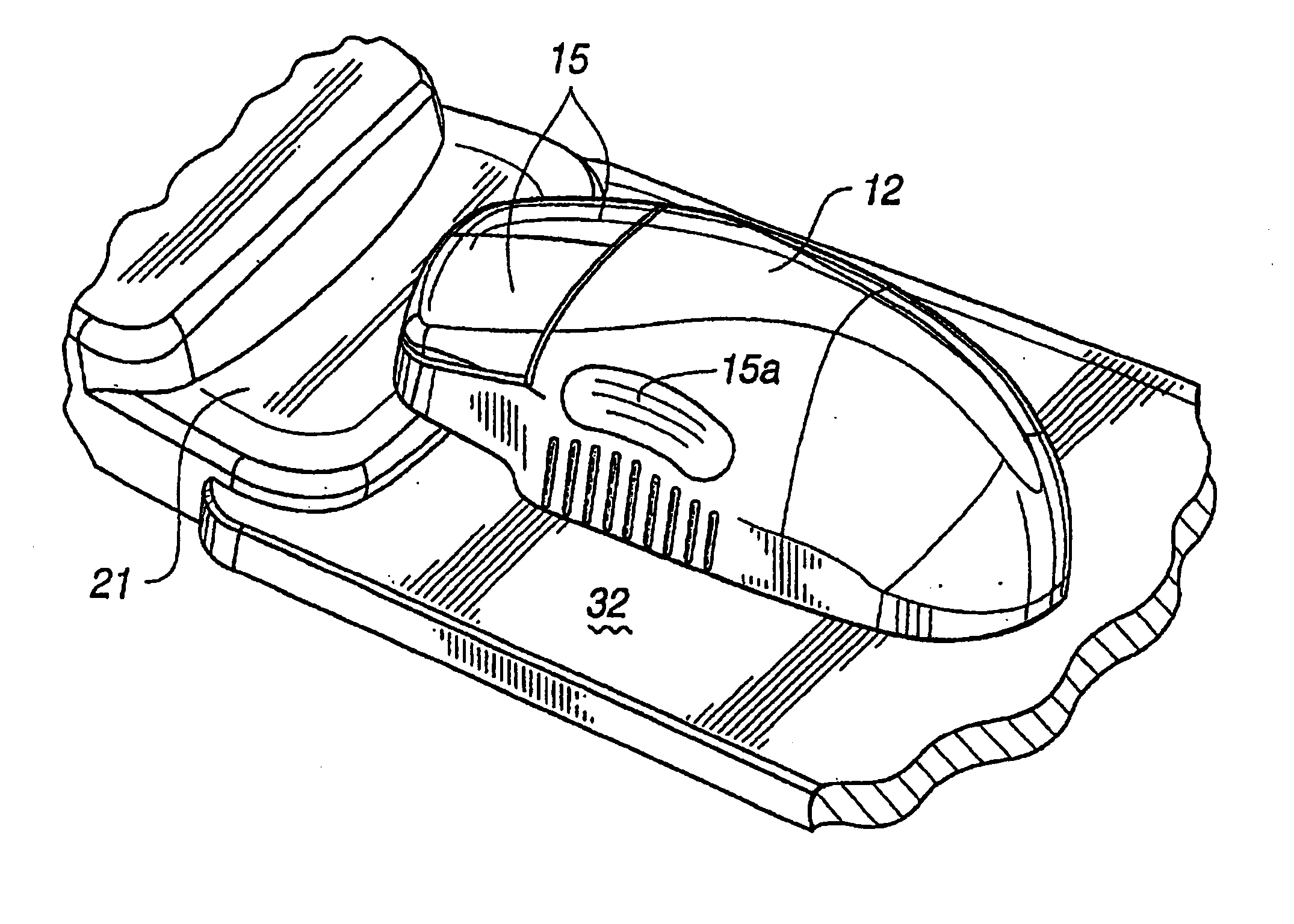
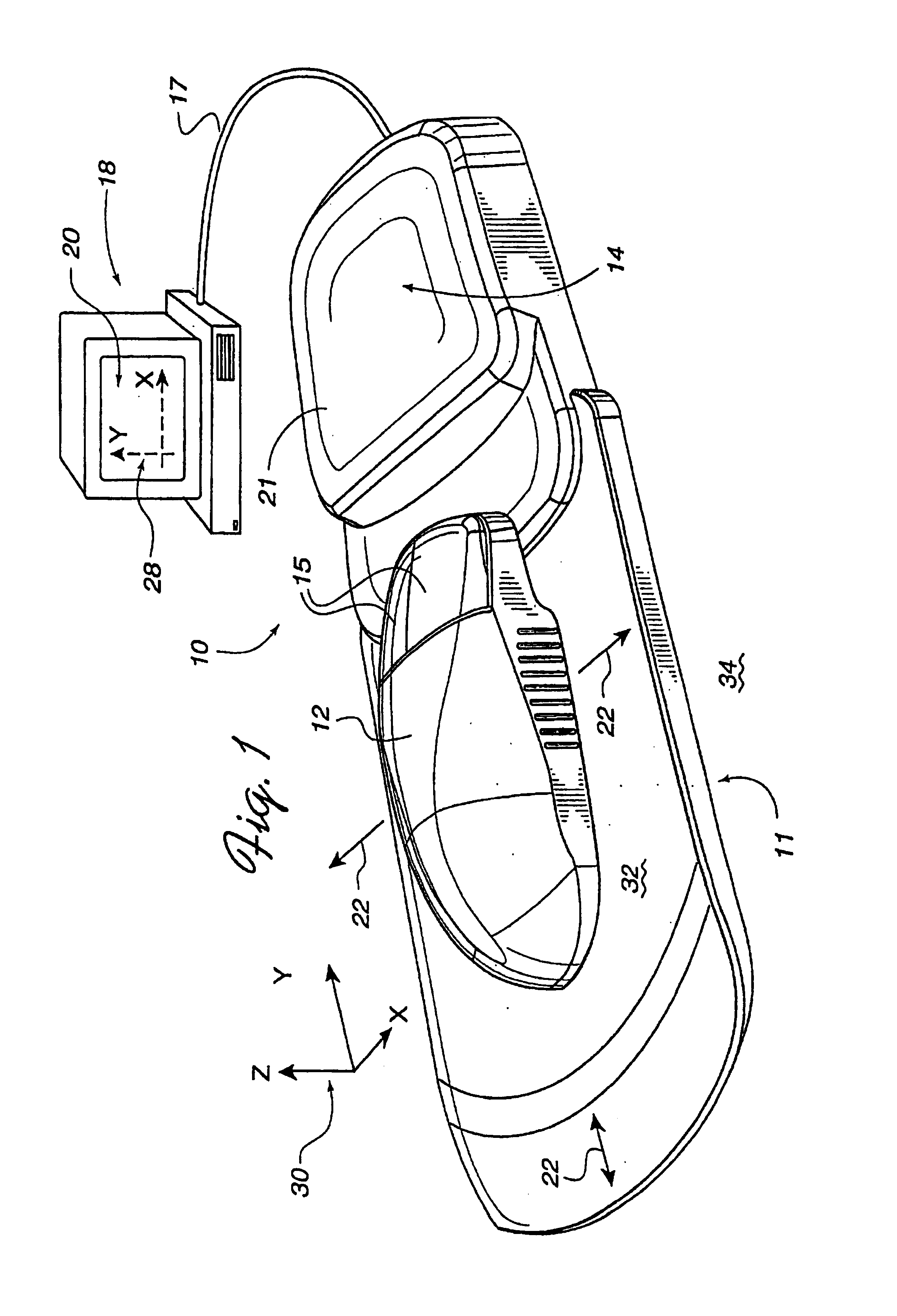
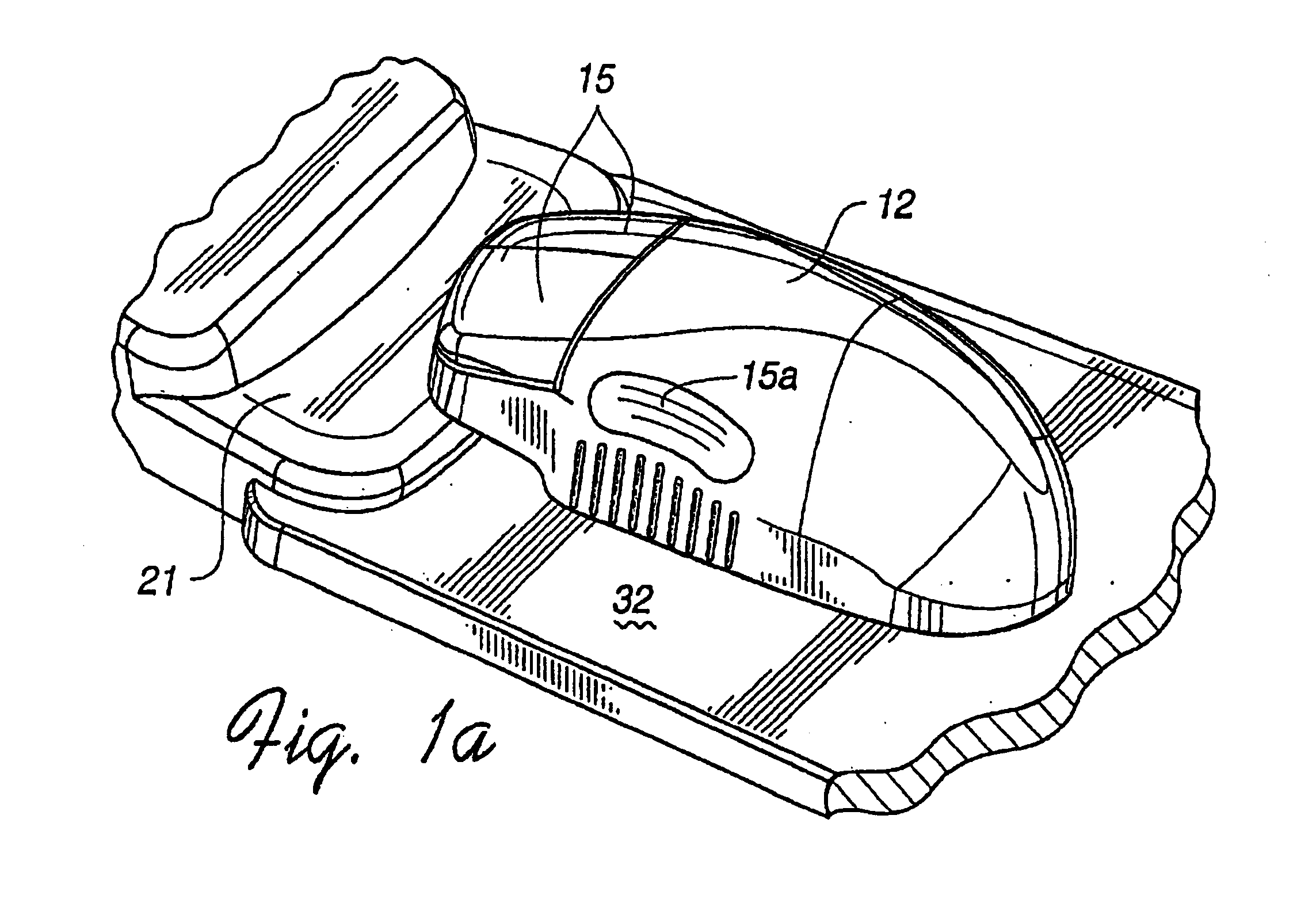
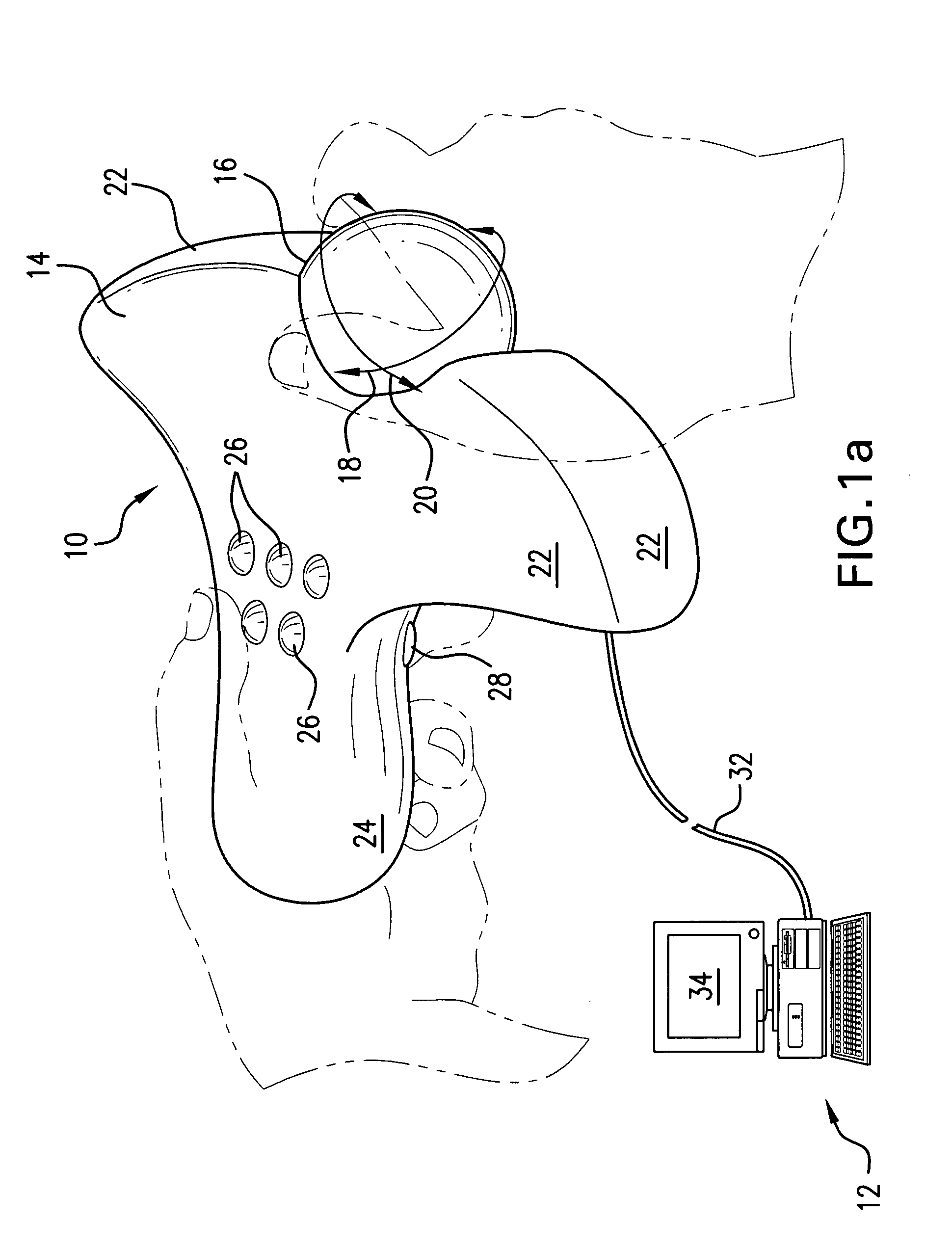
Image controller
InactiveUS20060028436A1Easy to controlAdvantage of versatility of complex movementsInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersViewpointsDisplay device
Owner:ANASCAPE
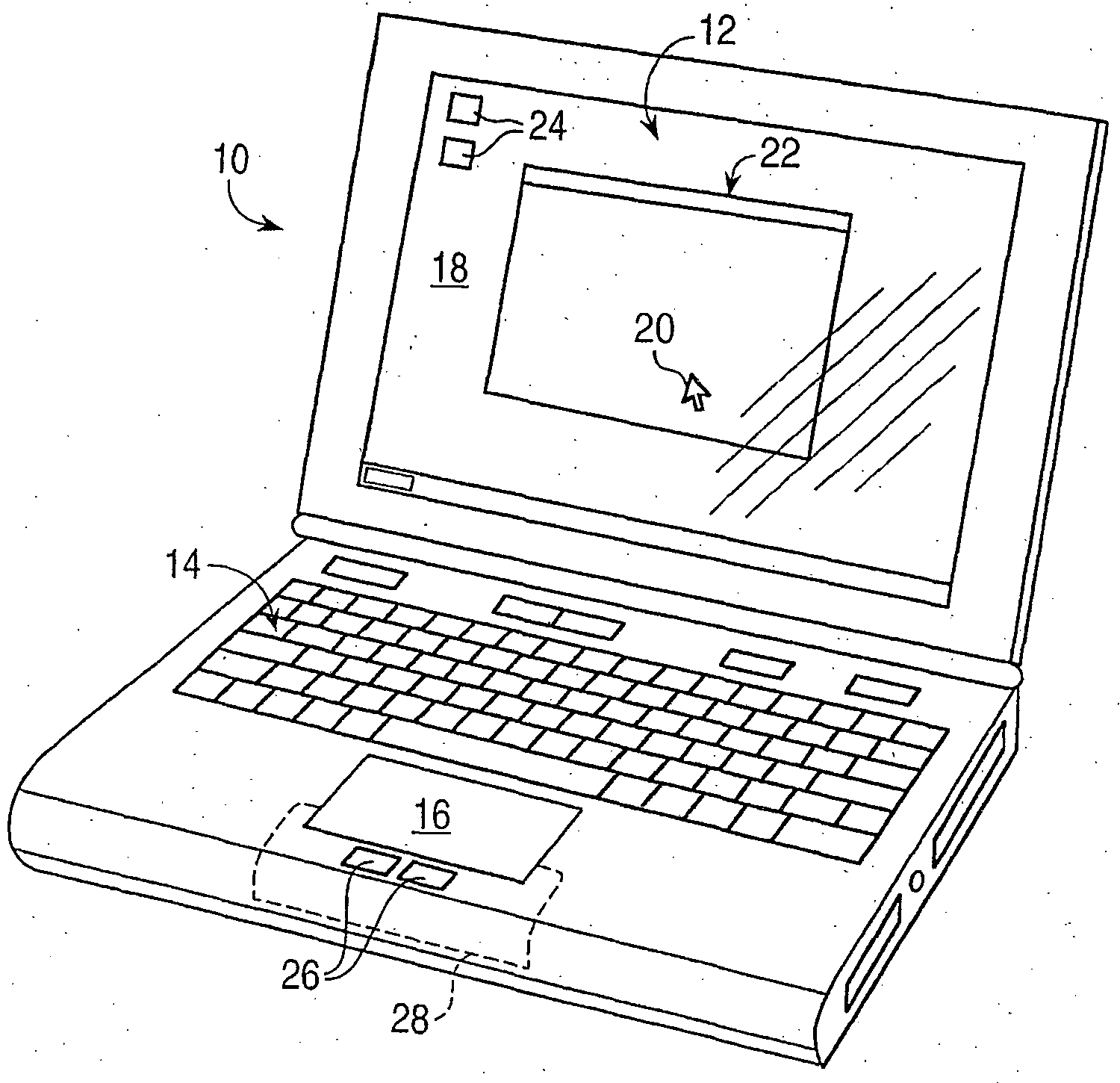
Haptic input devices
InactiveUS20050017947A1Enhanced interactionEnhance manipulationInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsPiezoelectric actuators
A haptic feedback touch control used to provide input to a computer. A touch input device includes a planar touch surface that provides position information to a computer based on a location of user contact. The computer can position a cursor in a displayed graphical environment based at least in part on the position information, or perform a different function. At least one actuator is also coupled to the touch input device and outputs a force to provide a haptic sensation to the user. The actuator can move the touchpad laterally, or a separate surface member can be actuated. A flat E-core actuator, piezoelectric actuator, or other types of actuators can be used to provide forces. The touch input device can include multiple different regions to control different computer functions.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
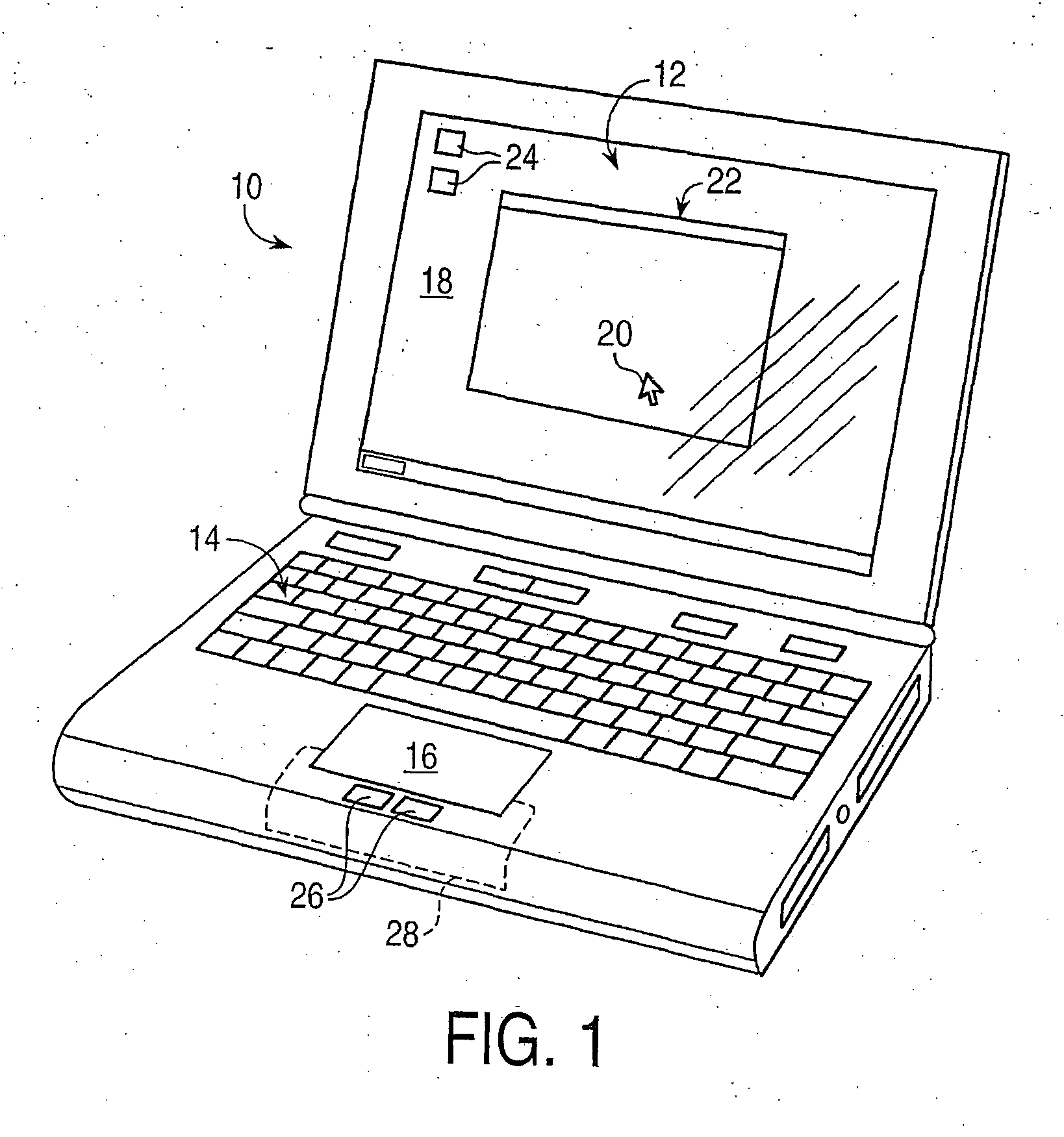
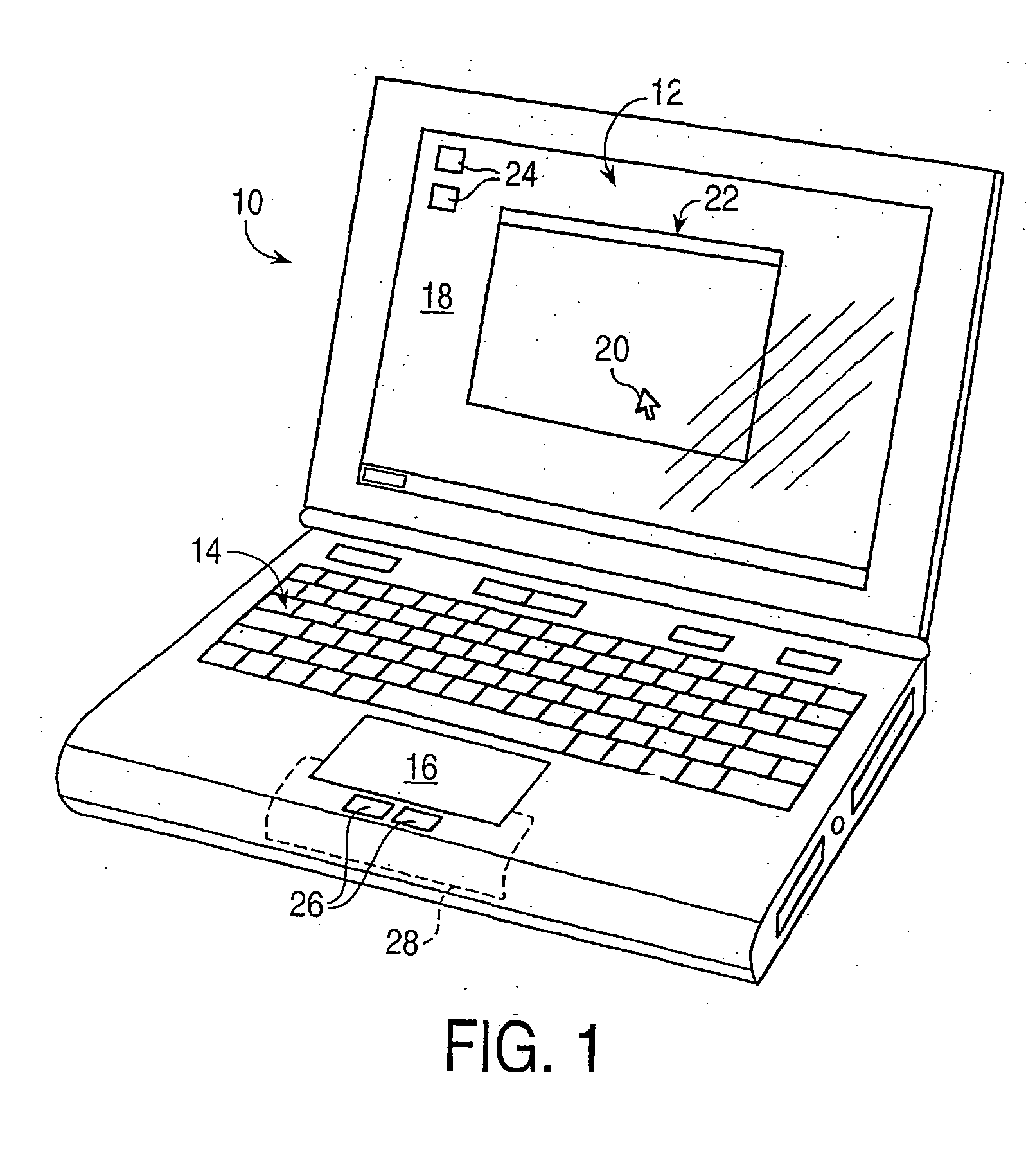
Providing force feedback to a user of an interface device based on interactions of a user-controlled cursor in a graphical user interface
InactiveUS7199790B2Easily moved onto targetFreedom of movementInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersGraphicsJoystick
A method and apparatus for providing force feedback to a user operating a human / computer interface device in conjunction with a graphical user interface (GUI) displayed by a host computer system. A physical object, such as a joystick or a mouse, controls a graphical object, such as a cursor, within the GUI. The GUI allows the user to interface with operating system functions implemented by the computer system. A signal is output from the host computer to the interface device to apply a force sensation to the physical object using one or more actuators. This desired force sensation is associated with at least one of the graphical objects and operating system functions of the graphical user interface and is determined by a location of the cursor in the GUI with respect to targets that are associated with the graphical objects. The graphical objects include icons, windows, pull-down menus and menu items, scroll bars (“sliders”), and buttons. The force sensation assists the user to select a desired operating system function or physically informs the user of the graphical objects encountered by the cursor within the GUI. A microprocessor local to the interface apparatus and separate from the host computer can be used to control forces on the physical object.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Variable sensor with tactile feedback
InactiveUS6344791B1Input/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersTouch PerceptionEngineering
Owner:ANASCAPE
Method and apparatus for providing tactile responsiveness in an interface device
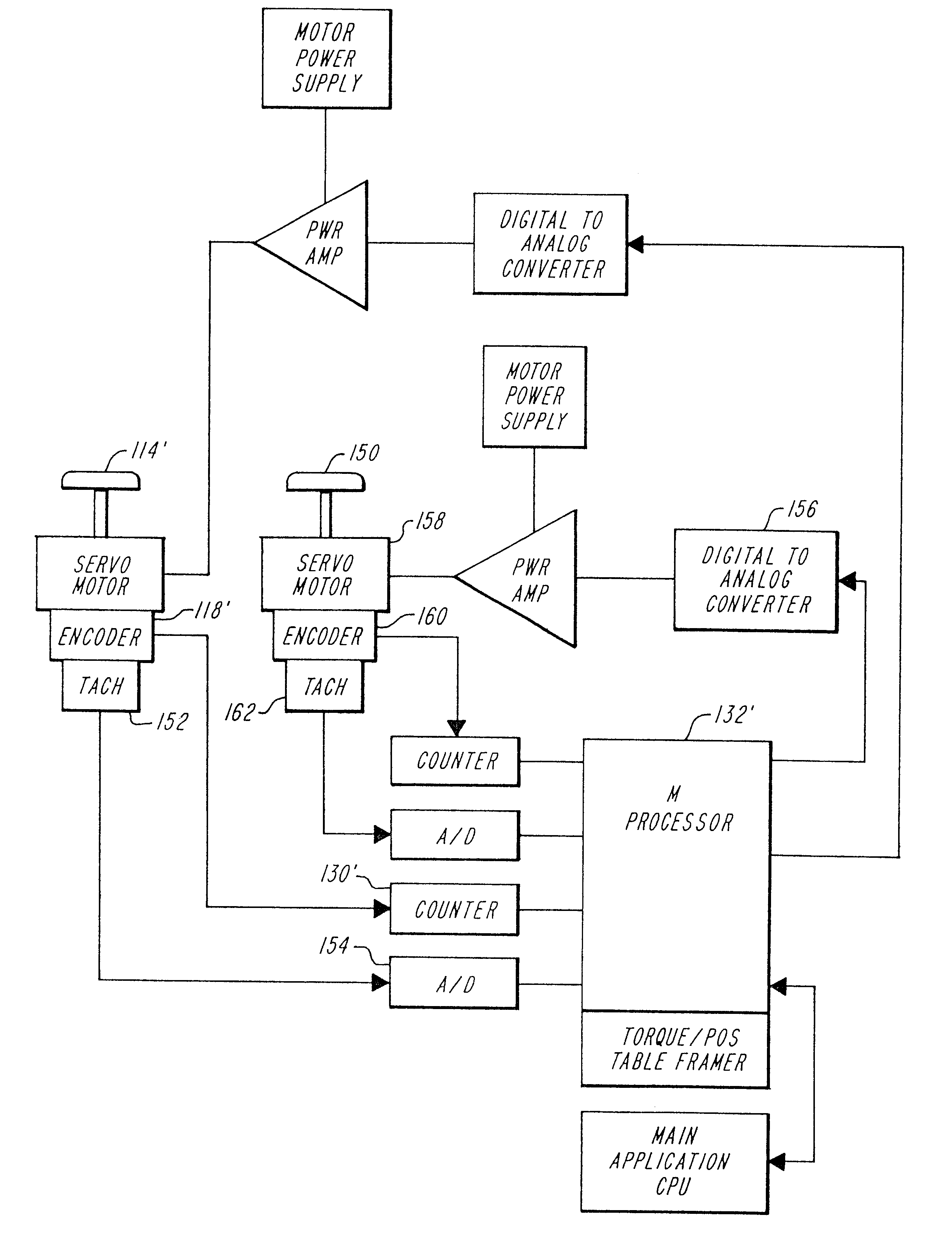
InactiveUS6876891B1Increasing and decreasing resistanceTo offer comfortInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingPosition dependentDisplay device
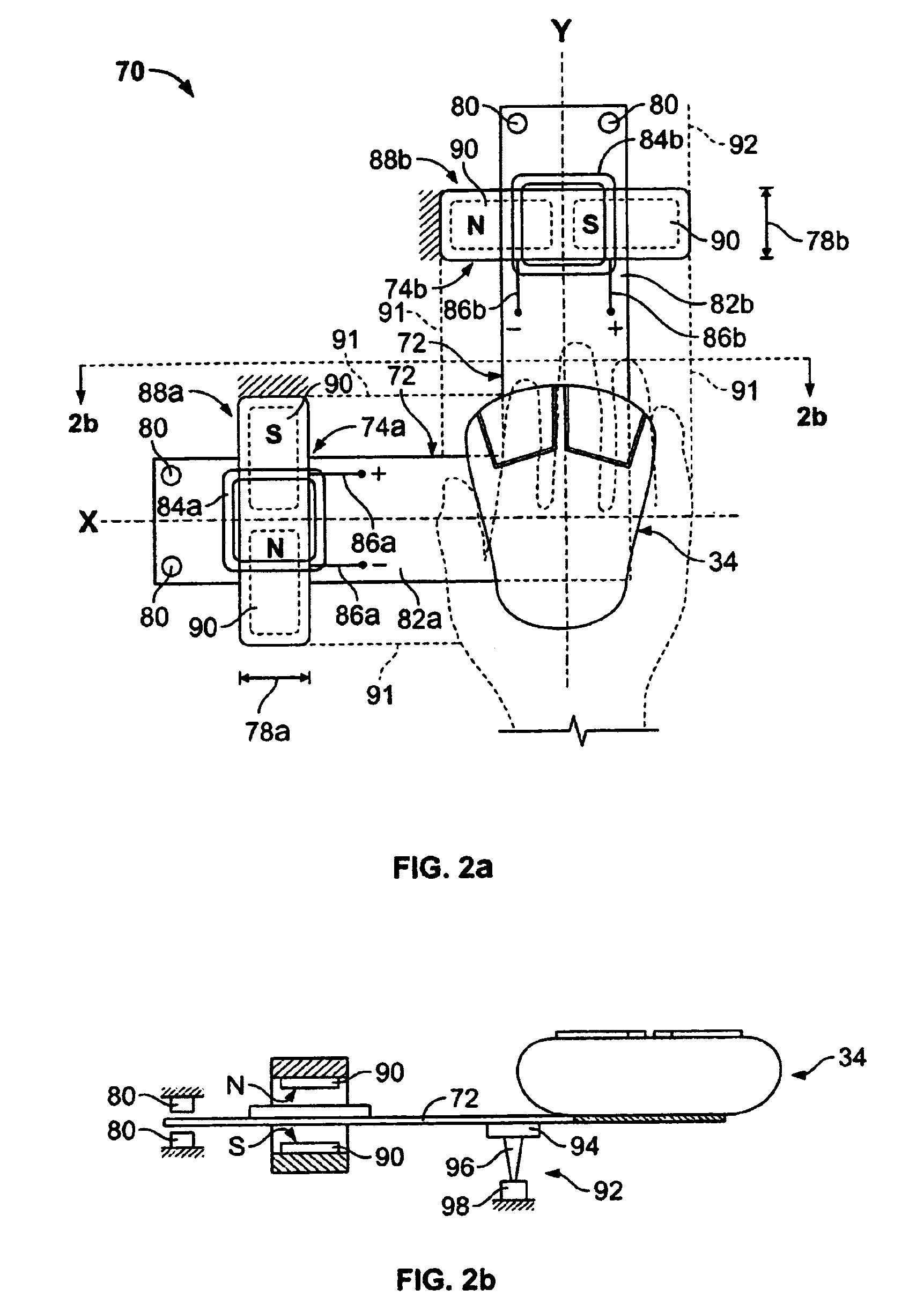
A method and apparatus implementing a user interface device, such as a mouse or trackball, having electronically controllable tactile responsiveness which is flexibly programmable. A user interface device effects positioning of a cursor within a limited area, such as on a display screen, with limits imposed by controllable tactile responsiveness. Programmable force-position characteristics relate the tactile responsiveness of the interface device to the position of the cursor within the limited area or on the display screen. In a described embodiment, the interface device includes at least two sets of wheels that move as the interface device is actuated. The at least two sets of wheels are aligned on mutually orthogonal axes. A servo motor is attached to each of the at least two sets of wheels. A position encoder is associated with each servo motor and outputs position information to a controller that has access to force-position relation information that is a function of a screen display on which the cursor is manipulated. The controller outputs a digital signal, in accordance with the force-display position relation information. The digital signal is converted to an analog current signal applied to the servo motor(s) to generate force in the servo motor. The force, presenting a tactile response to a human interacting with the user interface device, is perceived as a resistance, tactile pressure or lack thereof, or as a positive, assisted motion which is indicative of position on a screen display.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
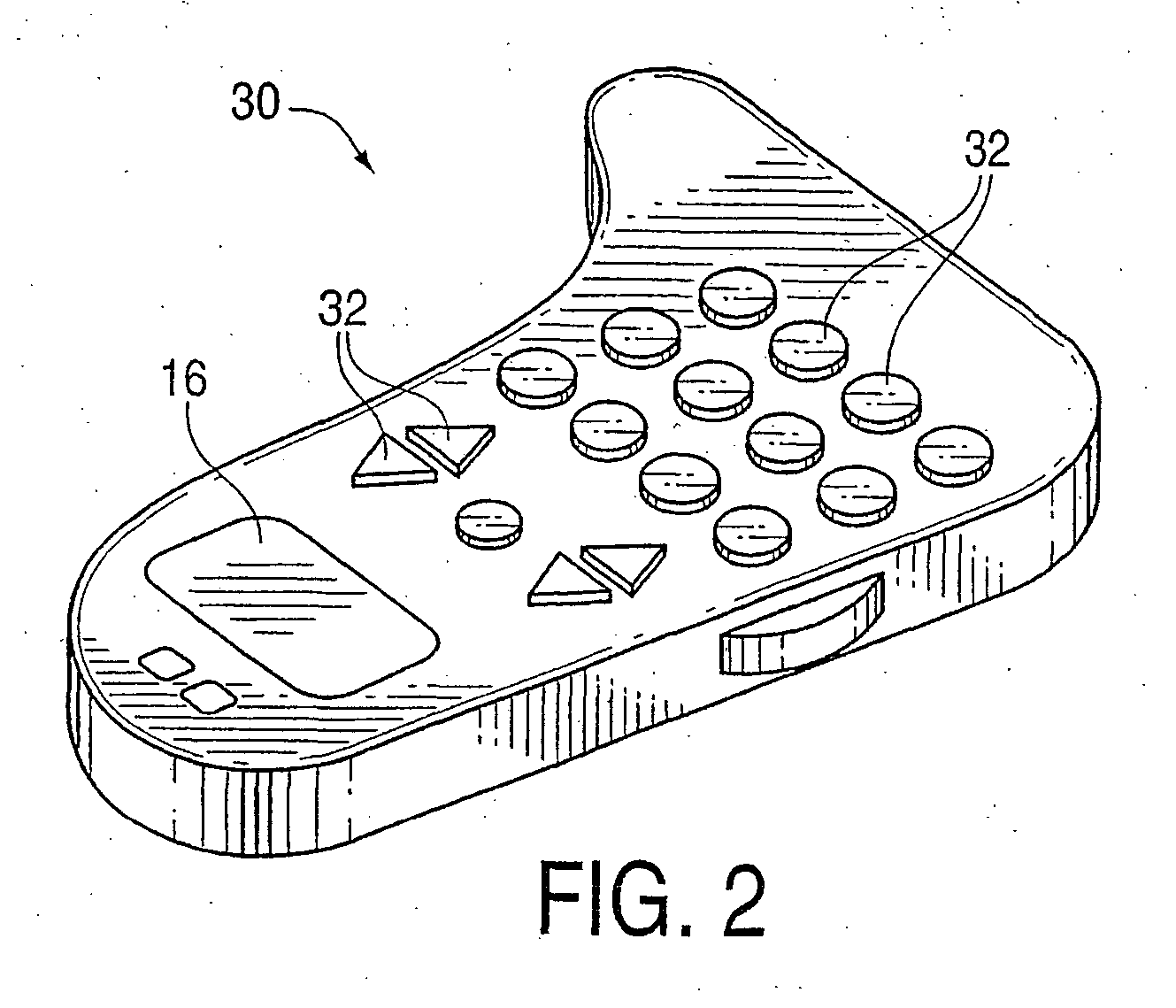
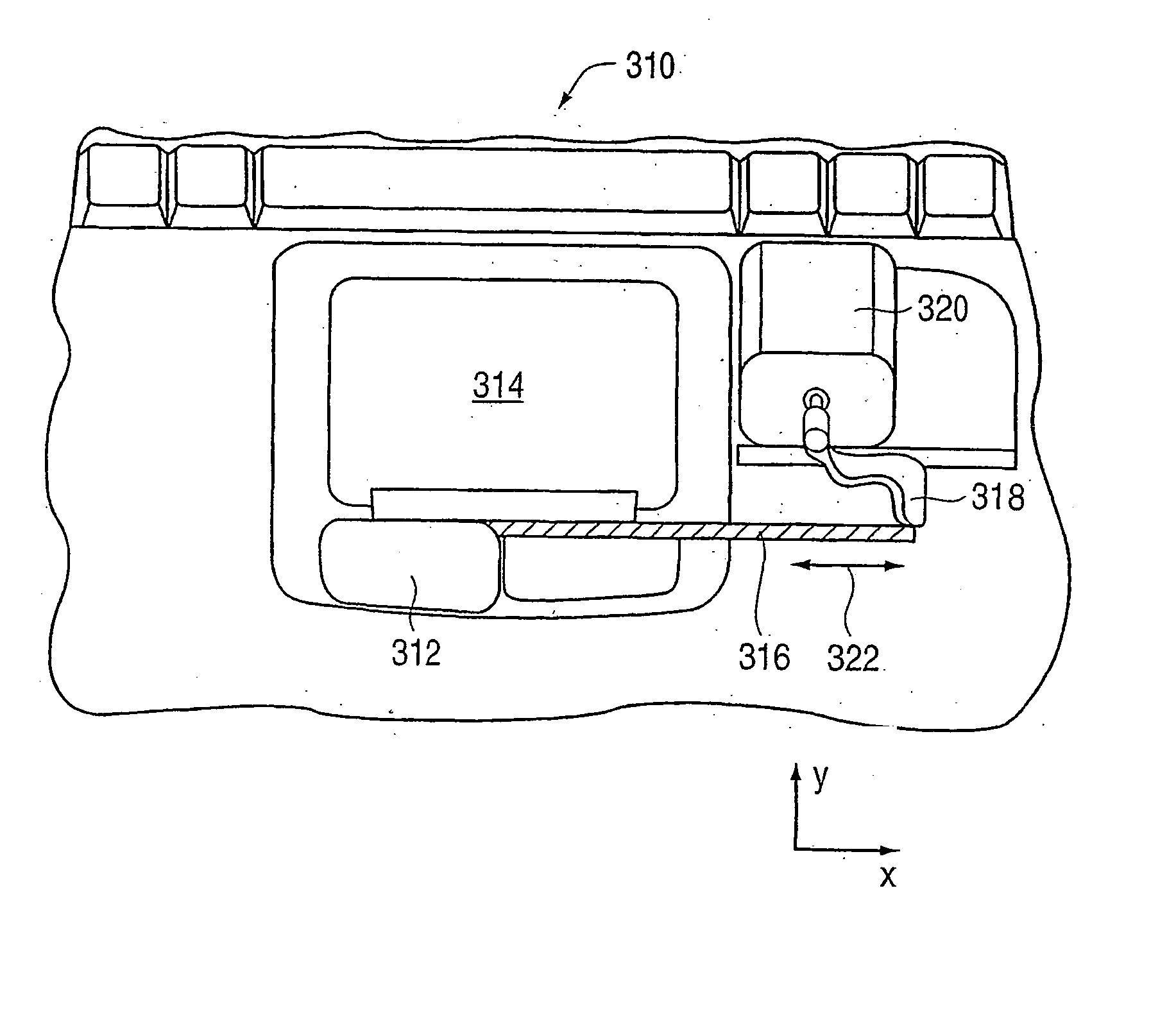
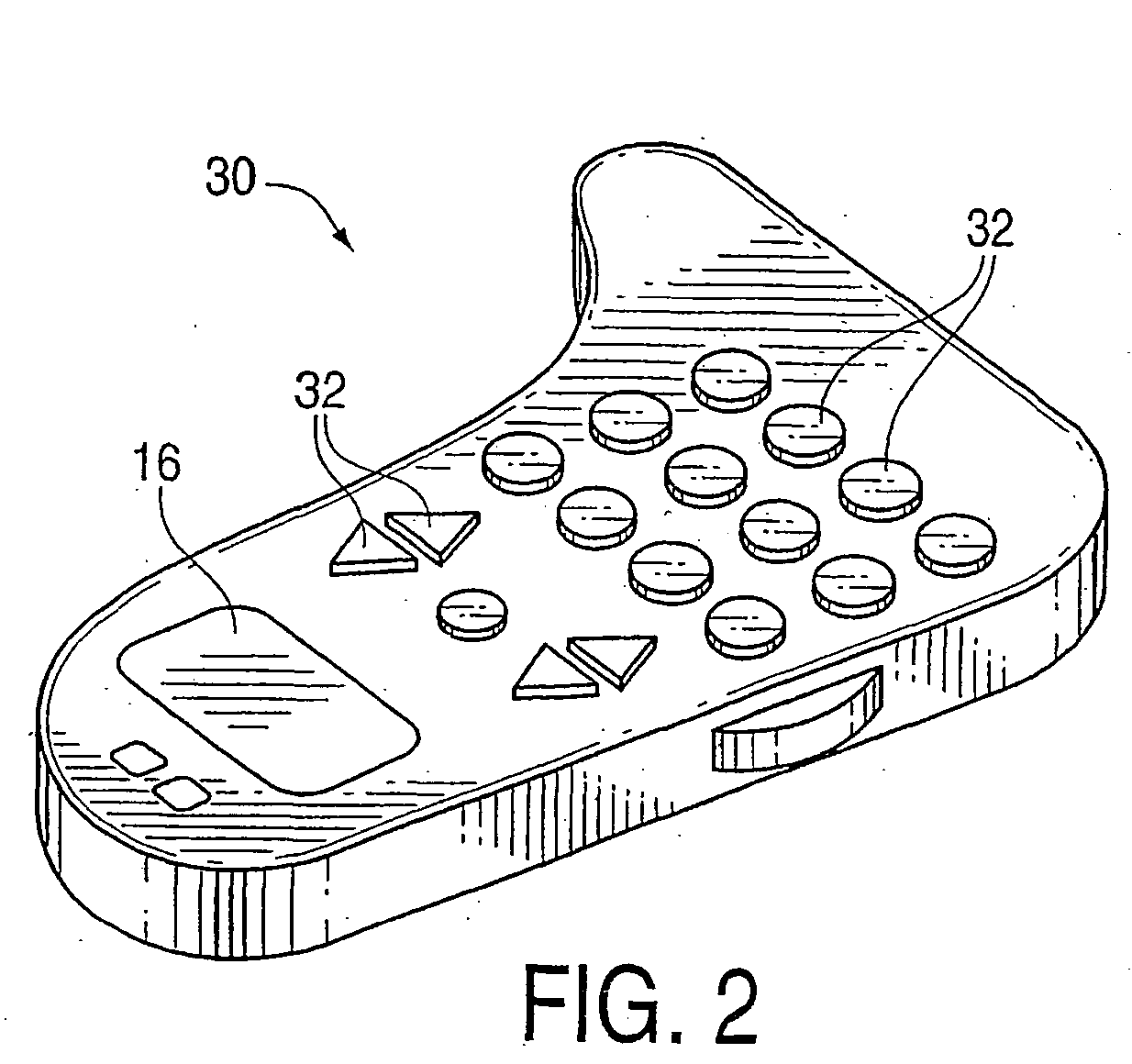
Image controllers with sheet connected sensors
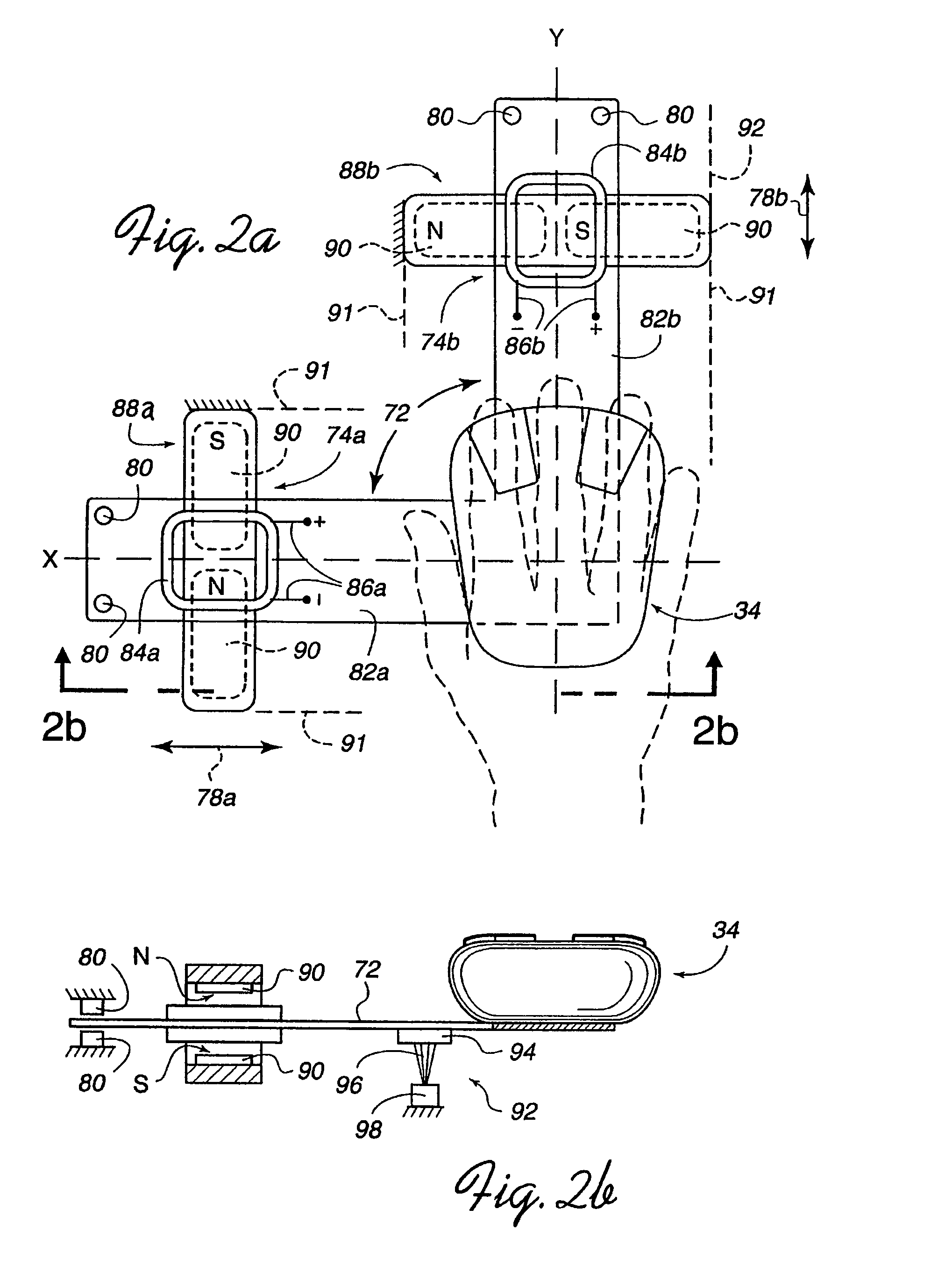
InactiveUS6222525B1Input/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersJoystickEngineering
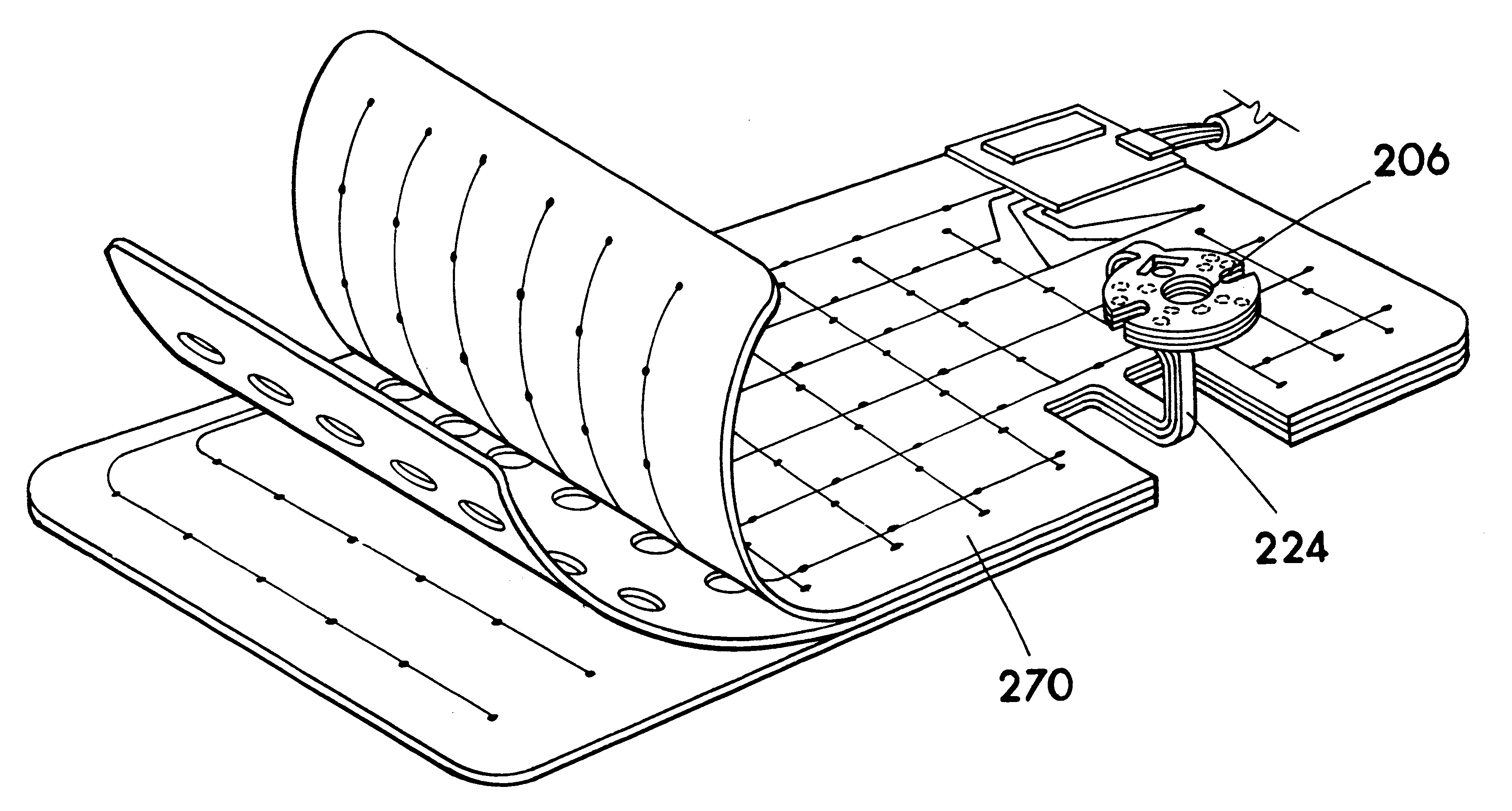
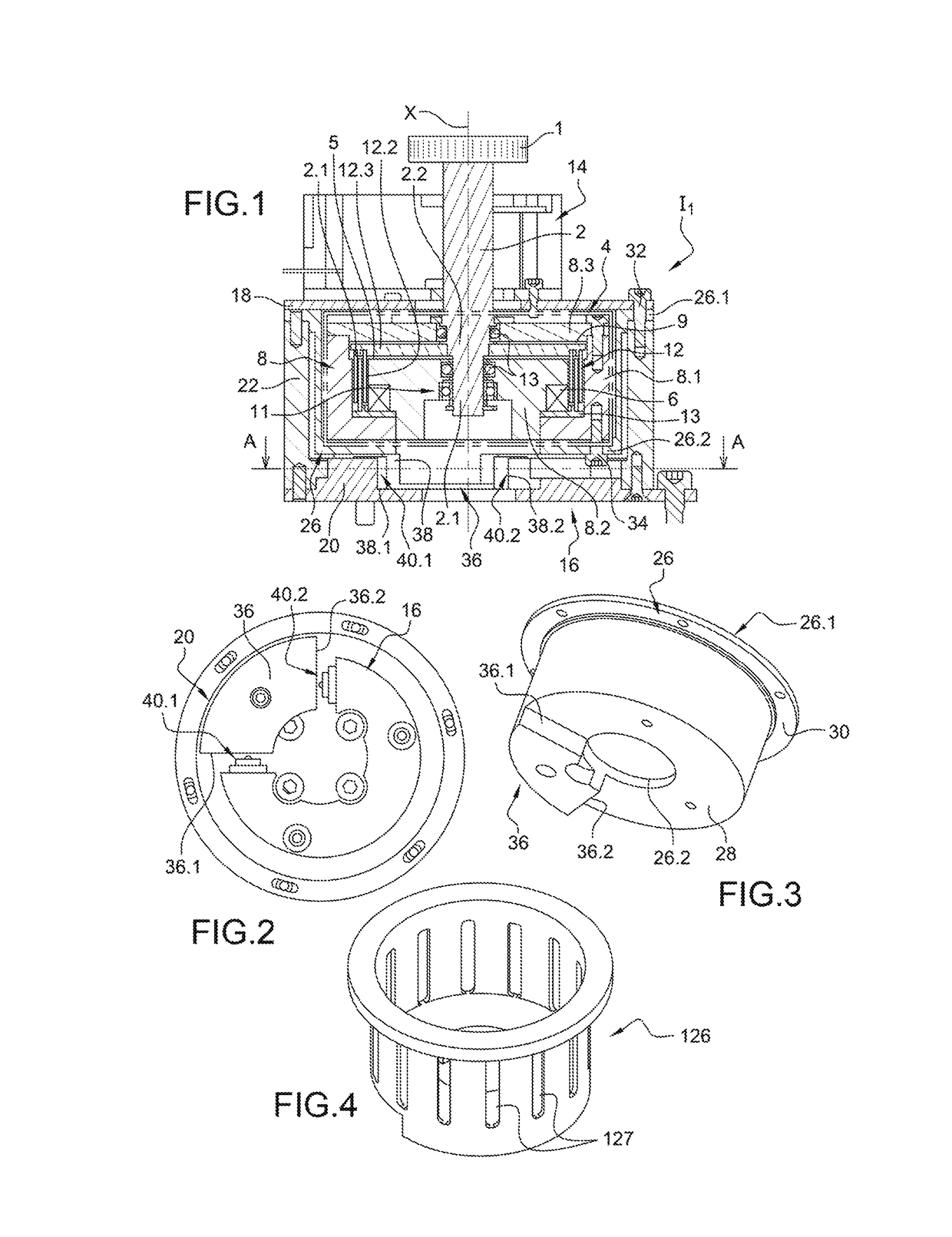
A sensor connecting sheet material for inclusion in appropriately structured multiple-axes controllers comprised of a single input member operable in 6 DOF relative to a reference member of the controller. The input member having return-to-center resiliency relative to the reference member on at least the three perpendicular linear axes. The input member can be of a continuously rotatable trackball-type or a limited rotation joystick-type, and the reference member can be a shaft, a base or a housing. The controllers include carriage structuring for influencing sheet connected sensors by hand-applied operation of the input member. The preferred structures provide cooperative interaction with movement or force influenced sensors in primarily a single area. Some, most, or all of the sensors are preferably supported on a generally single plane, such as on a printed flexible membrane sensor sheet or circuit board sheet. In an alternative embodiment, sensors and conductive traces are applied on a generally flat, flexible membrane sensor sheet, which is then bent into a three dimensional configuration which may in some cases reach a widely-spread 3-D constellation of 6 DOF and / or other sensor mountings. The use of sensors connected by a sheet member, whether finally applied in a flat or 3-D configuration, enables efficient circuit and sensor connection and placement during manufacture, resulting in low product costs and high reliability.
Owner:ANASCAPE +1
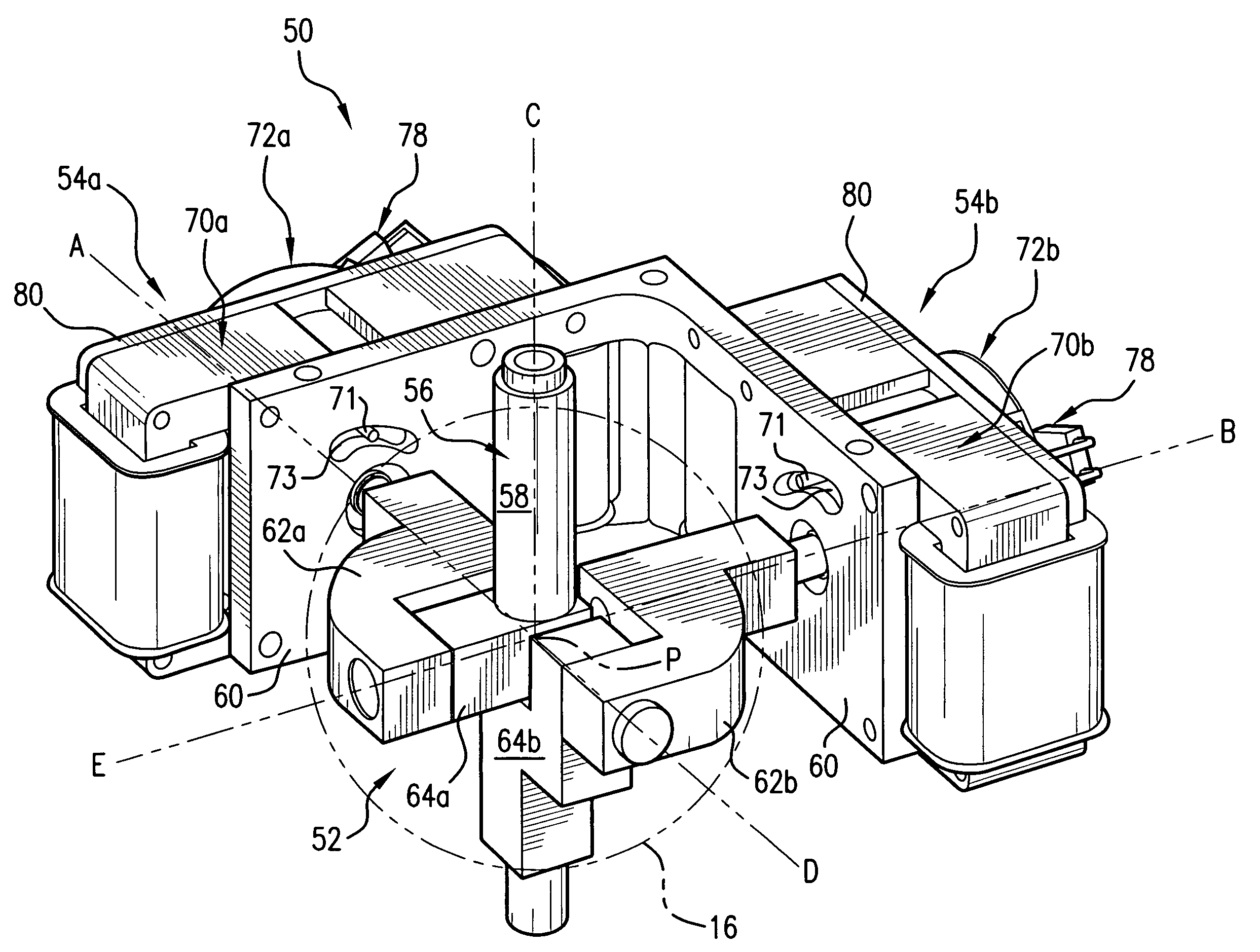
Mechanisms for control knobs and other interface devices
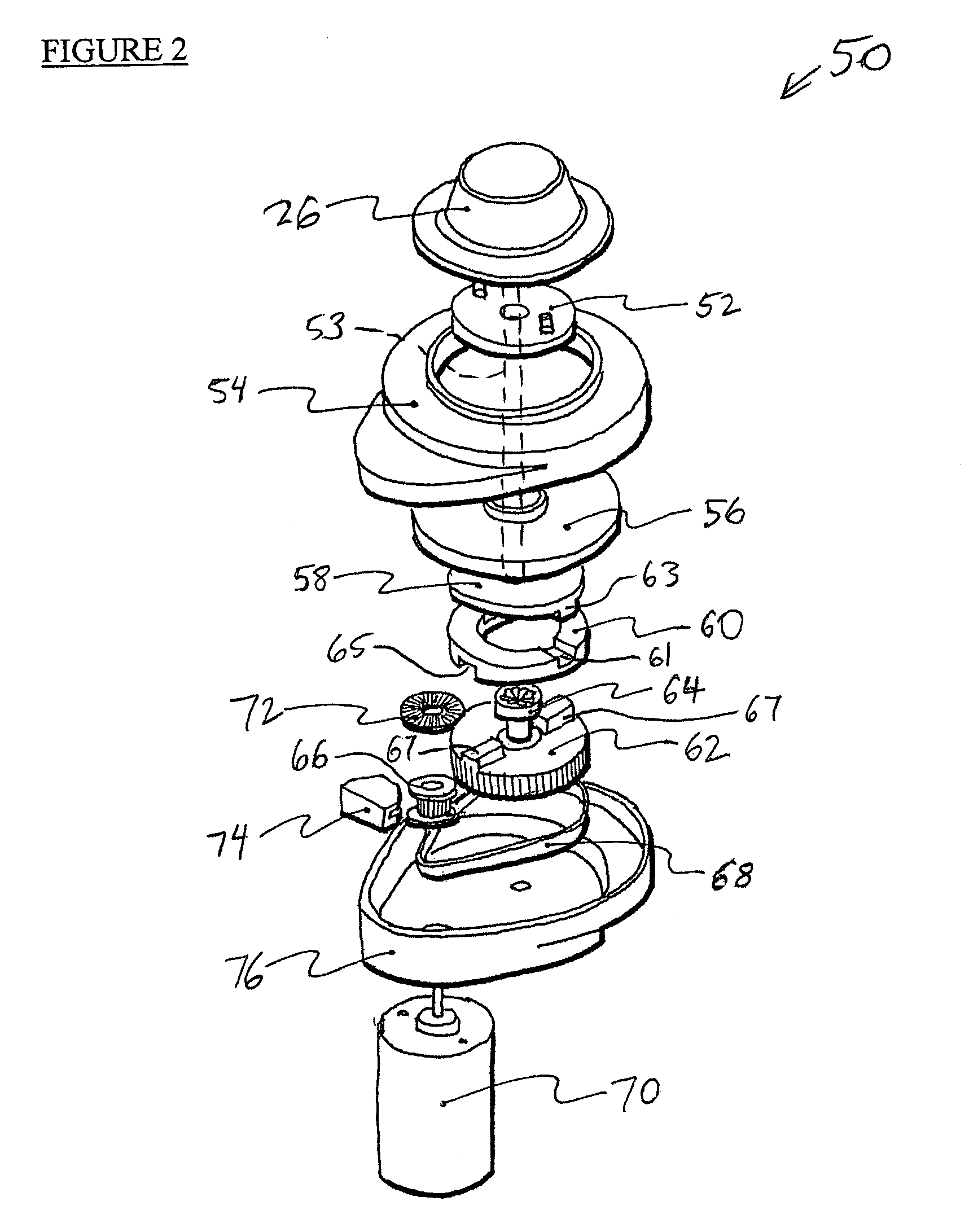
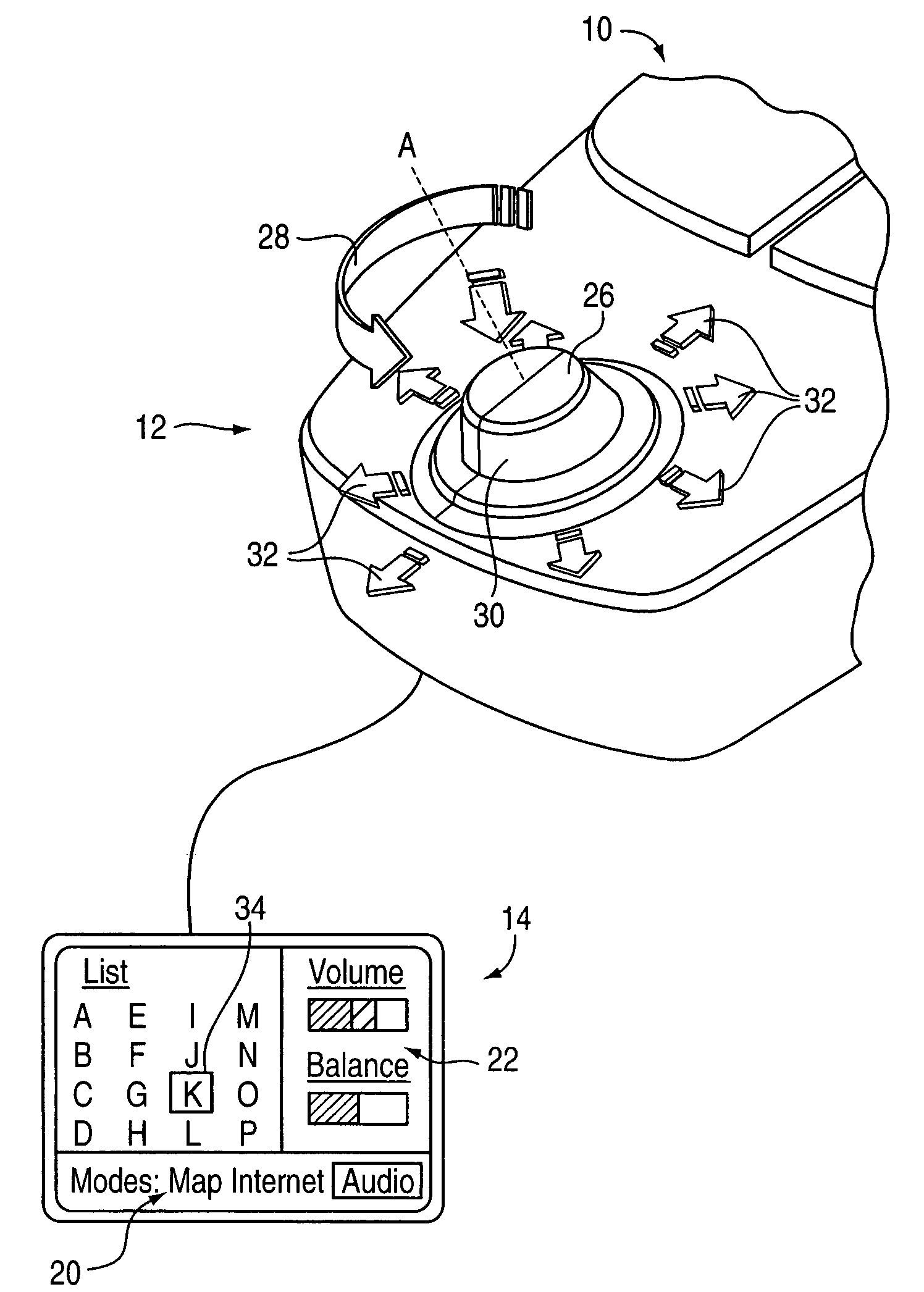
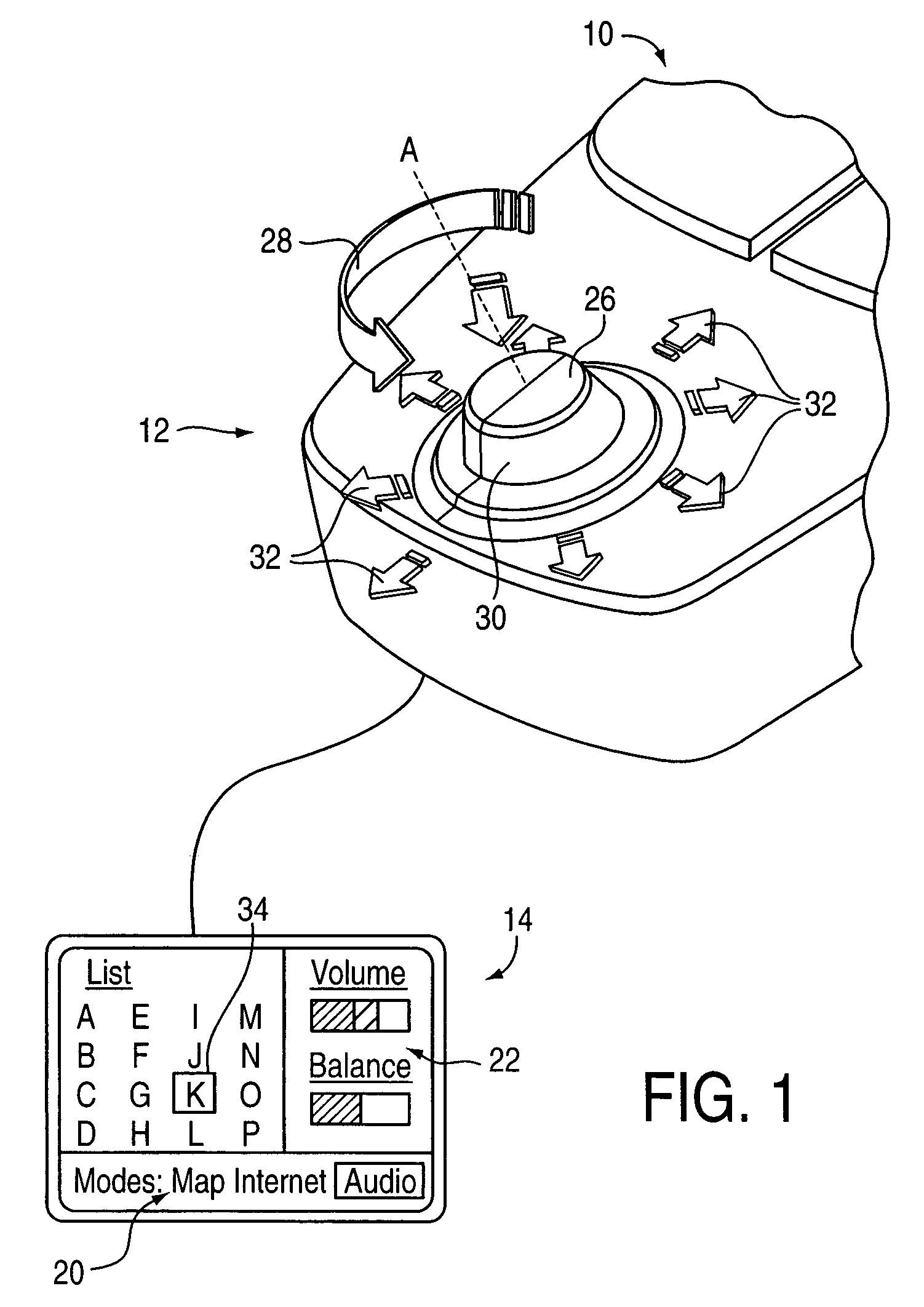
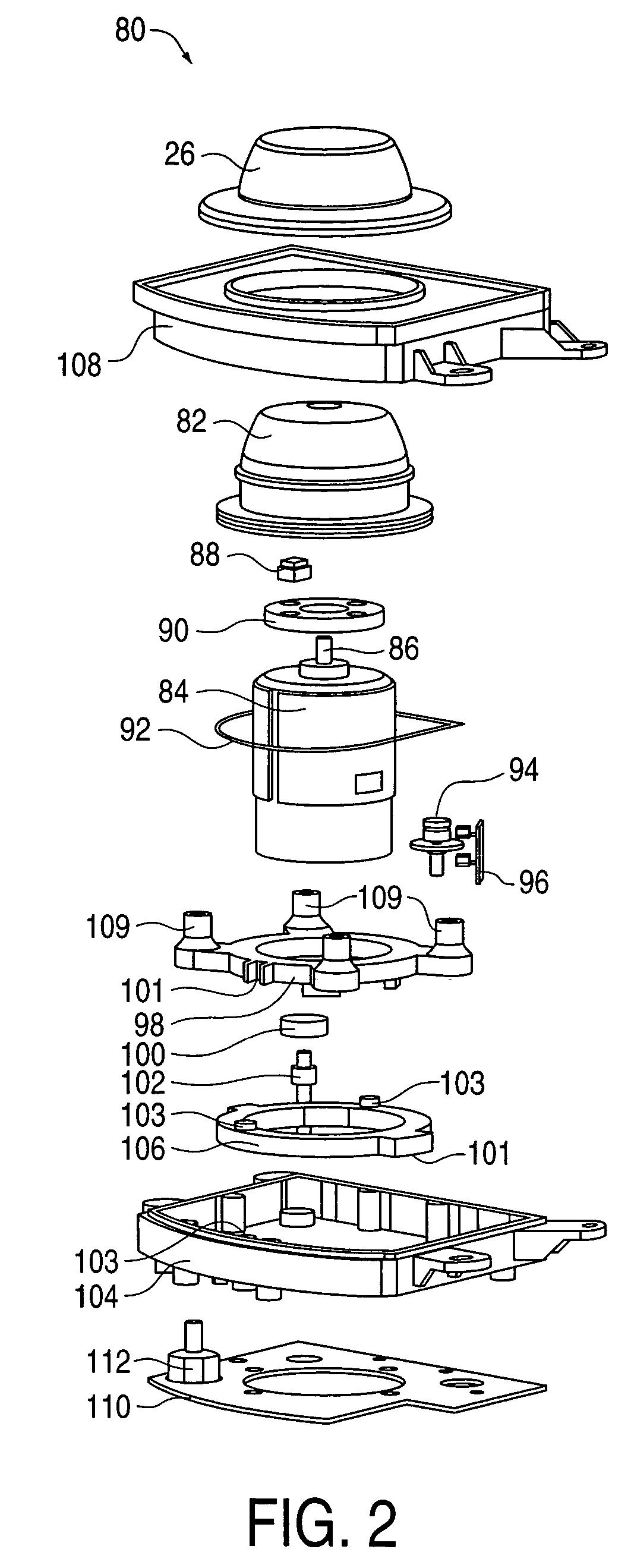
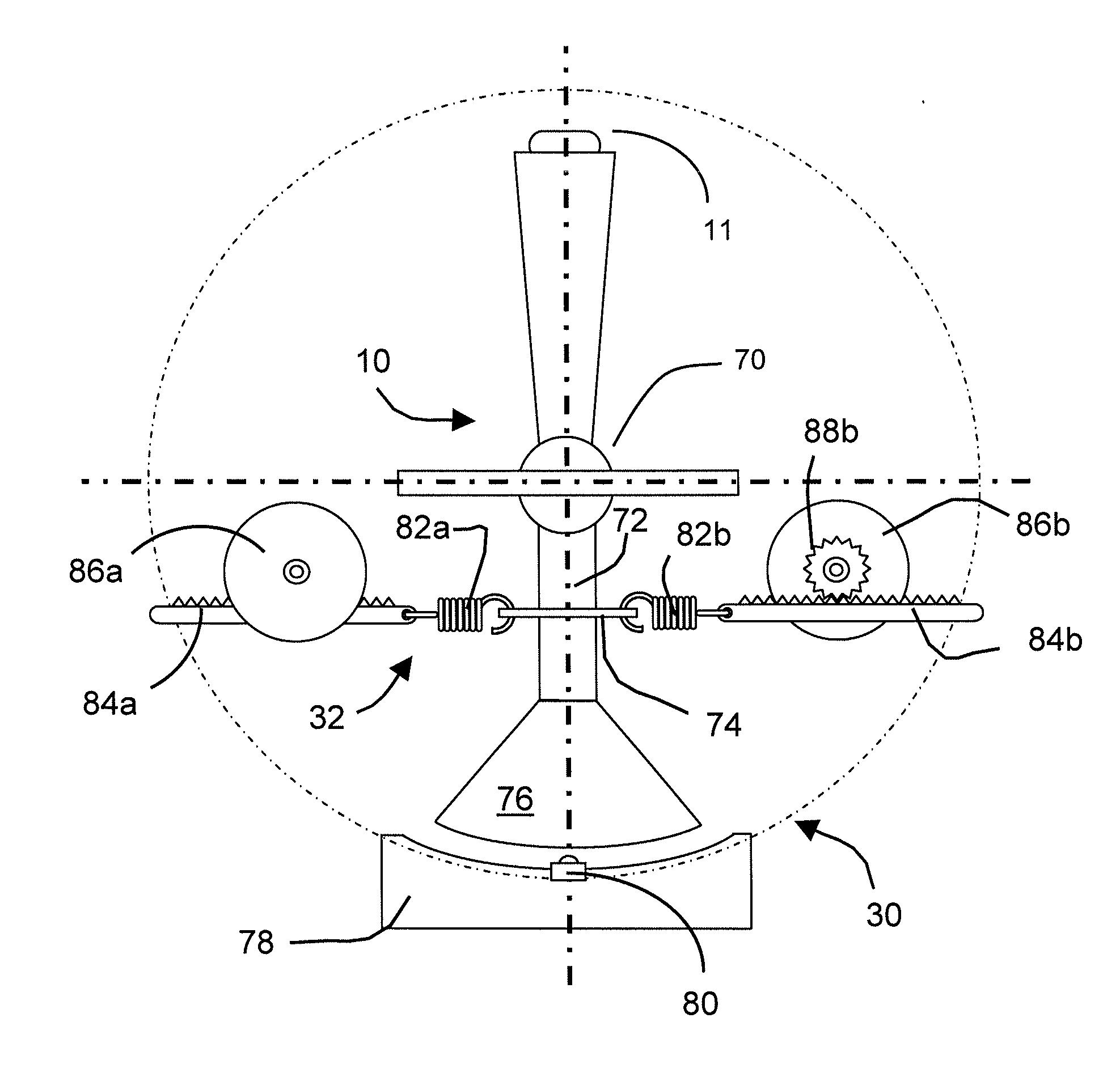
InactiveUS7038667B1Strong control functionGreat easeCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectrical haptic/tactile feedbackRotational axisLinear motion
Mechanisms for a control knob or other interface device providing additional degrees of freedom for the knob. One embodiment provides a rotatable knob moveable also in a lateral plane approximately perpendicular to the axis of rotation. A mechanism providing the lateral motion can include a gate member and a plunger member that engages grooves in the gate member. A rotational sensor detects a rotational position and a lateral sensor can detect a lateral position of the knob. Another embodiment provides an actuator that includes a shaft that is coaxial with the axis of rotation and which can be moved linearly along the axis of rotation with respect to actuator housing to accommodate linear motion of the knob. In another embodiment, a gear assembly including two interlocked gears is provided to transmit rotational motion from the knob to the sensor, and the interlocked gears translate with respect to each other when the knob is translated along the rotational axis.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Force feedback applications based on cursor engagement with graphical targets
InactiveUS7131073B2Input/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersGraphicsGraphical user interface
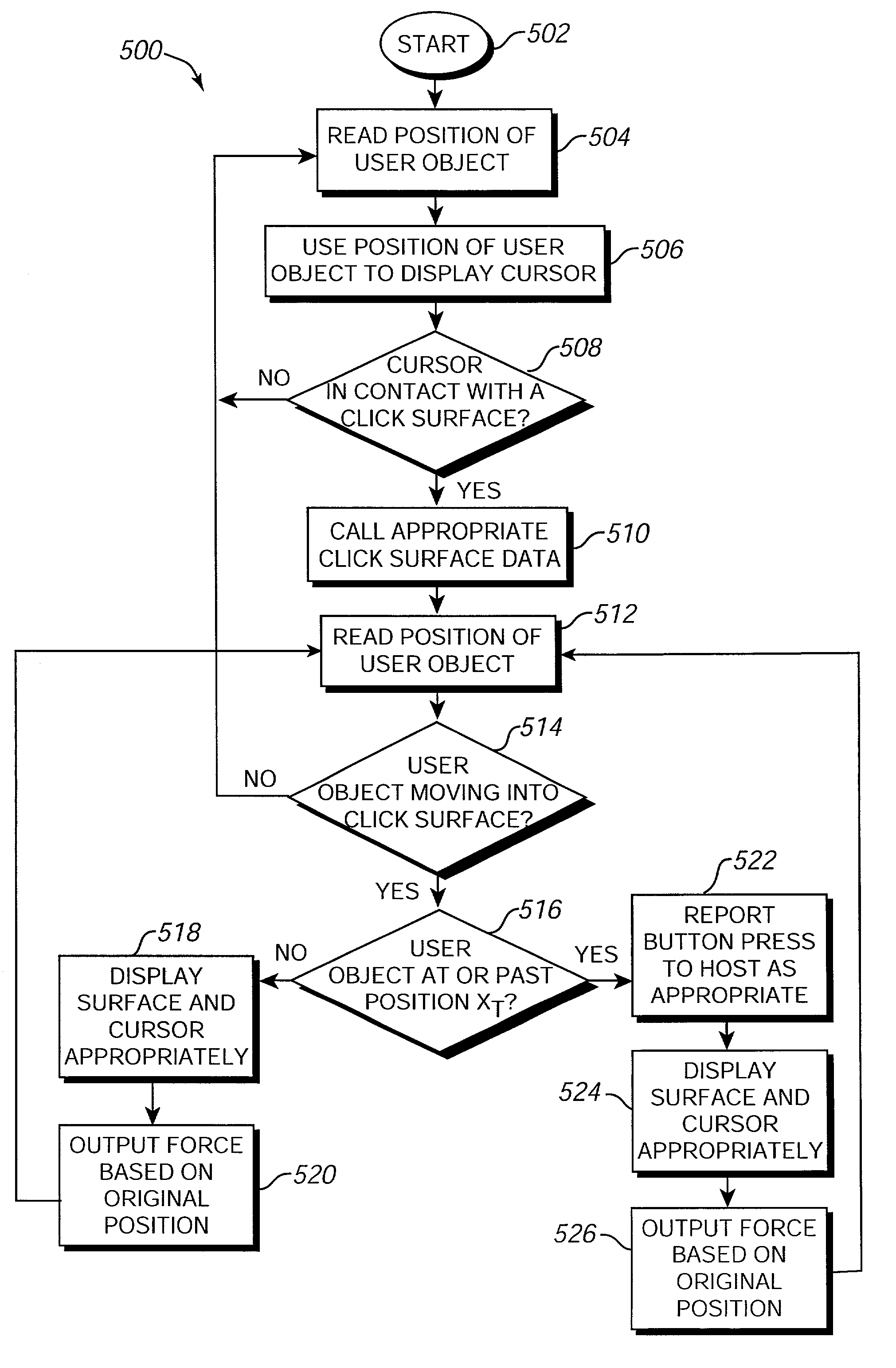
A method and apparatus for providing a click surface in a graphical environment, such as a graphical user interface, implemented on a host computer for use with a force feedback interface device. A displayed cursor is controlled by a user-moveable user object, such as a mouse, of the interface device. A click surface is displayed with an associated graphical object, such as a graphical button or an edge of a window, icon, or other object. When the click surface is contacted by the cursor, a force is output opposing movement of the user object in a direction into the click surface and into the graphical object. When the user object has moved to or past a trigger position past the contact with the click surface, a command gesture signal is provided to the host computer indicating that the graphical object has been selected as if a physical input device on the user object, such as a button, has been activated by the user. Preferably, the host computer displays the graphical environment including the click surface and cursor, while a microprocessor local to the interface device controls the force output of the click surface in parallel with the host display.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Interactions between simulated objects with force feedback
InactiveUS7158112B2More experienceInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersHuman–computer interactionComputer generation
A method and apparatus for providing force feedback to a user operating a human / computer interface device and interacting with a computer-generated simulation. In one aspect, a computer-implemented method simulates the interaction of simulated objects displayed to a user who controls one of the simulated objects manipulating a physical object of an interface device. The position of the simulated object, as provided within the simulation and as displayed, is mapped to the physical position of the user object. This mapping can be broken under conditions that are effective to provide force feedback to the user which imparts a physical sensation corresponding to the interaction of the simulated objects.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
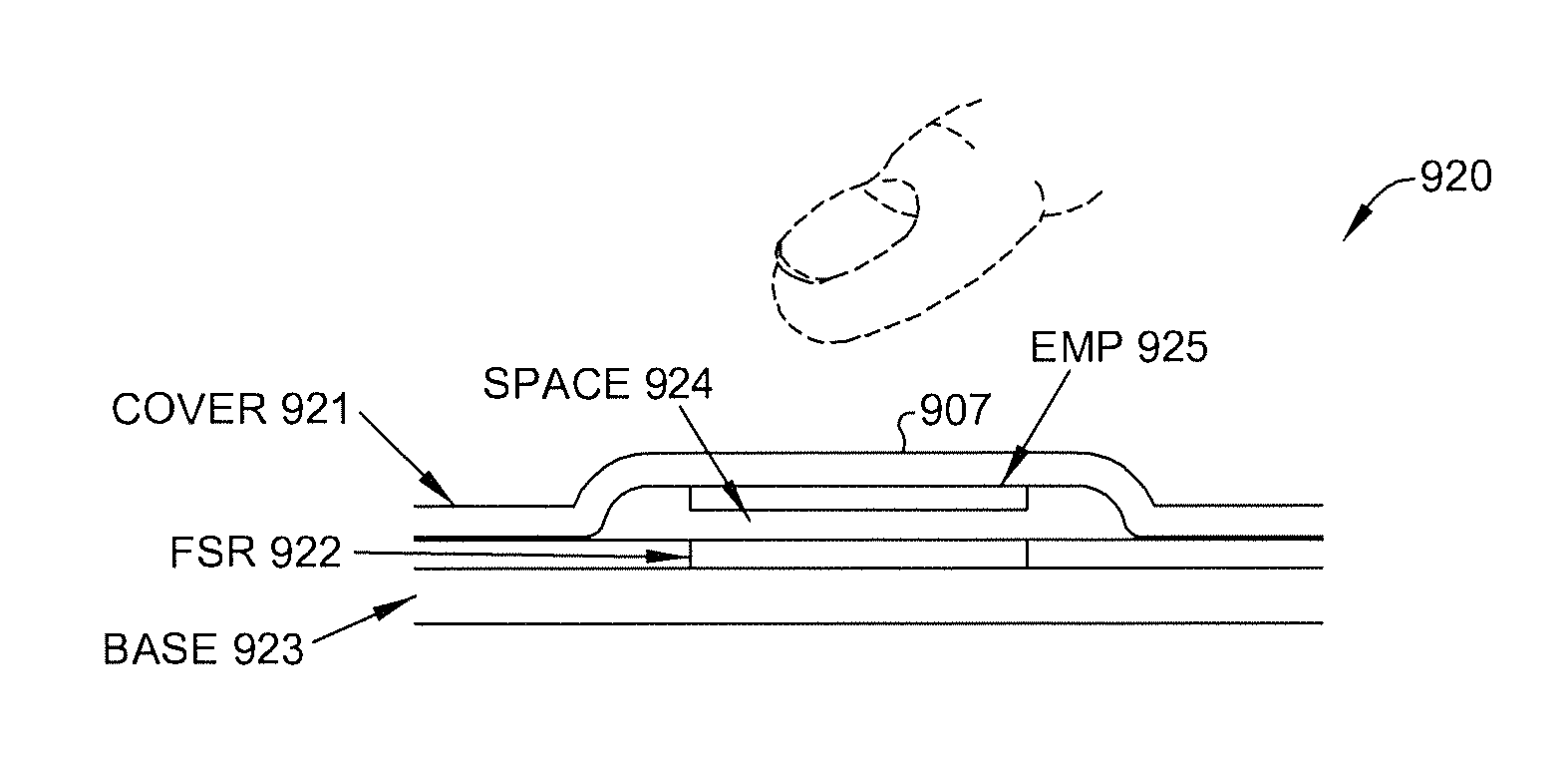
Thin profile user interface device and method providing localized haptic response
ActiveUS20140191973A1Input/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsGraphicsTransducer
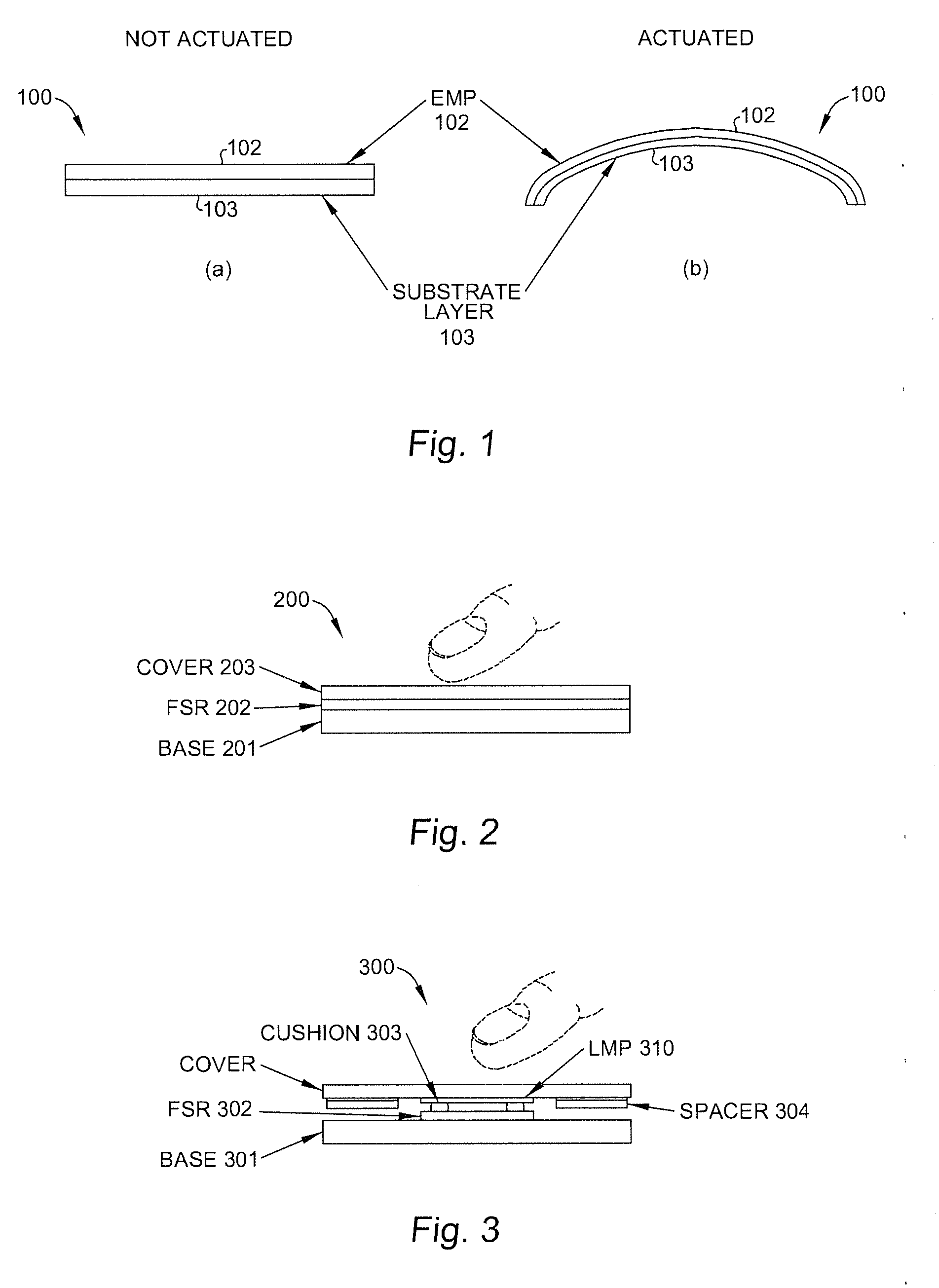
Electromechanical polymer (EMP) actuators are used to create haptic effects on a user interface deface, such as a keyboard. The keys of the keyboard may be embossed in a top layer to provide better key definition and to house the EMP actuator. Specifically, an EMP actuator is housed inside an embossed graphic layer that covers a key of the keyboard. Such a keyboard has a significant user interface value. For example, the embossed key provides the tactile effect of the presence of a key with edges, while allowing for the localized control of haptic vibrations. For such applications, an EMP transducer provides high strains, vibrations or both under control of an electric field. Furthermore, the EMP transducer can generate strong vibrations. When the frequency of the vibrations falls within the acoustic range, the EMP transducer can generate audible sound, thereby functioning as an audio speaker.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for providing dynamic force sensations for force feedback computer applications
InactiveUS7039866B1Simple and intuitive designPromoting further understandingInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersGraphicsJoystick
A method and apparatus for providing dynamic force sensations for use with a force feedback interface device. A force feedback interface device is connected to a host computer that implements a graphical environment. The host sends commands and command parameters to the interface device to initiate and characterize dynamic force sensations output on a user manipulatable object, such as a joystick. The interface device can include a local microprocessor for implementing force sensations by controlling actuators and reading sensors according to the host commands. A dynamic force routine can control the dynamic force sensations by implementing a simulated physical system including a simulated mass capable of motion independent of the user object. The physical system provides forces on the user object influenced by motion of both the user object and the simulated mass.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Method and apparatus for streaming force values to a force feedback device
InactiveUS7209117B2Minimal reduction in realismLess forceInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersPulse parameterEngineering
A method and apparatus for shaping force signals for a force feedback device. A source wave is provided and is defined by a set of control parameters (including a steady state magnitude, a frequency value and a duration value) and modified by a set of impulse parameters (including an impulse magnitude, and a settle time representing a time required for the impulse magnitude to change to the steady-state magnitude). Optionally, application parameters specifying a direction of force signal and trigger parameters specifying activating buttons can also be provided for the source wave. Using a host processor or a local processor, the force signal is formed from the source wave and the sets of control parameters and impulse parameters, where the force signal includes an impulse signal followed by a continual steady-state signal after an expiration of the settle time. A feel sensation is generated to a user of the force feedback device as physical forces produced by actuators on the force feedback device in response to the force signal. The steady-state magnitude value is lower than a magnitude value of a non-impulse-shaped force signal required to create a corresponding feel sensation having a similar apparent sensation to the user.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
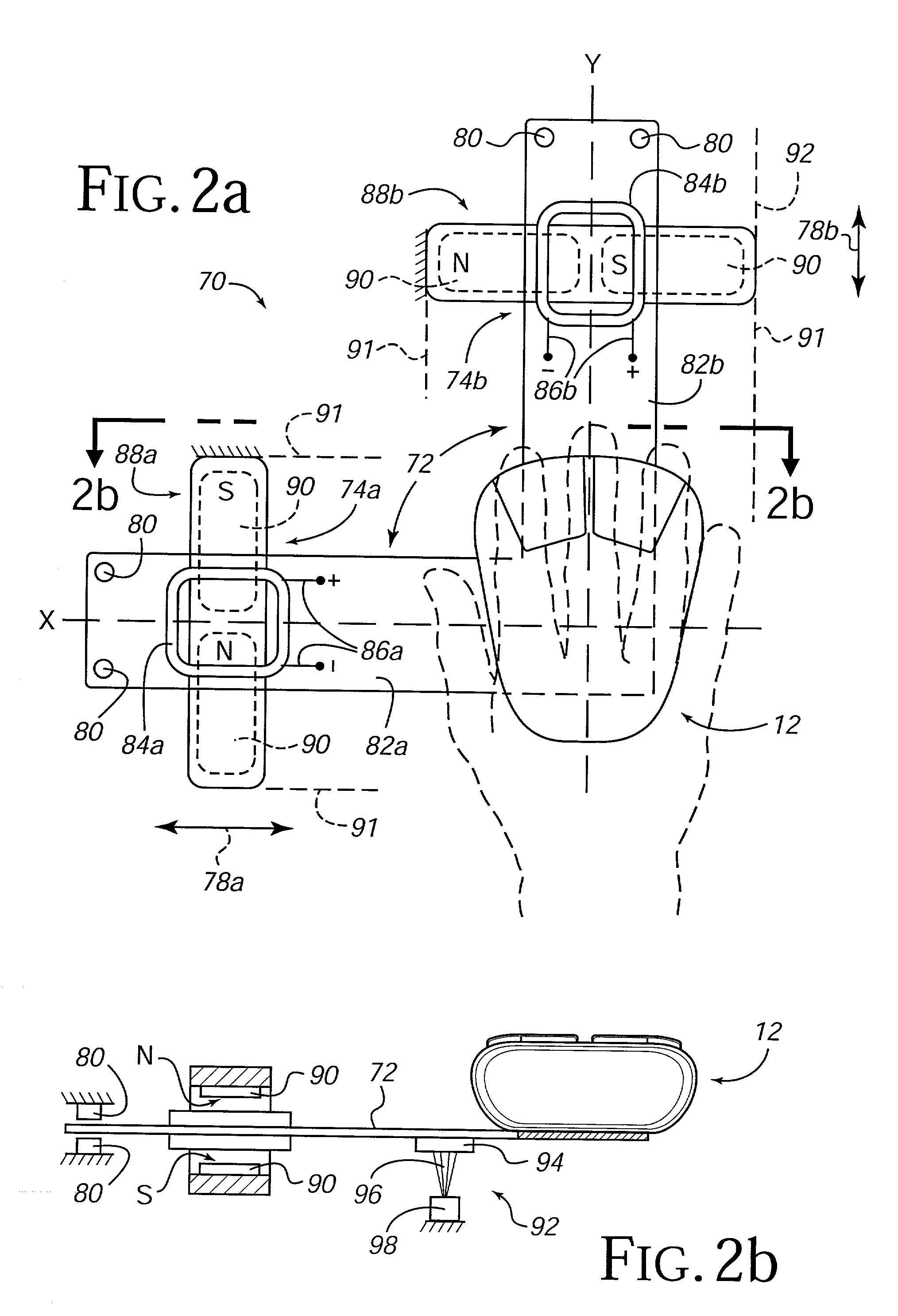
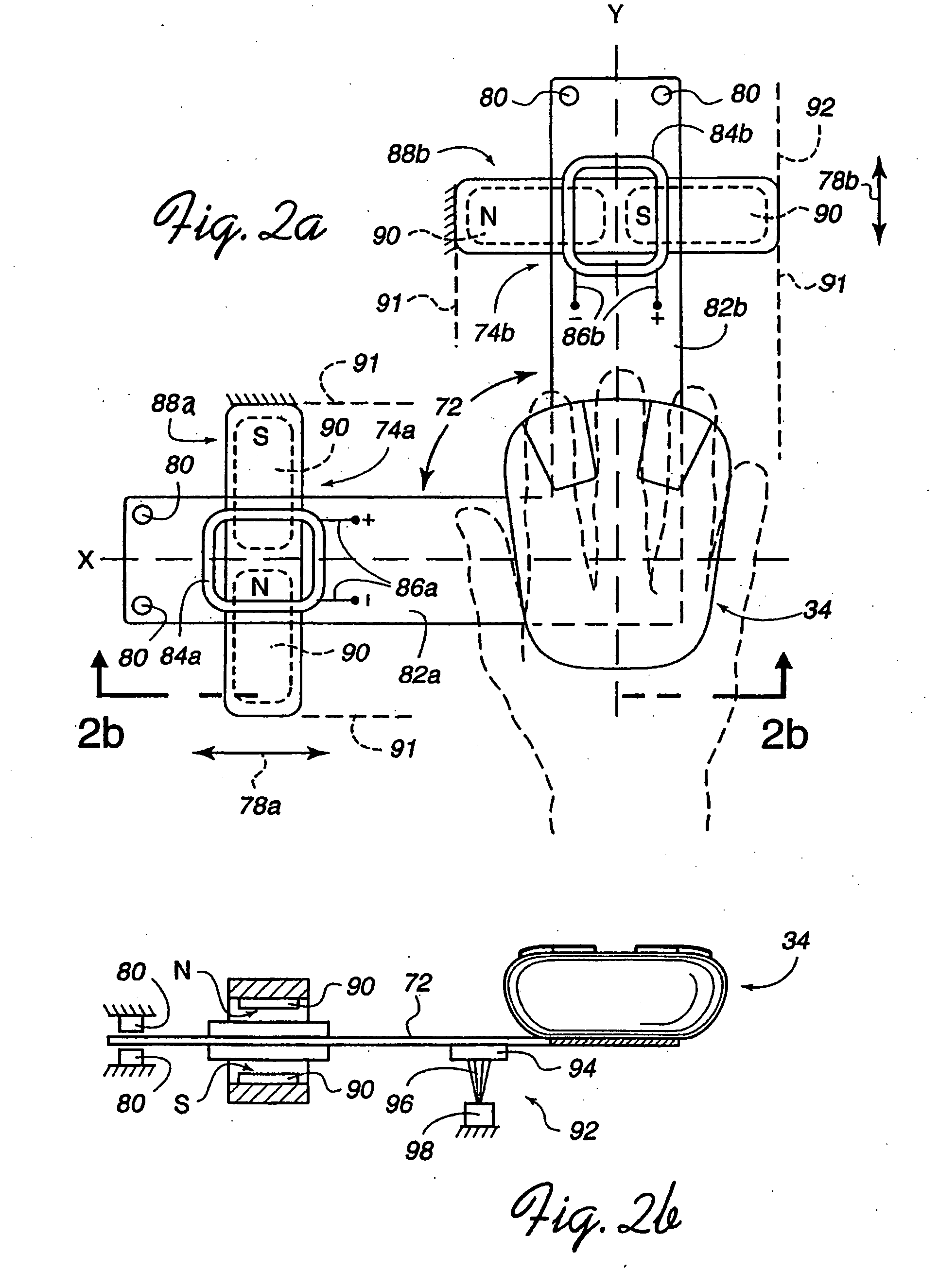
Force feedback interface device with force functionality button
InactiveUS7106313B2Low costSimple interfaceInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersClassical mechanicsWorkspace
A force feedback mouse interface device connected to a host computer and providing realistic force feedback to a user. The mouse interface device includes a mouse object and a linkage coupled to the mouse that includes a plurality of members rotatably coupled to each other in a planar closed-loop linkage, two of the members coupled to ground and rotatable about the same axis. Two actuators, preferably electromagnetic voice coils, provide forces in the two degrees of freedom of the planar workspace of the mouse object. Each of the actuators includes a moveable coil portion integrated with one of the members of the linkage and a magnet portion coupled to the ground surface through which the coil portion moves. At least one sensor is coupled to the ground surface that detects movement of the linkage and provides a sensor signal including information from which a position of the mouse object in the planar workspace can be determined.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Haptic interface for laptop computers and other portable devices
InactiveUS20050052430A1Enhanced interactionEnhance manipulationInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsPiezoelectric actuators
A haptic feedback touch control used to provide input to a computer. A touch input device includes a planar touch surface that provides position information to a computer based on a location of user contact. The computer can position a cursor in a displayed graphical environment based at least in part on the position information, or perform a different function. At least one actuator is also coupled to the touch input device and outputs a force to provide a haptic sensation to the user. The actuator can move the touchpad laterally, or a separate surface member can be actuated. A flat E-core actuator, piezoelectric actuator, or other types of actuators can be used to provide forces. The touch input device can include multiple different regions to control different computer functions.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
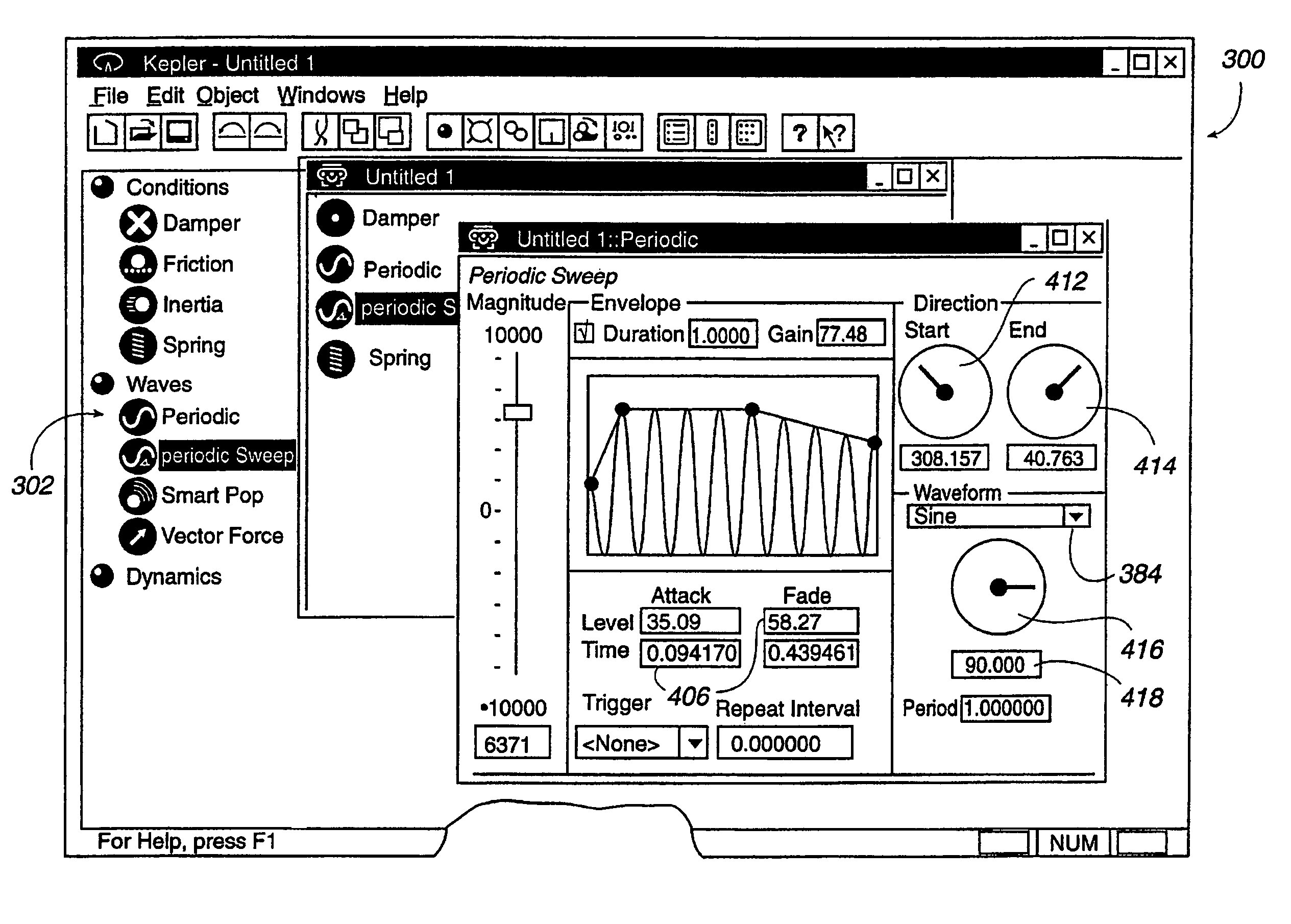
Designing force sensations for force feedback computer applications
InactiveUS7027032B2Simple and intuitive designEfficient use ofInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersGraphicsEngineering
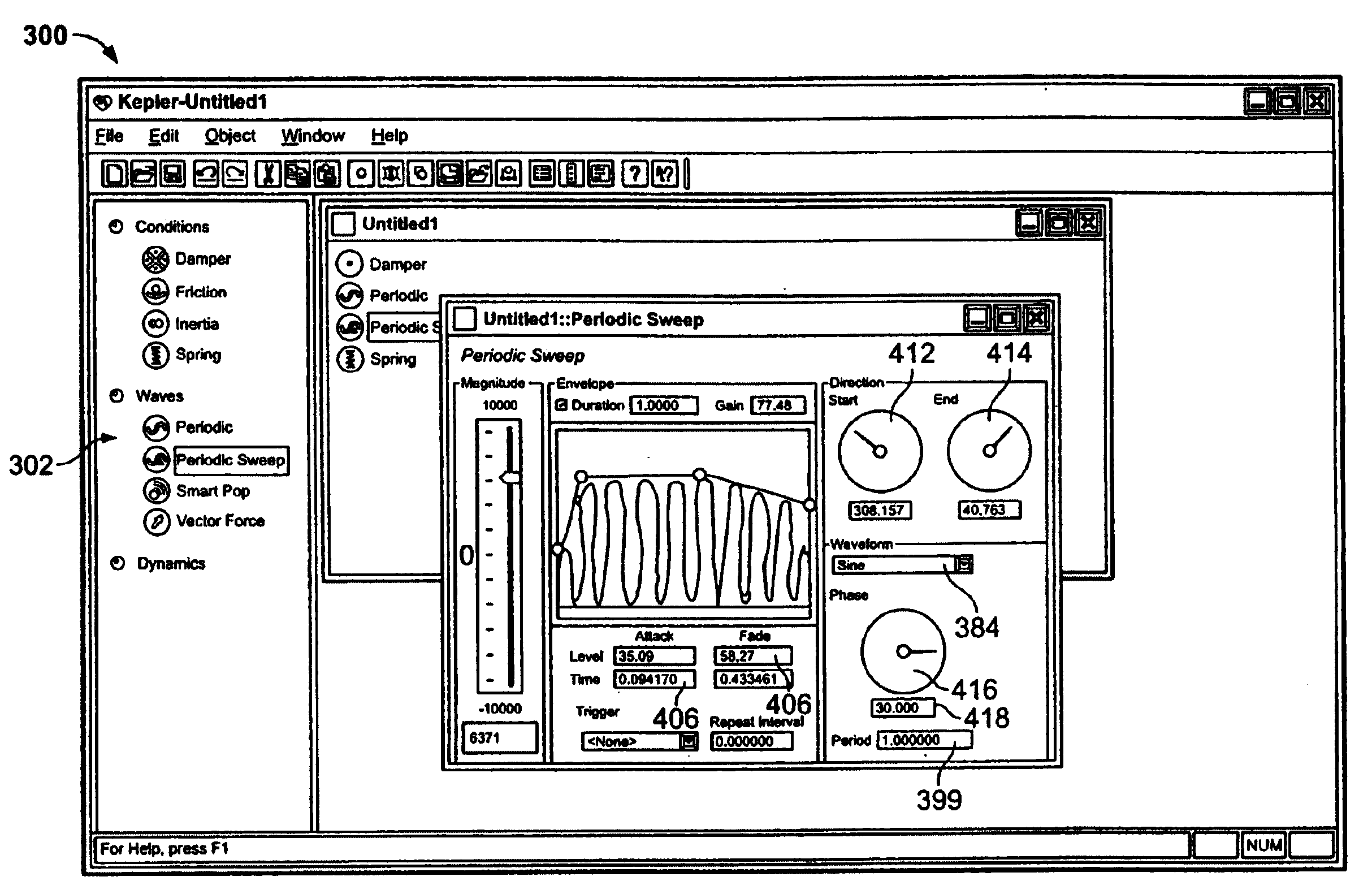
A design interface tool for designing force sensations for use with a host computer and force feedback interface device. A force feedback device is connected to a host computer that displays the interface tool. Input from a user is received in the interface to select a type of force sensation to be commanded by a host computer and output by a force feedback interface device. Input, such as parameters, is then received from the user which designs and defines physical characteristics of the selected force sensation. A graphical representation of the characterized force sensation is displayed on the host computer which provides a visual demonstration of a feel of the characterized force sensation so that the user can view an effect of parameters on said force sensation. The characterized force sensation is output to a user manipulatable object of the force feedback device so that the user can feel the designed force sensation, where the graphical representation is updated in conjunction with the output of the force sensation. The user can iteratively modify force sensation characteristics and feel the results, and store the characterized force sensations.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
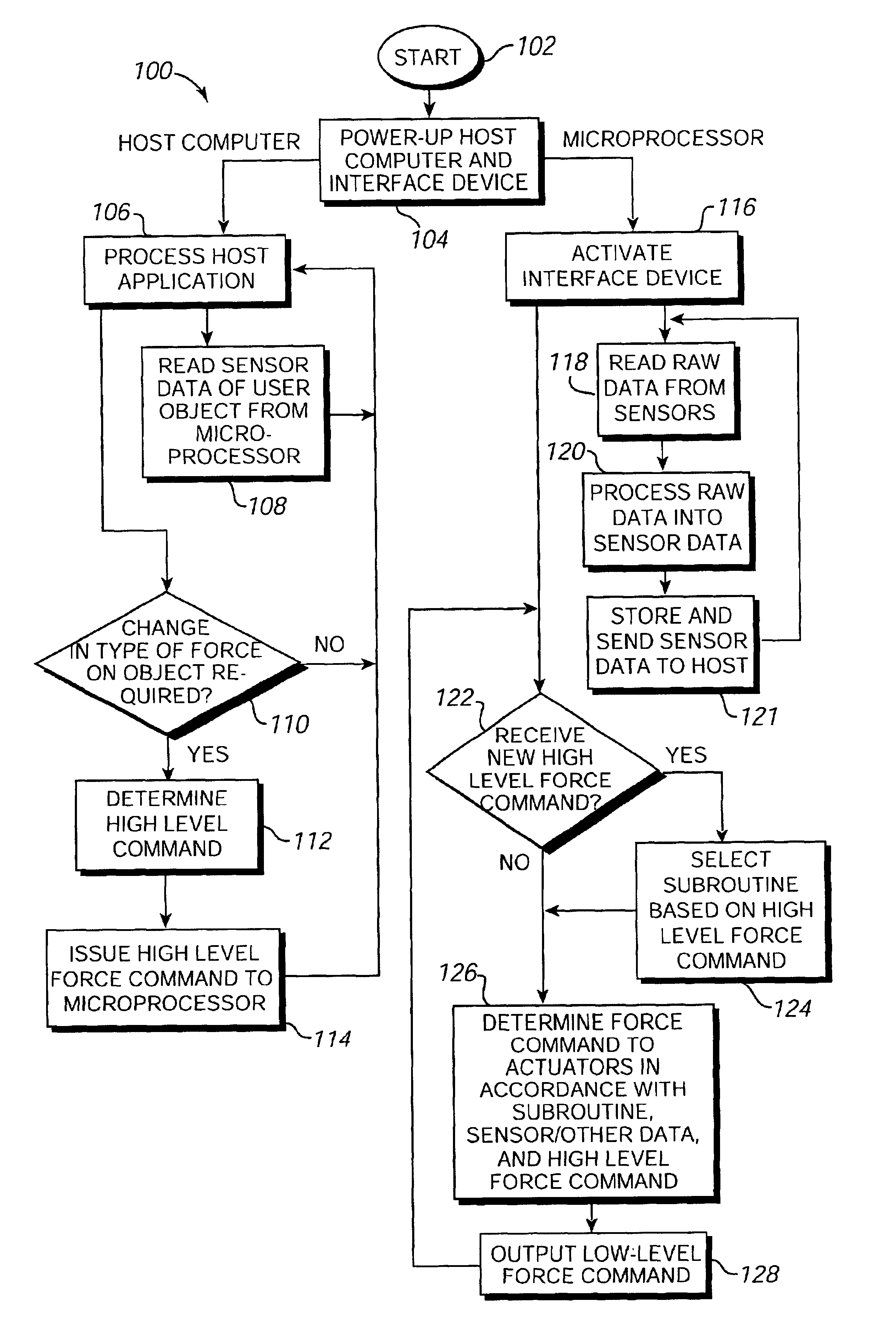
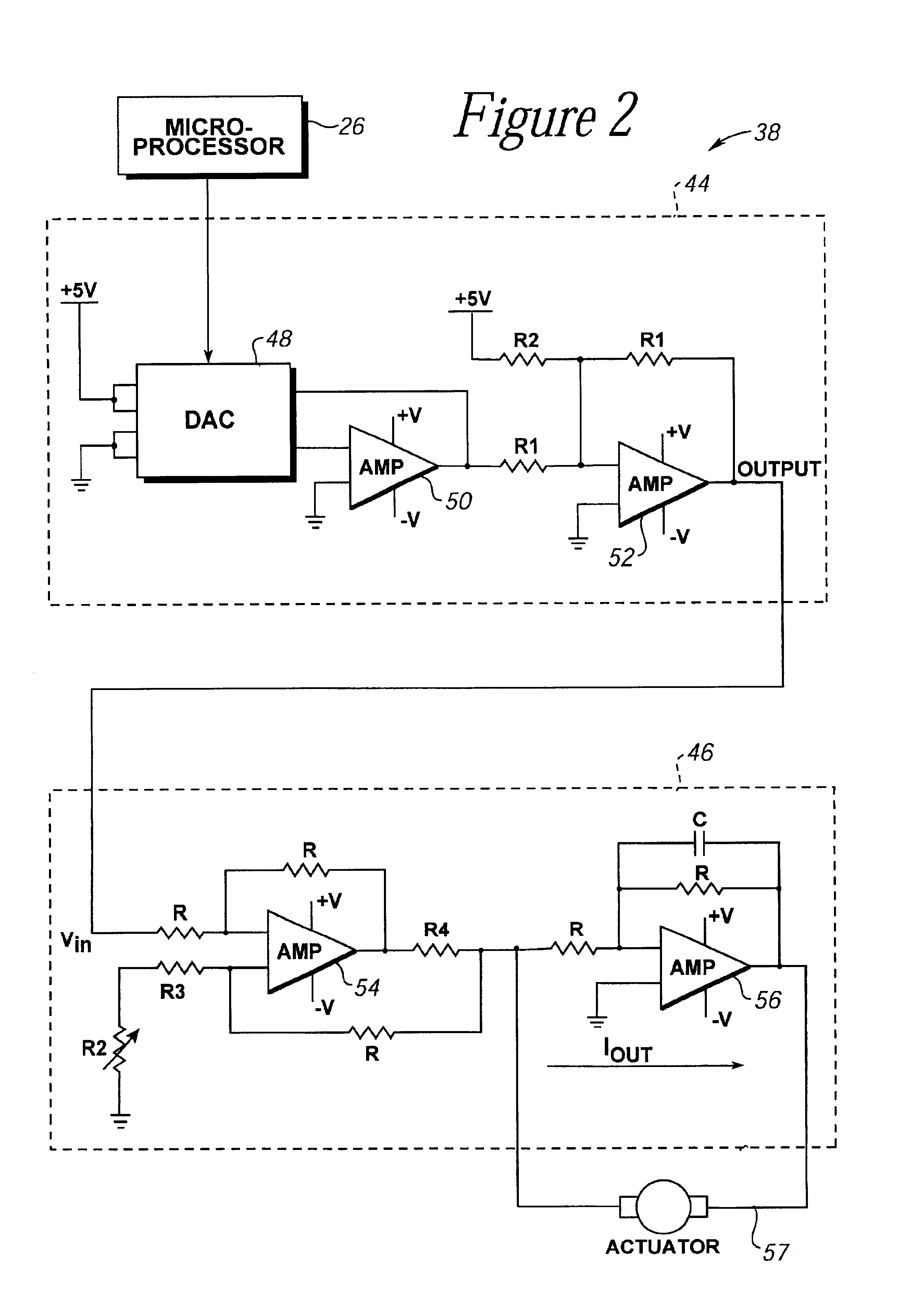
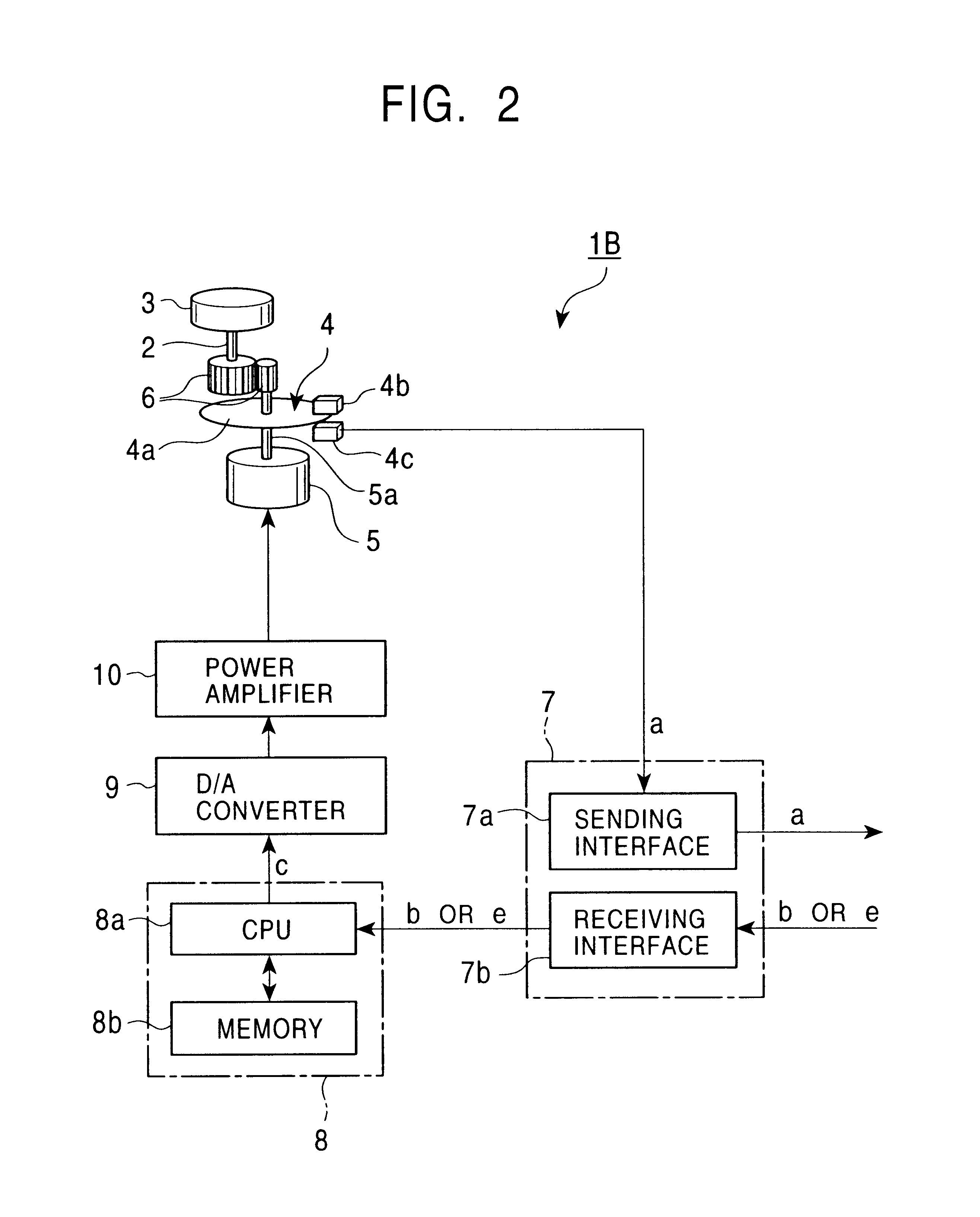
Force feedback device with microprocessor receiving low level commands
InactiveUS7061467B2Improve realismImprove accuracyInput/output for user-computer interactionProgramme-controlled manipulatorJoystickApplication software
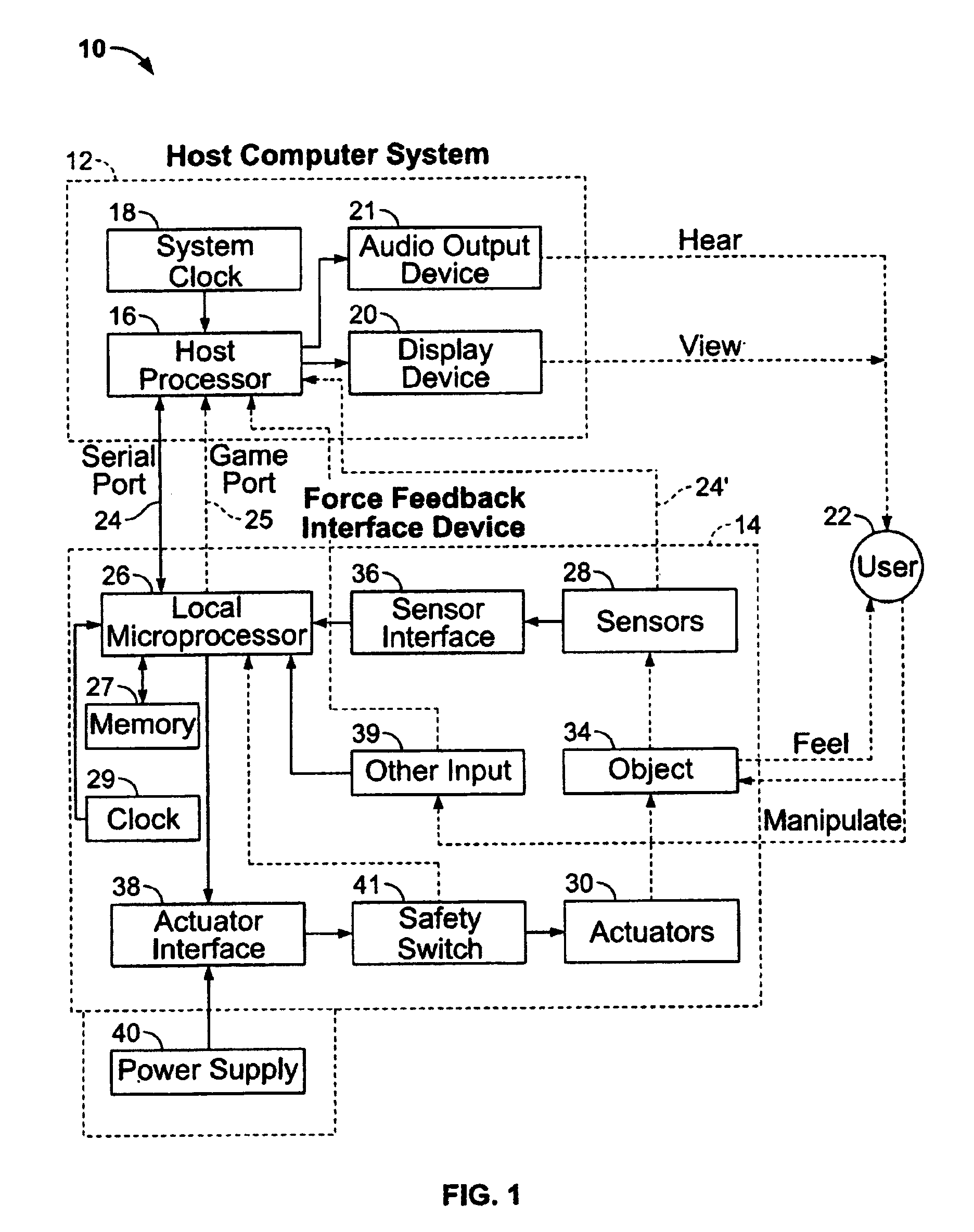
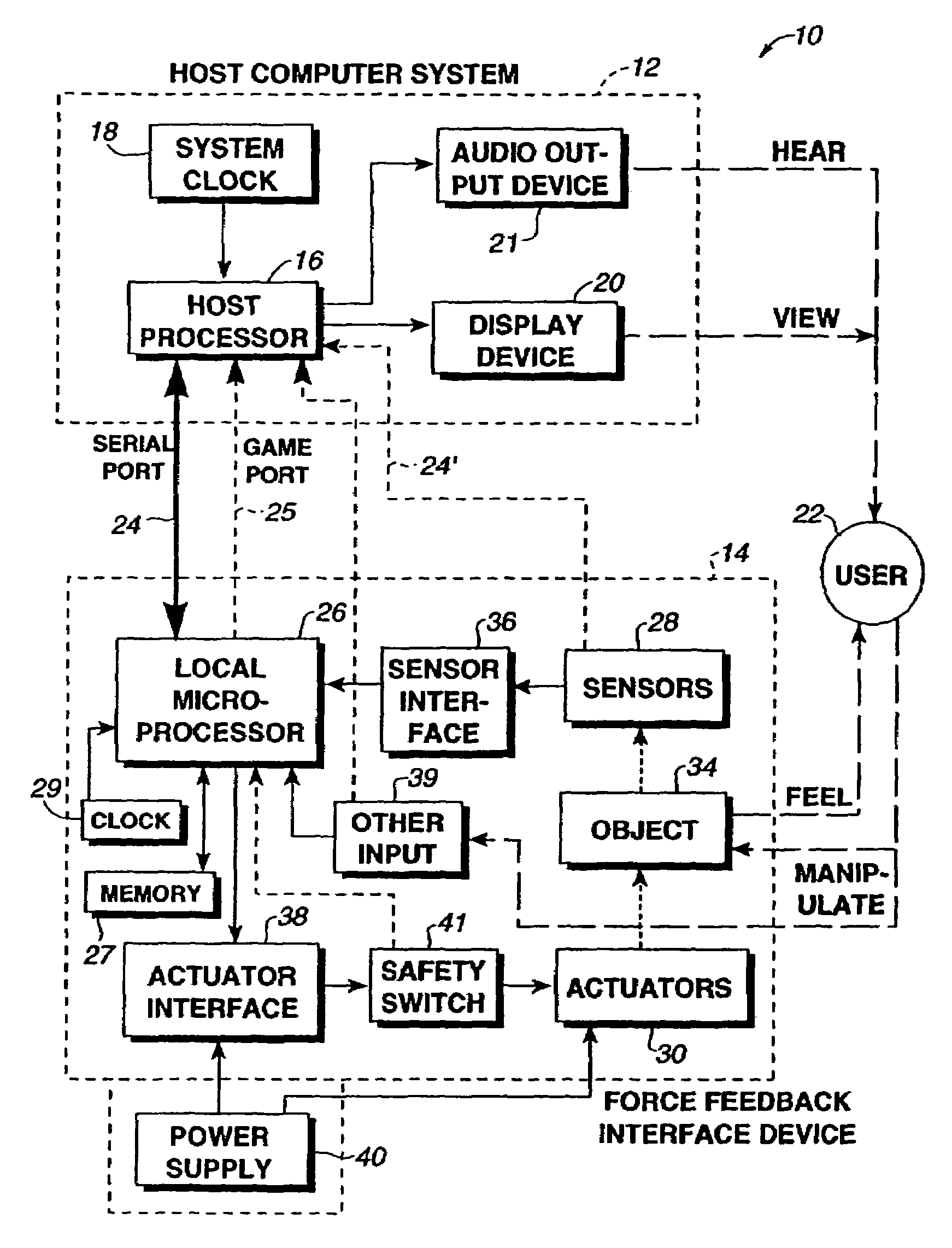
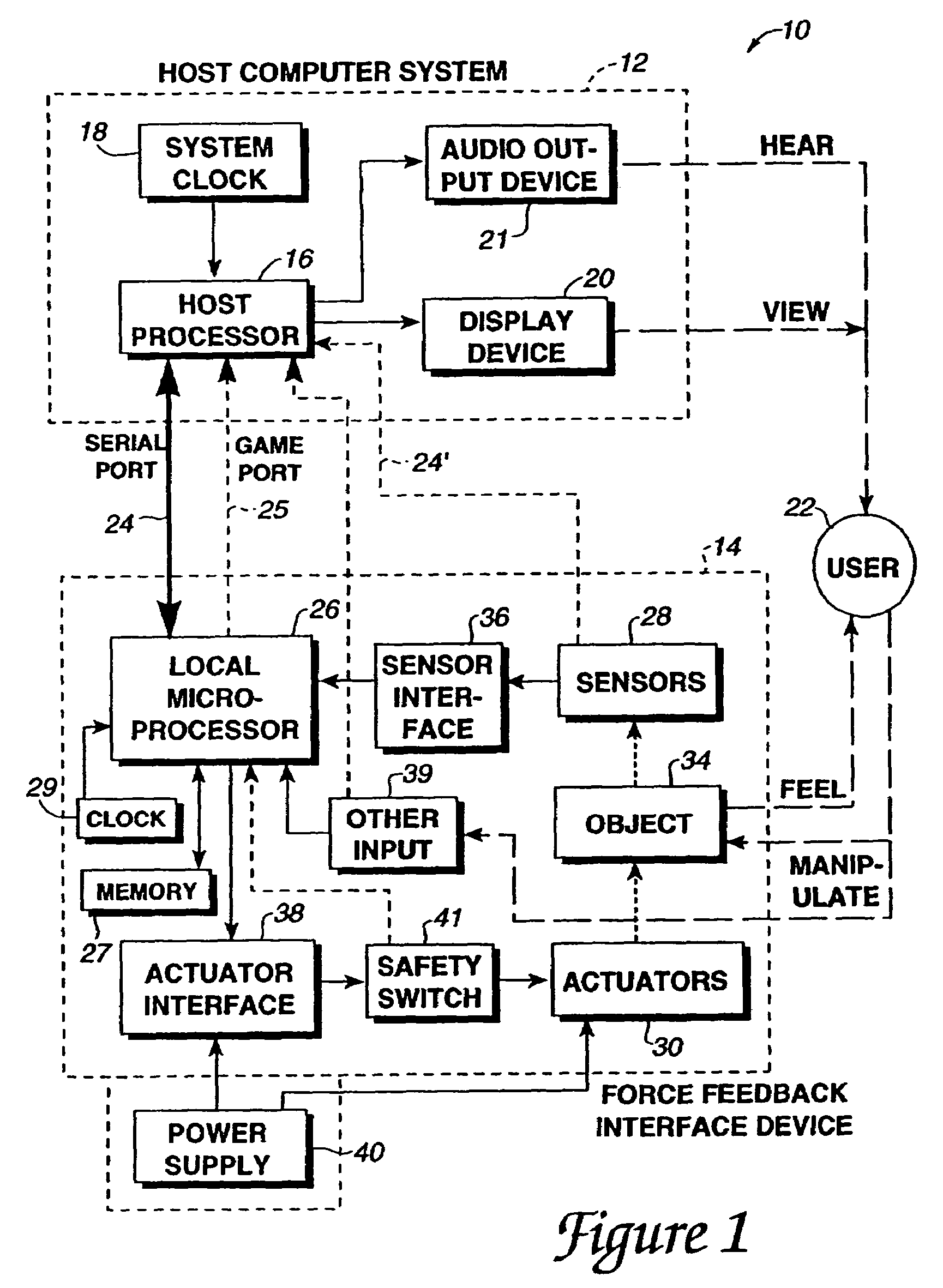
A method and apparatus for controlling and providing force feedback using an interface device manipulated by a user. A microprocessor is provided local to the interface device and reads sensor data from sensors that describes the position and / or other information about an object grasped and moved by the user, such as a joystick. The microprocessor provides the sensor data to a host computer that is coupled to the interface device by a communication bus that preferably includes a serial interface. In a “host-controlled” embodiment, the host computer calculates force values using the sensor data and other parameters of a host application program and sends the force values to the local microprocessor, which directly provides the force values to actuators to apply forces to the user object. In a “reflex” embodiment, the host computer sends high level supervisory commands to the local microprocessor, and the microprocessor independently implements a local process based on the high level command for reading sensor data and providing force values to the actuators using sensor data and other parameters.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
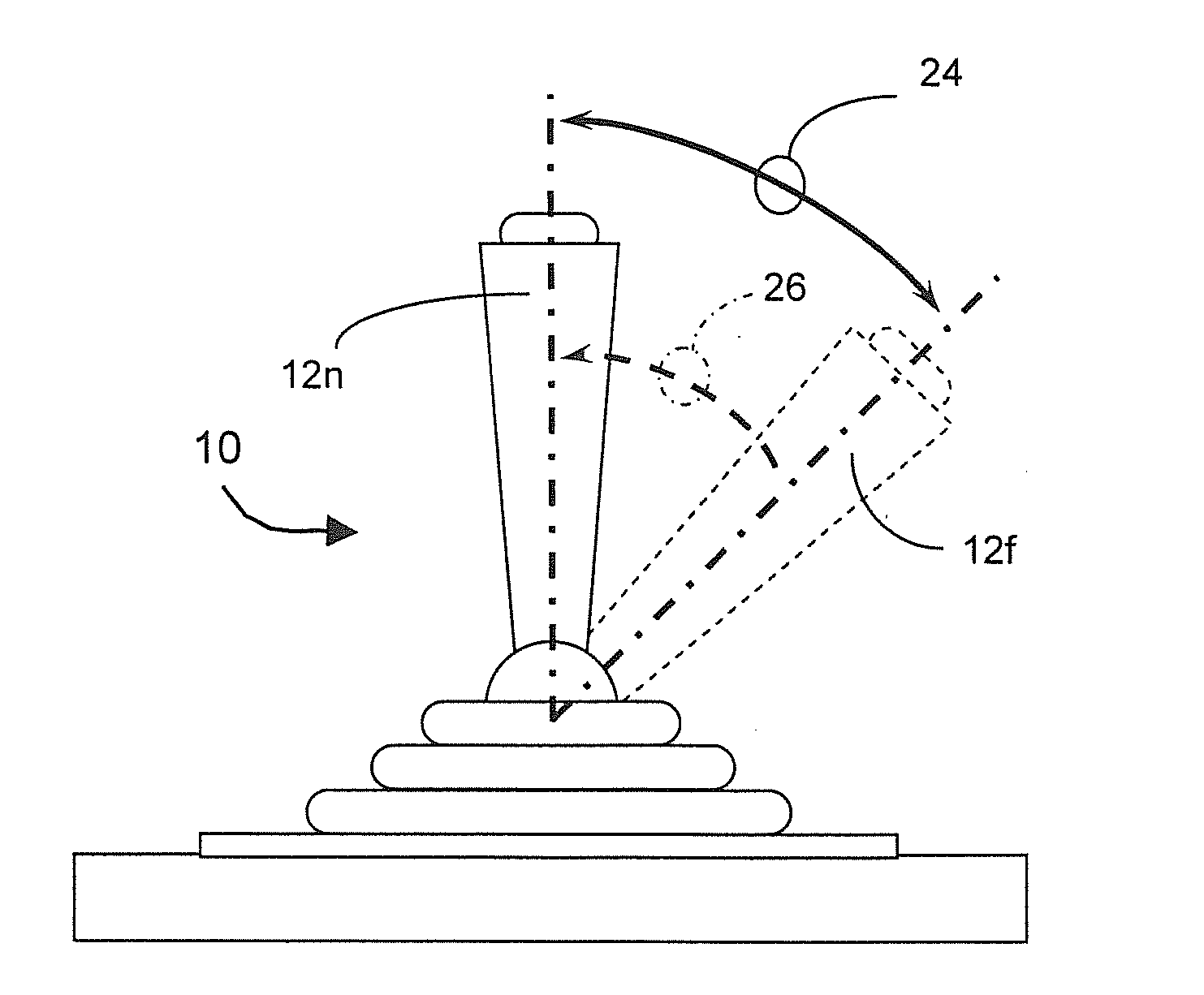
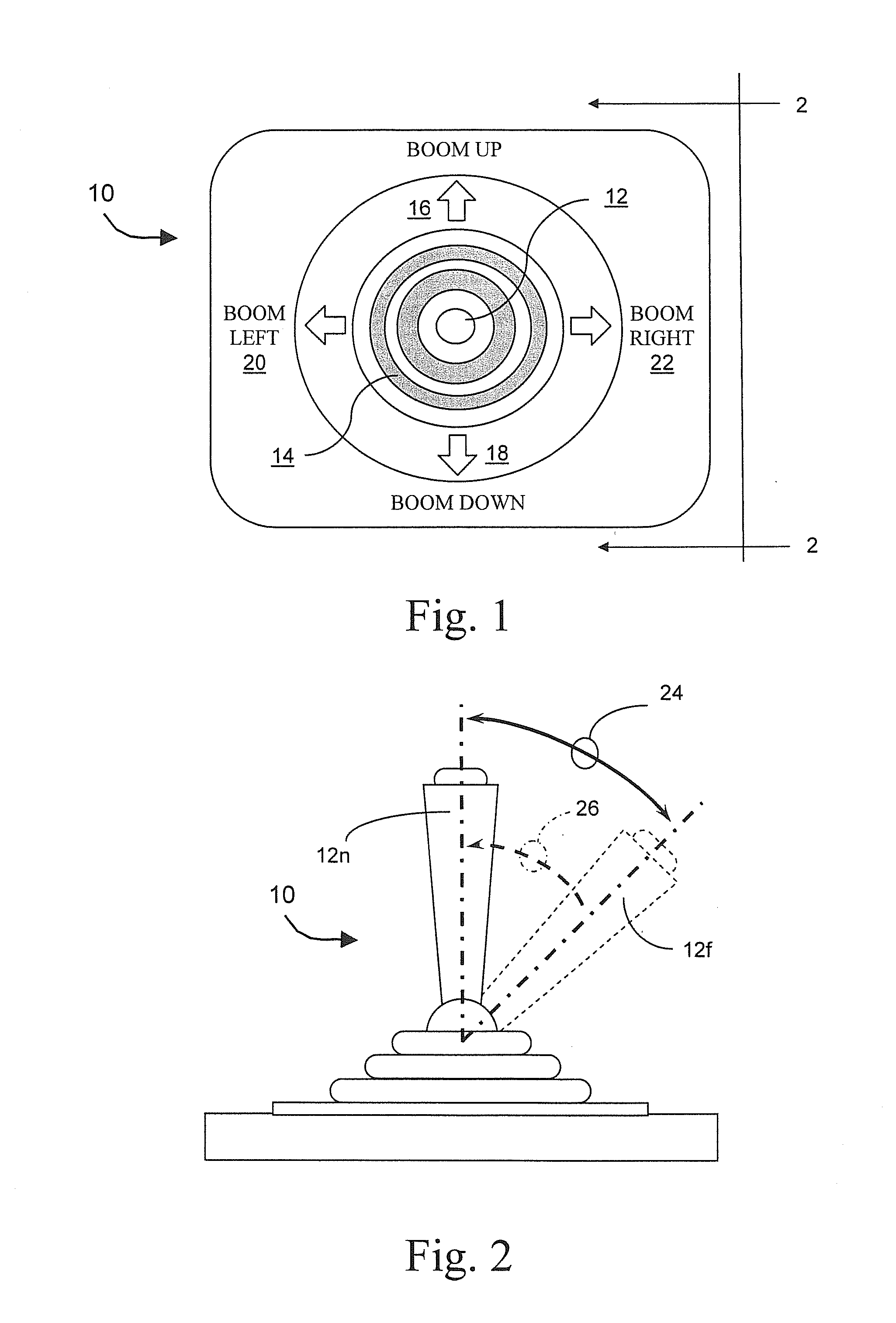
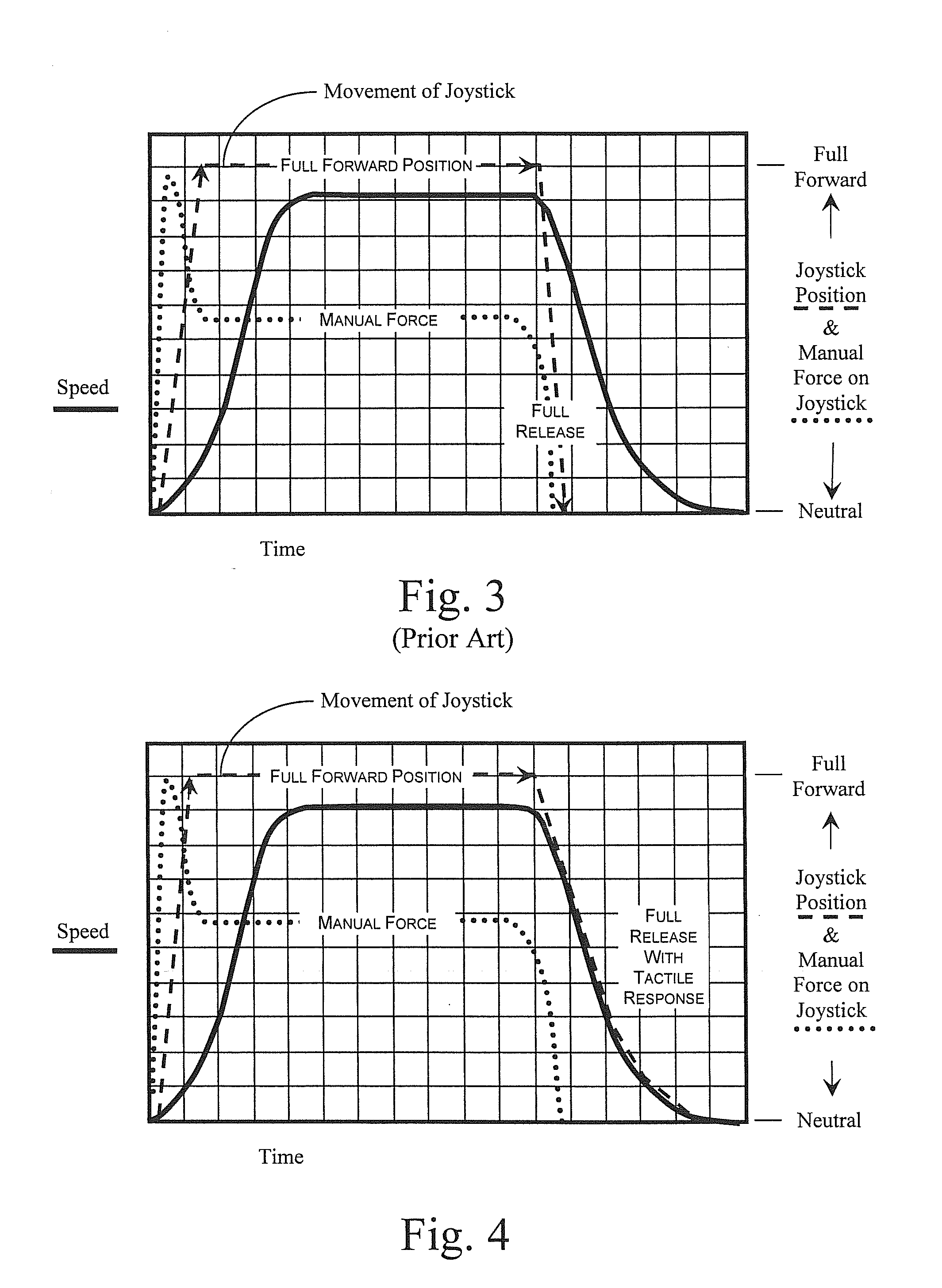
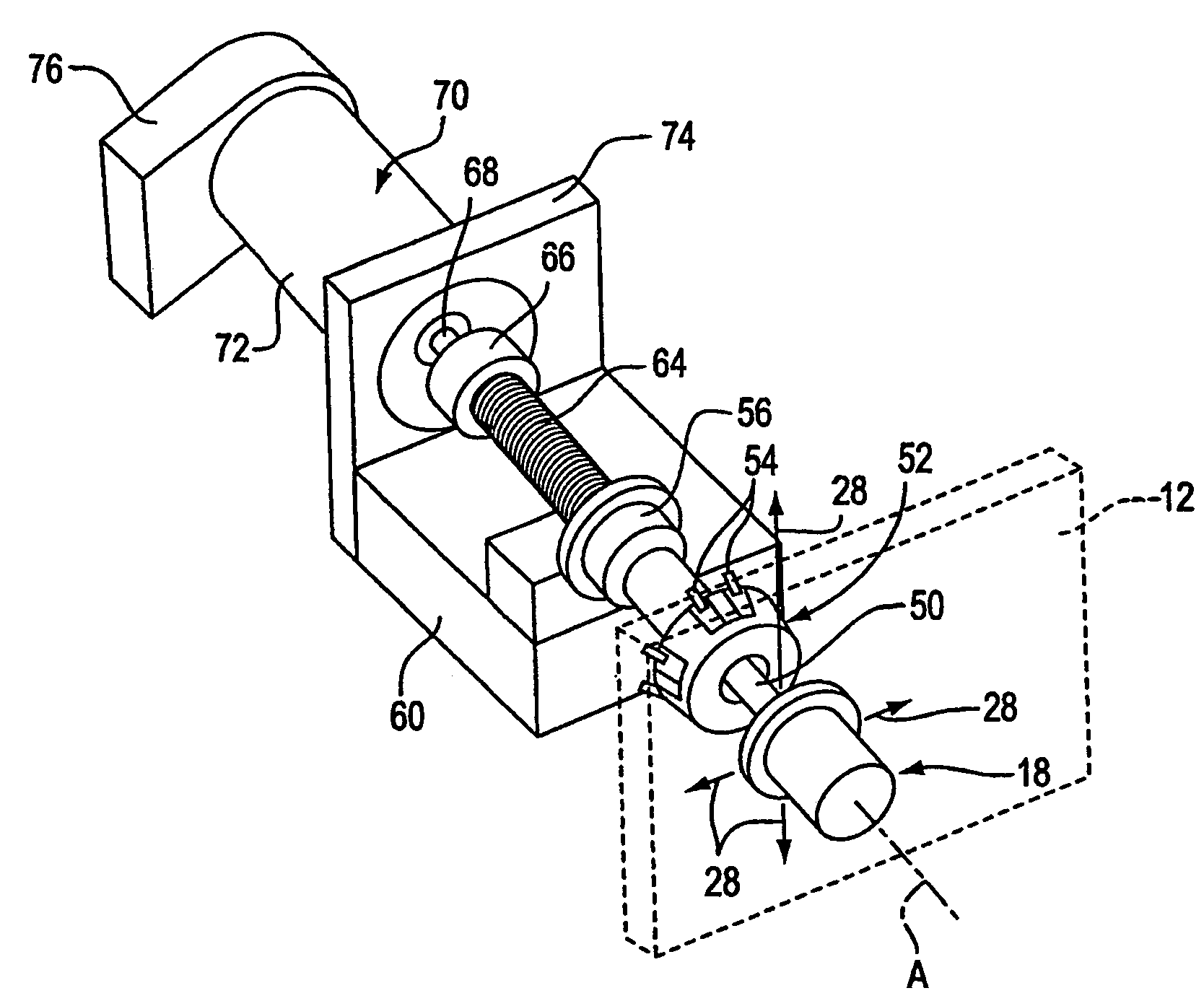
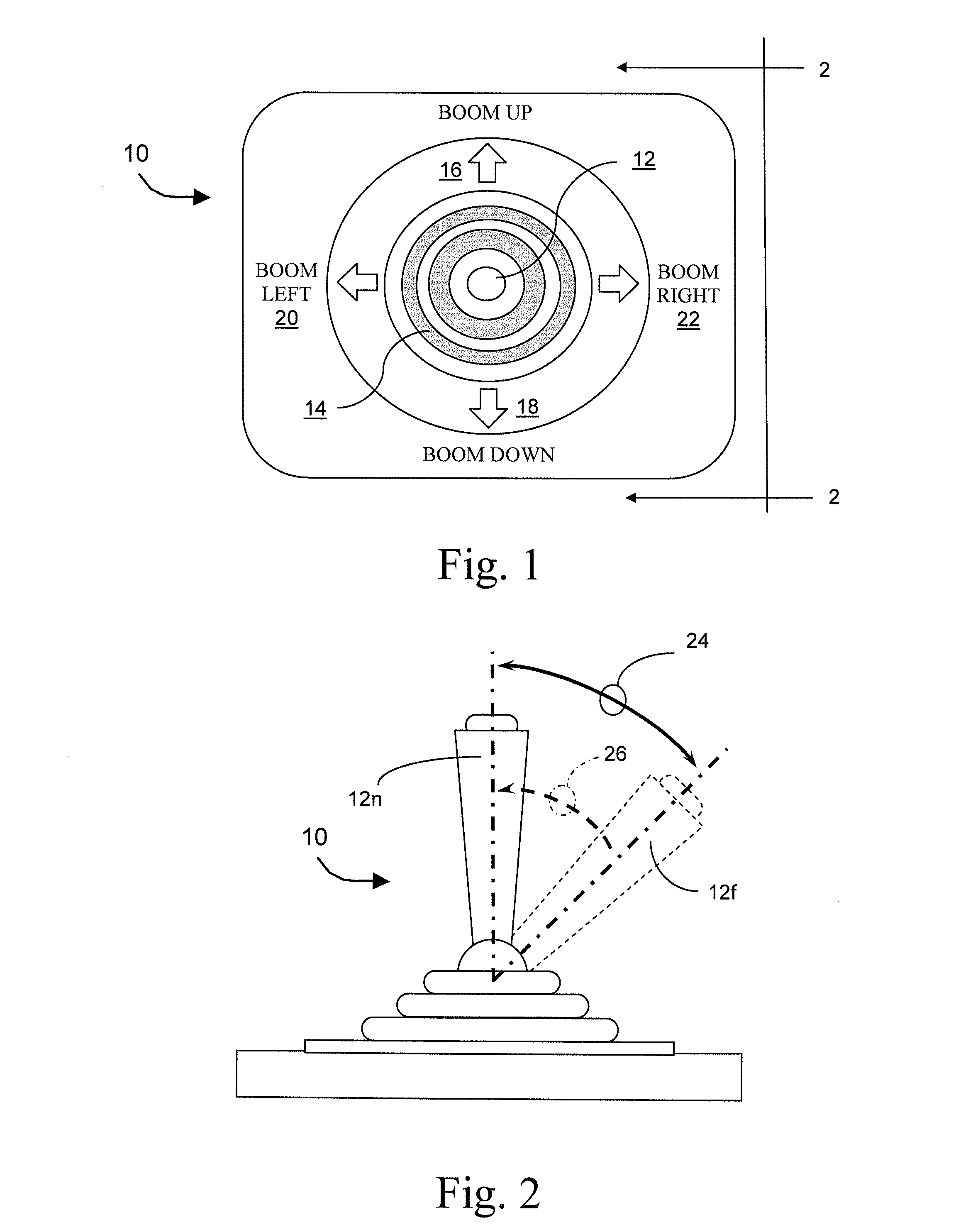
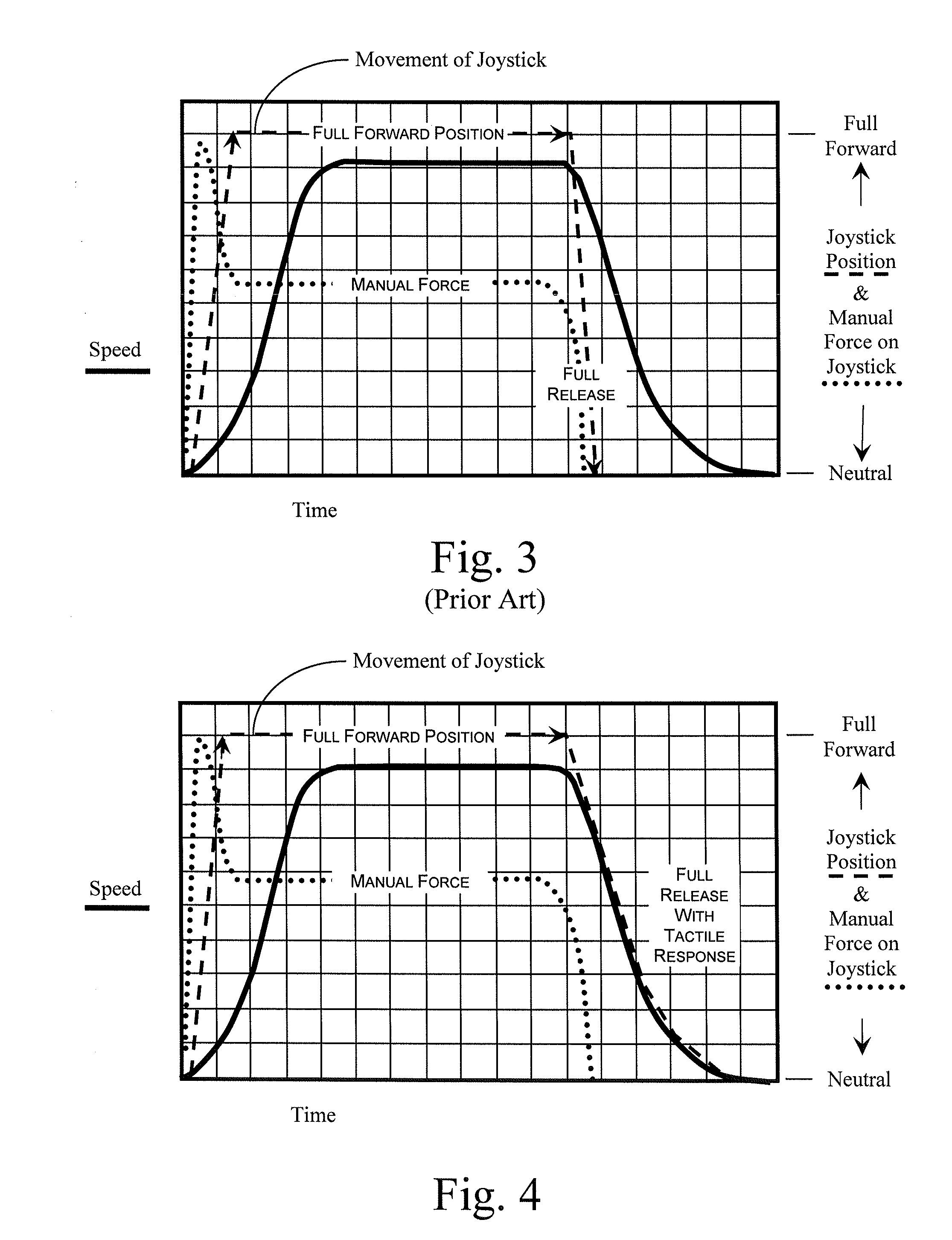
Tactile Feedback for Joystick Position/Speed Controls
InactiveUS20100302017A1Facilitate and adjustPrecise yet smooth speed controlManual control with multiple controlled membersMechanical apparatusJoystickControl system
The present invention includes a control system with a joystick controller for controlling the direction and speed of one or more controlled systems, such as a boom lift platform or the vehicle on which it rides. The joystick is neutrally-biased and effects a null velocity of the controlled system when the joystick is positioned in a neutral position. The joystick controller has motors, or the like, that provide intuitive tactile feedback to the joystick operator. The tactile feedback includes biasing the joystick away from the neutral position according to the controlled system's actual direction and speed but without generating a commanded direction and speed based on the biased position.
Owner:ENOVATION CONTROLS
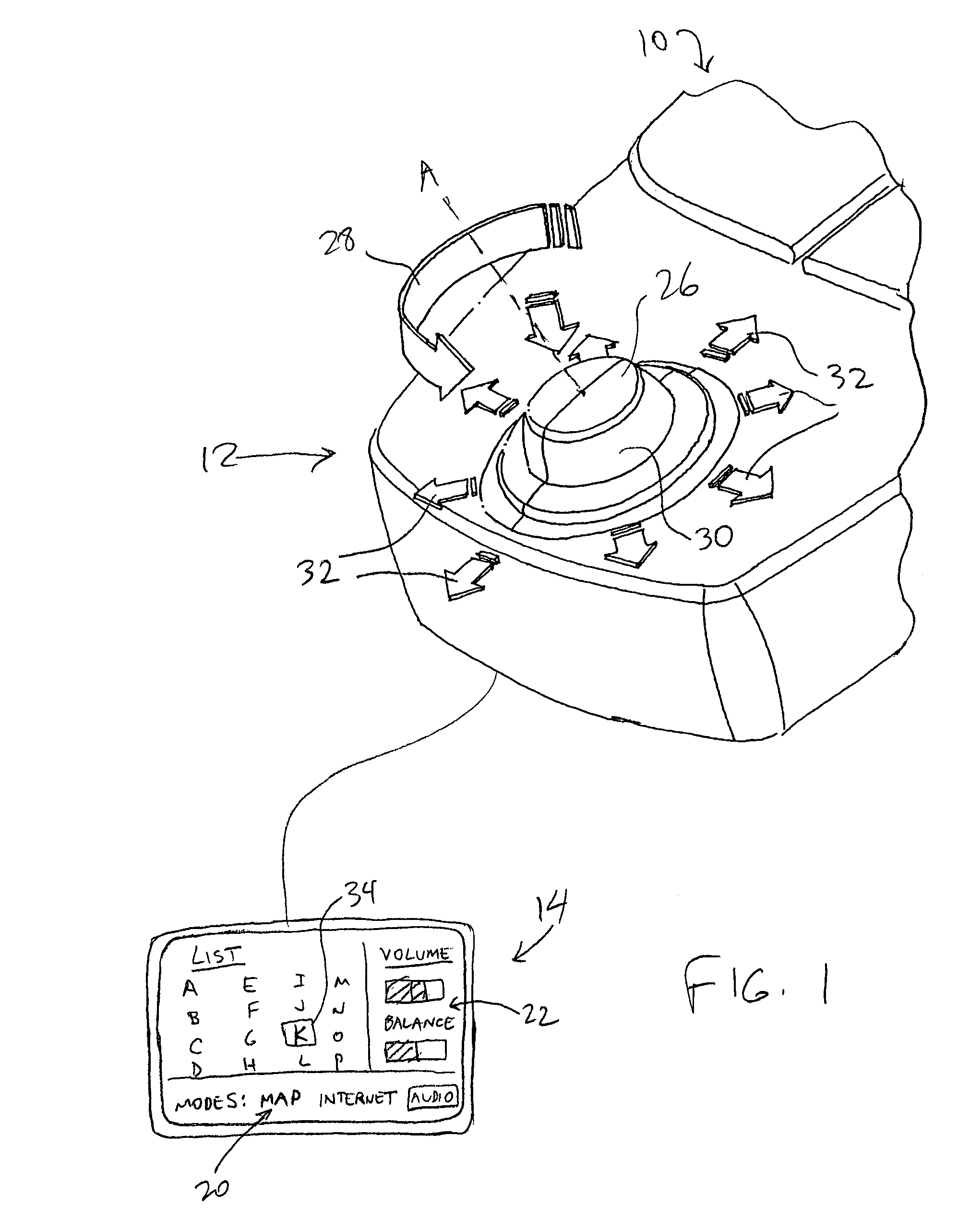
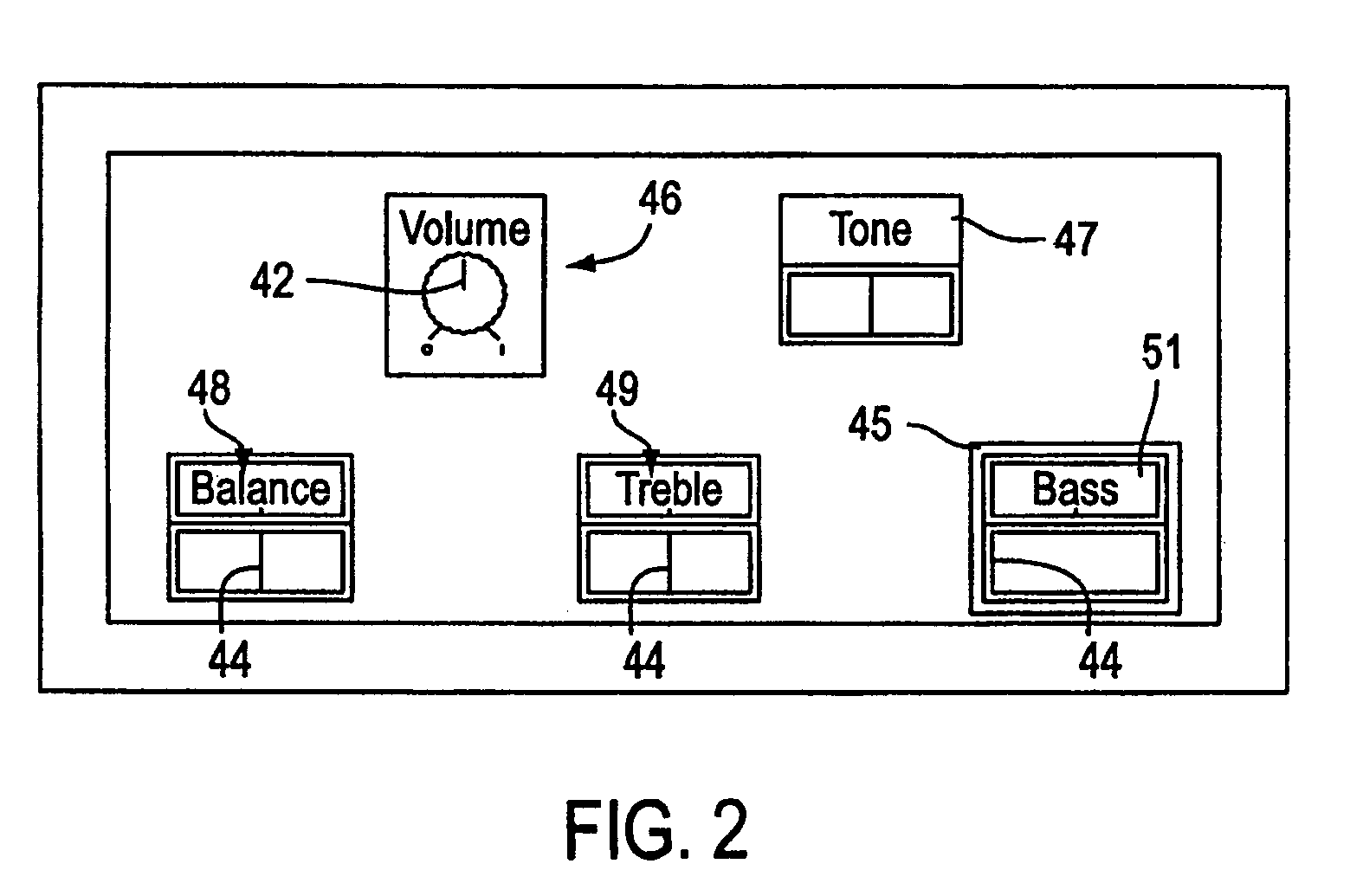
Control knob with multiple degrees of freedom and force feedback
InactiveUS7233313B2Strong control functionGreat caseInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersDetentDisplay device
The present invention provides a control knob on a device that allows a user to control functions of the device. In one embodiment, the knob is rotatable in a rotary degree of freedom and moveable in at least one transverse direction approximately perpendicular to the axis. An actuator is coupled to the knob to output a force in the rotary degree of freedom about the axis, thus providing force feedback. In a different embodiment, the knob is provided with force feedback in a rotary degree of freedom about an axis and is also moveable in a linear degree of freedom approximately parallel to the axis, allowing the knob to be pushed and / or pulled by the user. The device controlled by the knob can be a variety of types of devices, such as an audio device, video device, etc. The device can also include a display providing an image updated in response to manipulation of the knob. Detent forces can be provided for the knob by overlapping and adjusting ranges of closely-spaced detents in the rotary degree of freedom of the knob.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Force feedback device including single-phase, fixed-coil actuators
InactiveUS7061466B1Easily integrated intoManual control with multiple controlled membersNon-rotating vibration suppressionJoystickControl signal
A force feedback interface device that provides force feedback to a joystick handle manipulated by a user. A force feedback device inputs control signals to a computer and outputs forces to a user of the force feedback device. The device includes a housing gripped by the user of the force feedback device and a joystick handle manipulable in at least two rotary degrees of freedom by the user, such as a gamepad. Sensors detect a position of the joystick handle and two direct drive actuators each provide torque in a rotary degree of freedom. Each of the actuators is a brushless, single phase actuator having a grounded excitation coil and a moving magnetic material. The joystick is mechanically constrained to not move past either of two limits where the torque output by the actuator in an unenergized state changes direction. The joystick handle can be oriented such that a center position is substantially at a local minimum reluctance position of the actuator, where the joystick is mechanically constrained to not move substantially past either local maximum reluctance position adjacent to the local minimum reluctance position. The local minimum reluctance position can in some embodiments provide a centering spring force on the joystick handle.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
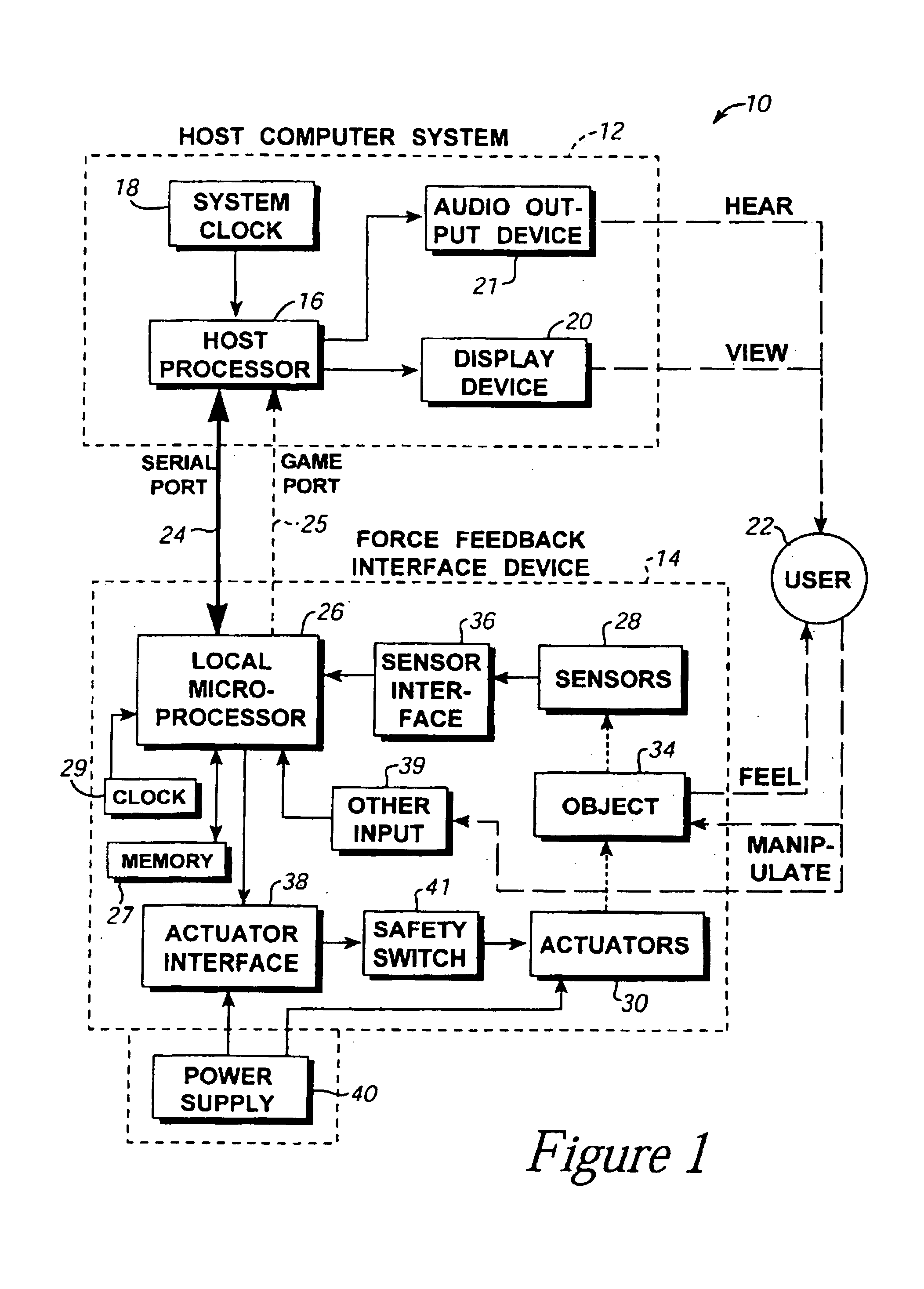
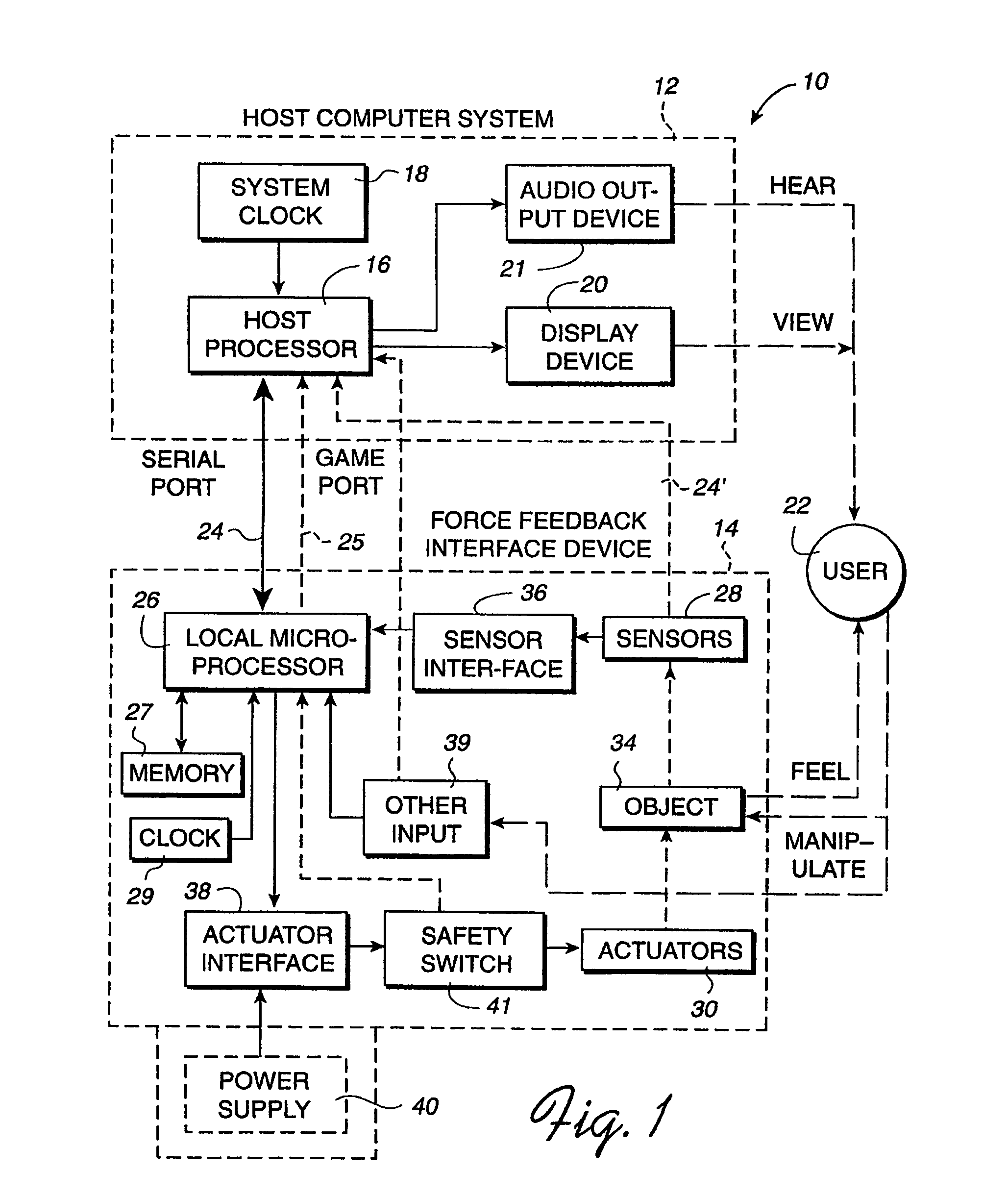
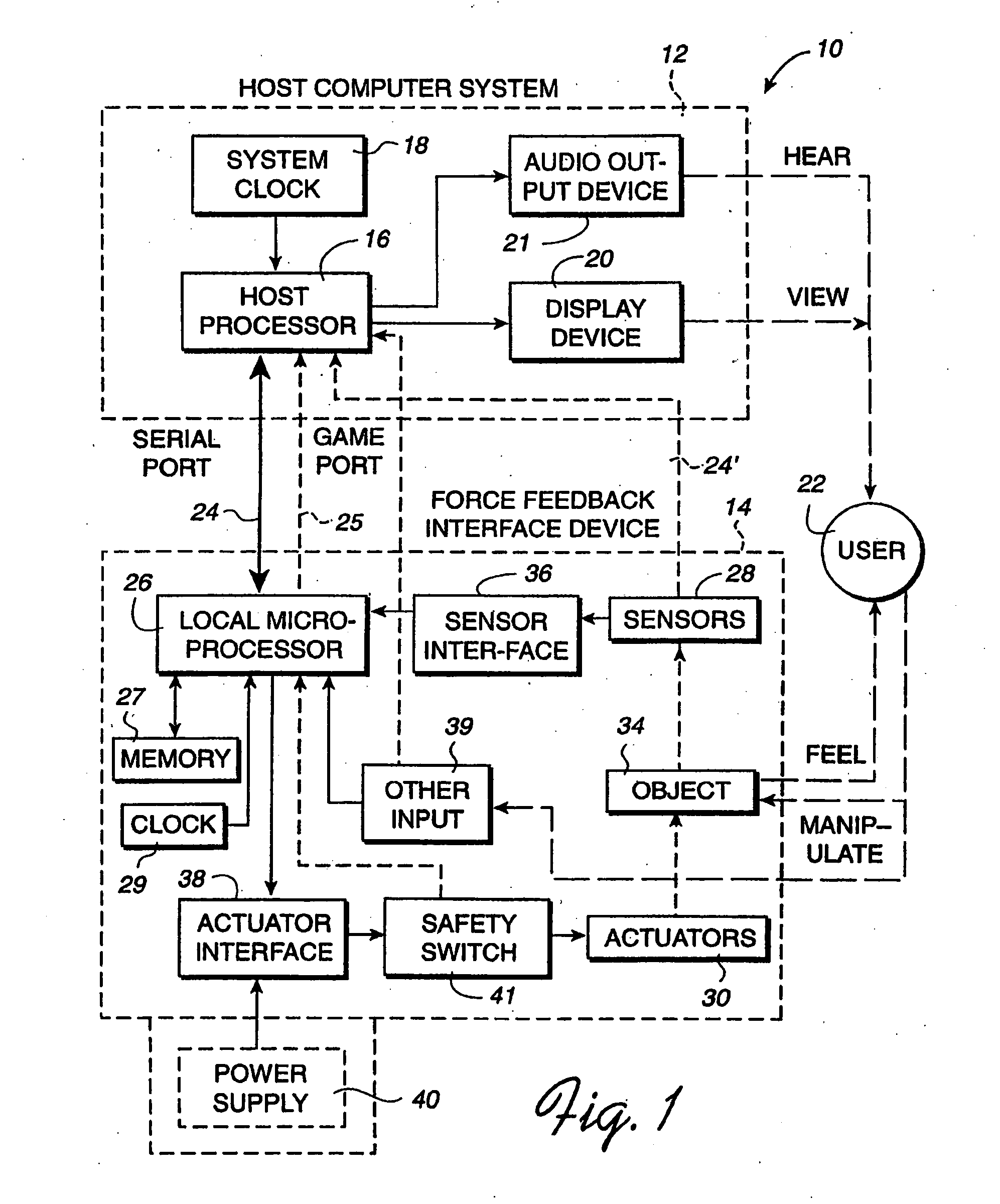
Method and apparatus for controlling force feedback interface systems utilizing a host computer
InactiveUS6982700B2Significant processing timeEasy to createInput/output for user-computer interactionProgramme-controlled manipulatorReflexJoystick
A method and apparatus for controlling and providing force feedback using an interface device manipulated by a user. A microprocessor is provided local to the interface device and reads sensor data from sensors that describes the position and / or other information about a user object moved by the user, such as a joystick. The microprocessor controls actuators to provide forces on the user object and provides the sensor data to a host computer that is coupled to the interface device. The host computer sends high level host commands to the local microprocessor, and the microprocessor independently implements a local reflex process based on the high level command to provide force values to the actuators using sensor data and other parameters. A provided host command protocol includes a variety of different types of host commands and associated command parameters. By providing a relatively small set of high level host commands and parameters which are translated into a panoply of forces, the protocol further shifts the computational burden from the host computer to the local microprocessor and allows a software developer to easily create force feedback applications.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Haptic feedback for touchpads and other touch controls
InactiveUS20060119589A1Enhanced interactionEnhance manipulationInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsTouchpad
A haptic feedback planar touch control used to provide input to a computer. A touch input device includes a planar touch surface that inputs a position signal to a processor of the computer based on a location of user contact on the touch surface. The computer can position a cursor in a displayed graphical environment based at least in part on the position signal, or perform a different function. At least one actuator is also coupled to the touch input device and outputs a force to provide a haptic sensation to the user contacting the touch surface. The touch input device can be a touchpad separate from the computer's display screen, or can be a touch screen. Output haptic sensations on the touch input device can include pulses, vibrations, and spatial textures. The touch input device can include multiple different regions to control different computer functions.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
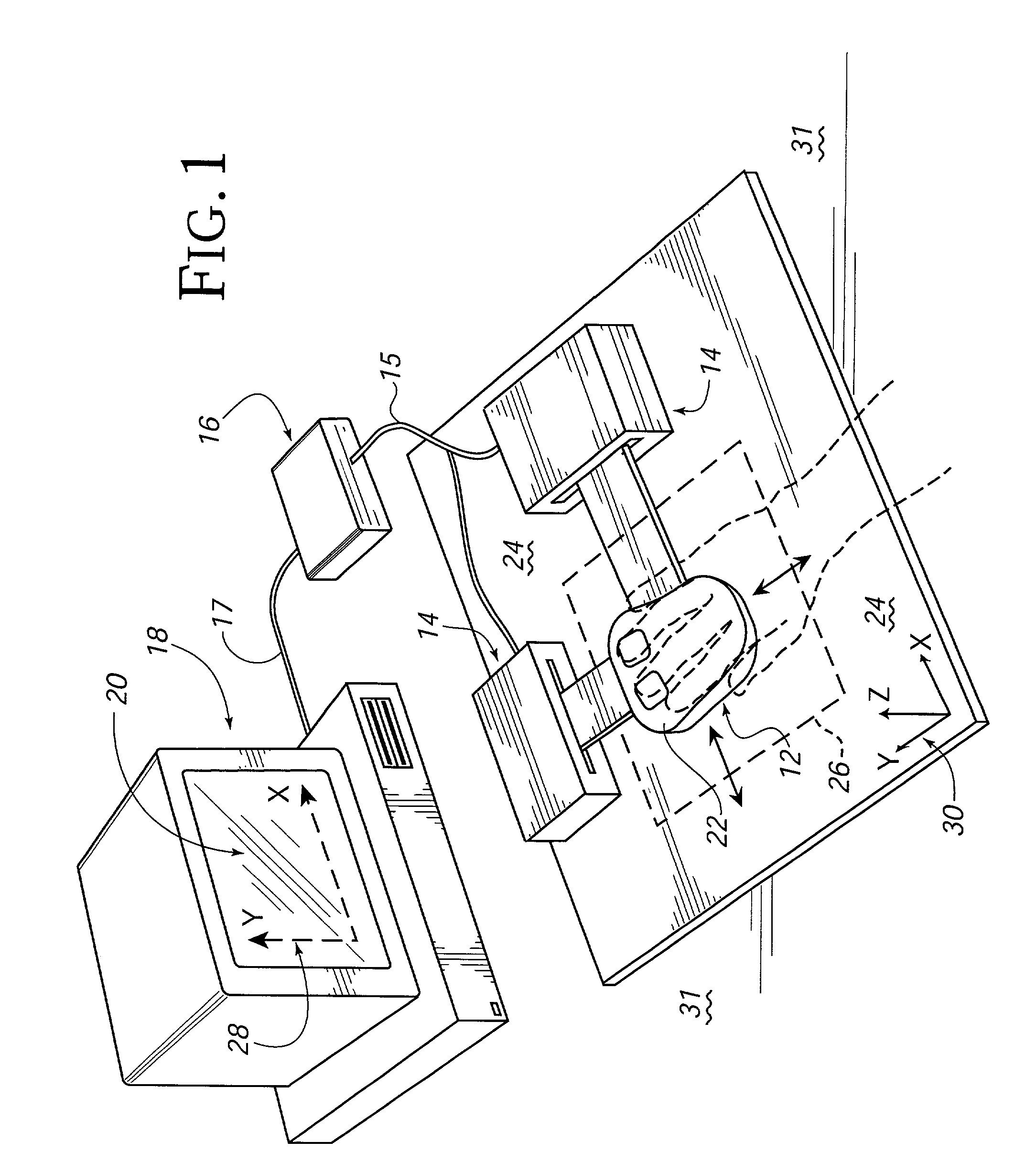
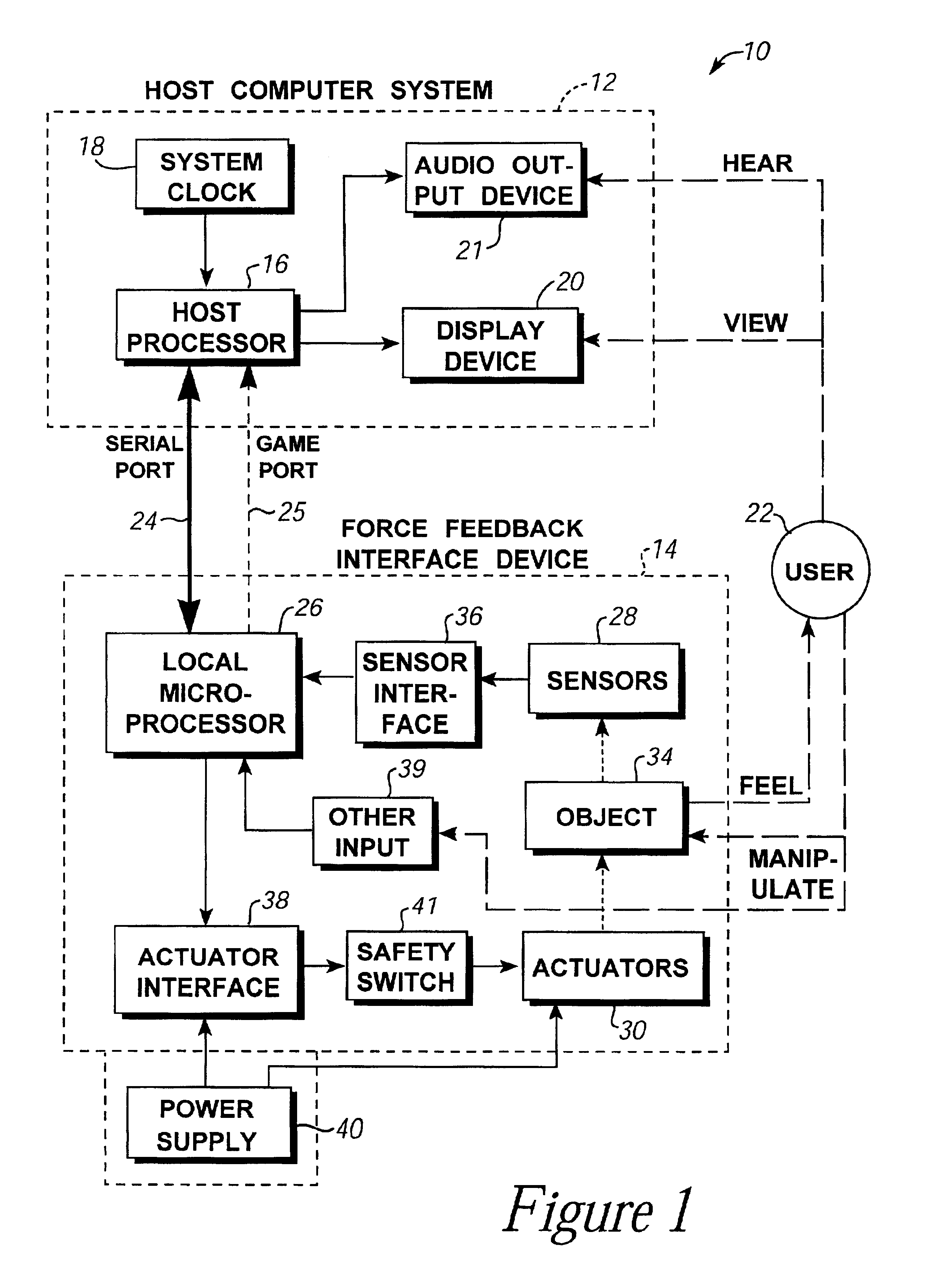
Interface device for sensing position and orientation and outputting force to a user
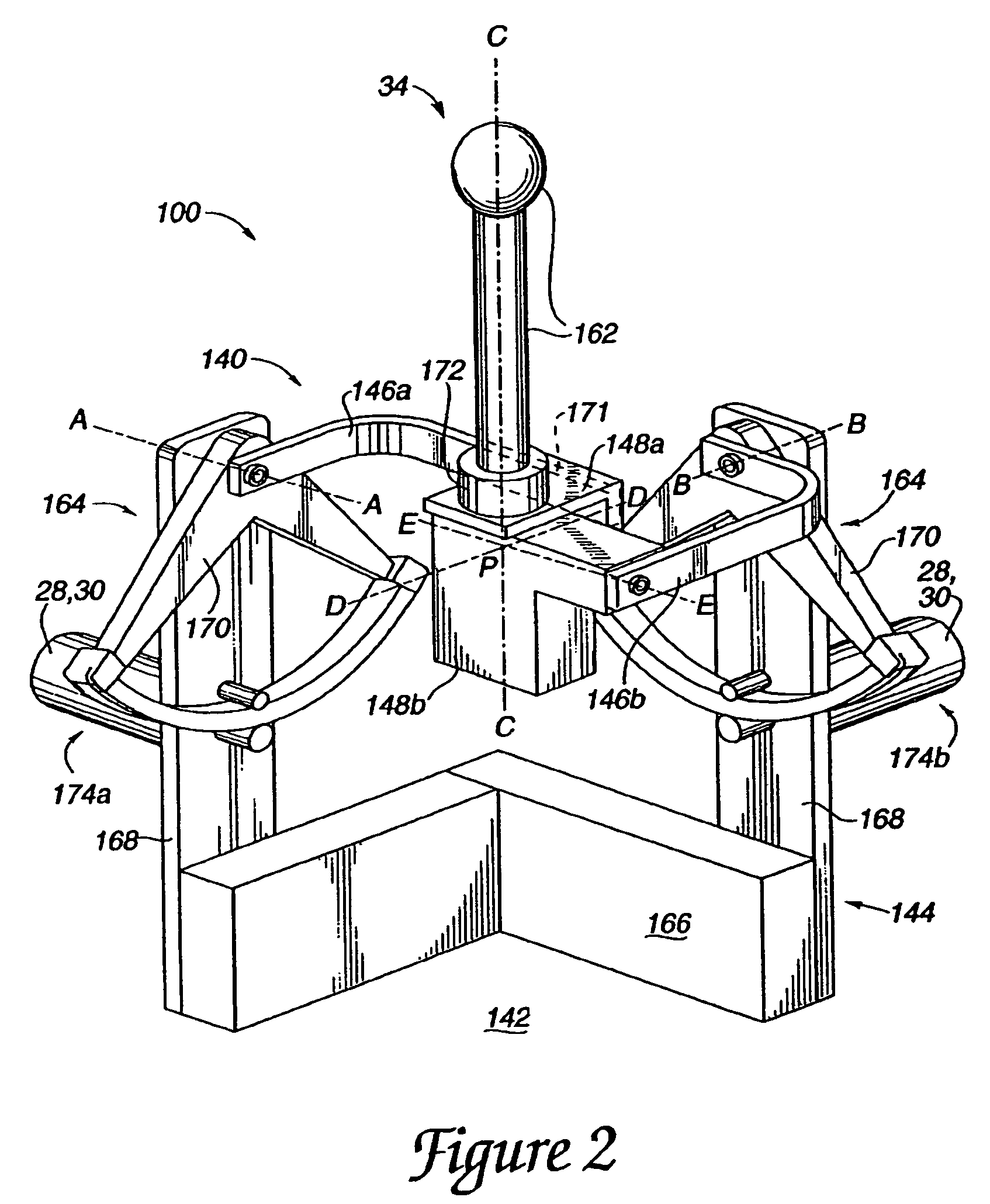
InactiveUS6987504B2Easy to operateReduce fatigueInput/output for user-computer interactionProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer graphics (images)Display device
An interface device for use with a computer that provides locative data to a computer for tracking a user manipulatable physical object and provides feedback to the user through output forces. The physical object is movable in multiple degrees of freedom and is tracked by sensors for sensing the location and orientation of the object. A device processor can be responsive to the output of the sensors and can provide the host computer with information derived from the sensors. The host computer can provides images on a display, where the computer responds to the provided sensor information and force feedback is correlated with the displayed images via force feedback commands from the host computer.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
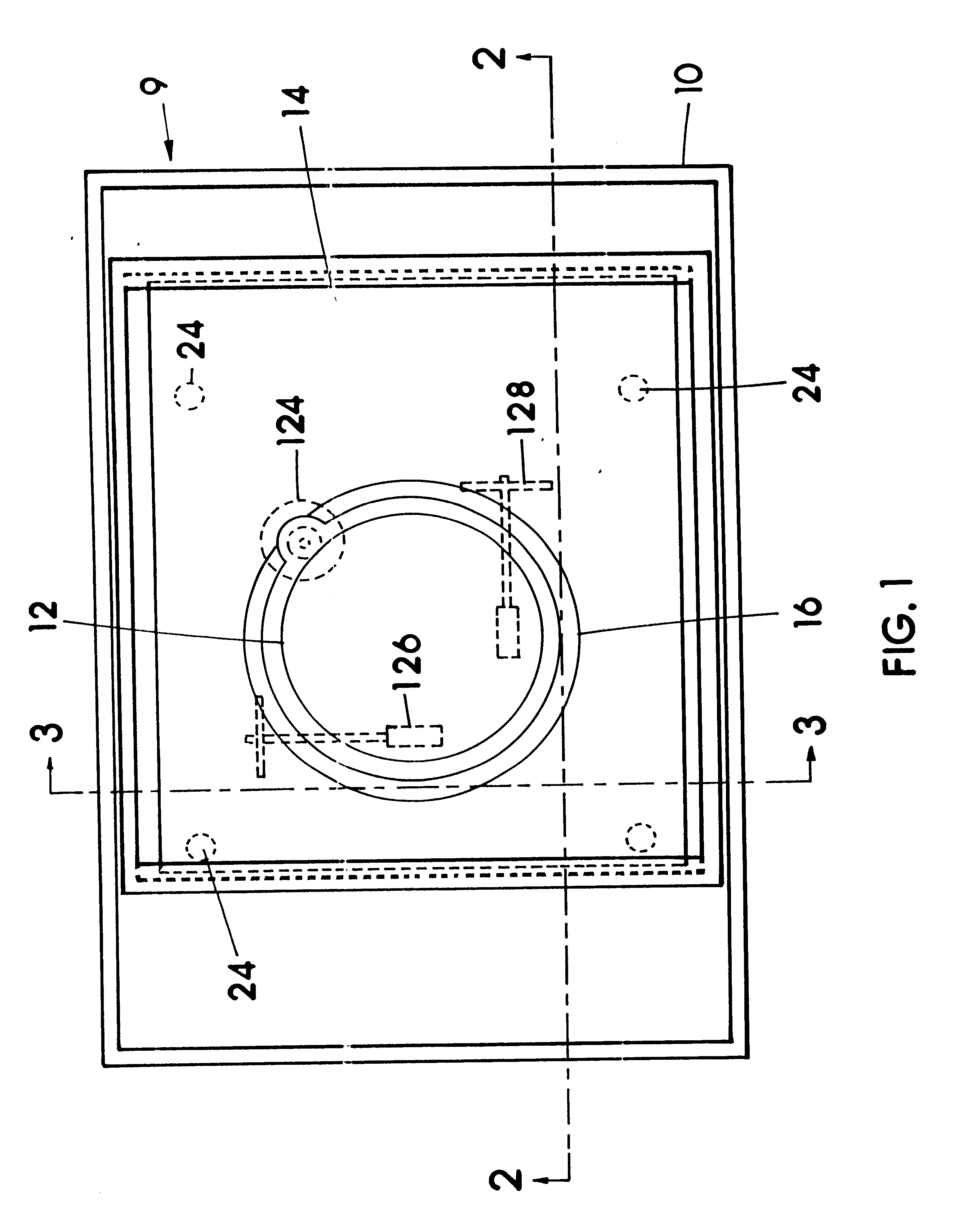
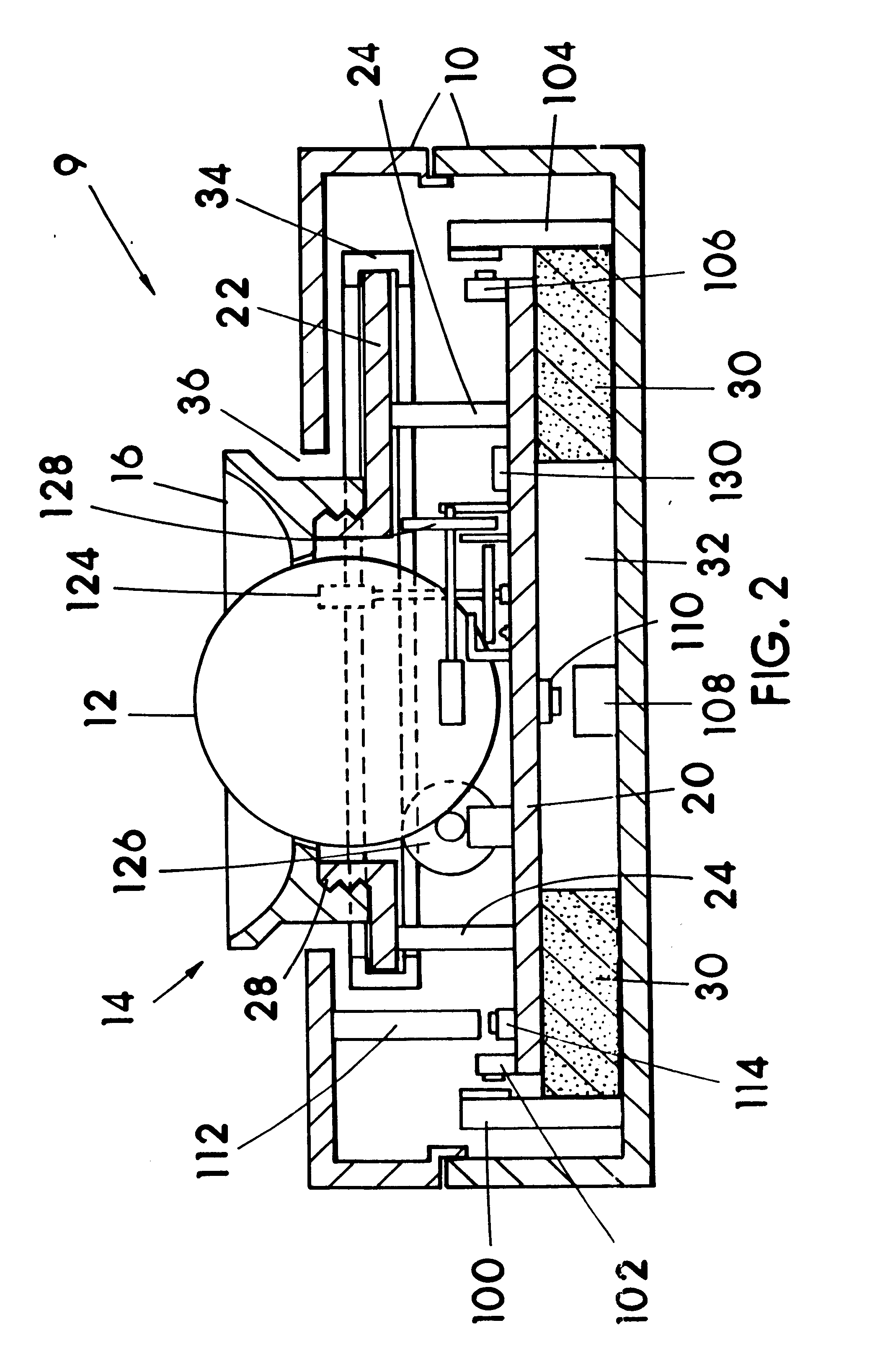
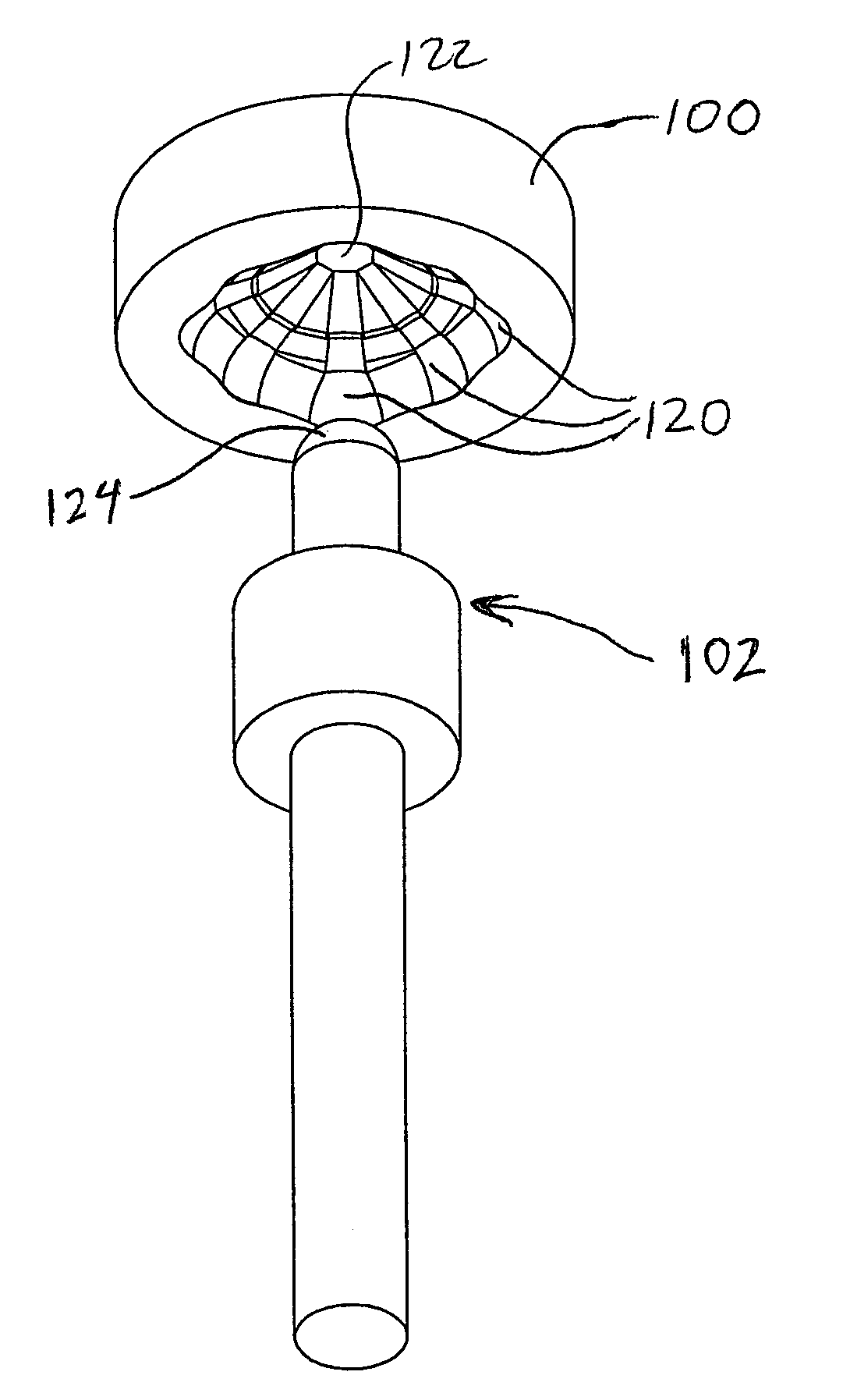
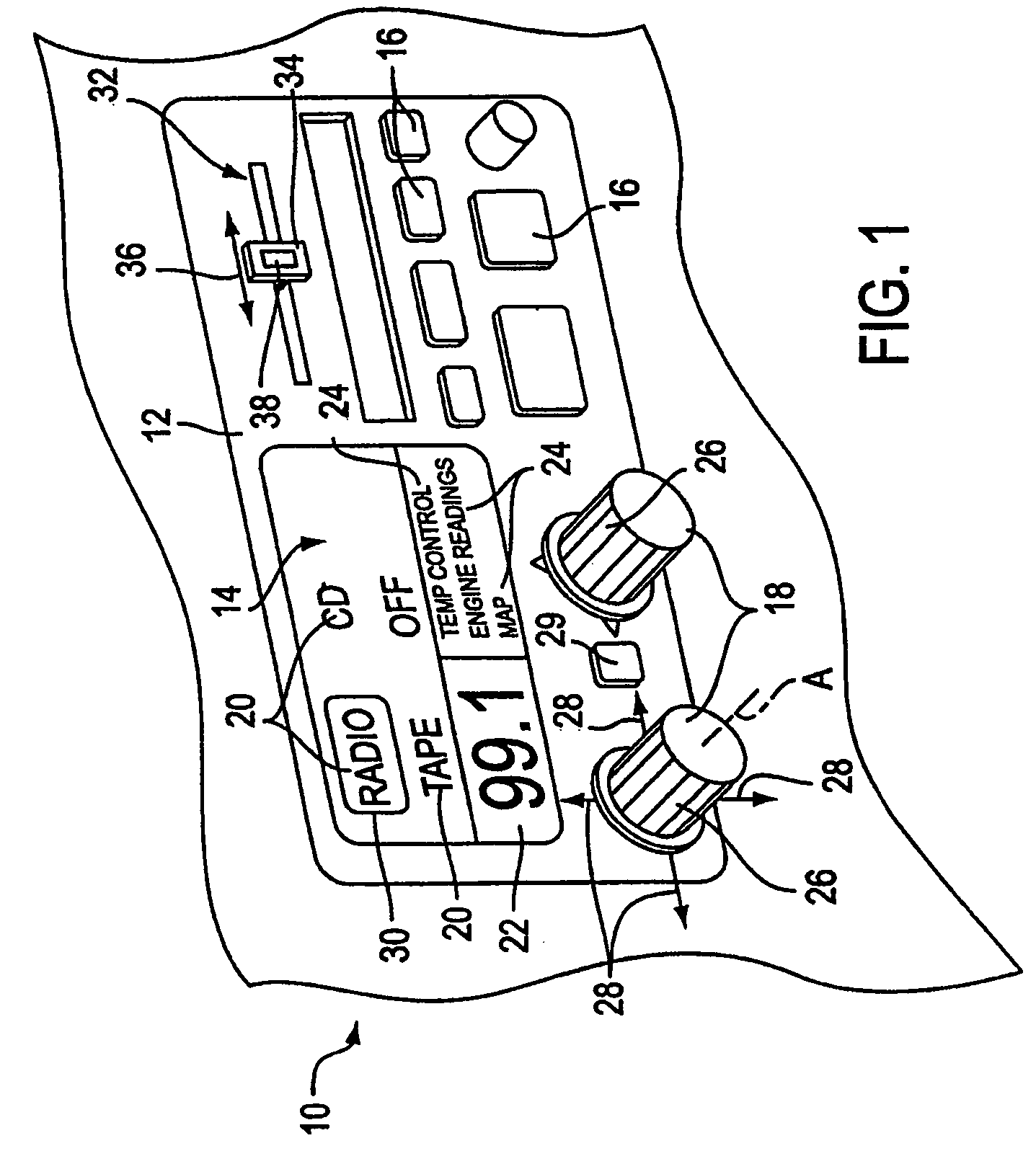
Manual input device with force feedback function and vehicle-mounted equipment controller using same
InactiveUS6591175B2Improve reliability and operabilityEliminate needDashboard fitting arrangementsDigital data processing detailsControl signalTransmitted power
A manual input device and a vehicle-mounted equipment controller are provided. The manual input device includes: a knob secured to an operation shaft and sensing portion for detecting the operation state of the operation shaft; an actuator to apply force to the knob; a power transmission portion for transmitting power between the operation shaft and a drive shaft of the actuator; and an input / output portion to send a first signal to the external device and to receive a second signal from an external device. The device further includes a control portion for generating a control signal for the actuator in accordance with an external signal outputted from an external sensing portion, or in accordance with control information generated in accordance with, at least, the external signal. The vehicle-mounted equipment controller includes selection switches for vehicle-mounted electric equipment, function selection switches, and the manual input device to adjust functions of the vehicle-mounted electric equipment selected.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Method and apparatus for designing force sensations in force feedback computer applications
InactiveUS20060187201A1Simple and intuitive designEfficient use ofInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersGraphicsEngineering
A design interface tool for designing force sensations for use with a host computer and force feedback interface device. A force feedback device is connected to a host computer that displays the interface tool. Input from a user is received in the interface to select a type of force sensation to be commanded by a host computer and output by a force feedback interface device. Input, such as parameters, is then received from the user which designs and defines physical characteristics of the selected force sensation. A graphical representation of the characterized force sensation is displayed on the host computer which provides a visual demonstration of a feel of the characterized force sensation so that the user can view an effect of parameters on said force sensation. The characterized force sensation is output to a user manipulatable object of the force feedback device so that the user can feel the designed force sensation, where the graphical representation is updated in conjunction with the output of the force sensation. The user can iteratively modify force sensation characteristics and feel the results, and store the characterized force sensations.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Predictive Force Sensitive Keypad
ActiveUS20110074691A1Improve text input efficiencyExcessive pressureInput/output for user-computer interactionEmergency actuatorsKey pressingText entry
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
Fluid haptic interface with improved haptic rendering using a torque or load sensor
ActiveUS9898032B2Improved haptic renderingReduce, or even suppress, a spatial and time delay in the control of the interfaceControlling membersSpringsMagnetic currentLow speed
A haptic interface, including: a button which can be rotated by a user; an interaction element interacting with a magnetorheological fluid, secured to the button; a mechanism measuring a current position of the button; a brake including a magnetorheological fluid and a generation system to generate a magnetic field in the fluid; a controller configured to generate orders for the system to generate a magnetic fluid to modify a value of the magnetic field; and a mechanism to detect torque exerted by a user on the button to know direction of the torque and whether the torque is greater than a given value for a given direction, the controller controlling generation of a magnetic field based on obtained information about the torque at least when the button indicates zero or low speed.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Pushbutton user interface with functionality preview
InactiveUS6976215B1Simpler and more understandableSimpler and more interfaceInput/output for user-computer interactionOperation facilitationTouch PerceptionDisplay device
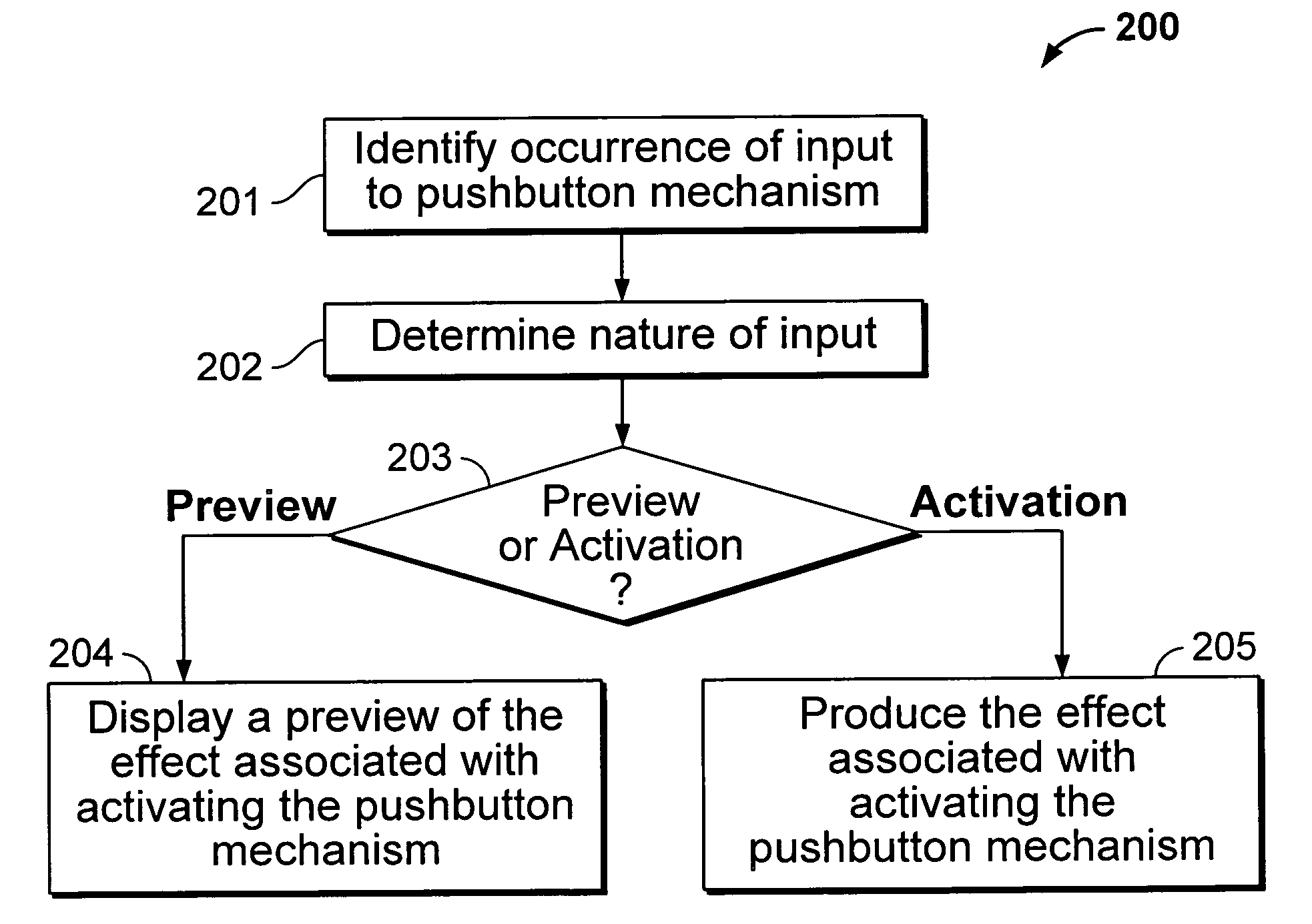
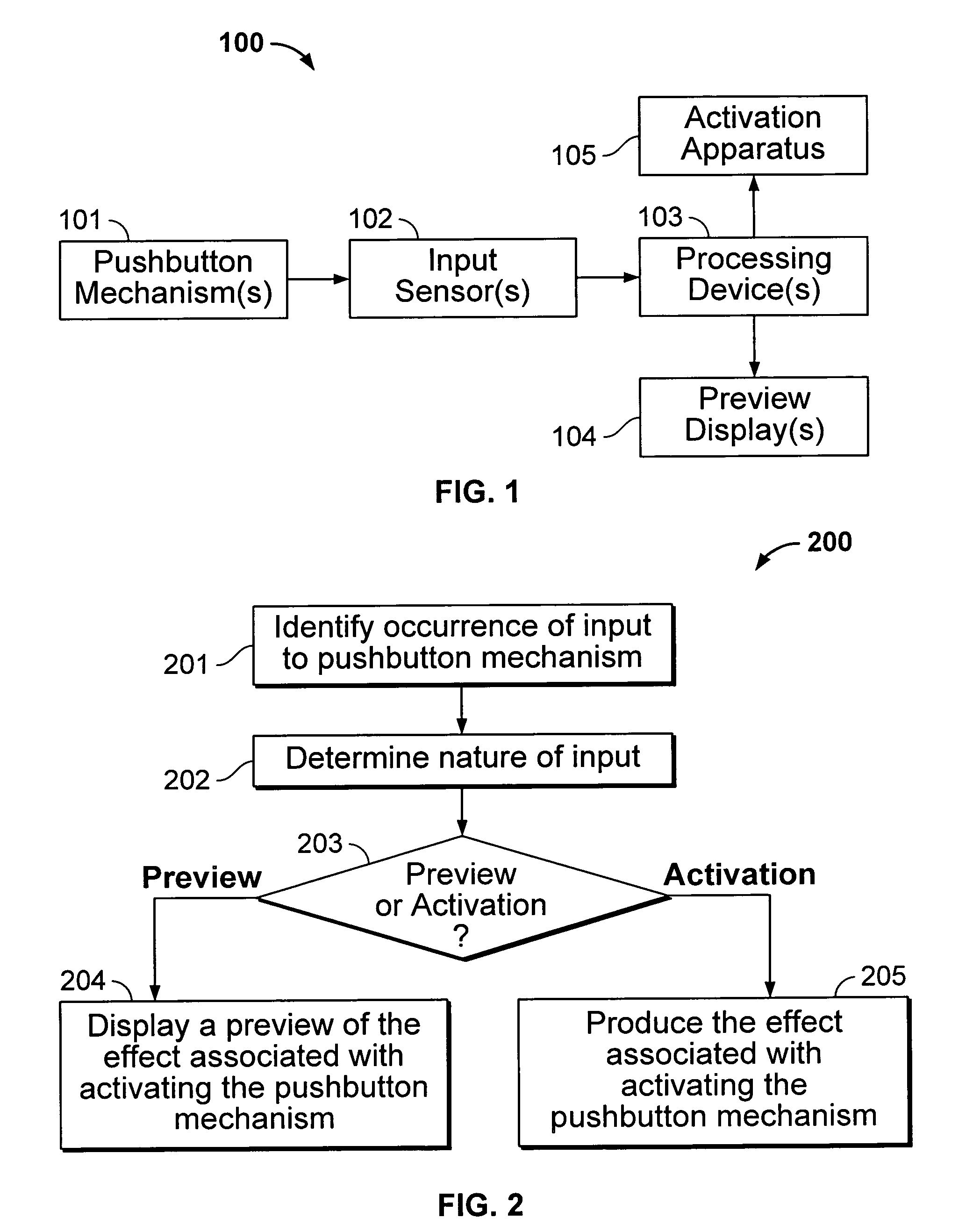
A pushbutton user interface enables a user to preview the effect of activating a pushbutton of the interface before the pushbutton is activated. The pushbutton user interface can be implemented so that an input (preview input) to the pushbutton that does not produce an activation of the pushbutton is sensed and, in response to the sensed input, a preview is displayed that indicates the effect of activating the pushbutton. The preview input can be sensed using, for example, a force-sensitive resistor, potentiometer or strain gauge. The preview display can include, for example, a visual display, an audio display, a haptic display, or a combination of two or three such displays. The pushbutton user interface can be implemented so that the preview input and an activation input (i.e., an input that produces an activation of the pushbutton) are sensed as a result of an input to the pushbutton along the same axis or along different (e.g., orthogonal) axes.
Owner:THINKLOGIX LLC
Haptic feedback effects for control knobs and other interface devices
InactiveUS7327348B2Easy to controlReduce overshootInput/output for user-computer interactionProgramme-controlled manipulatorFeedback effectDetent
The present invention provides haptic sensations for a haptic feedback device and especially for a rotational device such as a knob. Force effects such as a hill force effect and barrier force effect allow easier selection of menu items, menus, values, or other options by the user. Force models are also described to allow greater selection functionality, such as a scrolling list with detents and rate control borders, a jog shuttle, a push-turn model, a double-push model, and a cast control model.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Tactile Feedback for Joystick Position/Speed Controls
ActiveUS20160179128A1Minimize complexityReduce unnecessary costsManual control with multiple controlled membersControlling membersJoystickActuator
A joystick controller is disclosed for controlling movement of a boom lift platform, the controller having actuators or the like that provide one or more forms of tactile feedback that are intuitively interpreted and adjusted by the user of the joystick motion control, the joystick being neutrally-biased to effect a null movement when the joystick is positioned in a neutral position, but also being adapted with at least one form of tactile feedback by which the joystick controller conveys information about the boom lift's operation to the joystick operator, such as through resistive force or through vibrations or the like.
Owner:ENOVATION CONTROLS
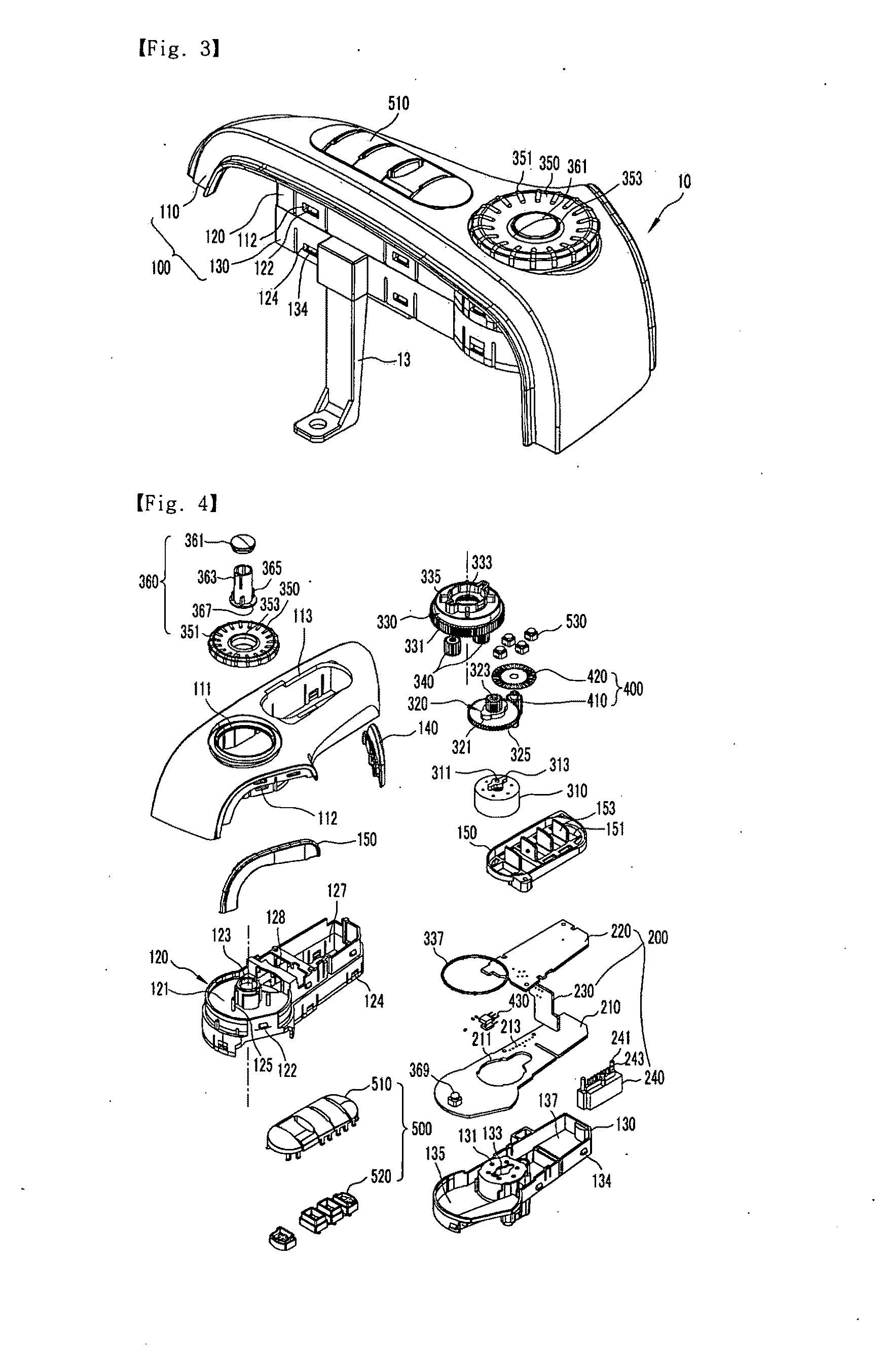
Haptic Steering Wheel Switch Device and Haptic Steering Wheel Switch System Including the Same
ActiveUS20100200375A1Avoid distractionAvoid inductionContact operating partsElectrical haptic/tactile feedbackElectric power transmissionSteering wheel
The present invention provides a haptic steering wheel switch device and a haptic steering wheel switch system including the same. The haptic steering wheel switch device comprises: a housing mounted in a steering wheel; a printed circuit board disposed inside of the housing; and a haptic rotary switch unit including a haptic rotary switch driver disposed in the housing and adapted to generate a rotational force in response to an electrical signal, a haptic rotary switching power transfer unit adapted to transfer the rotational force generated from the haptic rotary switch driver, and a haptic rotary switch knob exposed outside of the housing and connected to the haptic rotary switching power transfer unit to receive the rotational force from the haptic rotary switching power transfer unit.
Owner:LS AUTOMOTIVE TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com