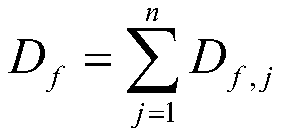Multi-axis variable-amplitude thermo-mechanical fatigue life prediction method based on critical surface damage
A thermomechanical fatigue and life prediction technology, which is applied in the direction of testing material strength by applying stable shear force, measuring device, and testing material strength by applying repetitive force/pulsation force, can solve the problem of high cost of thermomechanical fatigue test, Achieve the effect of clear physical meaning and low economic cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0047]The present invention is illustrated in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
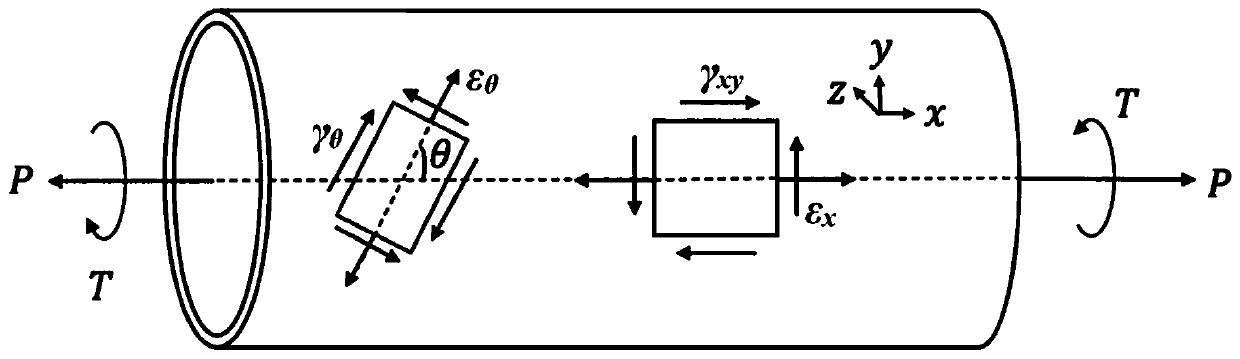
[0048] The present invention is further described through the axial-torsion multi-axial luffing thermal-mechanical fatigue test, and the test material is nickel-based superalloy GH4169.
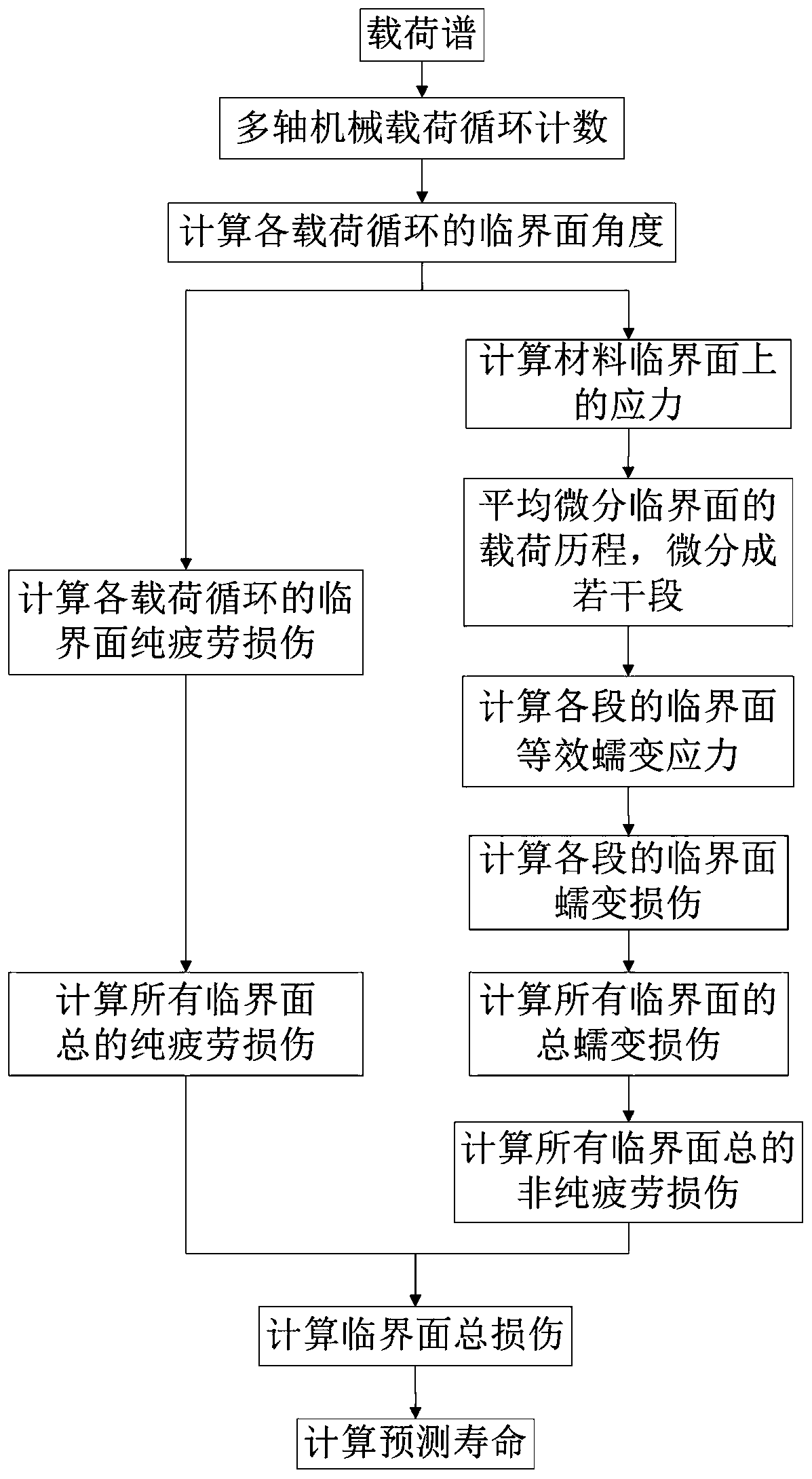
[0049] A damage mechanism based thermomechanical fatigue life prediction method for shaft-torsion multi-axis luffing, such as figure 1 As shown, the specific calculation method is as follows:
[0050] Step (1): Load cycle counting for shaft-torsional multi-axial mechanical loads. Under the action of axial torsional multiaxial thermomechanical loads, the Wang-Brown method is used to count the load cycles of the axial torsional mechanical loads, and determine the load interval of each load cycle;
[0051] Step (2): Calculate the critical plane angle for each load cycle. Under multiaxial loading, there are two planes that bear the maximum shear strain amplitude inside the material, but the directional ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com