Patents
Literature
177 results about "Laser beam transmission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
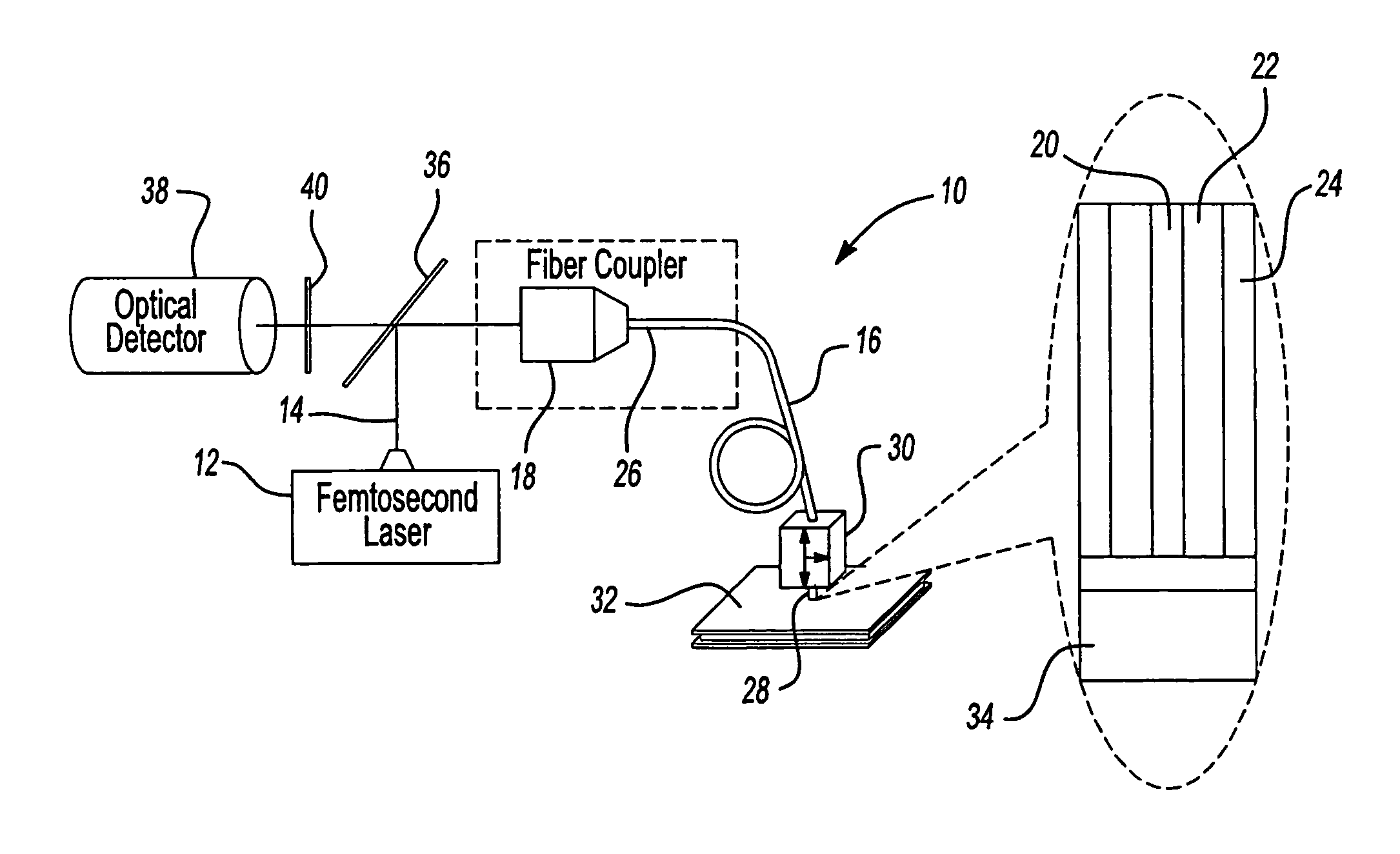
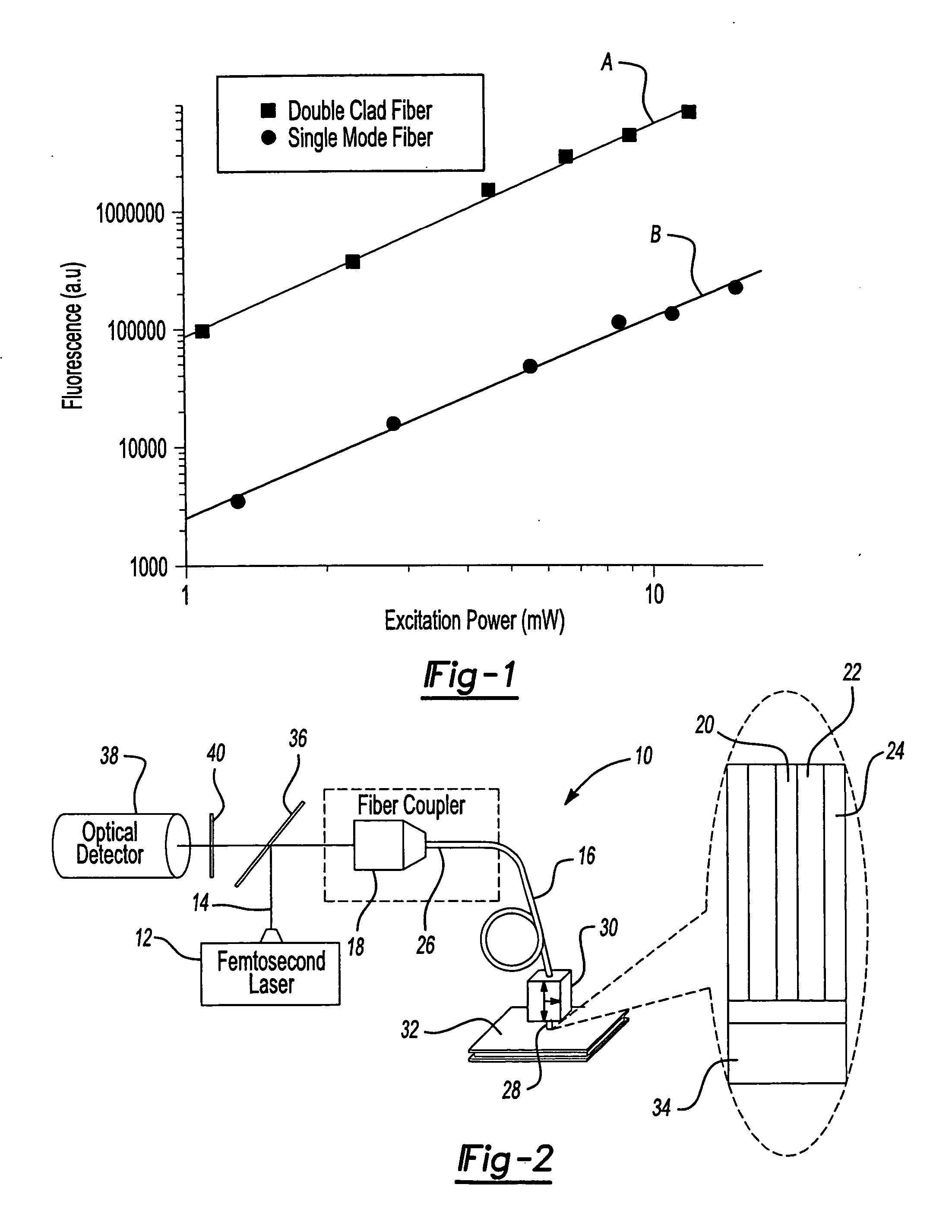
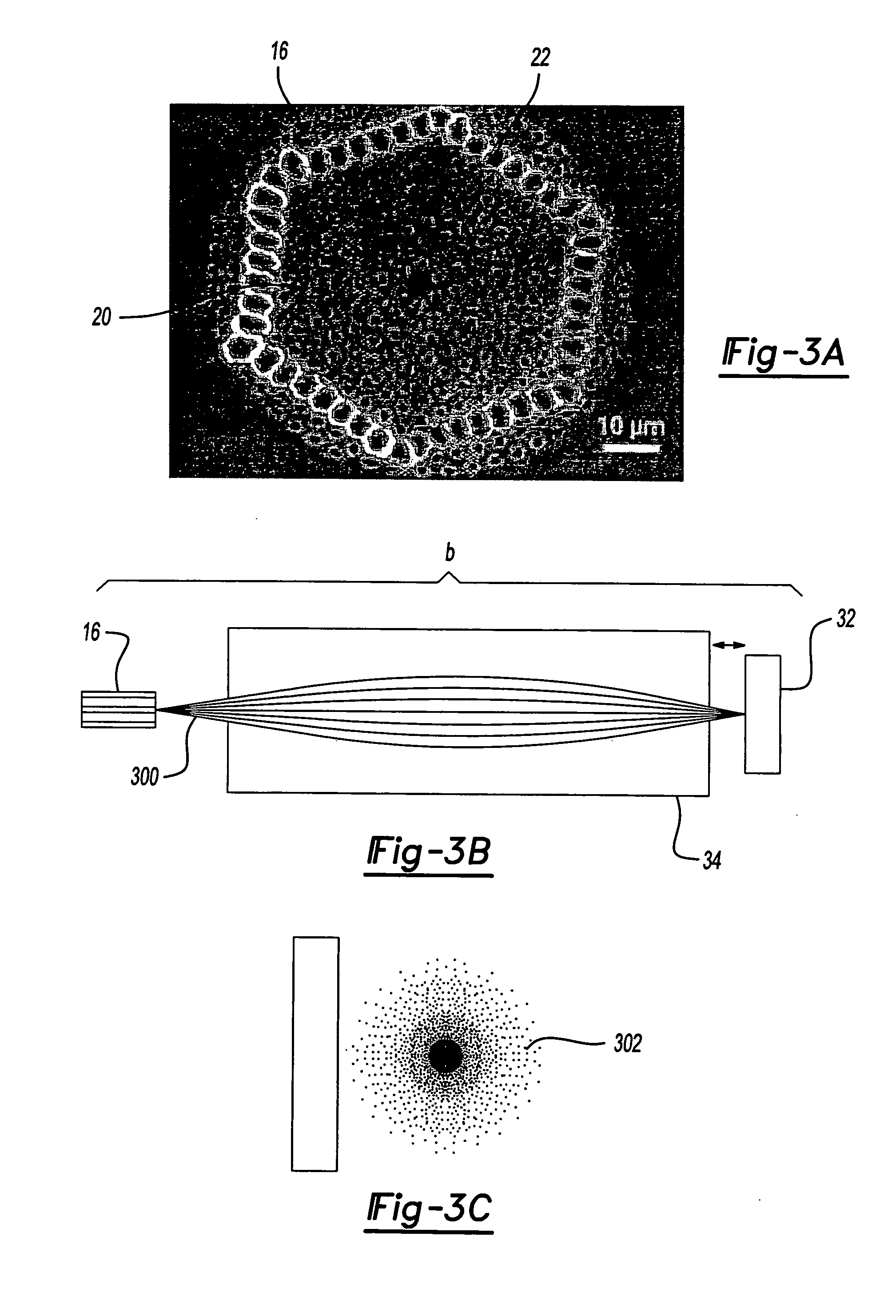
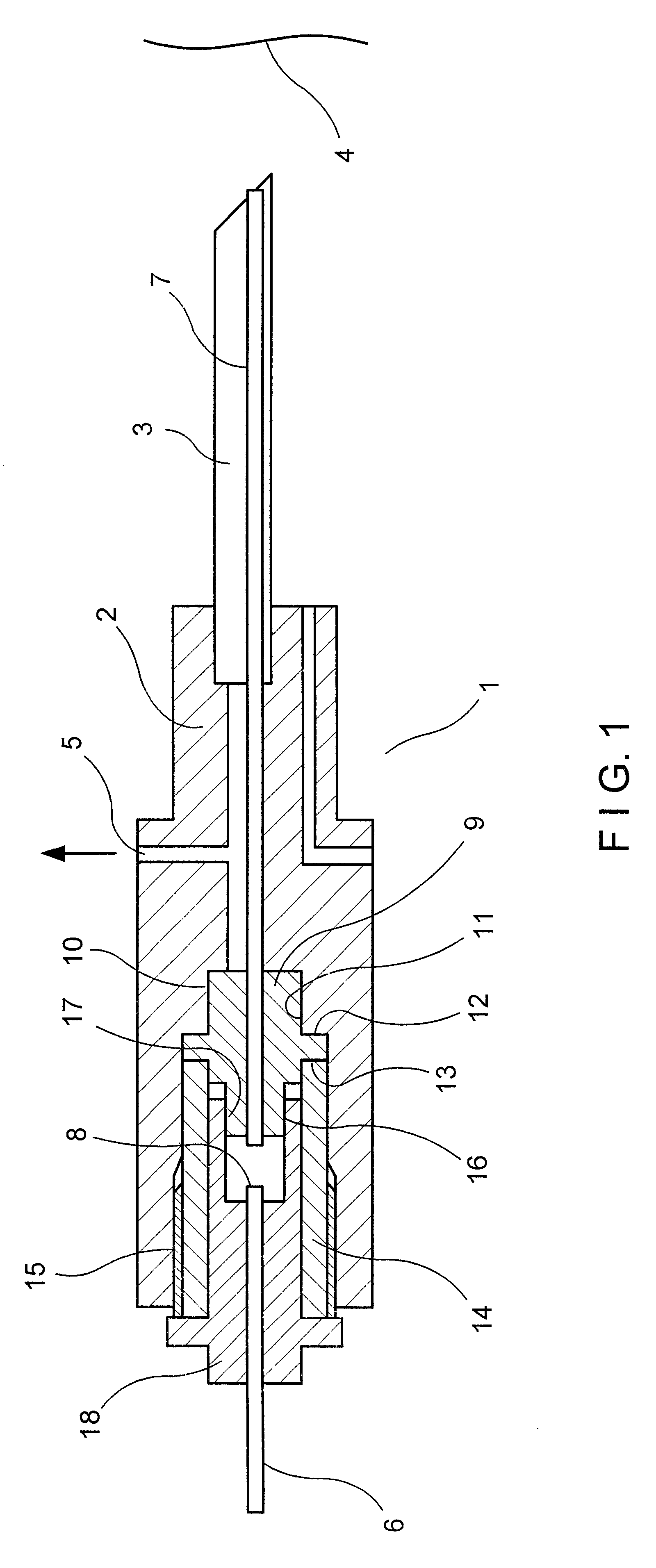
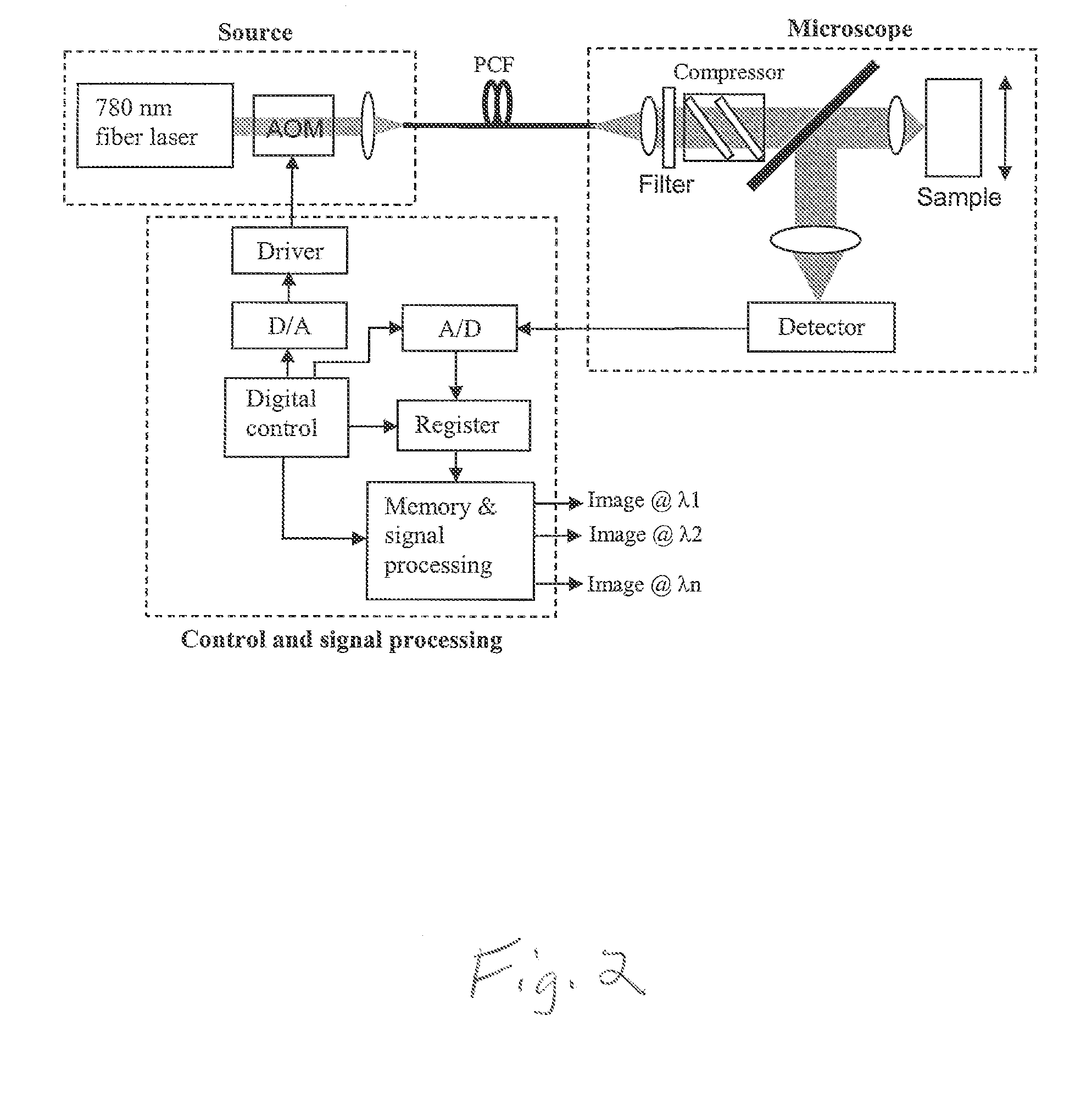
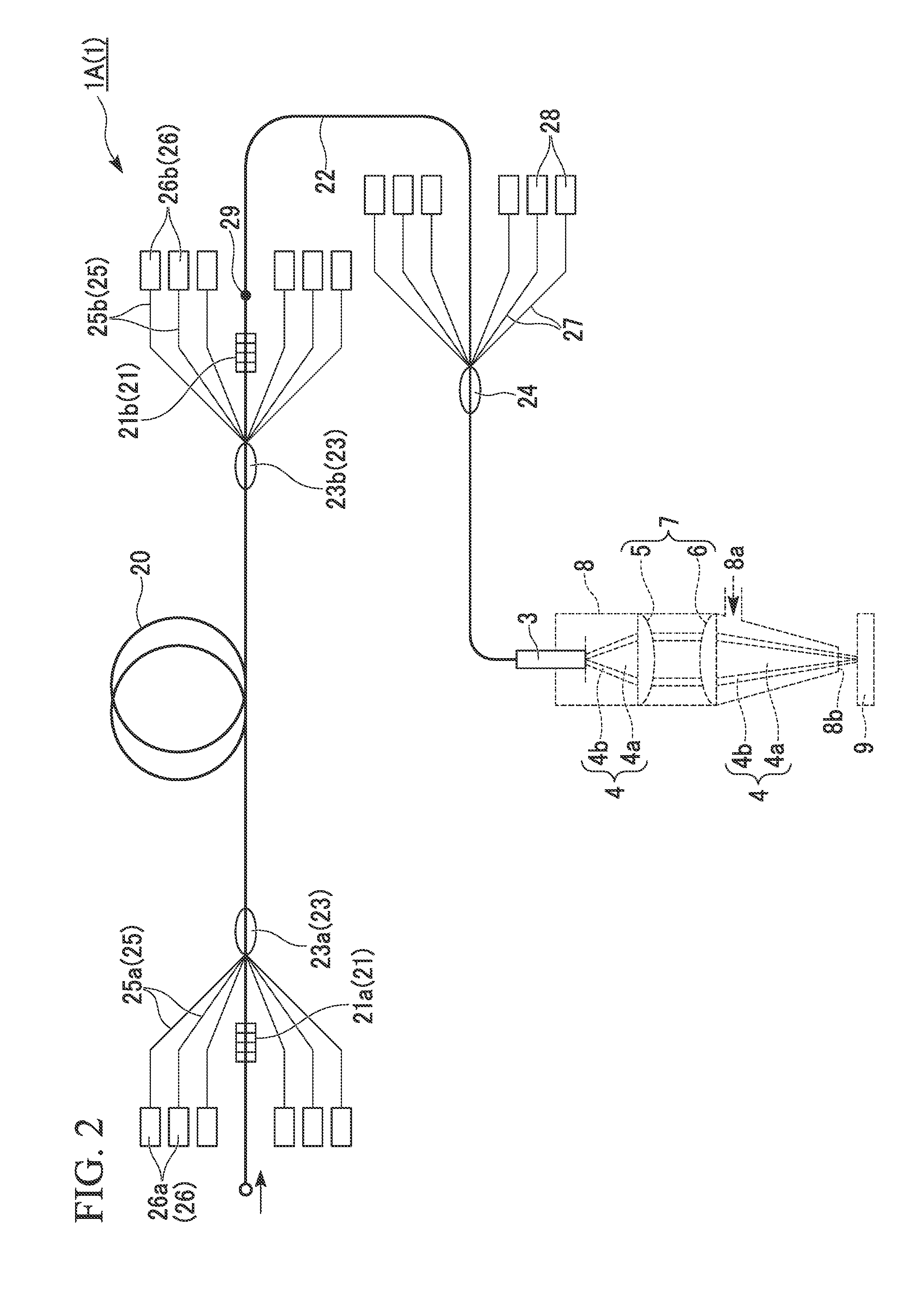
Double-clad fiber scanning microscope
ActiveUS20070002435A1High resolutionImprove detection efficiencyRaman scatteringMicroscopesFiberDouble-clad fiber
A scanning microscope having a laser outputting an excitation laser beam and a fiber member having a first core and a second core. The second core is generally disposed within the first core and is operable to receive the excitation laser beam from the laser and transmit the excitation laser beam to a sample to be tested. A moveable stage supports an end of the fiber member and / or a sample to be tested and is operable to move the end of the fiber member and the sample to be tested relative to each other.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Portable digital lidar system
A light detecting and ranging system and method for detecting airborne agents in which the system includes a laser which provides laser pulses of at least two wavelengths, a transmitter which transmits the laser pulses, a receiver which receives both elastically backscattered signals from airborne agents and fluorescence signals from the airborne agents, a common telescope which both focuses a laser beam transmission of the laser pulse from the transmitter to a far field and receives the elastically backscattered signals and the fluorescence signals from the far field, a digital detection system having at least one of a backscatter optical detector which detects the elastically backscattered signals and a fluorescence optical detector which detects the fluorescence signals from the airborne agents.
Owner:SCI & ENG SERVICES
Fiber optic infrared laser beam delivery system
ActiveUS7099533B1Lower Level RequirementsAccurately heldOptical resonator shape and constructionCoupling light guidesFiberPhotonics
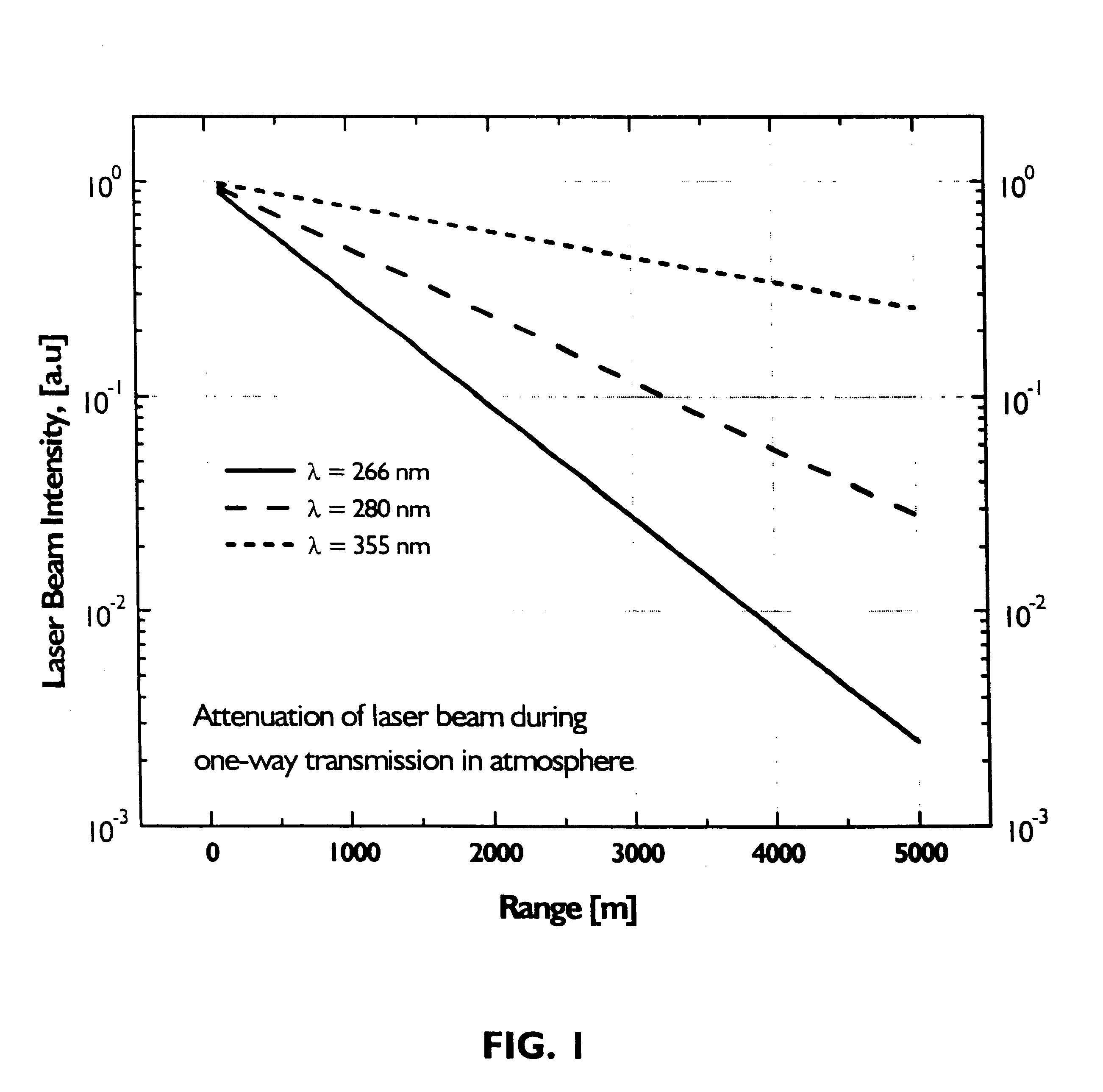
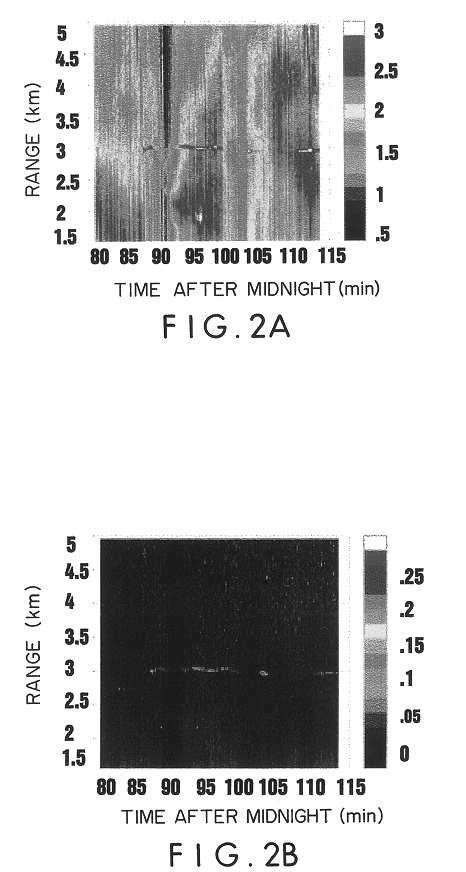
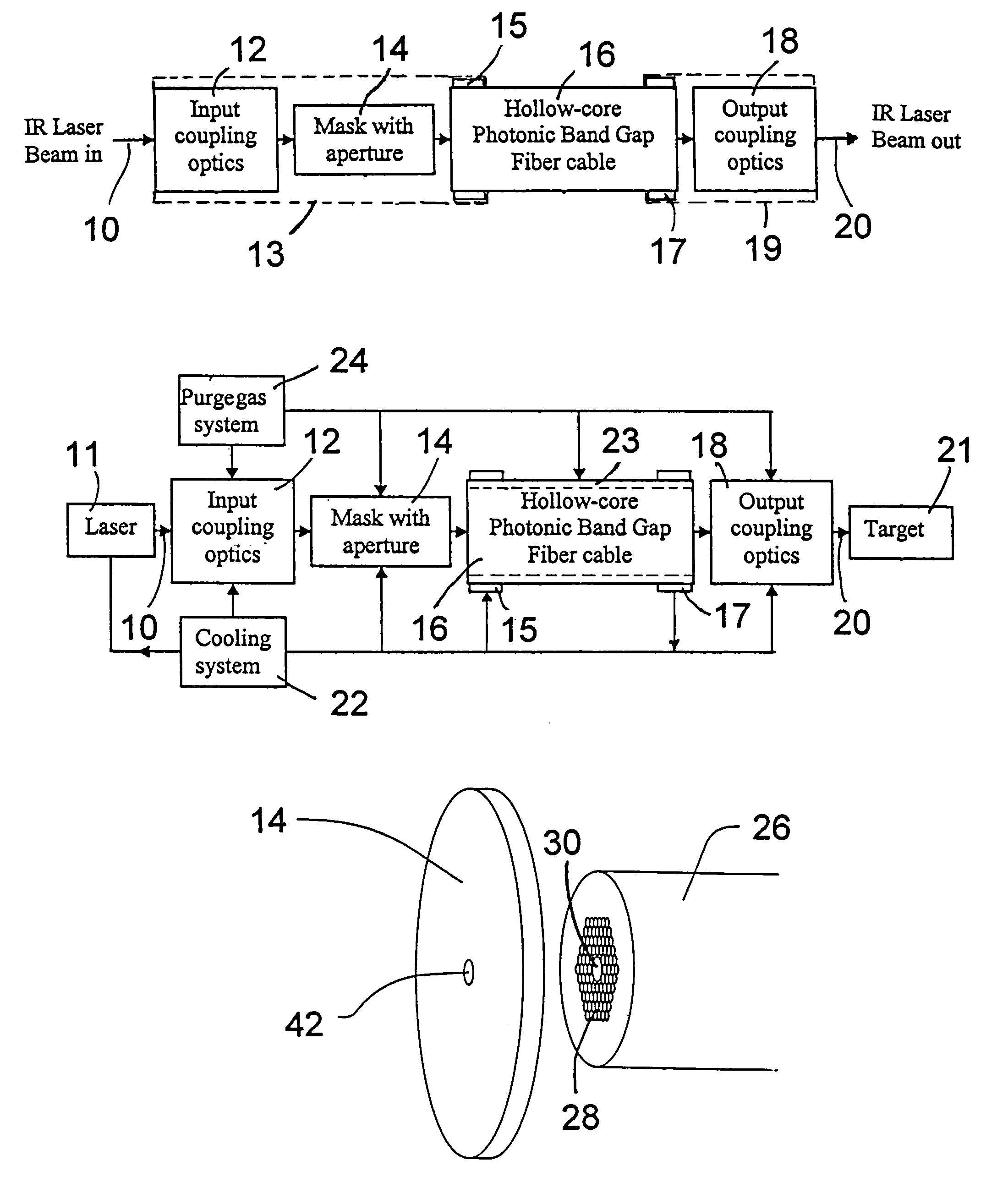
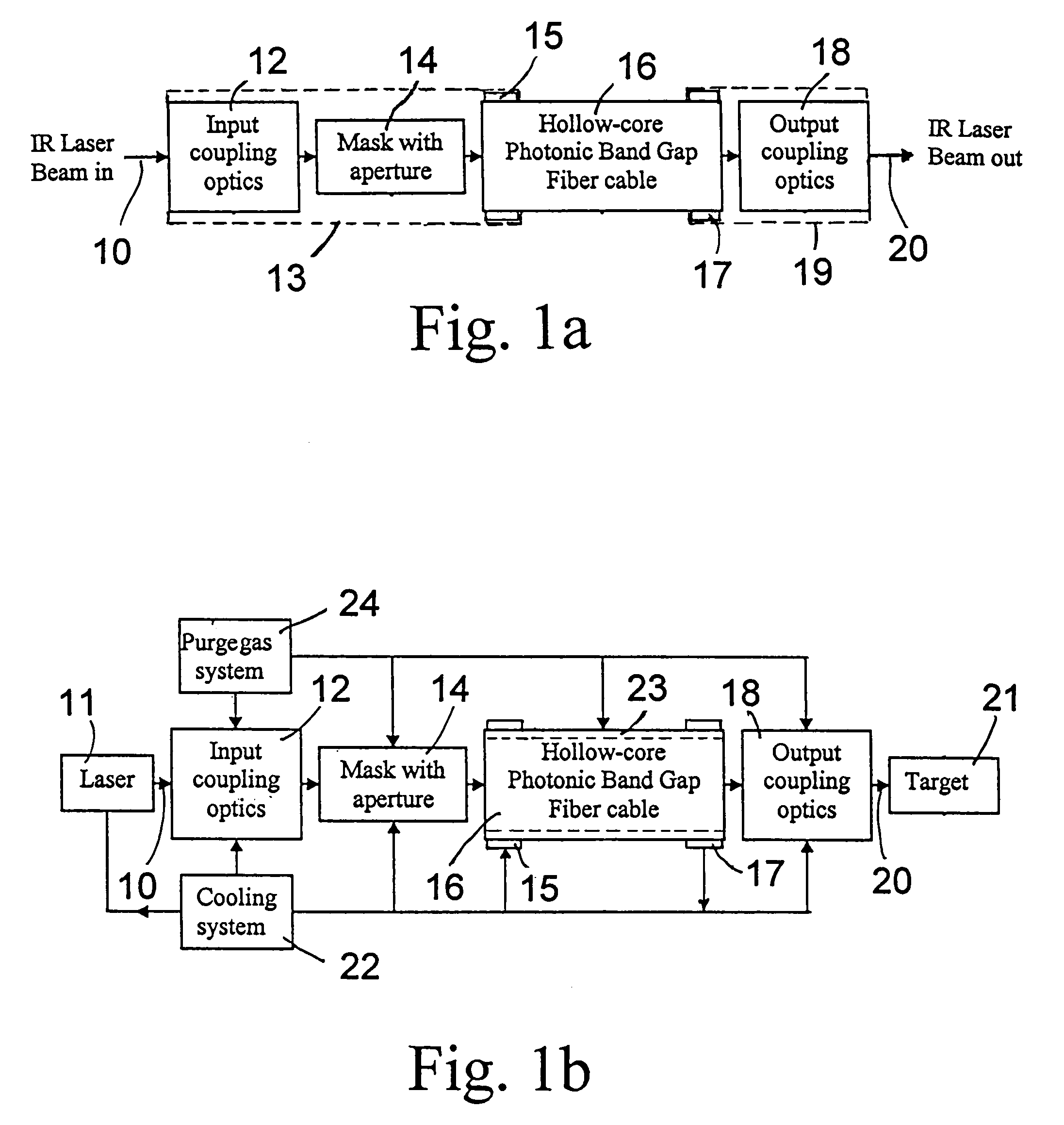
A laser beam delivery system is disclosed, which allows transmission of high-power infrared light through a hollow core photonic band gap (HC-PBG) fiber made of non-silica-based glass. In this system, the infrared beam first passes through input coupling optics which focus the beam onto the hollow core of the HC-PBG fiber. In front of the input end of the HC-PBG fiber, there is provided a mask with a hole aligned with the hollow core, and the infrared beam first passes through this hole before entering the hollow core of the HC-PBG fiber. This protects the photonic band gap structure from being damaged by the beam. After passing through the HC-PBG fiber, which may be from one to several hundred meters in length, the infrared beam exits at the output end of the fiber and passes through output coupling optics which collimate and focus the beam onto a desired target. The various components of the system may be water cooled during the operation or subjected to a gas purge to prevent condensation or gas ionization.
Owner:CHENARD FRANCOIS
Method and apparatus for wellbore perforation
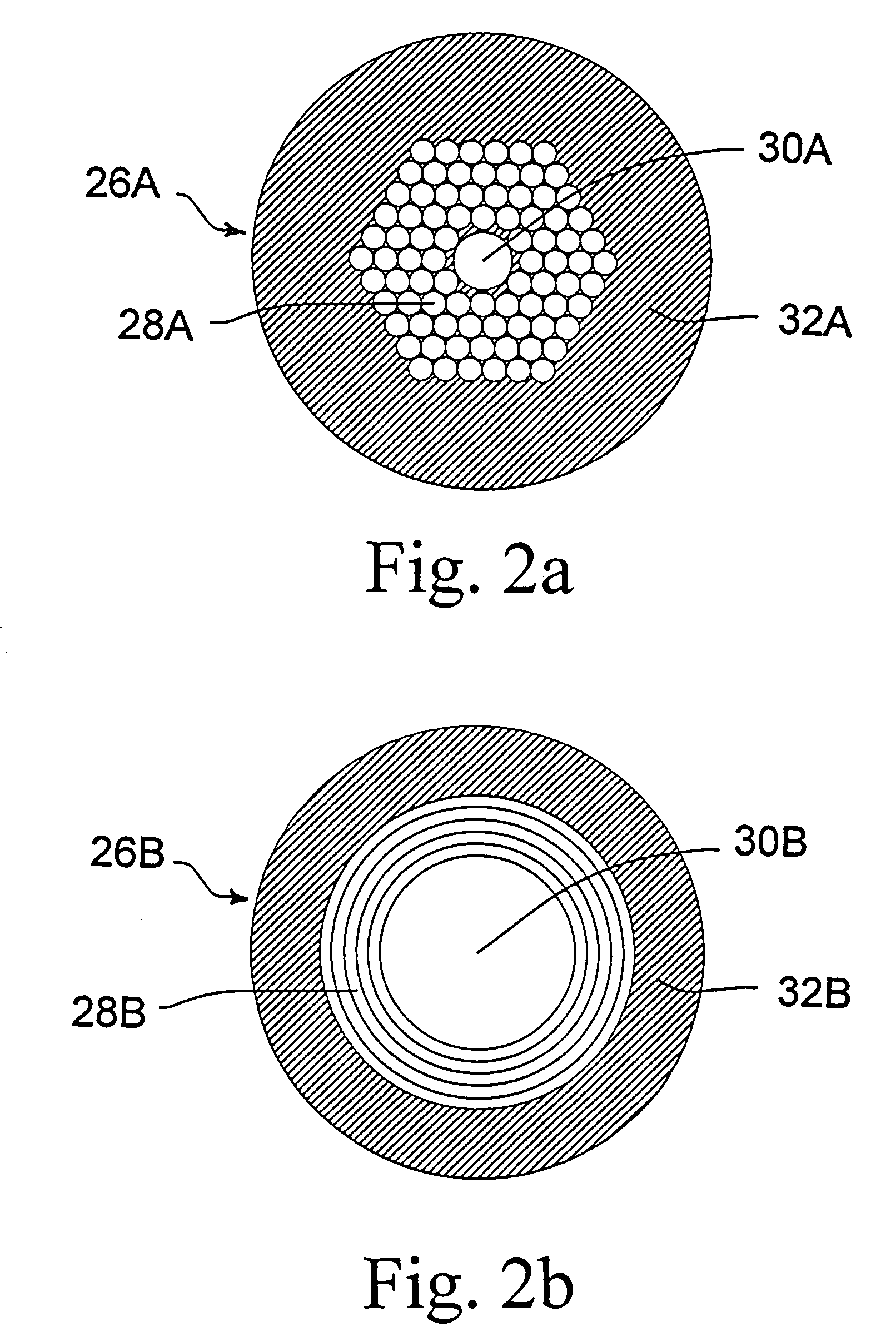
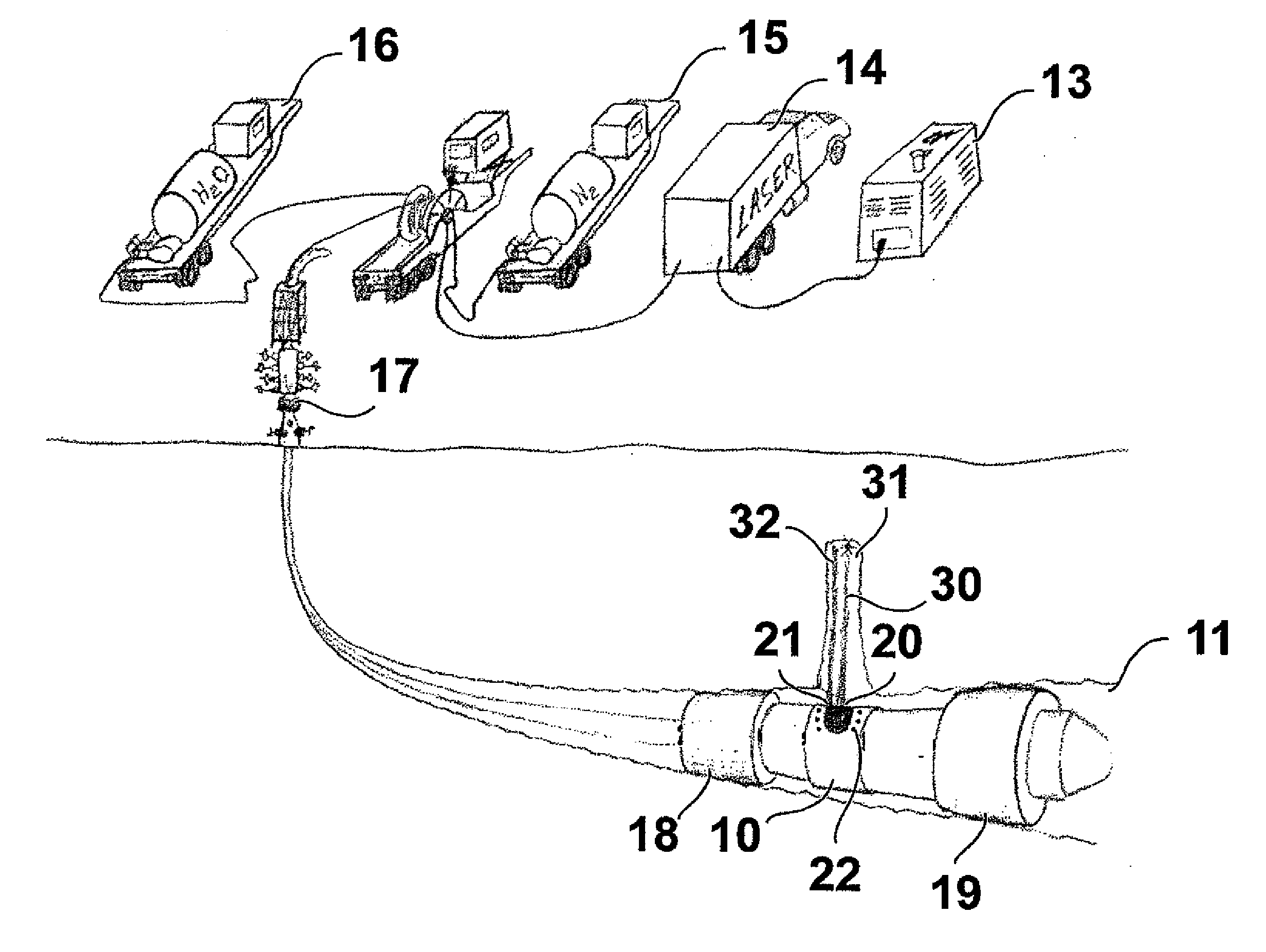
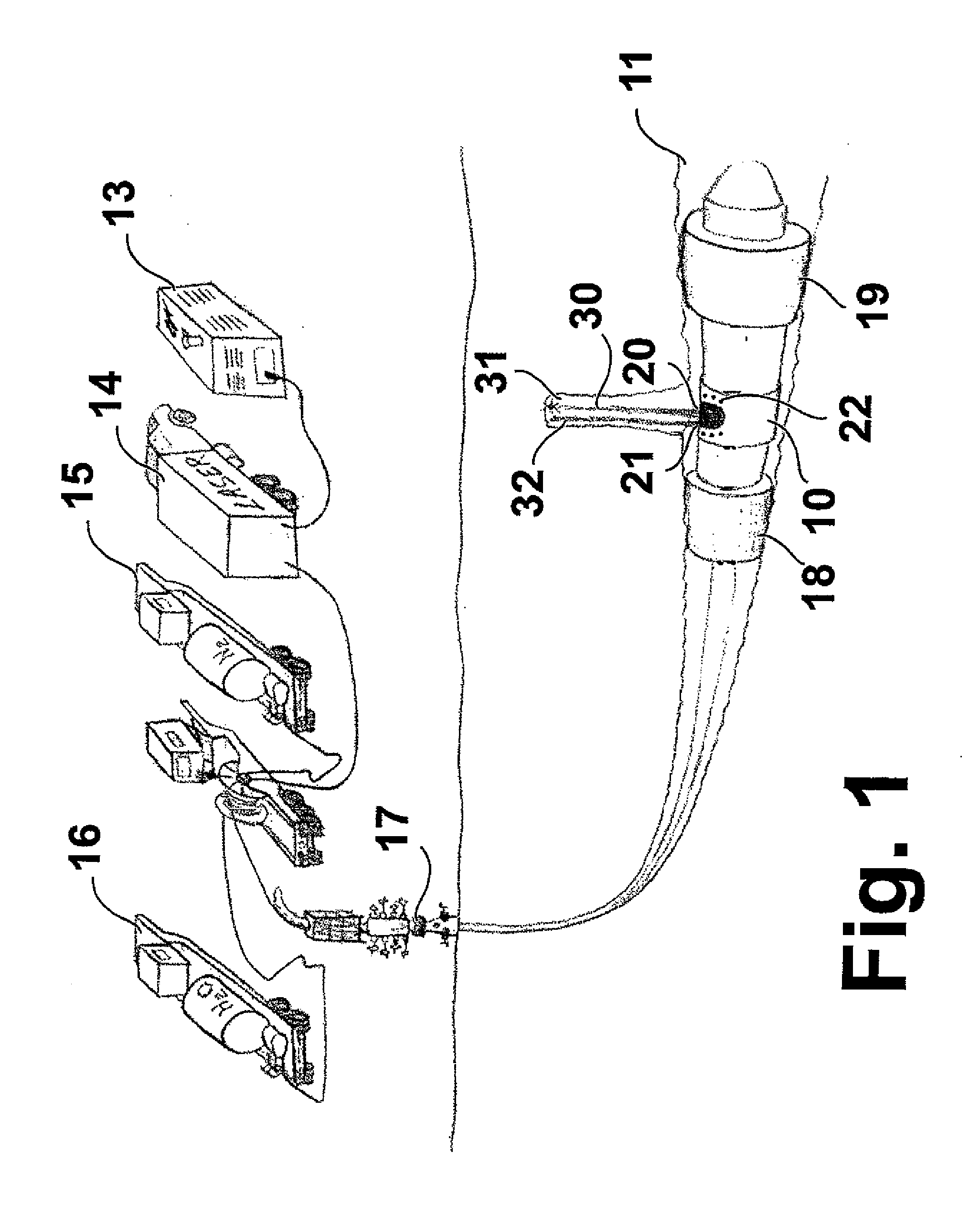
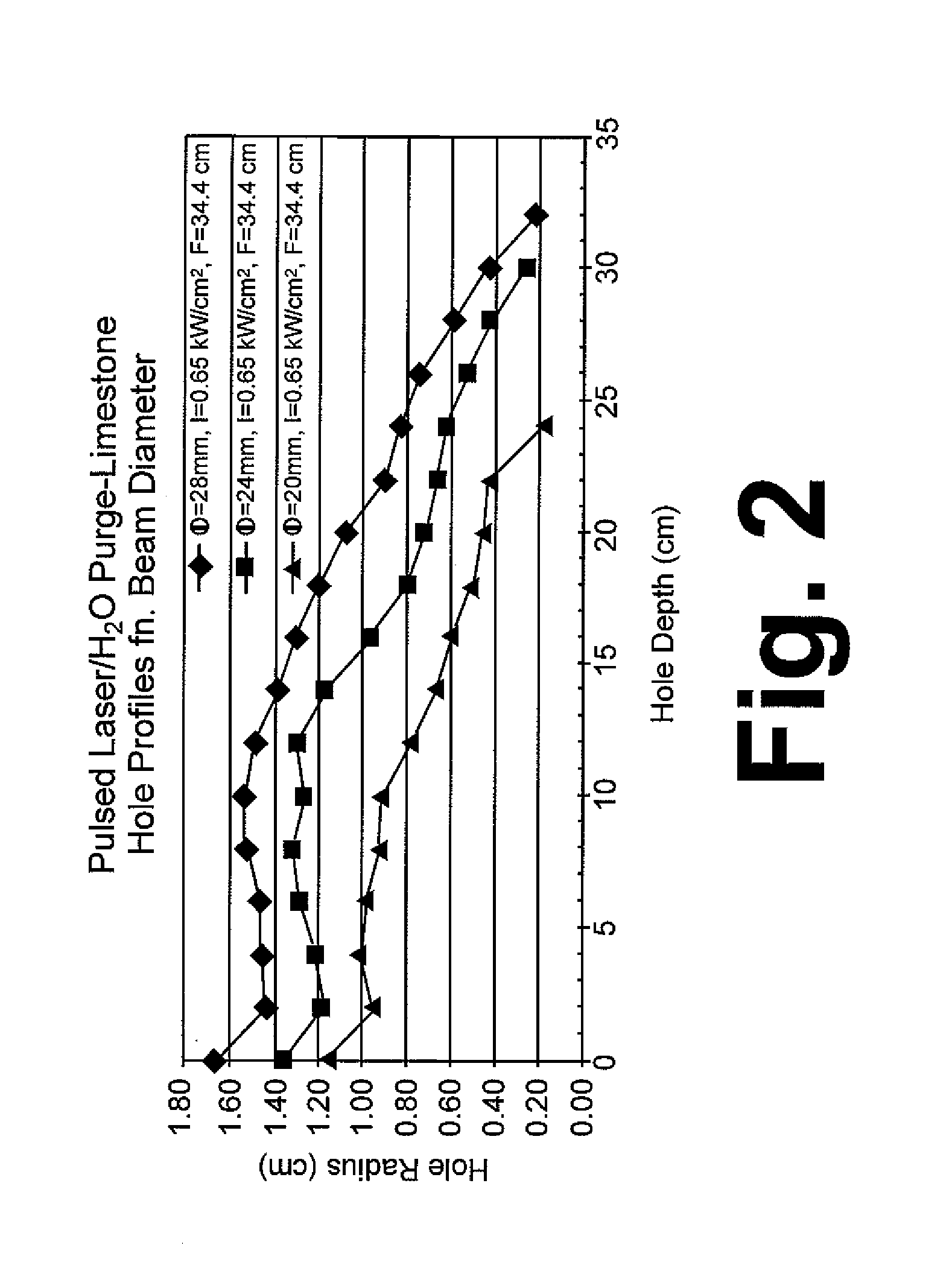
A method for wellbore perforation in which a section of the wellbore to be perforated is isolated and purged of wellbore fluid to provide a clear path for laser beam transmittal. A laser beam emitter in the purged wellbore section transmits a laser beam pulse from the laser beam emitter to a target area of a sidewall and formation lithology of the purged wellbore section, thereby altering a mechanical property of a material of the sidewall and formation lithology and producing material debris. A liquid jet pulse of a liquid is transmitted immediately following termination of the laser beam pulse to the target area, thereby removing the material debris from the target area. This cycle is then repeated until the desired perforation depth has been achieved.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC +1
Laser beam processing machine
ActiveUS20060266744A1Simple structureWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusLight beamOptoelectronics
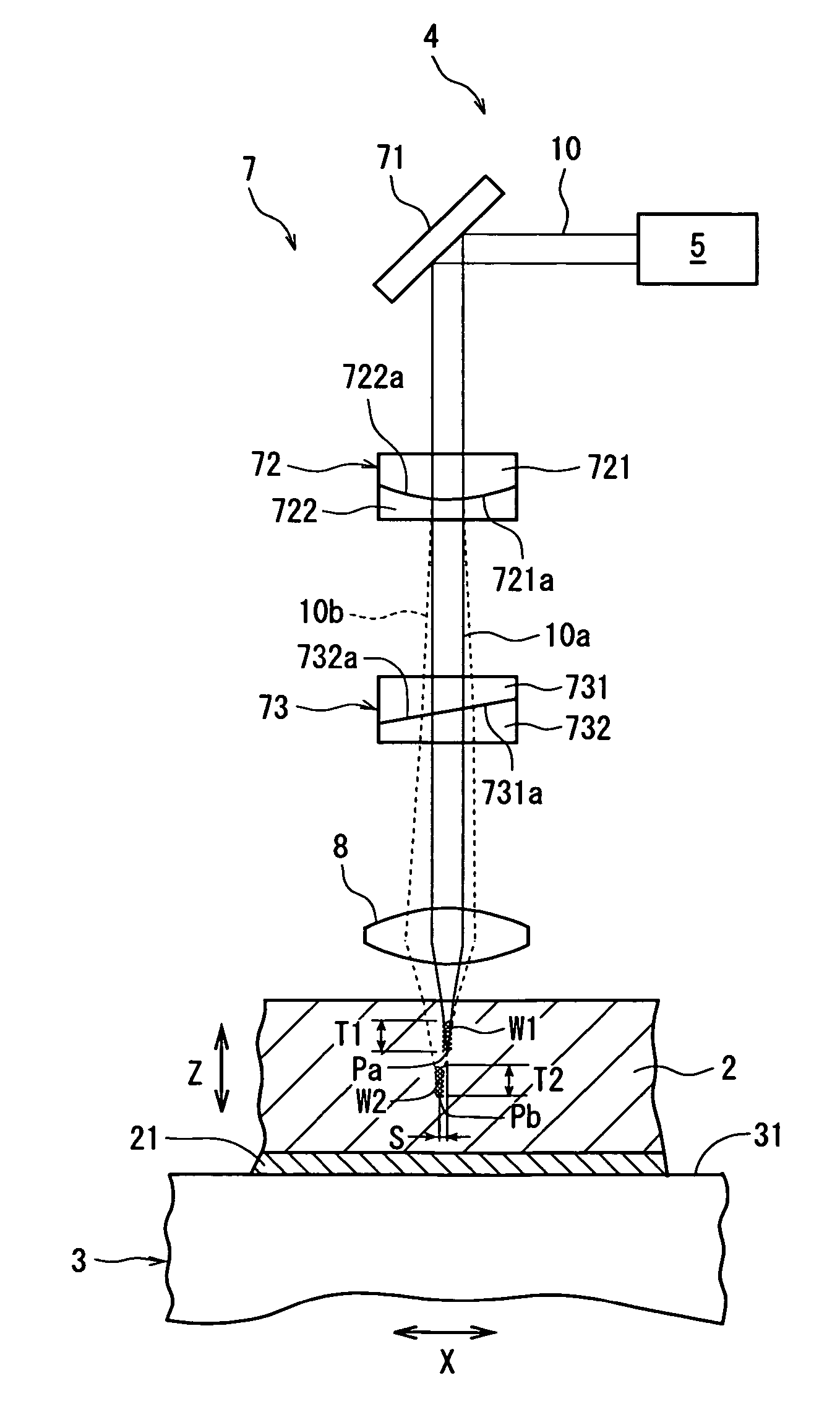
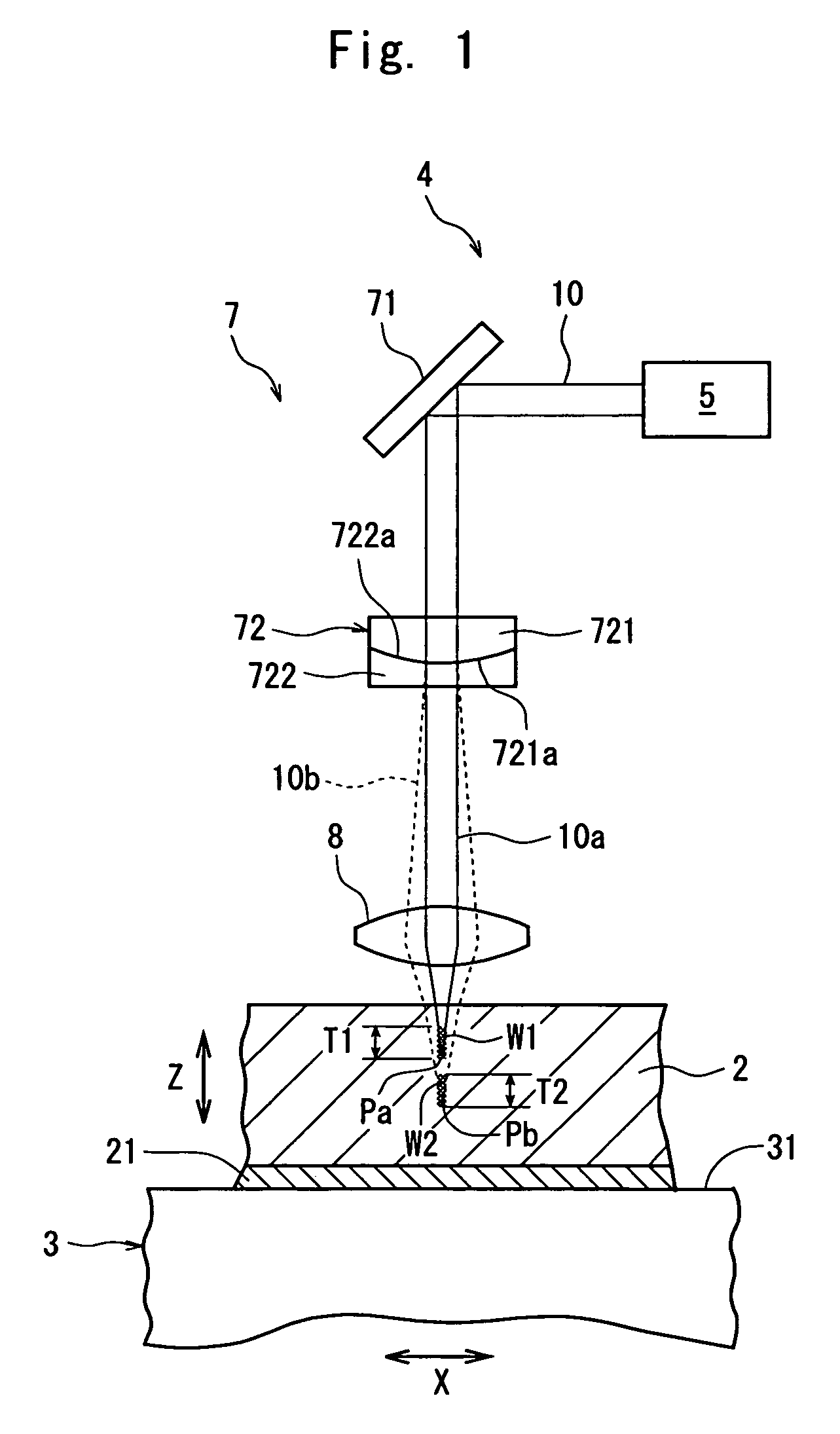
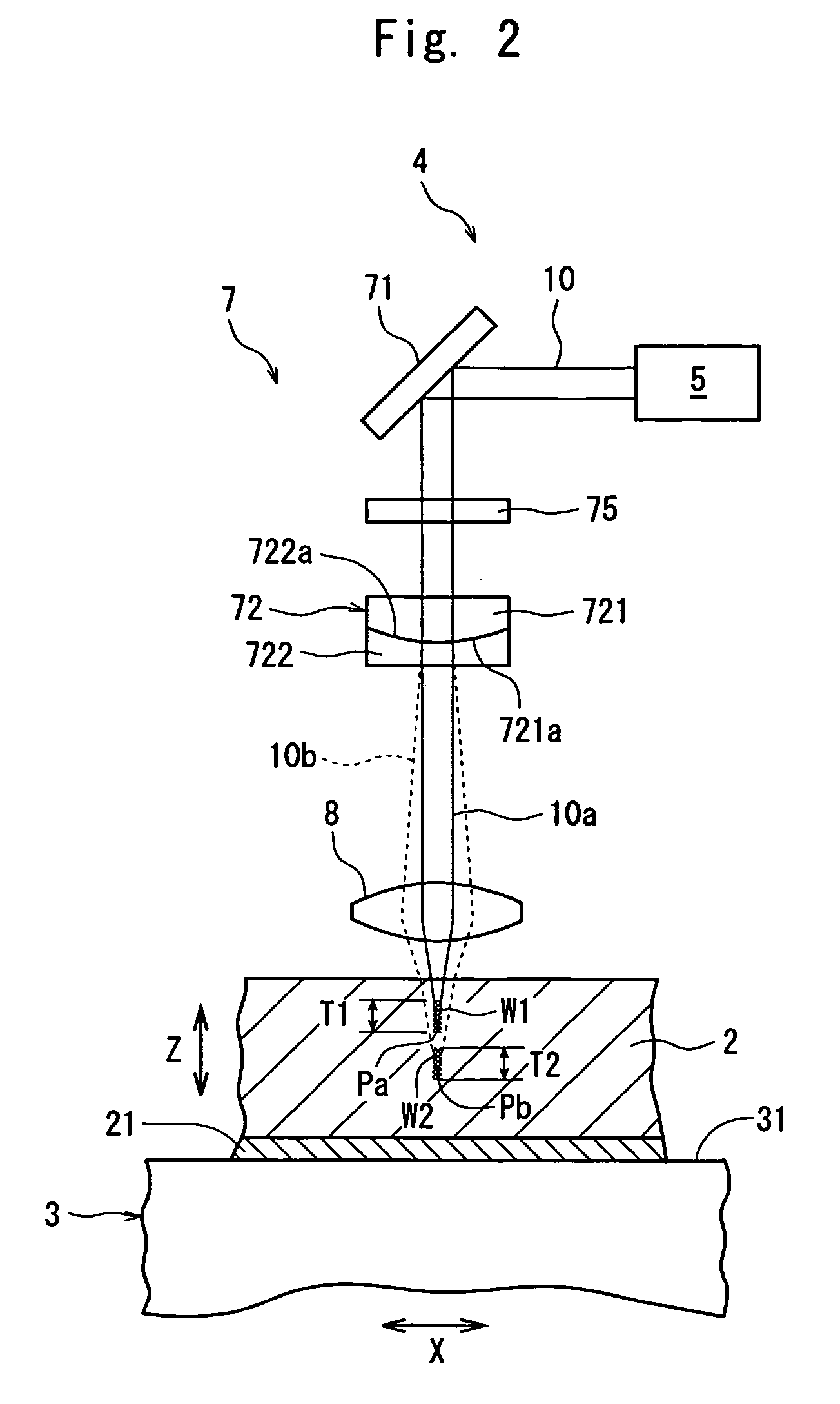
A laser beam processing machine comprising a chuck table for holding a workpiece, a laser beam application means for applying a laser beam capable of passing through the workpiece to the workpiece held on the chuck table, and a processing-feed means for moving the chuck table and the laser beam application means relative to each other, the laser beam application means comprising a laser beam oscillation means, an optical transmission means for transmitting a laser beam oscillated from the laser beam oscillation means and a condenser lens for converging a laser beam transmitted by the optical transmission means, wherein the optical transmission means comprises a birefringence lens for separating the laser beam oscillated from the laser beam oscillation means into normal light and abnormal light; and the condenser lens converges respectively the normal light and the abnormal light separated by the birefringence lens to form the focal point of the normal light and the focal point of the abnormal light.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Medical handpiece with a light guide which can be displaced in an axial direction
InactiveUS6461349B1Little manual effortIncrease the cross-sectional areaSurgical instrument detailsCoupling light guidesFiberLight guide
A medical handpiece for transmitting energy from a laser beam into biological tissue. An optical fiber for conveying the laser beam to the handpiece and a light guide for radiating the laser energy into the tissue are arranged in a base body. Means are provided for aligning the optical axis of the light guide in relation to the optical axis of the fiber and means for aligning the optical axis of the light guide in relation to the base body are also provided. The light guide can be displaced in an axial direction in relation to the base body and the alignment can be set according to the direction of displacement or maintained. The light guide is easy to replace and the device is easy to clean in accordance with all hygiene requirements.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Method and apparatus for transmitting energy via a laser beam
To transmit energy without direct mechanical or electrical contact, a transmitter unit emits a laser beam onto a radiation receiver of a receiver unit including a photovoltaic cell arrangement surrounded by a ring-shaped reflector. A portion of the laser beam is reflected from the reflector back to the transmitter unit, where the received reflected signal is evaluated to determine the position of the laser beam impinging on the radiation receiver. The transmitter unit deflects the laser beam as necessary to impinge directly on the photovoltaic cell arrangement and track any relative motion of the receiver unit. The receiver unit orients the radiation receiver to optimize the energy reception. The position of the laser beam is modulated and the resulting variation of the reflected signal is evaluated to determine therefrom the position of the laser beam on the radiation receiver.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
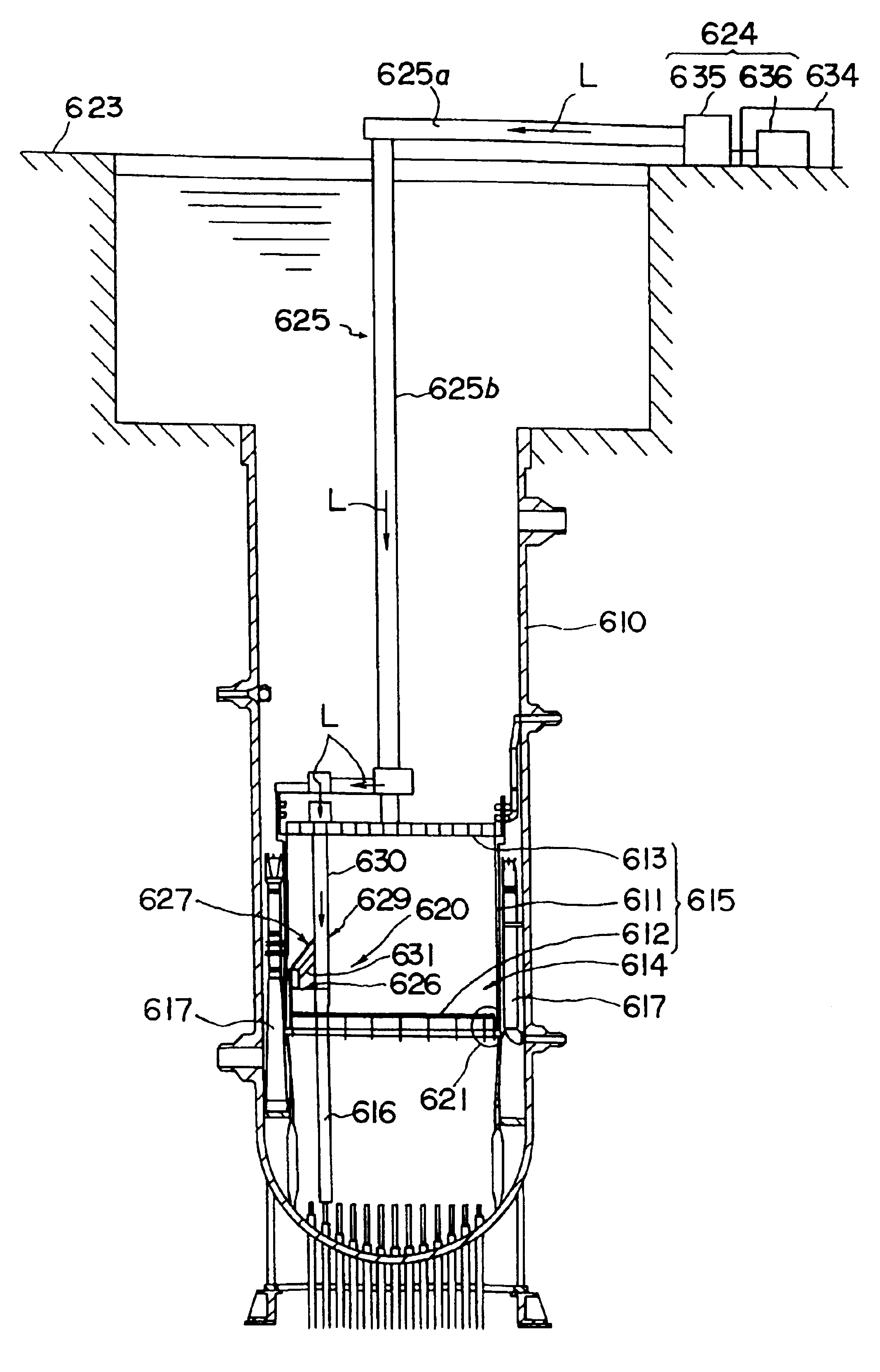
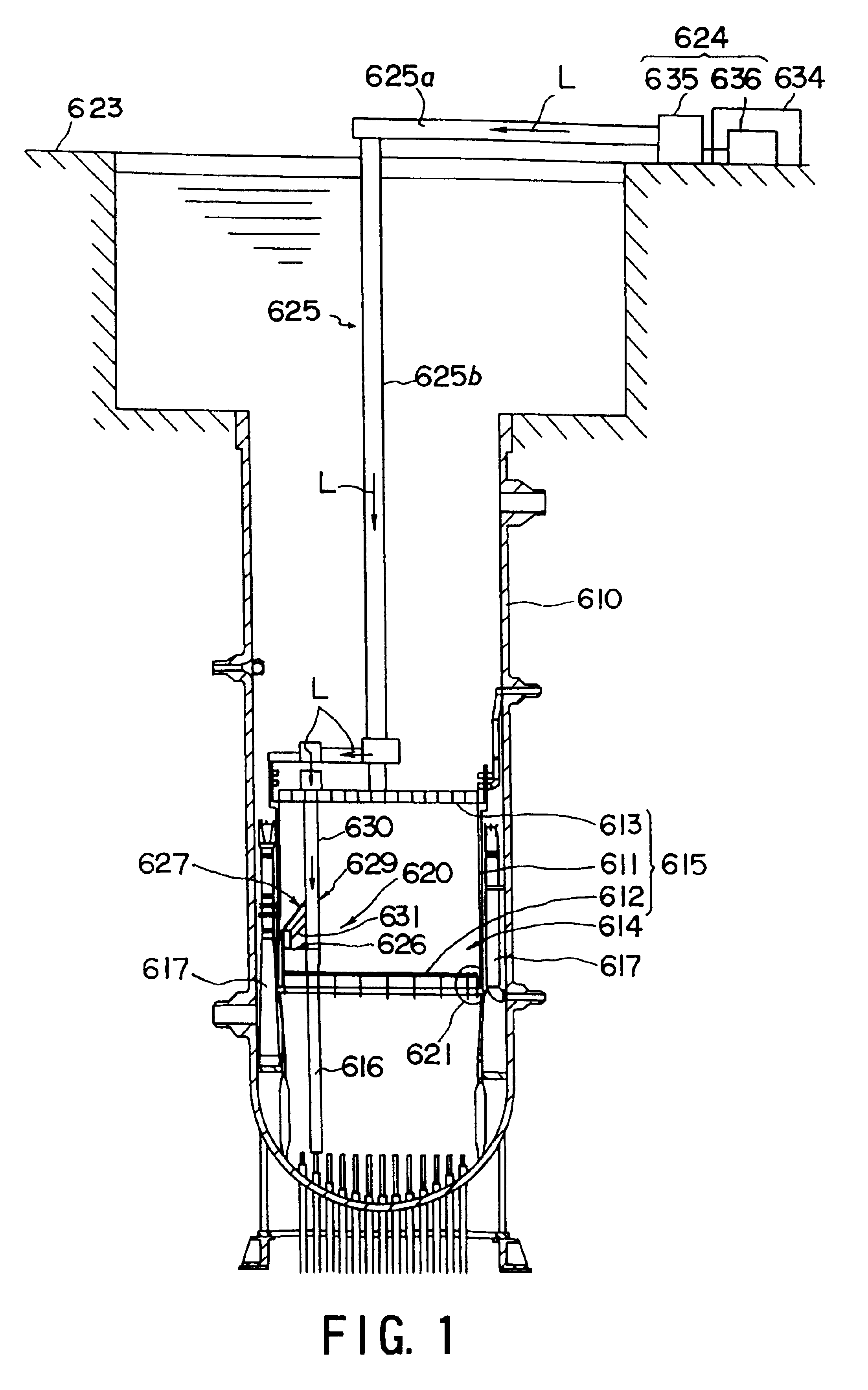
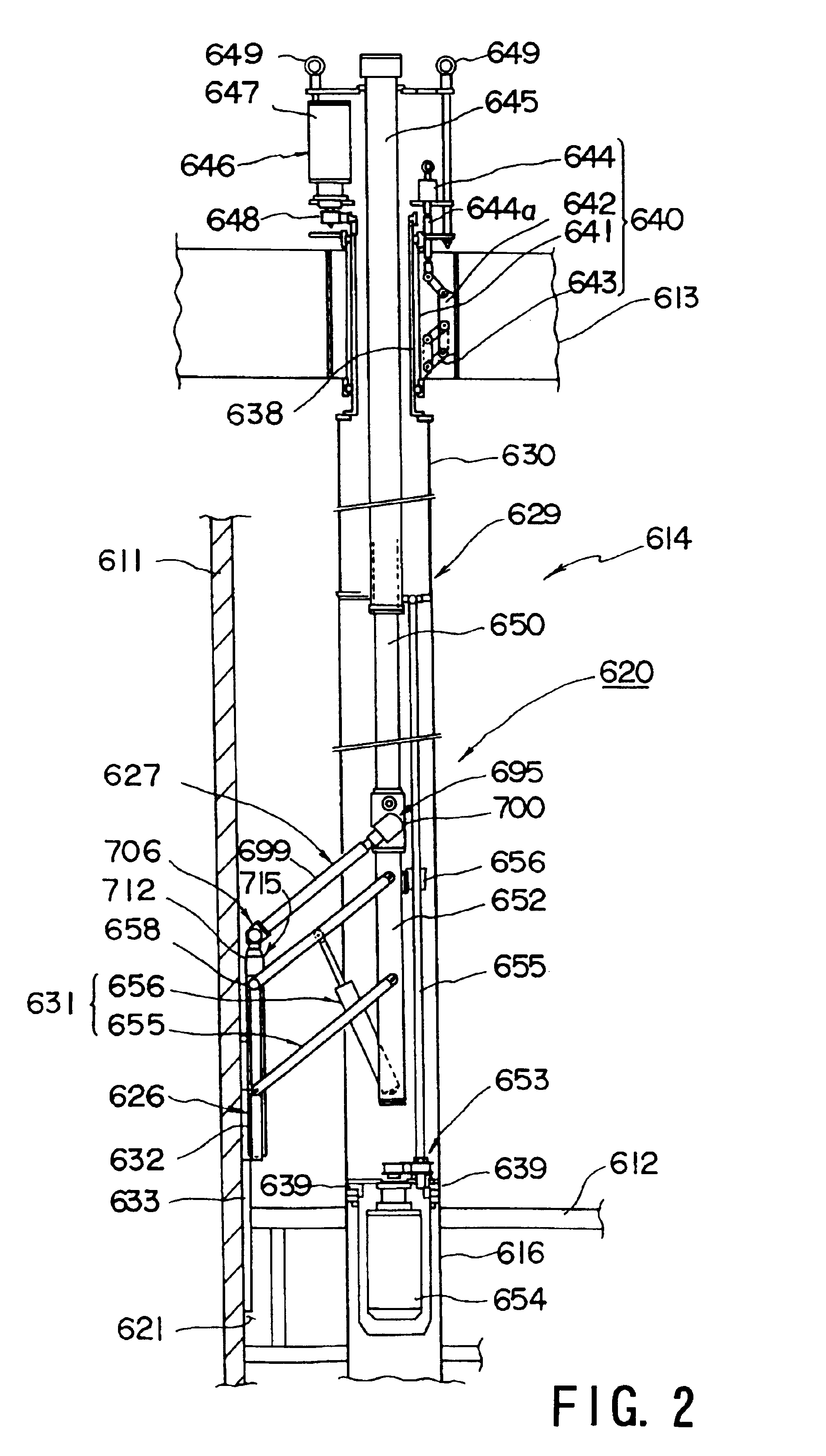
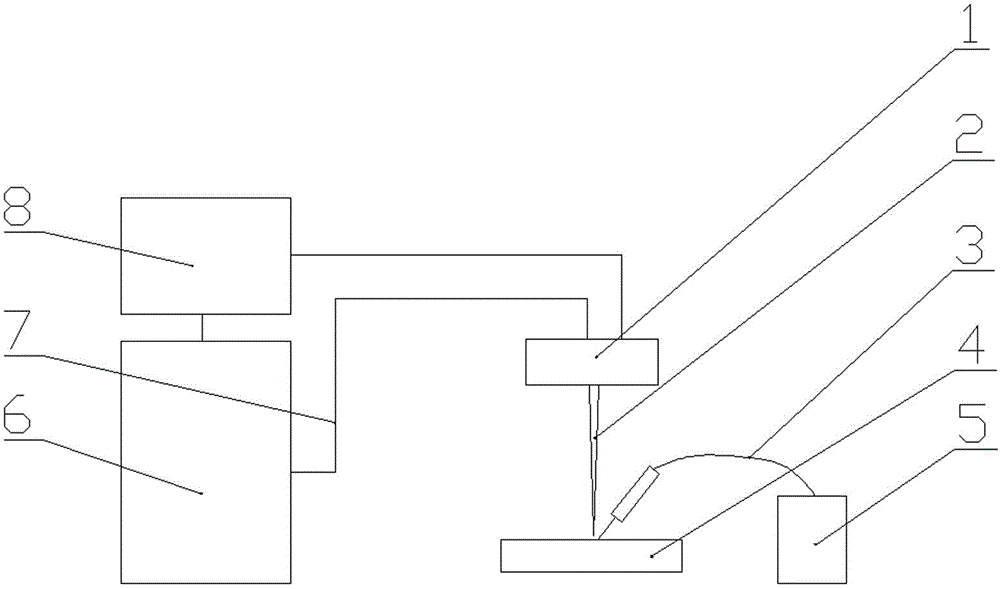
Laser emission head, laser beam transmission device, laser beam transmission device adjustment method and preventive maintenance/repair device of structure in nuclear reactor
InactiveUS6881925B1Deterioration in working can be preventedInhibit deteriorationLaser beam welding apparatusNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
A laser emitting head for irradiating a portion to be machined with laser beams outputted from a laser unit (624) incorporates an emitting head body having a light guide member (625) in the head for guiding the laser beams; a light converging lens (677) for converging the laser beams transmitted from the light guide member in the head; a reflecting mirror (678) for irradiating the portion to be machined with the converged laser beams; mirror rotating means (684) for holding the reflecting mirror to be rotative around the optical axis of the laser beam; distance-adjustment means (674) for adjusting the relative distance between the reflecting mirror and the converging lens; and moving means (665) for moving the reflecting mirror and the converging lens such that the relative distance is maintained so that the light guide member in the head. The converging lens and the reflecting mirror can be introduced / discharged with respect to a portion to be machined and formed in a narrow gap in an incore structure. As a result, a preventive-maintenance / repair operation using laser beams and arranged to be performed in a narrow gap in the incore structure can safely and efficiently be performed.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and apparatus for transmitting energy via a laser beam
To transmit energy without direct mechanical or electrical contact, a transmitter unit emits a laser beam onto a radiation receiver of a receiver unit including a photovoltaic cell arrangement surrounded by a ring-shaped reflector. A portion of the laser beam is reflected from the reflector back to the transmitter unit, where the received reflected signal is evaluated to determine the position of the laser beam impinging on the radiation receiver. The transmitter unit deflects the laser beam as necessary to impinge directly on the photovoltaic cell arrangement and track any relative motion of the receiver unit. The receiver unit orients the radiation receiver to optimize the energy reception. The position of the laser beam is modulated and the resulting variation of the reflected signal is evaluated to determine therefrom the position of the laser beam on the radiation receiver.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
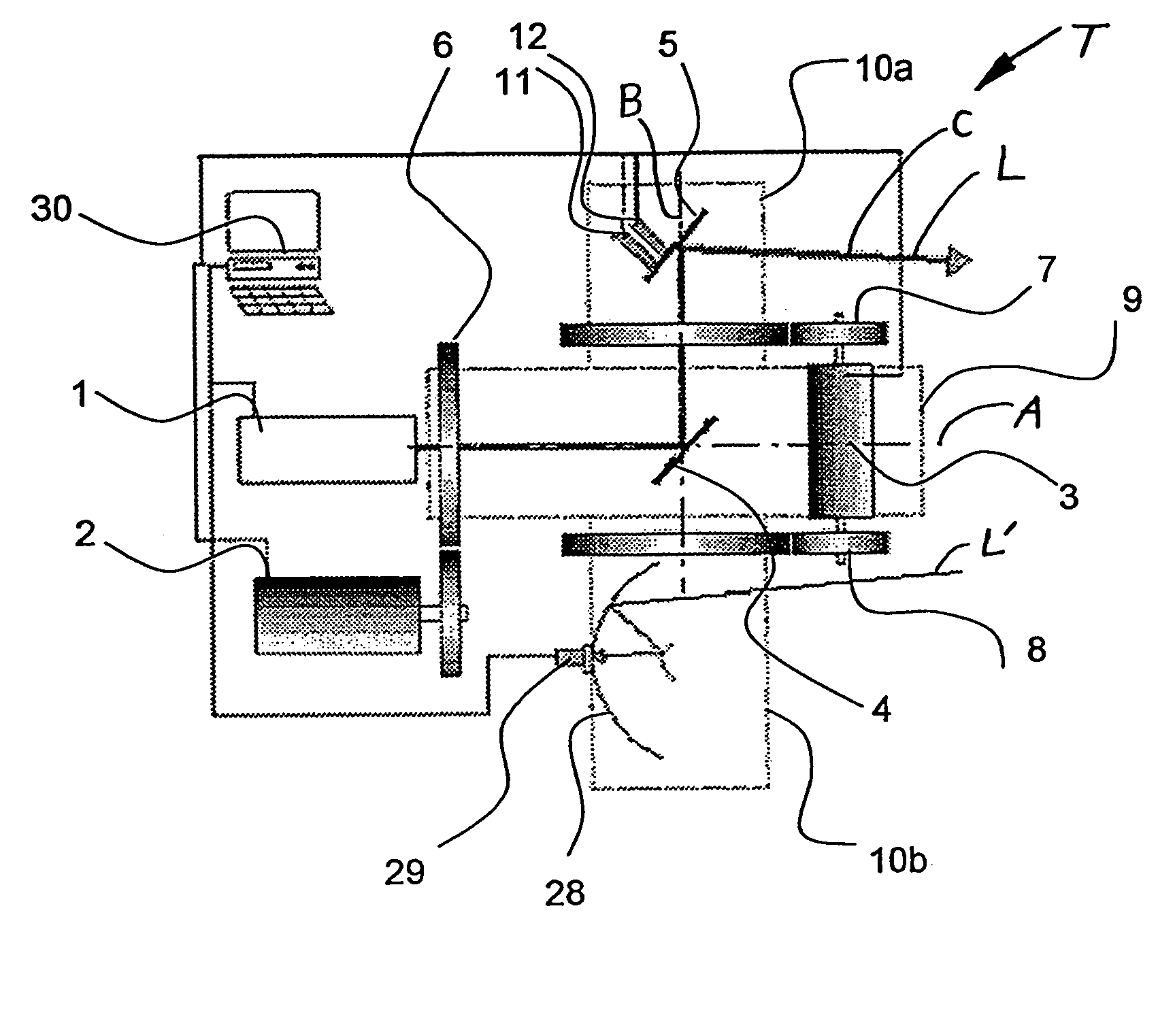
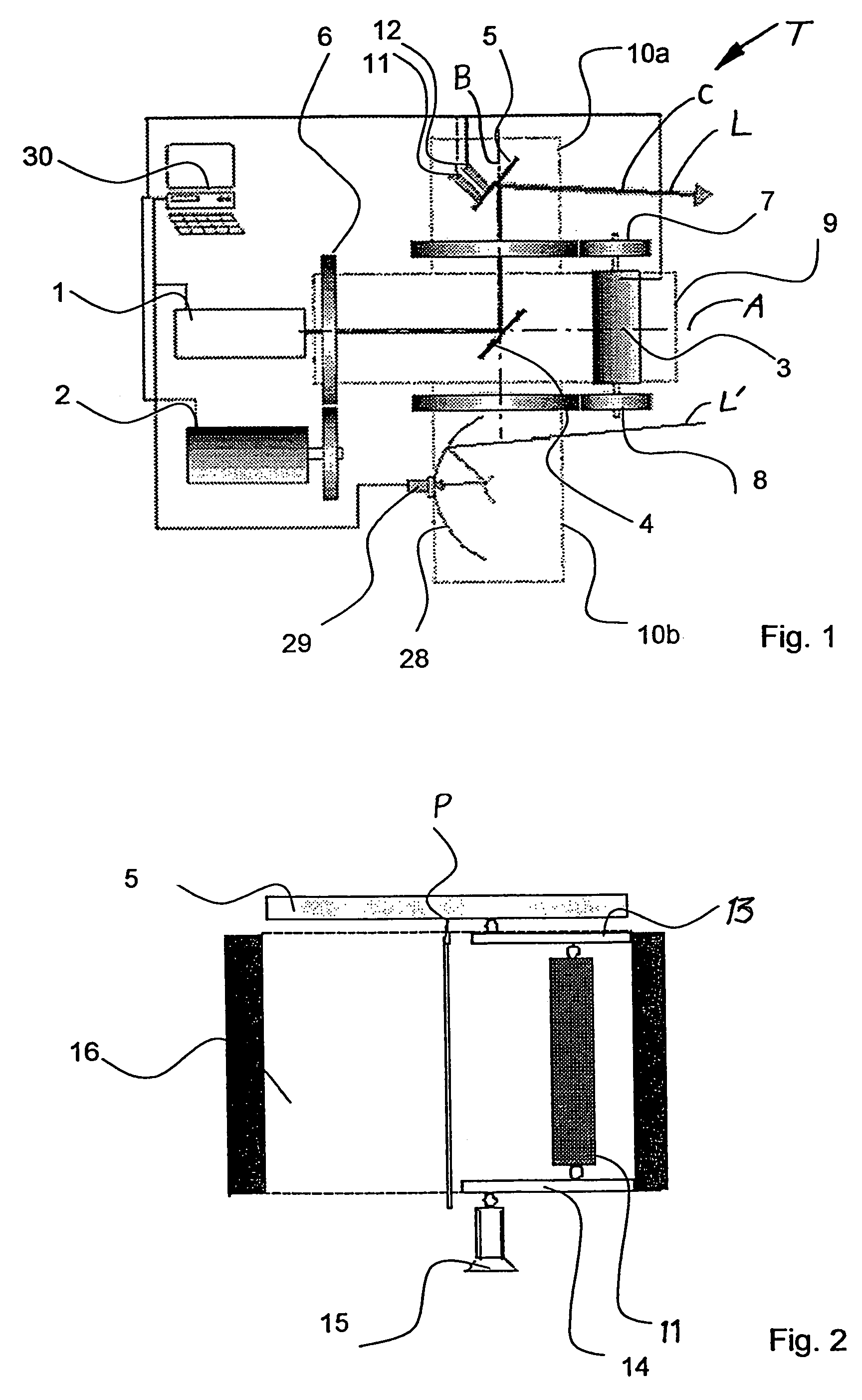
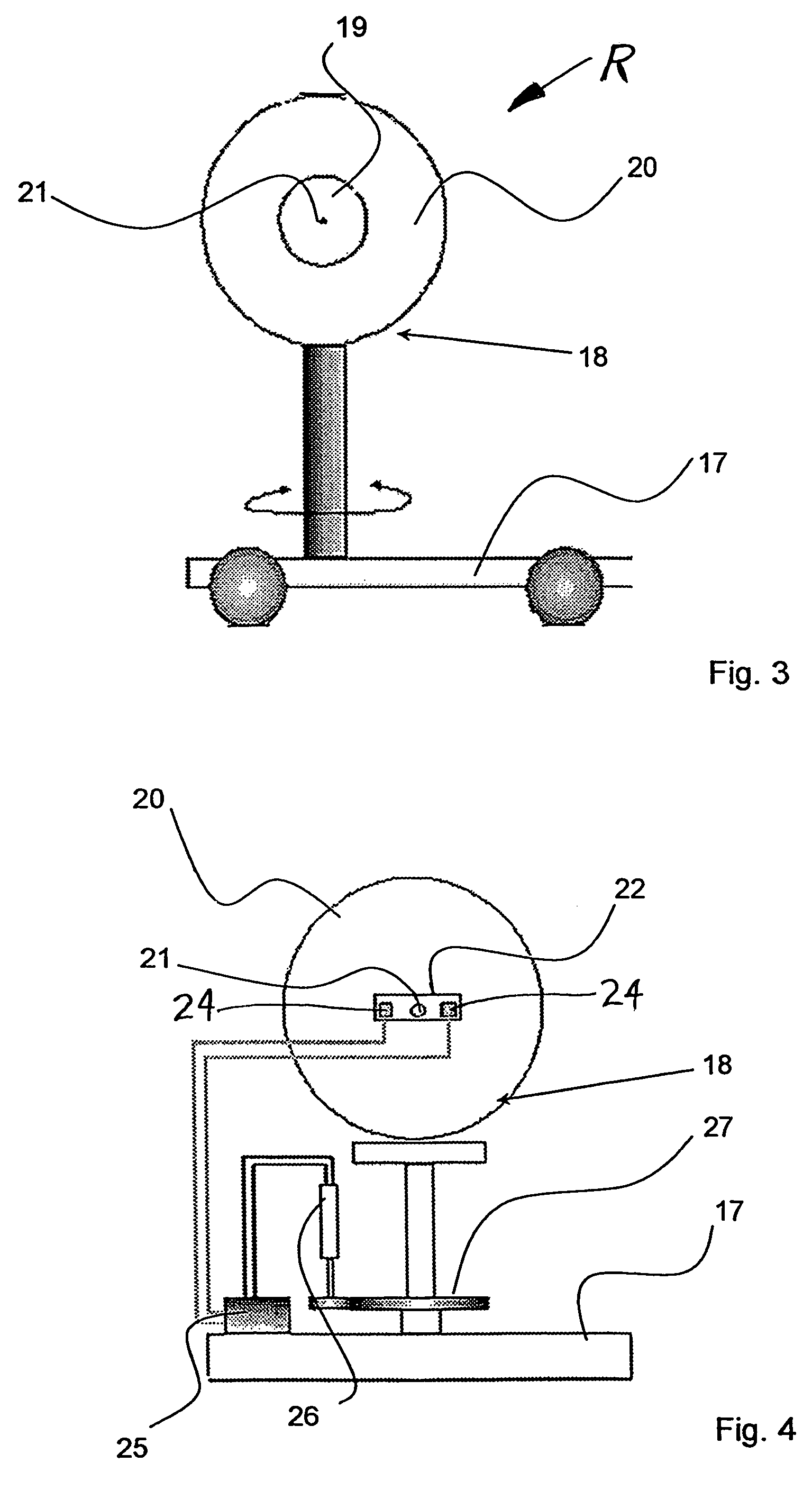
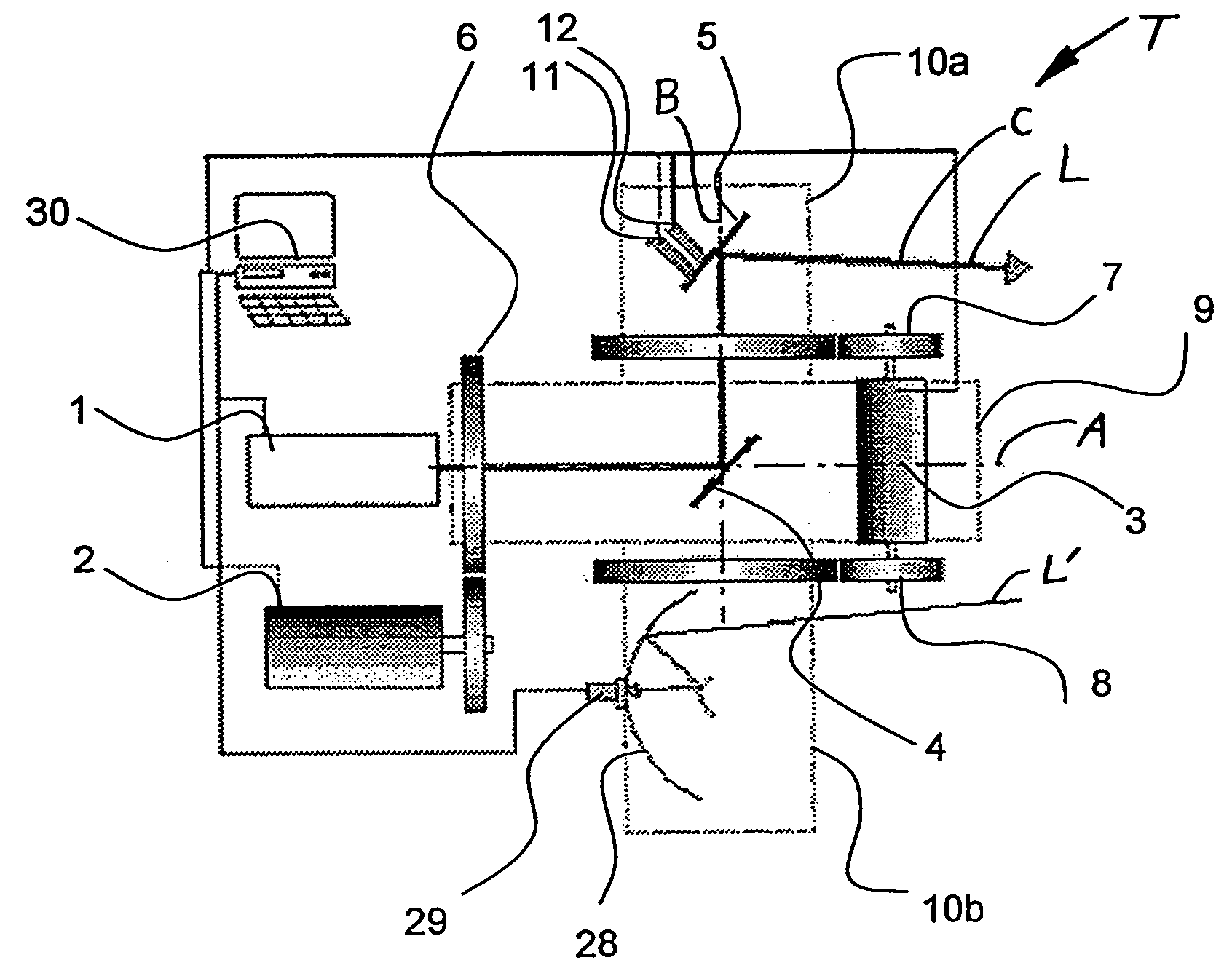
Medical system for treating deep surface targets
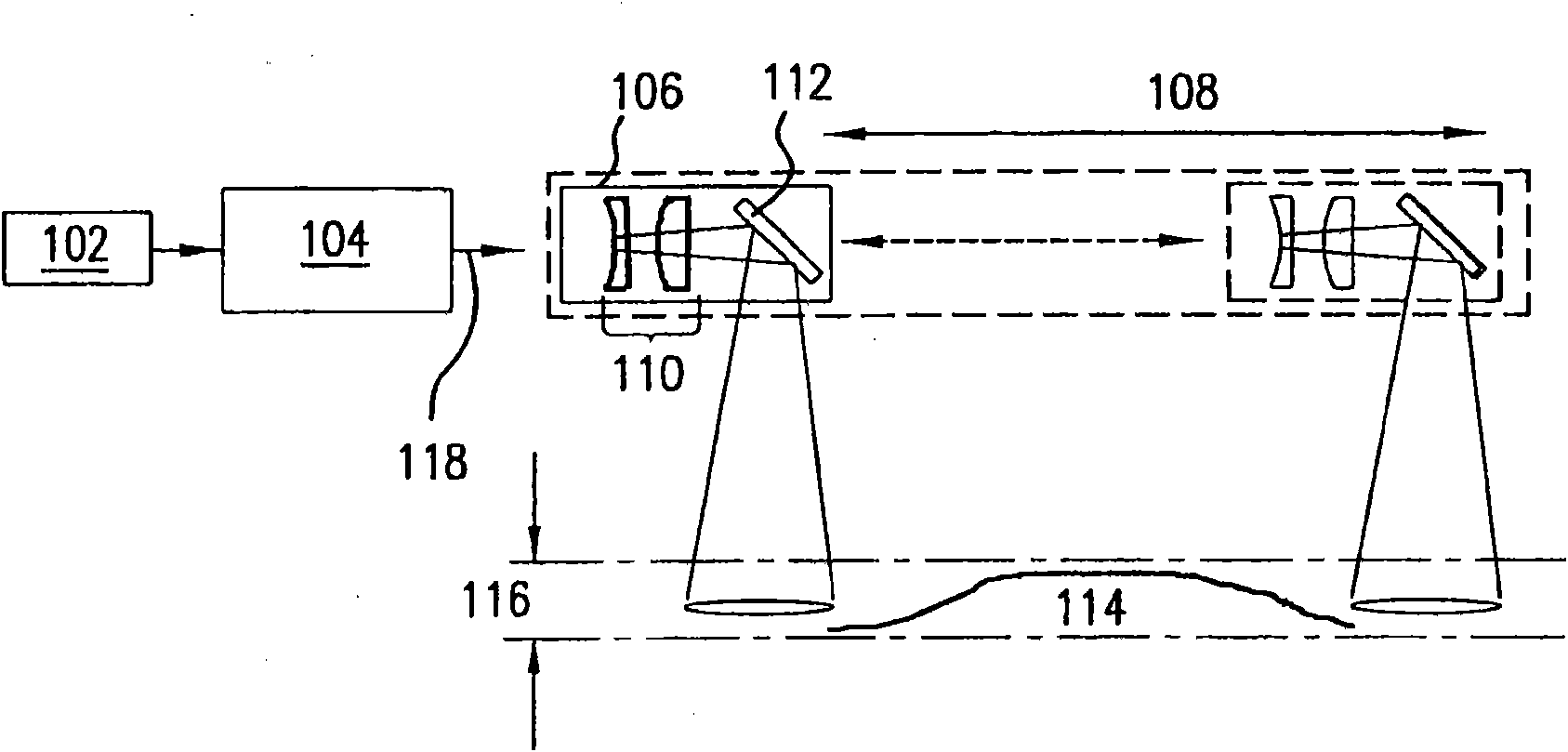
InactiveUS20150088105A1Sufficient energyInherent safety featureSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyLaser beam transmissionBlood vessel
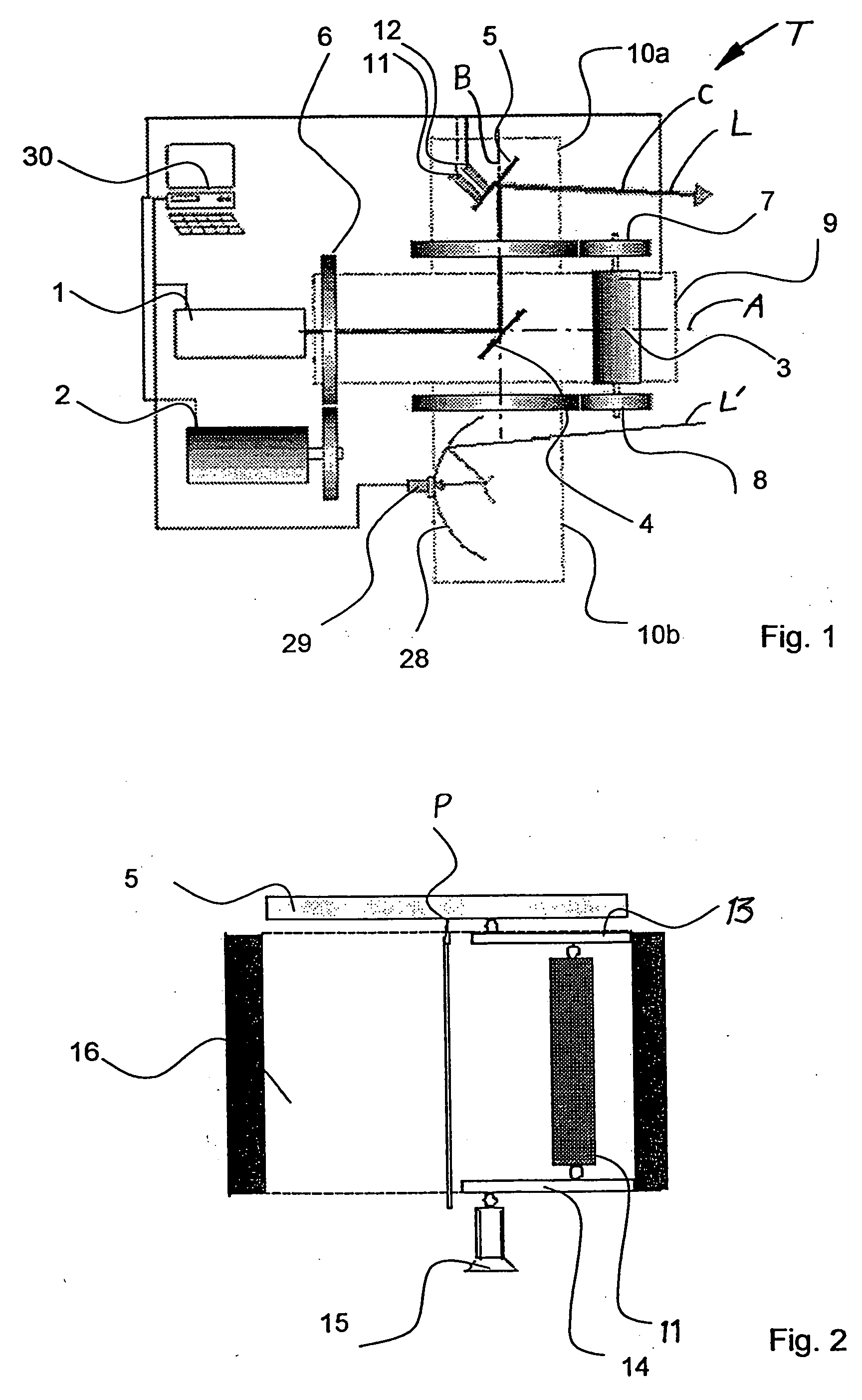
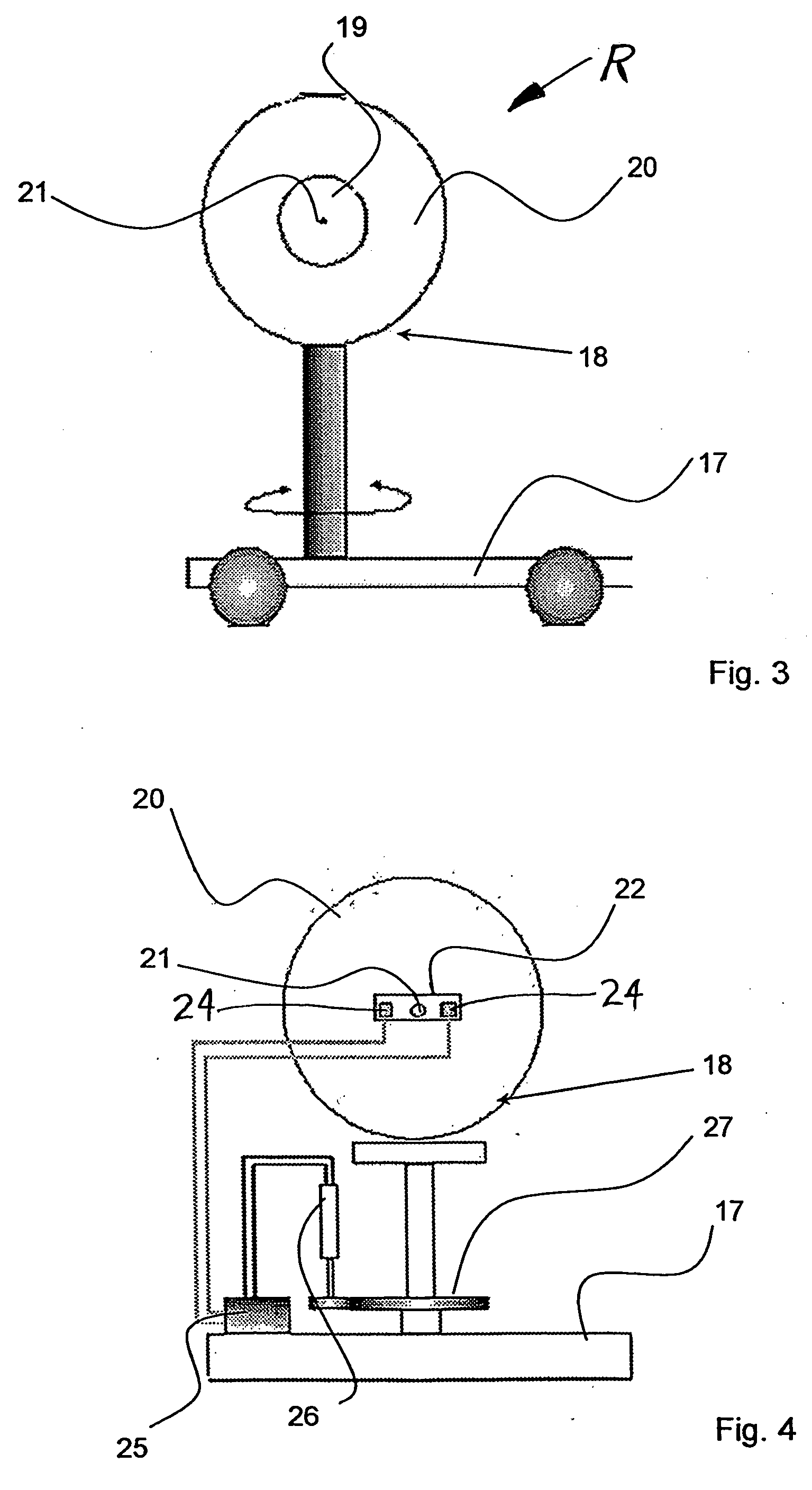
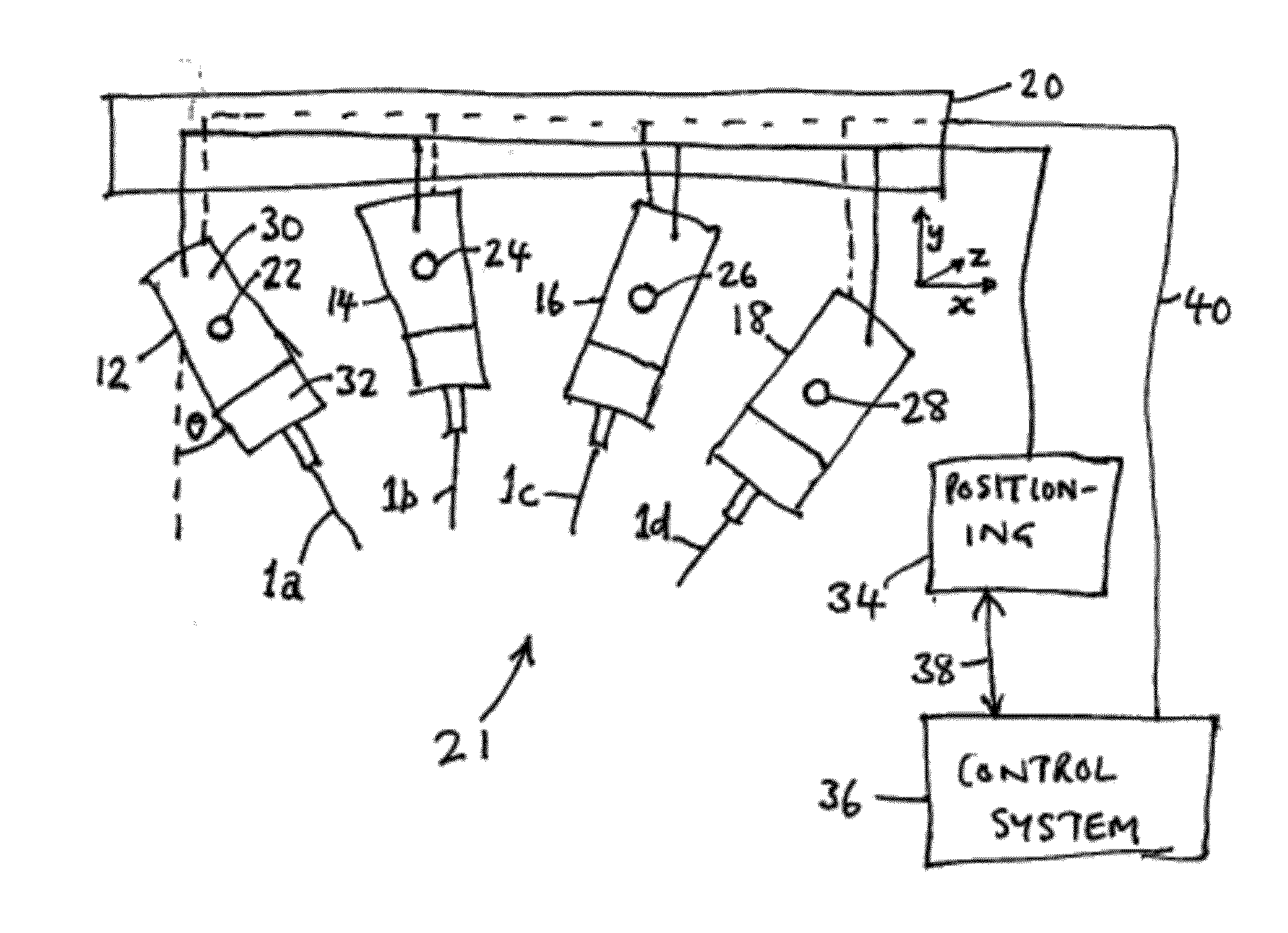
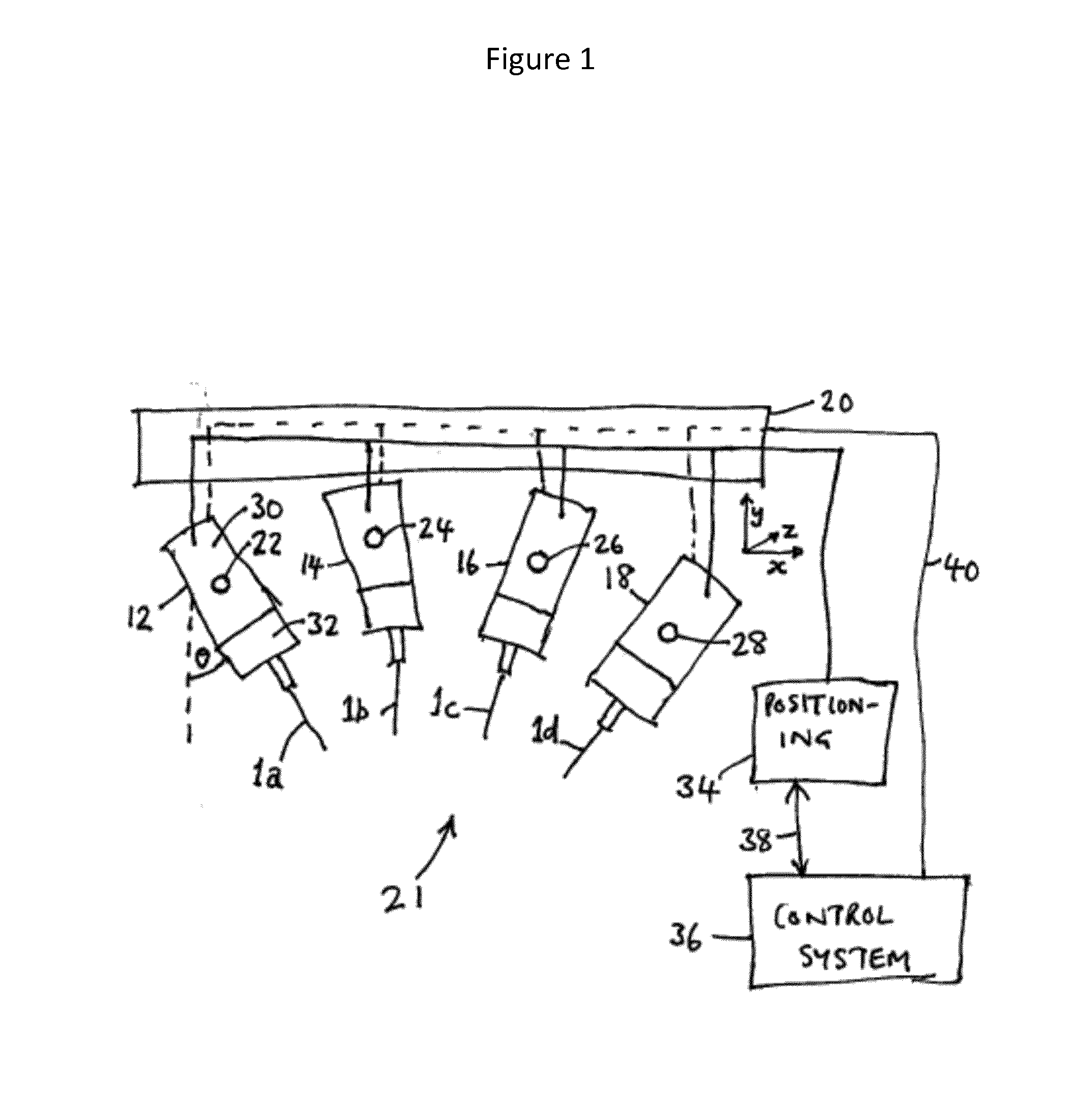
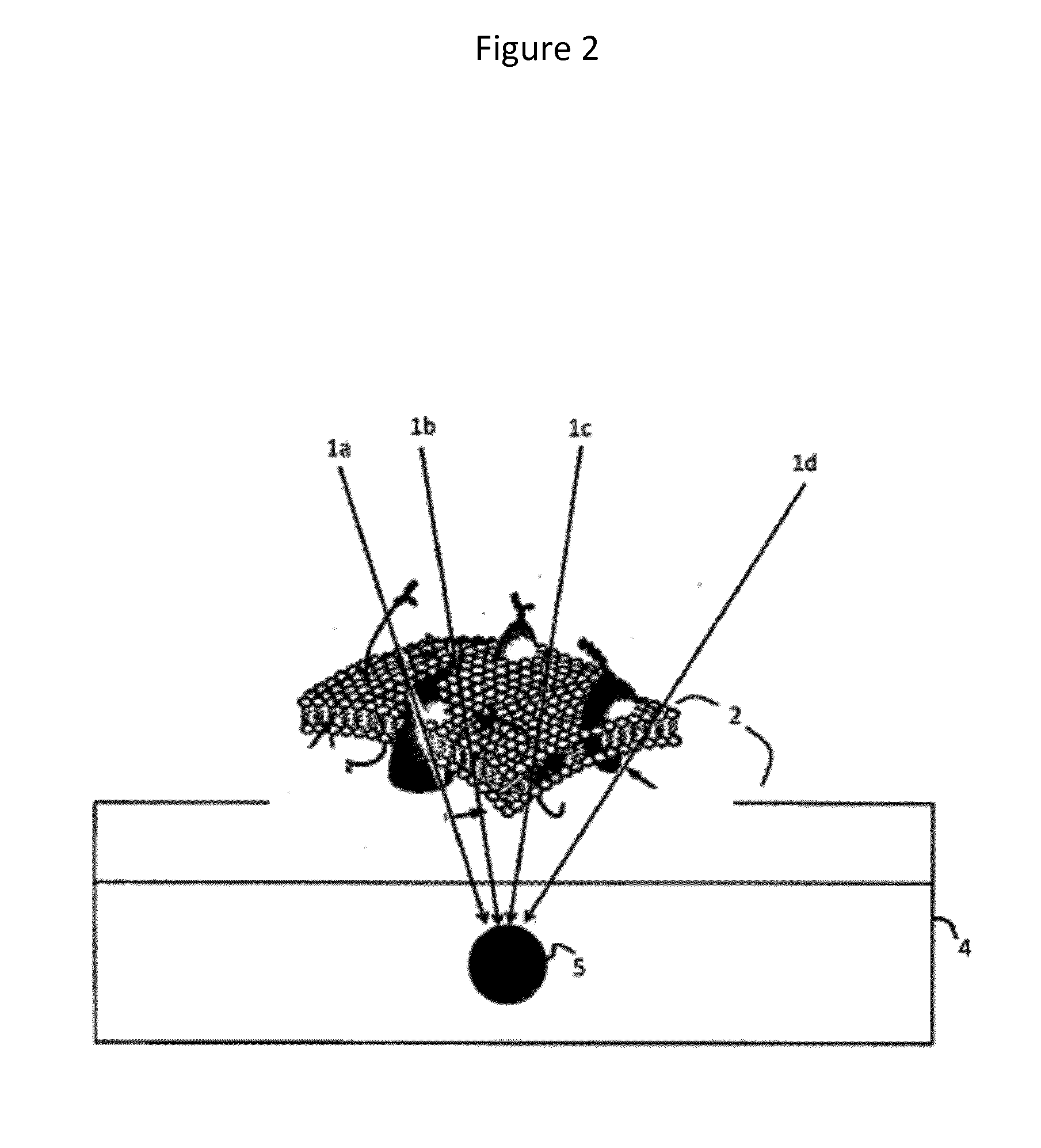
Disclosed herein are medical systems involving the novel use of lasers in a way to transfer a desired amount of energy to deeper tissues, such as deep dermis, fat, deep vessels, fascia, tumors and others, without burning the skin, in particular the skin surface. A medical system (10) comprises a laser beam delivery system (21) producing a plurality of laser beams (1a-1d) for simultaneously or alternately irradiating the deep tissue target structure (5) from multiple directions via the skin surface (2), wherein the laser beams (1a-1d) individually are individually adjusted to have an energy level insufficient to ablate and / or burn the skin (2). The target structure (5) comprises a deep tissue target structure (5). The laser beams (1a-1d) have a combined energy level at their point of intersection to achieve a preselected thermal gradient sufficient to treat the deep tissue target structure (5). The medical system (10) further comprises a cooling device for cooling the skin surface (2) during irradiation. A corresponding method and use is also disclosed.
Owner:FATEMI AFSCHIN
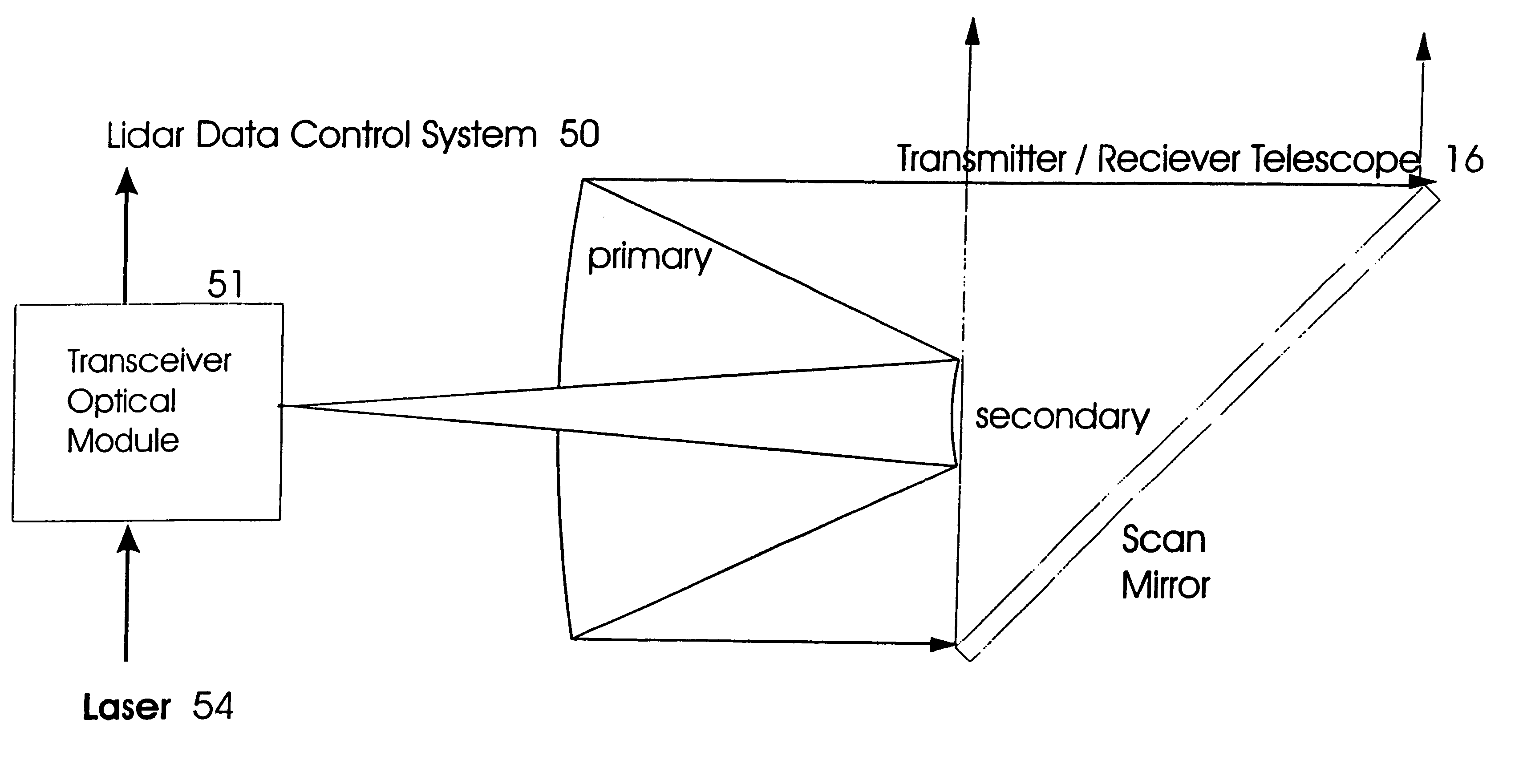
LIDAR Device Based on Scanning Mirrors Array and Multi-Frequency Laser Modulation
ActiveUS20180329037A1Maximize rangeReduce background noiseElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAmbiguityOptoelectronics
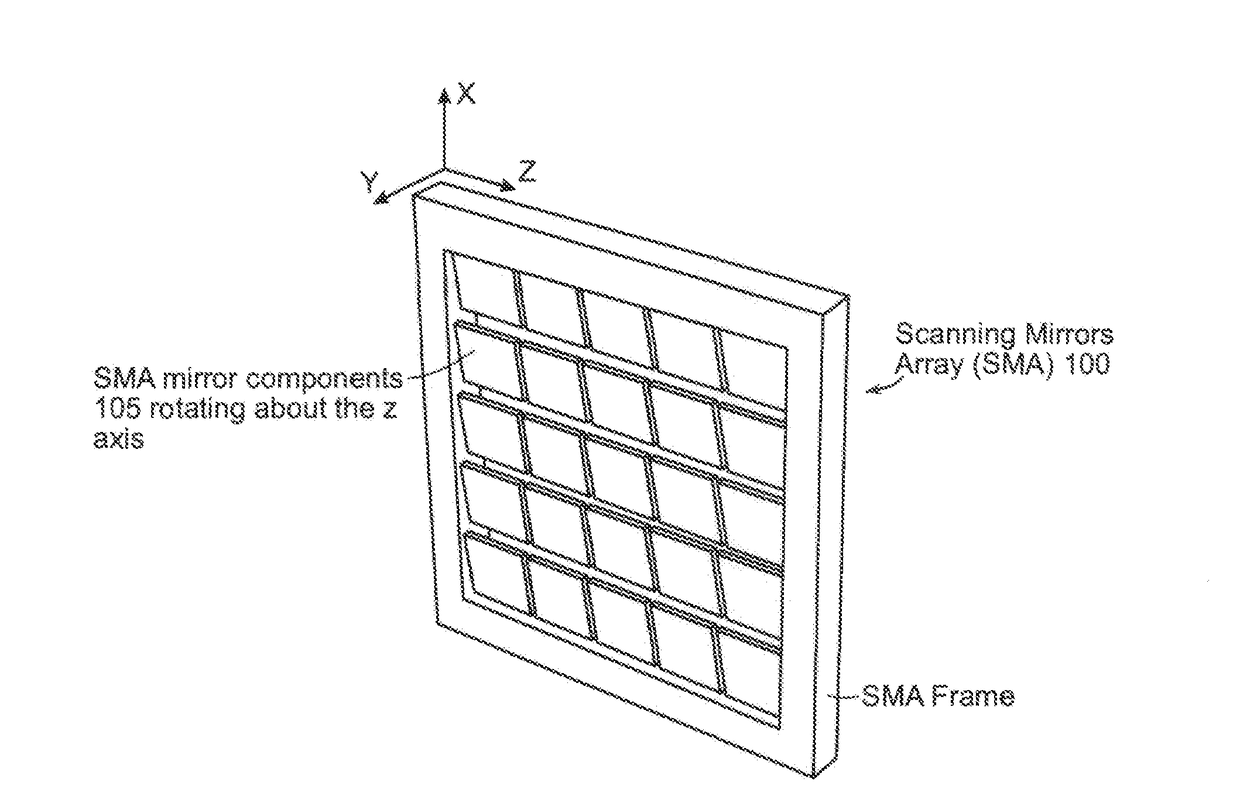
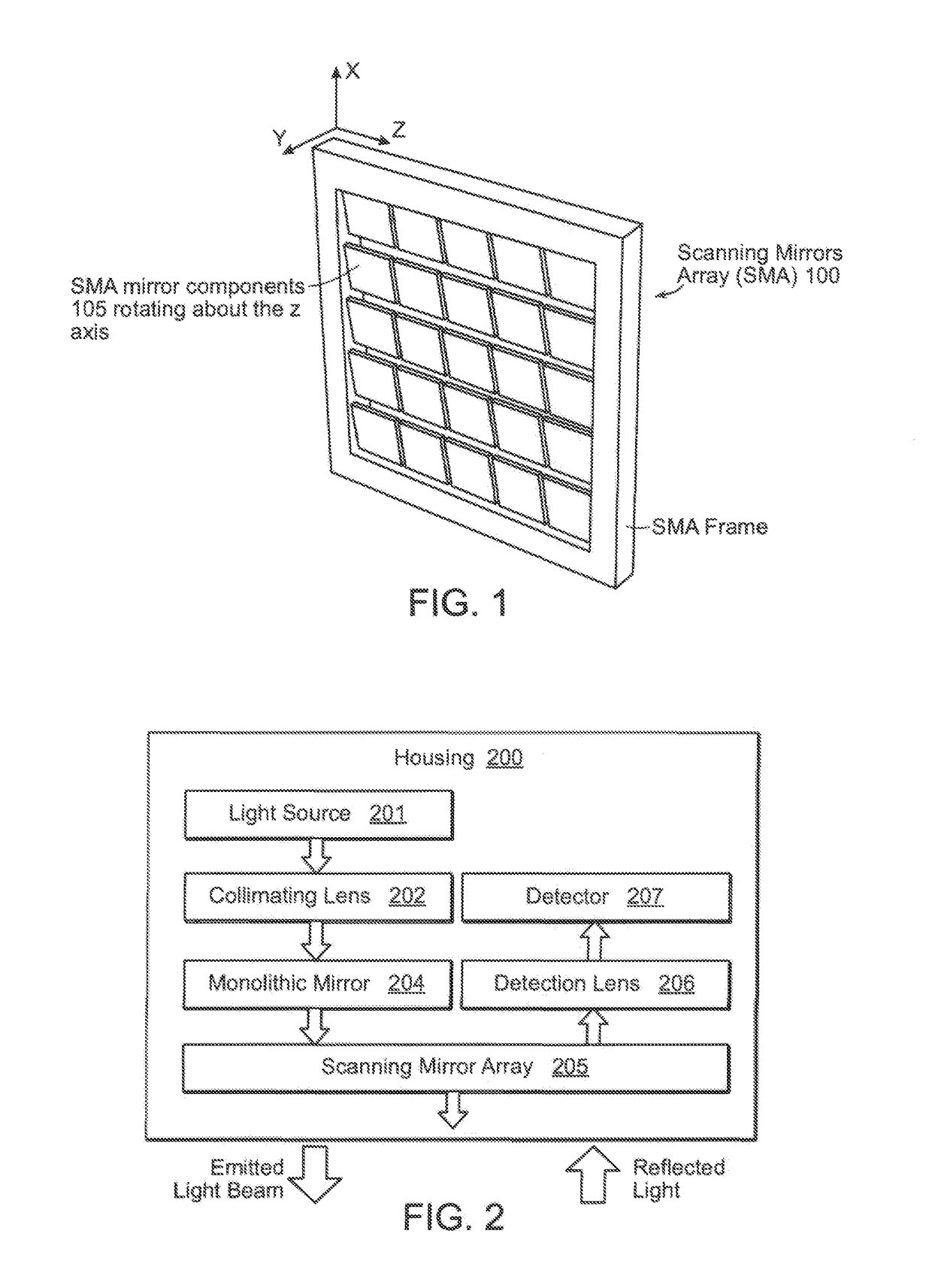
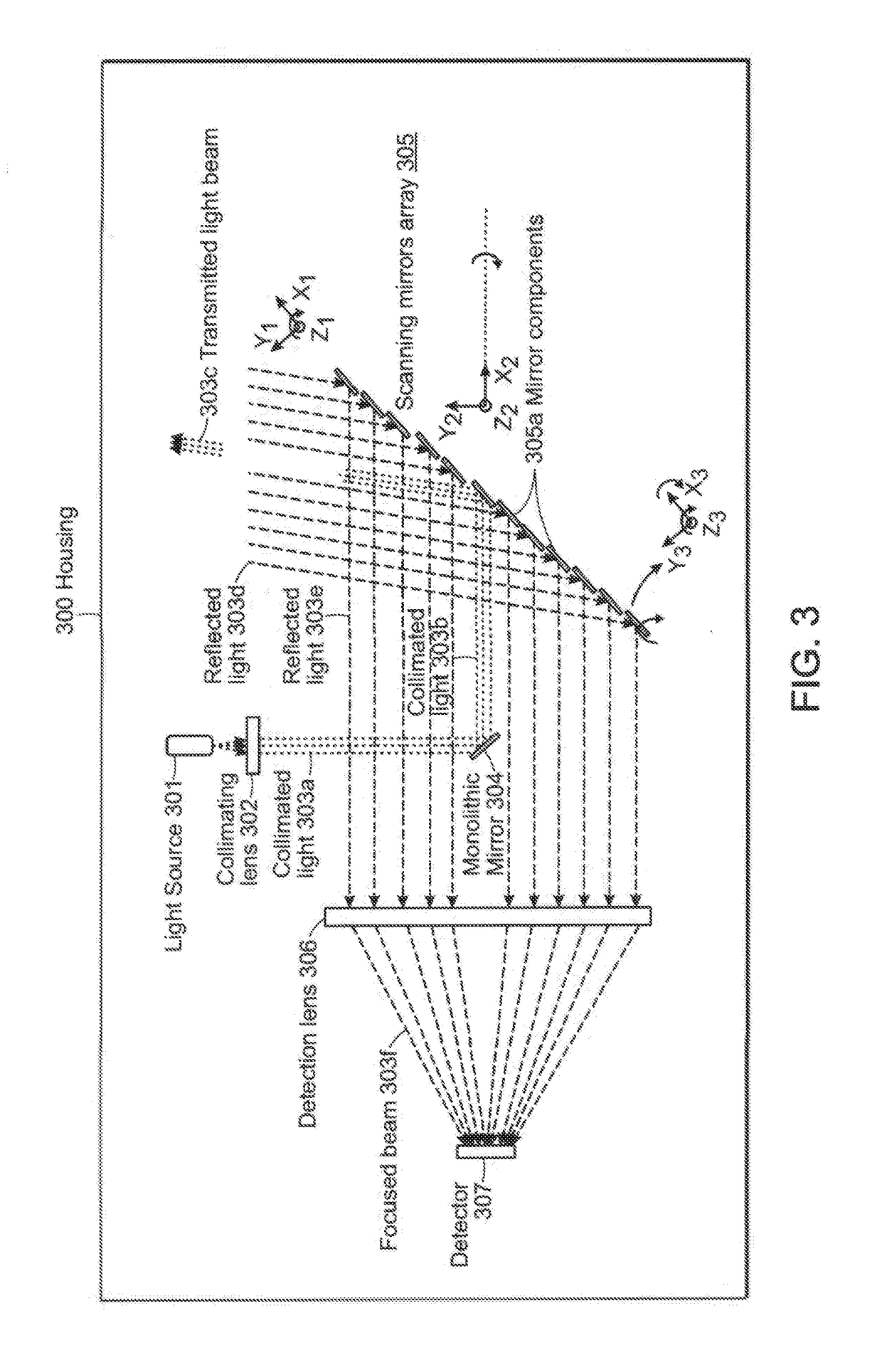
A LiDAR device that transmits a single or multiple continuous or intermittent laser beams to the environment and detects the reflected light on one or more detectors. The LiDAR device may include a scanning mirrors array composed of a single or multiple moving mirrors capable of changing the direction of the transmitted light. The scanning mirrors array may also include sensors and actuators which can be used to precisely control or measure the position of the mirrors. The LiDAR device may also include a lens that focuses the light captured by the mirror(s) onto a single or a multitude of detectors. The device may include laser sources and detectors operating in various wavelengths. The LiDAR device may also include laser power modulation mechanisms at a single or multitude of frequencies to improve signal detection performance and remove any ambiguity in range calculation.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Thick-plate narrow-gap laser scanning filler wire welding method
InactiveCN104551403AHigh energy density of laserImprove welding efficiencyWorkpiece edge portionsLaser beam welding apparatusThick plateLaser scanning
The invention relates to a thick-plate narrow-gap laser scanning filler wire welding method. The method comprises the steps: firstly arranging an I-type beveled edge or a deep U-type beveled edge with a thick truncated or a deep V-type beveled edge between two thick plates to be welded, transmitting laser beams to a weld seam by adopting a scanning galvanometer, carrying out the bottoming by virtue of laser self-melting welding, and then carrying out the laser scanning filler wire welding. In the filler wire welding process, the width of the beveled edge is detected in real time by adopting a visual detection system, and the deflection angle of the scanning galvanometer is further controlled, so that the laser beams can scan back and forth at two sides of the weld seam, a weld wire stretches into a gap of the beveled edge from the front of the laser beams, and the weld wire is molten by the laser which scans back and forth; the scanning galvanometer is driven by adopting a plane travel cart or an annular guide rail to move along the weld seam, and the scanning galvanometer is adjusted as the increment of welding beads, so that the laser can be focused in the plane of the weld seam to melt the weld wire. By adopting the thick-plate narrow-gap laser scanning filler wire welding method, the welding heat input can be reduced, the weld deformation can be alleviated, a thick-plate weld joint with small weld deformation and good gap side wall fusion can be obtained, and the welding efficiency and welding quality of the thick plate can be greatly improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL INST OF WELDING TECH GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL ACADEMY OF UKRAINE
Laser cutting device and cutting method
InactiveCN103551732AImprove finenessNo chippingGlass severing apparatusLaser beam welding apparatusLight beamOptoelectronics
The invention provides a laser cutting device which comprises a laser emission module, a focusing lens and a multifocal lens, wherein the multifocal lens is clung to the focusing lens and is arranged between the laser emission module and the focusing lens on the optical path of a laser beam; the laser beam passes through the multifocal lens and the focusing lens and form a plurality of focus points at intervals in the transmission direction of the laser beam. The ultrashort pulse laser beam is modulated through the multifocal lens and the focusing lens, the focus points are focused and formed at intervals in the internal laser beam transmission direction of a transparent material, a filament is formed in the transparent material through ablation by the focus points, a separation path of a filament array is quickly formed in combination with a worktable for moving and bearing the transparent material, and the effects of no fragmentation, high accuracy, high yield, irregular processing and no cumbersome follow-up steps can be achieved. The method has the characteristics of high simplicity in operation, high fineness and good quality of processed samples, high processing efficiency and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU DELPHI LASER
Donor film for laser induced thermal imaging method and organic electroluminescence display device fabricated using the film
InactiveUS20050136344A1Prevent penetrationPreventing a non-transfer defectElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
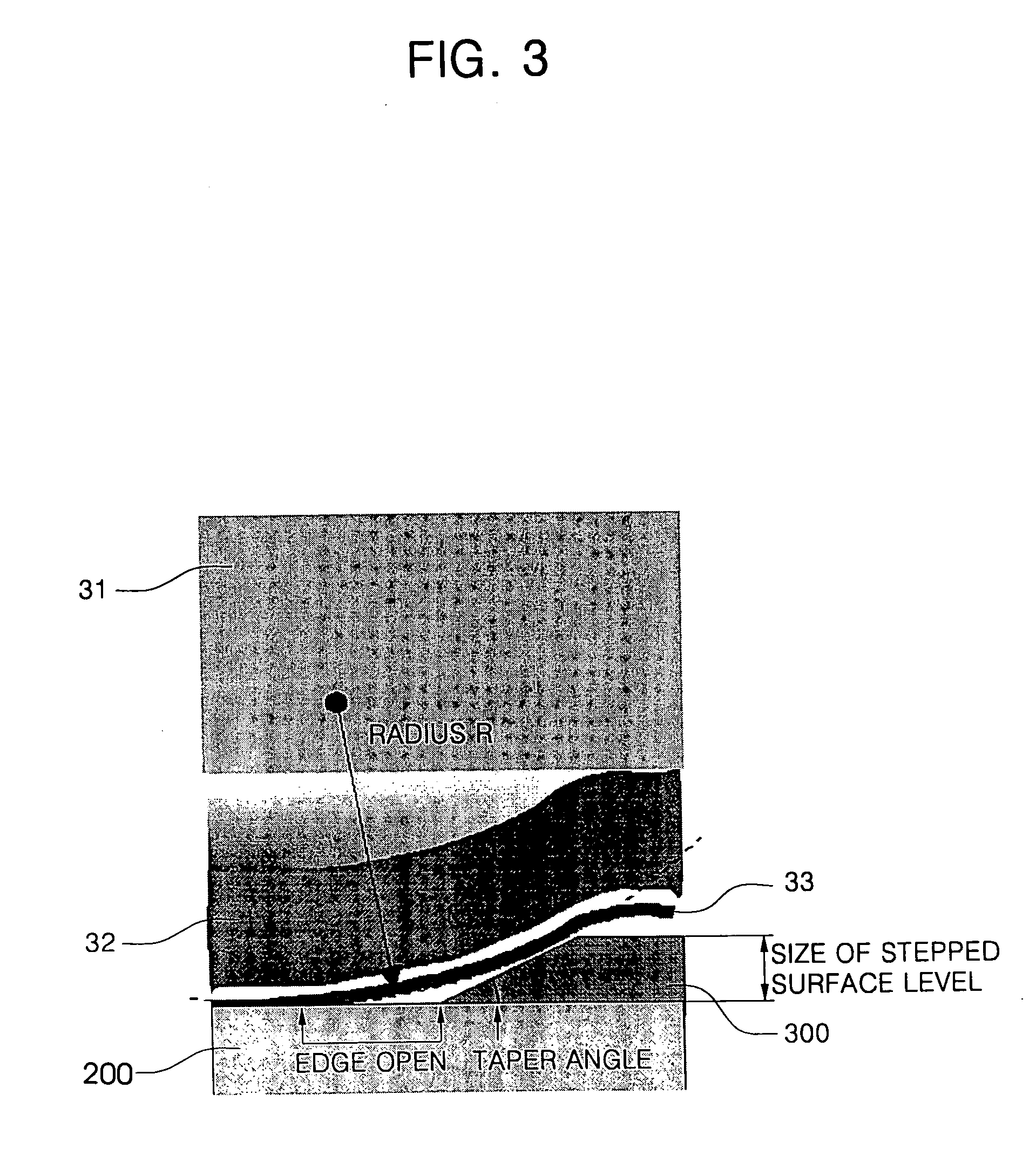
A donor film for laser induced thermal imaging method having a base film, a light-to-heat conversion layer formed on the base film, a reflection layer or a metal layer formed on the light-to-heat conversion layer, and a transfer layer formed on the reflection layer and formed of an organic material. The donor film is capable of reducing an edge open defect and increasing The amount of energy absorbed into the light-to-heat conversion layer by forming either the reflection layer or the metal layer between the light-to-heat conversion layer and the transfer layer, preventing damage of the substrate by not transmitting a laser beam to the substrate and prevents deterioration of the transfer layer by preventing gas generated from the light-to-heat conversion layer by heat from penetrating into the transfer layer and dissipating heat transferred to the transfer layer well into the transfer layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG MOBILE DISPLAY CO LTD
Method and device for suppressing signal fading in laser communication from ground to GEO (geosynchronous) satellite
ActiveCN102857294AAvoid Measuring Intensity Fluctuating WaveformsSuppress Turbulence Intensity FlickerSatellite communication transmissionRadio transmissionErbium lasersGround station
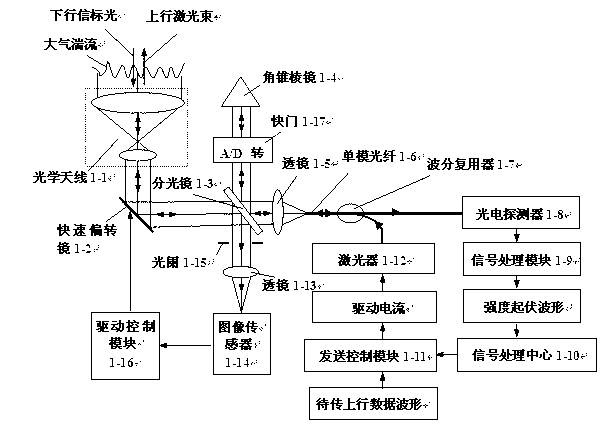
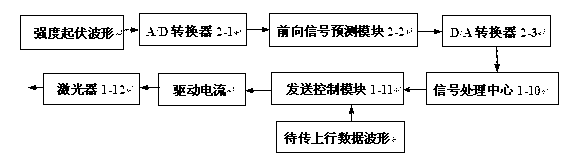
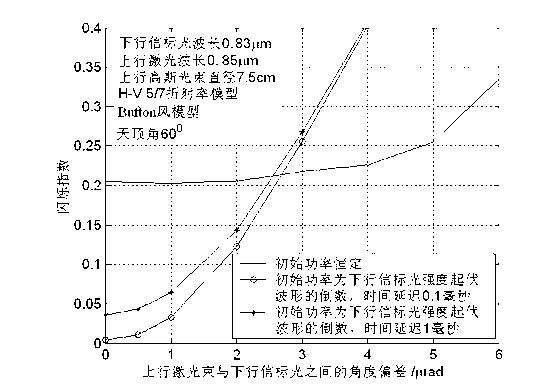
Disclosed are a method and a device for suppressing signal fading in laser communication from ground to a GEO (geosynchronous) satellite. The method includes: measuring intensity fluctuation waveform of downlink beacon light emitted from the GEO satellite by a single-mode fiber on a ground station, and transmitting uplink laser beam along a direction opposite to the downlink beacon light via the same single-mode fiber, and then emitting the uplink laser beam from an end face of the single-mode fiber; modulating to-be-transmitted uplink data waveform according to the reciprocal of the intensity fluctuation waveform of the downlink beacon light measured by the single-mode fiber, driving a laser to emit uplink laser, and transmitting the uplink laser beam to the GEO satellite. Accordingly, atmospheric turbulence and signal fading caused by alignment error of a ground transmitter can be eliminated automatically, and power of laser received by the satellite is stable. In addition, average transmission power of the uplink laser beam can be reduced on the condition of the rated fading probability.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
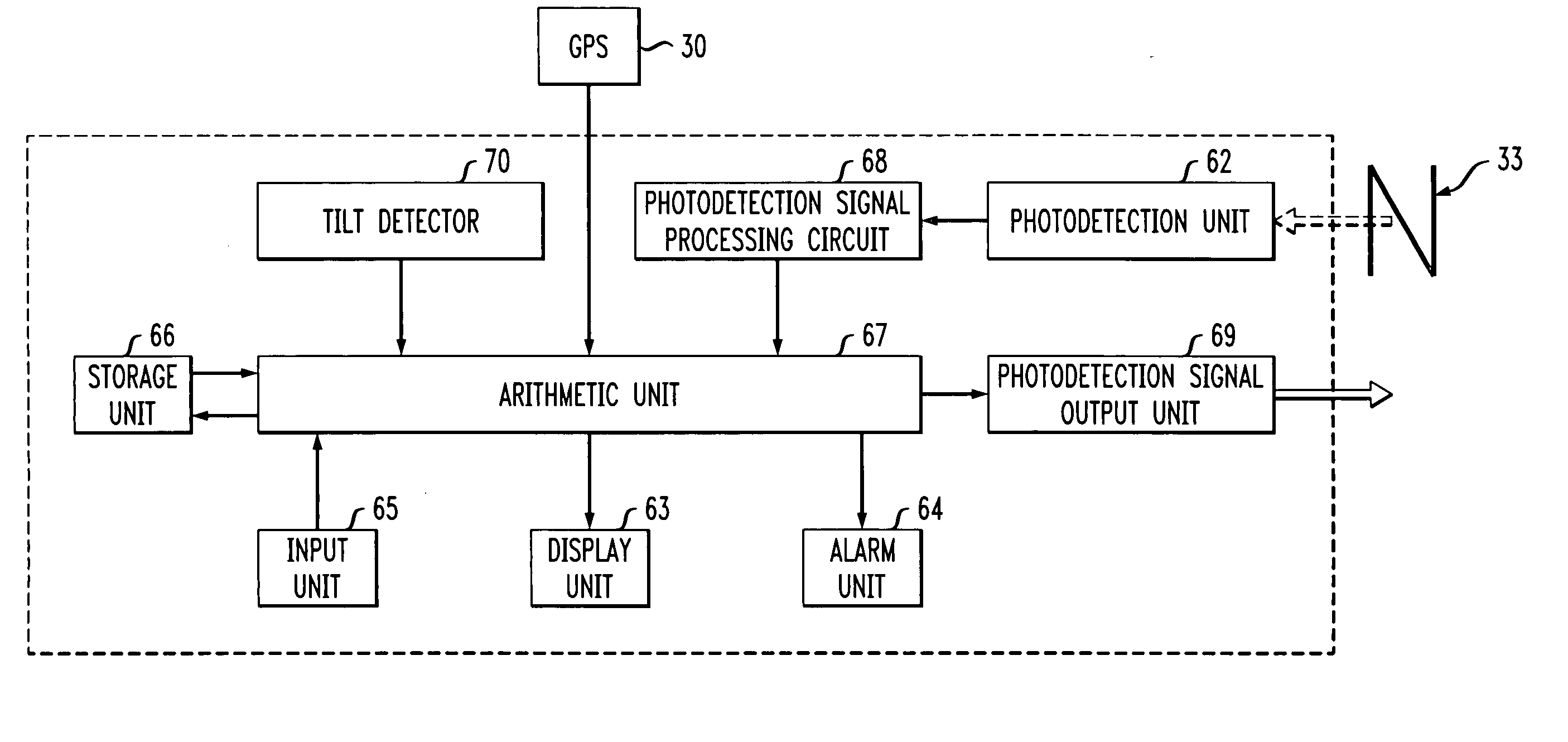
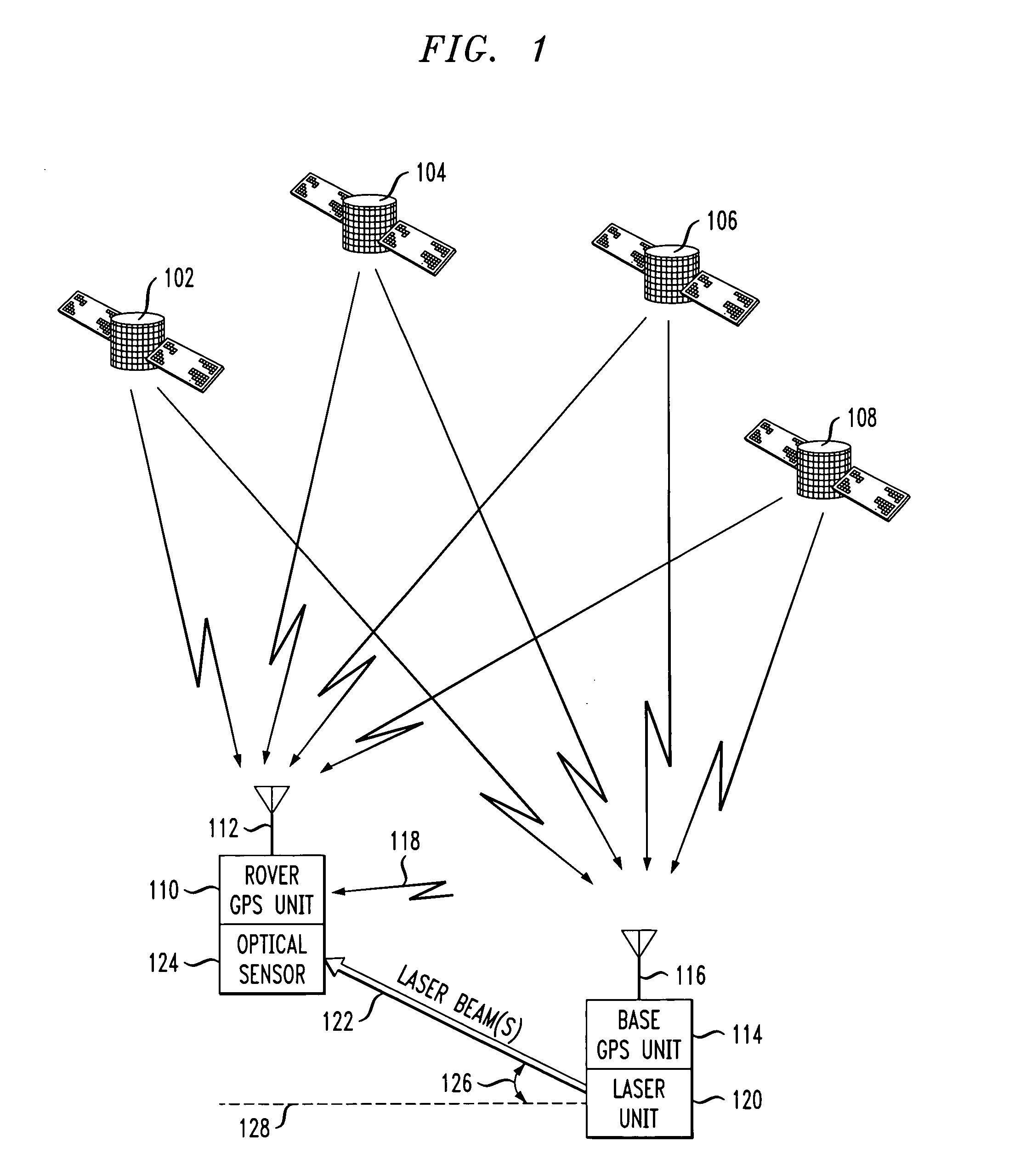
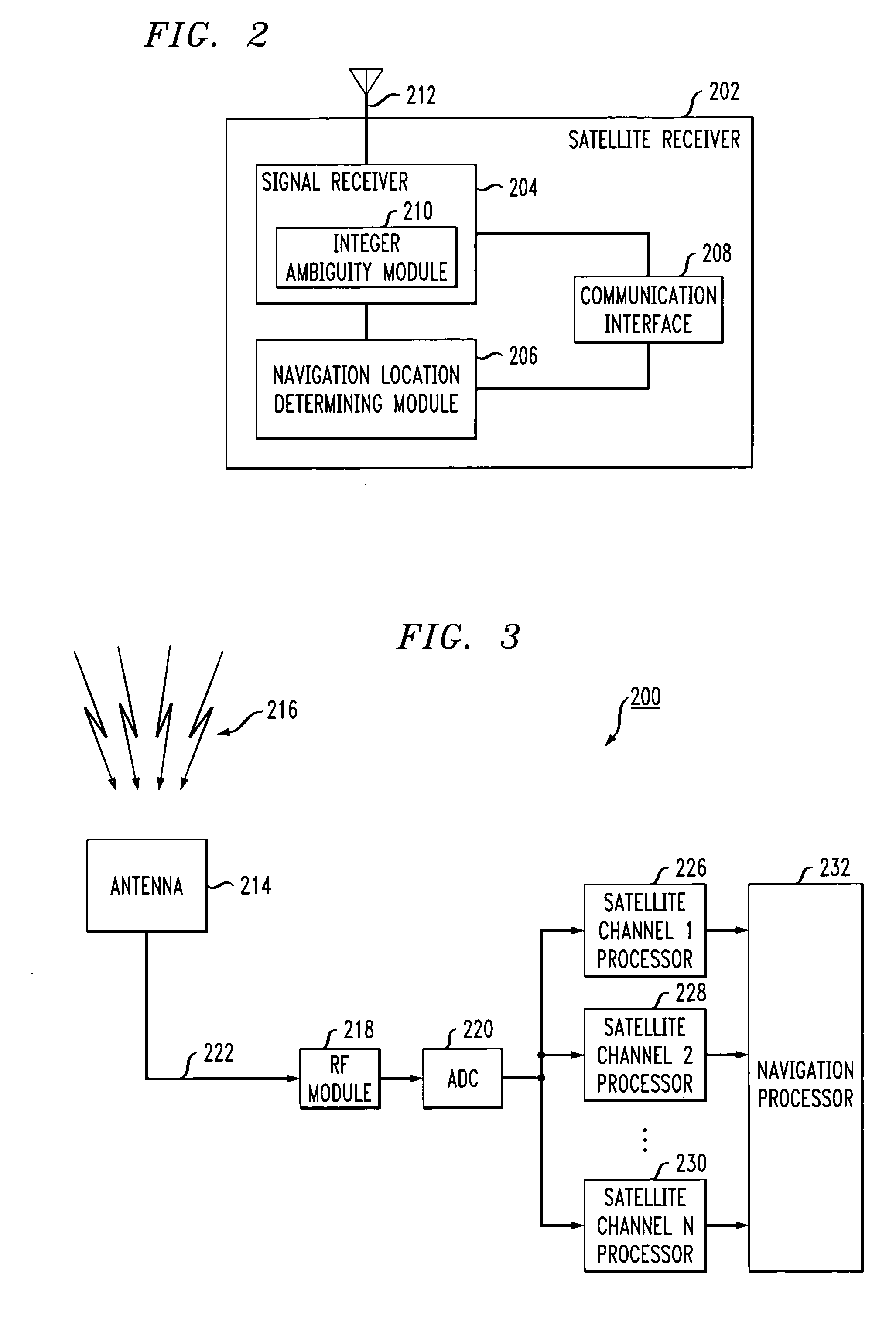
Estimation and resolution of carrier wave ambiguities in a position navigation system
ActiveUS20050264445A1Improve accuracyError minimizationActive open surveying meansPosition fixationElevation angleImage resolution
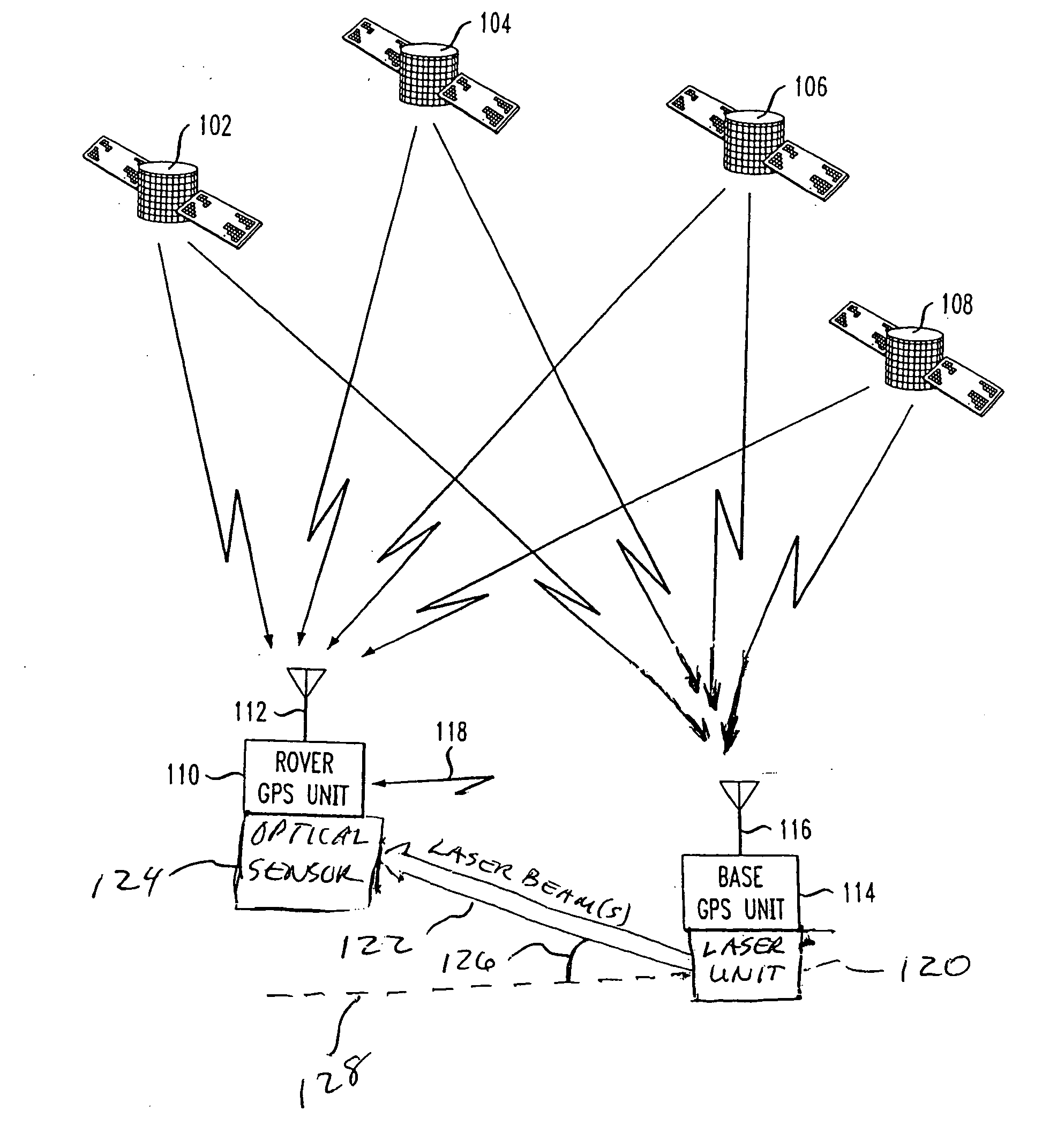
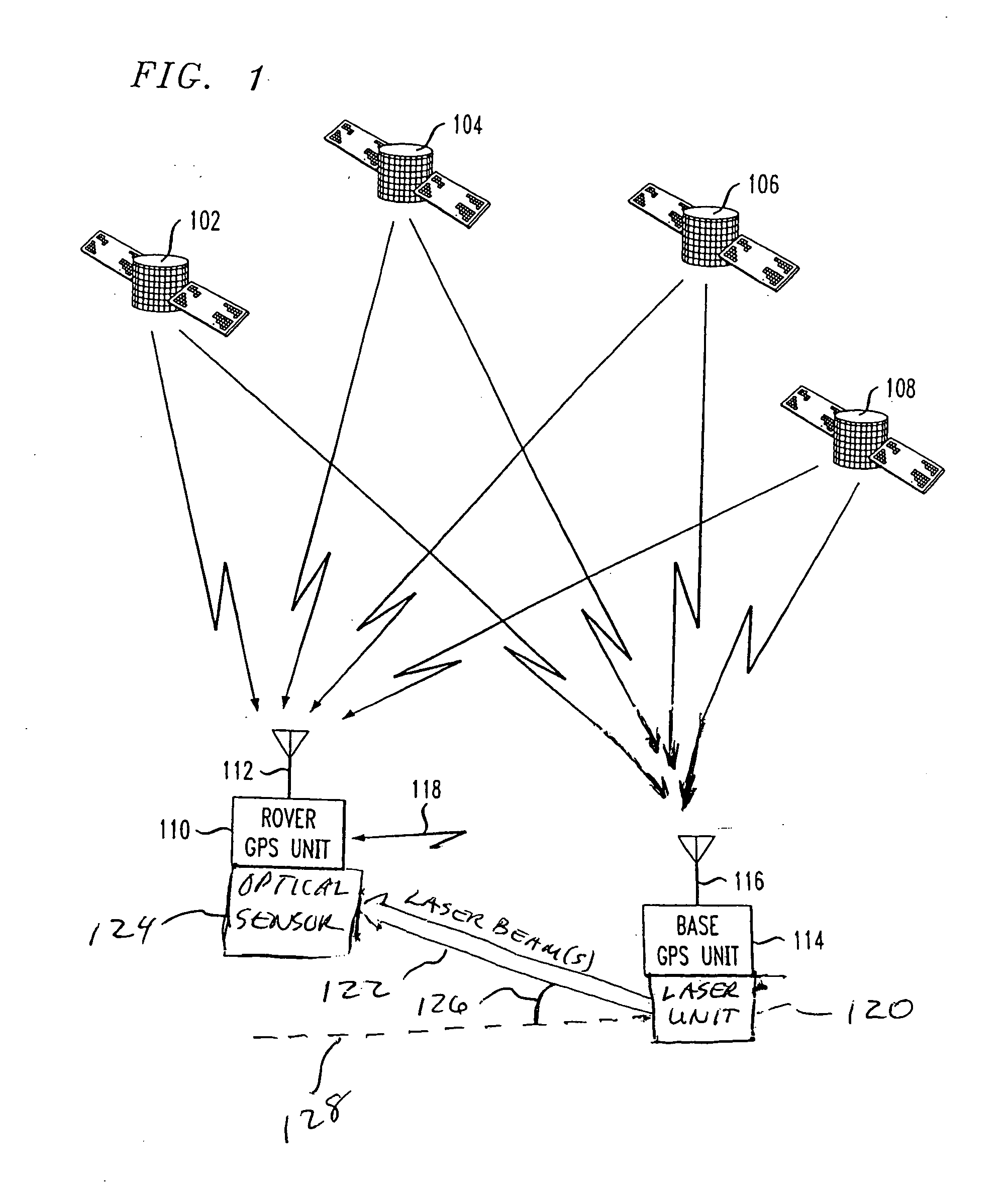
A method and apparatus for resolving floating point and integer ambiguities in a satellite position navigation system is disclosed. A rover station is periodically positioned at unknown locations and has a satellite receiver capable of receiving the navigation signals. By calculating relative position coordinates between a base station in a known location and the rover station, and by calculating other position parameters relative to the satellite position, a geometric constraint based on a measured elevation angle between the rover and base station can be incorporated into data computations and processing to help resolve carrier phase ambiguities. The elevation angle is measured by transmitting multiple laser beams to an optical sensor on the rover station. This technique results in greater precision in determining the location of the rover.
Owner:TOPCON GPS
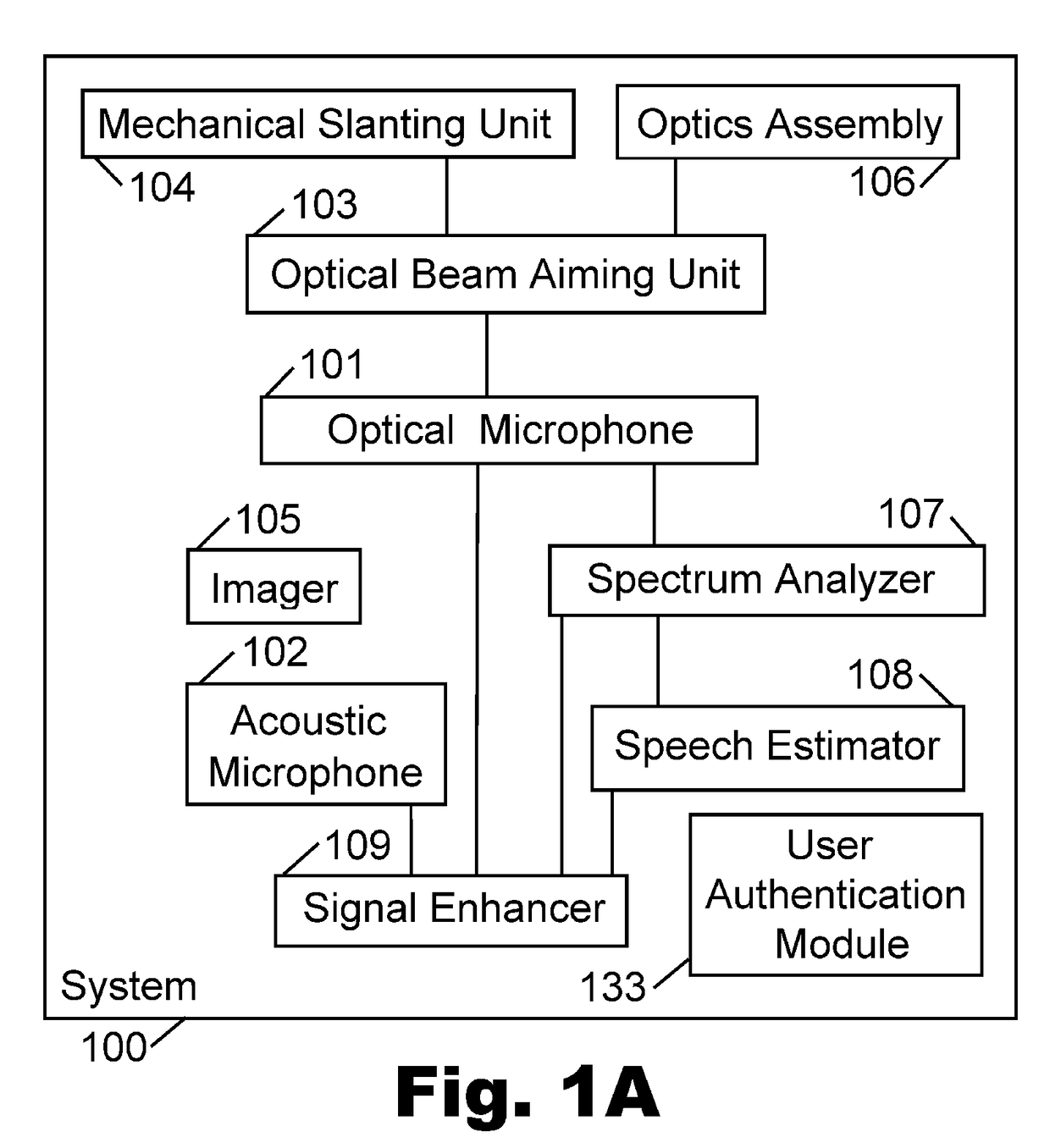
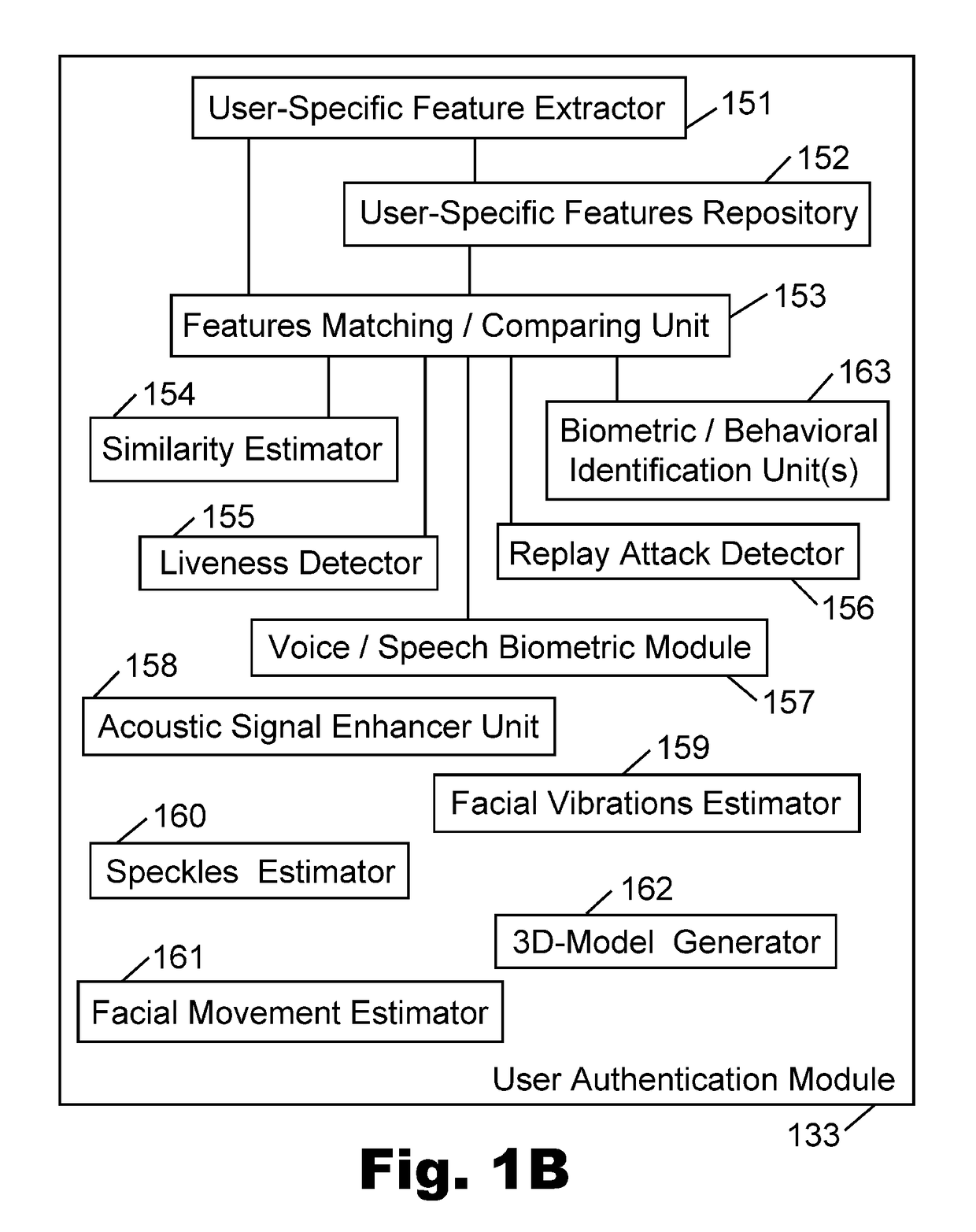
Device, system, and method of user authentication utilizing an optical microphone
InactiveUS20170351848A1Reduce and prevent attemptInternal/peripheral component protectionDigital data authenticationUser authenticationEngineering
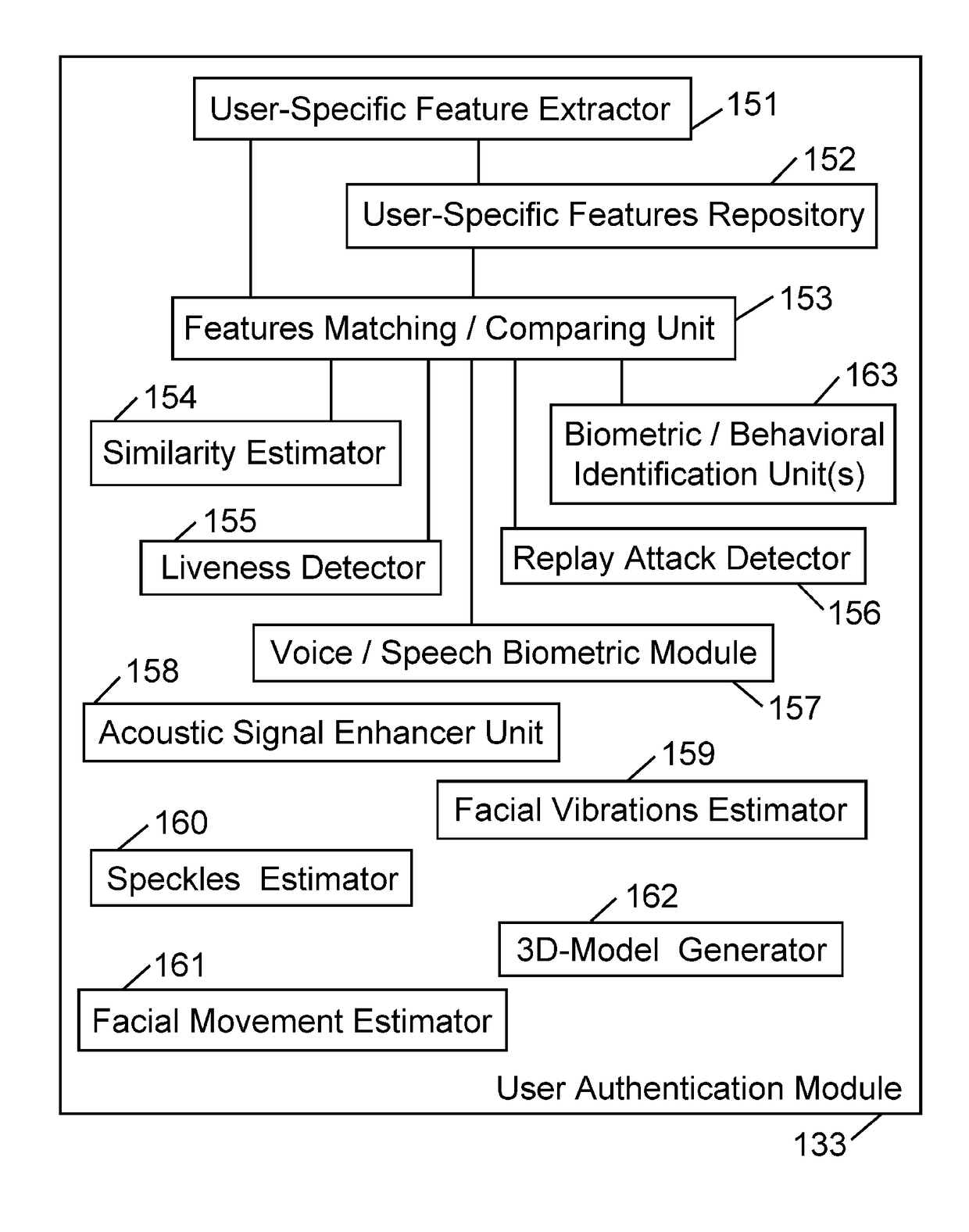
Device, system, and method of user authentication utilizing an optical microphone or laser-based microphone. An optical microphone transmits an outgoing optical signal or laser beam towards a face of a human speaker; receives an incoming optical feedback that is reflected back from the face of the human speaker; performs self-mix interferometry that is based on the outgoing optical signal and the incoming reflected optical signal; and generates a user-specific feature or characteristic that uniquely characterizes said human speaker. A user authentication module operates to authenticate the user for performing a privileged or an access-controlled action, based on the user-specific characteristic that was generated, optionally in combination with one or more biometric features or authentication requirements.
Owner:VOCALZOOM SYST
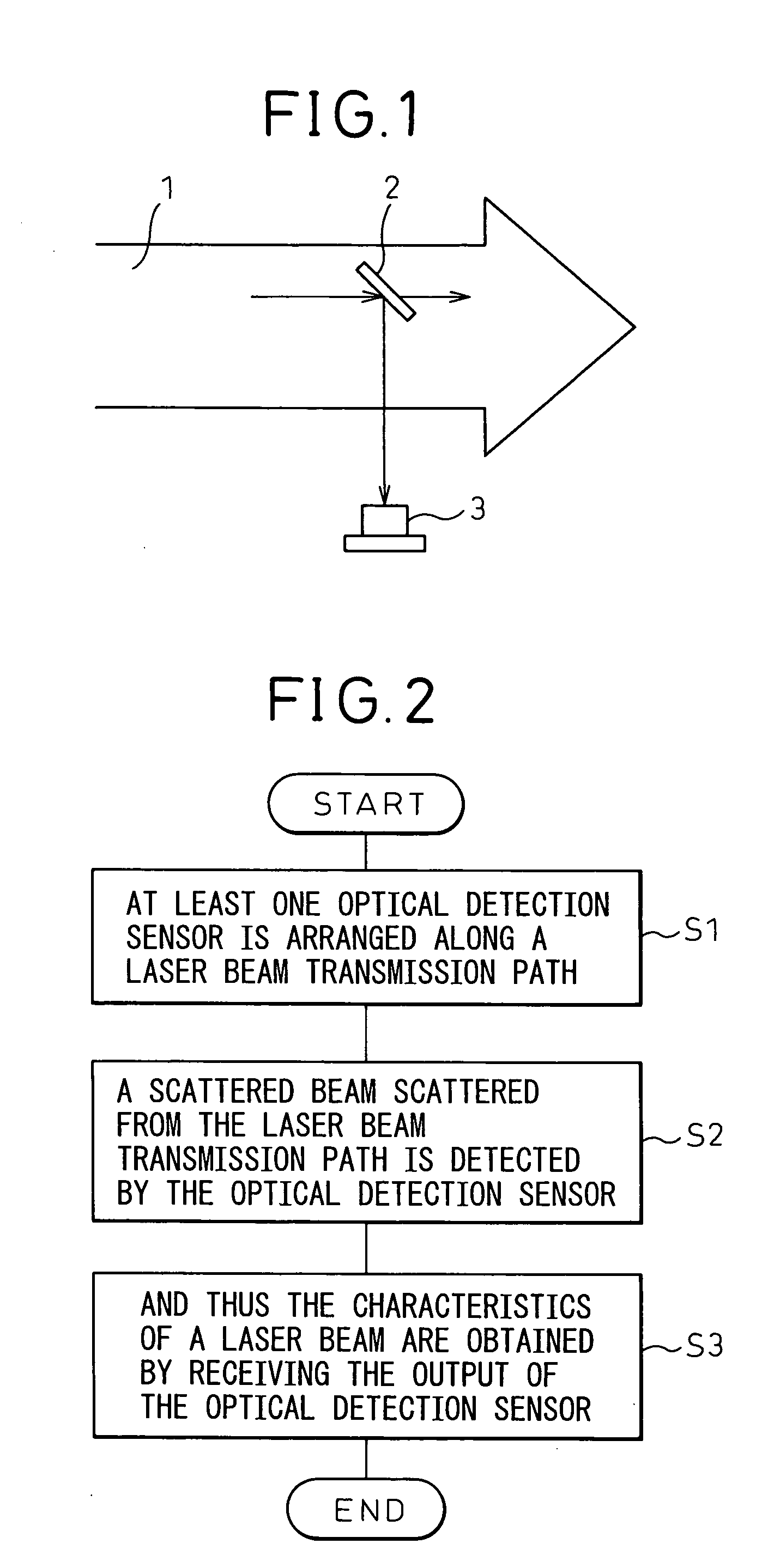
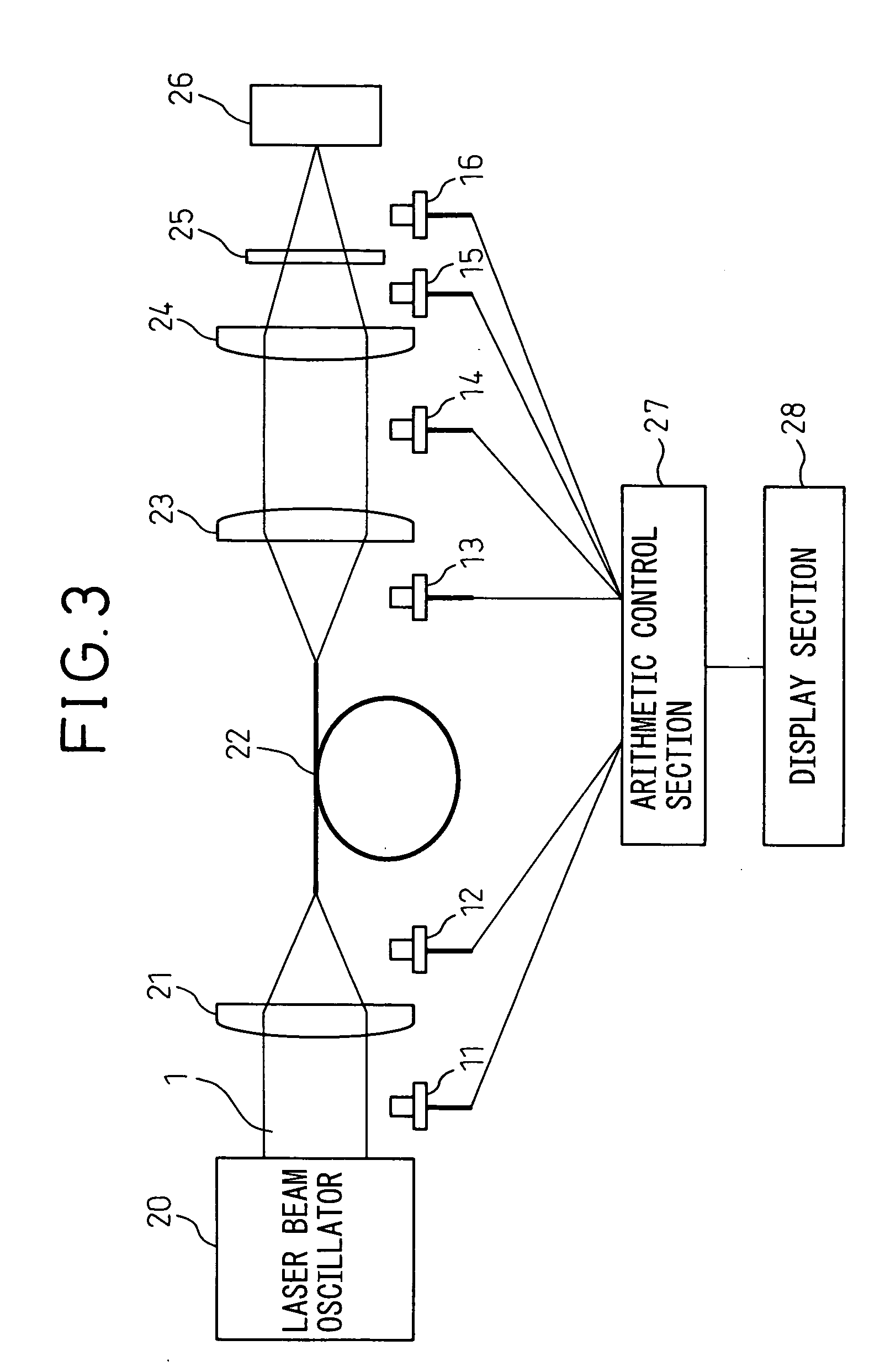
Method for controlling laser beam machine and laser beam machine
InactiveUS20050115940A1Maintenance conditionReal time monitoringLaser detailsPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsLight beamLaser beam machining
A laser beam machine and a laser beam machine capable of monitoring the effective energy of a laser beam oscillator, with which an object to be machined is irradiated, and the state of oscillation without affecting the properties of a laser beam, is disclosed. A laser beam machine comprises: a laser beam oscillator; a laser beam transmission path; a collimator lens; a machining condenser lens; at least one optical detection sensor provided along the laser beam transmission path; and an arithmetic control section for receiving the output of the optical detection sensor and performing a predetermined process to obtain the characteristic of a laser beam.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Dry cleaning system using a laser
InactiveCN1939643AEasy to removeAchieve clearingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusLight beamEngineering
The present invention relates to a dry cleaning system for removing the contamination from the cleaning object using a laser, and is directed to provide a dry cleaning system capable of removing contamination from the cleaning object effectively by using optical energy-laser, particularly removing contamination from the surface of the contact part of Semiconductor Test socket. According to the present invention, the dry cleaning system using laser is composed of: a laser generator for generating laser beam; a laser beam transmitting device for transmitting the laser beam generated from the laser generator; a laser beam irradiation device for adjusting the form of the laser beam transmitted by the laser beam transmitting device and irradiating the adjusted laser beam to the cleaning object; a scanning device for adjusting the irradiation position of the laser beam from the laser beam irradiation device.
Owner:IMT INC
Apparatus and method for processing micropore through filamentous laser
InactiveCN104959736AEasy to processSolve the problems that are difficult to control and difficult to process micro-holesLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingLight beam
The invention provides an apparatus for processing a micropore through filamentous laser. The apparatus comprises a computer control module, a laser, a laser beam transmission assembly, a focusing assembly and a processing platform. The laser beam transmission assembly and the focusing assembly are arranged along the optical path of laser in order, the computer control module is used for controlling parameters of laser emitted from the laser to produce filamentous laser, and the computer control module also can control the focusing assembly and the processing platform to work, so that the laser beam can modify the structure of material to be process on the processing platform. The apparatus for processing the micropore through filamentous laser can be used for processing a high-quality micropore whose aperture is less than 20 [mu]m at high efficiency, the problems that a conventional laser processing conicity is hard to control and a micropore is hard to process can be solved.
Owner:INNO LASER TECH CORP LTD
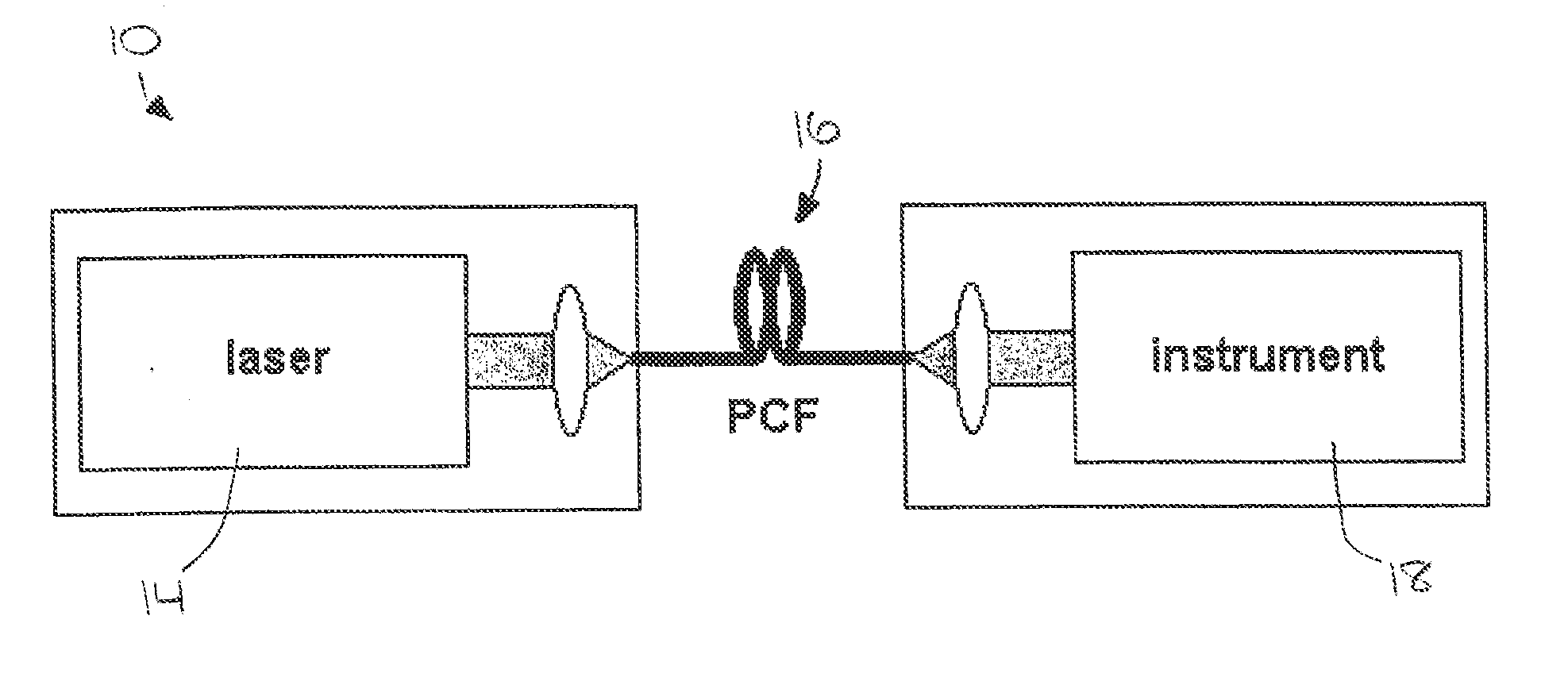
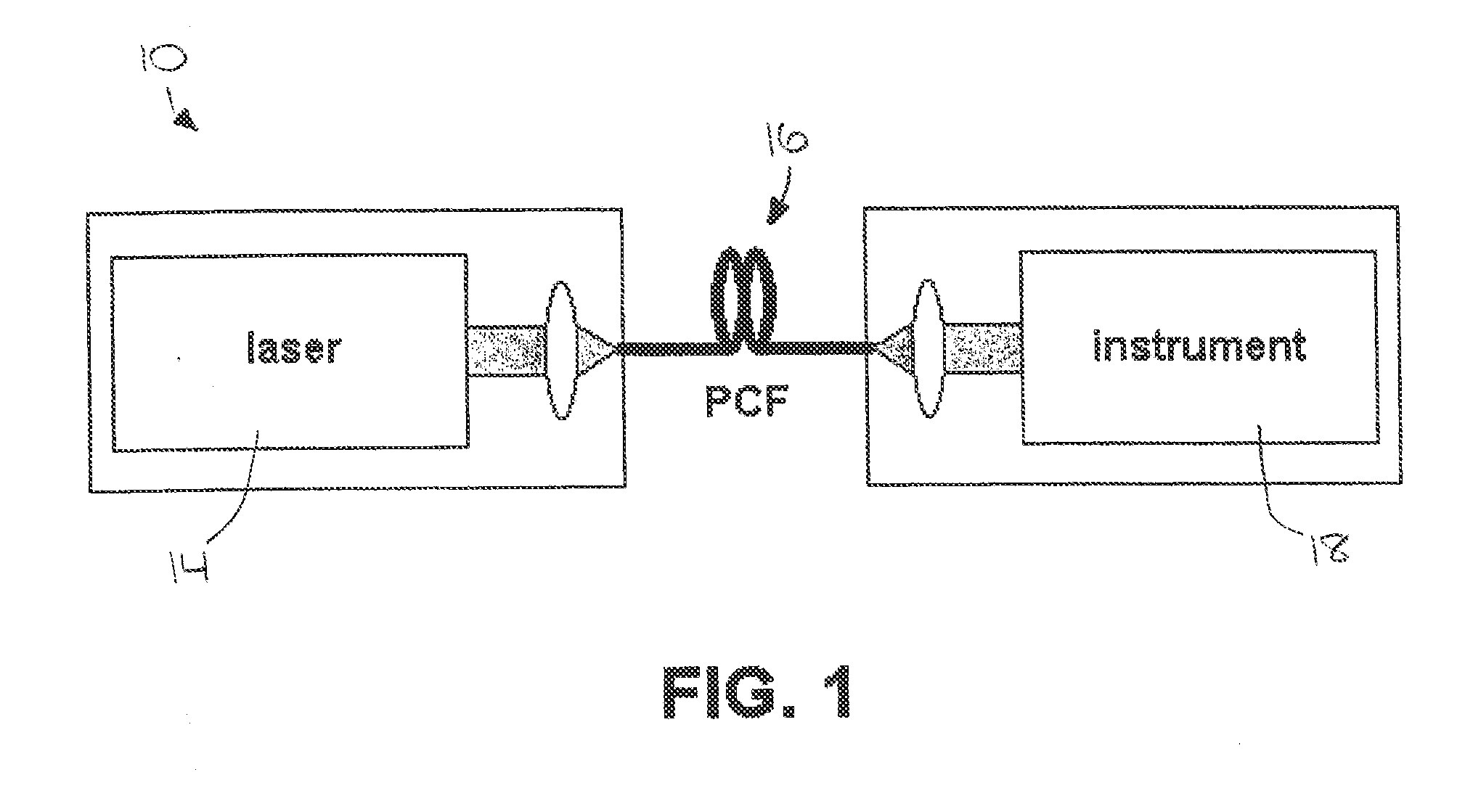
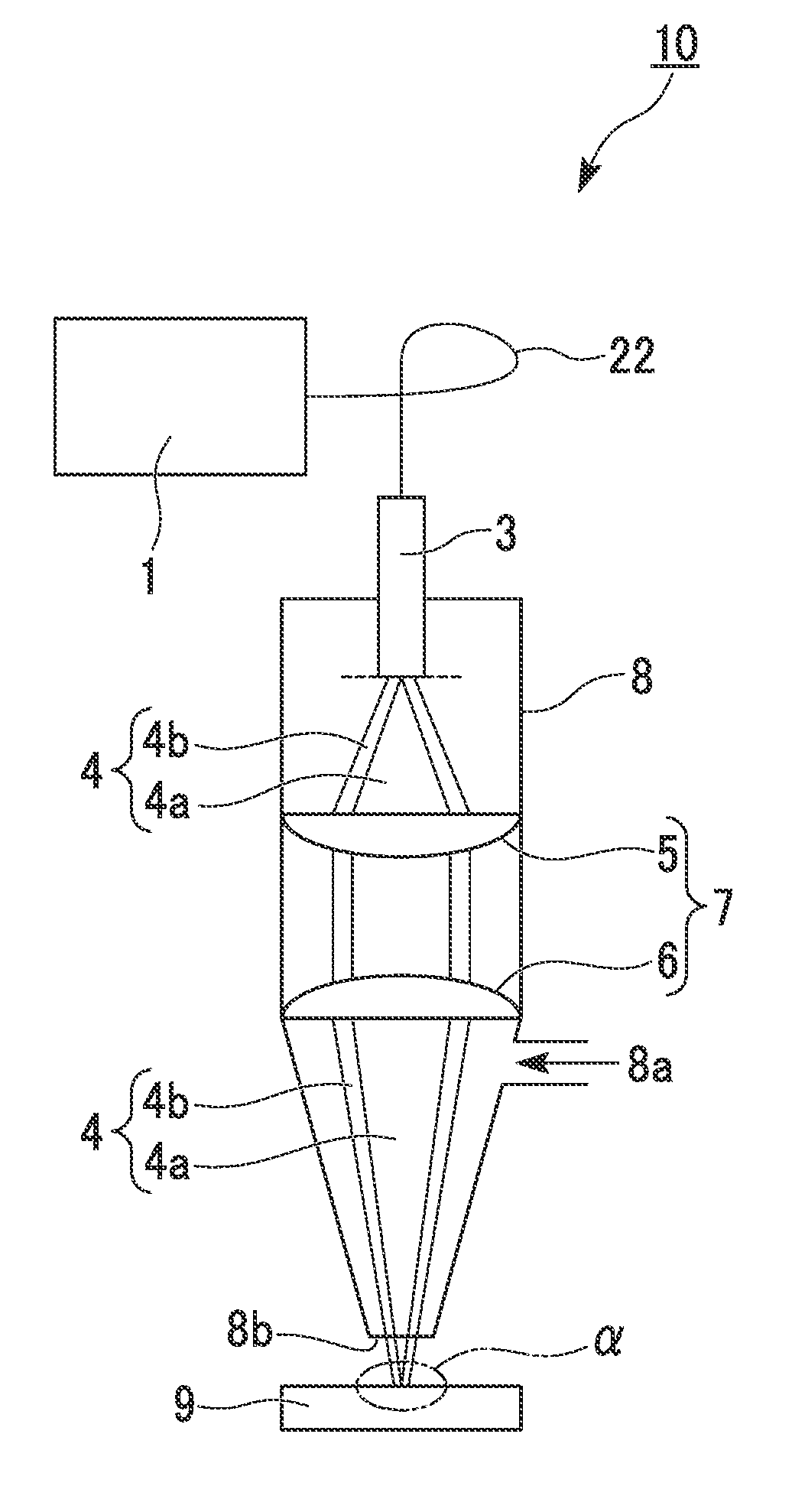
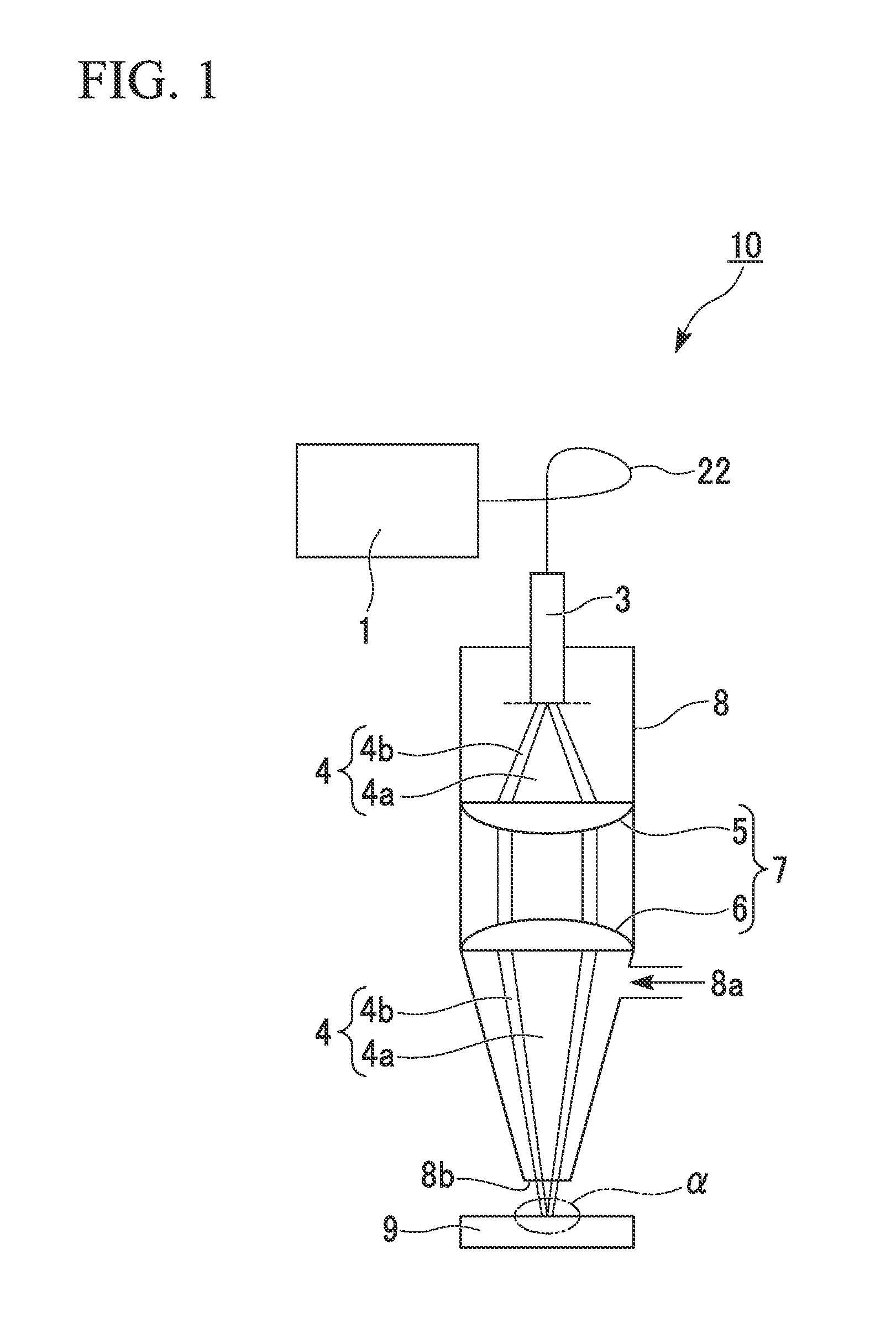
Laser system for photonic excitation investigation
A laser system (10) for use in photonic excitation investigation of a target object, in which the target object interacts with incident photons and emits a corresponding photon which is detected and used to generate an image of the target object. The laser system (10) includes a pulsed fiber laser (14) for producing a laser beam, and a non-linear photonic crystal fiber (16) for carrying the laser beam from the laser (14) to an instrument (18) for photonically exciting the target object. The photonic crystal fiber (16) allows for switching, or tuning, the wavelength of the laser beam. In two-photon microscopy, the laser system (10) allows for providing multiple wavelengths for exciting a plurality of different fluorophores simultaneously. In coherent Raman imaging and spectroscopy, the laser system (110) allows for using a single laser to provide two laser beams of different wavelengths.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
Estimation and resolution of carrier wave ambiguities in a position navigation system
ActiveUS20050212697A1Improve accuracyError minimizationActive open surveying meansPosition fixationElevation angleImage resolution
A method and apparatus for resolving floating point and integer ambiguities in a satellite position navigation system is disclosed. A rover station is periodically positioned at unknown locations and has a satellite receiver capable of receiving the navigation signals. By calculating relative position coordinates between a base station in a known location and the rover station, and by calculating other position parameters relative to the satellite position, a geometric constraint based on a measured elevation angle between the rover and base station can be incorporated into data computations and processing to help resolve carrier phase ambiguities. The elevation angle is measured by transmitting multiple laser beams to an optical sensor on the rover station. This technique results in greater precision in determining the location of the rover.
Owner:TOPCON GPS
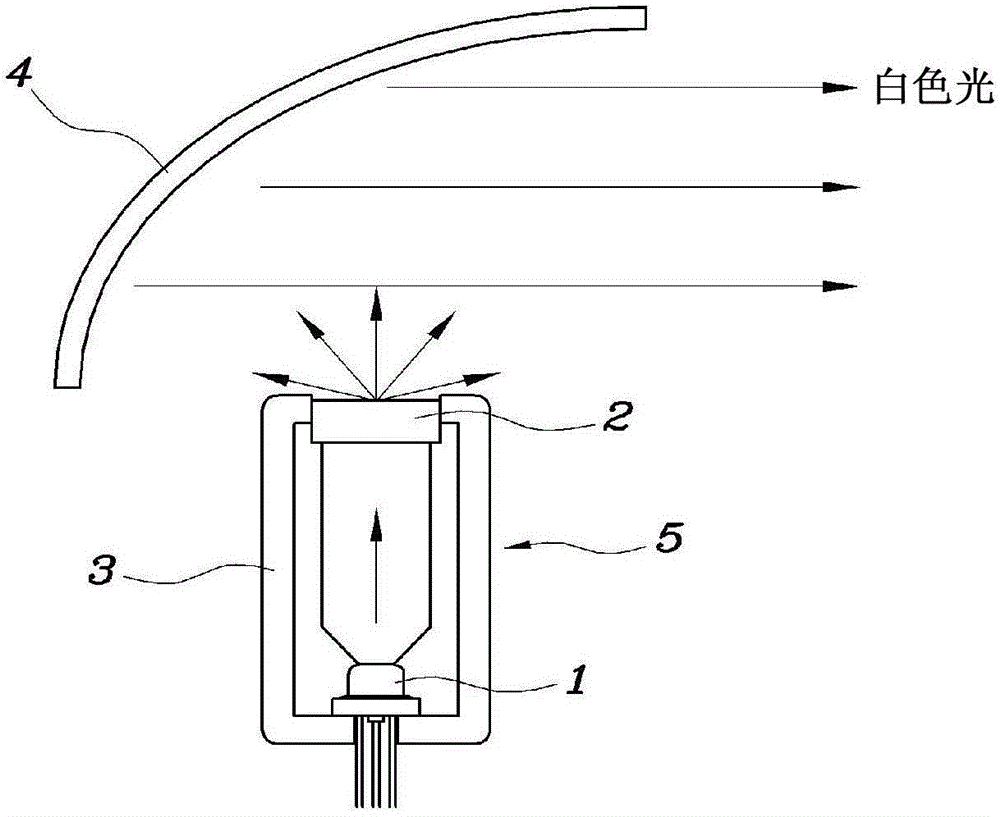
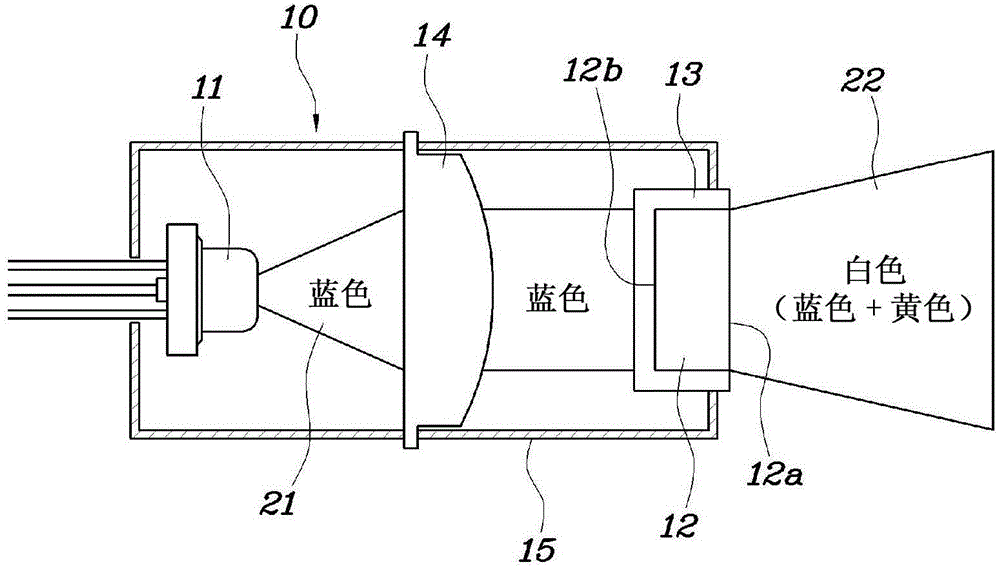
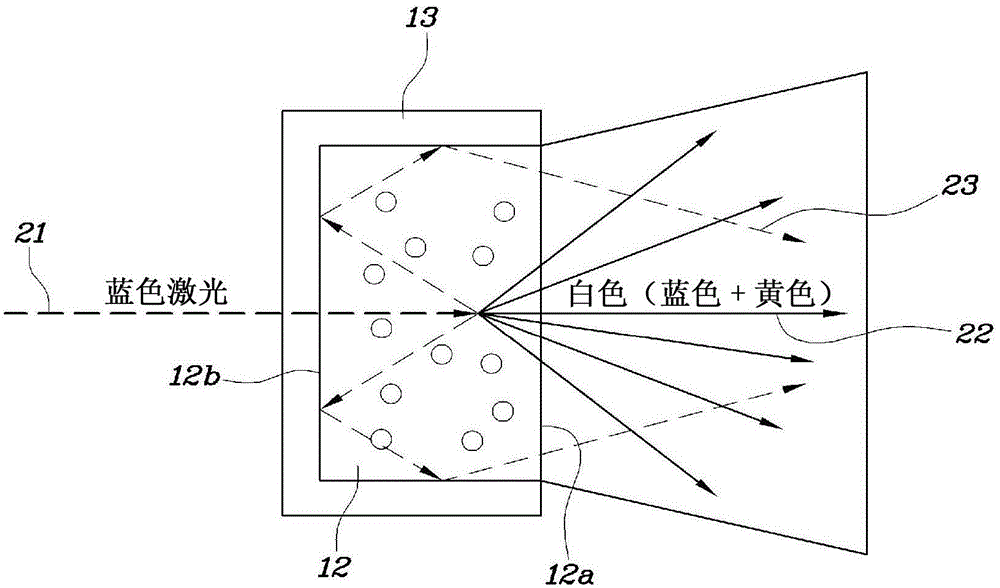
Head lamp for vehicle
A head lamp for a vehicle includes a laser light source module. The laser light source module comprises a laser diode generating a laser beam. A phosphor is mounted in front of the laser diode to react to light from the laser diode to output white light. A short wave pass filter is coupled with the phosphor to transmit a laser beam from the laser diode to the phosphor and retro-reflect light scattered in remaining directions avoiding a light emitting surface of the phosphor among the laser beam incident on the phosphor to the phosphor.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
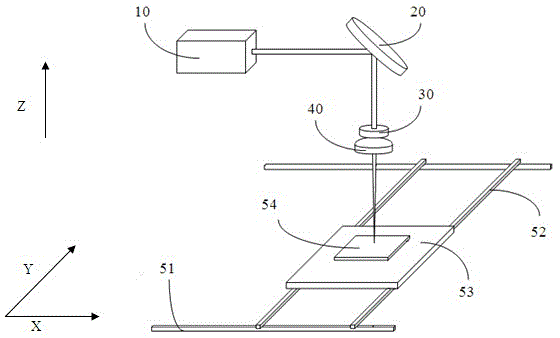
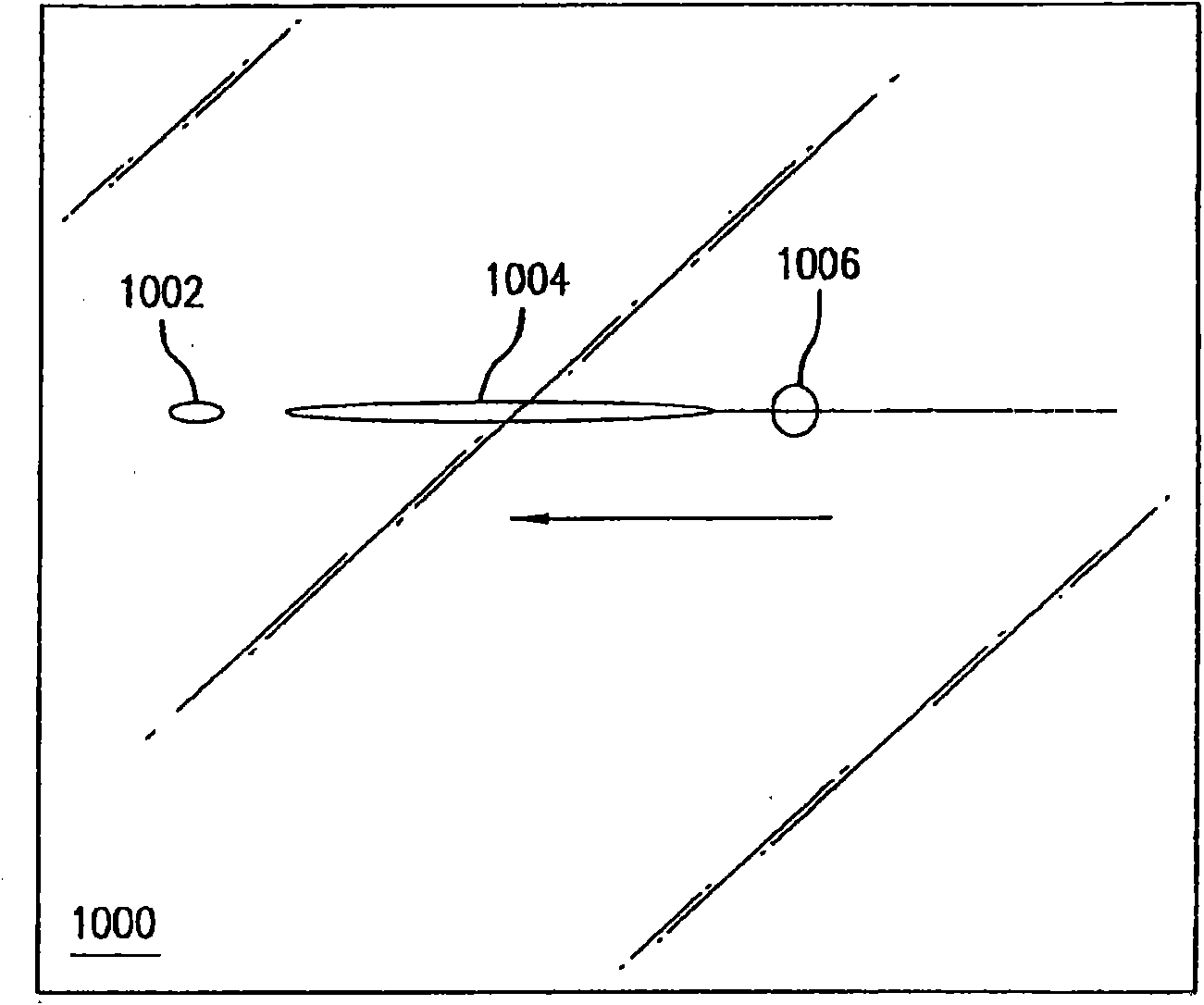
Scoring of non-flat materials
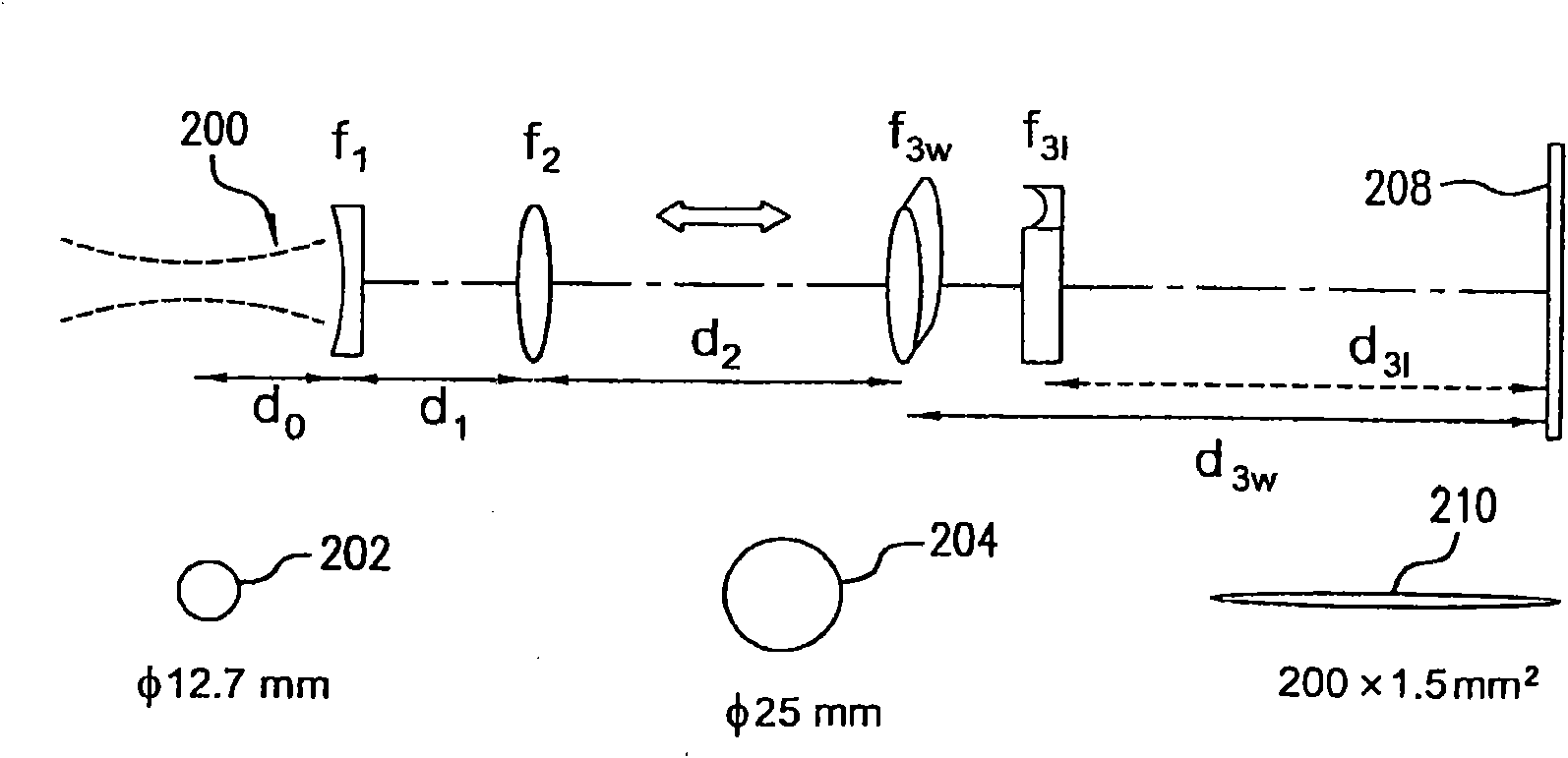
InactiveCN102046545AIncrease flight distanceExtended Beam SizeGlass severing apparatusLaser beam welding apparatusFlat glassBeam expander
Disclosed are systems for scoring non-flat materials including non-flat glass sheets (1000). In one embodiment, a laser scoring system is described. The laser scoring system includes a laser (102) and an optical head (106). The optical head is configured to receive output from the laser and focus the output into an elongated laser beam having a beam waist and an extended focal depth (116) of greater than + / - 5 mm relative to the center of the beam waist with a power density sufficient for scoring a material having at least a portion within the extended focal depth. In one aspect the system can include a beam expander (104). The beam expander receives the output from the laser, expands the output from the laser to an expanded laser beam, and transmits the expanded laser beam to the optical head.
Owner:CORNING INC
Laser apparatus and laser materials processing apparatus provided with same
ActiveUS20130215914A1Improve processing qualityReduce the amount requiredLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberDouble-clad fiber
A laser apparatus of the present invention has a first laser oscillator that emits a first laser beam; a passive fiber that is a double-clad fiber that transmits the first laser beam through a core; and a second laser oscillator that emits a second laser beam that is coupled into inner cladding of the passive fiber. Additionally, a laser materials processing apparatus of the present invention is provided with the laser apparatus; and an irradiation optical system having a collimating lens and a condenser lens.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
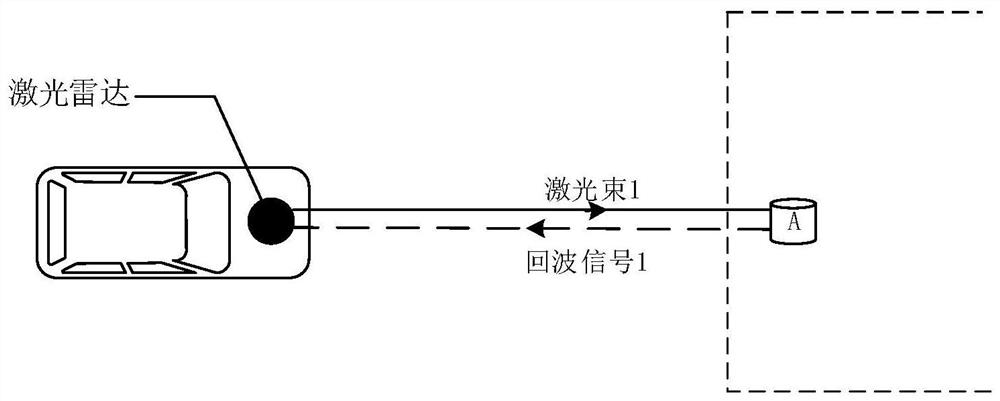
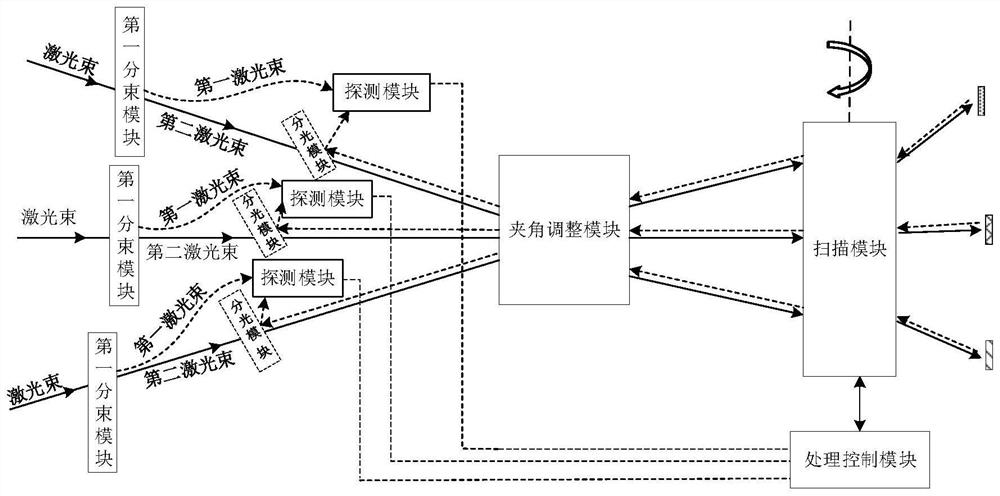
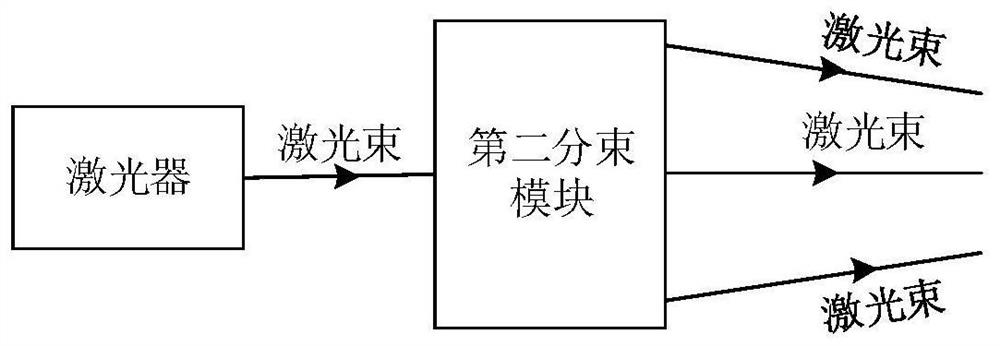
Laser radar and detection method of laser radar
The invention provides a laser radar and a detection method of the laser radar. The laser radar can be applied to the fields of automatic driving, networked vehicles and the like. The laser radar comprises a laser device, a first beam splitting module, an included angle adjusting module, a scanning module and a detection module, wherein the laser device is used for emitting N laser beams and transmitting the N laser beams to N first beam splitting modules; the first beam splitting module is used for splitting the received laser beams into first laser beams and second laser beams; the includedangle adjusting module is used for receiving the N second laser beams and adjusting an included angle between any two adjacent second echo signals in the N second laser beams to be greater than 0 degree and not greater than angular resolution; the scanning module is used for receiving the N second laser beams and emitting the N second laser beams at different detection angles; and the detection module is used for receiving the first laser beams and the corresponding echo signals, performing frequency mixing processing to obtain beat frequency signals and determining associated information of atarget object according to the beat frequency signals. Therefore, more associated information can be obtained, so that the point cloud density of a formed image can be improved, and the definition ofthe image is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Broadband Optical Phase Detection and Phase Noise Removal with an Optical Resonator
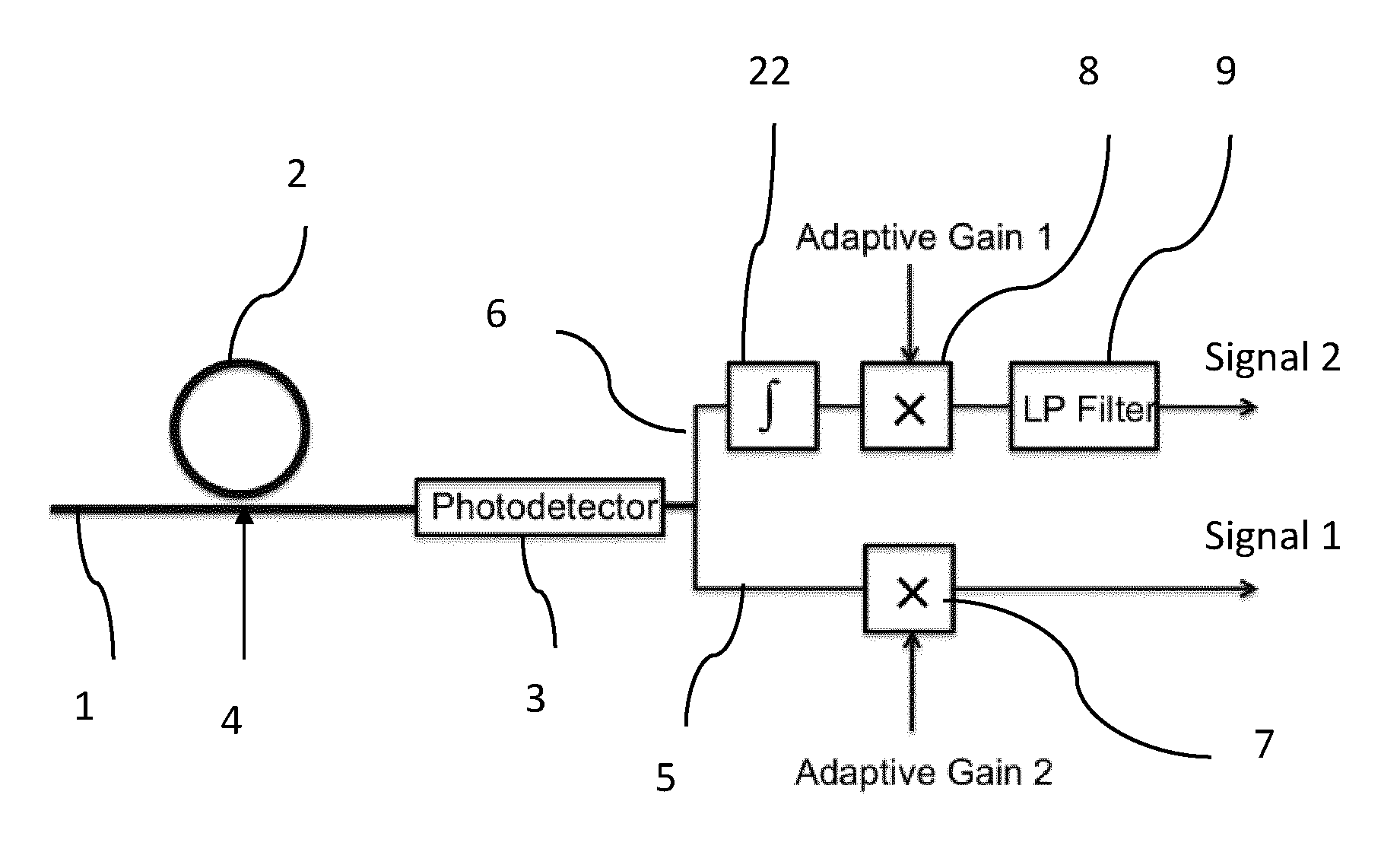
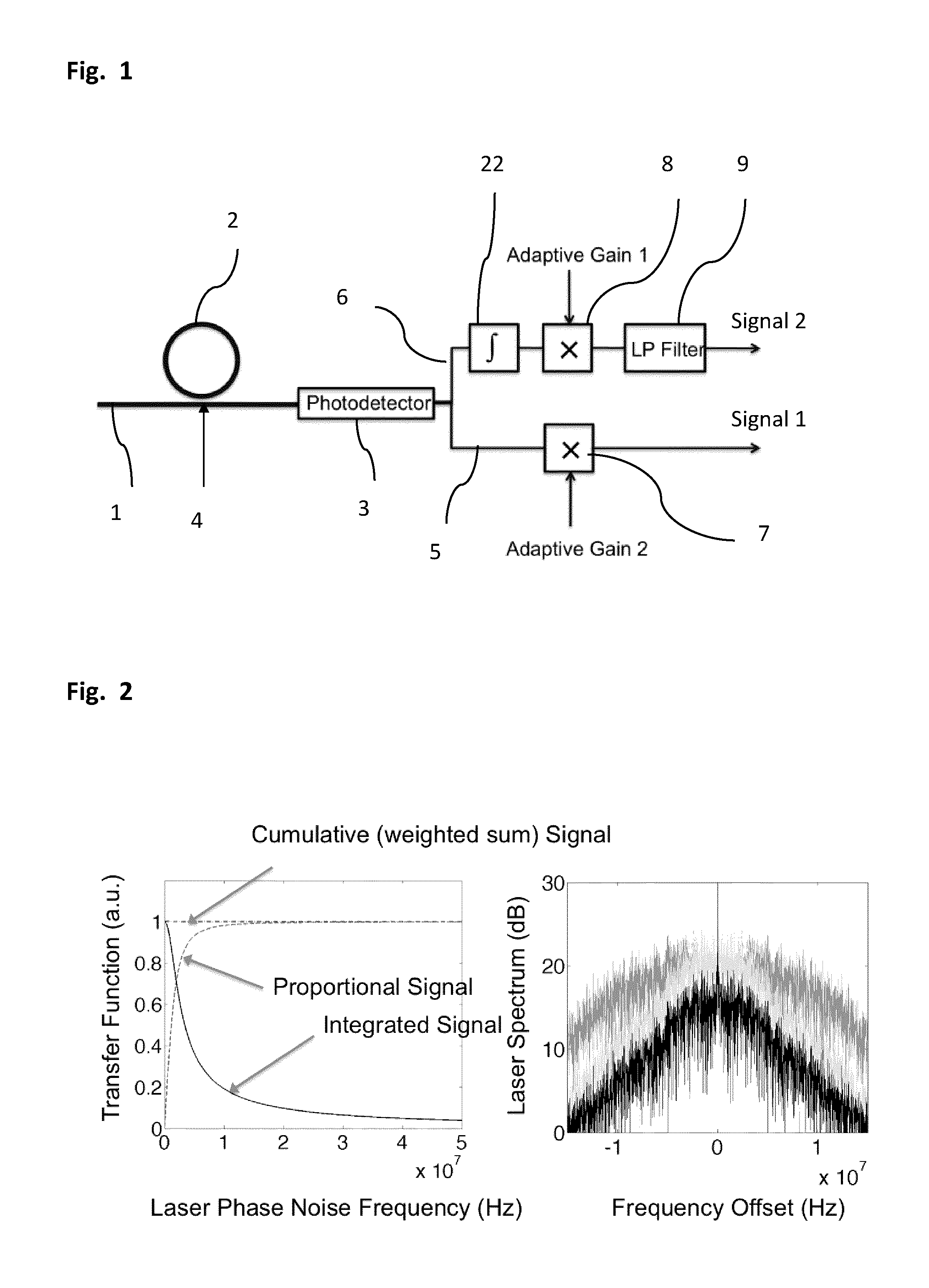
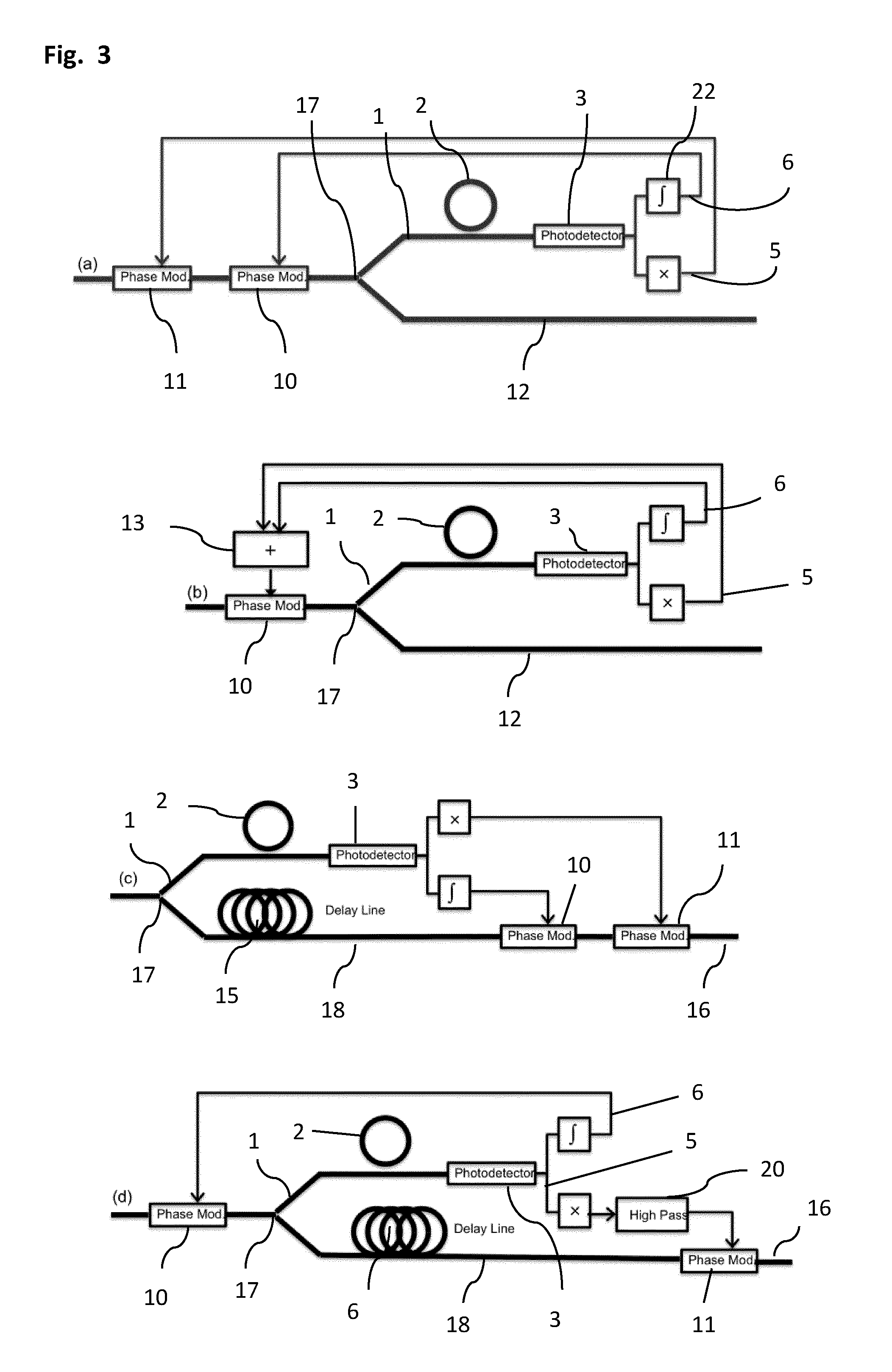
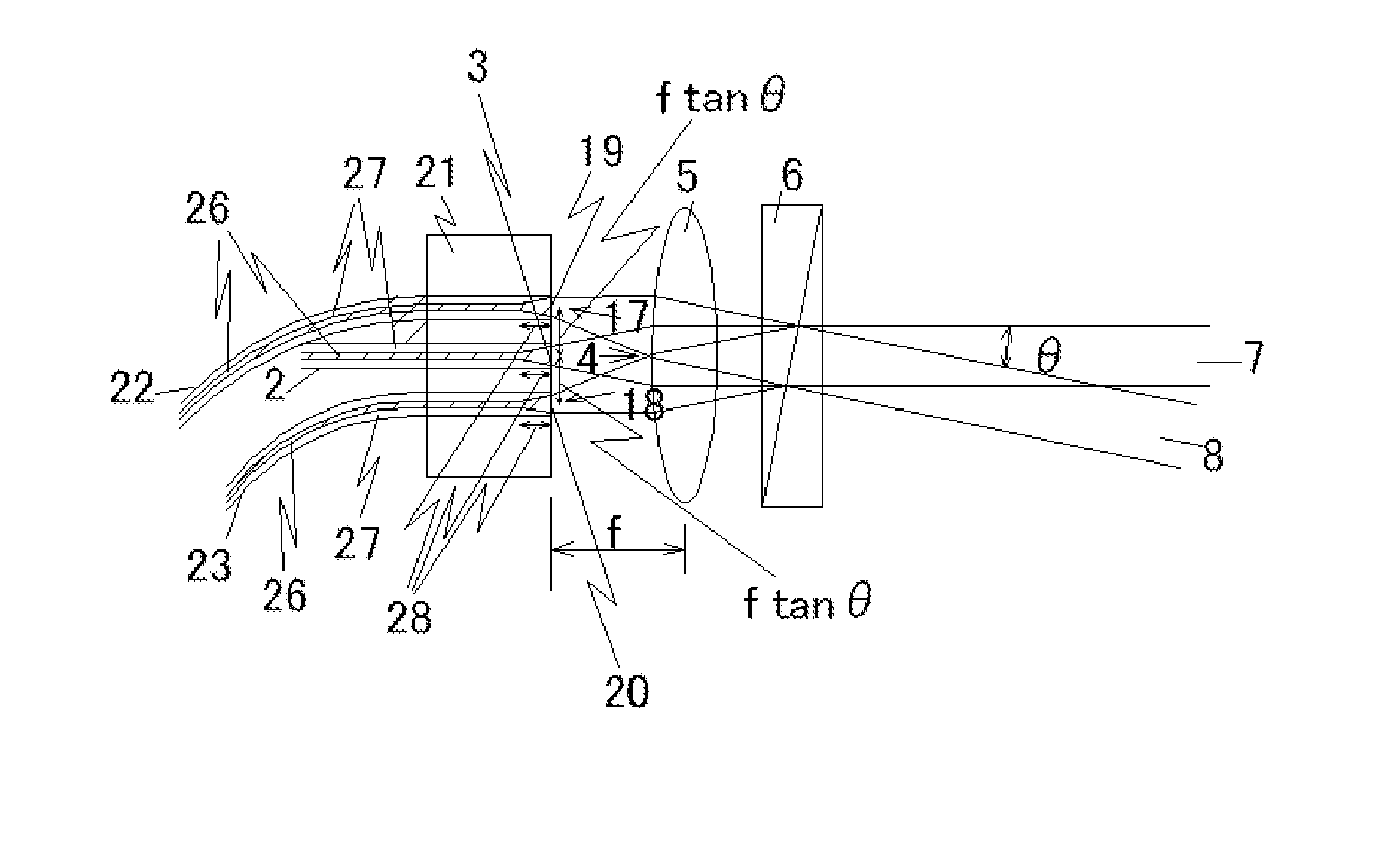
ActiveUS20130221211A1Improved noise detectionImprove phase noiseRadiation pyrometryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPhase noiseIntegrator
A phase noise detection apparatus comprises a laser beam, an optical resonator coupled thereto at a coupling point and a photodetector receiving light from the laser beam. The laser beam and the resonator coupled thereto convert phase noise of light transported by the laser beam prior to the coupling point into intensity noise of light transported by the laser beam thereafter. Intensity noise is converted into an electrical signal by the photodetector. The electrical signal is sent through a first signal path and a second signal path such that the first signal path transports a signal substantially proportional to the intensity noise, which is integrated in an integrator in the second path. Relative gain of the two signal paths can be adjusted and the overall gain of the signal path is preferably such that the optical phase modulator at least partially cancels said phase noise in the optical domain.
Owner:RWTH AACHEN UNIVERSITY
Collimator and optical isolator with collimator
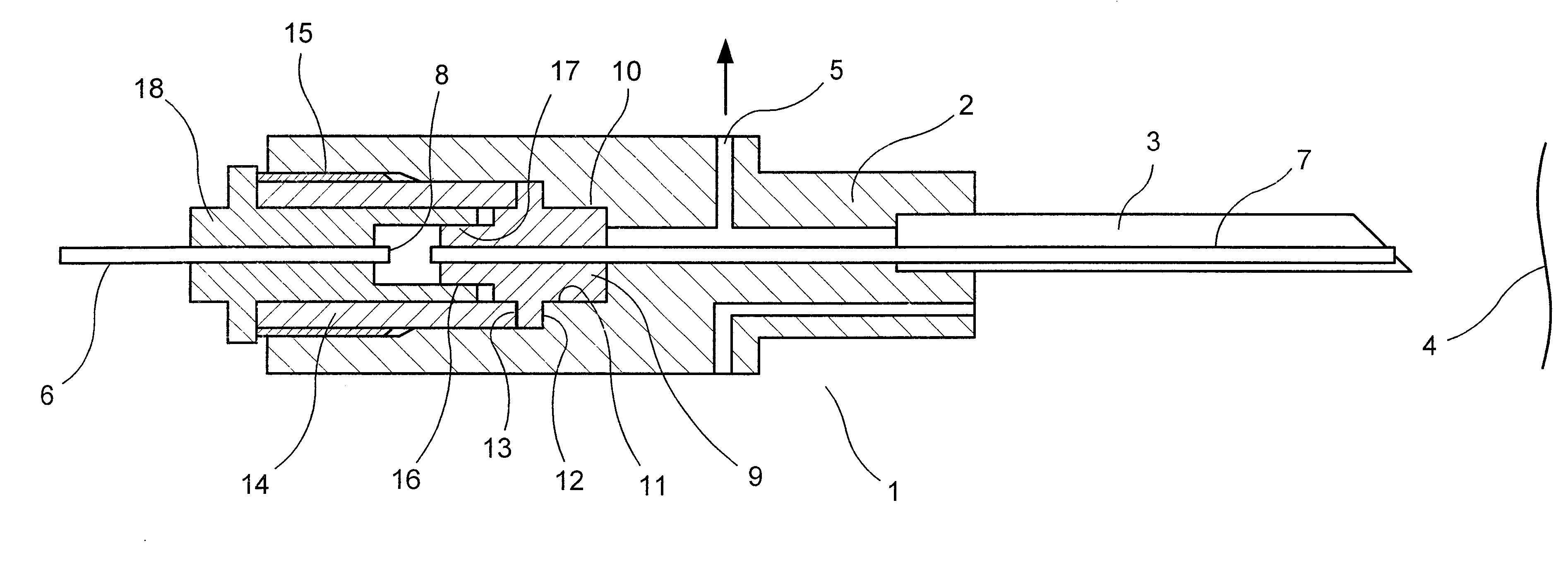
An optical isolator with a collimator which is used at the tip end of a laser beam transmitting fiber utilized in a laser processing. The optical isolator can provide solutions to the problems how to make return lights to be isolated from an incident light path and how to prevent the light energy from being conducted to an incident fiber, a laser oscillator, the collimator, and the optical isolator. The solutions comprise light-receiving fibers (22 and 23) disposed at focal points of a collimator lens (5) to which reflected lights from a workpiece return through the optical isolator. The return lights are then led to a ceramic tube (24) where the return light energy is converted to thermal energy and dissipated.
Owner:FURUUCHI KAGAKU
Laser processing system having auxiliary controller
ActiveUS20130126492A1Increase speedShorten the timeLaser detailsLaser beam welding apparatusNumerical controlLaser processing
A laser processing system includes: a numerical control device (1) outputting a laser output signal and a digital signal; a converter (231) converting the laser output signal to an analog signal; a pulse signal generator (22) generating a pulse signal for controlling the analog signal; an auxiliary controller (7) generating a logic signal which forcedly controls transmission / stop of a laser beam; a logical operation unit (28, 29) outputting a result of the logical operation between the pulse signal and the logic signal; a switching device (27) generating a laser drive signal for alternately transmitting / stopping the laser output on the basis of the logical operation result; and a sensor (6) for measuring intensity of light radiated or reflected from a workpiece irradiated with a laser beam. The auxiliary controller (7) generates the logic signal in accordance with the intensity of the light measured by the sensor (6).
Owner:FANUC LTD
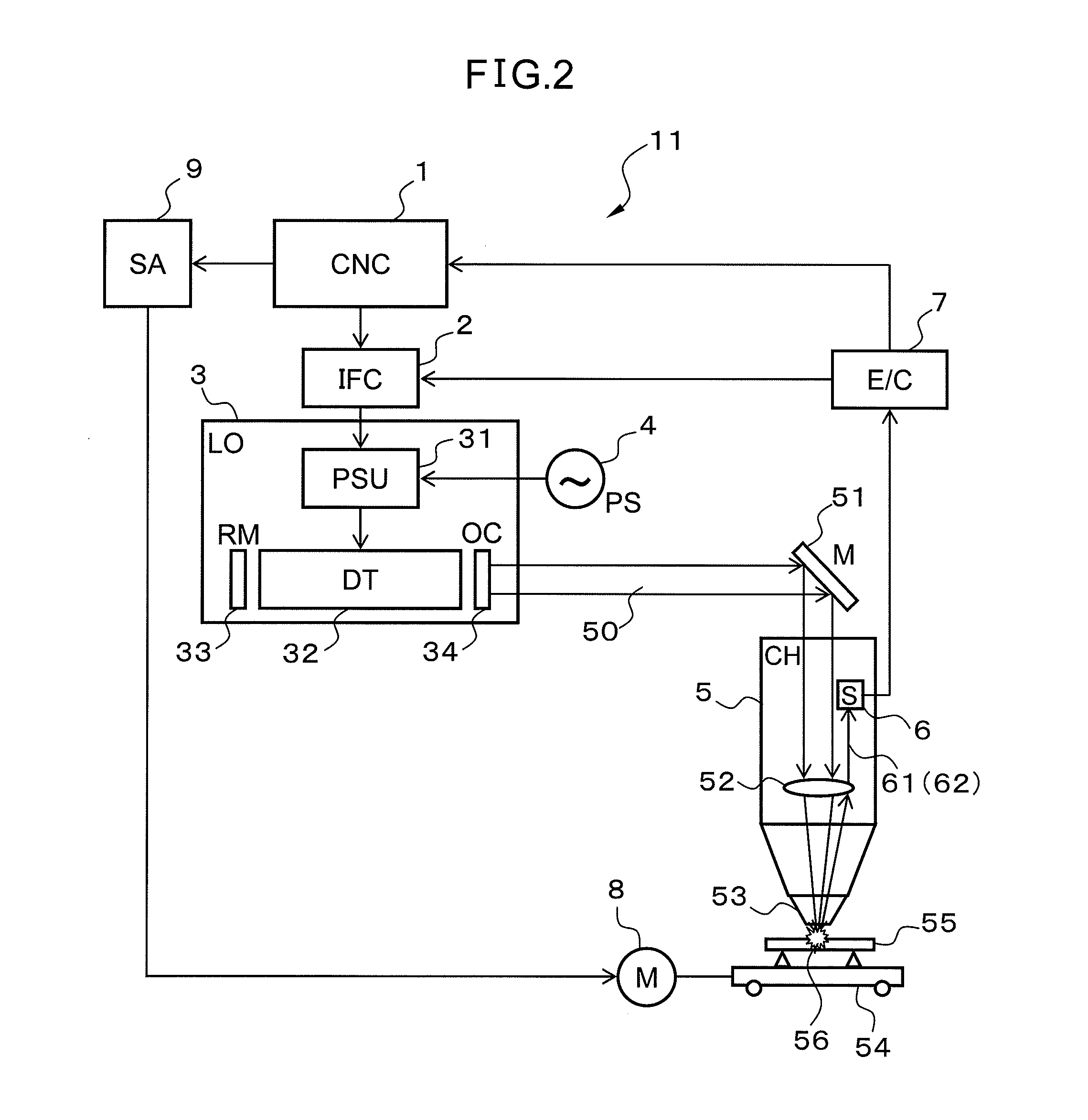
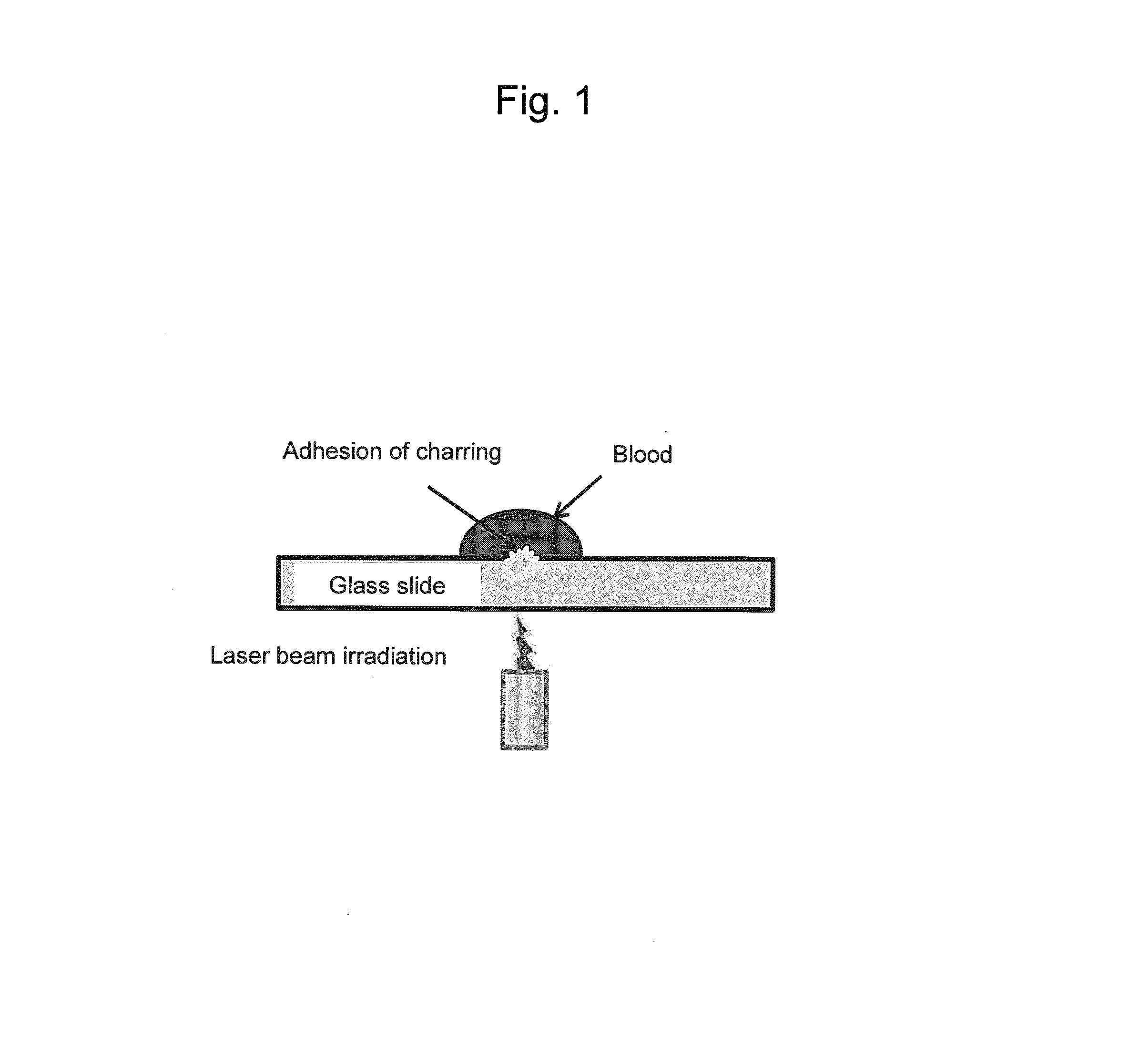
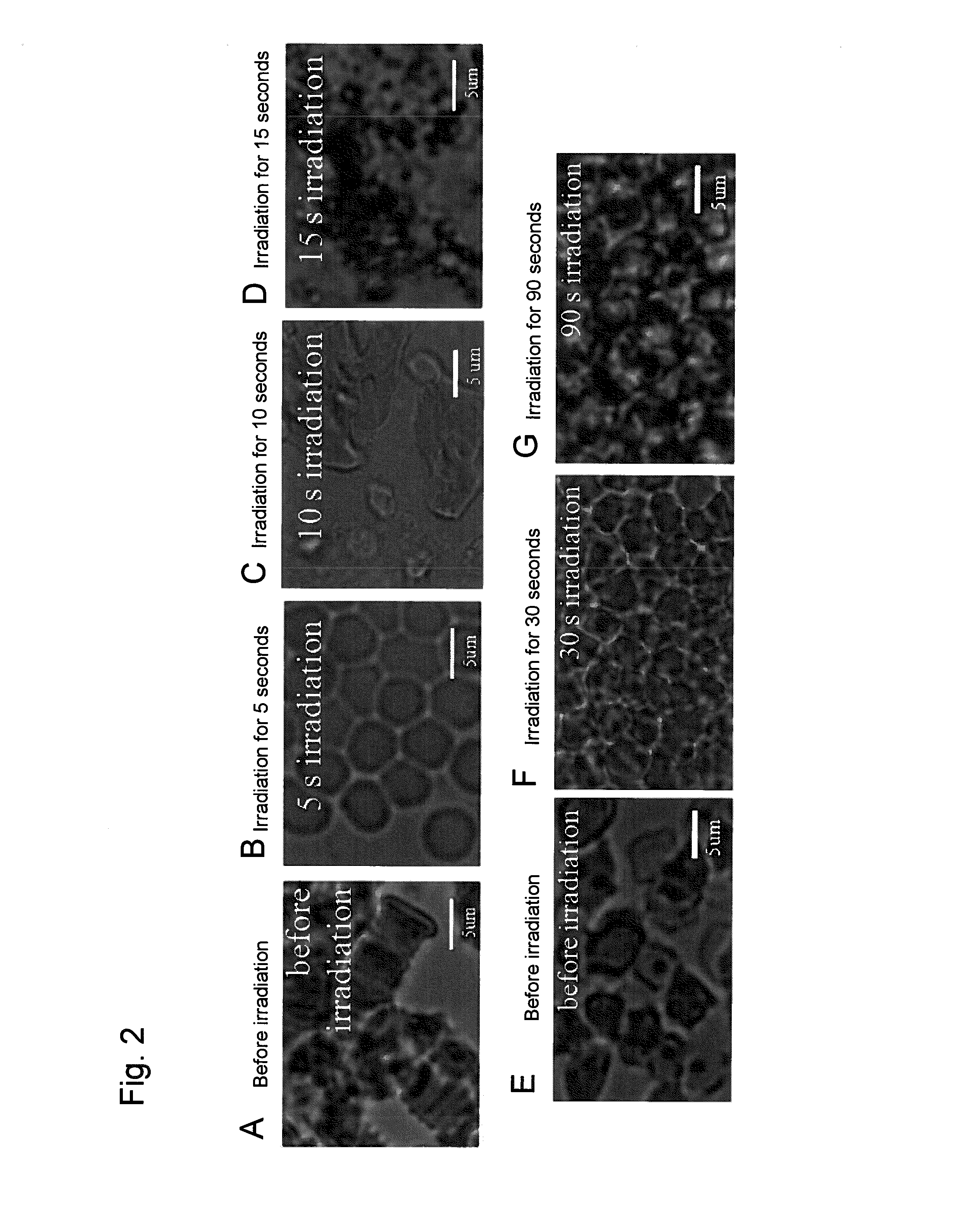
System for preventing blood charring at laser beam emitting site of laser catheter
InactiveUS20130046293A1Avoid charringBlood charringSurgical instrument detailsCatheterTemporal changeLight beam
This invention provides a method and a system for preventing charring at a laser beam emitting site during treatment or diagnosis using a laser catheter for applying a laser beam. The method is intended to control laser beam irradiation of an apparatus equipped with a laser catheter comprising a laser beam transmission means and a laser beam emitting site used for diagnosis or treatment with the irradiation of the inside of a blood vessel or heart cavity with a laser beam. The method for controlling laser beam irradiation is intended to prevent blood charring at a laser emission site of an apparatus equipped with a laser catheter, and the method comprises a step of controlling a laser beam output in accordance with temporal changes in the intensity of the diffuse reflected light beam by erythrocytes applied to the inside of a blood vessel or heart cavity.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com