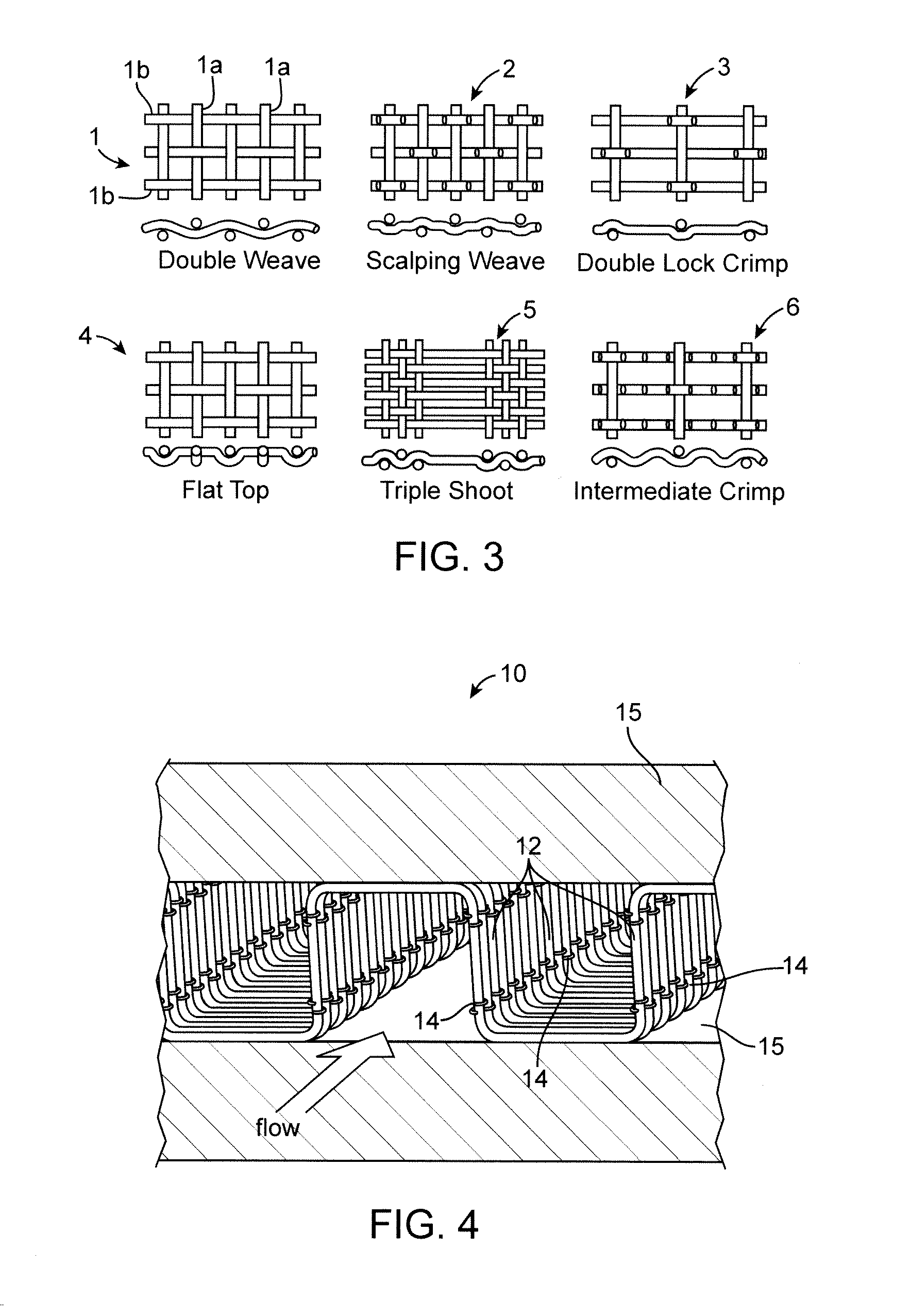
Patents
Literature
60results about How to "Excessive pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
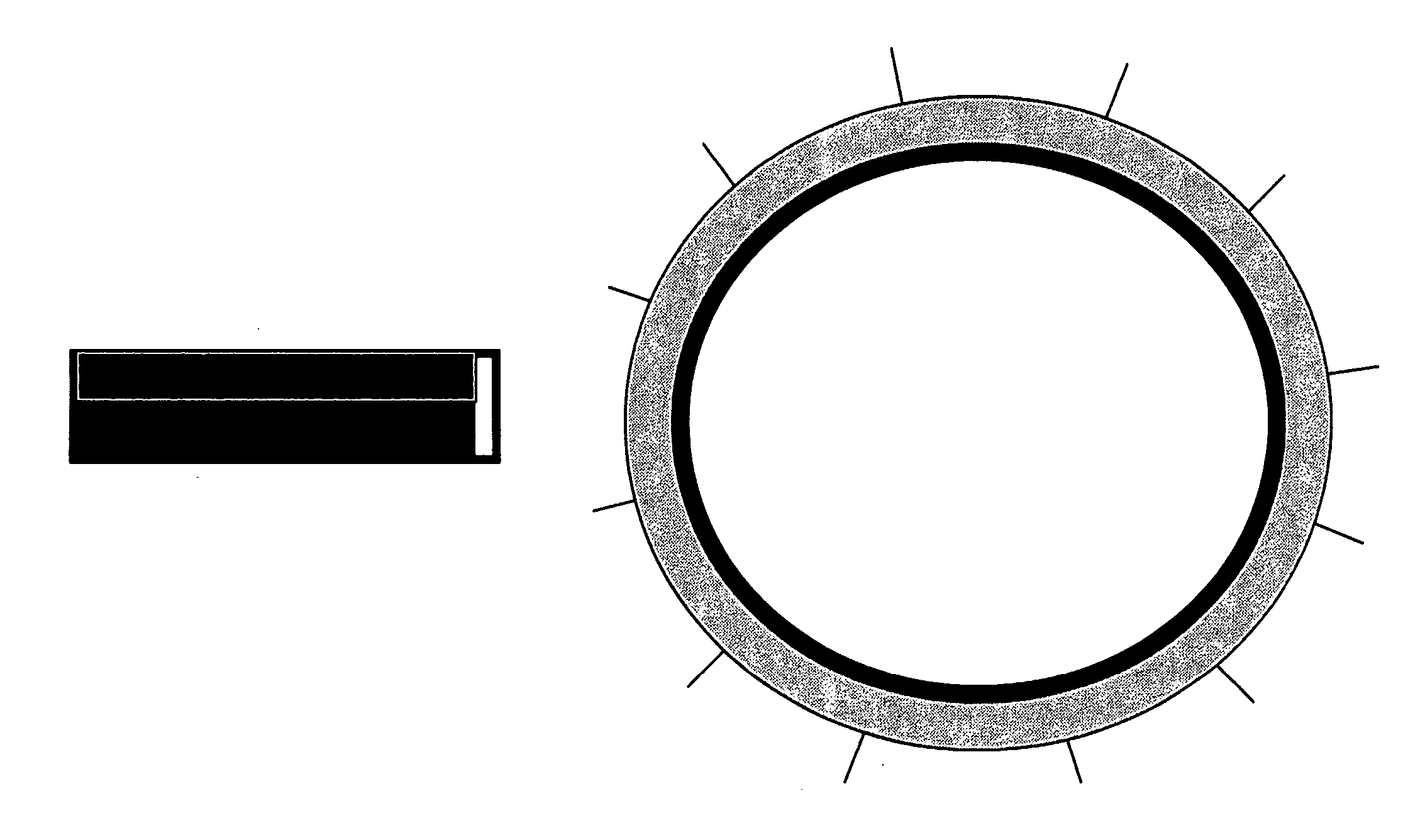
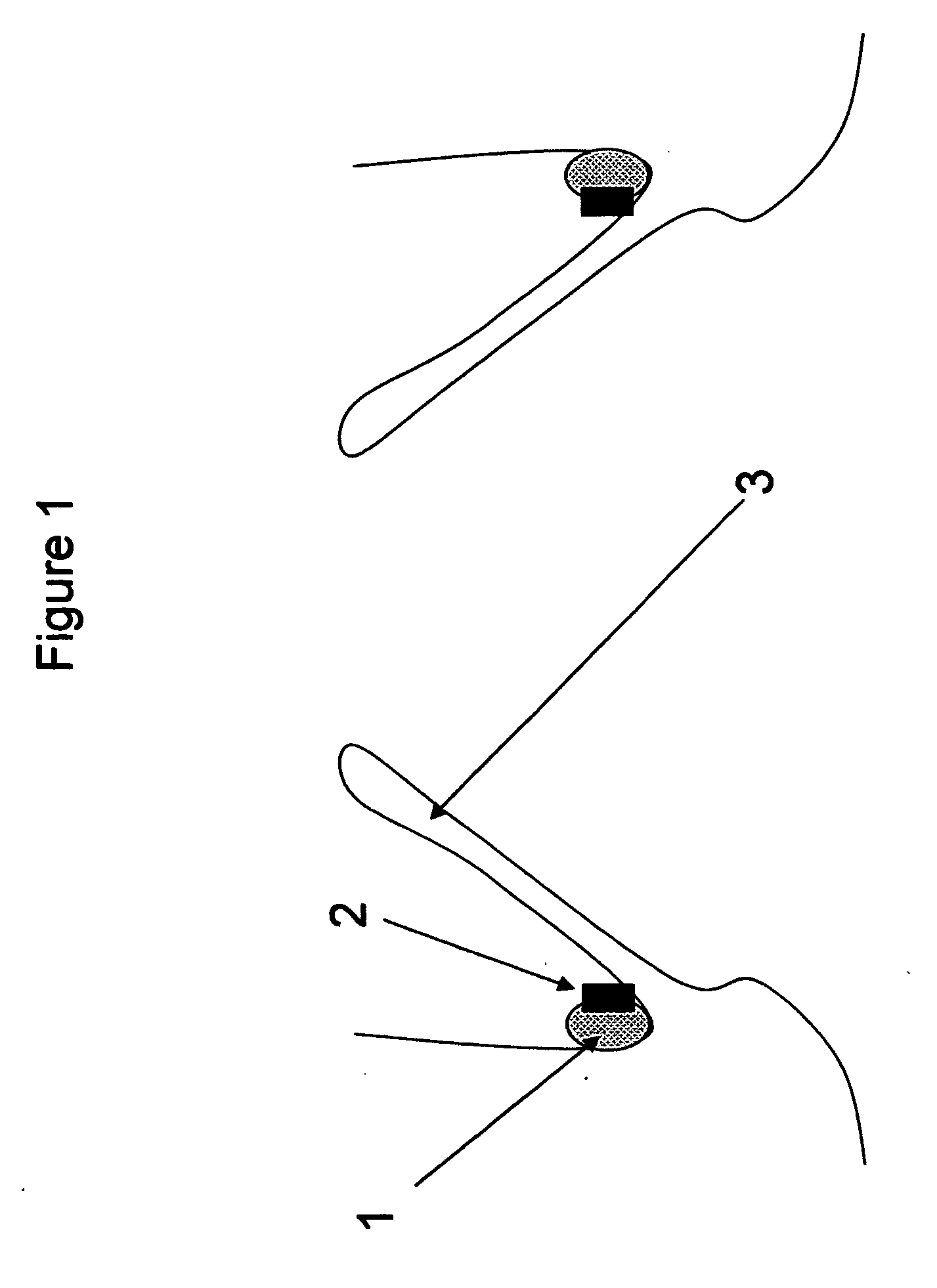
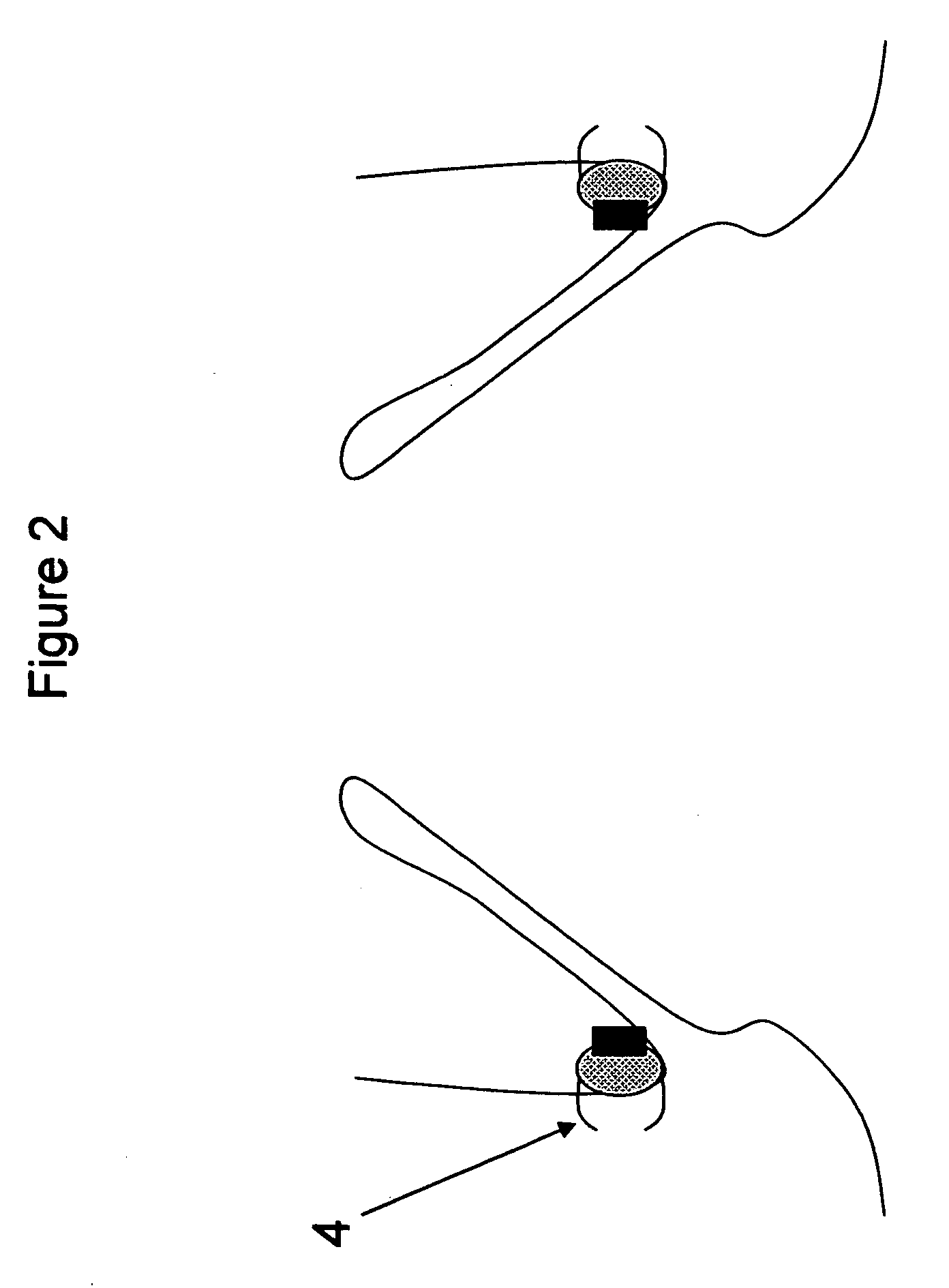
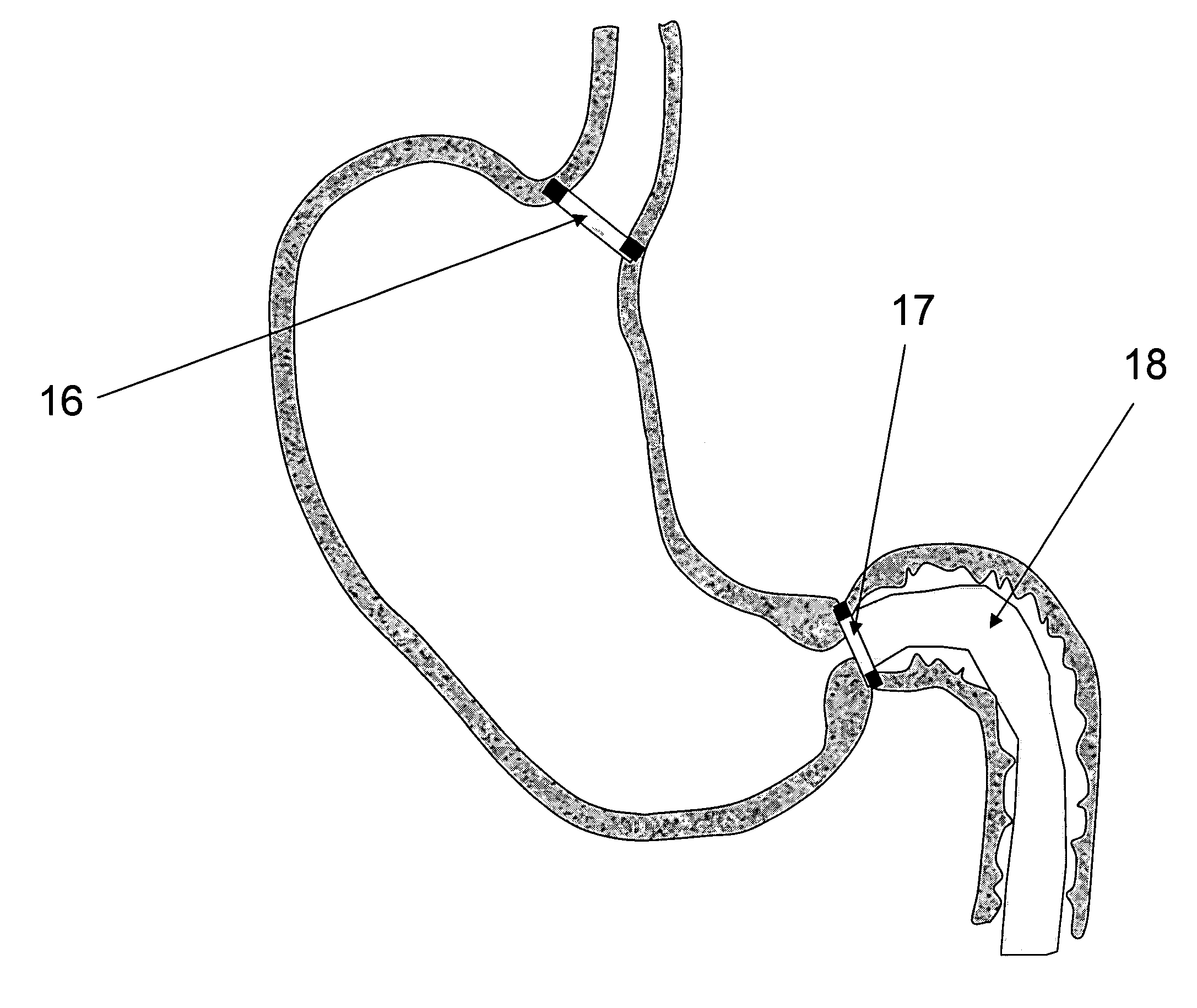
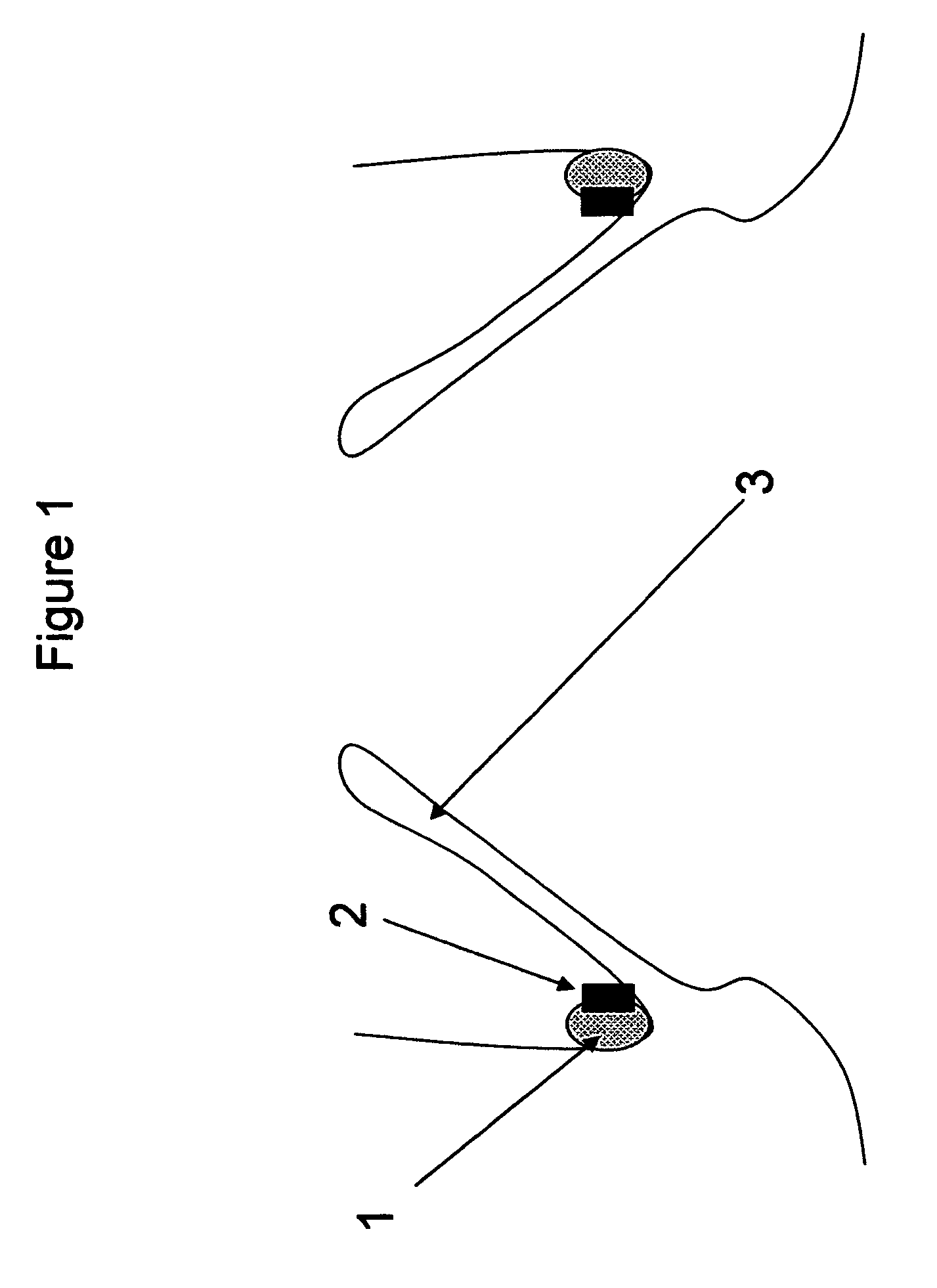
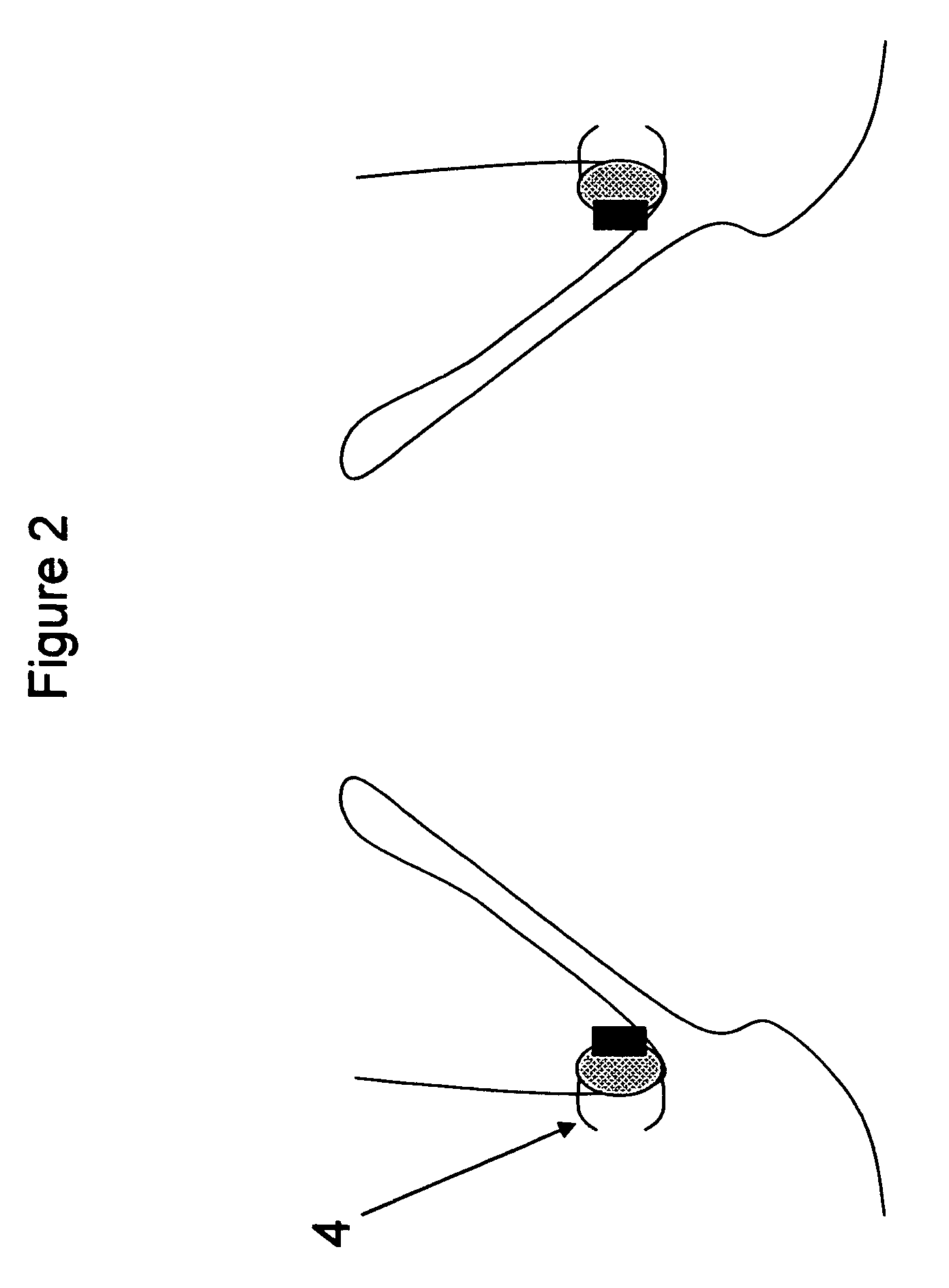
Method and apparatus for anchoring implants
InactiveUS20060069400A1Reduce risk of migrationReduce intrusionStentsHeart valvesLaparoscopyTherapeutic Devices
Methods, devices and systems facilitate retention of a variety of therapeutic devices. Devices generally include an anchoring element, which has been designed to promote fibrotic ingrowth, and an anchored device, which has been designed to firmly engage the complementary region of the anchoring element. The anchoring element may be placed in a minimally invasive procedure temporally separated from the deployment of the anchored device. Once enough time has passed to ensure appropriate fixation of the anchoring element by tissue and cellular ingrowth at the site of placement, the anchored device may then be deployed during which it firmly engages the complementary region of the anchoring element. In this manner, a firm attachment to the implantation site may be made with a minimum of required hardware. Some embodiments are delivered through a delivery tube or catheter and while some embodiments may require laparoscopy or open surgery for one or more of the placement procedures. Some embodiments anchor devices within the cardiovascular tree while others may anchor devices within the gastrointestinal, peritoneal, pleural, pulmonary, urogynecologic, nasopharyngeal or dermatologic regions of the body.
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
Method and apparatus for anchoring implants
InactiveUS7850704B2Low mechanical strengthReliable anchoringStentsHeart valvesSufficient timeTherapeutic Devices
Methods, devices and systems facilitate retention of a variety of therapeutic devices. Devices generally include an anchoring element, which has been designed to promote fibrotic ingrowth, and an anchored device, which has been designed to firmly engage the complementary region of the anchoring element. The anchoring element may be placed in a minimally invasive procedure temporally separated from the deployment of the anchored device. Once enough time has passed to ensure appropriate fixation of the anchoring element by tissue and cellular ingrowth at the site of placement, the anchored device may then be deployed during which it firmly engages the complementary region of the anchoring element. In this manner, a firm attachment to the implantation site may be made with a minimum of required hardware. Some embodiments are delivered through a delivery tube or catheter and while some embodiments may require laparoscopy or open surgery for one or more of the placement procedures. Some embodiments anchor devices within the cardiovascular tree while others may anchor devices within the gastrointestinal, peritoneal, pleural, pulmonary, urogynecologic, nasopharyngeal or dermatologic regions of the body.
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
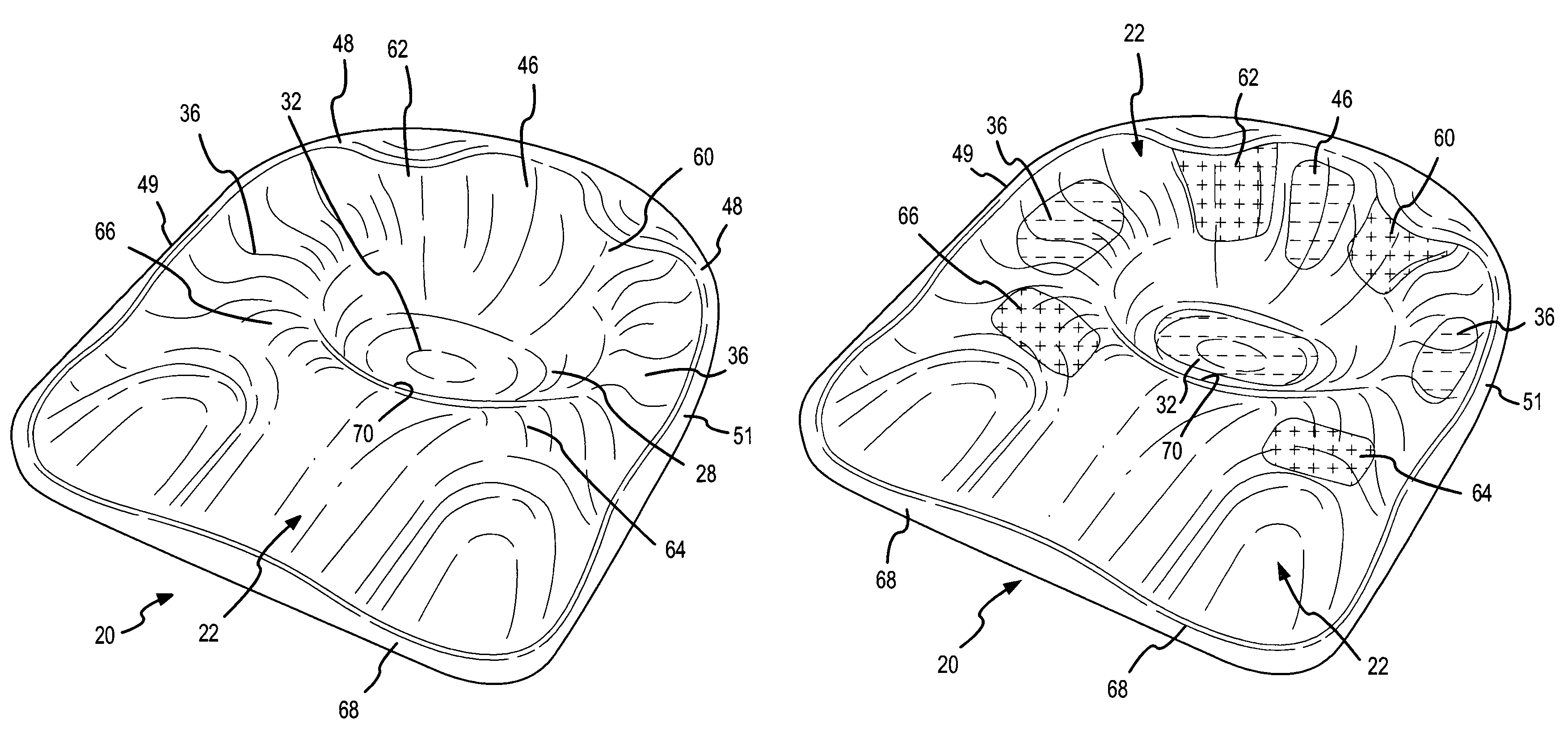
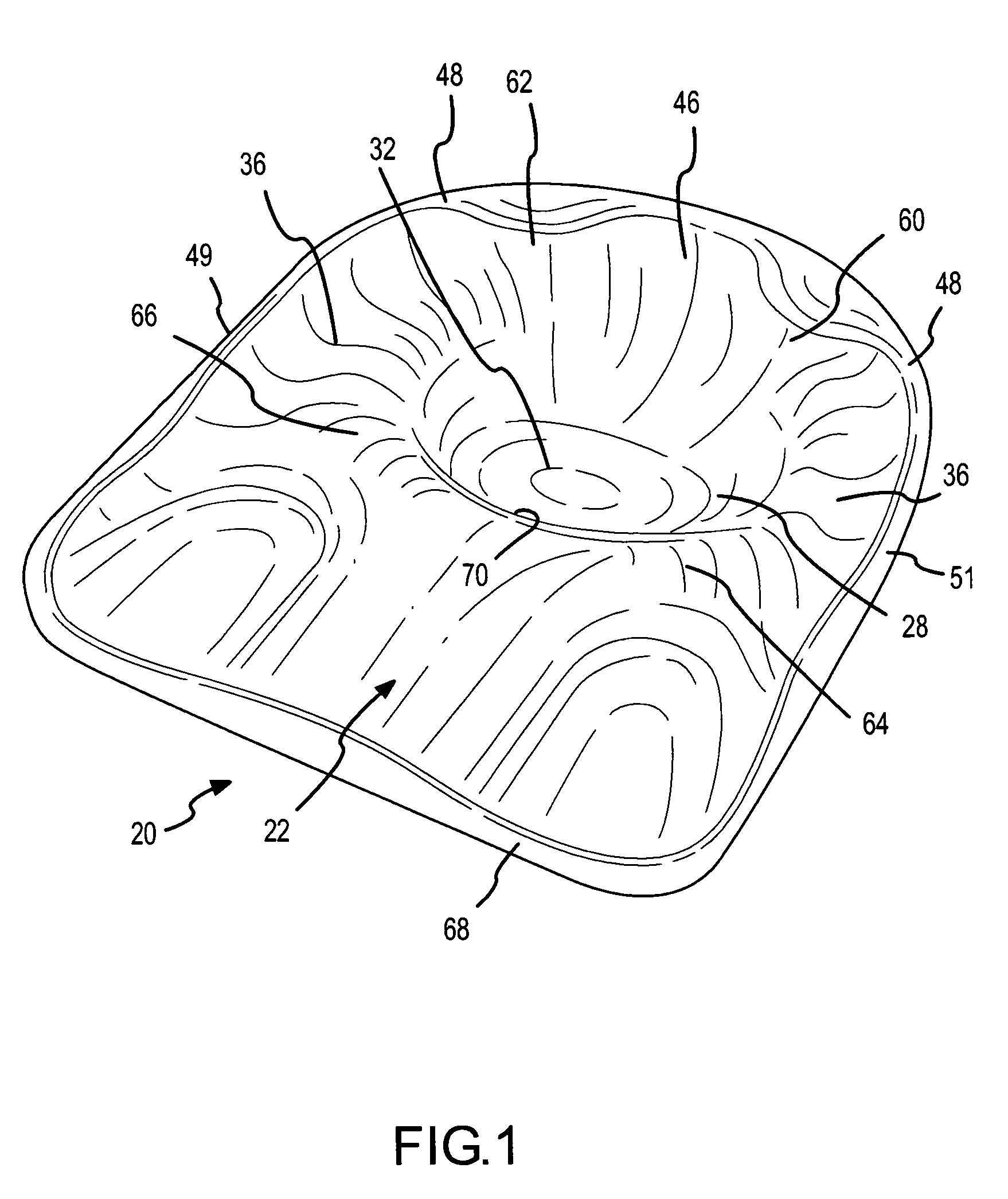
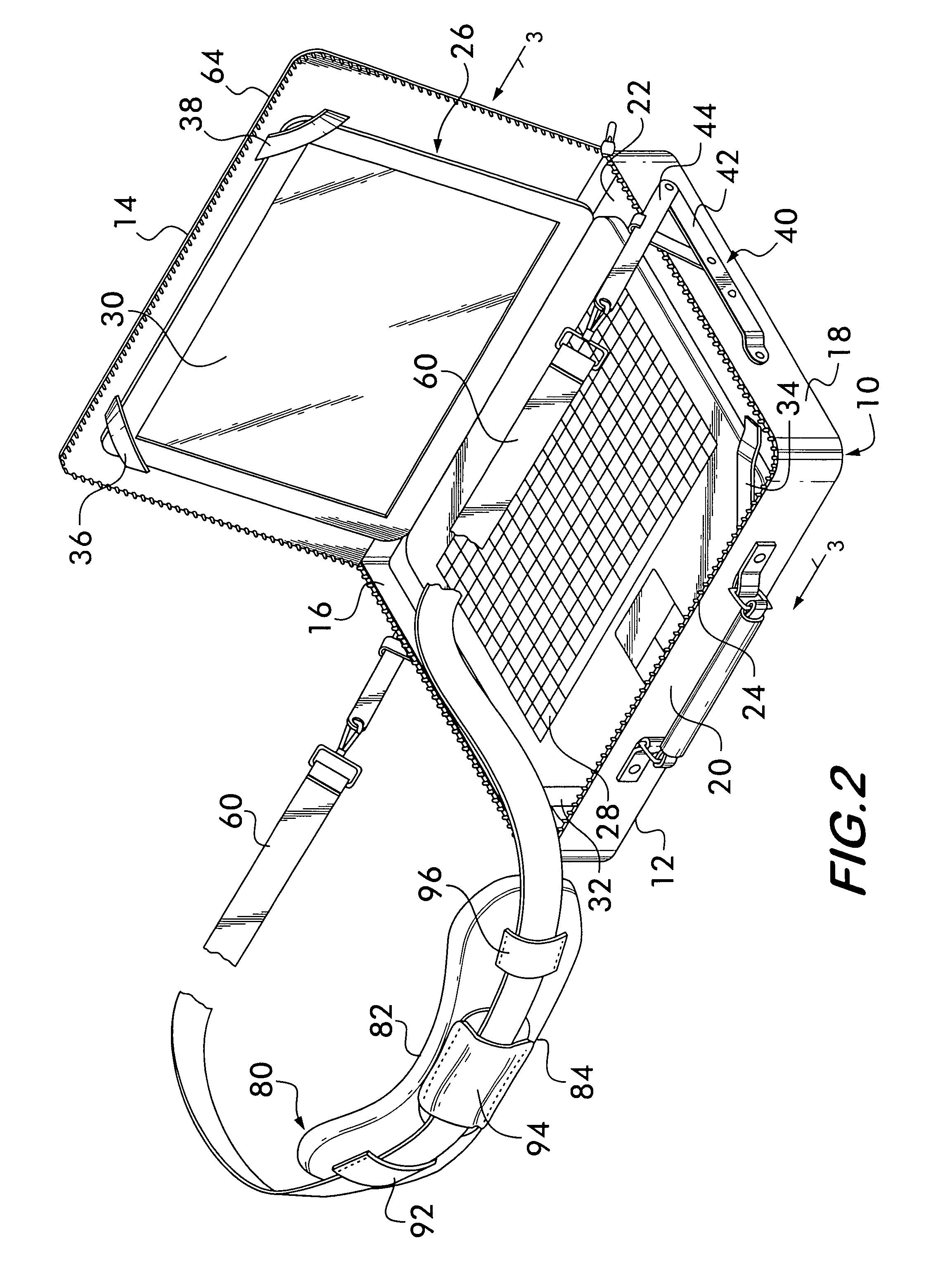
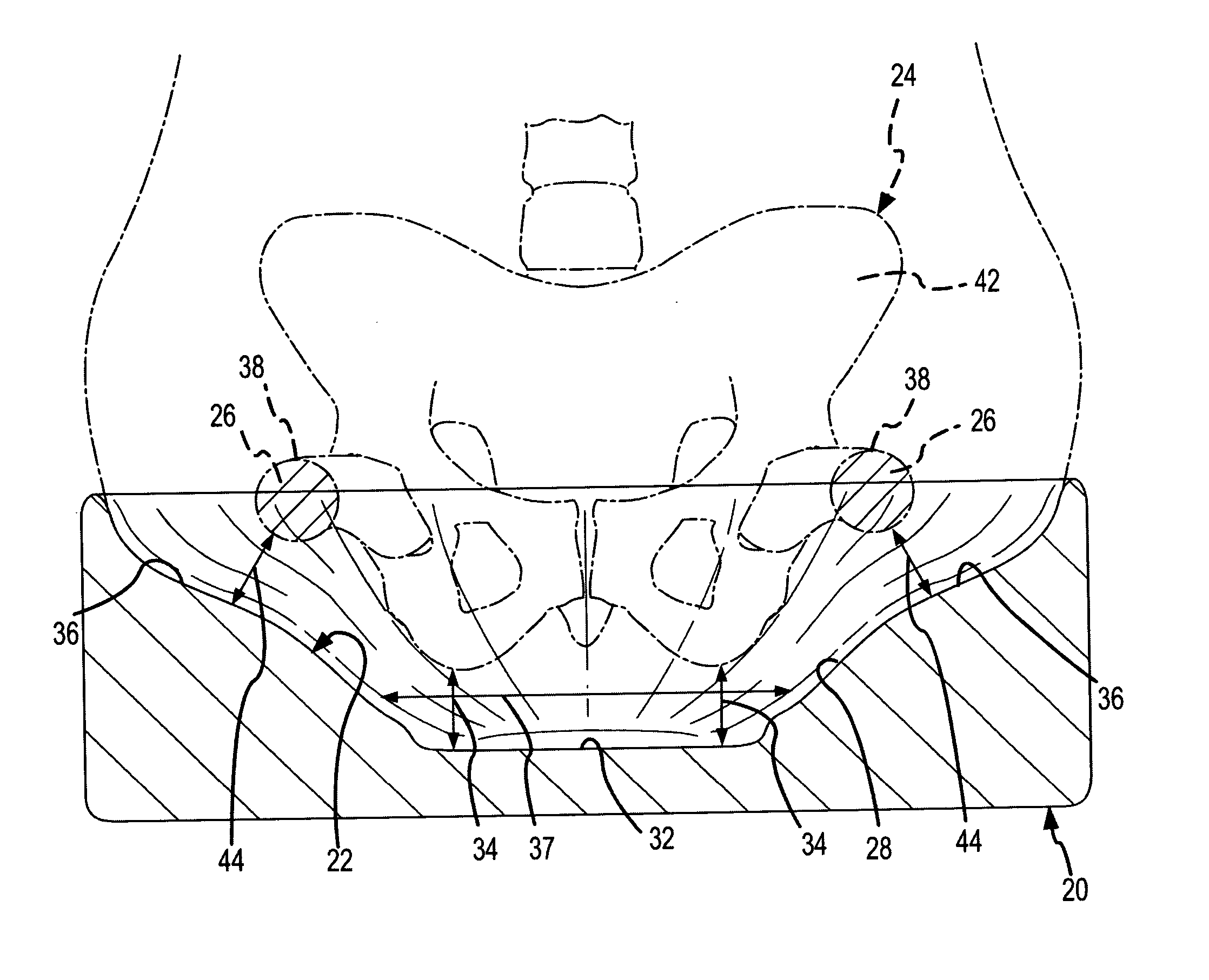
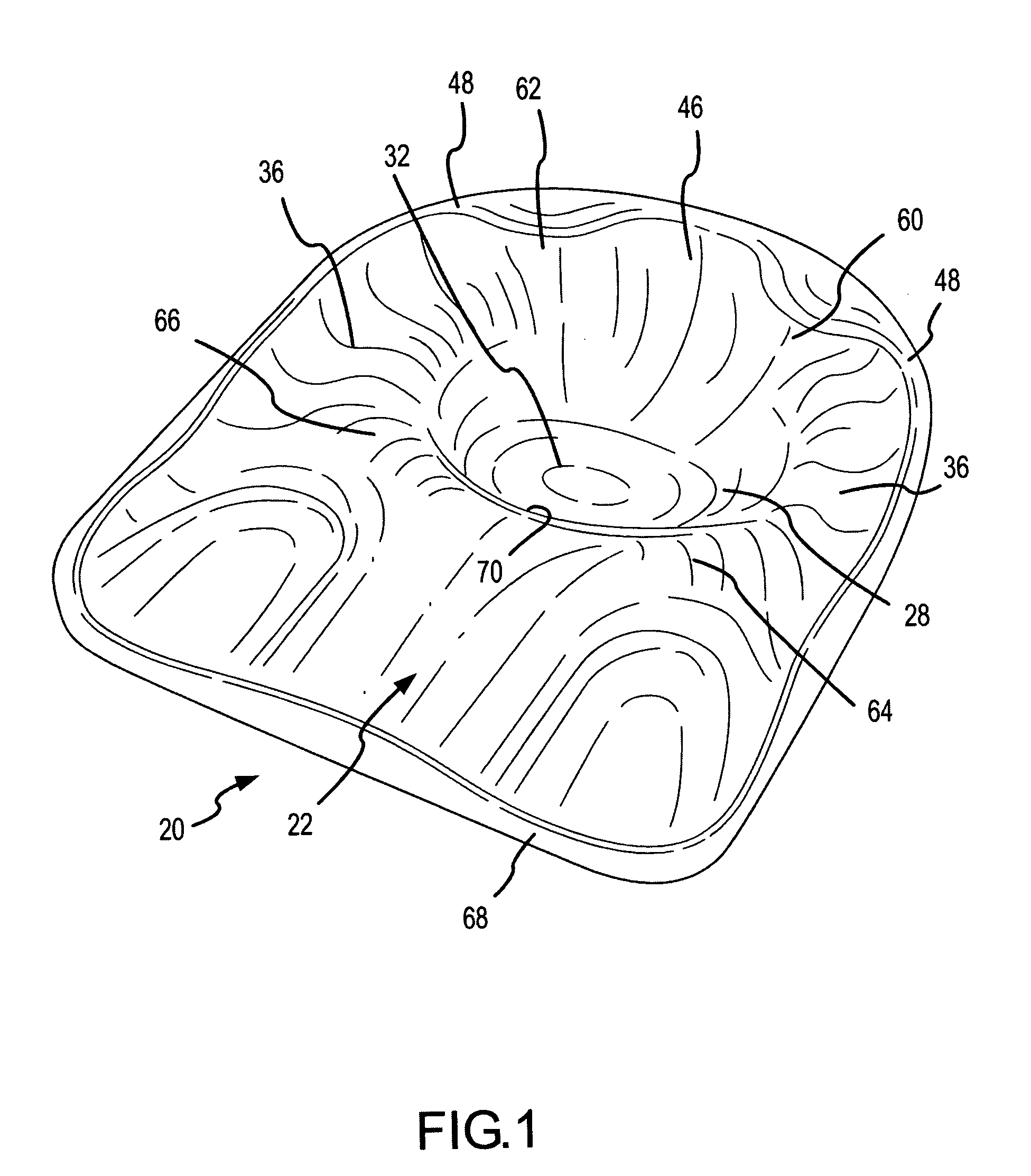
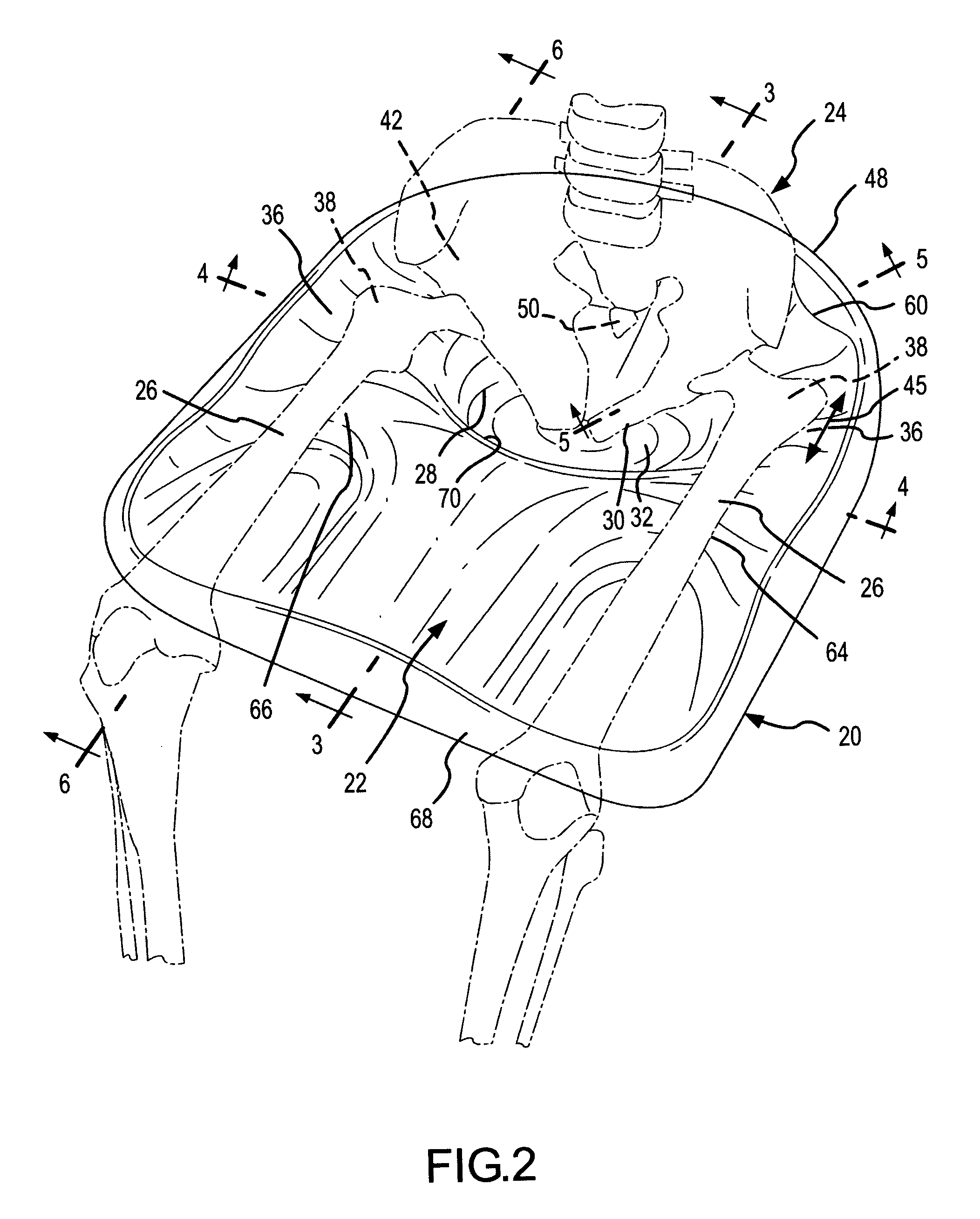
Contoured seat cushion and method for offloading pressure from skeletal bone prominences and encouraging proper postural alignment
InactiveUS7216388B2Reduce riskIncreased riskSofasWheelchairs/patient conveyanceSkin breakdownButtocks
A support contour of a cushion, such as a wheelchair cushion, defines relief areas at locations adjacent to skin covering the ischial tuberosities, the greater trochanters and the coccyx and sacrum of a person sitting on the support contour. Support areas of the support contour transfer force into the pelvic area adjacent to skin covering tissue masses on opposite lateral sides of the posterior buttocks and beneath the proximal thighs of the person. Greater clearance is also provided in the perineal area. Risks of pressure ulcers from pressure and shear forces on bony prominences is reduced while providing support at the broader areas without bony prominences in such a manner to encourage postural alignment. The risks of skin breakdown perineal are diminished.
Owner:ASPEN SEATING
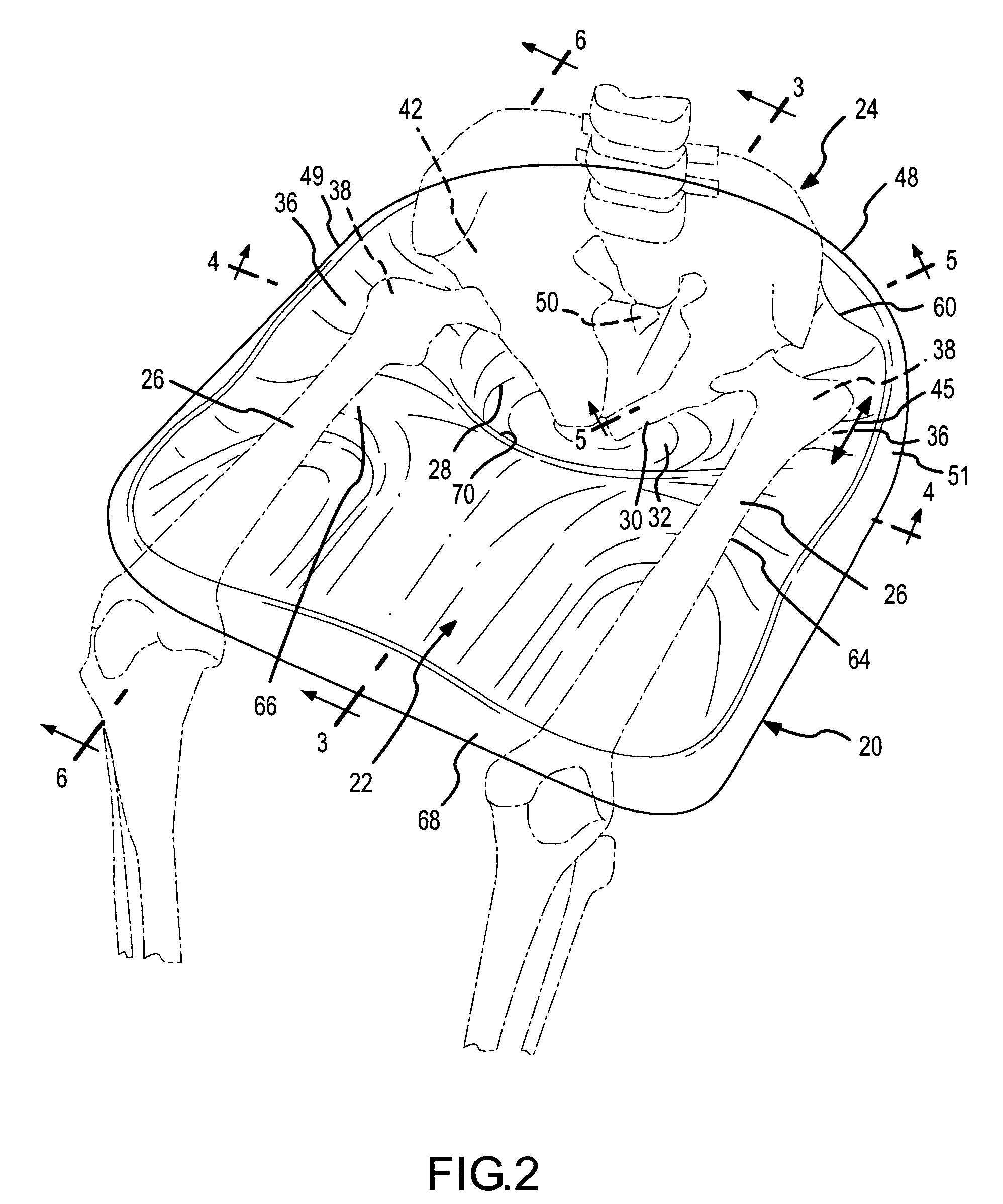
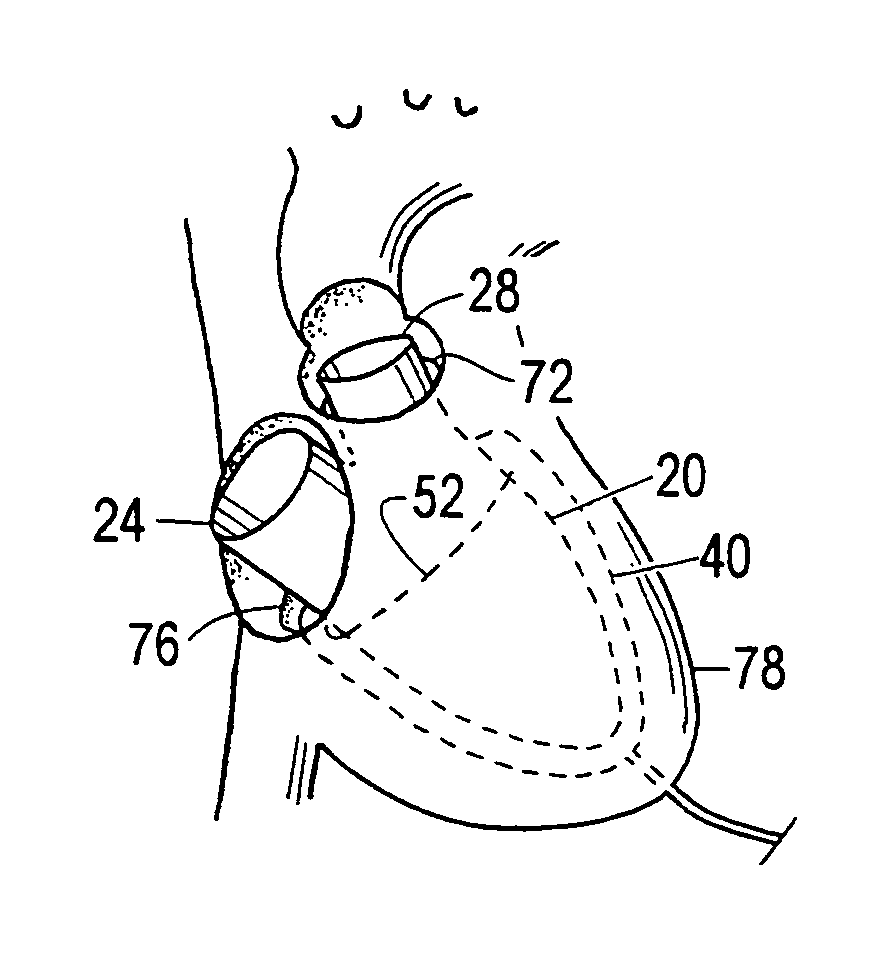
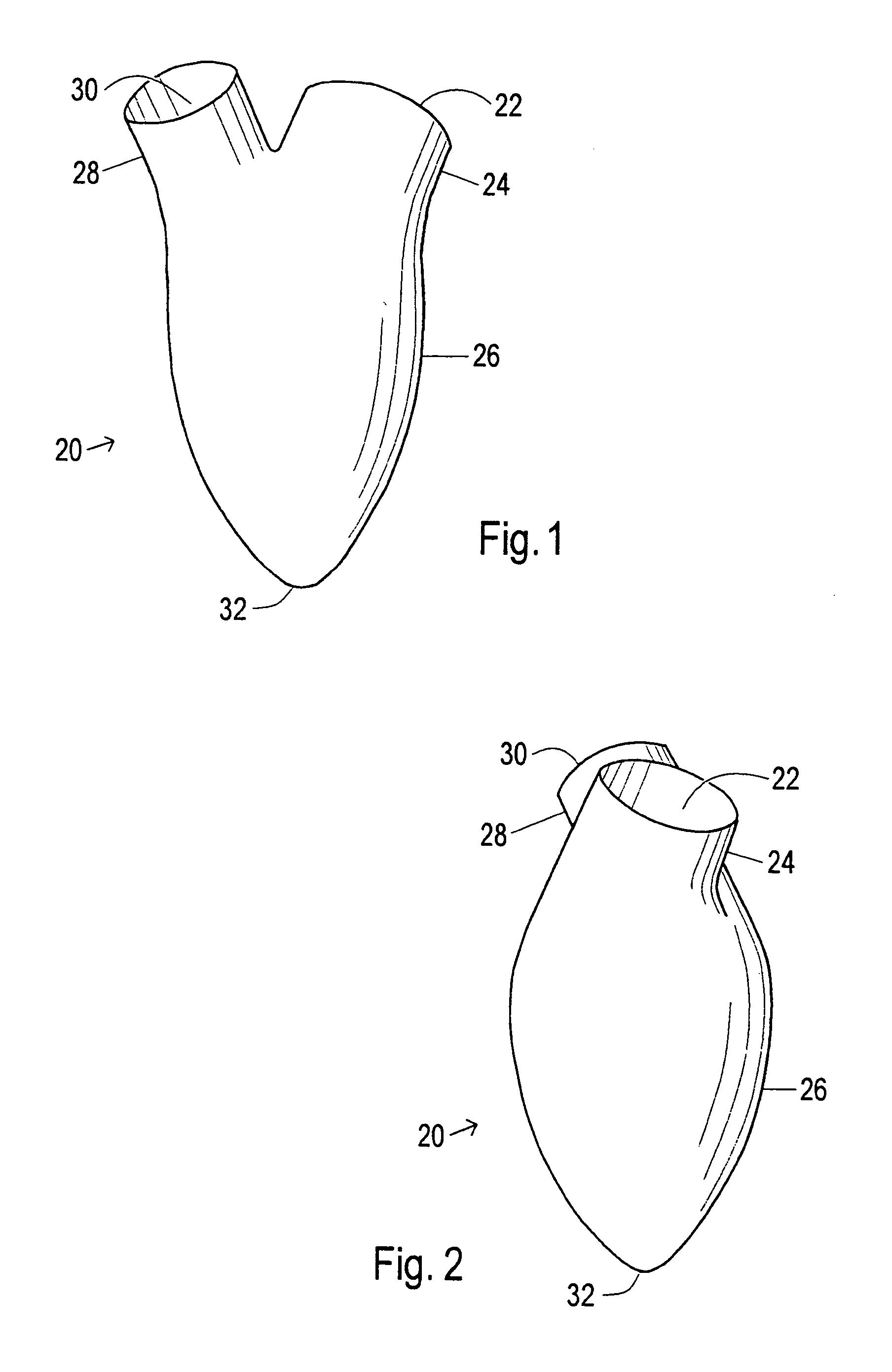
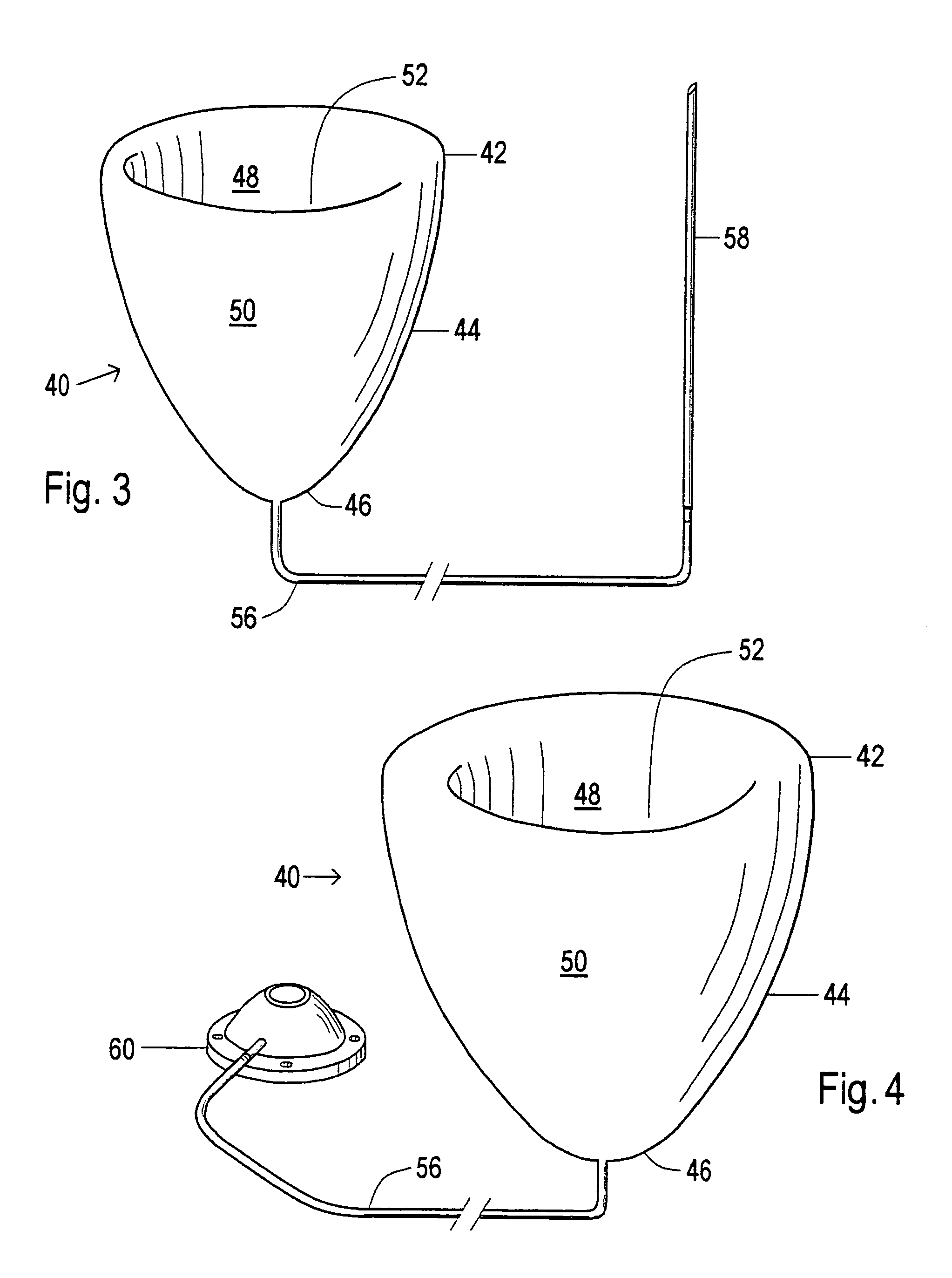
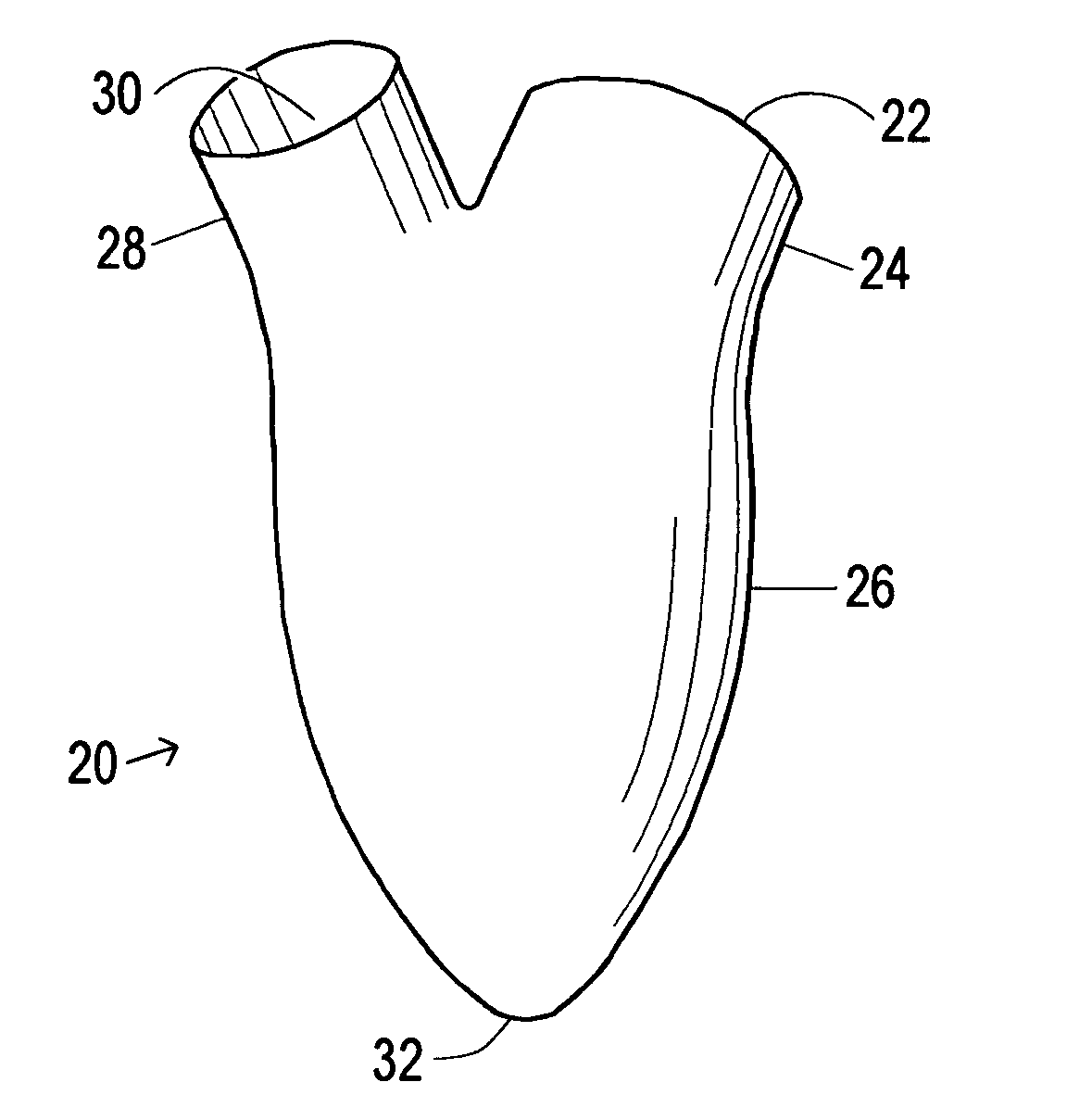
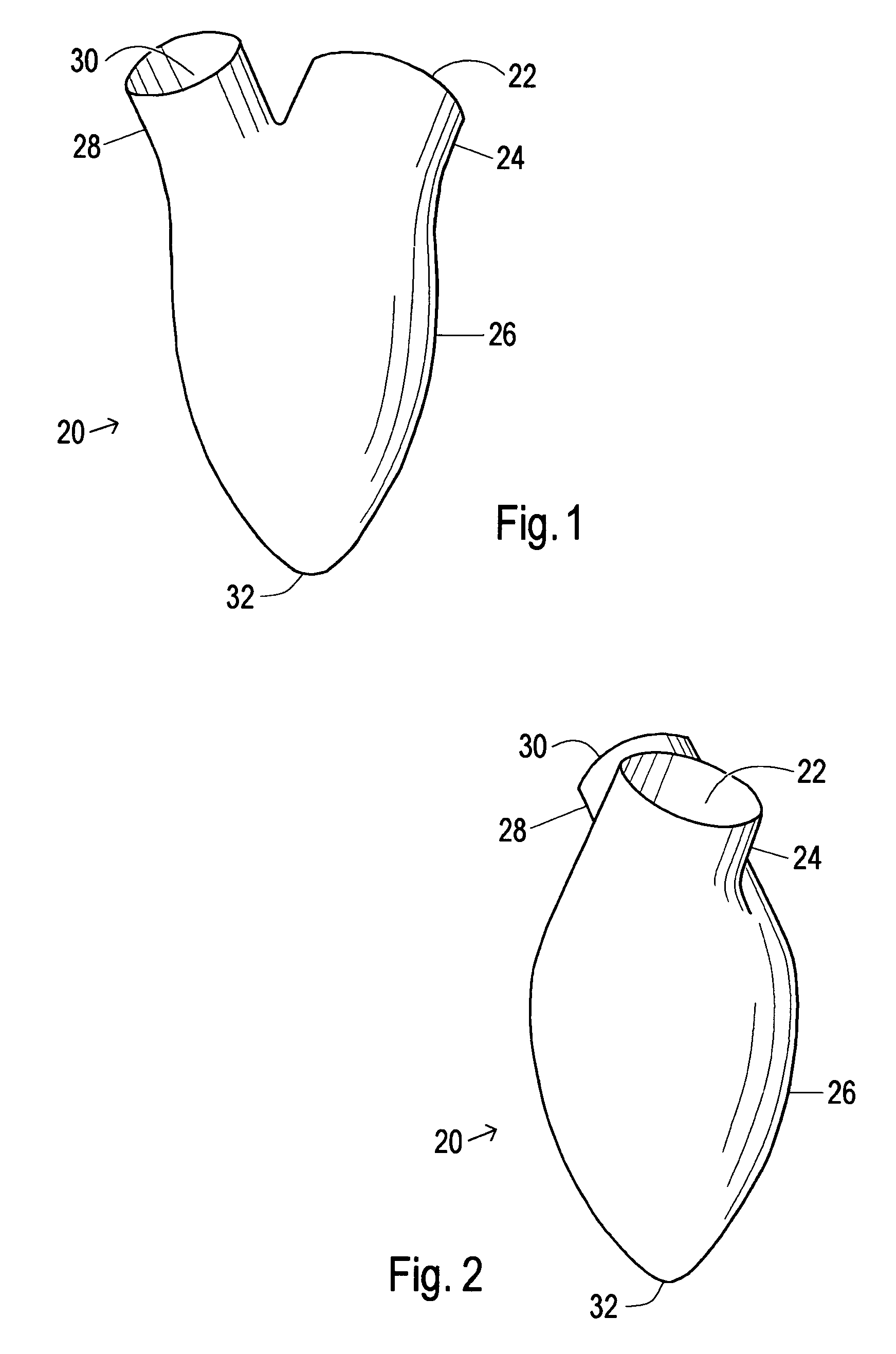
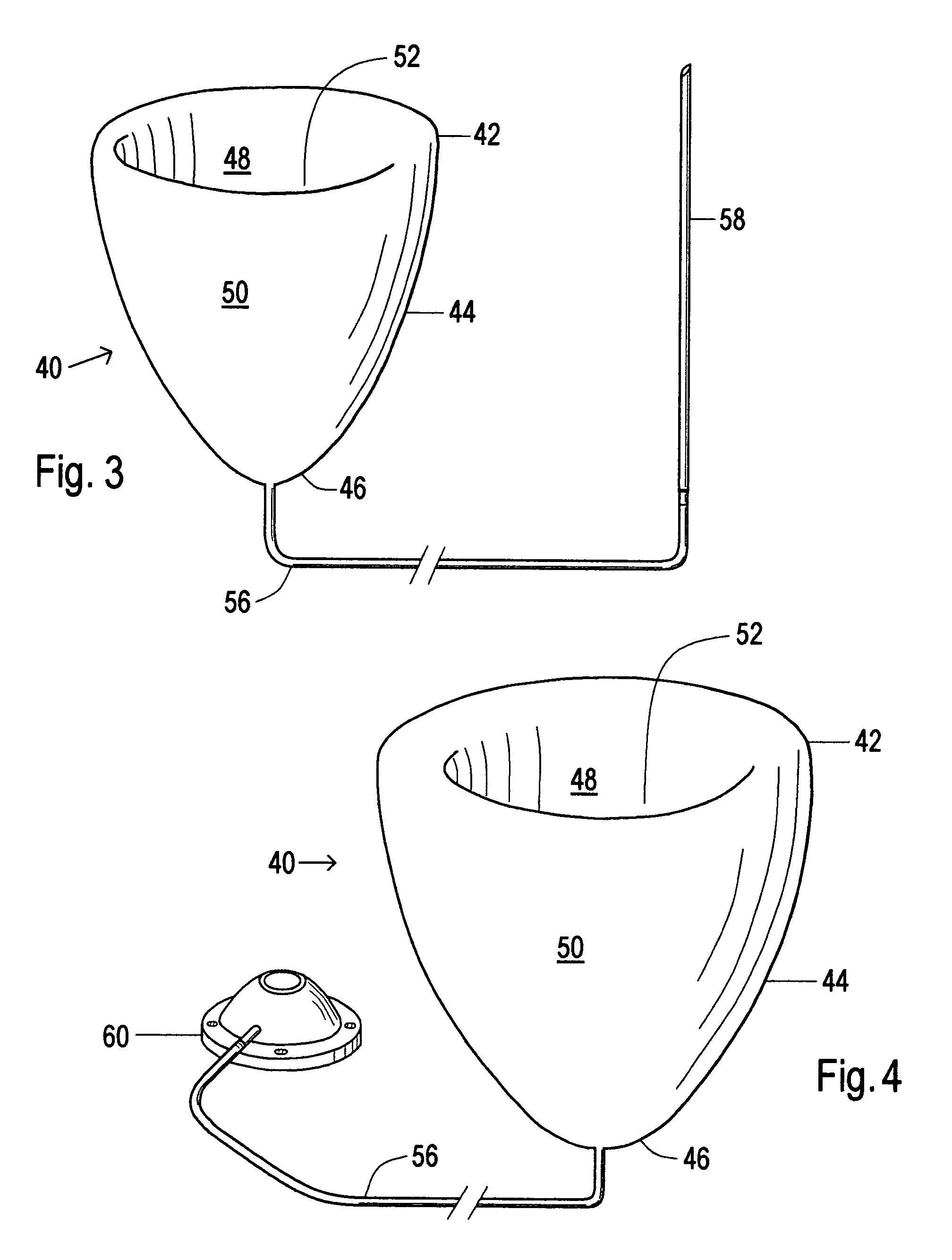
Device and method to control volume of a ventricle
ActiveUS7530998B1Small sizePrevent further enlargement of a diseased heartHeart valvesHeart stimulatorsCardiac cycleReverse remodeling
A device used to treat heart disease by decreasing the size of a diseased heart, or to prevent further enlargement of a diseased heart. The device works by limiting the volume of blood entering the heart during each cardiac cycle. The device partitions blood within the heart, and protects the heart from excessive volume and pressure of blood. The device is placed within the interior of the heart, particularly within a ventricular cavity. The device is a hollow sac, with two openings, which simulates the shape and size of the interior lining of a ventricle of a normal heart. It allows the ventricle to fill through one opening juxtaposed to the annulus of the inflow valve to a predetermined, normal volume, and limits filling of the heart beyond that volume. It then allows blood to be easily ejected through the second opening through the outflow valve. By limiting the amount of blood entering the ventricle, the ventricle is not subjected to the harmful effect of excessive volume and pressure of blood during diastole, the period of the cardiac cycle when the heart is at rest. This allows the heart to decrease in size, or to reverse remodel, and to recover lost function. In some applications, a second device may be simultaneously placed inside the heart to take up excessive space between the heart and the primary device.
Owner:STARKEY THOMAS DAVID
Device and method to limit filling of the heart
ActiveUS7341584B1Small sizeLimiting volume of bloodHeart valvesSurgical instrument detailsCardiac cycleReverse remodeling
A device used to treat heart disease by decreasing the size of a diseased heart, or to prevent further enlargement of a diseased heart. The device works by limiting the volume of blood entering the heart during each cardiac cycle. The device partitions blood within the heart, and protects the heart from excessive volume and pressure of blood. The device is placed within the interior of the heart, particularly within a ventricular cavity. The device is a hollow sac, with two openings, which simulates the shape and size of the interior lining of a ventricle of a normal heart. It allows the ventricle to fill through one opening juxtaposed to the annulus of the inflow valve to a predetermined, normal volume, and limits filling of the heart beyond that volume. It then allows blood to be easily ejected through the second opening through the outflow valve. By limiting the amount of blood entering the ventricle, the ventricle is not subjected to the harmful effect of excessive volume and pressure of blood during diastole, the period of the cardiac cycle when the heart is at rest. This allows the heart to decrease in size, or to reverse remodel, and to recover lost function. In some applications, a second device may be simultaneously placed inside the heart to take up excessive space between the heart and the primary device.
Owner:STARKEY THOMAS DAVID
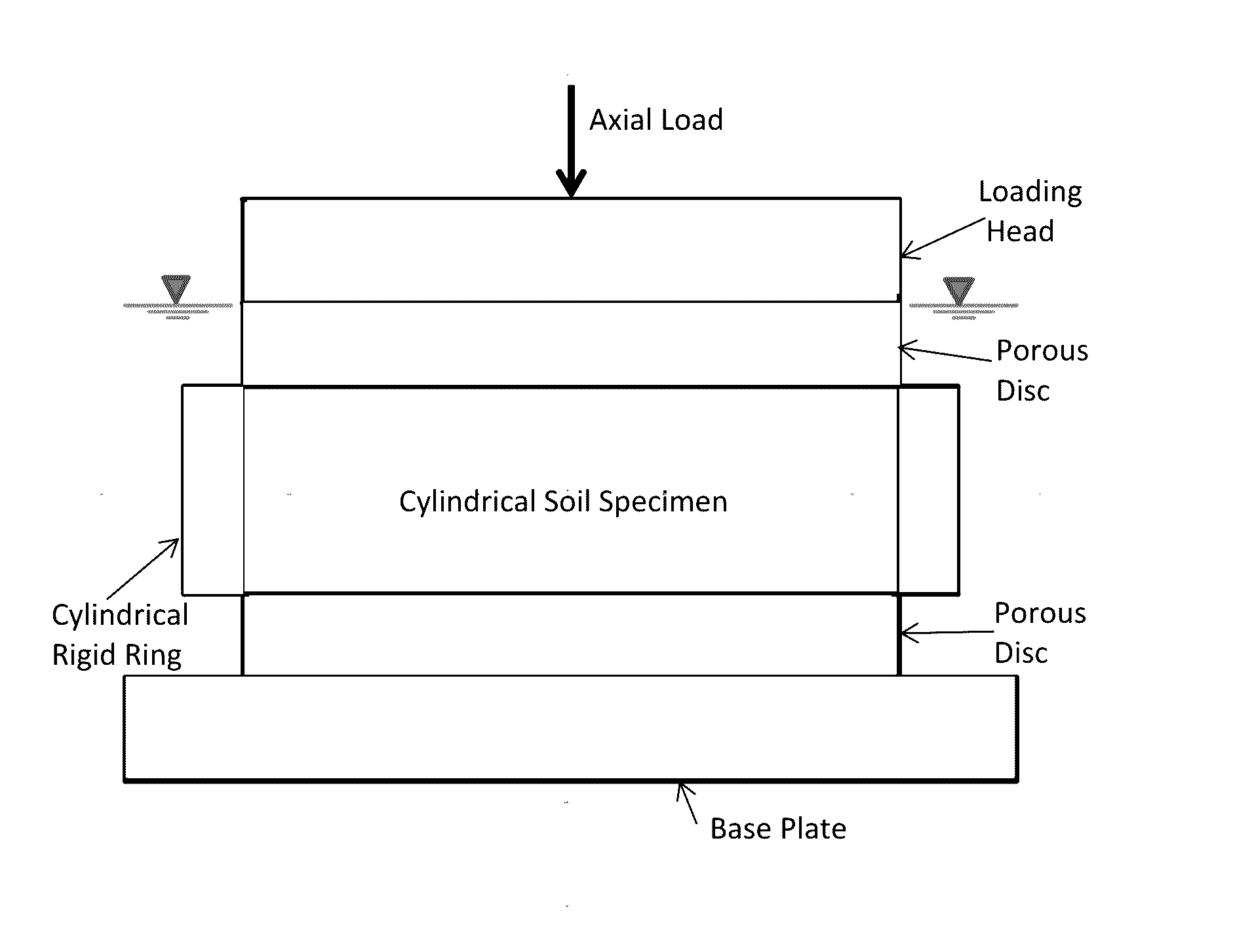
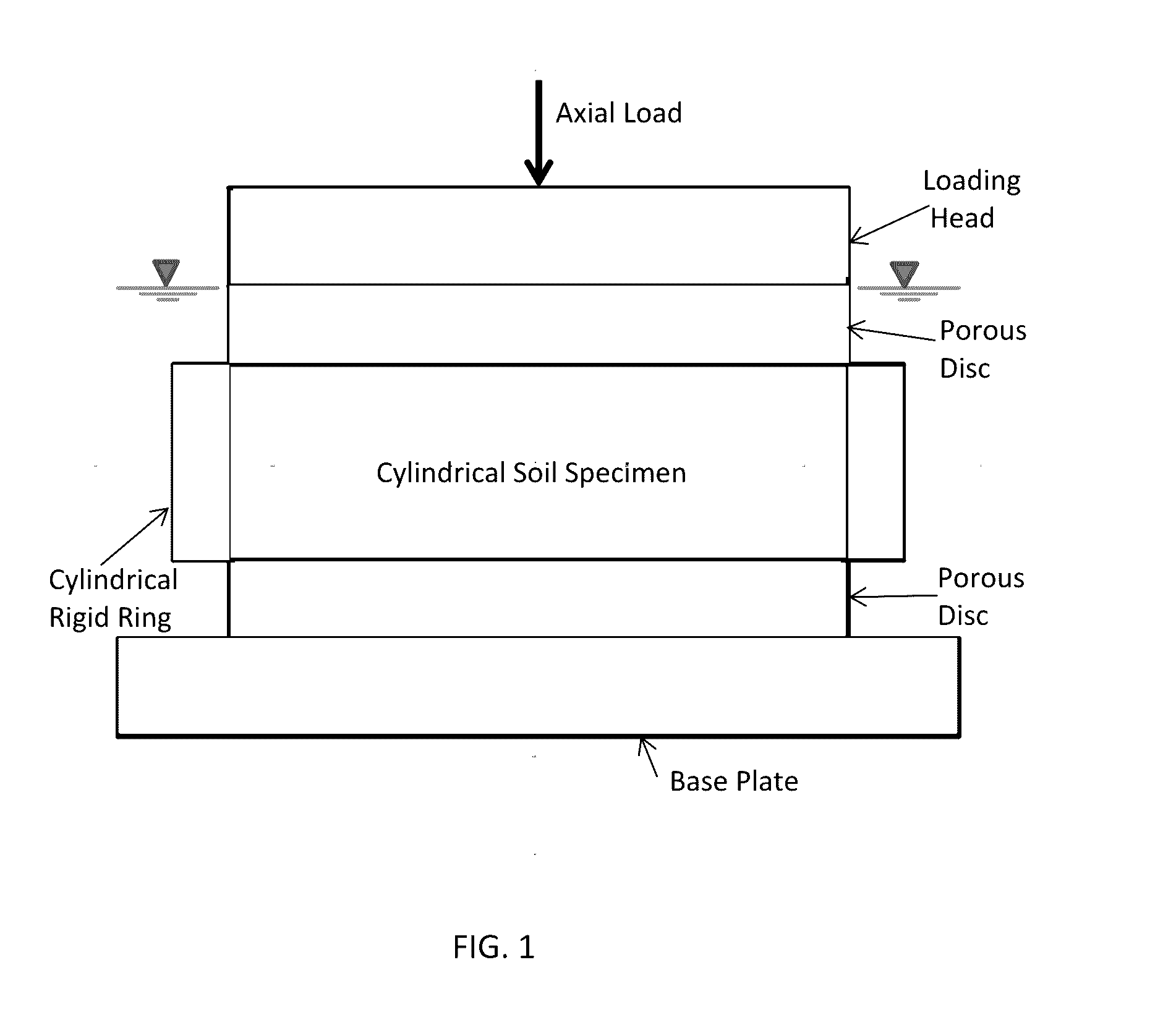
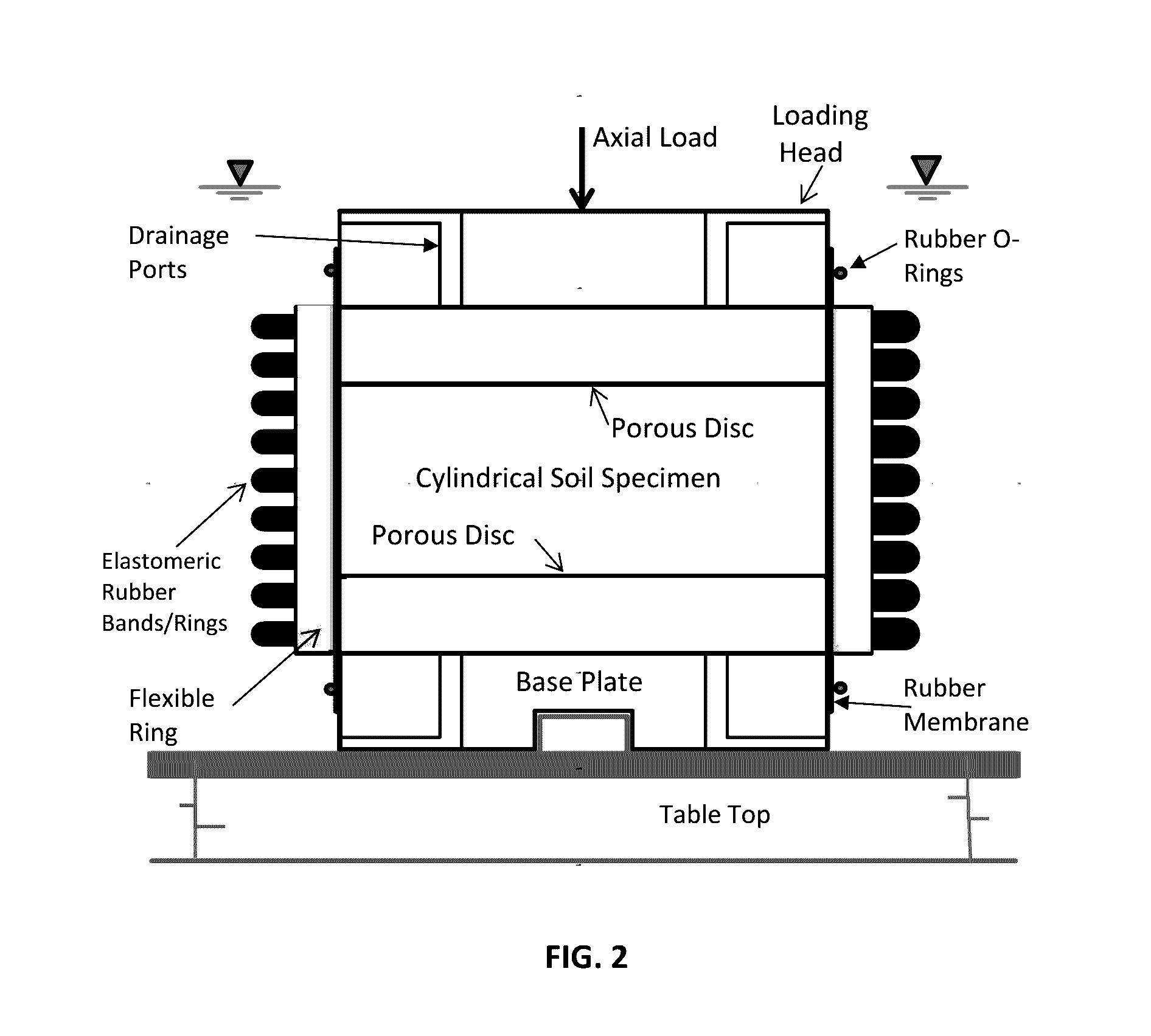
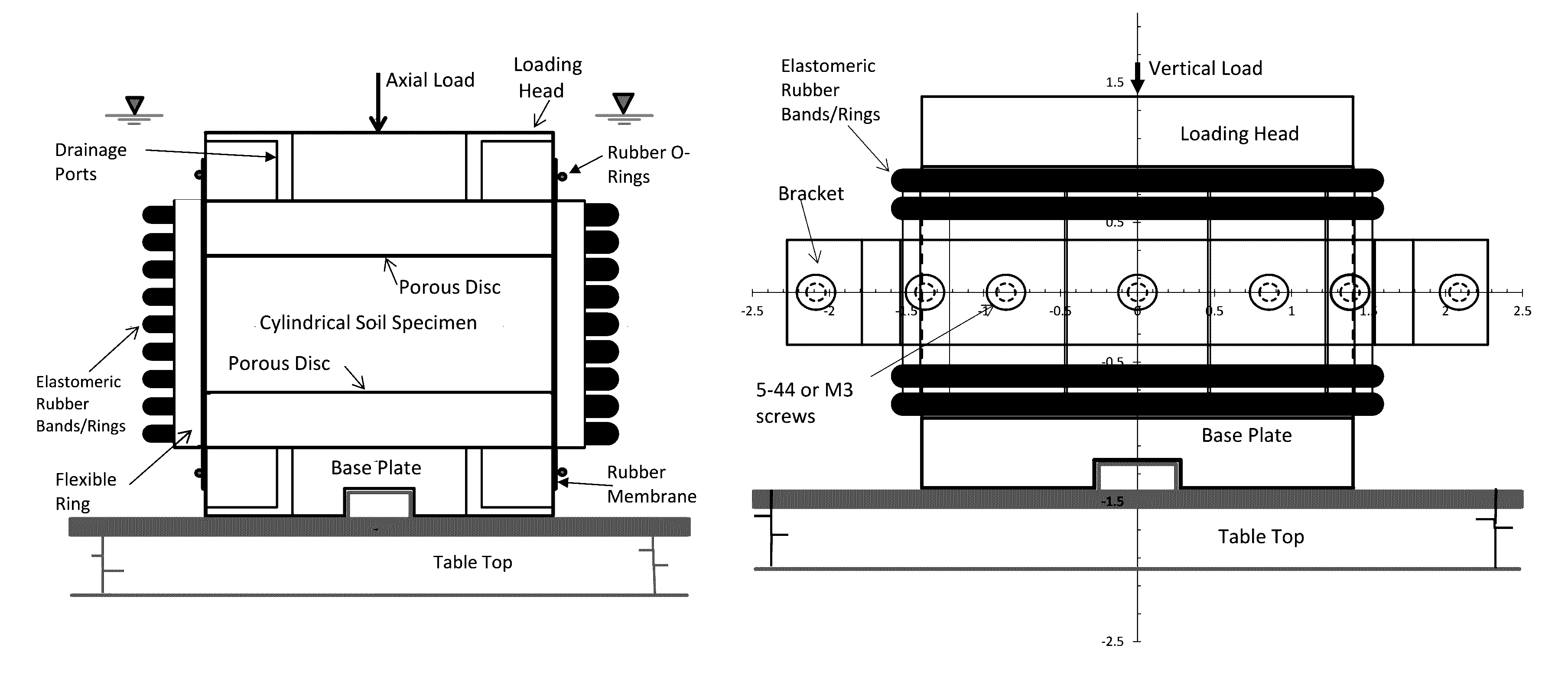
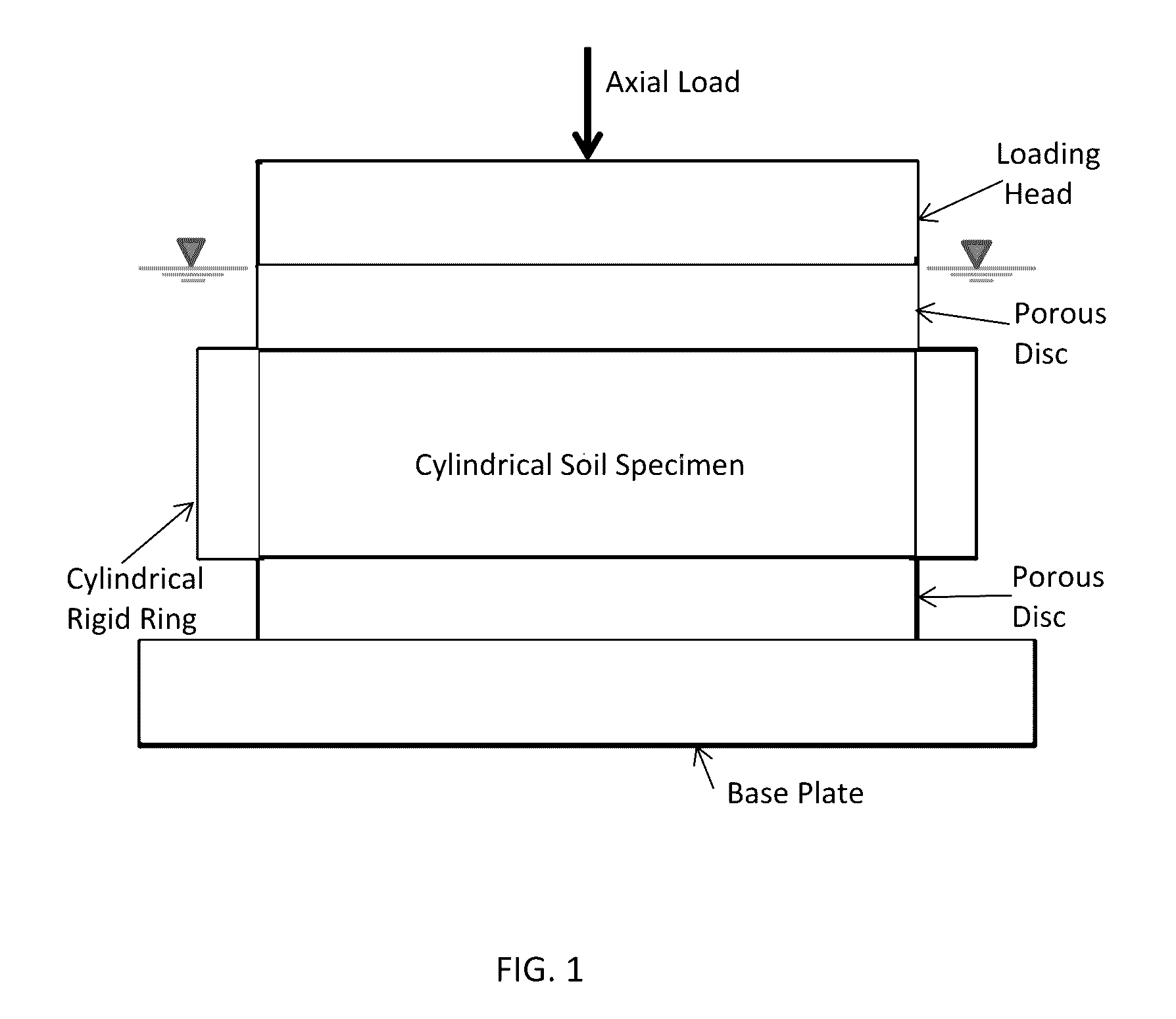
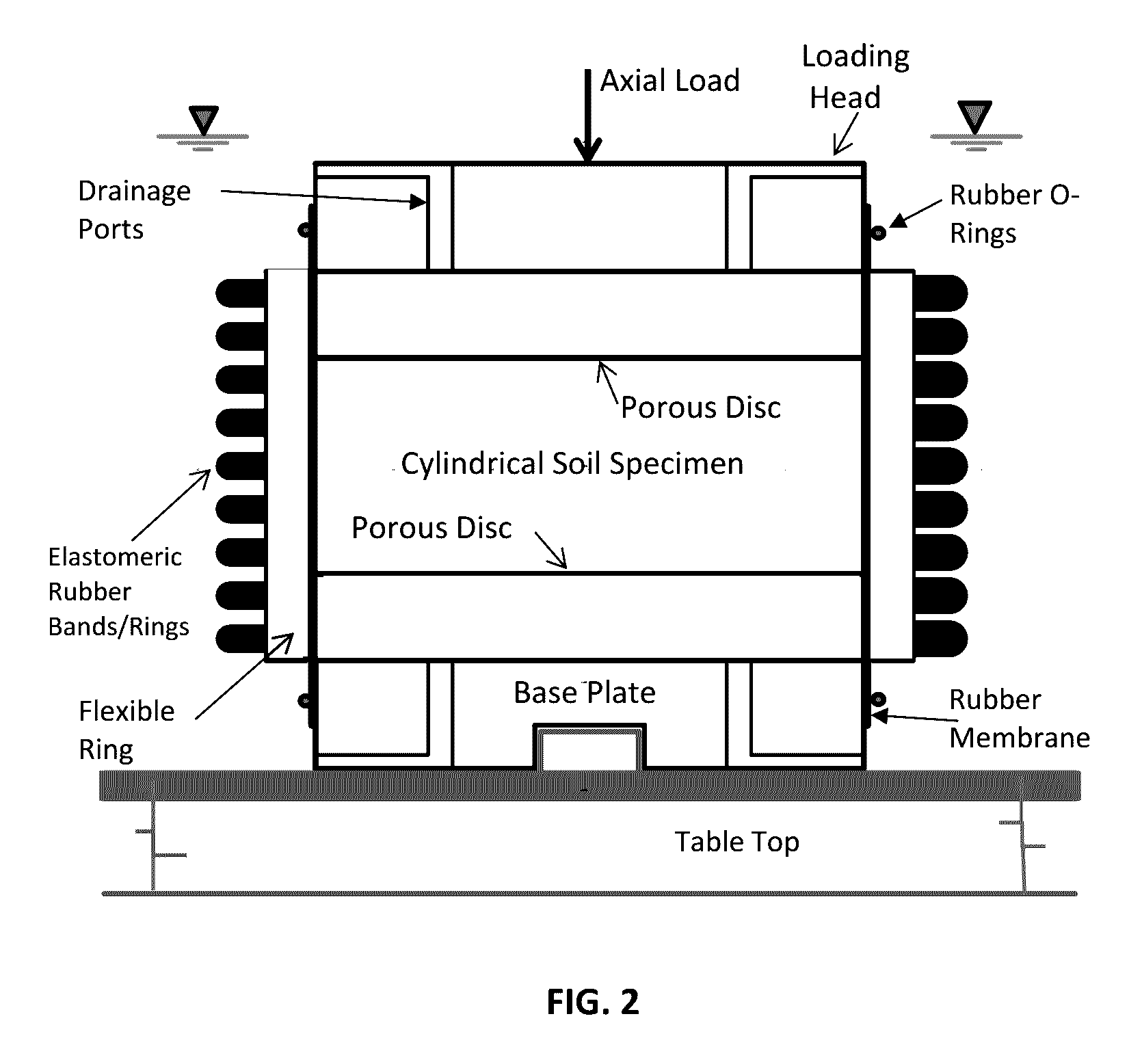
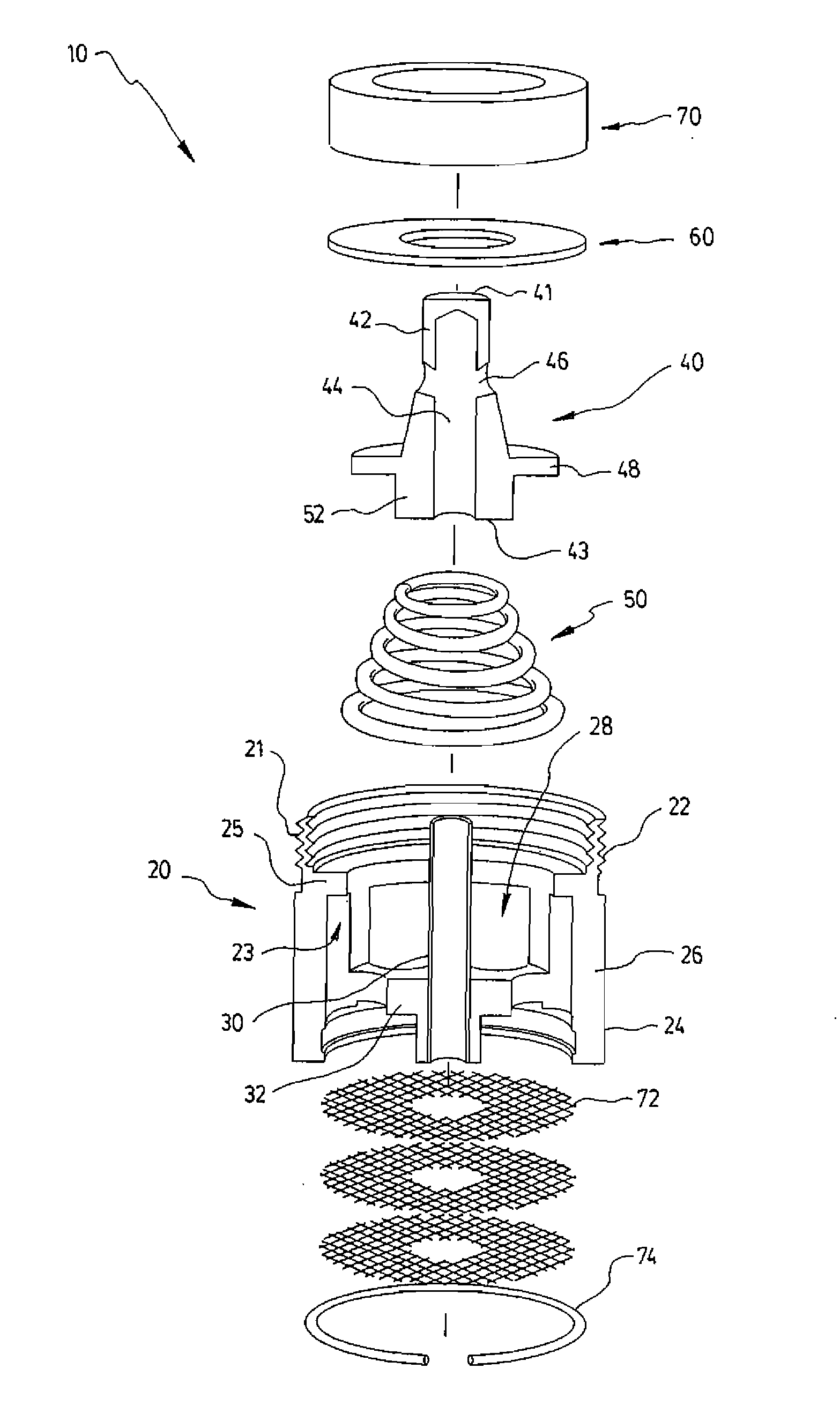
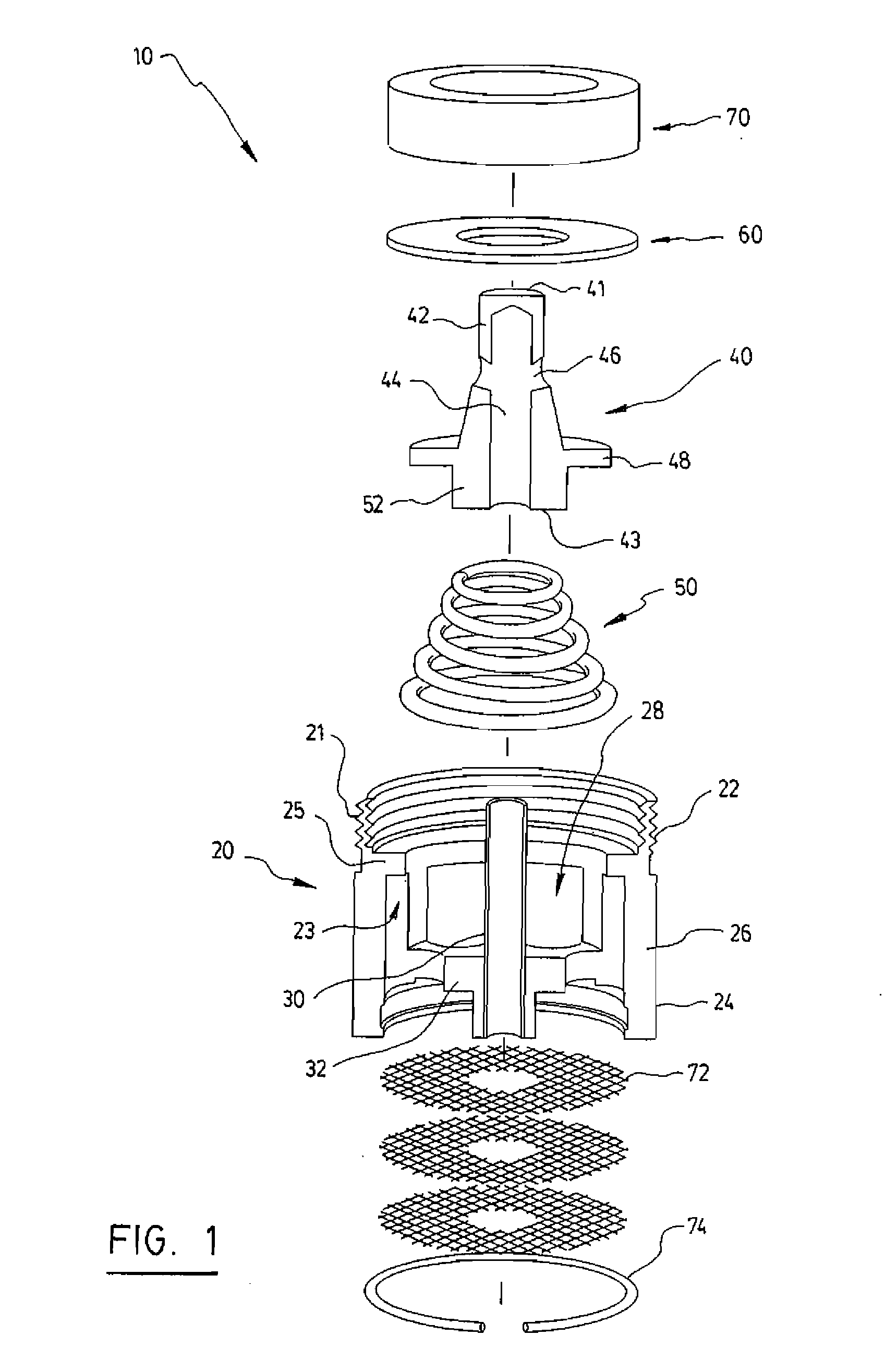
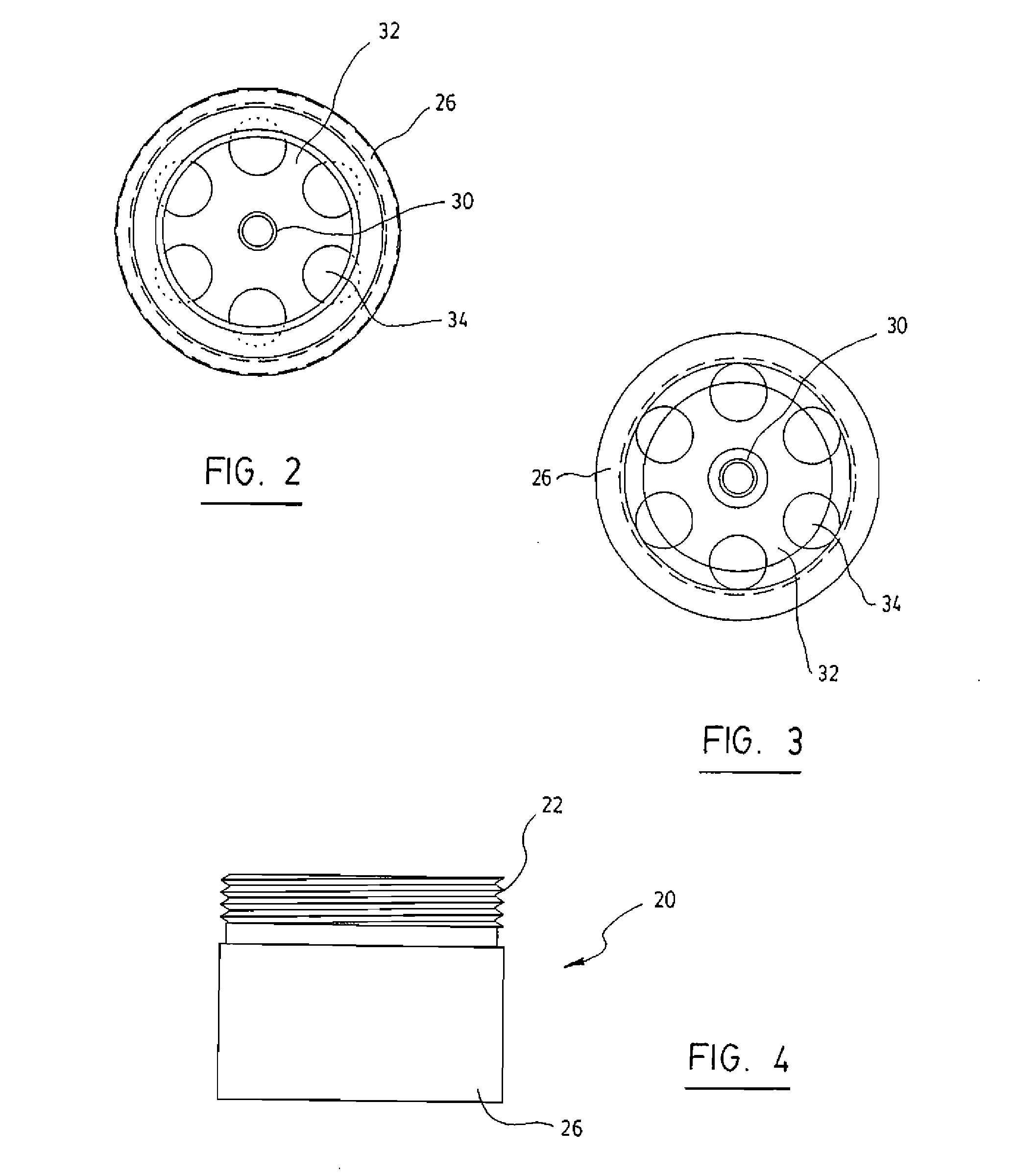
Test Device For Determining Three-Dimensional Consolidation Properties Of Soils
ActiveUS20160356685A1DissipationIncrease lateral resistanceEarth material testingMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSoil scienceRubber membrane
Standard test methods using a fixed ring for determining one-dimensional consolidation properties of soils represent a subsurface condition where settlement and dissipation of excess pore pressure is possible only in vertical direction. This subsurface condition never occurs, as settlements and dissipation of excess pore pressures always occur in horizontal and vertical directions. Dr. Ramesh Gupta has invented a test device for determining three-dimensional consolidation properties of soils, using a flexible ring permitting displacements and dissipation of excess pore pressures in both horizontal and vertical directions, and affording determination of coefficients of consolidation in horizontal and vertical directions including three-dimensional coefficient of consolidation, and modulus of elasticity. The test device consists of a flexible ring consisting of filter fabric around the soil specimen, rubber membrane around the filter, circular segmented metal plates around the membrane and rubber bands or rings around the plates. Both incremental or triaxial type loading can be used with this device.
Owner:GUPTA RAMESH CHANDRA
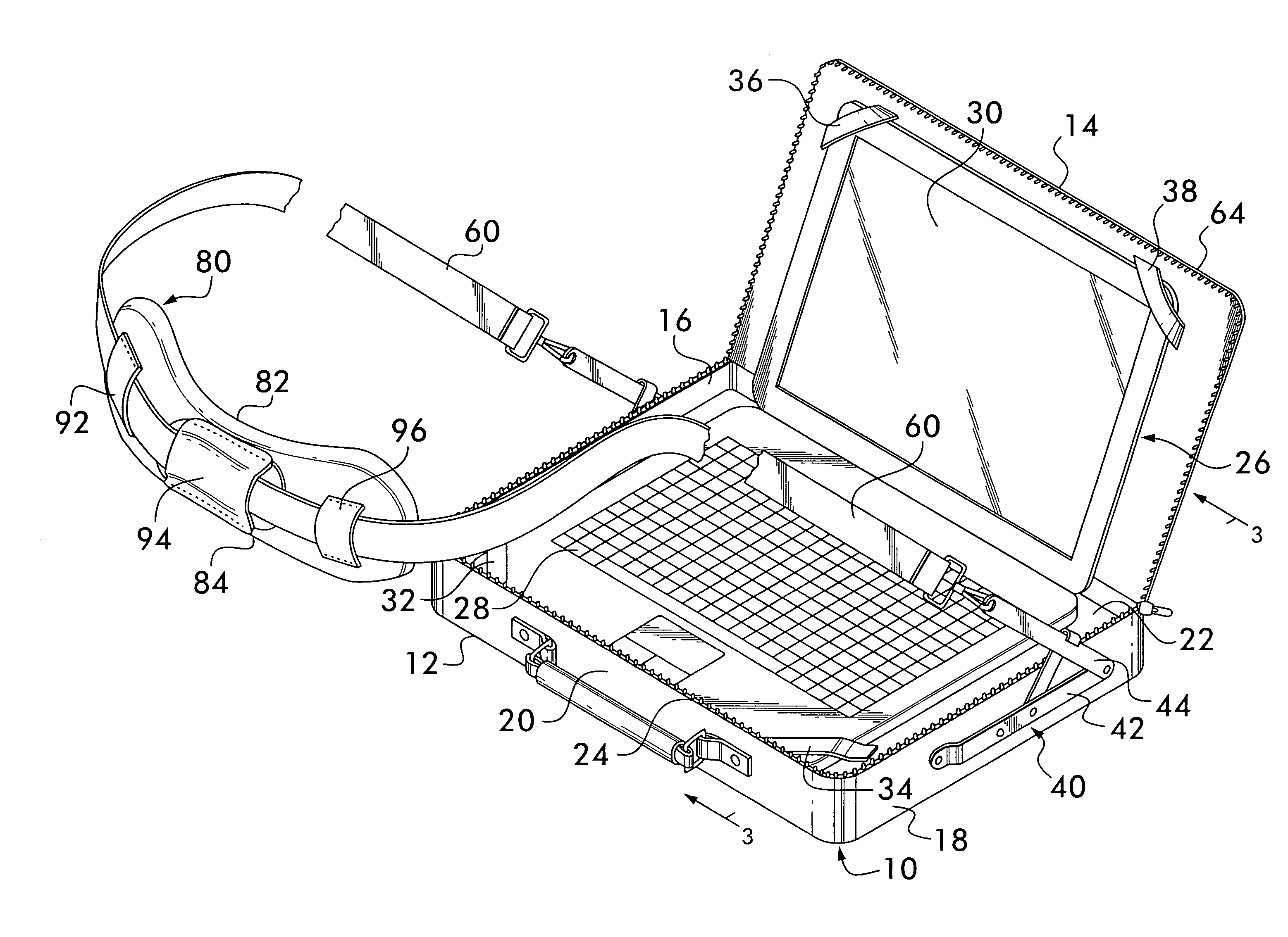
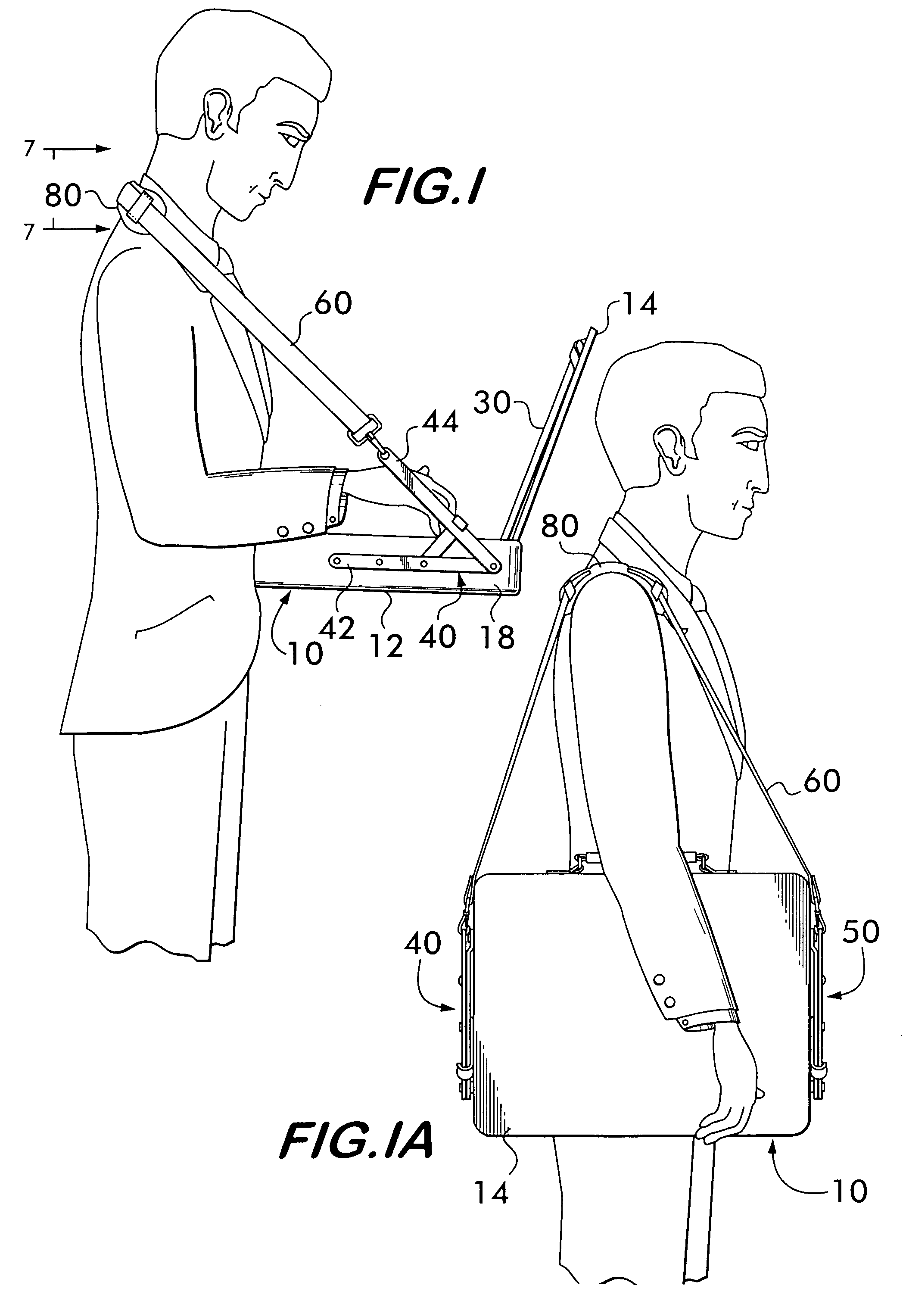
Laptop computer carrying case that transforms into a desk top
A laptop computer carrying case transforms into a desktop for use of a laptop or similar electronic device having a keyboard and a hingeably openable display. The laptop key board is held by bands in the lower portion of the case and the display is held in the top section of the case. Hinge structures are provided on the left and right sidewalls of the bottom section of the case. When the hinge structures are pivotally angularly separated, the bottom section containing the keyboard will be substantially horizontal enabling use of the laptop in a standing or mobile position. When the laptop is not being used, the case may be closed and the hinge structures closed with the laptop being carried by the strap over the shoulder. The hinge structure is provided with structure for limiting the amount by which the arms of the hinge may be pivotally angularly separated thereby providing stability to the laptop case in the desk top position. Detent means is provided to hold the arms of the hinge structure in aligned position when the case is being used to carry the laptop.
Owner:MITCHELL KEVIN
Contoured seat cushion and method for offloading pressure from skeletal bone prominences and encouraging proper postural alignment
InactiveUS20050022305A1Firm supportReduce riskSofasWheelchairs/patient conveyanceSkin breakdownButtocks
A support contour of a cushion, such as a wheelchair cushion, defines relief areas at locations adjacent to skin covering the ischial tuberosities, the greater trochanters and the coccyx and sacrum of a person sitting on the support contour. Support areas of the support contour transfer force into the pelvic area adjacent to skin covering tissue masses on opposite lateral sides of the posterior buttocks and beneath the proximal thighs of the person. Greater clearance is also provided in the perineal area. Risks of pressure ulcers from pressure and shear forces on bony prominences is reduced while providing support at the broader areas without bony prominences in such a manner to encourage postural alignment. The risks of skin breakdown perineal are diminished.
Owner:ASPEN SEATING
Apparatus, article and method for reducing pain during skin puncturing procedures
ActiveUS20120016292A1Easily and inexpensively utilizedOvercome disadvantagesGum massageAnaesthesiaInjections sitesSingle use
An instrument, article and method are provided for minimizing pain during administration by injection of a liquid, such as, an anesthetic. The instrument has a forward end. A lightpipe mounted freely for vibration projects out of the forward end. The article, a single use tip, is composed of a tip sleeve removably mounted on the forward end of the instrument and a tip member removably mounted on the projecting lightpipe to vibrate a preselected injection site on a human or animal. The tip sleeve and tip member are covered by an elastic overmold that enables the tip member to vibrate freely with respect to the tip sleeve and light from the lightpipe to illuminate the injection site. A vibration unit mounted in the instrument is coupled to the lightpipe. The method is carried out by imparting vibrations and illumination via the lightpipe to the tip member.
Owner:BING INNOVATIONS
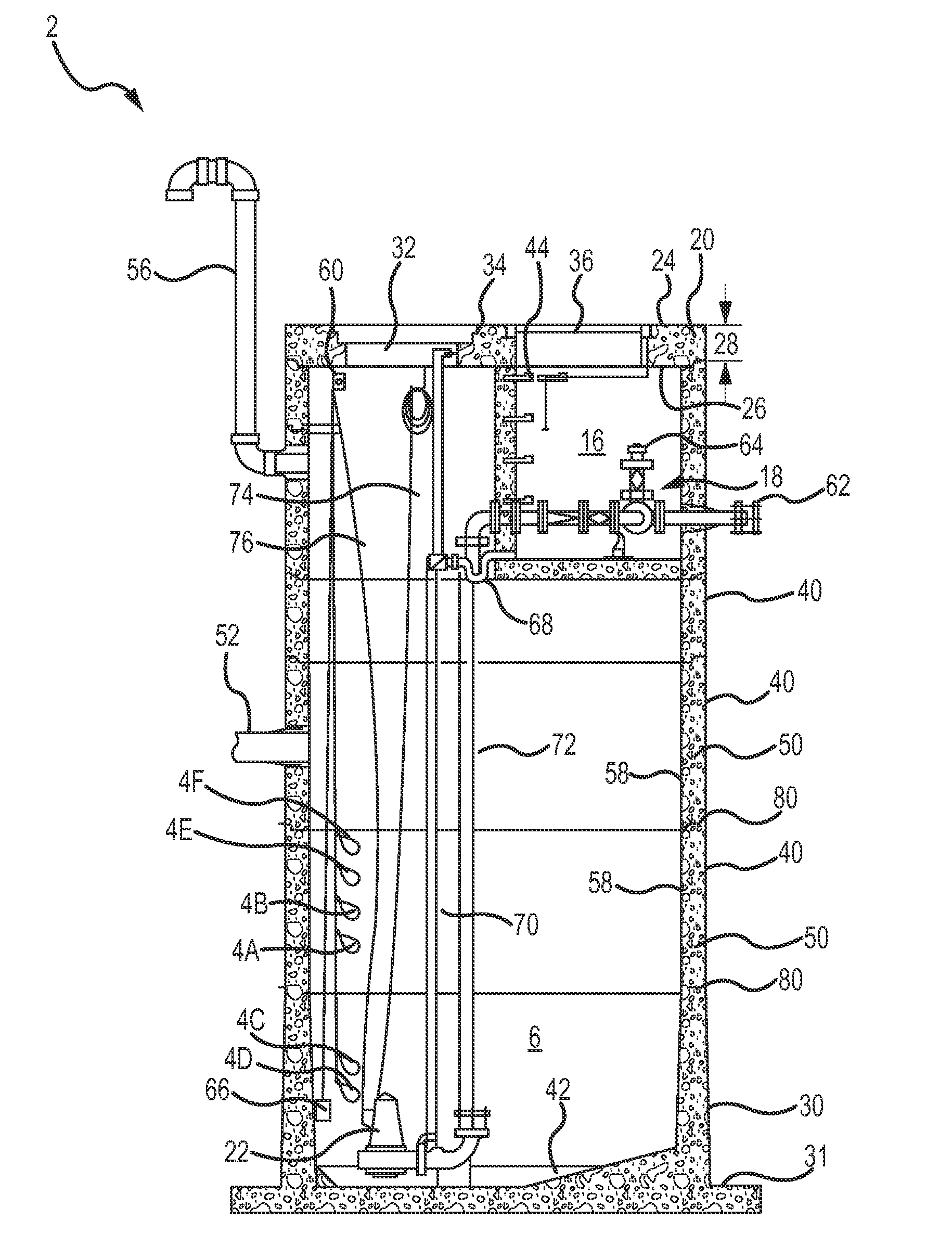
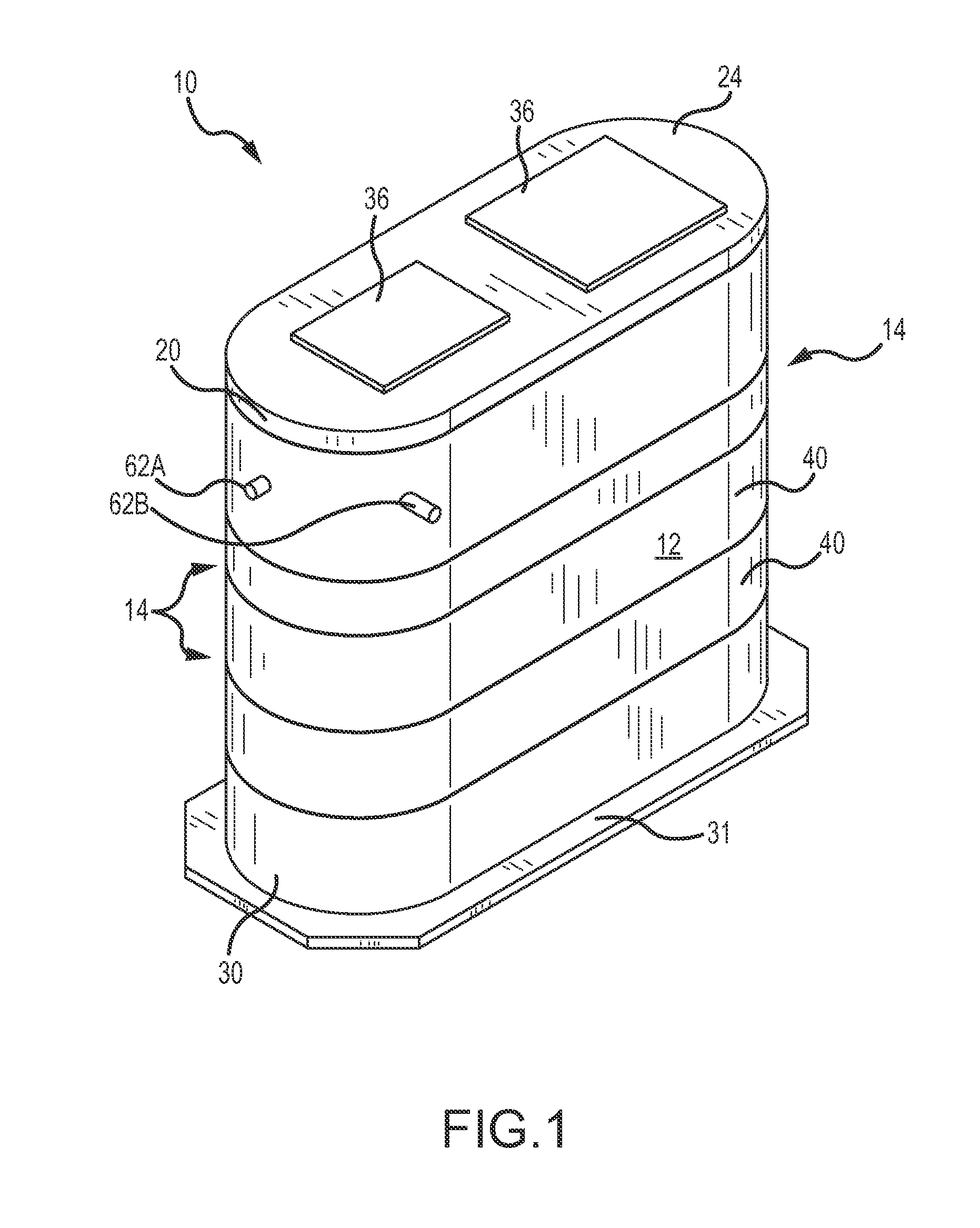
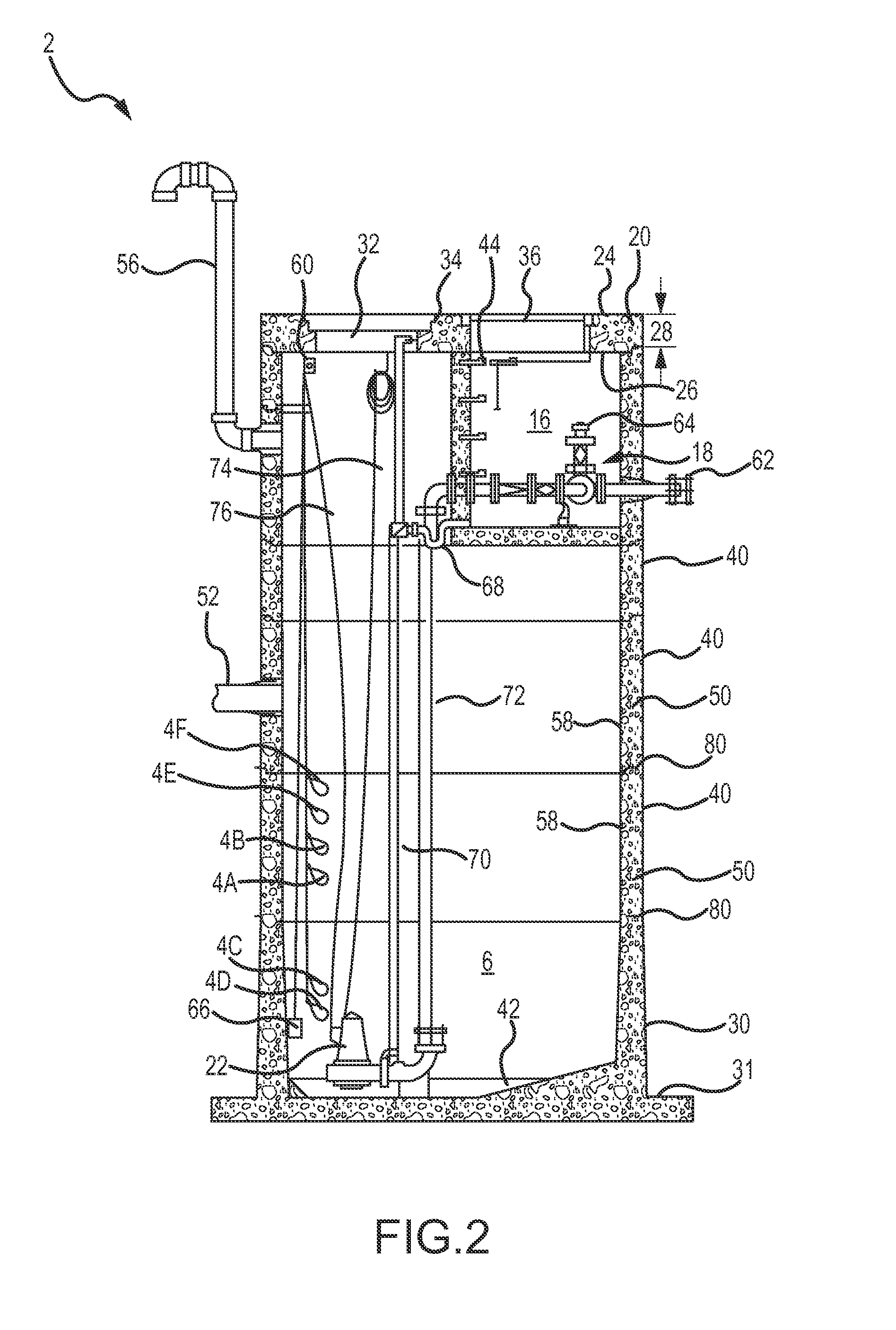
Water pumping station with an integral valve vault
ActiveUS20140326332A1Simple to fabricateEasy to installSewerage structuresPipesHigh elevationEffluent
A waste or storm water pumping station and system used to pump water from a lower elevation to a higher elevation during the process of moving or managing the water is disclosed herein. The pumping station has a wet well collection chamber with a sloped floor and an integral valve vault chamber cast within the pump station body, which results in increased storage capacity in the wet well chamber for pump station components. Additionally, the pumping station may be installed as a single unit of equal depth to eliminate differential settlement and multiple or uneven excavations.
Owner:OLDCASTLE PRECAST
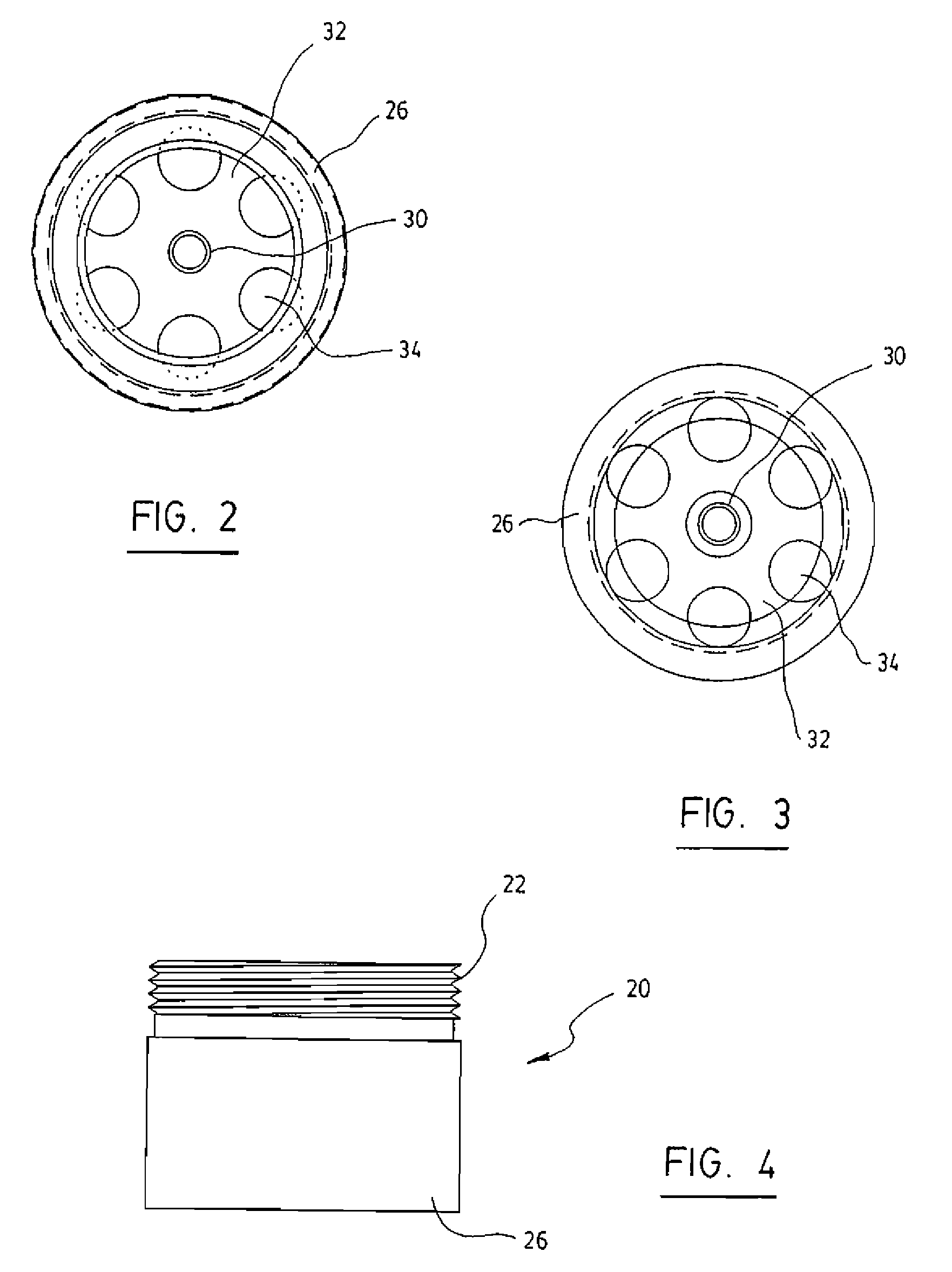
Tubular, especially can-shaped, receptacle for the accommodation of fluids, a method of manufacture, and use
ActiveUS7364047B2Improve pressure bearing capacityImprove stabilityBottlesLarge containersEngineering
Tubular, especially can-shaped, receptacle for the accommodation of fluids, especially drinks, with a tubular body and a base and top section attached to this, wherein the top section is constructed in the shape of a shoulder and is suitable for attaching a closure device, especially a resealable one. The shoulder-shaped top section is at least partially enclosed, especially in the shape of a shoulder, by an upper edge of the tubular body and sealed with this.
Owner:HUHTAMAKI RONSBERG ZWEIGNIEDERLASSUNG DER HUHTAMAKI DEUT
Lumbar support, cushion for seat, and seat structure
Owner:DELTA TOOLING CO LTD
System and method for pain reduction during skin puncture and breakable tip therefor
ActiveUS20120029422A1Easy and inexpensiveEliminate painDiagnosticsMedical devicesSingle useEngineering
An instrument, article and method are provided for minimizing pain during administration by injection of a liquid, such as, an anesthetic. The instrument has a forward end. A rod or lightpipe mounted freely for vibration projects out of the forward end. The article, a single use tip, is composed of a tip sleeve removably mounted on the forward end of the instrument and a tip member removably mounted on the projecting rod or lightpipe to vibrate a preselected injection site on a human or animal. The tip sleeve and tip member are covered by an elastic overmold that enables the tip member to vibrate freely with respect to the tip sleeve and light from the lightpipe to illuminate the injection site. The overmold of the single use tip is torn during removal of the single use tip from the instrument.
Owner:BING INNOVATIONS
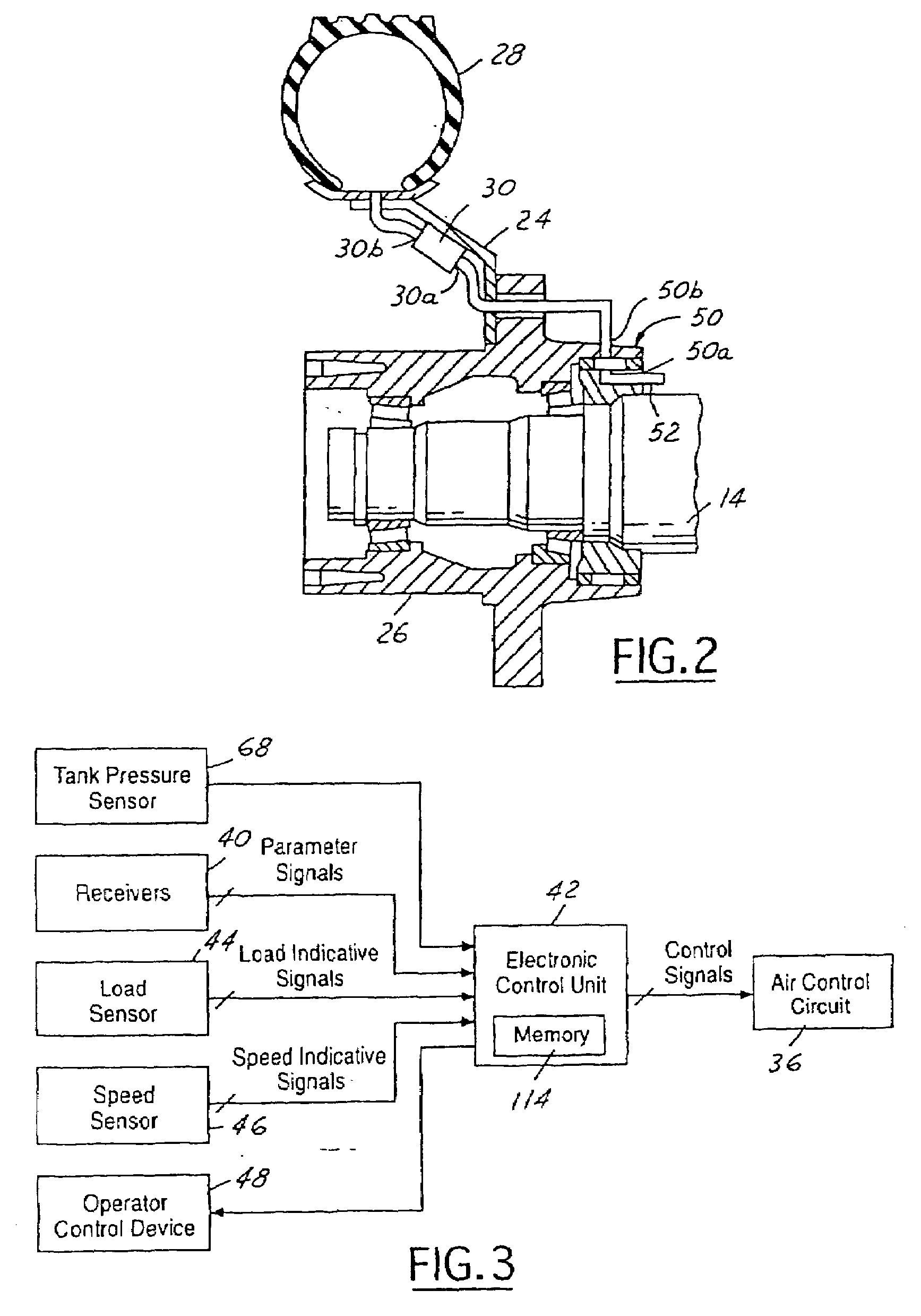
Tire inflation method
A tire inflation method is disclosed for moving air through a fluid control circuit to at least one tire that is below a target pressure. The dynamic pressure of the moving air in the fluid control circuit is monitored. A pressure control valve in the fluid control circuit is cycled on and off to prevent the dynamic pressure from reaching a predetermined amount over the target pressure.
Owner:DANA HEAVY VEHICLE SYSTEMS GROUP LLC
System and method for pain reduction during skin puncture and breakable tip therefor
ActiveUS20110319812A1Easily and inexpensively utilizedFree from painSurgeryMedical devicesInjection siteEngineering
An instrument, article and method are provided for minimizing pain during administration by injection of a liquid, such as, an anesthetic. The instrument has a forward end. A lightpipe mounted freely for vibration projects out of the forward end. The article, a single use tip, is composed of a tip sleeve removably mounted on the forward end of the instrument and a tip member removably mounted on the projecting lightpipe to vibrate a preselected injection site on a human or animal. The tip sleeve and tip member are covered by an elastic overmold that enables the tip member to vibrate freely with respect to the tip sleeve and light from the lightpipe to illuminate the injection site. The overmold of the single use tip is torn during removal of the single use tip from the instrument.
Owner:BING INNOVATIONS
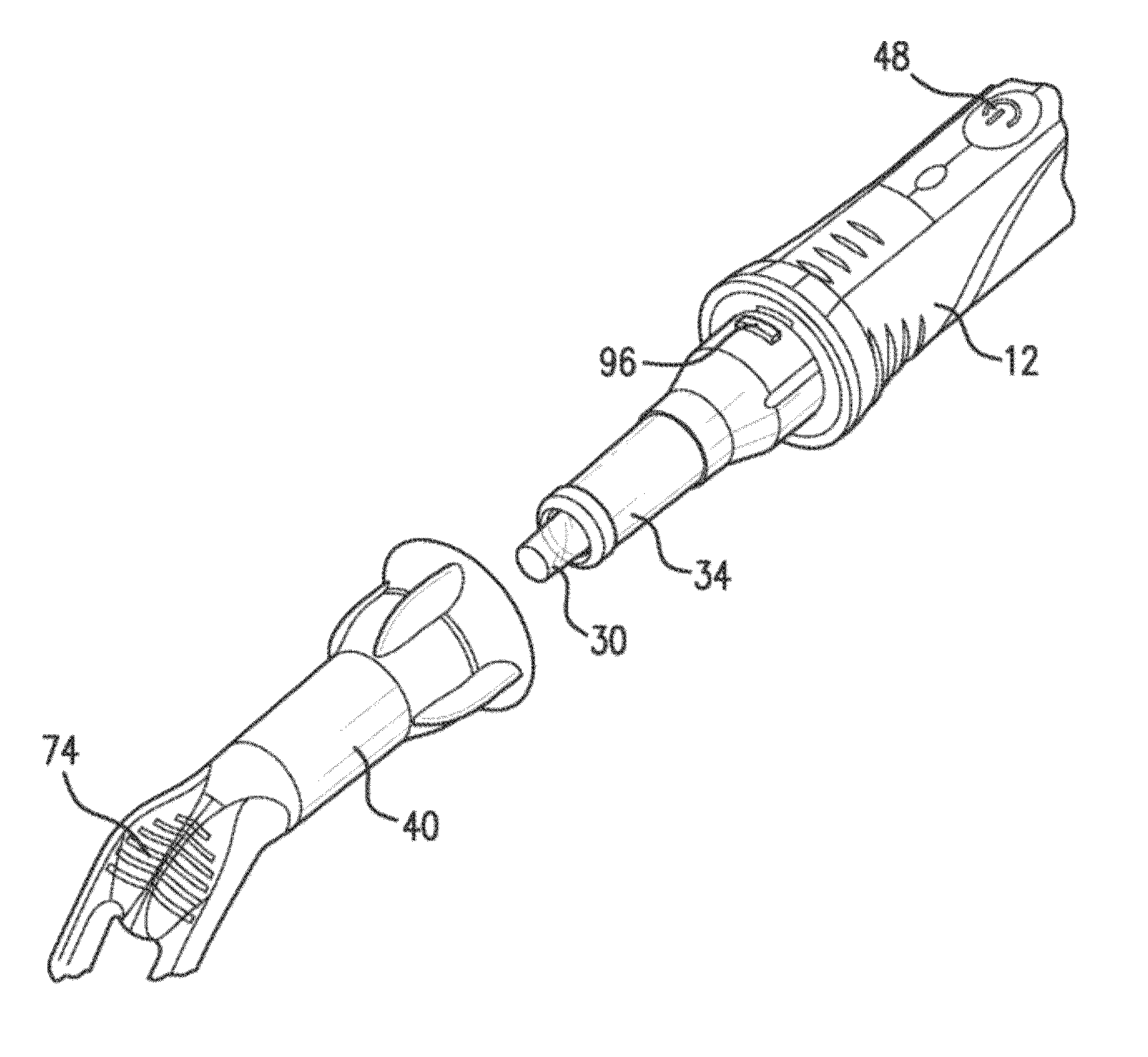
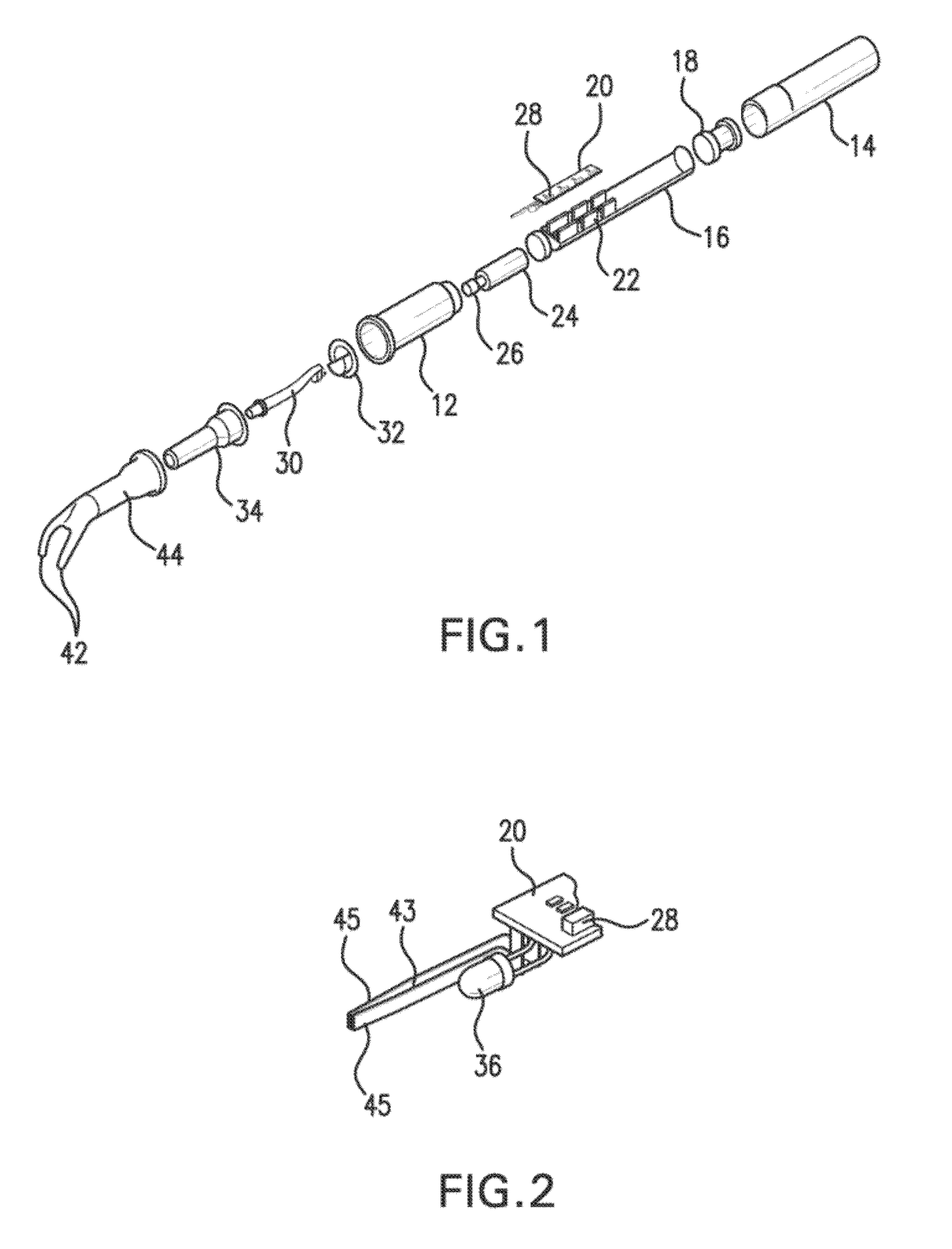
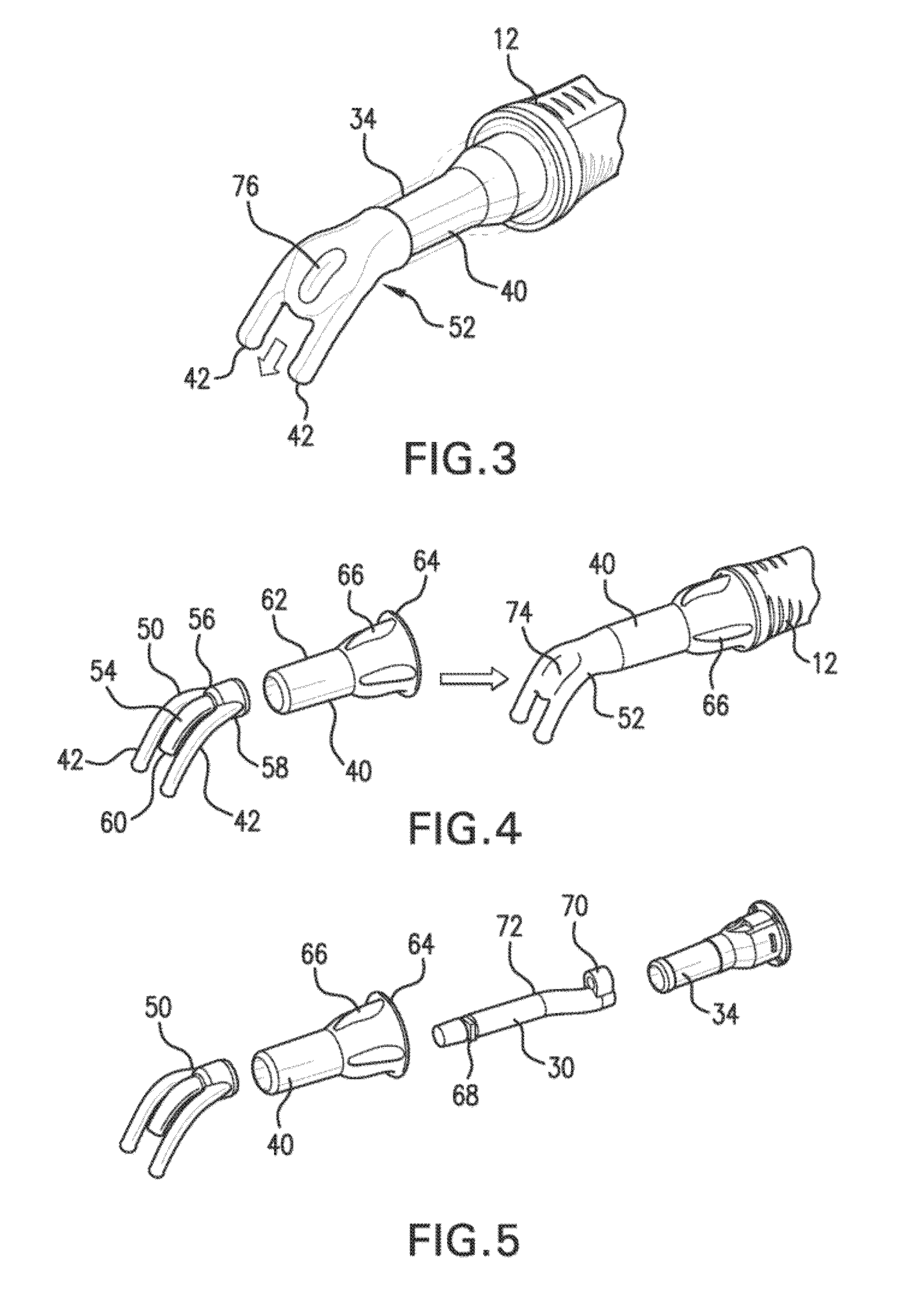
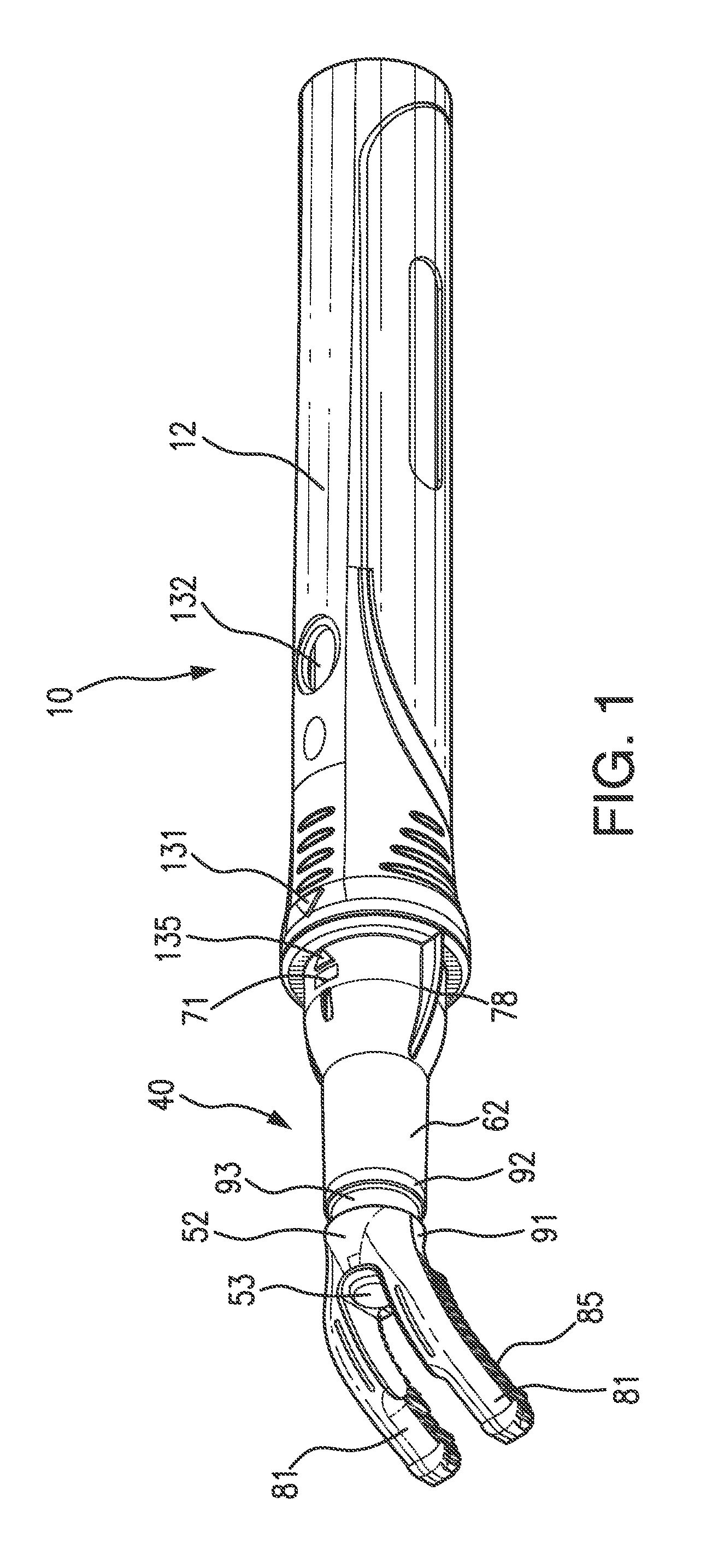
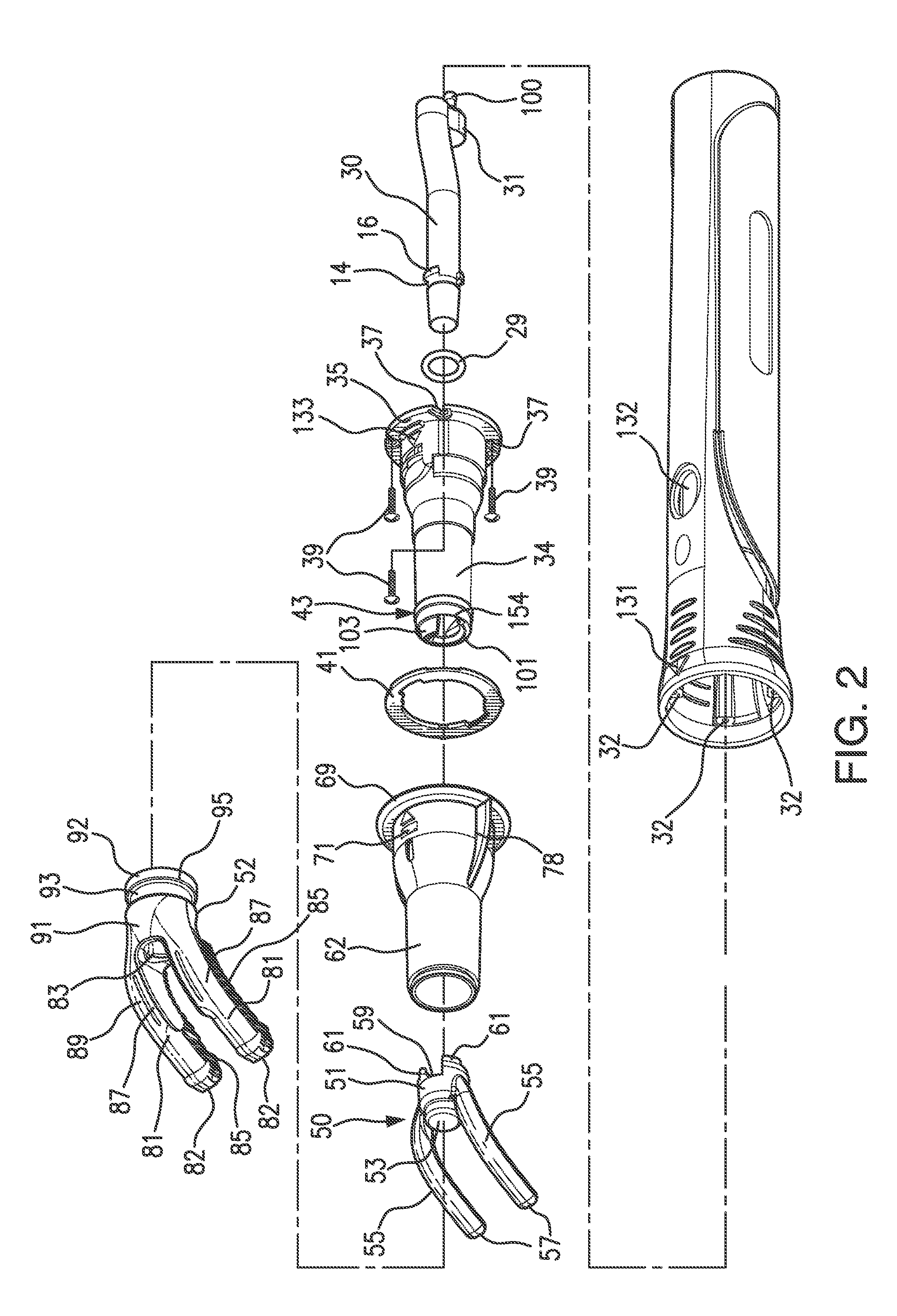
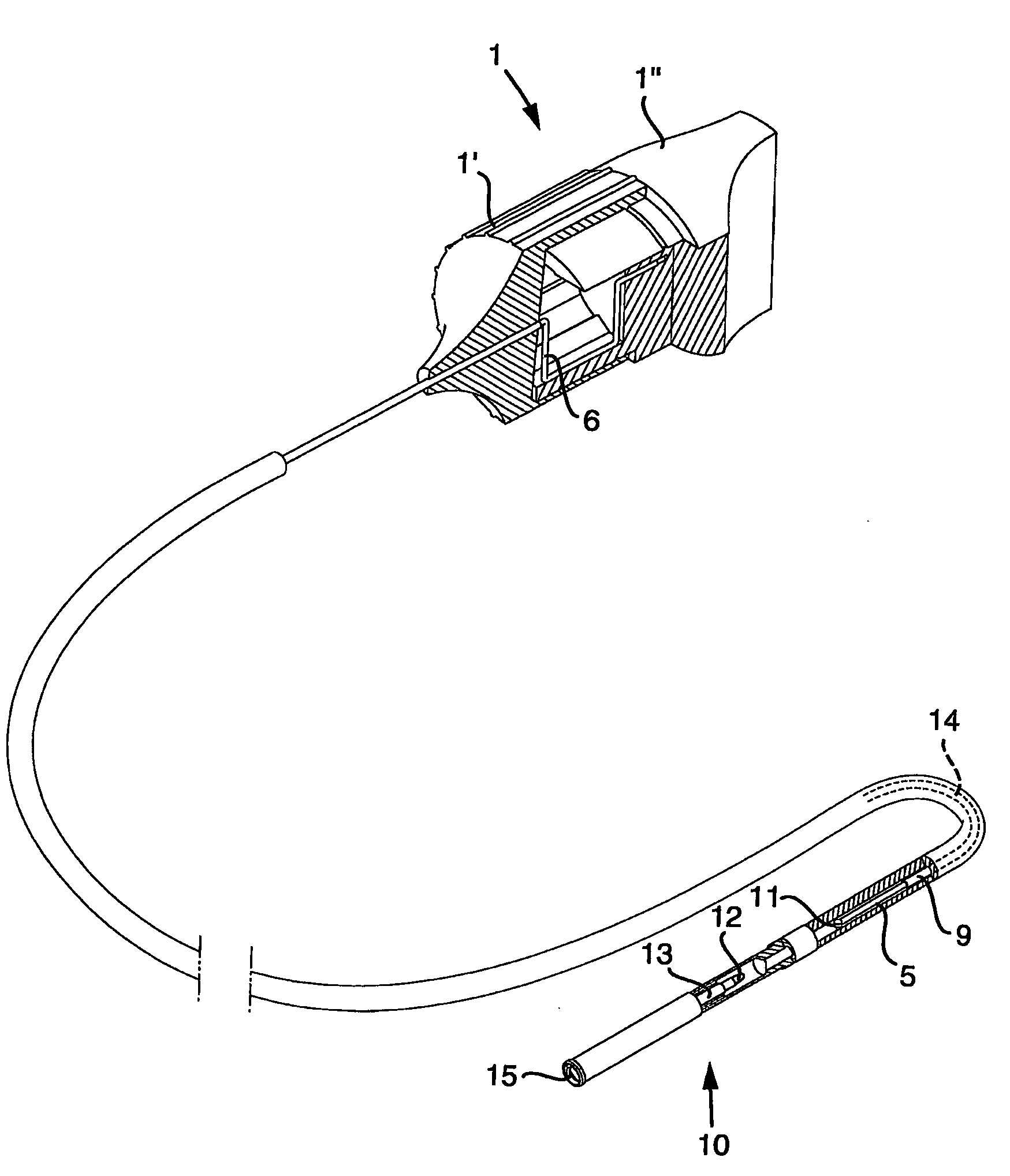
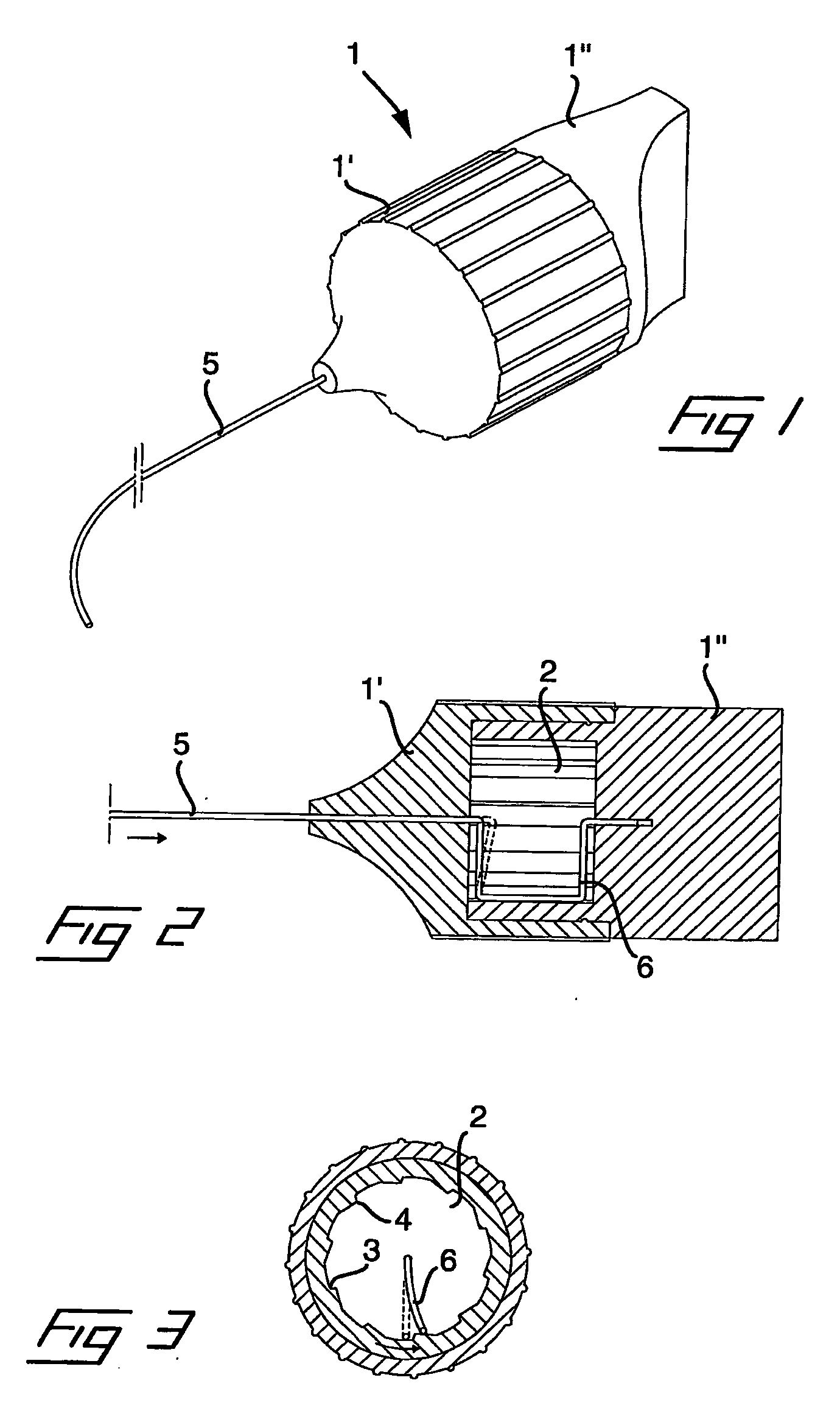
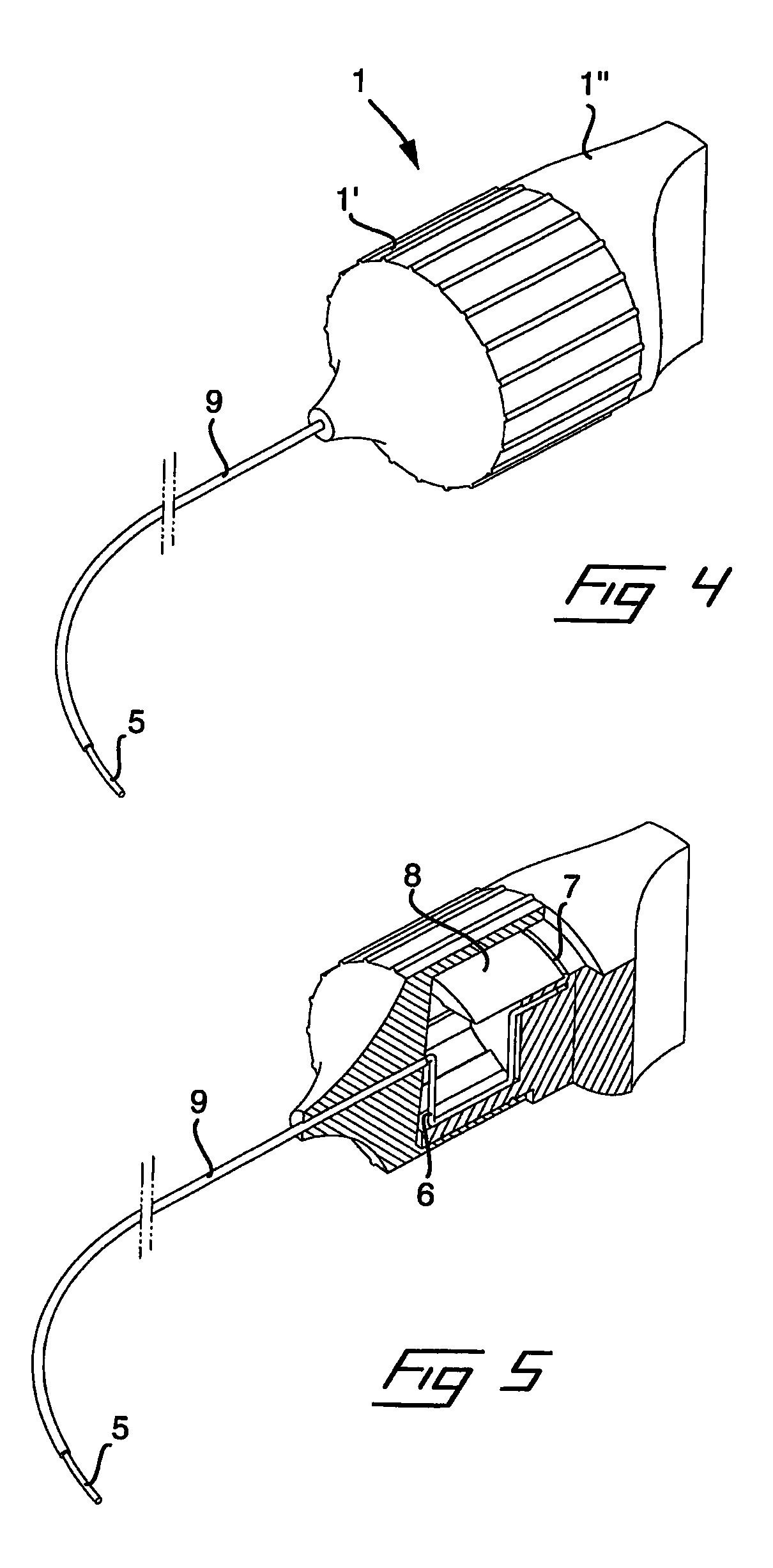
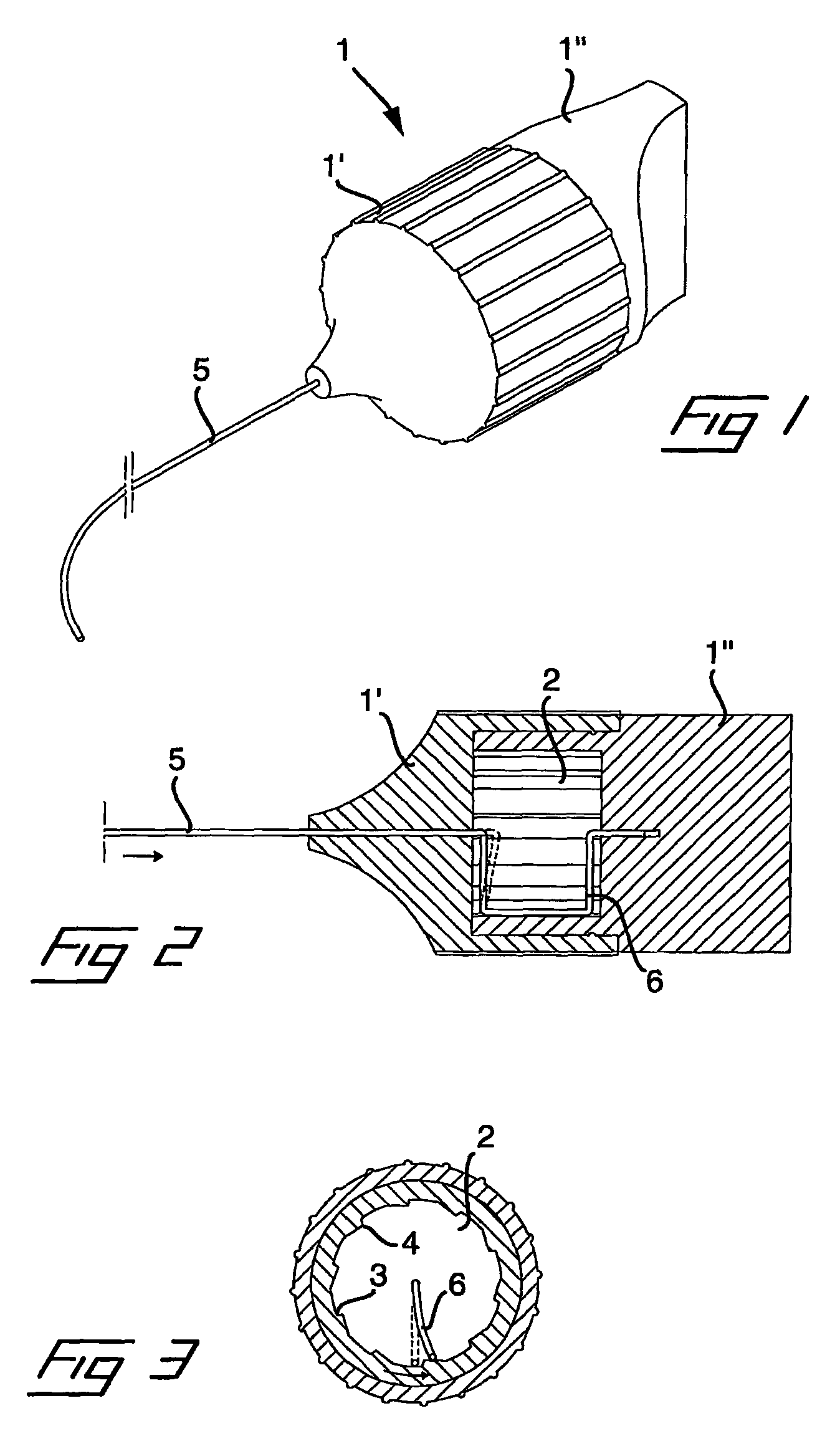
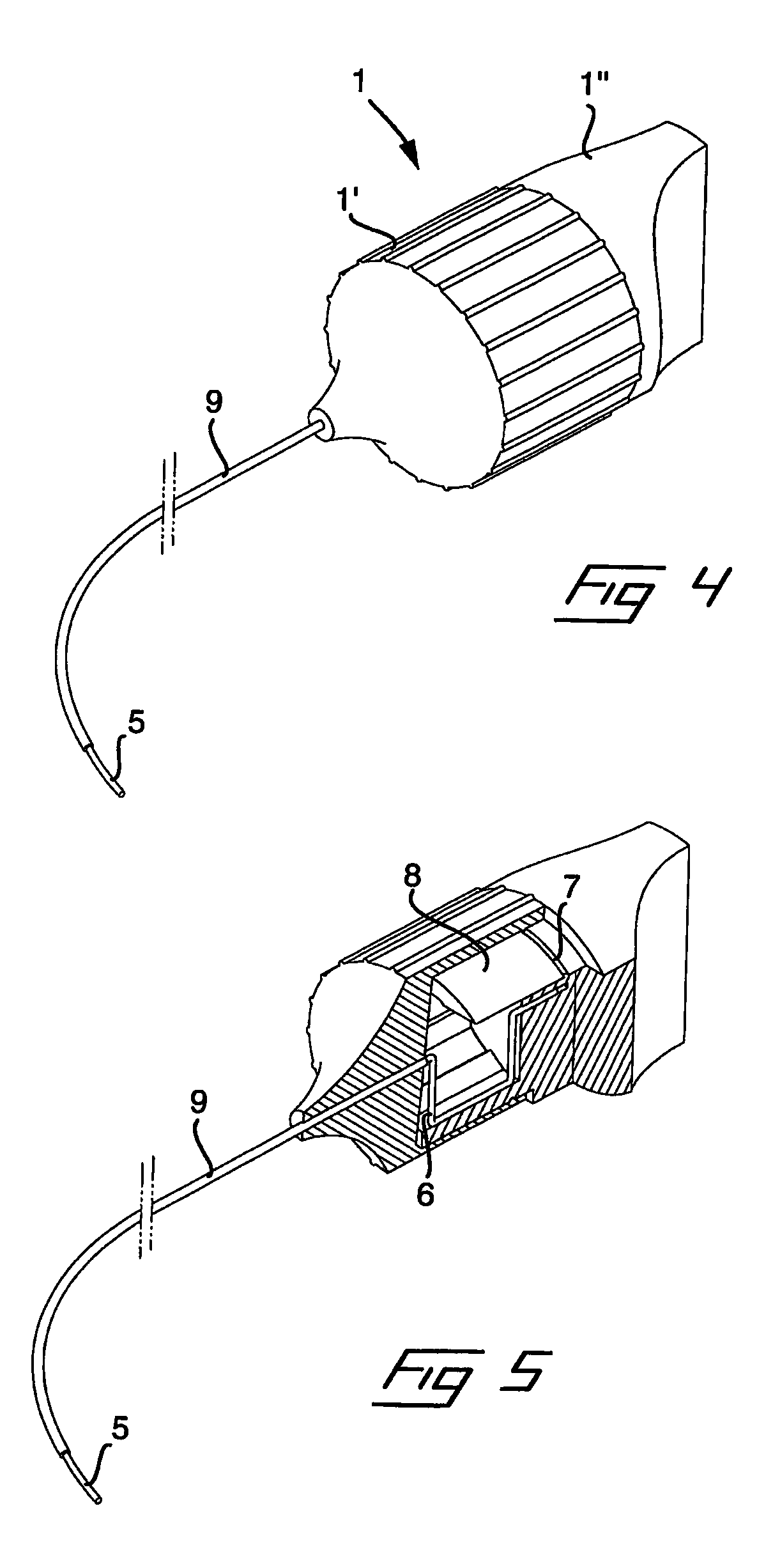
Tool and a Method for Attaching a Cardiac Stimulator Lead at a Desired Position Inside a Heart
InactiveUS20080234694A1Simple and inexpensive and reliableLimiting the torque transmitted to the helixEar treatmentTransvascular endocardial electrodesEngineeringHelix
For attaching a cardiac stimulator lead at a desired position inside a heart, the stimulator lead having a flexible tube from which a helix is extendible at a distal end thereof by a screw rotating motion and having a proximal end interconnected with an operating member, a tool has a flexible portion wire with an engagement formation at a distal end thereof that mates with a complimentary engagement formation at a proximal end of the operating member. The tool has a handle containing an internal cavity, with a proximal portion of the torsion wire being rotationally rotated by the handle in the internal cavity, and a resilient yoke is formed in the internal cavity, with at least a part of the yoke engaging grooves and ridges in a circumferential boundary surface of the internal cavity.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
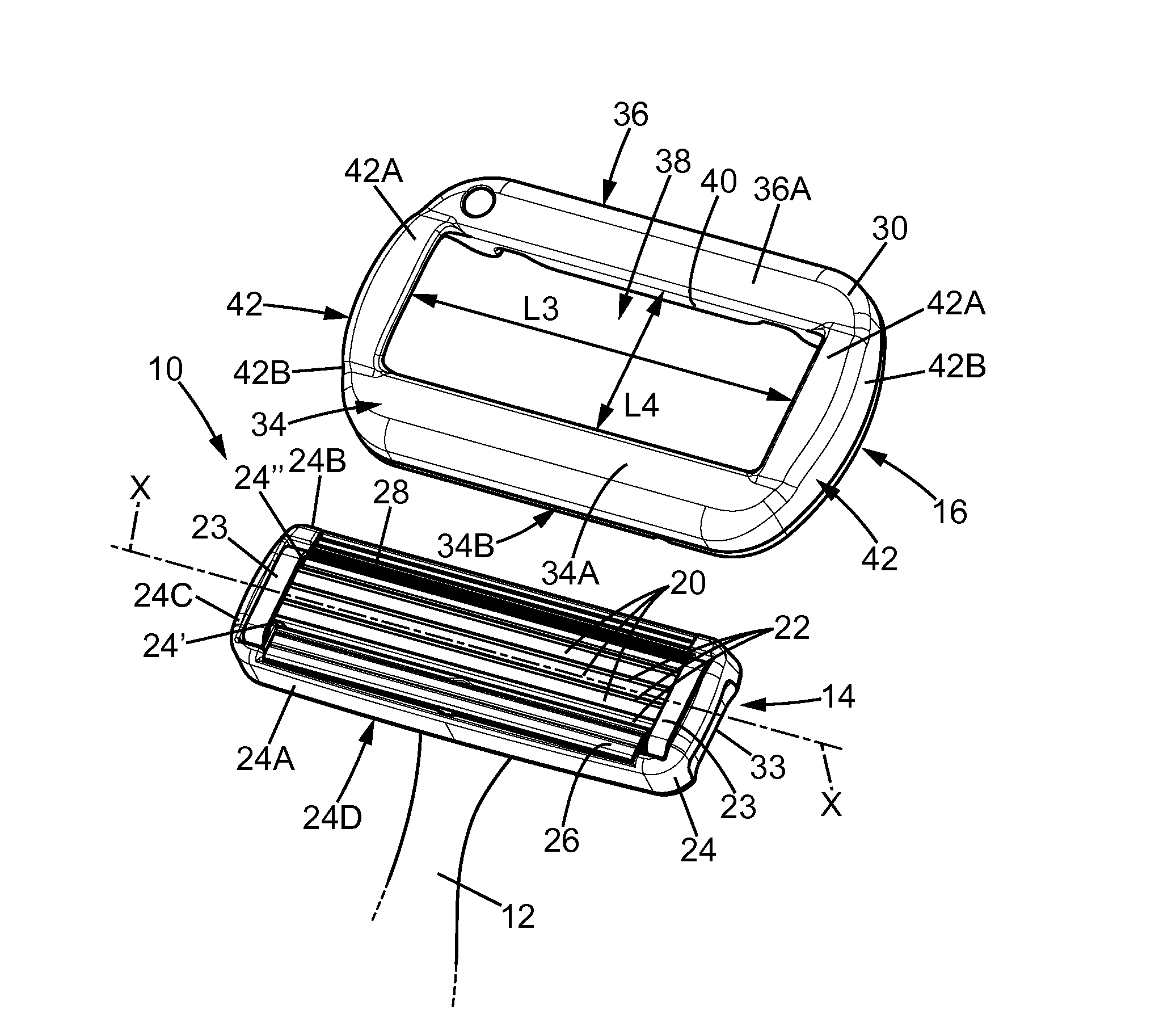
Shaving blade assembly with a blade unit and a skin contact member
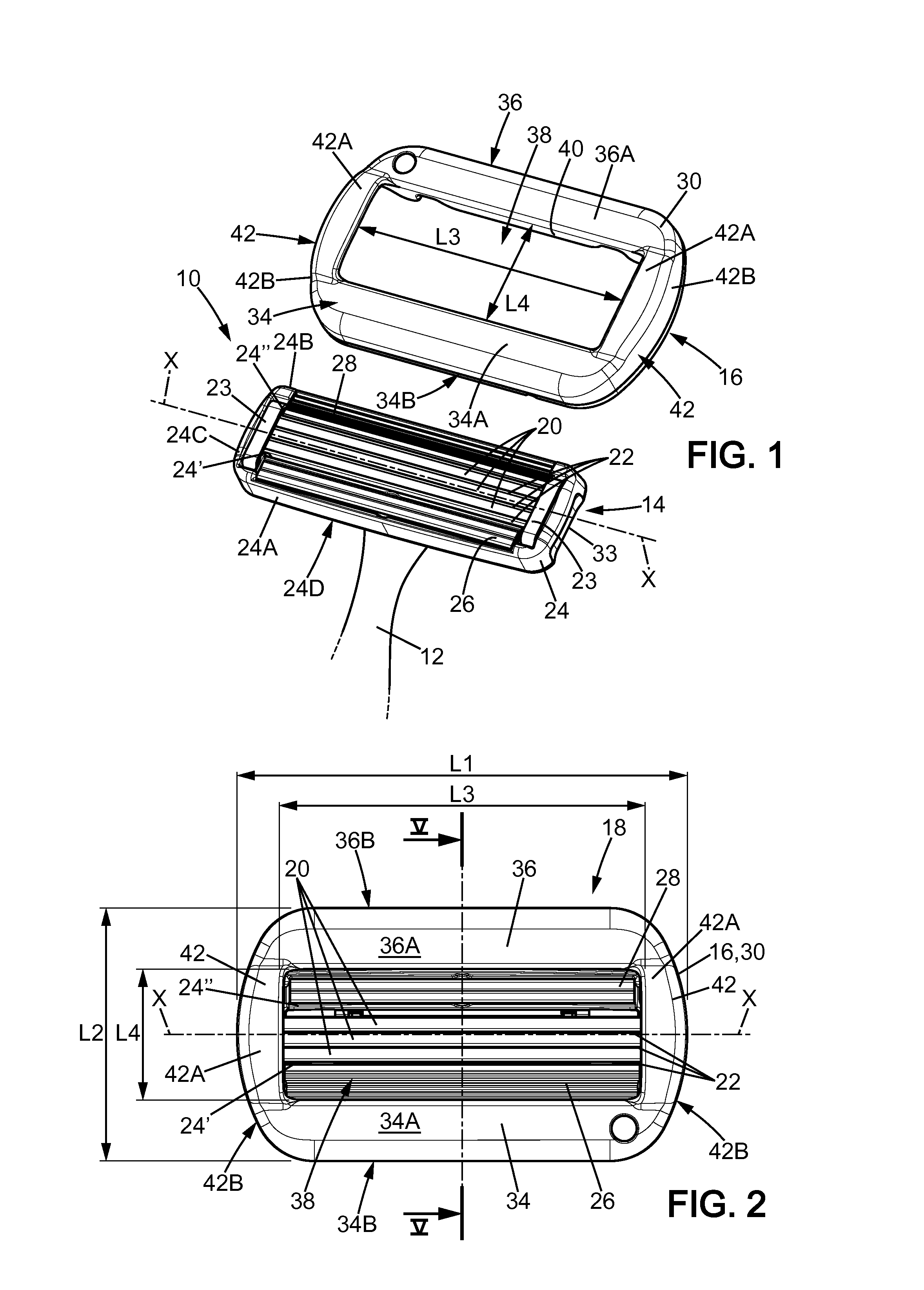
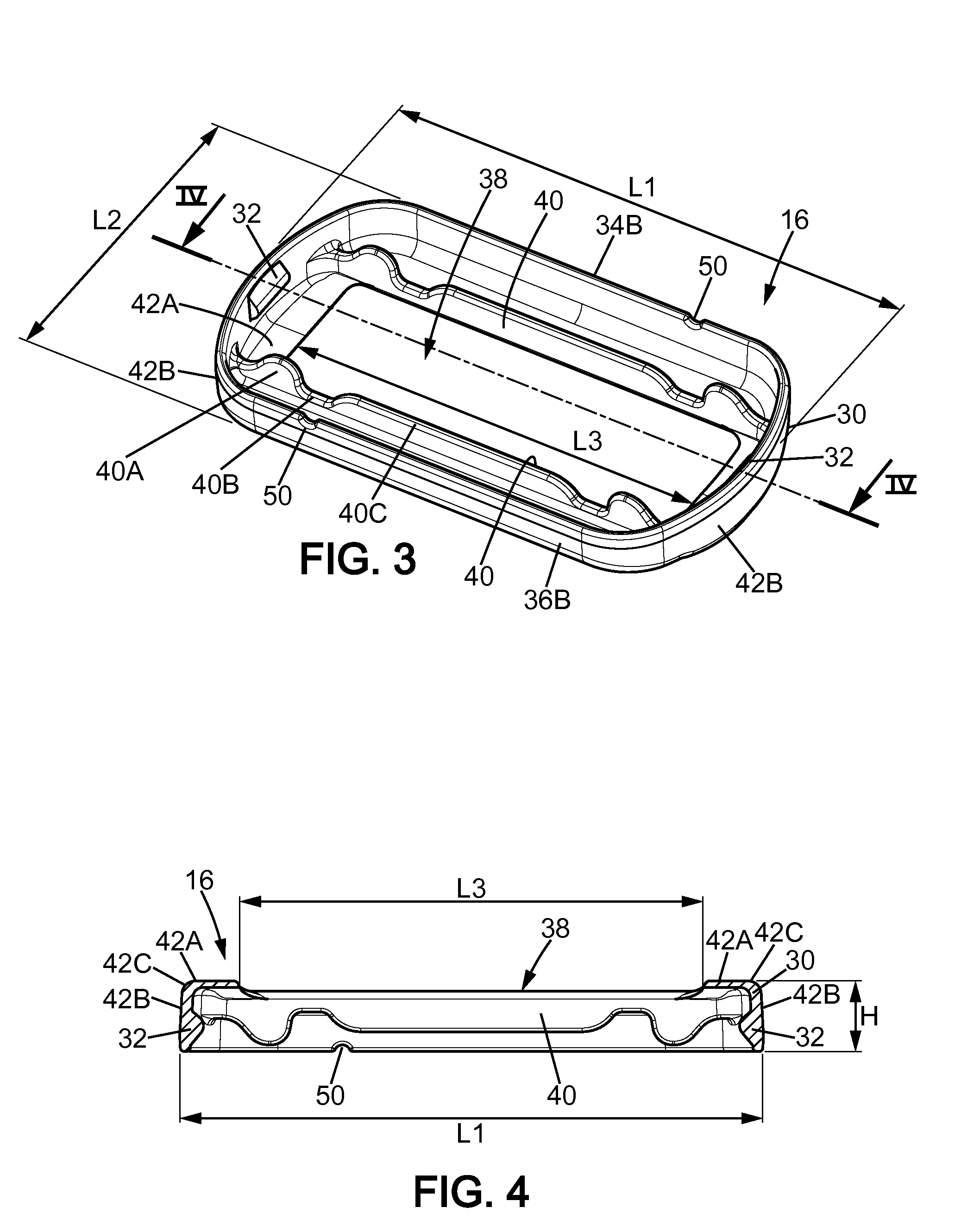
ActiveUS20140373362A1Prevent skinManufacturing costMetal working apparatusSkin contactBiomedical engineering
A shaving blade assembly including a blade unit and a skin contact member. A razor including a razor handle and such a shaving blade assembly. The blade unit includes at least one shaving blade having a cutting edge. The blade unit has a blade unit skin contact surface area, where the blade unit and the skin contact member have a shaving blade assembly skin contact surface area. The ratio between the shaving blade assembly skin contact surface area and the blade unit skin contact surface area is between approximately 2 and 3.1. The skin contact member can include a leading planar surface and a trailing planar surface defining a contact plane, and the contact plane and the shaving plane are parallel and the distance between the contact plane and the shaving plane is between approximately 0.2 mm and 0.6 mm.
Owner:BIC VIOLEX SA
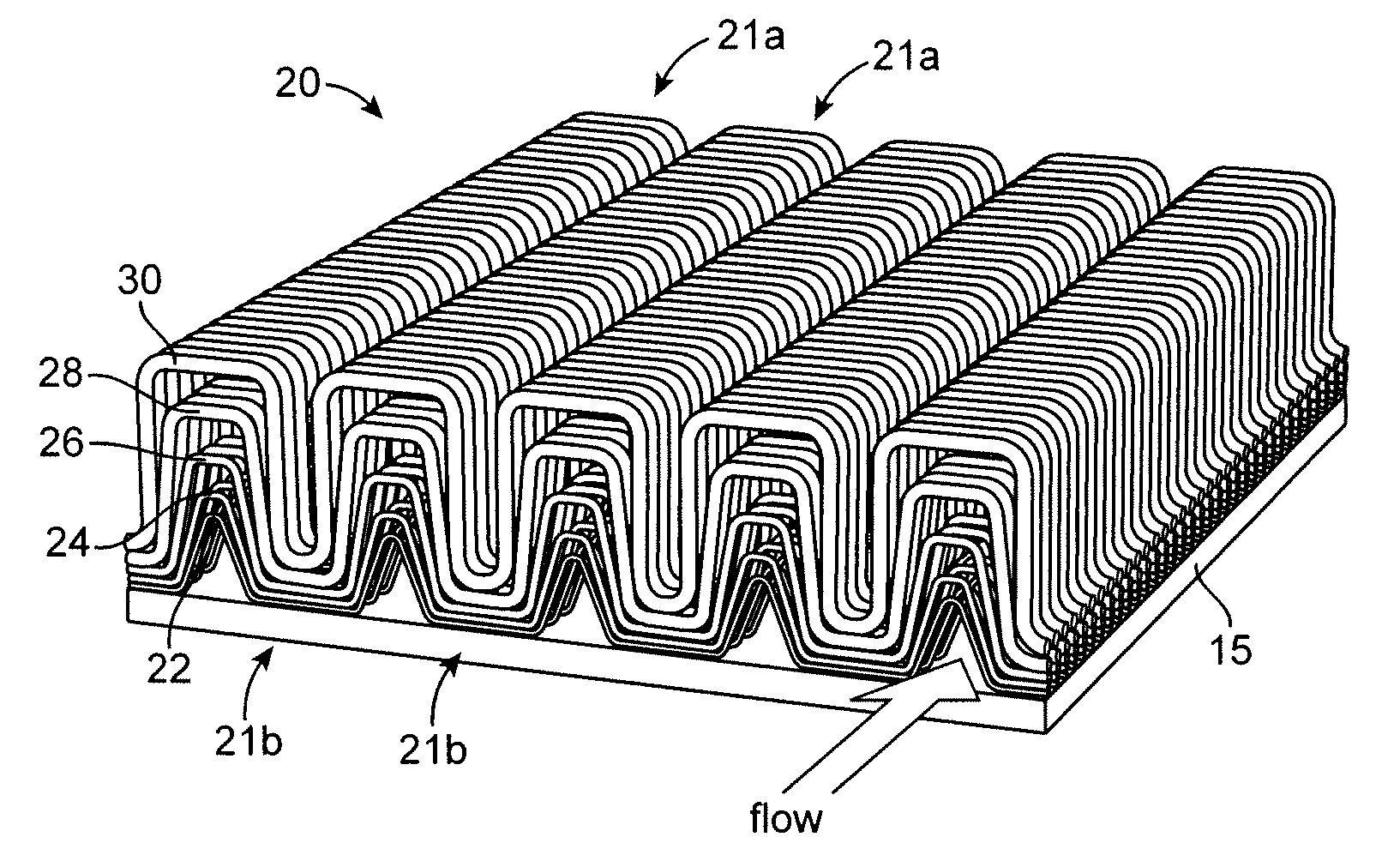
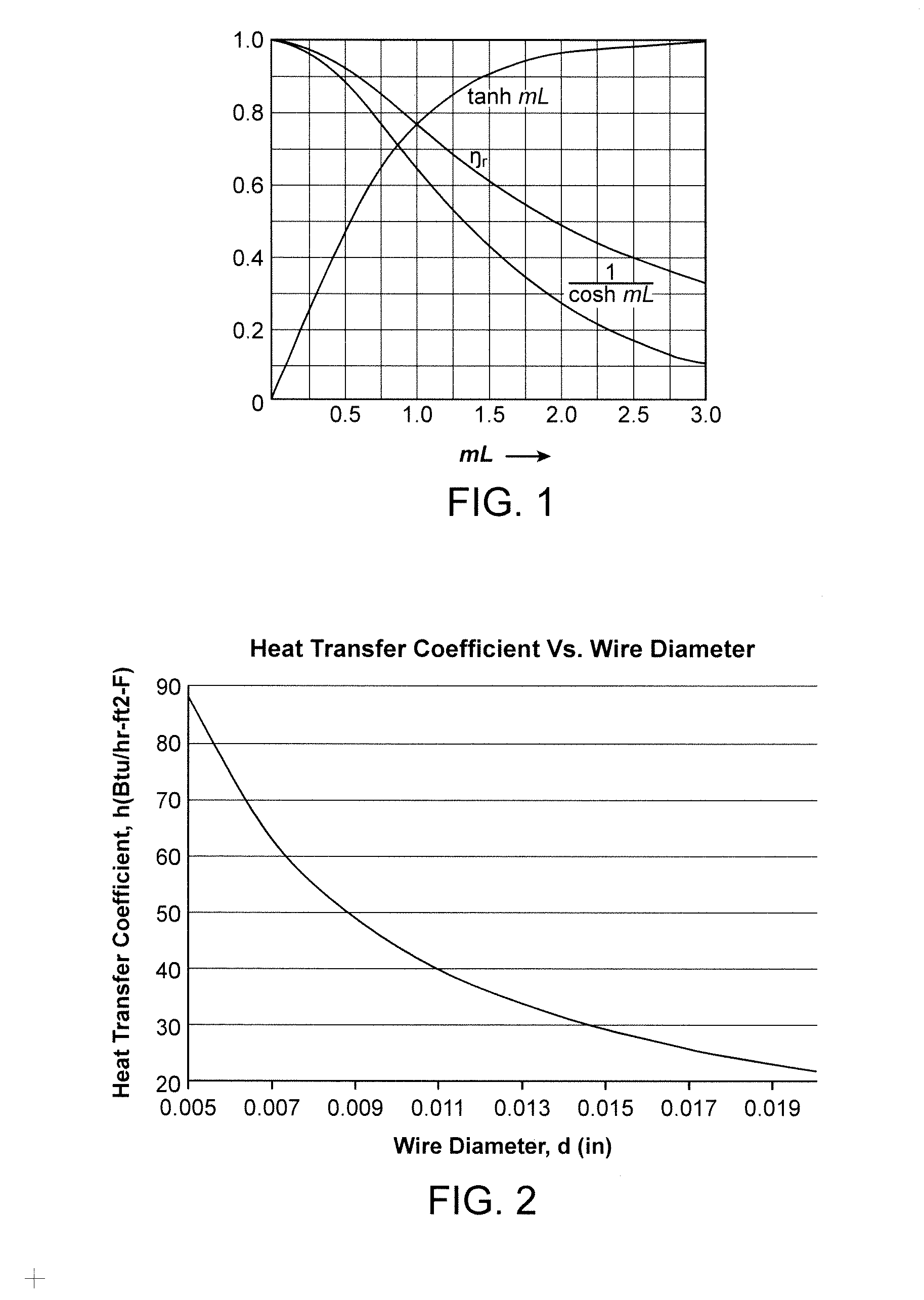
Non-Isotropic Structures for Heat Exchangers and Reactors
ActiveUS20120261106A1Substantial surface areaAugments heat flowMetal-working apparatusLaminated elementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:ALTEX TECH
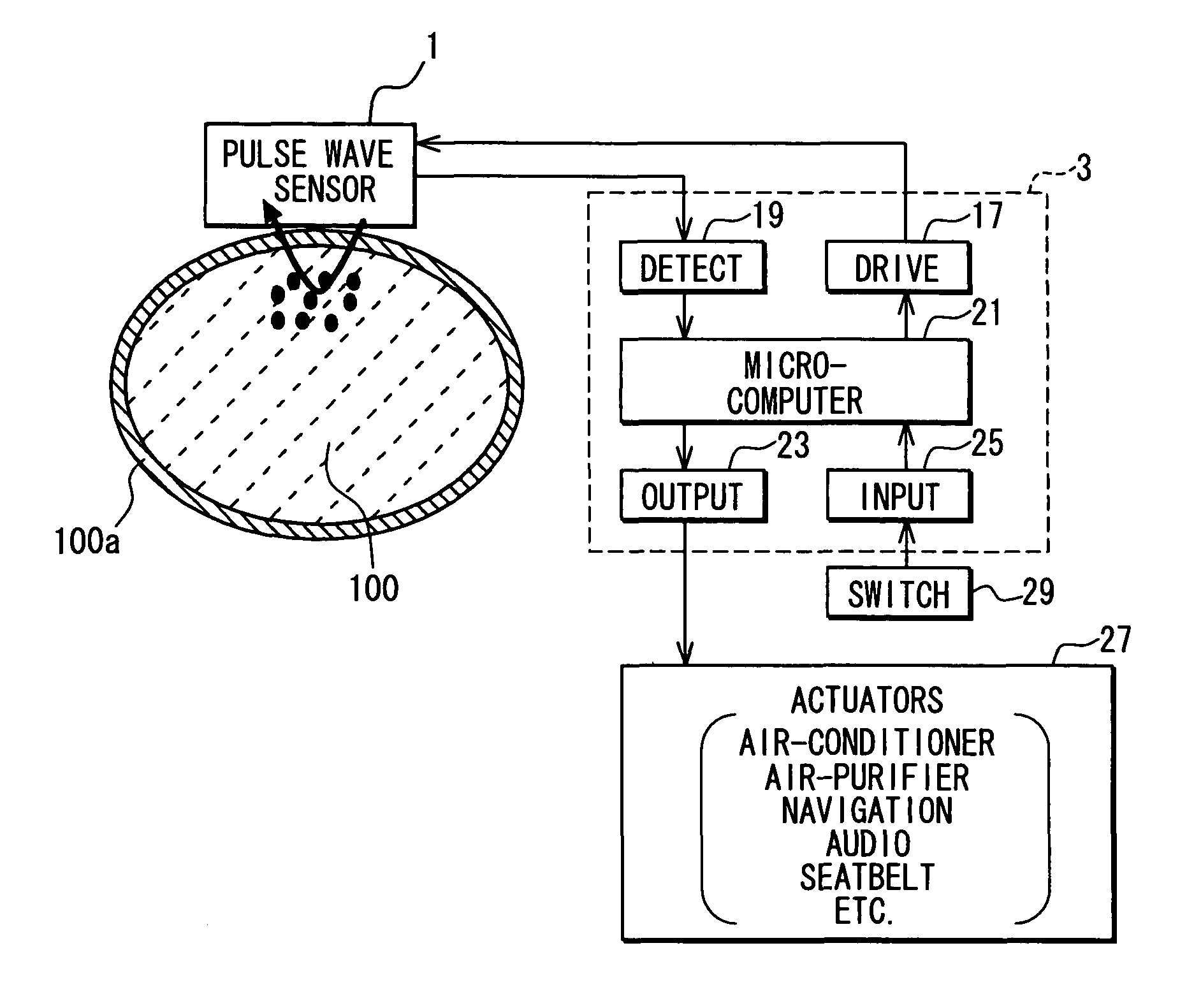
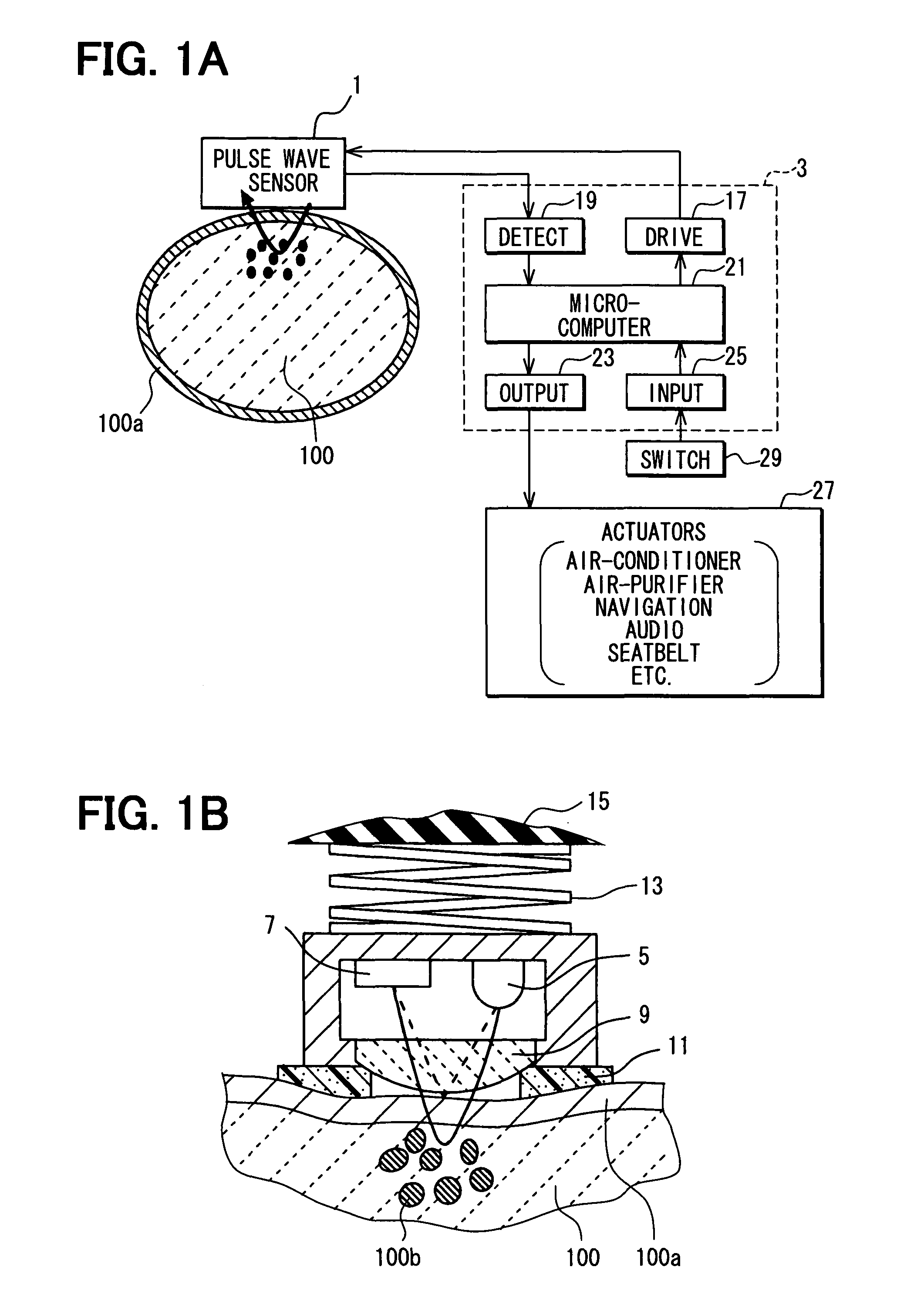
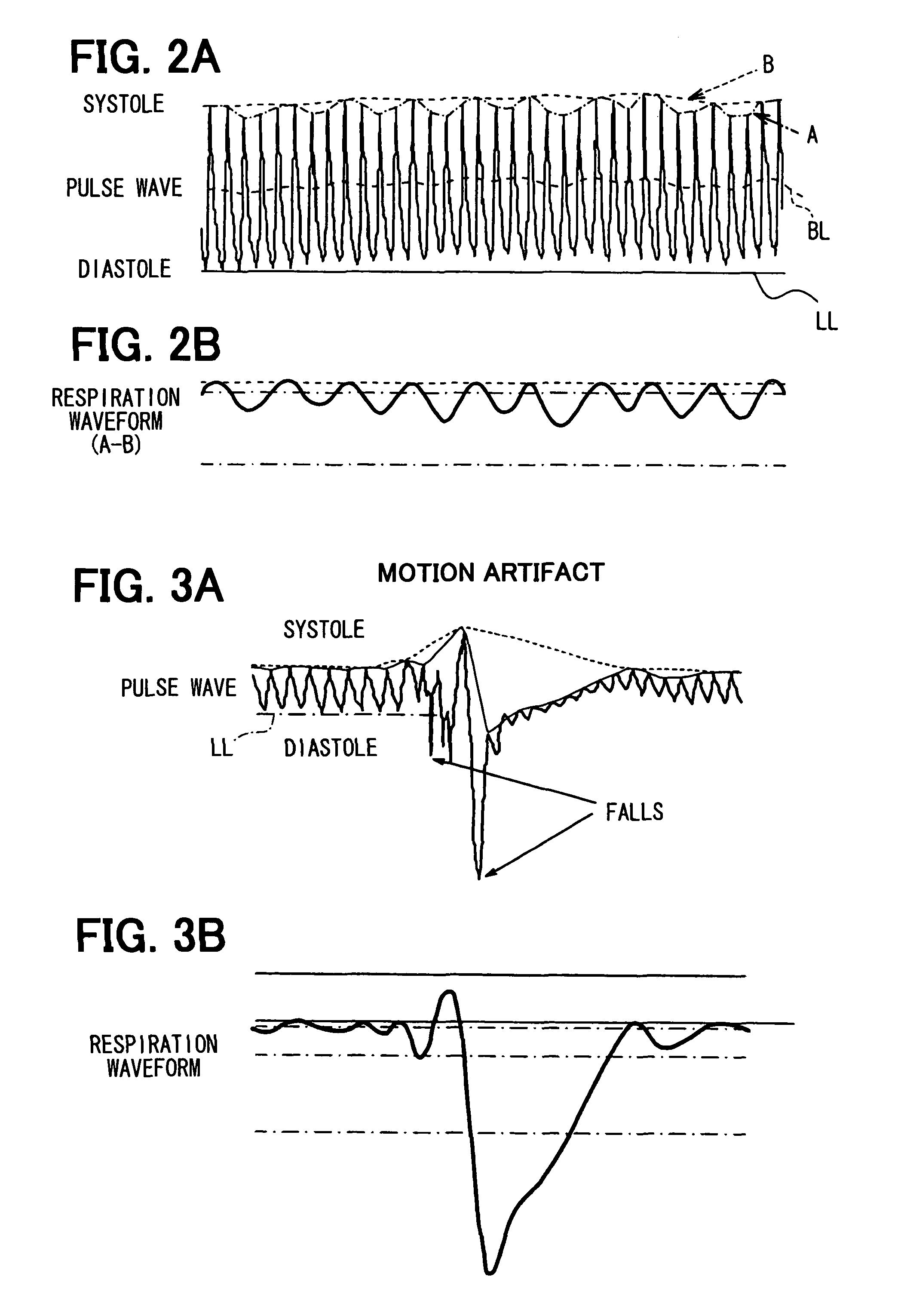
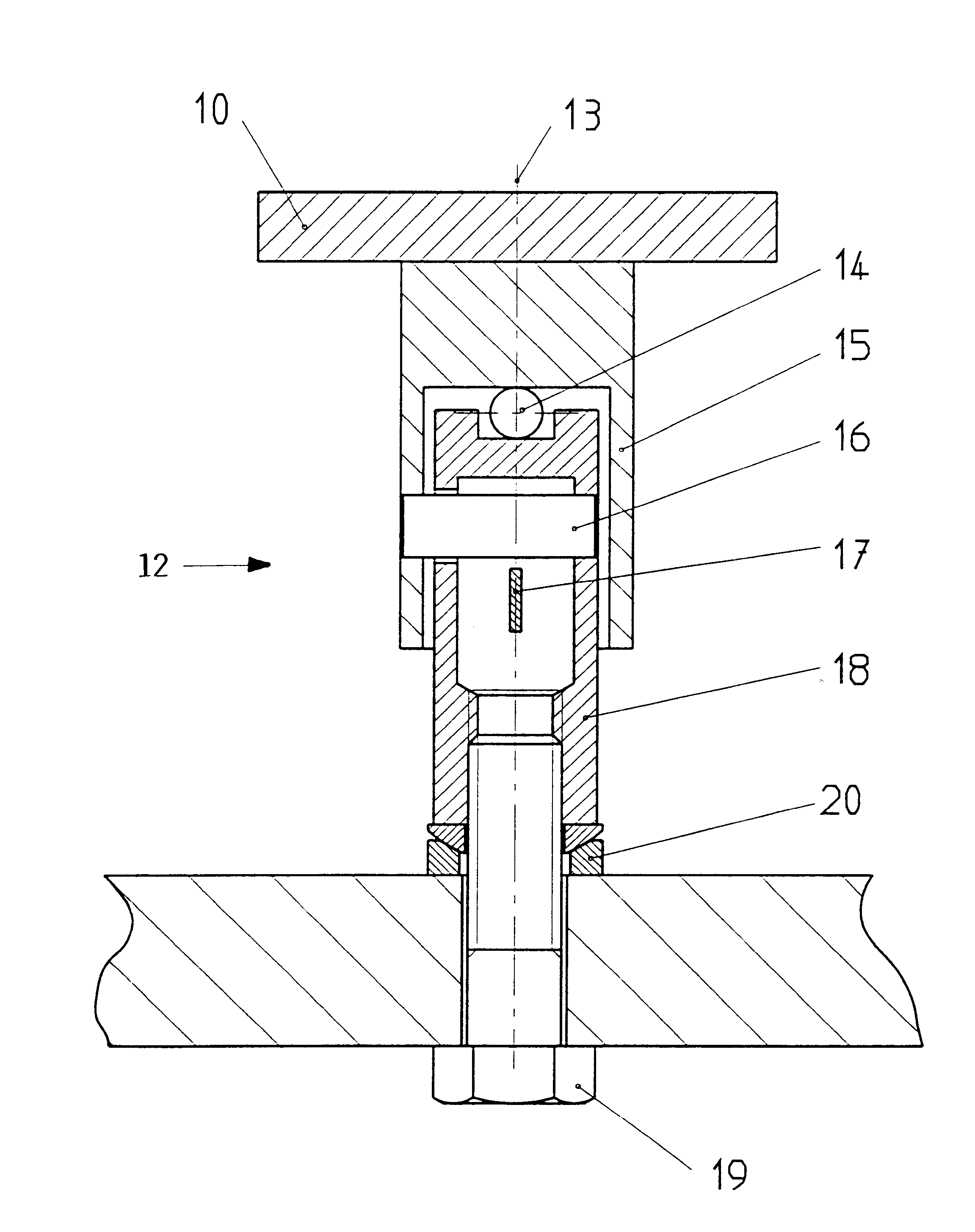
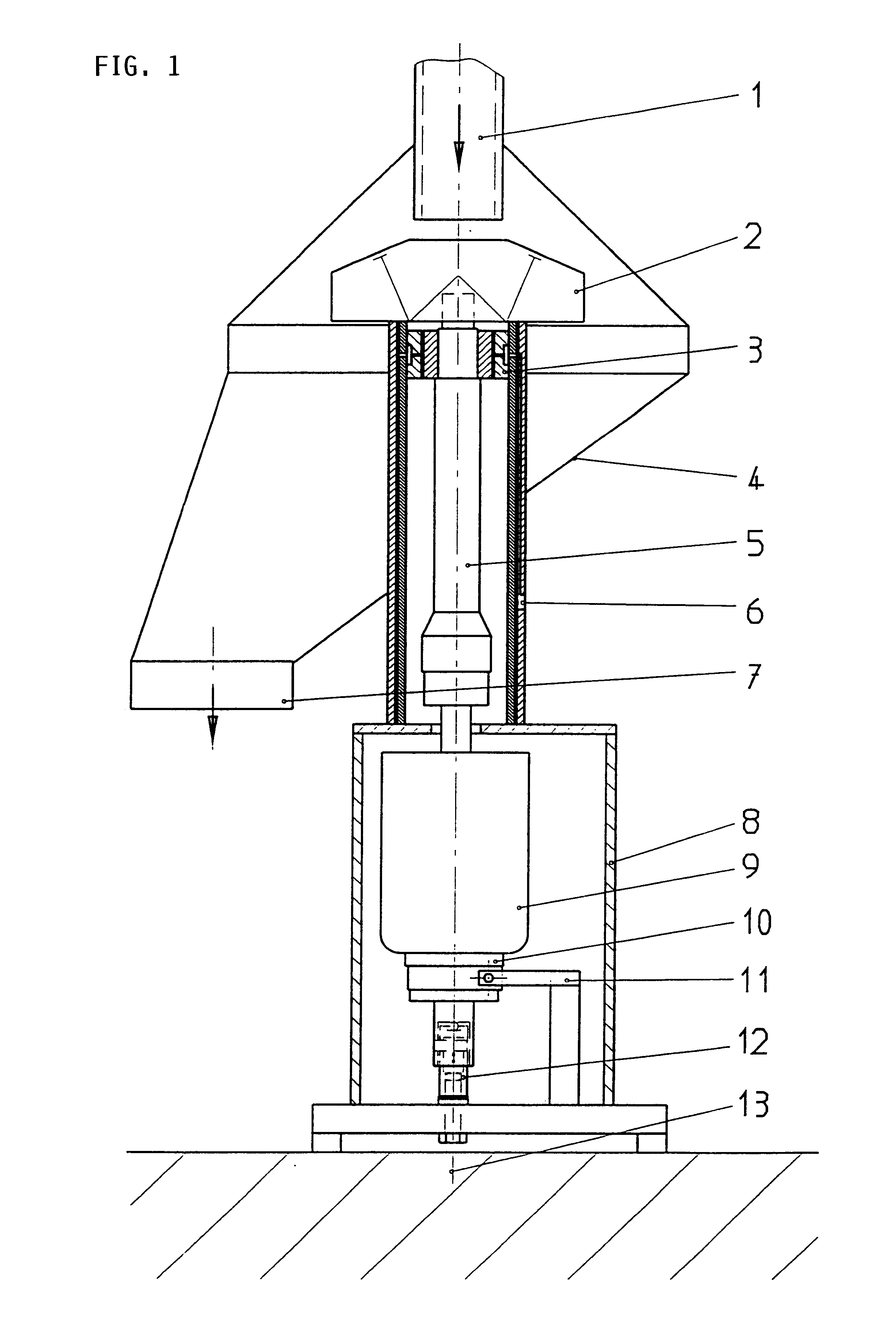
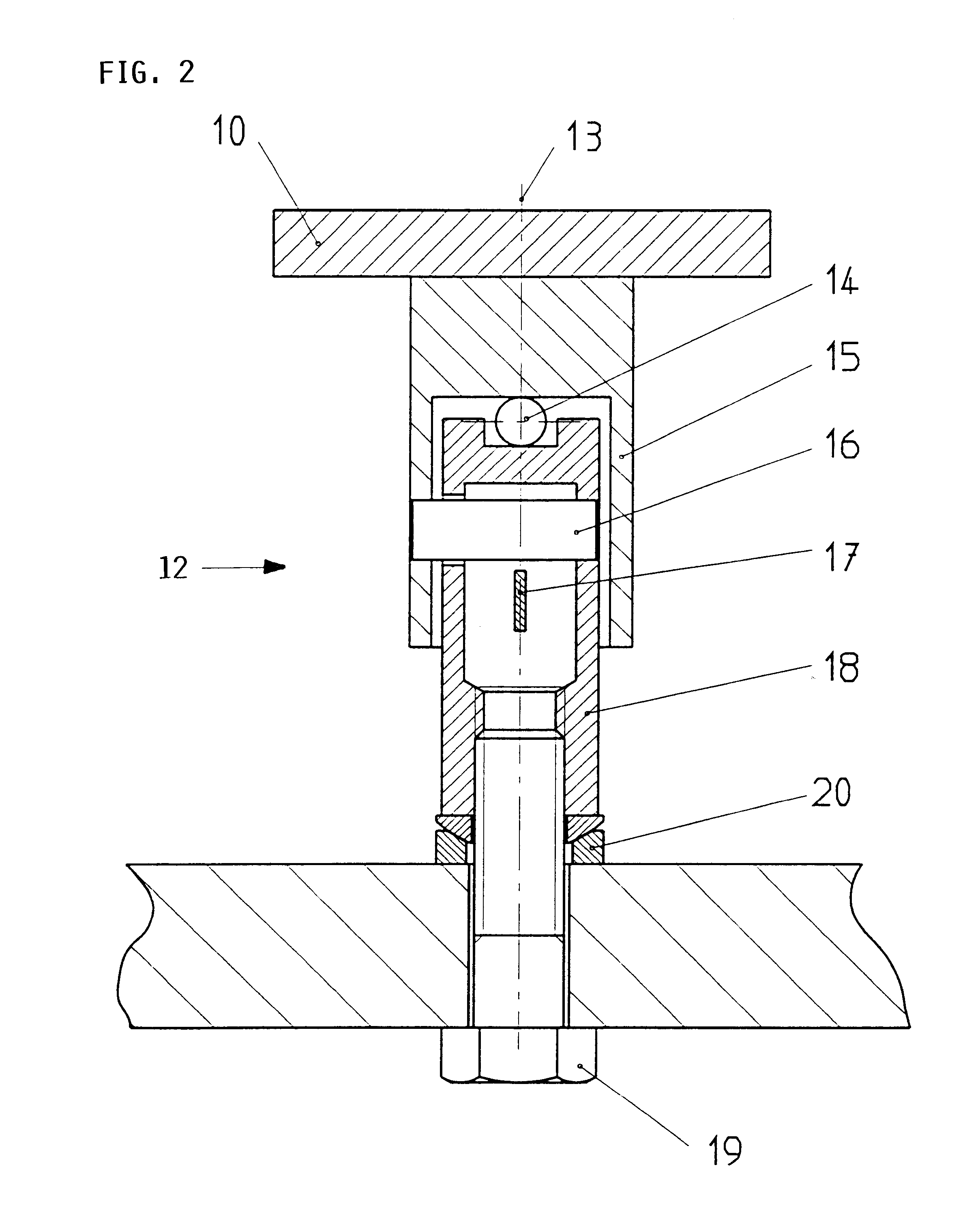
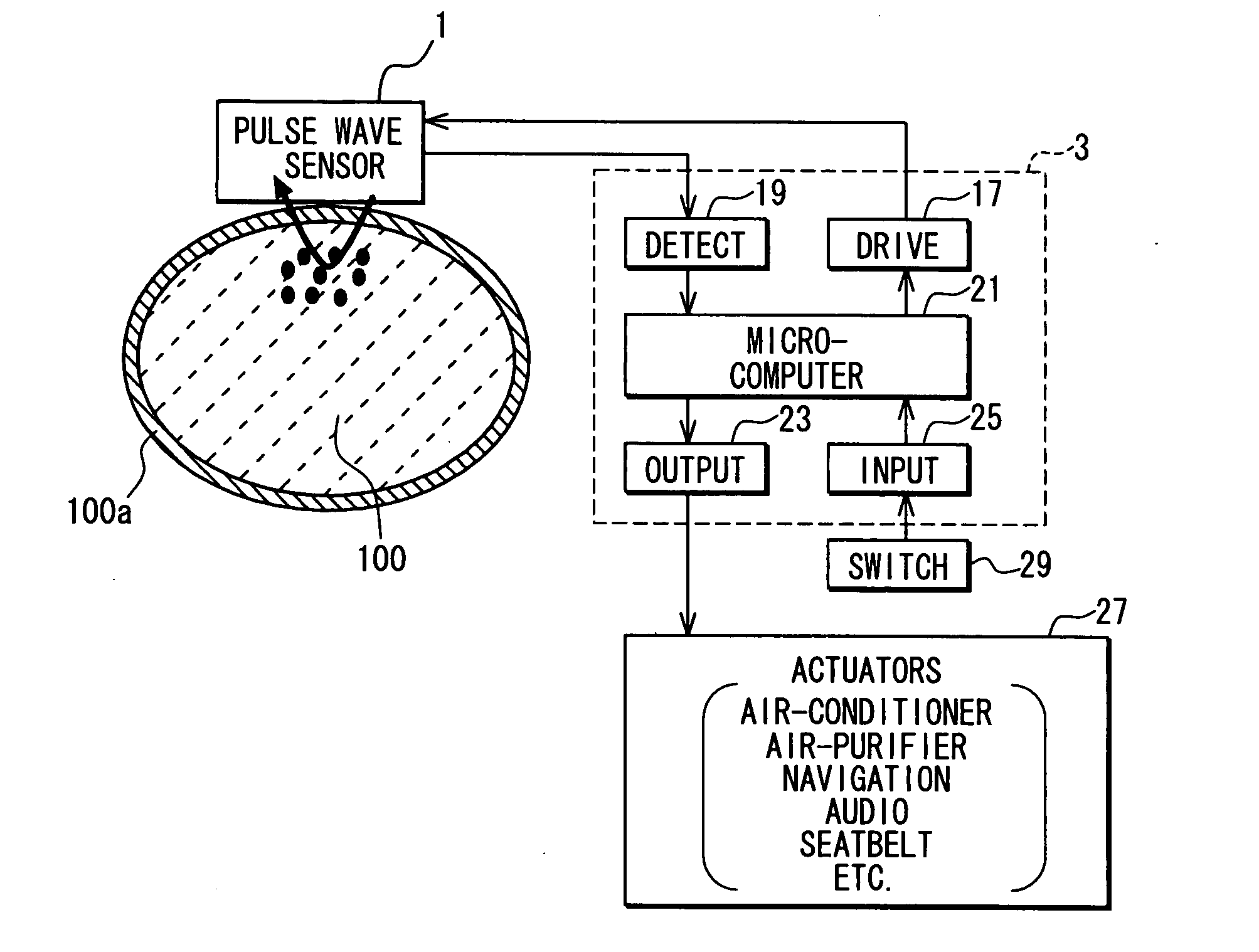
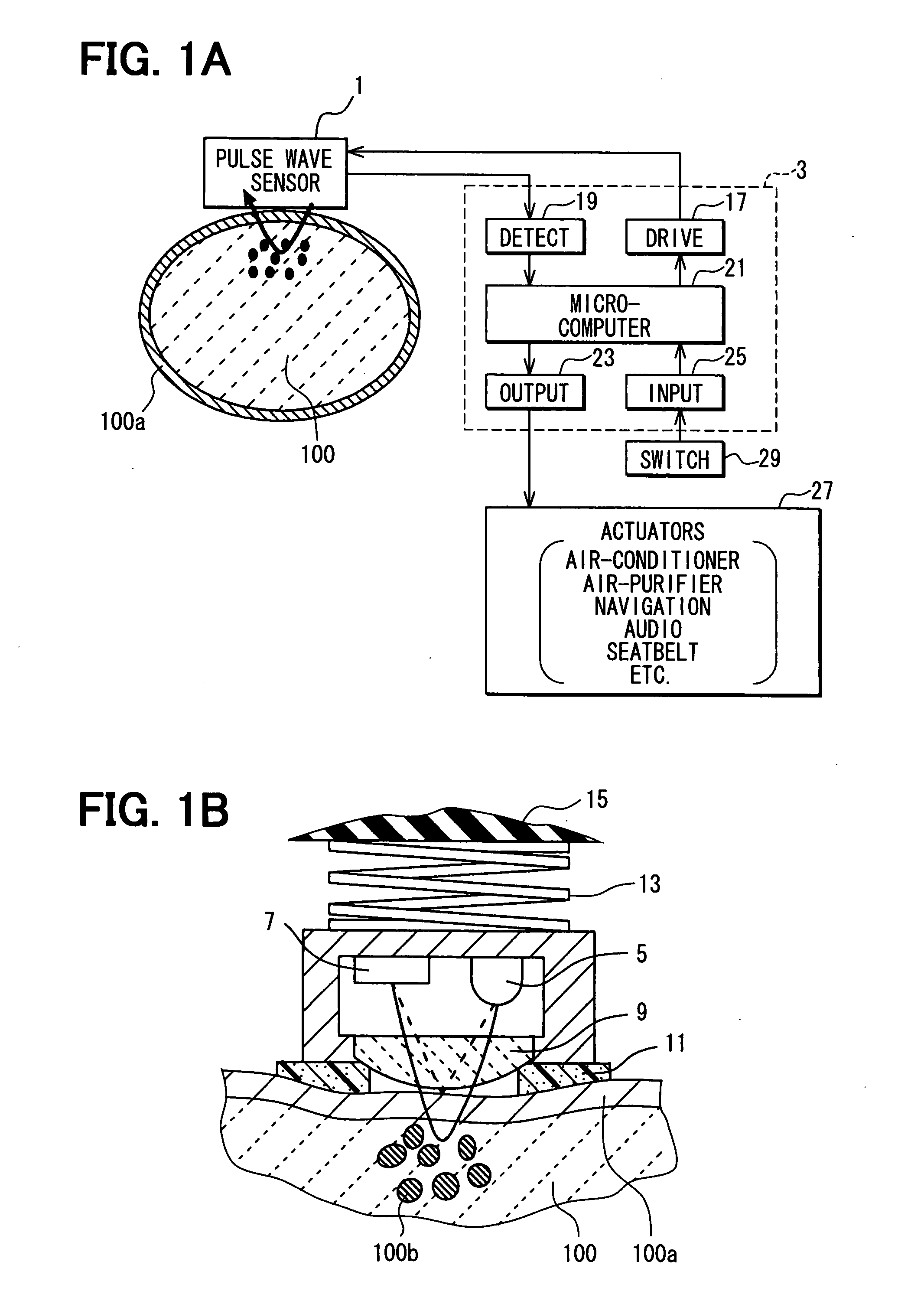
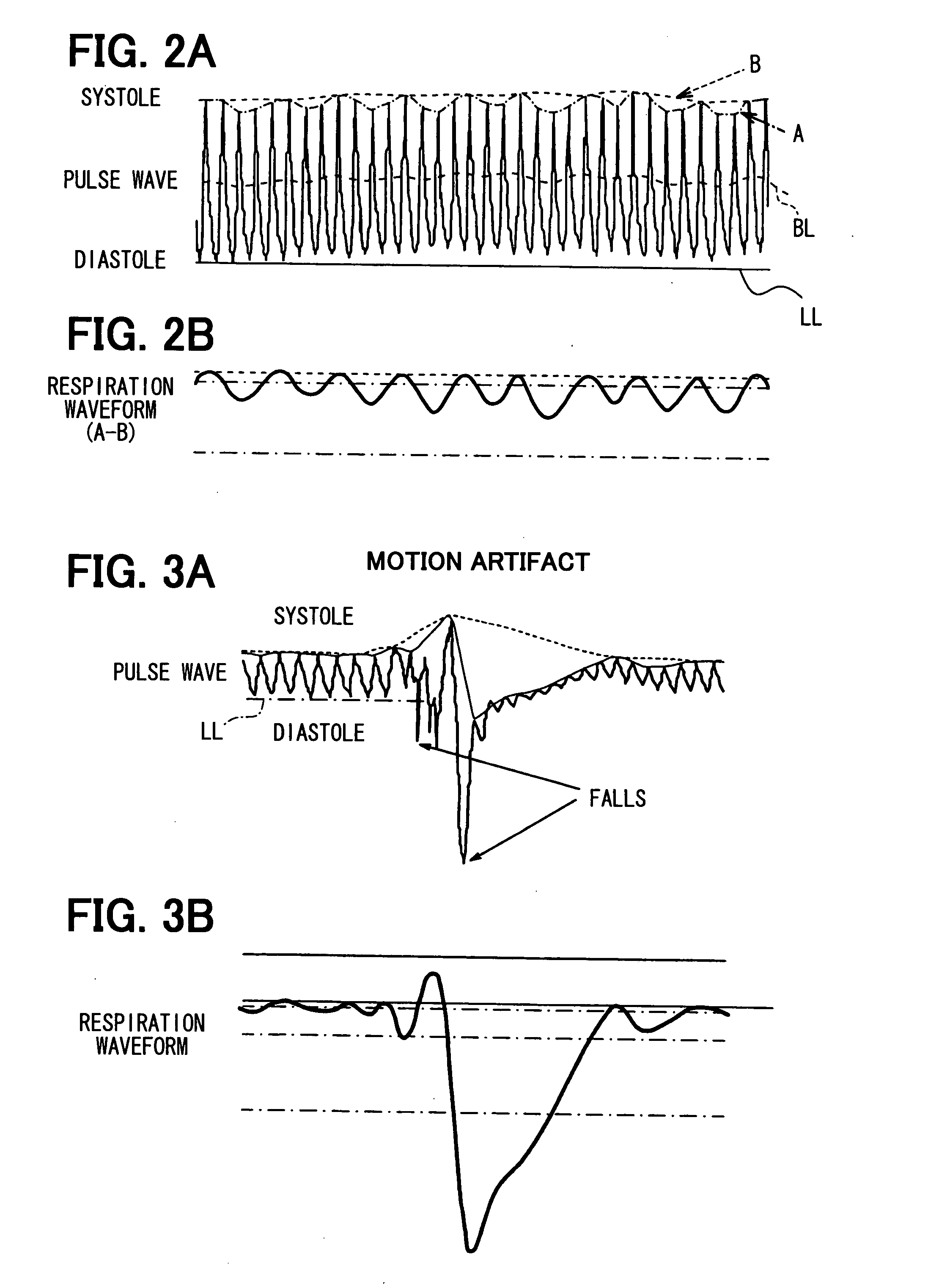
Apparatus for detecting vital functions, control unit and pulse wave sensor
ActiveUS8177720B2Accurate measurementExcessive pressureDiagnostics using lightPerson identificationYawnPulse wave
An apparatus for detecting vital functions has a pulse wave sensor attachable to a body and a control unit. The control unit checks if amplitude of pulse wave signals produced from the pulse wave sensor varies. The control unit further checks if a large change in the amplitude during a systolic phase of a pulse wave corresponding to the systolic phase of the heart. If a first large change in the amplitude during a diastolic phase of a pulse wave corresponding to the diastolic phase of the heart, it is highly probable that a motion artifact has occurred. Therefore, a motion artifact flag is set. Next, it is checked if the amplitude in the next diastole is changing by more than 30%. if it is presumed that the occurrence of cough is highly probable, a cough flag is set. if it is neither the motion artifact nor the cough, then a yawn flag is set.
Owner:SHIOMI TOSHIAKI +1
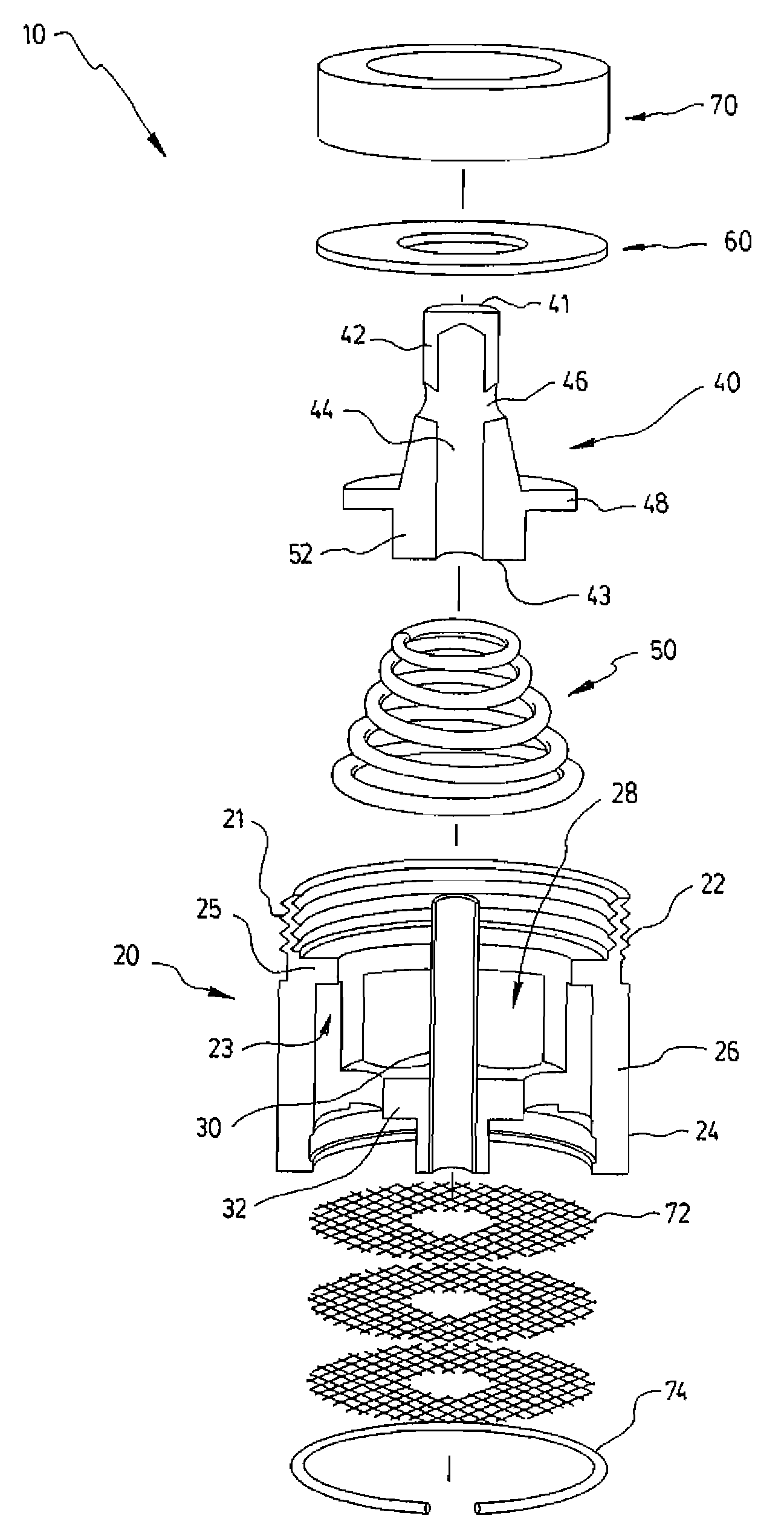
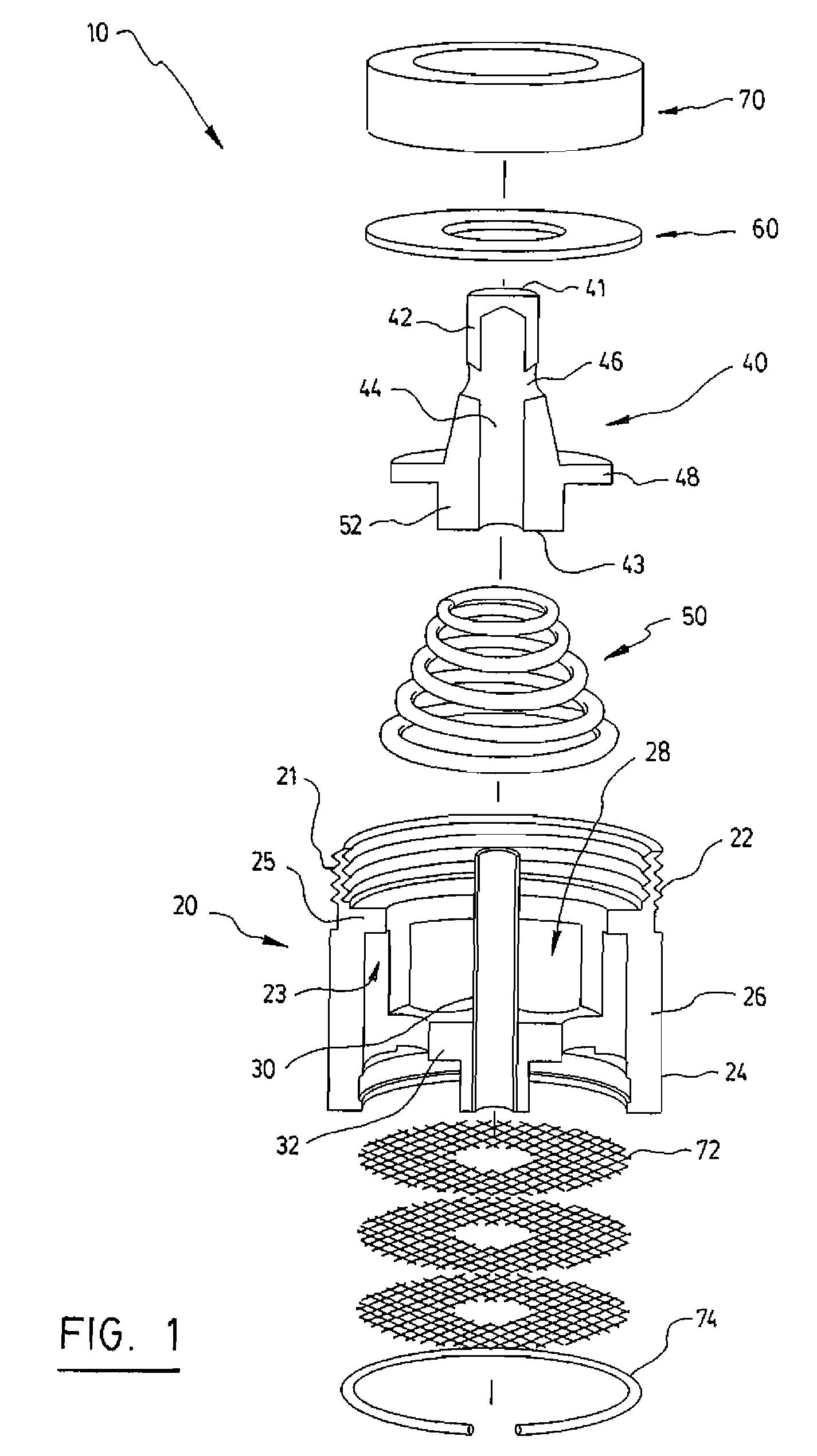
A food preparation capsule
ActiveUS20160052706A1Deformability is not impactedExcessive pressureReady-for-oven doughsContainers with multiple articlesPistonCavity pressure
The present invention concerns a capsule (11) containing a beverage ingredient, adapted to be functionally inserted in a food preparation machine (1), said capsule comprising walls (12) that define a cavity wherein said beverage is prepared by mixing said ingredient with a fluid injected therein under pressure by said machine, said capsule further comprising a dispensing opening (13), and opening means that open upon effect of the rise of pressure within said cavity, characterized in that said opening means comprise a flow-conducting channel (14) able to connect the capsule cavity to the dispensing opening (13) and a spring-mounted piston plug (15) that is movable in said channel between: (i) a closed position where said cavity pressure is below a first predetermined pressure Pc, the piston spring (16) is at rest, and the piston plug (15) seals against a sealing portion (19) of the channel walls, (ii) a dispensing position where said cavity pressure is equal or superior to Pc, the piston spring (16) is elastically deformed and the piston plug (15) is moved away from the channel walls so that beverage can flow outside of said capsule through said channel (14).
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090001386A1Effective reflectionExcessive pressureLaser detailsSolid-state devicesPressure relaxationDevice material
The present invention provides a semiconductor device realizing reduced occurrence of a defect such as a crack at the time of adhering elements to each other. The semiconductor device includes a first element and a second element adhered to each other. At least one of the first and second elements has a pressure relaxation layer on the side facing the other of the first and second elements, and the pressure relaxation layer includes a semiconductor part having a projection / recess part including a projection projected toward the other element, and a resin part filled in a recess in the projection / recess part.
Owner:SONY CORP
Tubular, especially can-shaped, receptacle for the accommodation of fluids, a method of manufacture, and use
ActiveUS20050262813A1Improve pressure bearing capacityImprove stabilityBottlesLarge containersEngineering
Tubular, especially can-shaped, receptacle for the accommodation of fluids, especially drinks, with a tubular body and a base and top section attached to this, wherein the top section is constructed in the shape of a shoulder and is suitable for attaching a closure device, especially a resealable one. The shoulder-shaped top section is at least partially enclosed, especially in the shape of a shoulder, by an upper edge of the tubular body and sealed with this.
Owner:HUHTAMAKI RONSBERG ZWEIGNIEDERLASSUNG DER HUHTAMAKI DEUT
Torque measuring device for a device measuring the flow of material
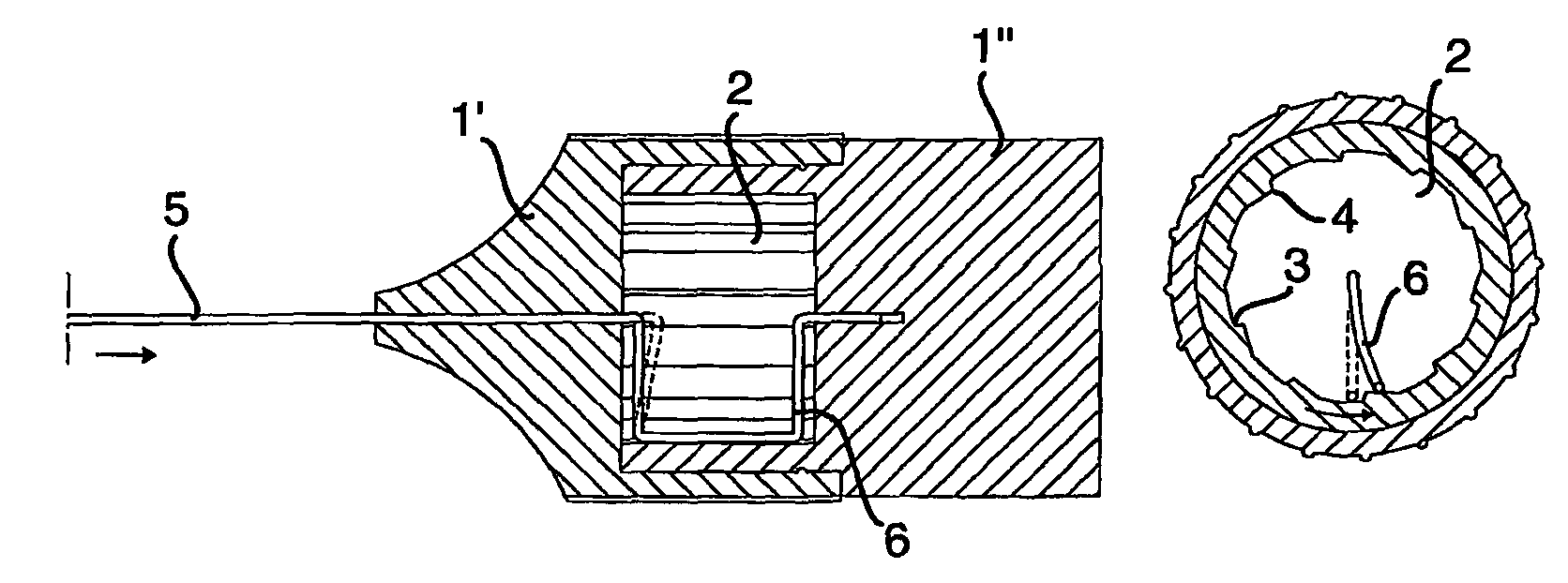
InactiveUS6705171B1Improved zero stabilityMeasuring value constantDirect mass flowmetersRotational axisImpeller
The invention relates to a device for measuring the flow of material, especially of a flow of bulk material, according to the Coriolis principle of measurement. The device has an impeller (2) which is driven by a motor (9) with a constant r.p.m. The flow of material is fed to the impeller (2) and is radially deflected. The driving torque is measured by a torque measuring sensor. The driving torque is transmitted to a force sensor (22) by a pivot bearing (12) for determining the torque. The force-sensing element (22) has at least two horizontal leaf springs (16, 17) which cross each other and which are arranged in such a way that the crossing point of the leaf springs (16, 17) coincides with a rotational axis (13). A thrust bearing (14) is integrated into the pivot bearing (12). The weight of the drive train is transmitted to a stationary housing (8) by the thrust bearing (14) with the help of a ball bearing or toe bearing. A frictionless air bearing (3) is provided for horizontally supporting the drive shaft (5) in order to improve the measuring accuracy.
Owner:SCHENCK PROCESS GMBH
Apparatus for detecting vital functions, control unit and pulse wave sensor
ActiveUS20070282227A1Simple methodAccurate measurementDiagnostics using lightPerson identificationYawnPulse wave
An apparatus for detecting vital functions has a pulse wave sensor attachable to a body and a control unit. The control unit checks if amplitude of pulse wave signals produced from the pulse wave sensor varies. The control unit further checks if a large change in the amplitude during a systolic phase of a pulse wave corresponding to the systolic phase of the heart. If a first large change in the amplitude during a diastolic phase of a pulse wave corresponding to the diastolic phase of the heart, it is highly probable that a motion artifact has occurred. Therefore, a motion artifact flag is set. Next, it is checked if the amplitude in the next diastole is changing by more than 30%. If it is presumed that the occurrence of cough is highly probable, a cough flag is set. If it is neither the motion artifact nor the cough, then a yawn flag is set.
Owner:SHIOMI TOSHIAKI +1
Test device for determining three-dimensional consolidation properties of soils
ActiveUS9546940B2Excessive pressureIncrease lateral resistanceEarth material testingMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesRubber membraneEngineering
Owner:GUPTA RAMESH CHANDRA
Faucet end piece
ActiveUS20090020628A1Excessive pressureLess waterDomestic plumbingSpray nozzlesWater flowEngineering
A faucet end piece connectable to a faucet nozzle is provided including a cylindrical body defining a cavity, a vertical pipe extending within the cavity, and an internal partition with water passages therethrough, extending across the cavity and connecting the vertical pipe to the body; a valve insertable in the cavity including a cap portion fitting over the vertical pipe and having at least one side orifice, a bore and a flange portion projecting transversally from the cap portion; a resilient element insertable inside the cavity between the body's internal partition and the valve flange portion. The valve is movable vertically under water pressure between an upper position wherein water flows through the cap portion side orifice, the bore and through the body vertical pipe, and a lower position where water flows around the cap portion through the internal partition water passages.
Owner:BELISLE CHRISTIAN
Apparatus And Method for Material Distribution
ActiveUS20120291319A1Reduce pressureExcessive pressureMachines/dredgers working methodsMechanical machines/dredgersEngineeringMaterial distribution
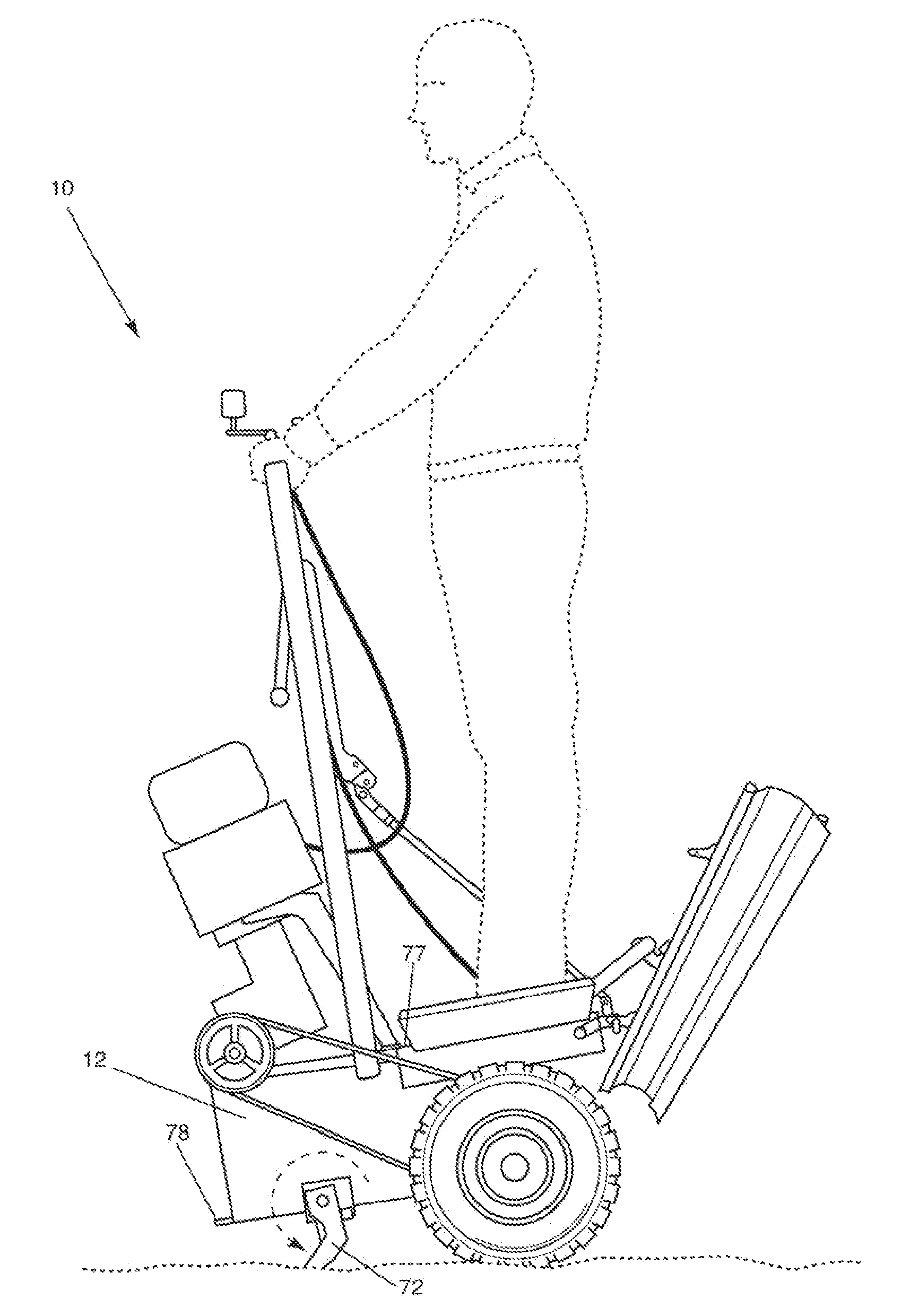
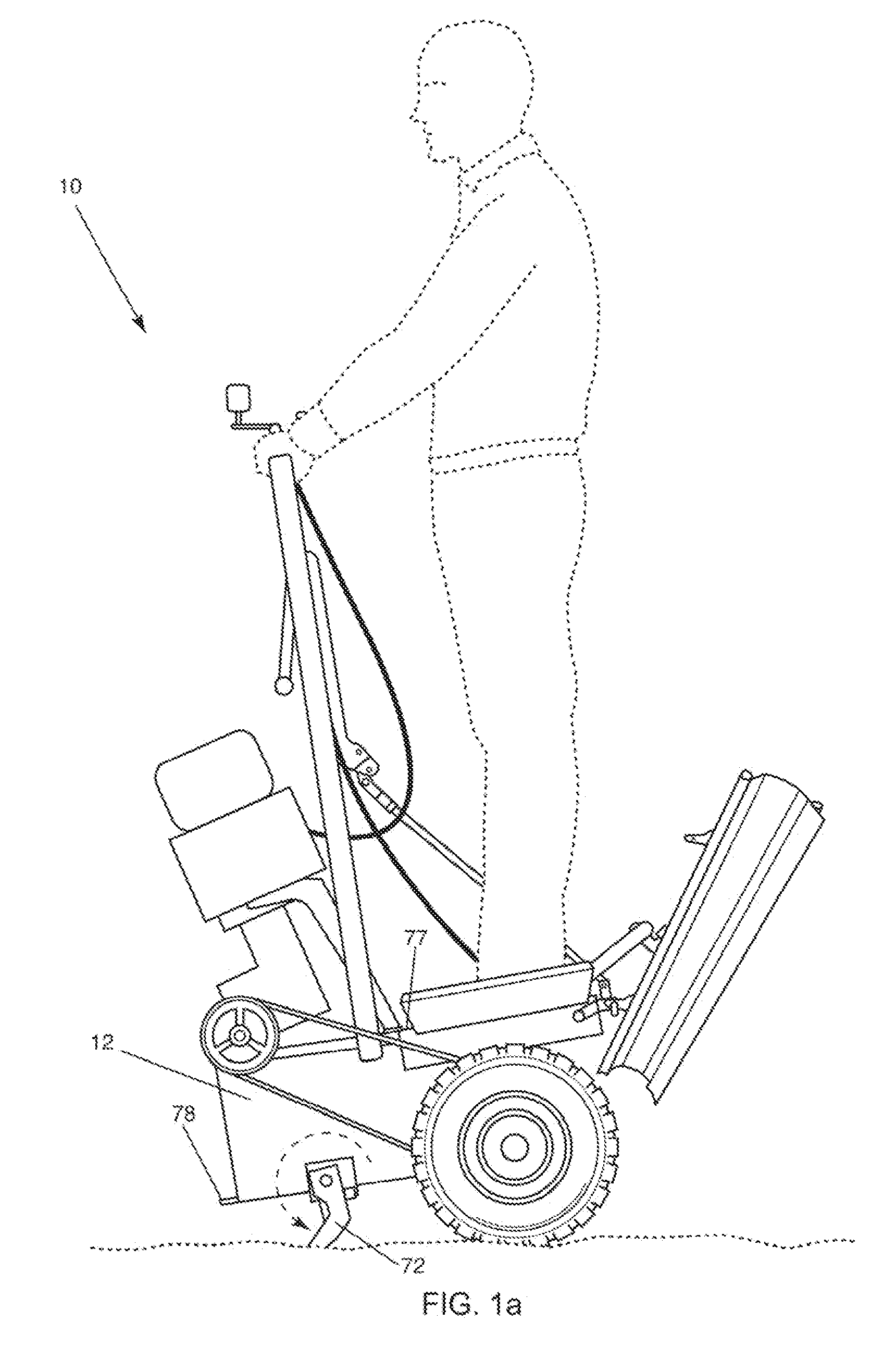
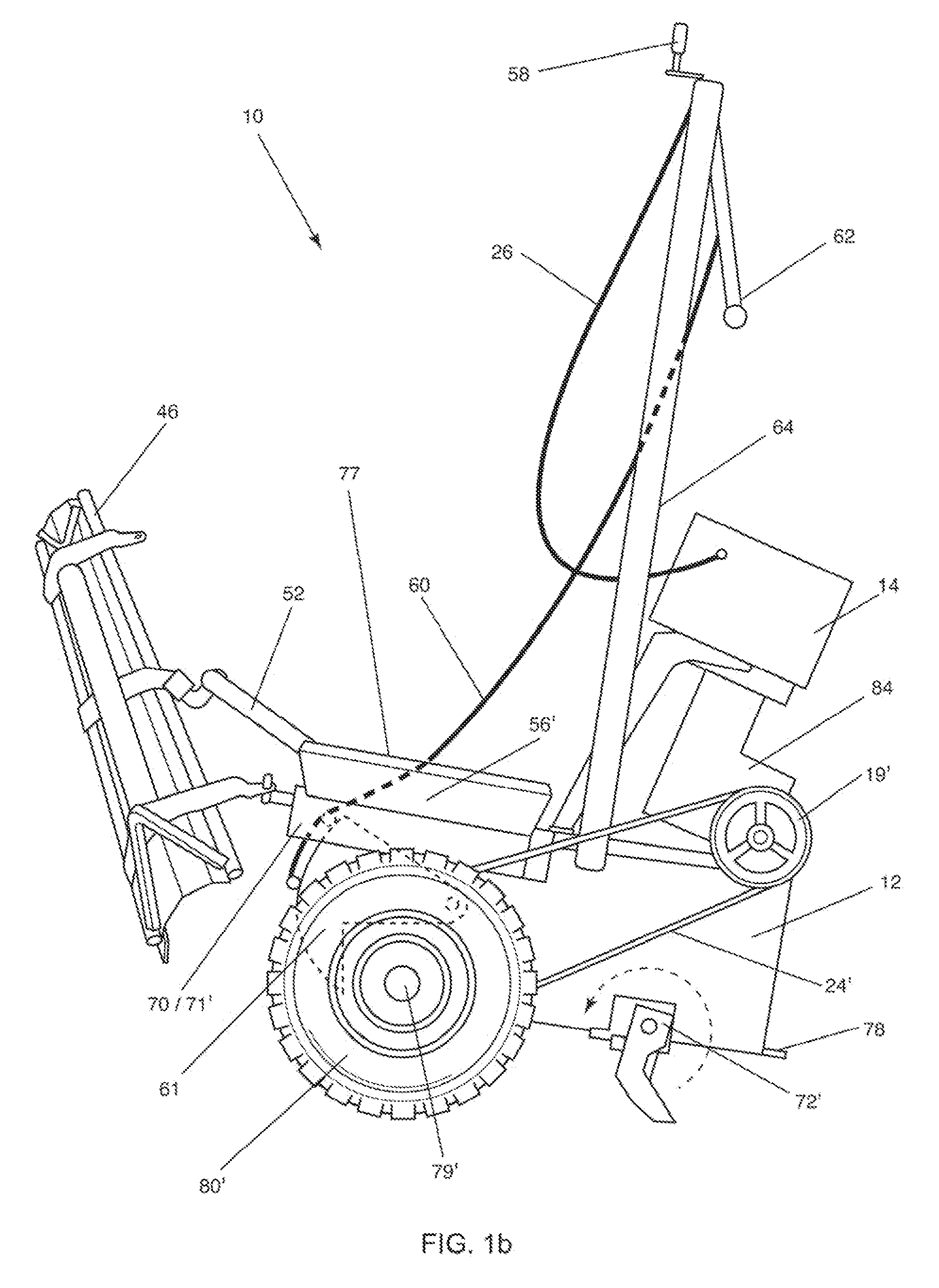
Apparatus and method for material distribution, including a draw-bar to which is fixedly connected a bucket body. Wheels are attached to the drawbar on opposite sides of the bucket body between an open side and a gate thereof. A lower edge of the open side of the bucket body, which can receive material, is in the form of a cutting blade or teeth. The gate, which is disposed opposite from the open side, can be opened and closed. At least part of a top side of the bucket body forms a platform for an operator. At least one engine is provided and is drivingly connected to the wheels. A handlebar is connected to the bucket body, forward of the platform, for pivoting the bucket body about the wheels so that the cutting blade or teeth can be brought into or out of contact with a surface.
Owner:JONES DAVID A
Tool and a method for attaching a cardiac stimulator lead at a desired position inside a heart
InactiveUS7981121B2Simple and inexpensive and reliableLimiting the torque transmitted to the helixTransvascular endocardial electrodesDiagnosticsEngineeringHelix
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Faucet end piece
ActiveUS7581685B2Excessive pressureLess waterSpray nozzlesDomestic plumbingPore water pressureWater flow
A faucet end piece connectable to a faucet nozzle is provided including a cylindrical body defining a cavity, a vertical pipe extending within the cavity, and an internal partition with water passages therethrough, extending across the cavity and connecting the vertical pipe to the body; a valve insertable in the cavity including a cap portion fitting over the vertical pipe and having at least one side orifice, a bore and a flange portion projecting transversally from the cap portion; a resilient element insertable inside the cavity between the body's internal partition and the valve flange portion. The valve is movable vertically under water pressure between an upper position wherein water flows through the cap portion side orifice, the bore and through the body vertical pipe, and a lower position where water flows around the cap portion through the internal partition water passages.
Owner:BELISLE CHRISTIAN
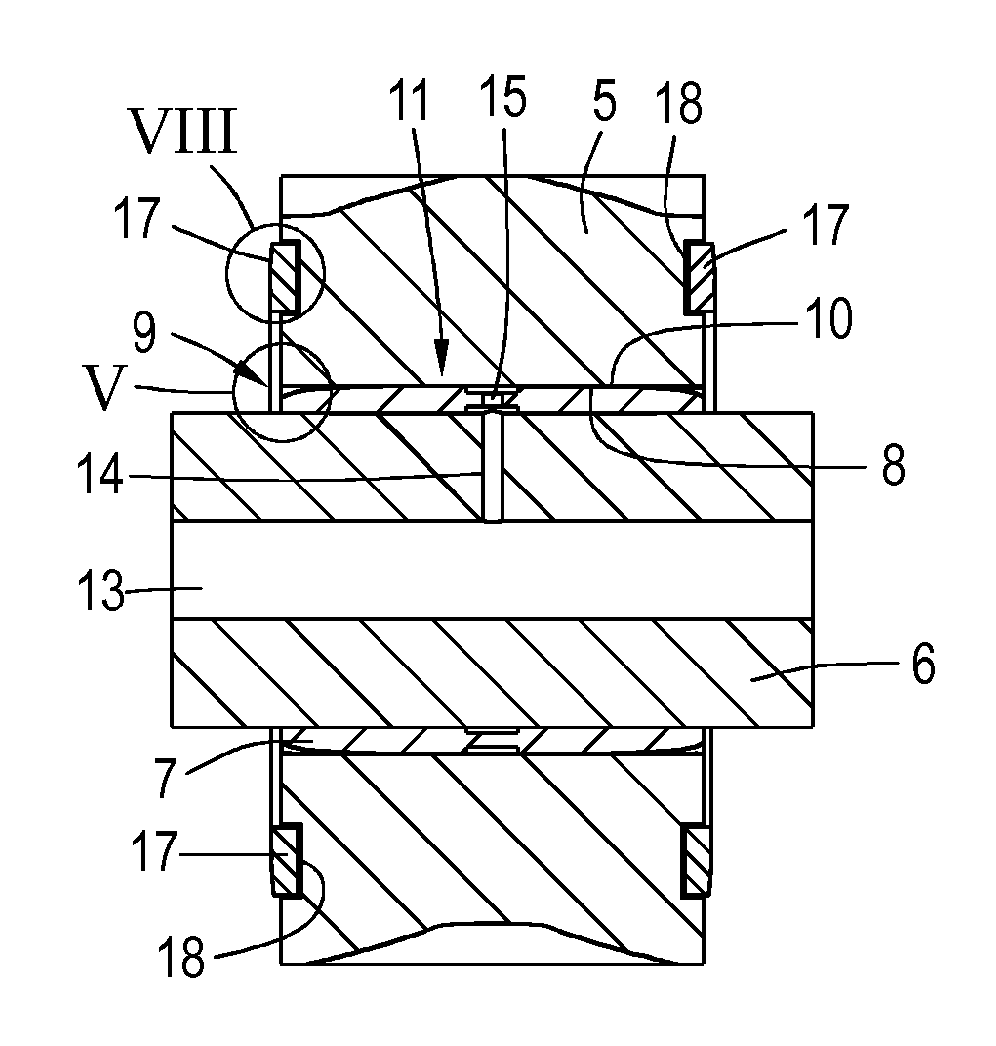
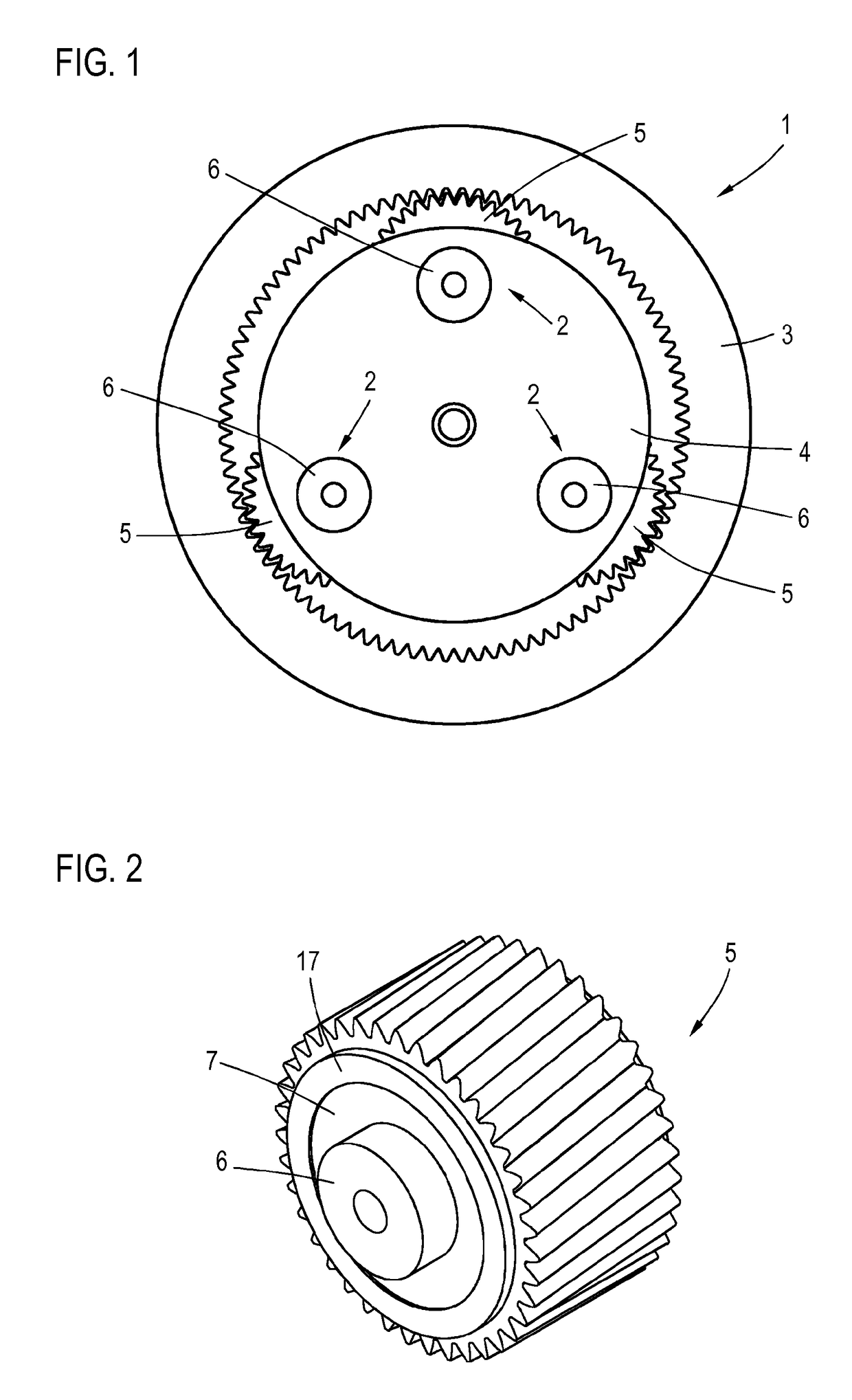
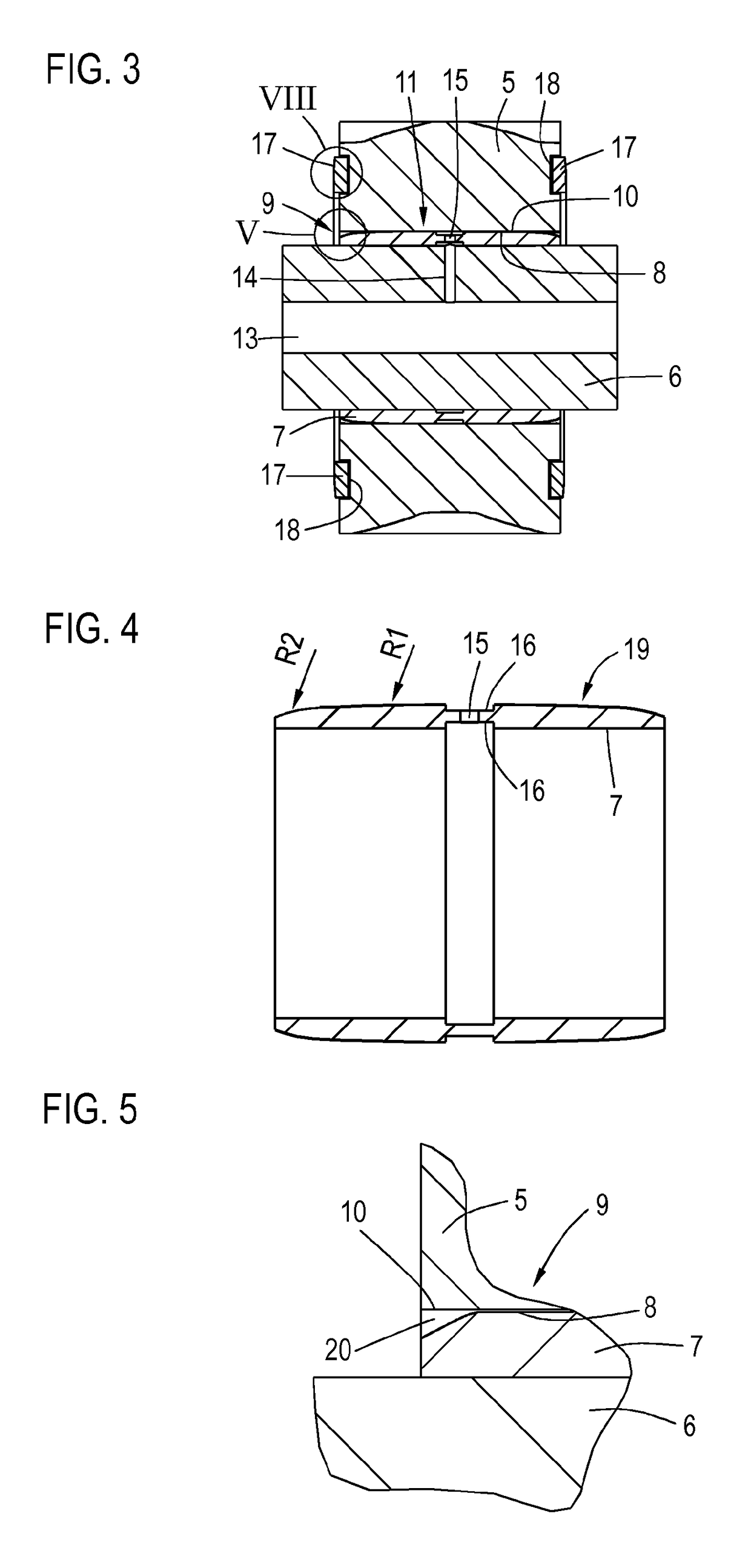
Planetary gear bearing arrangement
ActiveUS10047792B2Reduce edge stressExtreme wear resistanceEngine fuctionsShaftsFixed bearingGear wheel
A planetary gear bearing arrangement, including a planet carrier provided with a fixed bearing axis on which a planet gear is rotatably mounted via a sliding bearing that has a first antifriction layer on the axis side and a second antifriction layer on the gear side, wherein one of the two antifriction layers (8, 11) is created on a surface (10, 19) which is at least partially domed in the sliding region to reduce the edge pressure.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com