Method of designing golf club and golf club head
a golf club and design method technology, applied in the field of golf clubs and golf club heads, can solve the problems of insufficient restitution performance, excessive rigidity of the face part, low strength of the wood head, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the cost and the time required to execute computations, reducing the size of the sweet area, and easy design
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
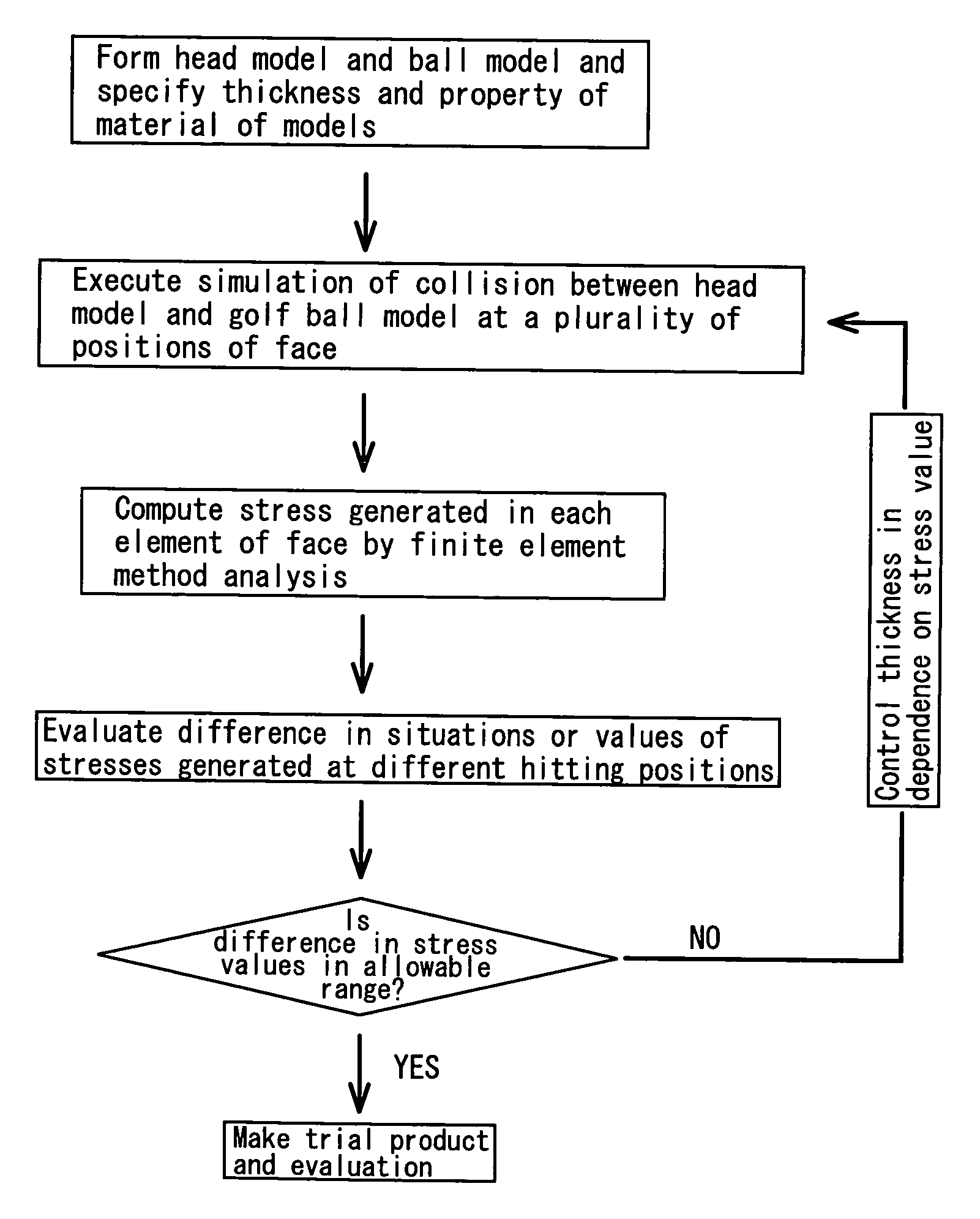
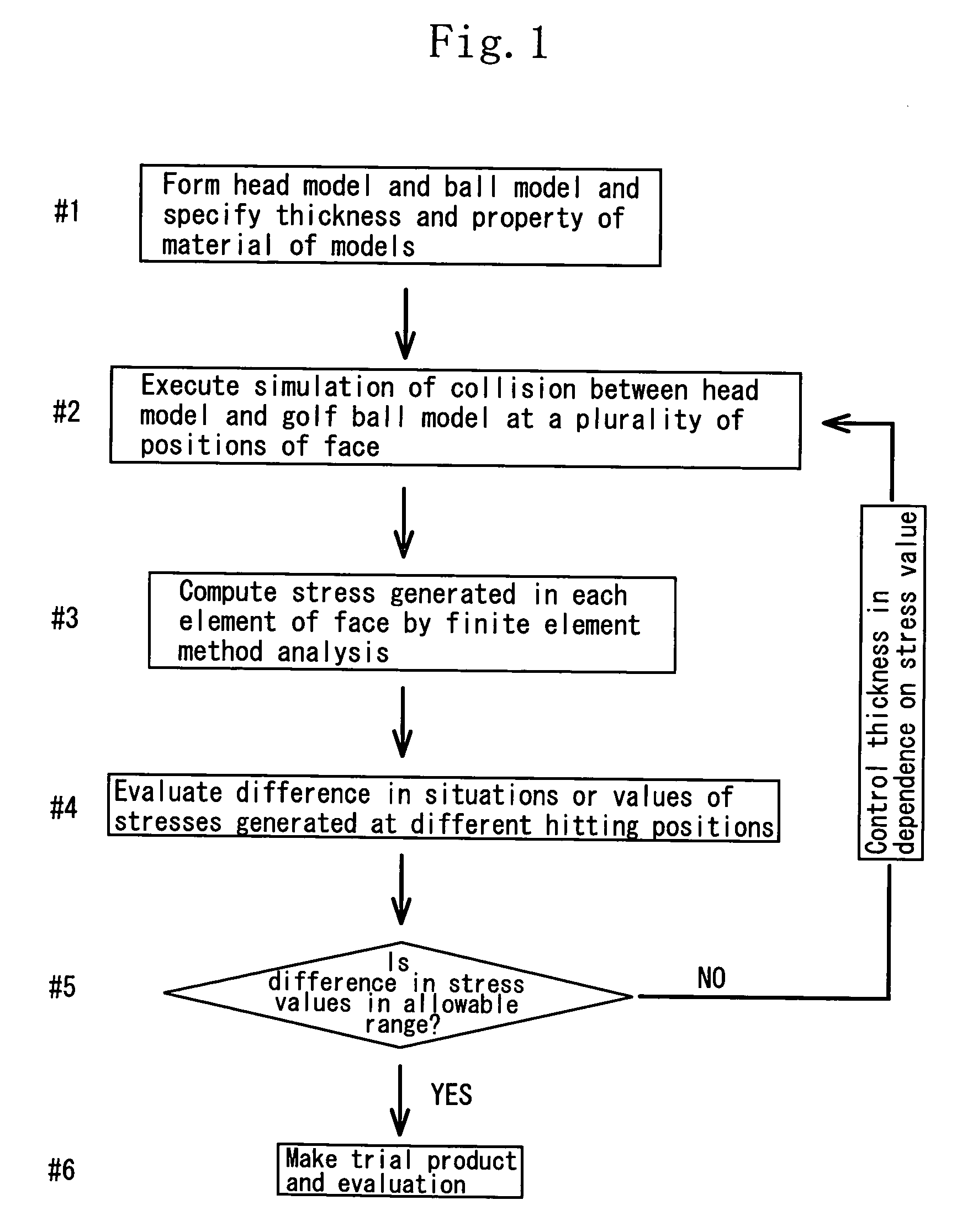
[0131] Golf club head models of the examples 1 through 8 shown in table 1 and golf club head models of the comparison examples 1 through 4 shown in table 2 were formed by using a computer. Simulation was executed by collision between ball models and the golf club head models. The coefficient of restitution of each golf club head model was determined to evaluate the performance of the golf club head models.
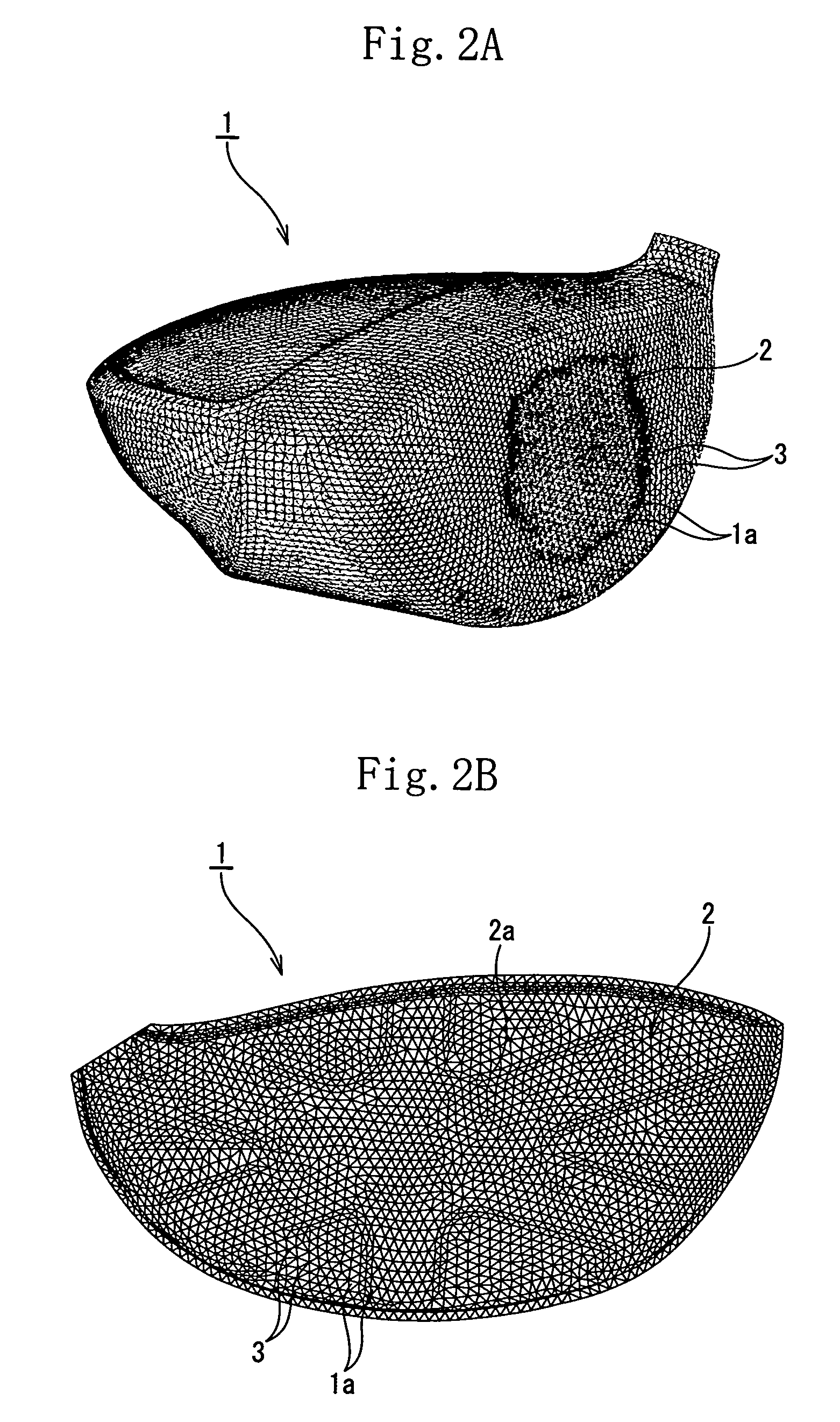
[0132] Excluding the reinforcing ribs of the face part, the golf club head models of all the examples and the comparison examples were prepared by using the same specification. More specifically, similarly to the embodiments shown in FIGS. 6 through 9, each of the hollow golf club head models made of a titanium alloy was formed by joining the face and body parts with each other to make them approximately cup-shaped. The head had a volume of 405 cc. The face part has an area of 4100 mm2. The thickness of the portion of the face part where the reinforcing ribs were not formed was se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com