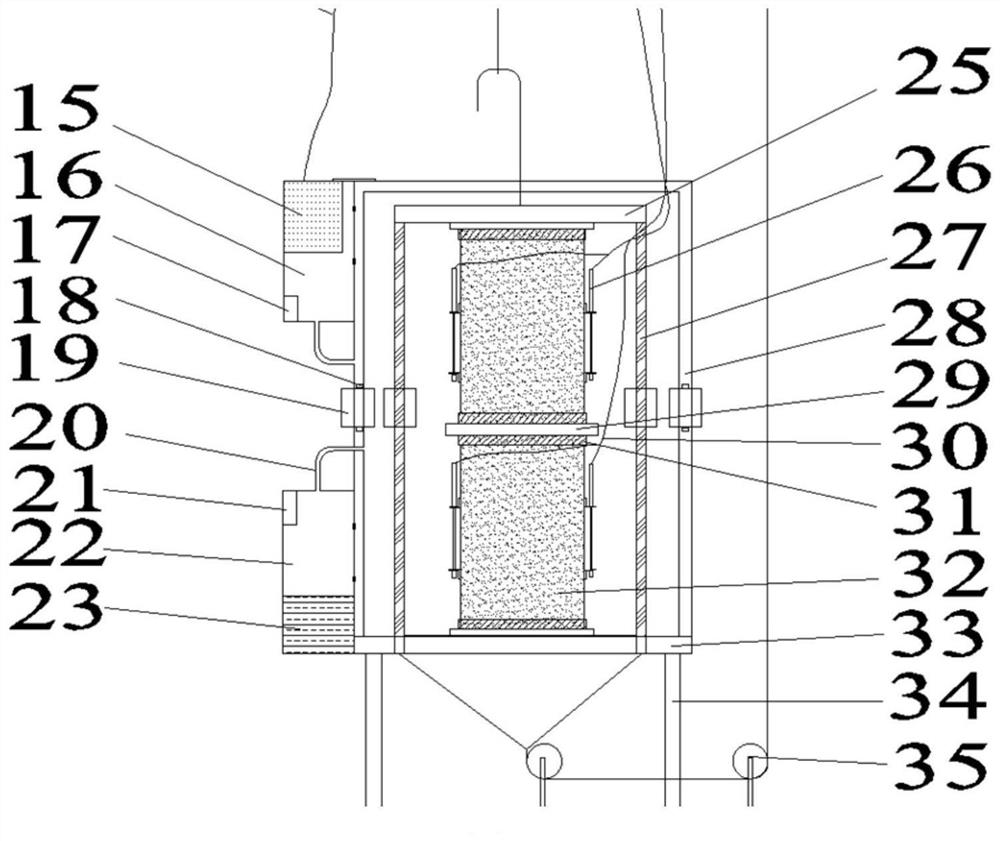
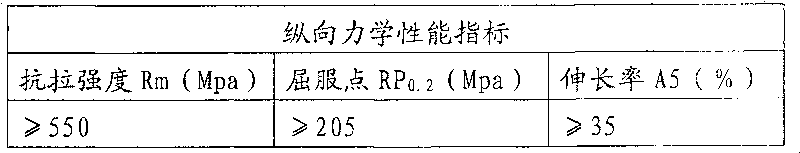
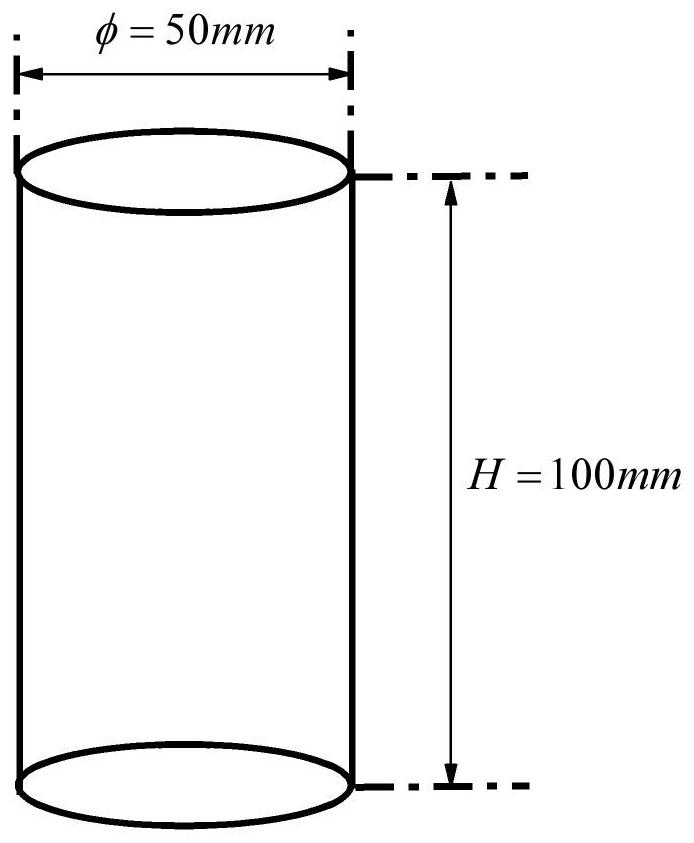
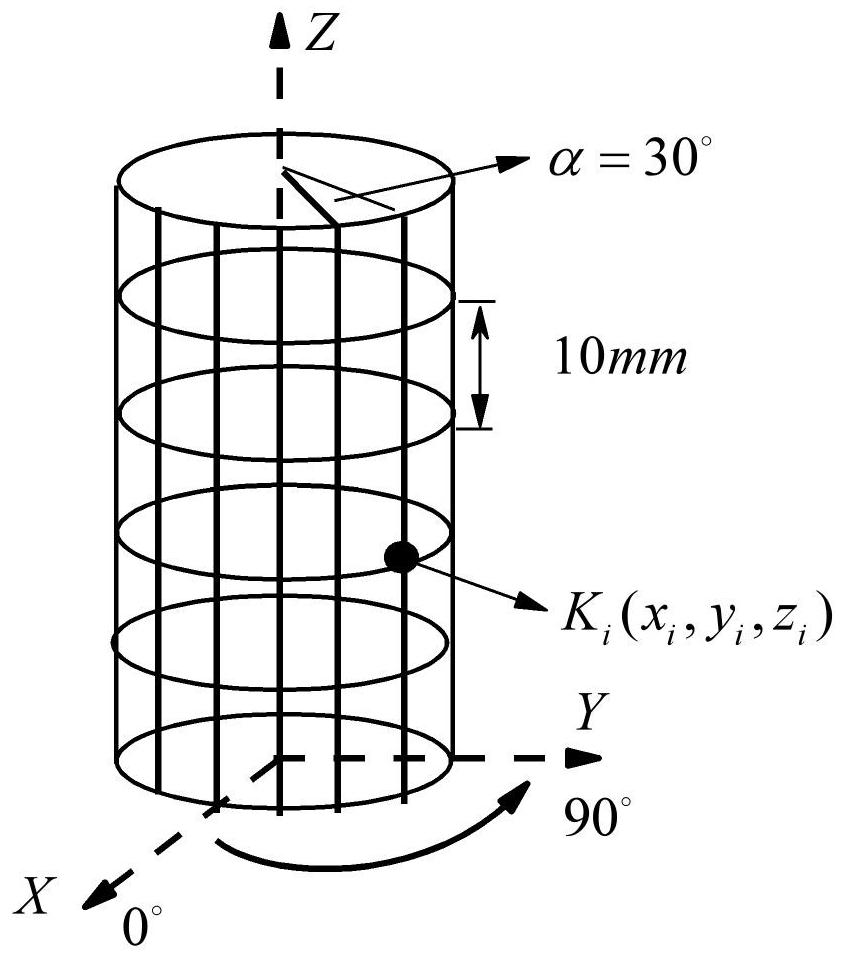
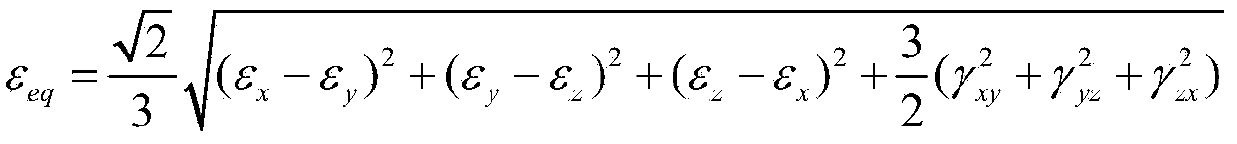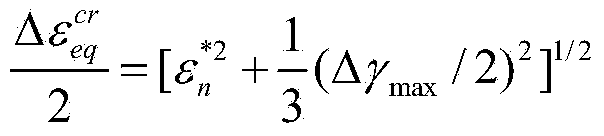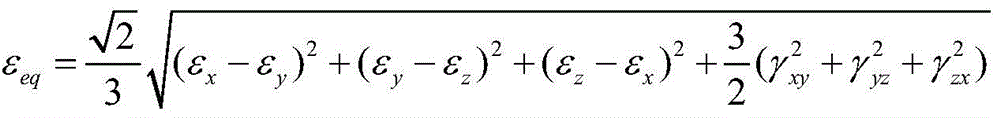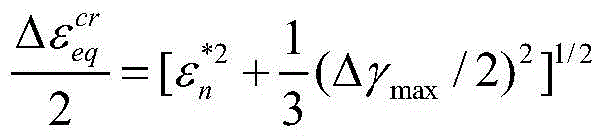Patents
Literature
46 results about "Creep stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Creep and Stress Rupture Properties Creep Properties Creep is a time-dependent deformation of a material while under an applied load that is below its yield strength. It is most often occurs at elevated temperature, but some materials creep at room temperature. Creep terminates in rupture if steps are not taken to bring to a halt.
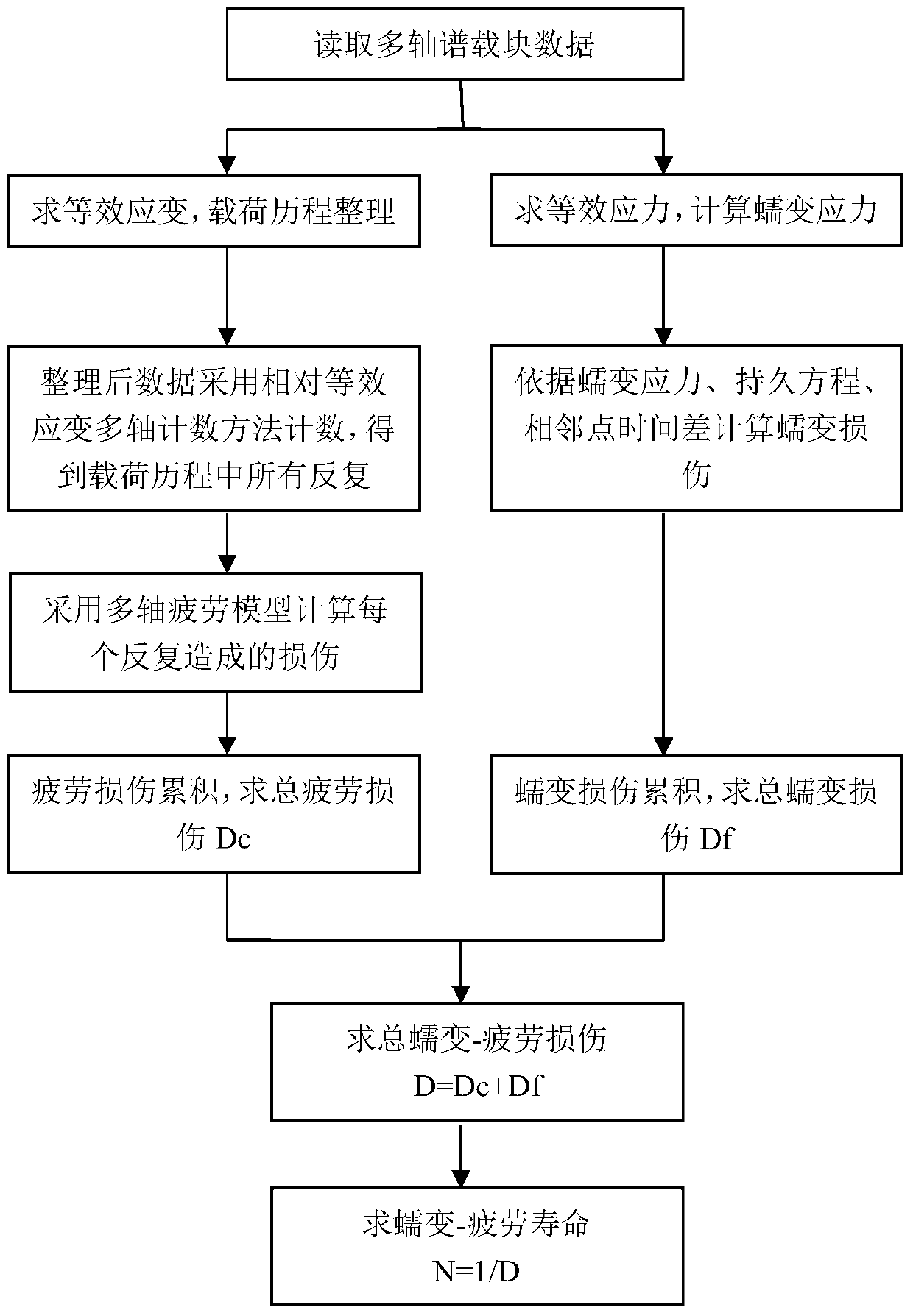
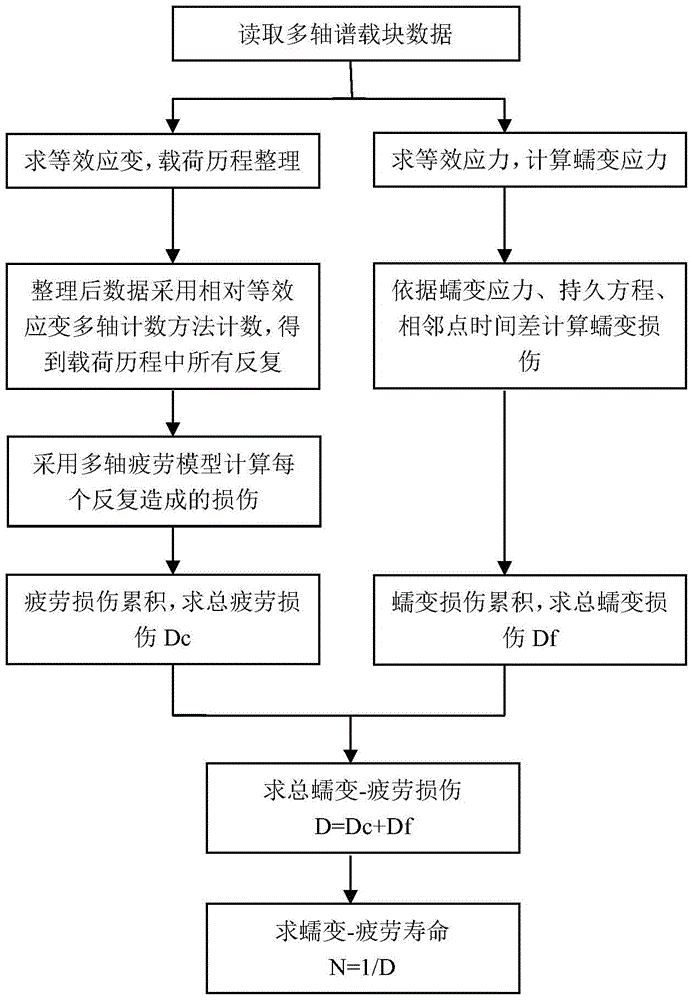
Low-cycle creep and fatigue life evaluation method under conditions of high temperature and multiaxial spectrum load
ActiveCN103926152AEasy accessReduce testing costsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFatigue damageCreep stress
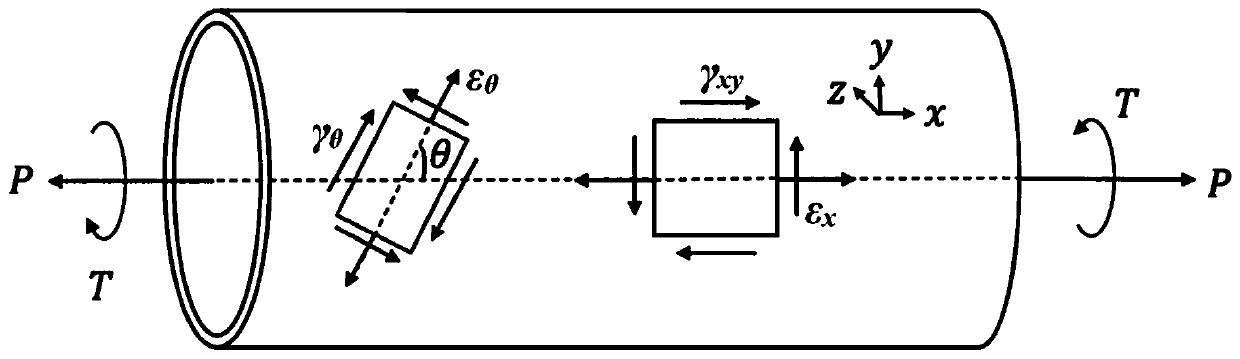
The invention relates to a low-cycle creep and fatigue life evaluation method under the conditions of high temperature and multiaxial spectrum load. The method comprises the following steps of reading a stress strain history in a multiaxial loading spectrum data block, working out equivalent strain, and finishing a loading history; repeatedly extracting by adopting a relative equivalent strain multi-axis counting method; working out all repeated fatigue damage by adopting a unified multiaxial fatigue damage life prediction model; accumulating the fatigue damage to work out the total fatigue damage; working out equivalent creep stress by utilizing the original loading history; working out creep damage Dc according to the equivalent creep stress and the stress history by combining a creep lasting equation; working out the total damage D caused by a multiaxial load spectrum block at the high temperature; and estimating the multiaxial creep and fatigue life. According to the method, the fatigue damage under the multiaxial stress and the creep damage under the multiaxial stress can be respectively calculated in the whole loading spectrum data block, the fatigue material constant at the room temperature is adopted in the calculation of the fatigue damage, and lasting equation material constant recommended by specification is adopted in the calculation of the creep damage; through experimental verification, the method has a good prediction effect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for manufacturing large-curvature aluminum alloy integral wall board component
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a large-curvature aluminum alloy integral wall board component. The method includes the steps that A, solution hardening is conducted on a wall board; B, the wall board obtained in the step A is arranged in a sealed environment formed by a thin film covering layer and a forming die jointly, the wall board is elastically deformed and plastically deformed in sequence under the vacuumized condition, and then the deformed wall board is obtained, wherein the temperature in the sealed environment where the wall board is located ranges from 15 DEG C to 35 DEG C, the vacuum degree ranges from -0.1 MPa to -0.05 MPa, and the treatment time ranges from 5 min to 60 min; C, in-situ creep stress relaxation aging is conducted on the deformed wall board obtained in the step B, wherein creep stress relaxation aging time is more than 2 h; D, unloading operation is conducted, and then the large-curvature aluminum alloy integral wall board component is obtained. When the method is used for manufacturing the large-curvature aluminum alloy integral wall board component, the residual stress of the product is greatly reduced, the strength of the product is improved, and the product with high forming accuracy and good performance is obtained.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
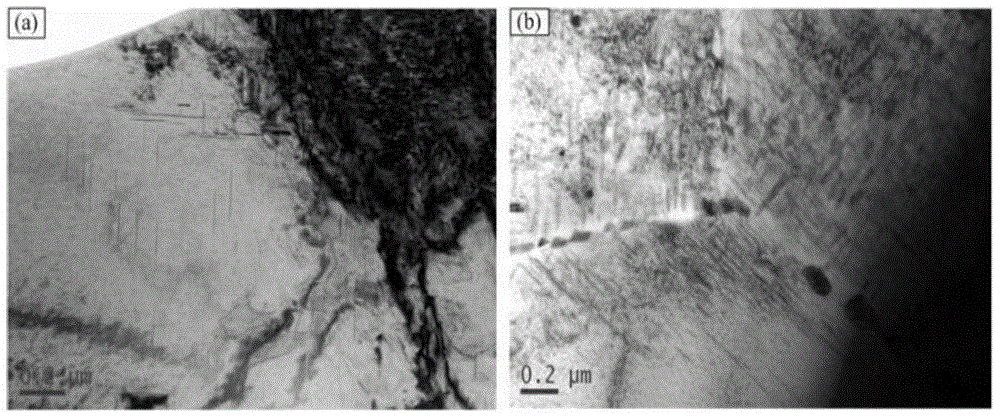
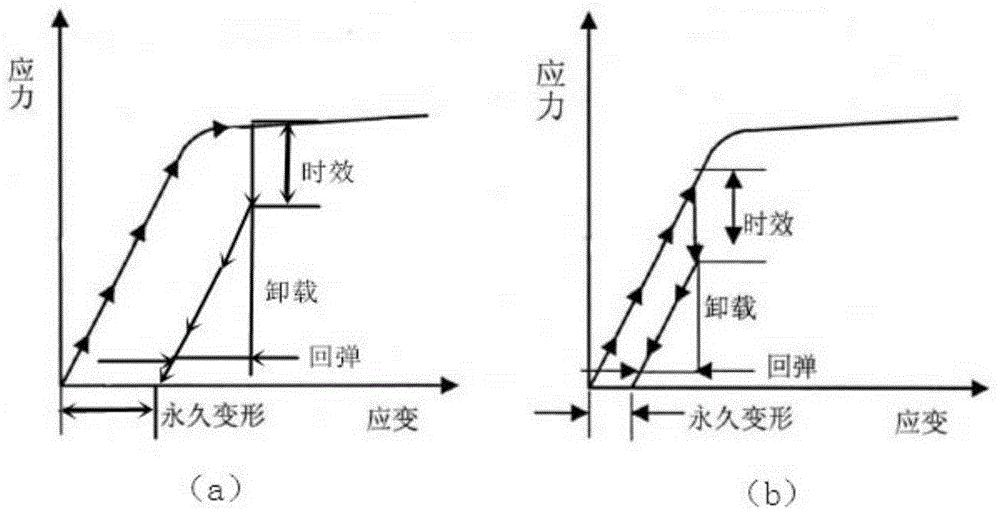
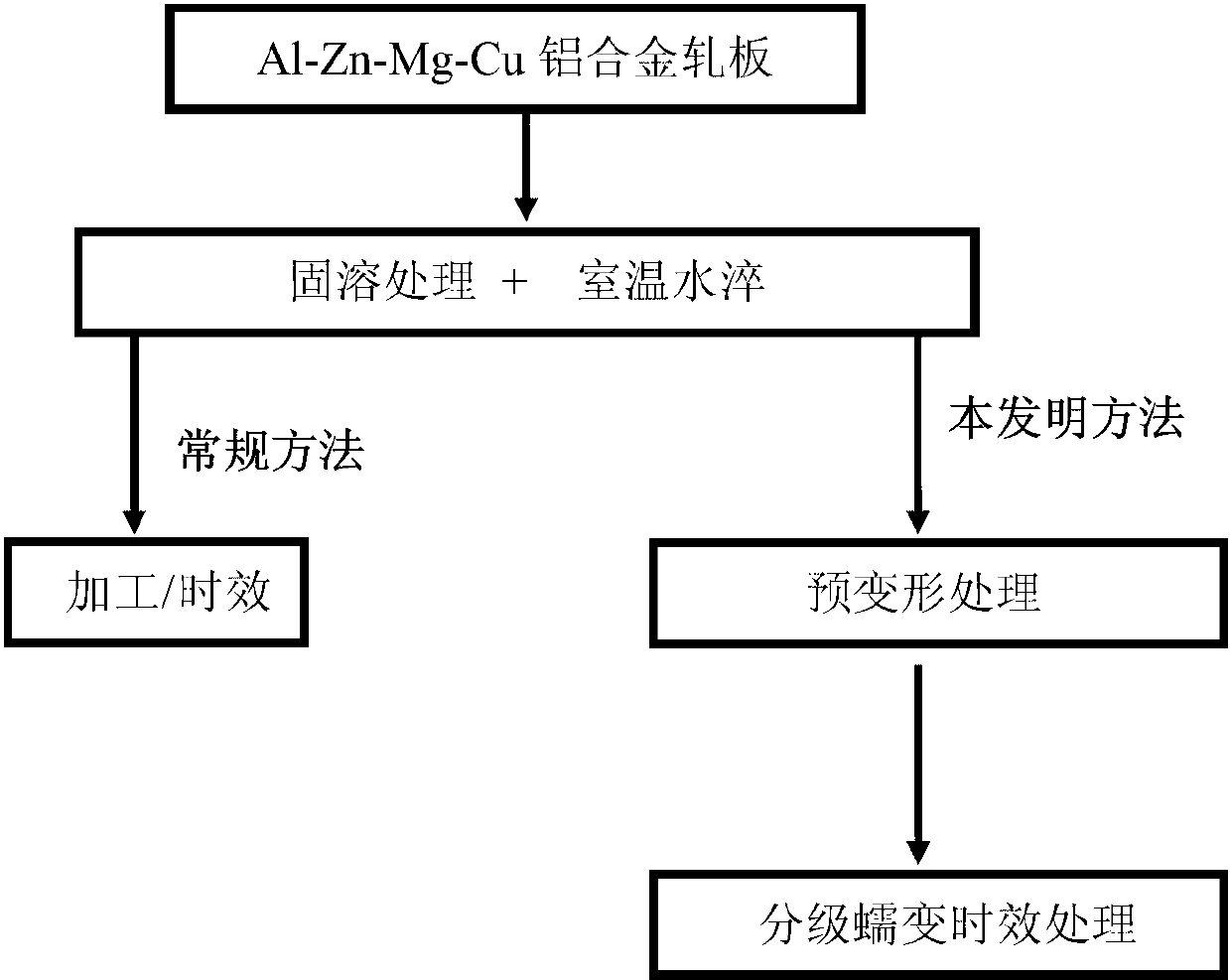
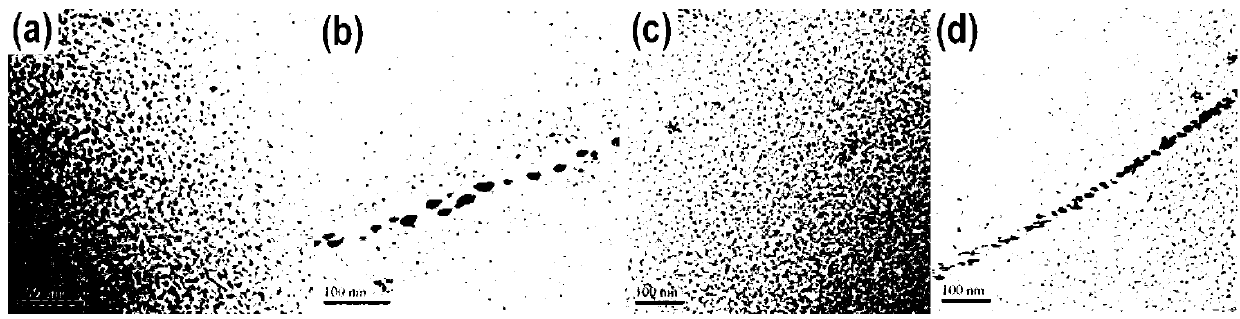
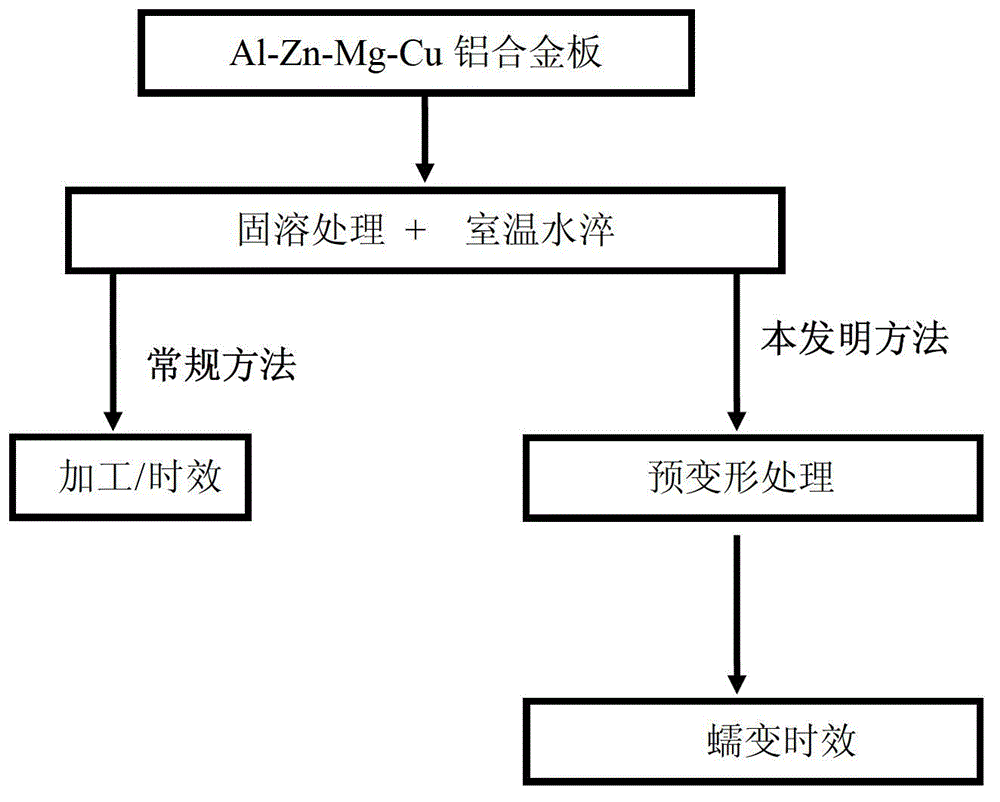
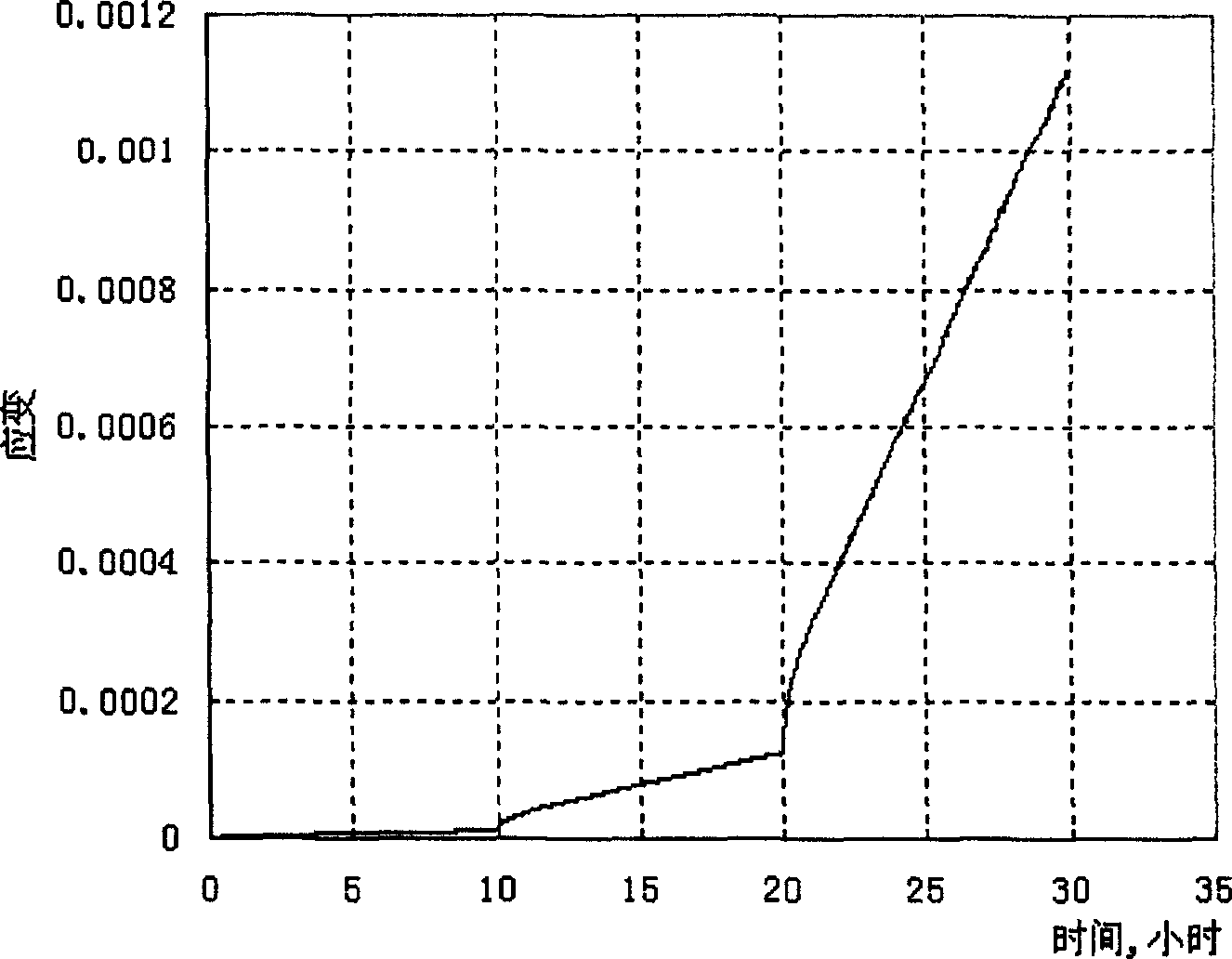
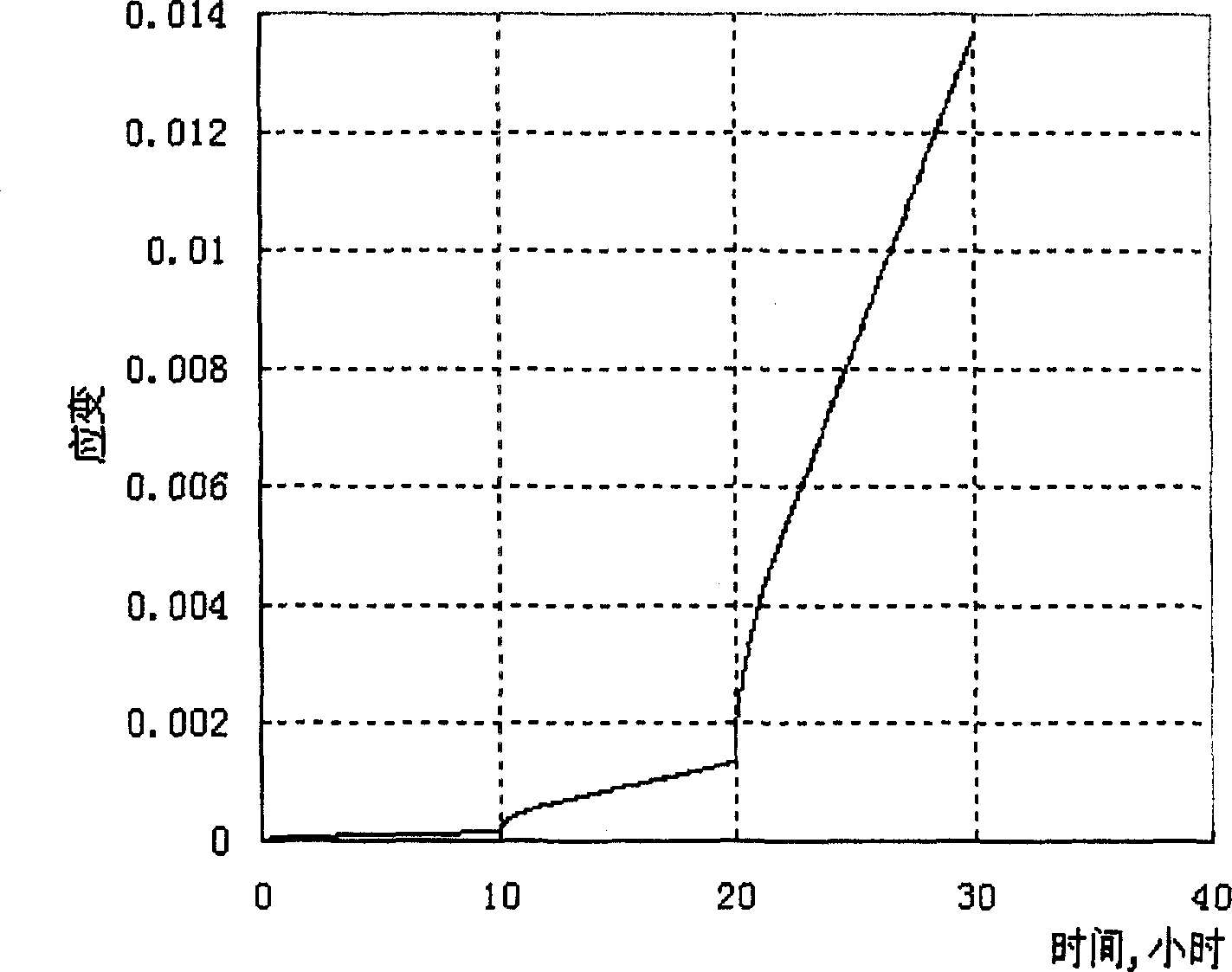
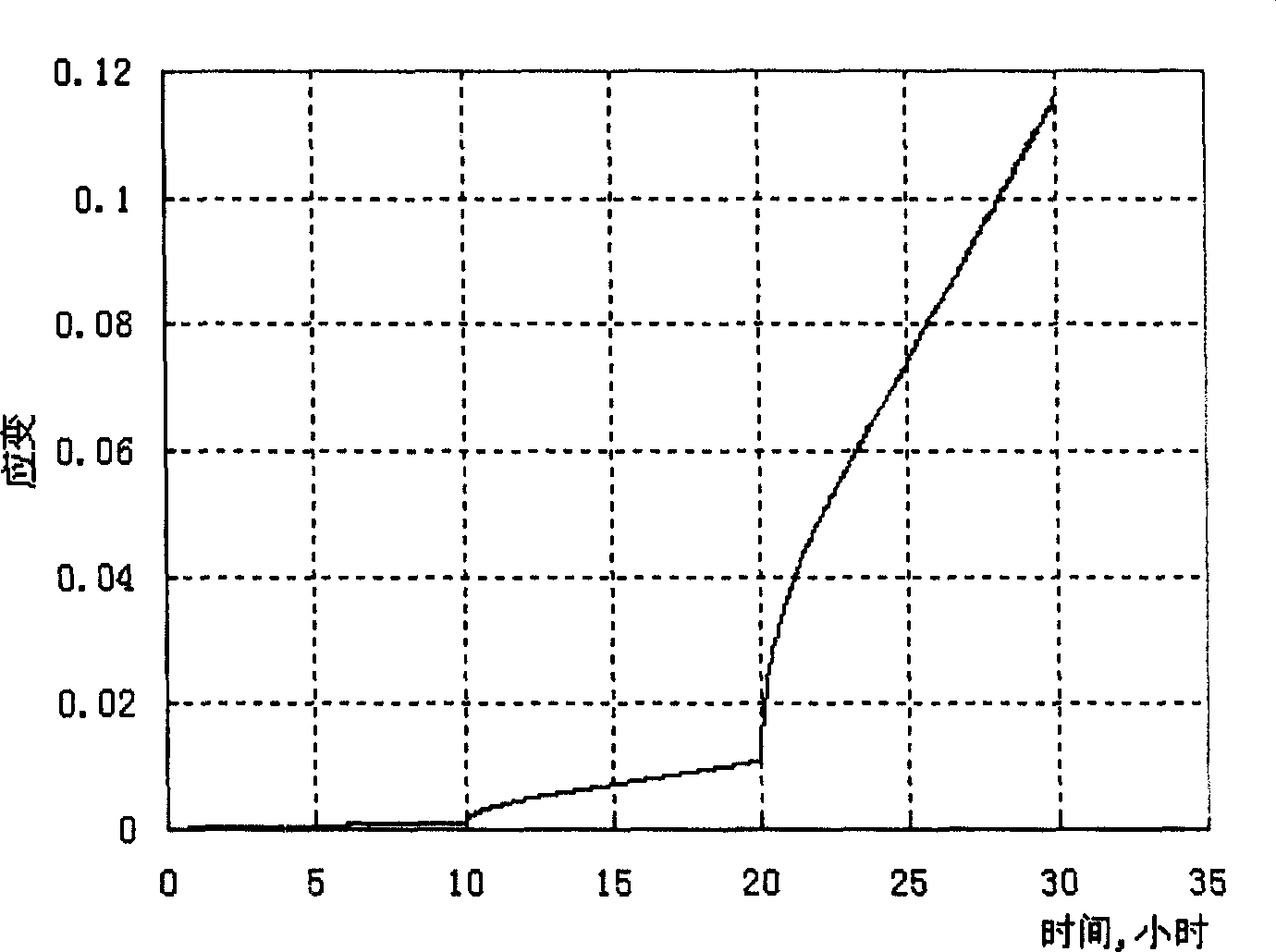
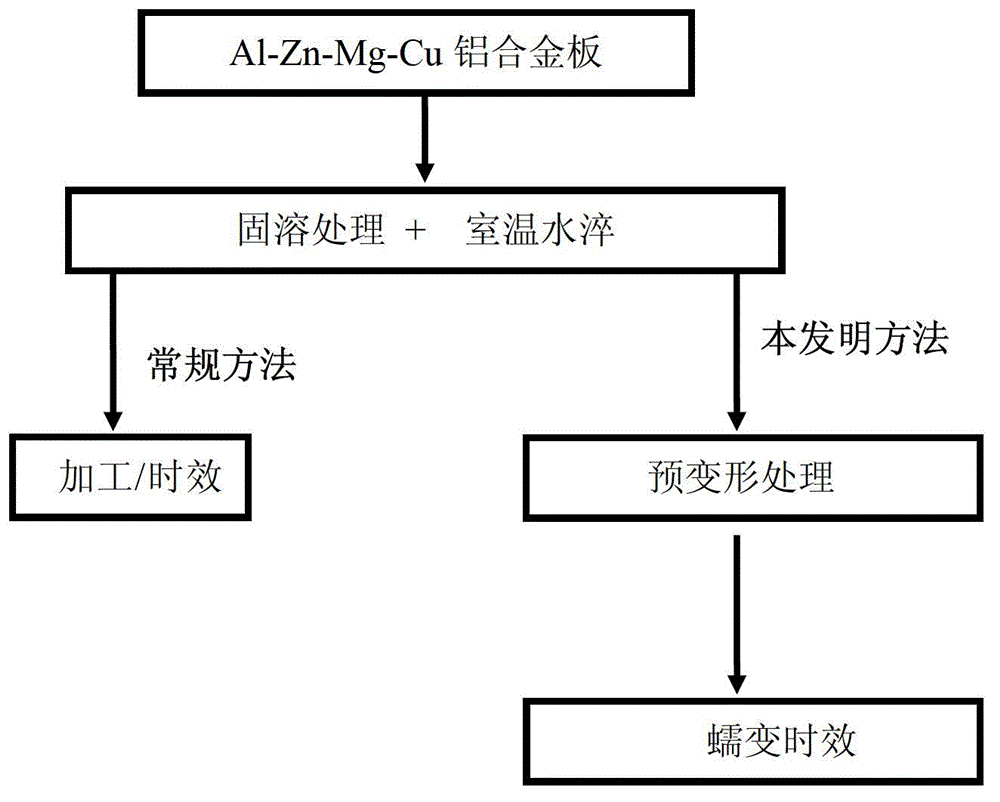
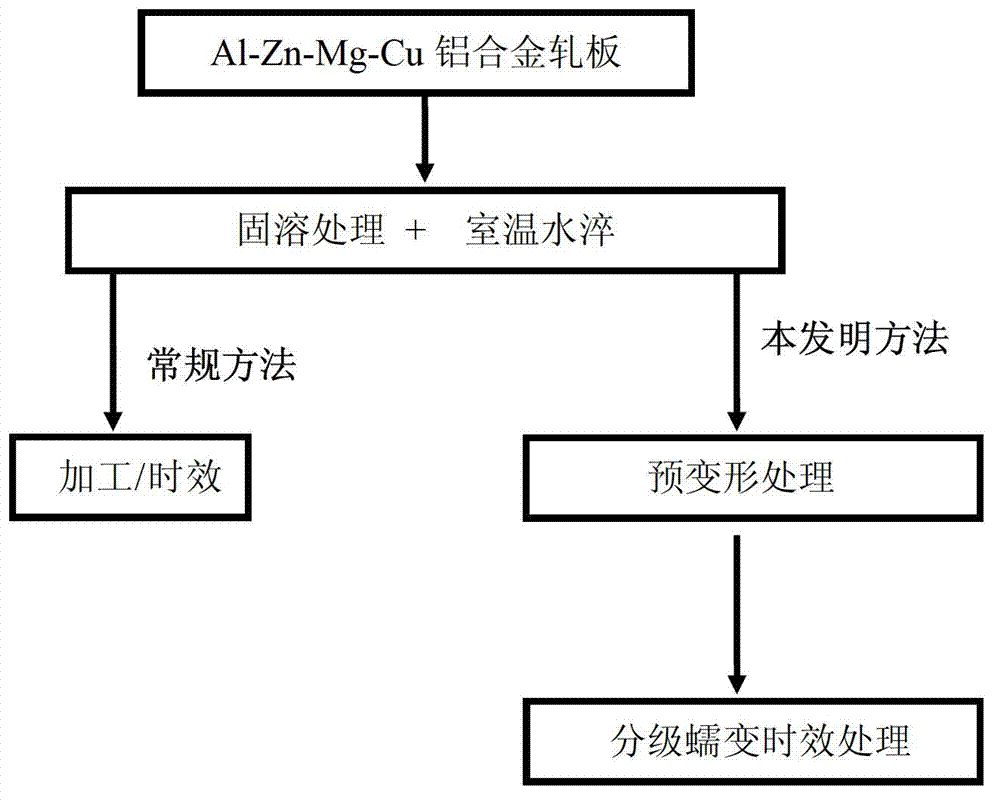
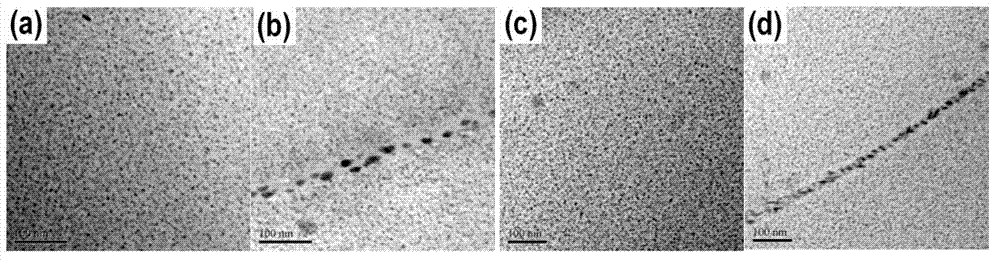
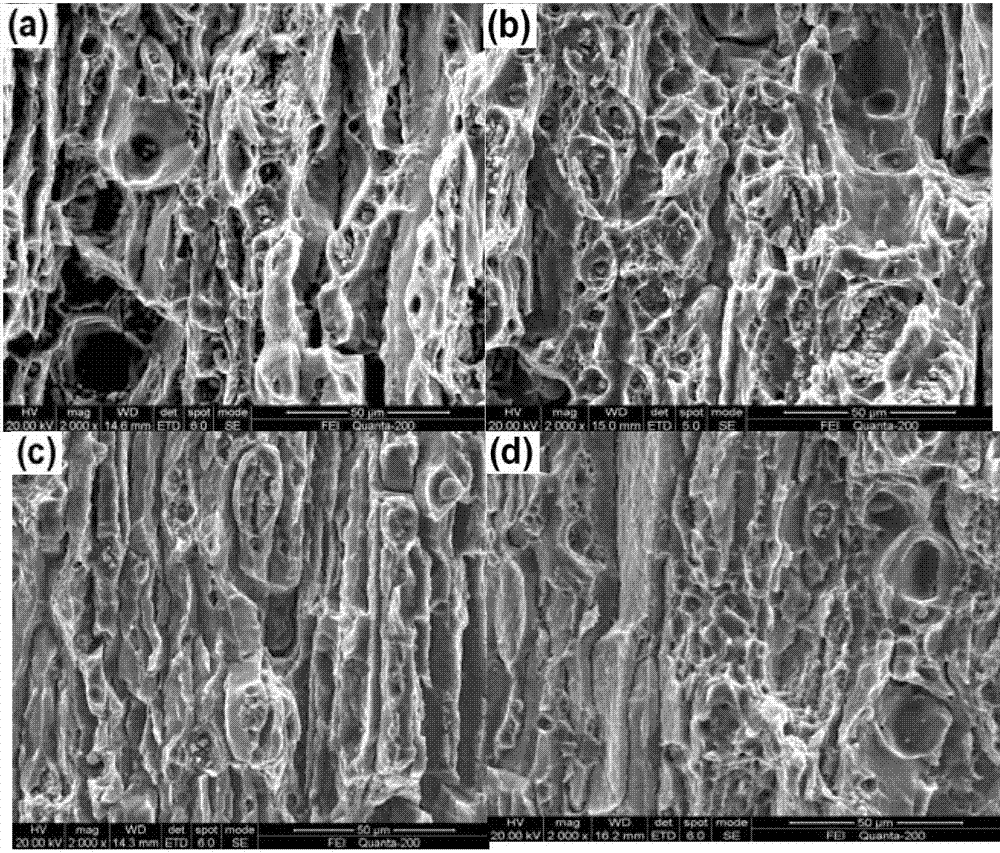
Method for multilevel creep age forming of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu series aluminium alloy plate
ActiveCN102978544AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove corrosion resistanceCreep stressThermal insulation
The invention relates to a method for multilevel creep age forming of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu series aluminium alloy plate. The method is characterized in that a reasonable solid solution-quenching-pretreating-multilevel creep aging system is adopted, is suitable for plates with the thickness of 2 millimeters-30millimeters and comprises the following steps that solid solution is carried out at 470-485 DEG C for 30 minutes-120 minutes, quenching is then carried out, the quenched plate is subjected to 0-10% predeformation treatment and creep aging at 120 DEG C and is thermally insulated for 24 hours, the creep return temperature is between 150 and 170 DEG C, return thermal insulation is carried out for 20-240 minutes, and another creep aging is thermally insulated at 120 DEG C for 24 hours, wherein the creep stress is between 100 and 150 mega pascals, and the forming bending radius is between 800 millimeters and 5000 millimeters. The method is utilized to treat Al-Zn-Mg-Cu series aluminium alloy, so that the alloy creep aging strengthening phase can be effectively regulated, the mechanical property of the alloy plate and the alloy creep formability are improved, the residual stress of the alloy plate is reduced, and the alloy exfoliation corrosion resistance is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for creep age forming of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu series aluminium alloy plate
InactiveCN102978545AImprove mechanical propertiesSimple and fast operationCreep stressSolid solution
The invention relates to a method for creep age forming of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu series aluminium alloy plate. The method is characterized in that a reasonable solid solution-quenching-pretreating-creep aging system is adopted, is suitable for plates with the thickness of 2 millimeters-30millimeters and comprises the following steps that solid solution is carried out at 470-485 DEG C for 30 minutes-120 minutes, quenching is then carried out, and the quenched plate is subjected to 0-10% predeformation treatment and creep aging at 120 DEG C-150 DEG C and is thermally insulated for 2-36 hours, wherein the creep stress is between 100 and 150 mega pascals, and the forming bending radius is above 1000 millimeters. The method is utilized to treat Al-Zn-Mg-Cu series aluminium alloy, so that the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu series aluminium creep formability can be effectively improved, and the residual stress of the alloy plate is reduced.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method of measuring reinforced concrete creep stress by using engineering safety monitoring rebar stressometer
Owner:BEIJING MILLENNIUM ENG TECH CO LTD +1
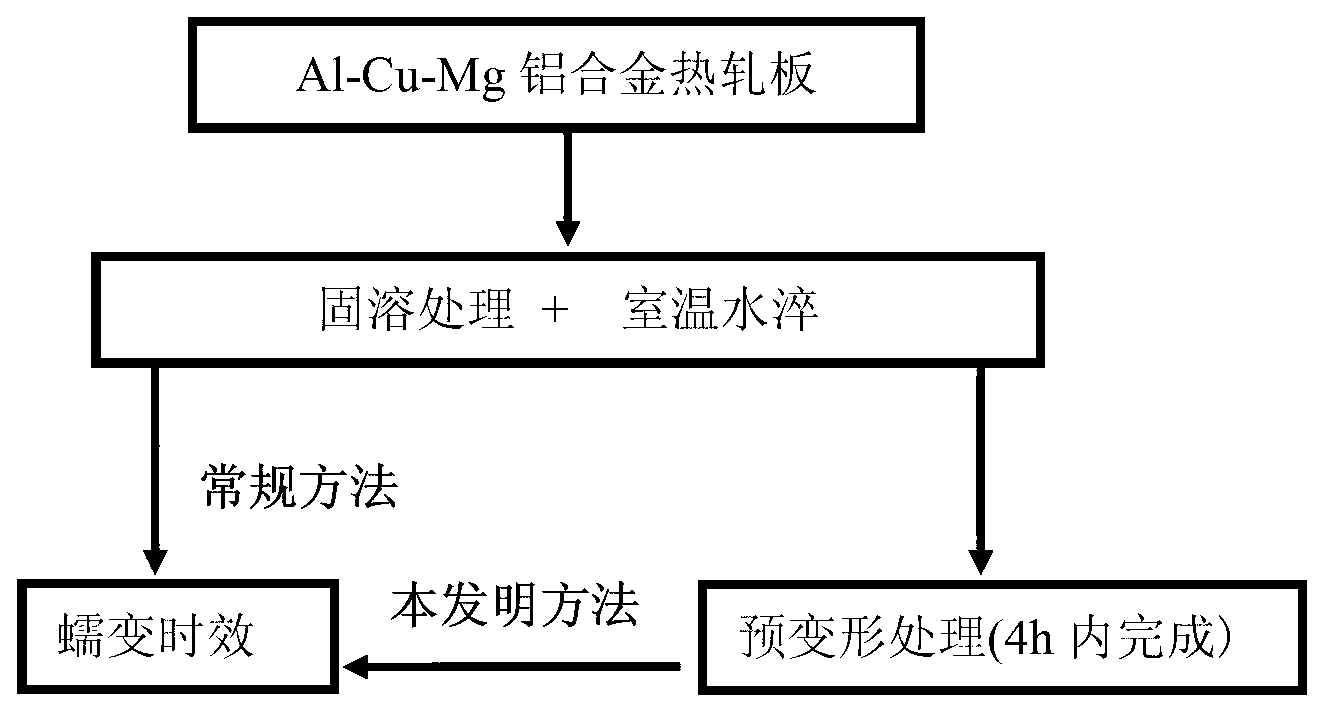
Creep aging forming method for Al-Cu-Mg alloy plate
ActiveCN103422035ASuppression of precipitation phase effectLittle difference in mechanical propertiesCreep stressRoom temperature
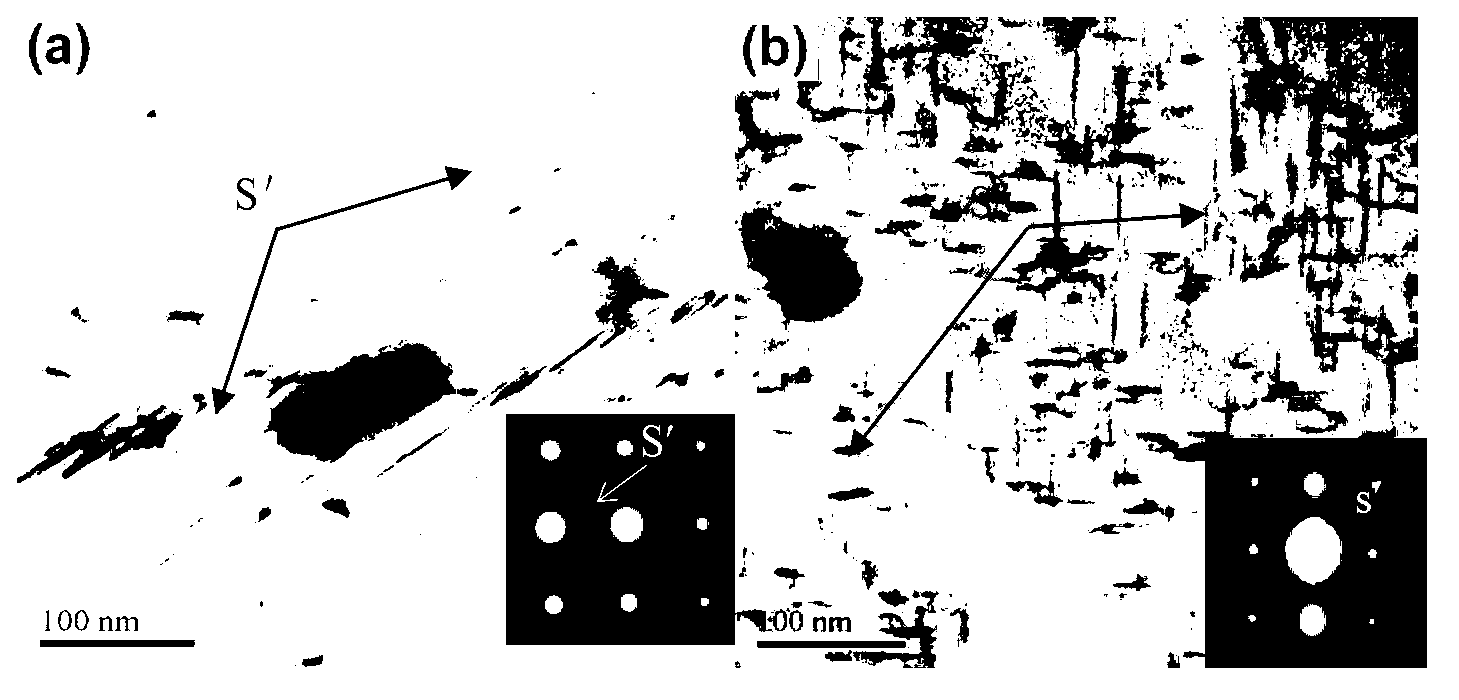
The invention discloses a creep aging forming method for an Al-Cu-Mg series alloy sheet material. The creep aging forming method relates to a heat treatment method for reducing creep aging anisotropy of the Al-Cu-Mg alloy sheet material and improving an alloy performance. The method comprises the following steps of: water quenching after adopting solid-solution treatment at 490-505 DEG C for 30-70 minutes, carrying out 2-10% of predeformation processing on a quenched sheet material, and then carrying out creep aging, wherein a creep temperature is 150-200 DEG C; creep time is 0-12 hours; creep stress is 150-300 MPa, and predeformation processing time is controlled within 4 hours. By adopting the creep aging forming method to process an Al-Cu-Mg alloy, a mechanical property of the alloy sheet material can be improved and a degree of anisotropy of the sheet material can be reduced by controlling precipitation of an alloy creep aging strengthening phase. Compared with common thermal treatment, tensile strength of a room temperature is improved by at least 10%, and the anisotropy is reduced by at least 10% by adopting the creep aging forming method to process the Al-Cu-Mg alloy. The technique is simple in operation, and remarkable in effect. Compared with improvement of alloy microstructure components by a microalloying manner, cost is saved; the method is easy to achieve in industrial production, and comprehensive benefit is obviously higher than that of a reported processing method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Method for designing salt rock stratum irregular-shaped sleeve
ActiveCN103195374AReduce effective stressPrevent casing damage accidentsDrilling rodsDrilling casingsCreep stressThick wall
The invention relates to a method for designing a salt rock stratum irregular-shaped sleeve. According to different salt rock stratum creep stress states, by changing the inner diameter or outer diameter of the irregular-shaped sleeve, the sleeve cross section shape suitable for a crustal stress level condition is determined. The irregular-shaped sleeve has the following two forms: an inner wall of the sleeve is circular, and an outer wall of the sleeve is oval; and an inner wall of the sleeve is oval, and an outer wall of the sleeve is circular. When the irregular-shaped sleeve is put into a shaft, the position with the maximum wall thickness and the direction of the maximum horizontal crustal stress are uniform. By means of the method, effective stress of a sleeve body under an uneven horizontal crustal stress state can be effectively reduced, the sleeve can be prevented from being damaged, and the technical problem that the strength of the sleeve with the existing wall thickness under the uneven horizontal crustal stress state is not enough and the sleeve can not be kept well in the follow-up production process is solved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Creep aging forming method for Al-Cu-Mg series alloy sheet material
InactiveCN102912268AImprove mechanical propertiesReduce the degree of anisotropyCreep stressRoom temperature
The invention discloses a creep aging forming method for an Al-Cu-Mg series alloy sheet material. The creep aging forming method relates to a heat treatment method for reducing creep aging anisotropy of the Al-Cu-Mg alloy sheet material and improving an alloy performance. The method comprises the following steps of: water quenching after adopting solid-solution treatment at 490-505 DEG C for 30-70 minutes, carrying out 2-10% of predeformation processing on a quenched sheet material, and then carrying out creep aging, wherein a creep temperature is 150-200 DEG C; creep time is 0-12 hours; creep stress is 150-300 MPa, and predeformation processing time is controlled within 4 hours. By adopting the creep aging forming method to process an Al-Cu-Mg alloy, a mechanical property of the alloy sheet material can be improved and a degree of anisotropy of the sheet material can be reduced by controlling precipitation of an alloy creep aging strengthening phase. Compared with common thermal treatment, tensile strength of a room temperature is improved by at least 10%, and the anisotropy is reduced by at least 10% by adopting the creep aging forming method to process the Al-Cu-Mg alloy. The technique is simple in operation, and remarkable in effect. Compared with improvement of alloy microstructure components by a microalloying manner, cost is saved; the method is easy to achieve in industrial production, and comprehensive benefit is obviously higher than that of a reported processing method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for overcomming creep of salt-rock layer by using ralation of drilling fluid density and chloride concentration
InactiveCN1814986ALower minimum burst pressureLower burst pressureFlushingDrilling compositionRelational modelCurve matching
Present invention refers to a method for overcoming salt rock layer creepage utilizing drilling fluid density and chlorides concentration relationship concentration relationship. It contains 1, to make hole boring with sampling and test sample processing, 2, taking four experiment test samples, to proceed creep test to each test sample, taking multiple level temperature and multiple level loading compound experiment mode to obtain creep test straining and timetable, 3, establishing salt rock creepage constitutive relation equation i.e. creep stress-rate of strain relation equation through curve matching method, 4, establishing well bore necked-in rate and drilling fluid density relation equation,5, taking the rest of four test samples, to proceed salting in experiment, corresponded salting in dissolution rate and chlorides pH indicator relation curve, establishing salting in rate and chlorides pH indicator relational model through nonlinear regression, 6, establishing drilling fluid density, temperature and chlorides pH indicator graph of relation edition, determining rational drilling fluid density and chlorides concentration to overcame salt bed creepage according to steps 6 graph of relation edition to salt bed well drilling in same zone block with experiment well core.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Creep aging forming method for Al-Zn-Mg-Cu aluminium alloy plate
The invention provides a creep aging forming method for an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu aluminium alloy plate. The key point is that the method adopts a reasonable solid solution-quenching-pretreatment-creep aging system and is suit for the plate with the thickness of 20 mm to 30 mm. The details are as follows: conducting solid solution for 30 min to 120 min at the temperature of 470 to 485 DEG C, and then quenching; conducting 0 to 10% of pretreatment for the plate after quenching; and then conducting creep aging insulation at the temperature of 120 DEG C to 150 DEG C for 2 to 36 h, wherein the creep stress adopts 100 to 150 Mpa and the forming bending radius is over 1000 mm. Through the adoption of the method to treat the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy, the creep formability of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu aluminium alloy can be effectively improved and the residual stress of the alloy plate is reduced.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
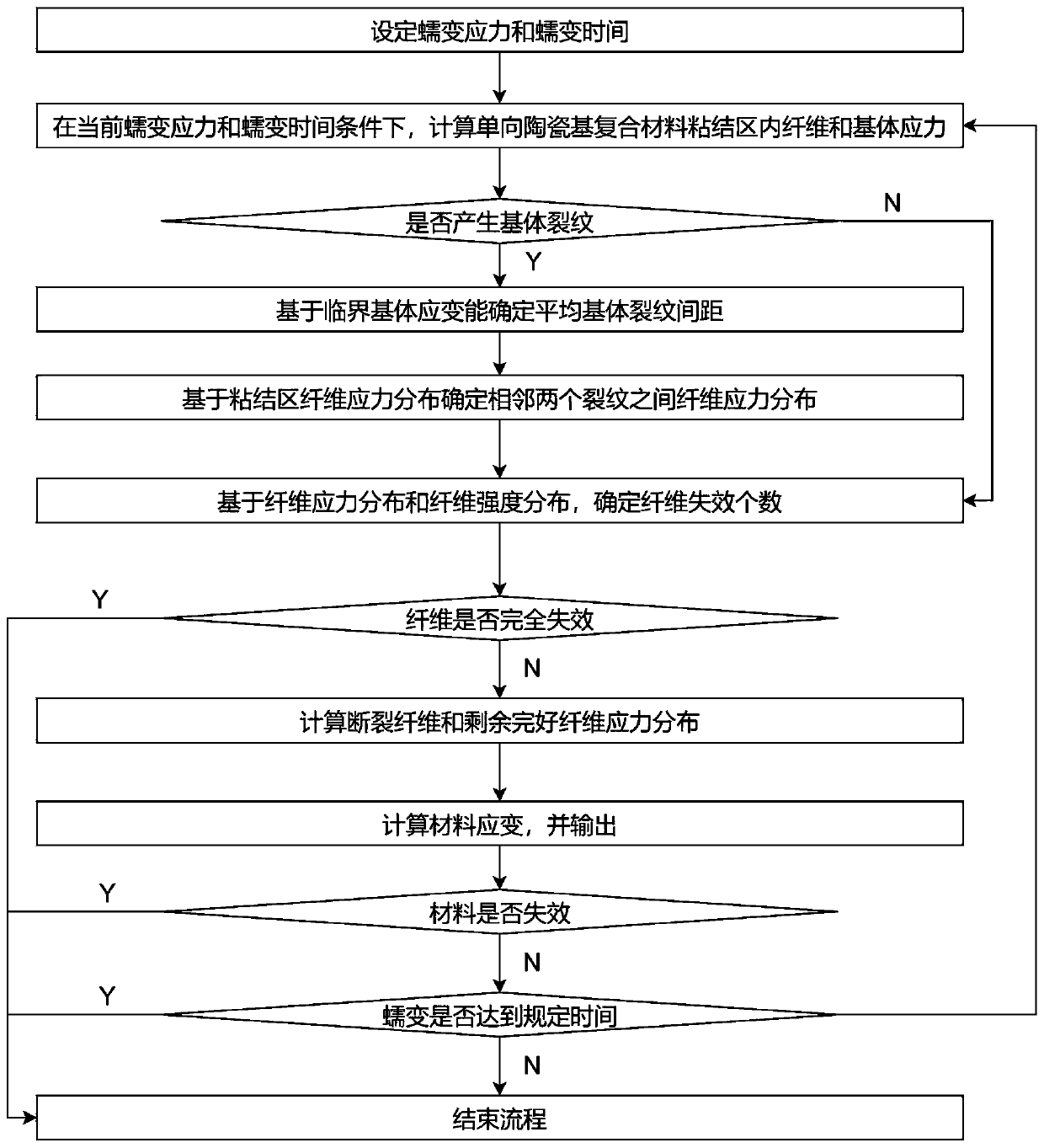
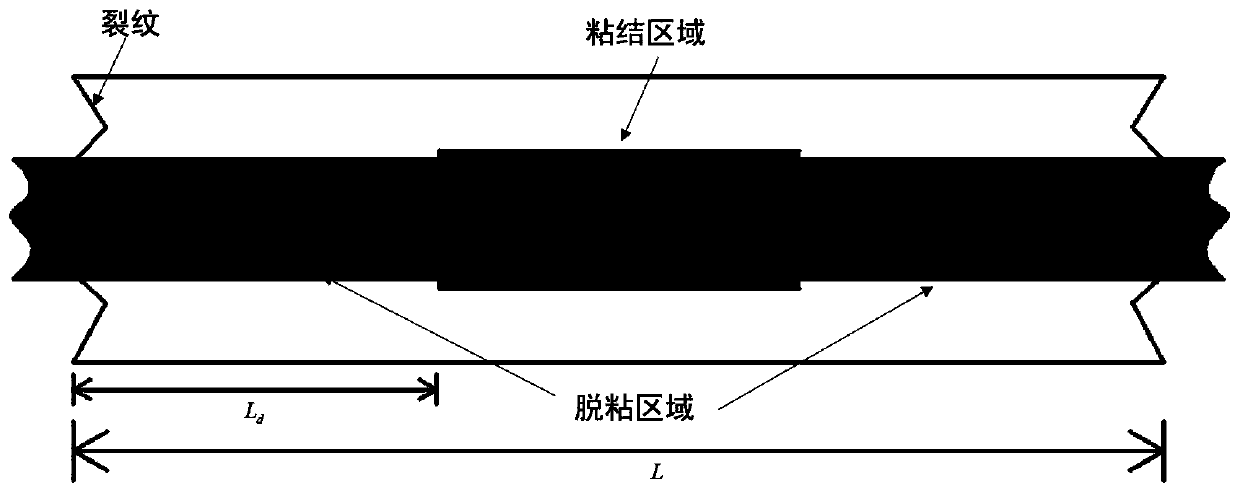
One-way ceramic matrix composite creep behavior prediction method
ActiveCN111024486AAccurately predict creep curvesRevealing Mesoscopic Failure MechanismsComputational materials scienceStrength propertiesCreep stressFailure mechanism
The invention discloses a one-way ceramic matrix composite creep behavior prediction method, which comprises the following steps: based on the same strain of bonding region fibers and a matrix, obtaining the stress of the bonding region fibers and the matrix under different creep stresses and times, and further obtaining the change of the matrix crack density. A shear-lag model is combined to obtain fiber stress change in the creep process, fiber failure and load borne by the failure fiber are considered, and finally a one-way ceramic matrix composite creep curve is calculated. According to the method, one-way ceramic matrix composite creep curves at different temperatures and creep stress levels can be accurately predicted, and the microscopic failure mechanism of material internal components is disclosed. On the other hand, the whole calculation process is concise and efficient, and the defects of high cost and long time consumption of an experimental method are overcome.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
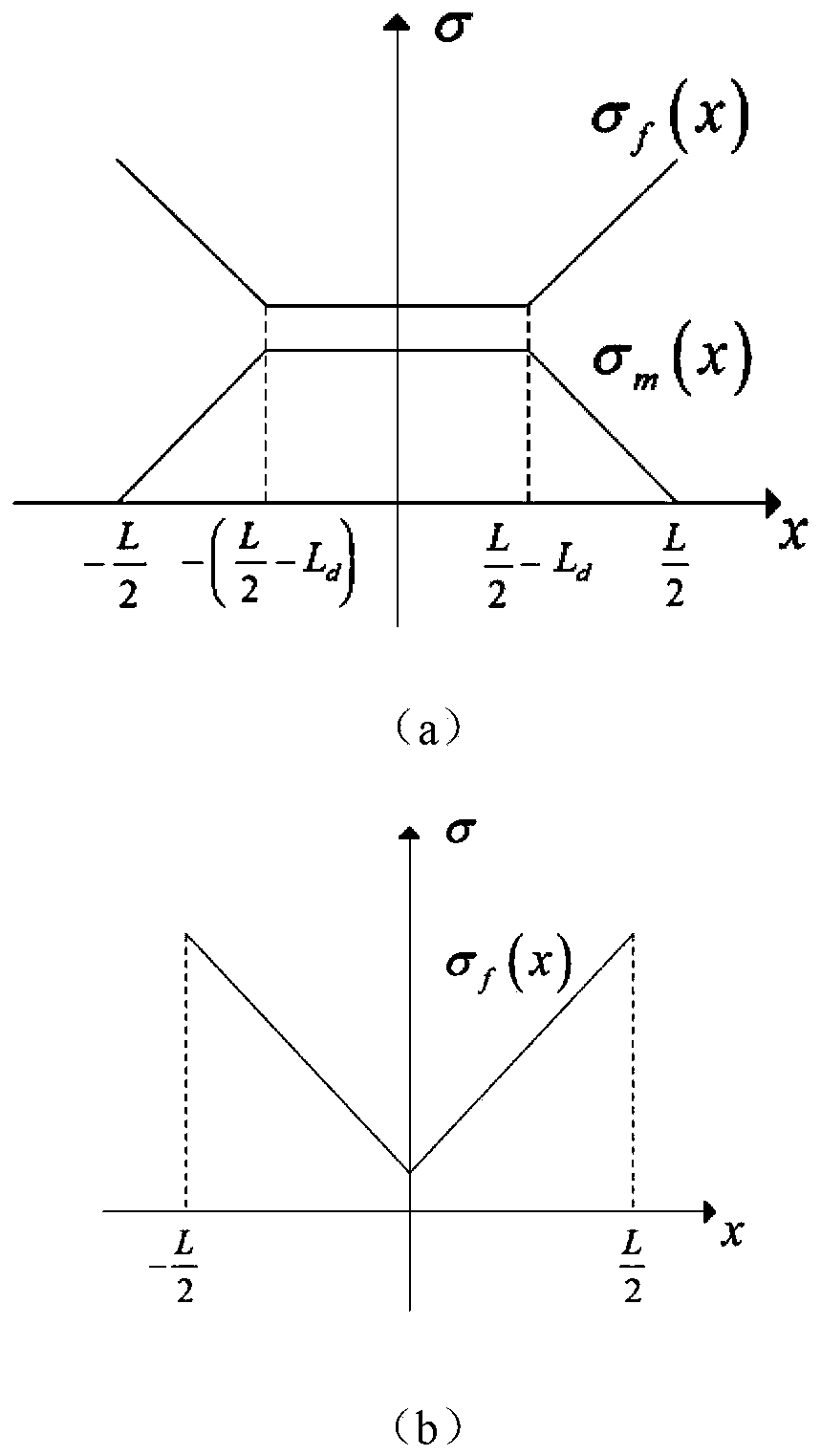
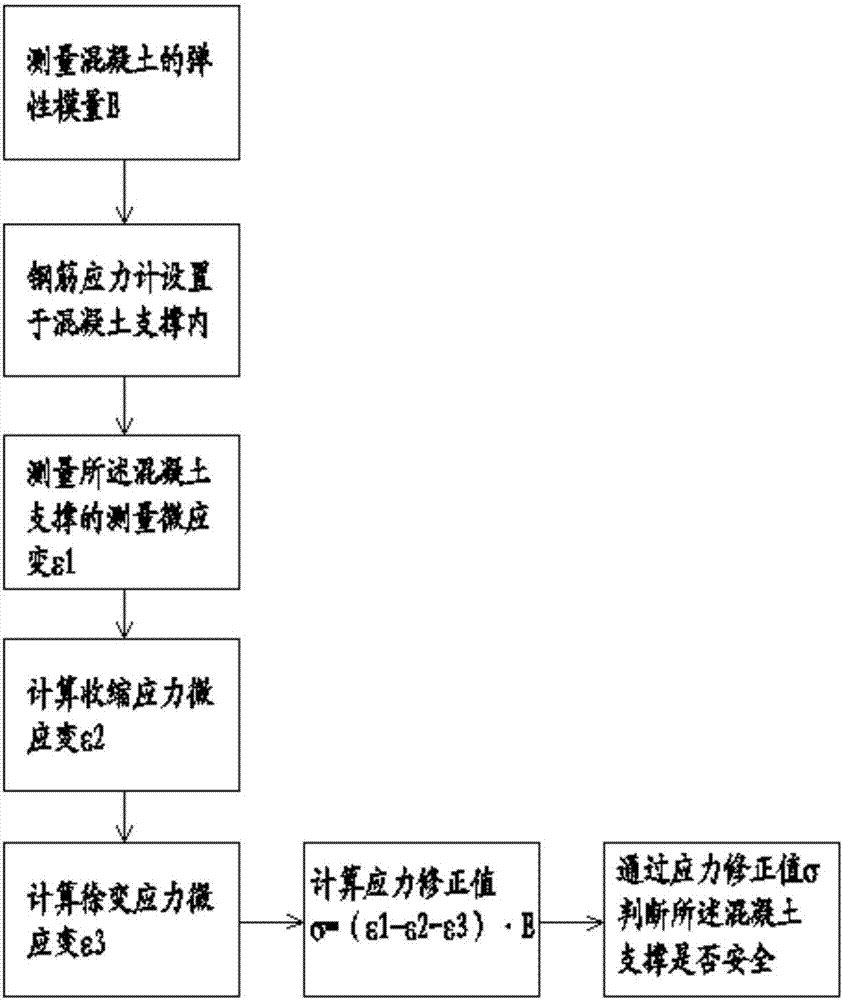
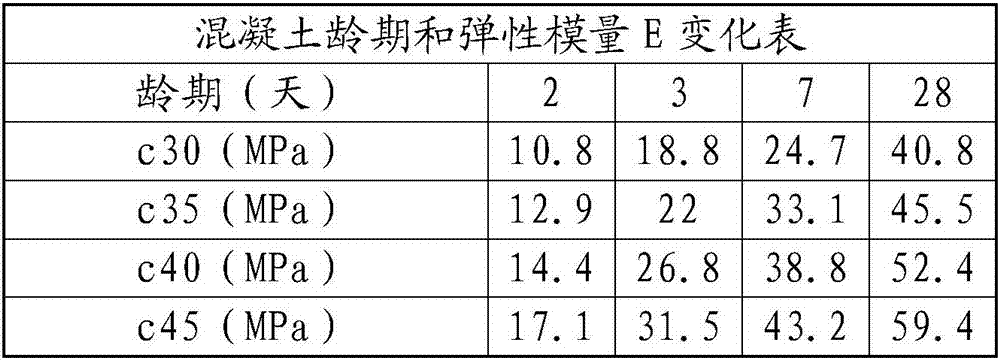
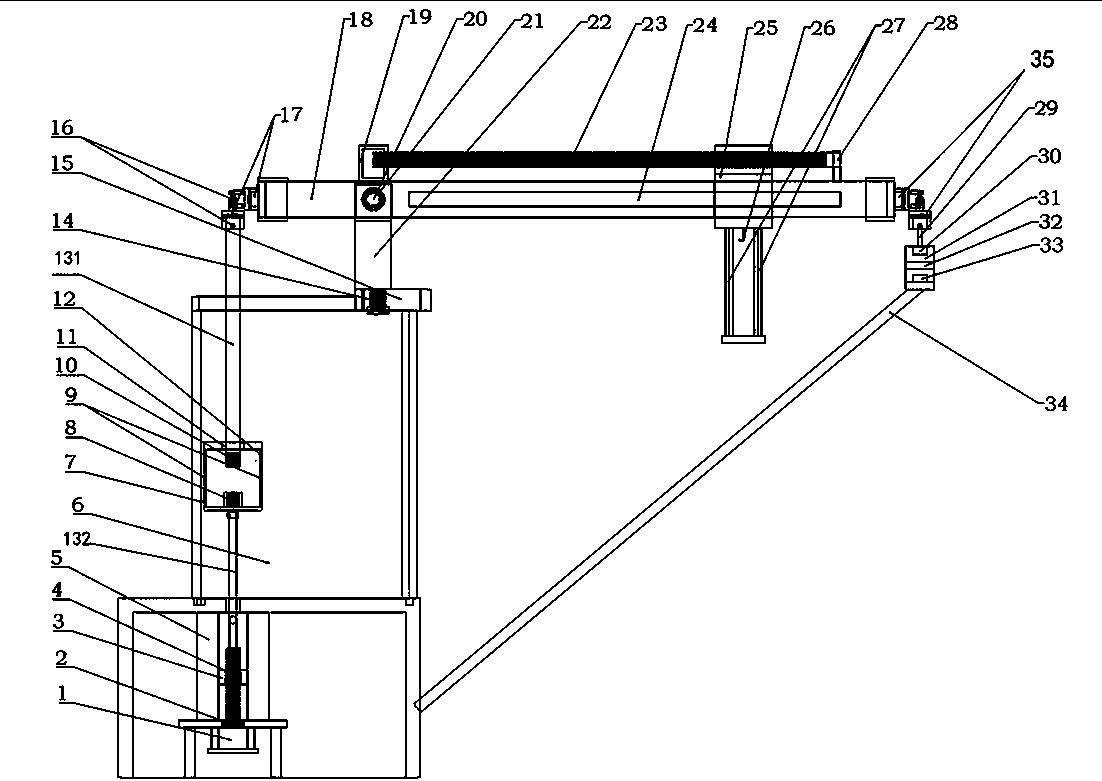
Concrete support stress monitoring data processing and optimization method
InactiveCN107478358AIncrease reflectionReliable construction basisForce measurement by permanent gauge deformationForce measurement by elastic gauge deformationStress conditionsCreep stress
The invention provides a concrete support stress monitoring data processing and optimization method; the method can better represent concrete support stress values, can better comply with engineering real conditions, and can provide more reliable construction basis for construction personnel. The method uses a stress correction value [sigma] to determine whether the concrete support is safe or not; the method considers an elastic modulus E changing with time, a contraction stress microstrain [Epsilon]2 formed by the contraction stress, and a creep stress microstrain [Epsilon]3 formed by the creep stress, thus better reflecting the concrete support truly received stress conditions, and providing more reliable construction basis for the construction personnel.
Owner:SHANGHAI CONSTRUCTION GROUP
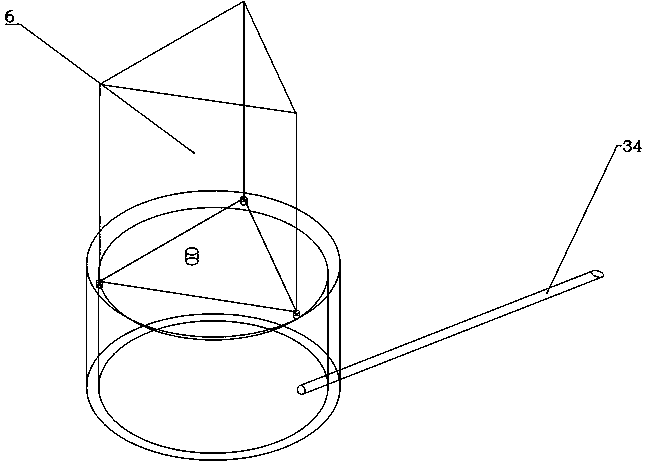
Lever-based slow tensile stress corrosion experimental device
ActiveCN109827897AReduce additional stressContinuous constant outputWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesCreep stressElectricity
The invention discloses a lever-based slow tensile stress corrosion experimental device. The device comprises a lever balance system, a corrosion test system and a feedback adjustment system; the lever balance system comprises a lever and a lever bracket for supporting the lever; the left end of the lever is connected with the corrosion test system; the right end of the lever is provided with a weight device; the corrosion test system includes an electrochemical corrosion tank; the electrochemical corrosion tank is used for simulating a corrosive environment and fixing a sample; the electrochemical corrosion tank is connected with the left end of the lever; the feedback adjustment system is connected between the lever balance system and the corrosion test system; and the feedback adjustment system is used for adjusting the balance of the lever. According to the lever-based slow tensile stress corrosion experimental device of the invention, the load of the weight can be amplified by thelever structure, and therefore, additional stress on a rod can be reduced; before an experiment is performed, different loads can be loaded or the position of the weight can be moved, and therefore,a variety of creep stress stretching conditions can be provided. The device has the advantages of simplicity and accurate measurement. With the device adopted, the real-time monitoring of creep stressand displacement under a constant force can be realized.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
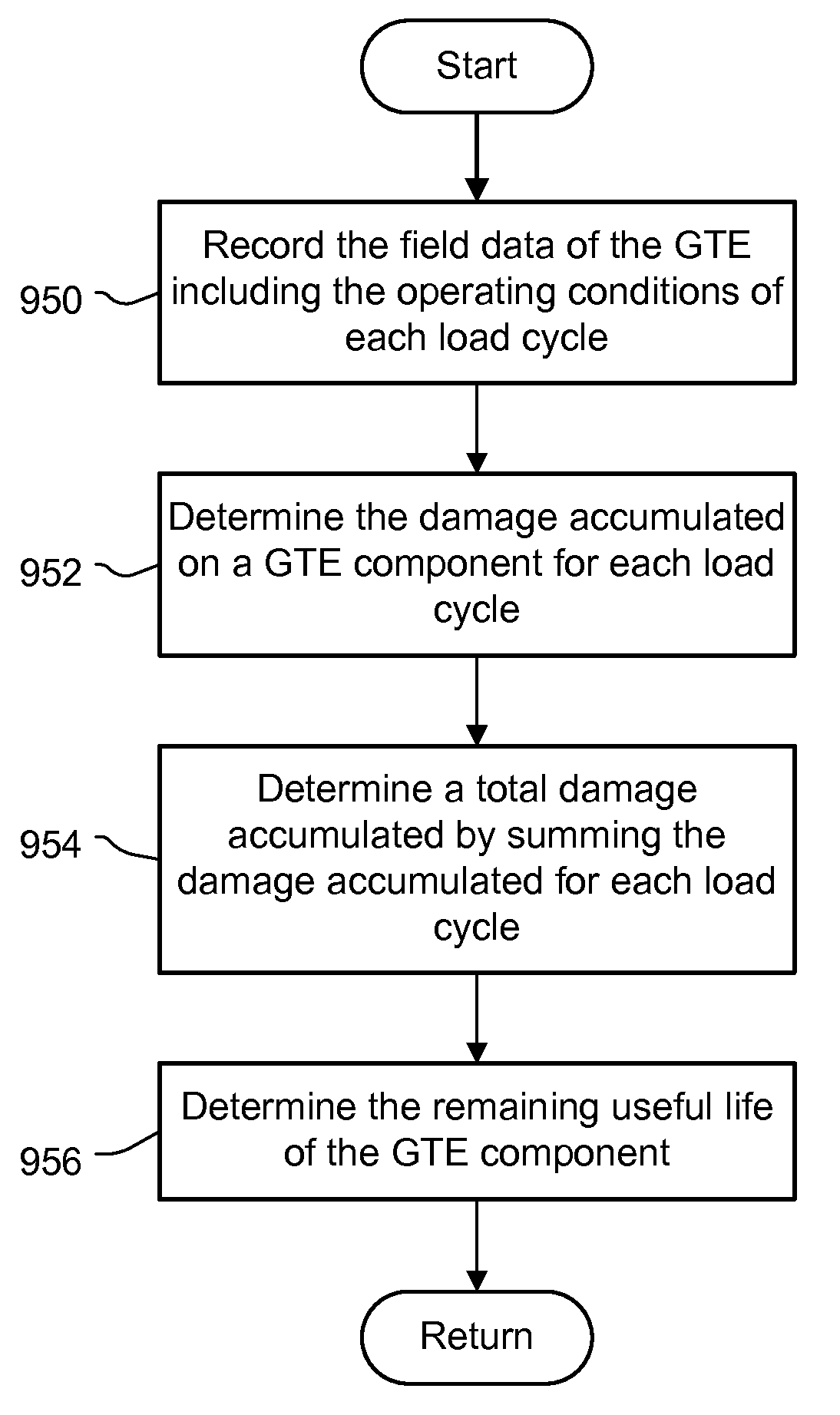
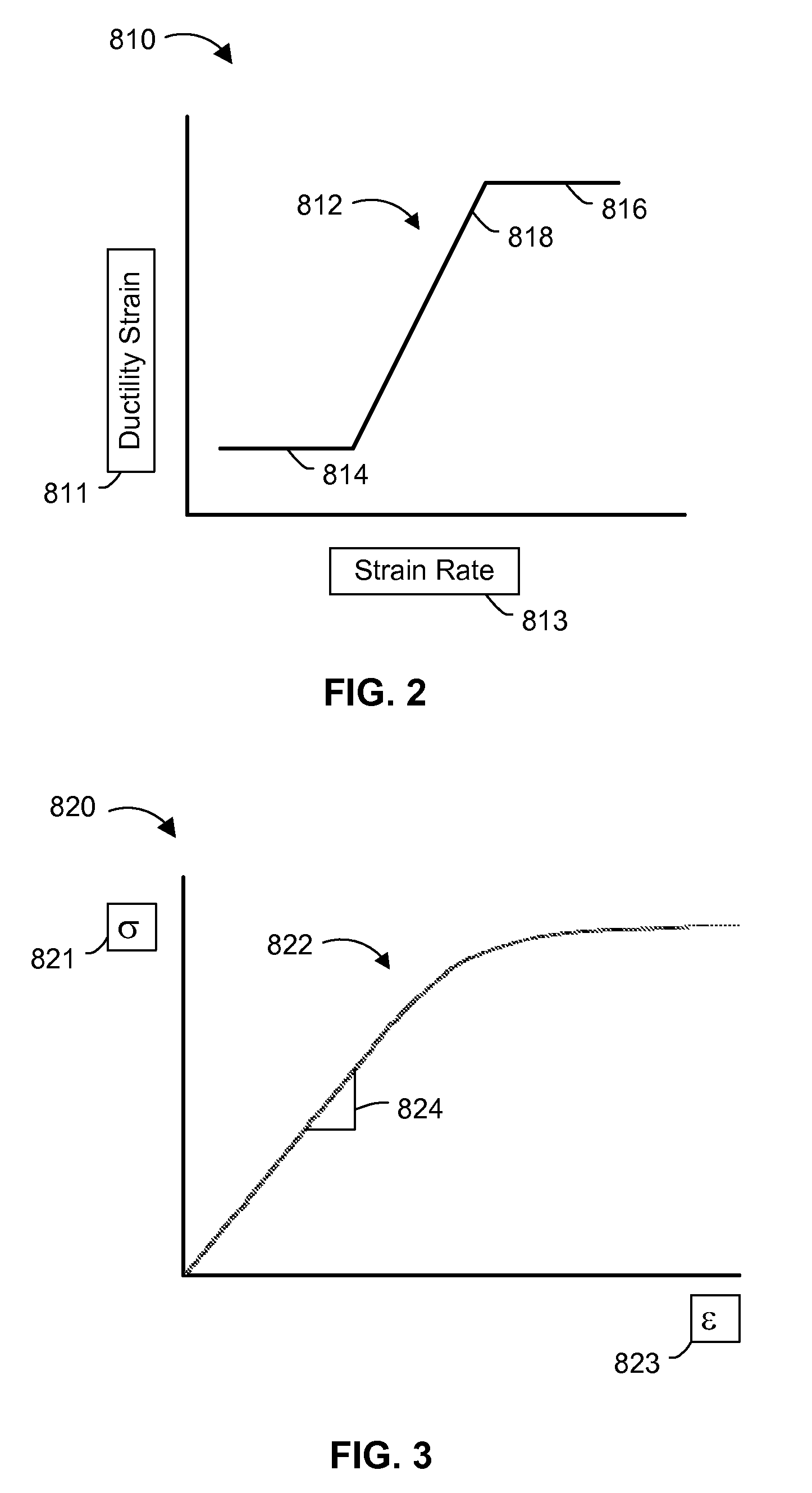
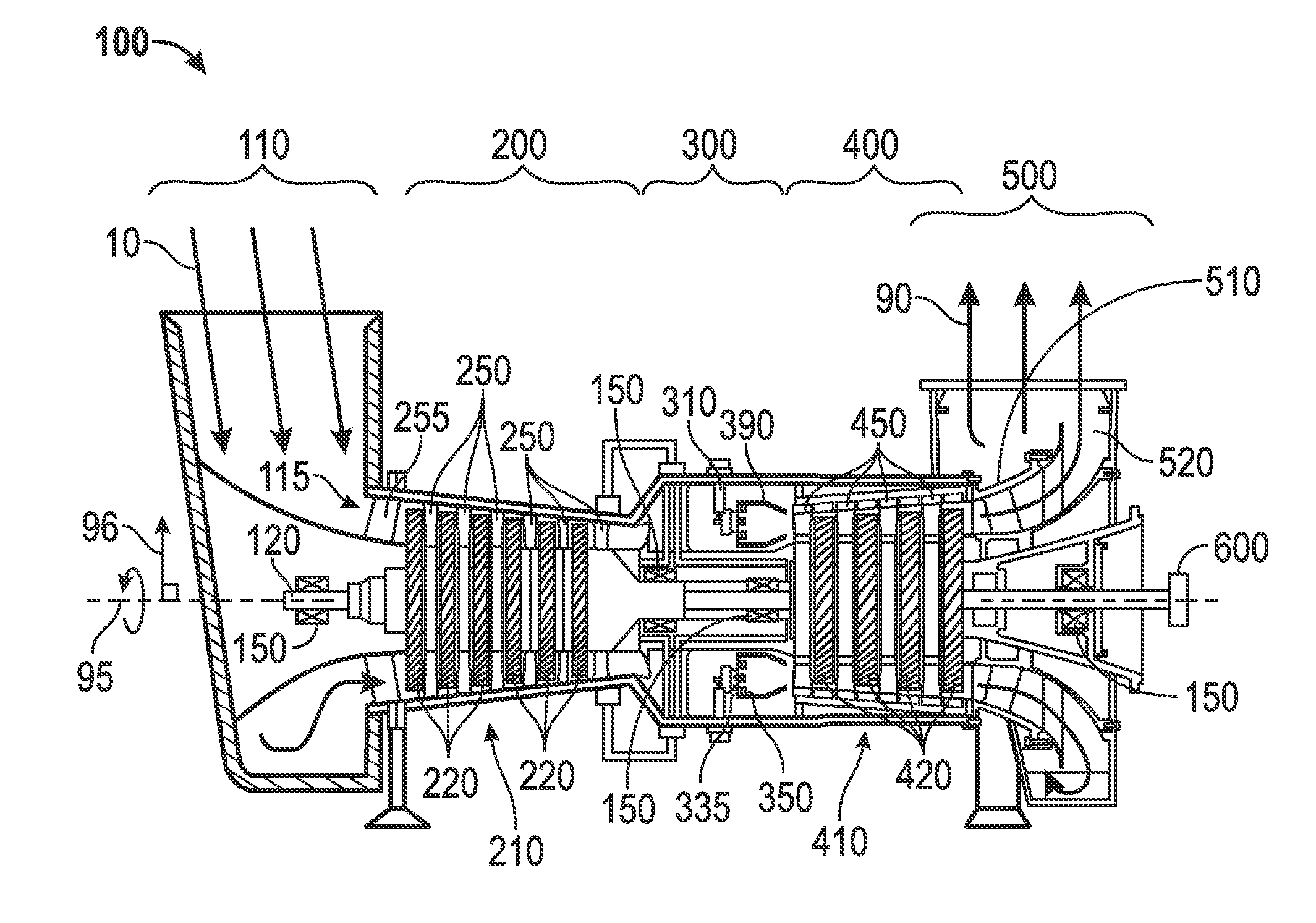
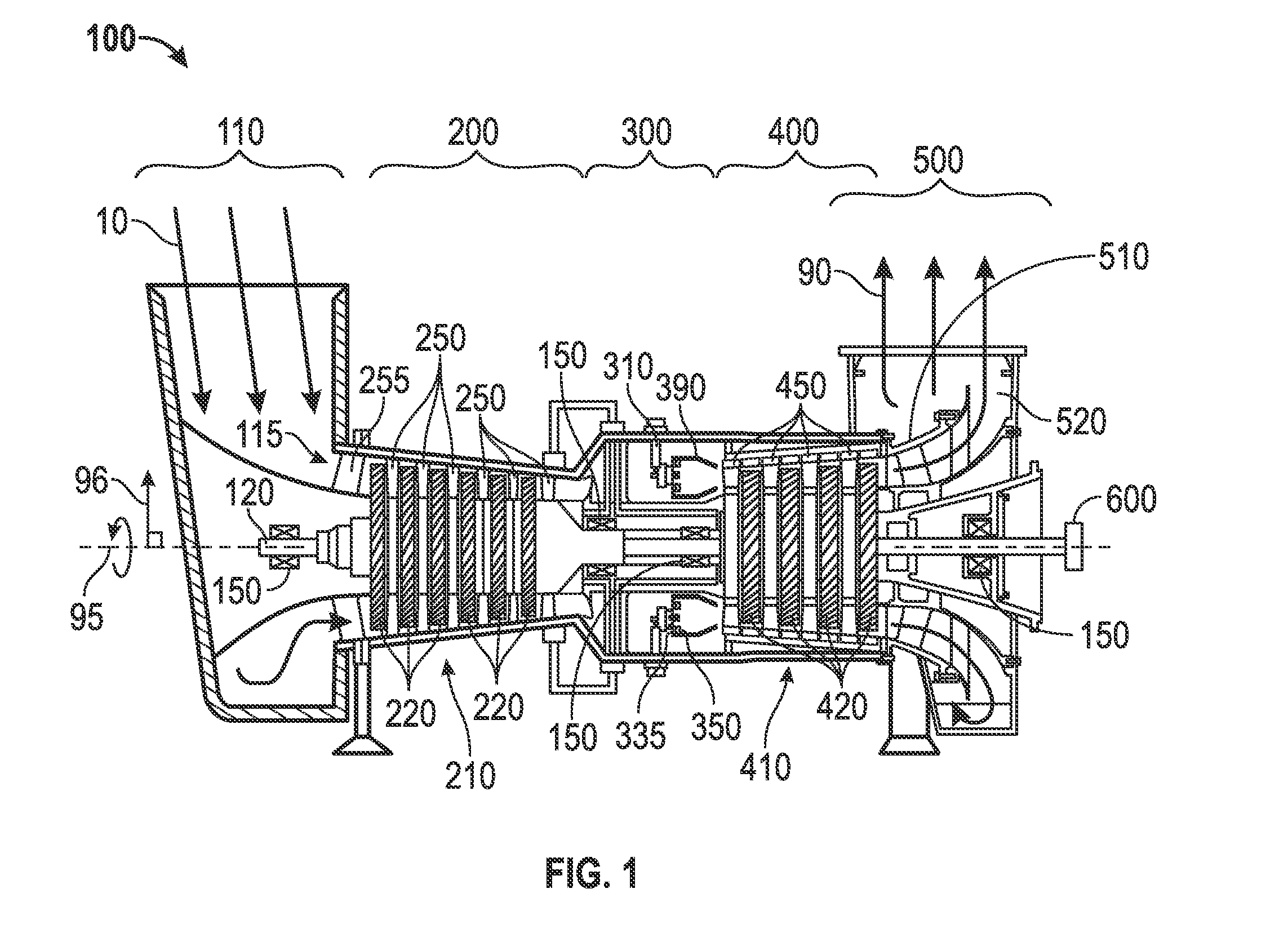
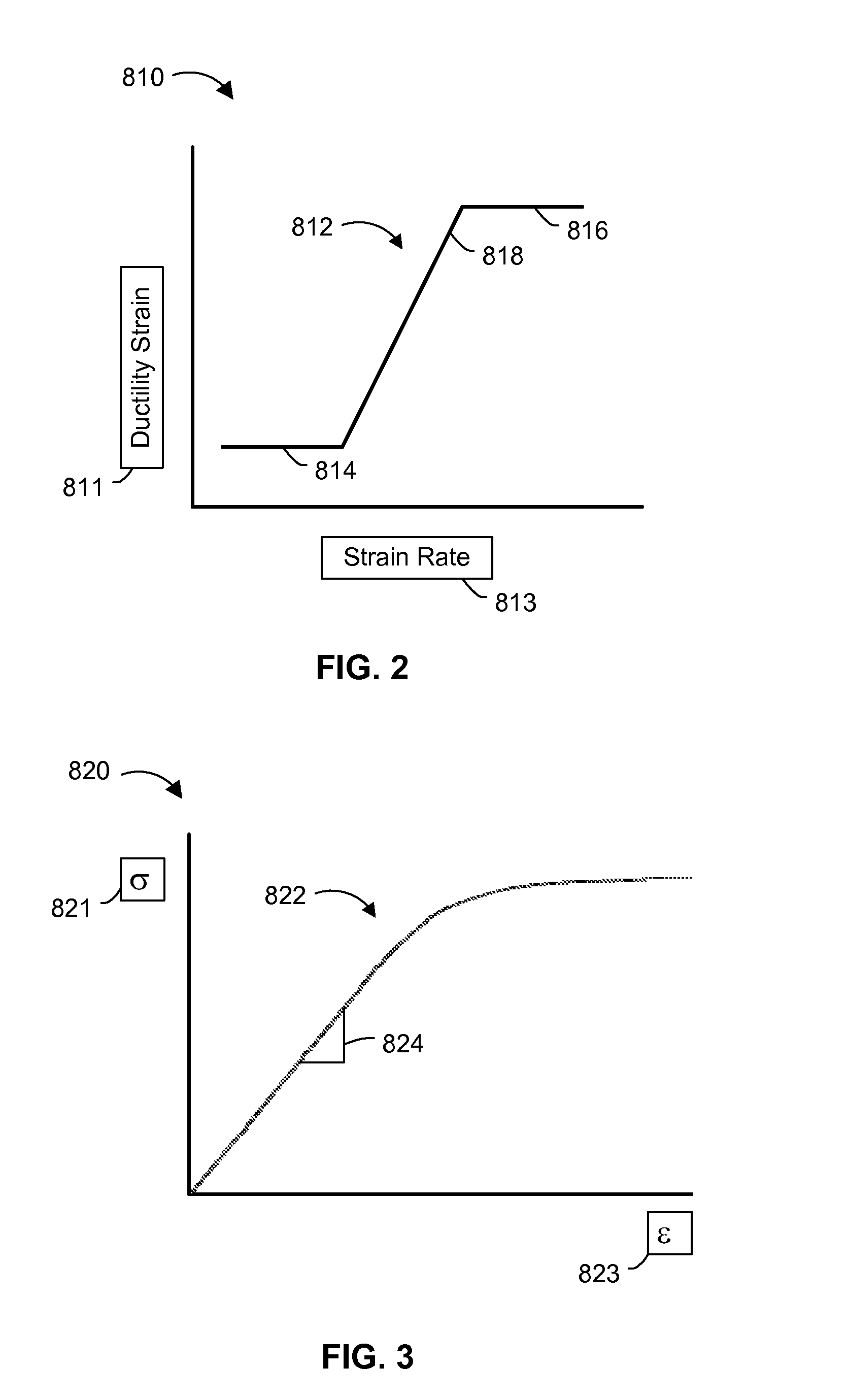
Condition based lifing of gas turbine engine components
ActiveUS9200984B2Gas-turbine engine testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesCreep stressLoad cycle
A system and methods for the condition based lifing of a gas turbine engine component is disclosed. The system and methods determine the stress and caused by fatigue and creep for each load cycle of the gas turbine engine, and use a ductility exhaustion method to combine the fatigue and creep strain rates determined from the fatigue and creep stresses to determine the remaining useful of the gas turbine engine component.
Owner:SOLAR TURBINES
Simply supported variable continuous bridge construction method with steel beam tensioning connector
ActiveCN108894118AReduced risk of corrosionReduce the impact of bearing capacityBridge erection/assemblyBridge materialsCreep stressT-beam
The invention discloses a simply supported variable continuous bridge construction method with a steel beam tensioning connector. The method includes the following steps that the steel beam tensioningconnector is pre-embedded in T-beams along the longitudinal direction of the T-beams, and tensions in a wet joint area between the T-beams; a curvilinear steel beam in the negative bending moment area of an existing pier top is transformed into a straight steel beam, which reduces the loss of prestress caused by the friction of a pipeline. However, a tensioning groove is transferred from the topof the prefabricated T-beam wing plate to the wet joint area, in the one hand, the disconnection of a reinforcing bar inside the T-beams is avoided, the impact of the reserved tensioning groove on thebearing capacity of the T-beams is greatly reduced; on the other hand, the difference of ages of concretes in and around the reserved tensioning groove is greatly shortened, and the concrete shrinkage and creep stress caused by age difference is greatly reduced. From the perspective of the construction process, the current construction procedure of steel beam tensioning is adjusted from 'tensioning before anchoring' to 'anchoring before tensioning', so that the prestress loss caused by anchorage retraction is eliminated.
Owner:CHONGQING JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Condition based lifing of gas turbine engine components
A system and methods for the condition based lifing of a gas turbine engine component is disclosed. The system and methods determine the stress and caused by fatigue and creep for each load cycle of the gas turbine engine, and use a ductility exhaustion method to combine the fatigue and creep strain rates determined from the fatigue and creep stresses to determine the remaining useful of the gas turbine engine component.
Owner:SOLAR TURBINES
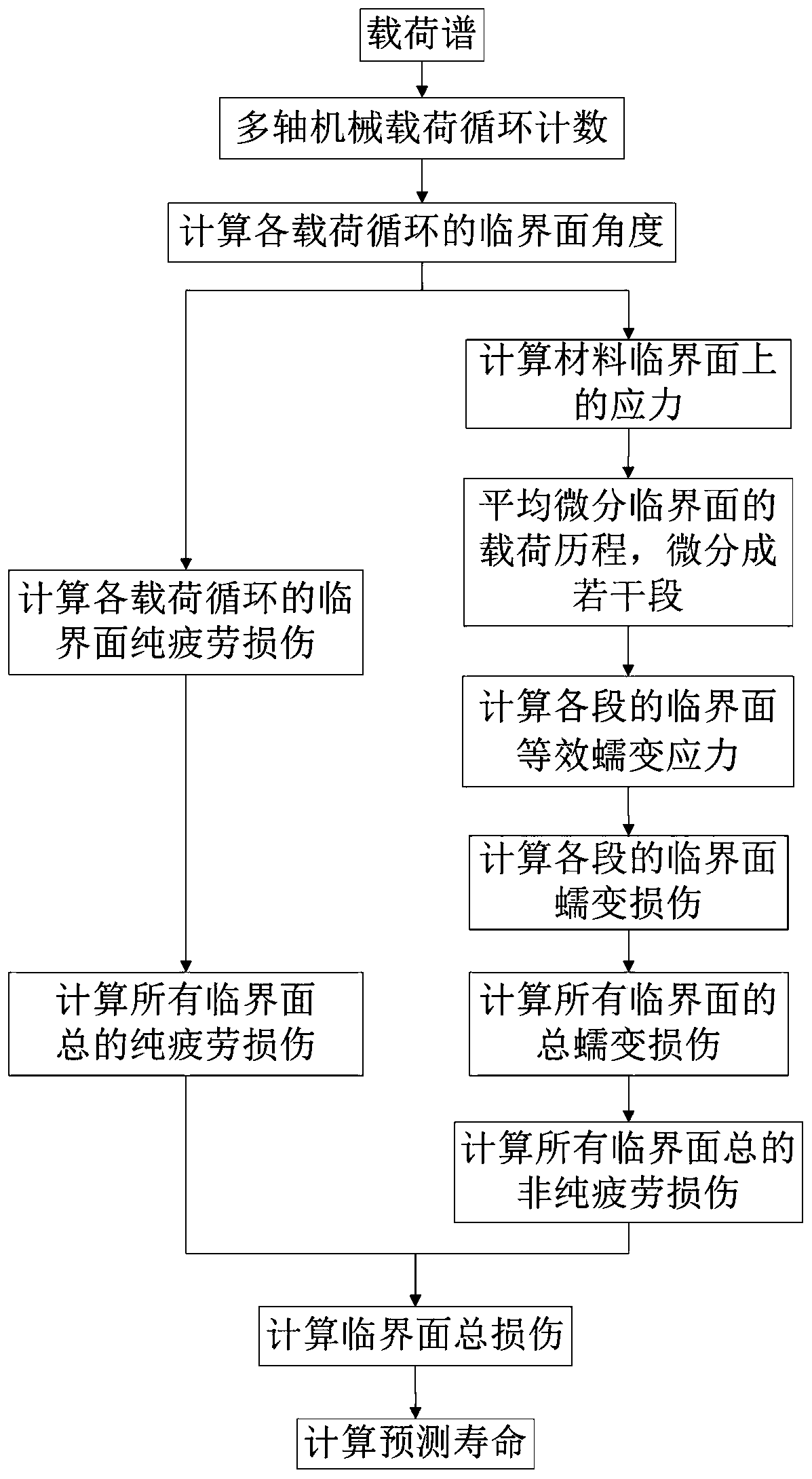
Multi-axis variable-amplitude thermo-mechanical fatigue life prediction method based on critical surface damage
ActiveCN110987675ALow economic cost of life predictionReduce economic costsMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesFatigue damageFatigue Intensity
The invention discloses a shaft torsional multi-axis variable-amplitude thermo-mechanical fatigue life prediction method based on material critical surface damage. The invention relates to the field of multi-axis thermo-mechanical fatigue strength theories. The method includes calculation of a multi-axis mechanical load cycle count, the critical surface angle of each load cycle, the critical surface pure fatigue damage of each load cycle, the total pure fatigue damage of the critical surfaces, stress on the critical surface of the material, an average differential critical surface load history, the critical surface equivalent creep stress of each section, the critical surface creep damage of each section, total creep damage of all critical surfaces, total non-pure fatigue damage of all critical surfaces, total damage of the critical surfaces and predicted service life. The proposed life prediction method can well predict the fatigue life of the alloy material under the shaft torsionalmulti-axis variable-amplitude thermo-mechanical loading.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for determining widths of partition coal pillars at slope based on creep test of coal sample
The invention provides a method for determining the widths of partition coal pillars at a slope based on the creep test of a coal sample. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a coal sample and determining the time of one stoping; with the time of one stoping as destroy time of the coal sample on a testing machine, setting normal stresses of different grades, setting horizontal stresses by using the Cheng' step loading method, carrying out creep fracture test on the coal sample within the time of one stoping, acquiring a creep stress-strain curve of the coal sample and a series of shear fracture strength data under the action of the normal stresses of different grades, and recording target time strength of the coal sample; subjecting the target time strength under the action of the normal stresses of different grades to fitting and determining the cohesive force and internal friction angle of the coal sample according to a fitting curve and Mohr' strength equation; setting the width range of the coal pillars, and simulating the vertical stress field distribution rule and plastic failure zone distribution rule of the coal pillars under the conditions of different coal pillar widths by using FLAC3D software according to the determined cohesive force and internal friction angle of the coal sample; and carrying out contrastive analysis so as to obtain the proper width range of the coal pillars.
Owner:扎鲁特旗扎哈淖尔煤业有限公司
Constant stress loaded hydrogen permeation experimental device and test method
ActiveCN110118695AContinuous constant outputSatisfies the case of stretched hydrogen permeation reactionMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesConstant loadHydrogen
The invention provides a constant stress loaded hydrogen permeation experimental device. The experimental device comprises a mechanical stress loading mechanism and a hydrogen permeation reaction mechanism; the mechanical stress loading mechanism comprises a force application mechanism, a spring, a passive sliding block and a force supplementing mechanism; the hydrogen permeation reaction mechanism comprises a test piece and a test piece stretching frame; the force application mechanism can produce tensile force on the spring so that the spring is deformed; the spring produces tensile force for the test piece stretching frame so as to realize the stretching of the test piece; the length is changed after the test piece is stretched, and the length of the spring is also changed, thereby causing a condition that the tensile force on the test piece by the spring is partially lost; the force supplementing mechanism can compensate the lost force so as to guarantee the constant force loadingof the test piece. The invention further provides a test method of the constant stress loaded hydrogen permeation experimental device. The compensation is performed through the force supplementing mechanism according to the tiny deformation of the test piece, thereby guaranteeing the constant load; and the device disclosed by the invention has strong applicability for the metal material stretching, is simple, accurate in measurement, low in cost, and capable of easily realizing the real-time monitoring on the creep stress and displacement under the constant force.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
Method for reducing longitudinal shrinkage joints of underground comprehensive pipe gallery
InactiveCN106049534AReduce generationImprove structural performanceArtificial islandsUnderwater structuresStress changeCreep stress
The invention relates to a method for reducing longitudinal shrinkage joints of an underground comprehensive pipe gallery. The method is characterized in that the stress change of the pipe gallery section is controlled, specifically, the stress making the underground comprehensive pipe gallery generate cracks is reduced through control over shrinkage stress, temperature stress and creep stress, and therefore, occurrence of the shrinkage joints is reduced; when sigma <ck>- sigma <pc> is smaller than or equal to f<tk>, the longitudinal shrinkage joints can be reduced, the sigma <ck> represents anti-crack edge concrete normal stress, and the sigma <pc> represents anti-crack edge concrete pre-pressure stress; through control over the shrinkage stress and the temperature stress in the construction stage, the purpose of reducing stress is achieved, and therefore, occurrence of the cracks is reduced; and through control over intelligent tensioning and by the adoption of cohesive pre-stressed concrete plates in the long-term maintenance stage, occurrence of the creep stress is reduced, and therefore, occurrence of the cracks is reduced.
Owner:江苏开来预应力工程有限公司
Negative bending moment steel bundle tensioning connector and bridge construction for simply supported continuous bridge
ActiveCN108978492AReduced risk of corrosionReduce the impact of bearing capacityBridge structural detailsBridge erection/assemblyCreep stressT-beam
The invention discloses a steel bundle tensioning connector and a bridge structure of a simply-supported transformed continuous bridge with a negative bending moment. The steel bundle tensioning connector is directly embedded in the T-beam along the longitudinal direction of the T-beam and tensioned in the wet joint area between the T-beams so that the existing pier top negative bending moment area of the curve steel bundle into a straight bundle, reduce the pipe friction caused by the loss of prestress. On the one hand, it avoids the steel bar breaking in the T-beam, and greatly reduces the influence of the reserved tension groove on the bearing capacity of T-beam, while the tension groove transfers from the top of the precast T-beam wing to the wet joint area. On the other hand, the agedifference of concrete in and around the reserved tensioning groove is greatly shortened, and the shrinkage and creep stress of concrete due to age difference is greatly reduced. From the view of construction process, the construction procedure of tensioning steel bundle is adjusted from tensioning before anchoring to anchoring before tensioning, which eliminates the prestress loss caused by the retraction of anchorage.
Owner:CHONGQING JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Digitalized construction site concrete prediction type anti-cracking method
ActiveCN110377981AThe calculation result is accurateSolve the problem of insufficient accuracyMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentCreep stressStress sensor
The invention discloses a digitalized construction site concrete prediction type anti-cracking method which comprises the following steps: firstly, arranging a temperature and stress sensor at a concrete sensitive position, then endowing concrete with a thermal parameter initial value, and then feeding back and analyzing a concrete thermodynamic parameter based on a particle swarm algorithm; calculating internal temperature predicted value and a stress predicted value in future 4-7 days according to a control equation of a three-dimensional unstable temperature field and a control equation ofa creep stress field; and finally, taking anti-cracking measures on the mass concrete according to the solved stress prediction value. According to the method provided by the invention, the calculation result is more accurate, and the concrete anti-cracking measure is adjusted according to the predicted future concrete temperature and stress development trend, so that the anti-cracking effect is the best.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
High-temperature-resistant and high-pressure-resistant creep die-casting magnesium alloy and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113337765AIncrease resistanceExcellent high temperature and high pressure creep performanceCreep stressMagnesium alloy
The invention discloses a high-temperature-resistant and high-pressure-resistant creep die-casting magnesium alloy and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of magnesium alloys. The problem that the creep resistance of the magnesium alloy in the prior art cannot completely meet the use requirement in the environment at the temperature of 200 DEG C or above is solved. The magnesium alloy comprises the following components including by weight, 1% to 6% of Zn, 0.5% to 4% of La, 0.5% to 6% of Y, 0% to 0.5% of Zr, 0% to 0.5% of Mn and the balance magnesium and inevitable impurity elements. The magnesium alloy contains Zn, La and Y, the Zn, the La and the Y form a continuous net-shaped second-phase structure in three-dimensional space distribution after being melted, a second phase has multiple structures, dislocation slippage and twin crystal formation can be effectively hindered under the high-temperature condition, the high-temperature creep resistance of the alloy is improved, it is verified that at the temperature of 250 DEG C, the creep stress of the alloy is 80 MPa, the lasting creep life is longer than 300 h, and the steady-state creep rate is less than 6*10<-9> / s.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A low-cycle creep-fatigue life evaluation method under high-temperature multi-axis spectral loading
ActiveCN103926152BEasy accessReduce testing costsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFatigue damageCreep stress
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
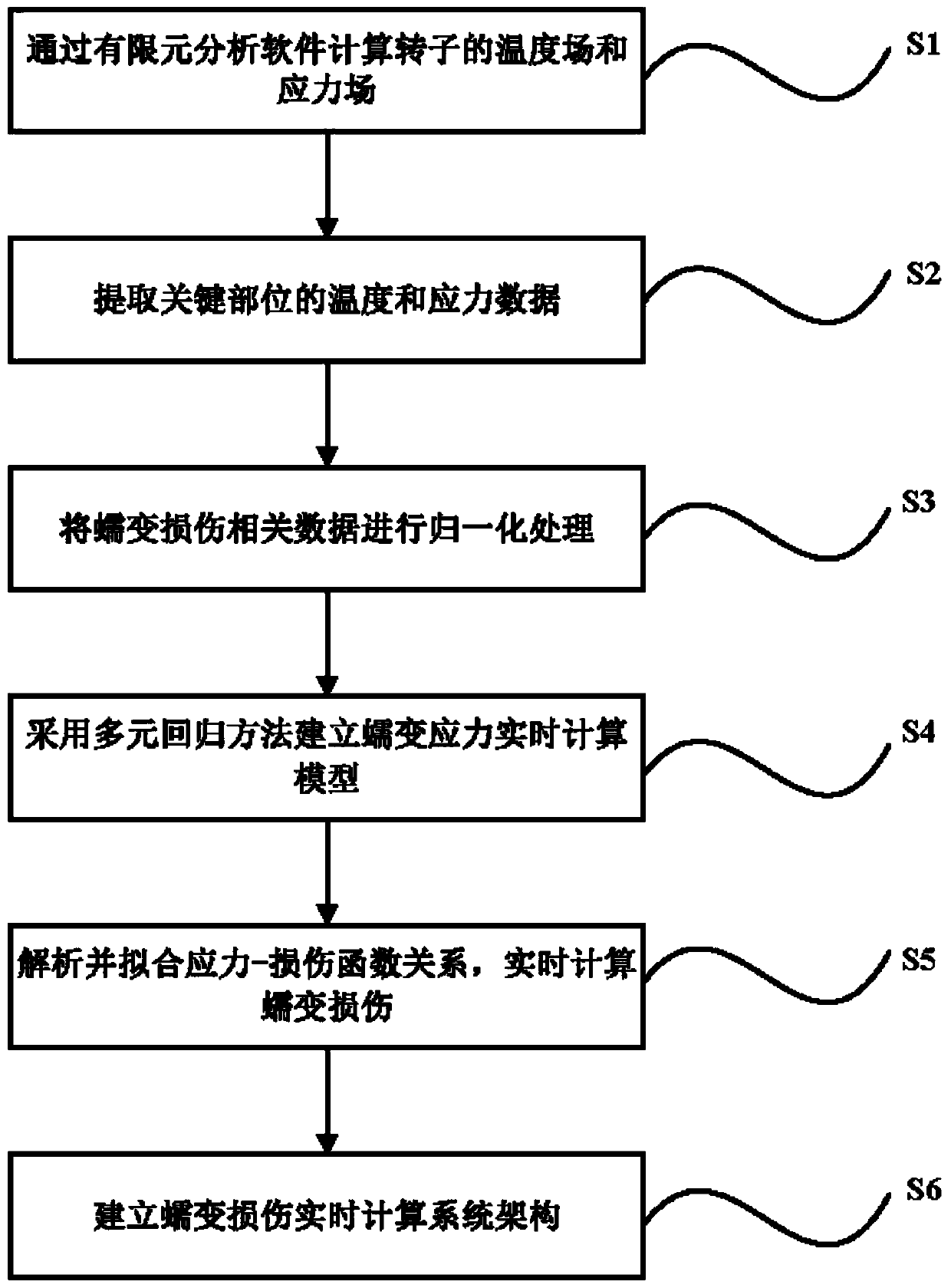
Turbine rotor creep damage real-time calculation method based on a finite element model
The invention provides a turbine rotor creep damage real-time calculation method based on a finite element model. The turbine rotor creep damage real-time calculation method comprises the steps that atemperature field and a stress field of a rotor are calculated through finite element analysis software; Extracting temperature and stress data of the key part; Performing normalization processing ontemperature, pressure, rotating speed and stress data related to creep damage calculation; Establishing a creep stress real-time calculation model by adopting a multivariate regression method; Analyzing and fitting stress; Calculating a damage function relationship, and calculating creep damage in real time; And establishing a creep damage real-time calculation system structure. The problem of real-time calculation of rotor creep damage in the prior art can be solved, and the method has high precision.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
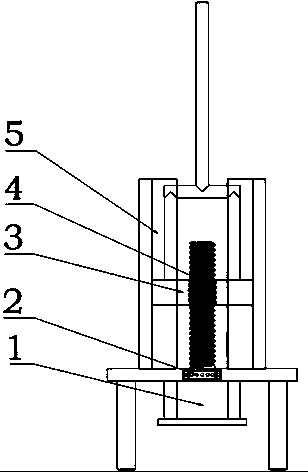
Cement-based material axial pressure creep testing device capable of regulating and controlling temperature, humidity and load
PendingCN113310811AEasy to installEasy to operateMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesCreep stressAxial pressure
The invention discloses a cement-based material axial pressure creep testing device capable of regulating and controlling temperature, humidity and load. The cement-based material axial pressure creep testing device comprises: an integral testing framework, wherein the integral testing framework consists of a fixed steel frame, a bearing support column, a bearing lever, a protecting device, a stabilizing device, bolts and the like; an axial pressure load regulation and control system composed of a slidable connecting device, a dead load counterweight device and a force transmission device; a test condition control system consisting of a temperature regulation and control device and a humidity regulation and control device; and a creep data acquisition and recording system consisting of a cement-based material sample, an axial pressure deformation measuring device and a data transmission and acquisition device. According to the invention, after a test piece and a deformation testing device are installed, the position of a bearing support column is adjusted, a counterweightblock matched with creep stress needed for testing is placed on a bearing tray, the needed temperature and humidity are set, and finally the temperature and humidity change is checked regularly and the creep degree progress is recorded; and the whole axial pressure creep testing device and method are simple and easy to implement, and the deformation characteristics of the cement-based material under various temperature and humidity and different creep stresses can be obtained.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Production method of seamless stainless steel tube for high-pressure boiler
InactiveCN101440428BAccelerated corrosionIncrease the grain size seriesFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesCreep stressAcid washing
The invention relates to a method for producing seamless stainless steel pipes for high-pressure boilers. The method comprises the following steps: adjusting weight ratio of carbon element in a raw material of TP347H type seamless stainless pierced billet to be 0.06 to 0.10 percent; and then carrying out truncating, acid washing, polishing, solid solution heat treatment, straightening, cold rolling, solid solution heat treatment, cold drawing, high-temperature creep stress conditioning, straightening and cutting pipes, and acid washing in turn on the pierced billet raw material, wherein the high-temperature creep stress conditioning is subjected to four groups of process temperature successively. The method improves level of grain size greatly based on the TP347H type seamless stainless steel, and the level of the grain size reaches 7 to 10; and at the same time, through adjusting the carbon element, the method improves corrosion resistance and steam oxidization resistance during use of the steel pipes at the environment of high temperature and high pressure, so that the seamless stainless steel pipes can be applied to supercritical boilers with large capacity and high parameters.
Owner:常州市新亚不锈钢管有限公司
Rock long-term strength determination method based on dominant acoustic emission source energy characteristics
PendingCN113866278AEasy to operateMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesProcessing detected response signalCreep stressAcoustic emission
The invention relates to the technical field of rock physical and mechanical property testing, and discloses a rock long-term strength determination method based on dominant acoustic emission seismic source energy characteristics, which comprises the following steps: carrying out longitudinal wave velocity testing on a standard rock test piece, arranging an acoustic emission sensor on the standard rock test piece; carrying out graded creep failure acoustic emission seismic source positioning test on the standard rock test piece, calculating P wave arrival time and initial motion amplitude corresponding to each acoustic emission seismic source, solving a moment tensor corresponding to each acoustic emission seismic source, classifying the acoustic emission seismic sources according to moment tensor characteristic values, and determining dominant acoustic emission seismic sources; picking up absolute energy of each stage of dominant acoustic emission source, calculating an absolute energy average value of each stage of creep dominant acoustic emission source, and drawing an absolute energy average value-creep stress curve; and taking a creep stress average value corresponding to the lowest point on the absolute energy-creep stress curve and a first data point after the lowest point as a rock average value being long-term strength sigma infinity.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for testing creep property of metal
PendingCN112649278AEfficient creep performanceEfficient creep performance testingStrength propertiesLinear variable differential transformerCreep stress
The invention provides a method for testing the creep property of metal. The method comprises the following steps: after loading initial axial stress to a sample, sequentially increasing the axial stress which is the same as the initial axial stress at the same time interval until the sample is broken; then, collecting stress and strain data in real time through a weighing sensor and a linear variable differential transformer, transmitting the data to a computer, processing the data through software, and drawing a creep curve of the sample; obtaining the minimum creep rate by utilizing the obtained creep curve, and drawing a minimum creep rate creep stress logarithm diagram according to a power law formula to obtain a creep index. According to the test method provided by the invention, the problems of more samples and long test time used for testing the metal creep property can be solved.
Owner:NINGXIA UNIVERSITY +1
Method for multilevel creep age forming of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu series aluminium alloy plate
ActiveCN102978544BImprove mechanical propertiesImprove corrosion resistanceCreep stressThermal insulation
The invention relates to a method for multilevel creep age forming of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu series aluminium alloy plate. The method is characterized in that a reasonable solid solution-quenching-pretreating-multilevel creep aging system is adopted, is suitable for plates with the thickness of 2 millimeters-30millimeters and comprises the following steps that solid solution is carried out at 470-485 DEG C for 30 minutes-120 minutes, quenching is then carried out, the quenched plate is subjected to 0-10% predeformation treatment and creep aging at 120 DEG C and is thermally insulated for 24 hours, the creep return temperature is between 150 and 170 DEG C, return thermal insulation is carried out for 20-240 minutes, and another creep aging is thermally insulated at 120 DEG C for 24 hours, wherein the creep stress is between 100 and 150 mega pascals, and the forming bending radius is between 800 millimeters and 5000 millimeters. The method is utilized to treat Al-Zn-Mg-Cu series aluminium alloy, so that the alloy creep aging strengthening phase can be effectively regulated, the mechanical property of the alloy plate and the alloy creep formability are improved, the residual stress of the alloy plate is reduced, and the alloy exfoliation corrosion resistance is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com